Abstract
Background:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) imposes a growing global burden, with hemodialysis (HD) patients facing high malnutrition rates (28% ~ 54%). Nutritional management is critical but challenging due to strict dietary restrictions and limited healthcare monitoring. Digital health technologies (DHTs) offer dynamic, personalized interventions, yet their efficacy remains inconsistent. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to assess the effects of DHT-based nutritional interventions on the nutritional status of hemodialysis patients.
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CINAHL, Scopus, CNKI, CBM, WanFang, and VIP databases from their inception to 21 March 2025, to investigate the impact of DHTs-based nutritional interventions on the nutritional status of hemodialysis patients. Outcomes included biochemical parameters, anthropometric measures, and Modified Quantitative Subjective Global Assessment (MQSGA). Risk-of-bias assessment used Cochrane criteria, and meta-analyses employed RevMan 5.4 with random/fixed-effects models.
Results:
A total of 23 literatures were included, involving 6 countries and 2,762 hemodialysis patients. DHT interventions improved the following 13 outcome measures: MQSGA, hemoglobin, albumin, prealbumin, phosphorus, potassium, BMI, mid-arm muscle circumference, triceps skinfold thickness, relative increase in body weight (%), weight gain, blood urea nitrogen, and serum creatinine. However, it had no significant effect on transferrin and calcium. The intervention forms are mainly applications and mobile platforms.
Conclusion:
Overall, DHT-based nutritional interventions effectively enhance multiple nutritional indicators in HD patients. However, variability in study quality, intervention formats, and regional disparities limits generalizability. Future research should prioritize high-quality, multicenter RCTs to optimize intervention protocols and explore emerging technologies.
Systematic review registration:
Identifier PROSPERO: CRD420251023133.
1 Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive disease characterized by a gradual decline in renal function, caused by various factors that induce chronic kidney structural and functional impairments, with a history of kidney damage lasting over 3 months. According to the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, CKD’s ranking in the list of global mortality causes has been rising steadily, securing the 13th position in 2016, climbing to 12th in 2017, and is projected to become the fifth leading cause of death globally by 2040 (1, 2). End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is the final stage of chronic kidney disease, characterized by toxin accumulation in the body, uremic symptoms, and various complications; patients in this stage often need dialysis (3, 4). Hemodialysis (HD) is a common method of renal replacement therapy for patients with acute and chronic renal failure. It involves periodically diverting blood outside the body via artificial means to remove metabolic waste and excess fluid, followed by the return of the purified blood to the body (5). Most Hemodialysis patients undergo regular long-term dialysis sessions lasting 3.5–4.5 h, three times a week. Globally, approximately 89% of ESRD patients undergo Hemodialysis (6). As of 2013, approximately one million individuals worldwide were undergoing hemodialysis, with the total number of patients receiving dialysis increasing at an annual rate of 10% (7). In China, the number of hemodialysis patients reached 910,000 by 2023 and is anticipated to continue rising significantly (8).
Hemodialysis patients, due to renal dysfunction, suffer from accumulated uremic toxins and insufficient erythropoietin production. Although long-term hemodialysis is life-saving, it is an invasive procedure that can induce chronic inflammation and increase nutritional consumption; additionally, these patients often require adherence to a low-protein diet, which may further contribute to malnutrition (9, 10). Studies indicate that the global malnutrition prevalence in such patients is as high as 28–54%, and in China, the rate of malnutrition in hemodialysis patients is even higher, ranging from 30.0 to 66.7% (11, 12). If hemodialysis patients are chronically malnourished, they may experience various adverse outcomes such as cognitive impairment, frailty, falls, disability, death, and a reduced quality of life (13, 14). Therefore, nutritional management for hemodialysis patients is crucial to prevent these adverse outcomes. At the same time, hemodialysis patients typically do not require constant hospitalization. After dialysis, they often return home, with some even undergoing treatment at home or in community settings. These challenges render continuous monitoring by healthcare professionals impractical. The strict dietary restrictions imposed on these patients make long-term adherence particularly difficult (15). Furthermore, existing nutritional interventions, which are typically guided by standardized protocols, are often challenging to implement rigorously due to significant individual differences among patients, such as age, comorbidities, and duration of dialysis (16).
The World Health Organization defined digital health as the field of knowledge and practice associated with the development and use of digital technologies to improve health in the “Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025” (17). Digital health technologies are those that can remotely access personal health-related information, including electronic health records, telemedicine or telehealth services, robotic technologies, and mobile health technologies supported by smartphones, wearable devices, applications, and various monitoring devices (17). The development of digital health technology provides new strategies for the nutritional management of hemodialysis patients. Compared with traditional methods, it features dynamic assessment, real-time feedback, efficiency, cross-spatiotemporal accessibility, precision, and personalization. In recent years, it has shown advantages in practical applications for hemodialysis patients. However, current research indicates inconsistent effects of digital health technology on the nutritional management of these patients. Some studies suggest it can improve hemoglobin, albumin, and BMI in hemodialysis patients, while others show no significant effects of the intervention (18, 19). Notably, hemoglobin is not only a key indicator of nutritional status but also the core marker for assessing anemia, one of the most common and clinically critical complications of hemodialysis, closely linked to malnutrition. Anemia affects 91.6–98.2% of hemodialysis patients (20), and its control directly impacts patients’ quality of life and prognosis. Thus, clarifying whether digital health technology-based nutritional interventions can effectively improve hemoglobin (and thereby alleviate anemia) is an essential part of confirming their overall value for nutritional management. This study uses meta-analysis to evaluate the effects of this technology on the nutritional intervention of hemodialysis patients. It aims to provide evidence-based support for developing feasible and effective intervention strategies, ultimately reducing malnutrition in hemodialysis patients.
2 Methods
We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses 2020 (PRISMA 2020) guidelines (21).
2.1 Literature search
Zhang Kai and Wang Ruixue searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CINAHL, Scopus, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Biology Medicine disc (CBMdisc), WanFang, and Weipu (VIP) databases. The search strategy integrated Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free terms and was customized for each database’s unique characteristics. Search terms included “hemodialysis,” “MHD,” “hemodialysis,” “renal dialysis,” “mobile applications,” “smartphone,” “wearable electronic devices,” “digital health,” “telemedicine,” “artificial intelligence,” “internet,” “mhealth,” “web,” “wechat,” “virtual reality,” “VR,” “virtual environment,” “virtual simulation,” “nutrition,” “nutri*,” “supplement*,” “diet therapy,” “diet*,” “dietary.” We conducted a manual search using the literature tracing method to comprehensively supplement the literature. Our search encompassed the period from the establishment of each database to 21 March 2025. The study is registered in PROSPERO: CRD420251023133. For illustration, the specific search strategy is detailed in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.2.1 Inclusion criteria
Population (P): Patients undergoing hemodialysis and age ≥18 years. Intervention (I): Nutrition interventions delivered through digital health technologies (core components including mobile health, artificial intelligence, telehealth, or virtual reality) specifically designed for HD patients. Comparison (C): Usual care, routine care, conventional care, or standard care without integration of m-health/digital health components. Outcomes (O): Nutritional outcomes included the following: Biochemical parameters (e.g., serum albumin, prealbumin, and phosphorus); anthropometric measurements (e.g., body mass index and mid-arm muscle circumference); scores from internationally recognized nutritional assessment scales (e.g., Modified Quantitative Subjective Global Assessment, MQSGA). Study type (S): Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) reporting means, standard deviations, and explicit sample sizes to allow effect size pooling for primary/secondary outcomes. Language: Studies published in Chinese or English.
2.2.2 Exclusion criteria
(1) Meetings, policy documents, or research proposals. (2) The interventions were not specific and were only follow-up interventions conducted via telephone, email, or WeChat. (3) Repeated publication.
2.3 Data extraction
Two researchers (Zhang Kai and Wang Ruixue), who had received training in evidence-based nursing, searched the literature independently. Two researchers independently read the title and abstract for preliminary screening and carefully read the full text. According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the literature, the included literature was determined. Two researchers extracted literature information, including the literature author, publication time, country, sample size, age, dialysis age, intervention cycle, carrier format, intervention content, and outcome measures. If there were any differences, the third researcher (Ni Cuiping) was consulted to assist in the judgment.
2.4 Risk-of-bias assessments
Three reviewers (Zhang Kai, Wang Ruixue, and Zhang Nan) assessed the quality of the studies according to the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for risk of bias, which included seven categories of risk of bias: randomized sequence generation, allocation concealment, participant blinding, outcome assessor blinding, incomplete data, selective reporting, and other bias (22). Each item was evaluated as “high risk,” “low risk,” and “unclear.” Disagreements were adjudicated by a fourth reviewer (Ni Cuiping). The methodological quality of the included trials was categorized into three tiers using the following evaluation framework: (1) Low-quality trials were defined as those exhibiting high risk of bias in either randomization procedures or allocation concealment, irrespective of other methodological domains; (2) High-quality trials required both robust randomization and allocation concealment, with all remaining methodological components demonstrating low or unclear risk; (3) Moderate-quality trials encompassed studies that neither satisfied the stringent criteria for high quality nor met the threshold for low-quality classification (23).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using Review Manager (RevMan) software version 5.4. All continuous outcomes were pooled using Standardized Mean Differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). This approach was chosen because the outcomes encompassed heterogeneous measures, including unitless comprehensive scores (MQSGA), biochemical parameters with differing units (e.g., albumin, phosphorus), and anthropometric measures (e.g., BMI, mid-arm muscle circumference). Although units were standardized for the same indicator where necessary, SMD allows for the comparison of effect magnitudes across these fundamentally different types of outcomes, thereby facilitating an integrated assessment of the intervention’s impact on multidimensional nutritional status. Heterogeneity was evaluated through the Chi-square test and Cochran’s Q statistic. A fixed-effects model was applied when heterogeneity was non-significant (p ≥ 0.1 and I2 < 50%), while a random-effects model was utilized in cases of substantial heterogeneity (p < 0.1 or I2 ≥ 50%). For heterogeneous outcomes (I2 ≥ 50%), subgroup analyses were conducted to explore potential sources of heterogeneity, stratified by 1. Digital health technology types (application program vs. mobile platform); 2. Intervention duration (≥ 6 months vs. < 6 months). Publication bias was assessed via funnel plot symmetry inspection. Sensitivity analyses were implemented through a leave-one-out approach to verify result robustness. Statistical significance was defined as a two-tailed p-value < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Literature screening process and results
A total of 1,838 records were identified from databases and registers, including CNKI (n = 89), WanFang (n = 529), VIP (n = 29), CBM (n = 92), PubMed (n = 146), Web of Science (n = 363), Cochrane Library (n = 72), Embase (n = 199), CINAHL (n = 31), and Scopus (n = 288). After removing 613 duplicate records, 1,225 records were screened, and 1,158 records were excluded because they were not relevant to the research topic. Subsequently, 67 reports were sought for retrieval, with none being unretrieved. Following eligibility assessment of these 67 reports, 45 were excluded for the following reasons: the study subjects were not eligible (n = 27), reviews or meta-analysis (n = 5), meeting abstracts (n = 3), self before-and-after control (n = 7), case analysis (n = 1), and outcome measures not presented as means and standard deviations (n = 2). Additionally, 3 records were identified by screening the reference lists of original studies; all 3 reports were retrieved successfully, and after eligibility assessment, 2 records were excluded because the study subjects were not eligible. Finally, a total of 23 studies were included in this review. This study adheres to the PRISMA guidelines, and the literature searching and screening process is outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1
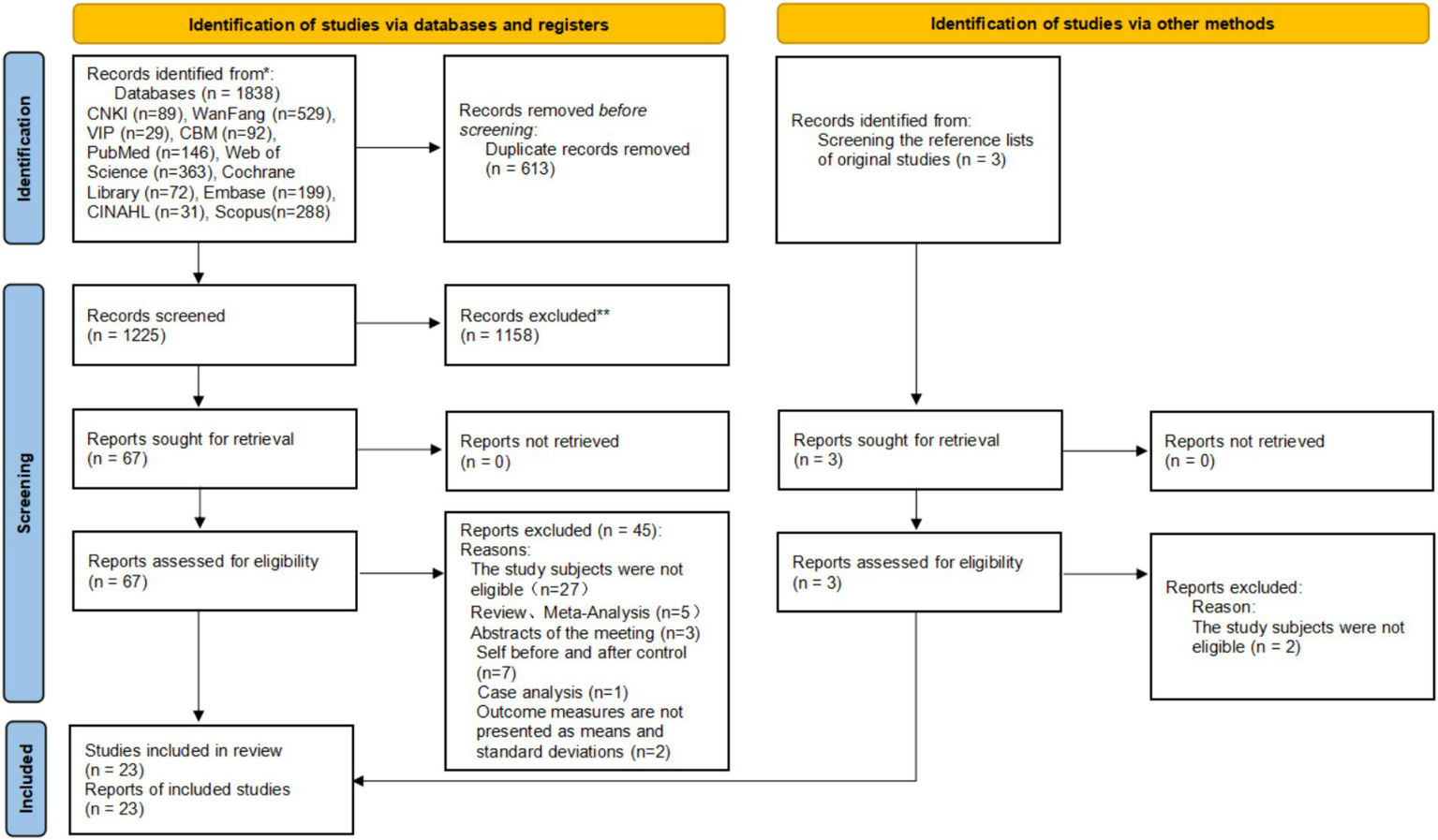
PRISMA diagram of searching and screening process.
3.2 The basic characteristics of the included literature
A total of 23 studies were included in the analysis, originating from 6 countries: China (n = 18) (18, 24–40), South Korea (n = 1) (19), Thailand (n = 1) (41), Iran (n = 1) (42), Malaysia (n = 1) (43), and the United States (n = 1) (44). In terms of publication timeframe, one study was published between 2011 and 2015 (44), four studies were published between 2016 and 2020 (24, 25, 27, 28), and 18 studies were published between 2021 and 2025 (18, 19, 26, 29–39, 41–43). These studies involved 2,762 hemodialysis patients in total, with 1,382 in the intervention group and 1,380 in the control group. Of the included studies, 19 focused on application-based interventions, including those utilizing WeChat and apps (19, 24–31, 33–35, 37, 38, 40–44). The remaining four studies adopted a mobile platform (18, 32, 36, 39). The basic characteristics of the included literatures are shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| Author, year | Country | Sample size (T/C) | Age (T/C) | Dialysis age (months) | Intervention cycle | Carrier format | Intervention content | Outcome measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kong YX, 2017 (24) | China | 50/50 | 45.45 ± 6.52 44.65 ± 6.78 |
- | 3 months | Application program (WeChat) | Conducted dietary education and answered questions via WeChat | Relative increase in body weight (%), Serum albumin, hemoglobin, potassium, and phosphorus |
| Wang J, 2020 (25) |
China | 250/250 | 36.45 ± 12.98 35.12 ± 12.81 |
- | 2 months | Application program (WeChat) | Delivered knowledge on disease and dialysis, provided diet and exercise guidance, and adjusted intervention plans based on nutritional status | Albumin, prealbumin, and transferrin |
| Fan JZ, 2022 (26) | China | 44/45 | 75.65 ± 10.78 75.45 ± 11.32 |
68.78 ± 30.25 69.32 ± 31.17 |
5 months | Application program (WeChat) | Provided nutrition education via WeChat and face-to-face, and developed personalized meal plans | Hemoglobin, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and transferrin; mid arm muscle circumference, triceps skinfold thickness, and BMI. |
| Zhang N, 2022 (18) | China | 79/79 | 67.07 ± 13.28 67.53 ± 12.12 |
36.57 ± 8.96 34.12 ± 8.52 |
3 months | Mobile platform | Nutrition team conducted a nutritional index assessment, precise nutrition and dry weight management, and provided targeted guidance based on a 3-day diet record analysis | Hemoglobin, prealbumin, albumin, phosphorus, potassium; MQSGA; BMI. |
| Zeng T, 2020 (27) | China | 50/50 | 51.10 ± 9.57 53.10 ± 9.56 |
- | 6 months | Application program (WeChat, QQ) | Nutrition management team provided psychological counseling, outcome feedback, meal planning, and personalized guidance | MQSGA, Albumin, transferrin, hemoglobin; mid arm muscle circumference, triceps skinfold thickness. |
| Deng FY, 2019 (28) | China | 61/61 | - | - | 6 months | Application program (WeChat) | The intervention was structured around five phases based on the Timing It Right theory. | Hemoglobin, serum protein, potassium, blood urea nitrogen, and serum creatinine. |
| Zhang JQ, 2024 (29) | China | 50/50 | 69.14 ± 3.11 69.28 ± 3.19 |
90.12 ± 13.44 91.68 ± 14.28 |
3 months | Application program (WeChat) | Conducted family education, provided diet management reports and family peer support, shared experiences, and kept diet diaries via WeChat | Hemoglobin, albumin, prealbumin, and transferrin. |
| Shi LR, 2023 (30) | China | 55/55 | 56.64 ± 9.39 57.38 ± 9.84 |
- | 3 months | Application program (WeChat) | Provided personalized nutrition guidance and regular nutrition knowledge dissemination, and carried out online interactive sharing and plan assessment-adjustment | Hemoglobin, albumin, triceps skinfold thickness. |
| Duan F, 2023 (31) | China | 74/74 | 54.79 ± 5.98 55.34 ± 5.21 |
2.25 ± 0.53 2.27 ± 0.48 |
2 months | Application program (WeChat) | Provided guidance via educational videos and personalized diet-lifestyle plans, and conducted dietary counseling and supervision via WeChat | Albumin, prealbumin; MQSGA |
| Shi SH, 2021 (32) | China | 79/79 | 50.68 ± 11.09 49.24 ± 12.68 |
57.81 ± 31.80 56.37 ± 33.44 |
3 months | Mobile platform | Provided comprehensive personalized dietary guidance and dietary tips, and implemented intervention via educational animation videos, doctor-patient video interaction, and patient experience-sharing sessions | MQSGA, serum albumin, hemoglobin, phosphorus, calcium, potassium, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen. |
| Dong XY, 2022 (33) | China | 74/74 | 53.22 ± 10.07 54.12 ± 9.51 |
56.11 ± 13.08 61.77 ± 18.89 |
6 months | Application program (WeChat) | Conducted comprehensive dietary education: 6–18 videos; monitoring for unhealthy habits; food discussions; patient peer exchange; video Q&A sessions | Hemoglobin, albumin, and prealbumin |
| Pack S, 2021 (19) | South Korea | 37/38 | 52.00 ± 10.01 50.66 ± 9.15 |
- | 8 weeks | Application program | Carried out dietary self-management in 3 phases: introduction, implementation, and maintenance | Phosphorus, potassium, and albumin. |
| Wang LJ, 2024 (34) | China | 110/110 | - | - | 3 months | Application program (WeChat) | Nutrition team conducted education via online consultation groups, needs assessment surveys, and PPT/video popularization, and adjusted diet via a food nutrient APP | Potassium, phosphorus, mid arm muscle circumference, albumin, prealbumin, transferrin, creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen, MQSGA |
| Teong LF, 2022 (43) | Malaysia | 33/33 | 47.5 ± 15.3 49.15 ± 13.63 |
- | 3 months | Application program (phosphate mobile app, MyKidneyDiet-Phosphate Tracker) | Provided dietary guidance via 6 animated educational videos and calculated personalized dietary intake | Phosphorus, calcium |
| Wu LF, 2021 (35) | China | 51/51 | 44.90 ± 10.02 45.43 ± 10.70 |
49.88 ± 23.01 51.27 ± 18.54 |
6 months | Application program (App) | The APP calculated recommended intake and monitored actual consumption, adjusted in a timely manner based on comparison, and provided food database queries | MQSGA, Relative increase in body weight (%), body Weight gain, albumin, hemoglobin, and mid-arm muscle circumference. |
| Thongsunti A, 2024 (41) | Thailand | 40/40 | - | - | 6 months | Application program (LINE application) | Watched 3 dietary education videos and received personalized dietary guidance and supervision | Phosphorus |
| Torabikhah M, 2023 (42) | Iran | 35/35 | 45.2 ± 1.4 46.7 ± 1.5 |
38.4 ± 2.4 40.8 ± 2.4 |
3 months | Application program (Di Care app) | Covered 7 topics via videos: the importance of HD, management of HD complications, diet, fluid intake restriction, physical activity, vascular access care, and medications | Potassium, phosphorus, albumin, ferritin, body weight gain |
| Zhou QQ, 2024 (36) | China | 30/30 | 55.08 ± 10.72 54.58 ± 10.27 |
108.36 ± 26.4 107.4 ± 25.8 |
2 months | Mobile platform | Carried out online consultation, doctor-patient interaction, health education and assessment, and developed precise nutrition and dry weight plans | Prealbumin, phosphorus. |
| Wei DM, 2024 (37) | China | 30/30 | 45.91 ± 7.53 46.72 ± 7.48 |
37.12 ± 10.33 36.98 ± 10.26 |
3 months | Application program (WeChat) | Nutrition team provided dietary guidance via articles/videos, conducted personalized nutrition assessment and counseling, and organized online educational lectures, Q&A, and diet log supervision | MQSGA, calcium and phosphorus |
| Welch JL, 2013 (44) | The United States | 24/20 | 53.0 ± 15.1 47.1 ± 11.5 |
6 weeks | Application program (DIMA) | Recorded food and beverage intake, and provided assessment and feedback based on the entered data to meet the prescribed nutritional intake | Body weight gain | |
| Zhu XB, 2021 (38) | China | 43/43 | 41.2 ± 14.9 40.4 ± 14. 8 |
141.6 ± 54 135.6 ± 55.2 |
6 months | Application program (WeChat) | Conducted one-on-one health education sessions every 3 weeks and developed personalized dietary plans | Albumin, hemoglobin |
| Li HT, 2024 (39) | China | 40/40 | 52.39 ± 6.53 50.14 ± 6.21 |
37.68 ± 5.76 36.64 ± 6.53 |
6 months | Mobile platform | Provided personalized plans and digital dietary education, conducted monitoring and interactive Q&A via the platform, and adjusted plans based on regular re-assessments | Phosphorus, calcium, albumin, and prealbumin |
| Yao DD, 2023 (40) | China | 43/43 | 44.53 ± 4.41 44.38 ± 4.37 |
13.59 ± 3.61 13.38 ± 3.57 |
3 months | Application program (WeChat) | Developed personalized low-phosphorus (<800 mg/day) and high-protein meal plans based on 3-day diet records (considering body fat, disease status, and calcium-phosphorus metabolism), and provided guidance on food selection and portion | Calcium, phosphorus |
Basic information of the included literature.
MQGSA, Modified Quantitative Subjective Global Assessment; BMI, Body Mass Index; HD, hemodialysis; Q&A, Question and Answer; -, no report.
3.3 The results of the risk of bias assessments
In total, 13 studies were assessed as having low risk of bias in randomized sequence generation (18, 25–29, 32, 39–44); 4 studies were rated as high risk due to the use of pseudo-randomization (24, 31, 34, 35); 6 studies, although stating the use of randomization, did not specify the type of randomization method used and were therefore rated as unclear (19, 30, 33, 36–38). Three studies reported allocation concealment and were rated as low risk (26, 32, 41); the remaining 20 studies were rated as unclear (18, 19, 24, 25, 27–31, 33–40, 42–44). Blind outcome assessment is challenging due to the unique nature of nutritional interventions, and 22 studies did not report blind outcome assessment, leading to unclear ratings (18, 19, 24–31, 33–44); one study reported blind outcome assessment, leading to low risk (32). Since the outcome measures in this study are mostly laboratory test results, which are relatively objective, the lack of blinding of outcome assessors has minimal impact on the results, and thus all 23 studies were rated as low risk (18, 19, 24–44). A total of 16 studies had complete outcome data and were rated as low risk (18, 24, 25, 27, 29–31, 33, 36–43); 7 studies reported reasons for dropout but did not describe whether an intention-to-treat analysis was conducted, resulting in an unclear rating (19, 26, 28, 32, 34, 35, 44). In total, 4 studies did not exhibit selective reporting and were rated as low risk (19, 41–43); 19 studies, although reporting both positive and negative results, did not report whether the RCT was registered, leading to an unclear rating (18, 24–40, 44). Three studies had no other biases and were rated as low risk (26, 28, 32); the remaining 20 studies did not report on quality control measures and were rated as unclear (18, 19, 24, 25, 27, 29–31, 33–44). The four studies were evaluated as low quality (24, 31, 34, 35), three studies as high quality (26, 32, 41), and the remaining 16 studies as medium quality (18, 19, 25, 27–30, 33, 36–40, 42–44). The figure of the risk of bias is shown in Supplementary Figure S1, while a summary of the risk of bias is shown in Supplementary Figure S2.
3.4 Meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Main outcome measures
3.4.1.1 MQSGA
Seven studies reported the MQSGA score (18, 27, 31, 32, 34, 35, 37). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect on the MQSGA score (SMD = −1.48, 95% CI: −1.93 to −1.03). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 95%, p < 0.001). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S3.
3.4.2 Biochemical indicators
3.4.2.1 Hemoglobin
A total of 11 studies reported hemoglobin levels (18, 24, 26–30, 32, 33, 35, 38). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect on the hemoglobin (SMD = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.67 to 1.05). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 80%, p < 0.001). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S4.
3.4.2.2 Serum albumin
A total of 18 studies reported serum albumin levels (18, 19, 24–35, 38, 39, 42, 43). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect on albumin (SMD = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.63 to 0.99). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 88%, p < 0.001). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S5.
3.4.2.3 Prealbumin
Seven studies reported prealbumin levels (18, 25, 29, 31, 33, 36, 39). The meta-analysis revealed a significant pooled effect on prealbumin (SMD = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.48 to 0.72). Heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 41%, P < 0.001). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S6.
3.4.2.4 Transferrin
Five studies reported serum transferrin levels (25–27, 29, 34). The meta-analysis showed no significant pooled effect on transferrin (SMD = 0.14, 95% CI: −0.84 to 1.11). Heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 98%, p = 0.78). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S7.
3.4.2.5 Calcium
Seven studies reported serum calcium levels (26, 32, 34, 37, 39, 40, 43). The meta-analysis showed no significant pooled effect on calcium (SMD = −0.04, 95% CI: −0.65 to 0.58). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 94%, p = 0.91). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S8.
3.4.2.6 Phosphorus
Thirteen studies reported serum phosphorus levels (18, 19, 24, 26, 32, 34, 36, 37, 39–43). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect on phosphorus (SMD = −0.71, 95% CI: −0.97 to −0.46). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 90%, p < 0.001). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S9.
3.4.2.7 Potassium
In total, 8 studies reported serum potassium levels (18, 19, 24, 26, 28, 32, 34, 42). The pooled effect size was statistically significant (SMD = − 0.67, 95% CI: −1.19 to −0.15). A high degree of heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 93%, p = 0.01). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S10.
3.4.3 Anthropometric indicators
3.4.3.1 Relative increase in body weight (%)
In total, 2 studies reported the relative increase in body weight (%) (24, 35). The meta-analysis showed a statistically significant effect (SMD = −1.00, 95% CI: −1.72 to −0.28). Heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 83%, p = 0.007). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S11.
3.4.3.2 Body weight gain
In total, 2 studies reported body weight gain (42, 44). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect (SMD = − 0.71, 95% CI: −1.12 to −0.31). Moderate heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 44%, p < 0.001). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S12.
3.4.3.3 BMI
In total, 2 studies reported body mass index (BMI) (18, 26). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect (SMD = 0.31, 95% CI: 0.06 to 0.56). Moderate heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 37%, p = 0.02). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S13.
3.4.3.4 Mid-arm muscle circumference
In total, 4 studies reported mid-arm muscle circumference (26, 27, 34, 35). The meta-analysis showed a significant effect (SMD = 1.92, 95% CI: 0.46 to 3.38). High heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 98%, p = 0.01). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S14.
3.4.3.5 Triceps skinfold thickness
In total, 2 studies reported triceps skinfold thickness (26, 27). The meta-analysis showed a significant effect (SMD = 1.16, 95% CI: 0.13 to 2.18). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 91%, p = 0.03). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S15.
3.4.4 Secondary outcome indicators
3.4.4.1 Urea nitrogen
In total, 3 studies reported blood urea nitrogen levels (26, 28, 32). The meta-analysis showed a significant effect (SMD = −0.27, 95% CI: −0.48 to −0.06). No heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 0%, p = 0.01). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S16.
3.4.4.2 Serum creatinine
In total, 3 studies reported serum creatinine levels (26, 28, 32). The meta-analysis showed a significant pooled effect (SMD = −0.80, 95% CI: −1.23 to −0.38). Considerable heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 74%, p < 0.01). The forest diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure S17.
3.5 Publication bias
For the outcomes with ≥ 10 included studies, funnel plots were used to assess publication bias for hemoglobin, albumin, and phosphorus. The funnel plots for hemoglobin and albumin showed slight asymmetry, indicating possible publication bias. This might be due to small sample sizes, low study quality, design differences, or reporting standardization in some included studies. The funnel plot for phosphorus was largely symmetric, suggesting minimal publication bias. The funnel plots are shown in Supplementary Figures S18–S20.
3.6 Sensitivity analyses
Sensitivity analyses were performed on outcome indicators with ≥ 3 studies by sequentially removing individual studies. For transferrin, after excluding a study by Wang LJ (34), the pooled effect size became statistically significant (p < 0.001). For mid-arm muscle circumference, excluding a study by Zeng T made the result non-significant (p = 0.08) (27). Similarly, for blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, removing studies by Fan JZ (26) and Shi SH (32), respectively, also led to non-significant results (p = 0.09 and p = 0.05). These four indicators showed unstable results. In contrast, results for the other indicators remained stable after sensitivity analysis. The differential sensitivity analyses are presented in Table 2.
Table 2
| Variable | Trials | Participants | Total | SMD (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transferrin | 5 | 504 | 1,009 | 0.14 (−0.84, 1.11) | 0.78 |
| After removing Wang LJ, 2024 (34) | 4 | 394 | 789 | 0.58 (0.39, 0.78) | <0.001 |
| Serum creatinine | 3 | 182 | 363 | −0.80 (−1.23, −0.38) | <0.001 |
| After removing Shi SH, 2021 (32) | 2 | 103 | 206 | −0.78 (−1.15, −0.00) | 0.05 |
| Urea nitrogen | 3 | 182 | 363 | −0.27 (−0.48, −0.06) | 0.01 |
| After removing Fan JZ, 2022 (26) | 2 | 138 | 274 | −0.21 (−0.44, 0.03) | 0.09 |
| Mid-arm muscle circumference | 4 | 255 | 511 | 1.92 (0.46, 3.38) | 0.01 |
| After removing Zeng T, 2020 (27) | 3 | 205 | 411 | 1.55 (−0.20, 3.29) | 0.08 |
Sensitivity analysis of the variable results with differences.
In this table, “Participants” refers to the number of participants in the intervention group, and “Total” refers to the total number of participants (including both intervention and control groups).
3.7 Subgroup analysis
3.7.1 MQSGA
Intervention duration: For ≥ 6 months, 202 patients, SMD = −3.06 (95% CI: −3.54 to −2.57, p < 0.001) (27, 35); for < 6 months, 743 patients, SMD = −0.84 (95% CI: −1.18 to −0.50, p < 0.001) (18, 31, 32, 34, 37). Digital health technology types: application program-based nutrition intervention involving 630 patients, SMD = -1.92 (95% CI: -2.81 to -1.03, p < 0.001); mobile platform-based nutrition intervention in 315 patients, SMD = -0.46 (95% CI: -0.68 to -0.24, p < 0.001) (18, 32). The subgroup analysis is shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S3.
Table 3
| Variable | Trials | Participants | Total | SMD (95% CI) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQSGA | |||||
| ≥ 6 months | 2 | 101 | 202 | -3.06 (-3.54, -2.57) | < 0.001 |
| <6 months | 5 | 372 | 743 | -0.84 (-1.18, -0.50) | < 0.001 |
| Application program | 5 | 315 | 630 | -1.92 (-2.81, -1.03) | < 0.001 |
| Mobile platform | 2 | 158 | 315 | -0.46 (-0.68, -0.24) | < 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin | |||||
| ≥ 6 months | 5 | 240 | 479 | 1.02 (0.53, 1.51) | < 0.001 |
| <6 months | 6 | 340 | 678 | 0.73 (0.41, 1.05) | < 0.001 |
| Application program | 9 | 422 | 842 | 0.99 (0.69, 1.28) | < 0.001 |
| Mobile platform | 2 | 158 | 315 | 0.36 (0.13, 0.58) | 0.002 |
| Albumin | |||||
| ≥ 6 months | 6 | 280 | 559 | 0.94 (0.51, 1.38) | < 0.001 |
| <6 months | 12 | 879 | 1757 | 0.74 (0.41, 1.08) | < 0.001 |
| Application program | 15 | 978 | 1957 | 0.87 (0.56, 1.18) | < 0.001 |
| Mobile platform | 3 | 198 | 395 | 0.51 (0.23, 0.79) | < 0.001 |
| Calcium | |||||
| Application program | 5 | 260 | 521 | 0.22 (-0.47, 0.90) | 0.54 |
| Mobile platform | 2 | 119 | 237 | -0.65 (-1.44, 0.14) | 0.11 |
| Phosphorus | |||||
| ≥6 months | 2 | 80 | 160 | -1.12 (-2.62, 0.39) | 0.15 |
| <6 months | 11 | 570 | 1141 | -0.65 (-1.03, -0.26) | 0.001 |
| Application program | 9 | 422 | 846 | -0.76 (-1.17, -0.35) | < 0.001 |
| Mobile platform | 4 | 228 | 455 | -0.62 (-1.38, 0.14) | 0.11 |
| Potassium | |||||
| Application program | 6 | 335 | 671 | -0.78 (-1.47, -0.09) | 0.03 |
| Mobile platform | 2 | 158 | 315 | -0.34 (-0.56, -0.11) | 0.003 |
The results of subgroup analysis of each outcome indicator.
In this table, “Participants” refers to the number of participants in the intervention group, and “Total” refers to the total number of participants (including both intervention and control groups).
3.7.2 Hemoglobin
Intervention duration: For ≥ 6 months of intervention involving 479 patients, the SMD = 1.02 (95% CI: 0.53 to 1.51, p < 0.001) (27, 28, 33, 35, 38); For < 6 months of intervention involving 678 patients, the SMD = 0.73 (95% CI: 0.41 to 1.05, p < 0.001) (18, 24, 26, 29, 30, 32). Digital health technology types: For application program-based nutritional interventions across 842 patients, the SMD = 0.99 (95% CI: 0.69 to 1.28, p < 0.001) (24, 26–30, 33, 35, 38); for mobile platform-based nutritional interventions across 315 patients, the SMD = 0.36 (95% CI: 0.13 to 0.58, p = 0.002) (18, 32). The subgroup analysis is shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S4.
3.7.3 Albumin
Intervention duration: For ≥ 6 months, 559 patients, SMD = 0.94 (95% CI: 0.51 to 1.38), p < 0.001 (27, 28, 33, 35, 38, 39); for < 6 months, 1757 patients, SMD = 0.74 (95% CI: 0.41 to 1.08), p < 0.001 (18, 19, 24–26, 29–32, 34, 42, 43). Digital health technology types: application program-based nutrition intervention, 1957 patients, SMD = 0.87 (95% CI: 0.56 to 1.18), p < 0.001; mobile platform-based nutrition intervention, 395 patients, SMD = 0.51 (95% CI: 0.23 to 0.79), p < 0.001 (18, 32, 39). The subgroup analysis is shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S5.
3.7.4 Calcium
Digital health technology types: application program-based nutrition intervention, 521 patients, SMD = 0.22 (95% CI: −0.47 to 0.90), p = 0.54 (26, 34, 37, 40, 43); mobile platform-based nutrition intervention, 237 patients, SMD = −0.65 (95% CI: −1.44 to 0.14), p = 0.11 (32, 39). The subgroup analysis is shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S8.
3.7.5 Phosphorus
Intervention duration: For ≥ 6 months, 160 patients, SMD = -1.12 (95% CI: −2.62 to 0.39), p = 0.15; for < 6 months, 1141 patients, SMD = -0.65 (95% CI: −1.03 to −0.26), p = 0.001 (18, 19, 24, 26, 32, 34, 36, 37, 40, 42, 43). Digital health technology types: application program-based nutrition intervention, 846 patients, SMD = −0.76 (95% CI: −1.17 to −0.35), p < 0.001 (19, 24, 26, 34, 37, 40–43); mobile platform-based nutrition intervention, 455 patients, SMD = −0.62 (95% CI: −1.38 to 0.14) (18, 32, 36, 39), p = 0.11. The subgroup analysis is shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S9.
3.7.6 Potassium
Digital health technology types: application program-based nutrition intervention, 671 patients, SMD = −0.78 (95% CI: −1.47 to −0.09), p = 0.03 (19, 24, 26, 28, 34, 42); mobile platform-based nutrition intervention, 315 patients, SMD = −0.34 (95% CI: −0.56 to −0.11), p = 0.003 (18, 32). The subgroup analysis is shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S10.
For other outcome indicators, subgroup analysis could not be conducted due to the small number of included studies.
4 Discussion
A total of 23 studies were included, of which four were low quality, three high quality, and 16 moderate quality. Overall, quality was acceptable but not high. The overall meta-analysis indicated that digital health technology-based nutrition interventions had no significant effects on transferrin and calcium but had significant effects on hemoglobin, albumin, prealbumin, phosphorus, potassium, MQSGA score, relative increase in body weight (%), weight gain, BMI, mid-arm muscle circumference, triceps skinfold thickness, blood urea nitrogen, and serum creatinine. This suggests these interventions may improve nutrition in hemodialysis patients. To further explore potential heterogeneity in the results, subgroup analyses were conducted on six outcomes: hemoglobin, albumin, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and MQSGA. For phosphorus, subgroup analyses found no significant difference in the ≥ 6-month intervention subgroup and no significant effect of mobile platform-based interventions, inconsistent with the overall meta-analysis. However, regarding this result, since only 2 studies were included in the subgroup analysis, the strength of evidence is unstable. Thus, this result should be interpreted with caution, and more follow-up studies with a duration of ≥ 6 months should be conducted in the future. Other subgroup analyses were generally in line with the overall results. Additionally, sensitivity analyses showed unstable results for transferrin, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and mid-arm muscle circumference. Caution is needed in interpreting the findings. More high-quality studies are required to validate these results.
Turning to the specific methods employed, the included studies primarily employed the following approaches: 1. Application programs: Mobile applications (Apps): Customized features such as dietary logging, nutrient calculation, and real-time feedback were used to deliver personalized guidance. For instance, Teong et al. (43) developed a hyperphosphatemia management app integrated with a food database and phosphorus intake tracker, enabling patients to generate daily phosphorus reports and receive adjustment recommendations. Similarly, Wu et al. (35) combined IoT-enabled smart water bottles and scales to monitor fluid and nutrient intake in real time, using algorithms to compare actual values with recommended targets and dynamically optimize dietary plans. Social media platforms (e.g., WeChat): These were utilized for health education, interactive consultations, and peer support. For example, Kong et al. (24) disseminated low-protein diet educational videos via WeChat and established patient groups for recipe sharing and management experience exchanges. Additionally, Wang et al. (34) employed a WeChat mini-program (“Food Nutrient Handbook”) to provide daily meal recommendations and dynamically assess patient needs through online questionnaires. 2. Mobile platforms: Remote monitoring and online education: Shi et al. (32) implemented an “Internet Plus” nutrition education model, uploading animated tutorials, hosting virtual classrooms, and facilitating video-based Q&A sessions between clinicians and patients, to identify nutritional gaps. Zhou et al. (36), meanwhile, made real-time adjustments to patients’ dry weight and dietary structures through online consultations and precision nutrition planning. Furthermore, Duan et al. (31) combined animated video education, face-to-face counseling, and WeChat-based supervision to enhance dietary adherence through phased interventions, while Li et al. (39) delivered personalized nutrition plans via web platforms and monitored patient activity levels, achieving diet management.
To understand how these interventions exert their effects, it is critical to examine key nutritional indicators. Biochemical indicators like hemoglobin, prealbumin, albumin, transferrin, calcium, potassium, and phosphorus are crucial for nutrition assessment in hemodialysis patients. The MQSGA is also a validated clinical nutrition evaluation tool (12, 45, 46). Overall, meta-analysis showed digital health technology-based nutrition interventions improved MQSGA, hemoglobin, albumin, prealbumin, phosphorus, and potassium but not transferrin and calcium. Specifically, for hemoglobin, while hemoglobin levels in hemodialysis patients are primarily influenced by erythropoietin (Epo) dosing, inflammatory status, and access-related blood loss, digital health interventions may provide supportive benefits. By offering personalized dietary guidance and promoting adherence to prescribed treatments, including medication and supplemental iron, digital tools may help optimize conditions for hemoglobin synthesis. It is important to note that intravenous iron is commonly used to manage iron deficiency in this population when indicated, and vitamin B12 deficiency is routinely screened for and is relatively uncommon. Thus, the role of digital interventions may lie mainly in enhancing overall treatment adherence and integrating nutritional support with medical management (47). Albumin and prealbumin: With the help of digital health technology, patients can more accurately control protein intake, avoid malnutrition caused by excessive restriction, and adjust dietary structure in time to ensure a sufficient high-quality protein supply, which is conducive to maintaining and improving serum albumin and prealbumin levels. Moreover, diet education helps patients understand protein metabolism, encouraging better adherence to diet plans. For phosphorus and potassium: Digital health technology monitors intake in real time and promptly reminds patients to adjust their diet within set safe ranges (48). For example, when the intake of phosphorus is close to the upper limit, the patient is reminded to reduce the intake of high-phosphorus foods, and at the same time, the patient is recommended to replace foods with low phosphorus and rich in other nutrients, so as to maintain the levels of phosphorus and potassium in a relatively stable range and avoid complications caused by abnormal phosphorus and potassium metabolism. However, transferrin is influenced by factors like inflammation, which is common in hemodialysis patients, potentially limiting improvement (49, 50). Meanwhile, calcium levels are regulated by complex mechanisms like PTH, vitamin D, and mineral metabolism, which may not be directly affected by nutritional interventions (51). Notably, sensitivity analysis showed unstable results for transferrin, which became significant after excluding a study by Wang LJ (34), indicating caution in interpreting results. More high-quality studies are needed. Subgroup analysis on phosphorus also showed no significant difference in the ≥ 6 months intervention subgroup or in mobile-platform-based interventions, inconsistent with the overall meta-analysis. Possible reasons include small sample sizes in subgroup analyses and reduced intervention effects due to declining patient compliance or adapted dietary habits over long-term interventions. Thus, future research should address compliance issues in long-term interventions, design 1- to 3-year follow-up studies, and conduct more large-sample, multicenter studies.
Beyond biochemical markers, anthropometric indicators provide complementary insights into nutritional status. In the context of anthropometric indicators, BMI is considered an independent predictor of mortality in MHD patients (52). Skinfold thickness measurement can be used to assess energy stored in the body in the form of fat, while mid-arm muscle circumference can reflect the retention of muscle protein (53). All of these are commonly used nutritional assessment indicators for hemodialysis patients. Nutrition interventions based on digital health technology can improve five outcome indicators during hemodialysis, namely the relative increase in body weight (%), weight gain, body mass index, mid-arm muscle circumference, and triceps skinfold thickness. Among these, for weight-related indicators, digital health technology can develop a personalized calorie intake plan for patients, combined with exercise guidance, to help patients control their body weight within a reasonable range. Regular weight monitoring and reminder functions enable patients to understand weight changes in a timely manner, adjust their diet and exercise habits, and thus effectively control weight gain. For BMI: By comprehensively considering the height, weight, and other information of patients, digital health technology can provide targeted diet and exercise advice to help patients maintain a healthy weight and body fat ratio, thereby improving BMI. For mid-arm muscle circumference and skinfold thickness: With the nutrition education function of digital health technology, patients can learn how to increase muscle protein intake through a reasonable diet, combined with appropriate resistance exercise, which can help increase muscle mass and improve mid-arm muscle circumference (54). At the same time, the precise control of fat intake can also help to regulate the distribution and thickness of subcutaneous fat and improve the skinfold thickness. However, for the outcome indicator of mid-arm muscle circumference, only four studies were included in the sensitivity analysis. The limited number of included studies resulted in a p ≥ 0.05, indicating poor stability of the results. Therefore, the study findings should be interpreted with caution. Future research should focus on conducting more high-quality studies to further explore this area.
For the secondary outcome of serum urea nitrogen levels, changes can reflect both the clearance efficiency of hemodialysis and the nutritional status of patients. In hemodialysis patients, the loss of renal function and decreased glomerular filtration rate, along with a chronic state of low-grade inflammation, can lead to elevated serum urea nitrogen levels. Serum creatinine is an important indicator of renal function, and in hemodialysis patients with compromised renal function, serum creatinine levels are often elevated. Specifically, for urea nitrogen, nutritional intervention reduces blood urea nitrogen production by improving the nutritional status of patients, increasing muscle protein synthesis, and reducing muscle breakdown (55). In addition, good nutritional support can enhance the patient’s immunity and overall body function, reduce the chronic inflammatory state, and also help to reduce urea nitrogen levels. Regarding serum creatinine, it is important to emphasize that serum creatinine levels are influenced by both muscle mass and dialysis clearance efficiency. Rational nutritional intake aims to improve the patient’s muscle mass and function. The reduction in serum creatinine observed in this study may be attributed primarily to the following mechanisms: diet management assisted by digital health technology optimizes fluid control and treatment compliance, significantly improving dialysis efficiency and enhancing creatinine removal; concurrently, nutritional support helps reduce pathological muscle breakdown, potentially moderating creatinine generation. Thus, the net effect is manifested as a decrease in serum creatinine levels (56). To further clarify the specific pathways by which DHT improves dialysis efficiency, its mechanisms can be broken down into three concrete aspects: (1) Real-time monitoring of nutritional intake (e.g., protein, fluids, potassium, and phosphorus) enables personalized dietary adjustments that prevent excessive inter-dialytic weight gain and solute accumulation, thus reducing the osmotic and volumetric burden during dialysis (57); (2) Medication and treatment reminders improve adherence to phosphate binders, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and dialysis sessions themselves, supporting more stable metabolic conditions (58); (3) Integration of serial biomarker trends (e.g., pre- and post-dialysis creatinine and urea reduction ratio) provides clinicians with actionable insights to adjust dialysis prescriptions, such as session duration, blood flow rate, or dialysate composition, enabling more precise and efficient solute clearance. It should be noted that serum creatinine is positively correlated with muscle mass (5). In healthy individuals or those with stable renal function, creatinine levels should correspond to muscle mass; low levels may indicate insufficient muscle tissue, while high levels may suggest impaired renal function (59). Therefore, the clinical goal is to maintain creatinine within a range that corresponds to adequate muscle mass and nutritional status, rather than simply reducing it. In this study, the overall meta-analysis results for serum urea nitrogen levels showed that nutrition interventions based on digital health technology can reduce both serum urea nitrogen and creatinine levels. However, the sensitivity analysis of these two outcomes included only three RCTs each. After sequentially excluding every one of these RCTs, the limited number of included studies resulted in poor stability of the results and no statistical significance. Therefore, more high-quality studies are still needed in the future to further validate these findings.
Notably, the core advantages of these digital health interventions lie in their dynamic adaptability, personalization, and accessibility: App-based algorithms enable real-time data analysis and instant feedback, social media platforms foster clinician-patient communication and behavioral monitoring, and remote technologies transcend spatiotemporal limitations of traditional care. However, their efficacy and widespread adoption are constrained by multiple practical and resource-related challenges. First, disparities in digital access and the complexity of digital solutions pose significant barriers. Since digital interventions rely on internet connectivity and smart devices, some patients, particularly those in resource-limited settings, may face obstacles in accessing such tools (60, 61). Additionally, developing specialized software or securing expert backend support demands substantial resources, complicating implementation (62, 63). Addressing these requires expanding digital infrastructure to ensure equitable access (64) and collaborating with information technology experts to design user-friendly applications with reliable systems, thereby minimizing technical barriers (65). Second, healthcare workforce constraints and workflow disruptions hinder adoption. Insufficient staff struggle to manage the extra workload introduced by digital interventions, such as data collection and follow-up (66, 67). Modifying workloads where feasible can help reduce disruptions and streamline integration. Third, broader economic, regulatory, and sociocultural factors impact viability. Excessively high costs for intervention groups (68), conflicts with local laws (65), and mismatches with cultural contexts (69) all impede uptake. Economic evaluations (e.g., cost–benefit analyses) can demonstrate long-term value, while adapting interventions to align with legal requirements and cultural norms is critical for acceptance. Looking ahead, future research should further leverage emerging technologies like AI-driven personalized recommendations and wearable biosensors, while exploring hybrid methodologies (e.g., gamification, family involvement) to enhance patient engagement. Prioritizing cultural adaptability, such as simplified interfaces for elderly users or multilingual support, will also be key to improving global applicability, alongside addressing the aforementioned barriers to ensure effective and equitable implementation.
5 Conclusion
The meta-analysis showed that digital health technology-based nutrition interventions can improve 13 indicators in hemodialysis patients: hemoglobin, albumin, prealbumin, phosphorus, potassium, MQSGA score, relative increase in body weight (%), weight gain, BMI, mid-arm muscle circumference, triceps skinfold thickness, blood urea nitrogen, and serum creatinine. However, no significant effects were found for transferrin and calcium. Due to the limited number of studies included for some outcomes and unstable results from sensitivity analyses and subgroup analyses, these findings should be interpreted with caution. Future research should focus on expanding the applications of digital health technologies, determining the optimal intervention methods, frequency, and duration, and conducting more large-scale, multicenter, high-quality randomized controlled trials to identify the best intervention protocols.
5.1 Limitations
(1) Due to the researchers’ language limitations, only Chinese and English studies were included. Moreover, most of the included studies were conducted in China, which indicates a geographical bias. Thus, the results of this study may have regional characteristics, and differences across regions need to be considered when generalizing the conclusions. (2) Among the 23 included studies, 4 were rated as low-quality, 3 as high-quality, and 16 as moderate-quality. The overall quality of the included studies was suboptimal, which might affect the stability of the results. (3) The studies were conducted in six countries, and differences in development, economy, and nursing environments may have influenced the findings. (4) Moreover, due to the limited number of included studies, subgroup analyses based on age and dialysis duration were not feasible. (5) Most included studies failed to adequately address or adjust for key baseline confounders (e.g., diabetes status and inflammatory markers), which significantly influence nutritional outcomes. This omission introduces a potential for confounding bias, meaning the observed effects may not be solely attributable to the digital interventions. (6) The analysis of some specific outcome measures may result in unstable estimates due to the small number of included studies.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
KZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. RW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. CN: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. It should be highlighted that AI tools such as ChatGPT and Grammarly were used in this study. Their primary function was to assist with text translation, improve clarity, and correct grammar. These tools were utilized solely to enhance the precision and grammatical accuracy of the text, not to create content.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1681161/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Kovesdy CP . Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int Suppl. (2022) 12:7–11. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2021.11.003
2.
Ke C Liang J Liu M Liu S Wang C . Burden of chronic kidney disease and its risk-attributable burden in 137 low-and middle-income countries, 1990-2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Nephrol. (2022) 23:17. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02597-3
3.
Ghanem S Hossri S Fuca N Granina E Saouma S Forte F . Patient-nephrologist prognostic awareness and discordance in end stage renal disease on renal replacement therapy. Int Urol Nephrol. (2020) 52:765–73. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02420-2
4.
Fidan C Ağırbaş İ . The effect of renal replacement therapy on health-related quality of life in end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis. Clin Exp Nephrol. (2023) 27:829–46. doi: 10.1007/s10157-023-02377-3
5.
National Kidney Foundation . KDOQI clinical practice guideline for hemodialysis adequacy: 2015 update. Am J Kidney Dis. (2015) 66:884–930. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.07.015
6.
Pecoits-Filho R Okpechi IG Donner JA Harris DCH Aljubori HM Bello AK et al . Capturing and monitoring global differences in untreated and treated end-stage kidney disease, kidney replacement therapy modality, and outcomes. Kidney Int Suppl. (2020) 10:e3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2019.11.001
7.
Eckardt KU Coresh J Devuyst O Johnson RJ Köttgen A Levey AS et al . Evolving importance of kidney disease: from subspecialty to global health burden. Lancet. (2013) 382:158–69. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60439-0
8.
Chen XM . (2025) Chinese mainland latest Dialysis data. Available online at: https://www.sohu.com/a/798151047_121948383 (Accessed July 9, 2025).
9.
Yao W . Construction of Hypoproteinemia risk prediction model for maintenance hemodialysis patients based on machine learning. Changchun: Ji Lin university (2023).
10.
Zhang J Wang HP Xun LL Zhang YY . Analysis on the risk factors of malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in elderly hemodialysis patients. Chin Evid Based Nurs. (2025) 11:1366–72.
11.
Carrero JJ Thomas F Nagy K Arogundade F Avesani CM Chan M et al . Global prevalence of protein-energy wasting in kidney disease: a Meta-analysis of contemporary observational studies from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J Ren Nutr. (2018) 28:380–92. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.08.006
12.
The Expert Collaboration Group on Nutrition Therapy Guidelines of the Kidney Disease Professional Committee of the China Association of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, and the Chinese Society of Nephrology, Chinese Medical Doctor Association . Clinical practice guideline for nutrition therapy in chronic kidney disease in China (2021 edition). Nation Med J China. (2021) 101:539–59. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20201211-03338
13.
Sahathevan S Khor BH Ng HM Abdul Gafor AH Mat Daud ZA Mafra D et al . Understanding development of malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: a narrative review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3147. doi: 10.3390/nu12103147
14.
Rotondi S Tartaglione L Pasquali M Ceravolo MJ Mitterhofer AP Noce A et al . Association between cognitive impairment and malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: two sides of the same coin. Nutrients. (2023) 15:813. doi: 10.3390/nu15040813
15.
Jin WY Zhang Y Feng CY Su CY . Influencing factors of hemodialysis patients'dietary behavior adherence: a qualitative study. Chinese journal of. Gen Pract. (2024) 22:508–12. doi: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003437
16.
Ikizler TA Burrowes JD Byham-Gray LD Campbell KL Carrero J-J Chan W et al . KDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in CKD: 2020 update. Am J Kidney Dis. (2020) 76:S1–S107. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006
17.
Xue P Bai AY Jiang Y Qiao YL . WHO global strategy on digital health and its implications to China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2022) 56:218–21. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20210616-00589
18.
Zhang N Lu XQ Ji YH Qiao YL . Application of precise management based on mobile medical model in elderly hemodialysis patients. Chin J Modern Nurs. (2022) 28:1792–6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115682-20210905-04020
19.
Pack S Lee J . Randomised controlled trial of a smartphone application-based dietary self-management program on haemodialysis patients. J Clin Nurs. (2021) 30:840–8. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15627
20.
Li JQ Yang Q Yuan DL Huang JJ Chang Q Nie JW et al . Effectiveness and safety of Roxadustat for renal Anemia in Dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: a Meta-analysis. Chin General Pract. (2023) 26:704–10. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0581
21.
Page MJ McKenzie JE Bossuyt PM Boutron I Hoffmann TC Mulrow CD et al . The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Br Med J. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
22.
Higgins JPT Green S .(eds.). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.1.0. Cochrane Collaboration website. (2011) Available at: http://training.cochrane.org/handbook (Accessed July 9, 2025).
23.
Zhao JG Zeng XT Wang J Liu L . Association between calcium or vitamin D supplementation and fracture incidence in community-dwelling older adults: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. (2017) 318:2466–82. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.19344
24.
Kong YX Chang XY . The application of wechat platform in dietary education for young and middle-aged hemodialysis patients. Henan Med Res. (2017) 26:2070–1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2017.11.106
25.
Wang J Zheng Y . Impact of WeChat platform continuous nursing intervention on nutritional status and nursing service satisfaction degree of uremic patients with maintenance hemodialysis. Clin Med Eng. (2020) 27:1661–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4659.2020.12.1661
26.
Fan JZ Cao XD Zhang Y Zhou W Du AY . Influence of family nutrition management system on nutritional status of elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients. Chin Evid Based Nurs. (2022) 8:3186–91. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.2095-8668.2022.23.012
27.
Zeng T Zhang N Yang LH Ding WJ . Influence of personalized nutrition management based on network plat-form on the patients with hemodialysis malnutrition. China Med Herald. (2020) 17:160–4. doi: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2020.02.040
28.
Deng FY . Construction and application of "internet+" transitional nursing intervention program for hemodialysispatients based on the opportunity theory. Hengyang: Nan Hua University (2019).
29.
Zhang JQ . Effects of dietary management based on family participation combined with dietary diary on dietary management behavior and nutritional status of elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients. Reflexol Rehabil Med. (2024) 5:155–8.
30.
Shi LR . Research on the impact of internet-based nutritional intervention on the frailty degree and physiological indicators of hemodialysis patients. Womens Health. (2023) 40:267–8.
31.
Duan F . The influence of animation education combined with feedback diet on the compliance of hemodialysis for renal failure. Guangming J Chin Med. (2023) 38:3703–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2023.19.005
32.
Shi SH Wang PL Zou QF You LJ Li YW Lin QH et al . Application of “internet +” nutrition education on patients with maintenance hemodialysis. Chin J Nurs. (2021) 56:33–9. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2021.01.005
33.
Dong XY Li W Ma XM Hu JJ Yan YL Ma XQ . The application of "internet +" nutrition education in regular outpatient hemodialysis patients. Health Vocat Educ. (2022) 40:139–41.
34.
Wang L Hu Y . Enhancing nutritional status and quality of life in hemodialysis patients: the impact of internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy. Curr Topics Nutraceut Res. (2024) 22:538–43. doi: 10.37290/ctnr2641-452X.22:538-543
35.
Wu LF Ye Y Li SM Zheng ZJ Chen LP . Effect of water and nutrition management system based on internet of things (IoT) technology in hemodialysis patients. J Nurs Sci. (2021) 36:26–8. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2021.20.026
36.
Zhou QQ . The improvement of precision management under Mobile healthcare mode combined with chain-like family care model to the nutritional status, self-care ability and Hope level of hemodialysis patients. Chin Pract J Rural Doct. (2024) 31:50–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7185.2024.10.016
37.
Wei DM Tan NN Wei B . Study of “internet +” nutrition education in maintenance hemodialysis patients. International journal of. Clin Res. (2024) 8:256. doi: 10.12208/j.ijcr.20240256
38.
Zhu XB Chang KL . Research on the impact of wechat platform intervention on the psychological and nutritional status of maintenance hemodialysis patients. People Milit Surg. (2021) 64:1271–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9736.2021.12.031
39.
Li HT Zhang LJ Xu H . Effect of individualized nutrition management intervention based on web platforms on the nutritional status and calcium-phosphate metabolism disorder in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. J Harbin Med Univ. (2024) 58:557–62. doi: 10.20010/j.issn.1000-1905.2024.05.0557
40.
Yan DD Niu Y . Effects of patient mutual help group based on WeChat platform combined with individualized diet structure management on fear of disease progression, calcium and phosphorus metabolism and dietary behavior in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Clin Res Pract. (2023) 8:171–4. doi: 10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202328043
41.
Thongsunti A Silpakit C Rattananupong T Kittanamongkolchai W Sumethpimolchai W Lohsoonthorn V . Effect of a transtheoretical model-based intervention and motivational interviewing on hyperphosphatemia management via telehealth (TMT program) among hemodialysis patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Public Health. (2024) 12:1361778. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1361778
42.
Torabikhah M Farsi Z Sajadi SA . Comparing the effects of mHealth app use and face-to-face training on the clinical and laboratory parameters of dietary and fluid intake adherence in hemodialysis patients: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Nephrol. (2023) 24:194. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03246-7
43.
Teong LF Khor BH Ng HM Sahathevan S Purba KR Narayanan SS et al . Effectiveness of a nutritional Mobile application for Management of Hyperphosphatemia in patients on hemodialysis: a multicenter open-label randomized clinical trial. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:961. doi: 10.3390/jpm12060961
44.
Welch JL Astroth KS Perkins SM Johnson CS Connelly K Siek KA et al . Using a mobile application to self-monitor diet and fluid intake among adults receiving hemodialysis. Res Nurs Health. (2013) 36:284–98. doi: 10.1002/nur.21539
45.
Chen WX Hu XY Li HR Xing L Wan LY Tang J et al . Comparison of the evaluation methods of nutritional status in patients with maintenance hemodialysis. Guangdong Med J. (2011) 32:3057–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2011.23.014
46.
Ye L Wang J Wei L Li CY Shen Y . Application and nursing countermeasure of modified SGA in maintenance hemodialysis patients nutritional assessment. Milit Nurs. (2014) 19:71–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9993.2014.19.024
47.
Sharma S Smitha MV Balakrishnan D . Telephonic intervention to combat non-adherence to oral iron-folic acid supplementation in pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. (2023) 20:100235. doi: 10.1016/j.eurox.2023.100235
48.
Chiu IM Wu PJ Zhang H Hughes JW Rogers AJ Jalilian L et al . Serum potassium monitoring using AI-enabled smartwatch electrocardiograms. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. (2024) 10:2644–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2024.07.023
49.
Zhong GZ Hu PF . The correlation of serum hepcidin and transferrin receptor contents with iron deficiency and micro-inflammatory response in patients with hemodialysis. J Hainan Med Univ. (2018) 24:30–3. doi: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20171211.005
50.
Duan XC Geng XM Zhao J Zhao WX Sun N Zhao XL et al . Research progress on exercise intervention of micro-inflammatory state in maintenance hemodialysis patients. J Nurs Sci. (2024) 39:110–4. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2024.16.110
51.
Loupy A Ramakrishnan SK Wootla B Chambrey R de la Faille R Bourgeois S et al . PTH-independent regulation of blood calcium concentration by the calcium-sensing receptor. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:3355–67. doi: 10.1172/JCI57407
52.
Leavey SF Strawderman RL Jones CA Port FK Held PJ . Simple nutritional indicators as independent predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. (1998) 31:997–1006. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.1998.v31.pm9631845
53.
Frisancho AR . New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr. (1981) 34:2540–5. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.11.2540
54.
Dorhout BG Wezenbeek N de Groot LCPGM Grootswagers P . Web-based exercise and nutrition intervention to improve leg muscle strength and physical functioning in older adults: pre-Post pilot study. JMIR Form Res. (2025) 9:e54392. doi: 10.2196/54392
55.
Hamidianshirazi M Shafiee M Ekramzadeh M Torabi Jahromi M Nikaein F . Diet therapy along with nutrition education can improve renal function in people with stages 3-4 chronic kidney disease who do not have diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr. (2023) 129:1877–87. doi: 10.1017/S0007114522002094
56.
Patel SS Molnar MZ Tayek JA Ix JH Noori N Benner D et al . Serum creatinine as a marker of muscle mass in chronic kidney disease: results of a cross-sectional study and review of literature. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2013) 4:19–29. doi: 10.1007/s13539-012-0079-1
57.
Wu L Ma W Zhang H Yang T Sun M Yang Z et al . Effect of intensive water-salt diet nursing intervention on blood pressure and volume load in patients with chronic renal failure. Ren Fail. (2025) 47:2474854. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2474854
58.
Kim SK Park SY Hwang HR Moon SH Park JW . Effectiveness of Mobile health intervention in medication adherence: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Med Syst. (2025) 49:13. doi: 10.1007/s10916-024-02135-2
59.
Groothof D Shehab NBN Erler NS Post A Kremer D Polinder-Bos HA et al . Creatinine, cystatin C, muscle mass, and mortality: findings from a primary and replication population-based cohort. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:1528–38. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13511
60.
Turoń-Skrzypińska A Tomska N Mosiejczuk H Rył A Szylińska A Marchelek-Myśliwiec M et al . Impact of virtual reality exercises on anxiety and depression in hemodialysis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:12435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39709-y
61.
Jakubowski KP Jhamb M Yabes J Gujral S Oberlin LE Bender FH et al . Technology-assisted cognitive-behavioral therapy intervention for end-stage renal disease. Transl Behav Med. (2020) 10:657–63. doi: 10.1093/tbm/ibz077
62.
Dawson J Tong A Matus Gonzalez A Campbell KL Craig JC Lee VW . Patients' experiences and perspectives of a mobile phone text messaging intervention to improve dietary behaviours in haemodialysis. Nutr Diet. (2021) 78:516–23. doi: 10.1111/1747-0080.12667
63.
Fakih El Khoury C Crutzen R Schols JMGA Halfens RJG Karavetian MA . A dietary Mobile app for patients undergoing hemodialysis: prospective pilot study to improve dietary intakes. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e17817. doi: 10.2196/17817
64.
Duncanson E Bennett PN Viecelli A Dansie K Handke W Tong A et al . Feasibility and acceptability of e-PROMs data capture and feedback among patients receiving haemodialysis in the symptom monitoring WIth feedback trial (SWIFT) pilot: protocol for a qualitative study in Australia. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e039014. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039014
65.
Agarwal N Shah KK Dansie K Bennett PN Greenham L Brown C et al . Feasibility of symptom monitoring WIth feedback trial (SWIFT) for adults on hemodialysis: a registry-based cluster randomized pilot trial. BMC Nephrol. (2023) 24:345. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03399-5
66.
Sandys V Edwards C McAleese P O’Hare E O’Seaghdha C . Protocol of a pilot-scale, single-arm, observational study to assess the utility and acceptability of a wearable hydration monitor in haemodialysis patients. Pilot Feasibility Stud. (2022) 8:17. doi: 10.1186/s40814-022-00976-7
67.
Kargar Jahromi M Javadpour S Taheri L Poorgholami F . Effect of nurse-led telephone follow ups (tele-nursing) on depression, anxiety and stress in hemodialysis patients. Glob J Health Sci. (2015) 8:168–73. doi: 10.5539/gjhs.v8n3p168
68.
Hudson JL Moss-Morris R Norton S Picariello F Game D Carroll A et al . Tailored online cognitive behavioural therapy with or without therapist support calls to target psychological distress in adults receiving haemodialysis: a feasibility randomised controlled trial. J Psychosom Res. (2017) 102:61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2017.09.009
69.
Nelson RG Pankratz VS Ghahate DM Bobelu J Faber T Shah VO . Home-based kidney care, patient activation, and risk factors for CKD progression in Zuni Indians: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 13:1801–9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06910618
Summary
Keywords
digital health technology, hemodialysis, nutrition, meta-analysis, systematic review
Citation
Zhang K, Zhang N, Wang R, Wei S and Ni C (2025) Impact of digital health technology-based nutritional interventions on the nutritional status of hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 12:1681161. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1681161
Received
07 August 2025
Accepted
30 September 2025
Published
29 October 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Dongliang Zhang, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, China
Reviewed by
Yun Zhang, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China
Marouane Ouirdani, Hassan Premier University, Morocco
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Wei and Ni.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cuiping Ni, cpni@cmu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Kai Zhang, orcid.org/0009-0002-5312-5010
Cuiping Ni, orcid.org/0009-0002-3535-9390
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.