- 1Department of Natural and Life Sciences, Faculty of Sciences, University of Algiers 1 Benyoucef Benkhedda, Algiers, Algeria
- 2Laboratoire de Recherche de Technologie Alimentaire et Nutrition Humaine - LRTANH, Ecole Nationale Supérieure Agronomique - ENSA, LRTANH, Algiers, Algeria
- 3Laboratory of Valorisation and Bioengineering of Natural Resources—LVBRN, Faculty of Sciences, University of Algiers 1 Benyoucef Benkhedda, Algiers, Algeria
- 4Physiologie de la Nutrition & Toxicologie, UMR INSERM U1231, CTM – Université Bourgogne Europe, Dijon, France
Obesity is a burning public health problem that affects both children and adult population all over the world. The incidence of obesity will increase in the coming years due to the urbanization of societies, which has led to unbalanced food intake and lack of physical activity among individuals. The efficacy of pharmaceutical interventions is limited, and a large number of drugs are known to trigger side effects, leading to their removal from the market. The use of natural products that exert least significant side effects can be a good alternative to prevent and manage obesity and its associated complications. These natural products include polyphenols, carotenoids and alkaloids that are recognized for their extensive range of biomedical applications and have been in practice for several decades. Administering low-to-moderate doses can yield a number of health benefits; thereby, enhancing their utility in clinical settings. Nevertheless, their direct application poses challenges due to several issues such as low bioavailability, scalability, environmental impact, clinical inconsistency, and toxicity at high doses. This review seeks to examine and identify the effects of some natural bioactive compounds (NBCs) in the management of obesity by targeting pathophysiological pathways, discuss the challenges associated with the use of NBCs including issues of bioavailability, dosage, toxicity and analysis of the efficacy of polyphenols in different models. It is necessary of address challenges associated with the use of NBCs by developing formulation strategies, establishing a safe concentration margin, employing humanized in vitro models to enhance translatability to clinical applications, optimizing dosage and harmonizing guidelines. The review also focuses on some conclusive studies demonstrating the potential anti-obesity effects of the most studied bioactive compounds in vitro, in vivo, and in clinical human trials through the regulation of appetite, adipogenesis, inflammation, thermogenesis and energy expenditure and gut microbiome.
1 Introduction
Obesity is a burning public health problem as it is associated with several complications, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis among others non-communicable diseases (1). The World Obesity Federation estimates that the economic impact of obesity will reach US$4.32 trillion by 2035, including healthcare costs of treatment with an impact on economic situation (decreased productivity, absenteeism, premature retirement or death), leading to the reduction of global gross world product by 2.9% (2). Obesity is mainly defined by body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or greater and described as a slow-motion disaster that has reached a pandemic level (3). Excessive BMI reflects a sustained energy imbalance due to high calorie intake and/or a decrease in energy expenditure, conducting to accumulation of energy reserves as fat depots (4). Obesity has a multifactorial etiology promoted by age, gender, genes, intake of high-calorie foods, dietary diversity, less physical exercise, and fat-rich food eating behavior (5–7).
The treatment of obesity is linked to body weight reduction through diet, exercise, pharmaceutical interventions, or bariatric surgery (8). In addition to the aforementioned anti-obesity approaches, there exists another crucial way to enhance energy metabolism. This approach involves the strategies that increase the body’s capacity to burn calories, generate heat, and utilize nutrients efficiently. Indeed, muscle tissue is metabolically active and spends more calories than adipocytes. Non—shivering thermogenesis (NST) is a mechanism that occurs at two sites of adaptive thermogenesis: brown adipose tissue (BAT) and skeletal muscle (SM). In SM, SERCA-based futile Ca2+-cycling and mitochondrial activities are the primary contributors to NST (9). Hence, targeting SM and NST may enhance energy metabolism and help combat obesity.
The efficacy of anti-obesity medicines is limited and their side effects include abdominal cramps, palpitations, increased blood pressure, diarrhea, insomnia and nausea (10). For example, fenfluramine an appetite suppressant used to control food intake via the central nervous system was removed from the market by the United States Food and Drug Administration (11). However, natural products exhibit anti-obesity activities with insignificant side effects (12). Consequently, the use of natural bioactive compounds (NBCs) from human diet is a good alternative to manage obesity. The NBCs exert anti-obesity-related actions, i.e., anti-inflammatory effects, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, and antihypertensive properties (13–15). Bioactive compounds or phytochemicals are no—nutrients constituents present in small amounts in fruits, vegetables and other plant-based food (16). They include polyphenols, carotenoids, alkaloids, dietary fibers, fatty acids, proteins, some carbohydrates vitamins and minerals (17).
Recognizing that NBCs may represent safe and effective alternatives to decrease obesity and its related comorbidities, this review seeks to: (1) examine and identify the effects of certain NBCs on obesity management by targeting pathophysiological pathways; (2) discuss the challenges associated with the use of NBCs including issues of bioavailability, concentration, and toxicity, and (3) analyze of the efficacy of polyphenols across different models. This review aims at providing with reliable data to enhance the quality of life and obesity management through the use of safe products and by considering formulations that target multiple pathways underlying obesity. This narrative review underscores the necessity of addressing challenges associated with the use of NBCs by developing formulation strategies, establishing a safe concentration margin, employing humanized in vitro models to enhance translatability to human applications, optimizing dosage and harmonizing guidelines. It will be pertaining to use new technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict compound activity, safety, and synergies. Besides, we summarize some conclusive studies showing the potential anti-obesity effects of the most studied bioactive compounds in vitro, in vivo, and in clinical human trials.
2 Methods
We conducted a comprehensive literature search by focusing on the most extensively studied NBCs with anti-obesity effects, particularly polyphenols. The mechanisms of action of these compounds have been thoroughly studied. We have focused on conclusive studies with insignificant side effects. Relevant keywords used were NBCs, polyphenols, carotenoids, alkaloids, clinical trial, obesity, and inflammation in the following databases: research gate, Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus and Web of Sciences. Relevant articles were included and reference lists of key papers were searched. We included in vitro, in vivo and clinical human studies without limiting period. A total of 183 papers were selected for further analysis. The selection process entailed the elimination of duplicate information, the screening of titles and abstracts, and a comprehensive full—text evaluation of potentially relevant articles. Both research and review articles written in English have been included in the manuscript.
3 Principles mechanisms underlying obesity
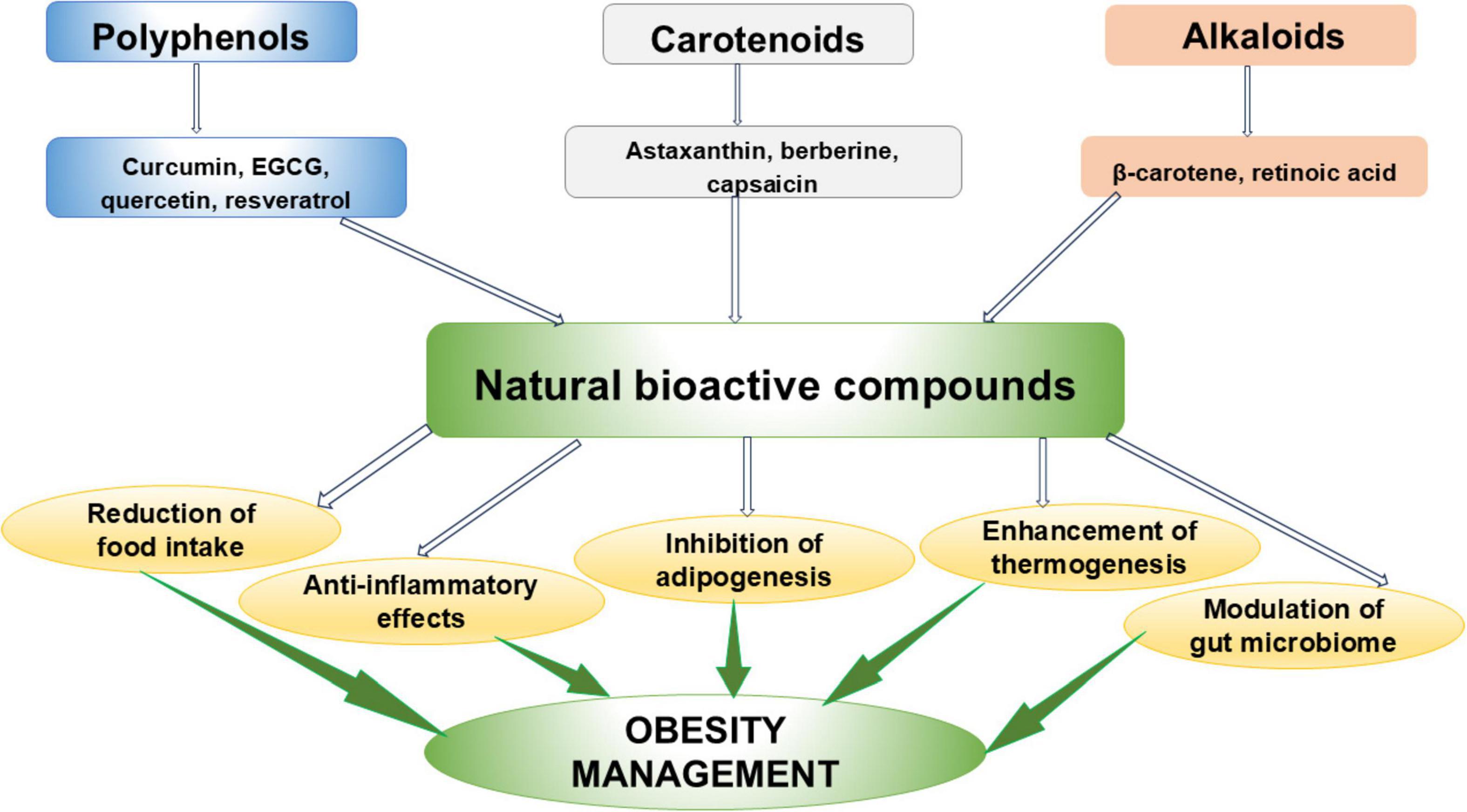
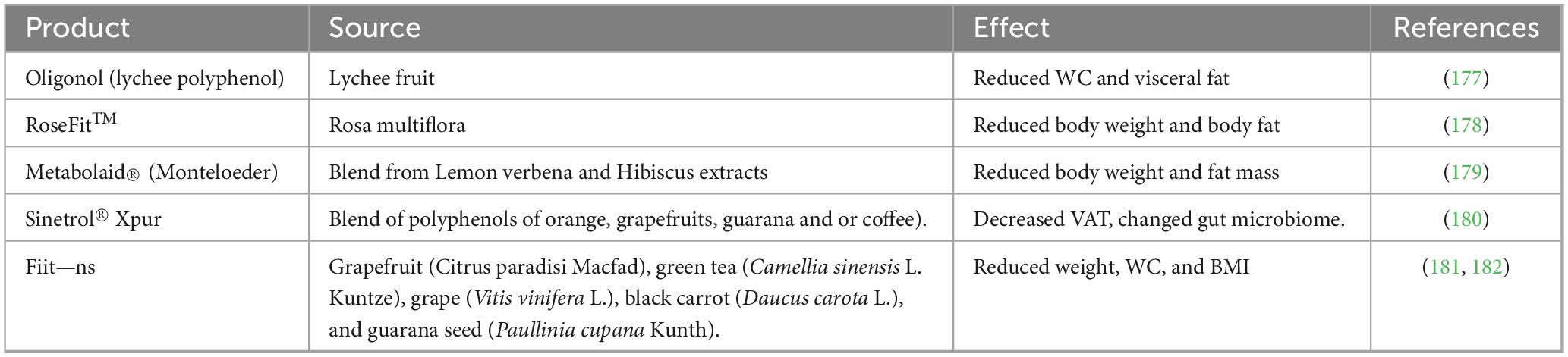
Several metabolic and signaling pathways are involved in the pathogenesis of obesity, mainly including the regulation of appetite and food intake, adipogenesis, inflammation, mitochondrial biogenesis and NST, and the regulation of gut microbiome. Figure 1 summarizes principles factors implicated in obesity.
Figure 1. Principles factors implicated in obesity. AgRP, agouti—related peptide; AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, adenosine mono phosphate-activated protein kinase; CART, cocaine- and amphetamine-related transcript protein; CCK, Cholecystokinin; C/EBPα, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; F/B, Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; IL-6, interleukin-1; JAK, Janus kinase-signal transducer; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa—B; NPY, neuropeptide Y; PGC-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; PYY, peptide YY; SERCA, Sarcolipin-mediated uncoupling of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; SIRT, Sirtuin; SREBP1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; UCP, uncoupling protein; ↑, upward arrow shows an increase; ↓ downward arrow shows a decrease.
3.1 Control of appetite and reduction of food intake
Energy homeostasis is regulated by a complex hormonal and neural pathways that involves gut—brain signaling mechanisms (18). Leptin, a satiating adipokine secreted mainly by adipose tissue has a central role in this regulation, it reduces food intake by acting in hypothalamus via the stimulation of anorexigenic pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine-and amphetamine-related transcript protein neurons (POMC/CART) (19) and inhibition of orexigenic neuropeptide Y/agouti-related peptide neurons (NPY/AgRP) neurons (20). Cholecystokinin (CCK), and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) are among major gut peptides involved in appetite suppression. They are released from enteroendocrine cells in response to ingested nutrients (21). CCK is a short—term satiety signal, suppresses appetite by exerting its action on POMC neurons (22), GLP-1 reduce appetite by stimulating POMC/CART and suppressing AgRP/NPY neurons through γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-dependent signal (23). Ghrelin mainly produced in the stomach, is an orexigenic hormone that stimulates hunger and favors weight gain (24). Obesity dysregulates the action of leptin in lateral hypothalamus, and the hyperleptinemia is a one of the characteristics of obese individuals (25). Targeting food intake regulation can deal with the physiopathology of obesity.
3.2 Adipogenesis
There are two forms of adipose tissues: white adipose tissue (WAT) and BAT. Obesity is characterized by an excessive accumulation of WAT, which occurs through increased adipocyte number (hyperplasia) or size (hypertrophy) (26). Adipogenesis is under the control of transcription factors including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) that are responsible for terminal adipocyte differentiation. Hormones like insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) are involved in the initiation of adipogenesis by their actions through the phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway (27). Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) is an important signaling pathway in adipogenesis (28).
The main regulators of cellular energy balance and gene expression are adenosine mono phosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the family of sirtuins, a highly conserved histone NAD-dependent deacetylases and/or ADP ribosyl transferases. The upregulation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and sirutin 2 (SIRT2) inhibits PPARγ transcriptional activity (29). Activation of AMPK inhibits adipogenesis by increasing body energy expenditure, promoting oxidation and inhibiting synthesis of fatty acid (30, 31). These actions occur via decreasing C/EBPβ and δ expression, downregulation of PPARγ, SREBP1, C/EBPα and adipogenic markers as well as acetyl-CoA-carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase (FAS) (32). As obesity is characterized by an excessive accumulation of WAT, the inhibition of adipogenesis can be one of the treatment strategies.
3.3 Inflammation
Obesity is characterized by a low-grade chronic inflammation, leading to the proliferation of macrophage, and entry of monocyte into tissues (33). As a result, there is continuous secretion of inflammatory cytokines, e.g., TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, leptin, resistin and MCP1, and cell adhesion molecules (CAM), like VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. The most inflammatory pathways activated are the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB), Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathways (34). The use of anti-inflammatory agents will be a good strategy to manage obesity.
3.4 Mitochondrial biogenesis and non-shivering thermogenesis
Thermogenesis in mammals depends on both shivering and NST. NST is generated by the UCP1 and ATP futile cycle process in BAT and SM (35, 36). UCP1 is expressed in the inner mitochondrial membrane more preferentially in BAT. We would like to recall that mitochondria is implicated in various functions as well as thermogenesis, apoptosis, and the production of free radicles (37). Thermogenesis is a process that generates heat in the body via oxidative phosphorylation which activates UCP-1 and UCP-3. It is mainly regulated by the leakage of protons (38). Mitochondrial dysfunctions like increased production of free radicles, decreased mitochondrial respiration, and apoptosis are involved in obesity development (39). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 (PGC-1) is a crucial regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis; it regulates the mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) expression. TFAM controls mitochondrial DNA replication and transcription via three processes; phosphorylation, methylation, and acetylation (40). High weight gain result from alteration of transcriptional activity in response to deacetylation of PGC-1α regulated by SIRT1 (37, 40). BAT is an important site of NST, it is is thermogenic adipocytes tissue with high expression of UCP-1 and mitochondria, it dissipates energy as heat (41). It is noteworthy that adipocyte browning is the process that makes WAT into brown-like adipocytes (beige or brite). The brite adipocytes exhibit the same thermogenic capacities as brown adipocytes in BAT (38). Signaling pathway AMPK/PGC1α is linked to adipocyte browning, differentiation, and thermogenesis (42).
As regards SM, it enhances energy expenditure through NST that occurs without muscle contractions (i.e., without shivering), thereby influencing weight gain. A Key mechanism in SM is the sarcolipin-mediated uncoupling of Sarcoplasmic—Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase (SERCA) (43). Shivering thermogenesis is an ATP-dependent mechanism that occurs through the contraction of SM, which generates heat. The heat production is mediated by myosin ATPase and SERCA activation (44, 45). However, NST is generated by the UCP1 and ATP futile cycle (36). The futile Ca2+ -cycling in the muscle is triggered by the leakage of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum via the ryanodine receptor (RYR)1 which subsequently activates SERCA. The ATP consumption and Ca2+ transport mediated by SERCA have been described as a “heat pump” (46). Targeting muscle-based thermogenesis is a promising research area for increasing energy expenditure. The enhancement of thermogenesis can be one of the anti-obesity strategies.
3.5 Regulation of gut microbiome
Gut microbiome is complex ecosystem with a pivotal role in the regulation of host metabolism. It is involved in several functions such as the control of satiety and lipogenesis, bile acid production, food digestion and the modulation of innate immunity (47). Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria are the major bacterial groups reported in human gastrointestinal (48). Through the fermentation of the incompletely hydrolyzed carbohydrates or indigestible materials like polyphenols and protein, gut microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that include propionate, acetate and butyrate (49). SCAFs inhibit cholesterol synthesis, increase energy expenditure, induce gut hormones secretion like peptide YY (PYY) and GLP-1 that reduce food intake (50, 51).
The ecosystem dysbiosis is related to obesity. In fact, a decrease in Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio can prevent obesity development and progression (52). In obese subjects, gut microbiome dysbiosis induce an increase in digestive energy uptake and a decrease in energy expenditure. The increase of F/B ratio has been reported to increase Clostridium ramosum that improve digestible energy uptake via enhancing the expression of CD36, the fatty acid translocase and GLUT2, a glucose transporter (53). However, decreased Bacteroides and Lactobacillus was found to decrease energy expenditure by reduction of bile acid (54), which regulates mitochondrial biogenesis in BAT (55). Dysbiosis must be targeted as one of the strategies for the management of obesity.
4 Anti-obesity effects of natural bioactive compounds
The use of natural products that exert no significant side effects can be a good alternative to prevent and manage obesity and its associated complications. These include polyphenols, carotenoids and alkaloids. Obesity management effects of some NBCs are shown in Figure 2.
4.1 Polyphenols
Polyphenols are natural components of the human diet. They are secondary metabolites composed from aromatic rings with various hydroxyl groups and are found in small quantities in plant foods, tea, coffee, legumes, and fruit (56, 57). They are mainly classified into three types: flavonoids, non-flavonoids and tannins. Flavonoid-type include flavanols or catechin (e.g., Epicatechin), flavonols (e.g., quercetin), isoflavones (e.g., genistein), flavanones (e.g., Hesperetin, naringenin), anthocyanins (e.g., cyanine pigments), and chalcones (e.g., Chalconarngenin). Non-flavonoids are categorized into phenolic acids (e.g., caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid), lignans (e.g., pinoresinol), and stilbenes (e.g., resveratrol) (56). Polyphenols as well as resveratrol, curcumin, catechins, quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, genistein, rutin, and anthocyanidins exert an anti-obesity effect (58).
4.1.1 Polyphenols decrease food intake
Flavonoid-rich extract of spinach leaf decreases food intake and weight gain in rats, by inducing a satietogenic effect via a quick release of CCK, the effect of 400 mg/kg dose is comparable to the standard drug fluoxetine (22). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) (Figure 3A) is a catechin of green tea that inhibits ghrelin secretion, enhances adiponectin levels and decreases nutrient absorption (59). EGCG and resveratrol (Figure 3B), suppress appetite and trigger starvation inhibitory effect via their stimulatory action on CCK and leptin release (60, 61). In healthy subjects, the intake of catechins at 1796 mg per day for 3 weeks was found to enhance fullness and to decrease appetite (62). Figure 4 summarizes anti-obesity mechanisms of some natural bioactive compounds
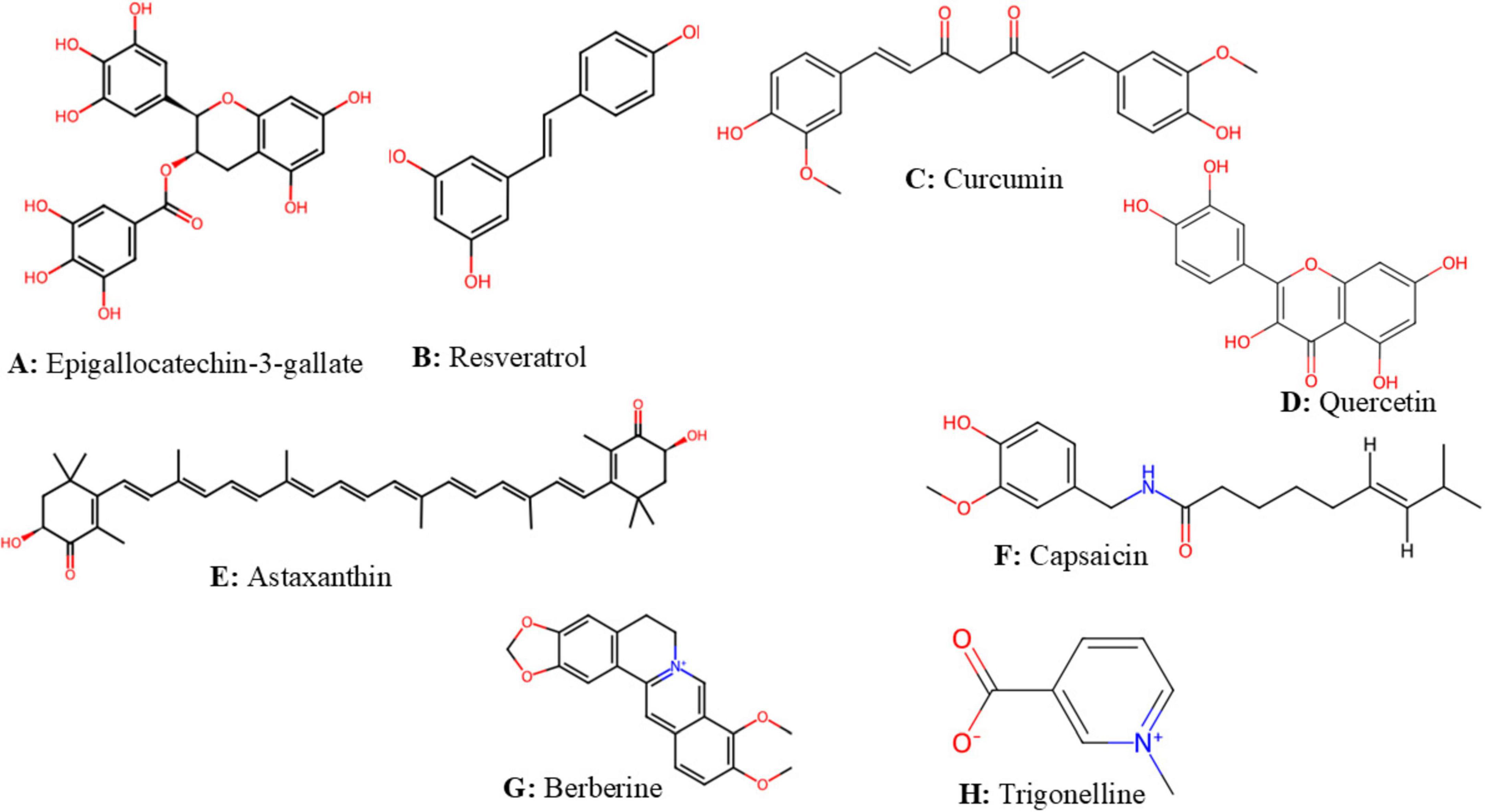
Figure 3. The structure of some natural bioactive compounds structures were downloaded from chemspider (pence and williams, 2010). (A) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate. (B) Resveratrol. (C) Curcumin. (D) Quercetin. (E) Astaxanthin. (F) Capsaicin. (G) Berberine; (H) Trigonelline.
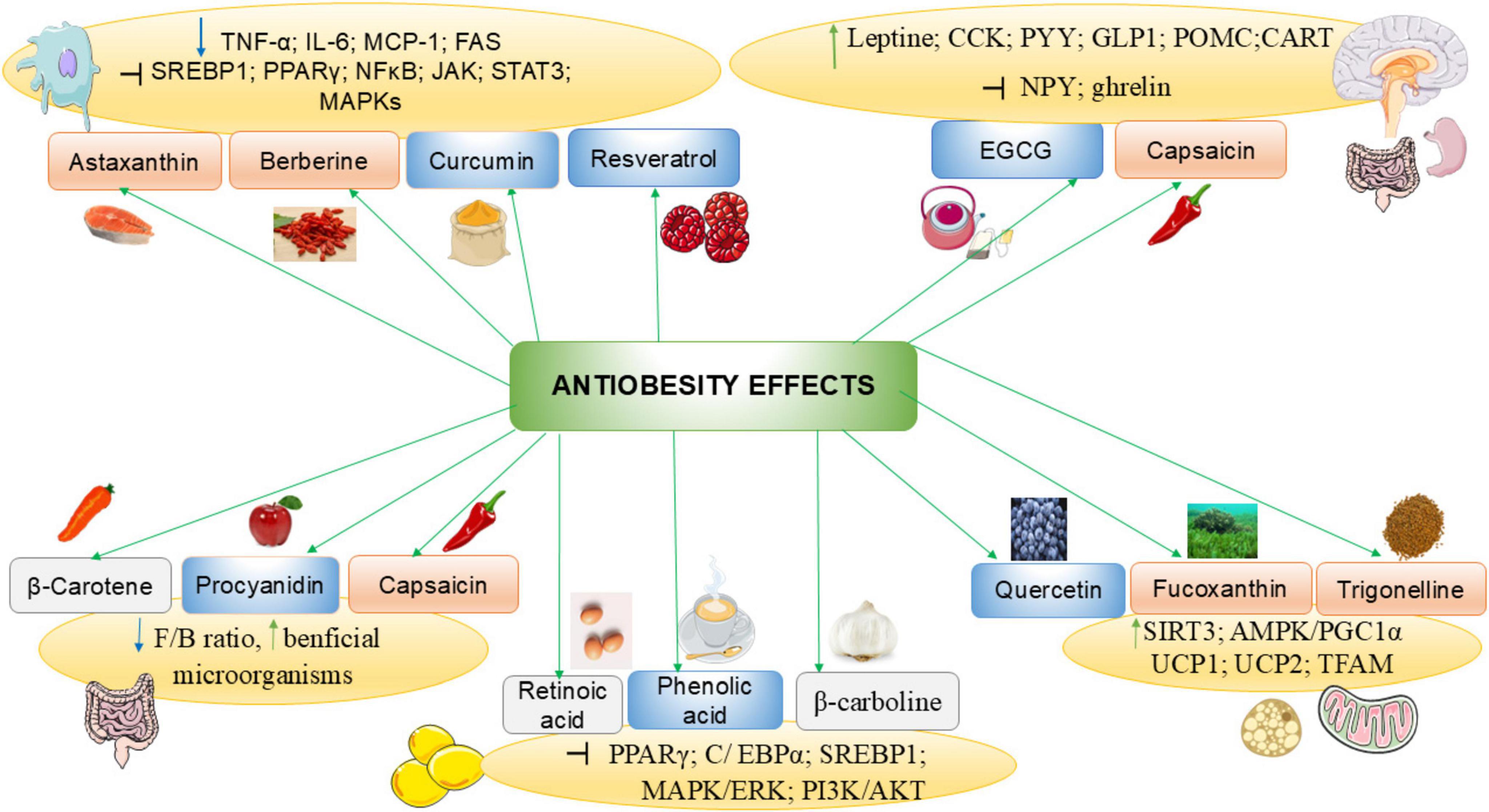
Figure 4. Anti-obesity mechanisms of some natural bioactive compounds. CART, cocaine- and amphetamine-related transcript protein; CCK, Cholecystokinin; C/EBPα, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha; F/B, Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; IL-6, interleukin-6; JAK, Janus kinase-signal transducer; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; NPY, neuropeptide Y; PGC-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator—activated receptor γ; PYY, peptide YY; SIRT, Sirtuin; SREBP1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; UCP: uncoupling protein. : decrease : increase; : inhibit; : polyphenols; : carotenoids; : alkaloids.
4.1.2 Polyphenols modulate adipogenesis
Polyphenols also regulate adipogenesis. The treatment of 3T3-L1 cells by resveratrol grape skin extracts decreases adipogenesis through the inhibition of PPARγ and C/EBPα protein expression, leading to the reduction in mRNA expression encoding PPARγ and C/EBPα and their target lipogenic genes SREBP1c, FAS, aP2, and SCD-1 (63). Clinical studies showed that resveratrol intake (150 mg/day) enhanced the number of small adipocytes in subcutaneous adipose tissue, reduced serum glucose and triglyceride levels in in obese participants (64).
EGCG inhibits 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation by PI3K-AKT signaling and has been reported to downregulate PPARγ and FAS expression levels in diet-induced obesity in the mouse and in cultured human adipocytes (65). Moreover, EGCG treatment of 3T3-L1 cells inhibits PPARγ and C/EBPα mRNA expression (66), abolishes adipocytes SREBP1 (67), and inhibits adipogenesis via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways (68). In 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, genistein blocks the transcriptional activity of C/EBPβ, and therefore inhibits C/EBPα and PPARγ expression at protein levels (69), and inhibits the phosphorylation of P38 MAPK (70).
4.1.3 Polyphenols exert anti-inflammatory effects
Grape polyphenols inhibit proinflammatory pathways involved in obesity, for instance, MAPK, NF-κB and transcription factor AP-1, and stimulate anti-inflammatory transcription factors as SIRT1 and PPAR, and also increase histone deacetylase activity (71). Resveratrol is known as an inhibitor of inflammation, clinical studies showed that in patients with metabolic syndrome, resveratrol supplementation at 150 mg/day decreased CRP and TNF-levels (72). In healthy men with obesity, 30 days supplementation at 150 mg per day enhanced SIRT1 and PGC-1α protein levels, activated AMPK, decreased circulating glucose and insulin levels, insulin resistance, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α concentrations (64). Curcumin (Figure 3C) pretreatment of human monocytic THP-1 cells before PMA-induced macrophages phenotype, reduces IL-1β secretion, and NF-κB activation (73). Moreover, curcumin supplementation at 4 g/kg diet added 2 days/week for 28 weeks decreases macrophage infiltration and inhibits NF-kB expression and activation of JNK pathway in adipose tissue of C57BL/6J mice (74). A randomized, controlled study showed that 30 days of curcumin supplementation in overweight subjects decreased body weight, fat mass, and BMI (75). Curcumin intake after meals at 40 mg capsules/twice a day for 3 months induce a decrease in TNFα, CRP, and IL-6 levels in overweight and obese patients (76). Curcumin upregulates adiponectin, downregulates leptin, suppresses NF-kB, STAT-3, and activates PPAR-γ signaling pathway. These interactions reverse inflammation linked to obesity (77).
4.1.4 Polyphenols enhance thermogenesis
4.1.4.1 Brown adipose tissue and mitochondria
EGCG treatment increased thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in mice leading to the reduction of body weight gain and plasma lipids, through the enhancement of body temperature and mitochondrial DNA content in BAT (78).
Epicatechin treatment at 1 mg/kg/day for 15 days mediated browning through the enhancement of UCP1 and UCP2 and mitochondrial proteins expression: SIRT1, SIRT3, PGC1α, and TFAM (79). Quercetin (a phenolic acid, Figure 3D) supplementation in HFD-fed obese mice increases the level of UCP1 either in WAT and BAT. Furthermore, this polyphenol increases the expression of PKA at protein level and phosphorylation of AMPK in WAT (80). Genistein, an isoflavone, found in legumes mainly in soybeans, increases browning in human visceral preadipocytes as well as upregulates UCP1 expression in human BAT and WAT via the activation of AKT and AMPK signaling pathways (81).
Epicatechin decreases the rate of weight gain via increasing the expression of PGC-1α, UCP1, and SIRT1 and 3 involved in mitochondrial energy expenditure in a rat model of HFD-induced obesity (82). Myricetin (flavonoid) reduces the acetylation of mitochondrial proteins and increases SIRT3 expression in adipose tissue of HFD-fed mice. This flavonoid increases energy expenditure by the upregulation of thermogenic protein PGC1-α and UCP1 in BAT of db/db mouse model of leptin deficiency (83). Vanillic acid (phenolic acid) reduces body weight gain and maintains body temperature by promoting thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis of BAT (84). Resveratrol stimulates mitochondrial activity via the increase in SIRT1 and PGC-1α levels (85).
4.1.4.2 Skeletal muscle
In patients with type 2 diabetes the intake of 3 g resveratrol for 12 weeks increased SIRT1 and AMPK expression in muscles thus regulated energy expenditure (86). Two meta-Analysis showed that the consumption of coffee reduced body weight, fat mass and WC. Chlorogenic acid is phenolic acid present in high amount in coffee might be responsible for these favorable actions in obesity (87).
Furthermore, resveratrol supplementation at a dosage of 2 mg/kg body weight per day during early postnatal life (days 2–20) and subsequent assignment to a HFD at 90 days of age for a duration of 10 weeks may aid in preventing diet-related disorders associated with ectopic lipid accumulation in muscle tissues. Mice treated with resveratrol exhibited protection in adulthood against HFD-induced triacylglycerol accumulation in SM, enhanced muscular capacities for fat oxidation and mitochondrial activity, and activation and enhancement of SIRT1 and AMPK in muscle. Several genes related to mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics were induced in the SM of adult mice, including TFAM and Ucp3 (88).
4.1.5 Polyphenols modulate gut microbiome
The polyphenol extract from chokeberry decreases the F/B ratio and increases the relative abundance of Bacteroides, Prevotella, Akkermansia in obese rats and prevents obesity, liver steatosis, and normalizes blood lipid levels (89). In HFD-induced mouse obesity, intake of tea infusion rich in catechin reduces body weight via decreases in Firmicutes and increases in Bacteroidetes (90).
Treatment with apple procyanidins, a non-absorbable flavonoid decreases the F/B ratio and increases the proportion of Akkermansia, which reduces obesity, inflammation and gut permeability in mice, maintained on a high-fat/high-sucrose diet (91). The intake of 5 g of mixed spice/day for 2 weeks enhances Bacteroidetes and reduces Firmicutes (92). The consumption of California strawberry powder at 26 g/day for 4 weeks increases Akkermansia muciniphila, and Bifidobacterium that are associated with lean body weight (93).
4.1.6 Comparative analysis of the efficacy of polyphenols across different models
Clinical outcomes regarding the efficacy of NBCs are inconsistent, as rodent models frequently yield promising results that do not successfully translate to human beings. Numerous trials are characterized by insufficient sample sizes and durations, and often utilize isolated compounds that may not replicate the effects of whole foods or natural preparations. A comparative analysis of the efficacy of some bioactive compounds, including quercetin and genistein across different models sheds light on this inconsistent efficacy. This review discusses the modulation of adipogenesis and inflammation by flavonoids through the regulation of transcription factors and the activation of AMPK. Genistein has been shown to inhibit adipogenesis and activate thermogenesis and β-oxidation in vitro (69, 81). However, despite being the most extensively studied isoflavone, no clinical studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in promoting weight loss in humans (69). Both quercetin and EGCG have been shown to exhibit anti–obesity effects in adipocyte cultures and animal models (65, 80). Nonetheless, quercetin supplementation does not appear to have beneficial effects on body weight but may reduce obesity-associated mortality by lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. This effect may be attributed to genetic polymorphisms in key enzymes involved in flavanol metabolism, which influence an individual’s sensitivity to catechins (65). Curcumin, derived from turmeric, suppresses adipogenesis and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in mice and human monocytic THP-1 cells (73, 74). Clinical trials in humans have shown modest reductions in body weight and improvements in metabolic markers (75, 76). These outcomes are partly due to the low bioavailability and poor solubility of curcumin, requiring formulation strategies for biomedical applications.
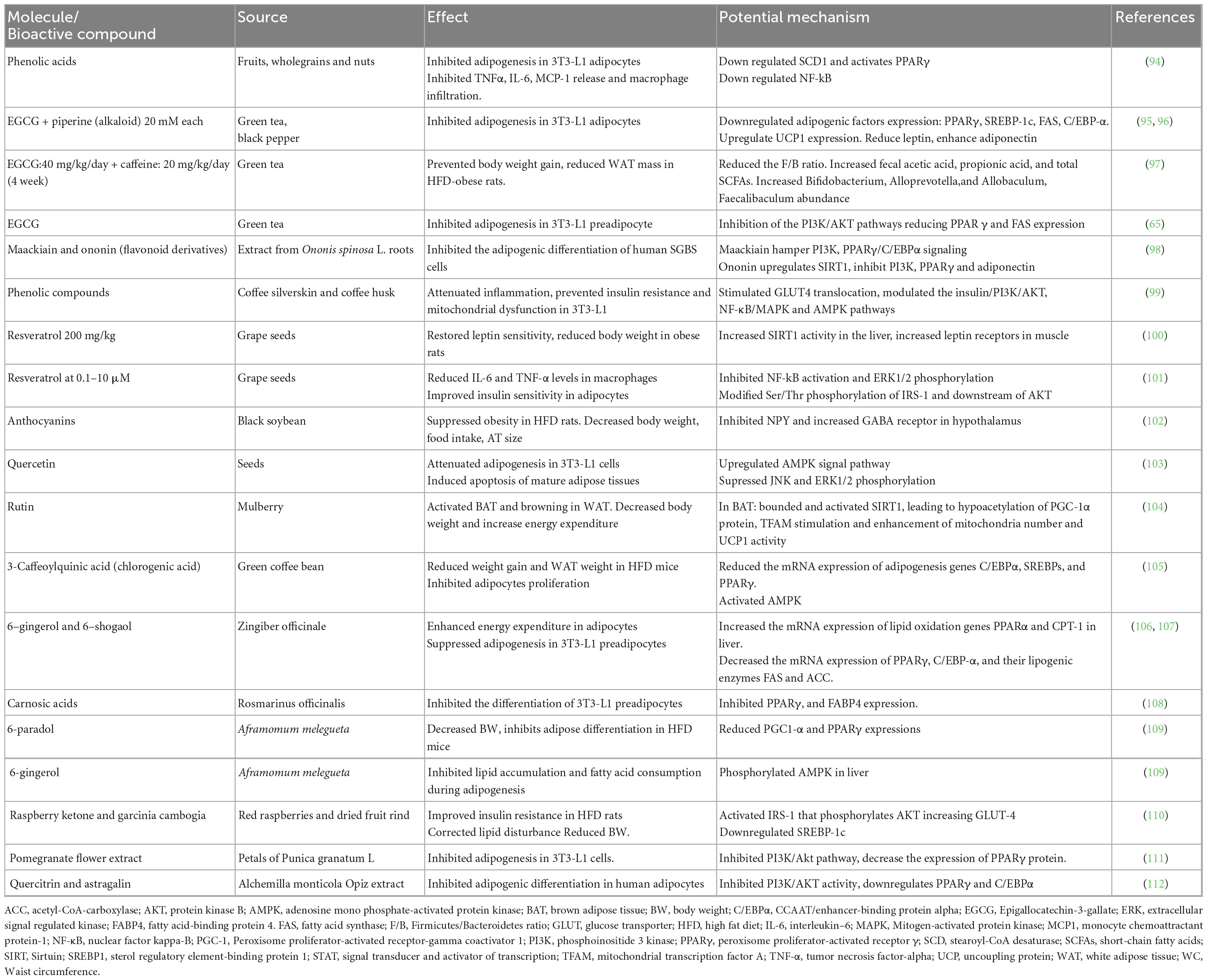
Others conclusive studies describing the anti-obesity mechanisms of polyphenols are summarized in Table 1.
4.2 Carotenoids
Carotenoids are fat-soluble pigments, synthetized by plants and microorganisms. Their primary sources are fruits and vegetables, eggs and salmon fish. They are classified into carotenes and xanthophylls and include numerous compounds as well as β-carotene, α-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, lutein, zeaxanthin, neoxanthin, capsanthin, bixin, and lycopene. Twenty carotenoids are significantly present in human plasma (113, 114). Certain carotenoids are precursors of vitamin A. Retinol is mainly derived from β-carotene under the action of β-carotene oxygenase 1 (BCO1) (115). BCO2 cleaves non-provitamin A carotenoids like lutein and lycopene (116). A meta-analysis showed an association between reduced serum carotenoid levels and obesity, and their low levels were a risk factor for obesity (117). Several studies have shown the anti-obesity effects of carotenoids and their derived products as retinoids (i.e., retinol, and retinoic acid) and vitamin A. Retinoids, which are intermediate products of vitamin A metabolism, prevent fat accumulation, inhibit adipogenesis and inflammation-related obesity.
4.2.1 Carotenoids anti-adipogenesis actions
The antiadipogenic effects of retinoic acid (RA) occur via RA binding to retinoic acid receptors (RARs), which inhibit the transcription of C/EBPα (118). Furthermore, RA inhibits the expression of ZFP423, a key transcription factor initiating adipogenesis that precedes PPARγ expression by blocking DNA demethylation in the promoter of Zfp423 (119). All-trans RA (ATRA) induces UCP1 expression through activation of RARs, which prevents fat accumulation (120).
4.2.2 Carotenoids anti-inflammatory effects
Astaxanthin (Figure 3E), a marine-derived carotenoid found in salmon fish, administration to HFD-fed C57BL/6J mice relieves hepatic inflammation through the reduction of TNF-α, IL1β levels and nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression (121). The involvement of RA in inflammation includes the repression of NF-κB transactivation via the activation of RAR and retinoid X receptor (122).
Crocin is an apocarotenoid derived from crocus flowers and is found in saffron extract. In a clinical trial, crocin treatment in patients with coronary artery disease reduced inflammation, enhanced SIRT1 and AMPK levels and decreased NF-κB expression (123).
In vivo animal studies showed that lycopene supplementation inhibits HFD induced obesity and inflammatory response. In pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats fed a HFD, the intake of 4.94 mg/day of lycopene for 20 days reduces the placental inflammation inhibiting IL-17, IL-6 and TNF-α (124). In C57BL/6J mice fed a HFD, the intake of tomato powder and lycopene at 10 mg/kg body weight/day for 12 weeks decreased TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-6 mRNA expression in the liver and adipose tissue. This treatment also decreased hepatic gene like FAS, SREBP-1c and PPARγ involved in lipid metabolism (125).
Lycopene reduces fat deposition in pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats, fed a HFD at 200 mg/kg of diet for 20 days, the effect was reported by enhancement of Lep gene and protein expression in placenta and the leptin level. It also ameliorated fetal weight (124).
Torularhodin, a fungal carotenoid reduces inflammations in HFD mice via PPARα signaling pathway. The administration of torularhodin (40 mg/kg diet/day for 12 weeks) to C57BL/6J mice, reduces TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β levels, downregulates proinflammatory proteins such as, osteopontin, protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta (PTK2B) and FAS-associated death domain protein, and upregulates anti-inflammatory proteins like STAT3, Fas cell surface death receptor (FAS), Bcl2-associated X (BAX) and ICAM1(126).
4.2.3 Carotenoids effects on gut microbiome
Astaxanthin treatment of BCO2-/- C57BL/6J mice showed a 385% enhancement of Akkermansia muciniphila in the mouse gut, in response to 10-fold increases in astaxanthin in the liver in response to the lack of BCO2-induced cleavage (127). Moreover, a human double-blinded trial showed a prebiotic effect of lycopene, at 7–30 mg/day for 1 month, on the gut microbiome in subjects with obesity, this polyphenol enhanced the abundance of Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Bifidobacterium longum (128). Furthermore, in BCO1 and BCO2 double knockout mouse models, lycopene supplementation enhanced Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium genera and reduced Bacteroides, Mucispirillum, Clostridium, and Parabacteroides populations (129).
β-Carotene supplementation (50 mg/kg body weight/day) for 7 days in a rat model of ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease, was found to lower colonic levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IFN-γ, decreased the expression of phosphorylated ERK and JNK. β-Carotene reduces inflammation by regulating the NF-κB/MAPK pathway and the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria, and enhances the abundance of Firmicutes and Actinobacteria. Moreover, it increased the levels of Faecalibacterium which inhibits the activation of intestinal epithelial NF-κB (130).
4.2.4 Comparative analysis of the efficacy of carotenoids across different models
Carotenoids demonstrate significant anti-obesity effects, particularly in in vitro and in vivo rat models, through mechanisms such as the inhibition of adipogenesis and inflammation, as well as the enhancement of metabolic profiles (detailed in section 3.2.). Nonetheless, human studies are limited and yield inconsistent results, underscoring the necessity for further research to validate these findings and to determine effective dosages and delivery methods for human applications. However, trials have indicated that supplementation with pure carotenoids or xanthophylls may help obesity prevention and management. Specifically, the supplementation of mixed carotenoids (β-carotene, α-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, lycopene, astaxanthin, and γ-tocopherol) in obese children over a 6-month period resulted in increased β-carotene levels and reductions in BMI z-score, waist-to-height ratio, and subcutaneous adipose tissue (131).
Additionally, the supplementation of paprika xanthophylls in healthy overweight participants for 12 weeks led to a reduction in abdominal fat area and BMI without any adverse effects (132). Moreover, inconsistent results have been reported in mice; the anti-obesity effect of β-carotene has been shown to be associated with its provitamin A activity in mice (133). In contrast, mice lacking β-carotene 15, 15’-monooxygenase (BCO) did not exhibit changes in adipose tissue weight (134).
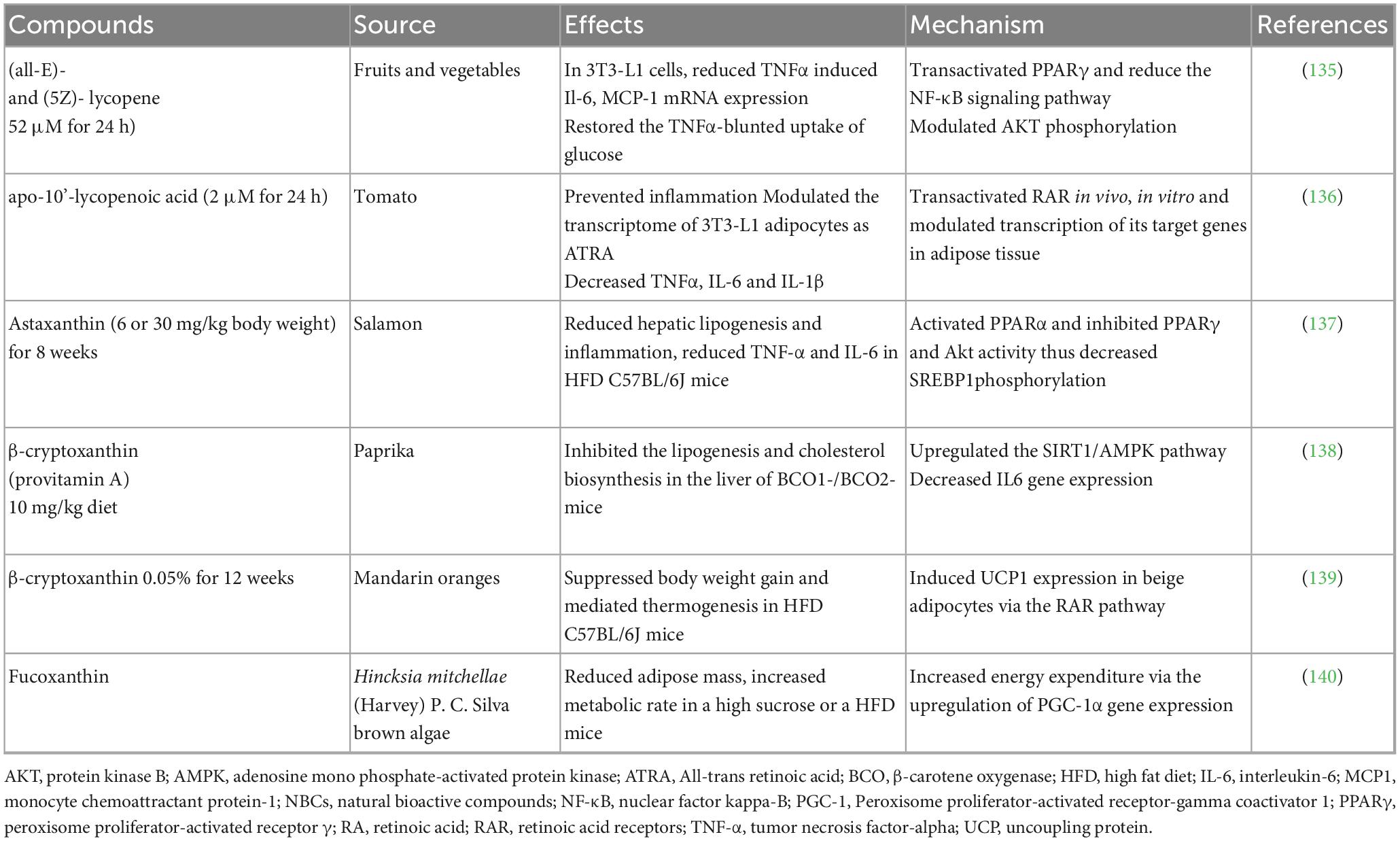
Conclusive studies describing anti-obesity effects of other carotenoids are summarized in Table 2.
4.3 Alkaloids
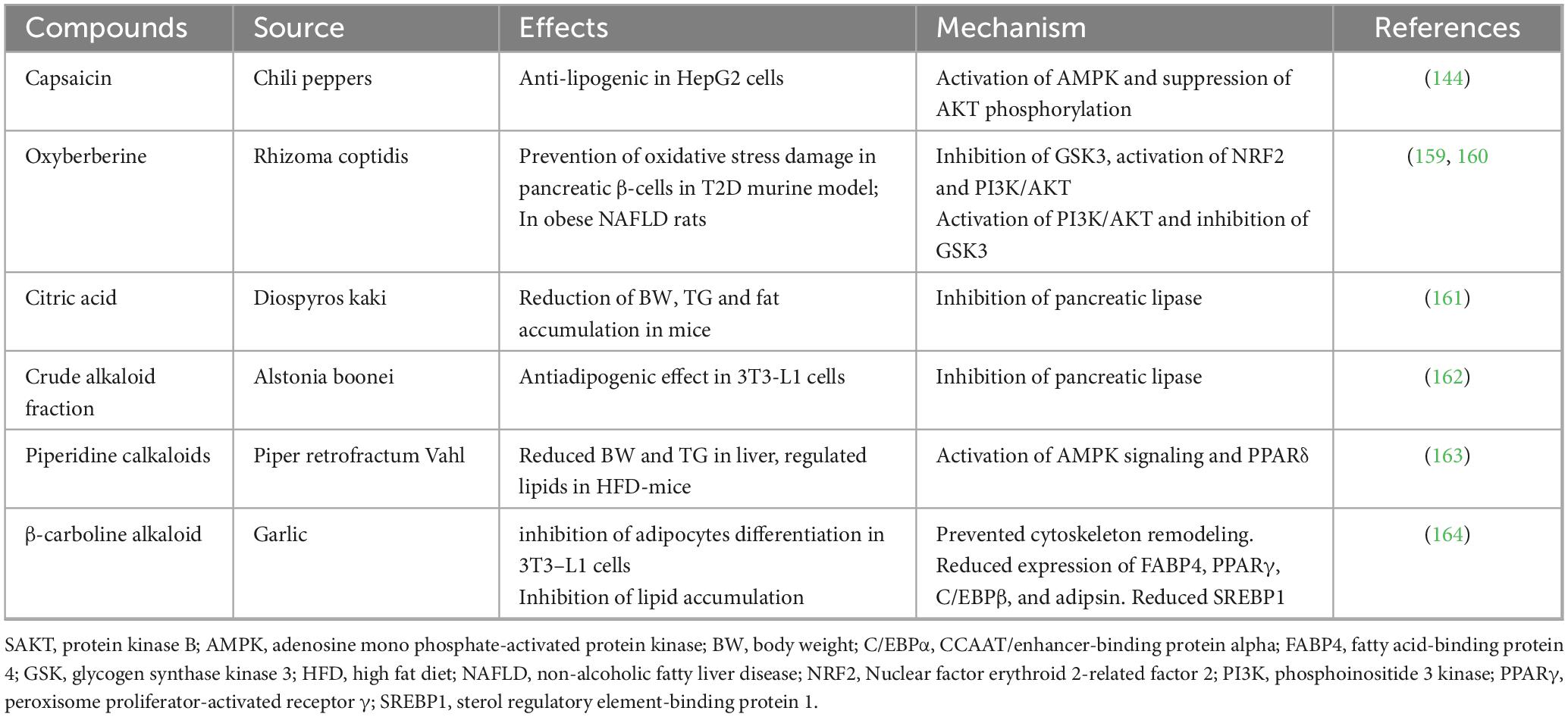
Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing secondary metabolites abundantly present in plants where they act against pathogens (141). They are mainly used as anesthetics, cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory agents (142). Studies showed anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory and anti-adipogenic effects of alkaloids, berberine and trigonelline. Capsaicin, a vanillin amide alkaloid present red in pepper, is used in the treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other diseases (143, 144). In vivo and in vitro data have demonstrated that capsaicinoids administration decreased weight gain and adiposity, in part, via decreasing lipogenesis and increasing thermogenesis (143).
4.3.1 Alkaloids reduce food intake
A human study showed that a lunch supplementation with capsaicin (Figure 3F) derived from the chili pepper fruit reduced levels of ghrelin and enhanced those of GLP-1 in participants with normal BMI or overweight (145). Another study conducted on obese mice showed that capsaicin increases GLP-1 release by enhancement of short-chain fatty acids in the intestine (146). In HFD fed mice, capsaicin decreased food ingestion via the activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1(TRPV1) in the hypothalamus. Furthermore, this leads to the upregulation of CART, PYY, and CCK expression in the hypothalamus, and downregulation of genes that promote appetite mostly cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R), ghrelin, and growth hormone secretagogue receptor (147). Another study showed a reduction in food intake and loss of weight in HFD mice, supplemented with capsaicin, along with enhanced the levels of acetic and propionic acids in the gut through the modification of number of bacteria producing these short chain fatty acids. This phenomenon also led to activate POMC and CART neurons in hypothalamus via PYY and GLP-1 action, and to inhibit NPY and AGRP neurons (148).
Capsaicinoids treatment in HFD obese mice decreased weight gain and enhanced leptin concentration in similarly to orlistat. The combination of green tea with capsaicinoid reduces hunger; a drink of 3.5 dl green tea per day containing 1795.5 mg catechins combined with capsaicin capsules that contain 1530 mg cayenne for 3 weeks decreases hunger and enhances satiety (62).
4.3.2 Alkaloids exert anti-adipogenic effects
Berberine (Figure 3G), an isoquinoline derivative alkaloid, has anti-adipogenic and anti-inflammatory properties. It induces browning in WAT (149), stimulates weight loss and mRNA expression of adiponectin (149, 150). Berberine inhibits adipogenesis via the inhibition of mRNA and protein levels of transcriptional factors like PPAR-γ and C/EBPα and their regulators (151, 152). It also decreased weight gain, food intake, triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels in HFD-induced obesity in the mouse (151) and suppressed the PPAR target genes as AP2, CD36, and LPL involved in adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells (152). Human studies showed that berberine intake improved obesity indices through significant decreases in BMI and WC (150). Moreover, in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, capsaicinoids lowered triacylglycerol and adipogenesis by the inhibition of PPAR-ɣ and fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4). These agents also increased thermogenesis via the induction of UCP1 and inhibited lipogenesis through decreasing gene expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) and FAS (143).
4.3.3 Alkaloids enhance thermogenesis
4.3.3.1 Brown adipose tissue and mitochondria
Trigonelline (Figure 3H), a major alkaloid component of fenugreek exerts anti-obesity effects by increasing browning in 3T3-L1 white adipocytes via upregulation of PGC-1α and UCP. This effect was reported via stimulation of β3-adrenergic receptor and the inhibition of PDE4 and p38 MAPK/ATF-2 (153). In Human clinical studies, trigonella extracted from herb fenugreek reduces blood sugar in patients with type 2 diabetes (154).
4.3.3.2 Skeletal muscle
Capsaicin treatment in HFD-induced obese mice reduces weight gain and upregulates the expression of UCP-2 and -3 and ATP-dependent thermogenic effectors through ATP-consuming calcium and creatine futile cycles. Both in in vitro and in vivo models, capsaicin treatment increased the expression of SERCA-1 and -2, ryanodine receptors (RYR-1 and RYR-2), UCP-2 and -3, creatine kinase B (CKB), and creatine kinase mitochondrial 2 (CKMT2), through activation of TRPV1, α 1-, β 2-, and β3-adrenergic receptors. Furthermore, capsaicin promotes myotube development and enhances lipid metabolism in C2C12 cells. Capsaicin increased mitochondrial Ca2+ concentrations, thus boosting the expression of oxidative phosphorylation protein complexes via the activation of the ATP-futile cycle (155).
4.3.4 Alkaloids modulate gut microbiome
Capsaicin was reported to reduce weight and intestinal permeability. In HFD mice, capsaicin supplementation enhanced the level of Bacteroides, Coprococcus, Prevotella, and Akkermansia in the gut and decreased body weight (148, 156). Besides, Capsaicin enhanced the concentration of acetic and propionic acids in intestinal tract (148).
4.3.5 Comparative analysis of the efficacy of alkaloids across different models
Numerous studies cited in this review have documented the anti–obesity properties of alkaloids through both in vivo and in vitro models. However, capsaicin supplementation may confer modest benefits in reducing body weight, BMI, and WC, particularly among obese individuals. It appears to enhance energy expenditure and fat oxidation. Animal studies have demonstrated that capsaicin, derived from chili peppers, induces weight loss in mice by activating TRPV1, which subsequently reduces food intake, stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, and enhances thermogenesis (147, 148). However, A meta–analysis of 15 human studies suggested that capsaicin supplementation may exert modest effects in reducing BMI, BW, and WC in obese or overweight individuals (157). A human study revealed that a 12–week high–dose capsaicin supplementation reduced appetite and decreased the waist–to–hip ratio without affecting total body adiposity or body mass (158). Nevertheless, the combination of green tea with capsaicin decreases hunger and enhances satiety (62) Capsaicin. bioavailability can be influenced by its absorption and metabolism in the body and factors may affect individual responses to capsaicin supplementation. Berberine exerts anti–obesity effects across various models by inhibiting adipogenesis in vitro, reducing body weight in vivo, and enhancing metabolic parameters and body weight in human clinical trials.
Table 3 has summarized more conclusive studies concerning the anti–obesity properties of carotenoids.
5 Challenges
NBCs hold potential in the management of obesity through mechanisms such as appetite suppression, fat metabolism, and anti–inflammatory properties. Nonetheless, several practical challenges, including limited bioavailability, scalability issues, environmental impact, toxicity concerns, and clinical inconsistency, require careful consideration. Bioavailability of these agents is dependent on digestion, absorption, metabolism, and their concentrations in food (165). Numerous NBCs exhibit poor absorption due to their rapid metabolism within the intestinal wall and liver (e.g., resveratrol, curcumin, and EGCG). Strategies such as nano formulations, encapsulation, or conjugation to carriers increase both cost and complexity. A systems–based approach is essential, encompassing sustainable sourcing methods (166), advanced formulation technologies, rigorous clinical trials, and ethical and ecological frameworks for production and utilization. Challenges include the overharvesting of wild plants, where increased demand poses threats to biodiversity and can damage ecosystems (167). The carbon and energy footprints associated with the industrial extraction, purification, and transport of bioactive compounds are notably energy–intensive. These practices have implications for ecological degradation, particularly when sourcing is unsustainable or involves monoculture farming. Furthermore, ethical concerns arise from bioprospecting without benefit–sharing, especially in developing countries, which can lead to equity issues.
It is crucial to acknowledge that bioactive compounds can exert adverse effects. At higher doses, these compounds may exhibit toxic properties. According to the European Food Safety Authority, the daily intake of EGCG should not exceed 800 mg, as higher doses can lead to liver damage and are associated with increased serum transaminase levels. Nevertheless, the moderate consumption of green tea infusion, which is rich in EGCG, at a rate of 1–2 cups per day, is deemed safe (168). Furthermore, several research reports have indicated that the toxicological threshold of blueberry polyphenols is ≥ 1,000 mg/kg bw/day in Sprague–Dawley rats over a 90–day period. This dosage corresponds to a 70 kg human ingesting approximately 10 g of blueberry polyphenols daily, a quantity that exceeds the levels currently found in dietary supplements (169). The study explored the efficacy of fisetin and luteolin, two polyphenolic compounds, in mitigating cell death and inflammation resulting from direct, non–oxidative DNA damage in human RPE–19 cells. When applied directly at a concentration of 50 μM, both luteolin and fisetin exhibited anti–inflammatory properties by reducing the secretion of IL–6 and IL–8. Nonetheless, these polyphenols also promoted apoptosis, diminished cell viability, and increased lactate dehydrogenase leakage. These findings imply that the cytoprotective effects of fisetin and luteolin are dependent on the specific stressors they need to counteract, whereas their anti–inflammatory potential is consistently observed across diverse experimental models (170).
In mice, oral administration of capsaicin at high doses (60 or 80 mg/kg) resulted in damage to gastrointestinal tissues and inflammation in the jejunum, ileum, and colon. Conversely, a lower dose (40 mg/kg) did not adversely affect the tissues. At 80 mg/kg, there was an increase in SCFAs, potentially linked to the regulation of the gut microbiome, particularly involving Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Faecalibacterium, and Butyricimonas (171).
The toxicity of berberine is contingent upon the species of animal, dosage, and route of administration. The risk associated with oral administration is lower compared to intraperitoneal (ip) administration. In a study by Mahmoudi et al. (172), ip administration of berberine at a dosage of 10 mg/kg/day over a period of 14 days resulted in the suppression of both cellular and humoral immune functions in BALB/c mice (172). Furthermore, previous research determined LD50 value for ip administered berberine to be 23 mg/kg in mice. An increase in the oral dosage of berberine from 20.8 to 41.6 g/kg was observed to elevate berberine blood concentration from 0.168 to 0.432 μg/mL, resulting in a 30% mortality rate (173).
The safe dosage for oral administration of berberine in mice is 20.8 g/kg, while in human beings it is 2.97 g/kg, which is 100 times higher than the typical doses prescribed in clinical trial studies (174).
5.1 Regulation challenges of compounds across the major countries
The regulation of bioactive compounds is complex and exhibits considerable variation across different countries. There is a lack of international consensus regarding definitions, terminology, and categorizations. Natural products are typically classified into two categories: “Supplements” or “Medicines.”Supplements are utilized with or without limited claims on therapeutic aspects, whereas medicines are employed for the treatment of illnesses, with health claims that differ according to jurisdiction in which it is manufactured and marketed. Although products are classified within the same category, regulatory requirements differ across countries. Particularly for those products “Classified as Supplements.” Green tea extract is classified as “Medicine” in Canada and Australia, whereas it is classified as “Supplement” in Japan, China, and the EU. In the US, it is utilized both as a botanical drug for topical application and as a dietary supplement. The chemical composition of green tea extracts differs from that of green tea itself (175). Various manufacturing processes can yield green tea extracts with distinct chemical compositions. Certain forms of green tea extract have been associated with reports of liver injury, prompting the issuance of warnings (176). Consequently, it is imperative to harmonize the methodologies for risk and safety assessment. Comprehensive knowledge of the herbal origins, as well as details regarding cultivation conditions, harvesting, handling, processing, labeling, and packaging, is essential.
6 Marketed formulation
Some formulations of NBCs are marketed as dietary supplements. These products are available in various markets and have been the focus of clinical research investigating their potential benefits in obesity management. Table 4 summarizes some marketed polyphenols with anti-obesity effects.
7 Conclusion
NBCs are recognized for their extensive range of biomedical applications and have been utilized for several decades. Administering low-to-moderate doses can yield numerous health benefits, thereby enhancing their utility in clinical settings. Nevertheless, their direct application poses challenges due to issues such as low bioavailability, scalability, environmental impact, clinical inconsistency, and toxicity at high doses. These challenges require the development of formulation strategies and the establishment of a safe concentration margin. Enhancing bioavailability is essential to increase their therapeutic potential in the prevention and management of obesity. Chemical and technological modifications, including the use of prodrugs, polymers, nanotechnology, liposomes, micelles, emulsions, and encapsulation, can safeguard and enhance their stability and bioavailability. The present review, based on conclusive in vitro, in vivo and clinical human trials, underscores the efficacy and safety of commonly available NBCs in obesity management by targeting pathophysiological mechanisms. However, the pathogenesis of obesity involves multiple pathways, including increased food intake, adipogenesis, inflammation, decreased thermogenesis, and gut microbiome dysbiosis. Functional foods can be developed from various NBCs to target these multiple pathways, combining these compounds may result in additive effects (e.g., the combination of EGCG with caffeine enhances fat oxidation). The use of humanized models in vitro, such as gut microbiome co-cultures, may enhance translatability to human applications. Further studies are required to ascertain the appropriate doses and duration of supplementation. Dose optimization is required through a defined therapeutic method using a suitable pharmacokinetic model. Harmonization of guidelines through the development of global regulatory frameworks for NBC standardization, particularly for nutraceuticals, is essential. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can be employed to predict compound activity, safety and synergies, and to integrate multi-omics data to map NBCs interactions with human biology. Despite the aforementioned challenges, NBCs anti-obesity actions remain physiologically significant.
Author contributions
HB: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AB: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. NK: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ACC, acetyl-CoA-carboxylase; AgRP, agouti-related peptide; AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, adenosine mono phosphate-activated protein kinase; ATRA, All-trans retinoic acid; BAX, Bcl2-associated X; BAT, brown adipose tissue; BCO, β-carotene oxygenase; BMI, Body mass index; CAM, cell adhesion molecules; CART, cocaine- and amphetamine-related transcript protein; CCK, Cholecystokinin; CD36, cluster of differentiation 36; C/EBP α, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha; DIO, diet-induced obesity; EGCG, Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; FABP4, fatty acid-binding protein 4; FAS, fatty acid synthase; F/B, Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GLUT, glucose transporter; HFD, high fat diet; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IL-6, interleukin-6; iNOS, nitric oxide synthase; JAK, Janus kinase-signal transducer; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCP1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; NBCs, natural bioactive compounds; NF- κ B, nuclear factor kappa-B; NPY, neuropeptide Y; PGC-1, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3 kinase; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; PPAR γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; PTK2B, protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta; PYY, peptide YY; RA, retinoic acid; RARs, retinoic acid receptors; SCD, stearoyl-CoA desaturase; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; SERCA, Sarcolipin-mediated uncoupling of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium ATPase; SIRT, Sirtuin; SREBP1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; TNF- α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; UCP, uncoupling protein; WAT, white adipose tissue; WC, Waist circumference.
References
1. Swinburn B, Sacks G, Hall K, McPherson K, Finegood D, Moodie M, et al. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet. (2011) 378:804–14. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60813-1
2. Mahase E. Global cost of overweight and obesity will hit $4.32tn a year by 2035, report warns. BMJ. (2023) 380:523. doi: 10.1136/bmj.p523
3. Chan M. Obesity and diabetes: The slow-motion disaster. Milbank Q. (2017) 95:11–4. doi: 10.1111/1468-0009.12238
4. González-Muniesa P, Mártinez-González M, Hu F, Després J, Matsuzawa Y, Loos R, et al. Obesity. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2017) 3:17034. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.34
5. Bounihi A, Saidi H, Bouazza A, Benbaibeche H, Azzouz M, Koceir E. Dietary diversity as a risk factor for obesity in algerian patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Healthcare (Basel). (2021) 9:1229. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9091229
6. Benbaibeche H, Hichami A, Oudjit B, Haffaf E, Kacimi G, Koceïr E, et al. Circulating mir-21 and mir-146a are associated with increased cytokines and CD36 in Algerian obese male participants. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2022) 128:1461–6. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2020.1775655
7. Koceïr E, Benbaïbeche H, Haffaf el M, Kacimi G, Oudjit B. [Metabolic syndrome and hormonal interaction in obese and type 2 diabetic Algerian subject: The behavior eating disorder impact]. Ann Biol Clin. (2009) 67:315–23. doi: 10.1684/abc.2009.0326
8. Burke L, Wang J. Treatment strategies for overweight and obesity. J Nurs Scholarsh. (2011) 43:368–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2011.01424.x
9. Pati B, Sendh S, Sahu B, Pani S, Jena N, Bal N. Recent advancements in pharmacological strategies to modulate energy balance for combating obesity. RSC Med Chem. (2023) 14:1429–45. doi: 10.1039/d3md00107e
10. Bessesen D, Van Gaal L. Progress and challenges in anti-obesity pharmacotherapy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2018) 6:237–48. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30236-X
11. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Requests the Withdrawal of the Weight-Loss Drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) From the Market. Silver Spring, MA: US Food and Drug Administration (2020).
12. Karri S, Sharma S, Hatware K, Patil K. Natural anti-obesity agents and their therapeutic role in management of obesity: A future trend perspective. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 110:224–38. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.076
13. Benbaibeche H, Ousmaal M, Rebah A, Akchiche Y, El Enshasy H, Dailin D, et al. Health Benefits of Mushrooms on Obesity and Chronic Diseases. Bioprospects of Macrofungi. Boca Raton: CRC Press (2023). p. 298–321.
14. Im J, Kim M, Park K. Association between the phytochemical index and lower prevalence of obesity/abdominal obesity in Korean adults. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2312. doi: 10.3390/nu12082312
15. Karasawa M, Mohan C. Fruits as prospective reserves of bioactive compounds: A review. Nat Prod Bioprospect. (2018) 8:335–46. doi: 10.1007/s13659-018-0186-6
16. Liu R. Health-promoting components of fruits and vegetables in the diet. Adv Nutr. (2013) 4:384S–92S. doi: 10.3945/an.112.003517
17. Pramila G, Jirekar D, Farooqui M, Naikwade S. Biological activity of aqueous extract of some medicinal plants. Der Chemica Sinica. (2014) 5:65–70.
18. Wachsmuth H, Weninger S, Duca F. Role of the gut-brain axis in energy and glucose metabolism. Exp Mol Med. (2022) 54:377–92. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00677-w
19. Schwartz M, Woods S, Porte D, Seeley R, Baskin D. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. (2000) 404:661–71. doi: 10.1038/35007534
20. Lam C, Chari M, Lam TK. CNS regulation of glucose homeostasis. Physiology (Bethesda). (2009) 24:159–70. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00003.2009
21. Gribble F, Reimann F. Enteroendocrine cells: Chemosensors in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. (2016) 78:277–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105439
22. Panda V, Shinde P. Appetite suppressing effect of Spinacia oleracea in rats: Involvement of the short term satiety signal cholecystokinin. Appetite. (2017) 113:224–30. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.02.030
23. Huang R, Ding X, Fu H, Cai Q. Potential mechanisms of sleeve gastrectomy for reducing weight and improving metabolism in patients with obesity. Surg Obes Relat Dis. (2019) 15:1861–71. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2019.06.022
24. Castañeda T, Tong J, Datta R, Culler M, Tschöp M. Ghrelin in the regulation of body weight and metabolism. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2010) 31:44–60. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2009.10.008
25. Benbaibeche H, Bounihi A, Koceir E. Leptin level as a biomarker of uncontrolled eating in obesity and overweight. Ir J Med Sci. (2021) 190:155–61. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02316-1
26. Haczeyni F, Bell-Anderson K, Farrell G. Causes and mechanisms of adipocyte enlargement and adipose expansion. Obes Rev. (2018) 19:406–20. doi: 10.1111/obr.12646
27. Mandl M, Wagner S, Hatzmann F, Mitterberger-Vogt M, Zwierzina M, Mattesich M, et al. Sprouty1 is a weight-loss target gene in human adipose stem/progenitor cells that is mandatory for the initiation of adipogenesis. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:411. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1657-3
28. Chang E, Kim C. Natural products and obesity: A focus on the regulation of mitotic clonal expansion during adipogenesis. Molecules. (2019) 24:1157. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061157
29. Perrini S, Porro S, Nigro P, Cignarelli A, Caccioppoli C, Genchi V, et al. Reduced SIRT1 and SIRT2 expression promotes adipogenesis of human visceral adipose stem cells and associates with accumulation of visceral fat in human obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). (2020) 44:307–19. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0436-7
30. Pollard A, Martins L, Muckett P, Khadayate S, Bornot A, Clausen M, et al. AMPK activation protects against diet induced obesity through Ucp1-independent thermogenesis in subcutaneous white adipose tissue. Nat Metab. (2019) 1:340–9. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0036-9
31. Feng S, Reuss L, Wang Y. Potential of natural products in the inhibition of adipogenesis through regulation of PPARγ expression and/or its transcriptional activity. Molecules. (2016) 21:1278. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101278
32. Choi E, Chun Y, Kim J, Ku S, Jeon S, Park T, et al. Modulating lipid and glucose metabolism by glycosylated kaempferol rich roasted leaves of Lycium chinense via upregulating adiponectin and AMPK activation in obese mice-induced type 2 diabetes. J Funct Foods. (2020) 72:104072. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104072
33. Rohm T, Meier D, Olefsky J, Donath M. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity. (2022) 55:31–55. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.12.013
34. Chen L, Teng H, Xie Z, Cao H, Cheang W, Skalicka-Woniak K, et al. Modifications of dietary flavonoids towards improved bioactivity: An update on structure-activity relationship. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 58:513–27. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1196334
35. Brownstein A, Veliova M, Acin-Perez R, Liesa M, Shirihai OS. ATP-consuming futile cycles as energy dissipating mechanisms to counteract obesity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2022) 23:121–31. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09690-w
36. Nowack J, Vetter S, Stalder G, Painer J, Kral M, Smith S, et al. Muscle nonshivering thermogenesis in a feral mammal. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:6378. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42756-z
37. Wood Dos Santos T, Cristina Pereira Q, Teixeira L, Gambero A, Villena J, Lima Ribeiro M. Effects of polyphenols on thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2757. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092757
38. Rosenwald M, Wolfrum C. The origin and definition of brite versus white and classical brown adipocytes. Adipocyte. (2014) 3:4–9. doi: 10.4161/adip.26232
39. de Mello A, Costa A, Engel J, Rezin G. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life Sci. (2018) 192:26–32. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.019
40. Fernandez-Marcos P, Auwerx J. Regulation of PGC-1α, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. (2011) 93:884S–90S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.001917
41. Morigny P, Boucher J, Arner P, Langin D. Lipid and glucose metabolism in white adipocytes: Pathways, dysfunction and therapeutics. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2021) 17:276–95. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00471-8
42. Zhang X, Zhang Q, Wang X, Zhang L, Qu W, Bao B, et al. Dietary luteolin activates browning and thermogenesis in mice through an AMPK/PGC1α pathway-mediated mechanism. Int J Obes (Lond). (2016) 40:1841–9. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2016.108
43. Periasamy M, Herrera J, Reis F. Skeletal muscle thermogenesis and its role in whole body energy metabolism. Diabetes Metab J. (2017) 41:327–36. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.327
44. Bal N, Periasamy M. Uncoupling of sarcoendoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase pump activity by sarcolipin as the basis for muscle non-shivering thermogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. (2020) 375:20190135. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0135
45. Blondin D, Haman F. Shivering and nonshivering thermogenesis in skeletal muscles. Handb Clin Neurol. (2018) 156:153–73. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63912-7.00010-2
46. Kjelstrup S, de Meis L, Bedeaux D, Simon J. Is the Ca2+-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum also a heat pump? Eur Biophys J. (2008) 38:59–67. doi: 10.1007/s00249-008-0358-0
47. Carrera-Quintanar L, López Roa R, Quintero-Fabián S, Sánchez-Sánchez M, Vizmanos B, Ortuño-Sahagún D. Phytochemicals that influence gut microbiota as prophylactics and for the treatment of obesity and inflammatory diseases. Mediators Inflamm. (2018) 2018:9734845. doi: 10.1155/2018/9734845
48. Davis H. Can the gastrointestinal microbiota be modulated by dietary fibre to treat obesity? Ir J Med Sci. (2018) 187:393–402. doi: 10.1007/s11845-017-1686-9
49. Canfora E, Jocken J, Blaak E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2015) 11:577–91. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.128
50. Jia R, Wu J, Luo D, Lin L, Chen C, Xiao C, et al. The beneficial effects of two polysaccharide fractions from sargassum fusiform against diabetes mellitus accompanied by dyslipidemia in rats and their underlying mechanisms. Foods. (2022) 11:1416. doi: 10.3390/foods11101416
51. Psichas A, Sleeth M, Murphy K, Brooks L, Bewick G, Hanyaloglu A, et al. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int J Obes (Lond). (2015) 39:424–9. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.153
52. Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhu J, Zhang M, Ho C, Huang Q, et al. Metagenomics analysis of gut microbiota in a high fat diet-induced obesity mouse model fed with (-)-epigallocatechin 3-O-(3-O-Methyl) gallate (EGCG3″Me). Mol Nutr Food Res. (2018) 62:e1800274. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800274
53. Woting A, Pfeiffer N, Loh G, Klaus S, Blaut M. Clostridium ramosum promotes high-fat diet-induced obesity in gnotobiotic mouse models. mBio. (2014) 5:e1530–1514. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01530-14
54. Ridlon J, Kang D, Hylemon P. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J Lipid Res. (2006) 47:241–59. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R500013-JLR200
55. Trauner M, Claudel T, Fickert P, Moustafa T, Wagner M. Bile acids as regulators of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism. Dig Dis. (2010) 28:220–4. doi: 10.1159/000282091
56. Bate-Smith EJ. The phenolic constituents of plants and their taxonomic significance. I. Dicotyledons. J Linn Soc Bot. (1962) 58:95–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8339.1962.tb00890.xC
57. Ziani B, Barros L, Boumehira A, Bachari K, Heleno S, Alves M, et al. Profiling polyphenol composition by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MSn and the antibacterial activity of infusion preparations obtained from four medicinal plants. Food Funct. (2018) 9:149–59. doi: 10.1039/c7fo01315a
58. Wang H, Xiang J, Qi Z, Du M. Plant extracts in prevention of obesity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 62:2221–34. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1852171
59. Lin Y, Shi D, Su B, Wei J, Găman M, Sedanur Macit M, et al. The effect of green tea supplementation on obesity: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother Res. (2020) 34:2459–70. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6697
60. Safahani M, Aligholi H, Noorbakhsh F, Djalali M, Pishva H, Mousavi S, et al. Resveratrol promotes the arcuate nucleus architecture remodeling to produce more anorexigenic neurons in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Nutrition. (2018) 50:49–59. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2017.10.019
61. Wang S, Moustaid-Moussa N, Chen L, Mo H, Shastri A, Su R, et al. Novel insights of dietary polyphenols and obesity. J Nutr Biochem. (2014) 25:1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.001
62. Reinbach H, Smeets A, Martinussen T, Møller P, Westerterp-Plantenga M. Effects of capsaicin, green tea and CH-19 sweet pepper on appetite and energy intake in humans in negative and positive energy balance. Clin Nutr. (2009) 28:260–5. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2009.01.010
63. Zhang X, Huang B, Choi S, Seo J. Anti-obesity effect of resveratrol-amplified grape skin extracts on 3T3-L1 adipocytes differentiation. Nutr Res Pract. (2012) 6:286–93. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2012.6.4.286
64. Timmers S, Konings E, Bilet L, Houtkooper R, van de Weijer T, Goossens G, et al. Calorie restriction-like effects of 30 days of resveratrol supplementation on energy metabolism and metabolic profile in obese humans. Cell Metab. (2011) 14:612–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.10.002
65. Wu M, Liu D, Zeng R, Xian T, Lu Y, Zeng G, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits adipogenesis through down-regulation of PPARγ and FAS expression mediated by PI3K-AKT signaling in 3T3-L1 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. (2017) 795:134–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.12.006
66. Chan C, Wei L, Castro-Muñozledo F, Koo W. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks 3T3-L1 adipose conversion by inhibition of cell proliferation and suppression of adipose phenotype expression. Life Sci. (2011) 89:779–85. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.09.006
67. Kim H, Hiraishi A, Tsuchiya K, Sakamoto K. (-) Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes through transcription factors FoxO1 and SREBP1c. Cytotechnology. (2010) 62:245–55. doi: 10.1007/s10616-010-9285-x
68. Hung P, Wu B, Chen H, Chen Y, Chen C, Wu M, et al. Antimitogenic effect of green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes depends on the ERK and Cdk2 pathways. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2005) 288:C1094–108. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00569.2004
69. Harmon A, Patel Y, Harp J. Genistein inhibits CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) activity and 3T3-L1 adipogenesis by increasing C/EBP homologous protein expression. Biochem J. (2002) 367:203–8. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020300
70. Zhang M, Ikeda K, Xu J, Yamori Y, Gao X, Zhang B. Genistein suppresses adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via multiple signal pathways. Phytother Res. (2009) 23:713–8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2724
71. Chuang C, McIntosh M. Potential mechanisms by which polyphenol-rich grapes prevent obesity-mediated inflammation and metabolic diseases. Annu Rev Nutr. (2011) 31:155–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145149
72. Tabrizi R, Saneei P, Lankarani K, Akbari M, Kolahdooz F, Esmaillzadeh A, et al. The effects of caffeine intake on weight loss: A systematic review and dos-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 59:2688–96. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1507996
73. Kong F, Ye B, Cao J, Cai X, Lin L, Huang S, et al. Curcumin represses NLRP3 inflammasome activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and P2X7R signaling in PMA-induced macrophages. Front Pharmacol. (2016) 7:369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00369
74. Shao W, Yu Z, Chiang Y, Yang Y, Chai T, Foltz W, et al. Curcumin prevents high fat diet induced insulin resistance and obesity via attenuating lipogenesis in liver and inflammatory pathway in adipocytes. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e28784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028784
75. Di Pierro F, Bressan A, Ranaldi D, Rapacioli G, Giacomelli L, Bertuccioli A. Potential role of bioavailable curcumin in weight loss and omental adipose tissue decrease: Preliminary data of a randomized, controlled trial in overweight people with metabolic syndrome. Preliminary study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2015) 19:4195–202.
76. Jazayeri-Tehrani S, Rezayat S, Mansouri S, Qorbani M, Alavian S, Daneshi-Maskooni M, et al. Nano-curcumin improves glucose indices, lipids, inflammation, and Nesfatin in overweight and obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutr Metab (Lond). (2019) 16:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12986-019-0331-1
77. Shehzad A, Ha T, Subhan F, Lee Y. New mechanisms and the anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in obesity and obesity-related metabolic diseases. Eur J Nutr. (2011) 50:151–61. doi: 10.1007/s00394-011-0188-1
78. Lee M, Shin Y, Jung S, Kim Y. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on thermogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis in brown adipose tissues of diet-induced obese mice. Food Nutr Res. (2017) 61:1325307. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1325307
79. Varela C, Rodriguez A, Romero-Valdovinos M, Mendoza-Lorenzo P, Mansour C, Ceballos G, et al. Browning effects of (-)-epicatechin on adipocytes and white adipose tissue. Eur J Pharmacol. (2017) 811:48–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.05.051
80. Choi H, Kim C, Yu R. Quercetin upregulates uncoupling protein 1 in white/brown adipose tissues through sympathetic stimulation. J Obes Metab Syndr. (2018) 27:102–9. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2018.27.2.102
81. Grossini E, Farruggio S, Raina G, Mary D, Deiro G, Gentilli S. Effects of genistein on differentiation and viability of human visceral adipocytes. Nutrients. (2018) 10:978. doi: 10.3390/nu10080978
82. Gutiérrez-Salmeán G, Ortiz-Vilchis P, Vacaseydel C, Garduño-Siciliano L, Chamorro-Cevallos G, Meaney E, et al. Effects of (-)-epicatechin on a diet-induced rat model of cardiometabolic risk factors. Eur J Pharmacol. (2014) 728:24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.053
83. Akindehin S, Jung Y, Kim S, Son Y, Lee I, Seong J, et al. Myricetin exerts anti-obesity effects through upregulation of SIRT3 in adipose tissue. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1962. doi: 10.3390/nu10121962
84. Han X, Guo J, You Y, Yin M, Liang J, Ren C, et al. Vanillic acid activates thermogenesis in brown and white adipose tissue. Food Funct. (2018) 9:4366–75. doi: 10.1039/c8fo00978c
85. Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, et al. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell. (2006) 127:1109–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.013
86. Goh K, Lee H, Lau D, Supaat W, Chan Y, Koh A. Effects of resveratrol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on skeletal muscle SIRT1 expression and energy expenditure. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. (2014) 24:2–13. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0045
87. Lee A, Lim W, Kim S, Khil H, Cheon E, An S, et al. Coffee intake and obesity: A meta-analysis. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1274. doi: 10.3390/nu11061274
88. Serrano A, Ribot J, Palou A, Bonet M. Long-term programming of skeletal muscle and liver lipid and energy metabolism by resveratrol supplementation to suckling mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2021) 95:108770. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108770
89. Zhu Y, Zhang J, Wei Y, Hao J, Lei Y, Zhao W, et al. The polyphenol-rich extract from chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa L .) modulates gut microbiota and improves lipid metabolism in diet-induced obese rats. Nutr Metab (Lond). (2020) 17:1–15. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00473-9
90. Zhang X, Zhang M, Ho CT, Guo X, Wu Z, Weng P, et al. Metagenomics analysis of gut microbiota modulatory effect of green tea polyphenols by high fat diet-induced obesity mice model. J Funct Foods. (2018) 46:268–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.05.003
91. Masumoto S, Terao A, Yamamoto Y, Mukai T, Miura T, Shoji T. Non-absorbable apple procyanidins prevent obesity associated with gut microbial and metabolomic changes. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:31208. doi: 10.1038/srep31208
92. Lu Q, Rasmussen A, Yang J, Lee R, Huang J, Shao P, et al. Mixed spices at culinary doses have prebiotic effects in healthy adults: A pilot study. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1425. doi: 10.3390/nu11061425
93. Ezzat-Zadeh Z, Henning S, Yang J, Woo S, Lee R, Huang J, et al. California strawberry consumption increased the abundance of gut microorganisms related to lean body weight, health and longevity in healthy subjects. Nutr Res. (2021) 85:60–70. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.12.006
94. Aranaz P, Navarro-Herrera D, Zabala M, Miguéliz I, Romo-Hualde A, López-Yoldi M, et al. Phenolic compounds inhibit 3T3-L1 Adipogenesis depending on the stage of differentiation and their binding affinity to PPARγ. Molecules. (2019) 24:1045. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061045
95. Ibitoye O, Ajiboye T. Dietary phenolic acids reverse insulin resistance, hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia, inflammation and oxidative stress in high-fructose diet-induced metabolic syndrome rats. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2018) 124:410–7. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2017.1415938
96. Lee W, Lee S, Son Y, Yun J. Gallic acid decreases inflammatory cytokine secretion through histone acetyltransferase/histone deacetylase regulation in high glucose-induced human monocytes. J Med Food. (2015) 18:793–801. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2014.3342
97. Oruganti L, Reddy Sankaran K, Dinnupati H, Kotakadi V, Meriga B. Anti-adipogenic and lipid-lowering activity of piperine and epigallocatechin gallate in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2023) 129:1152–9. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1908366
98. Mladenova S, Savova M, Marchev A, Ferrante C, Orlando G, Wabitsch M, et al. Anti-adipogenic activity of maackiain and ononin is mediated via inhibition of PPARγ in human adipocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 149:112908. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112908
99. Rebollo-Hernanz M, Zhang Q, Aguilera Y, Martín-Cabrejas M, Gonzalez de Mejia E. Phenolic compounds from coffee by-products modulate adipogenesis-related inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin resistance in adipocytes, via insulin/PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. (2019) 132:110672. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.110672
100. Ardid-Ruiz A, Ibars M, Mena P, Del Rio D, Muguerza B, Bladé C, et al. Potential involvement of peripheral Leptin/STAT3 signaling in the effects of resveratrol and its metabolites on reducing body fat accumulation. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1757. doi: 10.3390/nu10111757
101. Kang J, Park C, Kang J, Park Y, Park S. Randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of a newly developed formulation of phentermine diffuse-controlled release for obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2010) 12:876–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01242.x
102. Badshah H, Ullah I, Kim S, Kim T, Lee H, Kim M. Anthocyanins attenuate body weight gain via modulating neuropeptide Y and GABAB1 receptor in rats hypothalamus. Neuropeptides. (2013) 47:347–53. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2013.06.001
103. Ahn J, Lee H, Kim S, Park J, Ha T. The anti-obesity effect of quercetin is mediated by the AMPK and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2008) 373:545–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.06.077
104. Yuan X, Wei G, You Y, Huang Y, Lee H, Dong M, et al. Rutin ameliorates obesity through brown fat activation. FASEB J. (2017) 31:333–45. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600459RR
105. Choi B, Park S, Lee D, Lee H, Jin Y, Yang S, et al. Green coffee bean extract improves obesity by decreasing body fat in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Asian Pac J Trop Med. (2016) 9:635–43. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.05.017
106. Tzeng T, Liu I. 6-gingerol prevents adipogenesis and the accumulation of cytoplasmic lipid droplets in 3T3-L1 cells. Phytomedicine. (2013) 20:481–7. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.12.006
107. Suk S, Seo S, Yu J, Yang H, Jeong E, Jang Y, et al. A bioactive constituent of ginger, 6-shogaol, prevents adipogenesis and stimulates lipolysis in 3 T 3-L 1 adipocytes. J Food Biochem. (2016) 40:84–90. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12191
108. Gaya M, Repetto V, Toneatto J, Anesini C, Piwien-Pilipuk G, Moreno S. Antiadipogenic effect of carnosic acid, a natural compound present in Rosmarinus officinalis, is exerted through the C/EBPs and PPARγ pathways at the onset of the differentiation program. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2013) 1830:3796–806. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.03.021
109. Hattori H, Mori T, Shibata T, Kita M, Mitsunaga T. 6-Paradol acts as a potential anti-obesity vanilloid from grains of paradise. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2021) 65:e2100185. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202100185
110. Attia R, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Abdallah D, El-Abhar H, El-Maraghy N. Raspberry ketone and Garcinia Cambogia rebalanced disrupted insulin resistance and leptin signaling in rats fed high fat fructose diet. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 110:500–9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.079
111. Li T, Zhang L, Jin C, Xiong Y, Cheng Y, Chen K. Pomegranate flower extract bidirectionally regulates the proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of 3T3-L1 cells through regulation of PPARγ expression mediated by PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 131:110769. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110769
112. Mladenova S, Vasileva L, Savova M, Marchev A, Tews D, Wabitsch M, et al. Anti-adipogenic effect of alchemilla monticola is mediated Via PI3K/AKT signaling inhibition in human adipocytes. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:707507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.707507
113. Saini R, Prasad P, Lokesh V, Shang X, Shin J, Keum Y, et al. Carotenoids: Dietary sources, extraction, encapsulation, bioavailability, and health benefits-A review of recent advancements. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:795. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040795
114. Moran N, Mohn E, Hason N, Erdman J, Johnson E. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors impacting absorption, metabolism, and health effects of dietary carotenoids. Adv Nutr. (2018) 9:465–92. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy025
115. von Lintig J. Provitamin A metabolism and functions in mammalian biology. Am J Clin Nutr. (2012) 96:1234S–44S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.034629
116. Bandara S, Thomas L, Ramkumar S, Khadka N, Kiser P, Golczak M, et al. The structural and biochemical basis of apocarotenoid processing by β-carotene oxygenase-2. ACS Chem Biol. (2021) 16:480–90. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00832
117. Yao N, Yan S, Guo Y, Wang H, Li X, Wang L, et al. The association between carotenoids and subjects with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Funct. (2021) 12:4768–82. doi: 10.1039/d1fo00004g
118. Marchildon F, St-Louis C, Akter R, Roodman V, Wiper-Bergeron N. Transcription factor Smad3 is required for the inhibition of adipogenesis by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:13274–84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.054536
119. Wang B, Fu X, Zhu M, Du M. Retinoic acid inhibits white adipogenesis by disrupting GADD45A-mediated Zfp423 DNA demethylation. J Mol Cell Biol. (2017) 9:338–49. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjx026
120. Murholm M, Isidor M, Basse A, Winther S, Sørensen C, Skovgaard-Petersen J, et al. Retinoic acid has different effects on UCP1 expression in mouse and human adipocytes. BMC Cell Biol. (2013) 14:41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-41
121. Wu L, Mo W, Feng J, Li J, Yu Q, Li S, et al. Astaxanthin attenuates hepatic damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by up-regulating the FGF21/PGC-1α pathway. Br J Pharmacol. (2020) 177:3760–77. doi: 10.1111/bph.15099
122. Austenaa L, Carlsen H, Hollung K, Blomhoff H, Blomhoff R. Retinoic acid dampens LPS-induced NF-kappaB activity: Results from human monoblasts and in vivo imaging of NF-kappaB reporter mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2009) 20:726–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.07.002
123. Abedimanesh N, Motlagh B, Abedimanesh S, Bathaie S, Separham A, Ostadrahimi A. Effects of crocin and saffron aqueous extract on gene expression of SIRT1, AMPK, LOX1, NF-κB, and MCP-1 in patients with coronary artery disease: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res. (2020) 34:1114–22. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6580
124. Sun S, Cao C, Li J, Meng Q, Cheng B, Shi B, et al. Lycopene modulates placental health and fetal development under high-fat diet during pregnancy of rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2021) 65:2001148. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxac208
125. Fenni S, Hammou H, Astier J, Bonnet L, Karkeni E, Couturier C, et al. Lycopene and tomato powder supplementation similarly inhibit high-fat diet induced obesity, inflammatory response, and associated metabolic disorders. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61:1601083. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201601083
126. Li X, Cheng Y, Li J, Liu C, Qian H, Zhang G. Torularhodin alleviates hepatic dyslipidemia and inflammations in high-fat diet-induced obese mice via PPARα signaling pathway. Molecules. (2022) 27:6398. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196398
127. Wu L, Lyu Y, Srinivasagan R, Wu J, Ojo B, Tang M, et al. Astaxanthin-shifted gut microbiota is associated with inflammation and metabolic homeostasis in mice. J Nutr. (2020) 150:2687–98. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa222
128. Wiese M, Bashmakov Y, Chalyk N, Nielsen D, Krych Ł, Kot W, et al. Prebiotic effect of lycopene and dark chocolate on gut microbiome with systemic changes in liver metabolism, skeletal muscles and skin in moderately obese persons. Biomed Res Int. (2019) 2019:4625279. doi: 10.1155/2019/4625279
129. Xia H, Liu C, Li C, Fu M, Takahashi S, Hu K, et al. Dietary tomato powder inhibits high-fat diet-promoted hepatocellular carcinoma with alteration of gut microbiota in mice lacking carotenoid cleavage enzymes. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). (2018) 11:797–810. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-18-0188
130. Zhu L, Song Y, Liu H, Wu M, Gong H, Lan H, et al. Gut microbiota regulation and anti-inflammatory effect of β-carotene in dextran sulfate sodium-stimulated ulcerative colitis in rats. J Food Sci. (2021) 86:2118–30. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15684
131. Canas J, Lochrie A, McGowan A, Hossain J, Schettino C, Balagopal P. Effects of mixed carotenoids on adipokines and abdominal adiposity in children: A pilot study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 102:1983–90. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00185
132. Kakutani R, Hokari S, Nishino A, Ichihara T, Sugimoto K, Takaha T, et al. Effect of oral paprika xanthophyll intake on abdominal fat in healthy overweight humans: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Oleo Sci. (2018) 67:1149–62. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess18076
133. Amengual J, Gouranton E, van Helden Y, Hessel S, Ribot J, Kramer E, et al. Beta-carotene reduces body adiposity of mice via BCMO1. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e20644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020644
134. Lobo G, Amengual J, Li H, Golczak M, Bonet M, Palczewski K, et al. Beta,beta-carotene decreases peroxisome proliferator receptor gamma activity and reduces lipid storage capacity of adipocytes in a beta,beta-carotene oxygenase 1-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:27891–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.132571
135. Fenni S, Astier J, Bonnet L, Karkeni E, Gouranton E, Mounien L, et al. (all-E)- and (5Z)-lycopene display similar biological effects on adipocytes. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:e1800788. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800788
136. Gouranton E, Aydemir G, Reynaud E, Marcotorchino J, Malezet C, Caris-Veyrat C, et al. Apo-10′-lycopenoic acid impacts adipose tissue biology via the retinoic acid receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2011) 1811:1105–14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.09.002
137. Jia Y, Wu C, Kim J, Kim B, Lee S. Astaxanthin reduces hepatic lipid accumulations in high-fat-fed C57BL/6J mice via activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and inhibition of PPAR gamma and Akt. J Nutr Biochem. (2016) 28:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.09.015
138. Lim J, Liu C, Hu K, Smith D, Wu D, Lamon-Fava S, et al. Dietary β-cryptoxanthin inhibits high-refined carbohydrate diet-induced fatty liver via differential protective mechanisms depending on carotenoid cleavage enzymes in male mice. J Nutr. (2019) 149:1553–64. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz106
139. Hara H, Takahashi H, Mohri S, Murakami H, Kawarasaki S, Iwase M, et al. β-Cryptoxanthin induces UCP-1 expression via a RAR pathway in adipose tissue. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:10595–603. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01930
140. Wu M, Chou H, Huang C. Dietary fucoxanthin increases metabolic rate and upregulated mRNA expressions of the PGC-1alpha network, mitochondrial biogenesis and fusion genes in white adipose tissues of mice. Mar Drugs. (2014) 12:964–82. doi: 10.3390/md12020964
141. Ain Q, Khan H, Mubarak M, Pervaiz A. Plant alkaloids as antiplatelet agent: Drugs of the future in the light of recent developments. Front Pharmacol. (2016) 7:292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00292
142. Kurek J. Alkaloids: Their Importance in Nature and Human Life. Norderstedt: BoD–Books on Demand (2019).
143. Mariwala J, Rai D, Padigaru M, Ashok Morde A, Maddox E, Maalouf S, et al. Accumulating evidence to support the safe and efficacious use of a proprietary blend of capsaicinoids in mediating risk factors for obesity. Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 9:2823–35. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2122
144. Bort A, Sánchez B, Mateos-Gómez P, Díaz-Laviada I, Rodríguez-Henche N. Capsaicin targets lipogenesis in HepG2 cells through AMPK activation. AKT inhibition and PPARs regulation. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1660. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071660
145. Smeets A, Westerterp-Plantenga M. The acute effects of a lunch containing capsaicin on energy and substrate utilisation, hormones, and satiety. Eur J Nutr. (2009) 48:229–34. doi: 10.1007/s00394-009-0006-1
146. Song J, Ren H, Gao Y, Lee C, Li S, Zhang F, et al. Dietary capsaicin improves glucose homeostasis and alters the gut microbiota in obese diabetic ob/ob mice. Front Physiol. (2017) 8:602. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00602
147. Baboota R, Murtaza N, Jagtap S, Singh D, Karmase A, Kaur J, et al. Capsaicin-induced transcriptional changes in hypothalamus and alterations in gut microbial count in high fat diet fed mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2014) 25:893–902. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.04.004
148. Wang Y, Tang C, Tang Y, Yin H, Liu X. Capsaicin has an anti-obesity effect through alterations in gut microbiota populations and short-chain fatty acid concentrations. Food Nutr Res. (2020) 64:64. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v64.3525
149. Chen Q, Mo R, Wu N, Zou X, Shi C, Gong J, et al. Berberine ameliorates diabetes-associated cognitive decline through modulation of aberrant inflammation response and insulin signaling pathway in DM rats. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:334. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00334
150. Xiong P, Niu L, Talaei S, Kord-Varkaneh H, Clark C, Găman M, et al. The effect of berberine supplementation on obesity indices: A dose- response meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Clin Pract. (2020) 39:101113. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101113
151. Hu Y, Davies G. Berberine inhibits adipogenesis in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. Fitoterapia. (2010) 81:358–66. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2009.10.010
152. Huang C, Zhang Y, Gong Z, Sheng X, Li Z, Zhang W, et al. Berberine inhibits 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation through the PPARgamma pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2006) 348:571–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.095
153. Choi M, Mukherjee S, Yun J. Trigonelline induces browning in 3T3-L1 white adipocytes. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:1113–24. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6892
154. Lu F, Shen L, Qin Y, Gao L, Li H, Dai Y. Clinical observation on trigonella foenum-graecum L. total saponins in combination with sulfonylureas in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin J Integr Med. (2008) 14:56–60. doi: 10.1007/s11655-007-9005-3
155. Abdillah A, Lee J, Lee Y, Yun J. Modulatory roles of capsaicin on thermogenesis in C2C12 myoblasts and the skeletal muscle of mice. Chem Biol Interact. (2025) 407:111380. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2025.111380
156. Shen W, Shen M, Zhao X, Zhu H, Yang Y, Lu S, et al. Anti-obesity effect of capsaicin in mice fed with high-fat diet is associated with an increase in population of the gut bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:272. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00272
157. Zhang W, Zhang Q, Wang L, Zhou Q, Wang P, Qing Y, et al. The effects of capsaicin intake on weight loss among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. (2023) 130:1645–56. doi: 10.1017/S0007114523000697
158. Urbina S, Roberts M, Kephart W, Villa K, Santos E, Olivencia A, et al. Effects of twelve weeks of capsaicinoid supplementation on body composition, appetite and self-reported caloric intake in overweight individuals. Appetite. (2017) 113:264–73. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2017.02.025
159. Dou Y, Huang R, Li Q, Liu Y, Li Y, Chen H, et al. Oxyberberine, an absorbed metabolite of berberine, possess superior hypoglycemic effect via regulating the PI3K/Akt and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 137:111312. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111312
160. Li Q, Dou Y, Huang Z, Chen H, Li Y, Chen J, et al. Therapeutic effect of oxyberberine on obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rats. Phytomedicine. (2021) 85:153550. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153550
161. Kim G, Shin M, Shin S, Lee A, Lee J, Seo B, et al. Study of antiobesity effect through inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity of diospyros kaki fruit and citrus unshiu peel. Biomed Res Int. (2016) 2016:1723042. doi: 10.1155/2016/1723042
162. Anyanwu G, Ejike U, Gyebi G, Rauf K, Iqbal J. Phytochemical analysis, in vitro and in silico effects from Alstonia boonei De Wild stem bark on selected digestive enzymes and adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2023) 23:370. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04202-6
163. Kim K, Lee M, Jo K, Hwang J. Piperidine alkaloids from Piper retrofractum Vahl. protect against high-fat diet-induced obesity by regulating lipid metabolism and activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 411:219–25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.153
164. Baek S, Nam K, Yi S, Jo M, Lee K, Lee Y, et al. Anti-adipogenic Effect of β-carboline alkaloids from Garlic (Allium sativum). Foods. (2019) 8:673. doi: 10.3390/foods8120673
165. Iglesias-Carres L, Mas-Capdevila A, Bravo F, Aragonès G, Arola-Arnal A, Muguerza BA. comparative study on the bioavailability of phenolic compounds from organic and nonorganic red grapes. Food Chem. (2019) 299:125092. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125092
166. Mungwari C, King’ondu C, Sigauke P, Obadele B. Conventional and modern techniques for bioactive compounds recovery from plants. Sci Afr. (2024) 27:e02509. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2024.e02509
167. Theodoridis S, Drakou E, Hickler T, Thines M, Nogues-Bravo D. Evaluating natural medicinal resources and their exposure to global change. Lancet Planet Health. (2023) 7:e155–63. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00317-5
168. Stoeva S, Hvarchanova N, Georgiev K, Radeva-Ilieva M. Green tea: Antioxidant vs. pro-oxidant activity. Beverages. (2025) 11:64. doi: 10.3390/beverages11030064
169. Cladis D, Li S, Reddivari L, Cox A, Ferruzzi M, Weaver CMA. 90 day oral toxicity study of blueberry polyphenols in ovariectomized sprague-dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol. (2020) 139:111254. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111254
170. Hytti M, Szabó D, Piippo N, Korhonen E, Honkakoski P, Kaarniranta K, et al. Two dietary polyphenols, fisetin and luteolin, reduce inflammation but augment DNA damage-induced toxicity in human RPE cells. J Nutr Biochem. (2017) 42:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.12.014
171. Xiang Q, Tang X, Cui S, Zhang Q, Liu X, Zhao J, et al. Capsaicin, the spicy ingredient of chili peppers: Effects on gastrointestinal tract and composition of gut microbiota at various dosages. Foods. (2022) 11:686. doi: 10.3390/foods11050686
172. Mahmoudi M, Zamani Taghizadeh Rabe S, Balali-Mood M, Karimi G, Memar B, Rahnama M, et al. Immunotoxicity induced in mice by subacute exposure to berberine. J Immunotoxicol. (2016) 13:255–62. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2015.1058306
173. Mills S, Bone K. The Essential Guide to Herbal Safety. Amsterdam: Elsevier Health Sciences (2004).
174. Kheir M, Wang Y, Hua L, Hu J, Li L, Lei F, et al. Acute toxicity of berberine and its correlation with the blood concentration in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. (2010) 48:1105–10. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.01.033
175. Thakkar S, Anklam E, Xu A, Ulberth F, Li J, Li B, et al. Regulatory landscape of dietary supplements and herbal medicines from a global perspective. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. (2020) 114:104647. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104647
176. Mazzanti G, Menniti-Ippolito F, Moro P, Cassetti F, Raschetti R, Santuccio C, et al. Hepatotoxicity from green tea: A review of the literature and two unpublished cases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2009) 65:331–41. doi: 10.1007/s00228-008-0610-7
177. Nishihira J, Sato-Ueshima M, Kitadate K, Wakame K, Fujii H. Amelioration of abdominal obesity by low-molecular-weight polyphenol (Oligonol) from lychee. J Funct Foods. (2009) 1:341–8.
178. Sudeep H, Prithviraj P, Jestin T, Shyamprasad K. A polyphenol fraction from Rosa multiflora var. platyphylala reduces body fat in overweight humans through appetite suppression - A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Complement Med Ther. (2024) 24:197. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04487-1
179. Martínez-Rodríguez A, Martínez-Olcina M, Vicente-Martínez M, Asencio-Mas N, Navarro P, Caturla N, et al. Effectiveness of a polyphenol-enriched blend on weight management and metabolic syndrome-related parameters in healthy overweight adults. Appl Sci. (2024) 14:3882. doi: 10.3390/app14093882
180. Muralidharan J, Romain C, Chung L, Alcaraz P, Martínez-Noguera F, Keophiphath M, et al. Effect of Sinetrol® Xpur on metabolic health and adiposity by interactions with gut microbiota: A randomized, open label, dose-response clinical trial. Nutr Metab (Lond). (2024) 21:83. doi: 10.1186/s12986-024-00851-7
181. Cases J, Romain C, Dallas C, Gerbi A, Cloarec M. Regular consumption of Fiit-ns, a polyphenol extract from fruit and vegetables frequently consumed within the Mediterranean diet, improves metabolic ageing of obese volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, parallel trial. Int J Food Sci Nutr. (2015) 66:120–5. doi: 10.3109/09637486.2014.971229
Keywords: obesity, Natural products, anti-obesity agents, polyphenols, carotenoids, alkaloids
Citation: Benbaibeche H, Boumehira AZ and Khan NA (2025) Natural bioactive compounds and their mechanisms of action in the management of obesity: a narrative review. Front. Nutr. 12:1614947. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1614947
Received: 22 April 2025; Accepted: 09 June 2025;
Published: 26 June 2025.
Edited by:
Eric Gumpricht, Independent Researcher, Gilbert, AZ, United StatesReviewed by:
Mohammed Faris Abdulghani, University of Nineveh, IraqShashank Soni, Amity University, Lucknow, India
Copyright © 2025 Benbaibeche, Boumehira and Khan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hassiba Benbaibeche, aC5iZW5iYWliZWNoZUB1bml2LWFsZ2VyLmR6
 Hassiba Benbaibeche
Hassiba Benbaibeche Ali Zineddine Boumehira
Ali Zineddine Boumehira Naim Akhtar Khan
Naim Akhtar Khan