- 1Department of Nephrology, The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical School, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 3The Nephrology Department of Shanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
- 4The Fifth Clinical Medical School, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) have been demonstrated to be intricately linked in a multitude of research studies. The reclassification of MASLD has prompted a reevaluation of its epidemiological patterns and the associated risk of CKD. This is crucial as MASLD, focusing on cardiometabolic factors, might have a more pronounced association with CKD than NAFLD. Additionally, mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both MASLD and CKD. Studies on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis mouse models have revealed significant mitochondrial alterations, such as loss of cristae and impaired function in the kidneys, underscoring the critical importance of mitochondrial integrity in these pathologies. This review offers an extensive overview of the existing literature, covering the following key aspects: (a) presenting the latest epidemiological findings that elucidate the relationship between MASLD and CKD; (b) kidney pathological changes associated with MASLD; (c) mitochondrial alterations in MASLD and CKD, including oxidative stress, dynamics, and mitophagy; and (d) potential mitochondrial-targeted therapies.
Introduction
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) represent two major non-communicable diseases impacting global health. MASLD affects nearly 30% of the adult population (1), while CKD affects 8.2% (2). By the year 2031, it is projected that the incidence of MASLD will increase by 16.1% and that of CKD by 11.4% (3). This increase will significantly exacerbate the burden of these conditions, which are linked to poor prognosis, premature mortality, and reduced quality of life (4). A significant association exists between MASLD and CKD, characterized by notably lower glomerular filtration rates (GFR) among MASLD patients, indicating that MASLD may elevate the CKD risk (5, 6). Furthermore, in patients with MASLD, the proteinuria and the reduction in GFR are associated with the degree of hepatic fibrosis (7). Recent studies have introduced the term MLKD as an abbreviation to better encapsulate the relationship between MASLD and CKD (MLKD) (8).
In recent years, a notable shift has occurred in the field, marked by the reclassification from “non-alcoholic fatty liver disease” (NAFLD) to MASLD. Initially defined in the 1980s, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) was later broadened to encompass NAFLD (9). In 2020, the term “metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease” (MAFLD) was proposed (10, 11), requiring hepatic steatosis in conjunction with a minimum of one metabolic risk factor: type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), overweight/obesity, or evidence of metabolic dysfunction in individuals with lean or normal body weight (10). In 2023, “NAFLD” was redefined as “MASLD” (12). In contrast to the traditional definition, MASLD places increased emphasis on the metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors. CKD can emerge as a result of metabolic dysfunction. This implies that individuals with MAFLD or MASLD—manifested by hepatic steatosis in the presence of at least one metabolic factor—are at an increased risk of CKD (4) (Figure 1).
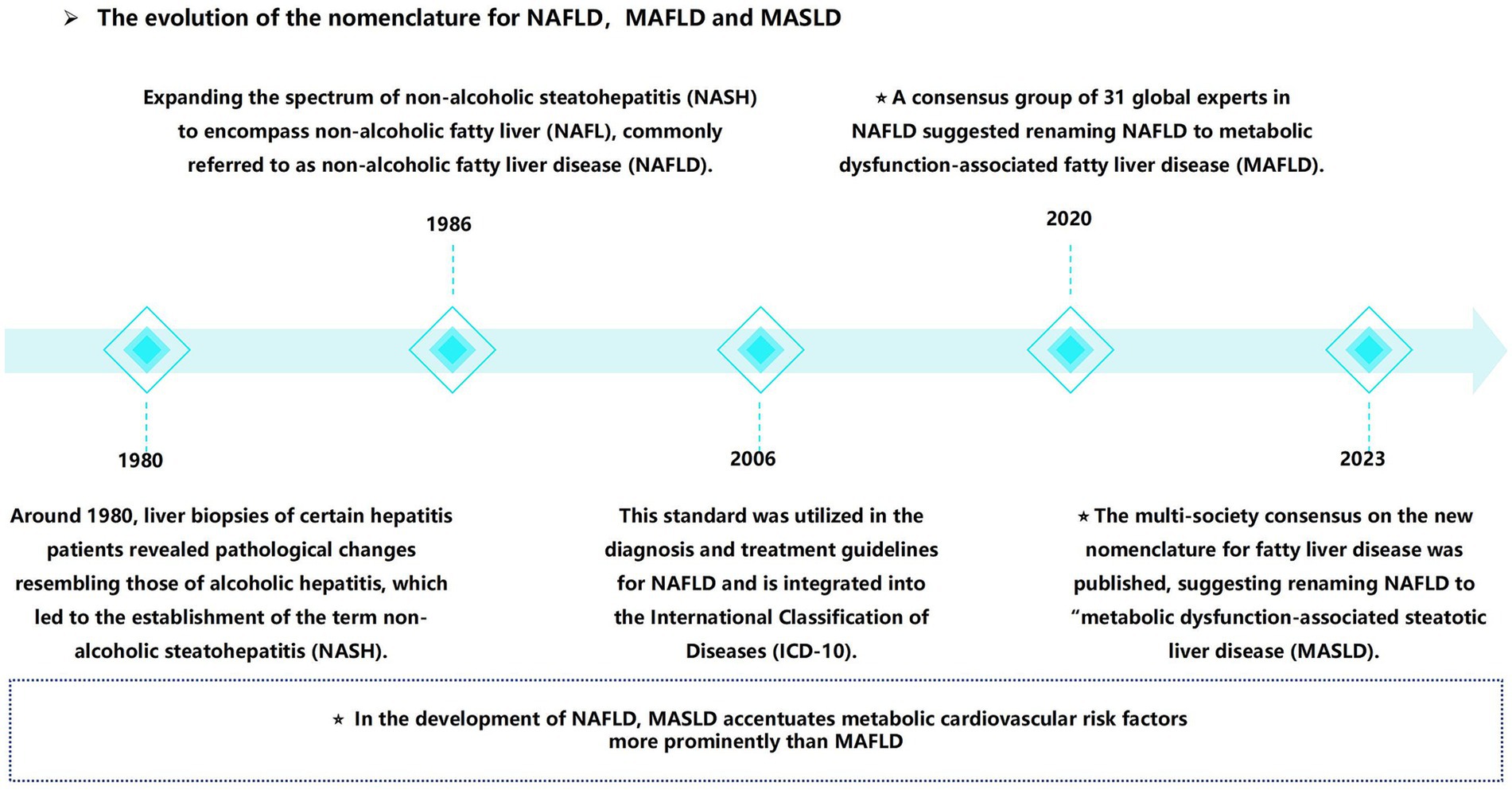
Figure 1. From non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) to metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), the naming evolution of MASLD.
Establishing a causal relationship between MLKD proves challenging; however, numerous research indicate that mitochondrial dysfunction is a key factor in the development of both conditions. Mitochondria play a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism, influencing energy production, redox balance, and apoptosis (13–15). Recent studies on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) have demonstrated mitochondrial swelling and loss of cristae, underscoring the crucial involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction in MLKD (16). This review aims to address a critical gap in the current literature regarding the interrelationship between MLKD, a condition that has garnered increasing attention yet remains underexplored. By offering an extensive overview of MLKD’s epidemiology, the kidney pathological changes associated with MASLD, and the mechanisms linking mitochondrial dysfunction to MLKD development, this review seeks to elucidate these connections. Ultimately, we hope to identify effective mitochondrial-targeted therapies to address this growing health challenge.
Epidemiological evidence of the association between MASLD and risk of CKD
Two studies published in 2008 (17, 18) first reported an increased risk of CKD among NAFLD patients, separate from typical factors associated with kidney dysfunction. Subsequent studies have further substantiated a notable correlation between NAFLD and the risk of CKD (4). An analysis synthesizing data included approximately 12 million middle-aged individuals, revealed that 28.1% of subjects in 13 longitudinal studies had NAFLD, which was associated with CKD (HR 1.43) (7). This analysis also revealed that the risk of CKD escalates as liver disease advances, particularly among those with more advanced liver conditions (7). The term “MAFLD” was introduced as a transitional term in 2020, while “MASLD” was formally adopted in 2023. Following the reclassification of MAFLD (10), several research investigated the influence of MAFLD on CKD risk, confirming an elevated risk of CKD among MAFLD patients (19–22).
As shown in Table 1, we focus on longitudinal studies from 2023 following the renaming to MASLD (12) that examine the association between MLKD. Heo et al.’s study including 57,785 Korean patients diagnosed with MASLD and with normal renal function at baseline, which revealed a CKD incidence of 11.31 per 104 person-years (23). Compared to non-MASLD individuals, those with MASLD exhibited a higher CKD risk (HR 1.21). In this study, MASLD was found to more effectively identify CKD and proteinuria risk compared to NAFLD (23). Gao et al. (6) recruited 79,540 participants who were diagnosed with hepatic steatosis through ultrasound, of which 19,062 were identified as having MASLD. The CKD incidence rate among MASLD patients was 22.4 per 103 person-years. After adjusting for confounders, MASLD exhibited a substantially elevated risk of CKD, with a HR of 1.15. The study also found that MASLD more effectively identifies CKD risk compared to conventional NAFLD, as demonstrated above (6). In a study by Mori et al. (24), which followed 3,187 Japanese patients with MASLD, the CKD incidence rate among MASLD patients was 28.3 per 103 person-years (24). MASLD subjects had a significantly higher incidence risk of CKD (HR 1.20) compared to those with non-steatotic liver disease (non-SLD) (24). Therefore, numerous epidemiological studies suggest that the definition of MASLD effectively identifies high-risk subgroups of patients who are likely to develop CKD. Moreover, MASLD appears to be a superior indicator of CKD risk compared to conventional NAFLD. This underscores the critical necessity of recognizing and addressing MLKD as a significant public health concern, while also highlighting the imperative for early identification and intervention to effectively mitigate this risk. Given the observational nature of the existing studies, the causal link between MASLD and increased CKD incidence remains uncertain. Additionally, the aforementioned study was conducted on an Asian population, highlighting the need for future studies to investigate other regions or ethnicities.
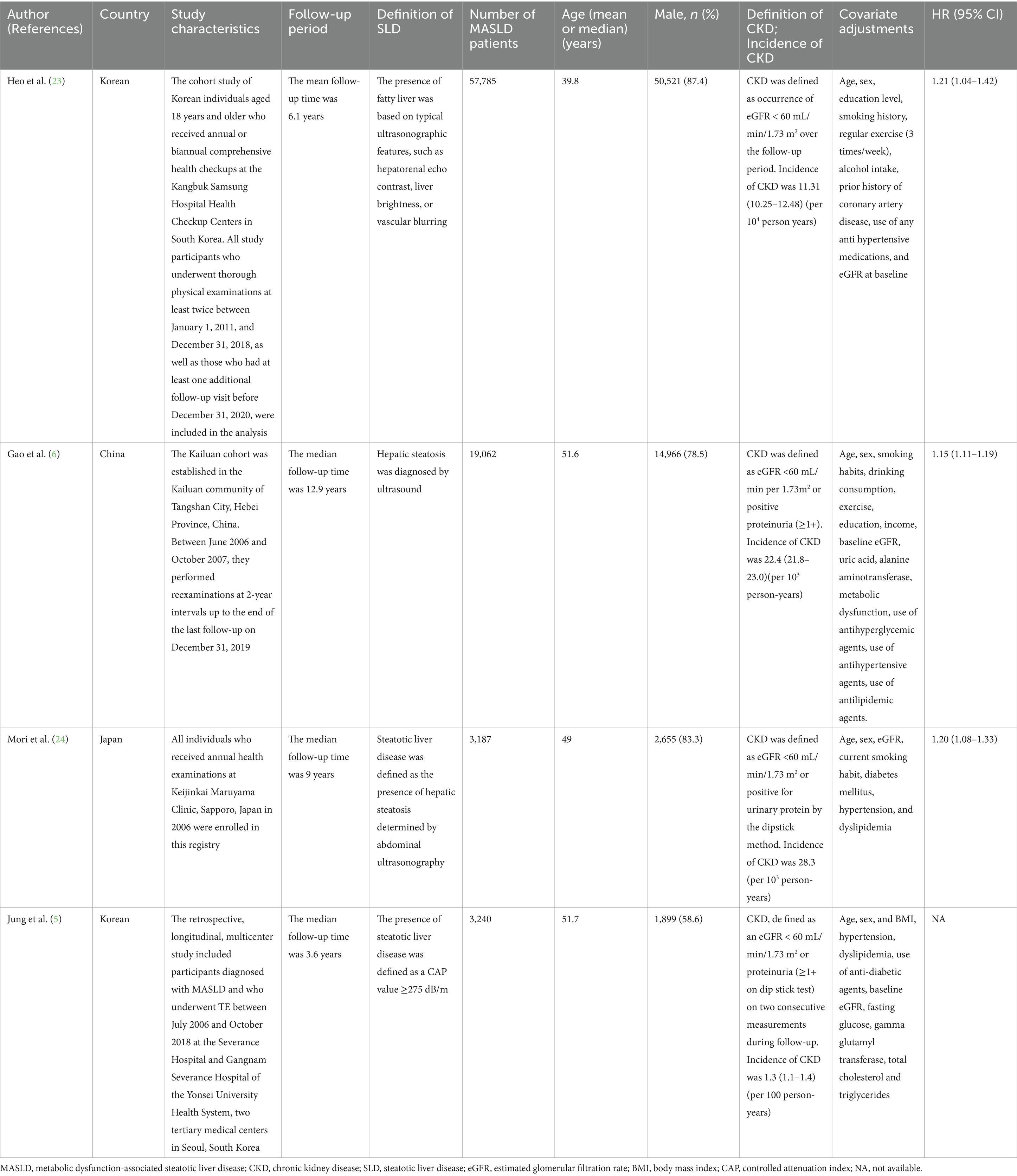
Table 1. Longitudinal studies evaluating the relationship between MASLD and CKD following the adoption of the new MASLD nomenclature in 2023.
Kidney pathological changes linked to MASLD
Animal evidence
In various MASLD mouse models, including those subjected to high-fat diet (HFD) (25, 26) combined or not with weekly low-dose CCl4 (16), significant pathological damage to the kidneys has been documented. The HFD model is known for its capacity to induce metabolic disturbances, including obesity, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia, which are central to the pathogenesis of MASLD (27). The combination of a high-fat diet with CCl4-induced liver injury provides a more comprehensive model that encompasses both metabolic and fibro-inflammatory aspects of the disease (28).
These injuries are characterized by glomerular enlargement, increased cross-sectional area of the glomeruli, a higher percentage of mesangial area, and renal fibrosis in both the tubules and interstitium (16, 25, 26). Electron microscopy reveals a marked loss of podocyte foot processes. However, Saito et al. (25) noted that the quantity of podocytes expressing WT-1 did not decrease, and they found no significant correlation between levels of proteinuria and the foot process loss. This suggests that factors beyond the loss of foot processes may contribute to the development of proteinuria (25). Mice subjected to a HFD exhibited a considerable accumulation of lipid droplets in the renal tubules, along with notable increases in neutral lipids in the interstitial cells of both the glomeruli and tubules (26).
Human correlates
Li et al. (16) reported a patient with a history of NASH who subsequently developed proteinuria. Similar to the pathological features of renal injury observed in the MASH mouse models, the pathology in this patient was characterized by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, increased mesangial matrix, glomerular enlargement, and tubular interstitial fibrosis with inflammatory infiltration (16). A number of non-atrophic tubules contained intracellular lipid and protein absorption droplets. Some podocyte foot processes mildly diminished, while the thickness of the glomerular basement membrane seemed normal. Abundant lipid inclusions were observed in podocytes, mesangial cells, and tubular epithelial cells (TECs) (16).
Mitochondrial structural alterations in MLKD
Mitochondria are organelles with double membranes that contain their own genetic material. Generally, their diameter ranges from approximately 0.5 to 1.0 μm, although size variations exist among different species. The outer mitochondrial membrane, which is smooth, functions as the boundary of the organelle. The inner mitochondrial membrane, characterized by its inward folds forming cristae, plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions (29).
The liver is particularly rich in mitochondria, with each liver cell containing between 1,000 and 2000 mitochondria (30, 31). Structural and functional impairments of mitochondria significantly contribute to the development of metabolic syndrome-related diseases (32–34). Patients with MASLD exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction characterized by mitochondrial swelling, cristae disorientation and fragmentation, mtDNA deletions, decreased activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes, and impaired mitochondrial β-oxidation (35). As the disease progresses, mitochondrial mass increases, while the maximum respiratory capacity measured using high-resolution respirometry decreases by 31 to 40% (36). Alterations in mitochondrial structure, elevations in oxidative stress, and reductions in ATP production were more pronounced (37).
The kidneys are the second most energy-consuming organs, with more than 80% of renal oxygen consumption attributed to Na/K-ATPase activity. Glomerular cells predominantly depend on glucose for energy, resulting in comparatively low mitochondrial density (38–40). Renal tubular cells mainly rely on fatty acids (FAs) for energy and have a high mitochondrial content. The proximal convoluted tubules (PCT) lack the enzymes necessary for glycolysis and depend entirely on mitochondrial oxidation of key substrates including FAs, lactate, citrate, and glutamate to produce energy (41). Under pathological conditions, PCT cells exhibit depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) (ΔΨm) (42, 43). Electron microscopy reveals mitochondrial damage, such as swelling and losing cristae. Notably, damaged mitochondria and lysosomes are observed surrounding myelin-like membranous inclusions within TECs (16). Mitochondrial abnormalities above have also been observed in individuals clinically diagnosed with MASH combined with CKD (16). This underlines the crucial involvement of the intricate and dynamic structure and functionality of mitochondria in the advancement of MLKD.
Metabolic reprogramming of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation
Under physiological conditions, tissues uptake FAs through various transport proteins, including scavenger receptor class B (CD36), fatty acid transport proteins (FATP), and fatty acid-binding protein (FABP). FATP are a class of multi-channel membrane proteins primarily responsible for transporting extracellular free fatty acids (FFAs) into cells while also participating in fatty acid metabolism (44). FABP, a family of intracellular proteins, recognizes long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) as substrates, is important in the metabolism and transport of FAs (44). CD36 primarily facilitates the transport of LCFAs into cells. As a transmembrane glycoprotein, CD36 is widely expressed across various cell types, including adipocytes, hepatocytes, and TECs. It is involved not only in the uptake and transport of FAs but also plays a role in signal transduction (44–46).
Fatty acid oxidation is a crucial component of energy metabolism, crucial for maintaining energy balance and regulating lipid storage. Most FAs are oxidized within the mitochondria (44), with mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (mtFAO) serving as essential pathway for reducing fat accumulation (47, 48). In the canonical pathway of mtFAO, FFAs are first activated to form acyl-CoA within the cytoplasm before being shifted into the mitochondrial matrix via carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 (CPT2) (45). Acyl-CoA is metabolized gradually by β-oxidation, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), producing a substantial amount of ATP.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) is extensively expressed in adipose tissue, liver, and kidneys. PPAR-γ regulates transport proteins, and its upregulation correlates with lipid accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis, thereby promoting metabolic reprogramming and the development of MLKD (Figure 2). In the liver, PPAR-γ influences the uptake and metabolism of FAs through promoting the expression of transport proteins such as CD36 (49). Selective deletion of PPAR-γ significantly reduces hepatic steatosis caused by a HFD in hepatocytes (50). Hepatic steatosis induced by a HFD in mice is closely associated with the expression of CD36, FATP2, and FATP5 (51, 52). Liver cell-specific deletion of CD36 can mitigate HFD-induced fatty degeneration in mice (53). Within the nephron, proximal renal tubules and glomeruli are particularly vulnerable to lipid accumulation, leading to renal damage. This susceptibility is linked to the upregulation of PPAR-γ and lipid uptake transporters such as CD36 and FABP (41). Elevated activity of FATP1, FATP4, and FATP2 results in an overload of FFAs in renal cells (44).
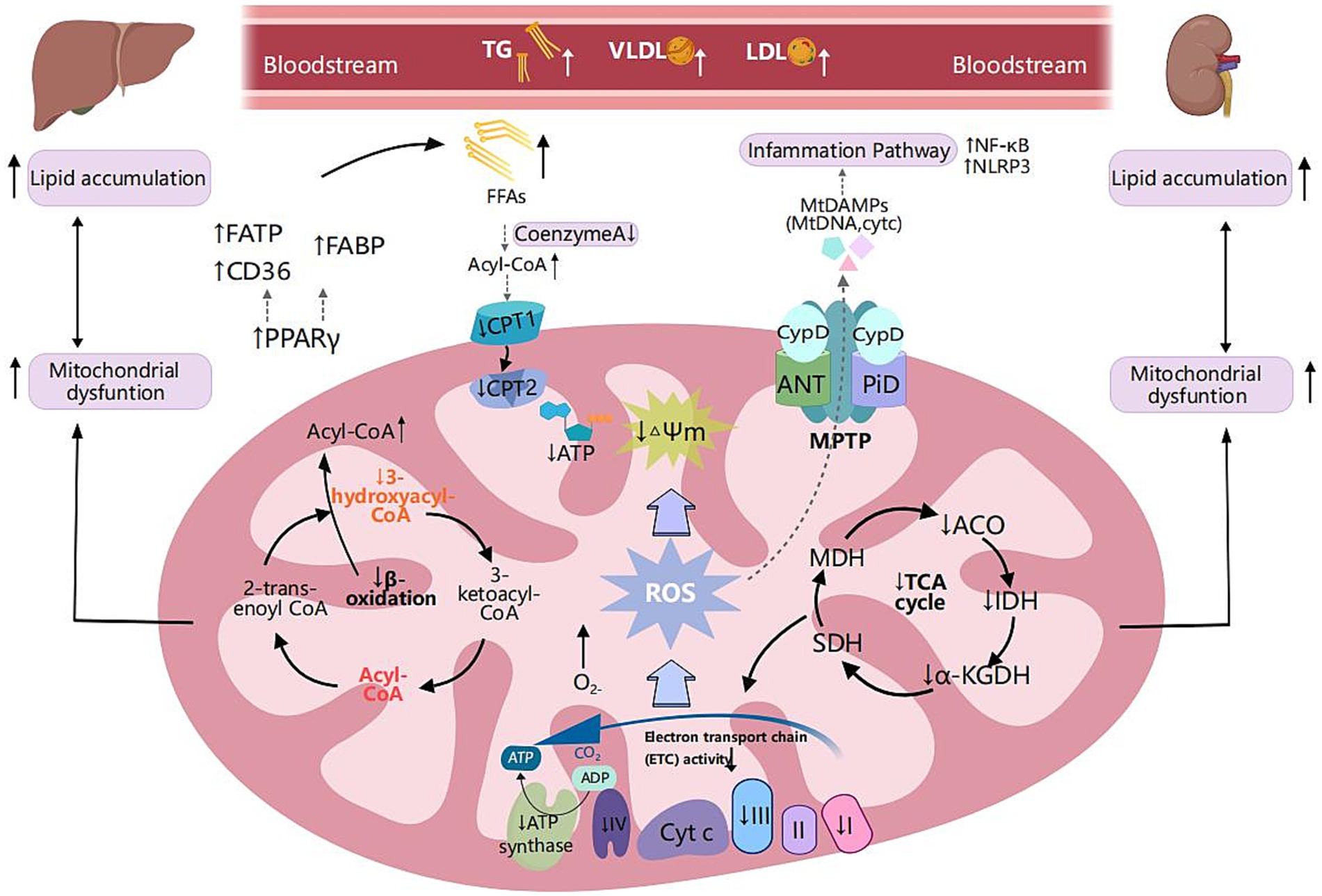
Figure 2. Metabolic reprogramming of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and shared pathogenic mechanisms in MASLD and CKD. Scavenger receptor class B (CD36), fatty acid transport proteins (FATP), and fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) are critical transport proteins involved in the uptake of fatty acids by tissues. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) is extensively expressed in adipose tissue, liver, and kidney. It regulates fatty acid transport proteins, and its upregulation is associated with lipid accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis, thereby facilitating metabolic reprogramming. In MLKD, the upregulation of PPAR-γ correlates with elevated expression levels of CD36, FATP, and FABP, which correlates with free fatty acid (FFA) overload in renal and hepatic cells. Decreased levels of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2 (CPT2) lead to reduced fatty acid oxidation, insufficient production of NADH, decreased activity of the electron transport chain (ETC), and inadequate levels of ATP, ultimately resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrial respiratory defects, specifically fatty acid oxidation (mtFAO) deficiency, can lead to chronic accumulation of FFAs and acyl-CoA, disrupting the function of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and mitochondrial respiration, leading to excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can induce oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and are associated with reduced mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and increased mitochondrial permeability exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, ROS can disrupt the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP), resulting in the leakage of mtDNA into the cytoplasm. ROS trigger downstream signaling pathways regulating inflammatory responses, including the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway and the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome pathway. This activation results in the production of substantial amounts of ROS, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation and oxidative damage. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn).
Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation respiratory deficiencies might significantly contribute to the progression of MLKD (Figure 2). Among the enzymes involved, β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase is particularly crucial in the β-oxidation pathway (54). Mary et al.’s study revealed a significant 40–50% reduction in β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity among MASLD patients compared to the control group, suggesting impaired β-oxidation (55). Furthermore, multiple studies have consistently shown decreased levels of CPT1 and CPT2 in animal models induced by a HFD (56–58). In obesity-related kidney disease models, the downregulation of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase-1 (ACSL1), a vital enzyme in fatty acid oxidation, is closely linked to heightened lipid accumulation in the kidneys (54). Notably, in CKD, the diminished expression of CPT1 and CPT2 also results in decreased fatty acid oxidation, inadequate NADH generation, impaired electron transport chain (ETC) activity, depleted ATP levels, culminating in mitochondrial dysfunction (59).
The prolonged presence of elevated FFAs and persistent buildup of acyl-CoA disrupt the TCA cycle and mitochondrial respiration, leading to excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (60). Moreover, compromised mitochondrial β-oxidation can prompt the peroxisomal and cytosolic oxidation of FFAs, giving rise to peroxidative byproducts and excess ROS levels (61). ROS can induce oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), resulting in a reduction in MMP and an increase in mitochondrial permeability (30), exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid peroxidation, thereby establishing a vicious cycle that favors metabolic reprogramming.
Oxidative stress
ROS are generated from various pathways within the mitochondria, involving a series of interconnected mechanisms. Initially, electrons leak from complexes of the ETC and interact with oxygen to produce superoxide radicals. Subsequently, these superoxide produce other ROS, including superoxide anions and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), through both enzymatic and non-enzymatic reactions. Dysfunction in the ETC or mitochondrial impairment can exacerbate this process, leading to an increased production of ROS (15, 62). The mitochondria possess several antioxidant defense mechanisms to mitigate ROS accumulation. Key antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, play crucial roles in ROS clearance (15, 63). Under physiological conditions, these enzymes convert superoxide radicals into H₂O₂ and water (64). A decline in antioxidant enzyme levels is a significant factor in the development of excessive oxidative stress.
As previously mentioned, lipid metabolism is a key factor in the oxidative stress associated with MLKD. Numerous studies have indicated that MASH patients exhibited elevated ROS (65–67). Additionally, some studies have confirmed an increase in mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) in CKD (68, 69), with FAs contributing to elevated ROS levels. A HFD increases CD36 expression in the kidneys of mice, while palmitic acid treatment enhances CD36 levels in podocytes in vitro (44). In contrast, treatment with the CD36 inhibitor has been shown to effectively reduce lipid accumulation and ROS production in podocytes (44, 70).
Elevated levels of ROS exacerbate oxidative stress associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to cellular damage and lipid peroxidation, which further aggravate the pathological state of MASLD (15) and the progression of CKD (14, 71) (Figure 2). Additionally, ROS can disrupt the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP), resulting in the leakage of mtDNA into the cytoplasm (72). ROS triggers downstream signaling pathways that regulate inflammatory responses, leading to increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (62, 73). TNF-α exacerbates oxidative damage and inflammatory responses while triggering the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). This results in the generation of substantial amounts of ROS, especially superoxide anions. The consequent oxidative stress not only exacerbates damage to cellular components but also stimulates the generation of additional TNF-α, perpetuating a cycle of inflammation and oxidative damage (62, 73).
Mitochondrial biogenesis
Mitochondrial biogenesis is a sophisticated process that enables cells to produce new mitochondria in order to satisfy their energy requirements and preserve cellular homeostasis. Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) is a crucial regulatory factor for mtDNA processes. By binding to mtDNA, TFAM promotes the production of mtDNA and proteins, transcribing and packaging them into nucleoids (74). The expression of TFAM is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), which connects the nuclear control of mitochondrial biogenesis with the maintenance and expression of mtDNA (14). AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) facilitates the activation of PGC-1α (75, 76).
In MASLD, the expression of key regulatory factors involved in mitochondrial biogenesis (77), such as Sirt3 and PGC-1α, is diminished. In models of CKD in mice, levels of PGC-1α (78, 79) and SIRT3 (80) are consistently reduced. The downregulation of SIRT3 results in the hyperacetylation of mitochondrial proteins, thereby promoting oxidative stress and fat accumulation in the liver (77). Additionally, low levels of PGC-1α are linked to a decline in antioxidant mechanisms (81). Inhibition of PGC-1α impedes mitochondrial biogenesis, leading to a decrease in mitochondrial quantity and impaired functionality, which may ultimately result in cellular energy metabolism disorders and apoptosis. Overall, mitochondrial biogenesis is suppressed during the progression of MLKD (Figure 3).
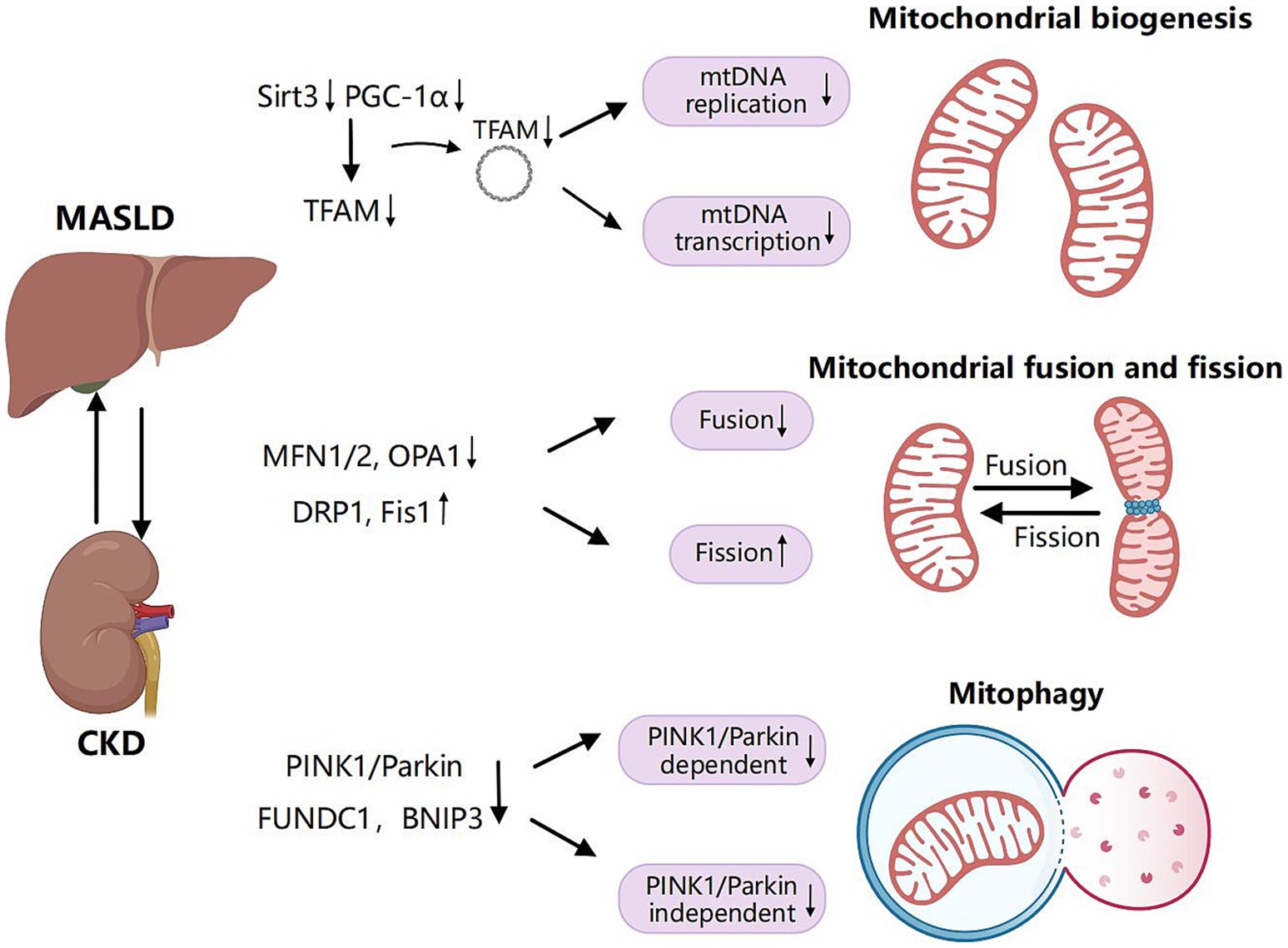
Figure 3. Shared pathogenic mechanisms of mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamics and mitophagy in MASLD and CKD. Mitochondrial biogenesis is a complex process through which cells generate new mitochondria to meet their energy demands and maintain cellular homeostasis. Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) serves as a pivotal regulatory factor in the transcription and replication of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The expression of TFAM is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α). Inhibition of PGC-1α and sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) impedes mitochondrial biogenesis, resulting in a reduction of mitochondrial quantity and impaired functionality during the progression of MLKD. Mitochondrial fusion refers to the process by which individual mitochondria within a cell merge through the fusion of their membranes and contents. In contrast, mitochondrial fission involves a single mitochondrion dividing into two or more smaller mitochondria. Key proteins involved in mitochondrial fusion include mitofusin 1 (MFN1), mitofusin 2 (MFN2), and optic atrophy 1 (OPA1). Mitochondrial fission is primarily regulated by dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) and mitochondrial fission protein 1 (Fis1). Decreased expression of MFN1, MFN2, and OPA1 in the liver and kidney, combined with the upregulation of DRP1 and Fis1 in MLKD, results in the inhibition of mitochondrial fusion and an increase in mitochondrial fission. Mitophagy is a specialized form of autophagy that specifically targets damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria to remove them and prevent the accumulation of harmful components. This process plays a crucial role in maintaining mitochondrial quality control and cellular homeostasis. Mitophagy encompasses ubiquitin-dependent pathways, including those involving phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and Parkin. Additionally, there are ubiquitin-independent pathways that involve receptors such as Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19-kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) and FUN14 domain-containing protein 1 (FUNDC1). A reduction in mitophagy-related proteins from both ubiquitin-dependent and independent pathways, including PINK1, Parkin, BNIP3, and FUNDC1, results in decreased mitophagy efficiency, exacerbating liver and kidney injury in MLKD. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn).
Mitochondrial dynamics: fusion and fission
Mitochondrial fusion is the process where individual mitochondria within a cell merge through the fusion of their membranes and contents. In contrast, mitochondrial fission refers to the division of one mitochondrion into multiple smaller units (14). Mitochondrial fusion is regulated by key proteins such as mitofusin 1 (MFN1) and mitofusin 2 (MFN2) on the outer mitochondrial membrane, which promote the connection and fusion of adjacent mitochondria, and optic atrophy 1 (OPA1) on the inner mitochondrial membrane, which controls inner membrane fusion (82). Mitochondrial fission is primarily regulated by dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) and mitochondrial fission protein 1 (Fis1). DRP1, a GTPase, forms spiral-like structures at the regions of mitochondrial constriction (15). Through mitochondrial fusion and fission, cells dynamically regulate the morphology and distribution of mitochondria to adapt to changing metabolic demands.
In patients with MASH, liver biopsies have shown a reduction in MFN2 levels (83). A HFD leads to a reduction in the levels of MFN1, MFN2, and OPA1. Concurrently, the expression of DRP1 is upregulated (84–86). FFA can increase the expression of Drp1 and Fis1 while reducing the expression of OPA1 and Mfn2 (87). The role of lipids in mitochondrial dysfunction associated with CKD has also received research support. Studies indicate that a HFD reduces the expression of MFN2 and OPA1 in the kidneys while increasing DRP1 expression (84, 88). Ko et al. (89) reported that in hypertensive kidney disease (HKD) rats, the expression of DRP1 was upregulated, whereas the expression of Mfn2 was downregulated. Acyl-CoA:lysocardiolipin acyltransferase-1 (ALCAT1) that regulates cardiolipin biosynthesis in mitochondrial. In a diabetic kidney disease (DKD) mouse model, the expression of MFN2 and OPA1 are diminished, whereas those of Drp1 and Fis1 are increased. Overexpression of ALCAT1 can enhance MFN2 and OPA1 expression while reducing Drp1 levels, which further mitigates the decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), thereby improving mitochondrial dynamics (90).
Disruption in the balance of mitochondrial fusion and fission impairs mitochondrial dynamics, leading to dysregulation of cellular homeostasis and mitochondrial function. As previously noted, key regulatory factors of mitochondrial fission and fusion include MFN, OPA1, DRP1, and Fis1. Alterations in the levels or function of these essential proteins disrupt the equilibrium between mitochondrial fission and fusion, leading to impaired mitochondrial structure and function, which in turn triggers inflammatory responses through various pathways (91, 92). Furthermore, mitochondrial dynamics are closely associated with cell death, particularly apoptosis, as some proteins linked to mitochondrial dynamics (e.g., Drp1 and Mfn2) directly regulate apoptotic processes (93, 94). The imbalance in mitochondrial dynamics, characterized by enhanced fission and suppressed fusion, leads to increased mitochondrial fragmentation, elevated permeability of the outer mitochondrial membrane, cytochrome leakage, and activation of caspases, ultimately inducing apoptosis (95) (Figure 3).
Mitophagy
Mitophagy, a specialized autophagic process, selectively targets and removes damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria to prevent the accumulation of harmful components (15). It encompasses ubiquitin-dependent pathways, including phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and Parkin. Additionally, there are ubiquitin-independent pathways involving receptors such as Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19-kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3), FUN14 domain-containing protein 1 (FUNDC1), and cardiolipin (96, 97). Dysregulation of mitophagy leads to the accumulation of damaged mitochondria, further exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction and contributing to the pathogenesis of MLKD. Disruptions in mitochondrial dynamics, such as imbalances in mitochondrial fusion and fission, can also affect mitophagy (98). These pathways ultimately form autophagolysosomes, facilitating the removal of damaged mitochondria (99).
Mitophagy is essential for regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and facilitating lipid β-oxidation within mitochondria (100). Conversely, impaired autophagy of damaged mitochondria fails to sustain an adequate number of healthy mitochondria, thereby contributing to hepatic steatosis and the progression of MASLD (101, 102). In experimental models of MASLD induced by a high-fat/high-calorie diet, the expression of PINK1 and Parkin is decreased, resulting in reduced mitophagy efficiency, exacerbating liver injury and ultimately progressing to MASH (37, 103). Insufficient FUNDC1-dependent mitophagy can drive the transition to HFD-induced MASLD (104). Data from Li R et al. indicated that liver injury induced by a HFD was linked to reduced Sirt3 expression, followed by inactivation of the ERK-CREB signaling and suppression of mitophagy driven by BNIP3, leading to mitochondrial-dependent cell death in hepatocytes (105).
Similarly, studies demonstrated that a HFD caused downregulation of PINK1 and Parkin expression in murine kidneys (106), resulting in impaired mitophagy, promoting mitochondrial injury in TECs, reducing MMP, and inducing apoptosis (107). In STZ-induced diabetic animal models, mitophagy-associated proteins from both ubiquitin-independent and non-independent pathways, such as FUNDC1, BNIP3 and PINK1 are reduced (98, 108). In a rat model of HKD established via 5/6 nephrectomy combined with DOCA-salt treatment (25 mg/kg, subcutaneous injection, twice weekly), the expression of PINK1/Parkin was upregulated (89).
The decreased stimulation of these pathways impairs the selective degradation of impaired mitochondria. Furthermore, the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria can result in elevated ROS production and intensified cellular stress, promoting persistent inflammation. Mitochondrial injury can trigger the release of mtDNA into the cytoplasm, which the immune mechanism recognizes as injury-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). This recognition further promotes inflammatory pathways and amplifies the inflammatory response (109) (Figure 3).
Mechanisms linking liver damage in MASLD to CKD development
While mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated, other critical factors such as the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), alterations in the gut microbiota, inflammation, and genetic predisposition likely also contribute. In MASLD, the liver, being the primary site for angiotensinogen synthesis, experiences increased production and release of angiotensinogen into the bloodstream due to its inflammatory and oxidative stress states. Angiotensinogen is subsequently converted to angiotensin I by renin and further to the potent vasoconstrictor angiotensin II by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II exacerbates liver injury by increasing intrahepatic resistance and elevates blood pressure through systemic vasoconstriction, emerging as a key risk factor for CKD development. Long-term excessive activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) induces renal ischemia, impairs renal filtration and electrolyte balance regulation, increases glomerular filtration membrane permeability, leading to proteinuria, and ultimately results in glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis, further weakening kidney function (110). Moreover, the vicious cycle initiated by RAAS activation in MASLD, driven by worsening liver injury and intensified RAAS activation, exacerbates renal ischemia and injury. The kidneys’ compromised ability to regulate fluid balance and blood pressure further stimulates RAAS activation, accelerating the progression of both diseases (111).
Intestinal microbiota imbalance is a hallmark pathological feature of both MASLD and CKD, significantly contributing to the pathogenesis of these conditions. In individuals with MASLD and CKD, the gut microbiota is characterized by reduced bacterial richness and diversity. Specifically, beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are diminished, while potentially pathogenic taxa like Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococcus are markedly enriched (8). This dysbiosis is closely associated with the disruption of intestinal epithelial tight junctions, leading to increased intestinal permeability. Consequently, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from the gut can translocate into the systemic circulation. LPS, a potent immune activator, triggers signaling pathways involving NF-κB and TLR2 and TLR4. This activation exacerbates inflammation in the liver and kidneys, thereby accelerating the progression of hepatic fibrosis and renal fibrosis. Moreover, intestinal microbiota imbalance is also closely associated with the production and metabolic changes of various intestinal metabolites, which play a significant role in the development of MASLD and CKD (112).
Genetic factors significantly influence the development and progression of MASLD and CKD, with various genetic polymorphisms and mutations potentially linking these two conditions. For instance, the I148M SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is strongly associated with increased hepatic fat accumulation and liver injury, predisposing carriers to severe liver disease. Research revealed that PNPLA3 mRNA and protein are expressed not only in the liver but also in the kidneys, particularly in renal tubular cells and podocytes (113). Podocyte activation during injury can drive renal fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis. The PNPLA3 GG variant may exacerbate injury and promote ectopic lipid accumulation under conditions of lipid excess, potentially leading to lipid nephrotoxicity by influencing podocyte activation (114).
Therapeutic strategies targeting mitochondria in MLKD
Given the significant overlap in pathogenesis between MLKD, treatment for one condition is likely to be effective for the other. As research on the association mechanism between MLKD progresses, some scholars have proposed the cardiac-kidney-liver (CKL) syndrome (115) or a framework referred to as the cardiovascular-renal-hepatic-metabolic (CRHM) syndrome (116). This management approach for heart, liver, and kidney functions by cardiology, endocrinology, nephrology, and hepatology is transitioning toward a more integrated model. This review focuses on the enhancement of oxidative stress mitigation, metabolic reprogramming, and mitochondrial homeostasis facilitated by antioxidants, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, PPAR-γ agonists, and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), along with their therapeutic roles in the management of MLKD.
Antioxidants
In patients with MLKD, elevated levels of ROS and decreased plasma antioxidant activity are observed in both the liver and kidneys. ROS-induced oxidative stress is recognized as one of the essential mechanisms underlying the onset and progression of MLKD, and multiple studies have emphasized the beneficial effects of antioxidants in treatment. Mitochondrial-targeted drugs, such as mitoTEMPO, elamipretide (SS-31) and mito-quinone (Mito-Q), have demonstrated potential therapeutic benefits in various diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, including MLKD (117, 118).
Mito-Q
Mito-Q is synthesized by covalently linking ubiquinone, an intrinsic electron carrier from the ETC, with the lipophilic molecule triphenylphosphine (TPP). Within cells, Mito-Q achieves high concentrations, approximately 100 times those found in the cytosol (117). As an antioxidant targeting mitochondria, Mito-Q acts a critical role in mitigating oxidative stress in mitochondria, stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis, and facilitating mitophagy. These processes are mediated through AMPK and its downstream signaling pathways, including mTOR, NF-κB, Nrf2, and SIRT1, ultimately contributing to the alleviation of symptoms associated with metabolic syndrome, such as obesity and insulin resistance (119).
Mito-Q has been shown to exert protective effects in rats fed a HFD, leading to reductions in body weight, hepatic steatosis, blood lipid levels, and insulin levels (120, 121). This effect correlates with elevated levels of mitochondrial cardiolipin content, thereby enhancing the activity of complexes II, III, and V (121). Furthermore, a phase II clinical trial targeting chronic hepatitis C revealed that Mito-Q can reduce hepatic transaminase levels, indicating its protective role against necrotizing liver inflammation (122). In kidney, Mito-Q reverses the changes in podocyte mitochondrial morphology and function induced by angiotensin II stimulation, including decreased MMP, excessive production of ROS, and ATP deficiency (123). In a recent pilot randomized controlled trial, Kirkman DL et al. revealed that Mito-Q enhanced macrovascular endothelial function, arterial hemodynamics, and microvascular function, partly by decreasing NADPH oxidase-mediated vascular dysfunction in CKD patients (118).
MitoTEMPO
MitoTEMPO is a mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant comprising the piperidine nitroxide (TEMPO) and TPP. TEMPO functions as a SOD mimic, capable of scavenging superoxide anions and alkyl radicals (117). In HFD-induced mice, MitoTEMPO improves liver lipid accumulation, alleviates inflammatory responses, and downregulates fibrosis-related gene expression (124). Moreover, MitoTEMPO inhibits ROS production, increases intrahepatic CD4+ T lymphocyte counts, and delays the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) induced by MASLD (125). Additionally, in human podocytes (HPC), MitoTEMPO stabilizes the MMP, while also mitigating the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome through the PINK1/Parkin-mediated autophagy pathway, thereby improving podocyte injury (126). Finally, mitoTEMPO significantly decreases markers of mitochondrial dysfunction, and levels of pro-fibrotic factors in mice with CKD, thereby enhancing renal function and mitigating renal fibrosis (127).
SS-31
Peptides targeting mitochondria, like Szeto-Schiller peptide 31 (SS-31), also known as elamipretide, are antioxidant peptides that selectively accumulate in the inner mitochondrial membrane (128, 129). Mechanistic studies demonstrate that SS-31 functions as a mitochondrial-targeted scavenger of mtROS, effectively mitigating oxidative stress while protecting cardiolipin from oxidative damage (90, 130, 131). In a mouse model of T2DM, SS-31 effectively prevents hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction by enhancing H₂O₂ metabolism, reducing lipid peroxidation and boosting ATP synthesis (132). Moreover, research by Hao et al. affirmed that SS-31 exhibited significant protective effects in mouse models of DKD by limiting cardiolipin oxidation and protecting podocytes (90). Szeto-schiller peptide 20 (SS-20) also demonstrates significant renal protective effects by reducing mtROS production and inflammatory responses (133).
SGLT2 inhibitors
Recent research on the interaction between MLKD has brought SGLT2 inhibitors into the spotlight as a promising therapeutic option. Honda et al. (134) demonstrated that ipragliflozin upregulates genes associated with fatty acid β-oxidation and lipid export in the liver, thereby accelerating hepatic lipid metabolism and decreasing liver lipid content in MASH mice, which alleviated liver steatosis. Dapagliflozin can reverse the decline in mtDNA copy number in the livers of diabetic mice while increasing the levels of Mfn2, Drp1and PGC1α. This process normalizes mitochondrial respiration control in hepatocytes, reduces lipid peroxidation, and prevents the activation of the MPTP (135). In human proximal tubular cells (HK-2), Zaibi N et al. measured ROS production in the cytoplasm and mitochondria under both normal and oxidative stress conditions with fluorescent probes. They found that dapagliflozin significantly mitigated the increase in ROS within the cytoplasm and mitochondria of proximal TECs during oxidative stress conditions and altered Ca2+ dynamics (136). Furthermore, dapagliflozin reduced macrophage infiltration in the kidneys of db/db mice, resulting in reduced expression of inflammatory cytokines and genes associated with oxidative stress, including monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and osteopontin (137).
In the clinical setting, initially introduced for the therapy of T2DM, SGLT2 inhibitorshave subsequently exhibited positive therapeutic effects in numerous trials targeting liver and kidney outcomes. Research have show that SGLT2 inhibitors can markedly decrease proteinuria, slow the progression of renal function decline, and decrease liver fat content; they also improve serum transaminase levels (138–140). A meta-analysis evaluated liver function and structure in patients with type 2 diabetes, comparing the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors with those of placebo or other oral hypoglycemic agents. The findings revealed that SGLT2 inhibitors effectively reduced serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (141). Furthermore, several large-scale cardio-renal outcome studies have demonstrated the renal advantages of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM (142–146).
GLP-1 receptor agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are increasingly recognized as novel therapeutic agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Their significant effects on metabolic regulation, weight management, and cardiovascular and renal protection have led to a growing focus on GLP-1RAs in the context of MLKD. Investigations have revealed that liraglutide reduces oxidative stress by increasing SOD levels. This includes decreasing serum malondialdehyde levels, MCP-1 expression, and NF-kB levels, while also inhibiting endogenous inflammatory responses (147, 148). Additionally, liraglutide enhances heme oxygenase-1 concentration in human serum, indicating a possible improvement in antioxidant capacity (149). Furthermore, semaglutide elevates serum and hepatic SOD levels in HFD-induced MASH mice, thus preventing hepatic lipid accumulation, exhibiting anti-inflammatory effects, and improving mitochondrial architecture by reducing mitochondrial swelling and promoting more ordered cristae (150). In the kidneys, exenatide reverses the downregulation of Sirt1 in FFA-induced TECs and prevents the increase in ROS. This intervention prevents declines in MMP and attenuates mitochondrial apoptosis (151).
In the early stages of MASLD treatment, GLP-1RAs as well as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and GLP-1 dual receptor agonists are commonly utilized (152). Although the specific benefits of these agents for liver fibrosis remain unclear, they indirectly enhance liver health by promoting weight loss, thus reducing hepatic fat and inflammation (153). The CGH-LiNASH study confirmed that liraglutide effectively reduces the weight of obese adult patients with MASLD and improves liver steatosis and hepatocyte apoptosis (154). In relation to kidney health, GLP-1RAs have been demonstrated to slow the progression of diabetic kidney disease, as evidenced by the LEADER study (155). The research investigated the impact of liraglutide on 23% of CKD patients, revealing a reduction in the risk of renal failure by approximately 25%, alongside decreased serum creatinine levels, reduced mortality risk due to kidney disease, and lower incidence of macroalbuminuria (155). Other GLP-1RAs, such as semaglutide, dulaglutide, efpeglenatide, lixisenatide, and the dual receptor agonist tirzepatide, have also demonstrated similar effects on macroalbuminuria (156).
PPAR-γ agonists
PPAR-γ is a nuclear receptor that regulates lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are categorized as PPAR-γ agonists, have been explored for their potential use in managing MLKD. As discussed earlier, TZDs, including pioglitazone, have the capacity to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and improve mitochondrial function (157). Their mechanism of action involves the induction of PGC-1α, a key transcriptional coactivator that regulates mitochondrial biogenesis, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid oxidation (158). They have demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in MLKD, and future research will further explore their clinical applicability in different disease states.
A systematic review indicated that pioglitazone treatment improved individual histological scores for MASH compared to placebo and increased the remission rate for MASH (159). Pioglitazone (45 mg/day for 72 weeks) was superior to placebo in improving fibrosis scores in MASH patients, particularly those with T2DM. In the context of DKD, a retrospective cohort study involving 742 patients revealed that pioglitazone did not significantly reduce the risk of composite renal endpoint events, although a non-significant reduction in proteinuria was noted (160). Further investigation is essential to thoroughly elucidate the therapeutic potential and clinical significance of pioglitazone in individuals with CKD.
Mesenchymal stem cells
MSCs are multipotent progenitor cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation. The versatility in sourcing of MSCs provides a strong basis for applications in cell-based therapy and regenerative medicine (161). Owing to their self-renewal, differentiation potential, regenerative, and immunomodulatory properties, MSCs have garnered attention as a promising therapeutic approach for the management of hepatic and renal disorders.
In recent years, the application of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) through transplantation has been utilized in various mouse models of MASLD. Studies have shown that BM-MSCs can effectively mitigate hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. They also enhance hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism, boost mitochondrial function, and decrease liver injury and apoptosis (162). BM-MSCs have the ability to transfer functional mitochondria to injured tissues via mechanisms like tunneling nanotubes, extracellular vesicles, and cell fusion, which subsequently enhances tissue repair (163). In MASLD mouse models, mesenchymal therapy has been shown to improve mitochondrial dysfunction through mitochondrial transfer, stimulate mitochondrial function and diminish calcium accumulation in steatotic hepatocytes, thereby alleviating hepatic steatosis (164). In the renal context, BM-MSCs promote the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) through phosphorylation (165), enhance mitochondrial function (166), and decrease the production of ROS, markedly suppressing oxidative stress and enhancing renal function (167). In DKD mouse models, BM-MSCs induce an anti-inflammatory phenotype in renal macrophages through mitochondrial transfer, which ameliorates kidney damage. This effect depends on PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and PGC-1α/TFEB-mediated lysosomal autophagy (168).
In clinical setting, a post-hoc analysis of a prospective clinical trial (NCT02302599) demonstrated that umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs) achieved a liver fat reversal rate of up to 45.45% in patients with T2DM complicated by MASLD after 20 weeks of treatment, significantly reducing body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose levels, triglycerides, and ALT levels (169). Additionally, an 18-month single-arm safety follow-up study (NCT02195323) indicated that the injection of a single dose of autologous MSCs in patients with CKD was safe and well-tolerated, although no statistically significant changes in renal function were observed (170). A randomized clinical trial by Perico et al. (NCT02585622) demonstrated that, compared to placebo, cell therapy significantly slowed the decline of eGFR over 18 months (171). Future studies should further investigate the mechanisms of MSCs, optimize treatment protocols, and address potential challenges in clinical applications to fully harness their therapeutic potential in the treatment of MLKD.
While BM-MSCs offer promising therapeutic potential, several challenges remain. These include issues related to graft rejection, limited cell engraftment, and difficulties in scaling up for clinical use. For instance, despite the immunomodulatory properties of MSCs, the risk of graft rejection cannot be entirely ruled out, especially in allogeneic settings (172). Additionally, achieving sufficient cell engraftment and long-term survival of transplanted cells remains a significant challenge, which can limit the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs (173). These challenges highlight the need for continued research and development to optimize MSC-based therapies.
Conclusion and future perspectives
An increasing amount of both experimental and clinical evidence indicates that the shared pathogenic pathways of mitochondrial dysfunction in MLKD have been extensively established. The intricate interplay among oxidative stress, mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamics, and mitophagy in both the liver and kidney is crucial for the progression of MLKD, and these processes are tightly interconnected. Several therapeutic agents, such as antioxidants, SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP-1RAs, PPAR-γ agonists, and MSCs, have shown promise in treating MLKD by modulating mitochondrial function. It is mentioned that the therapeutic benefits of these agents are not solely attributable to these mechanisms. Antioxidants and SGLT-2 inhibitors have been shown to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation (174), while GLP-1RAs and PPAR-γ agonists have demonstrated immune-modulatory properties (175). MSCs also exhibit anti-inflammatory effects through cytokine modulation and immune cell regulation (176). These additional mechanisms underscore the multifaceted nature of these agents’ therapeutic benefits and highlight their potential for addressing complex pathophysiological processes in MLKD.
Additionally, the mechanisms underlying MASLD-induced kidney injury and the liver-kidney crosstalk remain underexplored. Elucidating the molecular signaling pathways, cellular interactions, and shared inflammatory mechanisms between the liver and kidneys will be crucial for advancing our understanding of the association between the liver and kidneys. Further research is needed to elucidate these mechanisms and develop potential new therapies for MASLD-associated CKD.
Author contributions
JB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. LH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YZ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Shanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology, Key research and development projects (202302130501011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wong, VW, Ekstedt, M, Wong, GL-H, and Hagström, H. Changing epidemiology, global trends and implications for outcomes of NAFLD. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:842–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.04.036
2. Wang, L, Xu, X, Zhang, M, Hu, C, Zhang, X, Li, C, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in china: results from the sixth China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance. JAMA Intern Med. (2023) 183:298–310. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.6817
3. Bai, J, Zhang, L, Zhang, M, Hao, Y, Yi, Z, and Zhou, Y. Regional insights into the relationship between metabolic associated steatotic liver disease and chronic kidney disease: a socioeconomic perspective on disease correlation. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:993. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22188-3
4. Bilson, J, Mantovani, A, Byrne, CD, and Targher, G. Steatotic liver disease, MASLD and risk of chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Metab. (2024) 50:101506. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2023.101506
5. Jung, CY, Lee, JI, Ahn, SH, Kim, SU, and Kim, BS. Agile 3+ and Agile 4 scores predict chronic kidney disease development in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2024) 60:1051–61. doi: 10.1111/apt.18213
6. Gao, J, Li, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhan, X, Tian, X, Li, J, et al. Severity and remission of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty/steatotic liver disease with chronic kidney disease occurrence. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13:e032604. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032604
7. Mantovani, A, Petracca, G, Beatrice, G, Csermely, A, Lonardo, A, Schattenberg, JM, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: an updated meta-analysis. Gut. (2022) 71:156–62. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323082
8. Chen, WY, Zhang, JH, Chen, LL, Byrne, CD, Targher, G, Luo, L, et al. Bioactive metabolites: A clue to the link between MASLD and CKD? Clin Mol Hepatol. (2025) 31:56–73. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0782
9. Fan, JG, and Li, XY. NAFLD renaming to MAFLD, MASLD: background, similarities, differences, and countermeasures. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2023) 31:789–92. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230809-00042
10. Eslam, M, Newsome, PN, Sarin, SK, Anstee, QM, Targher, G, Romero-Gomez, M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039
11. Zheng, KI, Sun, DQ, Jin, Y, Zhu, PW, and Zheng, MH. Clinical utility of the MAFLD definition. J Hepatol. (2021) 74:989–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.12.016
12. Rinella, ME, Lazarus, JV, Ratziu, V, Francque, SM, Sanyal, AJ, Kanwal, F, et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. (2023) 78:1966–86. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000520
13. Zong, Y, Li, H, Liao, P, Chen, L, Pan, Y, Zheng, Y, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:124. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01839-8
14. Sun, A, Pollock, CA, and Huang, C. Mitochondria-targeting therapeutic strategies for chronic kidney disease. Biochem Pharmacol. (2025) 231:116669. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116669
15. Radosavljevic, T, Brankovic, M, Samardzic, J, Djuretić, J, Vukicevic, D, Vucevic, D, et al. Altered mitochondrial function in MASLD: key features and promising therapeutic approaches. Antioxidants (Basel). (2024) 13:906. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080906
16. Li, X, Bhattacharya, D, Yuan, Y, Wei, C, Zhong, F, Ding, F, et al. Chronic kidney disease in a murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Kidney Int. (2024) 105:540–61. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.12.009
17. Targher, G, Chonchol, M, Bertolini, L, Rodella, S, Zenari, L, Lippi, G, et al. Increased risk of CKD among type 2 diabetics with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2008) 19:1564–70. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007101155
18. Chang, Y, Ryu, S, Sung, E, Woo, HY, Oh, E, Cha, K, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease predicts chronic kidney disease in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic Korean men. Metabolism. (2008) 57:569–76. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2007.11.022
19. Jung, CY, Koh, HB, Park, KH, Joo, YS, Kim, HW, Ahn, SH, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: A nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab. (2022) 48:101344. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2022.101344
20. Wei, S, Song, J, Xie, Y, Huang, J, and Yang, J. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease can significantly increase the risk of chronic kidney disease in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2023) 197:110563. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110563
21. Kwon, SY, Park, J, Park, SH, Lee, YB, Kim, G, Hur, KY, et al. MAFLD and NAFLD in the prediction of incident chronic kidney disease. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:1796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27762-6
22. Tanaka, M, Mori, K, Takahashi, S, Higashiura, Y, Ohnishi, H, Hanawa, N, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease predicts new onset of chronic kidney disease better than fatty liver or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2023) 38:700–11. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfac188
23. Heo, JH, Lee, MY, Kim, SH, Zheng, MH, Byrne, CD, Targher, G, et al. Comparative associations of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease with risk of incident chronic kidney disease: a cohort study. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2024) 13:801–13. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-558
24. Mori, K, Tanaka, M, Sato, T, Akiyama, Y, Endo, K, Ogawa, T, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (SLD) and alcohol-associated liver disease, but not SLD without metabolic dysfunction, are independently associated with new onset of chronic kidney disease during a 10-year follow-up period. Hepatol Res. (2024) 55:34–45. doi: 10.1111/hepr.14097
25. Saito, H, Tanaka, T, Sugahara, M, Tanaka, S, Fukui, K, Wakashima, T, et al. Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) by JTZ-951 reduces obesity-related diseases in the liver, white adipose tissue, and kidney in mice with a high-fat diet. Lab Investig. (2019) 99:1217–32. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0239-4
26. Hamada, S, Takata, T, Yamada, K, Yamamoto, M, Mae, Y, Iyama, T, et al. Steatosis is involved in the progression of kidney disease in a high-fat-diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0265461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265461
27. Vacca, M, Kamzolas, I, Harder, LM, Oakley, F, Trautwein, C, Hatting, M, et al. An unbiased ranking of murine dietary models based on their proximity to human metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Nat Metab. (2024) 6:1178–96. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01043-6
28. Sodum, N, Rao, V, Cheruku, SP, Kumar, G, Sankhe, R, Kishore, A, et al. Amelioration of high-fat diet (HFD) + CCl4 induced NASH/NAFLD in CF-1 mice by activation of SIRT-1 using cinnamoyl sulfonamide hydroxamate derivatives: in-silico molecular modelling and in-vivo prediction. 3 Biotech. (2022) 12:147. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03192-5
29. Clare, K, Dillon, JF, and Brennan, PN. Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of MAFLD. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2022) 10:939–46. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00067
30. Zhang, R, Yan, Z, Zhong, H, Luo, R, Liu, W, Xiong, S, et al. Gut microbial metabolites in MASLD: Implications of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis and treatment. Hepatol Commun. (2024) 8:e0484. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000484
31. Fromenty, B, and Roden, M. Mitochondrial alterations in fatty liver diseases. J Hepatol. (2023) 78:415–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.020
32. Goedeke, L, and Shulman, GI. Therapeutic potential of mitochondrial uncouplers for the treatment of metabolic associated fatty liver disease and NASH. Mol Metab. (2021) 46:101178. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101178
33. Vezza, T, Abad-Jiménez, Z, Marti-Cabrera, M, Rocha, M, and Víctor, VM. Microbiota-mitochondria inter-talk: a potential therapeutic strategy in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Antioxidants (Basel). (2020) 9:848. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090848
34. Ramanathan, R, Ali, AH, and Ibdah, JA. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays central role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:7280. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137280
35. Kim, MB, Lee, J, and Lee, JY. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction for the prevention and treatment of metabolic disease by bioactive food components. J Lipid Atheroscler. (2024) 13:306–27. doi: 10.12997/jla.2024.13.3.306
36. Koliaki, C, Szendroedi, J, Kaul, K, Jelenik, T, Nowotny, P, Jankowiak, F, et al. Adaptation of hepatic mitochondrial function in humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver is lost in steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. (2015) 21:739–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.04.004
37. Deng, Y, Dong, Y, Zhang, S, and Feng, Y. Targeting mitochondrial homeostasis in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a review. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1463187. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1463187
38. Mapuskar, KA, Vasquez-Martinez, G, Mayoral-Andrade, G, Tomanek-Chalkley, A, Zepeda-Orozco, D, and Allen, BG. Mitochondrial oxidative metabolism: an emerging therapeutic target to improve CKD outcomes. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:1573. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061573
39. Bhargava, P, and Schnellmann, RG. Mitochondrial energetics in the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2017) 13:629–46. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.107
40. Brinkkoetter, PT, Bork, T, Salou, S, Liang, W, Mizi, A, Özel, C, et al. Anaerobic glycolysis maintains the glomerular filtration barrier independent of mitochondrial metabolism and dynamics. Cell Rep. (2019) 27:1551–1566.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.012
41. Lumpuy-Castillo, J, Amador-Martínez, I, Díaz-Rojas, M, Lorenzo, O, Pedraza-Chaverri, J, Sánchez-Lozada, LG, et al. Role of mitochondria in reno-cardiac diseases: A study of bioenergetics, biogenesis, and GSH signaling in disease transition. Redox Biol. (2024) 76:103340. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103340
42. Hall, AM, Rhodes, GJ, Sandoval, RM, Corridon, PR, and Molitoris, BA. In vivo multiphoton imaging of mitochondrial structure and function during acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. (2013) 83:72–83. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.328
43. Hall, AM, Unwin, RJ, Parker, N, and Duchen, MR. Multiphoton imaging reveals differences in mitochondrial function between nephron segments. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:1293–302. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008070759
44. Mitrofanova, A, Merscher, S, and Fornoni, A. Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2023) 19:629–45. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00741-w
45. Barnhart, S, Shimizu-Albergine, M, Kedar, E, Kothari, V, Shao, B, Krueger, M, et al. Type I IFN induces long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 to generate a phosphatidic acid reservoir for lipotoxic saturated fatty acids. J Lipid Res. (2025) 66:100730. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100730
46. Gaffar, S, and Aathirah, AS. Fatty-acid-binding proteins: from lipid transporters to disease biomarkers. Biomol Ther. (2023) 13:1753. doi: 10.3390/biom13121753
47. Nassir, F, and Ibdah, JA. Role of mitochondria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2014) 15:8713–42. doi: 10.3390/ijms15058713
48. Wang, Y, Yang, J, Zhang, Y, and Zhou, J. Focus on mitochondrial respiratory chain: potential therapeutic target for chronic renal failure. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:949. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020949
49. McTavish, PV, and Mutch, DM. Omega-3 fatty acid regulation of lipoprotein lipase and FAT/CD36 and its impact on white adipose tissue lipid uptake. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:386. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02376-7
50. Moran-Salvador, E, López-Parra, M, García-Alonso, V, Titos, E, Martínez-Clemente, M, González-Périz, A, et al. Role for PPARgamma in obesity-induced hepatic steatosis as determined by hepatocyte- and macrophage-specific conditional knockouts. FASEB J. (2011) 25:2538–50. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-173716
51. Doege, H, Baillie, RA, Ortegon, AM, Tsang, B, Wu, Q, Punreddy, S, et al. Targeted deletion of FATP5 reveals multiple functions in liver metabolism: alterations in hepatic lipid homeostasis. Gastroenterology. (2006) 130:1245–58. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.006
52. Falcon, A, Doege, H, Fluitt, A, Tsang, B, Watson, N, Kay, MA, et al. FATP2 is a hepatic fatty acid transporter and peroxisomal very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 299:E384–93. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00226.2010
53. Wilson, CG, Tran, JL, Erion, DM, Vera, NB, Febbraio, M, and Weiss, EJ. Hepatocyte-specific disruption of CD36 attenuates fatty liver and improves insulin sensitivity in HFD-fed mice. Endocrinology. (2016) 157:570–85. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1866
54. Jia, X, Zhu, L, Zhu, Q, and Zhang, J. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney injury and disease. Autoimmun Rev. (2024) 23:103576. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103576
55. Moore, MP, Cunningham, RP, Meers, GM, Johnson, SA, Wheeler, AA, Ganga, RR, et al. Compromised hepatic mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and reduced markers of mitochondrial turnover in human NAFLD. Hepatology. (2022) 76:1452–65. doi: 10.1002/hep.32324
56. Zhou, W, Deng, X, Zhu, X, Yan, Q, Zhou, N, du, S, et al. HtrA2/Omi mitigates NAFLD in high-fat-fed mice by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and restoring autophagic flux. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8:218. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01022-4
57. Lin, JJ, Liu, YC, Chang, CJ, Pan, MH, Lee, MF, and Pan, BS. Hepatoprotective mechanism of freshwater clam extract alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: elucidated in vitro and in vivo models. Food Funct. (2018) 9:6315–25. doi: 10.1039/C8FO01758A
58. Sangineto, M, Bukke, VN, Bellanti, F, Tamborra, R, Moola, A, Duda, L, et al. A novel nutraceuticals mixture improves liver steatosis by preventing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in a NAFLD model. Nutrients. (2021) 13:652. doi: 10.3390/nu13020652
59. Miguel, V, Tituaña, J, Herrero, JI, Herrero, L, Serra, D, Cuevas, P, et al. Renal tubule Cpt1a overexpression protects from kidney fibrosis by restoring mitochondrial homeostasis. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e140695. doi: 10.1172/JCI140695
60. Dewidar, B, Mastrototaro, L, Englisch, C, Ress, C, Granata, C, Rohbeck, E, et al. Alterations of hepatic energy metabolism in murine models of obesity, diabetes and fatty liver diseases. EBioMedicine. (2023) 94:104714. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104714
61. Li, Z, Li, Y, Zhang, HX, Guo, JR, Lam, CWK, Wang, CY, et al. Mitochondria-mediated pathogenesis and therapeutics for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:e1900043. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900043
62. Ma, Y, Lee, G, Heo, SY, and Roh, YS. Oxidative stress is a key modulator in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 11:91. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010091
63. Kowalczyk, P, Sulejczak, D, Kleczkowska, P, Bukowska-Ośko, I, Kucia, M, Popiel, M, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress-a causative factor and therapeutic target in many diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:13384. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413384
64. Ho, HJ, and Shirakawa, H. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Cells. (2022) 12:88. doi: 10.3390/cells12010088
65. Garcia-Martinez, I, Santoro, N, Chen, Y, Hoque, R, Ouyang, X, Caprio, S, et al. Hepatocyte mitochondrial DNA drives nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by activation of TLR9. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:859–64. doi: 10.1172/JCI83885
66. Karkucinska-Wieckowska, A, Simoes, ICM, Kalinowski, P, Lebiedzinska-Arciszewska, M, Zieniewicz, K, Milkiewicz, P, et al. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A complex relationship. Eur J Clin Investig. (2022) 52:e13622. doi: 10.1111/eci.13622
67. Ore, A, and Akinloye, OA. Oxidative stress and antioxidant biomarkers in clinical and experimental models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicina (Kaunas). (2019) 55:26. doi: 10.3390/medicina55020026
68. Cui, X, Shi, E, Li, J, Li, Y, Qiao, Z, Wang, Z, et al. GPR87 promotes renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by accelerating glycolysis and mitochondrial injury. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 189:58–70. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.07.004
69. Chen, H, Liu, Y, Zhang, T, Huang, T, Lang, Y, Sheng, Q, et al. Inhibition of the lncRNA 585189 prevents podocyte injury and mitochondria dysfunction by promoting hnRNP A1 and SIRT1 in diabetic nephropathy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2023) 578:112065. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2023.112065
70. Hua, W, Peng, L, Chen, XM, Jiang, XS, Hu, JG, Jiang, XH, et al. CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement. Open Med (Wars). (2024) 19:20240918. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0918
71. Chen, Y, Yang, Y, Liu, Z, and He, L. Adiponectin promotes repair of renal tubular epithelial cells by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Metabolism. (2022) 128:154959. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154959
72. Kent, AC, El, BK, and Hamrick, MW. Targeting the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to prevent age-associated cell damage and neurodegeneration. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:6626484. doi: 10.1155/2021/6626484
73. Liu, J, Han, X, Zhang, T, Tian, K, Li, Z, and Luo, F. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging biomaterials for anti-inflammatory diseases: from mechanism to therapy. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:116. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01512-7
74. Popov, LD. Mitochondrial biogenesis: An update. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:4892–9. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15194
75. Ding, Q, Qi, Y, Tsang, SY, and Biogenesis, M. Mitochondrial dynamics, and mitophagy in the maturation of cardiomyocytes. Cells. (2021) 10:2463. doi: 10.3390/cells10092463
76. Tang, JX, Thompson, K, Taylor, RW, and Oláhová, M. Mitochondrial OXPHOS biogenesis: co-regulation of protein synthesis, import, and assembly pathways. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3820. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113820
77. Zheng, Y, Wang, S, Wu, J, and Wang, Y. Mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: new insights from pathogenic mechanisms to clinically targeted therapy. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:510. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04367-1
78. Yang, T, Hu, Y, Chen, S, Li, L, Cao, X, Yuan, J, et al. YY1 inactivated transcription co-regulator PGC-1alpha to promote mitochondrial dysfunction of early diabetic nephropathy-associated tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39:391–413. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09711-7
79. Zhou, Y, Liu, L, Jin, B, Wu, Y, Xu, L, Chang, X, et al. Metrnl alleviates lipid accumulation by modulating mitochondrial homeostasis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. (2023) 72:611–26. doi: 10.2337/db22-0680
80. Juszczak, F, Arnould, T, and Decleves, AE. The role of mitochondrial sirtuins (SIRT3, SIRT4 and SIRT5) in renal cell metabolism: implication for kidney diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6936. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136936
81. Chimienti, G, Orlando, A, Russo, F, D’Attoma, B, Aragno, M, Aimaretti, E, et al. The mitochondrial trigger in an animal model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Genes (Basel). (2021) 12:1439. doi: 10.3390/genes12091439
82. Gao, S, and Hu, J. Mitochondrial fusion: the machineries in and out. Trends Cell Biol. (2021) 31:62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.09.008
83. Hernandez-Alvarez, MI, Sebastián, D, Vives, S, Ivanova, S, Bartoccioni, P, Kakimoto, P, et al. Deficient endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial phosphatidylserine transfer causes liver disease. Cell. (2019) 177:881–895.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.010
84. Zheng, P, Ma, W, Gu, Y, Wu, H, Bian, Z, Liu, N, et al. High-fat diet causes mitochondrial damage and downregulation of mitofusin-2 and optic atrophy-1 in multiple organs. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2023) 73:61–76. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.22-73
85. Gong, F, Gao, L, and Ding, T. IDH2 protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by alleviating dyslipidemia regulated by oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 514:593–600. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.069
86. Rodriguez, AG, Rodríguez, JZ, Barreto, A, Sanabria-Barrera, S, Iglesias, J, and Morales, L. Impact of acute high glucose on mitochondrial function in a model of endothelial cells: role of PDGF-C. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4394. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054394
87. J, Y, and Hwang, YC. 1599-P: regulation of mitochondrial dynamics ameliorates hepatic steatosis through TFEB Activation. Diabetes. (2023) 72:1599-P. doi: 10.2337/db23-1599-P
88. Ding, XQ, Jian, TY, Gai, YN, Niu, GT, Liu, Y, Meng, XH, et al. Chicoric acid attenuated renal tubular injury in HFD-induced chronic kidney disease mice through the promotion of mitophagy via the Nrf2/PINK/Parkin pathway. J Agric Food Chem. (2022) 70:2923–35. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07795
89. Ko, SF, Yang, CC, Sung, PH, Cheng, BC, Shao, PL, Chen, YL, et al. Dapagliflozin-entresto protected kidney from renal hypertension via downregulating cell-stress signaling and upregulating SIRT1/PGC-1α/Mfn2-medicated mitochondrial homeostasis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2023) 248:2421–39. doi: 10.1177/15353702231198087
90. Hao, Y, Fan, Y, Feng, J, Zhu, Z, Luo, Z, Hu, H, et al. ALCAT1-mediated abnormal cardiolipin remodelling promotes mitochondrial injury in podocytes in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:26. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01399-4
91. Tanriover, C, Copur, S, Ucku, D, Cakir, AB, Hasbal, NB, Soler, MJ, et al. The mitochondrion: a promising target for kidney disease. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:570. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020570
92. Li, L, Liu, F, Feng, C, Chen, Z, Zhang, N, and Mao, J. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in kidney disease: Insights from the cGAS-STING signaling pathway. Chin Med J. (2024) 137:1044–53. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003022
93. Qin, L, and Xi, S. The role of mitochondrial fission proteins in mitochondrial dynamics in kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:14725. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314725
94. Hao, Y, Zhao, L, Zhao, JY, Han, X, and Zhou, X. Unveiling the potential of mitochondrial dynamics as a therapeutic strategy for acute kidney injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2023) 11:1244313. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1244313
95. Chen, W, Zhao, H, and Li, Y. Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease: mechanisms and potential targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:333. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01547-9
96. Yang, K, Li, T, Geng, Y, Zou, X, Peng, F, and Gao, W. The role of mitophagy in the development of chronic kidney disease. PeerJ. (2024) 12:e17260. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17260
97. Wang, S, Long, H, Hou, L, Feng, B, Ma, Z, Wu, Y, et al. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:304. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01503-7
98. Yang, C, Yi, B, Yang, S, Li, A, Liu, J, Wang, J, et al. VDR restores the expression of PINK1 and BNIP3 in TECs of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Life Sci Alliance. (2024) 7:e202302474. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302474
99. Li, Y, Zheng, W, Lu, Y, Zheng, Y, Pan, L, Wu, X, et al. BNIP3L/NIX-mediated mitophagy: molecular mechanisms and implications for human disease. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 13:14. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04469-y
100. Casanova, A, Wevers, A, Navarro-Ledesma, S, and Pruimboom, L. Mitochondria: It is all about energy. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1114231. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1114231
101. Shin, S, Kim, J, Lee, JY, Kim, J, and Oh, CM. Mitochondrial quality control: its role in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J Obes Metab Syndr. (2023) 32:289–302. doi: 10.7570/jomes23054
102. Shetty, S, Anushree, U, Kumar, R, and Bharati, S. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant, mito-TEMPO mitigates initiation phase of N-Nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Mitochondrion. (2021) 58:123–30. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.03.001
103. Li, W, Cai, Z, Schindler, F, Afjehi-Sadat, L, Montsch, B, Heffeter, P, et al. Elevated PINK1/parkin-dependent mitophagy and boosted mitochondrial function mediate protection of HEPG2 cells from excess palmitic acid by hesperetin. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:13039–53. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09132
104. Lian, CY, Li, HJ, Xia, WH, Li, Y, Zhou, XL, Yang, DB, et al. Insufficient FUNDC1-dependent mitophagy due to early environmental cadmium exposure triggers mitochondrial redox imbalance to aggravate diet-induced lipotoxicity. Environ Pollut. (2024) 361:124724. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124724
105. Li, R, Xin, T, Li, D, Wang, C, Zhu, H, and Zhou, H. Therapeutic effect of Sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of the ERK-CREB pathway and Bnip3-mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol. (2018) 18:229–43. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.011
106. Han, YC, Tang, SQ, Liu, YT, Li, AM, Zhan, M, Yang, M, et al. AMPK agonist alleviate renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via activating mitophagy in high fat and streptozotocin induced diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:925. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04184-8
107. Sun, Y, Ge, X, Li, X, He, J, Wei, X, du, J, et al. High-fat diet promotes renal injury by inducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:914. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03122-4
108. Chen, H, Zhang, H, Li, AM, Liu, YT, Liu, Y, Zhang, W, et al. VDR regulates mitochondrial function as a protective mechanism against renal tubular cell injury in diabetic rats. Redox Biol. (2024) 70:103062. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103062
109. Liu, X, Lu, J, Liu, S, Huang, D, Chen, M, Xiong, G, et al. Huangqi-Danshen decoction alleviates diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by inhibiting PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Am J Transl Res. (2020) 12:989–998.
110. Lin, L, Tan, W, Pan, X, Tian, E, Wu, Z, and Yang, J. Metabolic Syndrome-Related Kidney Injury: A Review and Update. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:904001. Published 2022 Jun 23. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.904001
111. Orlic, L, Mikolasevic, I, Lukenda, V, Anic, K, Jelic, I, and Racki, S. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the renin-angiotensin system blockers in the patients with chronic kidney disease. Wien Klin Wochenschr. (2015) 127:355–62. doi: 10.1007/s00508-014-0661-y
112. Smirnova, E, Muthiah, MD, Narayan, N, Siddiqui, MS, Puri, P, Luketic, VA, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of the intestinal microbiome with functional bile acid changes underlie the development of NAFLD. Hepatology. (2022) 76:1811–24. doi: 10.1002/hep.32568
113. Mantovani, A, Taliento, A, Zusi, C, Baselli, G, Prati, D, Granata, S, et al. PNPLA3 I148M gene variant and chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetic patients with NAFLD: Clinical and experimental findings. Liver Int. (2020) 40:1130–41. doi: 10.1111/liv.14419
114. Sun, DQ, Zheng, KI, Xu, G, Ma, HL, Zhang, HY, Pan, XY, et al. PNPLA3 rs738409 is associated with renal glomerular and tubular injury in NAFLD patients with persistently normal ALT levels. Liver Int. (2020) 40:107–19. doi: 10.1111/liv.14251
115. Katsiki, N, Kolovou, G, Melidonis, A, and Banach, M. The Cardiac-Kidney-Liver (CKL) syndrome: the “real entity” of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Med Sci. (2024) 20:207–15. doi: 10.5114/aoms/183070
116. Theodorakis, N, and Nikolaou, M. From cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome to cardiovascular-renal-hepatic-metabolic syndrome: proposing an expanded framework. Biomol Ther. (2025) 15:213. doi: 10.3390/biom15020213
117. Zhang, T, Nie, Y, and Wang, J. The emerging significance of mitochondrial targeted strategies in NAFLD treatment. Life Sci. (2023) 329:121943. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121943
118. Kirkman, DL, Stock, JM, Shenouda, N, Bohmke, NJ, Kim, Y, Kidd, J, et al. Effects of a mitochondrial-targeted ubiquinol on vascular function and exercise capacity in chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled pilot study. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2023) 325:F448–56. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00067.2023
119. Yang, J, Suo, H, and Song, J. Protective role of mitoquinone against impaired mitochondrial homeostasis in metabolic syndrome. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 61:3857–75. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1809344
120. Feillet-Coudray, C, Fouret, G, Ebabe Elle, R, Rieusset, J, Bonafos, B, Chabi, B, et al. The mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant MitoQ ameliorates metabolic syndrome features in obesogenic diet-fed rats better than Apocynin or Allopurinol. Free Radic Res. (2014) 48:1232–46. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.945079
121. Fouret, G, Tolika, E, Lecomte, J, Bonafos, B, Aoun, M, Murphy, MP, et al. The mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant, MitoQ, increases liver mitochondrial cardiolipin content in obesogenic diet-fed rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2015) 1847:1025–35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.05.019
122. Gane, EJ, Weilert, F, Orr, DW, Keogh, GF, Gibson, M, Lockhart, MM, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant mitoquinone decreases liver damage in a phase II study of hepatitis C patients. Liver Int. (2010) 30:1019–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02250.x
123. Zhu, Z, Liang, W, Chen, Z, Hu, J, Feng, J, Cao, Y, et al. Mitoquinone protects podocytes from angiotensin II-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and injury via the keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:1394486. doi: 10.1155/2021/1394486
124. Wu, J, Zheng, L, Mo, J, Yao, X, Fan, C, and Bao, Y. Protective effects of MitoTEMPO on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via regulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells and inflammation in mice. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:9329427. doi: 10.1155/2020/9329427
125. Ma, C, Kesarwala, AH, Eggert, T, Medina-Echeverz, J, Kleiner, DE, Jin, P, et al. NAFLD causes selective CD4(+) T lymphocyte loss and promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Nature. (2016) 531:253–7. doi: 10.1038/nature16969
126. Liu, B, Wang, D, Cao, Y, Wu, J, Zhou, Y, Wu, W, et al. MitoTEMPO protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome via PINK1/Parkin pathway-mediated mitophagy. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 929:175136. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175136
127. Liu, Y, Wang, Y, Ding, W, and Wang, Y. Mito-TEMPO alleviates renal fibrosis by reducing inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:5828120. doi: 10.1155/2018/5828120
128. Zhao, K, Zhao, GM, Wu, D, Soong, Y, Birk, AV, Schiller, PW, et al. Cell-permeable peptide antioxidants targeted to inner mitochondrial membrane inhibit mitochondrial swelling, oxidative cell death, and reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:34682–90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402999200
129. Zhu, Y, Luo, M, Bai, X, Li, J, Nie, P, Li, B, et al. SS-31, a mitochondria-targeting peptide, ameliorates kidney disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:1295509. doi: 10.1155/2022/1295509
130. Szeto, HH. First-in-class cardiolipin-protective compound as a therapeutic agent to restore mitochondrial bioenergetics. Br J Pharmacol. (2014) 171:2029–50. doi: 10.1111/bph.12461
131. Yang, SK, Han, YC, He, JR, Yang, M, Zhang, W, Zhan, M, et al. Mitochondria targeted peptide SS-31 prevent on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via regulating mitochondrial ROS-NLRP3 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 130:110521. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110521
132. Bhatti, JS, Tamarai, K, Kandimalla, R, Manczak, M, Yin, X, Ramasubramanian, B, et al. Protective effects of a mitochondria-targeted small peptide SS31 against hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial abnormalities in the liver tissues of diabetic mice, Tallyho/JngJ mice. Mitochondrion. (2021) 58:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.02.007
133. Sun, L, Xu, H, Wang, Y, Ma, X, Xu, Y, and Sun, F. The mitochondrial-targeted peptide SBT-20 ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic renal failure. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:18238–50. doi: 10.18632/aging.103681
134. Honda, Y, Imajo, K, Kato, T, Kessoku, T, Ogawa, Y, Tomeno, W, et al. The selective SGLT2 inhibitor ipragliflozin has a therapeutic effect on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0146337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146337
135. Belosludtsev, KN, Starinets, VS, Belosludtsev, MN, Mikheeva, IB, Dubinin, MV, and Belosludtseva, NV. Chronic treatment with dapagliflozin protects against mitochondrial dysfunction in the liver of C57BL/6NCrl mice with high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Mitochondrion. (2021) 59:246–54. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.06.008
136. Zaibi, N, Li, P, and Xu, SZ. Protective effects of dapagliflozin against oxidative stress-induced cell injury in human proximal tubular cells. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0247234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247234
137. Terami, N, Ogawa, D, Tachibana, H, Hatanaka, T, Wada, J, Nakatsuka, A, et al. Long-term treatment with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, ameliorates glucose homeostasis and diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e100777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100777
138. Wanner, C, Inzucchi, SE, Lachin, JM, Fitchett, D, von Eynatten, M, Mattheus, M, et al. Empagliflozin and Progression of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:323–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1515920
139. Kuchay, MS, Krishan, S, Mishra, SK, Farooqui, KJ, Singh, MK, Wasir, JS, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on liver fat in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial (E-LIFT Trial). Diabetes Care. (2018) 41:1801–8. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0165
140. Ao, N, du, J, Jin, S, Suo, L, and Yang, J. The cellular and molecular mechanisms mediating the protective effects of sodium-glucose linked transporter 2 inhibitors against metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2025) 27:457–67. doi: 10.1111/dom.16043
141. Coelho, F, Borges-Canha, M, von Hafe, M, Neves, JS, Vale, C, Leite, AR, et al. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on liver parameters and steatosis: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2021) 37:e3413. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3413
142. Zelniker, TA, Bonaca, MP, Furtado, RHM, Mosenzon, O, Kuder, JF, Murphy, SA, et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: insights from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial. Circulation. (2020) 141:1227–34. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044183
143. Neal, B, Perkovic, V, and Matthews, DR. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in Type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2099. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1712572
144. Cannon, CP, Pratley, R, Dagogo-Jack, S, Mancuso, J, Huyck, S, Masiukiewicz, U, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1425–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2004967
145. Zinman, B, Wanner, C, Lachin, JM, Fitchett, D, Bluhmki, E, Hantel, S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:2117–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720
146. Wiviott, SD, Raz, I, Bonaca, MP, Mosenzon, O, Kato, ET, Cahn, A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:347–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812389
147. Liu, X, Huang, J, Li, J, Mao, Q, and He, J. Effects of liraglutide combined with insulin on oxidative stress and serum MCP-1 and NF-kB levels in type 2 diabetes. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. (2019) 29:218–21. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2019.03.218
148. Chen, WR, Shen, XQ, Zhang, Y, Chen, YD, Hu, SY, Qian, G, et al. Effects of liraglutide on left ventricular function in patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Endocrine. (2016) 52:516–26. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0798-0
149. Yao, MY, Li, LQ, Ma, JX, Xue, P, and Li, YK. Use of flash glucose-sensing technology in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with liraglutide combined with CSII: a pilot study. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2020) 53:e8652. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20198652
150. Niu, S, Chen, S, Chen, X, Ren, Q, Yue, L, Pan, X, et al. Semaglutide ameliorates metabolism and hepatic outcomes in an NAFLD mouse model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1046130. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1046130
151. Wang, Y, He, W, Wei, W, Mei, X, Yang, M, and Wang, Y. Exenatide attenuates obesity-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by activating SIRT1 in renal tubular cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:622737. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.622737
152. Targher, G, Mantovani, A, and Byrne, CD. Mechanisms and possible hepatoprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and other incretin receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:179–91. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00338-7
153. Mantovani, A, Byrne, CD, and Targher, G. Efficacy of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 7:367–78. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00261-2
154. Khoo, J, Hsiang, JC, Taneja, R, Koo, SH, Soon, GH, Kam, CJ, et al. Randomized trial comparing effects of weight loss by liraglutide with lifestyle modification in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. (2019) 39:941–9. doi: 10.1111/liv.14065
155. Imprialos, KP, Stavropoulos, K, and Doumas, M. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2196. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1713042
156. Mima, A, Nomura, A, and Fujii, T. Current findings on the efficacy of incretin-based drugs for diabetic kidney disease: A narrative review. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 165:115032. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115032
157. Kalavalapalli, S, Bril, F, Koelmel, JP, Abdo, K, Guingab, J, Andrews, P, et al. Pioglitazone improves hepatic mitochondrial function in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 315:E163–73. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00023.2018
158. Hodges, WT, Jarasvaraparn, C, Ferguson, D, Griffett, K, Gill, LE, Chen, Y, et al. Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier inhibitors improve metabolic parameters in diet-induced obese mice. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:101554. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101554
159. Mantovani, A, Byrne, CD, Scorletti, E, Mantzoros, CS, and Targher, G. Efficacy and safety of anti-hyperglycaemic drugs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with or without diabetes: An updated systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab. (2020) 46:427–41. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2019.12.007
160. Ho, CC, Yang, YS, Huang, CN, Lo, SC, Wang, YH, and Kornelius, E. The efficacy of pioglitazone for renal protection in diabetic kidney disease. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0264129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264129
161. Brown, C, McKee, C, Bakshi, S, Walker, K, Hakman, E, Halassy, S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Cell therapy and regeneration potential. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. (2019) 13:1738–55. doi: 10.1002/term.2914
162. Yi, S, Cong, Q, Zhu, Y, and Xu, Q. Mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cells in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Stem Cells Int. (2023) 2023:3919002. doi: 10.1155/2023/3919002
163. Torralba, D, Baixauli, F, and Sanchez-Madrid, F. Mitochondria know no boundaries: mechanisms and functions of intercellular mitochondrial transfer. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2016) 4:107. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00107
164. Bi, Y, Guo, X, Zhang, M, Zhu, K, Shi, C, Fan, B, et al. Bone marrow derived-mesenchymal stem cell improves diabetes-associated fatty liver via mitochondria transformation in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12:602. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02663-5
165. Wang, L, Qing, L, Liu, H, Liu, N, Qiao, J, Cui, C, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate oxidative stress-induced islet endothelium apoptosis and functional impairment via Wnt4-beta-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2017) 8:188. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0640-0
166. Lee, SE, Jang, JE, Kim, HS, Jung, MK, Ko, MS, Kim, MO, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial function in tubular epithelial cells. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0282-7
167. Wang, Y, Luo, P, and Wuren, T. Narrative review of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in renal diseases: mechanisms, clinical applications, and future directions. Stem Cells Int. (2024) 2024:8658246. doi: 10.1155/sci/8658246
168. Yuan, Y, Yuan, L, Li, L, Liu, F, Liu, J, Chen, Y, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from mesenchymal stem cells to macrophages restricts inflammation and alleviates kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy mice via PGC-1alpha activation. Stem Cells. (2021) 39:913–28. doi: 10.1002/stem.3375
169. Jian, Z, Yuepeng, W, Yu, H, Wangtian, M, Yiming, M, Weijun, G, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell infusion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: post facto analysis of a prospective clinical trial. J PLA Med Coll. (2019) 45:571–577+583.
170. Makhlough, A, Shekarchian, S, Moghadasali, R, Einollahi, B, Dastgheib, M, Janbabaee, G, et al. Bone marrow-mesenchymal stromal cell infusion in patients with chronic kidney disease: A safety study with 18 months of follow-up. Cytotherapy. (2018) 20:660–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.02.368
171. Perico, N, Remuzzi, G, Griffin, MD, Cockwell, P, Maxwell, AP, Casiraghi, F, et al. Safety and preliminary efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell (ORBCEL-M) therapy in diabetic kidney disease: a randomized clinical trial (NEPHSTROM). J Am Soc Nephrol. (2023) 34:1733–51. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000189
172. English, K, and Wood, KJ. Mesenchymal stromal cells in transplantation rejection and tolerance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2013) 3:a015560. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a015560
173. Kadri, N, Amu, S, Iacobaeus, E, Boberg, E, and Le Blanc, K. Current perspectives on mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for graft versus host disease. Cell Mol Immunol. (2023) 20:613–25. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01022-z
174. Tsai, KF, Chen, YL, Chiou, TT, Chu, TH, Li, LC, Ng, HY, et al. Emergence of SGLT2 inhibitors as powerful antioxidants in human diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 10:1166. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081166
175. Myasoedova, VA, Bozzi, M, Valerio, V, Moschetta, D, Massaiu, I, Rusconi, V, et al. Anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation: the key to unlocking the cardiovascular potential of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 receptor agonists. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 13:16. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010016
Keywords: metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, review
Citation: Bai J, Zhang L, He L and Zhou Y (2025) Altered mitochondrial function: a clue therapeutic strategies between metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and chronic kidney disease? Front. Nutr. 12:1613640. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1613640
Edited by:
Vladimir Lj Jakovljevic, University of Kragujevac, SerbiaReviewed by:
Jasmina Djuretić, University of Belgrade, SerbiaAnjali Srivastava, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Copyright © 2025 Bai, Zhang, He and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yun Zhou, emhvdXl1bl9zeEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jiang Bai
Jiang Bai Lijuan Zhang
Lijuan Zhang Letian He2
Letian He2 Yun Zhou
Yun Zhou