- The Second Hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, China
Introduction: As an important gas signaling molecule, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) exhibits therapeutic potential in inflammatory and oxidative stress-related diseases. This study developed and evaluated novel H2S donor derivatives based on the phenylphosphonothioic dichloride scaffold.
Methods: Derivatives were synthesized based on the phenylphosphonothioic dichloride scaffold. Compound 3b-1 was selected for its high H2S release capacity and favorable safety profile. Its anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated by measuring inhibition of TNF-α, TNF-β, and nitrite. Hepatoprotective effects were assessed in an H2O2-induced injury model using oxidative stress markers (MDA, SOD, GSH) and HSC activation. Cardioprotective effects were examined in an LPS-induced model by analyzing mitochondrial membrane potential, cardiac markers (LDH, CK-MB), and oxidative balance.
Results: Compound 3b-1 showed the highest H2S release capacity and inhibited TNF-α (86%), TNF-β (82%), and nitrite (67%). In the hepatocyte model, it reduced MDA (79%), enhanced SOD (49%) and GSH (76%), and suppressed HSC activation (55%). In the myocardial model, 3b-1 attenuated mitochondrial membrane potential dissipation, decreased LDH (34%) and CK-MB (24%), and restored GSH activity (73%) while reducing MDA (48%).
Discussion: The phosphorus-sulfur scaffold-based H2S donor 3b-1 demonstrates synergistic anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and organ-protective effects, highlighting its promise as a drug candidate for treating inflammation- and oxidative stress-related disorders.
1 Introduction
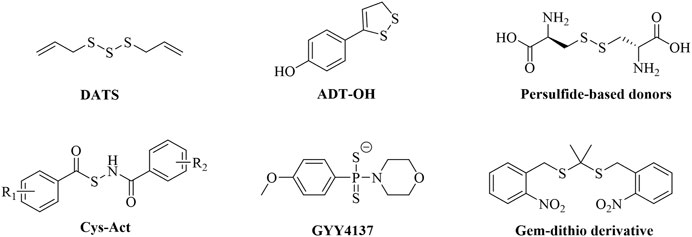
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has been identified as the third endogenous gaseous signaling molecule, following nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO). In recent years, it has been demonstrated to be widely involved in physiological and pathological processes such as cardiovascular homeostasis regulation, inflammation suppression, and hepatocyte metabolic regulation (Jin et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2020). Regarding the cardiovascular system, H2S inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by activating ATP-sensitive potassium channels, modulates myocardial ion channel function, and attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury (Kang et al., 2016). Furthermore, H2S has been shown to reduce myocardial fibrosis and collagen deposition within atherosclerotic plaques by inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGF-β1) signaling pathway, thereby delaying the process of vascular remodeling (Huang et al., 2023). In the field of inflammation regulation, low concentrations of H2S suppress the expression of pro-inflammatory factors such as Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) and Tumor Necrosis Factor Beta (TNF-β) by inhibiting the Nuclear Factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway (Lu and Wen, 2025). In the area of myocardial protection, the core mechanism of H2S lies in its dual capability to counteract apoptosis and promote tissue repair (Salloum, 2015). Despite this, current research on H2S donors still faces three major bottlenecks: poor chemical stability (e.g., the commonly used donor NaHS has an extremely short half-life), lack of tissue targeting, and uncontrollable release kinetics. An ideal H2S donor should release H2S only upon specific activation and with controlled, slow kinetics. To address this need, chemists have developed multiple novel types of H2S donors over the past decade that can be activated in response to different triggers, such as hydrolysis, biological thiols, light, pH, and enzymes (Figure 1) (Zhao et al., 2017). Major types include: natural donors (e.g., diallyl trisulfide (DATS) from garlic extracts) that release H2S in the presence of biological thiols (e.g., glutathione, GSH) and glucose (Chuah et al., 2007); hydrolysis-activated donors (e.g., ADT-OH) that primarily release H2S via hydrolysis (Wallace et al., 2007); persulfide donors that rapidly release H2S predominantly through exchange reactions with endogenous thiols (e.g., GSH) (Szczesny et al., 2014); thiol-triggered donors (e.g., Cys-Act) where H2S release occurs following nucleophilic addition by a thiol (Zhao et al., 2011); slow-release donors (e.g., GYY4137) that release H2S upon hydrolysis with controlled kinetics (Park et al., 2013); and photo-induced donors (e.g., gem-dithiol derivatives) where UV light exposure cleaves a photolabile protecting group, followed by hydrolysis to release H2S (Devarie-Baez et al., 2013). However, these donors also have limitations, such as uncontrolled release kinetics, limited trigger specificity, and significant toxicity, among others. Consequently, developing a new generation of disease microenvironment-responsive, controlled-release, and non-toxic H2S donors has become imperative to overcome current therapeutic limitations.
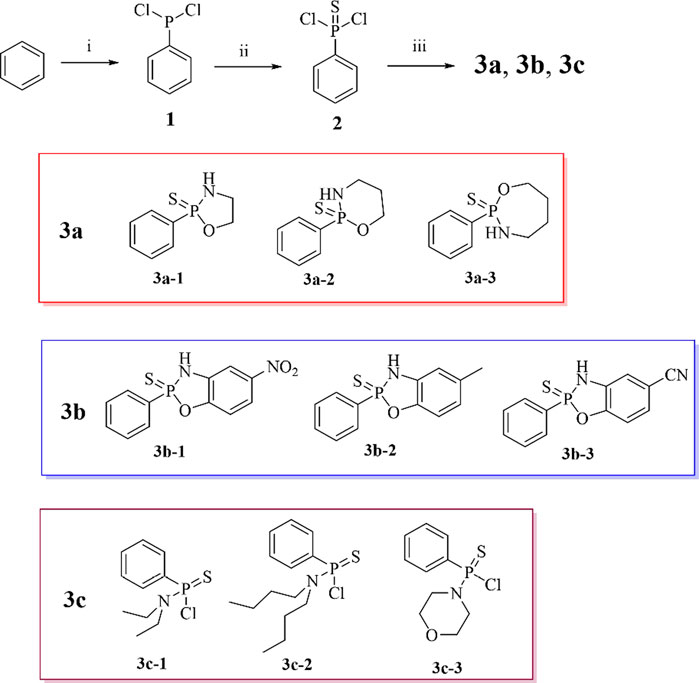
Scheme 1. Synthesis of H2S donor. Conditions and reagents: (i) AlCl3, PCl3, 75%; (ii) S, Benzene, 40%; (iii) Triethylamine, Monoethanolamine, 3-Aminopropanol, 4-Amino-1-butanol, 2-Amino-4-nitrophenol, 2-Amino-p-cresol, 2-Amino-4-cyanophenol, Diethylamine, Ethylbutylamine, Morpholine, 30%–45%.
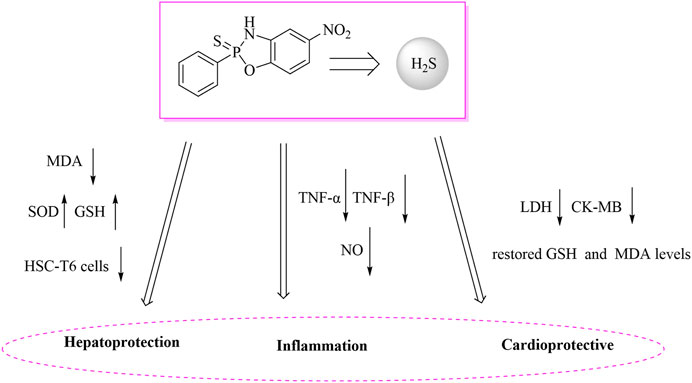
The liver, as the core organ for metabolism and detoxification, has its functional integrity vulnerable to damage from oxidative stress and fibrosis. H2S exhibits multi-layered physiological regulatory mechanisms in liver protection (Lee and Im, 2022). As illustrated in Figure 2, at the level of antioxidant defense, H2S effectively neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation products such as malondialdehyde (MDA) by enhancing glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis and boosting superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Studies demonstrate that exogenous H2S donors can significantly reduce MDA levels while elevating SOD and GSH in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis models, thereby maintaining redox homeostasis (Cirino et al., 2023). Septic cardiomyopathy, a fatal complication in critically ill patients with severe infections, is characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction and a systemic inflammatory storm, and currently lacks specific therapeutic interventions (Zhou et al., 2022). Endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), triggering NF-κB and NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome signaling pathways. This induces excessive production of NO, TNF-α, and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) in cardiomyocytes, ultimately leading to contractile dysfunction and cell death (Xia et al., 2023). During this process, a vicious cycle of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress further exacerbates myocardial injury—manifested by GSH depletion, MDA accumulation, and suppressed SOD activity (Cao et al., 2022). Although H2S demonstrates considerable therapeutic potential for myocardial protection through the mechanism illustrated in Figure 2, research on its application in septic myocardial injury remains limited. Existing studies predominantly focus on ischemia-reperfusion models. Traditional H2S donors (e.g., Na2S), due to their burst-release characteristics, cause significant concentration fluctuations and are unsuitable for meeting the sustained demands of the septic disease course (Wang, 2012). Therefore, developing novel donors with controllable release kinetics, enabling multi-target regulation simultaneously addressing cardiomyocyte redox balance (GSH/MDA) and inflammatory pathways, represents a promising strategy to overcome the therapeutic challenges in septic myocardial injury.
Based on the aforementioned research background and building on previous studies, this study synthesized a series of H2S donors featuring a phenylphosphonodithioate core structure, with the aim of overcoming the limitations of existing H2S donors. This breakthrough lays a solid foundation for the clinical translation of H2S-based therapeutics.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Chemical synthesis
As shown in Route 1, Starting from benzene, compounds 3a, 3b and 3c andwere synthesized as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors according to a previously reported method. Compounds 3a and 3b have been reported in the literature, while the 3c series remains undocumented (Xu et al., 2025; Zhang et al., 2019). Under AlCl3 catalysis, PCl3 is activated by Lewis acid to form the electrophile [Cl3P+] which attacks the benzene ring, proceeding through a σ-complex intermediate. Subsequent chlorine rearrangement of the transient intermediate phenylphosphorus trichloride (C6H5PCl3) yields phenyldichlorophosphine (1). Phenyldichlorophosphine (C6H5PCl2) then undergoes nucleophilic addition-elimination with elemental sulfur (S8) to form phenylthiophosphonyl dichloride (2). It is worth noting that sulfur-containing compounds are useful tools in medicinal chemistry (Akhlaghinia and Makarem, 2011; Morrison and Boyd, 2002). The reaction of phenylthiophosphonyl dichloride (C6H5P(S)Cl2) with nucleophiles (ethanolamine/2-amino-4-nitrophenol/diethylamine) follows an SN2 mechanism: nucleophilic groups (-NH2, -O-) attack the phosphorus atom to displace chlorine, affording C6H5P(S) (Nu)2-type products (3). The aromatic proton signals of the final product 3a (δ 7.30-8.80 ppm) aligned with literature data (Zhang et al., 2019), whereas the aromatic protons of donor 3b resonated at δ 8.00-7.30 ppm, exhibiting an upfield shift of 0.5 ppm relative to its precursor. This shift confirms that increased electron density on the phenyl ring attenuates deshielding effects. Donor 3c displayed analogous behavior. In summary, this study employed phenylthiophosphonyl dichloride (C6H5P(S)Cl2) as the key intermediate to efficiently construct a series of H2S donors (C6H5P(S) (Nu)2, 30%–45% yield) via SN2 nucleophilic substitution under weakly alkaline conditions (Et3N) in dichloromethane.
2.2 The toxicity of the compounds
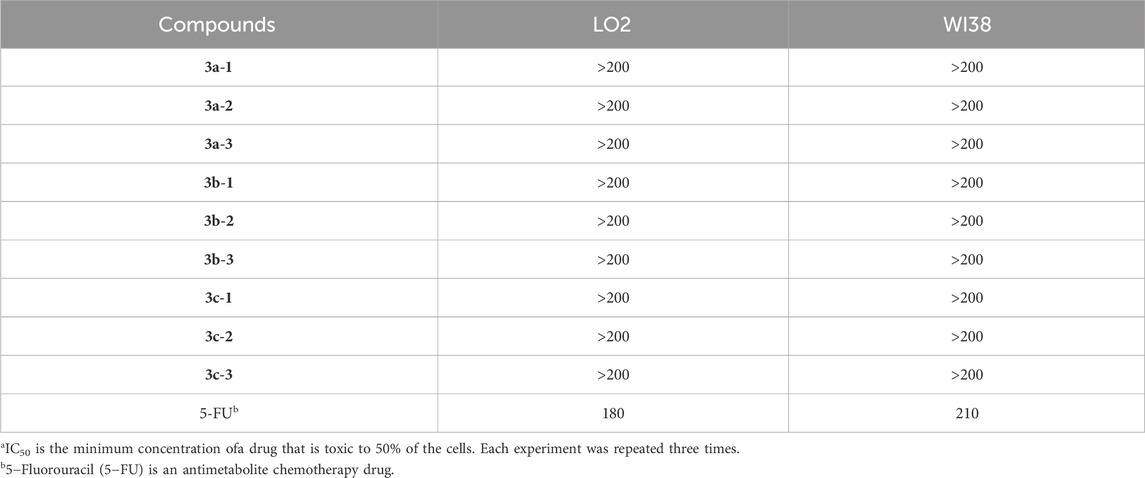
Drug safety is a prerequisite for subsequent experiments. We first evaluated the cytotoxicity of the hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donor compounds against normal liver cells (LO2) and WI38 (normal human lung fibroblasts) using the MTT assay (Xu et al., 2025). LO2 and WI38 cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well. Cell viability was measured 24 h after compound treatment, with untreated cells serving as the control. The experimental results (Table 1) demonstrated that: The H2S donor compounds exhibited no significant cytotoxicity against LO2 (normal hepatocytes) or WI38 (normal lung fibroblasts) within the tested concentration range. The toxicity of the test compound is much lower than that of the positive control drug 5-Fu. This indicates their low potential risk to normal liver tissue and non-target organs, providing a safety basis for further development. Regarding the rationale for using 5-FU in the LO2/WI38 models, our reasons are as follows: 5-Fluorouracil (5-Fu) is a classic antitumor chemotherapeutic drug with a long history of clinical application and a well-established mechanism of action. In in vitro cytotoxicity assays, 5-Fu is widely accepted and established as a standard positive control compound. 5-FU is recommended as a positive control agent by ISO 10993-5 (Biological evaluation of medical devices—Part 5: Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity), ensuring the reliability of cytotoxicity assessment results. This provides crucial historical reference benchmarks and comparability for experimental results. The inclusion of 5-Fu as a positive control serves as a vital means of monitoring experimental reproducibility and reliability.
2.3 H2S release ability of the compound and its influencing factors
Subsequently, we systematically evaluated the H2S release profiles of the novel hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donor drug under simulated physiological conditions in vitro. The results revealed that the compound exhibited favorable sustained-release characteristics in PBS buffer (pH 7.4) at 37 °C (Feng et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2019). As shown in Figure 3A, the 3b series compounds demonstrated higher cumulative H2S release. This enhanced release efficiency is likely attributed to the stronger electron-donating system inherent to the sulfur-phosphorus core-based H2S donors. The pH values vary across different human tissues and organs. For instance, the pH in the small intestine is approximately 8.0, whereas that of gastric fluid is as low as approximately 1.8. Therefore, we examined the hydrogen sulfide (H2S) release profile of compound 3b-1—which exhibits the strongest H2S-releasing capacity—under various pH conditions and its time-dependent release kinetics. As shown in Figure 3B, varying pH conditions had minimal impact on the H2S-releasing capacity of 3b-1. Time-course analysis (Figure 3C) revealed that H2S release increased progressively over the first 5 h and subsequently reached a plateau.
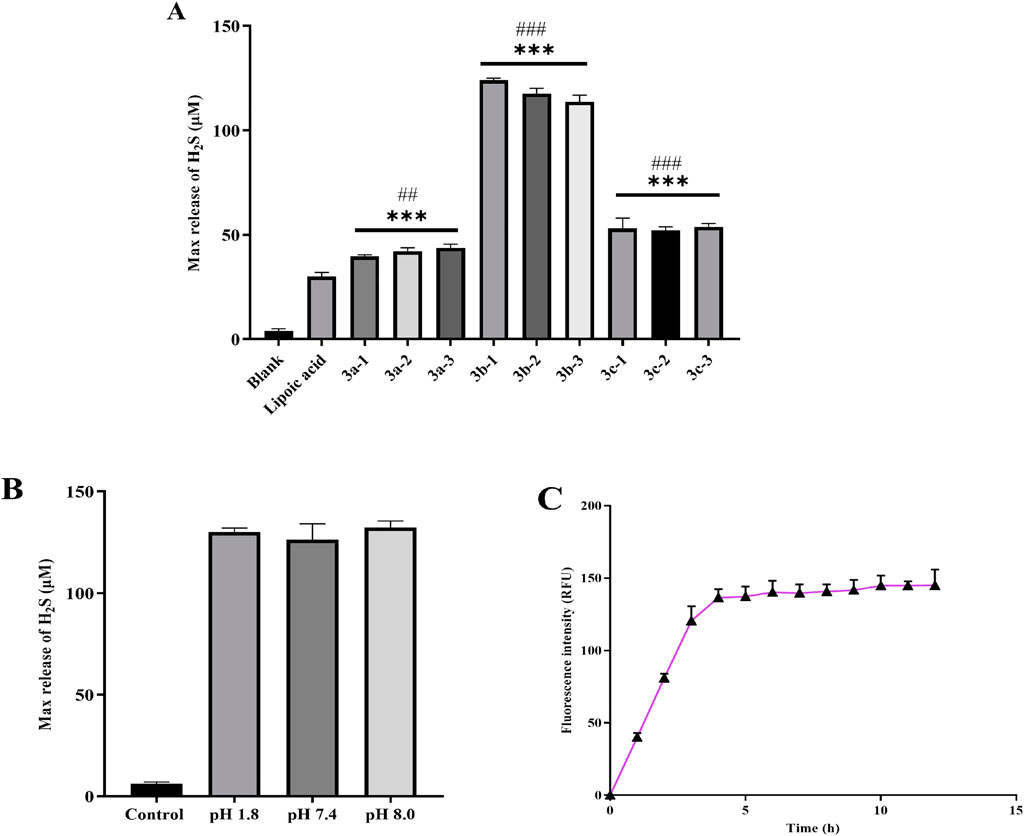
Figure 3. (A) Total H2S release by each compound over 6 h. (B) Total H2S release from Compound 3b-1 over 6 h under varying pH conditions. (C) The H2S amount released from 3b-1 within 12 h. Compared with the Blank group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. Lipoic acid group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
The H2S-releasing capacity of compounds is closely associated with their molecular structures. Specifically, the 3a series exhibits high stability, resulting in slow release kinetics and low H2S yield in PBS. Owing to the electron-donating effect of the benzene ring, the 3b series demonstrates facilitated H2S release. In contrast, H2S liberation from the 3c series is inhibited by the electron-withdrawing effect of the chlorine substituent. Based on these structure-activity relationships and supported by literature evidence, we propose the H2S release mechanism illustrated in Figure 4. Finally, we performed stability testing on compound 3b-1. As shown in Supplementary Figure S1, the detection results also provide additional support for the findings in Figure 3C, indicating that the compound decomposes within 5 h and subsequently plateaus.
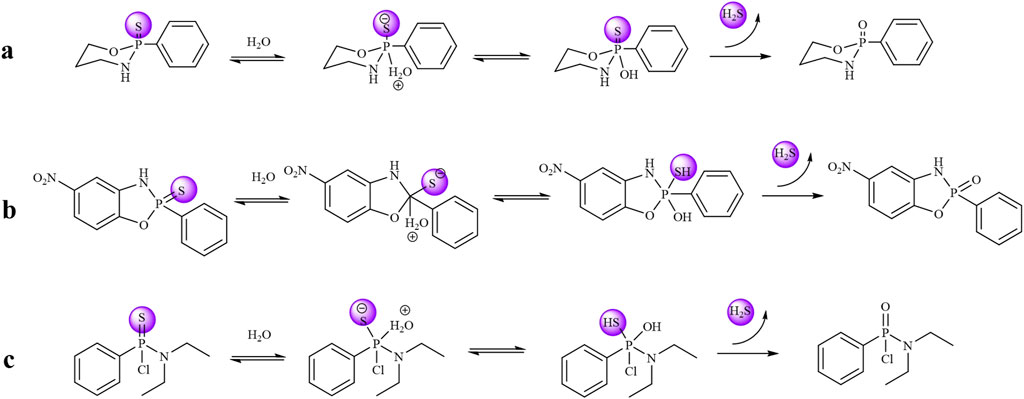
Figure 4. (a) Mechanism of compound 3a releasing hydrogen sulfide. (b) Mechanism of compound 3b releasing hydrogen sulfide. (c) Mechanism of compound 3c releasing hydrogen sulfide.
2.4 The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds
Initial screening of the nine newly synthesized compounds for anti-inflammatory activity was performed using LPS (1 μg/mL)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages over 24 h (Huang et al., 2016). As established, sustained inflammation drives hepatic pathology via Kupffer cell activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine cascades (e.g., TNF-α/IL-6), directly compromising hepatocyte viability. Similarly, septic cardiomyopathy involves TLR4-mediated hyperinflammation where cytokine storms (notably TNF-α, IL-1β) induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis and contractile dysfunction (Lu and Wen, 2025). Crucially, H2S confers organ protection through: (i) Suppression of NF-κB nuclear translocation and downstream pro-inflammatory gene expression; (ii) Modulation of inflammasome activity via inhibition of NLRP3 activation and caspase-1-dependent IL-1β maturation; (iii) Maintenance of redox homeostasis by attenuating inflammation-amplified oxidative stress through SOD/GSH pathways (Cirino et al., 2023). As shown in Figures 5A,B, the 3b-series compounds demonstrated superior suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, with compound 3b-1 exhibiting the most potent activity. Subsequent MTT assays confirmed low cytotoxicity for the 3b-series, with >95% cell viability maintained at 200 μg/mL (Figure 5C). Further evaluation of nitrite production (a marker of NO-mediated inflammation) revealed that 3b-1 most effectively attenuated inflammatory responses (Figure 5D). Given its highest H2S release capacity and superior anti-inflammatory efficacy, compound 3b-1 was selected as the lead candidate for subsequent mechanistic and in vivo studies.
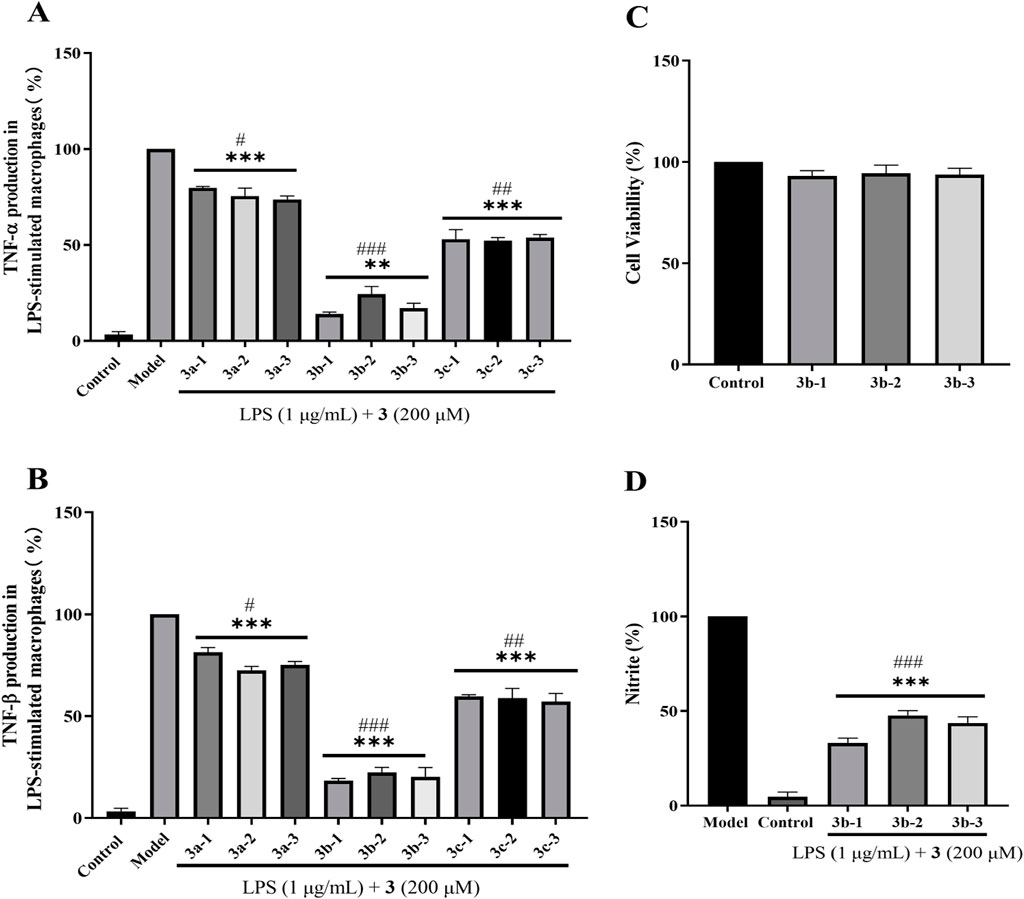
Figure 5. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory properties in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages treated with H2S donor compounds (200 μM). (A) Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α release by H2S donors. (B) Effects of H2S donors on RAW 264.7 macrophage viability. (C) Suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-β production by H2S donors. (D) Attenuation of nitrite accumulation by H2S donors. Compared with the control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. LPS model group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.5 Hepatoprotective effects
Chronic liver injury leads to excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM), driving the pathogenesis of liver diseases including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (Tacke and Zimmermann, 2014). Given the recognized antioxidant properties of hydrogen sulfide donors and their potential protective effects against hepatic disorders, we evaluated the cytoprotective activity of 3b-1 in both BRL-3A rat hepatocytes and HSC-T6 immortalized murine hepatic stellate cells. A cellular model of oxidative injury was established by treating BRL-3A cells with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 700 μM) for 24 h. As shown in (Figure 6A, H2O2 exposure significantly reduced cell viability compared to untreated controls. Pretreatment with 200 μM 3b-1 alone exhibited no cytotoxicity (Figure 6B). Compound 3b-1 dose-dependently restored viability in oxidatively damaged cells ((Figure 6C). Furthermore, 3b-1 treatment significantly reduced intracellular malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (p < 0.05) while enhancing superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and glutathione (GSH) content compared to the H2O2-injured group ((Figures 6D–F). These data demonstrate that 3b-1 protects hepatocytes against oxidative stress-induced damage. Hepatic fibrosis represents a wound-healing response characterized by ECM accumulation following chronic injury, with hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) serving as the primary ECM-producing cells (Roehlen et al., 2020). We thus assessed the anti-fibrotic potential of 3b-1 by examining its effects on TGF-β1-activated HSC-T6 cells. Compound 3b-1 dose-dependently suppressed HSC-T6 proliferation (Figures 6G,H). Collectively, 3b-1 protects against oxidative liver injury through reducing lipid peroxidation (MDA), enhancing antioxidant capacity (SOD, GSH), and inhibiting HSC activation. These dual mechanisms position 3b-1 as a promising therapeutic candidate for liver injury and fibrosis.
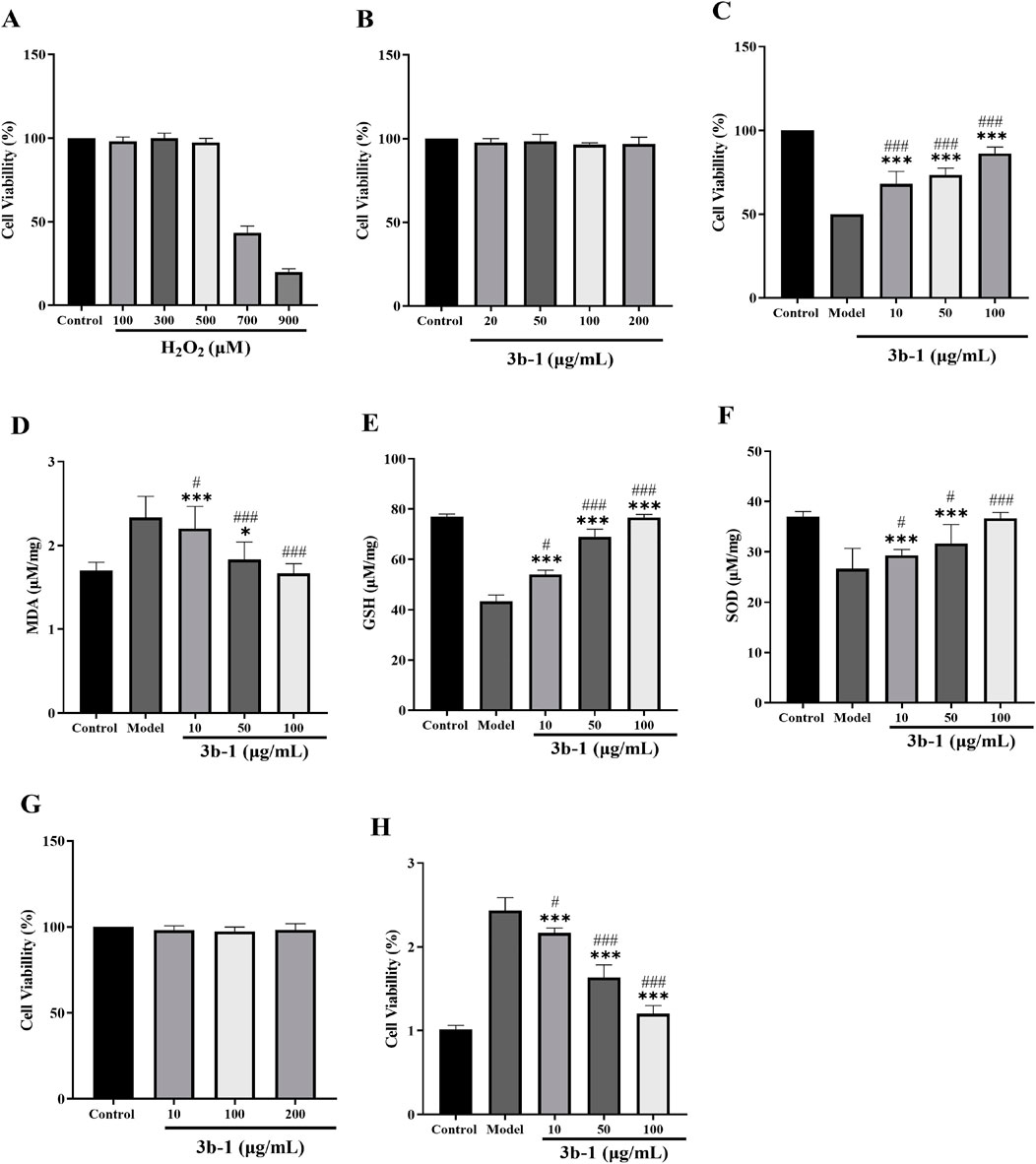
Figure 6. (A) Effect of H2O2 on the viability of BRL cells. (B) Effects of 3b-1 on the viability of BRL cells. (C) Effect of 3b-1 on restoring the cell growth in BRL cells exposed to H2O2. (D) Effect of 3b-1 on MDA in H2O2-treated BRL cells. (E) Effect of 3b-1 on GSH in H2O2-treated BRL cells. (F) Effect of 3b-1 on SOD in H2O2-treated BRL cells. (G) Effect of 3b-1 on the viability of HSC-T6 cells. (H) Effect of 3b-1 on the proliferation of HSC-T6 cells activated by TGF-β1. Compared with the control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. LPS model group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.6 Cardioprotective effects
In recent years, sepsis in its early stages has been recognized as a clinical syndrome characterized by a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) to infection. The heart is one of the organs most vulnerable to injury and dysfunction in sepsis, and sepsis-induced myocardial injury is relatively common in the ICU (Srzić et al., 2022). Previous studies have demonstrated that hydrogen sulfide (H2S) ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in septic rats by reducing cardiomyocyte injury caused by excessive autophagy through the activation of the AMPK/mTOR pathway (Yang et al., 2017).
To assess the cardioprotective capacity of compound 3b-1, we established an in vitro model of septic cardiomyopathy using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Initial dose-response analysis via CCK-8 assay (Figure 7A) demonstrated concentration-dependent cytotoxicity: 1 μg/mL LPS: Modest viability reduction versus control, 5 μg/mL LPS: Significant 51.6% viability decrease, 20 μg/mL LPS: Severe viability impairment. The intermediate LPS concentration (5 μg/mL) was selected for subsequent assays to maintain measurable pathological responses while ensuring experimental feasibility. To evaluate the protective effects of 3b-1, JC-1 probe analysis (Figure 7B) demonstrated that 3b-1 treatment effectively attenuated LPS-induced mitochondrial membrane potential disruption in cardiomyocytes. Subsequent measurements of cardiac injury markers (Figures 7C,D) showed that LPS stimulation significantly increased Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) and Creatine Kinase-Myocardial Band (CK-MB) release compared to the control group (P < 0.05), while 3b-1 administration significantly reduced these elevations (P < 0.05). Assessment of oxidative stress parameters (Figures 7E,F) revealed that LPS exposure significantly decreased GSH activity and increased MDA content relative to control (P < 0.05). Importantly, 3b-1 intervention restored GSH activity and reduced MDA levels (P < 0.05). These findings collectively demonstrate that the H2S donor 3b-1 effectively mitigates LPS-induced cardiomyocyte injury through preservation of mitochondrial function, reduction of cardiac injury markers, and attenuation of oxidative stress.
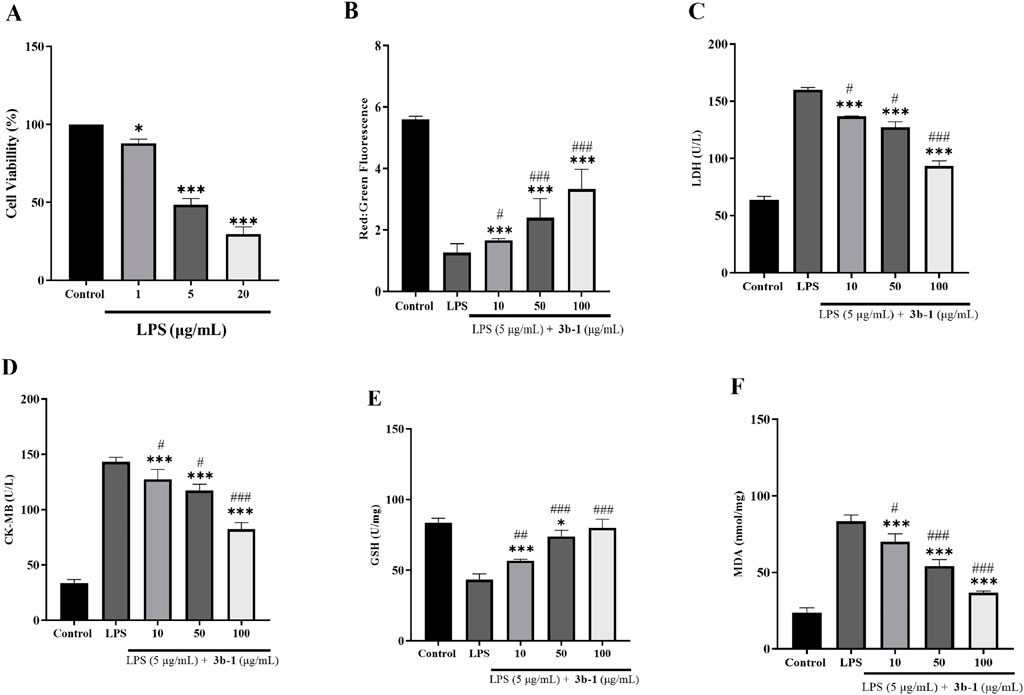
Figure 7. (A) Effect of varying LPS concentrations on H9c2 cell viability. (B) Impact of 3b-1 on mitochondrial membrane potential in LPS-stimulated cells. (C) Effect of 3b-1 on LDH release in LPS-treated cells. (D) Influence of 3b-1 on CK-MB levels in LPS-induced cells. (E) Effect of 3b-1 on GSH activity in LPS-stimulated cells. (F) Impact of 3b-1 on MDA production in LPS-exposed cells. Compared with the control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. LPS model group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
3 Conclusion
Building on previously reported compounds, this study synthesized a series of H2S-donor derivatives based on the phenylphosphonothioic dichloride scaffold using established synthetic methodologies. Among them, compound 3b-1 was identified as a highly efficient H2S donor and demonstrated significant in vitro anti-inflammatory activity, effectively reducing the levels of key inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, TNF-β, and nitrite. In an H2O2-induced oxidative injury model using BRL hepatocytes, 3b-1 exerted potent hepatoprotective effects by reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) production, enhancing the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH), and inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), collectively protecting against oxidative liver damage. This indicates its potential as a candidate for treating oxidative liver injury and liver fibrosis. Concurrently, in an LPS-induced cardiomyocyte injury model (mimicking septic cardiomyopathy), 3b-1 confirmed its distinct cardioprotective efficacy by preserving mitochondrial function, reducing the release of cardiac injury markers, and alleviating oxidative stress. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that 3b-1 is a multifunctional candidate molecule integrating efficient H2S release, potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and cardioprotective activities, providing a significant foundation for developing novel therapeutic strategies against related diseases such as liver injury, liver fibrosis, and septic cardiomyopathy.
4 Experimental section
4.1 Chemically synthetical experiments
All chemicals were of reagent grade or higher purity, purchased from Adamas and used directly without further purification. Solvents were used as received or dried over molecular sieves as appropriate. Column chromatography was performed using silica gel (100–200 mesh, Qingdao Ocean Chemical Factory), with reaction progress monitored by TLC (silica gel GF254 plates, Yantai Jiangyou Silica Gel Development Co., Ltd). All key intermediates and final products were characterized by 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) spectra recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 spectrometer. Chemical shifts are reported in ppm using residual solvent peaks as internal references (CDCl3: δ 7.26 ppm for 1H NMR, δ 77.16 ppm for 13C NMR). Products were further characterized by high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-HRMS) using an AB Sciex TripleTOF 5600+ mass spectrometer.
4.1.1 Dichloro(phenyl)phosphane (1)
Benzene (0.1 mmol), phosphorus trichloride (0.3 mmol), and aluminum chloride (0.12 mmol) were combined in a reaction flask and stirred under reflux for 5 h. Phosphorus trichloride (0.12 mol) and petroleum ether (45 mL) were then added, and stirring continued under reflux for 30 min. After cooling to room temperature, the mixture was filtered under reduced pressure. The filtrate was distilled at atmospheric pressure using petroleum ether, followed by distillation under reduced pressure. The fraction distilling at 100 °C was collected.
Yield, 75%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.94 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.61–7.51 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 140.72 (d, J=52.2 Hz), 132.79, 130.33 (d, J=31.3 Hz), 129.04 (d, J=7.9 Hz). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C6H6Cl2P+, 178.9506, found: 178.9511.
4.1.2 Phenylphosphonothioic dichloride (2)
Sulfur powder was added slowly in batches to the previous product (1) at 30 °C. Once most sulfur had dissolved and the solution became viscous, the temperature was raised to 80 °C and stirring continued for 1 h. Unreacted phosphorus trichloride and benzene were removed by distillation under atmospheric pressure followed by vacuum distillation. The fraction distilling at 90 °C was collected as phenyl phosphorothioic dichloride.
Yield, 40%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 8.13 (dd, J = 18.6, 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.63 (dt, J = 6.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.50 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 138.71 (d, J = 118.2 Hz), 133.87 (d, J = 4.0 Hz), 130.1 (d, J = 15.2 Hz), 128.85 (d, J = 18.2 Hz). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C6H6Cl2SP+, 210.9227, found: 210.9237.
4.1.3 2-phenyl-1,3,2-oxazaphospholidine 2-sulfide (3a-1)
2-Aminoethanol (2 mmol) and triethylamine (1 mL) were dissolved in dichloromethane. Phenylphosphonous dichloride (PhPCl2, 2 mmol) was added dropwise to the solution in an ice bath. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 8 h. The resulting precipitate was filtered off, and the filtrate was concentrated. The crude product was purified by column chromatography (PE/EA = 4:1) to afford a white solid.
Yield, 42%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.95–7.75 (m, 2H), 7.53–7.33 (m, 3H), 4.52–4.46 (m, 1H), 4.37–4.28 (m, 1H), 3.75–3.66 (m, 1H), 3.48–3.41 (m, 1H), 3.20–3.01 (m, J = 19 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 136.47 (d, J = 135.0 Hz), 132.15 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 130.96 (d, J = 12.4 Hz), 128.49 (d, J = 14.8 Hz), 77.16, 68.35, 43.97. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3265 (NH), 1436 (P=S), 1121 (C-O). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C8H11NOPS+, 200.0299, found: 200.0303.
4.1.4 2-phenyl-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinane 2-sulfide (3a-2)
Yield, 45%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.86–7.81 (m, J = 6.7, 2H), 7.50–7.48 (m, J = 4.8 Hz, 3H), 4.50–4.41 (m, 1H), 4.10–4.02 (m, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H), 3.46–3.13 (m, 3H), 2.10–2.02 (m, 1H), 1.62 (d, J = 14.3 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 134.34 (d, J = 133.7 Hz), 131.92 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 130.82 (d, J = 11.3 Hz), 129.03 (d, J = 14.1 Hz), 67.84, 41.33, 26.70. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3274 (NH), 1438 (P=S), 1120 (C-O). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C9H13NOPS+, 214.0455, found: 214.0462.
4.1.5 2-phenyl-1,3,2-oxazaphosphepane 2-sulfide (3a-3)
Yield, 50%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.92–7.81 (m, 2H), 7.48–7.39 (m, J = 2.7, 3H), 4.56 (m, 1H), 4.17 (m, J = 13.1, 1H), 3.46 (s, 1H), 3.16–3.03 (m, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.80–2.72 (m, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 1.97–1.69 (m, 3H), 1.64–1.47 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 135.13 (d, J = 148.6 Hz), 131.41 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 130.32 (d, J = 11.0 Hz), 128.37 (d, J = 14.5 Hz), 64.95, 42.65, 31.69, 29.70. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3436 (NH), 1438 (P=S), 1161 (C-O). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C10H15NOPS+, 228.0612, found: 228.0617.
4.1.6 Phenylphosphonothioic dichloride (3b-1)
Yield, 40%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.24–8.18 (m, 1H), 7.89 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 7.79–7.75 (m, 1H), 7.69–7.64 (m, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 12 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 147.68, 134.81 (d, J = 7.7 Hz), 134.12 (d, J = 3.1 Hz), 131.72 (d, J = 12.9 Hz), 128.91 (d, J = 15.6 Hz), 123.13, 117.18 (d, J = 4.0 Hz), 113.98. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3260 (NH), 1435 (P=S). 31P NMR (162 MHz, DMSO) 169.50. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. For C12H10N2O3PS+, 293.0150, found: 293.0148.
4.1.7 5-methyl-2-phenyl-3H benzo[d][1,3,2]oxazaphosphole 2-sulfide (3b-2)
Yield, 38%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.85–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.50–7.45 (m, 1H), 7.42–7.37 (m, 2H), 6.68 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 6.46 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 5.82 (d, J = 12 Hz, 1H), 2.17 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 146.28 (d, J = 7.4 Hz), 146.20, 133.84, 133.75, 132.16 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 132.13, 130.98 (d, J = 11.4 Hz), 130.87, 128.78 (d, J = 14.8 Hz), 124.83, 124.80, 121.53, 120.18 (d, J = 2.9 Hz), 116.40, 20.89. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3265 (NH), 1435 (P=S). TOF−MS, m/z: [M+H]+, calcd. for C13H13NOPS+, 262.0455, found: 262.0459.
4.1.8 2-phenyl-3H-benzo[d][1,3,2]oxazaphosphole-5-carbonitrile 2-sulfide (3b-3)
Yield, 41%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.86–7.80 (m, 2H), 7.49–7.37 (m, 1H), 7.42–7.37 (m, 2H), 6.84–6.79 (m, 2H), 6.67–6.63 (m, 1H), 5.99 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 145.65 (d, J = 7.8 Hz), 133.85, 132.18 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 130.88 (d, J = 11.5 Hz), 128.76 (d, J = 14.8 Hz), 127.91 (d, J = 3.1 Hz), 123.23, 121.14, 119.40 (d, J = 3.2 Hz), 115.58. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3265 (NH), 1433 (P=S). TOF−MS, m/z: [M+H]+, calcd. for C13H10N2OPS+, 273.0251, found: 273.0255.
4.1.9 Phenylphosphonothioic dichloride (3c-1)
Yield, 43%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.92–7.86 (m, 2H), 7.54–7.34 (m, 3H), 3.38–3.14 (m, 4H), 1.08 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 136.49 (d, J = 136.1 Hz), 132.02 (d, J = 3.6 Hz), 130.14 (d, J = 12.1 Hz), 128.53 (d, J = 15.8 Hz), 40.33 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 13.02 (d, J = 6.0 Hz). IR (KBr, cm-1): 1435 (P=S). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. For C10H16ClNPS+, 248.0429, found: 248.0433. The observed isotopic pattern is consistent with the theoretical distribution: experimental ratio [M + H]+: [M + H+2]+ = 3 : 1.
4.1.10 Phenylphosphonothioic dichloride (3c-2)
Yield, 45%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.96–7.90 (m, 2H), 7.48 (m, 3H), 3.28–3.06 (m, 4H), 1.60–1.52 (m, 2H), 1.47–1.39 (m, 2H), 1.25–1.15 (m, 4H), 0.83 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 137.27 (d, J = 136.0 Hz), 132.12 (d, J = 3.5 Hz), 130.58 (d, J = 12.0 Hz), 128.58 (d, J = 15.8 Hz), 46.10 (d, J = 2.0 Hz), 29.79 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 20.03 (d, J = 2.0 Hz), 13.76 (d, J = 2.0 Hz). IR (KBr, cm-1): 1435 (P=S). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. For C14H24ClNPS+, 304.1055, found: 304.1059. The observed isotopic pattern is consistent with the theoretical distribution: experimental ratio [M + H]+: [M + H+2]+ = 3 : 1.
4.1.11 Phenylphosphonothioic dichloride (3c-3)
Yield, 45%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 7.95–7.89 (m, 2H), 7.55–7.46 (m, 3H), 3.67 (t, J = 4.7 Hz, 4H), 3.44–3.36 (m, 2H), 3.08–3.00 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, Chloroform-d) δ 134.70 (d, J = 134.3 Hz), 132.01 (d, J = 3.0 Hz), 130.57 (d, J = 11.9 Hz), 128.90 (d, J = 15.7 Hz), 66.34 (d, J = 9.9 Hz), 45.31 (d, J = 2.8 Hz). IR (KBr, cm-1): 1435 (P=S). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. For C10H14ClNOPS+, 262.0222, found: 262.0225. The observed isotopic pattern is consistent with the theoretical distribution: experimental ratio [M + H]+: [M + H+2]+ = 3 : 1.
4.2 Cell viability
We used the CCK8 assay to detect cell viability. See Supplementary Material for more details (Xu et al., 2025).
4.3 H2S measurement
The release of hydrogen sulfide was detected by the methylene blue method. See Supplementary Material for more details (Zhao et al., 2019).
4.4 Treatment of compounds on LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages
See Supplementary Material for more details (Li et al., 2023).
4.5 Measurement of cytokines
Culture supernatants were analyzed for cytokine levels using commercial ELISA kits (e.g., mouse TNF-α) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. Absorbance was measured at [specify wavelength] nm using a microplate reader (Dogra, 2025).
4.6 Superoxide dismutase (SOD) measurement
3b-1 was determined using a commercial total SOD assay kit based on the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) method. See Supplementary Material for more details (Wen et al., 2022).
4.7 Hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic effects of 3b-1
See Supplementary Material for more details (Dogra, 2025; He et al., 2025).
4.8 H9c2 cell culture
See Supplementary Material for more details (Sun et al., 2022).
4.9 Measurement of cardiac enzymes (LDH and CK-MB)
See Supplementary Material for more details (Zheng et al., 2022).
4.10 Determination of compound 3b-1 stability in PBS
See Supplementary Material for more details.
4.11 Statistical analysis
The above experimental data are the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. SPSS 22.0 software was used to process the data, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to measure statistical differences between the two groups.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used. Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
DW: Software, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. YM: Supervision, Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft. YL: Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2025.1643663/full#supplementary-material
References
Akhlaghinia, B., and Makarem, A. (2011). Dithioacetalization of carbonyl compounds under catalyst-free condition. J sulfur Chem, 32(6), 575–581. doi:10.1080/17415993.2011.622394
Cao, G., Zeng, Y., Zhao, Y., Lin, L., Luo, X., Guo, L., et al. (2022). H2S regulation of ferroptosis attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 26 (5), 335. doi:10.3892/mmr.2022.12851
Chuah, S. C., Moore, P. K., and Zhu, Y. Z. (2007). S-allylcysteine mediates cardioprotection in an acute myocardial infarction rat model via a hydrogen sulfide-mediated pathway. Am. J. PHYSIOL-HEART C 293 (5), H2693–H2701. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00853.2007
Cirino, G., Szabo, C., and Papapetropoulos, A. (2023). Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide in mammalian cells, tissues, and organs. Physiol. Rev. 103 (1), 31–276. doi:10.1152/physrev.00028.2021
Devarie-Baez, N. O., Bagdon, P. E., Peng, B., Zhao, Y., Park, C. M., and Xian, M. (2013). Light-induced hydrogen sulfide release from “caged” gem-dithiols. Org. Lett. 15 (11), 2786–2789. doi:10.1021/ol401118k
Dogra, A. (2025). Baicalein: unveiling the multifaceted marvel of hepatoprotection and beyond. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 24, 1–13. doi:10.1080/10286020.2025.2481273
Feng, W., Teo, X. Y., Novera, W., Ramanujulu, P. M., Liang, D., Huang, D., et al. (2015). Discovery of new H2S releasing phosphordithioates and 2,3-Dihydro-2-phenyl-2-sulfanylenebenzo[d] [1,3,2]oxazaphospholes with improved antiproliferative activity. J. Med. Chem. 58 (16), 6456–6480. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00848
He, R., Lian, Z., Cheng, Z., Liu, Y., Peng, X., Wang, Y., et al. (2025). The phytochemical characterization of a cili (Rosa roxburghii) fruit low-temperature extract with hepatoprotective effects. Foods 14 (8), 1301. doi:10.3390/foods14081301
Huang, C. W., Feng, W., Peh, M. T., Peh, K., Dymock, B. W., and Moore, P. K. (2016). A novel slow-releasing hydrogen sulfide donor, FW1256, exerts anti-inflammatory effects in mouse macrophages and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 113 (PtA), 533–546. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.032
Huang, Y., Omorou, M., Gao, M., Mu, C., Xu, W., and Xu, H. (2023). Hydrogen sulfide and its donors for the treatment of cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury: a comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 161, 114506. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114506
Jin, Y. Q., Yuan, H., Liu, Y. F., Zhu, Y. W., Wang, Y., Liang, X. Y., et al. (2024). Role of hydrogen sulfide in health and disease. MedComm 5, e661. doi:10.1002/mco2.6615(9)
Kang, J., Li, Z., Organ, C. L., Park, C. M., Yang, C. T., Pacheco, A., et al. (2016). pH-Controlled hydrogen sulfide release for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Am. Chem. Soc.138(20) 138, 6336–6339. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b01373
Lee, J. H., and Im, S. S. (2022). Function of gaseous hydrogen sulfide in liver fibrosis. BMB Rep. 55 (10), 481–487. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2022.55.10.1242022.55.10.124
Li, F., Wang, X., Shi, J., Wu, S., Xing, W., and He, Y. (2023). Anti-inflammatory effect of dental pulp stem cells. Front. Immunol. 23 (14), 1284868. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1284868
Lu, W., and Wen, J. (2025). Anti-Inflammatory effects of hydrogen sulfide in axes between gut and other organs. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 42 (7-9), 341–360. doi:10.1089/ars.2023.0531
Morrison, R. T., and Boyd, R. N. (2002). Organic chemistry. 6th ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Park, C. M., Zhao, Y., Zhu, Z., Pacheco, A., Peng, B., Devarie-Baez, N. O., et al. (2013). Synthesis and evaluation of phosphorodithioate-based hydrogen sulfide donors. Mol. Biosyst. 9 (10), 2430–2434. doi:10.1039/c3mb70145j
Roehlen, N., Crouchet, E., and Baumert, T. F. (2020). Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives. Cells 9 (4), 875. doi:10.3390/cells9040875
Salloum, F. N. (2015). Hydrogen sulfide and cardioprotection–mechanistic insights and clinical translatability. Pharmacol. Ther. 152, 11–17. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.04.004
Srzić, I., Nesek, A. V., and Tunjić, P. D. (2022). Sepsis definition: what's new in the treatment guidelines. Acta Clin croat. 61 Suppl. l 1), 67–72. doi:10.20471/acc.2022.61.s1.11
Sun, L., Wang, H., Yu, S., Zhang, L., Jiang, J., and Zhou, Q. (2022). Herceptin induces ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in H9c2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 49 (2), 17. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2021.5072
Szczesny, B., Módis, K., Yanagi, K., Coletta, C., Le Trionnaire, S., Perry, A., et al. (2014). AP39 a novel mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide donor, stimulates cellular bioenergetics, exerts cytoprotective effects and protects against the loss of mitochondrial DNA integrity in oxidatively stressed endothelial cells in vitro. Nitric oxide 41, 120–130. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2014.04.008
Tacke, F., and Zimmermann, H. W. (2014). Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 60 (5), 1090–1096. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.025
Wallace, J. L., Caliendo, G., Santagada, V., Cirino, G., and Fiorucci, S. (2007). Gastrointestinal safety and anti-inflammatory effects of a hydrogen sulfide–releasing diclofenac derivative in the rat. Gastroenterology 132 (1), 261–271. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.042
Wang, R. (2012). Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide: a whiff exploration that blossomed. Physiol. Rev. 92 (2), 791–896. doi:10.1152/physrev.00017.2011
Wen, F., Tan, Z. G., and Xiang, J. (2022). Cu-Zn SOD suppresses epilepsy in pilocarpine-treated rats and alters SCN2A/Nrf2/HO-1 expression. Epileptic Disord. 24 (4), 647–656. doi:10.1684/epd.2022.1434
Xia, Y., Zhang, W., He, K., Bai, L., Miao, Y., Liu, B., et al. (2023). Hydrogen sulfide alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury through TLR4-NLRP3 pathway. Physiol. Res. 72 (1), 15–25. doi:10.33549/physiolres.934928
Xu, C., Yang, N., Yu, H., and Wang, X. (2025). Design and synthesis of phenylthiophosphoryl dichloride derivatives and evaluation of their antitumour and anti-inflammatory activities. Front. Chem. 21 (12), 1529211. doi:10.3389/fchem.2024.1529211
Yang, F., Zhang, L., Gao, Z., Sun, X., Yu, M., Dong, S., et al. (2017). Exogenous H2S protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by activating autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 43 (3), 1168–1187. doi:10.1159/000481758
Yang, N., Liu, Y., Li, T., and Tuo, Q. (2020). Role of hydrogen sulfide in chronic diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 39 (2), 187–196. doi:10.1089/dna.2019.5067
Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Li, J., Bai, Z., Zhao, Q., et al. (2019). Toxicity, bioactivity, release of H2S in vivo and pharmaco-kinetics of H2S-donors with thiophosphamide structure. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 15 (176), 456–475. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.05.017
Zhao, Y., Wang, H., and Xian, M. (2011). Cysteine-activated hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors. J. Am. Chem. Soc.133(1) 133, 15–17. doi:10.1021/ja1085723
Zhao, Y., Henthorn, H. A., and Pluth, M. D. (2017). Kinetic insights into hydrogen sulfide delivery from caged-carbonyl sulfide isomeric donor platforms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 (45), 16365–16376. doi:10.1021/jacs.7b09527
Zhao, Y., Steiger, A. K., and Pluth, M. D. (2019). Cyclic sulfenyl thiocarbamates release carbonyl sulfide and hydrogen sulfide independently in thiol-promoted pathways. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141 (34), 13610–13618. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b06319
Zheng, Q., Wang, H., Hou, W., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Use of anti-angiogenic drugs potentially associated with an increase on serum AST, LDH, CK, and CK-MB activities in patients with cancer: a retrospective Study. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 2 (8), 755191. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.755191
Keywords: hydrogen sulfide, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, phenylthiophosphonic dichloride
Citation: Wang D, Meng Y and Liu Y (2025) Activity evaluation of multifunctional H2S donors for anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and hepatoprotective applications. Front. Chem. 13:1643663. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1643663
Received: 09 June 2025; Accepted: 15 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ahmed A. Al-Karmalawy, University of Mashreq, IraqReviewed by:
Ata Makarem, University of Hamburg, GermanyAyman Abo Elmaaty, Port Said University, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Meng and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Donghe Wang, d2RoOTkxNDA4QDE2My5jb20=
 Donghe Wang
Donghe Wang Yujie Meng
Yujie Meng