Featured news
26 Sep 2022
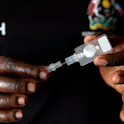
New research shows self-injectable contraception can enable women to take charge of their reproductive health
By Allen Namagembe, PATH, Uganda and Dr Jane Cover, PATH, US Image: PATH/Will Boase Allen Namagembe is a clinical epidemiologist, a biostatistician, and a global expert on self-injection. She is the Uganda Deputy Project Director and M&E Lead on the Uganda Self-Injection Scale-Up project at PATH. Dr. Jane Cover is a Research and Evaluation Manager on PATH’s Sexual and Reproductive Health team and the PATH-JSI DMPA-SC Access Collaborative. Now, they explain their team’s two studies, published in Frontiers in Global Women’s Health, where they used a human-centered design approach to develop and implement a pilot self-injection program in Uganda. Their results show how the program can increase women’s contraceptive access and options. For some, the term ‘self-care’ might conjure up images of skincare routines, bubble baths, and meditation. But in public health, self-care refers to the ability of individuals to self-manage aspects of their health care with the goal of promoting and sustaining health, preventing disease, and managing illness or disability. Grounded in evidence, agency, and equity, self-care interventions are key components of a holistic primary health care system and can help fill gaps in access to essential health services. We both conduct research in the sexual and reproductive health […]













