- 1School of Nursing, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 2School of Future Technology, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
- 3Shenzhen Eye Hospital, Shenzhen Eye Medical Center, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, China
Background: Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly accessed by lay users for medical advice. This study aims to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the responses generated by five large language models.
Methods: We identified 31 ophthalmology-related questions most frequently raised by patients during routine consultations and subsequently elicited responses from five large language models: ChatGPT-4o, DeepSeek-V3, Doubao, Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo, and Qwen. A five-point likert scale was employed to assess each model across five domains: accuracy, logical consistency, coherence, safety, and content accessibility. Additionally, textual characteristics, including character, word, and sentence counts, were quantitatively analyzed.
Results: ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 achieved the highest overall performance, with statistically superior accuracy and logical consistency (p < 0.05). Existing safety evaluations indicate that both Doubao and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo exhibit significant security deficiencies. Conversely, Qwen generated significantly longer outputs, as evidenced by greater character, word, and sentence counts.
Conclusion: ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 demonstrated the highest overall performance and are best suited for laypersons seeking ophthalmic information. Doubao and Qwen, with their richer clinical terminology, better serve users with medical training, whereas Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo most effectively supports patients’ pre-procedural understanding of diagnostic procedures. Prospective randomized controlled trials are required to determine whether integrating the top-performing model into pre-consultation triage improves patient comprehension.
1 Introduction
Advances in deep learning have enabled large language models (LLMs) to achieve substantial breakthroughs in natural language processing, demonstrating broad utility across text generation, semantic comprehension, translation, and inferential reasoning (1, 2). Recently, generative artificial intelligence has exhibited considerable promise within the healthcare sector, particularly in standardized examination simulation and clinical documentation, thereby invigorating contemporary medical practice (3–5). Advanced LLMs, exemplified by ChatGPT and DeepSeek, are now systematically deployed across diverse medical specialties and have demonstrated early efficacy in disease recognition, diagnostic support, and evidence-based clinical decision-making (6–8). LLMs have demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy and decision-making efficacy in subspecialties such as neuro-ophthalmology, glaucoma, and thyroid eye disease, underscoring their substantial application potential (9–11). Furthermore, large language models such as Qwen, Doubao, and Wenxin Yiyan exhibit substantial translational promise across clinical and research workflows (12, 13). These systems enhance healthcare service efficiency, mitigate clinician workload, and foster patient health literacy and equitable access to care (14).
Nevertheless, the deployment of LLMs in clinical settings faces several challenges, among which ‘model hallucination’ is particularly pronounced (15, 16). Such models may produce outputs that are structurally coherent yet factually erroneous, a limitation arising from outdated training corpora and restricted access to contemporary medical guidelines, ultimately compromising the comprehensiveness and authority of their knowledge bases (17, 18). Although initiatives such as DeepSeek seek to mitigate the black-box problem through enhanced transparency and interpretability, the medical community retains circumspection regarding their reliability (19, 20). The growing utilization of LLMs for unsupervised health self-diagnosis may expose lay users to inaccurate or unsafe information, thereby amplifying potential harms (21, 22). Besides, ophthalmology necessitates exceptionally high diagnostic precision, as even marginal deviations can adversely affect patient prognosis (23). Therefore, comprehensive performance evaluations within ophthalmological contexts are urgently required prior to their widespread clinical adoption (24). Existing studies focus primarily on different versions of ChatGPT, leaving a scarcity of comparative analyses across models (25).
This study systematically evaluates five LLMs (ChatGPT-4o, DeepSeek-V3, Qwen, Doubao, and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo) and focuses on their responses to ophthalmology-related questions from patients. Model outputs will be comprehensively assessed across five domains: accuracy, logical consistency, coherence, safety, and content accessibility. Additionally, quantitative text metrics (character, word, and sentence counts) will be extracted from Chinese-language outputs to elucidate their practical utility for patient education and clinical decision support.
2 Method
2.1 Ethical statement
This cross-sectional evaluation compared responses generated by five LLMs to 31 frequently encountered consultation questions in ophthalmology. The questions were derived from routine clinical inquiries collected by healthcare providers during patient encounters. Crucially, the study involved no patient-level data or personally identifiable information, thereby fully preserving individual anonymity and privacy.
2.2 Model selection
We purposefully selected five state-of-the-art LLMs: ChatGPT-4o, DeepSeek-V3, Qwen, Doubao, and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo. Selection criteria encompassed recent benchmark performance, public accessibility, the developers’ institutional credibility, and demonstrated suitability for medical question-answering.
2.2.1 ChatGPT-4o
ChatGPT-4o1 is OpenAI’s newest transformer-based large-scale language model. It leverages deep-learning techniques to deliver advanced generative and comprehension capabilities, and its multimodal architecture ensures robust performance across heterogeneous input modalities, encompassing text and images.
2.2.2 DeepSeek-V3
DeepSeek-V32 is engineered for high-performance information retrieval and open-domain question answering, integrating deep-learning and reinforcement-learning techniques to optimize retrieval efficiency and accuracy.
2.2.3 Qwen
Qwen3 is a conversational LLM optimized for interactive question-answering, emphasizing user engagement and real-time feedback.
2.2.4 Doubao
Doubao4 is specifically optimised for Chinese-language tasks, employing multi-layer attention mechanisms to capture nuanced semantics and cultural contexts.
2.2.5 Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo
Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo5 is tailored for Chinese natural-language processing, exhibiting strong generative and semantic-understanding capabilities.
2.3 Study design
We conducted a cross-sectional benchmarking study evaluating how the five selected LLMs respond to 31 frequently asked consultation questions covering retinal diseases, macular degeneration, glaucoma, dry eye and associated procedures. Questions were classified as definitional, causal, comparative, or procedural and reflect typical patient queries.
On 6 March 2025, two investigators jointly recorded the answer generated by each model in a single submission. Each question was submitted separately through the online platforms corresponding to the five models. No system prompts were provided, and responses were generated de novo from the query. Following response generation, the chat histories were manually reset to prevent carryover of context.
All outputs were independently verified by two researchers and transcribed into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Character, word, and sentence counts were automatically derived using the online text analytics tool Xiezuocat.6
Two board-certified vitreoretinal attending physicians with equivalent seniority (each with ≥5 years of subspecialty experience) independently rated each response across five domains: accuracy, logical consistency, coherence, safety, and content accessibility, using a five-point Likert scale (1 = poor, 5 = excellent). Detailed scoring criteria and the full question list are provided in the Supplementary material. All interactions were conducted within a controlled online environment following standardized operating procedures to maximize reproducibility.
2.4 Data analysis
All analyses were conducted in SPSS software (version 27.0). Inter-rater consistency of total scores was assessed with the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Normality was evaluated using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Normally distributed continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SD; non-normally distributed variables as median (IQR). Homogeneity of variances was evaluated using Levene’s test. Parametric comparisons among the five models employed one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA); non-parametric analyses utilized the Kruskal–Wallis H test. Where significant differences were detected, Bonferroni-corrected post-hoc pairwise comparisons were performed. p < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Comparative performance of five LLMs
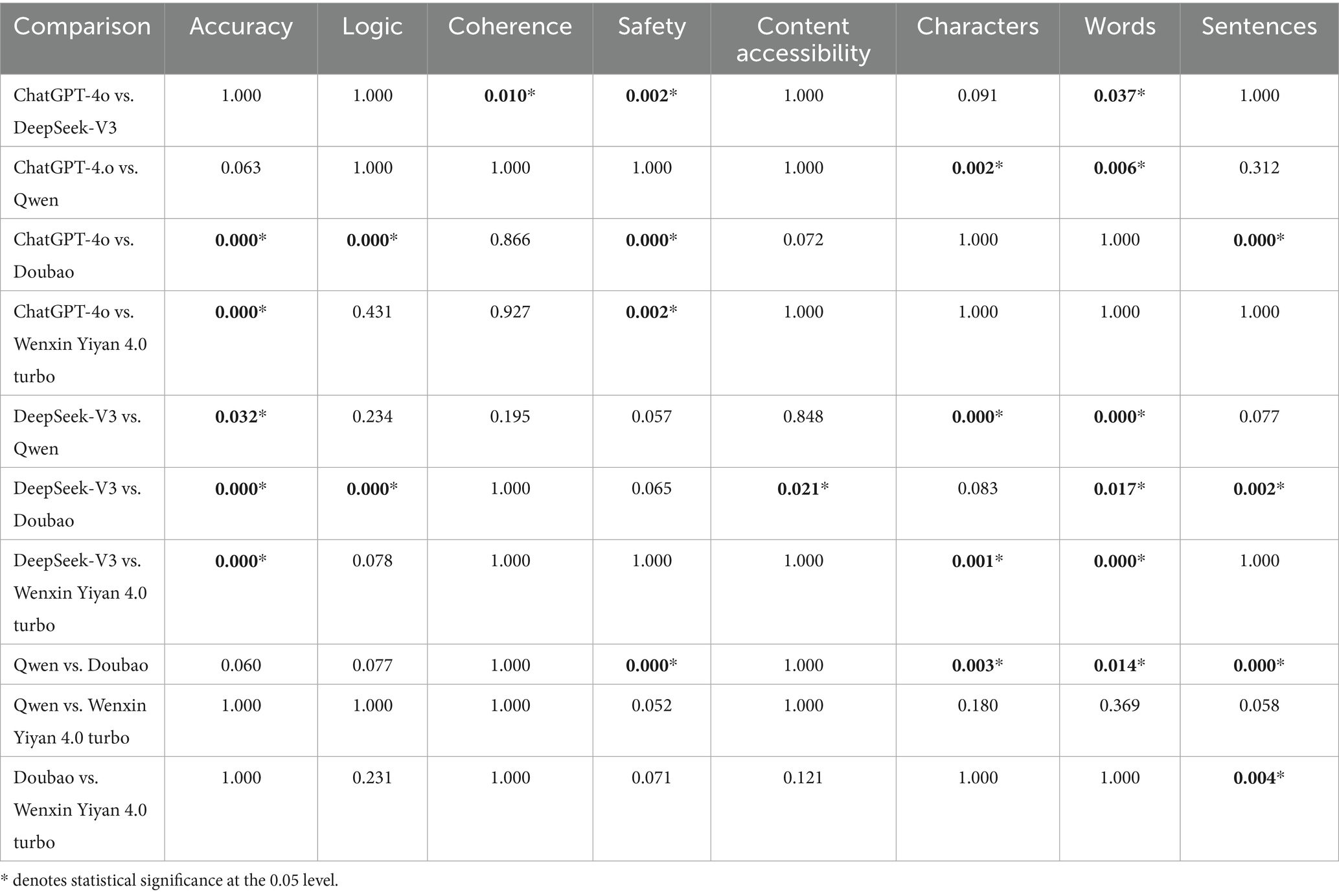
The ICC between the two raters was 0.87. Table 1 summarizes the median scores of the five LLMs across five domains: accuracy, logical consistency, coherence, safety, and content accessibility. Accuracy: ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 attained the maximum median score of 5.0, significantly surpassing the remaining models (H = 50.90, p < 0.05). Logical consistency: Likewise, ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 achieved a median of 5.0, significantly exceeding the others (H = 29.82, p < 0.05). Coherence: Scores differed modestly; nevertheless, ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 exhibited marginally higher stability (H = 11.69, P<0.05). Safety: ChatGPT-4o scored highest (4.0), whereas Doubao and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo recorded the lowest (3.0), with significant between-group differences (H = 52.30, p < 0.05). Content accessibility: ChatGPT, DeepSeek-V3 and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo performed best (4.0), while Qwen and Doubao scored lower (3.0); these differences were statistically significant (H = 12.54, p < 0.05). Detailed differences are provided in Table 2 and Figure 1.
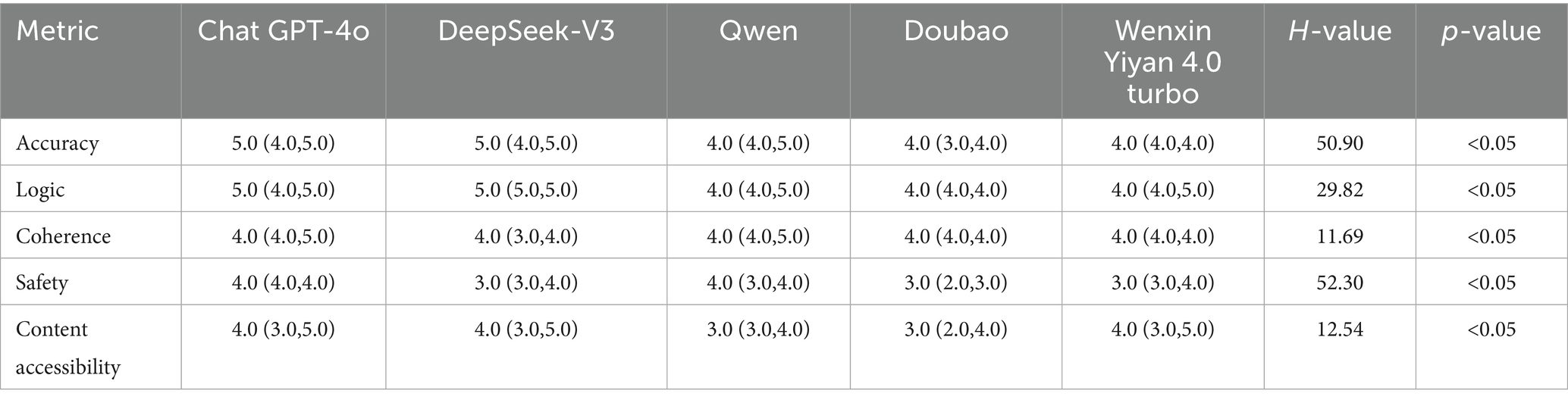
Table 1. Performance scores of five large language models across accuracy, logic, coherence, safety, and content accessibility.
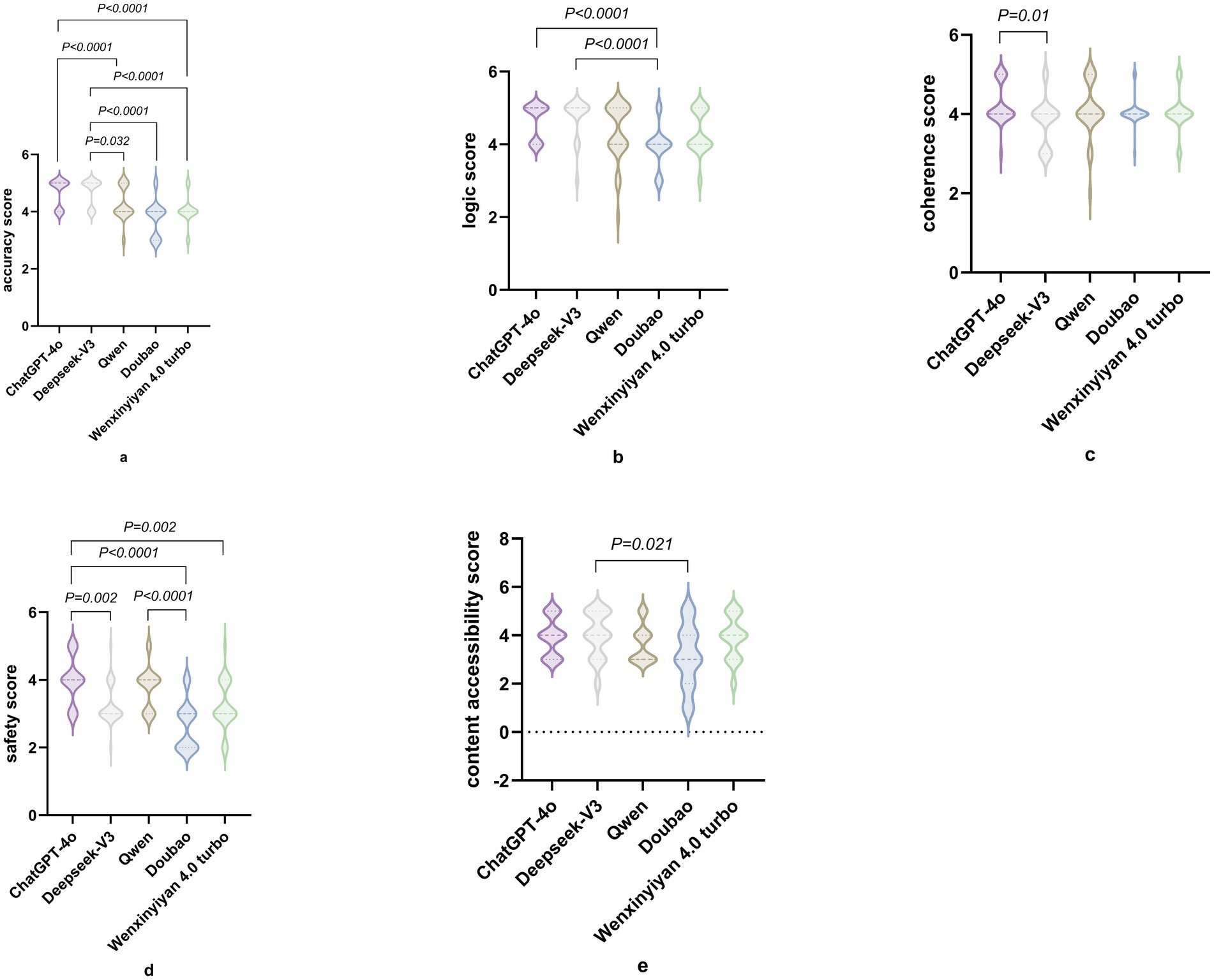
Figure 1. Pairwise comparisons between models. (a) Accuracy comparison; (b) Logic scores; (c) Coherence scores; (d) Safety scores; (e) Content accessibility scores.
3.2 Output length characteristics
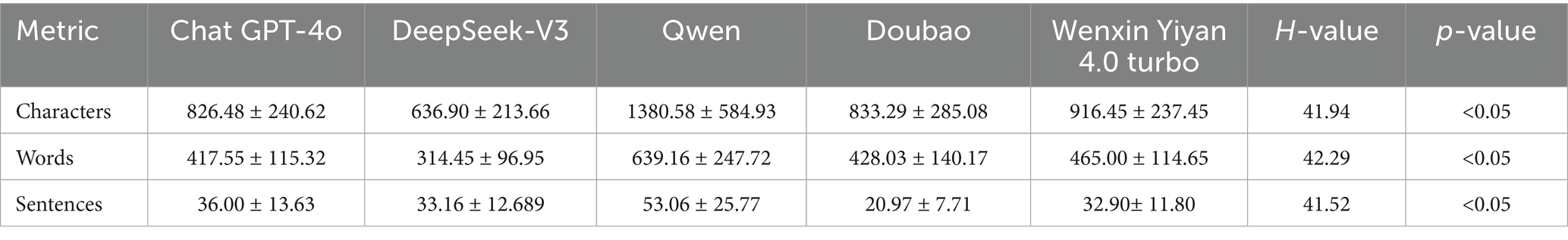
Table 3 and Figure 2 present descriptive statistics for character, word, and sentence counts. Qwen produced the longest responses (1,380.58), significantly exceeding ChatGPT-4o (826.48) and DeepSeek-V3 (636.90) (p < 0.05). Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo generated 916.45 words, approximating ChatGPT-4o. Similarly, Qwen yielded the highest token count (639.16), substantially surpassing DeepSeek-V3 (314.45) and ChatGPT-4o (417.55) (p < 0.05). Doubao and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo produced fewer tokens (428.03 and 465.00, respectively). Qwen also generated the greatest number of sentences (53.06), significantly exceeding DeepSeek-V3 (33.16) and ChatGPT-4o (36.00) (p < 0.05). Conversely, Doubao and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo produced the fewest sentences (20.97 and 32.90, respectively). Collectively, Qwen generated significantly more characters, words, and sentences than all other models (p < 0.05). Comprehensive pairwise comparisons are presented in Table 3 and Figure 2.
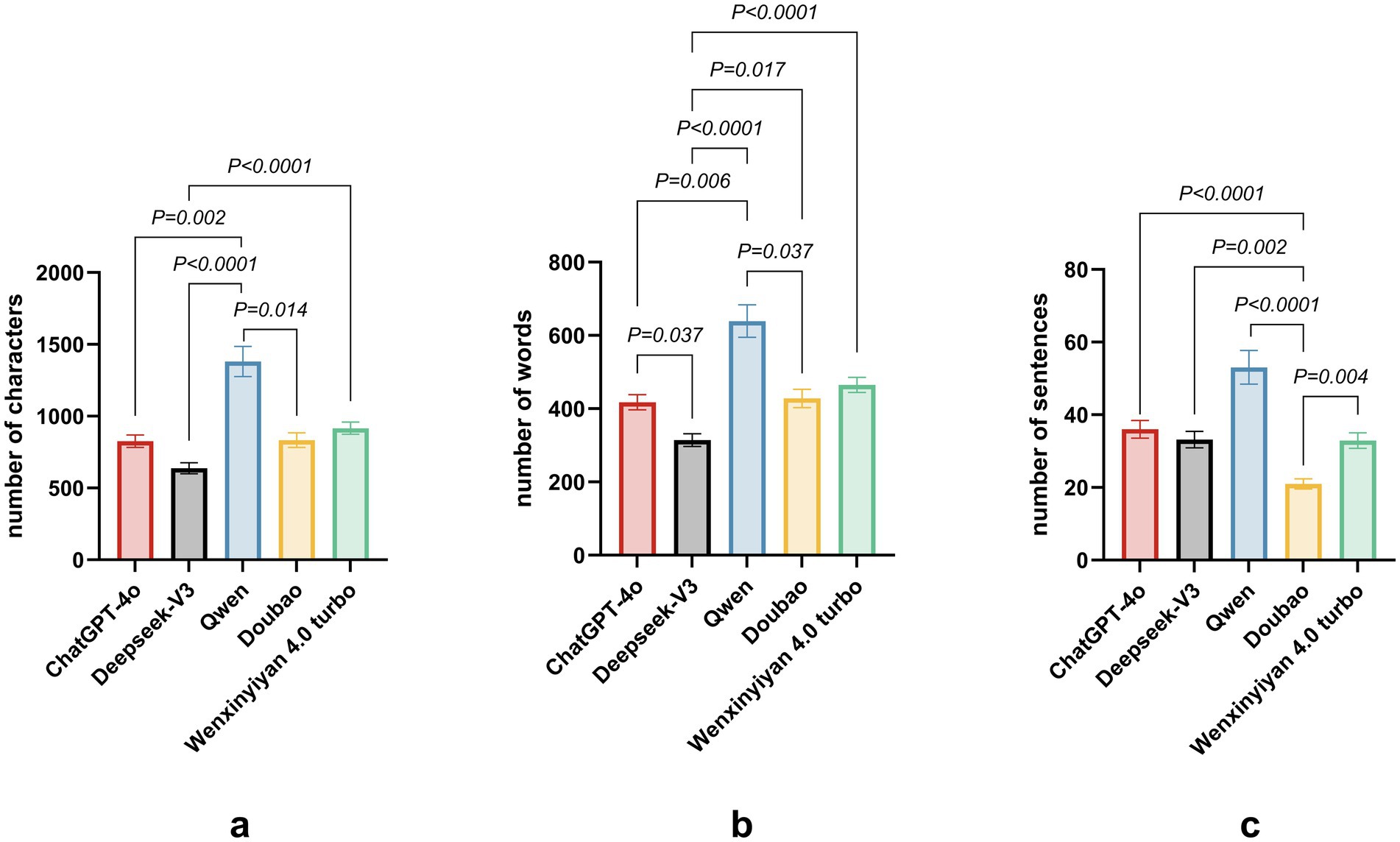
Figure 2. Response lengths of five large language models to 31 common consultation questions in ophthalmic practices. (a) Character count; (b) Word count; (c) Sentence count.
4 Discussion
As LLMs are increasingly adopted in ophthalmology, where diagnostic precision is paramount, their accuracy, safety, and clarity directly affect clinical decision support and patient education (26). Patients now commonly seek online health information and may obtain LLM-based advice without clinician oversight; therefore, these systems must meet rigorous quality standards before healthcare implementation.
Our findings demonstrate statistically significant inter-model heterogeneity, with ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 achieving superior overall performance. Consistent with earlier reports (23, 27), ChatGPT-4o exhibits near-expert proficiency in ophthalmological question-answering, while DeepSeek-V3 matches ChatGPT-4o in accuracy; both significantly outperform the remaining three models. This superiority may be attributable to: (1) the increased complexity of open-ended questions relative to prior multiple-choice formats; (2) delayed updates in competing models; and (3) advanced algorithmic architectures and curated training corpora employed by ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3.
Coherence scores were comparable across models, yet ChatGPT-4o and Qwen exhibited marginally superior stability (28), suggesting that architectural heterogeneity influences medical reasoning construction. We additionally assessed the inclusion of disclaimers intended to mitigate medical and legal risk. ChatGPT-4o and Qwen frequently appended disclaimers (e.g., “seek prompt medical attention” or “consult a qualified clinician”), indicating stronger safety-control mechanisms than their counterparts.
When addressing different query types, all models provided comprehensive descriptions of disease-related content, particularly for definitional questions. For diagnostic tasks, DeepSeek-V3 and Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo supplied extensive clinical context and complication analyses, whereas ChatGPT-4o remained concise yet superficial (14). Previous studies have not reported that Doubao and Qwen display broader stylistic variation than other models (29), whereas ChatGPT-4o, although clear and concise, shows limited stylistic flexibility.
Upon addressing the query “How does diabetes induce retinal damage?,” ChatGPT-4o first defined diabetic retinopathy and summarized its pathophysiology, then listed preventive measures (glycemic control, annual retinal screening, optimization of lipids and blood pressure, smoking cessation, limited alcohol intake, and supplementation with lutein, vitamins C and E, and ω-3 fatty acids). DeepSeek-V3 more deeply into the underlying molecular mechanisms while simultaneously elaborating on disease progression and clinical manifestations. Qwen and Doubao concentrate on a hierarchical analysis of pathological mechanisms, whereas clinical management recommendations are comparatively sparse. Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo first described the disease, then detailed relevant examinations such as optical coherence tomography. The examples of this study indicate that ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 are better suited for the general public seeking disease information, whereas Qwen, Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo, and Doubao employ more complex medical terminology that benefits clinical trainees but may hinder comprehension among non-specialists. Such complexity may impede information acquisition, emotional support, and interpersonal rapport among patients (30, 31).
Converging evidence from our multi-dimensional assessment described above suggests that the observed balance of accuracy, conciseness, and safety renders these models operationally viable for eye-care pathways.
Previous studies have demonstrated that ChatGPT demonstrates diagnostic accuracy comparable to, or even exceeding, that achieved by ophthalmology residents in distinguishing primary from secondary glaucoma (10). This study further demonstrated that ChatGPT-4o rapidly identified patients requiring immediate referral versus routine follow-up, consistent with earlier studies (32). Within hierarchical diagnostic and treatment settings, chatbots demonstrate a superior capacity to identify acute and severe conditions (33), substantially enhancing patient satisfaction and the overall care experience (34). In circumstances where a patient cannot attend a hospital or clinic in person, or requires expeditious triage to ascertain the urgency of professional medical attention, LLMs can be leveraged to provide case-specific recommendations (34).
The application of LLMs in ophthalmology is rapidly expanding across medical education, clinical support, research, and patient education (35). However, persistent challenges (inconsistent performance, algorithmic bias, hallucinations, data-privacy risks, and ethical dilemmas) remain (36). Patients with ophthalmic concerns should continue to consult certified eye-care professionals, ensuring adequate human oversight in clinical decision-making (26, 37). Future initiatives must prioritize iterative model refinement and interdisciplinary ethical governance to ensure responsible clinical deployment (24, 25). Empirical evidence confirms that well-crafted prompts enhance both output accuracy and contextual relevance (38–40), although prompt variation exerts limited influence on accuracy, it substantially modifies textual readability (41, 42). Consequently, readability remains pivotal for effective patient communication even when accuracy gains are marginal.
LLMs trained with domain-specific ophthalmological expertise outperform those trained on general corpora (43). Future validation pipelines for ophthalmology-focused LLMs should span multi-center, multi-tier institutions and establish an iterative cycle of fine-tuning, validation, and governance. Interdisciplinary experts in ophthalmology, law, and ethics will craft an adaptive governance framework, while curated multi-center datasets drive continuous model refinement. The integration of this model into medical education platforms can be used to generate immersive virtual patient cases that significantly bridge the gap between theory and clinical practice (44), while alleviating the healthcare burden in resource-limited regions (45, 46). We therefore recommend that the platform adopt a two-pronged strategy: first, encourage physicians to participate as cohesive teams to leverage peer-learning and collaborative mechanisms for enhancing overall service quality; second, embed robust privacy-preserving safeguards within personalized services so that patients can fully benefit from precision medicine without concerns about data security.
Our study has several limitations. First, each query was presented only once without priming or real-world outcome validation, potentially underestimating model capabilities. Second, analyses were restricted to Chinese-language responses, limiting generalizability. Third, we focused on the most common ophthalmic conditions, which may not fully capture the breadth of LLM functions. Future work should incorporate diverse, real-time datasets and develop validated tools for assessing linguistic complexity in Chinese LLMs to improve reliability, and should expand evaluation to additional models to clarify domain-specific strengths and limitations.
5 Conclusion
This study systematically evaluated five mainstream LLMs on ophthalmology question-answering tasks, revealing inter-model differences in accuracy, logical consistency, coherence, safety, and content accessibility. ChatGPT-4o and DeepSeek-V3 consistently outperformed the others, particularly in accuracy and logical consistency. Qwen produced the longest and most lexically rich outputs. Qwen, Wenxin Yiyan 4.0 Turbo, and Doubao employed complex medical terminology that may hinder comprehension among non-specialists. Continued technological advances and mitigation of current limitations will substantially enhance the clinical utility of LLMs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
MH: Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft. XW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. SZ: Validation, Software, Writing – original draft. XC: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Software, Writing – original draft. YX: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. WY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82571272) and Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZSM202411007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1673045/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^https://openai.com/index/hello-gpt-4o/
2. ^https://chat.deepseek.com/
References
1. Jin, Q, Leaman, R, and Lu, Z. PubMed and beyond: biomedical literature search in the age of artificial intelligence. EBioMedicine. (2024) 100:104988. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.104988
2. Health, TLD. Large language models: a new chapter in digital health. Lancet Digit Health. (2024) 6:e1. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00254-6
3. Stribling, D, Xia, Y, Amer, MK, Graim, KS, Mulligan, CJ, and Renne, R. The model student: GPT-4 performance on graduate biomedical science exams. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:5670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55568-7
4. Peng, Y, Rousseau, JF, Shortliffe, EH, and Weng, C. AI-generated text may have a role in evidence-based medicine. Nat Med. (2023) 29:1593–4. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02366-9
5. Ali, SR, Dobbs, TD, Hutchings, HA, and Whitaker, IS. Using ChatGPT to write patient clinic letters. Lancet Digit Health. (2023) 5:e179–81. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00048-1
6. Perlis, RH, and Fihn, SD. Evaluating the application of large language models in clinical research contexts. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e2335924. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35924
7. Jin, X, Zhang, J, Yang, J, Yang, S, Xue, D, and Zhang, Z. Every cloud has a silver lining: DeepSeek’s light through acute respiratory distress syndrome shadows. J Thorac Dis. (2025) 17:1109–13. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2025-381
8. Wei, J, Wang, X, Huang, M, Xu, Y, and Yang, W. Evaluating the performance of ChatGPT on board-style examination questions in ophthalmology: a meta-analysis. J Med Syst. (2025) 49:94. doi: 10.1007/s10916-025-02227-7
9. Yeganeh, M, Mohammad, D, Priscilla, A L, and Joseph, W F. ChatGPT assisting diagnosis of neuro-ophthalmology diseases based on case reports. (2024). Available online at: https://journals.lww.com/jneuro-ophthalmology/fulltext/9900/chatgpt_assisting_diagnosis_of_neuro_ophthalmology.723.aspx (Accessed April 10, 2025)
10. Delsoz, M, Raja, H, Madadi, Y, Tang, AA, Wirostko, BM, Kahook, MY, et al. The use of ChatGPT to assist in diagnosing Glaucoma based on clinical case reports. Ophthalmol Ther. (2023) 12:3121–32. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00805-x
11. Milad, D, Antaki, F, Milad, J, Farah, A, Khairy, T, Mikhail, D, et al. Assessing the medical reasoning skills of GPT-4 in complex ophthalmology cases. Br J Ophthalmol. (2024) 108:1398–405. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2023-325053
12. Liu, Y, Yuan, Y, Yan, K, Li, Y, Sacca, V, Hodges, S, et al. Evaluating the role of large language models in traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis and treatment recommendations. NPJ Digit Med. (2025) 8:466. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01845-2
13. Kang, D, Wu, H, Yuan, L, Shen, W, Feng, J, Zhan, J, et al. Evaluating the efficacy of large language models in guiding treatment decisions for pediatric refractive error. Ophthalmol Ther. (2025) 14:705–16. doi: 10.1007/s40123-025-01105-2
14. Lim, ZW, Pushpanathan, K, Yew, SME, Lai, Y, Sun, CH, Lam, JSH, et al. Benchmarking large language models’ performances for myopia care: a comparative analysis of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4.0, and Google bard. EBioMedicine. (2023) 95:104770. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104770
15. Farquhar, S, Kossen, J, Kuhn, L, and Gal, Y. Detecting hallucinations in large language models using semantic entropy. Nature. (2024) 630:625–30. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07421-0
16. Shen, Y, Heacock, L, Elias, J, Hentel, KD, Reig, B, Shih, G, et al. ChatGPT and other large language models are double-edged swords. Radiology. (2023) 307:e230163. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230163
17. Alberts, IL, Mercolli, L, Pyka, T, Prenosil, G, Shi, K, Rominger, A, et al. Large language models (LLM) and ChatGPT: what will the impact on nuclear medicine be? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2023) 50:1549–52. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06172-w
18. Tian, S, Jin, Q, Yeganova, L, Lai, P-T, Zhu, Q, Chen, X, et al. Opportunities and challenges for ChatGPT and large language models in biomedicine and health. Brief Bioinform. (2024) 25:bbad493. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad493
19. Normile, D. (2025) Chinese firm’s faster, cheaper AI language model makes a splash. Available online at: https://www.science.org/content/article/chinese-firm-s-faster-cheaper-ai-language-model-makes-splash (Accessed March 27, 2025)
20. Peng, Y, Malin, BA, Rousseau, JF, Wang, Y, Xu, Z, Xu, X, et al. From GPT to DeepSeek: significant gaps remain in realizing AI in healthcare. J Biomed Inform. (2025) 163:104791. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2025.104791
21. Temsah, A, Alhasan, K, Altamimi, I, Jamal, A, Al-Eyadhy, A, Malki, KH, et al. DeepSeek in healthcare: revealing opportunities and steering challenges of a new open-source artificial intelligence frontier. Cureus. (2025) 17:e79221. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79221
22. Kuehn, BM. More than one-third of US individuals use the internet to self-diagnose. JAMA. (2013) 309:756–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.629
23. Giannuzzi, F, Carlà, MM, Hu, L, Cestrone, V, Caputo, CG, Sammarco, MG, et al. Artificial intelligence with ChatGPT 4: a large language model in support of ocular oncology cases. Int Ophthalmol. (2025) 45:59–17. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03399-w
24. Moreno, AC, and Bitterman, DS. Toward clinical-grade evaluation of large language models. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2024) 118:916–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.11.012
25. Agnihotri, AP, Nagel, ID, Artiaga, JCM, Guevarra, MCB, Sosuan, GMN, and Kalaw, FGP. Large language models in ophthalmology: a review of publications from top ophthalmology journals. Ophthalmol Sci. (2024) 5:100681. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2024.100681
26. Cappellani, F, Card, KR, Shields, CL, Pulido, JS, and Haller, JA. Reliability and accuracy of artificial intelligence ChatGPT in providing information on ophthalmic diseases and management to patients. Eye. (2024) 38:1368–73. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02906-0
27. Mishra, V, Lurie, Y, and Mark, S. Accuracy of LLMs in medical education: evidence from a concordance test with medical teacher. BMC Med Educ. (2025) 25:443–8. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07009-w
28. Wu, X, Cai, G, Guo, B, Ma, L, Shao, S, Yu, J, et al. A multi-dimensional performance evaluation of large language models in dental implantology: comparison of ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Grok, Gemini and Qwen across diverse clinical scenarios. BMC Oral Health. (2025) 25:1272. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06619-6
29. Pan, Y, Tian, S, Guo, J, Cai, H, Wan, J, and Fang, C. Clinical feasibility of AI doctors: evaluating the replacement potential of large language models in outpatient settings for central nervous system tumors. Int J Med Inform. (2025) 203:106013. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2025.106013
30. Matin, RN, Linos, E, and Rajan, N. Leveraging large language models in dermatology. Br J Dermatol. (2023) 189:253–4. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad230
31. ElHawary, H, Gorgy, A, and Janis, JE. Large language models in academic plastic surgery: the way forward. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. (2023) 11:e4949. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004949
32. Waisberg, E, Ong, J, Zaman, N, Kamran, SA, Sarker, P, Tavakkoli, A, et al. GPT-4 for triaging ophthalmic symptoms. Eye. (2023) 37:3874–5. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02595-9
33. Zandi, R, Fahey, JD, Drakopoulos, M, Bryan, JM, Dong, S, Bryar, PJ, et al. Exploring diagnostic precision and triage proficiency: a comparative study of GPT-4 and bard in addressing common ophthalmic complaints. Bioengineering. (2024) 11:120. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020120
34. Betzler, BK, Chen, H, Cheng, CY, Lee, CS, Ning, G, Song, SJ, et al. Large language model and its impact in ophthalmology. Lancet Digit Health. (2023) 5:e917–24. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00201-7
35. Shah, NH, Entwistle, D, and Pfeffer, MA. Creation and adoption of large language models in medicine. JAMA. (2023) 330:866–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.14217
36. Cai, W. Feasibility and Prospect of privacy-preserving large language models in radiology. Radiology. (2023) 309:e232335. doi: 10.1148/radiol.232335
37. Yi, C, Niu, G, Zhang, Y, Rao, J, Liu, G, Yang, W, et al. Advances in artificial intelligence in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1356055. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356055
38. Lee, D, and Palmer, E. Prompt engineering in higher education: a systematic review to help inform curricula. Int J Educ Technol High Educ. (2025) 22:1–22. doi: 10.1186/s41239-025-00503-7
39. Patel, D, Raut, G, Zimlichman, E, Cheetirala, SN, Nadkarni, GN, Glicksberg, BS, et al. Evaluating prompt engineering on GPT-3.5’s performance in USMLE-style medical calculations and clinical scenarios generated by GPT-4. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:17341–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66933-x
40. Ranade, N, Saravia, M, and Johri, A. Using rhetorical strategies to design prompts: a human-in-the-loop approach to make AI useful. AI Soc. (2025) 40:711–32. doi: 10.1007/s00146-024-01905-3
41. Akkan, H, and Seyyar, GK. Improving readability in AI-generated medical information on fragility fractures: the role of prompt wording on ChatGPT’s responses. Osteoporos Int. (2025) 36:403–10. doi: 10.1007/s00198-024-07358-0
42. Campbell, DJ, Estephan, LE, Sina, EM, Mastrolonardo, EV, Alapati, R, Amin, DR, et al. Evaluating ChatGPT responses on thyroid nodules for patient education. Thyroid. (2024) 34:371–7. doi: 10.1089/thy.2023.0491
43. Luo, MJ, Pang, J, Bi, S, Lai, Y, Zhao, J, Shang, Y, et al. Development and evaluation of a retrieval-augmented large language model framework for ophthalmology. JAMA Ophthalmol. (2024) 142:798–805. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.2513
44. Sadeq, MA, Ghorab, RMF, Ashry, MH, Abozaid, AM, Banihani, HA, Salem, M, et al. AI chatbots show promise but limitations on UK medical exam questions: a comparative performance study. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:18859–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68996-2
45. Li, Z, Wang, Z, Xiu, L, Zhang, P, Wang, W, Wang, Y, et al. Large language model-based multimodal system for detecting and grading ocular surface diseases from smartphone images. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2025) 13:1600202. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1600202
Keywords: large language model, healthcare, consultation, ophthalmology, patient education
Citation: Huang M, Wang X, Zhou S, Cui X, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang W and Chi W (2025) Comparative performance of large language models for patient-initiated ophthalmology consultations. Front. Public Health. 13:1673045. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1673045
Edited by:
Xiaofei Zhang, Nankai University, ChinaReviewed by:
Peng Gao, Tongji University, ChinaMeng Wang, Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Wang, Zhou, Cui, Zhang, Xu, Yang and Chi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weihua Yang, YmVuYmVuMDYwNkAxMzkuY29t; Wei Chi, Y2hpd2VpQG1haWwuc3lzdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Mingxue Huang
Mingxue Huang Xiaoyan Wang
Xiaoyan Wang Shiqi Zhou
Shiqi Zhou Xinyu Cui2
Xinyu Cui2 Weihua Yang
Weihua Yang Wei Chi
Wei Chi