In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1 as published. The KLD and ULF bars were switched, but the numerical values within them, as well as other information presented in the figure and caption, were accurate.
The corrected Figure 1 and its caption appear below.
Figure 1
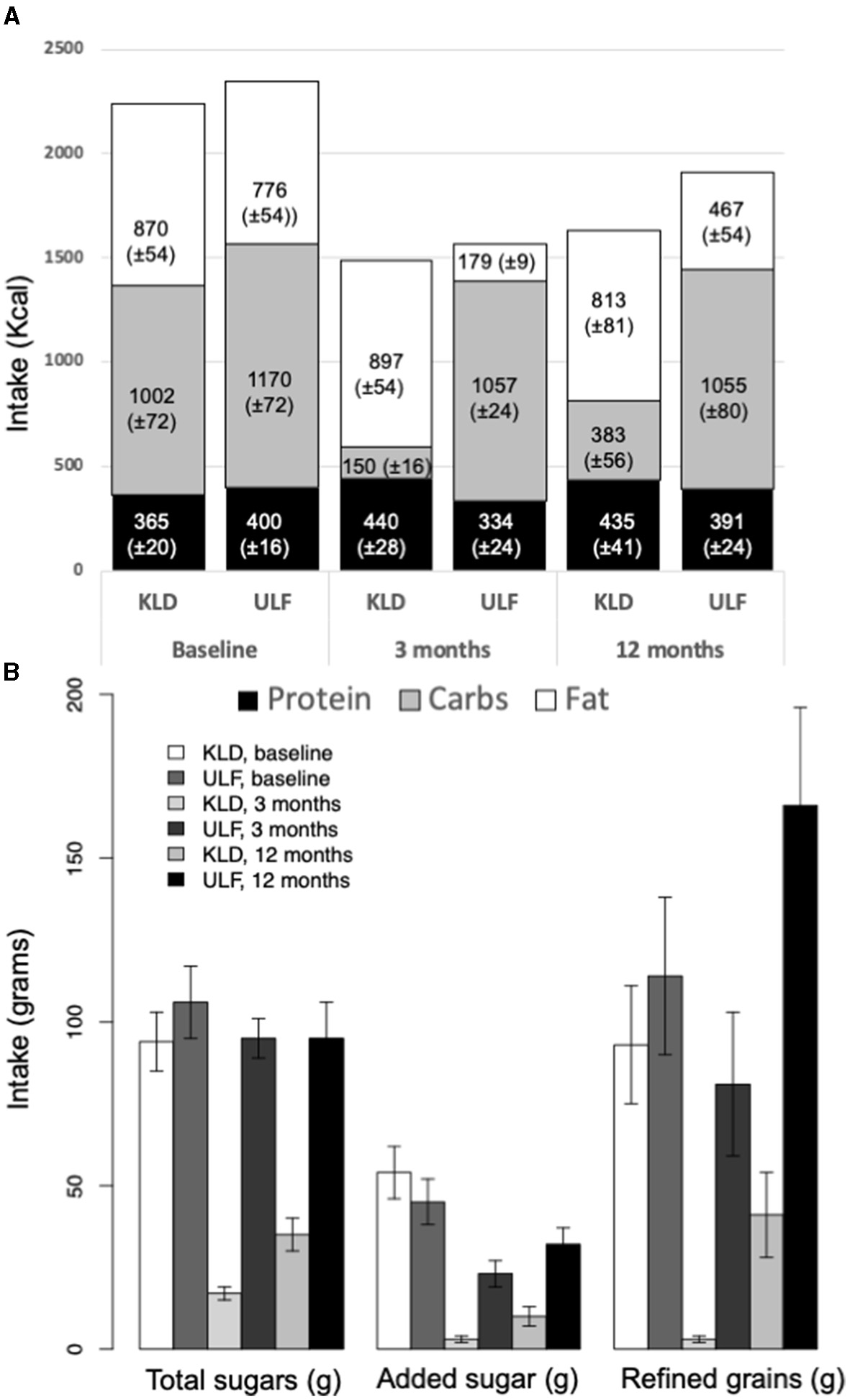
Macronutrient, added sugar, and refined grains intake for KLD and ULF. (A): Mean intake (Kcal/day; ± standard error of mean) of protein (black), carbohydrates (gray), and fat (white) for KLD and ULF at baseline, 3 months, and 12 months. (B): Mean intake (grams/day; ± standard error of mean) of total sugar, added sugars, and refined grains for KLD and ULF at baseline, 3 months, and 12 months. p-values for null hypothesis that nutrition variables are equivalent between diets at a given timepoint; from a linear mixed effects model including fixed effects for time, diet, and time*diet interaction, and a random effect for study participant.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Statements
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Summary
Keywords
ketogenic diet, ultra low-fat diet, low carbohydrate, low fat, weight loss, triglycerides/HDL ratio, insulin resistance, refined grains
Citation
Aronica L, Landry MJ, Rigdon J and Gardner CD (2023) Corrigendum: Weight, insulin resistance, blood lipids, and diet quality changes associated with ketogenic and ultra low-fat dietary patterns: a secondary analysis of the DIETFITS randomized clinical trial. Front. Nutr. 10:1275498. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1275498
Received
10 August 2023
Accepted
27 September 2023
Published
09 October 2023
Volume
10 - 2023
Edited and reviewed by
Iain Brownlee, Northumbria University, United Kingdom
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Aronica, Landry, Rigdon and Gardner.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Christopher D. Gardner cgardner@stanford.edu
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.