- Department of Cardiology, The Quzhou Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Quzhou People’s Hospital, Quzhou, China
Albuminuria, a core indicator of kidney injury, is closely associated with cardiovascular disease prognosis. Through multiple mechanisms, metabolic abnormalities, such as hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, obesity, and dyslipidemia, contribute to the onset and progression of albuminuria and significantly increase the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Based on recent clinical studies and basic experimental evidence, this review systematically elucidates how metabolic conditions are involved in the relationship between albuminuria and cardiac prognosis, encompassing several mechanisms, including chronic inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system overactivation, hemodynamic alterations, vascular endothelial dysfunction, mitochondrial dysfunction, and lipotoxicity. Additionally, it explores clinical intervention strategies. This review underscores the pivotal role of metabolic conditions in driving cardiorenal diseases and outlines evidence-based strategies for clinical management.
1 Introduction
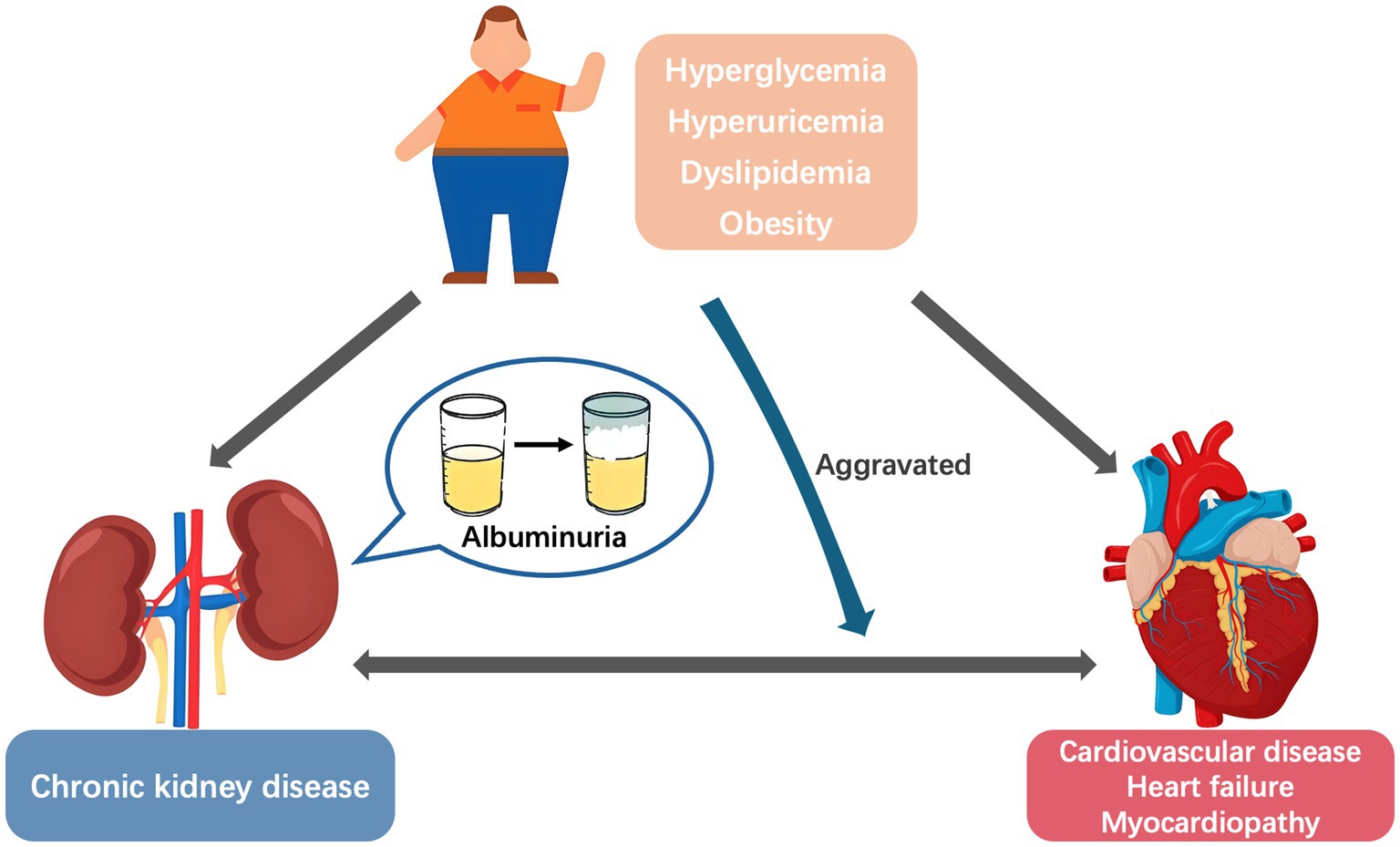
Albuminuria is a core indicator of kidney disease progression and an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and heart failure (HF) (1–3). With the rising incidence of metabolic diseases, the role of metabolic conditions in the relationship between albuminuria and adverse cardiovascular outcomes has gained increasing attention. Metabolic disorder, renal disease, and CVD often overlap and coexist in affected individuals. In a study involving 11,607 American adults, approximately 26.3% had at least one cardiac, renal, or metabolic disease, 8.0% had two of these conditions, and 1.5% had all three diseases simultaneously (4). Moreover, metabolic risk factors were the main CVD-attributable burdens in China, increasing from 62.80% in 1990 to 70.45% in 2019 (5). Common metabolic abnormalities, including hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, dyslipidemia, and obesity, not only share common pathophysiological mechanisms with cardiorenal diseases but also exacerbate disease progression when coexisting (6, 7). This interrelationship has led to the concept of Cardiovascular–Kidney–Metabolic syndrome (8, 9). However, metabolic abnormalities appear to be the primary driver, rather than mere contributors, of the “metabolic abnormalities–albuminuria–CVD” cycle. Metabolic abnormalities trigger albuminuria through kidney injury (10) while directly promoting vascular damage (11, 12), thereby initiating the progression of cardiorenal disease (Figure 1). Based on recent clinical research and basic experimental evidence, this research aimed to systematically elucidate the role of metabolic conditions as a driving factor in the relationship between albuminuria and cardiovascular prognosis, and explores the clinical intervention strategies.
2 Correlation between albuminuria and cardiac outcomes
Previously, a 24-h albumin excretion rate (AER) exceeding 30 mg was the gold standard for diagnosing albuminuria (13). However, given that 24-h urine collection is often impractical and causes patient burden, spot urine samples are now routinely used to estimate AER clinically (13). Assuming approximately 1 g of urinary creatinine is excreted daily, the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), calculated using spot urine samples, is used to determine the presence of albuminuria (14). Given that UACR remains relatively constant and is not influenced by changes in individual urine volume or body weight, it features high accuracy and reliability (14).
Currently, albuminuria, defined by the criterion of UACR >30 mg/g, is recognized as a critical indicator closely associated with the progression and adverse outcomes of chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly diabetic nephropathy (DN) (15). Mounting epidemiological evidence suggests that urinary albumin excretion is also linked to CVD incidence and mortality, with albuminuria being an independent risk factor for cardiovascular events (16, 17). A prospective cohort study examined 8,975 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) without pre-existing CVD at baseline and found that, after a median follow-up of 4.05 years and adjustment for potential confounders, participants with microalbuminuria exhibited a higher CVD risk, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.57 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.04–2.37) for myocardial infarction (MI) and 1.30 (95% CI: 1.07–1.57) for total CVD. Moreover, as the UACR increased, the risk also increased. Those with macroalbuminuria had an HR of 2.86 (95% CI: 1.63–5.00) for MI and 2.42 (95% CI: 1.85–3.15) for total CVD (18).
Traditionally, individuals who do not meet the diagnostic criteria for CKD (UACR < 30 mg/g, estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) are not considered to have high CVD risk. Nevertheless, recent retrospective clinical studies have presented contradictory findings, revealing a correlation between elevated UACR within the normal range and cardiorenal risk, independent of eGFR levels (19, 20). Research utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey demonstrated a near-linear relationship between continuous UACR levels and CVD risk, even among individuals without apparent cardiovascular disease, underscoring the continuum of risk and the importance of early intervention (19). Similarly, after adjusting for sociodemographic information, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, baseline eGFR, and related comorbidities, Kang et al. found that a UACR within 6.211–10.010 mg/g was already significantly associated with increased cardiac mortality (HR = 1.51, 95% CI: 1.12–2.03, p = 0.006). This association further intensified when UACR exceeded 10.010 mg/g (HR = 2.14, 95% CI: 1.62–2.82, p < 0.001) (21).
Chronic kidney injury reportedly elevates cardiovascular risk through multiple pathophysiological processes, including endothelial dysfunction, diffuse vascular damage, systemic inflammation, atherosclerosis, myocardial remodeling, and sodium and water retention (22–24). Interestingly, through Mendelian randomization analysis, Zhou et al. discovered that elevated UACR exhibited a causal relationship with increased risks for CAD (odds ratio [OR], 1.260; 95% CI: 1.042–1.523; p = 0.017) and MI (OR, 1.424; 95% CI: 1.137–1.783; p = 0.002). However, this causal relationship vanished after adjusting for metabolic factors such as blood pressure, blood glucose, and lipid levels (25), suggesting that the detrimental impact of UACR on CAD is mediated by these metabolic conditions.
3 Role of metabolic conditions in cardiorenal prognosis
Metabolic conditions such as hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, obesity, and hyperuricemia are well-established independent risk factors for albuminuria, driving its progression from microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria and from intermittent to persistent states.
A study by Sivanantham et al. demonstrated that microalbuminuria incidence was 27.7% (95% CI: 18.1–38.6) among patients with hypertension alone and 40.6% (95% CI: 29–52.2) among those with diabetes alone (26). In a survey conducted across 105 primary care units in Turkey, diabetes was significantly associated with an increased albuminuria risk (OR, 1.667; 95% CI: 1.205–2.309; p = 0.002). Moreover, albuminuria prevalence was significantly lower in patients with diabetes with controlled blood glucose than in those without controlled blood glucose (59.0% vs. 47.0%, p = 0.002) (27). Notably, when combined with metabolic abnormalities, the correlation between albuminuria and cardiovascular prognosis changes. A multicenter registry cohort study involving 5,960 patients with CAD demonstrated that an increased UACR had a more significant impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with T2DM than in those without T2DM. Furthermore, an interaction between glycemic status and UACR levels was observed in relation to cardiovascular and all-cause mortality (both interaction p-values < 0.001), even when UACR values were within the guideline-recommended normal range (23).
Regarding the relationship between hyperlipidemia and albuminuria, Hwang et al. found that UACR was positively correlated with total cholesterol and triglyceride levels but negatively correlated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels (28). Similarly, a higher ratio of non-HDL-C to HDL-C was significantly associated with an increased risk of macroalbuminuria (OR, 1.34; 95% CI: 1.13–1.59; p = 0.0007). A subgroup analysis revealed that this association was stronger among participants with a BMI of ≥30 kg/m2 (OR, 1.89; 95% CI: 1.44–2.47; p < 0.01), even after excluding those taking medications that affect lipid metabolism (29). Moreover, as BMI, waist circumference, and body fat content gradually increase, urinary albumin excretion also increases (30). In genetic studies, HindIII polymorphism in the LPL gene, a key enzyme in triglyceride metabolism, is significantly associated with increased microalbuminuria risk in patients with T2DM (31). Moreover, Shao et al. quantitatively analyzed HDL proteome alterations using isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry and found that low concentrations of the anti-atherosclerotic protein PON1 in the HDL proteome were associated with albuminuria and coronary artery calcification. In patients with T1DM manifesting albuminuria, reduced PON1 levels in the HDL proteome may partially mediate the increased CVD risk, increasing the possibility that HDL proteome alterations act as mediators of kidney disease and atherosclerosis risk (32).
A community-based prospective cohort study involving 1,862 middle-aged and older adult participants found that, over a 4-year follow-up period, after adjusting for confounding factors, each 1 mg/dL increase in serum uric acid (UA) was associated with a 1.42-fold higher risk of developing microalbuminuria (OR, 1.42; 95% CI: 1.27–1.59; p < 0.01). Thus, elevated serum UA can independently predict the onset of microalbuminuria (33). Additionally, Russo et al. conducted a retrospective investigation involving 21,963 patients from the URRAH study database. During a follow-up period of 215,618 person-years, they found that cardiovascular mortality stratified by all levels of eGFR was significantly higher in patients with hyperuricemia and proteinuria than in those with only one risk factor or no risk factors (34).
4 Mechanisms of metabolic conditions involved in cardiorenal diseases
Metabolic abnormalities deliver a “double hit” through renal injury (triggering albuminuria) and vascular damage (directly promoting atherosclerosis), creating a vicious “metabolic abnormalities–albuminuria–CVD” cycle. This multidimensional effect dominated by metabolic abnormalities may include the following specific underlying mechanisms (Figure 2).
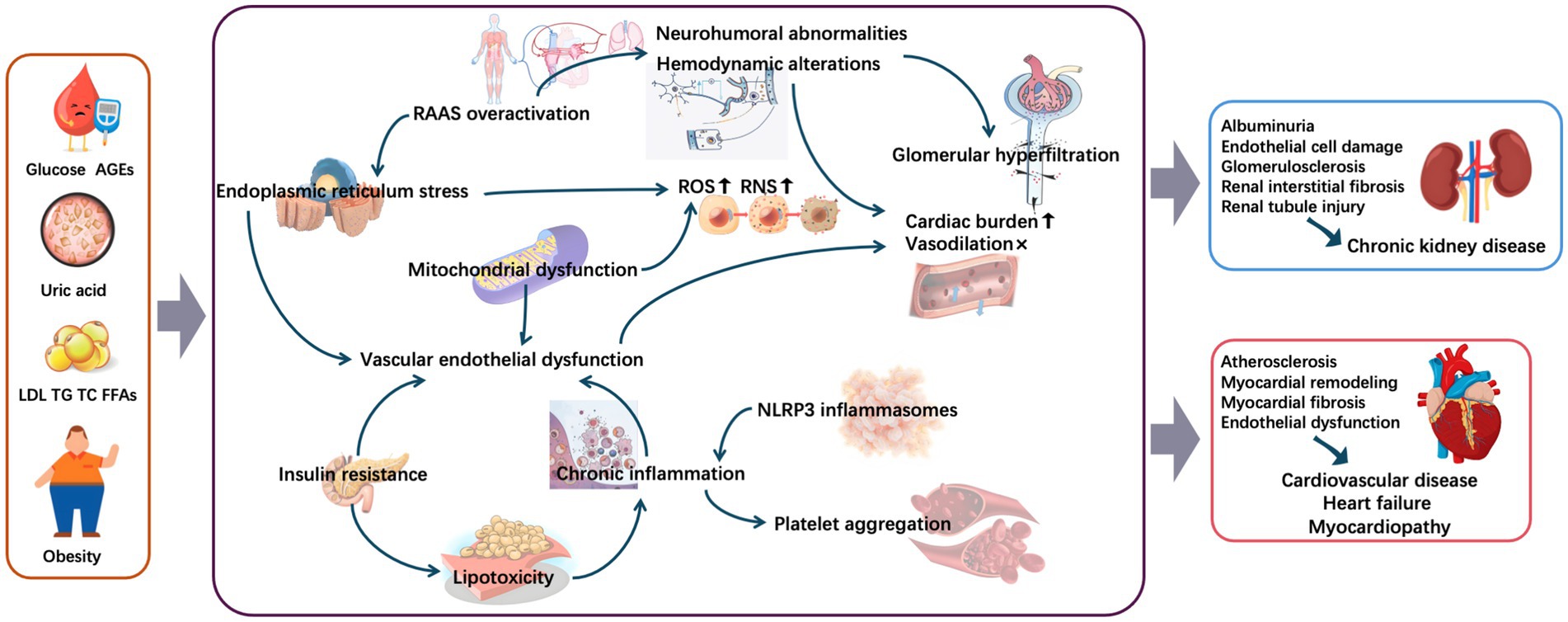
Figure 2. Mechanisms underlying metabolic conditions involved in cardiorenal diseases. AGEs, advanced glycation end-products; FFAs, free fatty acids; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; NLRP3, nodular receptor protein 3; RAAS, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.
4.1 Chronic inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Chronic low-grade inflammation induced by metabolic disorders exists in multiple organs or tissues, including the heart, brain, kidneys, and skeletal muscles and is characterized by the infiltration of immune cells, production of abnormal cytokines, and aberrant activation of inflammatory signaling pathways (35–38). Chronic inflammation is a fundamental feature of most renal pathologies, where inflammatory cell infiltration into the renal interstitium promotes fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, causing renal interstitial fibrosis—a crucial process leading CKD to end-stage renal disease (39–41). Moreover, metabolically mediated inflammation could accelerate glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis, causing gradual decline in renal function (40). Additionally, inflammation may compromise the structural and functional integrity of glomerular cells and injure renal tubular epithelial cells, thereby impairing reabsorption and secretion functions and accelerating the progression of CKD (42–44). In populations with diabetes and obesity, elevated glucose and lipid accumulation can promote inflammatory responses dependent of nodular receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes, inducing podocyte injury, a major factor in subsequent renal damage (45–49). Furthermore, inflammation with a high-specificity cellular and molecular response contributes to the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis (50). A high-fat diet can exacerbate atherosclerosis by elevating the neutrophil levels (51). Chronic inflammation associated with metabolic disorders can also damage vascular endothelial cells and promote lipid deposition and platelet aggregation, ultimately forming atherosclerotic plaques and increasing CAD risk (52, 53). In summary, chronic inflammation driven by metabolic dysregulation may be a key contributor to the development of cardiorenal diseases associated with metabolic abnormalities.
Several studies have demonstrated that excess nutrients and inflammatory cytokines associated with metabolic diseases can trigger or exacerbate ER stress and induce the overproduction of downstream reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen (54–57). ER stress disrupts the balance between nitric oxide and ROS, leading to oxidative stress, which aids in inducing endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis (58–60). Disruption of redox homeostasis leads to the accumulation of oxidative intermediates, which then attack unsaturated fatty acids in biological membranes, trigger lipid peroxidation, and further decompose into smaller oxides, including malondialdehyde; consequently, a series of structural and functional abnormalities involving the cardiovascular and renal systems occur (61–65). Thus, metabolically related ER stress facilitates the development of cardiorenal complications.
4.2 Overactivation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system
During obesity, adipose tissue secretes various adipokines (e.g., leptin and adiponectin), which can directly or indirectly activate the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) (66, 67). RAAS can also be activated by chronic hyperglycemia and hyperuricemia through the direct stimulation of renal renin secretion (68–71). This system is involved in blood pressure regulation, fluid homeostasis, and electrolyte balance. When it is overactivated, aldosterone secretion increases, promoting the renal tubular reabsorption of sodium and water, increasing volume load, and exacerbating cardiac burden (72). Angiotensin II induces plaque formation during the early stages, representing one of the most crucial impacts on atherogenesis from the RAAS (73). Additionally, the increased production of angiotensin II induces endothelin expression, which causes systemic vasoconstriction, blood pressure elevation, and cardiac and renal injury worsening (74, 75). Meanwhile, angiotensin II overexpression can induce oxidative stress, ER damage, and apoptosis by activating signaling pathways such as the mTOR/ERK pathway, leading to cardiorenal organ remodeling and dysfunction (76–78). Moreover, UA and angiotensin II synergistically increased inflammation and oxidative stress in human proximal tubular cells through the activation of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), in an additive manner (79). In summary, RAAS overactivation associated with metabolic abnormalities induces a vicious cycle of neurohumoral abnormalities, internal environment disturbances, and oxidative stress, further contributing in the development of cardiorenal disease.
4.3 Hemodynamic alterations
Obesity exhibits an increase in circulating blood volume and glomerular pressure, resulting in mechanical damage to the capillary walls. Prolonged exposure to elevated intraglomerular pressure can induce focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, which clinically presents as albuminuria and progressive decline in renal function (80, 81). In hyperglycemia, the secretion of vasoactive substances such as prostaglandins and nitric oxide increases, causing the afferent arterioles to excessively dilate and the renal blood flow to significantly increase, resulting in hyperfiltration (82, 83). Obesity and hyperglycemia promote the generation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which are deposited in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangial region; this deposition leads to the thickening of basement membranes, proliferation of mesangial matrix, and restricted dilation of the efferent arterioles, exacerbating the hyperfiltration state (84–86). Prolonged hyperfiltration mechanically damages the glomerular capillary walls and continuously activates mesangial and endothelial cells, which release profibrotic factors such as TGF-β and platelet-derived growth factor, ultimately promoting glomerulosclerosis (87–91). At the macro level, reciprocal communication between the renal microvasculature and the systemic circulation creates a vicious cycle that accelerates the progression of cardiorenal disease (92). Additionally, hemodynamic disturbances associated with metabolic dysfunction increase cardiac load and exacerbate HF symptoms (93).
4.4 Vascular endothelial dysfunction
Metabolic abnormalities, such as hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, and excessive release of free fatty acids (FFAs), adversely affect the vascular wall, leading to endothelial dysfunction (94–98). Vascular endothelial cells help maintain the barrier function between blood and the vascular wall; they also regulate the normal functioning of the circulatory system by balancing vasodilation and vasoconstriction (99). Vascular endothelial dysfunction is characterized by impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation, increased oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, increased permeability, and endothelial cell senescence, collectively hindering the physiological and protective functions of endothelial cells (100, 101). In endothelial dysfunction, vascular regulatory mechanisms are impaired, increasing the risk of cardiorenal diseases. Such dysfunction also leads to the decreased activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, resulting in reduced NO synthesis, which enhances vasoconstrictive capacity and increases peripheral resistance, thereby exacerbating cardiac load and causing renal diseases (102–105). High levels of glucose and UA, as well as AGEs, increase the permeability of glomerular endothelial cells, induce endothelial cell apoptosis, significantly alter the glomerular filtration barrier, and lead to albuminuria (84, 106). Therefore, improving endothelial function may help prevent or treat cardiorenal diseases associated with metabolic abnormalities.
4.5 Mitochondrial dysfunction
Mitochondrial quality control is a core regulatory system that maintains cellular energy homeostasis through three synergistic mechanisms (107). First, PGC-1α–mediated mitochondrial biogenesis continuously generates new mitochondria by activating the protein nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2. Second, mitochondrial dynamics—coordinately regulated by fusion proteins including mitofusins and fission proteins such as DRP1, ensure the clearance of damaged organelles and the renewal of healthy mitochondria with minimal resources and energy required. Finally, mitophagy mediated by PINK1/Parkin pathway, precisely identifies and eliminates damaged units with dissipated membrane potentials, thereby establishing a closed-loop system for mitochondrial quality control. This dynamic cycle—comprising biogenesis, remodeling, and clearance—provides adaptive support for cellular metabolism; however, when disrupted, it directly compromises the structural integrity of the ventricular myocardium and renal parenchyma, ultimately impairing cardiac and renal functions (108, 109).
Elevated levels of glucose, UA, and FFAs can induce mitochondrial dysfunction, which leads to ROS accumulation and exacerbates mitochondrial dynamic disturbances and mitochondrial DNA damage, forming a vicious cycle (110–114). High glucose levels can promote excessive mitochondrial fission in renal podocytes, leading to glomerular damage and renal dysfunction (115). Impairment of the mitochondrial antioxidant defense system, together with increased mitochondrial ROS production, can harm renal cell membrane lipids, proteins, and DNA, thereby inducing podocyte apoptosis and endothelial cell damage, which are common features of acute and chronic kidney injuries (116, 117). Moreover, mitochondrial dynamic imbalance contributes to the pathogenesis of various CVDs. Mitochondrial dynamic homeostasis is essential not only for the growth, apoptosis, and migration of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells but also for the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase production by monocytes and macrophages, as well as extracellular matrix degradation, which are important initiating factors for vascular remodeling (118–122). Abnormal mitochondrial dynamics can impair vascular cell function and accelerate the onset and progression of vascular remodeling diseases such as atherosclerosis (118, 121). Additionally, hyperglycemia can promote time-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes, potentially leading to diabetic cardiomyopathy (123). Given the important role of mitochondrial function in regulating cardiorenal injury, maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis during metabolic abnormalities is crucial.
4.6 Lipotoxicity and insulin resistance
In lipotoxicity during lipid metabolism disorders, FFA concentrations or intracellular lipid levels exceeds the storage capacity of adipose tissue and the oxidative capacity of various tissues for FFAs; consequently, lipid levels are abnormally elevated in the blood or are excessively deposited in nonadipose tissues, causing damage and toxicity to tissues and organs (124, 125). Lipotoxicity has been reported to increase CKD risk and considered as an independent risk factor for adverse cardiovascular events (126). It also increases the triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels; the deposition of these lipid components in the vascular wall leads to plaque formation, which causes vascular stenosis and obstruction, ultimately increasing the risk of atherosclerotic CVD (127). Lipotoxicity-induced liver inflammation may also lead to an imbalance in coagulation and fibrinolysis, making the blood hypercoagulable (128); consequently, cardiac and renal blood vessels develop thrombosis, which further promotes the onset and progression of cardiorenal diseases. Abnormal lipid metabolism also results in excessive FFA accumulation in nonadipose organs such as the heart and kidneys. When renal sinus fat abnormally accumulates, mechanical compression and inflammatory factor release can occur, triggering local hypoxia, oxidative stress, and fibrosis; consequently, nephron function is impaired (129, 130). Similarly, abnormal FFA buildup in cardiomyocytes activates ROS production, induces ER stress, and disrupts mitochondrial β-oxidation, leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis, interstitial fibrosis, and contractile function impairment; ultimately, lipotoxic cardiomyopathy develops (131, 132). Early prevention and control of lipotoxicity are essential to effectively maintain cardiorenal function.
Insulin resistance is a core feature of metabolic disorders and is crucial in CVD and CKD development by promoting myocardial fibrosis, endothelial dysfunction, and lipid metabolism disorders (133, 134). Insulin resistance can activate the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway, affecting the expression of insulin receptors in cardiac and renal tissues, reducing insulin sensitivity, and ultimately damaging such tissues (135–137). Pulakat et al. found that the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway was activated in the cardiovascular tissues of rodent models with nutrient excess; this activation is associated with weakened insulin metabolic signaling, impairing NO-mediated vasodilation, causing cardiac diastolic dysfunction, and promoting renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis (138). Insulin resistance can also contribute to peripheral microvascular and skeletal muscle dysfunction (139, 140), which are linked to increased HF risk (141, 142). A positive correlation was found between insulin resistance and HF risk in older adults with diabetes (143). Overall, insulin resistance directly or indirectly contributes to myocardial and renal tissue damage, and mitigating it may help alleviate its negative effects on the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
5 Therapeutic options
In this review, the analyses of observational studies and randomized trials have demonstrated that early metabolic regulation and subsequent albuminuria remission can accurately predict long-term improvements in cardiorenal clinical outcomes (144, 145). Metabolic conditions are not only a potent predictor of cardiorenal risk but also a modifiable therapeutic target. The following discussion focuses on the beneficial effects of metabolic regulation on cardiorenal diseases, with an emphasis on lifestyle interventions, pharmacological treatments, and novel targeted therapies (Figure 3).
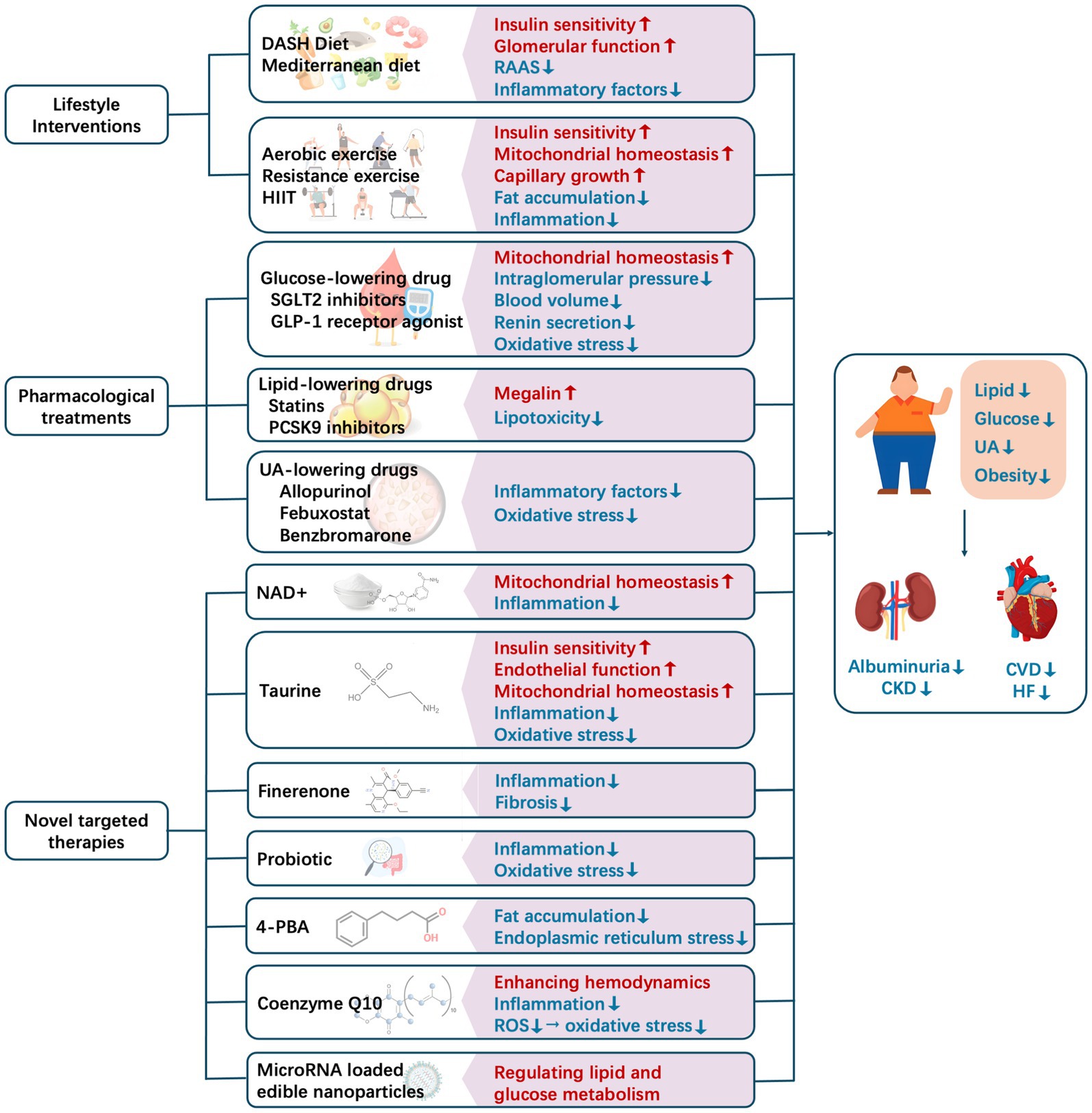
Figure 3. Current methods for intervening in and regulating metabolic conditions to improve cardiorenal outcomes. CKD, chronic kidney disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; DASH, Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension; HF, heart failure; HIIT, high-intensity interval training; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine nucleotide; RAAS, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; ROS, reactive oxygen species; UA, uric acid.
5.1 Lifestyle interventions
Lifestyle interventions, including dietary modification and exercise, are fundamental to the management of metabolic abnormalities. By improving energy metabolism balance, reducing oxidative stress, and mitigating inflammatory responses, they offer multidimensional protection to the renal and cardiovascular systems. The Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension diet emphasizes a high intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products while limiting saturated fat and cholesterol consumption (146). Mechanistically, its high levels of potassium, magnesium, and dietary fiber enhance insulin sensitivity and inhibit RAAS activation (147, 148), thereby alleviating glomerular hyperfiltration. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the intake of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), primarily from olive oil, fish, and nuts, to lower the inflammatory factor levels (149, 150). The CORDIOPREV study, which enrolled 1,002 patients with coronary heart disease, revealed that the crude incidence rate of major cardiovascular events per 1,000 person-years was 28.1 (95% CI, 27.9–28.3) in the Mediterranean diet group, which was significantly lower than 37.7 (95% CI, 37.5–37.9) in the low-fat diet group, with a log-rank p-value of 0.039 (151). The multivariate-adjusted HRs across the different models ranged from 0.719 (95% CI, 0.541–0.957) to 0.753 (95% CI, 0.568–0.998), indicating that the Mediterranean diet has cardiovascular protective effects (151). Furthermore, each one-point increase in the Mediterranean Diet Scale was associated with a 10% reduction in CKD risk (OR, 0.901; 95% CI, 0.868–0.935) (152), possibly because of MUFAs, which inhibit the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and reduce glomerular endothelial cell damage (153, 154).
Various types of exercise, including aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and comprehensive exercise training, can effectively prevent and significantly improve metabolic abnormalities. For example, moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (e.g., brisk walking and swimming) activates the AMPK/PGC-1α pathway, thereby enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and insulin sensitivity in both cardiac and skeletal muscles (155–157). For patients with metabolic abnormalities characterized by muscle loss and fat accumulation, resistance exercise can enhance muscle glucose uptake and reduce ectopic fat (158, 159). Furthermore, through alternating short bursts of high-intensity exercise and low-intensity recovery periods, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) significantly enhances mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation efficiency and capillary growth (160, 161), improving cardiac function (162). Additionally, HIIT benefits renal function by influencing kidney-specific mRNA expression of genes related to endogenous antioxidant enzyme activity (Gpx1, Sod1, and Cat) and inflammation (Kim1 and Tnfrsf1b) (163, 164).
5.2 Pharmacological treatments
Drug regimens should be tailored to specific metabolic disorders (e.g., hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and hyperuricemia) while providing renal and cardiovascular protection.
For instance, SGLT2 inhibitors promote urinary glucose excretion, reduce blood volume, and lower intraglomerular pressure by inhibiting SGLT2 in the proximal tubule (165, 166). The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin decreased the risk of kidney disease progression or cardiovascular death by 28% (95% CI 0.64–0.82, p < 0.0001) in the EMPA-KIDNEY trial (167). This drug also significantly reduced the risk of adverse cardiovascular events and hospitalization for HF in patients with T2DM in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME (168). GLP-1 receptor agonist, a glucose-lowering drug, enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion while inhibiting gastric emptying and appetite. A meta-analysis conducted by Kristensen et al. revealed that GLP-1 receptor agonist reduced the risks of MACE by 12% (95% CI, 0.82–0.94, p < 0.0001) and a broad composite kidney outcome by 17% (95% CI, 0.78–0.89; p < 0.0001), mainly resulting from the decreased excretion of urinary albumin (169). More importantly, both SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists exert cardiorenal protection through multiple mechanisms, including the regulation of mitochondrial function, inhibition of renin secretion, and reduction of oxidative stress (170, 171). SGLT2 inhibitors enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy by activating the AMPK-PGC-1α pathway, while directly suppressing renin release by restoring sodium delivery to the macula densa (170, 172). GLP-1 receptor agonists stabilize mitochondrial membrane potential and optimize energy metabolism via the cAMP-PKA signaling cascade; they also indirectly modulate the RAAS by regulating the sympathetic tone (170, 172). Furthermore, both drug classes could suppress ROS generation and regulate calcium homeostasis, thereby attenuating the unfolded protein response to block ER stress–driven apoptotic pathways (170, 171); ultimately, cytoprotective effects are exerted in the heart and kidneys.
Statins, which regulate lipids, inhibit oxidized LDL generation (173) and suppress macrophage infiltration, thereby delaying the progression of atherosclerosis and glomerulosclerosis (174, 175). Lipid-lowering drugs, particularly PCSK9 inhibitors, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events by lowering LDL-C and lipoprotein(a) levels (176, 177). PCSK9 exacerbates albuminuria by interacting with and downregulating megalin, a proximal tubule receptor essential for protein reabsorption in the kidneys (178, 179). In experimental models, inhibiting PCSK9 maintained megalin levels, reduced albuminuria, and improved renal disease phenotype (180).
The protective effects of UA-lowering therapy on cardiorenal diseases require further exploration, and pharmacological treatment for symptomatic hyperuricemia may hold greater significance (181–183). Allopurinol reduces UA production by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity, thereby blocking the conversion of hypoxanthine and xanthine into UA. A prospective cohort study by Goicoechea et al. demonstrated that allopurinol treatment significantly lowered serum UA and C-reactive protein levels, increased eGFR, and slowed the progression of kidney disease. Compared with the control group, allopurinol treatment reduced the risk of cardiovascular events by 71% (p = 0.026) (184). Similarly, the composite renal event rate was significantly lower in the febuxostat group than in the placebo group (relative risk [RR], 0.68; 95% CI 0.46–0.99), with a notably higher eGFR (mean difference: 2.89 mL/min/1.73 m2; 95% CI 0.69–5.09) (185). However, in high-risk patients such as those with diabetes or CKD, the impact of febuxostat on cardiovascular risk, compared with allopurinol, remains unclear in previous studies, with potential effects ranging from neutral to either reduced or increased risk; the underlying mechanisms are still unclear (186–188). In addition, in salt-induced hypertensive rat models, benzbromarone significantly reduced advanced oxidation protein products and attenuated oxidative stress, suggesting its substantial potential for preventing CVD and CKD (189).
5.3 Novel targeted therapies
Novel medications targeting multiple pathways, including chronic inflammation, ER stress, endothelial function, and mitochondrial function, are warranted.
Recently, nicotinamide adenine nucleotide (NAD+) has been discovered to regulate immune function and inflammation (190, 191). Treatment with nicotinamide riboside (NR), an NAD+ intermediate, in T2DM mice prevented the increase in albuminuria, urinary kidney injury molecule-1 excretion, and renal pathological changes; such prevention was due to reduced inflammation, at least partially by inhibiting the activation of the cGAS/STING signaling pathway (192). Additionally, NR increased SIRT3 activity and improved mitochondrial function, thereby reducing mitochondrial DNA damage (192). Moreover, through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, taurine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, helps alleviate endothelial dysfunction caused by metabolic abnormalities, prevent mitochondrial dysfunction, and help regulate vascular pressure (193–195). In patients with T2DM, taurine supplementation significantly reduces insulin resistance, oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial markers (193). Furthermore, finerenone, as a novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, is known to reduce inflammation and fibrosis, thereby exerting cardiorenal protective effects (196).
A previous study reported the interconnection between gut microbiota, metabolic abnormalities, and chronic inflammation (197). Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a metabolite of gut microbiota, activates the TLR4/NF-κB pathway, thereby exacerbating inflammation; it is also closely associated with atherosclerosis and renal pathological changes (198–200). Clinically, probiotic therapy has been shown to reduce TMAO levels in patients with unstable angina (201). In patients with DN, Dai et al. found that probiotics could improve glucose and lipid metabolism and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, thereby delaying the progression of albuminuria and renal function impairment (202).
The chemical 4-PBA alleviates ER stress by stabilizing protein folding; it also reduces fat accumulation in zebrafish fed a high-fat diet (203, 204). Several animal experiments have demonstrated that 4-PBA can reduce tubular cell apoptosis and renal fibrosis (205). Moreover, exogenous 4-PBA supplementation can inhibit atrial fibrosis in mice with atrial fibrillation induced by a high-fat diet (206), prevent cardiac rupture and remodeling in mice with MI (207), and inhibit myocardial hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis caused by pressure overload (208). Additionally, nutritional supplements such as coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a coenzyme in the mitochondrial respiratory chain, can reduce ROS production, thereby improving oxidative stress responses. Clinically, CoQ10 supplementation has beneficial effects on the lipid profile and helps lower blood pressure (209). It also helps prevent acute kidney injury in male diabetic rats, primarily by enhancing renal hemodynamics and reducing oxidative stress (210). Furthermore, CoQ10 can improve cardiovascular health, potentially by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, thereby decreasing fibrosis (211). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) participate in the epigenetic regulation of genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism, with some being dysregulated in metabolic and cardiorenal diseases (212–214). Research on miRNA-loaded edible nanoparticles offers promising new perspectives for clinical interventions targeting metabolic disorders and cardiorenal diseases (215).
Given that single-pathway interventions have limited efficacy, multi-pathway synergistic therapies have emerged as the core strategy for managing metabolic abnormalities. Regulating metabolism can effectively alleviate chronic inflammation, relieve ER stress, and optimize mitochondrial function, thereby improving cardiorenal outcomes. These mechanisms provide an important theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of complications related to metabolic abnormalities.
6 Conclusion
Given the associations among metabolic conditions, albuminuria, and CVD (Figure 4), early screening, comprehensive management, and targeted therapies are important. Targeted intervention in metabolic abnormalities may effectively control albuminuria, delay CVD progression, and improve the overall prognosis of cardiorenal disease. Future research should further explore the underlying mechanisms so that more precise prevention and treatment strategies can be developed, providing patients with more comprehensive health protection.
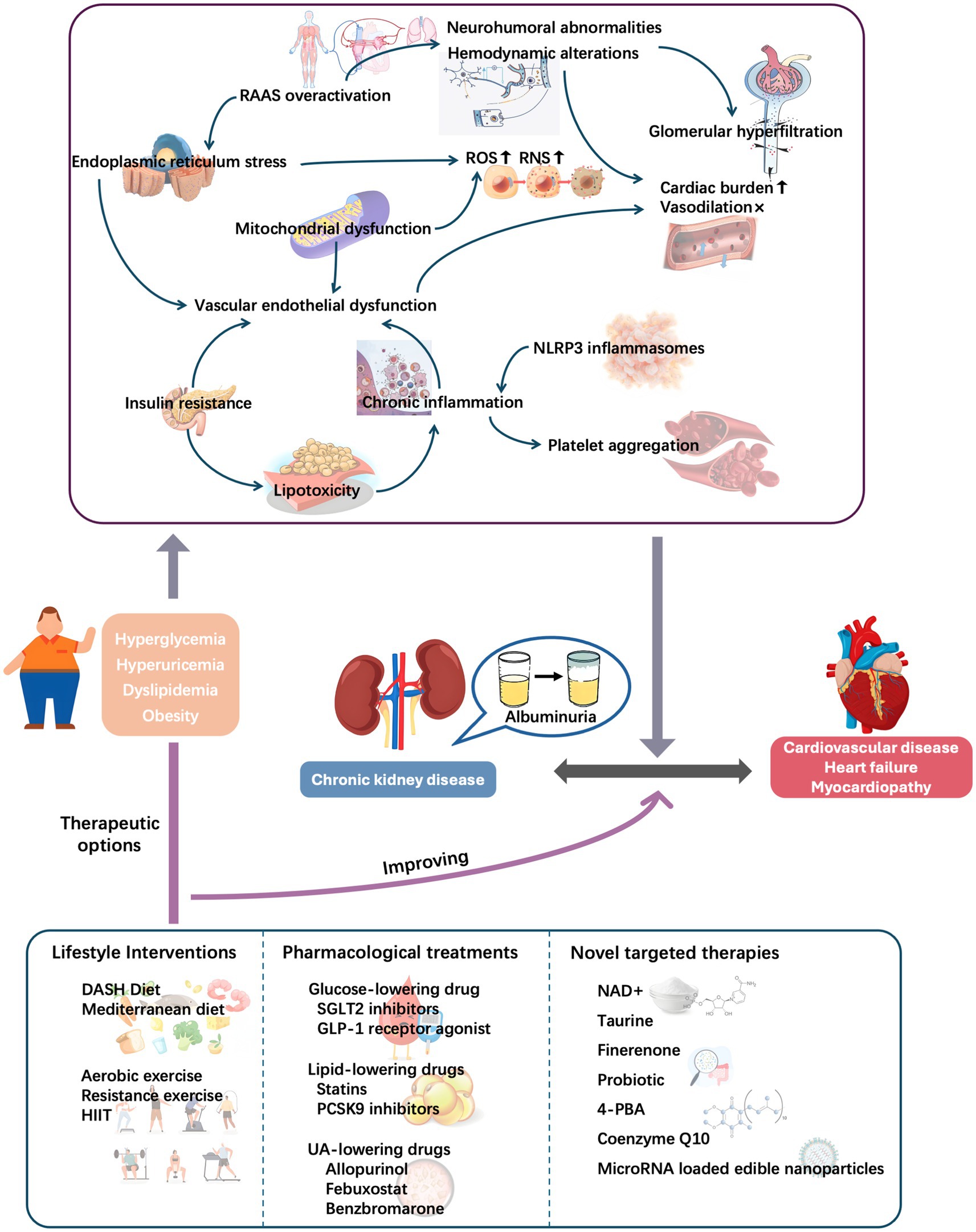
Figure 4. Role of metabolic conditions in cardiorenal diseases: Initiating pathways and therapeutic targeting. DASH, Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension; HIIT, high-intensity interval training; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine nucleotide; NLRP3, nodular receptor protein 3; RAAS, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; UA, uric acid.
Author contributions
YW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. HX: Methodology, Writing – original draft. XT: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZG: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission (2025KY1778) to YW and Competitive Healthcare Project for Science and Technology Research of Quzhou (2025K054) to ZG.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Barzilay, JI, Farag, YMK, and Durthaler, J. Albuminuria: an underappreciated risk factor for cardiovascular disease. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13:e030131. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.030131
2. Zoccali, C, and Mallamaci, F. Albuminuria and cardiovascular outcomes in early-stage chronic kidney disease. Heart. (2025) 111:490–2. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2024-325660
3. Min, KD, Matsumoto, Y, Asakura, M, and Ishihara, M. Rediscovery of the implication of albuminuria in heart failure: emerging classic index for cardiorenal interaction. ESC Heart Fail. (2024) 11:3470–87. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14811
4. Ahmad, FB, and Anderson, RN. The leading causes of death in the US for 2020. JAMA. (2021) 325:1829–30. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.5469
5. Zhang, J, Tong, H, Jiang, L, Zhang, Y, and Hu, J. Trends and disparities in China's cardiovascular disease burden from 1990 to 2019. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2023) 33:2344–54. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.07.039
6. Claudel, SE, Schmidt, IM, Waikar, SS, and Verma, A. Cumulative incidence of mortality associated with cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2025) 36:1343–51. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000637
7. Li, N, Li, Y, Cui, L, Shu, R, Song, H, Wang, J, et al. Association between different stages of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome and the risk of all-cause mortality. Atherosclerosis. (2024) 397:118585. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2024.118585
8. Marassi, M, and Fadini, GP. The cardio-renal-metabolic connection: a review of the evidence. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:195. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01937-x
9. Sebastian, SA, Padda, I, and Johal, G. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a state-of-the-art review. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2024) 49:102344. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102344
10. Rashidbeygi, E, Safabakhsh, M, Delshad Aghdam, S, Mohammed, SH, and Alizadeh, S. Metabolic syndrome and its components are related to a higher risk for albuminuria and proteinuria: evidence from a meta-analysis on 10,603,067 subjects from 57 studies. Diabetes Metab Syndr. (2019) 13:830–43. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.12.006
11. Liu, H, Wang, X, Gao, H, Yang, C, and Xie, C. Physiological and pathological characteristics of vascular endothelial injury in diabetes and the regulatory mechanism of autophagy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1191426. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1191426
12. Xu, R, Wang, Z, Dong, J, Yu, M, and Zhou, Y. Lipoprotein(a) and panvascular disease. Lipids Health Dis. (2025) 24:186. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02600-y
13. Fagerstrom, P, Sallsten, G, Akerstrom, M, Haraldsson, B, and Barregard, L. Urinary albumin excretion in healthy adults: a cross sectional study of 24-hour versus timed overnight samples and impact of GFR and other personal characteristics. BMC Nephrol. (2015) 16:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-16-8
14. Abdelmalek, JA, Gansevoort, RT, Lambers Heerspink, HJ, Ix, JH, and Rifkin, DE. Estimated albumin excretion rate versus urine albumin-creatinine ratio for the assessment of albuminuria: a diagnostic test study from the prevention of renal and vascular Endstage disease (PREVEND) study. Am J Kidney Dis. (2014) 63:415–21. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.10.061
15. Tang, WH, Hung, WC, Wang, CP, Wu, CC, Hsuan, CF, Yu, TH, et al. The lower limit of reference of urinary albumin/creatinine ratio and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:858267. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.858267
16. Bozkurt, B, Rossignol, P, and Vassalotti, JA. Albuminuria as a diagnostic criterion and a therapeutic target in heart failure and other cardiovascular disease. Eur J Heart Fail. (2025). doi: 10.1002/ejhf.3683
17. Song, Y, Yan, F, Yu, Y, Pan, J, Shen, W, Ni, H, et al. Significant association between elevated urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio and increased risk of acute coronary syndrome: a retrospective cross-sectional analysis. Ann Med. (2025) 57:2525393. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2525393
18. Tao, J, Sang, D, Zhang, X, Liu, X, Wang, G, Chen, S, et al. An elevated urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio increases the risk of incident cardia-cerebrovascular disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2024) 16:30. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01256-5
19. Mahemuti, N, Zou, J, Liu, C, Xiao, Z, Liang, F, and Yang, X. Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in Normal range, cardiovascular health, and all-cause mortality. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e2348333. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.48333
20. Pang, X, Dan, W, Lin, L, Li, H, Rao, X, and Li, S. Association of normal range of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio with all-cause mortality among diabetic adults with preserved kidney function: National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2003-2018. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2025) 27:2670–8. doi: 10.1111/dom.16269
21. Kang, M, Kwon, S, Lee, J, Shin, JI, Kim, YC, Park, JY, et al. Albuminuria within the Normal range can predict all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality. Kidney360. (2022) 3:74–82. doi: 10.34067/KID.0003912021
22. Gansevoort, RT, Correa-Rotter, R, Hemmelgarn, BR, Jafar, TH, Heerspink, HJ, Mann, JF, et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet. (2013) 382:339–52. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60595-4
23. Lin, X, Song, W, Zhou, Y, Gao, Y, Wang, Y, Wang, Y, et al. Elevated urine albumin creatinine ratio increases cardiovascular mortality in coronary artery disease patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicenter retrospective study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2023) 22:203. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01907-3
24. McCallum, W, and Sarnak, MJ. Cardiorenal syndrome in the hospital. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2023) 18:933–45. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000064
25. Zhou, X, Ruan, W, Zhao, L, Lin, K, Li, J, Liu, H, et al. Causal links between renal function and cardiac structure, function, and disease risk. Glob Heart. (2024) 19:83. doi: 10.5334/gh.1366
26. Sivanantham, P, Sahoo, JP, Lakshminarayanan, S, Bobby, Z, Loganathan, V, and Kar, SS. Prevalence and the factors associated with microalbuminuria among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and/or hypertension in the urban areas of Puducherry district: a cross-sectional study. Fam Pract. (2024) 41:18–24. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmad124
27. Fici, F, Bakir, EA, Beyaz, S, Makel, W, and Robles, NR. PAIT-survey-prevalence of albuminuria in patients with diabetes and hypertension in Turkey. Prim Care Diabetes. (2018) 12:558–64. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2018.08.008
28. Hwang, SW, Lee, T, Uh, Y, and Lee, JY. Urinary albumin creatinine ratio is associated with lipid profile. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:14870. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65037-w
29. Huang, D, and He, Y. Association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and macroalbuminuria: evidence from NHANES 1999-2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2025) 16:1503780. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1503780
30. Ren, M, Sun, K, Li, F, Qi, YQ, Lin, DZ, Li, N, et al. Association between obesity measures and albuminuria: a population-based study. J Diabetes Complicat. (2016) 30:451–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.12.007
31. Solini, A, Passaro, A, Fioretto, P, Nannipieri, M, and Ferrannini, E. Lipoprotein lipase gene variants and progression of nephropathy in hypercholesterolaemic patients with type 2 diabetes. J Intern Med. (2004) 256:30–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01332.x
32. Shao, B, Zelnick, LR, Wimberger, J, Himmelfarb, J, Brunzell, J, Davidson, WS, et al. Albuminuria, the high-density lipoprotein proteome, and coronary artery calcification in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39:1483–91. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312556
33. Chang, HY, Lee, PH, Lei, CC, Tung, CW, Hsu, YC, Huang, TJ, et al. Hyperuricemia is an independent risk factor for new onset micro-albuminuria in a middle-aged and elderly population: a prospective cohort study in Taiwan. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e61450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061450
34. Russo, E, Viazzi, F, Pontremoli, R, Barbagallo, CM, Bombelli, M, Casiglia, E, et al. Serum uric acid and kidney disease measures independently predict cardiovascular and Total mortality: the uric acid right for heart health (URRAH) project. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:713652. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.713652
35. Lee, YS, and Olefsky, J. Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease. Genes Dev. (2021) 35:307–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.346312.120
36. Saltiel, AR, and Olefsky, JM. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:1–4. doi: 10.1172/JCI92035
37. Varra, FN, Varras, M, Varra, VK, and Theodosis-Nobelos, P. Molecular and pathophysiological relationship between obesity and chronic inflammation in the manifestation of metabolic dysfunctions and their inflammation-mediating treatment options (review). Mol Med Rep. (2024) 29:29. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13219
38. Xu, S, Lu, F, Gao, J, and Yuan, Y. Inflammation-mediated metabolic regulation in adipose tissue. Obes Rev. (2024) 25:e13724. doi: 10.1111/obr.13724
39. Kadatane, SP, Satariano, M, Massey, M, Mongan, K, and Raina, R. The role of inflammation in CKD. Cells. (2023) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/cells12121581
40. Miguel, V, Shaw, IW, and Kramann, R. Metabolism at the crossroads of inflammation and fibrosis in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2025) 21:39–56. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00889-z
41. Qian, Q. Inflammation: a key contributor to the genesis and progression of chronic kidney disease. Contrib Nephrol. (2017) 191:72–83. doi: 10.1159/000479257
42. Chen, PP, Zhang, JX, Li, XQ, Li, L, Wu, QY, Liu, L, et al. Outer membrane vesicles derived from gut microbiota mediate tubulointerstitial inflammation: a potential new mechanism for diabetic kidney disease. Theranostics. (2023) 13:3988–4003. doi: 10.7150/thno.84650
43. Wang, Y, Jin, M, Cheng, CK, and Li, Q. Tubular injury in diabetic kidney disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic perspectives. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1238927. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1238927
44. Xiong, Y, Li, W, Jin, S, Wan, S, and Wu, S. Inflammation in glomerular diseases. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1526285. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526285
45. Gupta, A, Singh, K, Fatima, S, Ambreen, S, Zimmermann, S, Younis, R, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote NLRP3 Inflammasome activation and glomerular endothelial dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease. Nutrients. (2022) 14:14. doi: 10.3390/nu14142965
46. Huang, D, Kidd, JM, Zou, Y, Wu, X, Gehr, TWB, Li, PL, et al. Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome activation and inflammatory exosome release in Podocytes by acid sphingomyelinase during obesity. Inflammation. (2023) 46:2037–54. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01861-y
47. Jiang, XS, Liu, T, Xia, YF, Gan, H, Ren, W, and Du, XG. Activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway ameliorates hyperlipidemia-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury by inhibiting mtROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1342350. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342350
48. Shahzad, K, Fatima, S, Khawaja, H, Elwakiel, A, Gadi, I, Ambreen, S, et al. Podocyte-specific Nlrp3 inflammasome activation promotes diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2022) 102:766–79. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.06.010
49. Yang, X, Chen, Z, Luo, Z, Yang, D, Hao, Y, Hu, J, et al. STING deletion alleviates podocyte injury through suppressing inflammation by targeting NLRP3 in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Signal. (2023) 109:110777. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110777
50. Zhang, J, Ji, C, Zhai, X, Tong, H, and Hu, J. Frontiers and hotspots evolution in anti-inflammatory studies for coronary heart disease: a bibliometric analysis of 1990-2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1038738. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1038738
51. Lavillegrand, JR, Al-Rifai, R, Thietart, S, Guyon, T, Vandestienne, M, Cohen, R, et al. Alternating high-fat diet enhances atherosclerosis by neutrophil reprogramming. Nature. (2024) 634:447–56. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07693-6
52. Kong, P, Cui, ZY, Huang, XF, Zhang, DD, Guo, RJ, and Han, M. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: signaling pathways and therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:131. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00955-7
53. Wang, L, Cheng, CK, Yi, M, Lui, KO, and Huang, Y. Targeting endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2022) 168:58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.04.011
54. Fernandes-da-Silva, A, Miranda, CS, Santana-Oliveira, DA, Oliveira-Cordeiro, B, Rangel-Azevedo, C, Silva-Veiga, FM, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress as the basis of obesity and metabolic diseases: focus on adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas. Eur J Nutr. (2021) 60:2949–60. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02542-y
55. Ma, K, Zhang, Y, Zhao, J, Zhou, L, and Li, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: bridging inflammation and obesity-associated adipose tissue. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1381227. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1381227
56. Masenga, SK, Kabwe, LS, Chakulya, M, and Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097898
57. Rangel-Zuniga, OA, Haro, C, Perez-Martinez, P, Delgado-Lista, J, Marin, C, Quintana-Navarro, GM, et al. Effect of frying oils on the postprandial endoplasmic reticulum stress in obese people. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2014) 58:2239–42. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400401
58. Dong, Y, Fernandes, C, Liu, Y, Wu, Y, Wu, H, Brophy, ML, et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling in diabetic endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Diab Vasc Dis Res. (2017) 14:14–23. doi: 10.1177/1479164116666762
59. Sankrityayan, H, Rao, PD, Shelke, V, Kulkarni, YA, Mulay, SR, and Gaikwad, AB. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and renin-angiotensin system crosstalk in endothelial dysfunction. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2023) 16:139–46. doi: 10.2174/1874467215666220301113833
60. Yuan, C, Yu, B, Li, L, Chen, J, Qin, W, Zhou, Z, et al. SUCNR 1 promotes atherosclerosis by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated ER-Mito crosstalk. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 143:113510. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113510
61. Ayala, A, Munoz, MF, and Arguelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2014) 2014:360438. doi: 10.1155/2014/360438
62. Mendoza, A, Patel, P, Robichaux, D, Ramirez, D, and Karch, J. Inhibition of the mPTP and lipid peroxidation is additively protective against I/R injury. Circ Res. (2024) 134:1292–305. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323882
63. Nusken, E, Voggel, J, Saschin, L, Weber, LT, Dotsch, J, Alcazar, MAA, et al. Kidney lipid metabolism: impact on pediatric kidney diseases and modulation by early-life nutrition. Pediatr Nephrol. (2025) 40:1839–52. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06595-z
64. Tsikas, D, Tsikas, SA, Mikuteit, M, and Uckert, S. Circulating and urinary concentrations of malondialdehyde in aging humans in health and disease. Review and Discussion. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:11. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102744
65. Xu, Z, Jiang, F, Wu, X, Ren, B, Zhang, C, Lin, L, et al. ACAA2 protects against cardiac dysfunction and lipid peroxidation in renal insufficiency with the treatment of S-Nitroso-L-cysteine. Biomolecules. (2025) 15:15. doi: 10.3390/biom15030364
66. Allison, MA, Jenny, NS, McClelland, RL, Cushman, M, and Rifkin, D. The associations of adipokines with selected markers of the renin-angiotensinogen-aldosterone system: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J Hum Hypertens. (2015) 29:127–33. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2014.40
67. Lee, G, Kluwe, B, Zhao, S, Kline, D, Nedungadi, D, Brock, GN, et al. Adiposity, aldosterone and plasma renin activity among African Americans: the Jackson heart study. Endocr Metab Sci. (2023) 11:100126. doi: 10.1016/j.endmts.2023.100126
68. Gherghina, ME, Peride, I, Tiglis, M, Neagu, TP, Niculae, A, and Checherita, IA. Uric acid and oxidative stress-relationship with cardiovascular, metabolic, and renal impairment. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:23. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063188
69. Guerrero, A, Visniauskas, B, Cardenas, P, Figueroa, SM, Vivanco, J, Salinas-Parra, N, et al. Alpha-Ketoglutarate upregulates collecting duct (pro)renin receptor expression, tubular angiotensin II formation, and Na(+) reabsorption during high glucose conditions. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:644797. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.644797
70. Peng, H, Xing, YF, Ye, ZC, Li, CM, Luo, PL, Li, M, et al. High glucose induces activation of the local renin-angiotensin system in glomerular endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. (2014) 9:450–6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1855
71. Peti-Peterdi, J. High glucose and renin release: the role of succinate and GPR91. Kidney Int. (2010) 78:1214–7. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.333
72. Maryam,, Varghese, TP, and Tazneem, B. Unraveling the complex pathophysiology of heart failure: insights into the role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Curr Probl Cardiol. (2024) 49:102411. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102411
73. Poznyak, AV, Bharadwaj, D, Prasad, G, Grechko, AV, Sazonova, MA, and Orekhov, AN. Renin-angiotensin system in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and treatment of CVD. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:22. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136702
74. Becerra Calderon, A, Shroff, UN, Deepak, S, Izuhara, A, Trogen, G, McDonough, AA, et al. Angiotensin II directly increases endothelial calcium and nitric oxide in kidney and brain microvessels in vivo with reduced efficacy in hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13:e033998. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.033998
75. Iovino, M, Lisco, G, Giagulli, VA, Vanacore, A, Pesce, A, Guastamacchia, E, et al. Angiotensin II-vasopressin interactions in the regulation of cardiovascular functions. Evidence for an impaired hormonal sympathetic reflex in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Endocr Metab immune Disord drug. Targets. (2021) 21:1830–44. doi: 10.2174/1871530321666210319120308
76. Chen, LJ, Xu, YL, Song, B, Yu, HM, Oudit, GY, Xu, R, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 ameliorates renal fibrosis by blocking the activation of mTOR/ERK signaling in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Peptides. (2016) 79:49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2016.03.008
77. Essick, EE, Wilson, RM, Pimentel, DR, Shimano, M, Baid, S, Ouchi, N, et al. Adiponectin modulates oxidative stress-induced autophagy in cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e68697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068697
78. Jaimes, EA, Hua, P, Tian, RX, and Raij, L. Human glomerular endothelium: interplay among glucose, free fatty acids, angiotensin II, and oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2010) 298:F125–32. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00248.2009
79. Milanesi, S, Verzola, D, Cappadona, F, Bonino, B, Murugavel, A, Pontremoli, R, et al. Uric acid and angiotensin II additively promote inflammation and oxidative stress in human proximal tubule cells by activation of toll-like receptor 4. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:10868–76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27929
80. Xu, T, Sheng, Z, and Yao, L. Obesity-related glomerulopathy: pathogenesis, pathologic, clinical characteristics and treatment. Front Med. (2017) 11:340–8. doi: 10.1007/s11684-017-0570-3
81. Zbrzezniak-Suszczewicz, J, Winiarska, A, Perkowska-Ptasinska, A, and Stompor, T. Obesity-related Glomerulosclerosis-how adiposity damages the kidneys. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:26. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136247
82. Li, Y, Liu, ZS, Wei, R, Liu, ZW, Guo, LX, and Ren, JH. Renal elasticity and perfusion changes on ultrasonography in an early-stage diabetic rat model. Quant Imaging Med Surg. (2023) 13:7667–79. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-409
83. Schneider, MP, Ott, C, Schmidt, S, Kistner, I, Friedrich, S, and Schmieder, RE. Poor glycemic control is related to increased nitric oxide activity within the renal circulation of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2013) 36:4071–5. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0806
84. Dou, L, and Jourde-Chiche, N. Endothelial toxicity of high glucose and its by-products in diabetic kidney disease. Toxins (Basel). (2019) 11:578. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100578
85. Durak, S, Yilmazer, Y, Celik, F, Yesiloglu, E, Karakose, D, Dincol, S, et al. Investigation of advanced glycation end products in liver, adipose, and renal tissue of mice on a high-fat diet. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2024) 82:1101–8. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01260-6
86. Yang, PY, Li, PC, and Feng, B. Protective effects of gliclazide on high glucose and AGEs-induced damage of glomerular mesangial cells and renal tubular epithelial cells via inhibiting RAGE-p22phox-NF-kB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:9099–107. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201910_19313
87. Har, R, Scholey, JW, Daneman, D, Mahmud, FH, Dekker, R, Lai, V, et al. The effect of renal hyperfiltration on urinary inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in patients with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. (2013) 56:1166–73. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2857-5
88. Jia, T, Xu, T, Smeets, B, Buhl, EM, Moeller, MJ, Floege, J, et al. The role of platelet-derived growth factor in focal segmental Glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2023) 34:241–57. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022040491
89. Ketteler, M, Noble, NA, and Border, WA. Transforming growth factor-beta and angiotensin II: the missing link from glomerular hyperfiltration to glomerulosclerosis? Annu Rev Physiol. (1995) 57:279–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.001431
90. Liu, F, Cao, Y, Zhang, C, and Su, H. Decreased DANCR contributes to high glucose-induced extracellular matrix accumulation in human renal mesangial cell via regulating the TGF-beta/Smad signaling. FASEB J. (2023) 37:e22926. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300146R
91. Singh, J, Jain, A, Bhamra, R, Rathi, V, and Dhingra, AK. The mechanistic role of different mediators in the pathophysiology of nephropathy: a review. Curr Drug Targets. (2023) 24:104–17. doi: 10.2174/1389450124666221026152647
92. Zhang, X, Zhang, J, Ren, Y, Sun, R, and Zhai, X. Unveiling the pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches for diabetic nephropathy: insights from panvascular diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1368481. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1368481
93. Heegaard, B, Deis, T, Rossing, K, Ersboll, M, Kistorp, C, and Gustafsson, F. Diabetes mellitus and hemodynamics in advanced heart failure. Int J Cardiol. (2023) 379:60–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.03.015
94. Kong, Y, Niu, A, Yuan, W, Zhou, Y, Xia, M, Xiong, X, et al. Interaction of FOXO1 and SUMOylated PPARgamma1 induced by hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia favors vascular endothelial insulin resistance and dysfunction. Vasc Pharmacol. (2022) 147:107125. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2022.107125
95. Mallick, R, and Duttaroy, AK. Modulation of endothelium function by fatty acids. Mol Cell Biochem. (2022) 477:15–38. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04260-9
96. Ogiso, K, Shayo, SC, Kawade, S, Hashiguchi, H, Deguchi, T, and Nishio, Y. Repeated glucose spikes and insulin resistance synergistically deteriorate endothelial function and bardoxolone methyl ameliorates endothelial dysfunction. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0263080. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263080
97. Wang, B, Yu, Y, and Han, L. Adiponectin improves endothelial dysfunction caused by elevated FFAs levels, partially through cAMP-dependent pathway. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2012) 97:119–24. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.02.009
98. Wu, G, Liu, J, Ma, G, Wei, Q, and Song, X. Hyperuricemia facilitates uric acid-mediated vascular endothelial cell damage by inhibiting Mitophagy. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2025) 83:811–21. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01512-5
99. Augustin, HG, and Koh, GY. A systems view of the vascular endothelium in health and disease. Cell. (2024) 187:4833–58. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.012
100. Bloom, SI, Islam, MT, Lesniewski, LA, and Donato, AJ. Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial cell senescence. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20:38–51. doi: 10.1038/s41569-022-00739-0
101. Naderi-Meshkin, H, and Setyaningsih, WAW. Endothelial cell dysfunction: onset, progression, and consequences. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2024) 29:223. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2906223
102. Baaten, C, Vondenhoff, S, and Noels, H. Endothelial cell dysfunction and increased cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease. Circ Res. (2023) 132:970–92. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321752
103. Cho, ME, Brunt, VE, Shiu, YT, and Bunsawat, K. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: a clinical perspective. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2025) 329:H135–53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00908.2024
104. Engin, A. Endothelial dysfunction in obesity and therapeutic targets. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2024) 1460:489–538. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_17
105. Heo, KS, Phan, LP, Le, NTT, and Jin, Y. Mechanistic insights and emerging therapeutic strategies targeting endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Arch Pharm Res. (2025) 48:305–32. doi: 10.1007/s12272-025-01542-4
106. Asakawa, S, Shibata, S, Morimoto, C, Shiraishi, T, Nakamura, T, Tamura, Y, et al. Podocyte injury and albuminuria in experimental Hyperuricemic model rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:3759153. doi: 10.1155/2017/3759153
107. Liu, BH, Xu, CZ, Liu, Y, Lu, ZL, Fu, TL, Li, GR, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in human health and disease. Mil Med Res. (2024) 11:32. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00536-5
108. Jia, X, Zhu, L, Zhu, Q, and Zhang, J. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney injury and disease. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23:103576. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103576
109. Titus, AS, Sung, EA, Zablocki, D, and Sadoshima, J. Mitophagy for cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol. (2023) 118:42. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01009-x
110. Aluksanasuwan, S, Plumworasawat, S, Malaitad, T, Chaiyarit, S, and Thongboonkerd, V. High glucose induces phosphorylation and oxidation of mitochondrial proteins in renal tubular cells: a proteomics approach. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:5843. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62665-w
111. Cree-Green, M, Gupta, A, Coe, GV, Baumgartner, AD, Pyle, L, Reusch, JE, et al. Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes youth relates to serum free fatty acids and muscle mitochondrial dysfunction. J Diabetes Complicat. (2017) 31:141–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.10.014
112. Peng, D, He, X, Ren, B, Wang, Q, Peng, L, Jiang, Y, et al. JAK2/STAT3/HMGCS2 signaling aggravates mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in hyperuricemia-induced cardiac dysfunction. Mol Med. (2025) 31:184. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01246-x
113. Raja, AA, Dandare, A, Khan, MJ, and Khan, MJ. Free fatty acid overload targets mitochondria: gene expression analysis of palmitic acid-treated endothelial cells. Genes (Basel). (2022) 13:13. doi: 10.3390/genes13101704
114. Sharma, K, Zhang, G, and Saito, R. Suppresion of mitochondrial respiration is a feature of cellular glucose toxicity. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. (2023) 133:24–33.
115. Liu, S, Li, X, Wen, R, Chen, L, Yang, Q, Song, S, et al. Increased thromboxane/prostaglandin receptors contribute to high glucose-induced podocyte injury and mitochondrial fission through ROCK1-Drp1 signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2022) 151:106281. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2022.106281
116. Clark, AJ, and Parikh, SM. Mitochondrial metabolism in acute kidney injury. Semin Nephrol. (2020) 40:101–13. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2020.01.002
117. Ho, HJ, and Shirakawa, H. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Cells. (2022) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/cells12010088
118. Dumont, A, Lee, M, Barouillet, T, Murphy, A, and Yvan-Charvet, L. Mitochondria orchestrate macrophage effector functions in atherosclerosis. Mol Asp Med. (2021) 77:100922. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100922
119. Luo, Z, Yao, J, Wang, Z, and Xu, J. Mitochondria in endothelial cells angiogenesis and function: current understanding and future perspectives. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:441. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04286-1
120. Qin, HL, Bao, JH, Tang, JJ, Xu, DY, and Shen, L. Arterial remodeling: the role of mitochondrial metabolism in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2023) 324:C183–92. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00074.2022
121. Zhou, RH, Vendrov, AE, Tchivilev, I, Niu, XL, Molnar, KC, Rojas, M, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress in aortic stiffening with age: the role of smooth muscle cell function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2012) 32:745–55. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.243121
122. Zhu, T, Hu, Q, Yuan, Y, Yao, H, Zhang, J, and Qi, J. Mitochondrial dynamics in vascular remodeling and target-organ damage. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1067732. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1067732
123. Mordel, P, Fontaine, F, Dupas, Q, Joubert, M, and Allouche, S. Glucose fluctuation promotes mitochondrial dysfunctions in the cardiomyocyte cell line HL-1. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0289475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289475
124. Cheng, Y, Shao, S, Wang, Z, Guan, Q, Li, H, Liu, G, et al. From lipotoxicity to pan-lipotoxicity. Cell Discov. (2025) 11:27. doi: 10.1038/s41421-025-00787-z
125. Lipke, K, Kubis-Kubiak, A, and Piwowar, A. Molecular mechanism of lipotoxicity as an interesting aspect in the development of pathological states-current view of knowledge. Cells. (2022) 11:11. doi: 10.3390/cells11050844
126. D'Elia, JA, and Weinrauch, LA. Lipid toxicity in the cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome (CKMS). Biomedicine. (2024) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12050978
127. Djekic, D, Shi, L, Calais, F, Carlsson, F, Landberg, R, Hyotylainen, T, et al. Effects of a lacto-Ovo-vegetarian diet on the plasma Lipidome and its association with atherosclerotic burden in patients with coronary artery disease-a randomized, open-label, cross-over study. Nutrients. (2020) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/nu12113586
128. Valenti, L, Tripodi, A, La Mura, V, Pelusi, S, Bianco, C, Scalambrino, E, et al. Clinical and genetic determinants of the fatty liver-coagulation balance interplay in individuals with metabolic dysfunction. JHEP Rep. (2022) 4:100598. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100598
129. Luo, Z, Chen, Z, Hu, J, and Ding, G. Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury. Metabolism. (2024) 150:155718. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155718
130. Spit, KA, Muskiet, MHA, Tonneijck, L, Smits, MM, Kramer, MHH, Joles, JA, et al. Renal sinus fat and renal hemodynamics: a cross-sectional analysis. MAGMA. (2020) 33:73–80. doi: 10.1007/s10334-019-00773-z
131. Lim, S, and Meigs, JB. Ectopic fat and cardiometabolic and vascular risk. Int J Cardiol. (2013) 169:166–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.08.077
132. Ren, J, Wu, NN, Wang, S, Sowers, JR, and Zhang, Y. Obesity cardiomyopathy: evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Physiol Rev. (2021) 101:1745–807. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2020
133. Duan, M, Zhao, X, Li, S, Miao, G, Bai, L, Zhang, Q, et al. Metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population: evidence from NHANES 2001-2018. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2024) 23:243. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02334-8
134. Nakashima, A, Kato, K, Ohkido, I, and Yokoo, T. Role and treatment of insulin resistance in patients with chronic kidney disease: a review. Nutrients. (2021) 13:13. doi: 10.3390/nu13124349
135. Ancu, O, Mickute, M, Guess, ND, Hurren, NM, Burd, NA, and Mackenzie, RW. Does high dietary protein intake contribute to the increased risk of developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes? Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. (2021) 46:1–9. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2020-0396
136. Fraenkel, M, Ketzinel-Gilad, M, Ariav, Y, Pappo, O, Karaca, M, Castel, J, et al. mTOR inhibition by rapamycin prevents beta-cell adaptation to hyperglycemia and exacerbates the metabolic state in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (2008) 57:945–57. doi: 10.2337/db07-0922
137. Sun, JP, Shi, L, Wang, F, Qin, J, and Ke, B. Modified Linggui Zhugan decoction () ameliorates glycolipid metabolism and inflammation via PI3K-Akt/mTOR-S6K1/AMPK-PGC-1 alpha signaling pathways in obese type 2 diabetic rats. Chin J Integr Med. (2022) 28:52–9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3285-2
138. Pulakat, L, DeMarco, VG, Whaley-Connell, A, and Sowers, JR. The impact of Overnutrition on insulin metabolic signaling in the heart and the kidney. Cardiorenal Med. (2011) 1:102–12. doi: 10.1159/000327140
139. Blackwood, SJ, Tischer, D, van de Ven, MPF, Ponten, M, Edman, S, Horwath, O, et al. Elevated heart rate and decreased muscle endothelial nitric oxide synthase in early development of insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2024) 327:E172–82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00148.2024
140. Mooshage, CM, Tsilingiris, D, Schimpfle, L, Kender, Z, Aziz-Safaie, T, Hohmann, A, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with reduced capillary permeability of thigh muscles in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 109:e137–44. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad481
141. Gao, C, Xia, Y, Li, C, Zhou, T, Zhang, W, Cheng, H, et al. KMV-mediated cardiomyocyte-to-endothelial cell signaling drives capillary rarefaction to promote heart failure following pressure overload. Theranostics. (2025) 15:4970–88. doi: 10.7150/thno.104899
142. Tryfonos, A, Tzanis, G, Pitsolis, T, Karatzanos, E, Koutsilieris, M, Nanas, S, et al. Exercise training enhances angiogenesis-related gene responses in skeletal muscle of patients with chronic heart failure. Cells. (2021) 10:10. doi: 10.3390/cells10081915
143. Chen, L, Qian, L, and Liu, Y. Association between different insulin resistance indices and heart failure in US adults with diabetes mellitus. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. (2024) 29:e70035. doi: 10.1111/anec.70035
144. Liakopoulos, V, Franzen, S, Svensson, AM, Sattar, N, Miftaraj, M, Bjorck, S, et al. Renal and cardiovascular outcomes after weight loss from gastric bypass surgery in type 2 diabetes: Cardiorenal risk reductions exceed atherosclerotic benefits. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1276–84. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1703
145. Zannad, F, McGuire, DK, and Ortiz, A. Treatment strategies to reduce cardiovascular risk in persons with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. J Intern Med. (2025) 297:460–78. doi: 10.1111/joim.20050
146. Onwuzo, C, Olukorode, JO, Omokore, OA, Odunaike, OS, Omiko, R, Osaghae, OW, et al. DASH diet: a review of its scientifically proven hypertension reduction and health benefits. Cureus. (2023) 15:e44692. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44692
147. Campbell, TM, Campbell, EK, Attia, J, Ventura, K, Mathews, T, Chhabra, KH, et al. The acute effects of a DASH diet and whole food, plant-based diet on insulin requirements and related cardiometabolic markers in individuals with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2023) 202:110814. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110814
148. Maris, SA, Williams, JS, Sun, B, Brown, S, Mitchell, GF, and Conlin, PR. Interactions of the DASH diet with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Curr Dev Nutr. (2019) 3:nzz091. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzz091
149. Gantenbein, KV, and Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. Mediterranean diet as an antioxidant: the impact on metabolic health and overall wellbeing. Nutrients. (2021) 13:13. doi: 10.3390/nu13061951
150. Nani, A, Murtaza, B, Sayed Khan, A, Khan, NA, and Hichami, A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of polyphenols contained in Mediterranean diet in obesity: molecular mechanisms. Molecules. (2021) 26:26. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040985
151. Delgado-Lista, J, Alcala-Diaz, JF, Torres-Pena, JD, Quintana-Navarro, GM, Fuentes, F, Garcia-Rios, A, et al. Long-term secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet and a low-fat diet (CORDIOPREV): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2022) 399:1876–85. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00122-2
152. Hansrivijit, P, Oli, S, Khanal, R, Ghahramani, N, Thongprayoon, C, and Cheungpasitporn, W. Mediterranean diet and the risk of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrology (Carlton). (2020) 25:913–8. doi: 10.1111/nep.13778
153. Perez-Torres, A, Caverni-Munoz, A, and Gonzalez, GE. Mediterranean diet and chronic kidney disease (CKD): a practical approach. Nutrients. (2022) 15:15. doi: 10.3390/nu15010097
154. Zhou, Y, Tian, S, Wang, Q, Yao, S, Qian, L, Jiang, S, et al. DHA-enriched phosphatidylserine ameliorates high-fat diet-induced kidney injury in mice possibly by regulating TLR4/NF-kappaB and AMPK pathways. J Food Sci. (2022) 87:4233–49. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16284
155. Feng, L, Li, B, Cai, M, Zhang, Z, Zhao, Y, Yong, SS, et al. Resistance exercise alleviates the prefrontal lobe injury and dysfunction by activating SESN2/AMPK/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway and inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in mice with myocardial infarction. Exp Neurol. (2023) 370:114559. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114559
156. Liang, J, Zhang, H, Zeng, Z, Wu, L, Zhang, Y, Guo, Y, et al. Lifelong aerobic exercise alleviates sarcopenia by activating autophagy and inhibiting protein degradation via the AMPK/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. Meta. (2021) 11:11. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050323
157. Yang, B, Yu, Q, Chang, B, Guo, Q, Xu, S, Yi, X, et al. MOTS-c interacts synergistically with exercise intervention to regulate PGC-1alpha expression, attenuate insulin resistance and enhance glucose metabolism in mice via AMPK signaling pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2021) 1867:166126. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166126
158. Moller, LLV, Raun, SH, Fritzen, AM, and Sylow, L. Measurement of skeletal muscle glucose uptake in mice in response to acute treadmill running. J Biol Methods. (2022) 9:e162. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2022.385
159. Waters, DL, Aguirre, L, Gurney, B, Sinacore, DR, Fowler, K, Gregori, G, et al. Effect of aerobic or resistance exercise, or both, on intermuscular and visceral fat and physical and metabolic function in older adults with obesity while dieting. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2022) 77:131–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glab111
160. Fusagawa, H, Sato, T, Yamada, T, Naito, A, Tokuda, N, Yamauchi, N, et al. High-intensity interval training using electrical stimulation ameliorates muscle fatigue in chronic kidney disease-related cachexia by restoring mitochondrial respiratory dysfunction. Front Physiol. (2024) 15:1423504. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1423504
161. Molmen, KS, Almquist, NW, and Skattebo, O. Effects of exercise training on mitochondrial and capillary growth in human skeletal muscle: a systematic review and Meta-regression. Sports Med. (2025) 55:115–44. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-02120-2
162. Wang, Y, Yuan, J, Liu, H, Chen, J, Zou, J, Zeng, X, et al. Elevated meteorin-like protein from high-intensity interval training improves heart function via AMPK/HDAC4 pathway. Genes Dis. (2024) 11:101100. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.101100
163. Merces, EAB, Oliveira, CA, Portela, FS, Malheiro, LFL, Silva, HBL, Avila, JS, et al. High-intensity interval training elicits superior effects than continuous training to improve renal redox status via klotho and Nrf2 signaling in female rats with cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2025) 770:110480. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2025.110480
164. Tucker, PS, Briskey, DR, Scanlan, AT, Coombes, JS, and Dalbo, VJ. High intensity interval training favourably affects antioxidant and inflammation mRNA expression in early-stage chronic kidney disease. Free Radic Biol Med. (2015) 89:466–72. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.07.162
165. Wanner, C, Heerspink, HJL, Zinman, B, Inzucchi, SE, Koitka-Weber, A, Mattheus, M, et al. Empagliflozin and kidney function decline in patients with type 2 diabetes: a slope analysis from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 29:2755–69. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018010103
166. Heerspink, HJ, Perkins, BA, Fitchett, DH, Husain, M, and Cherney, DZ. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: cardiovascular and kidney effects, potential mechanisms, and clinical applications. Circulation. (2016) 134:752–72. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021887
167. Nangaku, M, Herrington, WG, Goto, S, Maruyama, S, Kashihara, N, Ueki, K, et al. Effects of empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease from Japan: exploratory analyses from EMPA-KIDNEY. Clin Exp Nephrol. (2024) 28:588–95. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02489-4
168. Fitchett, D, Inzucchi, SE, Cannon, CP, McGuire, DK, Scirica, BM, Johansen, OE, et al. Empagliflozin reduced mortality and hospitalization for heart failure across the Spectrum of cardiovascular risk in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Circulation. (2019) 139:1384–95. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037778
169. Kristensen, SL, Rorth, R, Jhund, PS, Docherty, KF, Sattar, N, Preiss, D, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2019) 7:776–85. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30249-9
170. Luna-Marco, C, Iannantuoni, F, Hermo-Argibay, A, Devos, D, Salazar, JD, Victor, VM, et al. Cardiovascular benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists through effects on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 213:19–35. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.01.015
171. Winiarska, A, Knysak, M, Nabrdalik, K, Gumprecht, J, and Stompor, T. Inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic kidney disease: the targets for SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:22. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910822
172. Puglisi, S, Rossini, A, Poli, R, Dughera, F, Pia, A, Terzolo, M, et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:738848. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.738848
173. Jamialahmadi, T, Baratzadeh, F, Reiner, Z, Mannarino, MR, Cardenia, V, Simental-Mendia, LE, et al. The effects of statin therapy on oxidized LDL and its antibodies: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7850659. doi: 10.1155/2022/7850659
174. Bussolati, B, Deregibus, MC, Fonsato, V, Doublier, S, Spatola, T, Procida, S, et al. Statins prevent oxidized LDL-induced injury of glomerular podocytes by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-signaling pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2005) 16:1936–47. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004080629
175. Wang, L, Yao, X, Li, Q, and Sun, S. Effect of simvastatin on lipid accumulation and the expression of CXCL16 and Nephrin in Podocyte induced by oxidized LDL. J Investig Surg. (2018) 31:69–74. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2016.1278057
176. Khan, SU, Yedlapati, SH, Lone, AN, Hao, Q, Guyatt, G, Delvaux, N, et al. PCSK9 inhibitors and ezetimibe with or without statin therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. (2022) 377:e069116. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-069116
177. Safarova, MS, and Kullo, IJ. Lipoprotein(a) lowering and cardiovascular risk reduction by PCSK9 inhibitors. Atherosclerosis. (2022) 361:30–1. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.10.010
178. Hummelgaard, S, Kresse, JC, Jensen, MS, Glerup, S, and Weyer, K. Emerging roles of PCSK9 in kidney disease: lipid metabolism, megalin regulation and proteinuria. Pflugers Arch. (2025) 477:773–86. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03069-5
179. Pavlakou, P, Liberopoulos, E, Dounousi, E, and Elisaf, M. PCSK9 in chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol. (2017) 49:1015–24. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1505-2
180. Skeby, CK, Hummelgaard, S, Gustafsen, C, Petrillo, F, Frederiksen, KP, Olsen, D, et al. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 targets megalin in the kidney proximal tubule and aggravates proteinuria in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. (2023) 104:754–68. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.06.024
181. Fiori, E, De Fazio, L, Pidone, C, Perone, F, Tocci, G, Battistoni, A, et al. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia: to treat or not a threat? A clinical and evidence-based approach to the management of hyperuricemia in the context of cardiovascular diseases. J Hypertens. (2024) 42:1665–80. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003807
182. Helget, LN, O'Dell, JR, Newcomb, JA, Androsenko, M, Brophy, MT, Davis-Karim, A, et al. Determinants of achieving serum urate goal with treat-to-target urate-lowering therapy in gout. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2024) 76:638–46. doi: 10.1002/art.42731
183. Stack, AG. Can we crystallize the role of urate-lowering treatment in chronic kidney disease? Kidney Int. (2025) 107:394–6. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.11.025
184. Goicoechea, M, de Vinuesa, SG, Verdalles, U, Ruiz-Caro, C, Ampuero, J, Rincon, A, et al. Effect of allopurinol in chronic kidney disease progression and cardiovascular risk. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2010) 5:1388–93. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01580210
185. Sapankaew, T, Thadanipon, K, Ruenroengbun, N, Chaiyakittisopon, K, Ingsathit, A, Numthavaj, P, et al. Efficacy and safety of urate-lowering agents in asymptomatic hyperuricemia: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Nephrol. (2022) 23:223. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02850-3
186. Huang, HH, Chen, YY, Fang, YW, Liou, HH, Wang, JT, and Tsai, MH. Comparative cardiovascular risks of Febuxostat and allopurinol in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Med Sci Monit. (2024) 30:e944314. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944314
187. Otani, M, Nonomiya, Y, Ihara, Y, Kawai, R, Taniuchi, S, Yoshida, H, et al. Association between Febuxostat use and the incidence of cardiovascular events, mortality, and kidney events in patients with chronic kidney disease compared to allopurinol: a study using a Japanese Nationwide database. Cureus. (2024) 16:e70351. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70351
188. Tsai, MH, Chen, YY, Liou, HH, Wang, JT, and Fang, YW. Febuxostat leads to better cardiovascular outcomes compared to allopurinol in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: a population-based cohort study. Am J Med. (2025) 138:e13:236–44. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2024.09.018
189. Muraya, N, Kadowaki, D, Miyamura, S, Kitamura, K, Uchimura, K, Narita, Y, et al. Benzbromarone attenuates oxidative stress in angiotensin II- and salt-induced hypertensive model rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:7635274. doi: 10.1155/2018/7635274
190. Damgaard, MV, and Treebak, JT. What is really known about the effects of nicotinamide riboside supplementation in humans. Sci Adv. (2023) 9:eadi4862. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4862
191. Yoshino, J, Baur, JA, and Imai, SI. NAD(+) intermediates: the biology and therapeutic potential of NMN and NR. Cell Metab. (2018) 27:513–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.11.002
192. Myakala, K, Wang, XX, Shults, NV, Krawczyk, E, Jones, BA, Yang, X, et al. NAD metabolism modulates inflammation and mitochondria function in diabetic kidney disease. J Biol Chem. (2023) 299:104975. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104975
193. Moludi, J, Qaisar, SA, Kadhim, MM, Ahmadi, Y, and Davari, M. Protective and therapeutic effectiveness of taurine supplementation plus low calorie diet on metabolic parameters and endothelial markers in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized, clinical trial. Nutr Metab (Lond). (2022) 19:49. doi: 10.1186/s12986-022-00684-2
194. Seneff, S, and Kyriakopoulos, AM. Taurine prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and protects mitochondria from reactive oxygen species and deuterium toxicity. Amino Acids. (2025) 57:6. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03440-3
195. Yildiz, O, and Ulusoy, KG. Effects of taurine on vascular tone. Amino Acids. (2022) 54:1527–40. doi: 10.1007/s00726-022-03198-6
196. Agarwal, R, Kolkhof, P, Bakris, G, Bauersachs, J, Haller, H, Wada, T, et al. Steroidal and non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal medicine. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:152–61. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa736
197. Scheithauer, TPM, Rampanelli, E, Nieuwdorp, M, Vallance, BA, Verchere, CB, van Raalte, DH, et al. Gut microbiota as a trigger for metabolic inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:571731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.571731
198. Hakhamaneshi, MS, Abdolahi, A, Vahabzadeh, Z, Abdi, M, and Andalibi, P. Toll-like receptor 4: a macrophage cell surface receptor is activated by trimethylamine-N-oxide. Cell J. (2021) 23:516–22. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7849
199. Wang, M, Li, XS, Wang, Z, de Oliveira Otto, MC, Lemaitre, RN, Fretts, A, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide is associated with long-term mortality risk: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:1608–18. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad089
200. Zheng, X, Huang, Y, Yang, M, Jin, L, Zhang, X, Zhang, R, et al. Vitamin D is involved in the effects of the intestinal flora and its related metabolite TMAO on perirenal fat and kidneys in mice with DKD. Nutr Diabetes. (2024) 14:42. doi: 10.1038/s41387-024-00297-z
201. Zhou, Z, Sun, L, Zhou, W, Gao, W, Yuan, X, Zhou, H, et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium reduces serum TMAO in unstable angina patients via the gut to liver to heart axis. Liver Res. (2025) 9:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2025.02.001
202. Dai, Y, Quan, J, Xiong, L, Luo, Y, and Yi, B. Probiotics improve renal function, glucose, lipids, inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. (2022) 44:862–80. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2079522
203. Dong, Y, Li, L, Xia, T, Wang, L, Xiao, L, Ding, N, et al. Oxidative stress can be attenuated by 4-PBA caused by high-fat or Ammonia nitrogen in cultured spotted seabass: the mechanism is related to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022):11. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071276
204. Xia, T, Liao, YQ, Li, L, Sun, LY, Ding, NS, Wu, YL, et al. 4-PBA attenuates fat accumulation in cultured spotted seabass fed high-fat-diet via regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Meta. (2022) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121197
205. Liu, SH, Yang, CC, Chan, DC, Wu, CT, Chen, LP, Huang, JW, et al. Chemical chaperon 4-phenylbutyrate protects against the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated renal fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:22116–27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7904
206. Zhang, Y, Yang, S, Fu, J, Liu, A, Liu, D, and Cao, S. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress prevents high-fat diet mediated atrial fibrosis and fibrillation. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:13660–8. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15816
207. Luo, T, Kim, JK, Chen, B, Abdel-Latif, A, Kitakaze, M, and Yan, L. Attenuation of ER stress prevents post-infarction-induced cardiac rupture and remodeling by modulating both cardiac apoptosis and fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. (2015) 225:90–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.032
208. Luo, T, Chen, B, and Wang, X. 4-PBA prevents pressure overload-induced myocardial hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Chem Biol Interact. (2015) 242:99–106. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.09.025
209. Li, Y, El-Sehrawy, A, Shankar, A, Srivastava, M, Mohammed, JS, Hjazi, A, et al. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Clin Ther. (2025) 47:235–43. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2024.12.010
210. Couto, SMF, da Fonseca, CD, Watanabe, M, and de Fatima Fernandes Vattimo, M. Protection of coenzyme Q10 against contrast-induced acute kidney injury in male diabetic rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2021) 13:69. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00689-6
211. Alehagen, U, Johansson, P, Svensson, E, Aaseth, J, and Alexander, J. Improved cardiovascular health by supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q10: applying structural equation modelling (SEM) to clinical outcomes and biomarkers to explore underlying mechanisms in a prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled intervention project in Sweden. Eur J Nutr. (2022) 61:3135–48. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-02876-1
212. Agbu, P, and Carthew, RW. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:425–38. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00354-w
213. Mahtal, N, Lenoir, O, Tinel, C, Anglicheau, D, and Tharaux, PL. MicroRNAs in kidney injury and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 18:643–62. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00608-6
214. Song, R, Dasgupta, C, Mulder, C, and Zhang, L. MicroRNA-210 controls mitochondrial metabolism and protects heart function in myocardial infarction. Circulation. (2022) 145:1140–53. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056929
Keywords: metabolic conditions, albuminuria, kidney injury, cardiovascular outcomes, mechanism, intervention strategies
Citation: Wu Y, Xu H, Tu X and Gao Z (2025) Role of metabolic conditions in cardiorenal diseases: initiating pathways and therapeutic targeting. Front. Nutr. 12:1701084. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1701084
Edited by:
Ian James Martins, University of Western Australia, AustraliaReviewed by:
Xu Zhai, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, ChinaAshwini Jagdale, Symbiosis International University, India
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Xu, Tu and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenyan Gao, Z2FvemhlbnlhbjgwQDE2My5jb20=
 Yeshun Wu
Yeshun Wu Hongqing Xu
Hongqing Xu Zhenyan Gao
Zhenyan Gao