- Shenzhen TCM Anorectal Hospital (Futian), Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Introduction: Previous studies have yielded conflicting results regarding the effect of probiotics on prediabetes. To address this, we did an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of existing studies to evaluate the effects of probiotics on prediabetes.
Methods: We conducted a thorough search for pertinent trials on the impact of probiotic supplementation on prediabetes using various databases such as PubMed, Medline, and Google Scholar.
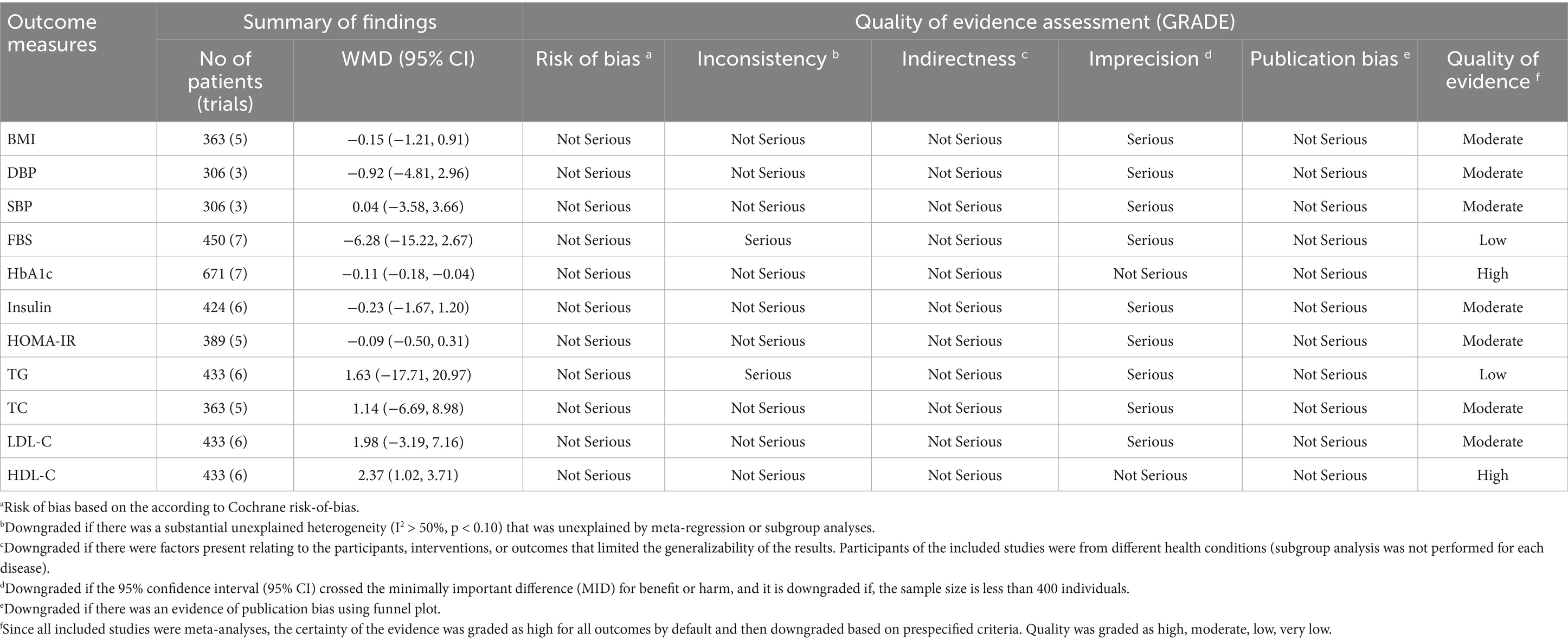
Results: Ten RCTs were included. Probiotic supplementation significantly reduced HbA1c (WMD = −0.11; 95% CI: −0.18, −0.04; p < 0.001; I2 = 0.0%) and increased HDL-C (WMD: 2.37; 95% CI: 1.02, 3.71; p < 0.001; I2 = 0.0%). Moreover, there were no significant effects of probiotic supplementation on FBS, insulin, HOMA-IR, LDL-C, TC, TG, BMI, SBP, and DBP. GRADE assessment showed high for HbA1c and HDL-C and moderate for BMI, SBP, DBP, insulin, HOMA-IR, TC, and LDL-C, and low for FBS and TG.
Conclusion: Probiotic supplementation reduces HbA1c levels and increases HDL-C in individuals with prediabetes. Future research involving large-scale, international RCTs is essential to further validate its therapeutic potential.
Introduction
Prediabetes occurs when fasting or postprandial blood sugar is elevated, though not enough to meet the criteria for full-blown diabetes (1). Prediabetes carries a significant risk of progression to type 2 diabetes (T2DM) (2). The prevalence of prediabetes is growing in countries at all economic levels, from advanced to emerging economies. In 2019, it was reported that an estimated 373.9 million people, or 7.5% of the global adult population aged 20–79 years, had prediabetes (3). Lifestyle changes and drug treatments both have their limitations and potential side effects in managing prediabetes (4). This highlights the urgent need for natural and safe solutions to control and delay the progression from prediabetes to diabetes (5). Notably, prediabetes is a reversible stage in clinical practice (6, 7). Recent studies have identified specific mechanisms that contribute to the progression from prediabetes to diabetes. Significant microbial changes occur in the gut during this process, impacting intestinal permeability, metabolic control, and insulin resistance mechanisms (8).
Probiotics have beneficial effects on the body by helping to regulate the balance of intestinal microbiota (9). Because of the close connection of gut microbiota to human health and the action of probiotics on gut microbiota, their supplementation can provide good health results (10). Increasing evidence indicates an inverse association between probiotics and hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension (11, 12). Certain probiotic bacterial strains have demonstrated efficacy in enhancing inflammation response, boosting immune function, and postponing the onset of diabetes (13). Several studies have shown the beneficial effects of particular probiotic bacterial strains on glycemic regulation (14–17). Additional metabolic effects, including reduced lipid concentrations, enhanced immune regulation, and diminished oxidative stress, have been found in research on diabetes involving probiotics (18, 19).
A meta-analysis study examined the effect of probiotics on prediabetes (20). First, all these studies were conducted before 2020. As a result of the publication of new clinical trial articles, there is a need to update the findings. Second, none of these studies performed a GRADE assessment, making it impossible to comment on the quality of the obtained evidence. Third, none of these studies have focused on adverse events. An updated review is needed to consolidate the varying results from previous studies regarding the impact of probiotic supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with prediabetes. The current meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) aims to provide a comprehensive view of the effects of probiotics on cardiometabolic health in patients with prediabetes.
Methods
Study design and protocol registration
The present research was performed in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (21). A detailed protocol outlining the study objectives, inclusion criteria, and analytical methods was registered in the PROSPERO database (CRD42023472957).
Eligibility criteria
RCTs evaluating the effects of probiotics on cardiometabolic health were included. The PICOS framework was used to determine the inclusion criteria. Participants (P) were individuals with prediabetes, defined as having fasting blood sugar (FBS) concentrations of 100–125 mg/dL, 2-h glucose tolerance test levels of 140–199 mg/dL, or HbA1c between 5.7 and 6.4%. The intervention (I) was probiotic supplementation at any dosage and duration. Comparators (C) included a placebo. Outcomes (O): Primary outcomes; BMI, FBS, HbA1c, insulin, HOMA-IR. Secondary outcomes: systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), HDL-C, and TG. Study design (S), RCTs were included. Observational studies, review articles, in vitro or in vivo studies, quasi-experimental studies, and non-randomized trials were excluded.
Search strategy
Relevant studies published up to August 2024 were searched in the PubMed, Medline, and Google Scholar databases using the following keywords: “probiotics,” “cardiovascular risk factors,” and “randomized controlled trials” (Supplementary material 1). Supplementary searches were conducted in trial registries (e.g., ClinicalTrials.gov) and the references in included articles. Our search was not limited to language or publication date. Both published articles and grey literature were considered.
Data extraction
The screening process was conducted independently by two researchers, and any disagreements were resolved by a third researcher. The extracted data included study characteristics (author, year, location, and design), participant details (sample size, age, gender, and baseline BMI), intervention specifics (probiotics dosage, duration, and administration method), and outcomes (the mean ± standard deviation (SD) changes of primary outcomes).
We followed the guidelines outlined for data extraction and conversion of quantitative outcomes (22). Continuous outcomes were extracted as means and standard deviations (SDs). When outcomes were reported in different units, they were converted to a uniform scale using the recommended methods in the handbook (23). We contacted the original study authors for clarification of missing or incomplete data. When medians and interquartile ranges (IQRs) were provided instead of means and SDs, we estimated the mean using the formula Mean≈Median and SD ≈ IQR/1.35. If the SD was not available but standard errors (SE) or confidence intervals (CIs) were reported, we calculated the SD using the formulas SD=SE× or SD = upper CI bound—lower CI bound/2 × 1.96 for a 95% CI (24). Additionally, for cases where only ranges were provided, we estimated SDs using the formula SD = Range/4, as applicable for normally distributed continuous data (23).
Risk of bias assessment and GRADE assessment
Two researchers conducted separate assessments to determine the potential for bias in every study. The Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool (ROB2) was used to evaluate methodological quality (25). Each domain was graded as “low risk,” “some concerns,” or “high risk.” Any differences of opinion were addressed and resolved with a third reviewer. We used the GRADE system to determine the certainty of the evidence for each measured outcome (26). Factors influencing certainty included publication bias, imprecision, indirectness, inconsistency, and risk of bias.
Statistical analysis
Stata version 14 was used for statistical analyses (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA), using a random-effects model for pooling the data (27). The overall effect size was calculated using the mean difference (MD) and SDs of changes in the outcome measures, with a correlation coefficient (r) set at 0.8. Meta-analyses were performed when at least three studies reported the same outcome. The weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated by combining data from all eligible RCTs (28). To quantify heterogeneity among the selected RCTs, we utilized the I2 statistic, interpreting results exceeding 50% as indicating considerable heterogeneity (29). Subgroup analysis was conducted to detect possible sources of heterogeneity. Subgroup analysis was also employed to demonstrate the effect size across various subgroups based on age and intervention duration. Sensitivity analyses were performed using the leave-one-out method to determine each study’s influence on the overall findings. Due to fewer than 10 included studies, Begg’s test was used to assess publication bias (30). A significant value was set as <0.05 in all analyses.
Results
Characteristics of included studies
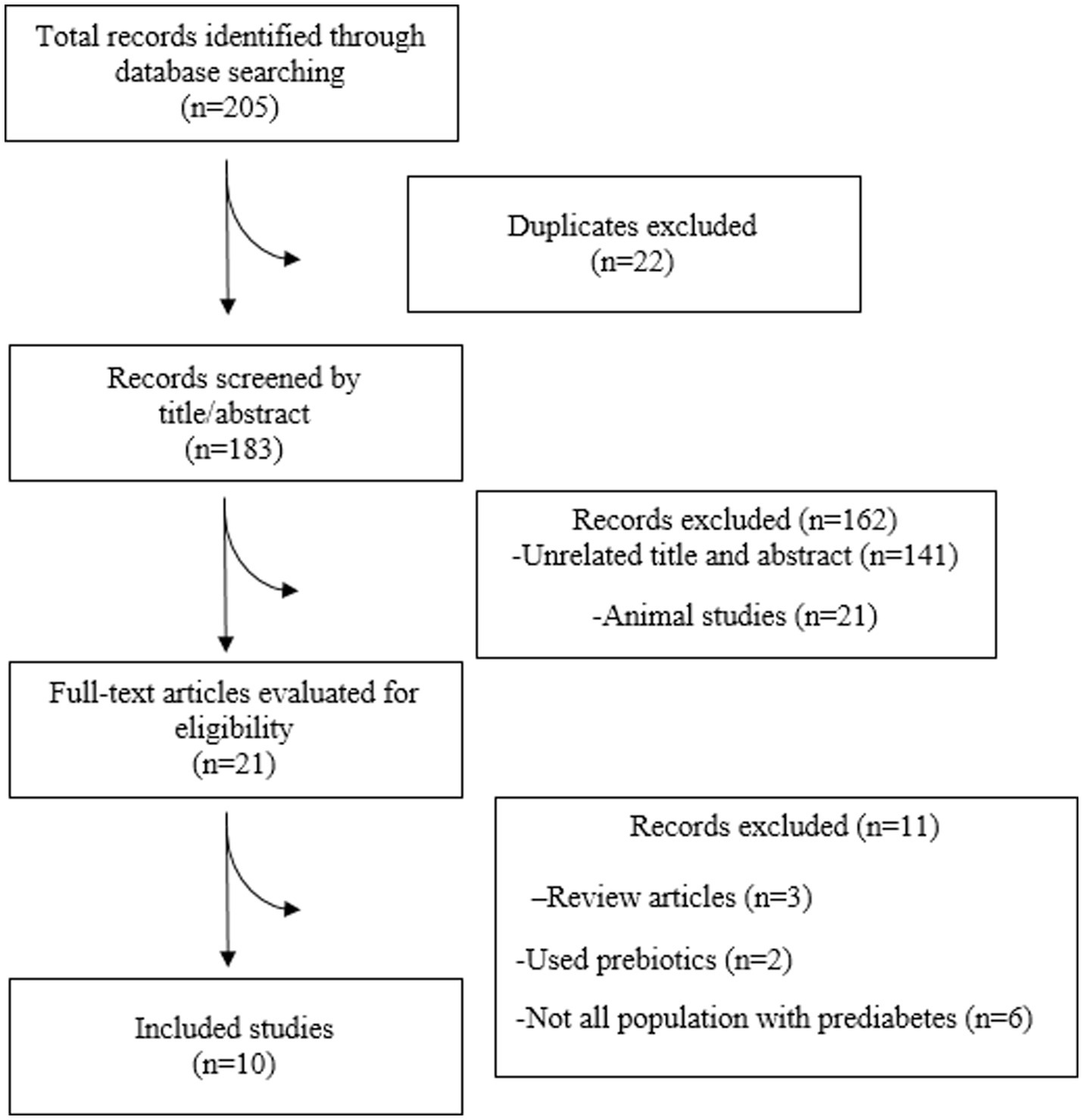
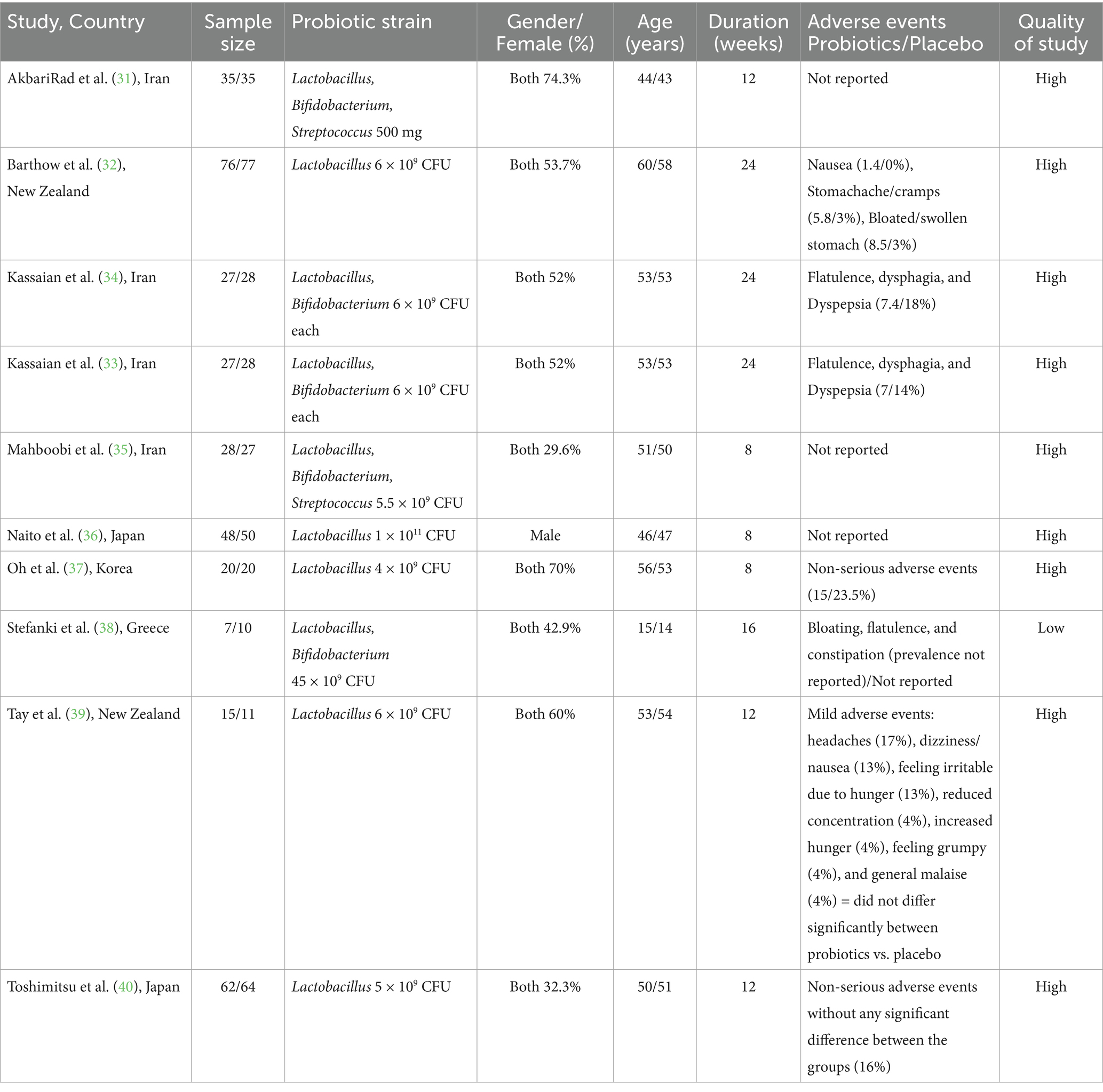
In total, 10 RCTs were incorporated into the present systematic review and meta-analysis (31–40) (Figure 1), which included 695 people with prediabetes. Of the 10 RCTs, 4 were conducted in Iran (31, 33–35), 2 in New Zealand (32, 39), 2 in Japan (36, 40), 1 in the Republic of Korea (37), and 1 in Greece (38). Except for one RCT, a double-blind approach was used. The observed sample sizes in the probiotic group ranged from 7 to 76, and in the placebo group, from 10 to 77. The follow-up duration in the RCTs ranged from 8 (35–37) to 24 (32–34) weeks. Five RCTs used capsules as the probiotic dosage form; three RCTs provided the probiotic in powder form, one RCT provided the probiotic in yogurt form, and the remaining RCTs included the probiotic in milk. The bacterial strains used in the included RCTs showed considerable diversity, with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium being the predominant probiotic components. All included RCTs used a placebo as a comparator (31–40). Background information for each assessed study is comprehensively presented in Table 1.
Risk of bias assessment
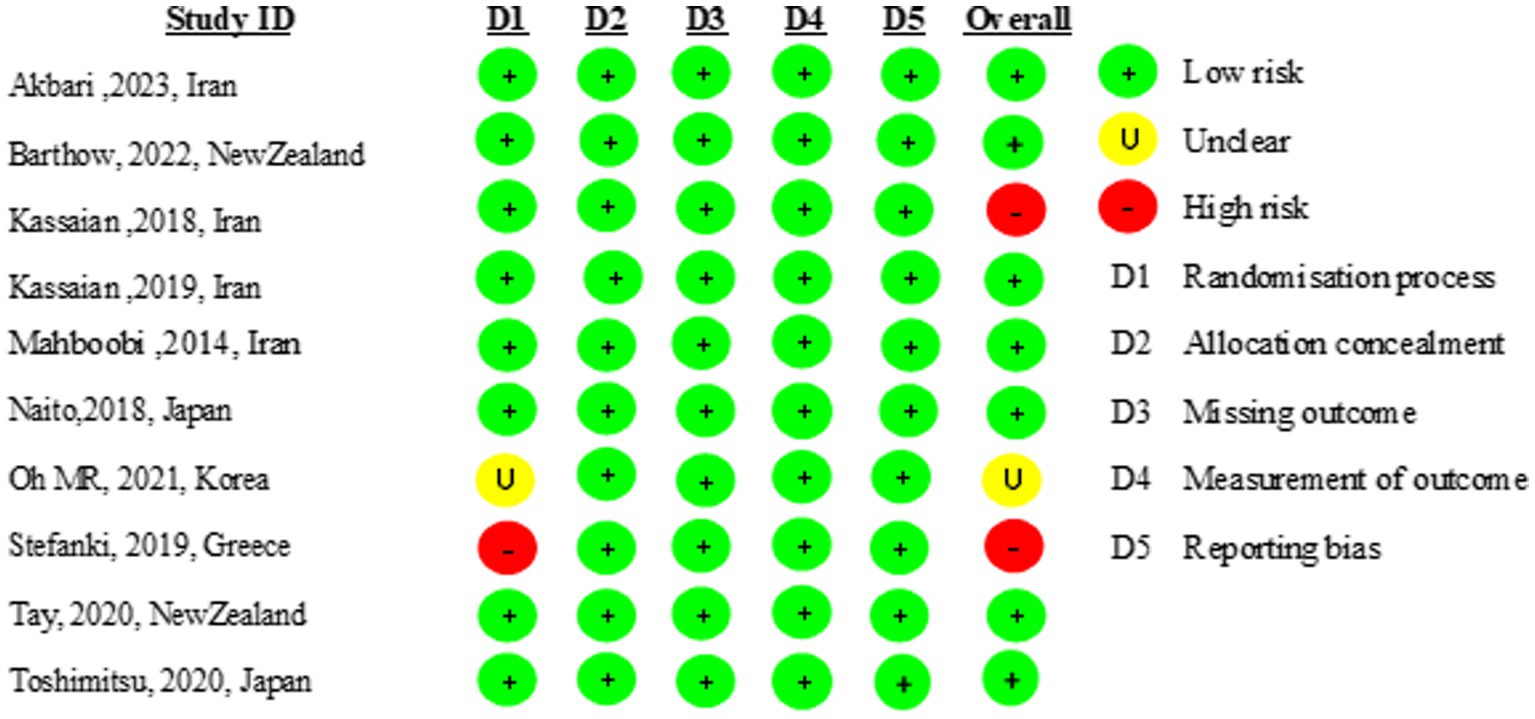
Nine of the 10 included studies were of high quality (31–37, 39, 40). One study did not report the randomization process. The risk of bias is presented in Figure 2.
Effect of probiotics on glycemic indices
The meta-analysis of comparisons from seven RCTs (n = 441) revealed that probiotic supplementation significantly reduced HbA1c (WMD = −0.11; 95% CI: −0.18, −0.04; p < 0.001), with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity = 0.77) (Figure 3A). However, probiotics did not have a significant effect on FBS (WMD = −6.28; 95% CI: −15.22, 2.67; p = 0.169; I2 = 94.0%, P-heterogeneity < 0.001) (Figure 3B), insulin (WMD = −0.23; 95% CI: −1.67, 1.20; p = 0.749; I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity = 0.931) (Figure 3C), and HOMA-IR (WMD = −0.09; 95% CI: −0.50, 0.31; p = 0.649; I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity = 0.894) (Figure 3D) compared to the control group. The results proved robust in sensitivity analyses, with no single trial exerting undue influence on the combined effect size (Supplementary Figures 1–3). However, the overall effects of probiotics on HbA1c were significantly altered when one trial was omitted during sensitivity analysis (WMD = −0.09; 95% CI: −0.19, 0.01; p > 0.05) (Supplementary Figure 4) (37). No evidence of publication bias was detected using Begg’s test (p > 0.05).
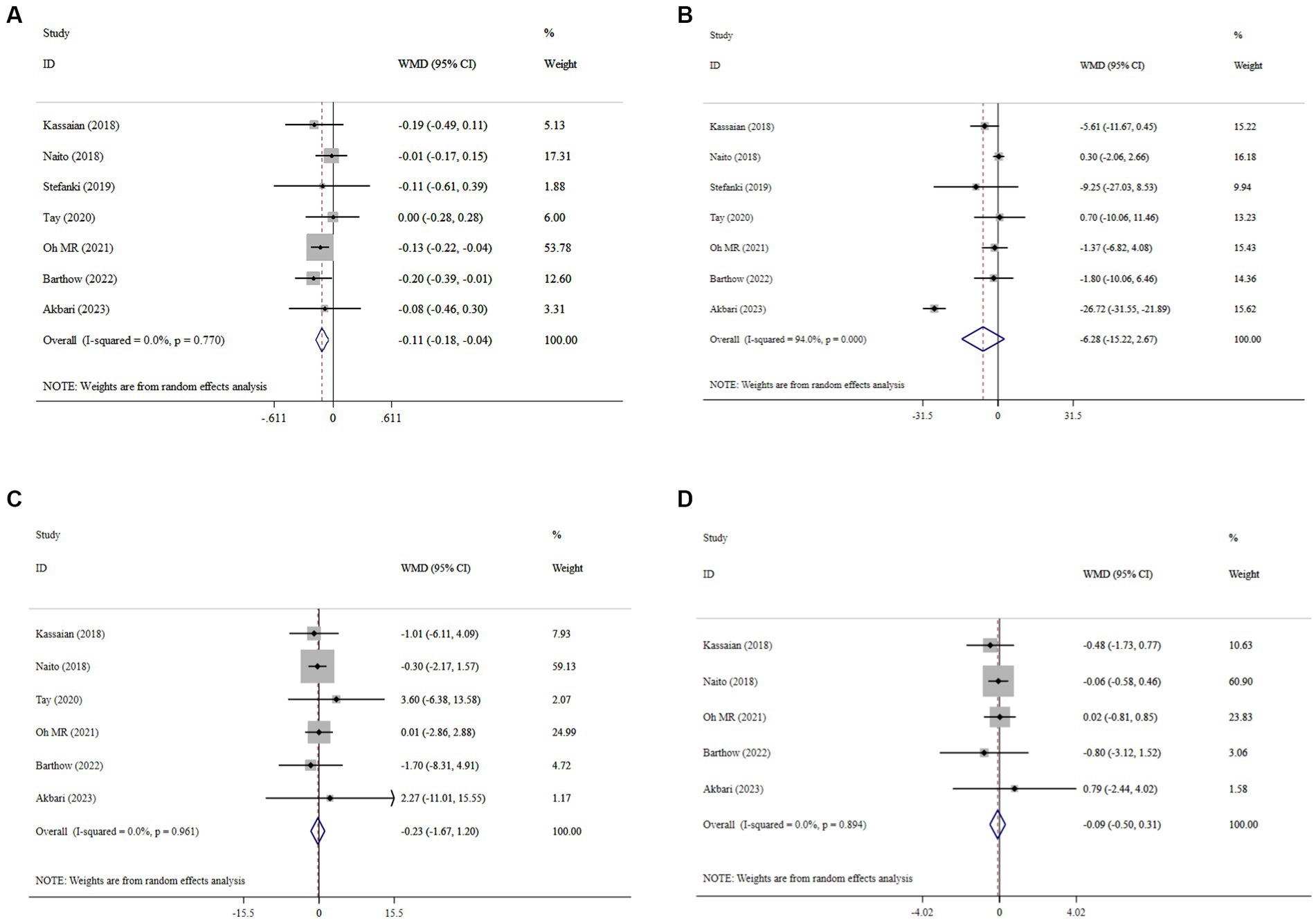
Figure 3. Forest plot details mean difference and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), the effects of probiotic supplementation on HbA1c (A), FBS (B), insulin (C), and HOMA-IR (D) levels.
Effect of probiotics on lipid profile
Probiotic supplementation significantly increased HDL-C, with a pooled WMD of 2.37 (95% CI: 1.02, 3.71; p < 0.001) and without substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity < 0.849) (Figure 4A). Moreover, probiotics did not have a significant effect on LDL-C (WMD = 1.98; 95% CI: −3.19, 7.16; p = 0.453; I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity = 0.874) (Figure 4B), TG (WMD = 1.63; 95% CI: −17.71, 20.97; p = 0.869; I2 = 55.9%, P-heterogeneity = 0.045) (Figure 4C), and TC (WMD = 1.14; 95% CI: −6.69, 8.98; p = 0.774; I2 = 14.8%, P-heterogeneity = 0.320) (Figure 4D) compared to the control group. Sensitivity analysis revealed that no individual study affected the overall effect size, and confirmed the overall results for the TC, TG, and LDL-C (Supplementary Figures 5–7). However, the overall effects of probiotics on HDL-C changed significantly by excluding the one RCT using sensitivity analysis (WMD = 1.31; 95% CI: −1.49, 4.09; p > 0.05) (Supplementary Figure 8) (35). No evidence of publication bias was detected using Begg’s test (p > 0.05).
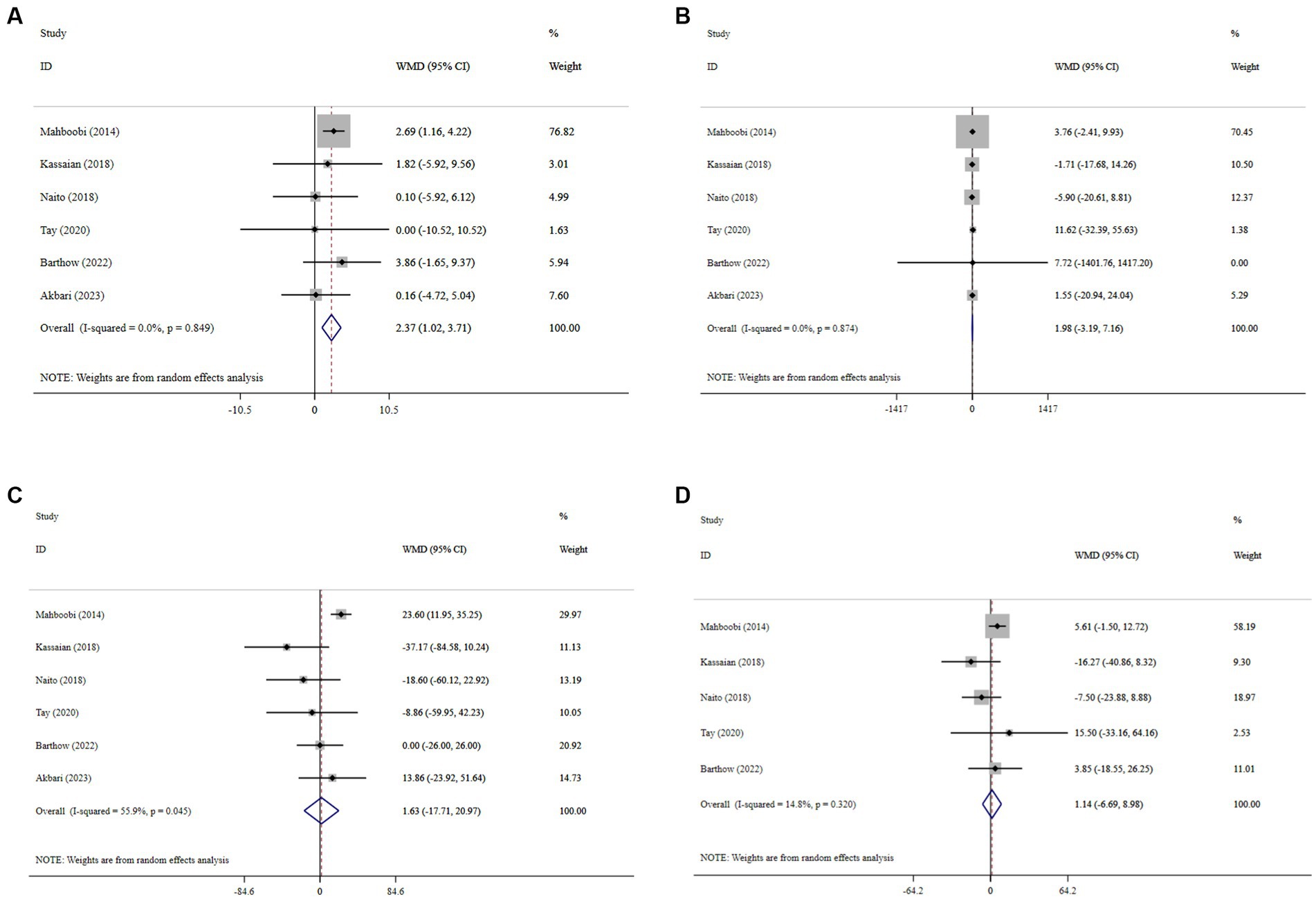
Figure 4. Forest plot details mean difference and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), the effects of probiotic supplementation on HDL-C (A), LDL-C (B), TG (C), and TC (D) levels.
Effect of probiotics on BMI and blood pressure
Overall, probiotic supplementation did not significantly reduce BMI (WMD = −0.15; 95% CI: −1.21, 0.91; p = 0.782; I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity = 0.998) (Figure 5A), SBP (WMD = −0.92; 95% CI: −4.81, 2.96; p = 0.641; I2 = 0.0%, P-heterogeneity = 0.410) (Figure 5B), and DBP (WMD = 0.04; 95% CI: −3.58, 3.66; p = 0.982; I2 = 43.6%, P-heterogeneity = 0.170) (Figure 5C). Sensitivity analysis showed that excluding any of the trials had no significant impact on the findings (Supplementary Figures 9–11). Begg’s test did not reveal publication bias (p > 0.05).
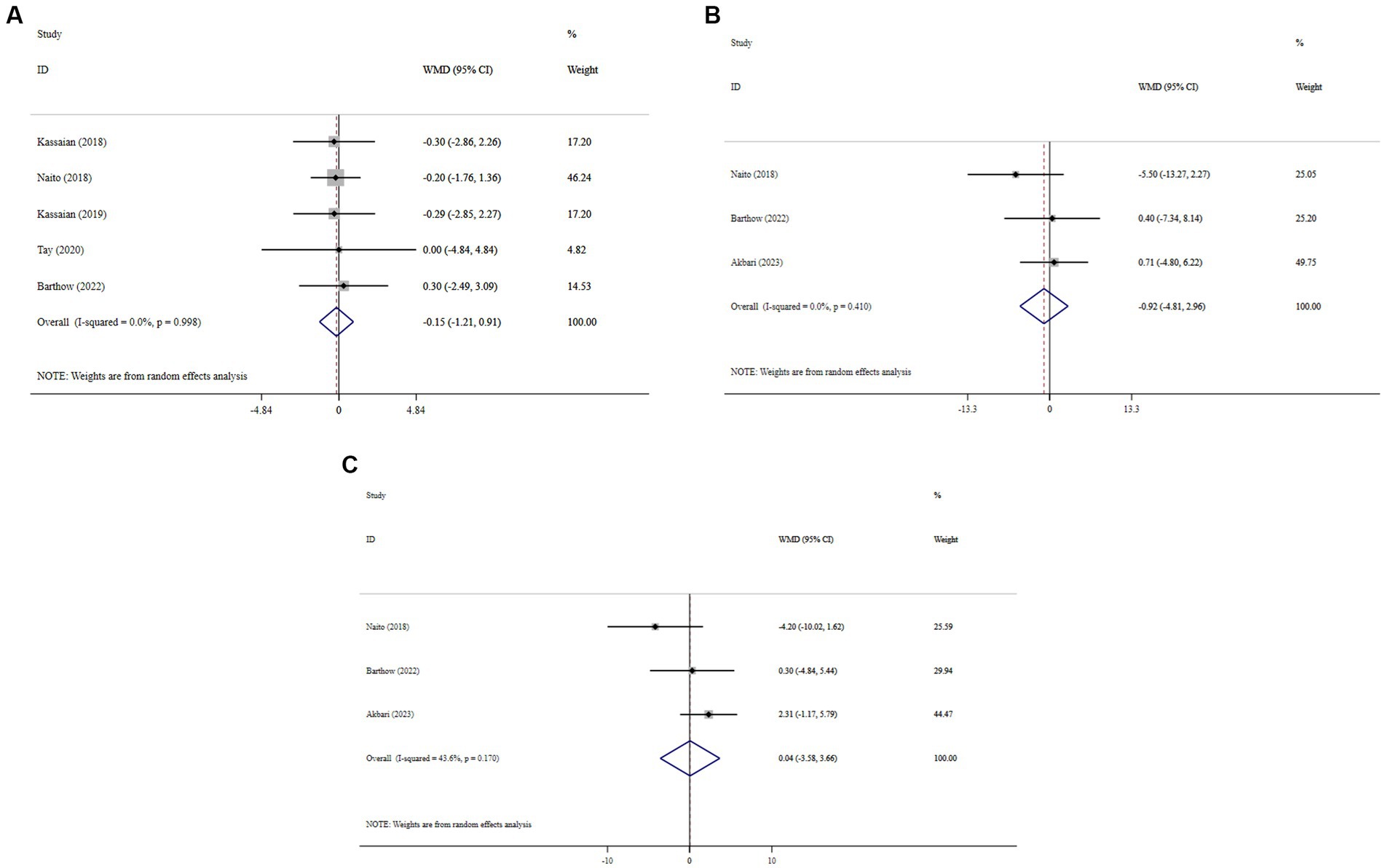
Figure 5. Forest plot detailing mean difference and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), the effects of probiotic supplementation on BMI (A), SBP (B), and DBP (C) levels.
GRADE assessment
The GRADE assessment revealed that the quality of evidence was high for HbA1c and HDL-C and moderate for HOMA-IR, insulin, BMI, SBP, DBP, TC, and LDL-C, and low for FBS and TG (Table 2).
Subgroup analysis
When stratified by mean age, studies showed more pronounced improvements in glycemic parameters—especially HbA1c levels—in older populations (>55 years) receiving probiotics versus younger individuals. Additionally, studies with larger sample sizes tended to have more significant results due to higher study power. The duration of intervention significantly influenced outcomes, with probiotic administration for more than 12 weeks demonstrating substantial HbA1c reduction compared to short-term supplementation. While HDL-C increased significantly only in the ≤12-week subgroup, study characteristics (sample size, dosage, and gender) showed no significant heterogeneity for HDL-C or HbA1c outcomes. This indicates time-dependent effects on HbA1c but suggests HDL-C responses may depend on additional factors beyond duration (see Table 3).
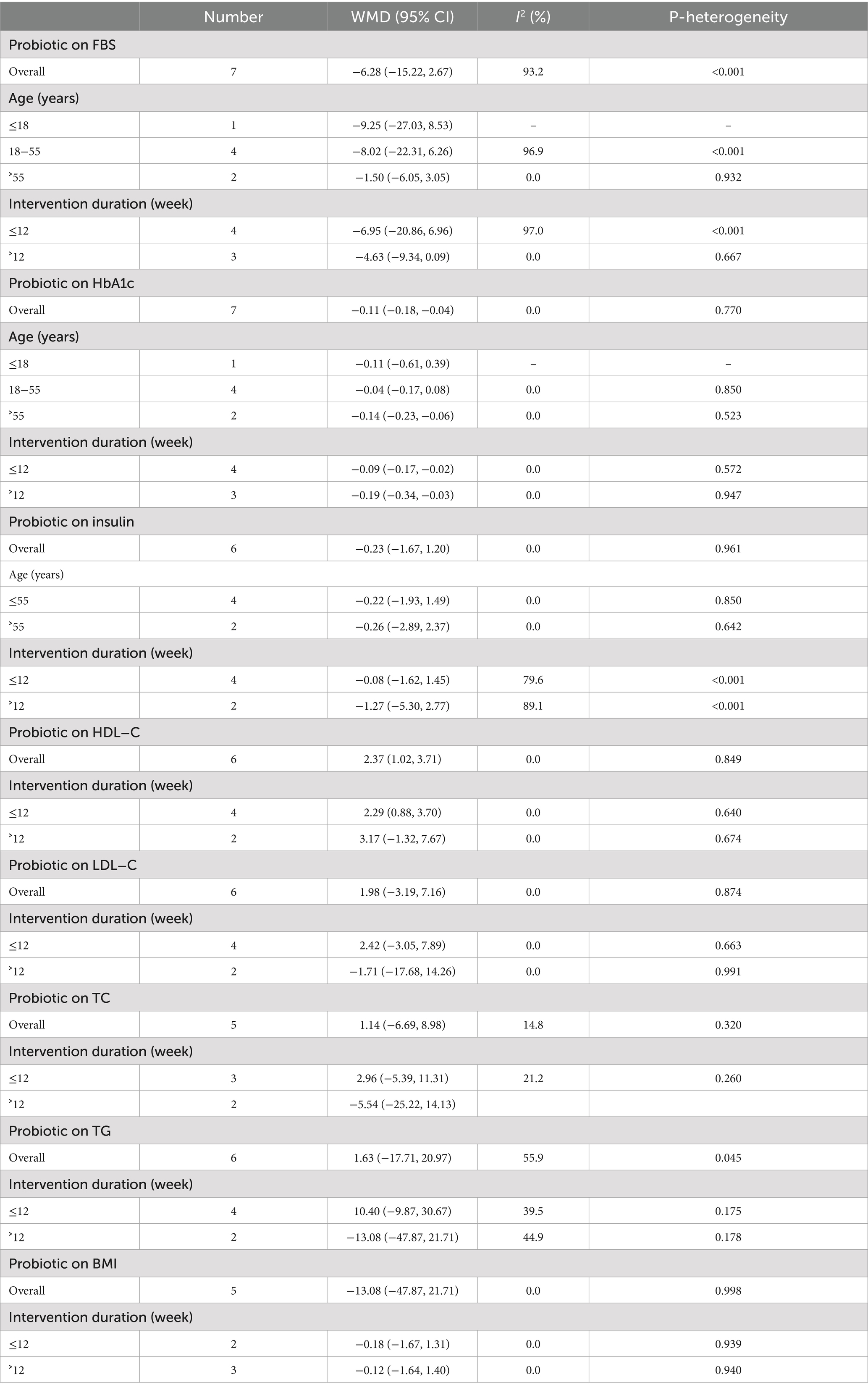
Table 3. Subgroup analyses for the effects of probiotics supplementation on patients with prediabetes.
Adverse events
The majority of adverse events were gastrointestinal in nature, including symptoms such as indigestion, abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, and changes in bowel habits. These adverse events were generally mild, self-limiting, and did not lead to discontinuation of treatment. The reported adverse events showed comparable incidence rates between the intervention and control arms across all six RCTs. Further details are provided in Table 1.
Discussion
Our comprehensive review revealed that probiotics in patients with prediabetes improved cardiometabolic health, including reduced HbA1c levels and increased HDL-C levels, compared to placebo therapy. However, no significant differences were observed between probiotic supplementation and placebo for other measured parameters, such as FBS, insulin, HOMA-IR, TC, LDL-C, TG, BMI, SBP, and DBP. Furthermore, regarding the safety profile, neither probiotics nor placebo showed significant differences in the occurrence of AEs. The non-significant effects on glycemic, lipid (TG, LDL-C, TC), and obesity (BMI) parameters could imply insufficient dosage/duration, interindividual microbiota differences, or a need for adjunct lifestyle therapies. Heterogeneity of results was high for FBS and TG. While subgroup analyses revealed potential sources of heterogeneity, these findings warrant cautious interpretation. This heterogeneity could stem from differences in study design, population characteristics, probiotics type and dosage, or intervention duration. However, the small number of available studies precluded subgroup analyses for all potential influencing factors. The certainty of the findings was evaluated using the GRADE rating, which was high for HbA1c and HDL-C and moderate for BMI, SBP, DBP, insulin, HOMA-IR, TC, and LDL-C, and low for FBS and TG.
The observed effect of probiotics on HbA1c but not on other glycemic parameters may be attributed to several factors. First, HbA1c reflects average blood glucose over a longer period (2–3 months), while FBS and insulin levels are influenced by short-term factors. Several short-term factors, such as recent meals, timing of food intake, physical activity, stress, and medication adherence, can significantly influence FBS and insulin levels. Furthermore, the low number of studies examining probiotics’ effects on glycemic control and lipid profile in prediabetes limits our understanding of their impact on various markers, making it difficult to generalize findings. The statistical power of our study may also be insufficient to detect small but clinically meaningful changes in fasting glucose or insulin resistance, as well as TG, TC, and LDL-C, which could explain the lack of significant changes in these parameters. Probiotic supplementation can enhance glycolipid control in patients with prediabetes by augmenting HDL-C levels and reducing HbA1c for various reasons. Blood glucose levels are elevated in patients with diabetes and prediabetes due to insulin resistance. Probiotics may decrease insulin resistance by promoting the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) (41). GLP-1 ameliorates insulin resistance by reducing body weight and augmenting the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin (42). The consumption of probiotics results in the synthesis of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the intestine, which subsequently interact with the G protein-coupled receptor family 43 (GPR43) and GPR41 (43). Inflammatory cytokines play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance (44). The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 contributes to insulin resistance through serine/threonine phosphorylation of IRS-1, thereby disrupting insulin signal transduction (45). Persistent inflammation is a significant catalyst for insulin resistance, leading to elevated glycosylated hemoglobin levels. Probiotics influence inflammatory responses by directly inhibiting the production of proinflammatory cytokines or indirectly reducing the prevalence of strains associated with proinflammatory processes (46, 47). The administration of probiotics has been demonstrated to substantially decrease the presence of Butyrivibrio crosscuts and Collinsella aerofaciens, which are involved in the pro-inflammatory response (38, 48). Probiotics can effectively impede the progression of insulin resistance by enhancing blood lipid levels. Probiotic supplementation demonstrates hepatoprotective effects against hypercholesterolemia-induced damage by downregulating gluconeogenic enzyme expression while upregulating glycogen synthase genes in hepatic tissue (49).
Although probiotic supplementation was associated with statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and HDL-C levels, it is not entirely clear which trials contributed most strongly to these effects. Some RCTs reporting substantial changes in these outcomes appeared to have relatively small sample sizes and higher standard deviations, suggesting that studies with less precision may have disproportionately influenced the pooled effect estimates (35, 37). This raises the possibility of small-study effects or publication bias, even in the presence of low statistical heterogeneity. Although the direction and magnitude of the effects were consistent, the robustness of these findings may still be limited by methodological variability and potential confounders not adjusted for in the primary studies. Future meta-analyses should consider influence diagnostics and sensitivity analyses to determine the extent to which individual studies affect overall estimates.
The findings of our investigation align with the meta-analysis mentioned above by Li et al. (20). Based on the findings, they suggested probiotics could provide metabolic advantages in prediabetes management by improving HbA1c and lipid parameters. Significant differences are evident between the previous meta-analysis by Li et al. (20) and our current meta-analysis. The initial distinction pertains to the number of studies included in the analysis. Li et al. (20) included only seven RCTs. Of the seven RCTs, one was published in Chinese and was excluded from prominent international databases. Thus, the validity and accuracy of its contents are uncertain. Our current meta-analysis includes 10 RCTs published in English and indexed in international databases. The second distinction is the inclusion of a greater number of outcomes compared to the previous meta-analysis by Li et al. (20) We specifically analyzed the BMI, SBP, HOMA-B, and DBP changes from the initial measurements not addressed in the previous study. The third difference is the inconsistent data entry by Li et al. (20), who calculated the HbA1c and HOMA-IR outcomes by subtracting baseline values from follow-up measurements in probiotic and placebo groups. Conversely, for other outcomes, including FBS, LDL-C, TC, HDL-C, and TG, only the values obtained during the follow-up period were recorded, without subtracting the baseline values from the follow-up values.
The strengths of this study include a rigorous methodology, adherence to PRISMA guidelines, and a comprehensive GRADE assessment to evaluate the certainty of evidence. We ensured robust and generalizable findings by using a random-effects model and conducting subgroup and sensitivity analyses. Additionally, including trials from diverse geographical locations enhances the external validity of our results. There were some limitations that must be mentioned. First, the relatively small number of included studies and participants, along with heterogeneity in probiotic strains, dosages, and formulations, may have impacted the reliability of the findings in this meta-analysis. Second, inadequate studies for gender-specific analysis. Third, most of the included trials did not account for potential confounding factors such as dietary habits, physical activity levels, smoking status, and other lifestyle-related variables that may influence cardiometabolic outcomes in individuals with prediabetes. Fourth, the non-significant glycemic and lipid profile changes might indicate that longer supplementation periods or higher dosages are needed to observe measurable outcome changes. Consequently, further well-designed RCTs are required to establish robust clinical evidence.
Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrate that probiotics supplementation can somewhat improve cardiometabolic health features by substantially decreasing HbA1c levels and increasing HDL-C levels in individuals with prediabetes. Moreover, probiotics did not have a significant effect on FBS, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, TC, LDL-C, TG, BMI, SBP, and DBP. Further studies are needed to determine the benefits of probiotics on patients with prediabetes. GRADE assessment showed high for HbA1c and HDL-C and moderate for BMI, SBP, DBP, insulin, HOMA-IR, TC, and LDL-C, and low for FBS and TG.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Author contributions
RL: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources, Formal Analysis, Validation, Project administration, Data curation, Supervision, Methodology. GW: Supervision, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Validation, Methodology, Visualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Investigation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1616476/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Neeland, IJ, Turer, AT, Ayers, CR, Powell-Wiley, TM, Vega, GL, Farzaneh-Far, R, et al. Dysfunctional adiposity and the risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in obese adults. JAMA. (2012) 308:1150–9. doi: 10.1001/2012.jama.11132
2. Bansal, N. Prediabetes diagnosis and treatment: a review. World J Diabetes. (2015) 6:296–303. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i2.296
3. Saeedi, P, Petersohn, I, Salpea, P, Malanda, B, Karuranga, S, Unwin, N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2019) 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
4. Ogurtsova, K, da Rocha Fernandes, JD, Huang, Y, Linnenkamp, U, Guariguata, L, Cho, NH, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2017) 128:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024
5. Lewis, S, and Burmeister, S. A double-blind placebo-controlled study of the effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus on plasma lipids. Eur J Clin Nutr. (2005) 59:776–80. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602139
6. Unwin, N, Shaw, J, Zimmet, P, and Alberti, KGMM. Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycaemia: the current status on definition and intervention. Diabet Med. (2002) 19:708–23. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00835.x
7. Lindström, J, Peltonen, M, Eriksson, JG, Ilanne-Parikka, P, Aunola, S, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S, et al. Improved lifestyle and decreased diabetes risk over 13 years: long-term follow-up of the randomised Finnish diabetes prevention study (DPS). Diabetologia. (2013) 56:284–93. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2752-5
8. Kassaian, N, Feizi, A, Rostami, S, Aminorroaya, A, Yaran, M, and Amini, M. The effects of 6 mo of supplementation with probiotics and synbiotics on gut microbiota in the adults with prediabetes: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Nutrition. (2020) 79:110854. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110854
9. Sánchez, B, Delgado, S, Blanco-Míguez, A, Lourenço, A, Gueimonde, M, and Margolles, A. Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61:1600240. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600240
10. Musazadeh, V, Zarezadeh, M, Ghalichi, F, Ahrabi, SS, Jamilian, P, Jamilian, P, et al. Anti-obesity properties of probiotics; a considerable medical nutrition intervention: findings from an umbrella meta-analysis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 928:175069. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175069
11. Liang, T, Wu, L, Xi, Y, Li, Y, Xie, X, Fan, C, et al. Probiotics supplementation improves hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update of meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 61:1670–88. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1764488
12. Zarezadeh, M, Musazadeh, V, Ghalichi, F, Kavyani, Z, Nasernia, R, Parang, M, et al. Effects of probiotics supplementation on blood pressure: an umbrella meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. (2023) 33:275–86. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2022.09.005
13. Sun, Z, Sun, X, Li, J, Li, Z, Hu, Q, Li, L, et al. Using probiotics for type 2 diabetes mellitus intervention: advances, questions, and potential. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 60:670–83. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1547268
14. Yadav, H, Jain, S, and Sinha, P. Antidiabetic effect of probiotic dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei in high fructose fed rats. Nutrition. (2007) 23:62–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2006.09.002
15. Hsieh, F-C, Lee, CL, Chai, CY, Chen, WT, Lu, YC, and Wu, CS. Oral administration of Lactobacillus reuteri GMNL-263 improves insulin resistance and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high fructose-fed rats. Nutr Metab. (2013) 10:1–14. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-10-35
16. Honda, K, Moto, M, Uchida, N, He, F, and Hashizume, N. Anti-diabetic effects of lactic acid bacteria in normal and type 2 diabetic mice. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2012) 51:96–101. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-07
17. Zarezadeh, M, Musazadeh, V, Faghfouri, AH, Roshanravan, N, and Dehghan, P. Probiotics act as a potent intervention in improving lipid profile: an umbrella systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 63:145–58. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.2004578
18. Kim, SH, Huh, C-S, Choi, I-D, Jeong, J-W, Ku, H-K, Ra, J-H, et al. The anti-diabetic activity of B ifidobacterium lactis HY 8101 in vitro and in vivo. J Appl Microbiol. (2014) 117:834–45. doi: 10.1111/jam.12573
19. Chen, P, Zhang, Q, Dang, H, Liu, X, Tian, F, Zhao, J, et al. Antidiabetic effect of Lactobacillus casei CCFM0412 on mice with type 2 diabetes induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Nutrition. (2014) 30:1061–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.03.022
20. Li, Y, Wu, Y, Wu, L, Qin, L, and Liu, T. The effects of probiotic administration on patients with prediabetes: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Transl Med. (2022) 20:498. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03695-y
21. Parums, DV. Review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analysis, and the updated preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. Med Sci Monit. (2021) 27:e934475. doi: 10.12659/MSM.934475
22. Cumpston, M, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (version 6.4) Cochrane (2023).
23. Jpt, H. (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Available online at: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org
24. Hozo, SP, Djulbegovic, B, and Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2005) 5:1–10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
25. Sterne, JA, Savović, J, Page, MJ, Elbers, RG, Blencowe, NS, Boutron, I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ Br Med J. (2019) 366:1–8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
26. Guyatt, GH, Oxman, AD, Vist, GE, Kunz, R, Falck-Ytter, Y, Alonso-Coello, P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. (2008) 336:924–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
27. Borenstein, M, Hedges, LV, Higgins, JPT, and Rothstein, HR. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2010) 1:97–111. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.12
29. Higgins, JP, and Thompson, SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
30. Higgins, J, Thomas, J, Chandler, J, Cumpston, M, Li, T, Page, MJ, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.2 Cochrane (2021).
31. AkbariRad, M, Shariatmaghani, SS, Razavi, BM, Majd, HM, Shakhsemampour, Z, Sarabi, M, et al. Probiotics for glycemic and lipid profile control of the pre-diabetic patients: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2023) 15:71. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01050-9
32. Barthow, C, Hood, F, Crane, J, Huthwaite, M, Weatherall, M, Parry-Strong, A, et al. A randomised controlled trial of a probiotic and a prebiotic examining metabolic and mental health outcomes in adults with pre-diabetes. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e055214. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055214
33. Kassaian, N, Feizi, A, Aminorroaya, A, Ebrahimi, MT, Norouzi, A, and Amini, M. Effects of probiotics and synbiotic on lipid profiles in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Funct Foods Health Dis. (2019) 9:494–507. doi: 10.31989/ffhd.v9i7.617
34. Kassaian, N, Feizi, A, Aminorroaya, A, Jafari, P, Ebrahimi, MT, and Amini, M. The effects of probiotics and synbiotic supplementation on glucose and insulin metabolism in adults with prediabetes: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Acta Diabetol. (2018) 55:1019–28. doi: 10.1007/s00592-018-1175-2
35. Mahboobi, S, Iraj, B, Maghsoudi, Z, Feizi, A, Ghiasvand, R, Askari, G, et al. The effects of probiotic supplementation on markers of blood lipids, and blood pressure in patients with prediabetes: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Prev Med. (2014) 5:1239.
36. Naito, E, Yoshida, Y, Kunihiro, S, Makino, K, Kasahara, K, Kounoshi, Y, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota-fermented milk on metabolic abnormalities in obese prediabetic Japanese men: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. (2018) 37:9–18. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.17-012
37. Oh, M-R, Jang, HY, Lee, SY, Jung, SJ, Chae, SW, Lee, SO, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 supplementation improves glycemic control in prediabetic subjects: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients. (2021) 13:2337. doi: 10.3390/nu13072337
38. Stefanaki, C, Michos, A, Mastorakos, G, Mantzou, A, Landis, G, Zosi, P, et al. Probiotics in adolescent prediabetes: a pilot RCT on glycemic control and intestinal bacteriome. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:1743. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101743
39. Tay, A, Pringle, H, Penning, E, Plank, LD, and Murphy, R. PROFAST: a randomized trial assessing the effects of intermittent fasting and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus probiotic among people with prediabetes. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3530. doi: 10.3390/nu12113530
40. Toshimitsu, T, Gotou, A, Sashihara, T, Hachimura, S, Shioya, N, Suzuki, S, et al. Effects of 12-week ingestion of yogurt containing Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 on glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation in prediabetic adults: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients. (2020) 12:374. doi: 10.3390/nu12020374
41. Wang, Y, Dilidaxi, D, Wu, Y, Sailike, J, Sun, X, and Nabi, XH. Composite probiotics alleviate type 2 diabetes by regulating intestinal microbiota and inducing GLP-1 secretion in db/db mice. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 125:109914. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109914
42. Yaribeygi, H, Sathyapalan, T, and Sahebkar, A. Molecular mechanisms by which GLP-1 RA and DPP-4i induce insulin sensitivity. Life Sci. (2019) 234:116776. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116776
43. Dalile, B, van Oudenhove, L, Vervliet, B, and Verbeke, K. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota–gut–brain communication. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:461–78. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0157-3
44. Wieser, V, Moschen, AR, and Tilg, H. Inflammation, cytokines and insulin resistance: a clinical perspective. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. (2013) 61:119–25. doi: 10.1007/s00005-012-0210-1
45. Kim, JH, Bachmann, RA, and Chen, J. Interleukin-6 and insulin resistance. Vitam Horm. (2009) 80:613–33. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(08)00621-3
46. Kim, Y, Keogh, J, and Clifton, P. Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and insulin sensitivity. Nutr Res Rev. (2018) 31:35–51. doi: 10.1017/S095442241700018X
47. Pintarič, M, and Langerholc, T. Probiotic mechanisms affecting glucose homeostasis: a scoping review. Life. (2022) 12:1187. doi: 10.3390/life12081187
48. Li, J, Hou, Q, Zhang, J, Xu, H, Sun, Z, Menghe, B, et al. Carbohydrate staple food modulates gut microbiota of Mongolians in China. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:484. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00484
Keywords: obesity, body weight, body mass index, meta-analysis, probiotics
Citation: Liu R and Wong G (2025) The effects of probiotic supplementation on cardiometabolic health in patients with prediabetes: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and GRADE assessment. Front. Nutr. 12:1616476. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1616476
Edited by:
Hui-Xin Liu, China Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ellen G. H. M. Van Den Heuvel, LLN NutriResearch, NetherlandsJaswinder Singh, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United States
Copyright © 2025 Liu and Wong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rongfang Liu, bHJmMTk2NUAxMjYuY29t
 Rongfang Liu*
Rongfang Liu* Gao Wong
Gao Wong