- 1Department of Nutrition, College of Medicine and Health Science, United Arab Emirates University, AlAin, United Arab Emirates
- 2Department of Biology, College of Science, United Arab Emirates University, AlAin, United Arab Emirates
The pharmacological potential of Nigella sativa and Ziziphus lotus, two medicinal plants native to the United Arab Emirates (UAE), is explored in the context of sustainable healthcare strategies. Both plants have demonstrated notable antidiabetic and antimicrobial effects in preclinical studies. For instance, thymoquinone from Nigella sativa has shown glucose-lowering efficacy comparable to metformin in rodent models, while Ziziphus lotus extracts have outperformed acarbose in inhibiting carbohydrate-digesting enzymes. This paper synthesizes findings from ethnobotanical surveys, pharmacological research, and clinical literature to assess their therapeutic relevance. Additionally, it addresses challenges in standardization, sustainable harvesting, and environmental influence on phytochemical composition. While current evidence is promising, gaps remain in clinical validation and regulatory integration. This review aims to inform future research and policy, supporting the incorporation of UAE-native medicinal plants into evidence-based healthcare practices.
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus and microbial infections remain two of the leading causes of mortality worldwide and pose an escalating public health crisis. According to the International Diabetes Federation (1), approximately 3.4 million deaths were attributable to diabetes in 2024 equating to one death every nine seconds with 43% of adults with diabetes remaining undiagnosed. The World Health Organization reported 1.6 million deaths directly caused by diabetes in 2021, nearly half of which occurred before the age of 70. With ageing populations, sedentary lifestyles, and the global rise in obesity, the number of adults living with diabetes has quadrupled since 1990 and now exceeds 800 million. Global prevalence has doubled from 7 to 14% between 1990 and 2022. This epidemic imposes a substantial economic burden, with global diabetes-related healthcare expenditure surpassing US$ 1 trillion annually and high blood glucose responsible for about 11% of cardiovascular deaths (1, 2).
Microbial infections and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) further intensify the threat. In 2019, infectious diseases accounted for 13.7 million deaths globally, with bacterial infections contributing to 7.7 million of these. Alarmingly, just five pathogens Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) were responsible for over half of the mortality (3). Furthermore, 4.95 million deaths were associated with bacterial AMR, with 1.27 million directly attributable to resistant pathogens. Forecasts suggest that without global intervention, multidrug-resistant (MDR) infections may cause up to 10 million deaths annually by 2050, while AMR is projected to contribute at least US$ 1 trillion in additional healthcare costs by mid-century (2, 4).
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are particularly vulnerable to microbial infections due to hyperglycemia-induced immune dysfunction, including reduced neutrophil activity and impaired antioxidant defenses (5, 6). Chronic hyperglycemia promotes tissue damage, poor wound healing, and microbial colonization—conditions that contribute to severe outcomes such as diabetic foot infections (DFIs), urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and sepsis. The clinical management of these infections has become increasingly difficult due to MDR organisms and the formation of biofilms, which enhance microbial persistence and antibiotic tolerance (7, 8).
Current treatment approaches for diabetic infections typically rely on broad-spectrum antibiotics, including beta-lactams, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and aminoglycosides. In severe or polymicrobial infections, agents such as piperacillin–tazobactam, linezolid, or carbapenems are commonly employed (9, 10). However, increasing resistance and the limited pipeline of new antimicrobials demand urgent exploration of alternative strategies.
Mechanistically, microbial resistance is driven by multiple factors: biofilm matrices limit drug penetration and harbor “persister” cells; efflux systems such as MexAB-OprM in P. aeruginosa expel a wide range of antibiotics; and enzymatic degradation via β-lactamases or oxidative stress responses further undermine treatment efficacy (8, 11, 12). Addressing these complex challenges requires innovative and integrated therapeutic solutions.
In response, recent advances highlight the potential of repurposed antidiabetic drugs (e.g., metformin, DPP-4 inhibitors) and plant-derived antimicrobials rich in flavonoids, alkaloids, and polyphenols, which exhibit both hypoglycemic and antibacterial effects (5, 6, 13). Compounds from plants such as Mangifera indica, Prunella vulgaris, and Camellia sinensis have demonstrated antimicrobial action against MDR strains of E. coli, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa (13). These emerging therapies not only reduce infection risk but also complement existing pharmacological regimens, offering promising alternatives in the fight against diabetes-related infections and the AMR crisis.
Medicinal plants (MP) have historically been pivotal in both traditional and modern medicine, offering a wide array of therapeutic benefits. The rising interest in plant-based treatments reflects the global pursuit of alternative and complementary solutions for addressing chronic health issues, including metabolic disorders, and infectious diseases (14, 15). The United Arab Emirates (UAE), characterized by its unique desert vegetation and rich tradition of herbal medicine, is home to pharmacologically significant plants such as Nigella sativa (N. sativa) (black seed) and Ziziphus lotus (Z. lotus) (sidr, jujube) (16).
Nigella sativa, widely cultivated in the UAE, is renowned for its bioactive compounds such as thymoquinone, quercetin, and p-cymene, which exhibit potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic properties. Similarly, Z. lotus, a native species thriving in the region’s harsh climate, contains diverse secondary metabolites, including flavonoids and saponins, known for their antidiabetic and antimicrobial activity (17–20). Notably, N. sativa and Z. lotus are rich in phytochemicals such as thymoquinone, flavonoids, alkaloids and saponins, which have demonstrated antidiabetic, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities in preclinical studies. These multifunctional properties make them attractive candidates for developing novel botanical therapeutics (14–20). The therapeutic potential of these plants aligns with the pressing need for innovative approaches to mitigate the growing burden of non-communicable diseases and antimicrobial resistance in the UAE (21–23).
This review integrates insights from ethnobotanical studies, pharmacological assays, and clinical research to highlight the antidiabetic and antimicrobial benefits of medicinal plants used in the UAE. By focusing on N. sativa and Z. lotus, which are deeply rooted in local traditional practices yet scientifically underexplored in a UAE-specific context, this work bridges the gap between ancestral knowledge and contemporary biomedical validation. The review also addresses critical challenges, including the lack of clinical standardization, sustainable harvesting practices, and limited regional data. By doing so, it offers a focused and culturally relevant perspective that contributes to global ethnopharmacological knowledge and supports the integration of native resources into modern therapeutic strategies (17–20).
A major strength of the present review lies in its focus on two medicinal plants, N. sativa and Z. lotus, which are native to the UAE and have demonstrated promising pharmacological potential in preclinical settings. By integrating ethnobotanical knowledge with scientific evidence, this review highlights the relevance of culturally rooted botanical therapies in addressing global health threats like diabetes and microbial resistance. However, one limitation of the current study is the lack of randomized clinical trials conducted within the UAE, as well as the exclusion of relevant non-English literature. To contextualize the urgency of this topic regionally, recent epidemiological data from a large cross-sectional study showed that nearly 30% of individuals with T2DM in the UAE had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (eASCVD), and over 99% had a high or very high 10-year risk for cardiovascular events (24). These alarming figures underscore the pressing need for sustainable, preventive therapeutic strategies that are locally available, affordable, and culturally acceptable.
To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive review that integrates pharmacological, phytochemical, and ethnobotanical data on N. sativa and Z. lotus within the specific cultural and environmental context of the UAE. While both plants have been studied individually in broader regional or global settings, their targeted evaluation in relation to the UAE’s unique healthcare challenges namely the dual burden of diabetes and antimicrobial resistance remains underexplored. This review is novel in its synthesis of UAE-specific data, such as regional prevalence of T2DM and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (24), alongside bioactivity evidence drawn from both traditional use and experimental studies. By linking local medicinal resources with global therapeutic needs, this work contributes a culturally relevant, sustainability-focused perspective that bridges traditional healing and modern scientific validation.
2 Scientific search methodology
A systematic literature search was conducted to retrieve peer-reviewed studies, reviews, and ethnobotanical reports focusing on the medicinal properties of UAE-native plants specifically N. sativa and Z. lotus. The search spanned June to December 2024, covering PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect databases. Search terms combined the botanical and common names of the plants (e.g., “Nigella sativa,” “black seed,” “Ziziphus lotus,” “jujube,” “sidr”) with specific keywords such as “antidiabetic,” “antimicrobial,” “traditional medicine UAE,” “bioactive compounds,” “thymoquinone,” and “sustainable therapy.”
Boolean operators (AND, OR) were used to broaden or refine search results. The search strategy also included manual screening of reference lists from relevant articles to identify additional sources. Only English-language publications or those with reliable translations were included to ensure data accuracy, from the last 20 years (2004–2024). Studies included were In vitro, In vivo, or clinical trials with clear pharmacological, phytochemical, or therapeutic data relevant to diabetes management and antimicrobial activity.
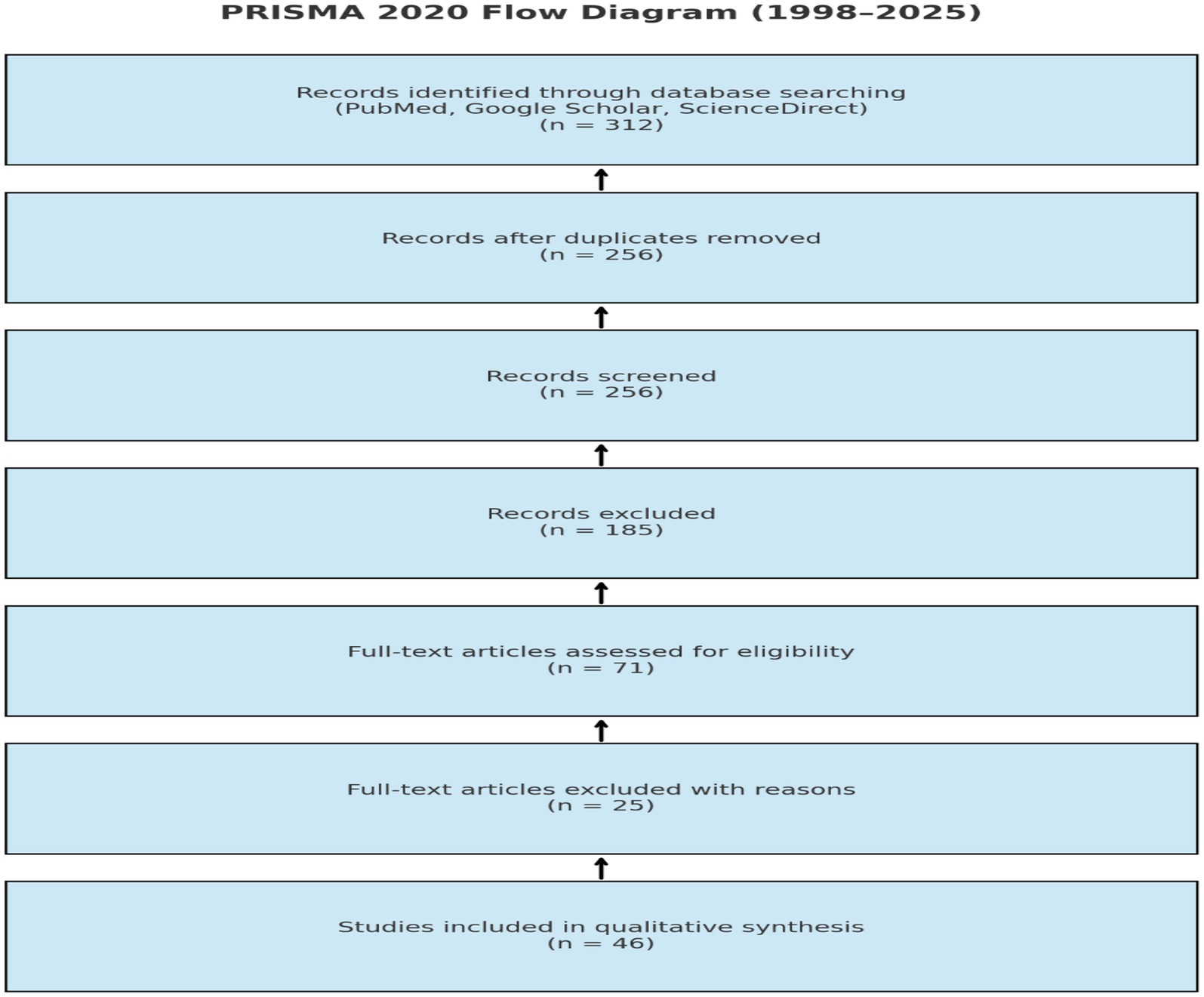
Articles that lacked sufficient data on medicinal effects, focused solely on nutrition or agriculture, or were not related to UAE flora were excluded to ensure regional relevance. A total of 312 studies were initially retrieved. After duplicate removal and eligibility screening based on inclusion/exclusion criteria, 46 articles were included in the final review (see PRISMA diagram, Figure 1, and VOSviewer software, Supplementary Figure 1).
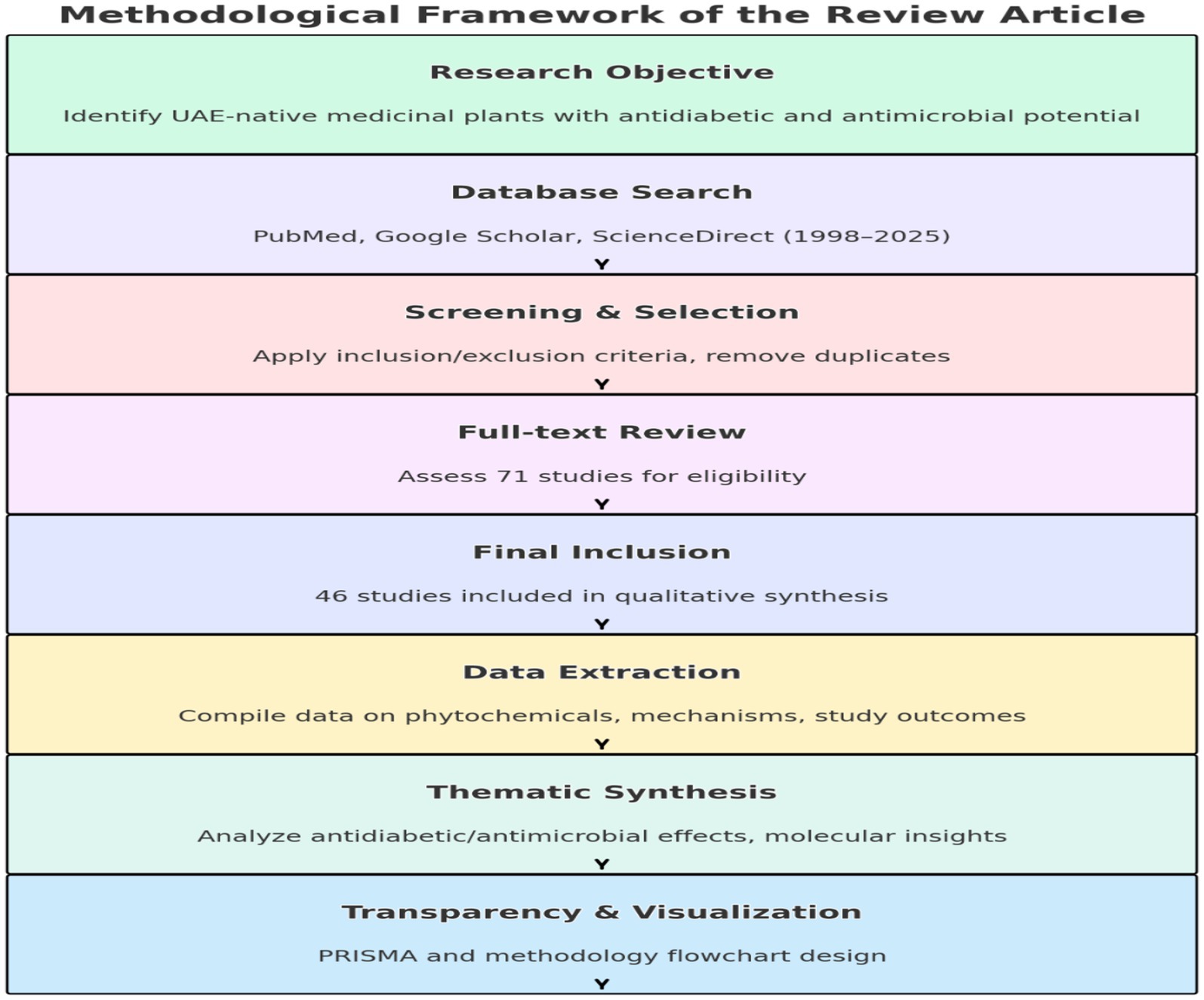
Figure 1. Methodological flowchart summarizing the steps followed in this systematic review, including search strategy, screening, data extraction, and synthesis.
2.1 Selection criteria
2.1.1 Data collection
Between June and December 2024, a comprehensive review of the flora of the UAE was conducted, utilizing a diverse range of references, including research and review articles as well as reputable online resources. The initial phase of the review involved compiling an extensive list of botanical names and their synonyms, which served as the foundation for a systematic and detailed literature review. Online platforms such as Google Scholar and databases like PubMed were utilized to identify relevant studies, focusing on plants that are either native to or naturalized within the UAE. The review emphasized the medicinal applications of these plants in both traditional and contemporary contexts. A systematic search strategy was employed, incorporating keywords that linked the botanical names and synonyms of each plant to specific medicinal uses, with particular emphasis on their roles in managing diabetes and combating bacterial infections. This methodical approach ensured a robust and comprehensive exploration of the therapeutic potential of UAE’s medicinal flora. Although several plants in the UAE exhibit potential medicinal properties, this review focuses on N. sativa and Z. lotus due to their extensive pharmacological documentation, cultural relevance, and strong evidence supporting their antidiabetic and antimicrobial effects. Additionally, comprehensive reviews on such native plants are limited in the UAE, further justifying our focused selection.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
This review includes studies that focus on the antidiabetic and antimicrobial properties of medicinal plants native to or widely utilized in the UAE. Studies were selected based on the following criteria:
Scope of Research: Peer-reviewed articles, experimental studies (In vitro and In vivo), observational studies, ethnobotanical surveys, and reviews that provide pharmacological, phytochemical, or ethnopharmacological insights into medicinal plants.
Relevance: Research explicitly addressing the medicinal applications of UAE flora, particularly in managing diabetes, and combating bacterial infections.
Phytochemical Data: Studies providing detailed analysis of active bio-compounds, mechanisms of action, and their demonstrated therapeutic efficacy.
Temporal Range: Articles published within the last 20 years, ensuring contemporary data and relevance.
Language: Publications in English or those with reliable translations to maintain the accuracy of data interpretation.
The 20-year temporal range was selected to encompass recent pharmacological advancements while retaining historical context relevant to traditional practices. They are widely utilized in the UAE, which refers to plants frequently cited in ethnobotanical surveys, traditional medicine literature, and regional healthcare practices. While every effort was made to ensure comprehensive coverage, the review may have excluded relevant non-English publications lacking reliable translations, which is acknowledged as a potential limitation in capturing all available data.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
Studies were excluded if they did not align with the following parameters:
Geographic Focus: Research on plants that are not native to or widely adapted for traditional or modern medicinal use in the UAE.
Medicinal Relevance: Articles focusing solely on nutritional, agricultural, or ornamental aspects of plants without discussing their medicinal applications.
Scientific Credibility: Non-peer-reviewed publications, anecdotal reports, or sources with limited scientific rigor were omitted to ensure data reliability.
Scope of Data: Studies lacking sufficient pharmacological or phytochemical data, such as those not identifying bioactive compounds, mechanisms of action, or relevant therapeutic outcomes.
Health Focus: Research that does not specifically address antidiabetic, or antimicrobial was excluded to maintain the study’s focus on key health challenges.
This rigorous inclusion and exclusion process ensures that the review synthesizes high-quality, relevant data to advance the understanding of UAE MPs’ therapeutic potential (Figure 1).
2.4 PRISMA flow and article selection summary
Following the PRISMA 2020 (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines, a systematic literature search was conducted across three major electronic databases: PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect. The search targeted studies published between 1998 and 2025, focusing on the antidiabetic and antimicrobial properties of N. sativa and Z. lotus. A total of 312 records were initially retrieved. After the removal of duplicates, 256 articles remained for title and abstract screening. Of these, 185 articles were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria. Subsequently, 71 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility, with 25 articles excluded due to methodological limitations or insufficient relevance. Ultimately, 46 studies were deemed suitable and were included in the qualitative synthesis. The full selection process is depicted in the PRISMA flow diagram (Figure 2), ensuring transparency, reproducibility, and methodological rigor.
3 Medicinal plants in the UAE overview
3.1 Nigella sativa
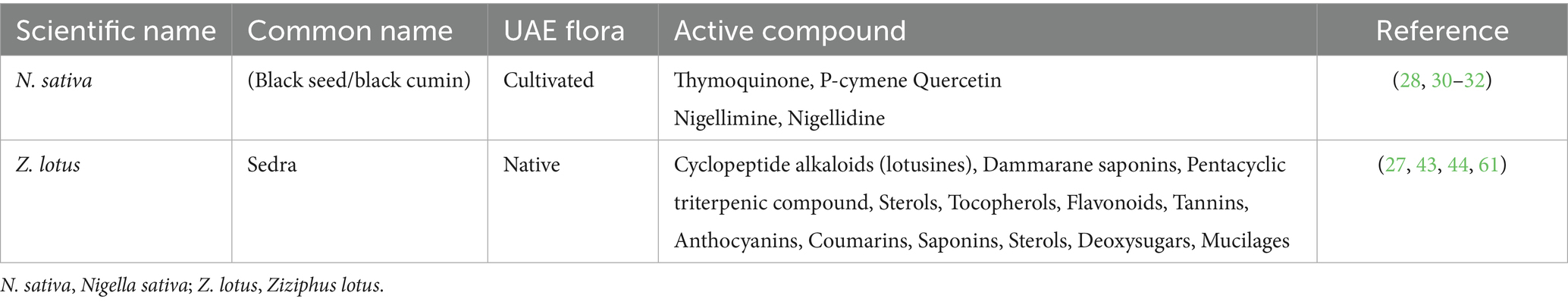
Nigella sativa, commonly known as black seeds or black cumin, is an annual herb belonging to the genus Nigella in the family Ranunculaceae. Cultivated on private farms in the UAE, N. sativa has been widely recognized for its applications in traditional and contemporary medicine, as well as in culinary uses (25–27). Its seeds are rich in bioactive compounds, including thymoquinone, p-cymene, carvone, citronellol, nigellimine, and nigellidine. These compounds contribute to its significant pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, and hepatoprotective effects (28–32).
Pharmacological studies have demonstrated its potential in managing diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and antimicrobials. Antimicrobial investigations have demonstrated its efficacy against a broad spectrum of pathogens, attributed to the presence of thymoquinone and thymol. This includes significant activity against S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa, in addition to its notable antifungal properties against Candida albicans (C. albicans) (33–36). Moreover, its antiviral effects, such as protection against murine cytomegalovirus, have been attributed to its ability to enhance macrophage function and interferon-gamma production (37). N. sativa also exhibits antidepressant and anticonvulsant properties, along with cytotoxic, anti-proliferative, and pro-apoptotic effects, supporting its potential use in cancer therapies (38–40).
Additionally, its hepatoprotective effects have been validated in experimental studies, where it showed protective effects against induced hepatotoxicity while improving serum lipid profiles (41). These findings affirm N. sativa as a valuable medicinal plant for preventive and therapeutic applications across a broad range of diseases (Table 1).
3.2 Ziziphus lotus
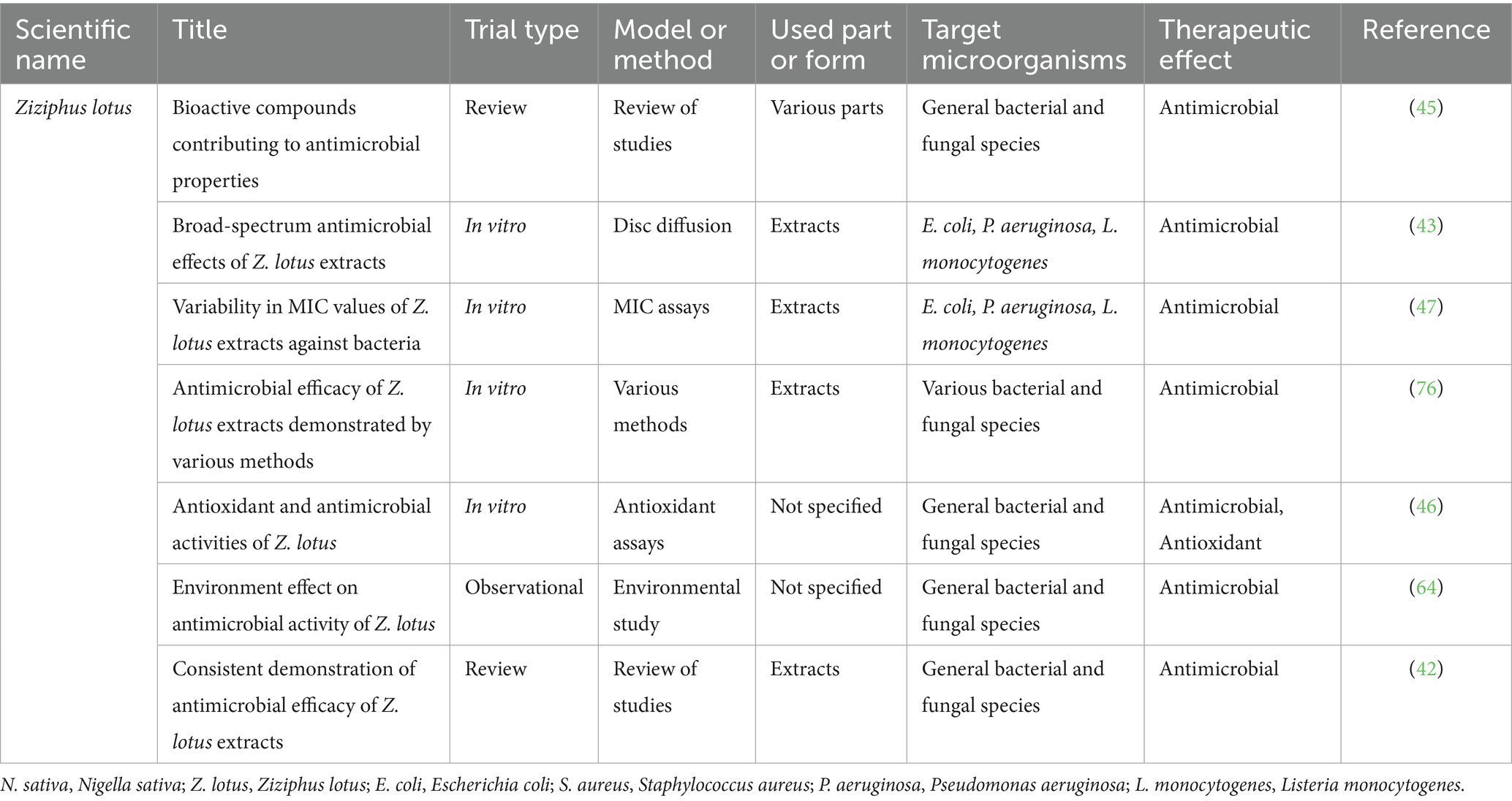
Ziziphus lotus, deciduous shrub commonly known as “jujube” and “sidr” belongs to the genus Zizyphus of the angiosperm Rhamnaceae family and is a perennial MP native to the UAE, thriving on stony slopes and alluvial plains (27, 42–44). This medicinal fruit, which flowers from March to April, has garnered significant scientific interest due to its rich composition of bioactive secondary metabolites, mainly phenolic compounds in various plant parts (27, 44). Extensive research has revealed various biological properties of Z. lotus polar extracts, including antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-ulcerogenic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antidiabetic, and antispasmodic activities (43–47). While the less polar fractions of Z. lotus remain relatively unexplored, studies have identified several unique compounds such as cyclopeptide alkaloids (lotusines), dammarane saponins, and a pentacyclic triterpenic compound in different plant tissues. Additionally, sterols and tocopherols have been evaluated in Z. lotus seed oils and whole fruits, though some analyses lack quantification (44). The diverse phytochemical profile and potential therapeutic applications of Z. lotus underscore its importance as a subject of ongoing research in the field of natural products and MPs (Table 1).
3.3 Traditional use and Ethnopharmacological relevance in the UAE
The use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) among patients with T2DM is notably high in the UAE, reflecting deep-rooted cultural practices and a growing inclination toward natural health solutions. A cross-sectional study involving T2DM patients from Dubai and Sharjah revealed that 39.3% had used CAM since diagnosis mainly folk foods and herbs often without physician guidance, and mostly influenced by family or social networks (48). N. sativa, one of the most widely recognized herbal medicines in the region, is acknowledged by community pharmacists in Dubai for its therapeutic potential despite regulatory and practice challenges (49). Likewise, Z. lotus, a native plant traditionally used to manage diabetes, infections, and skin conditions, has been shown to possess pharmacologically active compounds supporting these folk uses (27, 50). Recent comprehensive ethnopharmacological reviews have highlighted UAE-native plants such as Z. lotus, N. sativa, Phoenix dactylifera, Trigonella foenum-graecum, and Withania somnifera for their bioactive properties, showing relevance for addressing metabolic, cardiovascular, and antimicrobial conditions (51, 52). Additionally, a recent national study revealed strong public engagement with probiotics and prebiotics, especially among younger adults, reinforcing interest in plant-based functional products (53). Expanding the scope of plant-based medicine, modern technologies such as nano-drug delivery and 3D bioprinting are being explored to enhance the therapeutic delivery of natural compounds, including those used for conditions like alopecia underscoring the wider biomedical relevance of phytotherapy (54).
3.4 Geographical origin and phytochemical variability
The medicinal plants discussed in this review, particularly N. sativa and Z. lotus, are either native to the UAE or widely cultivated and used across the Middle East, Africa, and parts of Europe and Asia. Z. lotus, for example, is native to the arid and semi-arid regions of North Africa and the Mediterranean basin, including Algeria and Morocco, and is considered indigenous to the UAE (27). N. sativa, while widely cultivated in the UAE, is not native to the region but has a long history of traditional use across Asia, Eastern Europe, and North Africa (52, 55). Its seeds are extensively used in Middle Eastern and South Asian diets and ethnomedicine.
Geographical origin plays a significant role in the phytochemical profile of medicinal plants, influencing their bioactive potential and therapeutic efficacy. In the case of N. sativa, comparative studies have shown that seeds grown in different countries (India, Syria, Egypt, Poland) vary significantly in thymoquinone, tocotrienols, sterols, and terpene content, with some regions producing oil with higher antioxidant capacity and different antimicrobial potential (56). Similarly, the metabolic output of Z. lotus may be influenced by environmental conditions and microbial associations, including endophytic fungi, which differ by region and contribute to the antioxidant and antibacterial activity of the plant (14). These variations underscore the importance of location-specific studies and standardization, especially when formulating nutraceuticals or conducting comparative pharmacological research.
Thus, while the UAE context provides a unique environmental and cultural framework for the traditional use of these plants, the bioactive composition of N. sativa and Z. lotus can differ significantly depending on their country of origin, cultivation conditions, and ecological microbiota. Future studies should integrate chemical profiling with geographical data to ensure therapeutic consistency and efficacy across different formulations.
4 Overview of antidiabetic properties of medicinal plants in the UAE
4.1 Nigella sativa
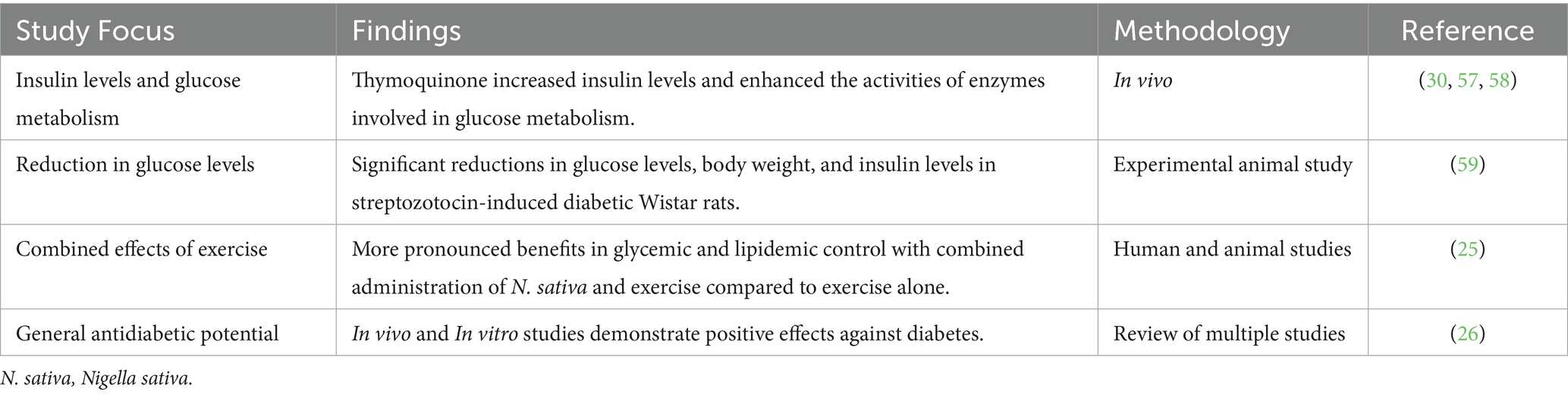
Nigella sativa contains thymoquinone, a principal bioactive compound that has demonstrated significant antidiabetic properties through multiple mechanisms of action. The administration of thymoquinone results in a marked reduction of plasma glucose levels. This hypoglycemic effect is thought to be mediated through two primary pathways: firstly, thymoquinone appears to increase insulin levels, potentially by stimulating insulin secretion or improving insulin sensitivity, and secondly, it enhances the activities of various cytosolic and mitochondrial enzymes involved in glucose metabolism. These enzymatic modulations likely contribute to improved glucose utilization and cell energy production (30, 57, 58). Increasing insulin availability and optimizing cellular glucose metabolism underscore thymoquinone’s potential as a promising natural compound for diabetes management. Research evidence supports the antidiabetic potential of N. sativa and its primary bioactive compound, thymoquinone (32). An experimental animal study using adult female streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats demonstrated significant reductions in glucose levels, body weight, and insulin levels following the administration of 10 mg/kg of N. sativa extract (thymoquinone) (59). Furthermore, administering 2 mL/kg of N. sativa oil for 30 days resulted in significant improvements in fasting blood glucose, insulin, and lipid profiles in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male Wistar rats (60). Additionally, the synergistic effect of N. sativa with exercise regimens has been explored, with two human studies and two animal studies showing that combined administration of N. sativa and exercise produced more pronounced benefits in glycemic and lipidemic control compared to exercise alone (25). Additionally, in vivo and in vitro studies have consistently demonstrated the positive effects of N. sativa against diabetes (26). These findings underscore the potential of N. sativa and its constituents as promising natural interventions for diabetes management, warranting further investigation in clinical settings (Table 2).
4.2 Ziziphus lotus
Ziziphus lotus is a rich source of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, tannins, anthocyanins, coumarins, saponins, sterols, deoxysugars, and mucilages, contributing to its diverse pharmacological properties (42, 61). These phytochemicals, particularly its high polyphenol content, are known for their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory effects (62). Research has demonstrated the significant anti-diabetic potential of Z. lotus extracts. In vivo studies showed that an aqueous extract of Z. lotus fruit (300 mg/kg) effectively controlled blood glucose levels in diabetic hamsters, with efficacy comparable to metformin (45). Furthermore, In vitro investigations revealed potent inhibitory effects of Z. lotus leaf and fruit extracts on α-amylase (IC50 = 20.40–31.91 μg/mL) and α-glycosidase (IC50 = 8.66–27.95 μg/mL), surpassing the efficacy of acarbose (45). The traditional use of Z. lotus as an anti-diabetic agent is supported by ethnobotanical surveys in Morocco, where it is among the plants used by traditional healers to treat diabetes (63). Environmental factors have been shown to significantly influence the plant’s secondary metabolites, affecting its bioactivities, which further supports the need for location-specific cultivation to optimize its medicinal value (64). Additionally, metabolomic studies have provided insights into the metabolic diversity and potent in-vitro antidiabetic potential of Z. lotus, identifying several bioactive metabolites that could contribute to its therapeutic effects (65). Moreover, the plant has shown significant effects on human T-cell proliferation, indicating its potential in modulating immune responses. The fruit pulp and seeds, in particular, were found to have higher concentrations of vitamins and fatty acids, which contributed to its notable antioxidant capacity and beneficial immunosuppressive effects, particularly in reducing excessive immune responses and inflammation (66). These findings underscore Z. lotus’s potential for nutraceutical/pharmaceutical applications in food formulations and pharmaceutical development, warranting further investigation in clinical settings (Table 3).
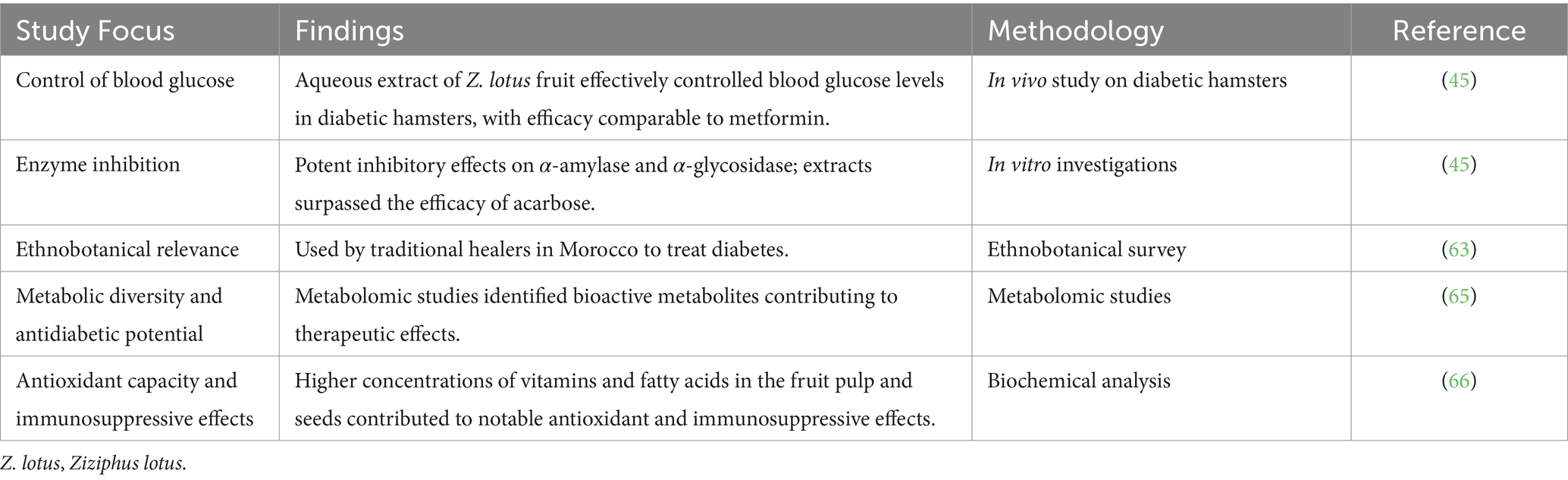
Table 3. Evaluation of Ziziphus lotus extracts for antidiabetic efficacy and biochemical properties.
5 Overview of antibacterial properties of medicinal plants in the UAE
5.1 Nigella sativa
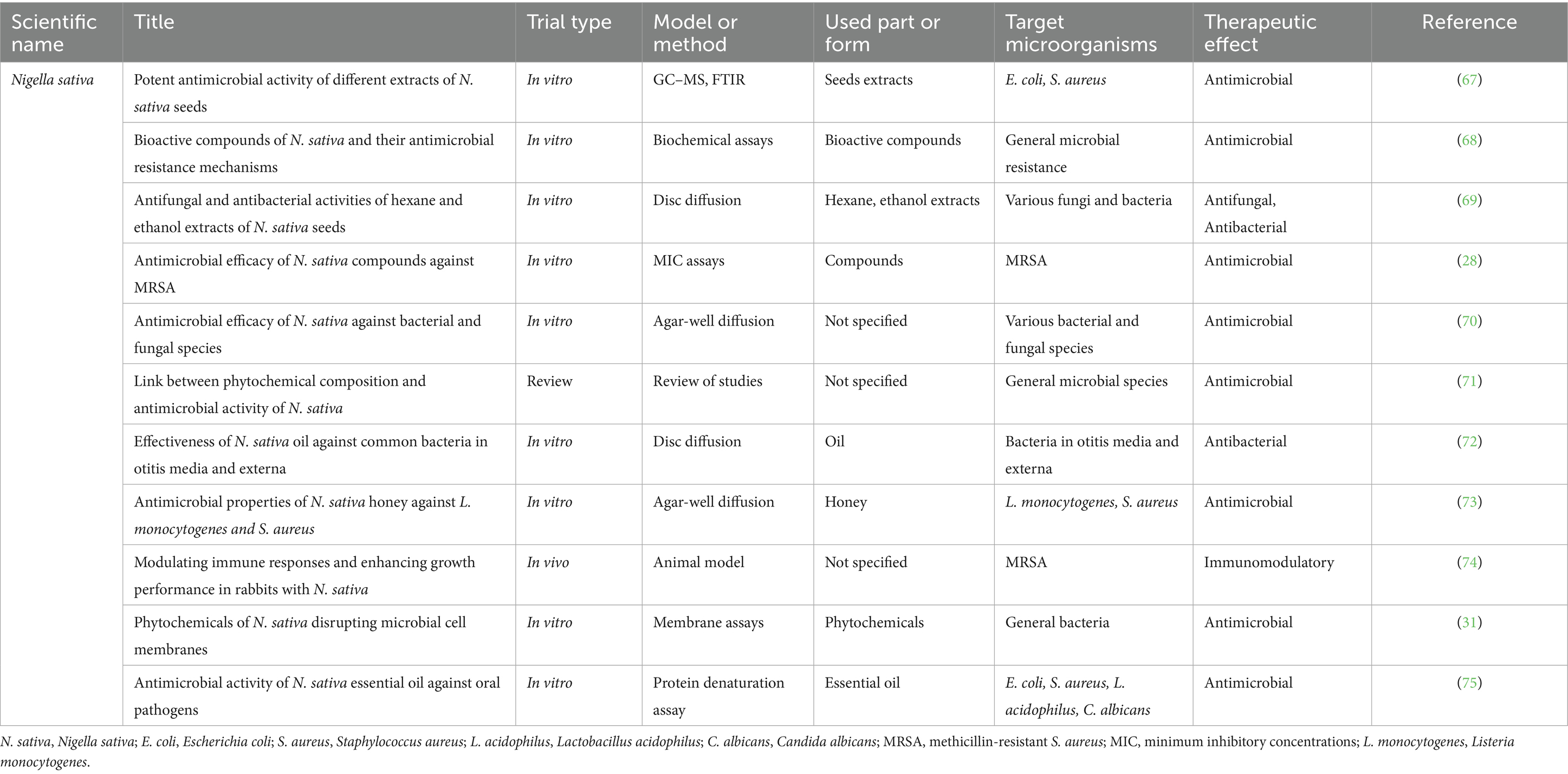
Nigella sativa has garnered substantial attention for its extensive antimicrobial properties, which have been rigorously documented in various studies. Shafodino et al. (67) highlighted the remarkable antimicrobial potential of N. sativa seed extracts, employing advanced techniques such as Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) to identify active compounds with significant activity against pathogens such as E. coli and S. aureus (67). In parallel, Hossain et al. (68) emphasized the role of key bioactive constituents, including thymoquinone, in combatting microbial resistance by inducing oxidative stress and triggering apoptosis in microbial cells (68).
Similarly, Al-Ameedy and Omran (69) demonstrated the potent antibacterial and antifungal activities of hexane and ethanol seed extracts, underscoring their potential in addressing infectious diseases (69). The work of Abbas et al. (28) further substantiates the plant’s therapeutic promise, showing that phytochemicals like quercetin in N. sativa achieve significant minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) against multidrug-resistant strains, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), thus highlighting the plant’s efficacy in addressing antibiotic resistance (28). Studies by Ashraf et al. (70) and Tiji et al. (71) lend additional credence to these findings, linking the antimicrobial effects of N. sativa to its diverse phytochemical composition and efficacy against a broad spectrum of bacterial and fungal species (70, 71).
Further expanding the evidence base, Kocoglu et al. (72) demonstrated the utility of N. sativa oil in effectively combating bacteria implicated in otitis media and external (72). Likewise, Kolayli et al. (73) revealed the unique antimicrobial properties of N. sativa honey, particularly against Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes) and S. aureus, further broadening its therapeutic applications (73). Elmowalid et al. (74) illustrated the immunomodulatory properties of N. sativa, showcasing its potential to enhance immune response and improve growth performance in rabbits exposed to MRSA infections (74).
Of particular interest, Bhatti et al. (31) explored the role of phytochemicals such as thymoquinone and p-cymene in disrupting microbial cell membranes and inhibiting cellular division, highlighting the plant’s environmentally friendly approach to combating microbial infections (31). In a similar vein, Bhavikatti et al. (75) elucidated the significant antimicrobial activity of N. sativa essential oil (NSEO) against oral pathogens. Their study revealed that NSEO inhibits protein denaturation and stabilizes cell membranes, demonstrating antimicrobial efficacy comparable to chlorhexidine against E. coli and S. aureus, with enhanced effects on Lactobacillus acidophilus and C. albicans. These findings underscore NSEO’s potential as a therapeutic agent for managing oral infections, particularly those resistant to conventional treatments. Collectively, these studies underscore the immense potential of N. sativa as a natural antimicrobial agent, advocating for further exploration into its broad-spectrum therapeutic applications. The cumulative evidence not only reinforces its role in addressing the global challenge of antibiotic resistance but also positions it as a cornerstone in the development of sustainable antimicrobial strategies (75) (Table 4; Figure 1).
5.2 Ziziphus lotus
Ziziphus lotus has been shown to contain a diverse array of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, tannins, anthocyanins, coumarins, saponins, sterols, deoxysugars, and mucilages (43, 45). These phytochemicals contribute to the plant’s significant antimicrobial properties, which have been demonstrated across multiple studies using various extracts and methodologies (42, 61). Notably, acetonic extracts of Z. lotus leaves exhibited potent antibacterial activity against several strains, including Notably, acetonic extracts of Z. lotus leaves exhibited potent antibacterial activity against several strains, including MRSA.
Methanolic and ethanolic extracts from different plant parts also showed broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and L. monocytogenes, with MIC values varying widely, from as low as 3.2 μg/mL to 200 mg/mL depending on the bacterial strain and extract type (47, 76). Additionally, the antimicrobial efficacy of Z. lotus extracts has been consistently demonstrated using various methods, including disc diffusion, agar-well diffusion, and microdilution techniques (46). These findings collectively underscore the potential of Z. lotus as a rich source of bioactive compounds. Its antimicrobial efficacy is notably influenced by environmental factors such as climate, soil conditions, and geographic origin, highlighting a critical area for future research to optimize medicinal value through location-specific cultivation strategies (42, 64) (Table 5; Figure 3).
Figure 3. Antibacterial Activity of Nigella sativa and Ziziphus lotus extracts against Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), and Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes).
6 Computational investigations
Recent computational investigations have significantly contributed to understanding the therapeutic potential of bioactive compounds from N. sativa and Z. lotus. For example, a network pharmacology and molecular docking study identified N. sativa compounds such as kaempferol and catechin as multi-target agents for diabetes and obesity management. These compounds exhibited strong binding affinities to AKT1 and other diabetes-related targets like IL6 and EGFR (77). In another study, components of N. sativa essential oil, such as α-phellandrene and thymol, showed notable inhibition of α-amylase and hemoglobin glycation, supported by in silico docking analyses (78).
A recent virtual screening of N. sativa phytoconstituents against the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) identified β-amyrin and taraxerol as potential candidates for diabetic-hypertensive therapy. Molecular dynamics simulations confirmed their stable binding and favorable pharmacokinetic profiles (79). Additionally, computational studies have explored the antiviral potential of dithymoquinone (DTQ) from N. sativa against SARS-CoV-2, with strong docking affinity to the ACE2 binding site, supported by MM-PBSA and molecular dynamics simulations (80, 81).
From an antimicrobial perspective, N. sativa extracts have been analyzed in silico for their interactions with bacterial quorum-sensing proteins such as LasR and PqsR. Thymol and thymoquinone displayed strong binding affinities, correlating with observed in vitro antimicrobial synergy (36). Another study combined in vitro and in silico evaluations of silver nanoparticles synthesized from N. sativa to demonstrate effective inhibition of CTX-M-15—a beta-lactamase enzyme linked to antibiotic resistance (82).
Similarly, Z. lotus has been computationally evaluated for its antidiabetic and antimicrobial potential. A metabolomics-based study identified bioactive metabolites such as caffeic acid, betulinic acid, quercetrin, and jujubogenin from Z. lotus and Zizphus spina-christi, which showed inhibitory effects against α-amylase and α-glucosidase in vitro. These findings were supported by multivariate analysis and molecular modeling (65). In a related study, betulin and betulinic acid isolated from Ziziphus spina-christi showed strong docking interactions with microbial targets, aligning with their antimicrobial activity (83).
Furthermore, the phenolic-rich stem bark extract of Z. lotus showed tyrosinase-inhibitory activity and potent antioxidant effects. Molecular docking confirmed the strong binding of these phytoconstituents to oxidative stress and skin-aging targets (84).
Collectively, these computational studies underscore the multifaceted therapeutic potential of phytoconstituents from N. sativa and Z. lotus, and highlight their relevance in drug discovery for metabolic, microbial, and viral diseases.
7 Molecular mechanisms of bioactive compounds: in vitro, in vivo, and clinical evidence
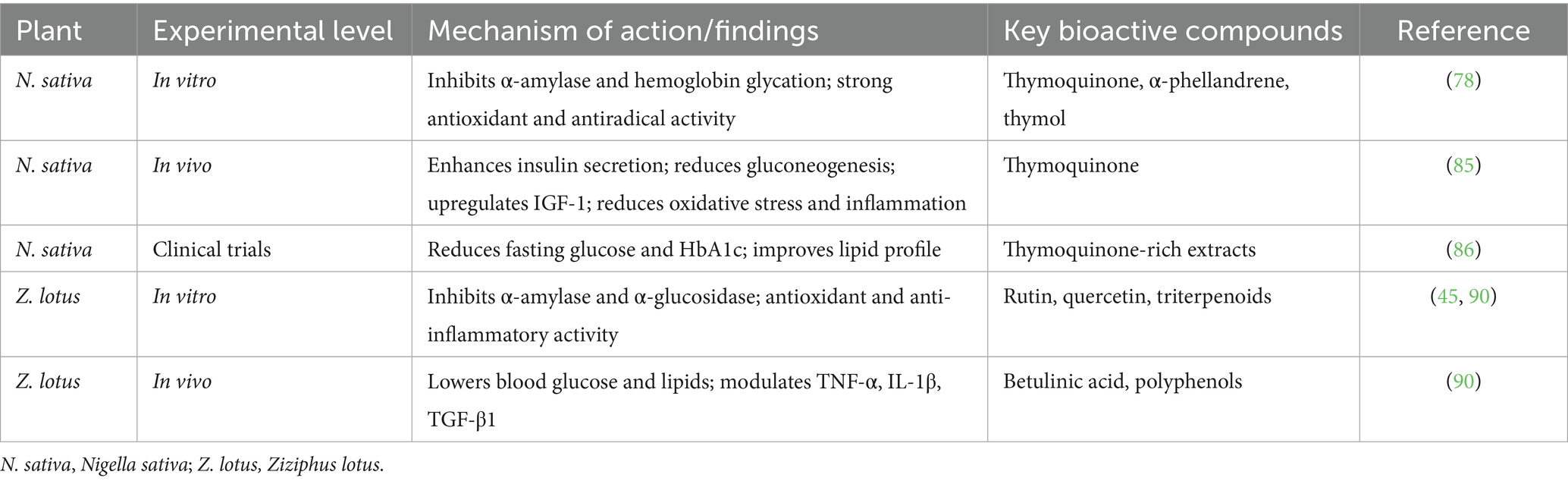
The therapeutic efficacy of N. sativa and Z. lotus is supported by mounting evidence spanning in vitro assays, animal models, and limited clinical trials. At the molecular level, the secondary metabolites of N. sativa, particularly thymoquinone, exhibit multifaceted biological activities. In vitro studies have demonstrated thymoquinone’s ability to inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase, reduce hemoglobin glycation, and scavenge free radicals (78). These effects correlate with its observed capacity to modulate oxidative stress pathways and improve insulin sensitivity in cell-based assays (85).
In vivo, thymoquinone improves glucose tolerance, reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis, and enhances antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD, CAT, GPx) in diabetic animal models (57, 85). It also upregulates insulin-like growth factor-1 and suppresses inflammatory mediators such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), supporting its anti-inflammatory and insulinotropic actions (85). Moreover, in silico studies have confirmed thymoquinone’s strong binding affinity to microbial virulence regulators (e.g., LasR, PqsR) and human diabetes-related targets (e.g., AKT1), supporting its dual application as an antidiabetic and antimicrobial agent (36).
Clinically, N. sativa supplementation has been shown to reduce fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, and improve lipid profiles in several small-scale trials, though more robust and inclusive studies are needed to validate its pharmacokinetics, therapeutic dose range, and long-term safety (85, 86).
Regarding Z. lotus, its bioactivity has been attributed to a diverse array of polyphenols, flavonoids, and triterpenoids. In vitro, extracts have demonstrated significant α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition, along with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (45, 87). Polyphenols such as rutin, hyperin, and isoquercitrin are known to regulate lipid metabolism, inhibit NF-κB signaling, and improve insulin resistance (88) Betulinic acid and related triterpenoids from Z. lotus also show promising in vitro antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects (83).
In vivo studies have confirmed the antihyperglycemic and hepatoprotective effects of Z. lotus extracts in diabetic and hyperlipidemic animal models, with upregulation of antioxidant enzymes and downregulation of TNF-α and IL-1β (88) Additionally, ethanolic extracts of Z. lotus showed potent antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, E. coli, and C. albicans in comparative MIC-based assays, validating its traditional use against infectious diseases (87, 89).
While clinical trials on Z. lotus remain limited, the plant’s ethnomedicinal record, chemical diversity, and consistent In vitro/In vivo data suggest its potential as a therapeutic candidate. Ongoing metabolomic and computational studies continue to validate its mechanisms, particularly in metabolic syndrome and microbial infections (65).
Collectively, the integration of In vitro, In vivo, and early-stage clinical findings supports the pharmacological versatility of both plants. These data reinforce the need for translational research and well-designed human trials to optimize bioavailability, safety, and therapeutic efficacy. A summary of the molecular mechanisms across In vitro, In vivo, and clinical trials is presented in Tables 6, 7.
8 Discussion and conclusion
This review highlights robust pharmacological evidence supporting the therapeutic applications of N. sativa and Z. lotus, two UAE-native medicinal plants. Notably, thymoquinone from N. sativa has demonstrated a glucose-lowering effect comparable to or exceeding metformin in animal models, with improvements in fasting glucose and lipid profiles. Z. lotus extracts showed potent inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase, surpassing acarbose in in vitro assays. Both plants also exhibited broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens such as MRSA, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa, attributed to their rich phenolic and flavonoid content.
Comparative evaluation suggests that N. sativa may possess a higher overall therapeutic potential due to its well-documented antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. Thymoquinone’s mechanisms include activation of AMPK, enhancement of insulin sensitivity, and modulation of oxidative and inflammatory pathways. Meanwhile, Z. lotus flavonoids and saponins demonstrate strong enzymatic inhibition and antimicrobial properties, though clinical and mechanistic evidence remains less extensive.
Both plants show targeted efficacy against T2DM, supported by streptozotocin-induced models and enzyme inhibition data. Their antimicrobial activity spans critical pathogens including MRSA, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and L. monocytogenes, supporting their relevance in managing diabetes-associated infections and antimicrobial resistance.
Recent molecular studies highlight the role of N. sativa compounds in regulating glucose uptake, oxidative stress (via SOD, CAT, GPx), and bacterial virulence pathways (e.g., quorum sensing, biofilm formation). In Z. lotus, bioactive constituents downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulate MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling, further supporting its dual therapeutic role.
Altogether, these findings reinforce the need for well-controlled clinical trials to confirm efficacy and safety in human populations. Variability in phytochemical content driven by environmental conditions also underscores the importance of standardized cultivation and extraction protocols. Bridging traditional herbal knowledge with scientific validation, these plants hold strong potential for integration into sustainable, evidence-based healthcare strategies (Figure 4).
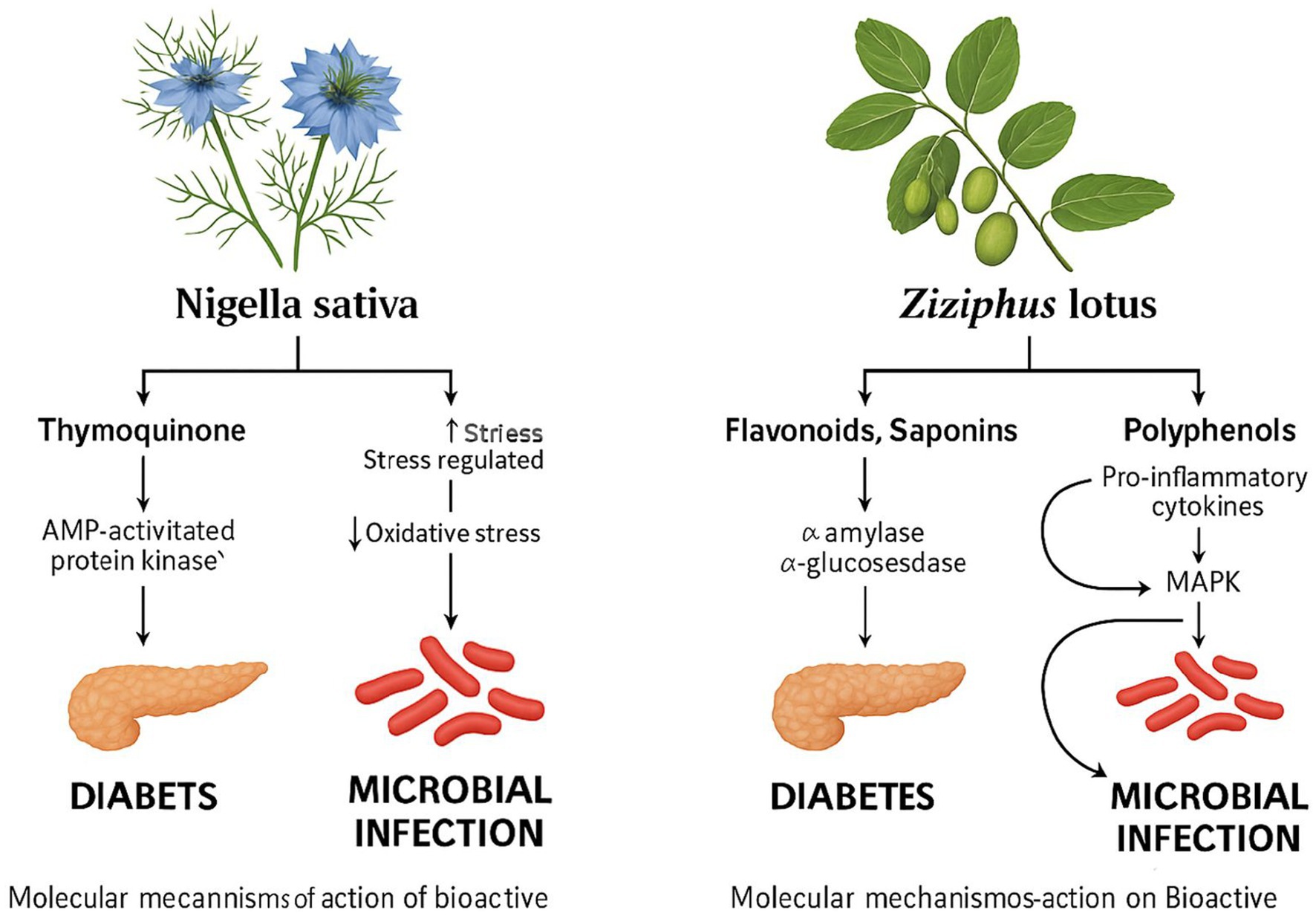
Figure 4. Molecular pathways illustrating the antidiabetic and antimicrobial effects of thymoquinone derived from Ziziphus lotus and Nigella sativa.
This diagram highlights how thymoquinone activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), enhances insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in the management of T2DM. Additionally, it shows thymoquinone’s role in microbial inhibition through membrane disruption, efflux pump inhibition, and suppression of quorum sensing, leading to reduced biofilm formation and virulence gene expression.
9 Future perspectives
Looking ahead, research on N. sativa and Z. lotus should prioritize clinical validation, particularly given their demonstrated antidiabetic and antimicrobial efficacy in preclinical models. N. sativa’s thymoquinone and Z. lotus extracts have shown results that exceed conventional treatments like metformin and acarbose in experimental settings, justifying human trials to confirm therapeutic relevance and optimize dosage. Environmental factors influencing phytochemical composition should be explored to develop cultivation strategies that maximize medicinal potency. Furthermore, efforts to establish standardized extraction protocols and regulatory frameworks will be essential for integrating these native plants into mainstream healthcare. Finally, increased public and professional awareness of their therapeutic benefits can support policy development and sustainable use.
Author contributions
AB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1592423/full#supplementary-material
References
1. International Diabetes Federation. (2024). The international diabetes federation’s guide for diabetes epidemiological studies - diabetes research and clinical practice. Available online at: https://www.diabetesresearchclinicalpractice.com/article/S0168-8227(20)30887-1/fulltext (Accessed December 3, 2024).
2. WHO. (2024). Noncommunicable diseases country profiles 2018. Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241514620 (Accessed May 25, 2025).
3. Zhang, C, Fu, X, Liu, Y, Zhao, H, and Wang, G. Burden of infectious diseases and bacterial antimicrobial resistance in China: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. (2023) 43:100972. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100972
4. O’Neill, J. (2016). Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations. Government of the United Kingdom. Available online at: https://apo.org.au/node/63983 (Accessed July 19, 2025).
5. Ahmed, S, Ahmed, MZ, Rafique, S, Almasoudi, SE, Shah, M, Jalil, NAC, et al. Recent approaches for downplaying antibiotic resistance: molecular mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. (2023) 2023:5250040. doi: 10.1155/2023/5250040
6. Hegazy, WAH, Rajab, AAH, Abu Lila, AS, and Abbas, HA. Anti-diabetics and antimicrobials: harmony of mutual interplay. World J Diabetes. (2021) 12:1832–55. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i11.1832
7. Du, F, Ma, J, Gong, H, Bista, R, Zha, P, Ren, Y, et al. Microbial infection and antibiotic susceptibility of diabetic foot ulcer in China: literature review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:881659. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.881659
8. Van Acker, H, Van Dijck, P, and Coenye, T. Molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial tolerance and resistance in bacterial and fungal biofilms. Trends Microbiol. (2014) 22:326–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.02.001
9. Deng, H, Li, B, Shen, Q, Zhang, C, Kuang, L, Chen, R, et al. Mechanisms of diabetic foot ulceration: a review. J Diabetes. (2023) 15:299–312. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13372
10. Senneville, É, Albalawi, Z, van Asten, SA, Abbas, ZG, Allison, G, Aragón-Sánchez, J, et al. IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2024) 40:e3687. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3687
11. Cloete, TE. Resistance mechanisms of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. (2003) 51:277–82. doi: 10.1016/S0964-8305(03)00042-8
12. Singh, S, Singh, SK, Chowdhury, I, and Singh, R. Understanding the mechanism of bacterial biofilms resistance to antimicrobial agents. Open Microbiol J. (2017) 11:53–62. doi: 10.2174/1874285801711010053
13. Tienda-Vázquez, MA, Melchor-Martínez, EM, Elizondo-Luévano, JH, Parra-Saldívar, R, Lara-Ortiz, JS, Luna-Sosa, B, et al. Antidiabetic plants for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated bacterial infections. PRO. (2023) 11:1299. doi: 10.3390/pr11051299
14. Eddouks, M, Lemhadri, A, Hebi, M, EL Hidani, A, Zeggwagh, NA, EL Bouhali, B, et al. Capparis spinosa L. aqueous extract evokes antidiabetic effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Avicenna J Phytomed. (2017) 7:191–8. doi: 10.22038/ajp.2016.7761
15. Kumar, A, Sreedharan, S, Kashyap, AK, Singh, P, and Ramchiary, N. A review on bioactive phytochemicals and ethnopharmacological potential of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.). Heliyon. (2022) 8:e08669. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08669
16. EL-Kamali, H. H., and Khalid, S. (1998). The most common herbal remedies in Dongola Province, northern Sudan. Fitoterapia. Available online at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-most-common-herbal-remedies-in-Dongola-Northern-EL-Kamali-Khalid/cc30ed2d3c2313b088e1465530fb9b0fe7e0d854 (Accessed December 2, 2024).
17. Accogli, R, Tomaselli, V, Direnzo, P, Perrino, EV, Albanese, G, Urbano, M, et al. Edible halophytes and halo-tolerant species in Apulia region (southeastern Italy): biogeography, traditional food use and potential sustainable crops. Plants. (2023) 12:549. doi: 10.3390/plants12030549
18. Joshi, T, Mandal, SK, Asati, V, Deepa, PR, and Sharma, PK. Arid/semi-arid flora as a treasure trove of bioactives and bioenergy: the case for underutilized desert legumes towards environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2024) 31:39025–36. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-29274-2
19. Meena, VS, Gora, JS, Singh, A, Ram, C, Meena, NK, Pratibha,, et al. Underutilized fruit crops of Indian arid and semi-arid regions: importance, conservation and utilization strategies. Horticulturae. (2022) 8:171. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae8020171
20. Mohammed, HA, Emwas, A-H, and Khan, RA. Salt-tolerant plants, halophytes, as renewable natural resources for Cancer prevention and treatment: roles of Phenolics and flavonoids in immunomodulation and suppression of oxidative stress towards Cancer management. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:5171. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065171
21. Al-Thani, H, El-Menyar, A, Consunji, R, Mekkodathil, A, Peralta, R, Allen, KA, et al. Epidemiology of occupational injuries by nationality in Qatar: evidence for focused occupational safety programmes. Injury. (2015) 46:1806–13. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2015.04.023
22. Bisht, R, Katiyar, A, Singh, R, and Mittal, P. Antibiotic resistance –a global issue of concern. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. (2009) 2. Available at: https://indexmedicus.afro.who.int/iah/fulltext/GLOBAL%20ISSUE%20OF%20CONCERN.pdf
23. Magliano, DJ, and Boyko, EJIDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition scientific committee. idf Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation (2021).
24. Awadi, FA, Rashid, F, Awada, G, Seifeldin, H, Sabbour, H, Aly, H, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular risk and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes in the United Arab Emirates: results from the prevalence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes across Middle East and African countries (PACT-MEA) study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. (2025) 19:103224. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2025.103224
25. Alyami, HH, and Al-Hariri, MT. Synergistic effects of Nigella sativa and exercise on diabetic profiles: a systematic review. Diabetes Ther. (2023) 14:467–78. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01362-5
26. Pop, RM, Trifa, AP, Popolo, A, Chedea, VS, Militaru, C, Bocsan, IC, et al. Nigella sativa: valuable perspective in the management of chronic diseases. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2020) 23:699–713. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.37734.8978
27. UAE Flora. (2023). Available online at: https://www.uaeflora.ae/ (Accessed December 2, 2024).
28. Abbas, M, Gururani, MA, Ali, A, Bajwa, S, Hassan, R, Batool, SW, et al. Antimicrobial properties and therapeutic potential of bioactive compounds in Nigella sativa: a review. Molecules. (2024) 29:4914. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204914
29. Abduallah, A., Alhimaidi, A., Adham, K., Rushdy, S., Sayed, M., and Gamaleldeen, A. (2017). The effect of Nigella sativa extract (Thymoquinone) on glucose insulin levels and body weight of induced diabetic female rats.
30. Ahmad, A, Husain, A, Mujeeb, M, Khan, SA, Najmi, AK, Siddique, NA, et al. A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: a miracle herb. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. (2013) 3:337–52. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60075-1
31. Bhatti, SA, Hussain, MH, Mohsin, MZ, Mohsin, A, Zaman, WQ, Guo, M, et al. Evaluation of the antimicrobial effects of Capsicum, Nigella sativa, Musa paradisiaca L., and Citrus limetta: a review. Front Sustain Food Syst. (2022) 6:1043823. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.1043823
32. Maideen, NMP. Antidiabetic activity of Nigella Sativa (black seeds) and its active constituent (Thymoquinone): a review of human and experimental animal studies. Chonnam Med J. (2021) 57:169–75. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2021.57.3.169
33. Chaieb, K, Kouidhi, B, Jrah, H, Mahdouani, K, and Bakhrouf, A. Antibacterial activity of Thymoquinone, an active principle of Nigella sativa and its potency to prevent bacterial biofilm formation. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2011) 11:29. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-29
34. Dosary, RAAQA. Antibacterial and alteration of drug resistance activities of black cumin seed (Nigella sativa) extracts against urinary pathogens. J Public Health Sci. (2023) 2:148–58. doi: 10.56741/jphs.v2i03.389
35. Forouzanfar, F, Bazzaz, BSF, and Hosseinzadeh, H. Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): a review on antimicrobial effects. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2014) 17:929–38. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4387228/pdf/IJBMS-17-929.pdf
36. Rahman, AU, Abdullah, A, Faisal, S, Mansour, B, and Yahya, G. Unlocking the therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa extract: phytochemical analysis and revealing antimicrobial and antioxidant marvels. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2024) 24:266. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04470-w
37. Shoaib, A, Javed, S, Wahab, S, Azmi, L, Tabish, M, Sultan, MH, et al. Cellular, molecular, pharmacological, and Nano-formulation aspects of Thymoquinone—a potent natural antiviral agent. Molecules. (2023) 28:5435. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145435
38. Ansary, J, Giampieri, F, Forbes-Hernandez, TY, Regolo, L, Quinzi, D, Gracia Villar, S, et al. Nutritional value and preventive role of Nigella sativa L. and its Main component Thymoquinone in Cancer: an evidenced-based review of preclinical and clinical studies. Molecules. (2021) 26:2108. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082108
39. Bin Sayeed, MS, Shams, T, Fahim Hossain, S, Rahman, MR, Mostofa, A, Fahim Kadir, M, et al. Nigella sativa L. seeds modulate mood, anxiety and cognition in healthy adolescent males. J Ethnopharmacol. (2014) 152:156–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.050
40. Çınar, İ, Gıdık, B, and Dirican, E. Determination of anti-cancer effects of Nigella sativa seed oil on MCF7 breast and AGS gastric cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. (2024) 51:491. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09453-1
41. Adam, GO, Rahman, MM, Lee, S-J, Kim, G-B, Kang, H-S, Kim, J-S, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of Nigella sativa seed extract against acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress. Asian Pac J Trop Med. (2016) 9:221–7. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.01.039
42. Abdoul-Azize, S. Potential benefits of jujube (Zizyphus Lotus L.) bioactive compounds for nutrition and health. J Nutr Metabol. (2016) 2016:2867470. doi: 10.1155/2016/2867470
43. Cadi, HE, Bouzidi, HE, Selama, G, Cadi, AE, Ramdan, B, Oulad El Majdoub, Y, et al. Physico-chemical and phytochemical characterization of Moroccan wild jujube “Zizyphus lotus (L.)” fruit crude extract and fractions. Molecules. (2020) 25:5237. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225237
44. Zazouli, S, Chigr, M, Ramos, PAB, Rosa, D, Castro, MM, Jouaiti, A, et al. Chemical profile of lipophilic fractions of different parts of Zizyphus lotus L. by GC-MS and evaluation of their Antiproliferative and antibacterial activities. Molecules. (2022) 27:483. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020483
45. Bencheikh, N, Radi, FZ, Fakchich, J, Elbouzidi, A, Ouahhoud, S, Ouasti, M, et al. Ethnobotanical, phytochemical, toxicological, and pharmacological properties of Ziziphus lotus (L.) lam.: a comprehensive review. Pharmaceuticals. (2023) 16:575. doi: 10.3390/ph16040575
46. Naili, MB, Alghazeer, RO, Saleh, NA, and Al-Najjar, AY. Evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Artemisia campestris (Astraceae) and Ziziphus lotus (Rhamnacea). Arab J Chem. (2010) 3:79–84. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.02.002
47. Yahia, Y, Benabderrahim, MA, Tlili, N, Bagues, M, and Nagaz, K. Bioactive compounds, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts from different plant parts of two Ziziphus mill. Species. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0232599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232599
48. Radwan, H, Hasan, H, Hamadeh, R, Hashim, M, AbdulWahid, Z, Hassanzadeh Gerashi, M, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine use among patients with type 2 diabetes living in the United Arab Emirates. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2020) 20:216. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03011-5
49. Rayes, IK, and Abrika, OSS. Community pharmacists knowledge and perspectives regarding the medicinal use of Nigella sativa seeds (Ranunculaceae),: a qualitative insight from Dubai, United Arab Emirates. JMPR. (2019) 13:518–22. doi: 10.5897/JMPR2019.6851
50. Farida, B, Maria Luísa, S, Farid, D, Malik, M, Nabil, K, Sofiane, D, et al. Ziziphus lotus (L.) lam. Plant treatment by ultrasounds and microwaves to improve antioxidants yield and quality: an overview. NAJFNR. (2021) 5:53–68. doi: 10.51745/najfnr.5.12.53-68
51. Al Raish, SM, Almasri, RS, and Bedir, AS. Ancient remedies, modern medicine: a review of antidiabetic, Cardioprotective, and antimicrobial activities of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), and Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera). Biology. (2025) 14:695. doi: 10.3390/biology14060695
52. Almasri, RS, Bedir, AS, and Al Raish, SM. Comprehensive ethnopharmacological analysis of medicinal plants in the UAE: Lawsonia inermis, Nigella sativa, Ziziphus spina-christi, Allium cepa, Allium sativum, Cymbopogon schoenanthus, Matricaria aurea, Phoenix dactylifera, Portulaca oleracea, Reichardia tingitana, Salvadora persica, Solanum lycopersicum, Trigonella foenum-graecum, Withania somnifera, and Ziziphus lotus. Nutrients. (2025) 17:411. doi: 10.3390/nu17030411
53. Alqaydi, TK, Bedir, AS, Abu-Elsaoud, AM, El-Tarabily, KA, and Al Raish, SM. An assessment of the knowledge, attitude, and practice of probiotics and prebiotics among the population of the United Arab Emirates. Foods. (2024) 13:2219. doi: 10.3390/foods13142219
54. Elnady, RE, Abdon, MS, Shaheen, HR, Eladawy, RM, Azar, YO, and Al Raish, SM. The future of alopecia treatment: plant extracts, Nanocarriers, and 3D bioprinting in focus. Pharmaceutics. (2025) 17:584. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050584
55. Goyal, S, Wani, MR, Raina, A, Laskar, RA, and Khan, S. Phenotypic diversity in mutagenized population of urdbean (Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper). Heliyon. (2021) 7:e06356. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06356
56. Dąbrowski, G, Czaplicki, S, and Konopka, I. Variation in the composition and quality of Nigella sativa L. seed oils—the underestimated impact on possible health-promoting properties. Molecules. (2024) 29:1360. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061360
57. Gholamnezhad, Z, Havakhah, S, and Boskabady, MH. Preclinical and clinical effects of Nigella sativa and its constituent, thymoquinone: a review. J Ethnopharmacol. (2016) 190:372–86. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.061
58. Kooti, W, Hasanzadeh-Noohi, Z, Sharafi-Ahvazi, N, Asadi-Samani, M, and Ashtary-Larky, D. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic uses of black seed (Nigella sativa). Chin J Nat Med. (2016) 14:732–45. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(16)30088-7
59. Abduallah, AM, Rashed, AA, Gamaleldeen, AK, and Sayed, SRM. The effect of Nigella sativa extract (Thymoquinone) on glucose insulin levels and body weight of induced diabetic female rats. Am J Life Sci. (2017) 5:52–6. doi: 10.11648/j.ajls.20170502.13
60. Maideen, NMP, Balasubramanian, R, and Ramanathan, S. Nigella Sativa (black seeds), a potential herb for the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Hypertension: a review. Curr Cardiol Rev. (2021) 17:e230421187786. doi: 10.2174/1573403X16666201110125906
61. Benali, T, Bakrim, S, Ghchime, R, Benkhaira, N, El Omari, N, Balahbib, A, et al. Pharmacological insights into the multifaceted biological properties of quinic acid. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. (2024) 40:3408–37. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2022.2122303
62. Rached, W, Barros, L, Ziani, BEC, Bennaceur, M, Calhelha, RC, Heleno, SA, et al. HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS screening of phytochemical compounds and the bioactive properties of different plant parts of Zizyphus lotus (L.) Desf. Food Funct. (2019) 10:5898–909. doi: 10.1039/C9FO01423C
63. Naceiri Mrabti, H, Bouyahya, A, Naceiri Mrabti, N, Jaradat, N, Doudach, L, and Faouzi, MEA. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used by traditional healers to treat diabetes in the Taza region of Morocco. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:1–16. doi: 10.1155/2021/5515634
64. Dahlia, F, Barouagui, S, Hemida, H, Bousaadia, D, and Rahmoune, B. Influence of environment variations on anti-glycaemic, anti-cholesterolemic, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of natural wild fruits of Ziziphus lotus (L.). S Afr J Bot. (2020) 132:215–25. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2020.04.033
65. Dawood, HM, Shawky, E, Zayed, M-AE, Tayea, ME, Ghareeb, DA, and Darwish, RS. Metabolomics and chemometrics approaches unravel the metabolic diversity and in-vitro antidiabetic potential of two Ziziphus species. Ind Crop Prod. (2024) 212:118288. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118288
66. Benammar, C, Hichami, A, Yessoufou, A, Simonin, A-M, Belarbi, M, Allali, H, et al. Zizyphus lotus L. (Desf.) modulates antioxidant activity and human T-cell proliferation. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2010) 10:54. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-10-54
67. Shafodino, FS, Lusilao, JM, and Mwapagha, LM. Phytochemical characterization and antimicrobial activity of Nigella sativa seeds. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0272457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272457
68. Hossain, MS, Sharfaraz, A, Dutta, A, Ahsan, A, Masud, MA, Ahmed, IA, et al. A review of ethnobotany, phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology and toxicology of Nigella sativa L. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 143:112182. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112182
69. Al-Ameedy, T. H., and Omran, R. (2019). Antimicrobial activity of Nigella sativa extract against some bacterial and fungal species.
70. Ashraf, S, Anjum, AA, Ahmad, A, Firyal, S, Sana, S, and Latif, AA. In vitro activity of Nigella sativa against antibiotic resistant Salmonella enterica. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. (2018) 58:54–8. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2017.12.017
71. Tiji, S, Rokni, Y, Benayad, O, Laaraj, N, Asehraou, A, and Mimouni, M. Chemical composition related to antimicrobial activity of Moroccan Nigella sativa L. extracts and isolated fractions. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2021/8308050
72. Kocoglu, E, Kalcioglu, MT, Uzun, L, Zengin, F, Celik, S, Serifler, S, et al. In vitro investigation of the antibacterial activity of Nigella sativa oil on some of the most commonly isolated bacteria in otitis media and externa. Eurasian J Med. (2019) 51:247–51. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2019.18386
73. Kolayli, S, Kazaz, G, Özkök, A, Keskin, M, Kara, Y, Demir Kanbur, E, et al. The phenolic composition, aroma compounds, physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of Nigella sativa L. (black cumin) honey. Eur Food Res Technol. (2023) 249:653–64. doi: 10.1007/s00217-022-04160-2
74. Elmowalid, GAE, Ahmad, AAM, El-Hamid, MIA, Ibrahim, D, Wahdan, A, El Oksh, ASA, et al. Nigella sativa extract potentially inhibited methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus induced infection in rabbits: potential immunomodulatory and growth promoting properties. Animals. (2022) 12:2635. doi: 10.3390/ani12192635
75. Bhavikatti, SK, Zainuddin, SLA, Ramli, RB, Nadaf, SJ, Dandge, PB, Khalate, M, et al. Insights into the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial potential of Nigella sativa essential oil against oral pathogens. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:11878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62915-1
76. Hammi, KM, Essid, R, Khadraoui, N, Ksouri, R, Majdoub, H, and Tabbene, O. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and antileishmanial activities of Ziziphus lotus leaves. Arch Microbiol. (2022) 204:119. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02733-5
77. Saleem, M, Fareed, MM, Saani, MSA, and Shityakov, S. Network pharmacology and multitarget analysis of Nigella sativa in the management of diabetes and obesity: a computational study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. (2024) 42:4800–16. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2222837
78. Dalli, M, Daoudi, NE, Abrigach, F, Azizi, S, Bnouham, M, Kim, B, et al. In vitro α-amylase and hemoglobin glycation inhibitory potential of Nigella sativa essential oil, and molecular docking studies of its principal components. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:1036129. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1036129
79. Vishwakarma, DK, Mishra, JN, Shukla, AK, Singh, AP, Vishwakarma, DK, Mishra, JN, et al. Phytosomes as a novel approach to drug delivery system In: Editor R. Pignatello wSmart drug delivery systems - futuristic window in cancer therapy. University of Catania, Italy. United Kingdom: IntechOpen (2024).
80. Ahmad, I, Wahab, S, Nisar, N, Dera, AA, Alshahrani, MY, Abullias, SS, et al. Evaluation of antibacterial properties of Matricaria aurea on clinical isolates of periodontitis patients with special reference to red complex bacteria. Saudi Pharm J. (2020) 28:1203–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.010
81. Ali, T, Hussain, F, Naeem, M, Khan, A, and Al-Harrasi, A. Nanotechnology approach for exploring the enhanced bioactivities and biochemical characterization of freshly prepared Nigella sativa L. nanosuspensions and their phytochemical profile. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:888177. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.888177
82. Hossain, MS, Seddique, AB, Sharmin, S, Rashid, MMO, Islam, A, and Hossain, MM. Nigella sativa oil improves motor skill learning of albino mice: in vivo and in Silico investigations. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2023) 2023:8498066. doi: 10.1155/2023/8498066
83. Ads, EN, Hassan, SI, Rajendrasozhan, S, Hetta, MH, Aly, SH, and Ali, MA. Isolation, structure elucidation and antimicrobial evaluation of natural pentacyclic triterpenoids and phytochemical investigation of different fractions of Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) stem bark using LCHRMS analysis. Molecules. (2022) 27:1805. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061805
84. Cacciola, A, D’Angelo, V, Raimondo, FM, Germanò, MP, Braca, A, and De Leo, M. Ziziphus lotus (L.) lam. As a source of health promoting products: metabolomic profile, antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory activities. Chem Biodivers. (2022) 19:e202200237. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200237
85. Shaukat, A, Zaidi, A, Anwar, H, and Kizilbash, N. Mechanism of the antidiabetic action of Nigella sativa and Thymoquinone: a review. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1126272. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1126272
86. Adam, SH, Mohd Nasri, N, Kashim, MIAM, Abd Latib, EH, Ahmad Juhari, MAA, and Mokhtar, MH. Potential health benefits of Nigella sativa on diabetes mellitus and its complications: a review from laboratory studies to clinical trials. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1057825. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1057825
87. Boudou, F, Guendouzi, A, Belkredar, A, and Rasheed, M. An integrated investigation into the antibacterial and antioxidant properties of propolis against Escherichia coli cect 515: a dual in vitro and in silico analysis. Not Sci Biol. (2024) 16:13837–7. doi: 10.55779/nsb16211837
88. Shady, NH, Soltane, R, Maher, SA, Saber, EA, Elrehany, MA, Mostafa, YA, et al. Wound healing and antioxidant capabilities of Zizyphus mauritiana fruits: in-vitro, in-vivo, and molecular modeling study. Plants (Basel). (2022) 11:1392. doi: 10.3390/plants11111392
89. Dhif, H, Salah-Abbès, J b, Al-Amiery, A, Chaieb, K, Calleja-Gómez, M, Berrada, H, et al. Comparative antimicrobial activity of ethanol and aqueous extracts of Ziziphus lotus against bacteria and fungi. Food Biosci. (2025) 71:107149. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2025.107149
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance, diabetes management, medicinal plants, phytochemical analysis, traditional medicine
Citation: Bedir AS, Almasri RS and Al Raish SM (2025) Therapeutic efficacy of Nigella sativa and Ziziphus lotus: sustainable strategies for diabetes, antimicrobial resistance, and health treatment. Front. Nutr. 12:1592423. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1592423
Edited by:
Marco Montemurro, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyReviewed by:
Hassan Rasouli, Tarbiat Modares University, IranSuriya Akter Shompa, University of Dhaka, Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Bedir, Almasri and Al Raish. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Seham M. Al Raish, c2VoYW0uYWxyYWlzaEB1YWV1LmFjLmFl
 Alaa S. Bedir1
Alaa S. Bedir1 Seham M. Al Raish
Seham M. Al Raish