Abstract
Tetrazoles are nitrogen-rich heterocycles that have attracted interest because of their numerous applications in pharmaceutical and medicinal chemistry. Four nitrogen atoms and one carbon atom make up these five-membered rings, which have special physicochemical and electrical characteristics, including acidity, resonance stabilization, and aromaticity. This article highlights the structure, spectroscopic characteristics, and physical and chemical characteristics of tetrazoles. It also describes how overlapping mechanisms, such as DNA replication inhibition, protein synthesis disruption, and oxidative stress induction, as well as similar therapeutic targets, enable inhibitors to serve as both antibacterial and anticancer agents. Tetrazole moieties have been fused with a range of pharmacophores, such as indoles, pyrazoles, quinolines, and pyrimidines, yielding fused derivatives that display substantial inhibitory activity against bacterial, fungal, and cancer cell lines, with certain compounds exhibiting efficacy comparable to or exceeding that of established therapeutic agents. The rational design of more efficacious tetrazole-based therapies is facilitated by structure–activity relationship analysis, which further highlights significant functional groups and scaffolds that contribute to increasing activity. We investigate the relationship between microbial inhibition and anticancer efficacy, opening up new avenues for the creation of multifunctional therapeutic agents. We hope that this study will offer significant guidance and serve as a valued resource for medicinal and organic researchers working on drug development and discovery in multifunctional therapeutics. The review involves a thorough investigation of tetrazole in recent years.
1 Introduction
1.1 Structure and spectroscopic properties
Tetrazoles are an instance of a heterocyclic compound that has a five-membered ring with one carbon atom and four nitrogen atoms. This unique arrangement makes them highly nitrogen-rich, leading to special chemical and energetic properties. Tetrazoles can theoretically exist in three tautomeric forms, like 1H, 2H, and 5H (Figure 1). Among these, the 1H and 2H tautomers of tetrazole are aromatic, each possessing a 6π-electron system that contributes to their stabilization. On the other hand, the 5H tautomer is not aromatic and is merely a proposed theoretical structure that lacks experimental proof (Kiselev et al., 2011). Tetrazole is found in the 1H form in the solid state, and the 1H tautomer predominates in polar solvents like dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). However, in the gas phase, the 2H tautomer is more prevalent (Bugalho et al., 2001). The tetrazole ring can act as a bioisostere for carboxylic acid groups (Biot et al., 2004), Cl-amidine rings (Subramanian et al., 2015), and furan rings in drug molecules because they share similar structural and electronic properties (Herr, 2002; Mohite et al., 2009) (Figure 2). Frequently, it enhances the metabolic stability and ADMET profile of compounds containing these functionalities. In drug design, tetrazoles can proficiently emulate carboxylic acids due to their comparable electronic distribution and hydrogen-bonding properties (Allen et al., 2012; Ballatore et al., 2013).
FIGURE 1

Tautomers of tetrazole.
FIGURE 2

Structure and bioisostere analog of tetrazole.
The two most significant isomers in terms of pharmacology and synthesis are 1H-tetrazole and 2H-tetrazole. The proton’s location on the nitrogen atom distinguishes the tautomer 1H- and 2H-tetrazoles (Uppadhayay et al., 2022). These two forms are tautomers, distinguished by the position of a proton on the nitrogen atom. Factors such as solvent polarity, pH, and temperature affect their dynamic equilibrium in solution. They remain thermodynamically stable in the solid state. This technique enhances both the thermodynamic stability and the aromatic character of the compound. The proton is on the N2 nitrogen in 2H-tetrazole, making it frequently more stable in polar liquids. Numerous kinds of bicyclic tetrazole systems have been developed through combining the tetrazole ring with heterocycles like pyridine, diazine, or triazine. Notable examples include tetrazolo [1,5-a]pyridine, tetrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine, and tetrazolo [1,5-b][1,2,4]triazine (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3
![Chemical structures for tetrazolo[1,5-a] pyridine, tetrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidine, and tetrazolo[1,5-b][1,2,4] triazine are shown. Each structure illustrates ring systems and nitrogen atoms in various configurations.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1700143/xml-images/fchem-13-1700143-g003.webp)
Some examples of substituted tetrazole bicycles fused with pyridine, diazine, or triazine.
Tetrazoles exhibit distinctive infrared absorption bands linked to different ring vibrations and specific functional groups. The N–H stretching band of 1H-tetrazole commonly shows up between 3,150 cm−1 and 3,400 cm−1. C=N stretching takes place in the 1600–1,500 cm−1 region, while N=N stretches are observed between 1,400 cm−1 and 1,300 cm−1. Moreover, in the range between 800 cm−1 and 1,000 cm−1, ring deformation and out-of-plane N–H bending vibrations take place (Billes et al., 2000). Tetrazoles exhibit prominent π→π* electronic transitions, often occurring at 210–230 nm in the ultraviolet spectrum. This technique is beneficial for exploring electronic effects and ring substitution. Modification of the tetrazole ring can lead to bathochromic changes, also known as red shifts, due to enhanced conjugation. Additionally, 1- and 2-substituted tetrazoles can be differentiated by their distinct UV absorption spectra. For example, 1-phenyltetrazole absorbs light at 236 nm, while 2-phenyltetrazole absorbs light at 250 nm. In contrast, NH-unsubstituted tetrazoles often exhibit altered absorption due to significant intermolecular interactions (Popova et al., 2017). Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in both one-dimensional (1H, 13C, 15N) and two-dimensional (COSY, HMBC, and HSQC) forms is one of the most effective methods for determining tetrazole structures and identifying regioisomers and tautomers (Shestakova et al., 2013). The 1H NMR method was used to characterize the free N–H bond in tetrazole. In 1H NMR spectroscopy, tetrazole had a peak downfield and a pKa value comparable to that of carboxylic acid. One signal was observed in 13C NMR spectroscopy at 155–160 ppm, depending on the substituted tetrazole ring. Tetrazole’s proton is highly aromatic and has the capacity to stabilize π-electron delocalization in a very acidic manner. The tetrazole anion is lipophilic, which is a crucial property for medication development (Elewa et al., 2020; Khurshid et al., 2022). Mass spectrometry of tetrazoles reveals distinct fragmentation behaviors in both positive and negative ion modes. In the positive ion mode, the molecule typically loses HN3, while in the negative ion mode, it tends to lose N2. As a result, these different ionization conditions lead to characteristic and differing fragmentation patterns during analysis (Liu et al., 2008).
1.2 Physical and chemical properties of tetrazoles
Tetrazole appears as a white to pale yellow crystalline powder with no detectable odor. It has a melting point of 155–157 °C, a density of 1.477 g/cm3, and a molar mass of 70.05 g/mol (Uppadhayay et al., 2022). Tetrazole is soluble in water, ethyl acetate, DMSO, and DMF. Tetrazole behaves as a weak acid with a pKa of approximately 4.89, comparable to propanoic acid (Jaiswal et al., 2024). Its acidic character arises from the pyridine-like nitrogen atom in the heteroaromatic ring, which enables delocalization of negative charge and coordination with metal ions. The substituent electrostatic properties strongly influence the acidity of 5-substituted tetrazoles; for example, 5-phenyltetrazole exhibits acidity similar to benzoic acid due to resonance stabilization of its conjugate base. Tetrazole anions readily form upon reaction with metal hydroxides and remain stable in aqueous or alcoholic media, even at elevated temperatures.
Chemically, tetrazoles react vigorously with strong acids, acid chlorides, anhydrides, oxidizing agents, and certain active metals, producing heat, toxic fumes, or explosive products. Upon heating or combustion, they decompose and release carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. In biochemical contexts, dilute 1H-tetrazole in acetonitrile is widely used as an activating agent in oligonucleotide synthesis. The tetrazole moiety functions as a carboxyl group bioisostere, improving pharmacokinetic profiles by enhancing solubility and bioavailability while reducing adverse effects. It also exhibits both electron-withdrawing (–I) and electron-donating (+M) effects, rendering tetrazole derivatives versatile in supramolecular chemistry and coordination complexes (Bissantz et al., 2010; Meyer et al., 2003; Movsisyan et al., 2016; Uppadhayay et al., 2022; Varala and Babu, 2018).
Pharmacologically, tetrazole-containing compounds display diverse biological activities, including antibacterial (Roszkowski et al., 2021), antifungal, anticancer (Slack et al., 2011), antiviral, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, antitubercular, antinociceptive, and hypoglycemic effects (Nammalwar et al., 2015). Prominent therapeutic applications include treatments for hypertension (Belz et al., 1999), allergies, infections, and seizures. Consequently, tetrazole and its derivatives are of significant interest across medicinal chemistry, biochemistry, and agricultural research.
1.3 Synthetic methods of tetrazole formation
1.3.1 From amine
The most basic method for synthesizing 1-substituted tetrazoles involves the reaction of an amine molecule with triethyl orthoformate in the presence of sodium azide using DMSO (Figure 4) (Dighe et al., 2009; Palimkar et al., 2003).
FIGURE 4

Synthesis of tetrazole from amine.
1.3.2 From cyano compounds
Nitriles or isocyanides are used as starting materials in a well-known and efficient approach for synthesizing substituted tetrazoles (Figure 5). 1-Substituted tetrazole was synthesized by reacting isocyanide with trimethylsilyl azide (1.5 eq) in 0.5 M methanol under acidic conditions at 60 °C (a) (Jin et al., 2004). Nitrile was treated with sodium azide, ammonium chloride, and lithium chloride in anhydrous dimethylformamide at 110 °C (b1) to afford 5-substituted tetrazole (Amanpour et al., 2012; Bond et al., 2012). Alternatively, the hydrothermal synthesis was carried out for the synthesis of 5-substituted tetrazole by reacting sodium azide with nitrile using NH4Cl, NH4F, and propane-1,2-diol (DPOL) for 48 h (b2) (Wang et al., 2013). The reaction of the azide ion with nitrile is the most practical way to obtain substituted tetrazole (c) (Wittenberger, 1994). Hydrazoic acid (HN3) and organic cyanides (d) were reacted to synthesize 5-substituted tetrazole for the first time through a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction (Mihina and HERBST, 1950; Vishwakarma et al., 2022).
FIGURE 5
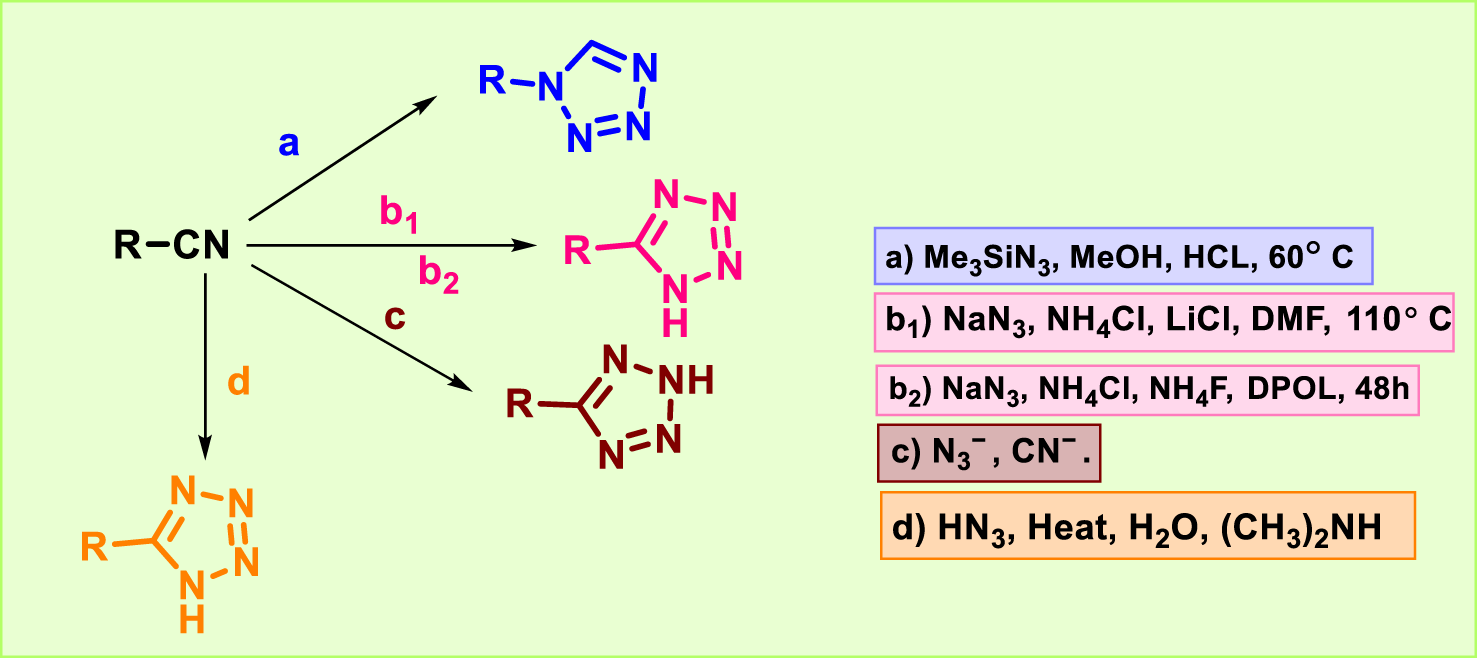
Synthetic route of tetrazoles from cyano compounds.
1.3.3 From amides
Figure 6 illustrates the synthesis of tetrazoles from acetanilide, formamide, and N-methyl benzamide. Tetrazoles were synthesized from acetanilide using DPPA or p-NO2DPPA in reflux conditions with pyridine (a, b). When the reaction was carried out at 90 °C with formamide, high yields of tetrazoles were achieved using either p-NO2DPPA with pyridine (d) or DPPA with pyridine (c) as the base. On the other hand, the use of p-NO2DPPA with pyridine (f) afforded high yields of tetrazoles from N-methyl benzamide, which contains a bulky substituent adjacent to the carbonyl group. Employing DPPA with 4-methylpyridine as the base (e) provided a comparable yield (Ishihara et al., 2020; Ishihara et al., 2022).
FIGURE 6

Synthesis of tetrazole from amide derivatives.
1.3.4 Alcohol and aldehydes
Primary alcohols and aldehydes were treated with iodine in aqueous ammonia under microwave irradiation to produce intermediate nitriles, followed by the [2 + 3] cycloaddition reaction in the presence of sodium azide to synthesize tetrazoles in high yields under microwave conditions (Shie and Fang, 2007). A simple and effective one-pot, three-component reaction was carried out involving aldehydes, hydroxylamine, and [bmim]N3 for the synthesis of the 5-substituted 1H-tetrazole derivative in Figure 7 (Heravi et al., 2012).
FIGURE 7
![Synthesis of tetrazole derivatives from alcohol and aldehyde using different reaction conditions. Firstly, alcohol and aldehyde derivatives are converted into their respective nitrile derivatives using different reaction conditions: iodine and 28% ammonia at 60°C for 15-30 minutes in a microwave synthesizer and Iodine, 28% ammonia at 25°C for 1 hour, respectively. Further, nitrile intermediates are converted into tetrazole in the presence of NaN3, ZnBr2, at 80°C for 10-45 minutes in a Microwave synthesizer. The aromatic aldehyde reacts with NH₂OH and [bmim]N₃ to yield an aromatic substituted tetrazole ring in the presence of Cu(OAc)₂, DMF, and reflux at 120°C for 12 hours.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1700143/xml-images/fchem-13-1700143-g007.webp)
Synthesis of tetrazole from alcohol and aldehydes.
1.3.5 From aryldiazonium salts
A highly efficient one-pot sequential approach has been developed for the direct synthesis of 2,5-disubstituted tetrazoles from aryldiazonium salts and amidines in Figure 8. This method is notable for its short reaction time, mild reaction conditions, and suitability for Gram-scale synthesis (Ramanathan et al., 2015).
FIGURE 8

Synthesis of tetrazole from aryldiazonium salts.
1.4 Correlation of anticancer and antimicrobial activity
Associating antimicrobial activity with anticancer activity is an area of growing interest in drug discovery and pharmaceutical research. The modes of action, molecular targets, and structural properties of antimicrobial and anticancer agents are quite similar (Figure 9). The anticancer and antimicrobial activities target distinct pathological conditions. Frequently, they have comparable mechanisms of action at the molecular and cellular levels (Martelli and Giacomini, 2018).
FIGURE 9

Illustrating the shared and distinct mechanisms of action for anticancer and antimicrobial agents: highlighting overlapping pathways such as DNA damage, protein synthesis inhibition, oxidative stress, and unique cellular targets relevant to therapeutic drug design.
1.4.1 Mechanism of action
1.4.1.1 DNA damage or inhibition of DNA replication
The key strategy in both anticancer and antimicrobial therapies is the mechanism of DNA damage or inhibition of DNA replication. These substances work directly by disrupting the replication or damaging the DNA, which eventually kills cancer cells or microbes (Puigvert et al., 2016). Anticancer agents exhibit anticancer activity by targeting the rapid DNA replication in cancer cells. Alkylating agents such as cyclophosphamide and cisplatin produce DNA crosslinks, followed by the prevention of replication. Double-strand breaks are caused by topoisomerase inhibitors like etoposide and doxorubicin. DNA replication is disrupted by antimetabolites such as 5-FU and methotrexate, which mimic or hinder nucleotide synthesis (Swift and Golsteyn, 2014). These actions make them selectively hazardous to rapidly dividing tumor cells at DNA damage checkpoints and trigger apoptosis.
Antibiotics have antimicrobial activity that targets microbial DNA replication to hinder growth. Quinolones/fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin are responsible for DNA breaks by inhibiting DNA gyrase/topoisomerase IV. In anaerobic environments, nitroimidazoles like metronidazole develop reactive species that damage DNA. Rifamycins such as rifampicin inhibit RNA polymerase, and sulfonamides and trimethoprim inhibit folate synthesis, resulting in nucleotide deficiency. These actions disrupt replication and transcription, resulting in bacteriostatic or bactericidal effects by exploiting rapid microbial cell division.
These mechanisms operate effectively on cancer cells and selectively target microbes that replicate faster than normal host cells. DNA damage and other irreversible damage lead to irreparable stress, which ultimately results in cell death (Roos et al., 2016). Repair inhibitors, such as PARP inhibitors, combine with DNA-damaging drugs to potentially enhance their effectiveness (Lodovichi et al., 2020). Tetrazole derivatives can bind to DNA or hinder the replication-related enzymes involved in replication. Structural features such as planar aromatic systems and hydrogen-bond donors enhance DNA binding. Future drug design and development can focus on creating dual inhibitors of cancer and bacterial topoisomerases (Bhattacharya and Chaudhuri, 2008).
1.4.1.2 Protein synthesis inhibition
The inhibition of protein synthesis is a vital mechanism in both anticancer and antimicrobial drug action. Protein synthesis is essential for cell survival, growth, and proliferation. Therefore, agents targeting this mechanism can selectively target cancer cells or other rapidly proliferating pathogens. Cancer cells need high protein synthesis to grow rapidly and exhibit anticancer activity. Rapamycin or other mTOR inhibitors prevent the synthesis of ribosomal proteins (Showkat et al., 2014). Translation initiation inhibitors such as silvestrol disrupt oncogene translation. Homoharringtonine and other elongation inhibitors effectively prevent protein elongation in the treatment of leukemia (Lindqvist and Pelletier, 2009). Proteasome inhibitors primarily inhibit protein degradation, which leads to ER stress and apoptosis (Fribley and Wang, 2006). These mechanisms cause apoptosis, suppress oncogene expression, and inhibit tumor development.
Bacterial ribosomes are different from human ones, which allows for the targeted inhibition of microbial protein synthesis in antimicrobial activity. Tetracyclines prevent the tRNA from binding to the 30S subunit, whereas aminoglycosides such as streptomycin misinterpret the mRNA (Chukwudi, 2016). Macrolides and chloramphenicol act on the 50S subunit, which hampers the peptide elongation or the development of a new bond. Initiation complex formation was inhibited by oxazolidinones, including linezolid. These bacteriostatic or bactericidal activities suppress protein synthesis. Disrupting translation causes stress and cell death because both microbes and cancer cells depend on a significant amount of protein synthesis. Researchers are developing tetrazole derivatives as dual-action inhibitors, which could potentially benefit cancer patients who also experience infection.
1.4.1.3 Oxidative stress generation
Many antibacterial and anticancer drugs with a tetrazole moiety rely significantly on oxidative stress in their mechanism of action. These compounds can make reactive oxygen species (ROS), killing both cancer and microbial cells by damaging their cells. Anticancer agents exploit this phenomenon by increasing ROS levels beyond the cell’s antioxidant defense capacity, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage, and the initiation of apoptosis or necrosis. Drugs like doxorubicin, arsenic trioxide, and cisplatin cause cell death by generating ROS directly or indirectly. Natural substances like curcumin and resveratrol also increase ROS, especially targeting cancer stem cells (Mirzaei et al., 2023). Redox imbalance, cell toxicity, and apoptotic activation all contribute to the limitation of tumor development. Additionally, ROS-induced signaling may activate caspase cascades, MAPKs, and p53, which could lead to cell cycle arrest or death (Kovacic and Osuna, 2000).
Several antimicrobial agents kill bacteria by triggering oxidative stress through the production of too many ROS. Bacteria have poor antioxidant defenses. Aminoglycosides like gentamicin induce protein misfolding and ROS accumulation (Han et al., 2024), fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin disrupt DNA (Fief et al., 2019), and nitroimidazoles like metronidazole release ROS under anaerobic environments. Silver nanoparticles and other metal-based agents also encourage the ROS formation (Chawla et al., 2023; Sánchez-López et al., 2020). This process leads to damage to bacterial DNA, proteins, and membranes, resulting in potent bactericidal effects that are particularly effective against resistant strains (Albesa et al., 2004; Mourenza et al., 2020; Varshneya et al., 2023).
The broad-spectrum and multitarget characteristics of ROS-based strategies are effective. These strategies can also overcome the problem of resistance. To increase the effectiveness of the drug, researchers can incorporate ROS-generating scaffolds and combine them with antioxidant defense inhibitors. Particularly for patients with impaired immune systems, dual-acting drugs that simultaneously target both cancer and infections hold significant promise.
1.4.2 Shared drug targets or pathways
1.4.2.1 Topoisomerase inhibitors
Topoisomerases are crucial enzymes that regulate the topological state of DNA by reducing the torsional strain generated during replication and transcription (Baranello et al., 2025). Inhibition of these enzymes disrupts critical DNA processes, which causes cell death in both bacteria and cancer cells. In the case of anticancer activity, topoisomerase inhibitors block enzymes essential for DNA replication. Topoisomerase I inhibitors (e.g., topotecan and irinotecan) stabilize single-strand breaks, which turn into lethal double-strand breaks during replication. Topoisomerase II inhibitors (e.g., doxorubicin and etoposide) trap the enzyme-DNA complex after double-strand cleavage, causing persistent DNA damage. These drugs respond against various solid tumors and blood cancers as they trigger apoptosis, especially in rapidly proliferating cancer cells (Liang et al., 2019; Yakkala et al., 2023). Bactericidal agents block the bacterial DNA gyrases topoisomerase II and topoisomerase IV, which inhibit DNA replication, followed by lethal double-strand breakdown for antimicrobial activity (D’Atanasio et al., 2020; Collins and Osheroff, 2024). The interruption of replication and transcription causes bacterial cell death. They are efficacious against a wide range of bacteria, but resistance may develop through gene mutations or efflux mechanisms (Ehmann and Lahiri, 2014). Topoisomerase inhibitors represent a common therapeutic strategy for both microbial and cancer treatment. However, their targets are different for bacterial enzymes in infections and human enzymes in malignant cells. This selectivity facilitated efficient treatment while minimizing toxicity to the host (Pommier et al., 2010).
1.4.2.2 Metabolic pathway inhibitors
Rapidly dividing cells, including bacteria and cancer cells, have a high demand for folate, which is essential for the synthesis of purines and thymidylate, which are the key components of DNA. In case of antimicrobial activity, sulfonamides inhibit dihydropteroate synthase, an enzyme unique to bacterial folate synthesis. Trimethoprim inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), which prevents the transformation of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate (Chawla et al., 2021; Tjampakasari, 2024). This dual blockade inhibits or kills bacteria by interfering with folate metabolism and impairs DNA synthesis. Methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolate from being reduced to tetrahydrofolate by selectively inhibiting the human DHFR, as per its anticancer activity. This procedure successfully interrupts tumor cell division by diminishing the crucial nucleotide precursors for DNA and RNA synthesis (Elgemeie and Mohamed-Ezzat, 2022). Sulfonamides/trimethoprim and methotrexate both target the folate-dependent pathways but inhibit specific enzymes in microbes or human cancer cells. Both drugs are effective against infection and malignancies by interfering with nucleotide synthesis and blocking DNA replication, respectively.
1.4.3 Structural similarities and repurposing potential
Many antimicrobial drugs have a similar type of structural features or mechanisms of action that are also efficient toward cancerous cells due to their common vulnerabilities (Karamanolis et al., 2024). This resemblance has led to significant efforts at cancer therapeutic repurposing. Numerous antimicrobial drugs possess characteristics that increase their anticancer potential, such as lipophilic or cationic structures that damage the cellular membranes and metal-chelating groups that encourage the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are responsible for oxidative damage (Malik et al., 2018).
Many antimicrobial drugs exhibit promising anticancer potential through various mechanisms. Salinomycin targets cancer stem cells (CSCs) by impairing mitochondrial activity and triggering ROS-mediated apoptosis (Qi et al., 2022). Clioquinol interrupts the proteasomal and NF-κB pathways by acting as a metal chelator (Yu et al., 2010). An antidiabetic with antimicrobial properties, metformin blocks mitochondrial complex I, stimulates AMPK, and suppresses mTOR, reducing cancer cell growth (Amengual-Cladera et al., 2024). Azoles such as ketoconazole are beneficial for hormone-dependent cancers by blocking steroid synthesis and drug efflux (Pejčić et al., 2023). Actinomycin D suppresses RNA synthesis for the treatment of pediatric cancers. Cisplatin and doxorubicin exhibit antibacterial efficacy by targeting bacterial topoisomerases and nucleic acid synthesis (Kathiravan et al., 2013). Imatinib inhibits the growth of pathogen replication and regulates immune responses. Structural and mechanistic similarities between antimicrobial agents and anticancer drugs support their repurposing as anticancer therapeutics (Pfab et al., 2021).
1.4.4 Disruption of the microbiome and cancer link
Certain microorganisms, such as Helicobacter pylori, are directly associated with the development of cancer by causing long-term inflammation, DNA damage, and increased cell proliferation. Eliminating these microbes is an important method of preventing cancer (Tsukamoto et al., 2017). Additionally, the gut microbiome plays a critical role in controlling the immune system and impacting cancer therapy (Shui et al., 2020). A healthy microbiome improves responses to immunotherapy and chemotherapy, while dysbiosis hinders the therapeutic efficacy and increases side effects (Chrysostomou et al., 2023). Therefore, managing the microbiome is a growing strategy in cancer prevention and treatment.
1.4.5 Immune modulation
In addition to treating infection, antibiotics show an effect on immune responses. Altering the gut microbiota and decreasing essential microbial metabolites and broad-spectrum antibiotics may cause immune modulation, followed by immunosuppression (Zhang and Chen, 2019). On the other hand, some antibiotics, such as macrolides and tetracyclines, have immunostimulatory effects. They exhibit anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties by regulating cytokine production and the activity of immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, and T-cells (Ruh et al., 2017). Some beneficial bacteria, including Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia muciniphila, facilitated antitumor immunity and improved immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) (Huang et al., 2023; Li et al., 2022). On the other hand, antibiotics have the potential to alter and disrupt the microbiome, which reduces the treatment efficacy and patient survival. Integrating microbiome-aware strategies is crucial for optimizing cancer therapy responses because both antibiotics and anticancer drugs showed an impact on the immune function and the microbiome. Antimicrobial and anticancer actions are interconnected through common mechanisms such as oxidative stress induction, metabolic inhibition, and DNA interference. This overlap makes it possible to build dual-activity drugs and comprehend the role of infectious agents in cancer development. Exploring these interconnections may accelerate the discovery of novel therapeutic agents.
Heterocyclic compounds are a valuable resource for discovering and developing new drugs for various medical conditions. More than 85% of chemical compounds with physiological action are heterocycles (Pal et al., 2024). Recently, the tetrazole scaffold has been used to produce promising antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Few review articles have reported on the medicinal importance of tetrazole derivatives as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Verma et al. (2022) reported synthetic approaches and biological activity of tetrazole analogs against different targets of cancer. Yuan et al. (2024) discussed the potential of tetrazole derivatives with their biological activities against several diseases, such as cancer, bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, asthma, hypertension, Alzheimer’s disease, malaria, tuberculosis, etc. In 2024, Jaiswal and group reported tetrazole derivatives and evaluated biological activities and structure–activity relationships against various neurological disorders, namely, Alzheimer’s, convulsion, depression, Parkinson’s, and diabetic neuropathy (Jaiswal et al., 2024). Atif and Ait Sir (2025) reported the different synthetic approaches of the tetrazole scaffold. These reviews cover either moiety-based aspects or synthetic-based approaches of the tetrazole scaffold. Recent synthetic approaches of tetrazole derivatives with deep insights into SAR for anticancer and antimicrobial activity were not elaborated and discussed in this recent review.
In the current updated review (2023–2025), we discuss recent advancements in synthetic approaches utilizing their core tetrazole moiety to develop compounds that exhibit significant antimicrobial and anticancer activities. The review emphasizes the perspective of structure and spectroscopic properties, physical and chemical properties, the synthetic method of tetrazole formation, the correlation between the mechanism of anticancer and antimicrobial activity, biological activity, and structure–activity relationship of tetrazole derivatives as anticancer and antimicrobial agents.
2 Antimicrobial derivatives
Rajeswari and coworkers designed and synthesized benzimidazole-linked tetrazole derivatives as antimicrobial agents. They substituted benzaldehyde 1 with 1,2-dibromoethane under basic conditions to produce compound 2. Substituted benzonitriles 3 were refluxed with sodium azide and ammonium chloride in DMF at 110 °C for 12 h to afford 5-substituted-1H-tetrazoles 4 via [3 + 2] cycloaddition. Intermediate 2 was reacted with substituted tetrazole derivatives 4 to yield intermediate 5. The key aldehyde intermediate 5 was condensed with o-phenylenediamine in the presence of sodium metabisulfite in DMF at 110 °C for 5 h. These conditions allowed the intramolecular cyclization to yield the anticipated benzimidazole-tetrazole derivatives 6 (Scheme 1). All the synthesized compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against Gram-positive (Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae) strains, and the findings revealed that compound 6b showed superior activity. Additionally, the researchers conducted antifungal activity tests, which revealed that compounds 6a and 6b exhibited significant activity. Antioxidant activity was determined via DPPH and nitric oxide (NO) radical scavenging assays. Compound 6a showed the most potent radical scavenging activity (IC50 = 54.1 μg/mL for DPPH; 75.75 μg/mL for NO) (Rajeswari et al., 2025).
SCHEME 1

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of benzimidazole-linked tetrazole derivatives as antimicrobial agents.
Saleh et al. designed and synthesized tetrazole derivatives with antibacterial and antifungal activity. Sulfanilamide derivative 7 was treated with hydrazine hydrate and carbon disulfide in the presence of ammonium hydroxide to synthesize intermediate thiosemicarbazide derivative 8. Then, it was reacted with substituted benzaldehyde to produce a hydrazone derivative via a condensation reaction. In the final step, intermediate 9 underwent a [3 + 2] cyclocondensation reaction in the presence of sodium azide to acquire tetrazole derivative 10 (Scheme 2). The findings of an antibacterial study demonstrated that compound 10 showed the highest activity against Staphylococcus aureus, with inhibition zones measuring 30 mm, 25 mm, and 18 mm at concentrations of 0.01 mg/mL, 0.001 mg/mL, and 0.0001 mg/mL, respectively. For E. coli, compound 10 exhibited moderate inhibition with a zone of inhibition of 10 mm across all tested concentrations. Antifungal activity was tested against Candida albicans, and compound 10 demonstrated significant activity with inhibition zones of 15 mm, 10 mm, and 5 mm at 0.01 mg/mL, 0.001 mg/mL, and 0.0001 mg/mL concentrations, respectively (Saleh et al., 2025).
SCHEME 2

Synthesis and structure–activity relationships study of tetrazole derivatives from sulfonamide.
Narkedimilli and coworkers designed and synthesized 1,2,3-triazole-incorporated tetrazoles as potent antitubercular agents. Substituted isothiocyanate 11 was reacted with sodium azide in aqueous conditions to yield substituted tetrazole derivatives 12, followed by reaction with propargyl bromide in the presence of tetrabutylammonium bromide to yield key intermediate 13 under an aqueous medium. Benzo [d]oxazole-2-thiol 14 was reacted with 1,2-dibromoethane 15 in the presence of sodium hydride in dry DMF under ice-cold conditions to yield 2-((2-bromoethyl)thio)benzo [d]oxazole 16, followed by nucleophilic substitution with sodium azide in DMF at 60 °C to obtain 2-((2-azidoethyl)thio)benzo [d]oxazole 17. In the final step, the click reaction was employed to couple the azide 17 and the appropriate alkyne-containing tetrazoles 13 to the synthesis of target compound 18 (Scheme 3). The reaction was carried out in a mixture of tert-butanol and water using copper (II) acetate and sodium ascorbate as the catalytic system at room temperature. Among all the synthesized compounds, compound 18a exhibited significant broad-spectrum antibacterial activity with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 3.8 μg/mL, 5.1 μg/mL, and 3.0 μg/mL against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Staphylococcus epidermidis, respectively. Conversely, compound 18b emerged as the most effective antitubercular agent, exhibiting an MIC of 3.0 μg/mL, which was superior to both streptomycin (5.0 μg/mL) and rifampin (3.9 μg/mL) against the H37Rv strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It also had remarkable antibacterial efficacy against P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and S. pyogenes, with MIC values of 3.0 μg/mL, 1.6 μg/mL, and 2.9 μg/mL, respectively (Narkedimilli et al., 2025).
SCHEME 3

Synthesis of 1,2,3-triazole-incorporated tetrazoles as potent antitubercular agents.
Nagaraju and colleagues developed tetrazole-fused pyrimidine derivatives to determine antimicrobial activity. In Scheme 4, ethyl acetoacetate 19, sulfur 20, and malononitrile 21 were dissolved in ethanol and triethylamine and refluxed for 12 h to synthesize 22 through Gewald synthesis. Compound 22 underwent cyclization in the presence of formic acid; the chlorination reaction was carried out to obtain 24. Morpholine and pyrrolidine were added to synthesize 25 from 24 through a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction, followed by ester hydrolysis and then esterification to form intermediate 27. In the next step, 4-methoxybenzaldehyde 28 is converted to 4-methoxybenzaldehyde oxime 29 using NH2OH.HCl and NaHCO3, followed by a Beckmann rearrangement reaction to yield compound 30. The mixture of benzonitrile, sodium azide, and ammonium chloride was refluxed at 120 °C to synthesize intermediate 31. Finally, intermediates 31 and 27 underwent a deprotonation process by nucleophilic substitution reaction to yield final derivatives 32. The researchers conducted antibacterial activity tests and found that compound 32a exhibited the highest activity against S. aureus and E. coli, with inhibition zone diameters of 18.0 mm and 17.70 mm, respectively, at a concentration of 50 μg/mL. Similarly, for B. subtilis andP. vulgaris, compound 32b showed the strongest activity with zone inhibition diameters of 16.30 mm and 19.7 mm at a 50 μg/mL concentration. At a 100 μg/mL concentration, compound 32b showed the most potent activity against B. subtilis and P. vulgaris with zone inhibition diameters of 18.6 mm and 21.07 mm, respectively. For S. aureus and E. coli, compound 32a showed excellent inhibitory activity with zone inhibitory diameters of 19.5 mm and 18.91 mm at a 100 μg/mL concentration. In vitro antimicrobial studies indicated that compound 32b showed the greatest activity, with MIC values of 0.07 μg/mL, 0.09 μg/mL, 0.04 μg/mL, and 0.11 μg/mL against B. subtilis, E. coli, A. niger, and R. oryzae, respectively, and 32a showed the highest activity with MIC values of 0.09 μg/mL and 0.13 μg/mL against E. coli and P. vulgaris, respectively (Nagaraju et al., 2024).
SCHEME 4

Synthesis of tetrazole-fused pyrimidine derivatives.
Aziz and coworkers designed and synthesized tetrazole-containing pyrrole derivatives as urease inhibitors. Initially, intermediate 35 was obtained by reacting furan-2,5-dione 34 with o-phenylenediamine 33 under ultrasonication. Intermediate 35 reacts with substituted benzaldehyde in the presence of acetic acid and ethanol to form Schiff base 36. Finally, tetrazole derivative 37 was synthesized by reacting sodium azide with Schiff base 36 in DMF via the cycloaddition reaction in Scheme 5. The results of an in vitro enzyme inhibitory assay against the urease enzyme revealed that compound 37 showed the highest activity with an IC50 value of 4.325 ppm (Muhammed Aziz and Ali Hassan, 2024).
SCHEME 5

Synthesis of 1-(2-(5-(4-nitrophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione.
Gailan and the group designed and developed a series of new tetrazole entities as an antimicrobial agent. The Schiff base 39 was prepared via a condensation reaction by mixing 1H-tetrazol-5-amine 38 with terephthalaldehyde, followed by the Schiff base undergoing a nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group of the succinic anhydride to produce the intermediate dipole molecule, which was then transformed into the final derivative 40 (Scheme 6). All the synthesized compounds were evaluated for antibacterial activity, and the results indicated that 40 exhibited the highest antibacterial activity among the tested compounds against Staphylococcus epidermis, with a zone of inhibition of 20 mm, while the reference antibiotic tetracycline showed an inhibition diameter of 10 mm at a concentration of 100 mg/mL (Gailan et al., 2024).
SCHEME 6

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of 2,2'-(1,4-phenylene)bis (3-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-1,3-oxazepane-4,7-dione).
Abualnaja et al. synthesized novel tetrazole derivatives and carried out antimicrobial activity. In the first step, 4-aminoacetophenone 41 and sodium azide were refluxed with triethyl orthoformate in an acidic medium to produce the precursor compound 1-(4-acetylphenyl)-1H-tetrazole 42, followed by electrophilic bromination, which afforded intermediate 43. Intermediate 43 underwent cyclization upon treatment with aromatic thiosemicarbazone 44 to furnish the targeting tetrazole-thiazole hybrids 45 via a Hantzsch-type reaction. Intermediate 43 facilitated the diazo coupling reaction with the diazonium salt obtained to furnish the hydrazonoyl bromide derivative 46 followed by treatment with thiocarbamoyl compound 47 to synthesize target compound 48 in the presence of dioxane and triethylamine (Scheme 7). The antimicrobial activity was tested against S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, S. typhimurium, and E. coli, and results demonstrated that compound 45 showed the highest activity with MIC values of 6.61 μg/mL and 7.92 μg/mL against Gram-positive bacteria such as S. aureus and S. pneumoniae, respectively. Meanwhile, 45 showed considerable activity with an MIC value of 28.65 μg/mL against A. fumigatus, compared to the reference miconazole MIC value of 25.29 μg/mL; no activity was observed against C. albicans. Compound 48 demonstrated the strongest activity against Gram-negative bacteria, S. typhimurium, and E. coli, with MIC values of 4.27 μg/mL and 5.28 μg/mL, respectively. However, it showed only meager efficacy against A. fumigatus and C. albicans (Abualnaja et al., 2024).
SCHEME 7

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of 2-(5-(4-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)benzoyl)-3-substituted-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile derivatives.
Devi et al. discovered tetrazole derivatives as antibacterial agents. Isotonic anhydride 49 reacted with para-amino benzonitriles 50 to synthesize ring-open intermediate 51, followed by a reaction with sodium azide and zinc bromide to obtain intermediate 52 by a cyclization reaction between nitrile and azide. Then, 52 was treated with 2-chloroacetyl chloride in basic media to obtain the desired compound 54 (Scheme 8). Synthesized compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus, and 54 showed the most inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 200 μg/mL and 200 μg/mL and MBC values of 390 μg/mL and 340 μg/mL, respectively. In contrast, the reference compound ampicillin exhibited IC50 values of 55 μg/mL against E. coli and 110 μg/mL against S. aureus, respectively (Devi et al., 2023).
SCHEME 8

Synthesis of 4-(4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[e][1,4]diazepine-2,5-dione.
Rajeswari et al. reported tetrazole-fused thiadiazole derivatives as antibacterial agents. In Scheme 9, benzyl nitrile 55 and sodium azide were used as starting materials to produce compound 56 through a cyclization reaction, followed by a nucleophilic substitution reaction involving ethyl bromoacetate and potassium iodide, and then ester hydrolysis was performed to obtain intermediate 58. Finally, an intramolecular cyclization reaction via nucleophilic attack was performed by involving 58 and thiosemicarbazone to produce the tetrazole derivative 59. All the synthesized compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against B. subtilis, S. aureus, E. coli, and S. aeruginosa. The results revealed that 59 showed MIC values of 6.25 μg/mL, 1.562 μg/mL, 3.125 μg/mL, and 3.125 μg/mL, respectively. When compared to the standard drug streptomycin, which showed MIC values of 6.25 μg/mL, 3.125 μg/mL, 3.125 μg/mL, and 6.25 μg/mL for the same targets, it appeared that compound 59 exhibited comparable or slightly better antibacterial activity at lower concentrations for some targets (Rajeswari et al., 2024).
SCHEME 9

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of tetrazole-fused thiadiazol derivatives.
Xu and coworkers developed tetrazole-linked quinazoline derivatives. In Scheme 10, 2-azido-5-chlorobenzaldehyde 60, t-BuCN 61, p-toluidine 62, and trimethylsilyl azide 63 were reacted in the presence of methanol to synthesize intermediate 64, which was further reacted with 2-phenylacetyl chloride 65 in the presence of PPh3 under basic conditions to synthesize final derivative 66. All the synthesized compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB905, and results showed that compound 66 showed a growth inhibitory value of 0.063 with 86% inhibition at 100 ppm concentration (Xu et al., 2024).
SCHEME 10

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of tetrazole-linked quinazoline derivative.
Oulous and coworkers developed tetrazole-fused pyrazole compounds and evaluated antimicrobial activity. Compound 67 and tBuOK were dissolved in DMF and refluxed for 1 h. The process was followed by benzylation to obtain compound 69 (Scheme 11). Six fungal strains, including Geotrichum candidum, Aspergillus niger, Penicillium digitatum, and Rhodotorula glutinis, as well as four bacterial strains, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and Listeria monocytogenes, were used to measure the effectiveness of all synthesized compounds. Among these synthesized compounds, 69 showed the highest inhibition potency against bacteria and fungi. For antibacterial activity, 69 showed significant inhibition toward S. aureus, L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa with inhibition zone diameters of 13 mm, 13 mm, 9 mm, and 9 mm, respectively. Tetracycline, used as a reference compound, showed inhibition potencies of 20 mm, 21 mm, 20 mm, and 22 mm diameter against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and L. monocytogenes, respectively. For antifungal activity, compound 69 exhibited the most potent inhibition against R. glutinis, Saccharomyces, G. candidum, Aspergillus niger, and C. albicans, with zone inhibition diameters of 18 mm, 11 mm, 14 mm, 12 mm, and 13 mm, respectively. In comparison, the reference compound cycloheximide displayed inhibition diameters of 30 mm, 27 mm, 30 mm, 31 mm, and 35 mm for the same fungi (Oulous et al., 2023).
SCHEME 11

Synthesis of tetrazole-fused pyrazole compounds.
El-sewedy and coworkers designed and synthesized tetrazole derivatives for dual activities, including antitumor and antimicrobial. In Scheme 12, target derivatives 72a and 72b were synthesized using substituted aldehyde 70 with malononitrile 21 and sodium azide 71 in ethanol via aza-Michael addition, followed by a 1,5-endo-dig cyclization reaction in TiO2. All the synthesized compounds were subjected to a cytotoxicity study, and results indicated that 72b showed the most potent antitumor activity against the BJ-1, A431, and HCT116 cell lines with IC50 values of 92.045 µM, 44.77 µM, and 201.45 µM, respectively. During antimicrobial screening, 72a exhibited minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 6.25 μg/mL and 1.56 μg/mL against K. pneumonia and S. aureus, respectively. The MIC value of compound 72b against C. albicans was 12.5 μg/mL. The researchers conducted an antioxidant activity test, which revealed that compound 72b exhibited the highest radical scavenging activity with percentage inhibitions of 71.7% and 72.5%, while the standard compound ascorbic acid showed inhibitions of 85.4% and 98% at concentrations of 50 mg/mL and 300 mg/mL, respectively, against DPPH. To conduct further research, the lethal dose was calculated for a toxicity study. The results indicated that compound 72b had a 50% mortality rate with an LD50 value of 2500 mg/kg, along with severe symptoms of toxicity, such as weight loss and malaise (El-Sewedy et al., 2023).
SCHEME 12

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of 3-(substituted phenyl)-2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)acrylonitrile.
Disli and colleagues developed tetrazole-fused hydroxy acetophenone derivatives and carried out antibacterial activity. 1-(2,4-dihydroxy-3-propylphenyl)ethan-1-one 73 underwent O-alkylation, then S-alkylation, followed by a cyclization reaction to produce tetrazole intermediate 74 in the presence of potassium carbonate, KI, NH4SCN, and NaN3/Et3N. To yield the target compound 75, intermediate 74 was subjected to a nucleophilic substitution (SN2) reaction in the presence of an alkyl halide under basic conditions (Scheme 13). Compound 75 exhibited the strongest inhibitory activity against various bacteria and fungi strains, with MIC values of 8 μg/mL against S. aureus, 4 μg/mL against S. epidermidis, 8 μg/mL against E. coli, 16 μg/mL against P. aeruginosa, 16 μg/mL against S. maltophilia, 16 μg/mL against C. albicans, and 4 μg/mL against A. fumigatus (Disli et al., 2023).
SCHEME 13

Synthesis of tetrazole-fused hydroxy acetophenone derivatives.
Husain and colleagues developed and synthesized novel Cu(II) and Co(II) complexes of a synthetic derivative of 2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)acetohydrazide using microwave technology. In Scheme 14, ethyl-1H-tetrazole acetate 76 was mixed intimately with hydrazine hydrate. This mixture was heated by MW irradiation for 2 min. The resulting colorless 2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)acetohydrazide was stirred well in ethanol at 0 °C to obtain ligand 77. The Co (78) and Cu (79) complexes of 2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) acetohydrazide were prepared by mixing the metal nitrate with the ligand using DMF solvent and irradiating for 2 minutes. Regarding the biological activity of spectroscopic studies of DNA interaction, the binding constant (Kb) values with ct-DNA were 0.39 × 10−3 M−1 for the ligand (77), 0.43 × 10−3 M−1 for the Co complex (78), and 0.41 × 10−3 M−1 for the Cu complex (79). The corresponding Ksv values were 0.09 × 10−1 M−1, 0.11 × 10−1 M−1, and 0.10 × 10−1 M−1, respectively. Similarly, the binding constant (Kb) values with BSA for the ligand (77), Co complex (78), and Cu complex (79) were 1.6 × 10−2 M−1, 3.08 × 10−2 M−1, and 2.27 × 10−2 M−1, respectively; the Ksv values were 7.2 × 10−3 M−1, 98.1 × 10−2 M−1, and 17.78 × 10−3 M−1, respectively. Further investigation was carried out using an antioxidant study. The results displayed that the ligand and its complexes demonstrated radical scavenging ability against DPPH, with the order being Co complex (78) > Cu complex (79) > ligand (77) as the concentration increased from 100 μg/mL to 500 μg/mL. This antioxidant activity was significantly lower than that of the well-recognized standard, ascorbic acid. According to antimicrobial investigations, the Co (II) complex 78 outperformed the control antibiotic streptomycin, which could kill opportunistic S. aureus, with a zone inhibition diameter of 16.2 mm. Due to their partially planar geometry, Co (II) complexes 78 exhibited the highest activity and potency in all the studies mentioned above. Tetrahedral Cu complexes (79) ranked second, followed by the free ligand (77) in third place (Husain et al., 2023).
SCHEME 14

Synthesis of Cu(II) and Co(II) complexes of a synthetic derivative of 2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)acetohydrazide.
Masood and coworkers reported tetrazole-containing biphenyl derivatives. Valsartan 80 underwent a condensation reaction in the presence of various phenols 81 to obtain target compounds 82 (Scheme 15). All the synthesized compounds were examined for their antihypertensive activity, and compound 82a demonstrated the greatest percentage of reduction (76.4%) of phenylephrine content on an isolated aorta. The mean systolic blood pressure of 80.17 was measured using the tail-cuff technique after administering compound 82b (80 mg/kg) to Wistar rats. They also carried out an enzyme inhibition assay on the urease enzyme. The results indicated that compound 82a displayed the highest inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 0.28 µM, whereas the standard drug thiourea showed an IC50 value of 4.24 µM. Additionally, they reported antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, Bacillus pumilus, and E. coli; unfortunately, none of the synthesized compounds showed antibacterial efficacy (Masood et al., 2023).
SCHEME 15

Synthesis of modified valsartan derivatives.
Bourhou and colleagues synthesized tetrazole derivatives to evaluate their antimicrobial properties. Initially, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde 83 was refluxed with dibromomethane 84 in ethanol under basic conditions to yield compound 85. In the second step, these dialdehydes 85 underwent a Michael addition reaction by removal of water and then the formation of a dicyanovinyl group in the presence of malononitrile 21 and ammonium hexafluorophosphate to form 86. Finally, key intermediate 86 was converted to the corresponding tetrazolic compound 87 via a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction in the presence of sodium azide in DMF at 110 °C (Scheme 16). The researchers conducted antibacterial activity tests, and the results revealed that compound 87 exhibited the highest activity against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, Listeria innocua, G. candidum, C. albicans, R. glutinis, A. niger, and S. aureus, with zone inhibition diameters of 14.90 mm, 11.5 mm, 13.45 mm, 12.65 mm, 14.5 mm, 11.25 mm, and 13.65 mm, respectively (Bourhou et al., 2023).
SCHEME 16

Synthesis of 3,3'-((hexane-1,6-diylbis (oxy))bis (4,1-phenylene))bis (2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)acrylonitrile).
Ali et al. developed tetrazole derivatives for antimicrobial activity. First, Schiff base derivative 90 was synthesized using amino benzothiazole derivative 88 and substituted benzaldehyde 89 in absolute ethanol under acetic conditions; this was followed by a [2 + 2] cycloaddition or Staudinger reaction, and then a nucleophilic substitution reaction was performed to produce compound 92. Lastly, targeted tetrazole derivative 93 was synthesized using the azide-nitrile cycloaddition approach from 92 (Scheme 17). They examined antimicrobial activity against bacteria like E. coli and S. aureus and fungi such as C. albicans. The results indicated that compound 93 exhibited the highest level of activity, as demonstrated by its respective MIC values of 75 μg/mL, 125 μg/mL, and 150 μg/mL. Fluconazole had an MIC value of 250 μg/mL against C. albicans, while ampicillin demonstrated MIC values of 100 μg/mL against both E. coli and S. aureus(Ali et al., 2023).
SCHEME 17

Illustrates the synthesis and structure–activity relationship of 4-(substituted phenyl)-3-(5-hexyl-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1-(5-methoxybenzo [d]thiazol-2-yl)azetidin-2-one.
Singh and coworkers developed pyrimidine-fused tetrazole derivatives as antimicrobial agents. In Scheme 18, 1-phenylbutane-1,3-dione 94 and hydrazine carbothioamide 95 were reacted in distilled water in the presence of ionic liquid to produce pyrimidine ring derivative 96 through condensation and cyclization, followed by reaction with aromatic aldehyde 97 to yield 98. Finally, 98 was treated with sodium azide in the presence of distilled water to produce the desired tetrazole-containing complex heterocyclic 99 through the cyclization process. Compound 98b showed the highest activity with zone inhibition diameters of 17 mm and 19 mm against S. paratyphi-A and S. aureus, respectively. Compound 99a showed the highest activity against E. coli and B. subtilis with zone inhibition diameters of 18 mm and 18 mm, respectively. For antifungal activity, similarly, compound 98c showed the strongest inhibitory activity against F. molaniforme, with a percentage inhibition of 77.22%. Against A. niger, compound 99a showed a percentage inhibition of 69.40%. In contrast, the reference compound Griseofulvin showed percentage inhibition 86% and 81% against F. molaniforme and A. niger respectively. Other reference compound Fungiguard displayed percentage inhibition 78% and 77% against F. molaniforme and A. niger respectively (Singh et al., 2023).
SCHEME 18

Synthesis of pyrimidine-fused tetrazole derivatives as antimicrobial agents.
Megha et al. developed novel tetrazole-containing biphenyl derivatives and showed dual antimicrobial and anticancer activity. In the first step, a reaction between 4-(bromomethyl)biphenyl-2-carbonitrile 100 and ethyl 4-aminobenzoate 101 underwent a nucleophilic substitution reaction to form the intermediate compound 102, followed by treatment with substituted 1-bromo-3-phenylpropan-2-one derivatives 103 to generate the compound 104 via nucleophilic substitution reaction (Scheme 19). The cyclization process was carried out to form the tetrazole derivatives 105 in the presence of sodium azide. They exhibited antibacterial activity against S. aureus, B. subtilis, S. typhi, and P. aeruginosa. The results indicated that 105a exhibited the highest activity with zone of inhibition diameter values of 15.2 mm, 15.0 mm, 15.0 mm, and 15.3 mm, respectively, at higher concentrations (100 μg/mL), which is similar to the standard drug gentamycin. The researchers also conducted a cytotoxicity study, revealing that compound 105b exhibited the strongest inhibitory action, with IC50 values exceeding 8.47 μg/mL against the A549 cell line, which is very close to the standard drug doxorubicin’s IC50 value of 7.60 μg/mL. Additionally, they looked into the anti-tuberculosis activity, and the results showed that compound 105c had high sensitivity with MIC values of 3.12 μg/mL, which was similar to the reference standard pyrazinamide (MIC = 3.12 μg/mL) (Megha and Bodke, 2023).
SCHEME 19

Synthesis of tetrazole-containing biphenyl derivatives through nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Cherfi and coworkers developed pyrazole-fused tetrazole derivatives. In Scheme 20, a mixture of 106 and tBuOK in THF was heated under reflux in the presence of 1-bromopropane 107 to obtain intermediate 108 via N-alkylation. Intermediate 108 underwent ester reduction in the presence of LiAlH4 to synthesize compound 109. All synthesized compounds were tested for antifungal activity, and results demonstrated that compound 109 showed the highest activity with inhibition diameters of 15 mm, 15 mm, 15 mm, and 14 mm against G. candidum, A. niger, P. digitatum, and R. glutinis, respectively. Additionally, they investigated the vasorelaxant action on an isolated rat aorta, and the outcomes revealed that compound 108 had the most significant activity with a maximum effect (Emax) of 60.26%. Carbachol and verapamil were employed in this investigation as positive controls and showed Emax values of 85.52% and 91.62%, respectively (Harit et al., 2023).
SCHEME 20

Synthesis and structure–activity relationships of (4-methyl-1-((2-propyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)methyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)methanol.
Beebany and coworkers developed new phenylene-bis-tetrazole derivatives and tested them against bacteria. First, intermediate bisimine 112 was synthesized from the reaction between aldehydes 111 and amines 110 using absolute ethanol as a solvent. These imines have been transformed into heterocyclic derivative 113 via the cyclocondensation reaction of imines with phthalic anhydride and sodium azide (Scheme 21). They carried out an antibacterial activity against Gram-negative E. coli and Gram-positive S. aureus to assess their potential as antibacterial agents. The results showed that compound 113 showed the highest inhibition performance against the growth of the applied bacteria. Furthermore, compound 113 exhibited increased activity at higher concentrations, resulting in a larger inhibition zone. These data suggest that its antibacterial effectiveness is dose-dependent, with higher concentrations leading to enhanced inhibition of bacterial growth. Compound 113 showed MIC values of 31 mm and 21 mm at 0.01 μg/mL concentration and MIC values of 12 mm and 13 mm at 0.0001 μg/mL concentration against E. coli and S. aureus, respectively (Beebany, 2023).
SCHEME 21

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of phenylene-bis-tetrazole derivatives.
Gujja and coworkers focused on the development of triazolyl tetrazole-bearing indazole derivatives as antimicrobial agents. Phenyl isothiocyanate 114 underwent a cyclization reaction in the presence of sodium azide to give 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiol 115, followed by deprotonation and a nucleophilic substitution reaction to produce derivative 116. In the presence of catalytic amounts of sodium nitrite, 1-methyl-1H-indazol-5-amine 117 was converted to compound 118 under a nitrogen atmosphere, which underwent Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition or click reaction, involving intermediate 116, to yield compounds 119 in the presence of DMF and copper sulfate under a nitrogen atmosphere (Scheme 22). All the synthesized compounds were tested for antimicrobial activity. The results showed that compound 119a showed superior inhibitory activity against S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and A. flavus with MIC values of 5 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, 12 μg/mL, 13 μg/mL, and 18 μg/mL, respectively, and compound 119b demonstrated the highest activity against M. Luteus and M. gypseum with MIC values of 9 μg/mL and 11 μg/mL, respectively (Gujja et al., 2023).
SCHEME 22

Synthesis of triazolyl tetrazole-bearing indazole derivatives as antimicrobial agents.
Loganathan et al. designed and synthesized tetrazole derivatives that were screened for dual antimicrobial and anticancer activity. In Scheme 23, a mixture of equivalent moles of 2-(1H-imidazole-5-yl)ethanamine 120, 1H-tetrazole 121, and benzaldehyde 122 or 3-methylbut-2-enal 123 in ethanol with HCl was refluxed for 2 h at 60 °C to form compounds 124 and 125, respectively, through a condensation reaction. All the synthesized compounds were tested for antibacterial activity against S. aureus, E. coli, E. faecalis, P. aeruginosa, and K. pneumoniae. The results showed that compound 124 showed the highest activity with MIC values of 2 μg/mL, 4 μg/mL, 8 μg/mL, 32 μg/mL, and 8 μg/mL, respectively. Those showed similar activity to the reference compound, cefazolin. For antifungal activity, compound 124 showed the highest inhibitory activity against A. niger, M. audouinii, C. albicans, and C. neoformans, with MIC values of 2 μg/ML, 1 μg/mL, 16 μg/mL, and 32 μg/mL, respectively. To further investigate, the researchers conducted cytotoxicity assays, which revealed that compound 124 exhibited remarkable efficacy against the HeLa cell line with a GI50 value of 0.01 µM, while compound 125 demonstrated superior activity against the HepG2 and MCF7 cell lines with GI50 values of 0.02 µM and 0.04 µM, respectively. The standard compound doxorubicin showed GI50 values of 0.01 µM against the HepG2 cell line, 0.02 µM against the MCF7 cell line, and 0.04 µM against the HeLa cell line, respectively (Loganathan et al., 2024).
SCHEME 23

Synthesis of imidazole-containing tetrazole derivatives.
Jagadeesan and coworkers developed N-acyl indole-substituted tetrazole derivatives that screened for dual antimicrobial and anticancer activity. 2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)acetic acid 126 underwent a chloroacetylation reaction in the presence of SOCl2 to prepare intermediate 127, followed by a nucleophilic substitution reaction with indole derivative 128 to produce the desired compound 129 (Scheme 24). Synthesized derivatives were tested for in vitro antibacterial activity against S. aureus MTCC 737, K. planticola MTCC 2277, B. cereus MTCC 430, S. aureus MLS16 MTCC 2940, E. coli MTCC 1687, and P. aeruginosa MTCC 424. The results revealed that compound 129 showed the highest activity with MIC values of 18.75 μg/mL, 9.37 μg/mL, 37.5 μg/mL, 9.37 μg/mL, 1.67 μg/mL, and 18.75 μg/mL, respectively. They tested antifungal activity, and according to their data, compound 129 showed superior inhibitory activity against A. niger, equal to that of the standard miconazole’s MIC value of 9.37 μg/mL. The results of a cytotoxicity study showed that compound 129 demonstrated the highest activity against the HeLa, A549, MCF-7, and K562 cell lines with IC50 values of 3.8 µM, 47.5 µM, 2.4 µM, and 6.9 µM, respectively (Jagadeesan and Karpagam, 2023).
SCHEME 24

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of N-acyl indole-substituted tetrazole derivatives.
Henches and coworkers developed tetrazole-containing sulfonyl acetamide moieties as inhibitors of M. tuberculosis and Mycobacterium marinum. This synthetic route in Scheme 25 started with the commercially available 5-mercapto-1-substituted tetrazole 130, which was S-alkylated with compound 131 to afford intermediate 132. The use of UHP and TFAA in acetonitrile resulted in the predominant formation of the desired sulfones (133). All the synthesized compounds were tested for in vitro inhibitory activity against M. tuberculosis and M. marinum. The results demonstrated that compound 133 showed the highest activity with MIC90 values of 1.25 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL, respectively, while the standard drug rifampin showed superior efficacy with MIC90 values of 0.06 μg/mL and 0.2 μg/mL for the same targets (Henches et al., 2023).
SCHEME 25

Synthesis and structure–activity relationships of tetrazole-containing sulfonyl acetamides congeners.
Zala and coworkers developed pyrazolyl pyrazoline-clubbed tetrazole hybrids as promising anti-tuberculosis agents. In Scheme 26, 5-chloro-4-(1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole 135 was synthesized by reaction with derivative 134 and ethylene glycol using p-toluene sulfonic acid (p-TSA) in toluene under reflux conditions via acetalization reaction, followed by nucleophilic substitution reaction, then deprotection to yield compound 137. Finally, 137 was reacted with 2-acetyl furan 138 and hydrazide derivative 139 in an ethanolic NaOH solution to synthesize compound 140 through nucleophilic addition and cyclization reaction. All the synthesized compounds were tested for in vitro antitubercular activity against the M. tuberculosis H37Rv strain. The results demonstrated that compound 140 showed the highest activity, with MIC values of 12.5 μg/mL and a percentage inhibition of 99% (Zala et al., 2023).
SCHEME 26

Synthesis of pyrazolyl pyrazoline-clubbed tetrazole hybrids as anti-TB agents.
Khramchkhin et al. developed tetrazole-fused quinoline derivatives and evaluated their antiviral activity. In Scheme 27, 2-propyl-2H-tetrazol-5-amine 142 has a nucleophilic amine group, which attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the 2-mercaptoquinolin-3-carbaldehyde 141 to create azomethine derivatives 143. Compound 143 further reacted with 3-phenylpropiolaldehyde 144 to synthesize the final compound 145 in triethylamine and DMF through conjugate addition (Michael addition) followed by an intramolecular cyclization process. Among these synthesized compounds, 145 showed excellent potency against the influenza A/Puerto Rico/8/34 virus in the MDCK cell line with IC50 values of 18.4 µM and a selectivity ratio (SI) value of >38. A drug with a higher SI ratio is likely to be safer and more effective in treating a viral infection. In contrast, the standard drug oseltamivir carboxylate has an IC50 value of 0.17 µM and an SI value greater than 588 (Khramchikhin et al., 2023).
SCHEME 27

Synthesis of tetrazole-fused quinoline derivatives.
3 Anticancer derivatives
Vellaiyan et al. designed and synthesized 1,2,3‒triazole-fused tetrazole hybrids as anticancer agents. The process begins with material 2-(2-fluoro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl) propanoic acid 146, followed by a nucleophilic addition reaction using lithium aluminum hydride in THF at room temperature to obtain intermediate 147. This stage is then followed by a nucleophilic substitution to form alkyl azide 148 by reacting diphenyl phosphoryl azide (DPPA) in the presence of DIAD and PPh3. In the final step, Cu(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition was carried out between the terminal alkyne of 149 and the azide of intermediate 148 to form a regioselective 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole ring formation and yield target compound triazole-fused tetrazole derivatives 150 (Scheme 28). The antiproliferative assay revealed that compound 150a exhibited the highest activity against the HepG2, HuH7, and MCF-7 cell lines with IC50 values of 1.83 μM, 1.46 μM, and 1.35 μM, respectively, and compound 150b showed activity against the T-47D cell line with an IC50 value of 3.55 μM (Vellaiyan et al., 2025).
SCHEME 28

Synthesis of 1,2,3‒triazole-fused tetrazole hybrids as anticancer agents.
Olejarz and coworkers designed and developed novel tetrazole derivatives as Bcl-2 apoptosis regulators for the treatment of cancer. Initially, 3,3′-dimethoxybenzidine 151 was treated with various aryl or alkyl isothiocyanates 152 in dry acetonitrile under ambient conditions for 1–6 h, resulting in bis-thiourea intermediates 153. It was followed by a cyclization reaction with sodium azide to synthesize the final target compound 154 in the presence of mercuric chloride, dry DMF, and triethylamine (Scheme 29). All the synthesized compounds were tested against human cancer cell lines like HTB-140, A549, HeLa, and SW620. The findings revealed that compound 154b showed the highest activity against respective cell lines with IC50 values of 23.5 μM, 34.2 μM, 20.3 μM, and 21.3 μM. Flow cytometric analysis using annexin V/7-AAD staining revealed that 154c showed the highest late apoptotic activity in A549 cells (92.1% late apoptosis). Molecular docking studies identified compound 154a as a potent Bcl-2 protein inhibitor (Olejarz et al., 2025).
SCHEME 29

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of tetrazole derivatives.
Manwar and coworkers developed novel tetrazole derivatives as anticancer agents. Phenyl pyrazole derivative 155 and aniline derivative 160 were reacted with chloroacetyl chloride to obtain corresponding chloroacetamide derivatives 156 and 161, which reacted with sodium azide (NaN3) in a mixture of ethanol and water to synthesize azide intermediates 157 and 162. The azide intermediates were treated with 4-bromobenzonitrile 158 in a sealed vial at 130 °C for 72 h under solvent-free conditions to obtain final derivatives. The regioselective [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction produced 1-substituted-5-aryl tetrazole derivatives 159 and 163 (Scheme 30). All the synthesized compounds were tested for in vitro cytotoxicity assays against two human cancer cell lines, HT-29 and MDA-MB-231. The findings showed that compound 163 showed the highest activity against the HT29 cell line, and compound 159 showed superior activity against the MDA-MB-231 cell line with IC50 values of 69.99 μg/mL and 86.73 μg/mL, respectively (Manwar et al., 2025).
SCHEME 30

Synthesis of pyrazole clubbed tetrazole derivatives as anticancer agents.
Rahman and coresearchers developed benzimidazole-triazole-tetrazole derivatives as anticancer agents targeting breast cancer. Hydrazine derivative 164 reacts with acetic acid to form compound intermediate 165 via an intramolecular cyclization reaction. The Michael addition reaction, followed by a [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction, was carried out to synthesize compound 167 in the presence of sodium azide and ammonium chloride. Thereafter, intermediate 167 underwent an N-alkylation reaction via the SN2 mechanism in the presence of ethyl chloroacetate under basic conditions to yield ester derivative 168, followed by hydrazinolysis in the presence of hydrazine hydrate to form hydrazide derivative 169. In the final step, the hydrazide derivative 169 reacted with furfural to form the target compound, the Schiff base derivative 170 (Scheme 31). An in vitro cytotoxicity assay revealed that compound 170 demonstrated superior activity against the MCF-7 cell line with an IC50 value of 0.29 μM, whereas 5-fluorouracil showed an IC50 value of 0.11 μM. A molecular docking study was also performed, and compound 170 showed the highest binding affinity against the 8GVZ protein with a binding affinity of −6.68 kcal/mol and formed a hydrogen bond with the Thr1782 amino acid residue (Abdel-Rahman et al., 2025).
SCHEME 31

Synthesis of benzimidazole–triazole–tetrazole derivatives as anticancer agents targeting breast cancer.
Kaur and coworkers developed indole-based tetrazole derivatives as an anti-breast cancer agent. The N-position of the initial compound 1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde 171 underwent benzylation reactions using benzyl chlorides 172 in basic conditions to yield compound 173. Furthermore, the aldehyde-to-nitrile transformation reaction was performed using an ammonia-based condensation followed by an oxidation reaction to yield intermediate 174 with iodine. Following this, an azide-nitrile cycloaddition reaction formed a tetrazole derivative 175. In the final step, N-benzylation of indole–tetrazoles 175 in the presence of KOH using substituted benzyl chlorides occurred with excellent yields of 2-benzylated tetrazole derivatives 177 (Scheme 32). All the synthesized compounds were subjected to an antiproliferative assay, and results revealed that compound 177b showed the highest activity with IC50 values of 3.83 µM, 7.83 µM, and 15.7 µM against the T-47D, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cell lines, respectively. Compound 177a showed the second-highest inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 10.00 µM, 7.95 µM, and 19.4 µM against the T-47D, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cell lines, respectively. The most active compounds, 177a and 177b, were selected to determine their cytotoxicity against normal human embryonic kidney cells, HEK-293. Compound 177a was found to have non-significant cytotoxicity against the HEK-293 cells, while compound 177b has much less cytotoxicity (IC50 = 108.6 µM) against the normal cells than the standard drug bazedoxifene (IC50 = 38.48 µM). To determine the ER-α binding affinity, compounds 177a and 177b were tested for the ER-α competitor assay. Based on the competitive binding experiment findings, compounds 177a and 177b showed IC50 values of 5.826 nM and 110.6 nM, respectively, demonstrating stronger binding affinity and greater efficiency for ER-α than the standard drug bazedoxifene, which has an IC50 of 339.2 nM. For further investigation, they carried out Western blotting, and according to the results, compound 177a induced 46.06% expression of ER-α protein in T-47D cells. This result suggests that the compound 177a inhibited the expression of ER-α protein in T-47D cells to exhibit its anticancer activity (Kaur et al., 2024).
SCHEME 32

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of indole-based tetrazole derivatives as anti-breast cancer agents.
Asiri and colleagues designed and developed tetrazole ring-incorporated oxazole-pyrimidine derivatives as anticancer agents. In Scheme 33, 2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-oxoacetaldehyde 178 was reacted with pyrimidin-5-yl-methanamine 179 in the presence of Ag2CO3 to produce the pure compound 5-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-(pyrimidin-5-yl)oxazole 180 through a cyclization reaction, followed by reduction to yield amine intermediate 181. Under the Sandmeyer reaction conditions, intermediate 181 was changed into azide intermediate 182, followed by a cyclization reaction in the presence of substituted benzonitrile 183 and ZnBr2, which produced compound 184 in good yields. In vitro cytotoxicity assay revealed that, among these synthesized compounds, compound 184 exhibited the highest inhibitory activity against the PC3, A549, MCF-7, and DU-145 cell lines with IC50 values of 0.08 µM, 0.04 µM, 0.01 µM, and 0.12 µM, respectively. The standard compound etoposide showed IC50 values of 2.39 µM, 3.08 µM, 2.11 µM, and 1.97 µM, respectively (Asiri et al., 2024).
SCHEME 33

Synthesis of tetrazole ring-incorporated oxazole-pyrimidine derivatives.
Al-Samrai et al. developed a platinum complex containing tetrazole derivatives as a promising anticancer agent. Complex 185 was prepared by reacting two equivalents of 1-methyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole-5-thiol 130 with one equivalent of K2PtCl4 in the presence of Et3N as a basic medium. Additionally, an equivalent molar amount of complex 185 and diphosphine ligands (diphos = dppe) was reacted in dichloromethane as a solvent, yielding complex 186 (Scheme 34). Researchers evaluated the enzyme inhibition assay against alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and the finding revealed that complex 186 exhibited the inhibitory percentage (84.02%) at a concentration of 10–4 mol/L. For additional investigation, they conducted cell line activity against the HepG2 cell line, and findings indicated that complex 185 demonstrated the highest activity, with an IC50 value of 34.78 μM (Al-Samrai et al., 2024).
SCHEME 34

Synthesis of platinum complex containing tetrazole derivatives as promising anticancer agents.
Metre and coworkers developed pyrazole-fused tetrazole derivatives as promising dual-active anticancer and antifungal agents. In Scheme 35, the starting material N-arylsydnone 187 was converted to 188 in the presence of acrylonitrile and chloranil, followed by cyclization and nucleophilic substitution. Further, the reaction was carried out to yield the targeted compound 191 in the presence of substituted 4-bromomethyl coumarin 190. All the synthesized compounds were subjected to an anticancer study, and results revealed that compound 191 showed IC50 values of 67.69 μg/mL and 27.85 μg/mL against the L929 and HCT116 cell lines, respectively. They tested its antifungal activity against C. albicans, and results demonstrated that compound 191 showed superior activity with MIC values of 4 μg/mL (Metre et al., 2024).
SCHEME 35

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of 7-methyl-4-((5-(1-substituted-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)-4a,8a-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-one.
Yerga et al. designed and synthesized novel tetrazole derivatives targeting tubulin. N-methylation of 5-nitroindole 128 produced N-methyl-5-nitroindole 193 under basic conditions with phase transfer catalysis. Then, compound 193 was reduced to yield the corresponding amine 194. In the next step, a coupling reaction was carried out between compound 194 and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid 192 to yield amide intermediate 195. The amide functionality in 195 was then transformed into a 1,5-disubstituted tetrazole ring using a tetrachlorosilane-azide system, resulting in compound 196. The addition of a methylsulfanyl group to the pyridine ring was achieved via reaction with methanethiolate, giving compound 197. Finally, a formyl group was introduced at the 3-position of the indole ring in compound 197 through a Vilsmeier–Haack reaction, resulting in the formation of the carbaldehyde derivative 198 (Scheme 36). First, they tested antiproliferative activity against the HeLa, MCF7, U87 MG, T98G, HepG2, HCT8, HT-29, and HEK-293 cell lines. The finding demonstrated that compound 198 showed the highest activity with IC50 values of 0.024 µM, 0.026 µM, 0.012 µM, 0.019 µM, 0.031 µM, 0.029 µM, 0.033 µM, and 2.27 µM, respectively. In further investigation, compounds were subjected to a tubulin polymerization inhibition assay, and results demonstrated that compound 198 showed the highest activity, with IC50 values of 0.8 µM. Flow cytometry studies revealed that the compound 198 targets tubulin and arrests cells at the G2/M phase, and thereafter undergoes apoptotic induction (Gallego-Yerga et al., 2023).
SCHEME 36

Synthesis of indole pyridine clubbed tetrazole derivatives as anticancer agents.
He et al. designed and synthesized furan-containing tetrazole derivatives as potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. The key intermediate 202 was synthesized using substituted aniline 199 and furoic acid 201 as starting substrates. Intermediate 202 reacts with thionyl chloride to yield the second intermediate 203 via an acylation reaction. Compound 204 was treated with 203 in basic media to produce the target compound 205 via nucleophilic substitution reaction (Scheme 37). All the synthesized compounds were subjected to an enzyme inhibition assay. The results showed that compound 205 demonstrated the highest inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 4.6 µM and 78% inhibition at 50 µM concentrations against α-glucosidase kinase. The researchers conducted a cytotoxicity assay, revealing that compound 205 exhibited the highest activity against the HEK293, RAW264.7, and HepG2 cell lines, with percentage inhibitions of 22.3%, 33.9%, and 37.6%, respectively (He et al., 2023).
SCHEME 37

Synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of S-(1-methyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl) 5-(substituted phenyl)furan-2-carbothioate.
Vanam and Anireddy invented and synthesized tetrazole-fused imidazopyridine compounds as anticancer agents. In Scheme 38, a mixture of 2-aminopyridine 206 and 4-bromocinnamaldehyde 207 was stirred at 60 °C for 8 h to yield intermediate 208 through a copper-catalyzed cyclization reaction, followed by reduction in the presence of NaBH4 to afford compound 209, and then mesylation and substitution by the azide ion to produce compound 210. Finally, the cyclization reaction was performed between substituted benzonitrile 211 and azide 210 to produce the final tetrazole derivatives 212. All the synthesized compounds were subjected to cytotoxicity studies against the MCF-7, A549, and MDA-MB-231 cell lines. The results revealed that compound 212 showed the highest activity with IC50 values of 1.66 μM, 1.90 μM, and 2.89 μM, whereas reference compound doxorubicin showed IC50 values of 3.12 μM, 2.10 μM, and 3.41 μM, respectively (Vanam and Anireddy, 2023).
SCHEME 38

Synthesis of tetrazole-fused imidazopyridine compounds.
Pokhodylo et al. developed a tetrazole containing a benzylthiazol moiety as a promising anti-leukemic agent. 2-amino-5-benzyl-1,3-thiazole derivatives 217a and 217b were synthesized via the Meerwein reaction of the arene diazonium chlorides, which are prepared from the corresponding aniline with acrolein, yielding 3-aryl-2-chloropropanals, and the following cyclocondensation with thiourea. (1H-tetrazol-1-yl)benzoic acids 219 were obtained by the reaction of substituted 4-aminobenzoic acid 218 with triethyl orthoformate and sodium azide, followed by acylation of the reaction with compound 217b in the presence of oxalyl chloride to yield compound 220. The tetrazole acid 222 was prepared through a one-pot reaction involving amido-ester derivatives 221, phosphorus oxychloride, and sodium azide. The present process was followed by hydrolysis of the ester moiety to form a carboxyl group and then acylation with compound 217a in the presence of oxalyl chloride to yield compound 223 (Scheme 39). Synthesized compounds were subjected to an MTT assay for measurement of cell viability, and results revealed that compound 220 showed the highest activity against the K-562 cell line, with an IC50 value of 0.70 μM. Compound 223 showed promising activity against the HaCaT and J774.2 cell lines, with IC50 values of 6.00 μM and 3.61 μM, respectively. Compound 220 showed a significant effectiveness in inhibiting cell growth at nanomolar concentrations against both leukemia K-562 cells and melanoma UACC-62 cells, with IC50 values of 56.4 nM and 56.9 nM, respectively, as determined by the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay. However, at nanomolar concentrations, compound 220 exhibited extreme cytotoxicity across a wide range of tumor cell lines, including K-562, NCI-H460, HCT-15, KM12, SW-620, LOX IMVI, M14, UACC-62, CAKI-1, and T47D. In the leukemic K-562 cells, the alkaline comet test identified that the compound 220 led to DNA single-strand damage. In K-562 cells treated with 220 at 70 nM, 1.1% of DNA was found in the tail of the comets, and 5.1% of DNA was found in the comet tails in cells treated with 220 at a 700 nM concentration. The reference drug, doxorubicin, caused less DNA damage than the derivative 220 (Pokhodylo et al., 2023).
SCHEME 39

Synthesis of a tetrazole containing a benzylthiazol moiety.
Mikolaichuk et al. developed tetrazole-fused morpholine derivatives as anticancer agents. In Scheme 40, cyanuric chloride 224 reacted with 5-methyltetrazol-1-ylacetic acid hydrazide 225 through a nucleophilic substitution reaction to produce compounds 226, which have the tetrazole cycle connected to 1,3,5-triazine by an acetohydrazide linker. The resulting compound 226 was further used to synthesize targeted derivatives of morpholin-4-yl-1,3,5-triazines 227 under basic conditions. All the synthesized compounds were subjected to cytotoxicity studies against the Huh-7 and A549 tumor cell lines. Results demonstrated that compound 227 showed the highest inhibitory activity with a 49% and 51% inhibition percentage, respectively. The additional findings from the antioxidant analysis indicated that compound 227 did not interact with nitric oxide (NO) radicals and did not show any photoinduced hemolysis effect (Mikolaichuk et al., 2023).
SCHEME 40

Synthesis of N'-(4,6-substituted-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-2-(5-methyl-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)acetohydrazide derivatives.
Gandham and the group developed tetrazolo pyrrolidine analogs as potent anticancer agents. Intermediate 233 was synthesized by reaction with 231 and 232 in dichloromethane for 4 h through nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction, followed by the formation of a tosylate 234 from a hydroxyl group in the presence of 4-tolylsulfonyl chloride, which was further treated with sodium azide to provide azide intermediate 235 via SN2 reaction. Phenyl isothiocyanate 228 underwent a cyclization reaction in the presence of sodium azide to give 1-phenyl-1H-tetrazole-5-thiol 229, followed by deprotonation and a nucleophilic substitution reaction to produce the derivative 230. The synthesis of new tetrazolyl triazole pyrrolidine derivative 236 was accomplished via click chemistry of appropriate substituted tetrazole alkynes 230 with pyrrolidine azide 235 in the presence of L-sodium ascorbate and CuSO4 (Scheme 41). All the synthesized compounds were tested for anticancer activity against the HeLa, MCF-7, HCT-116, and HepG2 cell lines, and results showed that compound 236 exhibited the highest activity with IC50 values of 1.00 µM, 3.83 µM, 1.66 µM, and 1.92 µM, respectively. In comparison, the standard drug doxorubicin displayed lower activity than 236 with IC50 values of 2.34 µM, 3.02 µM, 1.96 µM, and 2.08 µM against the same cell lines (Gandham et al., 2023).
SCHEME 41

Synthesis of tetrazolo pyrrolidine analogs as potent anticancer agents.
Jarupula and coworkers developed novel 1,2,3-triazole-linked tetrazole congeners as a promising anticancer agent. In Scheme 42, 4-aminophenol 237 reacted with carbon disulfide in the presence of triethylamine in THF, followed by the addition of H2O2 at 40 °C to afford 4-isothiocyanatophenol 238. Cyclization was carried out in the presence of sodium azide to afford 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-5H-tetrazole-5-thione 239, which was methylated and followed by a nucleophilic substitution reaction to produce intermediate 241. Further reaction with substituted aryl azides 242 led to the formation of targeted derivatives 243 via a click reaction. All the synthesized compounds were screened for anticancer activity against the A549 and MCF-7 cell lines. Results revealed that compound 243 exhibited superior inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 18.06 µM and 25.13 µM against the A549 and MCF-7 cell lines, respectively, compared to the standard drug doxorubicin, which had IC50 values of 20.48 µM and 27.18 µM against the same cell lines (Jarupula et al., 2023).
SCHEME 42

Synthesis of novel 1,2,3-triazole-linked tetrazole congeners.
Ulular and group-synthesized Ni(II) and Pt (II) complexes of tetrazole derivatives. 5-aminotetrazole 38 refluxed with 5-bromosalicyaldehyde 248 in ethanol to produce intermediate (E)-2-(((1H-tetrazol-5-yl)imino)methyl)-4-bromophenol 249. A further reaction proceeds with K2 [PtCl4] to yield the target complex 250 (Scheme 43). The group screened the target derivatives for dual activities against cancer (binding properties of ct-DNA) and microbial strains. The binding properties of ct-DNA were investigated using ultraviolet-visible region spectroscopy and viscometry experiments. UV-region spectroscopy demonstrated that the molecules showed interaction with DNA, either electrostatic or binding to the minor/major grooves between base pairs of DNA and aromatic chromophore. Viscometry experiments suggested that all Schiff bases and complexes might also have intercalation-type interactions with DNA. The researchers also performed antimicrobial activity by the well-diffusion method. The complex 250 is the only ligand that was active against all microbial strains, both Gram-negative (S. epidermis, S. aureus, and B. cereus) and Gram-positive (P. putida, E. aerogenes, S. typhi, E. coli, P. vulgaris, and C. albicans). The complex showed a significant zone of inhibition with diameters of 22 mm, 23 mm, and 16 mm toward the respective Gram-negative strains and 26 mm, 14 mm, 20 mm, 19 mm, 10 mm, and 30 mm toward the respective Gram-positive strains mentioned above (Ulular et al., 2024).
SCHEME 43
![Chemical reaction diagram showing the synthesis of compound 250. Starting materials include 5-aminotetrazole (38) and brominated salicylaldehyde (248) in the presence of ethanol (EtOH) to form compound 249. Further reaction with potassium tetrachloroplatinate (K₂[PtCl₄]) produces compound 250.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1700143/xml-images/FCHEM_fchem-2025-1700143_wc_sch43.webp)
Synthesis of Pt(II) complexes of tetrazole derivatives.
Disli et al. synthesized tetrazole-containing donepezil derivatives and investigated multiple activities, such as anticancer, antimicrobial, and antibiofilm (Scheme 44). Substituted phenyl isothiocyanate 251 underwent a cyclization reaction in the presence of sodium azide to give substituted 1-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-5H-tetrazole-5-thione 252, which was further reacted with 5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one 253 to yield the target derivatives 254a-c in the presence of iodine and methanol. The synthesized derivatives were screened against antibacterial (E. coli ATCC 25,922 & S. aureus ATCC 29,213) and antifungal (C. albicans ATCC 10,231) strains. Compounds 254a and 254b showed excellent antimicrobial activity against E. coli (MIC = 0.1 and 0.2 mg/mL), S. aureus (MIC = 0.02 and 0.2 mg/mL), and C. albicans (MIC = 0.2 and 0.05 mg/mL) strains. The researcher performed an antibiofilm activity assay using the crystal violet method, and the results indicated that 254a showed the highest biofilm inhibition rate of 90% and 98.74% in the S. aureus and C. albicans strains, respectively, at 0.2 mg/mL concentration. The anticancer activity was also examined using the MTT assay. All compounds were screened against the MDA-MB-231 cell line. The result showed that compounds showed moderate cytotoxicity, with IC50 values ranging from 475.36 to 589.18 µM. The researchers then tested a combination of doxorubicin and synthesized compounds and found that the compounds showed a synergistic effect. In combination, 254c showed the highest activity against the MBA-MB-231 cell line, with the IC50 value of 1.14 µM. These results suggest that 254c may enhance the anticancer potential of doxorubicin, which can be used as adjuvant combination chemotherapy targeting TNBC (Dişli et al., 2025).
SCHEME 44

Synthesis of tetrazole-containing donepezil derivatives with multiple activities.
4 Challenges and future perspectives
Tetrazole-based agents have enormous potential as antibacterial and anticancer therapeutics, but several obstacles prevent their clinical translation and extensive usage. Their adverse physicochemical profile is one of the main challenges. Because of their strong acidity and polarity, tetrazoles have poor membrane permeability and, as a result, low oral bioavailability. Their poor solubility, ineffective absorption, and occasionally high metabolism and excretion all limit their therapeutic efficacy, which reinforces this issue. Apart from pharmacokinetic problems, safety considerations are also important. Some tetrazole compounds have limited selectivity between impaired and healthy tissues, exhibiting cytotoxicity against normal cells. There may also be dangers of genotoxicity, mutagenicity, or hepatotoxicity, depending on the substitution pattern. In 2024, Kaur et al. reported indole-based tetrazole derivatives and screened for anti-breast cancer activity. Targeted derivatives displayed measurable cytotoxicity against the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines, but they also showed toxicity against normal human embryonic kidney cells (HEK-293), which indicates imitated selectivity (Kaur et al., 2024). In 2025, Vellaiyan et al. synthesized triazole–tetrazole conjugates that demonstrated potential antiproliferative effects on the HepG2 and HuH7 cancer cell lines while also damaging normal fibroblast cell lines at greater concentrations (Vellaiyan et al., 2025). Husain et al. reported copper (II) and cobalt (II) tetrazole complexes in 2023. These complexes exhibited robust DNA-binding and anticancer properties. However, their lack of selectivity resulted in considerable toxicity in normal cell models and oxidative stress in non-malignant tissues (Husain et al., 2023). Abdel-Rahman et al. (2025) synthesized benzimidazole-clubbed tetrazoles and screened them against the breast cancer cell line (MCF-7). The synthesized derivatives showed significant activity against the cancer cell line MCF-7, but also damaged the normal epithelial cells at the same concentrations. In antimicrobial applications, off-target toxicity may arise, and certain derivatives can disrupt the host microbiome, consequently diminishing therapeutic efficacy.
Structural factors also make things more challenging. Tetrazole rings often serve as bioisosteres for carboxylic acids and amides in drug design; however, this mimicry can lead to off-target interactions, increasing the risk of unintended side effects. For example, anticancer tetrazole derivatives may attack healthy cells that are dividing quickly, which can cause problems like bone marrow suppression, gastrointestinal toxicity, etc. Similarly, antimicrobial tetrazoles may be less effective against resistant strains or ineffective against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Chemical stability is another issue because some tetrazole derivatives can break down in water, become unstable in acidic or basic conditions, or break down in a way that depends on the pH. These problems make them less effective and shorten their shelf lives.
Even though there have been promising results in vitro and in vivo, only a small number of tetrazole derivatives have made it to clinical trials. Several strategies have been suggested to address these problems. Prodrug design may increase solubility and oral bioavailability. Combining tetrazoles with other pharmacophores in hybrid drug designs is a promising way to make drugs stronger and avoid resistance. In addition, computer-aided drug design (CADD) and other computational methods can help improve selectivity and reduce toxicity. Finally, rational structural changes can be made to fine-tune the balance between hydrophilicity and lipophilicity, which will improve the drug-like properties and overall therapeutic potential.
5 Conclusion
Tetrazoles, with their distinct nitrogen-rich heterocyclic structure, are still very promising for new drug development because of their wide range of biological activity, excellent physicochemical characteristics, and ease of synthetic accessibility. This study highlights the dual pharmacological potential, structure–activity correlations, and varied synthesis techniques of tetrazoles as antibacterial and anticancer drugs. The present study also summarizes the correlation between antimicrobial and anticancer activities, which will be beneficial for the design and development of multi-targeting candidates because anticancer and antimicrobial agents share their molecular targets and overlapping mechanisms, including DNA damage, protein synthesis inhibition, metabolic pathway interference, etc. Tetrazole’s potential in therapeutic development has been supported by recent research because several of the compounds discussed here have shown exceptional efficacy in antimicrobial and anticancer investigations. Certain compounds demonstrated broad-spectrum antibacterial activity with low MIC values, while others showed notable cytotoxicity against numerous cancer cell lines with IC50 values in the nanomolar range (Table 1). The increasing amount of data encourages more research and improvement of tetrazole templates, especially using hybridization techniques and structure-based design methodologies. According to these outcomes, tetrazole derivatives have much potential for the discovery and creation of novel therapeutic candidates.
TABLE 1
| S. No. | Compounds | MIC (µg/mL) or IC50 (µM) | Cell line or strain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
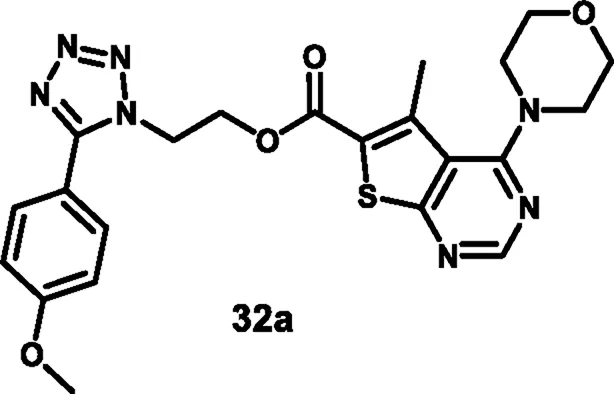
|
0.09 μg/mL 0.13 μg/mL |
E. coli
P. vulgaris |
| 2 |
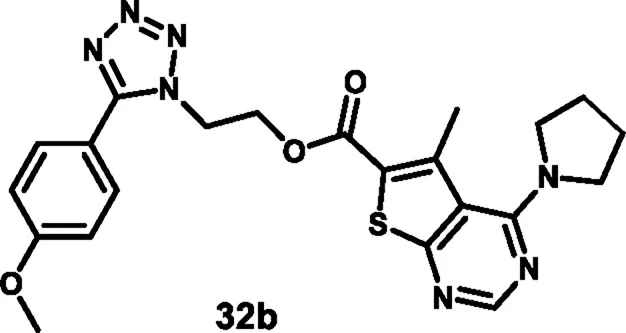
|
0.07 μg/mL 0.09 μg/mL 0.04 μg/mL 0.11 μg/mL |
B. subtilis
E. coli A. niger R. oryzae |
| 3 |
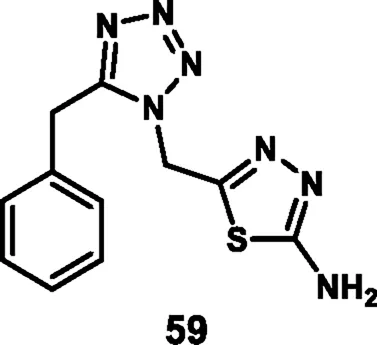
|
1.562 μg/mL |
S. aureus |
| 4 |
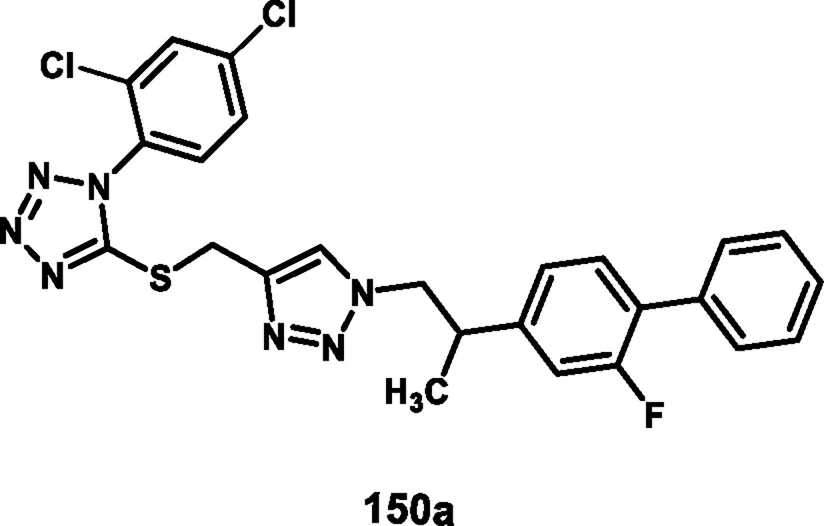
|
1.35 µM |
MCF-7 |
| 5 |
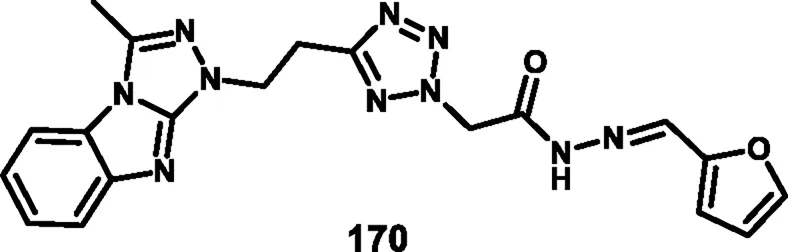
|
0.29 μM |
MCF-7 |
| 6 |
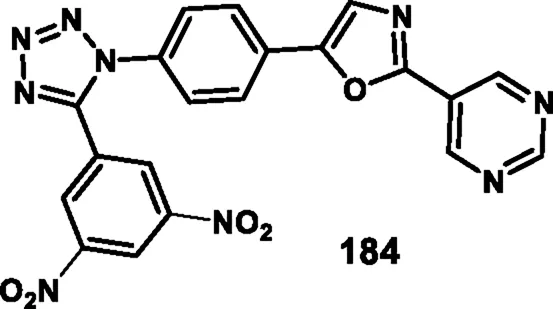
|
0.08 μM 0.04 μM 0.01 μM 0.12 μM |
PC3 A549 MCF-7 DU-145 |
| 7 |
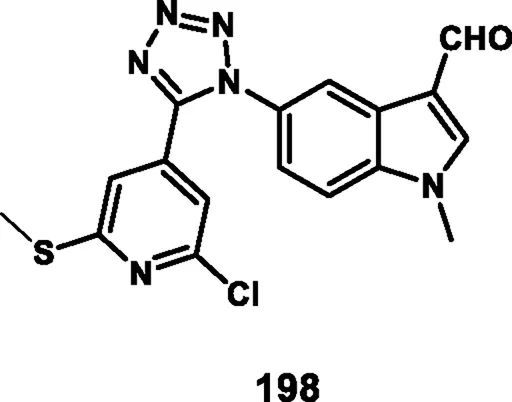
|
0.024 μM 0.026 μM 0.012 μM 0.019 μM 0.029 μM |
HeLa MCF-7 U87 MG T98G HCT8 |
| 8 |
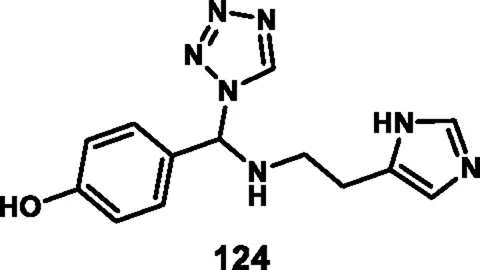
|
2 μg/mL 1 μg/mL GI50: 0.01 μM |
S. aureus
M. audouinii HeLa |
| 9 |
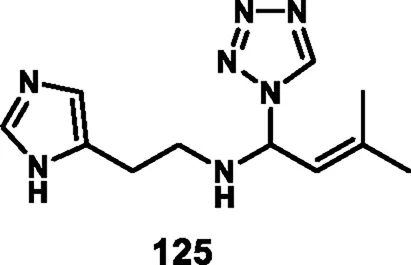
|
GI50: 0.02 μM GI50: 0.04 μM |
HepG2 MCF-7 |
| 10 |
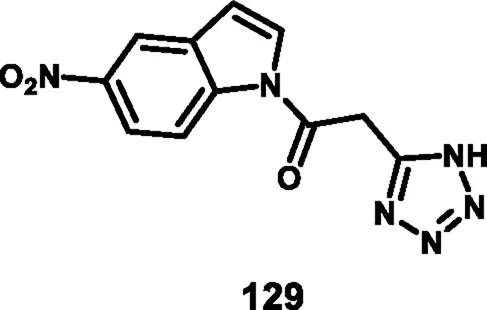
|
1.67 μg/mL 2.4 μM |
E. coli
MCF-7 |
Summary of the most potent derivatives with MIC or IC50 and their respective strain or cell line.
Statements
Author contributions
LM: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Investigation. GT: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. RP: Writing – review and editing, Data curation. NM: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. PS: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. GM: Writing – review and editing. MR: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. VS: Writing – review and editing, Validation. KM: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Project administration.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are heartily thankful to the management of SRM College of Pharmacy Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences (SRM Institute of Science and Technology), Sri Balaji Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University), School of Pharmacy (Sangam University), Geetanjali University, and Acharya and BM Reddy College of Pharmacy for constant encouragement, support, and motivation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abdel-Rahman A. H. Zaid I. F. Salama W. M. Hawatah M. A. Zaki Y. H. Farag B. et al (2025). Design and evaluation of novel Benzimidazolo-Triazole-Tetrazole derivatives as anticancer agents against MCF-7 cells. Russ. J. Gen. Chem.95 (6), 1530–1542. 10.1134/s1070363225602066
2
Abualnaja M. M. Alalawy A. I. Alatawi O. M. Alessa A. H. Qarah A. F. Alqahtani A. M. et al (2024). Synthesis of tetrazole hybridized with thiazole, thiophene or thiadiazole derivatives, molecular modelling and antimicrobial activity. Saudi. Pharm. J.32 (3), 101962. 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.101962
3
Al-Samrai O. a.A. Samarrai O. R. A. Yousef T. A. Abou-Krisha M. M. Alhalafi M. H. Al-Janabi A. S. (2024). Synthesis, spectroscopic, DFT, anticancer evaluation and enzyme inhibition studies of platinum (II) complexes with 1-methyl-1H-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrazole-5-thiol and phosphine ligands: crystal structure of [pt (mtzt) 2 (dppe)]. Chem. Phys. Impact8, 100581. 10.1016/j.chphi.2024.100581
4
Albesa I. Becerra M. C. Battán P. C. Páez P. L. (2004). Oxidative stress involved in the antibacterial action of different antibiotics. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.317 (2), 605–609. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.03.085
5
Ali J. M. Shaheed D. Q. Radhi A. J. Alkhafaji H. A. A. R. A. Kadhim H. (2023). Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of tetrazole derivatives. Int. J. Adv. Chem. Res.5 (1), 41–46. 10.33545/26646781.2023.v5.i1a.142
6
Allen F. H. Groom C. R. Liebeschuetz J. W. Bardwell D. A. Olsson T. S. Wood P. A. (2012). The hydrogen bond environments of 1 H-tetrazole and tetrazolate rings: the structural basis for tetrazole–carboxylic acid bioisosterism. J. Chem. Inf. Model52 (3), 857–866. 10.1021/ci200521k
7
Amanpour T. Mirzaei P. Bazgir A. (2012). Isocyanide-based four-component synthesis of ferrocenyl 1, 5-disubstituted tetrazoles. Tetrahedron Lett.53 (11), 1421–1423. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.01.038
8
Amengual-Cladera E. Morla-Barcelo P. M. Morán-Costoya A. Sastre-Serra J. Pons D. G. Valle A. et al (2024). Metformin: from diabetes to Cancer—Unveiling molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Biology13 (5), 302. 10.3390/biology13050302
9
Asiri Y. I. Syed T. Maringanti T. C. Eppakayala L. Puli V. S. (2024). Synthesis and biological evaluation of tetrazole ring incorporated oxazole-pyrimidine derivatives as anticancer agents. Synth. Commun.54 (10), 802–814. 10.1080/00397911.2024.2331922
10
Atif A. Ait Sir H. (2025). Progress in the synthesis of tetrazoles. A brief review. Org. Prep. Proced. Int., 1–16. 10.1080/00304948.2025.2543253
11
Ballatore C. Huryn D. M. Smith III A. B. (2013). Carboxylic acid (bio) isosteres in drug design. ChemMedChem8 (3), 385–395. 10.1002/cmdc.201200585
12
Baranello L. Kouzine F. Levens D. (2025). Topoisomerase regulation of cancer gene expression. Annu. Rev. Biochem.94, 333–359. 10.1146/annurev-biochem-091724-010717
13
Beebany S. (2023). Synthesis, characterization of New Phenylene Bis Tetrazole and Bis benzoxazepinedione derivatives from some Bis imines with its biological activity assessment. Kirkuk J. Sci.18 (3), 21–31. 10.32894/kujss.2023.143144.1119
14
Belz G. G. Butzer R. Kober S. Mang C. Mutschler E. (1999). Time course and extent of angiotensin II antagonism after irbesartan, losartan, and valsartan in humans assessed by angiotensin II dose response and radioligand receptor assay. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.66 (4), 367–373. 10.1053/cp.1999.v66.a101162
15
Bhattacharya S. Chaudhuri P. (2008). Medical implications of benzimidazole derivatives as drugs designed for targeting DNA and DNA associated processes. Curr. Med. Chem.15 (18), 1762–1777. 10.2174/092986708785133013
16
Billes F. Endrédi H. Keresztury G. (2000). Vibrational spectroscopy of triazoles and tetrazole. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem.530 (1-2), 183–200. 10.1016/S0166-1280(00)00340-7
17
Biot C. Bauer H. Schirmer R. H. Davioud-Charvet E. (2004). 5-substituted tetrazoles as bioisosteres of carboxylic acids. Bioisosterism and mechanistic studies on glutathione reductase inhibitors as antimalarials. J. Med. Chem.47 (24), 5972–5983. 10.1021/jm0497545
18
Bissantz C. Kuhn B. Stahl M. (2010). A medicinal chemist’s guide to molecular interactions. J. Med. Chem.53 (14), 5061–5084. 10.1021/jm100112j
19
Bond A. D. Fleming A. Gaire J. Kelleher F. McGinley J. McKee V. et al (2012). Coordination studies of copper (II), cobalt (II) and iron (II) with isomeric pyridyl–tetrazole ligands. Polyhedron.33 (1), 289–296. 10.1016/j.poly.2011.11.038
20
Bourhou C. Benouda H. Bellaouchi R. Merzouki M. Fraj E. Harit T. et al (2023). Synthesis of novel tetrazolic derivatives and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. J. Mol. Struct.1278, 134913. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.134913
21
Bugalho S. C. Maçôas E. M. Cristiano M. L. S. Fausto R. (2001). Low temperature matrix-isolation and solid state vibrational spectra of tetrazole. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.3 (17), 3541–3547. 10.1039/b103344c
22
Chawla P. Teli G. Gill R. K. Narang R. K. (2021). An insight into synthetic strategies and recent developments of dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors. ChemistrySelect6 (43), 12101–12145. 10.1002/slct.202102555
23
Chawla P. A. Teli G. Pathania S. Singh S. Srivastava V. (2023). Exploration of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer potential of substituted 4-thiazolidinone derivatives: synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd.43 (1), 597–618. 10.1080/10406638.2021.2019796
24
Chrysostomou D. Roberts L. A. Marchesi J. R. Kinross J. M. (2023). Gut microbiota modulation of efficacy and toxicity of cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Gastroenterology164 (2), 198–213. 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.10.018
25
Chukwudi C. U. (2016). rRNA binding sites and the molecular mechanism of action of the tetracyclines. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.60 (8), 4433–4441. 10.1128/aac.00594-16
26
Collins J. A. Osheroff N. (2024). Gyrase and topoisomerase IV: recycling old targets for new antibacterials to combat fluoroquinolone resistance. ACS Infect. Dis.10 (4), 1097–1115. 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00128
27
Devi M. Jaiswal S. Yaduvanshi N. Kaur N. Kishore D. Dwivedi J. et al (2023). Design, synthesis, antibacterial evaluation and docking studies of triazole and tetrazole linked 1, 4‐benzodiazepine nucleus via click approach. ChemistrySelect8 (6), e202204710. 10.1002/slct.202204710
28
Dighe S. N. Jain K. S. Srinivasan K. V. (2009). A novel synthesis of 1-aryl tetrazoles promoted by employing the synergy of the combined use of DMSO and an ionic liquid as the solvent system at ambient temperature. Tetrahedron. Lett.50 (45), 6139–6142. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.08.063
29
Disli A. Yucesoy E. E. Ozturk A. Dilek G. (2023). Synthesis and biological studies of novel hydroxyacetophenone-tetrazole hybrids. Org. Commun.16 (2), 86. 10.25135/acg.oc.148.2302.2696
30
Dişli A. Aksu E. Doyduk D. Akdoğan N. Cuhaci U. Özadam N. et al (2025). Design, synthesis, computational insights, and evaluation of Tetrazole containing donepezil derivatives as antibiofilm, antimicrobial, and anticancer agents with Doxorubicin. J. Mol. Struct.1349, 143713. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2025.143713
31
D’Atanasio N. Capezzone de Joannon A. Di Sante L. Mangano G. Ombrato R. Vitiello M. et al (2020). Antibacterial activity of novel dual bacterial DNA type II topoisomerase inhibitors. PLoS One15 (2), e0228509. 10.1371/journal.pone.0228509
32
Ehmann D. E. Lahiri S. D. (2014). Novel compounds targeting bacterial DNA topoisomerase/DNA gyrase. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.18, 76–83. 10.1016/j.coph.2014.09.007
33
El-Sewedy A. El-Bordany E. A. Mahmoud N. F. Ali K. A. Ramadan S. K. (2023). One-pot synthesis, computational chemical study, molecular docking, biological study, and in silico prediction ADME/pharmacokinetics properties of 5-substituted 1 H-tetrazole derivatives. Sci. Rep.13 (1), 17869. 10.1038/s41598-023-44615-4
34
Elewa S. I. Fatthallah N. A. Nessim M. I. El-Farargy A. F. (2020). Synthesis and characterization of some tetrazoles and their prospective for aerobic micro-fouling mitigation. Arab. J. Chem.13 (12), 8750–8757. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.10.005
35
Elgemeie G. H. Mohamed-Ezzat R. A. (2022). New strategies targeting cancer metabolism: anticancer drugs, synthetic analogues and Antitumor agents. Elsevier.
36
Fief C. A. Hoang K. G. Phipps S. D. Wallace J. L. Deweese J. E. (2019). Examining the impact of antimicrobial fluoroquinolones on human DNA topoisomerase IIα and IIβ. ACS omega4 (2), 4049–4055. 10.1021/acsomega.8b03428
37
Fribley A. Wang C.-Y. (2006). Proteasome inhibitor induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer. Biol. Ther.5 (7), 745–748. 10.4161/cbt.5.7.2971
38
Gailan M. H. Hussein M. S. Elmasry G. F. (2024). Synthesis, ADME profiling, antibacterial screening and molecular docking of some new tetrazole‐heterocycle hybrids. ChemistrySelect9 (22), e202401118. 10.1002/slct.202401118
39
Gallego-Yerga L. Chiliquinga A. J. Peláez R. (2023). Novel tetrazole derivatives targeting tubulin endowed with antiproliferative activity against glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (13), 11093. 10.3390/ijms241311093
40
Gandham S. K. Kudale A. A. Allaka T. R. Chepuri K. Jha A. (2023). New tetrazolopyrrolidine-1, 2, 3-triazole analogues as potent anticancer agents: design, synthesis and molecular docking studies. Mol. Divers.28 (5), 3313–3329. 10.1007/s11030-023-10762-z
41
Gujja V. Sadineni K. Epuru M. R. Rao Allaka T. Banothu V. Gunda S. K. et al (2023). Synthesis and in silico studies of some new 1, 2, 3‐Triazolyltetrazole bearing indazole derivatives as potent antimicrobial agents. Chem. Biodivers.20 (12), e202301232. 10.1002/cbdv.202301232
42
Han L. Wang Z. Wang D. Gao Z. Hu S. Shi D. et al (2024). Mechanisms and otoprotective strategies of programmed cell death on aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol.11, 1305433. 10.3389/fcell.2023.1305433
43
Harit T. Dib I. Yahyaoui M. I. Asehraou A. Yahyi A. Ziyyat A. et al (2023). Pyrazole-tetrazole hybrid compounds: synthesis, characterization and their biological activities. Chem. Data. Collect.45, 101026. 10.1016/j.cdc.2023.101026
44
He M. Li Y.-J. Shao J. Fu C. Li Y.-S. Cui Z.-N. (2023). 2, 5-Disubstituted furan derivatives containing imidazole, triazole or tetrazole moiety as potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem.131, 106298. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106298
45
Henches R. Ozga T. Gao Y. Tu Z. Zhang T. Francis C. L. (2023). Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-(Tetrazol-5-yl) sulfonylacetamides as inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium marinum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.92, 129391. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129391
46
Heravi M. M. Fazeli A. Oskooie H. A. Beheshtiha Y. S. Valizadeh H. (2012). Click synthesis of 5-substituted 1H-tetrazoles from aldehydes, hydroxylamine, and [bmim] N3 via one-pot, three-component reaction. Synlett23 (20), 2927–2930. 10.1055/s-0032-1317671
47
Herr R. J. (2002). 5-Substituted-1H-tetrazoles as carboxylic acid isosteres: medicinal chemistry and synthetic methods. Bioorg. Med. Chem.10 (11), 3379–3393. 10.1016/s0968-0896(02)00239-0
48
Huang J. Gong C. Zhou A. (2023). Modulation of gut microbiota: a novel approach to enhancing the effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol.15, 17588359231204854. 10.1177/17588359231204854
49
Husain A. Devi C. S. Anupama B. (2023). Synthesis, characterization, DNA binding, protein binding, antioxidant and anti microbial activity of tetrazole ring based complexes. J. Mol. Struct.1291, 135963. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135963
50
Ishihara K. Shioiri T. Matsugi M. (2020). An expeditious approach to tetrazoles from amides utilizing phosphorazidates. Org. Lett.22 (16), 6244–6247. 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01890
51
Ishihara K. Ishihara K. Tanaka Y. Shioiri T. Matsugi M. (2022). Practical synthesis of tetrazoles from amides and phosphorazidates in the presence of aromatic bases. Tetrahedron108, 132642. 10.1016/j.tet.2022.132642
52
Jagadeesan S. Karpagam S. (2023). Novel series of N-acyl substituted indole based piperazine, thiazole and tetrazoles as potential antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant and cytotoxic agents, and their docking investigation as potential Mcl-1 inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct.1271, 134013. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134013
53
Jaiswal S. Verma K. Dwivedi J. Sharma S. (2024). Tetrazole derivatives in the management of neurological disorders: recent advances on synthesis and pharmacological aspects. Eur. J. Med. Chem.271, 116388. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116388
54
Jarupula V. E P. K. Bujji S. Shivarathri P. Neeradi S. Morthad M. et al (2023). Synthesis of novel hybrids containing 1, 2, 3-triazole-linked tetrazole moieties, evaluation of anticancer activity and molecular docking studies. Russ. J. Gen. Chem.93 (Suppl. 4), S849–S857. 10.1134/s1070363223170012
55
Jin T. Kamijo S. Yamamoto Y. (2004). Synthesis of 1-substituted tetrazoles via the acid-catalyzed [3+ 2] cycloaddition between isocyanides and trimethylsilyl azide. Tetrahedron Lett.45 (51), 9435–9437. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2004.10.103
56
Karamanolis N. N. Kounatidis D. Vallianou N. G. Dimitriou K. Tsaroucha E. Tsioulos G. et al (2024). Unraveling the anti-cancer mechanisms of antibiotics: current insights, controversies, and future perspectives. Antibiotics14 (1), 9. 10.3390/antibiotics14010009
57
Kathiravan M. K. Khilare M. M. Nikoomanesh K. Chothe A. S. Jain K. S. (2013). Topoisomerase as target for antibacterial and anticancer drug discovery. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem.28 (3), 419–435. 10.3109/14756366.2012.658785
58
Kaur K. Verma H. Gangwar P. Dhiman M. Jaitak V. (2024). Design, synthesis, in vitro and in silico evaluation of indole-based tetrazole derivatives as putative anti-breast cancer agents. RSC Med. Chem.15 (4), 1329–1347. 10.1039/d3md00730h
59
Khramchikhin A. V. Skryl’nikova M. A. Gureev M. A. Zarubaev V. V. Esaulkova I. L. Ilyina P. A. et al (2023). Novel 1, 2, 4-Triazole-and Tetrazole-Containing 4 H-Thiopyrano [2, 3-b] quinolines: synthesis based on the Thio-Michael/aza-Morita–Baylis–Hillman Tandem reaction and investigation of antiviral activity. Molecules28 (21), 7427. 10.3390/molecules28217427
60
Khurshid M. N. Jumaa F. H. Jassim S. S. (2022). Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the biological activity of tetrazole compounds derived from the nitrogenous base uracil. Mater. Today Proc.49, 3630–3639. 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.203
61
Kiselev V. G. Cheblakov P. B. Gritsan N. P. (2011). Tautomerism and thermal decomposition of tetrazole: high-level ab initio study. J. Phys. Chem. A115 (9), 1743–1753. 10.1021/jp112374t
62
Kovacic P. Osuna J. A. (2000). Mechanisms of anti-cancer agents emphasis on oxidative stress and electron transfer. Curr. Pharm. Des.6 (3), 277–309. 10.2174/1381612003401046
63
Li X. Zhang S. Guo G. Han J. Yu J. (2022). Gut microbiome in modulating immune checkpoint inhibitors. EBioMedicine82, 104163. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104163
64
Liang X. Wu Q. Luan S. Yin Z. He C. Yin L. et al (2019). A comprehensive review of topoisomerase inhibitors as anticancer agents in the past decade. Eur. J. Med. Chem.171, 129–168. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.034
65
Lindqvist L. Pelletier J. (2009). Inhibitors of translation initiation as cancer therapeutics. Future Med. Chem.1 (9), 1709–1722. 10.4155/fmc.09.122
66
Liu W. Guo Y. Han C. Huang X. (2008). Characteristic fragmentation behavior of 5-[1-aryl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-1H-tetrazole by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Life Sci. J.5 (2), 25–29.
67
Lodovichi S. Cervelli T. Pellicioli A. Galli A. (2020). Inhibition of DNA repair in cancer therapy: toward a multi-target approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (18), 6684. 10.3390/ijms21186684
68
Loganathan V. Akbar I. Ahamed A. Alodaini H. A. Hatamleh A. A. Abuthkir M. H. S. et al (2024). Synthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of tetrazole N-Mannich base derivatives: investigation of DFT calculation, molecular docking, and Swiss ADME studies. J. Mol. Struct.1300, 137239. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.137239
69
Malik M. A. Dar O. A. Gull P. Wani M. Y. Hashmi A. A. (2018). Heterocyclic Schiff base transition metal complexes in antimicrobial and anticancer chemotherapy. MedChemComm9 (3), 409–436. 10.1039/c7md00526a
70
Manwar H. Q. Al-Shuhaib Z. Hussein K. A. Ismael S. M. (2025). Synthesis, computational and anti-cancer activity studies of new 5-substituted tetrazole-1-yl acetamides. Chem. Afr.8 (4), 1271–1286. 10.1007/s42250-025-01207-1
71
Martelli G. Giacomini D. (2018). Antibacterial and antioxidant activities for natural and synthetic dual-active compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem.158, 91–105. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.009
72
Masood A. Khan M. A. Ahmad I. Breena Raza A. Ullah F. et al (2023). Synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of 2-(N-(2′-(2H-tetrazole-5-yl)-1, 1′-biphenyl-4yl-methyl)-pentanamido)-3-methyl Butanoic acid derivatives. Molecules28 (4), 1908. 10.3390/molecules28041908
73
Megha G. Bodke Y. (2023). Synthesis of new 4-{2′-(2 H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-1, 1′-biphenyl-4-yl methyl}(2-R-2-oxoethyl) amino benzoic acid derivatives as potent biological agents with docking studies. Russ. J. Gen. Chem.93 (6), 1535–1546. 10.1134/s1070363223060269
74
Metre T. V. Kamble R. R. Kodasi B. R. Bheemayya L. Nadoni V. B. Nayak M. R. et al (2024). Design, synthesis and characterization of novel 1, 5-and 2, 5-coumarin-4-yl-methyl regioisomers of 5-pyrazol-3-yl-tetrazoles as promising anticancer and antifungal agents. J. Mol. Struct.1312, 138541. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.138541
75
Meyer E. A. Castellano R. K. Diederich F. (2003). Interactions with aromatic rings in chemical and biological recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.42 (11), 1210–1250. 10.1002/anie.200390319
76
Mihina J. S. Herbst R. M. (1950). The reaction of nitriles with hydrazoic acid: synthesis of monosubstituted tetrazoles. J. Org. Chem.15 (5), 1082–1092. 10.1021/jo01151a027
77
Mikolaichuk O. Protas A. Popova E. Lutsev M. Smirnov E. Y. Golotin V. et al (2023). Synthesis and Study of some properties of new tetrazole-containing derivatives of Morpholin-4-yl-1, 3, 5-triazine and 4-Methylpiperidin-1-yl-1, 3, 5-triazine. Russ. J. Gen. Chem.93 (5), 1050–1063. 10.1134/s1070363223050055
78
Mirzaei S. Gholami M. H. Zabolian A. Saleki H. Bagherian M. Torabi S. M. et al (2023). Resveratrol augments doxorubicin and cisplatin chemotherapy: a novel therapeutic strategy. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol.16 (3), 280–306. 10.2174/1874467215666220415131344
79
Mohite P. Pandhare R. Khanage S. Bhaskar V. (2009). A novel approach for synthesis of substituted tetrazoles. Dig. J. Nanomat. Biostruct. 4, 803–807.
80
Mourenza Á. Gil J. A. Mateos L. M. Letek M. (2020). Oxidative stress-generating antimicrobials, a novel strategy to overcome antibacterial resistance. Antioxidants9 (5), 361. 10.3390/antiox9050361
81
Movsisyan M. Delbeke E. Berton J. Battilocchio C. Ley S. Stevens C. (2016). Taming hazardous chemistry by continuous flow technology. Chem. Soc. Rev.45 (18), 4892–4928. 10.1039/c5cs00902b
82
Muhammed Aziz D. Ali Hassan S. (2024). Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of Tetrazole derivatives with Pyrrole‐2, 5‐Dione moieties as urease inhibitors: exploring structure‐activity relationships and computational insights. ChemistrySelect9 (23), e202401259. 10.1002/slct.202401259
83
Nagaraju B. Rajeswari M. Mounika T. Rajitha G. Kumar G. S. Rao C. V. et al (2024). Synthesis and anti-microbial studies of new series of 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrazole integrated thieno [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct.1295, 136485. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136485
84
Nammalwar B. Muddala N. P. Pitchimani R. Bunce R. A. (2015). OSU-6: a highly efficient, metal-free, heterogeneous catalyst for the click synthesis of 5-benzyl and 5-aryl-1 H-tetrazoles. Molecules20 (12), 22757–22766. 10.3390/molecules201219881
85
Narkedimilli V. K. K. Allaka T. R. Balli R. Bhoomandla S. Purumandla S. R. Venkateswarlu K. (2025). Design, synthesis, in vitro and in silico studies of 1, 2, 3-triazole incorporated tetrazoles as potent antitubercular agents. J. Mol. Struct.1327, 141242. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.141242
86
Olejarz W. Sadowski K. Roszkowski P. Bielenica A. Wiśniewski M. Struga M. et al (2025). Design and in vitro evaluation of novel tetrazole derivatives of dianisidine as anticancer agents targeting Bcl-2 apoptosis regulator. Sci. Rep.15 (1), 17634. 10.1038/s41598-025-02781-7
87
Oulous A. Harit T. Yahyaoui M. I. Asehraou A. Malek F. (2023). New family of tetrazole-pyrazole compounds: synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activity and docking study. Arab. J. Chem.16 (11), 105268. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105268
88
Pal R. Teli G. Akhtar M. J. Matada G. S. P. (2024). Synthetic product-based approach toward potential antileishmanial drug development. Eur. J. Med. Chem.263, 115927. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115927
89
Palimkar S. S. Siddiqui S. A. Daniel T. Lahoti R. J. Srinivasan K. V. (2003). Ionic liquid-promoted regiospecific Friedlander annulation: novel synthesis of quinolines and fused polycyclic quinolines. J. Org. Chem.68 (24), 9371–9378. 10.1021/jo035153u
90
Pejčić T. Todorović Z. Đurašević S. Popović L. (2023). Mechanisms of prostate cancer cells survival and their therapeutic targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (3), 2939. 10.3390/ijms24032939
91
Pfab C. Schnobrich L. Eldnasoury S. Gessner A. El-Najjar N. (2021). Repurposing of antimicrobial agents for cancer therapy: what do we know?Cancers13 (13), 3193. 10.3390/cancers13133193
92
Pokhodylo N. Finiuk N. Klyuchivska O. Stoika R. Matiychuk V. Obushak M. (2023). Bioisosteric replacement of 1H-1, 2, 3-triazole with 1H-tetrazole ring enhances anti-leukemic activity of (5-benzylthiazol-2-yl) benzamides. Eur. J. Med. Chem.250, 115126. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115126
93
Pommier Y. Leo E. Zhang H. Marchand C. (2010). DNA topoisomerases and their poisoning by anticancer and antibacterial drugs. Chem. Biol.17 (5), 421–433. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.04.012
94
Popova E. A. Protas A. V. Trifonov R. E. (2017). Tetrazole derivatives as promising anticancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem.17 (14), 1856–1868. 10.2174/1871520617666170327143148
95
Puigvert J. C. Sanjiv K. Helleday T. (2016). Targeting DNA repair, DNA metabolism and replication stress as anti‐cancer strategies. FEBS J283 (2), 232–245. 10.1111/febs.13574
96
Qi D. Liu Y. Li J. Huang J. H. Hu X. Wu E. (2022). Salinomycin as a potent anticancer stem cell agent: state of the art and future directions. Med. Res. Rev.42 (3), 1037–1063. 10.1002/med.21870
97
Rajeswari M. Nagaraju B. Yasmintaj S. Muralidhar P. Rao C. V. Karunakar P. et al (2024). Design, synthesis, biological evolution and in silico studies of a novel 1, 2, 3, 4‐tetrazole fused with 1, 3, 4‐thiadiazole‐2‐amine derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem.61 (7), 1116–1124. 10.1002/jhet.4831
98
Rajeswari M. Nagaraju B. Balaji H. Ali S. Balaji M. Karunakar P. et al (2025). Design, synthesis, biological activity, molecular docking and dynamic studies of novel benzimidazole‐integrated 1, 2, 3, 4‐Tetrazole derivatives. Chem. Biodivers.22 (9), e202500353. 10.1002/cbdv.202500353
99
Ramanathan M. Wang Y.-H. Liu S.-T. (2015). One-pot reactions for synthesis of 2, 5-substituted tetrazoles from aryldiazonium salts and amidines. Org. Lett.17 (23), 5886–5889. 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03068
100
Roos W. P. Thomas A. D. Kaina B. (2016). DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer.16 (1), 20–33. 10.1038/nrc.2015.2
101
Roszkowski P. Szymańska-Majchrzak J. Koliński M. Kmiecik S. Wrzosek M. Struga M. et al (2021). Novel tetrazole-based antimicrobial agents targeting clinical bacteria strains: exploring the inhibition of staphylococcus aureus dna topoisomerase iv and gyrase. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (1), 378. 10.3390/ijms23010378
102
Ruh C. Banjade R. Mandadi S. Marr C. Sumon Z. Crane J. K. (2017). Immunomodulatory effects of antimicrobial drugs. Immunol. Investig.46 (8), 847–863. 10.1080/08820139.2017.1373900
103
Saleh M. J. Ahmed S. E. Saleh J. N. (2025). Synthesis, characterization of Tetrazole derivatives, and evaluation of bacterial and fungal activity. Asian. J. Chem. Sci.15 (2), 123–134. 10.9734/ajocs/2025/v15i2364
104
Sánchez-López E. Gomes D. Esteruelas G. Bonilla L. Lopez-Machado A. L. Galindo R. et al (2020). Metal-based nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: an overview. Nanomaterials10 (2), 292. 10.3390/nano10020292
105
Shestakova T. S. Shenkarev Z. O. Deev S. L. Chupakhin O. N. Khalymbadzha I. A. Rusinov V. L. et al (2013). Long-Range 1H–15N J couplings providing a method for direct studies of the structure and Azide–Tetrazole equilibrium in a series of azido-1, 2, 4-triazines and Azidopyrimidines. J. Org. Chem.78 (14), 6975–6982. 10.1021/jo4008207
106
Shie J.-J. Fang J.-M. (2007). Microwave-assisted one-pot tandem reactions for direct conversion of primary alcohols and aldehydes to triazines and tetrazoles in aqueous media. J. Org. Chem.72 (8), 3141–3144. 10.1021/jo0625352
107
Showkat M. Beigh M. A. Andrabi K. I. (2014). mTOR signaling in protein translation regulation: implications in cancer genesis and therapeutic interventions. Mol. Biol. Int.2014 (1), 1–14. 10.1155/2014/686984
108
Shui L. Yang X. Li J. Yi C. Sun Q. Zhu H. (2020). Gut microbiome as a potential factor for modulating resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol.10, 2989. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02989
109
Singh L. P. Gugulothu S. Perusomula R. Mishra A. Bhavani P. D. Singh S. et al (2023). Synthesis of some Tetrazole and Thiazolidine-4-One derivatives of schiff base by using ionic liquids as catalyst and evaluation of their antifungal and antibacterial activity. Eur. Chem. Bull.12, 281–297.
110
Slack J. L. Causey C. P. Thompson P. R. (2011). Protein arginine deiminase 4: a target for an epigenetic cancer therapy. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci.68, 709–720. 10.1007/s00018-010-0480-x
111
Subramanian V. Knight J. S. Parelkar S. Anguish L. Coonrod S. A. Kaplan M. J. et al (2015). Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of tetrazole analogs of Cl-amidine as protein arginine deiminase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem.58 (3), 1337–1344. 10.1021/jm501636x
112
Swift L. H. Golsteyn R. M. (2014). Genotoxic anti-cancer agents and their relationship to DNA damage, mitosis, and checkpoint adaptation in proliferating cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci.15 (3), 3403–3431. 10.3390/ijms15033403
113
Tjampakasari C. R. (2024). Dihydrofolate reductase (dfr) and dihydropteroate synthase (sul) gene mutations in Escherichia coli trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistance. IJOBB8 (1), 51–59.
114
Tsukamoto T. Nakagawa M. Kiriyama Y. Toyoda T. Cao X. (2017). Prevention of gastric cancer: eradication of Helicobacter pylori and beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci.18 (8), 1699. 10.3390/ijms18081699
115
Ulular M. Sarı N. Han F. Öğütçü H. Hasanoğlu Özkan E. (2024). Synthesis, antimicrobial, and DNA-binding evaluation of novel schiff bases containing tetrazole moiety and their Ni (II) and Pt (II) complexes. Pharm. Chem. J.57 (10), 1609–1620. 10.1007/s11094-024-03056-7
116
Uppadhayay R. Kumar A. Teotia J. Singh A. (2022). Multifaceted chemistry of tetrazole. Synthesis, uses, and pharmaceutical applications. Russ. J. Org. Chem.58 (12), 1801–1811. 10.1134/s1070428022120090
117
Vanam N. R. Anireddy J. S. (2023). Synthesis and biological evaluation of tetrazole fused imidazopyridine derivatives as anticancer agents. Chem. Data. Collect.48, 101092. 10.1016/j.cdc.2023.101092
118
Varala R. Babu B. H. (2018). “A click chemistry approach to tetrazoles: recent advances,” in Molecular docking. London: IntechOpen.
119
Varshneya M. M. Chawlab P. A. Telib G. Hussainc A. (2023). Synthesis, characterization, in vitro antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory evaluations of {5’-(substituted aryl)-2-furanyl}-3, 4-dihydro-1h-pyrimidine-2-one derivatives. Indian Drugs60 (03), 17–29. 10.53879/id.60.03.13669
120
Vellaiyan V. Allaka T. R. Bhoomandla S. Vudari B. Chepuri K. Nagarajaiah H. (2025). Design, synthesis, and computational docking techniques of novel 1, 2, 3‒triazole‒tetrazole hybrids as potential leads in the development of anticancer agents. J. Mol. Struct.1327, 141189. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.141189
121
Verma A. Kaur B. Venugopal S. Wadhwa P. Sahu S. Kaur P. et al (2022). Tetrazole: a privileged scaffold for the discovery of anticancer agents. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des.100 (3), 419–442. 10.1111/cbdd.14103
122
Vishwakarma R. Gadipelly C. Mannepalli L. K. (2022). Advances in tetrazole Synthesis–an overview. ChemistrySelect7 (29), e202200706. 10.1002/slct.202200706
123
Wang W.-X. Cai H.-L. Xiong R.-G. (2013). Hydrothermal synthesis method of 5-(4′-methylbiphenyl-2-yl)-1H-tetrazole. Chin. Chem. Lett.24 (9), 783–785. 10.1016/j.cclet.2013.04.041
124
Wittenberger S. J. (1994). Recent developments in tetrazole chemistry. A review. Org. Prep. Proced. Int.26 (5), 499–531. 10.1080/00304949409458050
125
Xu Y. Yuan D. Zhang Y. Zhang Y. He P. Ren Z.-L. (2024). Design and synthesis of tetrazole-linked quinazoline derivatives and their bioactivities against Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB905. Tetrahedron Lett.140, 155046. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2024.155046
126
Yakkala P. A. Penumallu N. R. Shafi S. Kamal A. (2023). Prospects of topoisomerase inhibitors as promising anti-cancer agents. Pharmaceuticals16 (10), 1456. 10.3390/ph16101456
127
Yu H. Lou J. R. Ding W.-Q. (2010). Clioquinol independently targets NF-kappaB and lysosome pathways in human cancer cells. Anticancer Res.30 (6), 2087–2092.
128
Yuan Y. Li M. Apostolopoulos V. Matsoukas J. Wolf W. M. Blaskovich M. A. et al (2024). Tetrazoles: a multi-potent motif in drug design. Eur. J. Med. Chem.279, 116870. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116870
129
Zala M. Vora J. J. Khedkar V. M. (2023). Synthesis, characterization, antitubercular activity, and molecular docking studies of pyrazolylpyrazoline-clubbed triazole and tetrazole hybrids. ACS Omega8 (23), 20262–20271. 10.1021/acsomega.2c07267
130
Zhang S. Chen D.-C. (2019). Facing a new challenge: the adverse effects of antibiotics on gut microbiota and host immunity. Chin. Med. J.132 (10), 1135–1138. 10.1097/cm9.0000000000000245
Summary
Keywords
tetrazole, anticancer, antimicrobial, synthetic strategy, structure–activity relationships
Citation
Maji L, Teli G, Pal R, Maheshwari N, Soni PK, Matada GSP, Rathore MS, Saravanan V and Muthukumaradoss K (2025) Exploring tetrazole chemistry: synthetic techniques, structure–activity relationship, and pharmacological insights in antimicrobial and anticancer therapy. Front. Chem. 13:1700143. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1700143
Received
06 September 2025
Revised
17 October 2025
Accepted
20 October 2025
Published
08 December 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Anthony J. Burke, University of Coimbra, Portugal
Reviewed by
Pedro Brandão, Egas Moniz Center for Interdisciplinary Research (CiiEM), Portugal
Ronaldo De Oliveira, Federal Rural University of Pernambuco, Brazil
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Maji, Teli, Pal, Maheshwari, Soni, Matada, Rathore, Saravanan and Muthukumaradoss.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kathiravan Muthukumaradoss, kathirak@srmist.edu.in; Ghanshyam Teli, ghanshyamsahu203@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.