Abstract
The biosynthesis of nanoparticles (NPs) has attracted significant interest due to their diverse biological applications. However, the potential for NPs synthesis using plant resources from Vicia monantha Retz remains largely unexplored. Notably, this study marks the first use of this specific plant for the biosynthesis of chromium oxide nanoparticles (Cr2O3NPs). In the present study, the single phase of Cr2O3 was confirmed at a calcination temperature 700 °C for the synthesized NPs. The crystallite sizes increased from 14 nm to 20 nm with the increase in the calcination temperature to 900 °C for 2 h. Ultraviolet–visible (UV–VIS) light spectroscopy revealed that the samples are semiconductor materials, according to the observed values of energy band gap. The developed Cr2O3NPs did not show any toxicity toward NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. The results demonstrated that Cr2O3NPs exhibited good antimicrobial activity against two bacterial strains (Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus) and two fungal strains (Candida albicans and Aspergillus sp.), producing clear inhibition zones of 0.26 cm, 0.21 cm, 0.28 cm, and 0.3 cm, respectively, after 24 h. The Cr2O3NPs exhibit successful green synthesis, notable biocompatibility, and antimicrobial properties, making them highly promising for various applications and opening possibilities for the utilization of nanoparticles in antimicrobial systems.
1 Introduction
Bio-nanotechnology has become a significant area within nanotechnology because of its environmental sustainability, simplicity, and economic efficiency (Shahcheraghi et al., 2022). The combination of metallic and botanical structures creates an effective basis for the production of nanoparticles (NPs) with a variety of properties (Sawalha et al., 2021). Nanoparticles have been used in a variety of fields, including cosmetics, sensors, biomedicine, pathogen detection, diagnostics, antigen detection, enzymes, vaccines, and radiology, because of their high-density corners, chemical stability, and exceptional magnetic, catalytic, and electrical properties (Iqbal et al., 2020a). Nanoparticles such as zinc oxide, silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, silver, and carbon nanotubes are harmful to the environment and humans. These NPs can cause cell death, oxidative stress, DNA damage, apoptosis, and inflammation (Sengul and Asmatulu, 2020; Srivastava et al., 2015). These issues necessitate safer nanoparticles. Chromium oxide nanoparticles (Cr2O3NPs) offer a promising alternative due to their unique physicochemical properties. Cr2O3 NPs are unique among metal oxide nanoparticles due to their extraordinary stability, hardness, high resistivity, higher melting temperature, and 3.4 eV band gap (Iqbal et al., 2020b). Nanoparticles are characterized by a high surface area to volume ratio, which is a contributing factor to their distinctive physicochemical properties (Joudeh and Linke, 2022). This surface area also enhances their antimicrobial effectiveness and reactivity, rendering them suitable for use in medical devices and antimicrobial coatings (Rezić and Meštrović, 2023). Cr2O3NPs have several uses, including catalysis, photonics, coatings, and complex colorants (Karimian and Piri, 2013). The most stable of the chromium oxides are the trivalent Cr2O3NPs (Horie et al., 2013). Despite their promise, Cr2O3NPs have limited biological uses due to reported harmful effects in several studies (Alqarni et al., 2022).
Antimicrobial nanoparticles, including silver and copper, demonstrate significant bactericidal efficacy (Fan et al., 2021). Nonetheless, these nanoparticles present cytotoxic risks to cells (Fan et al., 2021; Tortella et al., 2022). Chromium oxide nanoparticles demonstrate the ability to improve antimicrobial properties while reducing cytotoxic effects. Cr2O3 nanoparticles compromise bacterial membranes and impede enzyme function, resulting in significant antimicrobial efficacy (Khan et al., 2021). The biocompatibility of Cr2O3NPs is critical for their application in a variety of biological systems. Coating or functionalizing the surfaces of Cr2O3NPs with biogenic compounds might mitigate their negative effects. A possible strategy is to cover the surface of Cr2O3NPs with biogenic phytomolecules derived from plants (Khan et al., 2021). Thus, green nanoparticle manufacturing has emerged as a viable alternative to traditional physical and chemical approaches, with the potential to mitigate some of their negative impacts (Ahmad et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2021). Green synthesis is an interesting method for manufacturing nanoparticles since it is straightforward, inexpensive, and ecologically benign (Khan et al., 2021). In cancer therapy, biologically synthesized metallic nanoparticles function as cytotoxic agents (Patil and Chandrasekaran, 2020). Plant extracts, unlike bacteria and fungi, offer a straightforward and effective method for producing large-scale nanoparticles (Singh et al., 2018).
Numerous researchers are currently focusing on the green manufacture of Cr2O3NPs using plant extracts (Zheng et al., 2021). Plant extracts include a variety of phytochemicals, including phenols, flavonoids, and terpenoids, which possess natural reducing and stabilizing properties. These compounds can effectively convert metal salts into nanoparticles under mild reaction conditions, reducing the need for hazardous chemicals and high-energy procedures. This approach produces nanoparticles with a precise size distribution and remarkable stability (Adeyemi et al., 2022). Because of its environmentally friendly methodology and broad applicability, green nanoparticle production utilizing plant extracts has a lot of potential in nanotechnology (Khan et al., 2021). Cr2O3NPs have significant antibacterial activity. Their ability to suppress microbial development makes them ideal for medical applications such as medication delivery systems and medical device coatings. Research has demonstrated that these nanoparticles may successfully target a variety of pathogens, including bacteria and fungi, enhancing their potential for infection management (Adfar et al., 2023). Although further research is needed to completely understand the reasons and enhance nanoparticle-based treatments, these improvements provide intriguing possibilities for novel treatment options. Vicia sativa L. is an important crop often known as common or garden vetch. It is a grain legume with excellent seed yield, which may reach 250 kg per hectare. The seeds are high in protein, carbohydrates, and minerals, making them suitable for both human diet and animal feed (Aloweidat, 2014). Common vetch also has several pharmacological characteristics. V. sativa has lately been used as a fertilizer to increase soil nitrogen availability, and it may be cultivated all-year to provide green manure (Ramírez-Parra and De la Rosa, 2023). V. sativa is also known as a powerful medicinal plant due to its high concentration of flavonoids, phenolics, saponins, tannins, and terpenoids (Ahmed et al., 2019).
The current study comprehensively describes the reaction conditions, synthesis technique, and properties of Cr2O3NPs. Cr2O3NPs were first biosynthesized from chromium acetate, with an aqueous leaf extract of V. sativa serving as a reducing and stabilizing agent. Furthermore, Cr2O3NPs were characterized using a variety of approaches. In addition, numerous of its biological activities were studied, including cytotoxicity and antibacterial testing. The sustainable production of Cr2O3NPs offers a promising method for creating environmentally benign materials with important applications in catalysis, environmental remediation, and biomedicine. Characterization and assessment of their qualities are critical for realizing their full potential while maintaining safety and efficacy.
2 Empirical procedure
2.1 Preparation of the aqueous plant extract for nanoparticle synthesis
Two grams of the plant powder obtained from Vicia monantha was dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water and placed in an ultrasonic bath at 80 °C for 40 min. The solid material was then removed and filtered twice using Whatman filters to eliminate any residual solids. The filtrate was stored at 25 °C until it was used for the biosynthesis of Cr2O3NPs.
2.2 Synthesis of chromium nanoparticles
Cr2O3NPs were synthesized using chromium chloride (CrCl3) as a precursor. A mixture of the plant extract and 0.2 M CrCl3 solution (3:7 ratio) was stirred magnetically at 100 °C for 1.5 h in a 250-mL conical flask. Nanoparticle formation was monitored via color change. After cooling, Cr2O3NPs were separated by centrifugation (13,500 rpm at 4 °C) and dried at 80 °C. The nanoparticle concentration was determined using ultraviolet–visible (UV–VIS) spectrophotometry (Zainab et al., 2022). The prepared sample was ground completely using a mortar and pestle to obtain a fine powder. The powdered sample was divided into different parts to be calcined at different calcination temperatures (500 °C, 700 °C, and 900 °C).
2.3 Instrumentations and measurements
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the as-prepared and calcined samples were obtained using an X-ray diffractometer (Philips model pw1710, Cu-Kα radiation, and λ = 1.54 Å) in the range of 10–80̊ (step 0.02) for 2θ. The average crystallite size (D) of Cr2O3 was calculated using Scherrer’s equation (Abd elfadeel et al., 2022):where k, βhkl, λ, and θ are the shape factor (0.9), the full width at half of the maximum intensity of the diffraction peak in radian, the wavelength of the used X-ray beam, and Bragg’s refractive angle, respectively.
Specific surface area (SSA), which refers to the area per unit mass, is considered an important factor to present the bulk rates of such reactions (m2/g). It is a significant parameter for nanoparticles because their large surface-to-volume ratio decreases with an increase in particle size. It can be calculated using the following formula (Al-Saadi and Hameed, 2015; Theivasanthi and Alagar, 2011; 2012):where ρ presents the density of Cr2O3NPs (5.23 g cm-3).
Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were recorded in the range of 400 cm-1–4,000 cm-1 using a double-beam spectrometer (Nicolet iS 10) with the KBr pellet method. The optical properties were determined using a computerized double-beam UV-Vis spectrophotometer (JASCO V-670). The absorbance spectrum of Cr2O3, both as prepared and calcined at different temperatures (500 °C, 700 °C, and 900 °C for 2 h) were recorded in the range of 200 nm–800 nm at room temperature. The energy band gap was calculated using Tauc’s formula (Venkatachalapathy et al., 2023):where α, h, ν, A, and Eg are the absorbance constant, Planck constant, the frequency of the incident photons, the transition constant, and the energy band gap, respectively (Venkatachalapathy et al., 2023).
2.4 Antibacterial activity
The antibacterial activity of Cr2O3NPs was evaluated using the disc diffusion method, as previously reported, against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus sp. (Atta et al., 2021). In brief, nutrient agar medium or yeast–peptone–dextrose–agar (YPDA) medium was used to cultivate all the microbial strains. Cr2O3NP suspensions were applied to the 8-mm-diameter paper discs and then UV-sterilized. Following that, the dried discs were placed on top of the agar culture plates containing a specific set of bacteria and fungi that had been incubated for 24 h at 37 °C and 72 h at 30 °C, respectively. Finally, the inhibition zones’ diameters were measured. The negative and positive controls were dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and chromium nitrate, respectively.
2.5 Toxicity analysis
The cytotoxicity of Cr2O3NPs on NIH-3T3 (mouse embryonic fibroblast cells obtained from China Infrastructure of Cell Line Resources) (Adhikari et al., 2024; Atta et al., 2021; 2022) was assessed using the MTT assay. NIH-3T3 cells were cultured in high-glucose (4.5 g/L) DMEM flasks supplemented with L-glutamine, pyruvate (110 g/L), 10% FBS (Gibco, United States), and 1% penicillin/streptomycin and incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. The culture medium was replaced daily until confluence was achieved. For toxicity assessment, the Cr2O3NPs were positioned in a 96-well microplate, inoculated with 1 × 10^4 cells per well, and incubated in a 5% CO2 environment. Following 24 h–48-h of incubation, the samples were washed thrice with PBS and subsequently placed into fresh DMEM growth medium containing MTT (3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H tetrazolium bromide) reagent at a concentration of 5 mg/mL in a 10:1 ratio. The samples were re-incubated at 37 °C for 4 h. Subsequently, the medium was eliminated, and formazan, along with 150 mL of DMSO, was introduced. Absorption was ultimately quantified at 570 nm utilizing a multi-scan spectrophotometer (Tecan, Infinite F50, Germany). The cells cultured solely in the medium served as a reference, and their viability was regarded as 100% (Atta et al., 2022).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Physicochemical investigations
The extract of Vicia monantha is essential in nanoparticle synthesis because its active compounds stabilize the nanoparticles, inhibit agglomeration, and improve crystallization, as demonstrated in a previous study (Nasr et al., 2024). The combination of metallic components and plant extracts improves the product’s functional and environmental performance, offering benefits such as biocompatibility, material stability, and increased metal strength (Jeevanandam et al., 2022). Plant-based materials have biodegradable and eco-friendly properties, which improve sustainability (Hano and Abbasi, 2021). Although pure metallic systems may provide greater durability, they lack the inherent benefits of plant extracts (Dikshit et al., 2021). Green synthesis improves the properties of Cr2O3 nanoparticles (Yasmeen et al., 2023). Our findings show that the plant extract significantly influences particle agglomeration and crystallization, thereby improving the overall stability and functionality of the nanoparticles.
The XRD patterns of Cr2O3 as prepared and calcined at different temperatures (500 °C, 700 °C, and 900 °C for 2 h) are shown in Figure 1. The broad peaks observed in the XRD analysis of the material synthesized and calcined at 500 °C indicate a low degree of crystallinity. The crystallinity of the calcined materials showed an improvement with an increase in Tc (Abdel-Ghany et al., 2012; Abd elfadeel et al., 2023). The observed narrow XRD peaks with higher intensities were achieved as a function of Tc. This means that the maximum crystallinity percentage can be obtained at a calcination temperature in the range of 700 °C ≤ Tc ≤ 900 °C. The XRD spectrum displayed distinct and intense peaks, confirming the crystalline nature and single-phase formation of Cr2O3NPs. The peaks of the XRD spectrum of the samples at calcination temperatures of 700 °C and 900 °C showed excellent agreement with those mentioned in previous works for Cr2O3 (Hao et al., 2019; Sackey et al., 2021).
FIGURE 1

XRD patterns of Cr2O3 as prepared and calcined at different temperatures.
Figure 1 clearly shows that the XRD pattern is dominated by diffraction peaks 0 1 2, 1 0 4, 1 1 0, 0 0 6, 1 1 3, 2 0 2, 0 2 4, 1 1 6, 1 2 2, 2 1 4, 3 0 0, 1 0 10, 2 2 0, and 3 0 6 that correspond to 2θ at 24.22°, 33.33°, 35.92°, 39.42°, 41.20°, 43.82°, 49.92°, 54.57°, 58.13°, 63.14°, 64.79°, 72.66°, 76.57°, and 79.04°, respectively. The noticeably strong and narrow diffraction peaks in the pattern of XRD are ascribed to the elevated crystallinity of the Cr2O3NPs. It is completely indexed in the space group R c symmetry of the rhombohedral structure. No impurity peaks were detected, which is consistent with the reference value of JCP No. 00-006-0504.
The crystallite size increased from 14 nm to 20 nm as the calcination temperature was increased to 900 °C for 2 h. The increase in crystallite size is attributed to the growth of the magnetic domain as a function of the calcination temperature Tc for all samples (Mazen et al., 2015). It is noted that the obtained small crystallite size for the pure phase of α-CrO3 (14 nm–20 nm) is smaller than that of samples prepared by the microwave irradiation method (Meenambika et al., 2013).
Specific surface area values of Cr2O3NPs are presented in Table 1. SSA decreases slightly as the particle size and calcination temperature increase, which can be attributed to the generation of agglomeration as a result of the heat treatment occurring in the material (Al-Saadi and Hameed, 2015; Theivasanthi and Alagar, 2011; 2012).
TABLE 1
| Tc (°C) | As prepared | 500 ℃ | 700 ℃ | 900 ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal size D (nm) | 14 | 19 | 20 | 20 |
| SSA (m2.g−1) | 78.5 | 58 | 54.2 | 54.2 |
| Abs. edge (nm) | 294 | 325 | 312 | 316 |
| Eg (eV) | 4.2 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
Crystallite size (D), optical absorption edge, SSA, and band gap (Eg) of Cr2O3 powder nanoparticles at different calcination temperatures (Tc).
The FT-IR absorption spectra of Cr2O3 as prepared and calcined at different temperatures of 500 °C, 700 °C, and 900 °C for 2 h in the range of 4,000 cm-1–400 cm-1 are shown in Figure 2. Several vibrational modes were observed. The spectra represent absorption bands at 414, 451, 563, 629, 901, 952, 1,141, 1,633, and 3,441 cm−1, respectively. All the observed peaks are in good agreement with the previously reported results (Bumajdad et al., 2017; Ahmed Mohamed et al., 2020; Rasheed et al., 2020; Sone et al., 2016). The metal oxide generally represents the peaks caused by interatomic vibrations that are below 1,000 cm−1. So, in the present investigation, the vibrations positioned at 414, 451, 563, 629, 901, and 952 cm−1 can be attributed to the Cr–O stretching vibrations (Abdullah et al., 2014; Bumajdad et al., 2017; Hassan et al., 2019). The relatively weak absorption band at 414 cm−1 and the strong absorption band at 563 cm−1 can be attributed to Cr–O bonds in the bending mode, while the strong absorption band at 629 cm−1 provides clear evidence for the presence of crystalline α-Cr2O3 (Bumajdad et al., 2017; Jaswal et al., 2014; Sone et al., 2016). The relatively strong broad band observed at 3,441 cm−1 can be attributed to O–H stretching modes of what could be waters of hydration. The weak broad band at 1,633 cm−1 may be attributed to the presence of adsorbed moisture on the surface of the α-Cr2O3 powder (Adnan and Mohammed, 2024; Hassan et al., 2019; Jaswal et al., 2014; Ahmed Mohamed et al., 2020; Sone et al., 2016). The spectra of the calcination products (at 500 °C–900 °C) are significantly different from that of the as-prepared Cr2O3. The spectrum of Cr2O3 only exhibits two sharp, strong bands at 629 and 563 cm−1, in addition to a much weaker absorption at 901, 1,141, 1,633, and 3,441 cm−1 (Bumajdad et al., 2017). As the calcination temperature increases, it is observed that the broad peak groups associated with O–H stretching vibration shrink, while the stretching peaks of Cr2O3 grow and become significant. The spectrum of the calcined samples reveals the corresponding vibration bands of Cr–O only, which in turn depicts the successful removal of impurity during calcinations and the high purity of the as-grown Cr2O3 nanostructures. The high intensity of the peaks of the Cr2O3 bands indicates the good crystalline nature of the materials (Abdullah et al., 2014; Rasheed et al., 2020).
FIGURE 2

FT-IR spectra of Cr2O3 as prepared and calcined at different temperatures.
The values of crystallite size (D), optical absorption edge, and the band gap (Eg) of the Cr2O3 powder nanoparticles at different calcination temperatures (Tc) are listed in Table 1.
Sangwan and Kumar (2017) reported the optical characteristics of chromium oxide and observed that the energy gap of the electronic transitions is located in the photon energy range of 4.19 eV. The absorption wavelength of chromium oxide was noted in the visible light region, as shown in Figures 3a–d. The calculated values of the band gap were noted to be 4.2, 3.8, 3.9, and 3.9 eV, respectively. The values of the investigated absorption edges and the energy gap of Cr2O3NPs are in good agreement with the previous studies (Ahmad et al., 2018; Hassan et al., 2019; Kamble et al., 2019; Sangwan and Kumar 2017). It was observed that the value of the band gap decreased as the calcination temperature increased. The decrease in the optical band gap with increasing crystallinity confirms the quantum size effect, which is consistent with previous findings (Shobana et al., 2019). The peaks observed at approximately 375, 465, and 669 nm can be attributed to the 3-d electronic transitions of Cr3+ ions, which are situated in six-coordinate geometry with octahedral symmetry (Khalaji and Pavel Machek, 2022).
FIGURE 3

(a–d) UV–VIS absorption spectrum and the inserted Tauc’s plot for the band gap of as-prepared Cr2O3 and calcined Cr2O3 at different temperatures.
Figures 4a–d demonstrate the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of Cr2O3 nanoparticles, both as-prepared and calcined at 700 °C. The images show that Cr2O3NPs mainly exhibit a spherical morphology, with some rod-shaped NPs also observed in the as-prepared sample. At a calcination temperature of 700 °C, Cr2O3NPs became agglomerated, which is in agreement with a previous work (Khalaji, 2021). It can be noted that the Cr2O3NP size determined by TEM ranged from ∼5 nm to 60 nm. The results show a strong similarity with the previous studies (Adnan and Mohammed, 2024; Mohammed et al., 2020). The biosynthesized NPs, in addition to the heat treatment, revealed more enhancements. According to the single phase, smaller crystalline size, and optical band gap, in addition to higher crystallinity, the study revealed the improvement of physiochemical characteristics better than those prepared through different methods in previous studies (Adnan and Mohammed, 2024; Ahmad et al., 2018; Hao et al., 2019; Khalaji, 2021; Ahmed Mohamed et al., 2020; Sackey et al., 2021). Furthermore, the observed enhancements of the achieved materials make them promising in photocatalytic applications (Khalaji and Pavel Machek, 2022).
FIGURE 4

TEM images of Cr2O3NPs, both as-prepared (a,b) and calcined at 700 °C (c,d).
3.2 Antibacterial activity of Cr2O3NPs
The Cr2O3NPs are known to possess strong antimicrobial activity and high inhibitory effects toward different microbes, such as Escherichia coli. Earlier studies have demonstrated the successful development of antimicrobials with a variety of nanoparticles, such as Zn, Ag, Cu, and TiO2 (Ali et al., 2021; Atta et al., 2021). The result obtained indicates that Cr2O3 in the nanoparticles enhances their antimicrobial activity. Additionally, during the reaction, superoxide radical (ROS) O2 is formed (Gyawali et al., 2024), which kills the microbes. This outcome is comparable to that of another study (Hasanin et al., 2023), which found that superoxide radical activity in the presence of Cr2O3NPs significantly disrupted microbial cell organelles such as the cell membrane, cytoplasmic fluid, and nucleic acids, resulting in cellular destruction.
In the present study, the antimicrobial activity of Cr2O3NPs was evaluated against four pathogens, including two bacterial strains, Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli, and two fungal species, Candida albicans and Aspergillus sp., along with the negative control (DMSO) and positive control (chromium nitrate), and the results are shown in Figure 5. The selected microbial strains for the determination of the antimicrobial activity of Cr2O3NPs are generally associated with human health. The antimicrobial activity evaluation through the disc diffusion method showed that the Cr2O3NPs discs produced inhibition zones of 0.26, 0.21, 0.28, and 0.3 cm for E. coli, S. aureus, C. albicans, and Aspergillus sp., respectively. These values are significantly better than the positive control (*p < 0.05) and higher than the negative control (**p < 0.01). In contrast, chromium nitrate (i.e., positive control) produced inhibition zones of 0.24, 0.19, 0.21, and 024 cm against the same set of microbial strains. On the other hand, filter paper with DMSO (i.e., negative control) did not produce any inhibition zones against the selected microbial strains, indicating that the antibacterial activity was exclusively attributed to the Cr2O3NPs (green synthesis), surpassing the antibacterial activity of the chemically synthetized form of Cr2O3NPs represented by chromium nitrate (as a positive control) (Dridi et al., 2018; Yasmeen et al., 2023).
FIGURE 5
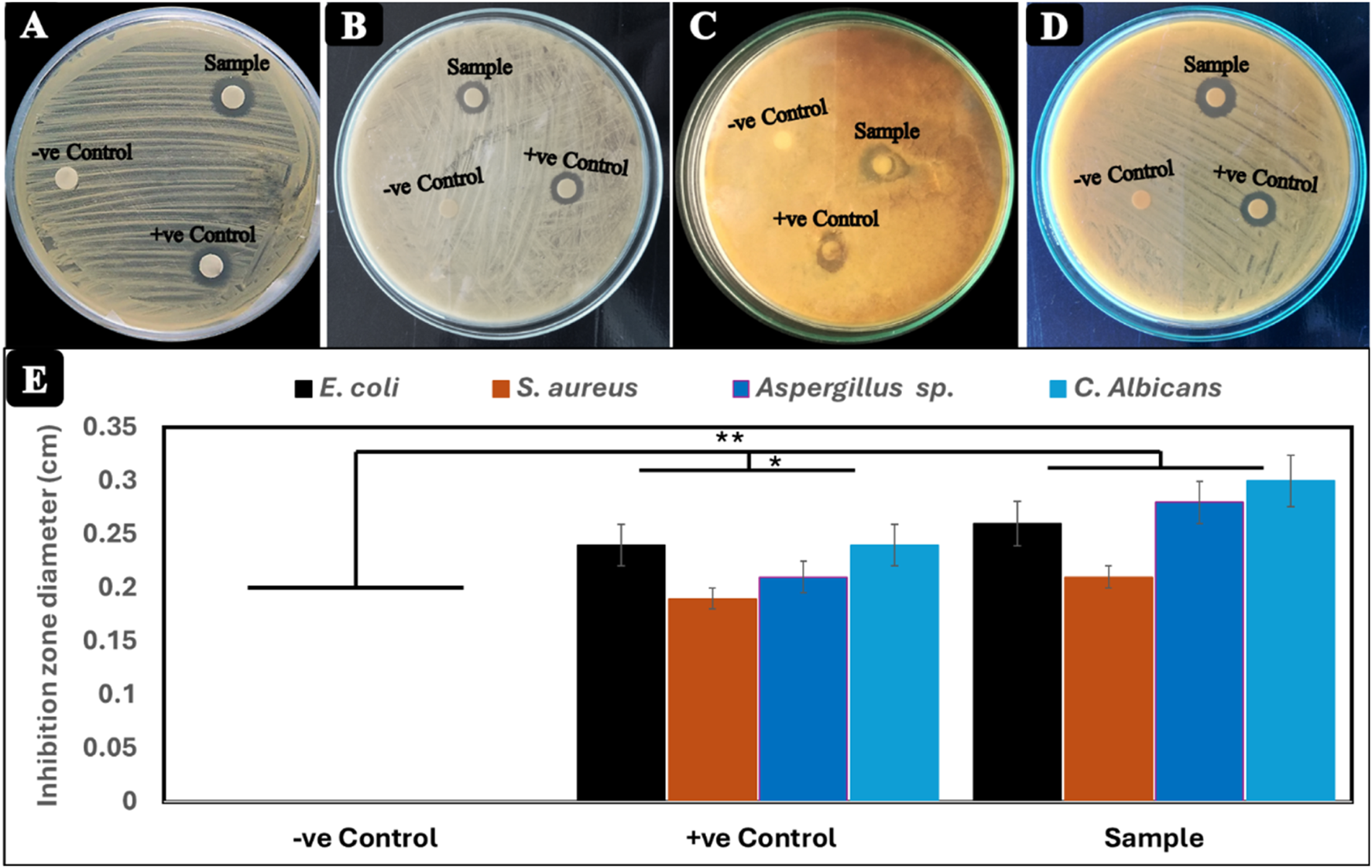
Antimicrobial activity of Cr2O3NPs film (test film), chromium nitrate (positive control), and filter paper with DMSO (negative control) against (A)Escherichia coli, (B)Staphylococcus aureus, (C)Aspergillus sp., and (D)Candida albicans.(E) Diameter (cm) of the inhibition zone.
Additionally, the study evaluated the effectiveness of Cr2O3NPs in inhibiting biofilm formation by persister cells from microbial isolates. The average inhibitory rate of Cr2O3NPs against microbial isolates was determined. Cr2O3NPs significantly reduced biofilm formation. Cr2O3NPs had a significant impact on biofilms formed by persister cells from all selected isolates (Al Marjani et al., 2021). Several factors influence the antibacterial mechanism of Cr2O3NPs, including the nanoparticles’ size and surface properties, the specific microbial strain, and the nanoparticles’ mode of action. Cr2O3NPs have the potential to induce oxidative stress in bacterial cells, leading to damage of DNA, proteins, and lipids. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion radicals (), can cause oxidative stress by interacting with and damaging cellular components (Benfield and Henriques, 2020; Rangayasami et al., 2020; Reygaert, 2018). The interaction of nanoparticles with the lipid bilayer of the bacterial membrane has the potential to change and disrupt the membrane structure. Figure 5 illustrates the mechanism of the antibacterial action of Cr2O3NPs.
3.3 Biocompatibility testing of Cr2O3NPs
The synthesis of Cr2O3NPs for antimicrobial product development must ensure biocompatibility and non-toxicity. This study assessed the cytotoxicity of Cr2O3NPs on NIH-3T3 fibroblasts using the MTT assay, and the results are depicted in Figure 6. The viability of NIH-3T3 fibroblasts on Cr2O3NPs after 12 h was 98%, 80%, and 64% for concentrations of 10, 50, and 100 μg/mL, respectively, indicating no cytotoxic effect at low concentrations and low toxicity at high concentrations of the nanoparticles toward the cells (Figure 6). With continuous incubation for 24 h, viability gradually declines, reaching 93%, 74%, and 58% for Cr2O3NPs. The diminished cell viability may result from nutrient depletion in the growth medium. The results demonstrate satisfactory cell viability of Cr2O3NPs, with cell survival exceeding 90% relative to the control, indicating the acceptable cytotoxicity of Cr2O3NPs toward NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. The findings agree with a prior study indicating that Cr2O3NPs facilitated the proliferation of L929 cells while maintaining an acceptable toxicity threshold (Alarifi et al., 2016). Some studies indicated that chromium nitrate exhibits the highest toxicity, while others demonstrated that chromium synthesized through green methods has low toxicity (Hassan et al., 2019; Puerari et al., 2016; Sharma and Sharma, 2021; Sone et al., 2016). The current study’s findings indicate that Cr2O3NPs are predominantly non-toxic to mammalian cells, exhibiting toxicity only at elevated concentrations due to their diminutive size and volatile properties (Ahmed Mohamed et al., 2020). The present study does not permit the assessment of time-dependent cytotoxicity beyond the duration of 24 h. This represents a limitation of our study, which we will rectify in future research to deliver a more thorough evaluation of cytotoxicity over prolonged durations. Furthermore, we have elucidated the definitions of “low” and “high” concentrations in the manuscript. “Low concentrations” denote doses under 10 μg/mL, exhibiting no significant cytotoxicity, whereas “high concentrations” indicate levels exceeding this threshold, where cytotoxic effects are more evident.
FIGURE 6

Viability of NIH-3T3 cells cultured in Cr2O3NPs in a 96-well plate. Absorption was recorded at 570 nm for all samples; *p < 0.05.
4 Conclusion
In this study, Cr2O3NPs were successfully synthesized through a green method using the leaf extract of Vicia monantha Retz as both a reducing and capping agent. The synthesized Cr2O3NPs were thoroughly characterized using XRD, TEM, FT-IR spectroscopy, and UV–VIS spectroscopy. The green-synthesized Cr2O3NPs exhibited inhibitory activity against Aspergillus sp. and Candida albicans, with moderate effects observed against S. aureus and E. coli. Furthermore, the study suggests that Cr2O3NPs are predominantly non-toxic to mammalian cells, although some toxicity was noted under specific conditions. These findings indicate that green-synthesized Cr2O3NPs have potential applications in the medical field as effective antibacterial and antifungal agents. With further exploration, these nanoparticles could emerge as promising therapeutic agents in the future.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
EHE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. GAe: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. XL: Formal analysis, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft. EAE: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. AS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. TT: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing. OF: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. OA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Methodology. W-ZL: Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was financially supported by the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (Nos. JCYJ20241202123900001 and JCYJ20240813104925034).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abd elfadeel G. Venkatachalapathy R. Saddeek Y. Manoharan C. Venkateshwarlu M. (2022). Synthesis, structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties of Li2−2xNixAl2xFe2−2xO4, (x = 0,0.4, and 0.5) nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.13, 045008. 10.1088/2043-6262/aca0ef
2
Abd elfadeel G. Manoharan C. Saddeek Y. Venkateshwarlu M. Venkatachalapathy R. (2023). Effect of calcination temperature on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of synthesized α-LiFeO2 nanoparticles through solution-combustion. J. Alloys Compd.944, 169097. 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169097
3
Abdel-Ghany A. E. Mauger A. Groult H. Zaghib K. Julien C. M. (2012). Structural properties and electrochemistry of α-LiFeO2. J. Power Sources197, 285–291. 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.09.054
4
Abdullah M. M. Rajab F. M. Al-Abbas S. M. (2014). Structural and optical characterization of Cr2O3 nanostructures: evaluation of its dielectric properties. AIP Adv.4, 027121–11. 10.1063/1.4867012
5
Adeyemi J. O. Oriola A. O. Onwudiwe D. C. Oyedeji A. O. (2022). Plant extracts mediated metal-based nanoparticles: synthesis and biological applications. Biomolecules12, 627. 10.3390/biom12050627
6
Adfar Q. Aslam M. Maktedar S. S. (2023). “A compendium of metallic inorganic fillers’ properties and applications employed in polymers,” in Nanofillers (CRC Press), 25–68. 10.1201/9781003279389-2
7
Adhikari M. Atta O. M. Kishta M. S. Maboruk M. Shi Z. Yang G. (2024). Lysozyme-enhanced cellulose nanofiber, chitosan, and graphene oxide multifunctional nanocomposite for potential burn wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.280, 135668. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135668
8
Adnan W. G. Mohammed A. M. (2024). Green synthesis of chromium oxide nanoparticles for anticancer, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun.159, 111683. 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111683
9
Ahmad Z. Shamim A. Mahmood S. Mahmood T. Khan F. U. (2018). Biological synthesis and characterization of chromium (iii) oxide nanoparticles. Eng. Appl. Sci. Lett.1 (2018), 23–29. 10.30538/psrp-easl2018.0008
10
Ahmad W. Bhatt S. C. Verma M. Kumar V. Kim H. (2022). A review on current trends in the green synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles, characterizations, and their applications. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. and Manag.18, 100674. 10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100674
11
Ahmed M. Ji M. Qin P. Gu Z. Liu Y. Sikandar A. et al (2019). Phytochemical screening, total phenolic and flavonoids contents and antioxidant activities of Citrullus colocynthis L. and Cannabis sativa L. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res.17. 10.15666/aeer/1703_69616979
12
Ahmed Mohamed H. E. Afridi S. Khalil A. T. Zohra T. Ali M. Alam M. M. et al (2020). Phyto-fabricated Cr2O3 nanoparticle for multifunctional biomedical applications. Nanomedicine15, 1653–1669. 10.2217/nnm-2020-0129
13
Al Marjani M. Aziz S. N. Rheima A. M. Abbas Z. S. (2021). Impact of chromium oxide nanoparticles on growth and biofilm formation of persistence Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Nano Biomed. Eng.13, 321–327. 10.5101/nbe.v13i3.p321-327
14
Al-Saadi T. M. Hameed N. A. (2015). Synthesis and structural characterization of Cr2O3 nanoparticles prepared by using Cr(NO3)3. 9H2O and triethanolamine undermicrowaveirradiation. Synthesis44.
15
Alarifi S. Ali D. Alkahtani S. (2016). Mechanistic investigation of toxicity of chromium oxide nanoparticles in murine fibrosarcoma cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine11, 1253–1259. 10.2147/IJN.S99995
16
Ali S. Q. Aziz W. J. Sabry R. S. (2021). Fabrication of Cr2O3 nanoparticles using okra plant extract for antimicrobial activity. J. Kufa-Physics13, 41–50. 10.31257/2018/JKP/2021/130206
17
Aloweidat M. Y. (2014). Growth performance and yield components of five legume crops under rain-fed conditions.
18
Alqarni L. S. Alghamdi M. D. Alshahrani A. A. Nassar A. M. (2022). Green nanotechnology: recent research on bioresource-based nanoparticle synthesis and applications. J. Chem.2022, 1–31. 10.1155/2022/4030999
19
Atta O. M. Manan S. Ul-Islam M. Ahmed A. A. Q. Ullah M. W. Yang G. (2021). Silver decorated bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as antimicrobial food packaging materials. ES Food Agrofor.6, 12–26. 10.30919/esfaf590
20
Atta O. M. Manan S. Ul-Islam M. Ahmed A. A. Q. Ullah M. W. Yang G. (2022). Development and characterization of plant oil-incorporated carboxymethyl cellulose/bacterial cellulose/glycerol-based antimicrobial edible films for food packaging applications. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater.5, 973–990. 10.1007/s42114-021-00408-9
21
Benfield A. H. Henriques S. T. (2020). Mode-of-action of antimicrobial peptides: membrane disruption vs. intracellular mechanisms. Front. Med. Technol.2, 610997. 10.3389/fmedt.2020.610997
22
Bumajdad A. Al-Ghareeb S. Madkour M. Sagheer F.Al (2017). Non-noble, efficient catalyst of unsupported α- Cr2O3 nanoparticles for low temperature CO oxidation. Sci. Rep.7, 14788. 10.1038/s41598-017-14779-x
23
Dikshit P. K. Kumar J. Das A. K. Sadhu S. Sharma S. Singh S. et al (2021). Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: applications and limitations. Catalysts11, 902. 10.3390/catal11080902
24
Dridi R. Dhieb C. Cherni S. N. Boudjada N. C. Zouaoui N. S. Zid M. F. (2018). A new supramolecular chromium (III) complex: synthesis, structural determination, optical study, magnetic and antibacterial activity. J. Mol. Struct.1152, 294–302. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.09.111
25
Fan X. Yahia L. Sacher E. (2021). Antimicrobial properties of the Ag, Cu nanoparticle system. Biology10, 137. 10.3390/biology10020137
26
Gyawali N. Kandel R. Lee I. Shrestha S. Pandey A. Akter J. et al (2024). Silver decoration of Cr2O3 nanoparticles: facile preparation of Cr2O3 nanoparticles and Ag-Cr2O3 nanocomposites and characterization of their antibacterial activity and ability to photocatalytically degrade organic wastes under visible light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem.447, 115251. 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2023.115251
27
Hano C. Abbasi B. H. (2021). Plant-based green synthesis of nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Biomolecules12, 31. 10.3390/biom12010031
28
Hao G. Xiao L. Hu Y. Shao F. Ke X. Liu J. et al (2019). Facile preparation of Cr2O3 nanoparticles and their use as an active catalyst on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J. Energetic Mater.37, 251–269. 10.1080/07370652.2019.1593551
29
Hasanin M. S. Elhenawy Y. Abdel-Hamid S. M. S. Fouad Y. Monica T. Al-Qabandi O. A. et al (2023). New eco-friendly, biocompatible, bactericidal, fungicidal and anticancer-activity-exhibiting nanocomposites based on bimetallic TiO2@ Cr2O3 nanoparticle core and biopolymer shells. J. Compos. Sci.7, 426. 10.3390/jcs7100426
30
Hassan D. Khalil A. T. Solangi A. R. El-Mallul A. Shinwari Z. K. Maaza M. (2019). Physiochemical properties and novel biological applications of callistemon viminalis-mediated α-Cr2O3 nanoparticles. Appl. Organomet. Chem.33, 1–13. 10.1002/aoc.5041
31
Horie M. Nishio K. Endoh S. Kato H. Fujita K. Miyauchi A. et al (2013). Chromium (III) oxide nanoparticles induced remarkable oxidative stress and apoptosis on culture cells. Environ. Toxicol.28, 61–75. 10.1002/tox.20695
32
Iqbal J. Abbasi B. A. Ahmad R. Shahbaz A. Zahra S. A. Kanwal S. et al (2020a). Biogenic synthesis of green and cost effective iron nanoparticles and evaluation of their potential biomedical properties. J. Mol. Struct.1199, 126979. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.126979
33
Iqbal J. Abbasi B. A. Munir A. Uddin S. Kanwal S. Mahmood T. (2020b). Facile green synthesis approach for the production of chromium oxide nanoparticles and their different in vitro biological activities. Microsc. Res. Tech.83, 706–719. 10.1002/jemt.23460
34
Jaswal V. S. Arora A. K. Kinger M. Gupta V. D. Singh J. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of chromium oxide nanoparticles. Orient. J. Chem.30, 559–566. 10.13005/ojc/300220
35
Jeevanandam J. Kiew S. F. Boakye-Ansah S. Lau S. Y. Barhoum A. Danquah M. K. et al (2022). Green approaches for the synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles using microbial and plant extracts. Nanoscale14, 2534–2571. 10.1039/D1NR08144F
36
Joudeh N. Linke D. (2022). Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: a comprehensive review for biologists. J. Nanobiotechnology20, 262. 10.1186/s12951-022-01477-8
37
Kamble B. B. Naikwade M. Garadkar K. M. Mane R. B. Sharma K. K. K. Ajalkar B. D. et al (2019). Ionic liquid assisted synthesis of chromium oxide (Cr2O3) nanoparticles and their application in glucose sensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron.30, 13984–13993. 10.1007/s10854-019-01748-5
38
Karimian R. Piri F. (2013). Synthesis and investigation the catalytic behavior of Cr2O3 nanoparticles. J. Nanostructures3, 87–92. 10.1186/2193-8865-3-52
39
Khalaji A. D. (2021). Structural, optical and magnetic studies of Cr2O3 nanoparticles prepared by microwave-assisted synthesis. Nanochemistry Res.6, 18–24. 10.22036/NCR.2021.01.003
40
Khalaji A. D. Pavel Machek M. J. (2022). Cr2O3 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, optical, magnetic properties and their photocatalytic degradation of methyl Orange. J. Nanoanalysis9, 175–181. 10.22034/jna.2021.1943565.1276
41
Khan S. A. Shahid S. Hanif S. Almoallim H. S. Alharbi S. A. Sellami H. (2021). Green synthesis of chromium oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial, antioxidant anticancer, and biocompatibility activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22, 502. 10.3390/ijms22020502
42
Mazen S. A. Abu-Elsaad N. I. Nawara A. S. (2015). Influence of silicon substitution and annealing temperature on the microstructure and magnetic properties of lithium ferrite. J. Alloys Compd.648, 690–697. 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.018
43
Meenambika R. Ramalingom S. Chithambara Thanu T. (2013). Effect of calcinations temperature on the structure of Cr2O3 nanoparticles prepared by novel solvent free synthesis. ICANMEET2013, 324–327. 10.1109/ICANMEET.2013.6609303
44
Mohammed M. A. Rheima A. M. Jaber S. H. Hameed S. A. (2020). The removal of zinc ions from their aqueous solutions by Cr2O3 nanoparticles synthesized via the UV-irradiation method. Egypt. J. Chem.63, 425–431. 10.21608/ejchem.2019.17003.2042
45
Nasr A. Elshazly E. H. Slima D. F. Elnosary M. E. Sadek A. M. Khamis M. et al (2024). Bioactive compounds from Vicia sativa L. and Vicia monantha retz. With unveiling antiviral potentials in newly green synthesized CdO nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol.26, 497–512. 10.2174/0113892010305452240427044346
46
Patil S. Chandrasekaran R. (2020). Biogenic nanoparticles: a comprehensive perspective in synthesis, characterization, application and its challenges. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol.18, 67. 10.1186/s43141-020-00081-3
47
Puerari R. C. da Costa C. H. Vicentini D. S. Fuzinatto C. F. Melegari S. P. Schmidt É. C. et al (2016). Synthesis, characterization and toxicological evaluation of Cr2O3 nanoparticles using Daphnia magna and Aliivibrio fischeri. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf.128, 36–43. 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.011
48
Ramírez-Parra E. De la Rosa L. (2023). Designing novel strategies for improving old legumes: an overview from common vetch. Plants12, 1275. 10.3390/plants12061275
49
Rangayasami A. Kannan K. Joshi S. Subban M. (2020). Bioengineered silver nanoparticles using Elytraria acaulis (Lf) Lindau leaf extract and its biological applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol.27, 101690. 10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101690
50
Rasheed R. T. Easa H. A. Jassim L. S. (2020). Preparation and characterization of Cr2O3 nanoparticle prepared by chemical method. AIP Conf. Proc., 020202. 10.1063/5.0000124
51
Reygaert W. C. (2018). An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol.4, 482–501. 10.3934/microbiol.2018.3.482
52
Rezić I. Meštrović E. (2023). Characterization of nanoparticles in antimicrobial coatings for medical Applications-A review. Coatings13, 1830. 10.3390/coatings13111830
53
Sackey J. Morad R. Bashir A. K. H. Kotsedi L. Kaonga C. Maaza M. (2021). Bio-synthesised black α- Cr2O3 nanoparticles; experimental analysis and density function theory calculations. J. Alloys Compd.850, 156671. 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156671
54
Sangwan P. Kumar H. (2017). Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activities of chromium oxide nanoparticles against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res.10, 206–209. 10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i2.15189
55
Sawalha H. Abiri R. Sanusi R. Shaharuddin N. A. Noor A. A. M. Ab Shukor N. A. et al (2021). Toward a better understanding of metal nanoparticles, a novel strategy from eucalyptus plants. Plants10, 929. 10.3390/plants10050929
56
Sengul A. B. Asmatulu E. (2020). Toxicity of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett.18, 1659–1683. 10.1007/s10311-020-01033-6
57
Shahcheraghi N. Golchin H. Sadri Z. Tabari Y. Borhanifar F. Makani S. (2022). Nano-biotechnology, an applicable approach for sustainable future. 3 Biotech.12, 65. 10.1007/s13205-021-03108-9
58
Sharma U. R. Sharma N. (2021). Green synthesis, anti-cancer and corrosion inhibition activity of Cr2O3 nanoparticles. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem.11, 8402–8412. 10.33263/BRIAC111.84028412
59
Shobana M. K. Kim K. Kim J. H. (2019). Impact of magnesium substitution in nickel ferrite: optical and electrochemical studies. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostructures108, 100–104. 10.1016/j.physe.2018.12.013
60
Singh A. Singh N. Afzal S. Singh T. Hussain I. (2018). Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a review of their biological synthesis, antimicrobial activity, uptake, translocation and biotransformation in plants. J. Mater. Sci.53, 185–201. 10.1007/s10853-017-1544-1
61
Sone B. T. Manikandan E. Gurib-Fakim A. Maaza M. (2016). Single-phase α-Cr2O3nanoparticles’ green synthesis using Callistemon viminalis red flower extract. Green Chem. Lett. Rev.9, 85–90. 10.1080/17518253.2016.1151083
62
Srivastava V. Gusain D. Sharma Y. C. (2015). Critical review on the toxicity of some widely used engineered nanoparticles. Industrial and Eng. Chem. Res.54, 6209–6233. 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b01610
63
Theivasanthi T. Alagar M. (2011). Electrolytic synthesis and characterization of silver nanopowder. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1111.02604. 10.5101/nbe.v4i2.p58-65
64
Theivasanthi T. Alagar M. (2012). Konjac bio-molecules assisted, rod-spherical shaped lead nano powder synthesized by electrolytic process and its characterization studies. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1212.57955. 10.5101/nbe.v5i1.p10-19
65
Tortella G. R. Pieretti J. C. Rubilar O. Fernández-Baldo M. Benavides-Mendoza A. Diez M. C. et al (2022). Silver, copper and copper oxide nanoparticles in the fight against human viruses: progress and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol.42, 431–449. 10.1080/07388551.2021.1939260
66
Venkatachalapathy R. Manoharan C. Venkateshwarlu M. Abd elfadeel G. Saddeek Y. (2023). Solution combustion route for Ni and Al co-doped lithium ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, the effect of doping on the structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int.49, 6594–6607. 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.212
67
Yasmeen G. Hussain S. Tajammal A. Mustafa Z. Sagir M. Shahid M. et al (2023). Green synthesis of Cr2O3 nanoparticles by Cassia fistula, their electrochemical and antibacterial potential. Arabian J. Chem.16, 104912. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104912
68
Zainab Ahmad S. Khan I. Saeed K. Ahmad H. Alam A. et al (2022). A study on green synthesis, characterization of chromium oxide nanoparticles and their enzyme inhibitory potential. Front. Pharmacol.13, 1008182. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1008182
69
Zheng H. Jiang J. Xu S. Liu W. Xie Q. Cai X. et al (2021). Nanoparticle-induced ferroptosis: detection methods, mechanisms and applications. Nanoscale13, 2266–2285. 10.1039/D0NR08478F
Summary
Keywords
structure properties, optical properties, cytotoxicity, antimicrobial, physical activity
Citation
Elshazly EH, Abd elfadeel G, Yang L, Li X, Ewais EA, Sadek AM, Taha TM, Fathy O, Atta OM and Liu W-Z (2025) Sustainable biosynthesis, physiochemical characterization, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial evaluation of novel chromium oxide nanoparticles. Front. Chem. 13:1584199. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1584199
Received
27 February 2025
Accepted
03 September 2025
Published
24 September 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Timur Sh. Atabaev, Nazarbayev University, Kazakhstan
Reviewed by
Kadriye Özlem Saygi, Gaziosmanpaşa University, Türkiye
Dong-Wook Han, Pusan National University, Republic of Korea
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Elshazly, Abd elfadeel, Yang, Li, Ewais, Sadek, Taha, Fathy, Atta and Liu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wen-Zong Liu, liuwenzong@hit.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.