Abstract
Introduction:
Building upon previous research, this study focuses on the replication and evaluation of a series of hydrazone derivatives derived from isoniazid.
Methods:
The lead compound, identified as C5, was assessed for its antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, notably Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. Its hemolytic potential, cytotoxicity (against VERO cells), and ability to induce resistance were evaluated. Mechanistic studies included assays for membrane depolarization (using DiSC35 fluorescence), membrane integrity (via SYTOX Green uptake), measurement of intracellular ATP levels, and detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Additional investigations examined its effect on LPS-induced NO/TNF-α release in macrophages and its activity against S. aureus biofilms.
Results:
Compound C5 exhibited potent antibacterial activity (MIC = 16 μg/mL against S. aureus ATCC 29213). It demonstrated no hemolysis and low cytotoxicity (IC50 > 128 μg/mL). A time-kill assay achieved complete eradication of S. aureus within 16 hours at 8× MIC, and the compound showed a low tendency to induce resistance. The mechanistic studies revealed that C5 disrupts the bacterial membrane, causing depolarization, loss of integrity, and leakage of proteins/DNA. It also induced ROS accumulation and significantly reduced ATP levels. Furthermore, C5 suppressed LPS-induced NO/TNF-α release in macrophages (p < 0.01) and inhibited/disrupted S. aureus biofilms.
Discussion:
These results demonstrate that C5 possesses a multifunctional mechanism of action, combining direct bactericidal activity through membrane targeting with anti-biofilm efficacy and immunomodulatory properties. This multifaceted profile highlights its strong potential as a promising candidate for combating resistant bacterial infections.
1 Introduction
Antibiotic resistance in Gram-positive bacteria has become a critical global public health threat (Asenjo et al., 2021). The latest World Health Organization (WHO) report indicates that methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) now surpasses HIV infection in mortality rates (Lakhundi and Zhang, 2018). Moreover, the pipeline for novel traditional antibiotics is nearing depletion: among antibacterial new molecular entities currently entering Phase I clinical trials, only approximately one-third target Gram-positive bacteria. Furthermore, the vast majority are derivatives of existing antibiotics, lacking truly groundbreaking mechanisms of action (Mohr, 2016). While traditional antibiotics like vancomycin remain the ‘last line of defense’ against MRSA infections, their nephrotoxicity and the rising prevalence of resistance (exemplified by the emergence of vancomycin-resistant S. aureus VRSA strains) underscore the urgent need for novel antibacterial agents with distinct mechanisms of action (Cheung et al., 2021; García-Castro et al., 2023).
Against this backdrop, isoniazid (INH), a first-line tuberculosis drug, has garnered significant interest due to its unique hydrazine (-NHNH2) pharmacophore (Ridahunlang et al., 2023). However, the antibacterial spectrum of isoniazid is relatively narrow, exhibiting high efficacy primarily against Mycobacteria, while its activity against many common Gram-positive bacteria (such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, etc.) and Gram-negative bacteria is limited (Bhowmik et al., 2023; Poulton and Rock, 2022). This is largely attributed to its strong hydrophilicity, which hinders effective penetration through the dense peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive bacteria as well as the outer membrane barrier of Gram-negative bacteria. However, the highly reactive hydrazine moiety within the INH molecule provides an ideal platform for structural modification (Sodré-Alves et al., 2024). Studies demonstrate that constructing Schiff bases via aldehyde-amine condensation can confer amphiphilic character to the resulting molecules. This modification enhances penetration through the cell membranes of Gram-positive bacteria while simultaneously evading recognition by efflux pumps (Hong et al., 2025). Consequently, developing novel Schiff base derivatives based on the INH scaffold represents not only a rational strategy to overcome its inherent antibacterial spectrum limitations but also an innovative approach to combat infections caused by drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria.
Schiff bases possess diverse biological activities, including antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant effects, making them highly valuable research targets (Udhayakumari and Inbaraj, 2020; Rana et al., 2024; Presenjit et al., 2024). The unique structure of the Schiff base linkage (-C=N-) offers a triple advantage in antibacterial drug design: Membrane Targeting: The electron delocalization characteristic of the imine bond facilitates molecular intercalation into the bacterial phospholipid bilayer, disrupting membrane potential through electrostatic interactions (Fontana et al., 2022). Metal Chelation Capacity: The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom enables the chelation of metal ions such as Mg2+ and Zn2+, interfering with the function of metalloenzymes (e.g., DNA polymerase, peptide deformylase) (Kaur et al., 2023). ROS-Inducing Effect: Schiff bases substituted with nitro/hydroxyl groups can act as electron shuttles, disrupting respiratory chain complex I and triggering a burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Barua et al., 2024). It is worth noting that Schiff bases are important compounds in synthetic processes and drug discovery (Han et al., 2025; Klika et al., 2022; Kopka et al., 2019).
Therefore, this study adopted a molecular hybridization strategy. Condensing isoniazid with aromatic aldehydes to form Schiff bases. The introduced aromatic aldehydes serve as hydrophobic groups to enhance lipophilicity, thus improving the ability to penetrate the thick peptidoglycan layer of Gram-positive bacteria. This approach led to the discovery of compound C5 (N'-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide), which exhibits potent antibacterial activity. Compound C5 rapidly eradicates Staphylococcus aureus by disrupting cell membrane integrity and activating the endogenous ROS pathway (Figure 1). This work provides a chemical entity (NCE) for developing drugs against drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria. Furthermore, it establishes a theoretical foundation for the rational design of Schiff base-based antibacterial agents.
FIGURE 1

Antibacterial mechanism diagram of Isoniazid Schiff Base derivatives.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Chemical synthesis
Building on established synthetic approaches, this process employs ethyl isonicotinate as the starting material, as outlined in Scheme 1 (Backes et al., 2015; Ji et al., 2018; Rouzi et al., 2024). Hydrazinolysis with hydrazine hydrate in ethanol solvent affords the key intermediate, isoniazid. This step features simple operation under mild, well-controlled conditions, delivering isoniazid in 86% isolated yield with high efficiency. Subsequently, the reactive hydrazine group of isoniazid undergoes condensation with structurally diverse aldehyde derivatives in ethanol. This transformation also proceeds under mild conditions with excellent reaction compatibility, successfully yielding varying target products C. For compound B, the signal for the hydrazinyl proton was observed at δ 12.06 (s, 1H), which is consistent with literature values. For compound C, the set of signals in the aromatic region (δ 9.0-7.0) for the phenyl protons also agreed well with reported data (Backes et al., 2015; Ji et al., 2018; Rouzi et al., 2024). With the exception of compound C7, all other compounds have been previously synthesized and were not first developed in this study (Backes et al., 2015; Ji et al., 2018; Rouzi et al., 2024). Critically, all intermediates and final products C are purified to high purity via straightforward recrystallization, eliminating the need for tedious, time-consuming, and costly column chromatography. This purification strategy significantly streamlines the workflow, enhances process economy, and improves scalability, collectively highlighting the substantial potential of this route for industrial-scale applications.
SCHEME 1

Synthesis of Isoniazid derivatives. Conditions and reagents: (i) ethanol, NH2NH2, reflux, yield 86%; (ii) ethanol, different aldehyde groups, reflux, yield 81%–92%.
2.2 Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration
Reportedly, some Schiff base derivatives exhibit promising in vitro antibacterial activity (Hong et al., 2025). Therefore, this study employed the broth microdilution method to determine the in vitro antibacterial activity (MIC) against the following strains: Gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 43300, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 33731, Staphylococcus aureus MRSA2, Bacillus Subtilis ATCC6633. Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis SM012. The antibacterial results for all compounds are summarized in Table 1. Among the tested compounds: C5 (16 μg/mL) exhibited inhibitory activity against all tested S. aureus strains. C1 (64 μg/mL) also inhibited all tested S. aureus strains. The remaining compounds demonstrated poor antibacterial activity, likely attributable to their overall poor solubility.
TABLE 1
| MIC a (μg/mL) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | R | E. coli ATCC 25922 | S. enteritidis SM012 | S. aureus ATCC 29213 | S. aureus ATCC 43300 | S. aureus ATCC 33731 | S. aureus MRSA2 | B. Subtilis ATCC6633 |
| Vancomycinb | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Enrofloxacinc | - | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | - | - | - | - | - |
| C1 |
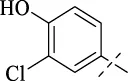
|
>256 | >256 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 128 | 128 |
| C2 |
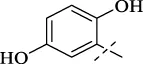
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C3 |
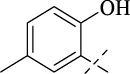
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C4 |
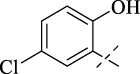
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C5 |
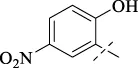
|
>256 | >256 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| C6 |
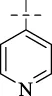
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C7 |
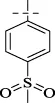
|
>256 | >256 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 |
| C8 |
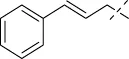
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C9 |
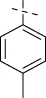
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C50 |
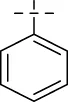
|
>256 | >256 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 256 | 256 |
| C11 |
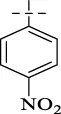
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C12 |
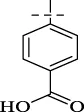
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C13 |
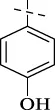
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C14 |
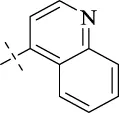
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| C15 |
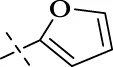
|
256 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 256 |
| C16 |
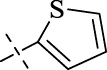
|
>256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
The antibacterial activity of Isoniazid derivatives.
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration that completely inhibits microbial growth after 16–24 h. Each experiment was repeated three times.
vancomycin is a clinical drug against Gram-positive bacteria.
Enrofloxacin is a broad-spectrum quinolone-based antibiotic.
2.3 Time-killing curve determinations and drug resistance study
To evaluate the bactericidal efficacy of C5 against S. aureus ATCC 29213, we determined the time-kill kinetics of the compound by enumerating bacterial colonies at various time points, using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as the negative control (Xiao et al., 2024). As shown in Figure 2A, the growth of S. aureus ATCC 29213 was completely inhibited at 4 × MIC. Schiff bases exhibit a low propensity for resistance development due to their multi-target mechanism of action and membrane-disrupting effects. Consistent with this, resistance development studies demonstrated a low spontaneous resistance frequency for C5 against S. aureus ATCC 29213. As depicted in Figure 2B, after 28 serial passages, the MIC value for S. aureus ATCC 29213 increased by no more than 8-fold. These results indicate that C5 effectively kills bacteria while minimizing the development of resistance.
FIGURE 2

(A) Time-kill kinetics of C5 against S. aureus ATCC 29213. (B) Resistance development of C5. Data are presented as means ± SEM (Standard Error of Mean) from three independent experiments.
2.4 The toxicity of the compounds
To evaluate compound safety, hemolysis assays were first performed for all test compounds. A 1% Triton X-100 solution served as the positive control, and sterile PBS was used as the negative control. As shown in Figure 3A, no hemolysis was observed for compound C5 across the concentration range of 2–256 μg/mL. This indicates that C5 exhibits no hemolytic activity against rabbit erythrocytes at concentrations effective for its antibacterial action. Subsequently, the cytotoxicity of the active compound C5 against African green monkey kidney (VERO) cells was assessed using the CCK-8 assay.The results (Figure 3B) demonstrate that C5 exhibited no cytotoxicity towards VERO cells at concentrations up to 256 μg/mL.
FIGURE 3

(A) Percentage of hemolysis of rabbit blood cells at various C5 concentrations, The values represented by the bars from left to right are: 3, 100, 17, 11, 9, 5, and 5. (B) Cytotoxicity of compound C5 against Vero cells after 24 h. Difference is considered significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
2.5 Antimicrobial mechanism investigation
2.5.1 Membrane depolarization and permeabilization assay
Studies indicate that the antibacterial activity of Schiff base compounds is associated with their hydrophobic interactions (Caldés et al., 2013; Hong et al., 2025). Based on the Schiff base group and hydrophobic characteristics inherent in compound C5’s structure, we hypothesized that it likely exerts its antibacterial effect by targeting the bacterial cell membrane. The specific mechanism may involve inducing alterations in membrane depolarization and permeability. To investigate the direct impact of C5 on the bacterial membrane, this study employed fluorescent probes: The cationic dye 3,3′-dipropylthiadicarbocyanine iodide (DiSC35) was used to monitor changes in bacterial membrane potential (depolarization). The nucleic acid stain SYTOX Green, which cannot penetrate intact cell membranes, was utilized to assess changes in membrane permeability (integrity), evaluating C5’s disruptive effect on membrane function.
Within 10 min of adding compound C5, a sustained increase in fluorescence intensity was observed in suspensions of S. aureus ATCC 29213 pre-loaded with either the DiSC35 or SYTOX Green probes (Figures 4A,B). When C5 reached concentrations of 4 × MIC or 32 × MIC, the fluorescence intensity of the bacterial mixtures at 35 min was significantly enhanced compared to the initial value. In contrast, the fluorescence intensity of the blank control (without C5) remained stable. These findings demonstrate that C5 disrupts the polarized state of the bacterial cell membrane (i.e., the distribution of positive and negative charges across the membrane), leading to increased membrane permeability. In conclusion, C5 exerts its bactericidal effect by mediating membrane damage through alterations in the polarization state and permeability of the bacterial cell membrane.
FIGURE 4

(A) Cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization by C5 assessed using SYTOX Green uptake. (B) Cytoplasmic membrane depolarization by C5 measured with the DiSC35 probe. The blank control was bacteria without compound treatment. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.5.2 Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ATP
During antibiotic treatment, disruption of membrane equilibrium often leads to the accumulation of ROS, a common mechanism of action for bactericidal antibiotics (Tu et al., 2022). Furthermore, membrane depolarization is also linked to ROS generation (Hong et al., 2025). Therefore, we examined changes in ROS accumulation in bacteria following treatment with compound C5. Within 30 min, a significant increase in ROS levels was observed in the C5-treated group (Figure 5A). The elevation in bacterial ROS levels corresponded with an increase in the proportion of dead bacteria. Studies indicate a strong correlation between the bactericidal effects of antibiotics and enhanced bacterial respiratory activity (Dörner et al., 2024; Islam and Reid, 2024). Consequently, we assessed the impact of C5 treatment on intracellular ATP levels in bacteria. As shown in Figure 5B, intracellular ATP levels decreased significantly following treatment with C5.
FIGURE 5
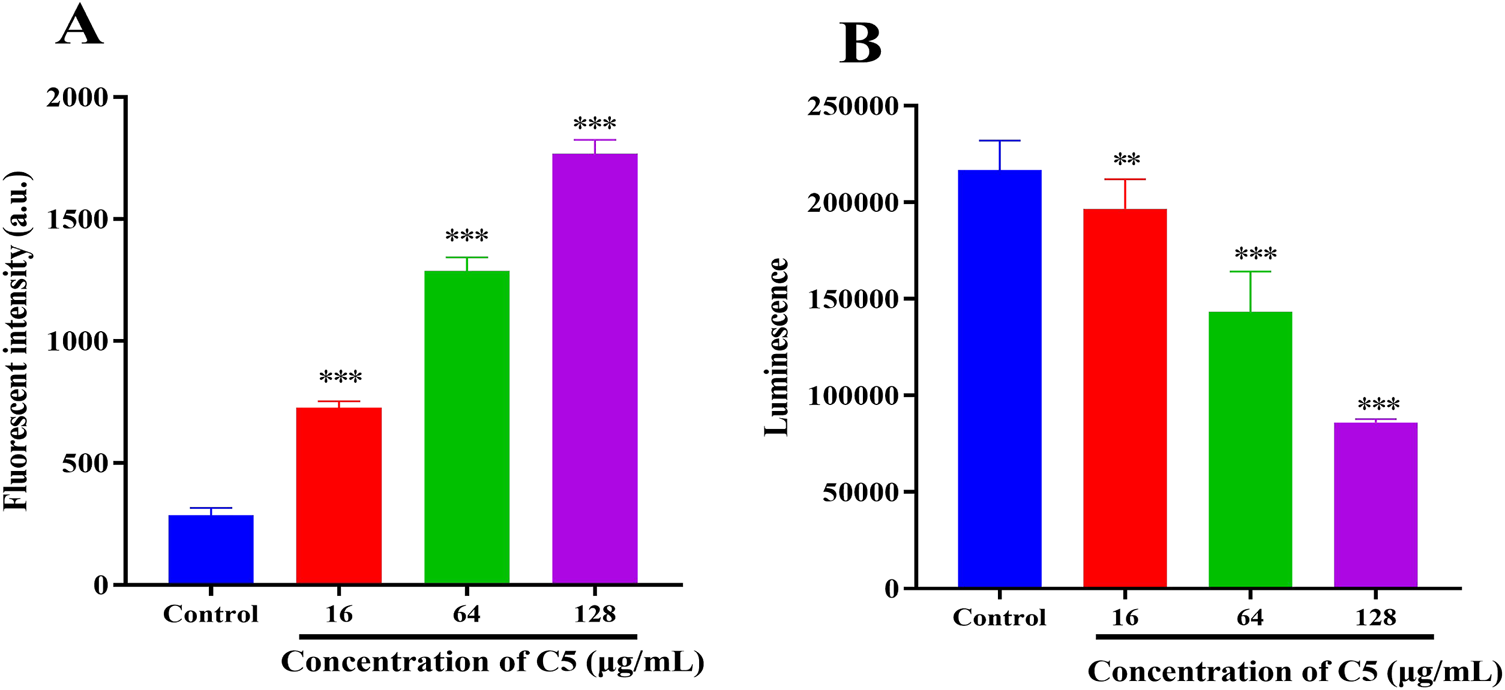
(A) Effect of C5 treatment on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in S. aureus ATCC 29213. (B) Effect of C5 treatment on intracellular ATP levels in S. aureus ATCC 29213. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.5.3 Leakage of proteins and DNA
To further evaluate the impact of compound C5 on bacterial membrane integrity, we measured changes in the concentration of proteins and DNA in the extracellular culture medium of S. aureus ATCC 29213 following treatment with different concentrations of C5. The results demonstrated that compared to the blank control group, the concentrations of extracellular proteins and DNA were significantly elevated in the C5-treated bacterial suspensions. This effect occurred in a dose-dependent manner (Figures 6A,B). These findings directly demonstrate that C5 disrupts the cell membrane integrity of S. aureus ATCC 29213, leading to the leakage of intracellular contents (proteins and DNA).
FIGURE 6

(A) Protein leakage caused by the treatment of C5 on S. aureus ATCC 29213. (B) DNA leakage resulting from the treatment of C5 on S. aureus ATCC 29213. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.6 The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds
Inflammation commonly accompanies infections. Given that Schiff Base derivatives have been demonstrated to possess anti-inflammatory effects, we further evaluated the impact of compound C5 on the levels of inflammatory factors NO and TNF-α (Hu et al., 2022). As shown in Figure 7, compared to the control group, LPS stimulation alone significantly increased the production of NO and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells. However, treatment with compound C5 significantly suppressed this production. At a concentration as low as 64 μg/mL, compound C5 effectively reduced the generation of both NO and TNF-α.
FIGURE 7

Anti-inflammatory activity of the C5 compounds in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells was evaluated in the LPS-enhanced leukocyte migration assay. (A) C5 affects the level of NO. (B) C5 affects the level of TNF-α. Compared with the LPS model group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ###p < 0.001 vs. control group. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments.
2.7 Inhibitory effects towards S. Aureus biofilm formation
Over 80% of chronic bacterial infections in humans are associated with biofilms. Biofilms are structured communities of bacteria encased within a protective extracellular polymeric matrix, exhibiting significantly enhanced tolerance to antimicrobial agents and host defense systems. In contexts such as medical devices (e.g., catheters, implants), chronic wounds, and cystic fibrosis lungs, biofilm-associated infections are characterized by their persistent, recurrent, and recalcitrant nature (Sirinirund et al., 2023; Vyas et al., 2020). Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop agents capable of effectively preventing biofilm formation and eradicating established biofilms. Building upon this, we investigated the ability of compound C5 to inhibit biofilm formation by S. aureus ATCC 29213. Quantitative analysis of biofilms was performed using the crystal violet assay. Figure 8A illustrates the inhibitory effects of C5 at various concentrations. C5 exhibited dose-dependent inhibition of S. aureus ATCC 29213 biofilm formation: 23% (16 μg/mL, 1 × MIC), 84% (64 μg/mL, 4 × MIC), and 91% (256 μg/mL, 8 × MIC). Subsequently, we further evaluated the eradication efficacy of C5 against pre-formed S. aureus ATCC 29213 biofilms (Figure 8B). C5 effectively disrupted established biofilms with eradication rates of 10% (1 × MIC), 35% (4 × MIC), and 66% (8 × MIC), confirming its potency against biofilm-embedded S. aureus.
FIGURE 8

(A) Inhibition rate of C5 on S. aureus ATCC 29213 biofilm formation. (B) Biofilm dispersion of C5 on S. aureus ATCC 29213 biofilm. Difference is considered significant at *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, vs. control group. Data are presented as means ± SD from three independent experiments.
3 Conclusion
Based on compounds synthesized by other researchers, this study discovered the antibacterial activity of the isoniazid-based Schiff base agent, featuring a lead compound (MIC = 16 μg/mL) with outstanding properties: potent and rapid bactericidal activity achieving complete eradication within 16 h at 8 × MIC coupled with low resistance potential; a defined multi-mechanistic antibacterial action involving disruption of bacterial membrane integrity (as confirmed by DiSC35) depolarization and SYTOX Green uptake) leading to intracellular content leakage, interference with energy metabolism via ATP depletion, and induction of oxidative stress through ROS accumulation; significant anti-biofilm efficacy; a unique anti-inflammatory function suppressing the production of key macrophage mediators NO and TNF-α; and an excellent safety profile demonstrating no hemolysis and extremely low mammalian cytotoxicity (IC50 > 128 μg/mL). This combined “antibacterial–anti-inflammatory–anti-biofilm” triple synergistic effect positions the compound as a highly promising multifunctional candidate for combating drug-resistant staphylococcal infections.
4 Experimental section
4.1 Chemically synthetical experiments
All chemicals were of reagent grade or higher and used as received from Adamas without further purification. Solvents were employed as supplied or dried over molecular sieves when necessary. Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (100–200 mesh, Qingdao Ocean Chemical). Reaction progress was monitored by TLC on silica gel GF254 plates (Yantai Jiangyou). 1H NMR (400 MHz) and 13C NMR (100 MHz) spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 spectrometer, with chemical shifts reported relative to residual solvent signals (CDCl3: δH 7.26 ppm, δC 77.16 ppm). High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were acquired on an AB Sciex TripleTOF 5600+ instrument using electrospray ionization (ESI).
4.1.1 Isonicotinohydrazide (B)
Ethyl isonicotinate (1 mmol, 151 mg) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol. Hydrazine hydrate (3 mmol) was then added, and the solution was heated to reflux at 80 °C for 8 h. After completion of the reaction, isoniazid was obtained by recrystallization from ethanol.
119 mg, Yield, 86%. White solid powder. M.P. 171 °C–173 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.07 (s, 1H), 8.71–8.64 (m, 3H), 7.74–7.68 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 164.54, 150.63, 140.72, 121.49. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C6H8N3O+, 138.0667, found: 138.0669.
4.1.2 N'-(3-chloro-4-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C1)
Compound C1 was synthesized analogously to compound B. Compound B (1 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol, followed by the addition of 4-chloro-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1 mmol). The solution was heated to reflux at 80 °C for 8 h. Upon reaction completion, the product was obtained by recrystallization from ethanol.
248 mg, Yield, 90%. White solid powder. M.P. 232 °C–235 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.06 (s, 1H), 8.80 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 8.36 (s, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.06 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.38, 155.19, 149.85, 148.04, 141.06, 128.64, 127.51, 126.34, 121.84, 120.42, 116.96. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H11ClN3O2+, 276.0540, found: 276.0544.
4.1.3 N'-(2,5-dihydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C2)
232 mg, Yield, 90%. White solid powder. M.P. 259 °C–261 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.46 (s, 1H), 11.12 (s, 1H), 8.83 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 2H), 8.69 (s, 1H), 7.92 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 7.69 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.97 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.05, 150.28, 149.87, 149.69, 148.55, 140.57, 121.73, 119.34, 118.89, 117.11, 113.46. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H12N3O3+, 258.0878, found: 258.0853.
4.1.4 N'-(2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C3)
217 mg, Yield, 85%. White solid powder. M.P. 189 °C–191 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.26 (s, 1H), 10.83 (s, 1H), 8.80 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 8.64 (s, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (s, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 2.25 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.21, 155.30, 150.19, 149.04, 139.83, 132.28, 129.07, 127.85, 121.39, 118.13, 116.17, 19.76. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C14H14N3O2+, 256.1086, found: 256.1088.
4.1.5 N'-(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C4)
223 mg, Yield, 81%. White solid powder. M.P. 189 °C–191 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.24 (s, 1H), 8.81 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 8.64 (s, 1H), 7.89 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.04 (s, 1H), 6.76 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.27, 156.19, 149.56, 146.89, 140.76, 131.14, 127.37, 123.15, 122.05, 120.68, 118.31. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H11ClN3O2+, 276.0540, found: 276.0542.
4.1.6 N'-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C5)
252 mg, Yield, 88%. White solid powder. M.P. 242 °C–245 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.44 (s, 1H), 12.19 (s, 1H), 8.90–8.67 (m, 3H), 8.61 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (dd, J = 9.1, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.85, 161.76, 150.34, 145.36, 140.35, 140.18, 127.05, 123.69, 121.94, 120.21, 117.34. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3265 (NH), 1650 (CO), 1600 (NH). TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H11N4O4+, 287.0780, found: 287.0782.
4.1.7 N'-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide (C6)
183 mg, Yield, 81%. White solid powder. M.P. 230 °C–232 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.49 (s, 1H), 8.80 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 8.69 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 8.54 (s, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.48, 150.78, 150.04, 146.81, 142.49, 140.55, 122.12, 121.85. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C12H11N4O+, 227.0933, found: 227.0937.
4.1.8 N'-[4-(methylsulfonyl)benzylidene]isonicotinohydrazide (C7)
270 mg, Yield, 89%. White solid powder. M.P. 209 °C–211 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.41 (s, 1H), 8.84 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 8.59 (s, 1H), 8.10–7.86 (m, 4H), 3.89 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.07, 149.83, 147.75, 142.18, 141.69, 139.24, 128.39, 128.04, 122.62, 43.89. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C14H14N3O3S+, 304.0756, found: 304.0759.
4.1.9 N'-[(1E,2E)-3-phenylallylidene]isonicotinohydrazide (C8)
213 mg, Yield, 85%. White solid powder. M.P. 164 °C–166 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.07 (s, 1H), 8.82 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 8.29 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 7.64 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.53–7.29 (m, 3H), 7.10 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.20, 151.22, 149.45, 141.33, 140.03, 135.80, 129.05, 128.87, 127.24, 125.39, 122.04, 39.52. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C15H14N3O+, 252.1137, found: 252.1141.
4.1.10 N'-(4-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C9)
196 mg, Yield, 82%. White solid powder. M.P. 186 °C–188 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.99 (s, 1H), 8.78 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 8.43 (s, 1H), 7.82 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 2.35 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.58, 150.33, 149.13, 140.56, 140.29, 131.36, 129.50, 127.29, 121.56, 21.06. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C14H14N3O+, 240.1137, found: 240.1141.
4.1.11 N′-benzylideneisonicotinohydrazide (C10)
203 mg, Yield, 90%. White solid powder. M.P. 191°C–193°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.29 (s, 1H), 8.85 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.98, 149.24, 148.61, 141.80, 133.83, 130.26, 128.72, 127.12, 122.23, 39.52. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H12N3O+, 226.0980, found: 226.0983.
4.1.12 N'-(4-nitrobenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C11)
243 mg, Yield, 90%. White solid powder. M.P. 237 °C–239 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.61 (s, 1H), 8.87 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H), 8.66 (s, 1H), 8.31 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 8.01 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 4H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.70, 149.11, 148.30, 147.04, 141.86, 140.46, 128.47, 124.33, 122.64. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H11N4O3+, 271.0831, found: 271.0835.
4.1.13 4-[(2-isonicotinoylhydrazineylidene)methyl]benzoic acid (C12)
237 mg, Yield, 88%. White solid powder. M.P. 313 °C–315 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.45 (s, 1H), 8.86 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 8.61 (s, 1H), 8.01 (dd, J = 12.6, 7.2 Hz, 4H), 7.87 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 167.34, 161.70, 148.99, 148.68, 146.87, 142.64, 138.45, 132.52, 130.31, 127.81, 123.05. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C14H12N3O3+, 270.0878, found: 270.0881.
4.1.14 N'-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (C13)
210 mg, Yield, 87%. White solid powder. M.P. 244 °C–246 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.04 (s, 1H), 8.81 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 8.42 (s, 1H), 7.93 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.80, 159.65, 149.50, 149.02, 141.65, 128.98, 124.79, 121.96, 115.66, 39.52. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C13H12N3O2+, 242.0929, found: 242.0933.
4.1.15 N'-(quinolin-4-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide (C14)
248 mg, Yield, 90%. White solid powder. M.P. 204 °C–206 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.81 (s, 1H), 9.32 (s, 1H), 9.05 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 8.84 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 2H), 8.74 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.15 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 8.03–7.85 (m, 5H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.40, 150.48, 149.63, 146.73, 146.28, 141.12, 139.91, 131.42, 128.94, 128.58, 125.06, 122.62, 120.50. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C16H13N4O+, 277.1089, found: 277.1094.
4.1.16 N'-(furan-2-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide (C15)
176 mg, Yield, 82%. White solid powder. M.P. 257 °C–259 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.51 (s, 1H), 8.91 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 3H), 8.52 (s, 1H), 8.13 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 2H), 6.65 (dd, J = 3.3, 1.7 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 159.96, 148.67, 146.50, 145.29, 138.86, 122.94, 114.25, 111.95. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C11H10N3O2+, 216.0773, found: 216.0776.
4.1.17 N'-(thiophen-2-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide (C16)
194 mg, Yield, 84%. White solid powder. M.P. 217 °C–219 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.04 (s, 1H), 8.78 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 8.69 (s, 1H), 7.81 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 7.69 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.51 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.11 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.93, 150.76, 144.56, 140.88, 139.20, 132.00, 129.88, 128.39, 121.94. TOF-MS, m/z: [M + H]+, calcd. for C11H9N3OS+, 232.0544, found: 232.0547.
4.2 Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Stratev and Fasulkova, 2024).
4.3 Time-killing kinetics
Time-Kill Kinetics The time-kill kinetics of compound C5 against S. aureus ATCC 29213 were assessed by the viable plate count method. Detailed procedures followed those described in previous reports.
4.4 Drug resistance study
The drug resistance study of compound C5 was performed by following the protocol of previous study. The initial MIC values of C5 against S. aureus ATCC 29213 was determined according to method described above. The process was repeated continuously for 28 days.
4.5 Hemolysis assay
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Hong et al., 2025; Sæbø et al., 2023).
4.6 Cytotoxicity assay
Cytotoxicity was assessed using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Beyotime, Shanghai, China), following established methods with minor modifications. Cell viability was calculated as follows: Cell viability (%) = [(OD450,sample - OD450,blank)/(OD450,control - OD450,blank)] × 100% (Mine et al., 2020).
4.7 Biofilm formation assay
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Li et al., 2024).
4.8 The anti-inflammatory activity of the compounds
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Moudgil and Venkatesha, 2022).
4.9 Membrane depolarization study
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Hong et al., 2025).
4.10 DNA and protein leakage
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Hong et al., 2025).
4.11 ROS detection assay
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Zhang et al., 2022).
4.12 Intracellular ATP measurement
For detailed procedures, refer to the Supplementary Material (Morciano et al., 2020).
4.13 Statistical analysis
The above experimental data is the average ±SEM (Standard Error of Mean) independent experiment of at least three data points. SPSS 21.0 software was used to analyze the data, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to process the statistical differences between the two groups.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
YL: Investigation, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Data curation, Supervision. LH: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Validation, Data curation, Project administration. BL: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization. ZQ: Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Software, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1706525.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2025.1654358/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Asenjo A. Oteo-Iglesias J. Alós J. I. (2021). What's new in mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria of clinical origin?Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin.39, 291–299. 10.1016/j.eimce.2020.02.017
2
Backes G. L. Jursic B. S. Neumann D. M. (2015). Potent antimicrobial agents against azole-resistant fungi based on pyridinohydrazide and hydrazomethylpyridine structural motifs. Bioorg Med. Chem.23, 3397–3407. 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.04.040
3
Barua M. Bandyopadhyay S. Wasai A. Ghosh M. Roy I. Ghosh P. et al (2024). A trinuclear Zn (II) schiff base dicyanamide complex attenuates bacterial biofilm formation by ROS generation and membrane damage and exhibits anticancer activity. Microb. Pathog.188, 106548. 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106548
4
Bhowmik P. Modi B. Roy P. Chowdhury A. (2023). Strategies to combat Gram-negative bacterial resistance to conventional antibacterial drugs: a review. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect.14, 333–346. 10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0323
5
Caldés C. Vilanova B. Adrover M. Donoso J. Muñoz F. (2013). The hydrophobic substituent in aminophospholipids affects the formation kinetics of their schiff bases. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett.23, 2202–2206. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.01.100
6
Cheung G. Y. C. Bae J. S. Otto M. (2021). Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence12, 547–569. 10.1080/21505594.2021.1878688
7
Dörner P. J. Anandakumar H. Röwekamp I. Fiocca-Vernengo F. Millet B. Krzanowski M. et al (2024). Clinically used broad-spectrum antibiotics compromise inflammatory monocyte-dependent antibacterial defense in the lung. Nat. Commun.15, 2788. 10.1038/s41467-024-47149-z
8
Fontana R. Marconi P. C. R. Caputo A. Gavalyan V. B. (2022). Novel chitosan-based schiff base compounds: Chemical characterization and antimicrobial activity. Molecules27, 2740. 10.3390/molecules27092740
9
García-Castro M. Sarabia F. Díaz-Morilla A. López-Romero J. M. (2023). Approved antibacterial drugs in the last 10 years: from the bench to the clinic. Explor. Drug Sci.3, 180–209. 10.37349/eds.2023.00013
10
Han J. Klika K. D. Makarem A. (2025). Byproducts in the synthesis of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11. Nat. Protoc.18. 10.1038/s41596-025-01164-6
11
Hong S. Lu H. Tian D. Chang Y. Lu Q. Gao F. (2025). Discovery of triazole derivatives for biofilm disruption, anti-inflammation and metal ion chelation. Front. Chem.26, 1545259. 10.3389/fchem.2025.1545259
12
Hu C. W. Chang Y. C. Liu C. H. Yu Y. A. Mou K. Y. (2022). Development of a TNF-α-mediated trojan horse for bacteria-based cancer therapy. Mol. Ther.30, 2522–2536. 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.04.008
13
Islam N. Reid D. (2024). Inhaled antibiotics: a promising drug delivery strategies for efficient treatment of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) associated with antibiotic resistant biofilm-dwelling and intracellular bacterial pathogens. Respir. Med.227, 107661. 10.1016/j.rmed.2024.107661
14
Ji Y. Dai F. Zhou B. (2018). Designing salicylaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazones as Cu(II) ionophores with tunable chelation and release of copper for hitting redox achilles heel of cancer cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med.129, 215–226. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.017
15
Kaur M. Kumar S. Yusuf M. Lee J. Malik A. K. Ahmadi Y. et al (2023). Schiff base-functionalized metal-organic frameworks as an efficient adsorbent for the decontamination of heavy metal ions in water. Environ. Res.236, 116811. 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116811
16
Klika K. D. Alsalim R. Eftekhari M. Makarem A. (2022). Synthesis of a polyaminocarboxylate-based aluminum complex and its structural studies using 1H{13C}-HMBC NMR and a Karplus-type function. Dalton Trans.51, 12436–12441. 10.1039/d2dt01702d
17
Kopka K. Makarem A. Sarvestani M. K. Klika K. D. (2019). A multifunctional HBED-type chelator with dual conjugation capabilities for radiopharmaceutical development. Synlett30, 1795–1798. 10.1055/s-0039-1690194
18
Lakhundi S. Zhang K. (2018). Methicillin-Resistant staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev.31, e00020-18–18. 10.1128/CMR.00020-18
19
Li M. Cruz C. D. Ilina P. Tammela P. (2024). High-throughput combination assay for studying biofilm formation of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Arch. Microbiol.206, 344. 10.1007/s00203-024-04029-w
20
Mine Y. Suga M. Mimura S. Minoda M. Murayama T. Nikawa H. et al (2020). Cytotoxicity assay using a human pluripotent stem cell-derived cranial neural crest cell model. Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim.56, 505–510. 10.1007/s11626-020-00491-0
21
Mohr K. I. (2016). History of antibiotics research. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol.398, 237–272. 10.1007/82_2016_499
22
Morciano G. Imamura H. Patergnani S. Pedriali G. Giorgi C. Pinton P. (2020). Measurement of ATP concentrations in mitochondria of living cells using luminescence and fluorescence approaches. Methods Cell Biol.155, 199–219. 10.1016/bs.mcb.2019.10.007
23
Moudgil K. D. Venkatesha S. H. (2022). The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of natural products to control autoimmune inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 95. 10.3390/ijms24010095
24
Poulton N. C. Rock J. M. (2022). Unraveling the mechanisms of intrinsic drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.17, 997283. 10.3389/fcimb.2022.997283
25
Presenjit P. Chaturvedi S. Singh A. Gautam D. Singh K. Mishra A. K. (2024). An insight into the effect of schiff base and their d and f block metal complexes on various cancer cell lines as anticancer agents: a review. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem.24, 488–503. 10.2174/0118715206280314231201111358
26
Rana M. S. Rayhan N. M. A. Emon M. S. H. Islam M. T. Rathry K. Hasan M. M. et al (2024). Antioxidant activity of schiff base ligands using the DPPH scavenging assay: an updated review. RSC Adv.14, 33094–33123. 10.1039/d4ra04375h
27
Ridahunlang N. Bisht R. Rishanlang N. (2023). Isoniazid derivatives as anti-tubercular agents: from structural design to clinical investigations. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets223, e041022209552. 10.2174/1871526522666221004152324
28
Rouzi K. Altay A. Bouatia M. Yeniçeri E. Islam M. S. Oulmidi A. et al (2024). Novel isoniazid-hydrazone derivatives induce cell growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via mitochondria-dependent caspase activation and PI3K/AKT inhibition. Bioorg Chem.150, 107563. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107563
29
Sæbø I. P. Bjørås M. Franzyk H. Helgesen E. Booth J. A. (2023). Optimization of the hemolysis assay for the assessment of cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 2914. 10.3390/ijms24032914
30
Sirinirund B. Siqueira R. Li J. Mendonça G. Zalucha J. Wang H. L. (2023). Effects of crown contour on artificial biofilm removal efficacy with interdental cleaning aids: an in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implants Res.34, 783–792. 10.1111/clr.14105
31
Sodré-Alves B. M. C. Toledo M. M. Zimmermann I. R. Araújo W. N. Tavares N. U. L. (2024). Isoniazid use, effectiveness, and safety for treatment of latent tuberculosis infection: a systematic review. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop.25, e004022024. 10.1590/0037-8682-0504-2023
32
Stratev D. Fasulkova R. (2024). Minimum inhibitory concentration of doxycycline for Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Indian J. Med. Microbiol.48, 100532. 10.1016/j.ijmmb.2024.100532
33
Tu C. Lu H. Zhou T. Zhang W. Deng L. Cao W. et al (2022). Promoting the healing of infected diabetic wound by an anti-bacterial andnano-enzyme-containing hydrogel with inflammation-suppressing, ROS-scavenging, oxygen and nitric oxide-generating properties. Biomaterials286, 121597. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121597
34
Udhayakumari D. Inbaraj V. (2020). A review on schiff base fluorescent chemosensors for cell imaging applications. J. Fluoresc.30, 1203–1223. 10.1007/s10895-020-02570-7
35
Vyas N. Grewal M. Kuehne S. A. Sammons R. L. Walmsley A. D. (2020). High speed imaging of biofilm removal from a dental implant model using ultrasonic cavitation. Dent. Mater36, 733–743. 10.1016/j.dental.2020.03.003
36
Xiao X. Huan Q. Huang Y. Liu Z. Liu Y. Li R. et al (2024). Gramine sensitizes Klebsiella pneumoniae to tigecycline killing. Phytomedicine126, 155421. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155421
37
Zhang X. Zheng X. Ying X. Xie W. Yin Y. Wang X. (2022). CEBPG suppresses ferroptosis through transcriptional control of SLC7A11 in ovarian cancer. J. Transl. Med.21, 334. 10.1186/s12967-023-04136-0
Summary
Keywords
isoniazid, schiff base, antibacterial activity, anti biofilm, anti inflammatory
Citation
Liu Y, Hu L, Liu B and Qu Z (2025) Membrane-targeting antibacterial isoniazid schiff base against S. aureus and biofilms . Front. Chem. 13:1654358. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1654358
Received
26 June 2025
Accepted
26 August 2025
Published
09 September 2025
Corrected
09 October 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Marco Paolino, University of Siena, Italy
Reviewed by
Prashant Murumkar, Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, India
Ata Makarem, University of Hamburg, Germany
Diana Camelia Nuta, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Miguel Garcia Castro, University of Malaga, Spain
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liu, Hu, Liu and Qu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yaguang Liu, h418561754@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.