- 1College of Biological and Food Engineering, Jilin Engineering Normal University, Changchun, China
- 2Department of Gastrointestinal Colorectal and Anal Surgery, The China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 3Laboratory of Micro and Nano Biosensing Technology in Food Safety, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Food Science and Biotechnology, College of Food Science and Technology, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China
- 4Department of Orthopedics, The China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 5Jilin Province Hua En Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Changchun, Jilin, China
- 6Department of Neurology, Jilin City Central Hospital, Jilin, China
- 7Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, China-Japan Union Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, China
Fermented quinoa has emerged as a promising functional food owing to its enhanced nutritional profile, improved bioactive compound bioavailability, and favorable sensory attributes. Key fermentation parameters-microbial selection, process conditions, and substrate pretreatment-that govern the quality and functionality of fermented quinoa products. It highlights microbial-driven biotransformation of polyphenols and flavonoids, which enhances antioxidant activity and bioavailability. Fermentation also modulates sensory profiles and promotes gut health through enrichment of beneficial genera. These data provide a foundational framework for process standardization, scale-up, and industrial adaptation, particularly highlighting the versatility of lactic acid bacteria and the need for mechanized fermentation technologies to enhance commercial viability. Future research should focus on multi-omics approaches to decipher microbial consortia dynamics, in vivo validation of health benefits, development of clean-label formulations, and exploration of sustainable fermentation technologies. This review provides a scientific foundation for optimizing quinoa-based biotransformation processes and accelerating the development of next-generation fermented quinoa products with enhanced nutritional and health-promoting properties.
1 Introduction
Quinoa, a low-glycemic index (GI) crop native to the Andes Mountains, has been cultivated for over 5,000 years. Known as the “super grain,” “future food,” and “mother of food” (1), it is prized for its exceptional nutritional value. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations recognizes quinoa as the one of the most critical single crop that provides all essential amino acids, trace elements, and vitamins humans need (2). Its balanced amino acid composition and comprehensive nutrition have made it a key research focus (3).
Despite growing market demand for quinoa-fermented products, knowledge gaps remain regarding fermentation processes and key influencing factors. This study comprehensively reviews quinoa-fermented products developed globally, providing an overview of the current product landscape. It also analyzes fermentation processes of representative products to identify optimal parameters and highlights critical factors affecting fermentation, essential for quality control and product improvement.
By addressing these areas, this research aims to guide future development of quinoa-fermented products, enhancing their nutritional value, quality, and market competitiveness. The findings not only bridge existing knowledge gaps but also support advancements in the quinoa deep-processing industry.
2 Nutritional value and function of quinoa
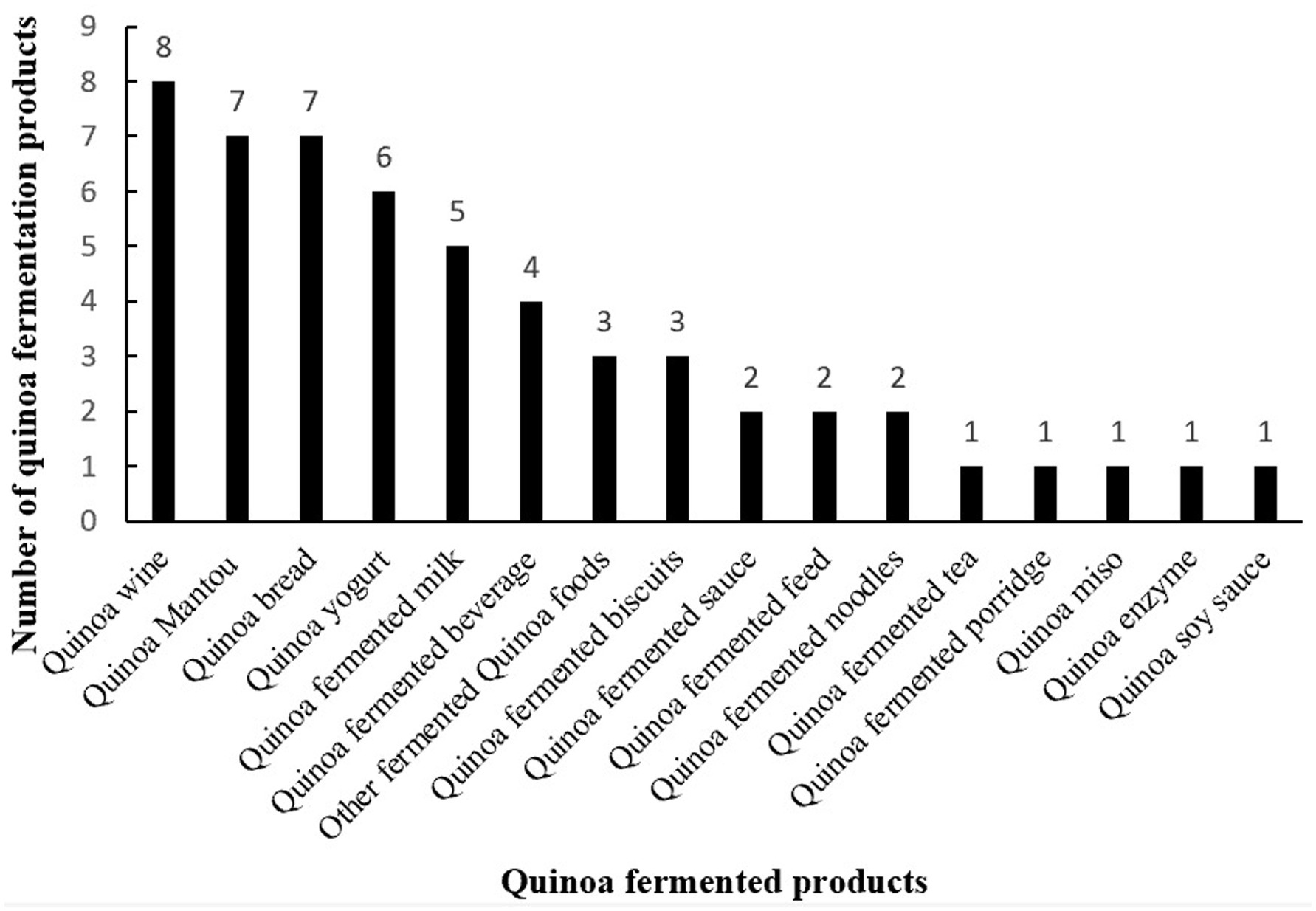
Quinoa is a nutrient-rich crop, providing high-quality protein, essential amino acids, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids. Its gluten-free nature makes it an ideal food for individuals with Crohn’s disease (CD) (4). As shown in Figure 1A, quinoa’s primary nutritional components are starch, protein, and amino acids. Its starch has a small particle size (0.4–2.0 μm) and high amylopectin content (5), giving it superior gelatinization and fermentation properties compared to other cereals. Quinoa contains 2.0–9.5% fat, 80% of which is unsaturated fatty acids, including squalene, which aids in fat reduction (6, 7). It also provides a well-balanced amino acid profile with over 17 types, making it the most nutritionally complete whole grain (8). Figure 1B shows that quinoa’s lysine content is double that of wheat and corn and 25% higher than rice, while its histidine levels match corn and exceed rice and wheat (9). Rich in minerals, vitamins, and soluble dietary fiber (1.53%), quinoa meets the nutritional needs of pregnant women in later stages, particularly for K, Fe, Zn, VE, and folic acid (10). It also contains at least 26 phenolic compounds, such as vanillic and ferulic acids (11), along with functional components like flavonoids, rutin, quercetin, and phytosterols (12). These compounds help combat fatigue, boost immunity, and support chronic disease management, positioning quinoa as a promising functional food.
Figure 1. Chart of quinoa nutritional content. (A) Description of the specific nutrient composition in quinoa; (B) Comparing the content of major nutrients across different coarse grains.
Despite its benefits, quinoa’s coarse texture and bitter-tasting compounds-such as saponins and phytic acid-limit its appeal. Saponins, concentrated in the pericarp, contribute to its strong bitterness (13), with up to 87 different types identified (14) and levels in the outer layer reaching 13.39% (15). Processing is required to reduce saponin levels below 0.06% for improved taste (16). Flavonoids and polyphenols also contribute to bitterness and astringency (17), while antinutritional factors like phytates (7.92–8.93 g/kg) hinder mineral absorption (18, 19). Fermentation offers an effective solution by converting saponins into less bitter derivatives like polysaccharides (20), enhancing nutrient bioavailability. It also generates antioxidants that stabilize free radicals, prevent oxidation, and improve flavor (21). Beneficial fermentation microbes aid digestion and nutrient absorption, while fermented quinoa products exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and gut health benefits (22). These advantages highlight fermentation’s potential to transform quinoa into a more palatable and nutritionally optimized food.
3 Quinoa-fermented beverages
3.1 Quinoa alcoholic beverages
Quinoa alcoholic beverages are brewed primarily from quinoa, yielding various fermented drinks such as beer, liquor, fruit wine, and yellow wine through different fermentation methods and ingredient combinations. During fermentation, microorganisms break down quinoa’s sugars into alcohol, organic acids, and aromatic compounds while preserving many of its natural nutrients. This enhances both the nutritional value and flavor profile of the beverages. Beyond retaining quinoa’s health benefits, these fermented drinks stimulate digestive enzyme secretion, boost appetite, and aid digestion (23). The fermentation process also develops unique aromatic qualities, significantly improving their sensory characteristics.
3.1.1 Quinoa beer
Beer is the world’s most popular alcoholic beverage, but traditional beer contains gluten, making it unsuitable for individuals with CD (22). Quinoa-based gluten-free beer offers a smoother taste, rich foam, and distinctive aroma, setting it apart from conventional beers (24). Quinoa beer has been widely researched globally.
The first quinoa beer was developed in 2005 by Zweytick et al. using quinoa and German malt yeast (25). Prasad et al. (26) later created a non-alcoholic quinoa beer (<0.5% vol.) with antioxidant properties using wild quinoa and Burmese Pichia pastoris. Dezelak (27) produced quinoa beer with buckwheat, noting that quinoa beer contained higher amino acid levels (25% more than buckwheat beer) and abundant metal cations. Saccharomyces pastorianus tum 34/70 was used for fermentation, and according to pierce classification, it showed that different fermentation strains had selectivity for amino acid absorption of different raw materials, which directly affected the nutritional composition of beer. Bian et al. (28) found that fermentation temperature and yeast quantity significantly affect beer quality, though gluten-free grains like quinoa yield lower alcohol and flavonoid content than barley-based beers.
Quinoa beer production involves processing, saccharification, fermentation, and packaging (26), with fermentation being the most critical stage. Yeast selection and fermentation conditions greatly influence beer quality (Table 1), affecting flavor and color, the main and secondary factors of total flavonoids content were fermentation temperature > feed water ratio > pH value. Lower fermentation temperatures increase flavonoid levels, enhancing antioxidant activity (29). Polyphenols possess antioxidant properties. During the fermentation process, a portion of polyphenols bind with proteins to form precipitates, resulting in a decrease in their content. β-Glucan undergoes degradation by β-glucanase during wort preparation and fermentation. Incomplete degradation can impact beer filtration and flavor (25). Bogdan et al. (30) observed that quinoa beer fermentation generates significant fatty and amino acids. In the fermentation process, phenolic compounds (conjugates with carbohydrates, fatty acids and proteins) existing in bound state will be transformed into free state under the action of chemical bond breaking of grain cell wall components and a variety of enzymes (β-glucosidase, decarboxylase, esterase, hydrolase and reductase). Free phenolic compounds have higher biological accessibility, and the released free aglycones can significantly improve antioxidant activity.
3.1.2 Quinoa liquor
As a traditional Chinese distilled beverage, liquor undergoes solid-state fermentation through natural microbial inoculation with simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (31). Quinoa has proven to be an exceptional base material for liquor production. Yang et al.—developed China’s first strong-flavor quinoa liquor (“quinoa grain liquid”) using pure quinoa and medium-temperature wheat Daqu for saccharification and fermentation (32). This innovative spirit features a sweet, clean taste with a refreshing finish and remarkable persistence. While maintaining the characteristic robust, smooth profile of strong-flavor liquors, quinoa varieties develop unique flavor notes due to their specialized production methods. The choice of saccharifying and fermenting agents critically impacts the fermentation process. Consequently, brewers must carefully control koji fermentation parameters, duration, and temperature, as these factors directly determine the final product’s taste profile, aroma characteristics, and production yield (33).
3.1.3 Quinoa fruit wine
Fermented fruit wine is typically made from fresh fruit through crushing, adjunct addition, fermentation, and aging. Many producers use mixed cultures of yeast and lactic acid bacteria to create more complex flavor profiles (34). The choice of yeast strain is particularly important as it directly affects the wine’s sugar and alcohol content. Kong et al. (35) developed quinoa ginseng wine by mixing quinoa and ginseng fruit (2:1 ratio), followed by liquefaction and saccharification. When the sugar concentration reached 25°Brix, they added 4% dry yeast and fermented the mixture at 32 °C for 9 days. The resulting wine had a golden hue, smooth taste, and unique blended flavor, with 11.2% alcohol content. Since quinoa contains high starch levels, amylase treatment is necessary for liquefaction and saccharification before fermentation. This process converts starch into fermentable sugars. While single-yeast fermentation yields higher sugar and alcohol concentrations, it often produces less complex aromas. In contrast, mixed yeast cultures degrade carbohydrates and proteins in raw materials through synergistic fermentation. Yeasts generate various esters via biosynthesis and the reaction between alcohols and free acids, thereby endowing the wine with characteristic flavors such as wine aroma, fruit aroma, and floral aroma. For instance, phenylethane exhibits a rose-like floral scent, while ethyl octanoate has an apricot aroma. These collectively result in a more balanced and richer flavor (35).
3.1.4 Quinoa yellow wine
Yellow wine, a low-alcohol fermented beverage, preserves beneficial nutrients through fermentation. Liu (36) showed quinoa yellow wine contains higher essential amino acid levels than non-quinoa varieties, with superior nutritional and antioxidant properties compared to traditional millet yellow wine. Zhang et al. (37) developed quinoa wine using Qingli No. 2 through liquefaction (α-amylase 6 U/g at 95 °C for 50 min) and saccharification (glucoamylase 100 U/g at 70 °C for 150 min), followed by fermentation (4.0% yeast at 30C, 1:4 material-water ratio). Antioxidant activity peaked on day 3, with residual activity maintained thereafter. The initial fermentation phase (boiling chyme → mixing → fermentation → separation) is crucial for active compound formation, requiring stable temperatures. The liquefaction method’s slow fermentation with high yeast amounts yields lower alcohol content but better preserves quinoa proteins, it can also improve the fluidity of the wine body (37). Beyond these varieties, Jeon et al. (38) created Korean “makgeolli” using equal quinoa-rice proportions, demonstrating antibacterial, antioxidant and antitumor activities. These applications illustrate quinoa’s global potential as a wine fermentation substrate.
3.2 Quinoa-fermented dairy products
3.2.1 Quinoa yogurt
Quinoa yogurt is produced through a standardized process involving quinoa preparation (soaking, boiling, blending), milk mixing, homogenization, sterilization, and fermentation with typical yogurt cultures (S. thermophilus and L. bulgaricus) (39, 40). Critical process parameters include fermentation time (6–8 h), inoculation amount (3.3–4%), and stabilizer addition (0.2% sodium alginate or Hansheng gum), which significantly influence product texture and flavor profiles (40, 41). Studies demonstrate that quinoa addition (optimal 0.6%) and sugar content (7%) are the most influential factors, affecting fermentation kinetics, acidity development, and final product viscosity (42–47). The recommended fermentation temperature ranges between 39 and 45 °C to ensure optimal microbial activity and product characteristics. Research indicates that quinoa incorporation modifies yogurt properties through multiple mechanisms: reducing pH, accelerating acidification, and enhancing texture by increasing the consistency coefficient (44–46). While quinoa substitution can shorten fermentation time by up to 25% compared to traditional formulations, excessive quinoa (>1%) or sugar concentrations may impair microbial growth and sensory attributes (45–47). Current optimization strategies focus on balancing quinoa content (0.6–1.0%), sugar levels (6–7%), and fermentation duration (6–8 h) to achieve ideal viscosity, flavor intensity, and nutritional enhancement while maintaining typical yogurt fermentation kinetics (43–47). During the fermentation process, proteases secreted by different fermenting bacteria decompose proteins in the raw materials into small-molecular peptides and amino acids. Small-molecular peptides possess a certain umami taste, while amino acids may participate in the Maillard reaction, thereby affecting the color and flavor of yogurt (41).
3.2.2 Quinoa-fermented milk
Quinoa-fermented milk products are typically produced by lactic acid bacteria fermentation using quinoa pulp and reconstituted milk (48). Studies demonstrate that these products exhibit enhanced functional properties compared to conventional fermented milks. Chen et al. developed a “fruit and vegetable-kefir” quinoa-fermented milk with significantly higher polyphenol and flavonoid contents, along with superior antioxidant capacity (hydroxyl radical, DPPH radical, and superoxide anion radical scavenging rates) and iron reduction ability (48). Optimization studies by Zhang et al. identified fermentation temperature as the most critical factor affecting superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in sugar-free quinoa-fermented milk (prepared with 30% quinoa pulp, 5% xylitol, and a 2:1 L. plantarum to L. acidophilus ratio at 38 °C for 8 h) (49). The incorporation of quinoa pulp has been shown to modify milk’s physicochemical properties while boosting antioxidant activity (50, 51). Beyond traditional lactic acid bacteria, innovative applications utilize probiotic strains (Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) to develop functional variants like quinoa-enriched MILK KISHK, with demonstrated improvements in protein content (52) and shelf life (53). The fermentation process naturally reduces water activity (AW) and pH, inhibiting spoilage microorganisms while promoting beneficial flora that enhance intestinal health and mineral absorption. Nutrients such as polysaccharides, polyphenols, saponins, and bioactive peptides in quinoa, after being fermented by intestinal flora, can selectively promote the proliferation of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. Meanwhile, the content of dietary fiber in fermented quinoa remains undegraded, which is beneficial for maintaining intestinal health. These findings underscore the importance of starter culture selection in optimizing both product quality and health-promoting properties.
In summary, quinoa-based fermented dairy products, including yogurt and fermented milk, demonstrate enhanced nutritional and functional properties through optimized fermentation processes. These products represent promising functional food innovations that combine traditional dairy fermentation with quinoa’s nutritional advantages, though careful control of formulation parameters remains crucial for optimal quality and sensory acceptance.
3.3 Other quinoa-fermented drinks
3.3.1 Quinoa-fermented tea
Quinoa fermented tea demonstrates superior nutritional and bioactive properties compared to traditional baked or stir-fried quinoa tea. Quinoa leaves contain valuable components including 3.3% ash, 1.9% fiber, 0.4% nitrate, and 0.29% vitamin E, along with abundant proteins and lipids, making them ideal for tea production (54). Quinoa tea can be processed into two types: black tea and green tea. The manufacturing process of quinoa green tea is as follows: spreading and air-drying → de-enzyming → drying. Among these steps, de-enzyming is critical. Enzymes are inactivated at a high temperature of 230–250 °C to retain the green color and nutrients of the tea, which is finally dried at 100–140 °C. The manufacturing process of quinoa black tea involves withering → rolling → fermentation → drying. The fermentation is carried out under conditions of different temperatures (38–50 °C) and humidities (20–80%) to activate enzyme activity and promote the transformation of substances in the tea, and the final product is obtained by drying at 80–100 °C. The characteristics of quinoa tea are essentially the result of the combined effects of “physical treatment—enzyme activity regulation—substance transformation” during the tea-making process. Green tea is centered on “inhibiting enzyme activity and retaining natural components,” while black tea is keyed on “guiding enzymatic reactions and reorganizing functional substances.” The rich chemical changes during these fermentation processes endow quinoa tea with unique nutritional properties and flavors.
Fermentation enhances flavor profiles, with He et al. (55) identifying 17 distinct flavor compounds in fermented quinoa compared to only 16 in unfermented samples. A notable preparation method developed by Ling et al. (56) involves combining quinoa with Monascus, incubating at 31 °C for 10 days to produce red yeast rice-quinoa fermented powder, which when mixed with cooked quinoa (1:25 ratio) yields tea with significantly higher antioxidant activity than conventional baked quinoa tea. The fermentation process substantially increases soluble phenolic compounds including vanillic acid, protocatechuic acid, and rutin (56), while simultaneously reducing bitterness and improving overall quality (57). However, challenges include potential flavor loss and susceptibility to mildew during fermentation, necessitating strict control of humidity and fermentation duration to maintain product quality and stability. These findings highlight the importance of optimized fermentation parameters for developing high-quality quinoa tea products with enhanced nutritional and sensory characteristics.
3.3.2 Quinoa-fermented non-alcoholic beverages
Quinoa-fermented non-alcoholic beverages, produced through microbial fermentation, offer notable health benefits including gastrointestinal regulation and improved digestion, Glutamate decarboxylase from fermentative bacteria catalyzes the conversion of glutamic acid in quinoa to GABA, and GABA possesses physiological activities such as reducing blood pressure and improving sleep. The standardized production process involves quinoa processing, microbial inoculation, fermentation, broth preparation, and flavor blending (58–60). Microbial selection critically determines beverage characteristics, as demonstrated by Yang et al. (60) using 4% lactic acid bacteria (34 °C, 24 h) to achieve balanced sour–sweet flavors, while Liu et al. (61) combined Auricularia auricula with quinoa and 5 g/L lactic acid bacteria (37 °C) for natural flavor development. Novel strains like P 31891 significantly enhance fermentation efficiency (62), and L. plantarum 299 V (37 °C, 9 h) reduces phytase content, potentially improving mineral absorption (19). These microbial metabolic processes transform carbohydrates into organic acids, the decrease in pH activates endogenous phytase in quinoa, promoting phytate degradation and thereby enhancing the absorption of nutrients. Both enzymatic reactions and microbial activities can significantly improve antioxidant activity while altering flavor characteristics (63). Optimal strain selection thus enables tailored development of beverages with specific functional and sensory properties.
Overall, quinoa-fermented tea and non-alcoholic beverages represent innovative functional products where microbial fermentation significantly enhances both nutritional value and sensory quality. Future research should focus on strain-specific metabolic pathways to further optimize the fermentation-mediated bioconversion of quinoa’s unique phytochemicals, particularly exploring synergistic effects between traditional tea-processing techniques and modern microbial fermentation technologies for developing next-generation functional beverages. This approach could bridge traditional consumption patterns with contemporary health demands while addressing current challenges in flavor consistency and process standardization.
4 Quinoa-fermented foods
Quinoa has emerged as a valuable raw material for diverse food products due to its rich nutritional profile and suitability for low-GI formulations. However, its high dietary fiber content often results in technical challenges including low specific volume, dry texture, and coarse mouthfeel, which negatively impact sensory quality. Fermentation presents an effective solution to these limitations, simultaneously enhancing palatability while boosting nutritional value and bioactive properties. During the fermentation of quinoa, the content of free phenolic acids and flavonoids will significantly increase, the content of total polyphenols will increase by 46.56%, the content of total flavonoids will increase by 57.28%, and the content of bound phenols and polymers will decrease, so the antioxidant capacity of quinoa after fermentation will be significantly improved (p < 0.05) (60). The demonstrated improvements in both organoleptic characteristics and functional benefits suggest quinoa-fermented foods hold significant potential for future food development, warranting expanded research efforts in this promising field.
4.1 Quinoa-fermented instant porridge
While quinoa porridge serves as a nutritious low-GI food option, its inherent hardness presents textural challenges that conventional processing methods fail to adequately address while remaining time-consuming. Fermented instant porridge technology emerges as an effective solution, significantly improving both convenience and palatability (64). Under the slow action of quinoa’s own endogenous enzymes, starch is decomposed into maltose, oligosaccharides, etc., which slows down the postprandial blood glucose rise. The water-soluble dietary fibers abundant in quinoa absorb water and swell to form a viscous gel layer, which wraps starch granules and hinders the contact between amylase and starch, thereby delaying the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Advanced formulations utilizing specialized starters like selenium- and chromium-enriched S. cerevisiae demonstrate particular promise, offering enhanced nutritional balance and metabolic benefits that make them especially suitable for individuals managing hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes. These technological advancements position fermented quinoa porridge as a practical and health-promoting food alternative.
4.2 Quinoa-fermented noodles
Quinoa’s nutritional profile, characterized by high dietary fiber and low GI value, makes it particularly suitable for developing healthy noodle products (65). Fermentation significantly enhances the structural and nutritional qualities of quinoa-based pasta, with studies demonstrating improved elasticity and reduced phytase content through lactic acid bacteria processing (66, 67). Notably, specific L. plantarum strains (CRL1964 and CRL2107) enable effective vitamin B2 and B9 biofortification, offering potential solutions for micronutrient deficiencies as evidenced in animal studies (68, 69). Successful quinoa noodle production requires strategic selection of both raw materials and fermentation strains to optimize both nutritional value and consumer acceptability, with current research primarily focused on lactic acid bacteria applications for quality enhancement.
4.3 Quinoa-fermented bread
Quinoa-enriched bread has emerged as a nutritionally superior alternative to conventional wheat bread, offering enhanced aroma, texture, and functional properties (70). The fermentation process and final product quality are influenced by multiple factors including quinoa flour ratio (optimal 12%), butter content (0.7–5.48%), and specialized starter cultures (71, 72). Recent innovations include gluten-free formulations using L. plantarum CRL 778 for celiac patients (73), improved textural properties through lactic acid bacteria fermentation (reduced hardness, enhanced phytase activity) (74), and superior crumb structure via exopolysaccharide-producing Weissella MG1 (75, 76). Advanced techniques like microbial transglutaminase fermentation significantly increase protein/fiber content while improving dough rheology (77). Optimal production parameters involve two-stage fermentation systems [35–38 °C, 75–90% Relative humidity (RH)] with precisely controlled ingredient ratios (71, 72), where temperature primarily affects cohesiveness/elasticity and butter concentration determines hardness. During the fermentation process, organic acids in quinoa can inhibit starch retrogradation, thereby reducing the staling rate of quinoa bread. Additionally, organic acids can ferment in sucrose to synthesize dextran, which acts as a hydrocolloid to improve the water-holding capacity of dough and increase the porosity of bread simultaneously. These technological advancements, combined with strict process control to prevent structural defects, position quinoa bread as a promising functional bakery product with enhanced nutritional value, sensory quality, and extended shelf stability.
4.4 Quinoa-fermented steamed buns
The growing demand for nutritious bakery options has spurred the development of low-GI quinoa steamed buns, with research demonstrating significant improvements in formulation and processing techniques. Optimal proofing conditions (temperature 28–38 °C, humidity 75–80%) critically influence texture and fluffiness (78), while specialized yeast strains enhance water-binding capacity and viscoelasticity (79). Innovative formulations include konjac-quinoa-protein blends (34 °C, 75% RH, 30 min) for increased fiber/protein content (80) and okra-quinoa combinations (28 °C, 80% RH, 20 min) for nutritional enhancement (81). Studies establish ideal parameters as 10–20% quinoa flour with 0.75–1% yeast and 15–35 min proofing times (82–84), where black quinoa (20% incorporation) shows superior antioxidant activity (83). Maintaining quinoa content below 20% preserves gluten network integrity, while standardized yeast concentrations (1%) ensure optimal texture. These advancements enable production of functional steamed buns with improved nutritional profiles, sensory qualities, and reduced proofing times through controlled temperature/humidity conditions.
4.5 Quinoa-fermented cookies
Traditional fermented biscuits often suffer from nutritional imbalances, featuring excessive carbohydrates, sugars and fats alongside insufficient vitamins and quality proteins. Quinoa incorporation addresses these limitations while enhancing functional properties. Zhou et al. developed Monascus-fermented quinoa biscuits using tea byproduct culture media, achieving desirable crispness and distinctive tea aroma suitable for low-GI diets (85). Sandez Penidez et al. created lactic acid bacteria-fermented variants with elevated antioxidant activity, potentially replacing synthetic antioxidants (86). Qiu et al. pioneered high-fiber quinoa bran biscuits (10.8% dietary fiber) through triple fermentation of wheat flour, quinoa flour and bran (87). These advancements demonstrate quinoa-fermented biscuits’ superior nutritional profiles, improved sensory characteristics, and functional benefits including enhanced antioxidant capacity, delayed lipid/protein oxidation, and extended shelf stability, positioning them as healthier alternatives in the baked goods sector (86).
4.6 Other quinoa-fermented foods
Quinoa has been successfully adapted to diverse fermented food applications beyond traditional products. In Turkish tarhana production, partial substitution of wheat flour with quinoa enhances nutritional and rheological properties while preserving sensory acceptability (88, 89). Fermentation effectively transforms quinoa’s characteristic earthy flavor into pleasant fermented notes, as evidenced in Väkeväinen et al.’s development of probiotic-enriched vegan quinoa snacks (90). Additionally, Chiş et al. demonstrated quinoa’s potential in specialized dietary products through L. plantarum ATCC 8014-fermented quinoa flour muffins, which exhibit reduced carbohydrates alongside elevated organic and folic acid content (91). These applications highlight quinoa’s versatility in meeting contemporary food innovation demands while improving nutritional profiles.
Quinoa fermentation technology effectively addresses the inherent textural and sensory limitations of quinoa-based foods while significantly enhancing their nutritional and functional properties. Future research should focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying fermentation-induced nutrient transformations, particularly the interplay between microbial consortia and quinoa’s unique phytochemical matrix, to develop next-generation functional foods targeting specific metabolic disorders. This approach will facilitate the transition from empirically optimized processes to rationally designed fermentation systems that maximize both nutritional and commercial potential.
5 Quinoa-fermented condiments
5.1 Quinoa miso
Quinoa has been successfully adapted for miso production (known as “doenjang” in China), a traditional Japanese fermented condiment valued for its nutritional benefits, immune-modulating properties, and potential cancer-preventive effects (92). Liu et al. developed an optimized production protocol involving: (1) quinoa cooking and Aspergillus oryzae inoculation (30 °C koji production), followed by (2) mixing with cooked soybeans (2:1 ratio) and (3) anaerobic fermentation with yeast/lactic acid bacteria (28–32 °C, 4–5 months) to yield a glossy, aromatic reddish-brown product (93). Critical parameters include strict temperature control (28–32 °C) and anaerobic maintenance to prevent undesirable yeast byproducts (92). This quinoa incorporation not only enhances miso’s nutritional profile but also expands product diversity, demonstrating significant potential for fermented food industry innovation.
5.2 Quinoa sauce
Quinoa sauce quality and flavor development depend critically on koji preparation, fermentation techniques, and aging processes, with the aging stage being particularly vital for protein denaturation and enzymatic hydrolysis (94). Nakamura et al. developed an innovative mushroom mycelium-derived fermentation enzyme (25 °C, 14-day cultivation) that significantly enhances quinoa’s flavor profile (95). Comparative studies by Dong et al. demonstrated extrusion puffing as the optimal aging method, producing sauce with superior moisture content (15–18%), total acidity (1.2–1.5%), amino acid nitrogen (0.8–1.2 g/100 g), and reducing sugars (3.5–4.0%) while maintaining ideal pH (4.5–5.0) and salt levels (12–14%) (94). Fermentation reduces the hardness of quinoa products by 25–40% by degrading cellulose and pectin. The organic acids (lactic acid, acetic acid) produced by fermentation increase the acidity value. At the same time, the alcohols and esters produced by fermentation impart a floral and fruity aroma, which can mask the grassy taste of the original quinoa. These technological advances not only improve nutritional value and flavor complexity but also create new opportunities in the growing multigrain condiment market, particularly for health-conscious consumers seeking innovative fermented products.
5.3 Quinoa soy sauce
Quinoa-enriched soy sauce merges traditional fermentation techniques with modern nutritional enhancement, employing distinct regional methods: high-salt dilute-state fermentation (Japan/Korea) and combined high-salt/low-salt approaches (China) (96). The production process combines quinoa with steamed soybeans using A. oryzae and specialized yeast strains, yielding products with improved nutritional profiles and unique flavor characteristics. Technological advancements include temperature-controlled mechanical ventilation for optimized koji production and low-temperature fermentation to enhance A. oryzae activity (97). The incorporation of salt-tolerant Torulopsis yeast and Rhodotorula species further improves lipid metabolism and aroma development (97), demonstrating quinoa’s potential to expand both functional and sensory properties in traditional soy sauce fermentation while maintaining authentic production methods.
Quinoa-fermented condiments, including miso, sauce, and soy sauce, demonstrate significant potential in combining traditional fermentation techniques with modern nutritional enhancement. The incorporation of quinoa not only diversifies product offerings but also addresses growing consumer demand for innovative, health-promoting fermented foods while maintaining traditional production authenticity. Future research should focus on standardizing processes and exploring additional functional benefits of quinoa in fermented condiments.
6 Other quinoa-fermented products
6.1 Quinoa enzymes
Microbial fermentation employing lactic acid bacteria, molds, and yeasts drives essential biochemical conversions that produce bioactive enzymes and metabolites (98). This process significantly enhances product quality by modifying flavor profiles, intensifying coloration, reducing irritant compounds, and generating novel bioactive substances including flavonoids and organic acids. In quinoa-specific applications, Tian et al. established optimal fermentation conditions (37 °C, 48-h duration, 20% yeast inoculum) that maximize these beneficial transformations, demonstrating the potential for precisely controlled microbial processes in developing functional quinoa-based food products with enhanced nutritional and sensory properties (99).
6.2 Quinoa-fermented feed
Quinoa straw offers superior nutritional characteristics and digestibility compared to corn straw due to its lower lignin content (100). Fermentation processing enhances these properties, improving texture and palatability while increasing nutritional value. Lv et al. determined the key fermentation parameters in order of significance: lactic acid bacteria concentration > moisture content > duration, with optimal conditions (12 mg/kg inoculum, 60% moisture, 24.5 days) yielding 6.93% crude protein (100). Comparative studies by Yu et al. demonstrated fermentation’s nutritional benefits, including 2.70% crude protein increase, approximately 3% higher soluble sugars, and enhanced cellulose degradation versus unfermented feed (101). These improvements position fermented quinoa straw as a viable alternative feed source with enhanced digestibility and nutritional profile.
7 Key technologies and applications of quinoa fermentation
7.1 Impact of the sensory properties of fermented quinoa products on consumer preferences
The application of fermented quinoa products has garnered increasing attention; however, the relationship between their sensory characteristics and consumer preferences exhibits complexity, influenced not only by the inherent properties of quinoa but also by processing techniques, incorporation ratios, and regional cultural differences (102). Studies indicate that the texture and flavor of fermented quinoa products are critical determinants of consumer acceptance, with negative sensory attributes such as off-flavors and grittiness significantly reducing preference (103). Meanwhile, the use of flavoring agents, such as adding raspberry syrup to fermented quinoa beverages, can markedly enhance product acceptability (104).
Furthermore, the incorporation ratio of quinoa exhibits a threshold effect on consumer preference, with low-to-moderate levels (5–30%) generally being well-accepted, whereas exceeding a certain limit leads to decreased acceptability (102). Cross-cultural studies have also demonstrated significant regional variations in preferences for quinoa-based products, underscoring the importance of market-specific optimization (105). Notably, while quinoa can enhance the nutritional profile of food products, this improvement may sometimes come at the expense of sensory quality, particularly in low-fat or gluten-free formulations (106).
In summary, during the development of fermented quinoa products, maintaining sensory quality alongside nutritional enhancement is essential, and formulations should be tailored to the specific demands of target markets. Future research should focus more on balancing the health benefits of quinoa with sensory acceptability, particularly in product development for children, aiming to foster long-term consumption habits (102, 106).
7.2 Impact of fermented quinoa products on human health
Fermented quinoa products demonstrate significant potential in modulating gut microbiota, enhancing the biotransformation of bioactive compounds, and improving human health. Studies indicate that quinoa-derived polysaccharides and dietary fibers act as prebiotics, reducing intestinal pH to promote the proliferation of beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium while inhibiting pathogens like Escherichia coli (6). Additionally, quinoa flavonoids can modulate gut microbiota composition by increasing the abundance of Firmicutes while reducing Bacteroidetes, thereby improving microbial balance (22). The short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced during fermentation not only help maintain intestinal barrier integrity but also regulate immune and inflammatory responses by activating G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) (107, 108).
Regarding the biotransformation of bioactive compounds, microbial fermentation significantly enhances the total phenolic content and bioavailability in quinoa, particularly elevating the levels of flavonoids such as quercetin and kaempferol, which strengthens antioxidant activity (23, 109). Fermentation also degrades toxic alkaloids in quinoa saponins, generating low-molecular-weight sapogenins, while hydrolyzing polysaccharides into readily fermentable oligosaccharides, further promoting SCFA production (22, 110). These metabolites exert beneficial effects on human health, including ameliorating intestinal disorders, mitigating metabolic diseases, and providing systemic protection. For instance, SCFAs have been shown to alleviate intestinal damage in models of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer, while modulating the gut-brain axis to improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) (22, 62, 107).
Despite challenges such as dose-dependent potential toxicity and individual variability, the therapeutic effects of fermented quinoa products on metabolic disorders—including obesity, diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)—have been preliminarily validated in animal studies (22, 111). Future research should focus on elucidating the interaction mechanisms between fermentation strains and quinoa components, optimizing the synbiotic effects of prebiotics and probiotics, and conducting long-term human clinical trials to validate the health benefits of fermented quinoa products (22, 62).
7.3 Effects of bacterial strains during quinoa fermentation
Specific microbial strains play pivotal roles in quinoa biotransformation through multiple mechanisms that promote growth, enhance stress resistance, suppress diseases, and regulate metabolic processes. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) such as Bacillus licheniformis QA1 and Enterobacter asburiae QF11 secrete organic acids to solubilize insoluble phosphates in soil, improving phosphorus availability and thereby stimulating quinoa root development and biomass accumulation (112). Additionally, nitrogen-fixing strains can fix atmospheric nitrogen, providing supplemental nitrogen nutrition that significantly enhances plant height, panicle weight, and grain yield (113, 114).
The synthesis and signaling of phytohormones constitute another critical mechanism influencing quinoa growth. For instance, Pseudomonas sp. M30-35 produces indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), directly stimulating cell division and root elongation to improve nutrient uptake efficiency (115). Seed coating with Trichoderma harzianum TE-7/TE-126 activates phytohormone signaling pathways, increasing shoot dry weight and yield by 2- to 3-fold (116).
In terms of stress resilience enhancement, specific strains significantly improve quinoa’s tolerance to environmental challenges. Under salt stress, Pseudomonas sp. M30-35 maintains photosynthetic efficiency by increasing chlorophyll a/b content while promoting root activity and saponin accumulation to counteract phosphorus deficiency (115). Furthermore, the mineral-solubilizing bacterium Pontibacter lucknowensis Cq-48 enhances water-use efficiency by improving transpiration rates and leaf area (114).
Biocontrol and disease suppression represent another key function. Trichoderma spp. exhibit mycoparasitism by coiling around and lysing pathogenic hyphae, reducing downy mildew incidence, while their volatile organic compounds (VOCs) demonstrate significant inhibitory effects against Botrytis cinerea (117, 118). Endophytic bacteria secrete antimicrobial metabolites to mitigate bacterial leaf spot severity (119). Additionally, these microbes induce systemic resistance by upregulating defense-related genes, strengthening quinoa’s tolerance to pathogens (119).
Finally, fermentation enhancement mechanisms reveal that lactic acid bacteria (LAB) such as Lactobacillus fermentum and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus can significantly elevate α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activities during quinoa seed fermentation, thereby improving anti-hyperglycemic functionality (120).
In summary, specific microbial strains exert multifaceted interactions to drive quinoa biotransformation. Future research should focus on optimizing their application strategies to achieve sustainable quinoa production (113, 115, 116).
7.4 Industrial and therapeutic applications of quinoa fermented products
Quinoa, as a highly nutritious pseudocereal, demonstrates remarkable potential in industrial applications and therapeutic uses through its fermented products. Rich in bioactive components including proteins, polyphenols, saponins, and dietary fibers, quinoa undergoes microbial biotransformation during fermentation, thereby enhancing its functional properties (121).
In industrial applications, fermented quinoa beverages not only exhibit improved foam stability but also serve as wine-clarifying agents to enhance product texture and sensory characteristics (18). Furthermore, fermented quinoa byproducts can be utilized to produce bio-preservatives, emulsifiers, or food carriers, suitable for baked goods and plant-based milk alternatives, offering new options for lactose-intolerant individuals (121, 122).
Regarding therapeutic applications, fermentation significantly enhances the antioxidant, antihypertensive, and antidiabetic activities of quinoa extracts (121). Studies indicate that probiotic fermentation of quinoa water-soluble extracts increases polyphenol and peptide content, effectively scavenging free radicals while inhibiting α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase, suggesting potential interventions for metabolic disorders (121). Additionally, saponins and polysaccharides in fermented quinoa products exhibit anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, making them promising candidates for neuroprotective agents or immune enhancers (121, 123).
Future research should prioritize the following key areas: First, novel bioactive compounds-particularly phytochemicals from diverse quinoa genotypes or regional varieties-need to be isolated and characterized, with emphasis on their transformation mechanisms during fermentation (121). Second, green and sustainable processes should be optimized to recycle quinoa byproducts, reducing industrial costs and environmental footprints (121). Third, clinical validation and safety assessments are critical, as current studies predominantly rely on in vitro or animal models; human clinical trials are warranted to confirm the safety and therapeutic efficacy of fermented products (121). Lastly, expanding applications in emerging fields-such as nanocarriers for drug delivery or edible films-and integrating biotechnology to enhance stress-resistant quinoa varieties should be explored (121, 122).
In summary, fermented quinoa products exhibit broad prospects in industrial and therapeutic applications. However, future research must address bottlenecks including varietal diversity, process optimization, and clinical translation to facilitate the transition from laboratory to market (121, 122) (Figure 2).
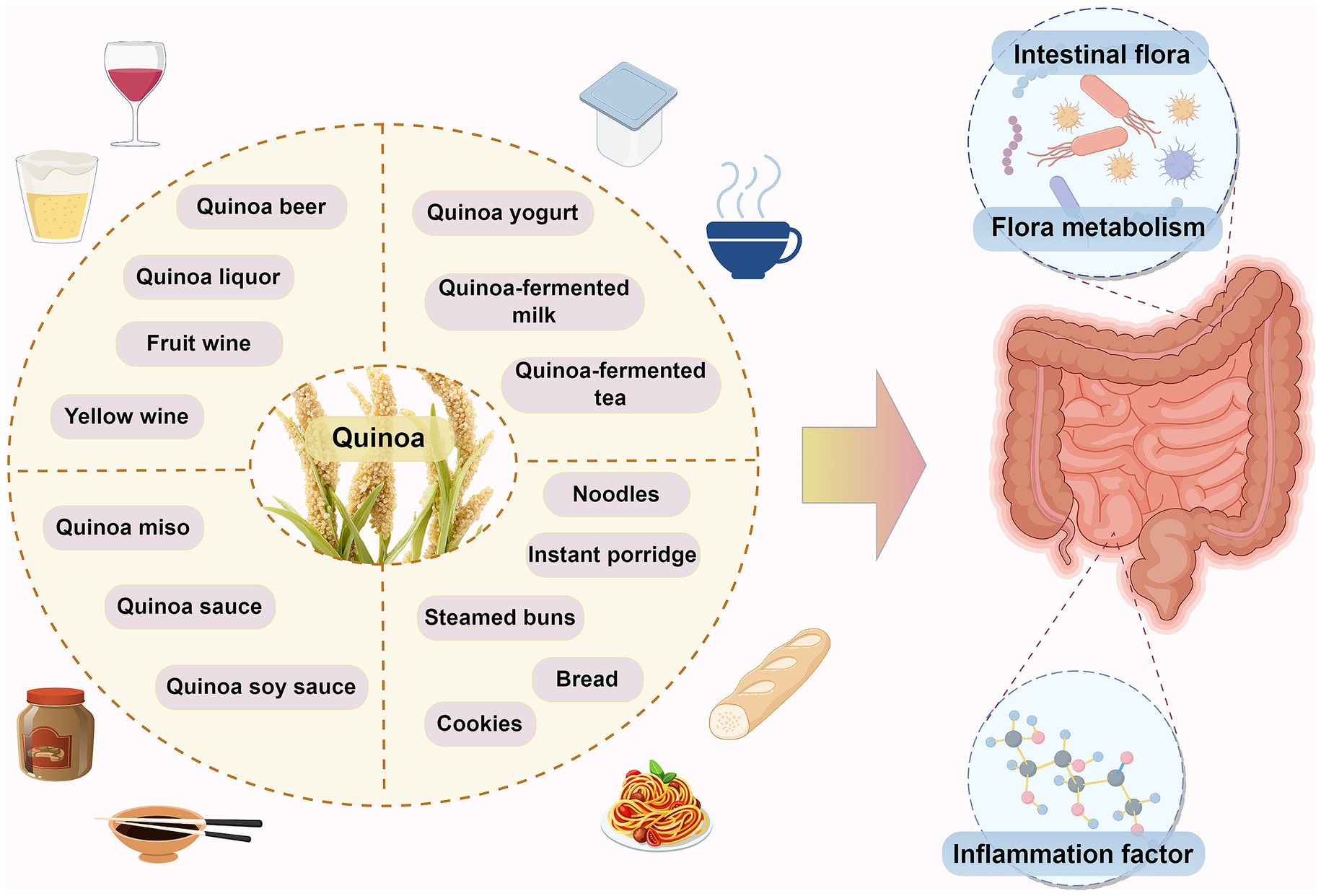
Figure 2. A summary of the findings discussed in this review. This figure was drawn by Figdraw.com and some images by OpenClipArt-vectors and Tshirtshophoplix via Pixabay.com.
8 Future perspectives and innovations
Current research has primarily focused on grain wines and dairy products, with fermented teas and condiments receiving comparatively less attention. To advance this field, future efforts should focus on three key directions:
(1) Process optimization and standardization
Given the substantial variation in fermentation parameters, systematic optimization is critical to enhance efficiency and reproducibility. Reducing processing time by 30–50% through strain selection, enzyme supplementation, or dynamic fermentation control could significantly improve economic viability, which is currently hampered by a 20–40% cost increase due to prolonged fermentation.
(2) Sensory and nutritional enhancement
Further research should elucidate the microbial mechanisms governing flavor development and texture modulation to align with regional dietary preferences. Targeted fermentation using functional strains may concurrently improve palatability, gut health benefits, and nutrient bioavailability.
(3) Market-driven product diversification
Expanding beyond conventional formats, localized adaptations-such as savory condiments for Asian markets or high-protein fermented snacks for Western consumers-could boost market penetration. Integrating multi-omics approaches will accelerate strain screening and process design, facilitating scalable production while preserving nutritional advantages.
9 Conclusion
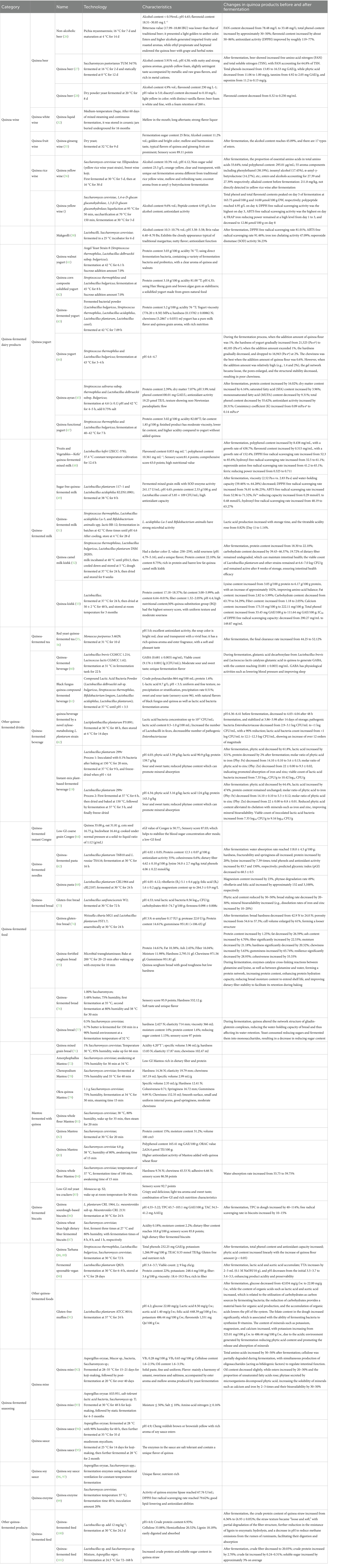
This study systematically cataloged 54 quinoa fermented products developed worldwide (Figure 3). Analysis of these products revealed distinct fermentation protocols: alcoholic products employ low-temperature fermentation (<30 °C) with specific microbial consortia (yeast for beer/fruit wine, Daqu for Baijiu, combined enzymes/yeast for yellow wine), while dairy products utilize thermophilic bacteria (S. thermophilus/L. bulgaricus at 42 °C for 6–8 h for yogurt; Lactobacillus/L. plantarum at 37–42 °C for fermented milk). Bakery products demonstrate optimal fermentation at 30–38 °C with 75–80% RH for 15–40 min. This comprehensive process inventory establishes critical reference parameters for: (1) nutrient preservation through optimized temperature control, (2) standardization of microbial starter cultures, and (3) industrialization potential assessment. The findings particularly highlight lactic acid bacteria’s dual utility in both human food and animal feed fermentation, suggesting cross-industry applications. These documented processes provide a foundational framework for scaling production while maintaining product quality, addressing current challenges in quinoa fermentation standardization and commercial viability. Future research should focus on mechanization adaptations of these optimized protocols to facilitate industrial adoption.
Author contributions
CheL: Validation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Resources. TL: Software, Writing – original draft. XiaoL: Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Project administration. WG: Writing – original draft, Investigation. JL: Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. GH: Resources, Writing – original draft. ChuL: Validation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. FL: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XianL: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. XM: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Department of Science and Technology of Jilin Province (nos. 20220202076NC, 20220402078GH, 20240601010RC) and the Education Department of Jilin Province (no. JJKH20251206KJ). The APC was funded by XL.
Conflict of interest
ChuL and XM were employed by Jilin Province Hua En Biotechnology Co. Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors we have use Editage for English language editing.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Maradini, AM, Pirozi, MR, Borges, JTD, Sant'Ana, HMP, Chaves, JBP, and Coimbra, JSDR. Quinoa: nutritional, functional, and antinutritional aspects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2017) 57:1618–30. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2014.1001811
2. He, LY, Wang, L, and Lv, JM. Research progress on nutritional composition and biological function of quinoa. Grain Oil. (2022) 35:11–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2022.04.004
3. Pathan, S, and Siddiqui, RA. Nutritional composition and bioactive components in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) greens: a review. Nutrients. (2022) 14:558. doi: 10.3390/nu14030558
4. Zevallos, VF, Herencia, IL, Chang, F, Donnelly, S, Ellis, JH, and Ciclitira, PJ. Gastrointestinal effects of eating quinoa (Chenopodium quinoawilld.) in celiac patients. Off J Am College Gastroenterol. (2014) 109:270–8. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.431
5. Yang, S, Dong, YJ, Zhu, KT, Guan, SS, and Xiao, Y. Research progress on quinoa starch. Cereals Oils. (2023) 36:1. 4,8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2023.04.001
6. Liu, X, Song, JJ, and Lin, XH. Research progress on nutrition and bioactive components of quinoa. Food Saf Guide. (2022) 7:135–7. doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2022.07.036
7. Ruiz, GA, Xiao, W, Van Boekel, M, Minor, M, and Stieger, M. Effect of extraction pH on heat-induced aggregation, gelation and microstructure of protein isolate from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Food Chem. (2016) 209:203–10. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.04.052
8. Zhang, Q, Gao, Y, Pan, X, Qian, F, and Wu, XY. Amino acid composition and nutritional evaluation of quinoa harvested in two seasons on the Chengdu plain [J/OL]. Food Ferment Ind. (2023) 9:1–15. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.033324
9. Hussain, MI, Farooq, M, Ishaq, A, Al-Ghamdi, AA, and Hatamleh, AA. Botany, nutritional value, phytochemical composition and biological activities of quinoa. Plants (Basel). (2021) 10:2258. doi: 10.3390/plants10112258
10. Jiao, HY, Gao, WG, and Chen, LW. Determination of nutritional composition of quinoa and its promoting effect on the health of pregnant women. Grassroots Med Forum. (2018) 22:1902–3. doi: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2018.14.018
11. Wang, J, Zhou, SX, Chang, SJ, Zhao, LY, and Chen, GT. Comparison and application of nutritional and functional active ingredients in different varieties of quinoa. J Food Saf Qual Test. (2022) 13:681–7. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2022.03.002
12. Ren, G, Teng, C, Fan, X, Guo, S, Zhao, G, Zhang, L, et al. Nutrient composition, functional activity and industrial applications of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Chem. (2022) 410:135290. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135290
13. Suárez-Estrella, D, Torri, L, Pagani, MA, and Marti, A. Quinoa bitterness: causes and solutions for improving product acceptability. J Sci Food Agric. (2018) 98:4033–41. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8980
14. Mroczek, A. Phytochemistry and bioactivity of triterpene saponins from Amaranthaceae family. Phytochem Rev. (2015) 14:577–605. doi: 10.1007/s11101-015-9394-4
15. Lim, JG, Park, HM, and Yoon, S. Analysis of saponin composition and comparison of the antioxidant activity of various parts of the quinoa plant (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 8:694–702. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1358
16. El Hazzam, K, Hafsa, J, Sobeh, M, Mhada, M, Taourirte, M, EL Kacimi, K, et al. An insight into saponins from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd): a review. Molecules. (2020) 25:1059. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051059
17. Song, LM, Yu, Y, Du, LD, Ji, XY, Gao, H, Cai, YQ, et al. Does saponin in quinoa really embody the source of its bitterness? Food Chem. (2024) 437:137872. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137872
18. Castro-Alba, V, Lazarte, CE, Perez-Rea, D, Carlsson, NG, Almgren, A, Bergenståhl, B, et al. Fermentation of pseudocereals quinoa, canihua, and amaranth to improve mineral accessibility through degradation of phytate. J Sci Food Agric. (2019) 99:5239–48. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9793
19. Ayub, M, Castroc-Alba, V, and Lazarte, CE. Development of an instant-mix probiotic beverage based on fermented quinoa with reduced phytate content. J Funct Foods. (2021) 87:104831. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104831
20. Li, Q, Yu, D, Dong, GL, and Du, XW. Research progress on the mechanism of microbial fermentation transformation of saponin compounds Chinese herbal medicine Chin Herb Med. (2022) 53:7264–78. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.22.031
21. Karlund, A, Gomez-Gallego, C, Korhonen, J, Palo-oja, O-M, El-Nezami, H, and Kolehmainen, M. Harnessing microbes for sustainable development: food fermentation as a tool for improving the nutritional quality of alternative protein sources. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1020. doi: 10.3390/nu12041020
22. Huang, H, Jia, C, Chen, X, Zhang, L, Jiang, Y, Meng, X, et al. Progress in research on the effects of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) bioactive compounds and products on intestinal flora. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1308384. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1308384
23. Melini, F, and Melini, V. Impact of fermentation on phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of quinoa. Fermentation. (2021) 7:20. doi: 10.3390/fermentation7010020
24. Chen, H, Suo, R, Liu, YQ, Zhang, YX, Lv, W, and Wang, J. GC-MS and GC-IMS analysis of characteristic volatile flavor components in quinoa wine. Chin J Food Sci. (2023) 23:268–80. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2023.12.028
25. Yang, D, and Gao, X. Progress of the use of alternatives to malt in the production of gluten-free beer. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 62:2820–35. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1859458
26. Prasad, DGC, Vidyalakshmi, R, Baskaran, N, and Anand, TM. Influence of Pichia myanmarensis in fermentation to produce quinoa based non-alcoholic beer with enhanced antioxidant activity. J Cereal Sci. (2022) 103:103390. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2021.103390
27. Dezelak, M, Zarnkow, M, Becker, T, and Kosir, IJ. Processing of bottom-fermented gluten-free beer-like beverages based on buckwheat and quinoa malt with chemical and sensory characterization. J Inst Brew. (2014) 120:360–70. doi: 10.1002/jib.166
28. Bian, M, and Zhou, GT. Study on the saccharification process of quinoa beer. China Brewing. (2017) 36:180–4. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2017.11.039
29. Adebo, OA, and Medina-Meza, IG. Impact of fermentation on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of whole cereal grains: a mini review. Molecules. (2020) 25:927. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040927
30. Bogdan, P, Kordialikk-Bogack, AE, Czyzowska, A, Oracz, J, and Żyżelewicz, D. The profiles of low molecular nitrogen compounds and fatty acids in wort and beer obtained with the addition of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.), amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus L.) or maltose syrup. Foods. (2020) 9:1626. doi: 10.3390/foods9111626
31. Yang, HB, Yu, FY, and Li, X. Research on the key technology of dry sauce baijiu brewing. Wine Making. (2022) 49:131–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8110.2022.03.035
32. Yang, MC. The fragrance of the fine wine "Chenopodium cereals liquid" overflows the capital city. Chin Liquor. (2018) 12:78–9.
33. Zheng, W, Xue, JL, Zhang, L, Yang, G, Fan, HJ, Yang, Y, et al. Study on the technology of brewing compound flavor baijiu with different saccharification and fermentation agents. Food Ferment Ind. (2022) 48:61–6. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.030576
34. Zhao, GH, Hu, MQ, Lu, XW, Peng, LT, Wang, YR, and Zhao, FL. Research progress in the processing technology of fermented fruit wine. China Brewing. (2022) 41:27–31. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.04.005
35. Kong, ZM, Yang, XJ, Dang, B, Zhang, J, Zhang, WG, and Chi, DZ. Optimization of fermentation process and analysis of aroma components of quinoa ginseng fruit wine. Agric Prod Process. (2021) 7:39–44. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2021.04.010
36. Liu, H. Quality evaluation of naked oats and brewing of oat yellow wine. Chinese Acad Agric Sci. (2015) 40–7. doi: 10.7666/d.Y2787571
37. Zhang, WG, Zhang, J, Dang, B, and Yang, XJ. Optimization of fermentation process and antioxidant properties of quinoa yellow wine. Food Mach. (2019) 35:174–178+226. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.12.032
38. Jeron, EB, Song, MG, Kim, SH, Choi, JS, Lee, JS, and Park, SY. Quality characteristics and antioxidant activities of Korean traditional rice and quinoa-based wine “Makgeolli”. Cereal Chem. (2023) 100:473–83. doi: 10.1002/cche.10626
39. Tribby, D, and Teter, V. The sensory evaluation of dairy products. Cham: Springer International Publishing, (2023): 199–234.
40. Zheng, M, Du, JJ, Lu, Y, and Bai, YY. Research progress on the application of functional yogurt. Modern Food. (2022) 28:48–50. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2022.13.012
41. Li, X, Jiang, FG, Ling, YK, Deng, X, Xu, YS, and Zhao, G. Optimization of fermentation process for quinoa walnut yogurt using response surface methodology. Food Res Dev. (2020) 41:131–6. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.23.022
42. Yang, SX, Zhu, ZJ, and Li, N. Research on the process of corn quinoa compound solidified yogurt. Agric Prod Process. (2022) 18:51–4. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.09.051
43. Quan, F, Zhu, WX, Zang, Q, Hong, D, Wang, JN, and Wu, SQ. Optimization of quinoa fermented yogurt process using response surface methodology. Food Res Dev. (2022) 43:133–9. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.08.018
44. Codina, GG, Framciuc, SG, and Mironeasa, S. Rheological characteristics and microstructure of milk yogurt as influenced by quinoa flour addition. J Food Qual. (2016) 39:559–66. doi: 10.1111/jfq.12210
45. Akkoyun, Y, and Arslan, S. The impact of quinoa flour on some properties of ayran. Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 8:5410–8. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1832
46. Alkobeisi, F, Varidi, MJ, Varidi, M, and Nooshkam, M. Quinoa flour as a skim milk powder replacer in concentrated yogurts: effect on their physicochemical, technological, and sensory properties. Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 10:1113–25. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2771
47. Du, JJ, Bai, YY, Lu, Y, Zheng, M, and Yu, SY. Study on the production process of quinoa functional yogurt. Modern Food. (2022) 28:68–72. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2022.19.020
48. Chen, SJ, and Wang, WR. Development and antioxidant properties analysis of fruit vegetable kefir quinoa fermented mixed freeze-dried food. Preserv Process. (2021) 21:58–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2021.11.009
49. Zhang, Y, Wang, Y, Li, ZF, Wang, D, Zhang, YL, Zhang, H, et al. The physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of sugar free quinoa fermented milk. Food Mach. (2021) 37:18–22+92. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2021.10.004
50. Zhang, Y, Wang, Y, Li, ZF, Wang, D, Zhang, YL, and Zuo, ZH. Optimization of the composite fermentation process and quality analysis of sugar free quinoa fermented milk. Food Ind Technol. (2021) 42:209–2016. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021020126
51. Casarotti, SN, Carneiro, BM, and Penna, ALB. Evaluation of the effect of supplementing fermented milk with quinoa flour on probiotic activity. J Dairy Sci. (2014) 97:6027–35. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8197
52. Abd-Rabou, HS, Shehata, MG, EL Sohaimy, SA, and Awad, A. Functional probiotic quinoa camel milk kishk. J Food Process Preserv. (2020) 44:e14681. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.14681
53. Ismail, HA, and Rayan, AM. Preparation and evaluation of Quinoa-Kishk as a novel functional fermented dairy product. J Food Sci Technol. (2022) 59:1063–74. doi: 10.1007/s13197-021-05110-8
54. Luo, XX. Analysis of the main nutritional functional components and antioxidant evaluation of quinoa tea. Chinese Acad Agric Sci. (2018) 17–47.
55. He, SL, Lin, YD, Deng, RY, Xiong, J, Zhou, LN, and Zhou, YF. Study on the adaptability of quinoa substrate in monascus fermentation. Chin Season. (2020) 45:92–7.
56. He, SL, Lin, YD, Tian, D, Zhou, LN, Zhao, XL, Luo, LN, et al. Study on the compound technology and antioxidant activity of red koji quinoa fermented tea. Grain Oil. (2022) 35:143–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2022.05.033
57. Zhou, XY, Yue, T, Wei, ZF, Yang, LY, Zhang, LH, Wu, BM, et al. Tea-making technology by using quinoa raw materials. Food Sci Technol. (2023) 43:e117422. doi: 10.1590/fst.117422
58. Lu, Y. Optimization of quinoa fermented beverage formula by response surface methodology. Grain Process. (2022) 47:53–8.
59. Lei, Q, Wang, J, Li, Q, Li, J, Wang, X, Mao, N, et al. Effects of Latilactobacillus delbrueckii fermentation on the bioconversion and antioxidant capacity of phenolic compounds in quinoa sprouts. Food Biosci. (2024) 59:104190. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104190
60. Yang, TY, Liu, YQ, and Ma, TJ. Optimization of the fermentation process for quinoa fermented beverage rich in gamma aminobutyric acid food industry technology. Food Ind Technol. (2019) 40:169. 175,180. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.16.028
61. Liu, XY, Yang, GL, Kong, XH, and Wang, B. Study on the processing technology and stability of black fungus quinoa compound fermented beverage. China Brewing. (2018) 37:193–8. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.06.038
62. Canaviro-Pza, P, Oscarsson, E, Kjelistrom, A, Olsson, H, Jois, C, Hakansson, A, et al. Effects on microbiota composition after consumption of quinoa beverage fermented by a novel xylose-metabolizing L. plantarum strain. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3318. doi: 10.3390/nu13103318
63. Meng, FB, Zhou, L, Li, JJ, Li, YC, Wang, M, Zou, LH, et al. The combined effect of protein hydrolysis and Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on antioxidant activity and metabolomic profiles of quinoa beverage. Food Res Int. (2022) 157:111416. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111416
64. Yu, Z, Cao, YL, Han, D, Zhu, YY, Wu, C, Yu, YJ, et al. Optimization of low GI quinoa multigrain porridge formula by D-optimal mixture design. Food Res Dev. (2022) 43:117–22. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.15.016
65. Zhang, X, Ren, YY, Meng, ZK, and Zou, Y. Study on the extrusion process and in vitro digestion characteristics of low GI quinoa noodles. Food Ferment Technol. (2021) 57:57–62+85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-506X.2021.04.008
66. Lorusso, A, Verni, M, Montemurro, M, Coda, R, Gobbetti, M, and Rizzello, CG. Use of fermented quinoa flour for pasta making and evaluation of the technological and nutritional features. LWT. (2017) 78:215–21. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.12.046
67. Dallagnol, AM, Pescuma, M, De Valdez, GF, and Rollán, G. Fermentation of quinoa and wheat slurries by Lactobacillus plantarum CRL 778: proteolytic activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. (2013) 97:3129–40. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4520-3
68. Carrizo, SL, De LeBlanc, AM, Leblanc, JG, and Rollán, GC. Quinoa pasta fermented with lactic acid bacteria prevents nutritional deficiencies in mice. Food Res Int. (2020) 127:108735. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108735
69. Montemurro, M, Coda, R, and Rizzello, CG. Recent advances in the use of sourdough biotechnology in pasta making. Foods. (2019) 8:129. doi: 10.3390/foods8040129
70. Paucean, A, Man, SM, Chis, MS, Mureşan, V, Pop, CR, Socaci, SA, et al. Use of pseudocereals preferment made with aromatic yeast strains for enhancing wheat bread quality. Foods. (2019) 8:443. doi: 10.3390/foods8100443
71. Hao, TT, Tang, LQ, Liu, Y, and Fu, LH. Study on the technology of novel quinoa mixed grain bread. Agric Prod Process. (2017) 2:24–8. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2017.01.044
72. Chen, HF, Chen, J, Li, W, et al. Optimization of ripening process of pre awakened frozen raw embryo Mantou food research and development (2024) 45:137–45.
73. Jagelaviciute, J, and Cizeikiene, D. The influence of non-traditional sourdough made with quinoa, hemp and chia flour on the characteristics of gluten-free maize/rice bread. LWT. (2021) 137:110457. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110457
74. Wolter, A, Hager, AS, Zannini, E, Czerny, M, and Arendt, EK. Influence of dextran-producing Weissella cibaria on baking properties and sensory profile of gluten-free and wheat breads. Int J Food Microbiol. (2014) 172:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.11.015
75. Castillejos, GR, Ortega, CL, Pérez, AG, García, NM, and Salazar, RR. Effects of transglutaminase on the proximal and textural properties of gluten-free bread of sorghum and quinoa. Revista de la Facultacd de Agronomia. (2018) 35:188–201. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329571592
76. Wei, W. Optimization of the formula and processing technology of quinoa bread using response surface methodology. Food Ind. (2022) 43:67–71.
77. Zhou, XC, Zhang, XT, Ye, JD, Zhao, WL, Zhou, XY, and Li, H. Research on the technology of quinoa bread. Food Res Dev. (2019) 40:74–9. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.20.014
78. Lu, HM, Wang, QY, Yuan, M, and Zhang, HF. Effects of different yeasts on the characteristics and quality of quinoa Mantou dough Chinese food additives (2023) 34:126–31. doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2023.11.017
79. Cheng, WX, Wang, YJ, Wang, F, and Long, WL. Study on technological conditions of konjac Mantou grain processing Grain Process. (2023) 48:32–6.
80. Xu, XB, Pang, M, Wu, ZS, and You, XL. Development of okra quinoa Mantou. Grain Process. (2023) 48:34–8.
81. Wei, X, and Han, WY. The effect of quinoa whole flour on the quality of Mantou. Modern Food. (2021) 16:121–4. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2021.16.034
82. Cheng, KY, Sun, JX, Zhao, WL, Liu, J, Liao, ZY, and Li, H. Optimization of processing technology and analysis of quality characteristics of quinoa Mantou. China Fruit Veg. (2021) 41:16–20. doi: 10.19590/j.cnki.1008-1038.2021.02.004
83. Chen, YH, Yang, XS, Guo, HM, Ren, GX, and Li, JC. The effect of different varieties of quinoa wheat flour on the quality and antioxidant activity of Mantou. Food Ferment Ind. (2020) 46:157–64. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.021861
84. Zhang, F, Zhao, L, Jing, Z, Gao, TY, Yu, H, Zhang, NH, et al. Characteristics of quinoa wheat mixed flour dough and processing technology of quinoa Mantou. Food Sci. (2019) 40:323–32. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180822-235
85. Zhou, Y. Process optimization of low GI red koji tea biscuits. Fujian Agric Sci Technol. (2021) 52:43–8. doi: 10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2021.04.008
86. Sandez Penidez, SH, Velasco Manini, MA, LeBlanc, JG, Gerez, CL, and Rollán, GC. Quinoa sourdough-based biscuits with high antioxidant activity fermented with autochthonous lactic acid bacteria. J Appl Microbiol. (2022) 132:2093–105. doi: 10.1111/jam.15315
87. Qiu, LM. A study on the processing technology of high dietary fiber fermented biscuits with quinoa wheat bran. Food Saf Guide. (2023) 17:142–144148. doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2023.17.043
88. Çevik, A, and Ertas, N. Effect of quinoa, buckwheat and lupine on nutritional properties and consumer preferences of tarhana. Qual Assur Saf Crops Foods. (2019) 11:145–55. doi: 10.3920/QAS2018.1305
89. Demir, MK. Use of quinoa flour in the production of gluten-free tarhana. Food Sci Technol Res. (2014) 20:1087–92. doi: 10.3136/fstr.20.1087
90. Vakevainen, K, Ludena-Urquizo, F, Korkala, E, Lapveteläinen, A, Peräniemi, S, Von, WA, et al. Potential of quinoa in the development of fermented spoonable vegan products. LWT. (2020) 120:108912. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108912
91. Chiş, MS, Păucean, A, Man, SM, Vodnar, DC, Teleky, BE, Pop, CR, et al. Quinoa sourdough fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 8014 designed for gluten-free muffins—a powerful tool to enhance bioactive compounds. Appl Sci. (2020) 10:7140. doi: 10.3390/app10207140
92. Wu, HL, Wu, CS, and Ding, XW. Comparison between Japanese traditional fermented food miso and Chinese fermented soybean Chinese seasoning. China Condim. (2014) 39:134–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2014.02.032
93. Liu, XY, and Yang, GL. The brewing process of quinoa miso and the development of its sauce powder. Chin Season. (2017) 42:93–96+99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2017.02.020
94. Dong, P, Xu, CJ, Wang, XT, Yuan, FM, Wu, HC, and Deng, J. The effect of different ripening methods on the quality of quinoa sauce. Food Ind Technol. (2022) 43:60–8. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120205
95. Kazuo, N, and Song, G. Brewing quinoa sauce by inoculating mushroom hyphae on quinoa. China Brewing. (2016) 35:169.
96. Yamana, T, Taniguchi, M, Nakahara, T, Ito, Y, Okochi, N, Putri, SP, et al. Component profiling of soy-sauce-like seasoning produced from different raw materials. Meta. (2020) 10:137. doi: 10.3390/metabo10040137
97. Lu, ZY, and Wei, KQ. Summary of high salt dilute fermentation technology for "brewing soy sauce". Chin Season. (2006) 1:28–31+42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2006.01.006
98. Suo, JY, Zhu, YJ, Chen, L, and Chen, XZ. Research and development prospect analysis of edible enzymes. Food Ferment Ind. (2020) 46:271–83. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024617
99. Yu, T, Hu, YC, Peng, LX, Zou, L, Zhao, G, and Sun, YL. Preparation process and activity of quinoa enzyme. Food Ind. (2020) 41:156–60.
100. Lv, J, Wu, ZY, Guo, XN, Feng, YL, Lu, JX, Chai, WW, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for quinoa straw by lactic acid bacteria based on response surface methodology. Zhejiang Agric J. (2022) 34:1866–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.09.06
101. Yu, XF, Guo, XN, Zhang, Y, Liu, ZW, Zhang, XW, Xu, KX, et al. Optimization of fermentation process for quinoa straw feed using response surface methodology. J Grassland Ind. (2021) 30:155–64. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2020203
102. Eduardo, K, Bedoya-Perales, N, Escobedo-Pacheco, E, and Saldaña, E. Sensory and consumer science as a valuable tool to the development of quinoa-based food products: more than three decades of scientific evidence. Scientia Agropecuaria. (2024) 15:251–67. doi: 10.17268/sci.agropecu.2024.019
103. Cizeikiene, D, Gaide, I, and Basinskiene, L. Effect of lactic acid fermentation on quinoa characteristics and quality of quinoa-wheat composite bread. Foods. (2021) 10:171. doi: 10.3390/foods10010171
104. Karovičová, J, Kohajdová, Z, Minarovičová, L, Lauková, M, Greifová, M, Greif, G, et al. Utilisation of quinoa for development of fermented beverages. Slov J Food Sci. (2020) 14:465–72. doi: 10.5219/1323
105. Prescott, J, and Bell, G. Cross-cultural determinants of food acceptability: recent research on sensory perceptions and preferences. Trends Food Sci Technol. (1995) 6:201–5. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2244(00)89055-X
106. Srujana, MNS, Kumari, BA, Maheswari, KU, Devi, KBS, and Suneetha, WJ. Sensory quality characteristics of gluten-free products prepared with germinated quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa wild). Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. (2017) 6:3507–14. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.419
107. Xi, X, Fan, G, Xue, H, Peng, S, Huang, W, and Zhan, J. Harnessing the potential of quinoa: nutritional profiling, bioactive components, and implications for health promotion. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:829. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070829
108. Koistinen, VM, Hedberg, M, Shi, L, Johansson, A, Savolainen, O, Lehtonen, M, et al. Metabolite pattern derived from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-fermented rye foods and in vitro gut fermentation synergistically inhibits bacterial growth. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2022) 66:e2101096. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202101096
109. Liu, N, An, XP, Wang, Y, and Qi, JW. Metabolomics analysis reveals the effect of fermentation to secondary metabolites of Chenopodium album L. based on UHPLC-QQQ-MS. Fermentation. (2023) 9:100. doi: 10.3390/fermentation9020100
110. Xu, LN, Guo, S, and Zhang, SW. Effects of solid-state fermentation on the nutritional components and antioxidant properties from quinoa. Emirat J Food Agric. (2019) 31:39–45. doi: 10.9755/ejfa.2019.v31.i1.1898
111. Lu, HY. Study on the preparation of fermented beverage from germinated quinoa and its improving effects on lipid metabolism and intestinal flora in high-fat mice. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technology (2023).
112. Mahdi, I, Fahsi, N, Hafidi, M, Allaoui, A, and Biskri, L. Plant growth enhancement using rhizospheric halotolerant phosphate solubilizing bacterium Bacillus licheniformis QA1 and Enterobacter asburiae QF11 isolated from Chenopodium quinoa willd. Microorganisms. (2020) 8:948. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060948
113. Ortuño, N, Castillo, JA, Claros, M, Navia, O, Angulo, M, Barja, D, et al. Enhancing the sustainability of quinoa production and soil resilience by using bioproducts made with native microorganisms. Agronomy. (2013) 3:732–46. doi: 10.3390/agronomy3040732
114. Rafique, E, Mumtaz, MZ, Ullah, I, Rehman, A, Qureshi, KA, Kamran, M, et al. Potential of mineral-solubilizing bacteria for physiology and growth promotion of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Front Plant Sci. (2022) 13:1004833. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1004833
115. Cai, D, Xu, Y, Zhao, F, Zhang, Y, Duan, H, and Guo, X. Improved salt tolerance of Chenopodium quinoa Willd. contributed by Pseudomonas sp. strain M30-35. PeerJ. (2021) 9:e10702. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10702
116. Leon Ttacca, B, Ortiz Calcina, N, Pauro Flores, L, Borja Loza, R, Mendoza-Coari, P, and Palao Iturregui, L. Inoculation methods of native strains of Trichoderma sp. and their effect on the growth and yield of quinoa. Revista de la Facultacd de Agronomia. (2022) 39:e223955. doi: 10.47280/RevFacAgron(LUZ).v39.n4.10
117. Leon Ttacca, B, Ortiz Calcina, N, Condori Ticona, N, and Chura Yupanqui, E. Cepas de Trichoderma con capacidad endofitica sobre el control del mildiu (Peronospora variabilis Gäum.) y mejora del rendimiento de quinua. Revista de Investigaciones Altoandinas. (2018) 20:19–30. doi: 10.18271/ria.2018.327
118. Tian, M, Peng, YF, Lü, H, Qing, N, Ren, L, Yin, H, et al. Trichoderma Afroharzianum LMNS-M9: identification, biological characteristics, and growth-promoting effect on quinoa. Microbiol China. (2023) 50:3848–65. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.230144
119. Badran, A, Eid, NA, Hassan, AR, and Mahmoudi, H. Differential responses in some quinoa genotypes of a consortium of beneficial endophytic bacteria against bacterial leaf spot disease. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1167250. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1167250
120. Jafarpour, D, and Hashemi, SMB. Pure and co-fermentation of quinoa seeds by Limosilactobacillus fermentum and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus: bioactive content, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities. Fermentation. (2023) 9:80. doi: 10.3390/fermentation9020080
121. Casalvara, RFA, Ferreira, BMR, Gonçalves, JE, Yamaguchi, NU, Bracht, A, Bracht, L, et al. Biotechnological, nutritional, and therapeutic applications of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) and its by-products: a review of the past five-year findings. Nutrients. (2024) 16:840. doi: 10.3390/nu16060840
122. Mu, H, Xue, S, Sun, Q, Shi, J, Zhang, D, Wang, D, et al. Research progress of quinoa seeds (Chenopodium quinoa wild.): nutritional components, technological treatment, and application. Foods. (2023) 12:2087. doi: 10.3390/foods12102087
Keywords: quinoa, fermentation process, nutritional value, beverages, dairy products, condiments
Citation: Li C, Liu T, Li X, Gao W, Lv J, Hu G, Li C, Liu F, Liu X and Meng X (2025) Review of quinoa fermentation: product diversity, process optimization, and nutritional enhancement. Front. Nutr. 12:1605558. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1605558
Edited by:
Tanaji Kudre, Central Food Technological Research Institute (CSIR), IndiaReviewed by:
Seydi Yıkmış, Namik Kemal University, TürkiyeAbdul Waheed, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China
Umesh Patil, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Li, Liu, Li, Gao, Lv, Hu, Li, Liu, Liu and Meng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xianglong Meng, bWVuZ3hsamR5eUBqbHUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Chen Li
Chen Li Tong Liu2†
Tong Liu2† Xianjun Liu
Xianjun Liu Xianglong Meng
Xianglong Meng