- 1Department of Gynecology, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China
- 2Affiliated Women and Children's Hospital, School of Medicine, UESTC Chengdu Women's and Children's Central Hospital, Chengdu, China
Oxidative stress plays a central role in reproductive disorders, with food bioactive compounds offering therapeutic potential through their antioxidant properties. This review examines antioxidant active ingredients from plant-based foods and their protective mechanisms in reproductive system oxidative stress management. Key phytochemicals including polyphenols (flavonoids, phenolic acids such as curcumin, resveratrol, and EGCG), carotenoids (lycopene, lutein), and organosulfur compounds demonstrate potent free radical scavenging capacity, regulate antioxidant enzyme activity, and inhibit lipid peroxidation through Nrf2 pathway activation and NF-κB inhibition. These natural food ingredients provide anti-inflammatory effects and metabolic benefits including improved insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial protection. Clinical evidence shows lycopene supplementation (4–8 mg/day) improves sperm motility and reduces DNA fragmentation in male infertility, resveratrol (150 mg/day) enhances ovarian reserve markers in female fertility, and curcumin reduces inflammatory markers (IL-8, TNF-α) in endometriosis while improving assisted reproductive outcomes. However, poor bioavailability limits therapeutic efficacy, with most compounds showing < 10% absorption. Advanced delivery technologies, including nanoencapsulation (5–30 fold enhancement), phospholipid complexation, and formulation with absorption enhancers (e.g., piperine), can substantially improve the bioavailability of these compounds for functional foods and dietary supplements. Emerging single-cell and multi-omics approaches provide powerful tools to unravel tissue-specific mechanisms, while future progress also depends on establishing uniform dosage standards and conducting rigorous safety assessments to address potential pro-oxidant effects and long-term interactions. Given that infertility affects 17.5% of adults globally, food-derived antioxidant interventions represent accessible strategies for managing reproductive disorders, supporting the development of nutraceuticals and novel foods for reproductive health protection.
1 Introduction
Global reproductive health has emerged as a pressing concern, posing multifaceted challenges not only to individual wellbeing but also to public health systems and demographic stability. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 8%−12% of reproductive-age couples experience fertility issues, with recent data indicating that infertility affects nearly 17.5% of adults globally—an alarming and escalating global health challenge (1, 2).
The implications of fertility problems extend far beyond clinical diagnoses. Affected individuals frequently experience psychological distress, such as anxiety, depression, and diminished self-esteem (3, 4). Families may endure prolonged infertility treatments that are emotionally taxing and financially burdensome, especially in healthcare systems with limited insurance coverage (4, 5). On a societal level, declining fertility contributes to demographic challenges including accelerated population aging, workforce shortages, and intergenerational imbalance (6, 7). These overlapping burdens highlight an urgent need for accessible and effective reproductive health interventions.
Emerging evidence increasingly implicates environmental deterioration, lifestyle modifications, unbalanced diets, and chronic psychological stress as contributing factors to fertility impairments (8–10). Redox imbalance has been recognized as a central pathological nexus linking these diverse risk factors to reproductive impairments (9, 11). This state arises when the cellular balance between reactive oxygen/nitrogen species production and antioxidant defense is disrupted, leading to cumulative molecular damage (12).
The reproductive system is particularly vulnerable to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced stress due to its unique structural and metabolic characteristics. Sperm membranes are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids that are readily oxidized, while oocyte maturation and fertilization demand high mitochondrial activity, increasing sensitivity to oxidative imbalance (13, 14). Substantial research has demonstrated that oxidative stress contributes to the pathogenesis of a wide array of reproductive disorders, including oligoasthenozoospermia, ovarian insufficiency, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and prostatitis, as well as reproductive impairments associated with systemic metabolic conditions such as diabetes (13, 15, 16).
Conventional therapeutic approaches, including hormonal treatments and assisted reproductive technologies, remain the primary strategies for infertility management (17–19). However, these interventions are often limited by side effects, variable success rates, and accessibility challenges, particularly in resource-limited settings, highlighting the need for alternative or complementary approaches (20–22).
Plant-derived foods contain a variety of bioactive compounds with strong antioxidant capacities (23). These natural agents confer protection via multiple mechanisms: directly scavenging free radicals, enhancing endogenous antioxidant systems, modulating redox-sensitive signaling pathways, and preserving mitochondrial integrity (24–26). Compared to synthetic antioxidants, their multifunctional nature, better safety profile, and broader cellular targets offer distinct therapeutic advantages (24, 25).
In light of the growing fertility-related burden and the limitations of current treatment modalities, plant-based interventions present a compelling research focus. Herein, this review synthesizes current knowledge on the regulatory effects of bioactive components from plant-derived foods on oxidative imbalance in the reproductive system. We further explore their potential in mitigating inflammation-related and metabolism-associated reproductive disorders and examine translational strategies to enhance bioavailability and promote functional food development for reproductive health protection.
2 Molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress in the reproductive system
Oxidative stress constitutes a critical pathological axis linking environmental exposures, metabolic imbalance, and reproductive disorders. Clarifying the underlying molecular mechanisms is essential to understand how redox imbalance alters gamete integrity, hormonal regulation, and tissue homeostasis. This framework provides a foundation for interpreting both physiological processes and pathological outcomes in reproductive health.
2.1 Generation of ROS and reproductive vulnerability
Oxidative stress arises in reproductive tissues through a convergence of mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammatory activation, and environmental insults, with profound implications for gamete viability and hormonal regulation (27–29). Mitochondrial electron leakage during oxidative phosphorylation and NADPH oxidase activation serve as the primary endogenous sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in both male and female gonads (30, 31). Inflammatory leukocyte infiltration during ovulation and in the epididymal or seminal environment adds further ROS burden, especially under pathologic conditions (27, 29, 32). Exogenous contributors—including bisphenol A, heavy metals, ionizing radiation, and high-fat diets—amplify ROS generation or suppress antioxidant enzyme systems, tipping the redox balance toward cellular injury (33–36).
Notably, the structural composition of reproductive cells renders them uniquely vulnerable to oxidative damage: sperm membranes are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), which undergo rapid lipid peroxidation; spermatozoa also possess minimal cytoplasm, lacking significant antioxidant defense reservoirs (32, 37–41). Oocytes, while comparatively robust, contain a high density of metabolically active mitochondria and demand high ATP throughput, increasing both ROS production and mitochondrial stress under suboptimal conditions (31, 42, 43). Erectile tissues show similar vulnerability due to their dependence on nitric oxide (NO) signaling and high PUFA content in vascular smooth muscle membranes (44, 45). The corpus cavernosum contains high concentrations of polyunsaturated fatty acids in smooth muscle cell membranes, making them susceptible to lipid peroxidation. Additionally, the intricate vascular network required for erectile function depends on endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity, which is particularly sensitive to ROS-mediated inactivation and endothelial dysfunction.
The genomic and epigenomic integrity of gametes further raises the stakes: even subthreshold ROS-induced lesions may result in fertilization failure, impaired embryo development, or transgenerational genomic instability (42, 43, 46–48).
2.2 Physiological roles of ROS in reproduction
Far from being solely destructive, reactive oxygen species (ROS) at physiological concentrations are essential modulators of reproductive processes (49, 50). In males, ROS are involved in sperm capacitation through cholesterol efflux, membrane hyperpolarization, and tyrosine phosphorylation—prerequisites for acrosomal exocytosis and zona pellucida binding (49, 51, 52). In females, ROS facilitate follicular rupture, corpus luteum formation, and endometrial remodeling during the periovulatory phase, partly by enhancing matrix metalloproteinase activity and promoting local prostaglandin release (29, 53, 54). These coordinated redox changes act in tandem with inflammation-like signaling required for ovulation and implantation (53, 55). In erectile tissues, physiological ROS levels support normal vascular responses, but excess ROS rapidly inactivate nitric oxide, impairing erectile function (56).
Intracellularly, ROS serve as secondary messengers activating the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase), PI3K/Akt (phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B), and JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) pathways, which regulate cytoskeletal remodeling, steroid biosynthesis, and controlled apoptosis (55, 57–59). The Keap1–Nrf2–ARE pathway (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1–Nuclear factor erythroid 2–Antioxidant Response Element), transiently activated during ovulation and implantation, induces antioxidant enzymes such as HO-1 (heme oxygenase-1) and NQO1 (NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1), thereby providing cytoprotection without suppressing the physiological ROS signaling essential for fertilization and embryo development (60–64). The balance between beneficial and detrimental redox activity is depicted in Figure 1, which contextualizes ROS as both drivers and modulators of fertility-related cellular functions.
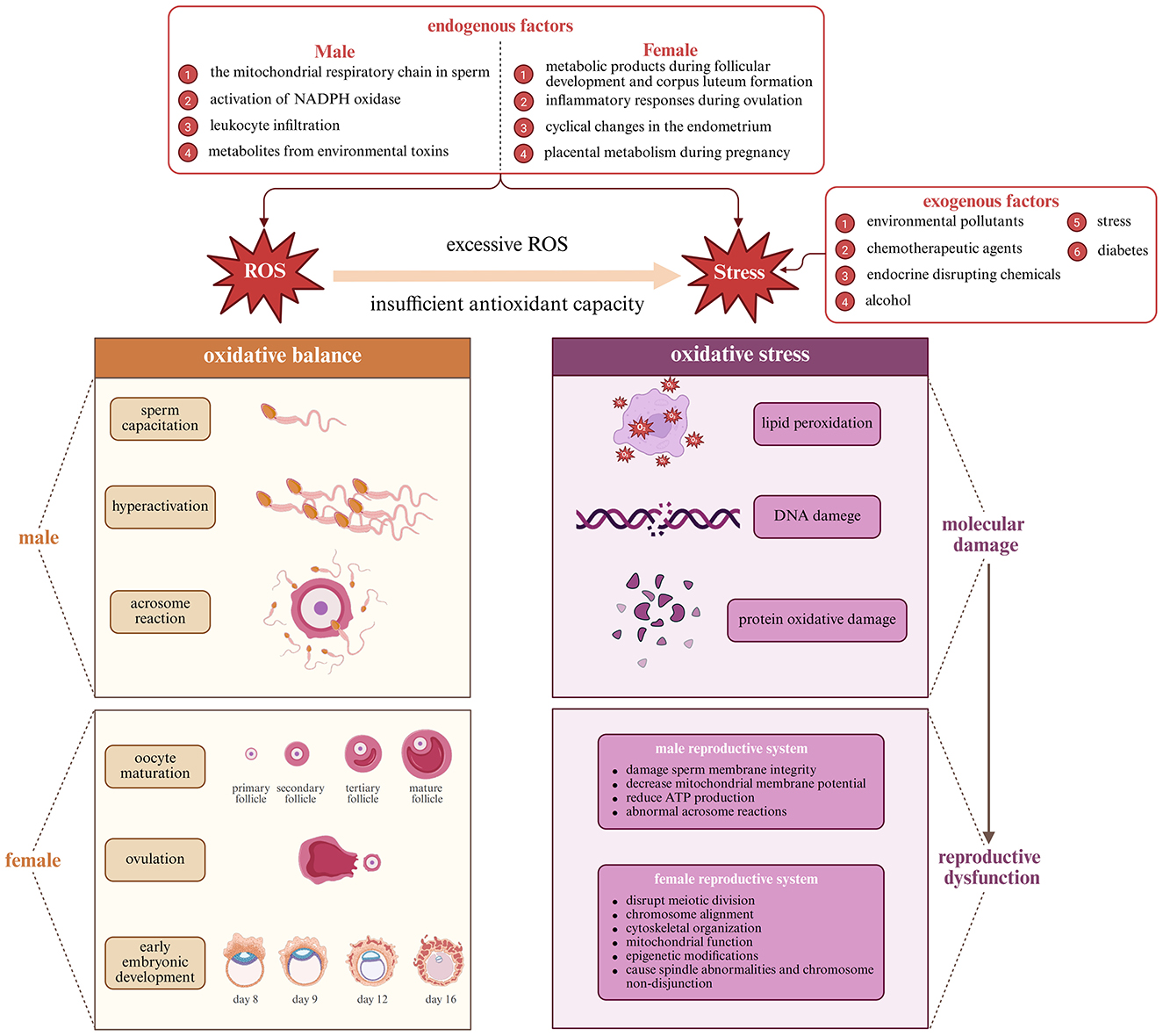
Figure 1. Antioxidant mechanisms of polyphenolic compounds (Created with BioRender.com).
2.3 Oxidative stress-mediated reproductive dysfunction
Excessive accumulation of ROS disrupts reproductive function by impairing gamete integrity, altering hormonal signaling, and promoting chronic inflammation (65–67). In sperm, ROS-driven lipid peroxidation compromises membrane fluidity, reduces mitochondrial membrane potential, and elevates DNA fragmentation—all of which impair motility and fertilization capacity (32, 39, 68). Oocytes subjected to oxidative insult exhibit disrupted spindle microtubule assembly, chromosomal missegregation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, contributing to aneuploidy and embryo arrest (66, 69, 70). In parallel, ROS dysregulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis by inhibiting GnRH pulsatility, suppressing gonadotropin secretion, and impairing steroidogenic enzyme function in the gonads. Follicular atresia and testicular germ cell apoptosis are accelerated, thereby reducing ovarian reserve and sperm output (32, 39, 65, 68, 71). ROS also amplify inflammation by activating NF-κB, which induces cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, creating a self-perpetuating inflammatory-oxidative feedback loop that degrades reproductive tissues over time (71–73). The cumulative impact of these mechanisms is diagrammed in Figure 1, highlighting the systemic nature of ROS-induced reproductive failure.
2.4 Oxidative damage biomarkers in the reproductive system
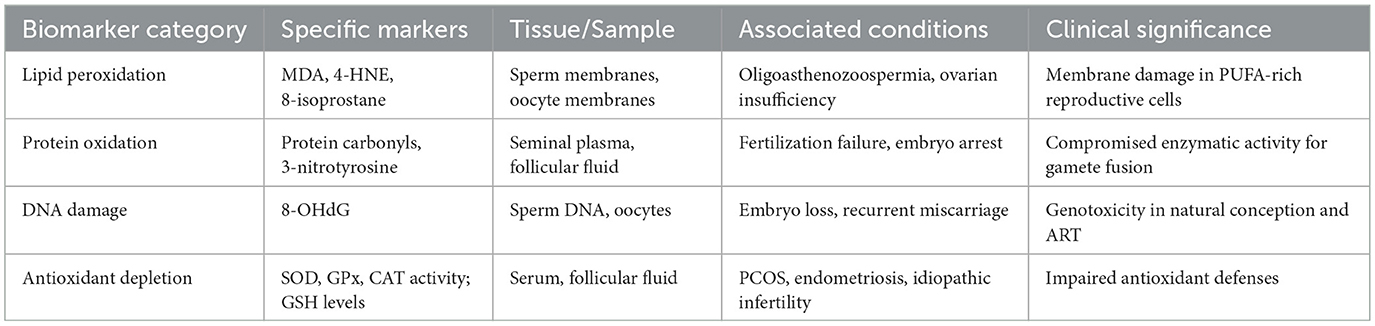
Biochemical markers of oxidative damage provide important diagnostic and mechanistic insights into redox imbalance in reproductive biology (29, 74). Among these, lipid peroxidation indicators, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), and 8-isoprostane, are frequently used to assess oxidative damage in sperm and oocyte membranes (75–77). Protein oxidation products, including protein carbonyls and nitrated residues like 3-nitrotyrosine, can compromise enzymatic activity essential for gamete fusion and fertilization (77–82). The DNA oxidation marker 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) is widely recognized as a surrogate indicator of ROS-mediated genotoxicity and has been associated with embryo loss and recurrent miscarriage in both natural conception and assisted reproductive technology (ART) settings (76, 83, 84). Impaired antioxidant defenses, characterized by reduced activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase (CAT), along with decreased glutathione levels, are commonly observed in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and idiopathic infertility (43, 77, 85–87). Figure 2 classifies these biomarkers based on their molecular origin and functional relevance, highlighting their value in assessing oxidative damage and monitoring therapeutic outcomes. Table 1 provides a comprehensive overview of these oxidative stress biomarkers, their tissue distribution, associated reproductive conditions, and clinical significance for diagnostic and therapeutic monitoring.
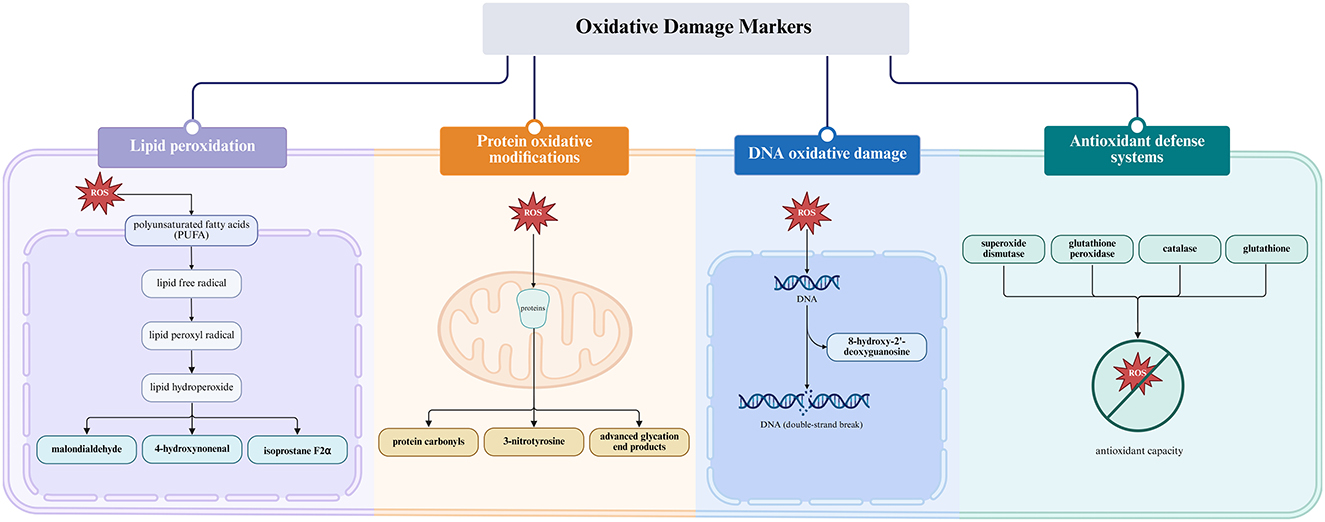
Figure 2. Oxidative balance and oxidative stress in reproductive systems (Created with BioRender.com).
3 Major plant-derived food bioactive substances and their antioxidant properties
3.1 Polyphenols: chemical structure and antioxidant mechanisms
Polyphenolic compounds represent nature's most diverse and abundant antioxidants, characterized by their multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups attached to aromatic rings (88, 89). These plant secondary metabolites comprise several major structural classes including flavonoids (quercetin, kaempferol, and apigenin), catechins (epigallocatechin gallate, epicatechin), anthocyanins (cyanidin, delphinidin), and phenolic acids (caffeic acid, ferulic acid) (90–92). The antioxidant capacity of polyphenols correlates directly with their chemical structure, particularly the number and position of hydroxyl groups, presence of extended conjugation, and spatial configuration (92, 93).
Polyphenols exert antioxidant effects through multiple mechanisms beyond simple free radical neutralization. At the molecular level, their phenolic hydroxyl groups readily donate hydrogen atoms to neutralize reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, forming relatively stable phenoxyl radicals through resonance delocalization across aromatic rings (94–97). Additionally, many polyphenols effectively chelate transition metals such as iron and copper, preventing Fenton reactions that generate highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (94, 98–100).
Beyond direct chemical interactions with ROS, polyphenols modulate cellular signaling pathways that regulate oxidative homeostasis. A particularly significant mechanism involves activation of the Keap1-Nrf2 (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-Nuclear factor erythroid 2) pathway (101, 102). Polyphenols modify Keap1 through covalent interactions or phosphorylation events, releasing Nrf2 from cytoplasmic sequestration (101, 102). Translocated to the nucleus, Nrf2 binds to Antioxidant Response Element (ARE) sequences in the promoter regions of numerous antioxidant enzymes, including glutathione S-transferase, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1, and heme oxygenase-1, effectively amplifying endogenous antioxidant capacity (103, 104).
Simultaneously, many polyphenols inhibit pro-oxidant enzymes like xanthine oxidase, NADPH oxidase, and lipoxygenase, further reducing ROS generation at its source (105–110). This multi-level intervention in oxidative processes contributes to their potent protective effects in reproductive tissues. These antioxidant mechanisms of polyphenolic compounds are illustrated in Figure 3.
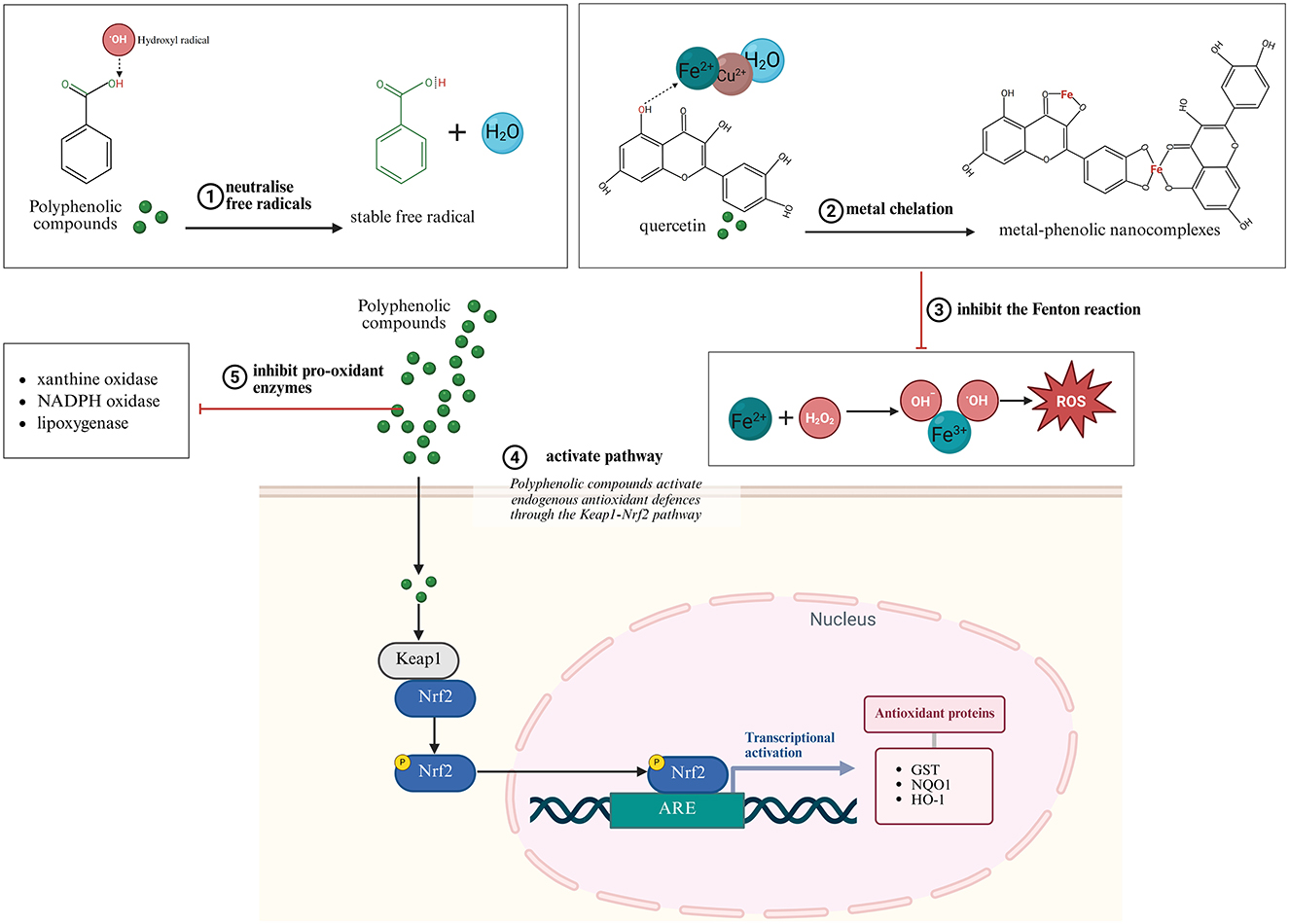
Figure 3. Biomarkers of oxidative stress (Created with BioRender.com).
3.2 Carotenoids: lycopene and lutein
Carotenoids constitute a family of lipophilic pigments characterized by a polyisoprenoid structure with an extensive conjugated double bond system (111). This chemical architecture enables carotenoids to quench singlet oxygen and neutralize peroxyl radicals particularly efficiently, with their antioxidant activity correlating directly with the number of conjugated double bonds (112, 113). The most biologically relevant carotenoids for reproductive health include lycopene (predominant in tomatoes) and lutein (abundant in green leafy vegetables), and β-carotene (found in orange and yellow vegetables) (111–115). The structural classification and distinct functional properties of major reproductive-relevant carotenoids are illustrated in Figure 4.
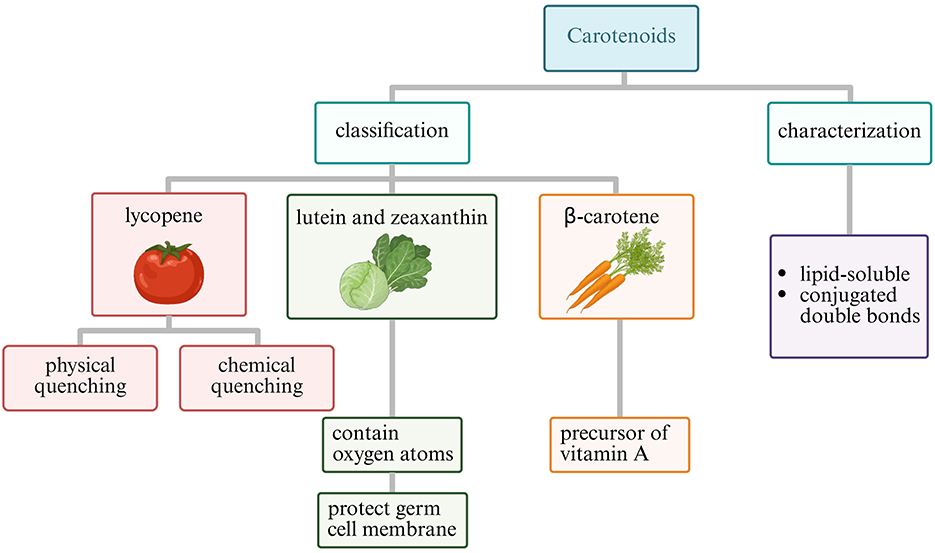
Figure 4. Classification of carotenoids relevant to reproductive health (Created with BioRender.com).
Lycopene, containing 11 conjugated and two non-conjugated double bonds, demonstrates the highest singlet oxygen quenching capacity among common carotenoids—approximately twice that of β-carotene (116). Its acyclic structure contributes to its exceptional antioxidant properties (117). Particularly noteworthy is lycopene's tissue-specific accumulation pattern, with concentrations in the prostate gland reaching levels up to 10-fold higher than those in serum, suggesting specialized uptake mechanisms and particular relevance for male reproductive health (116, 118–121).
Mechanistically, lycopene functions through both physical and chemical quenching of reactive species (122–124). In physical quenching, the carotenoid absorbs energy from singlet oxygen, transitioning to an excited triplet state before dissipating the energy as heat, returning to ground state without chemical alteration (122, 123). This process can be repeated multiple times, allowing a single lycopene molecule to deactivate numerous singlet oxygen molecules (122, 124, 125). Chemical quenching involves electron transfer or addition reactions with free radicals, effectively terminating radical chain reactions but resulting in lycopene oxidation (126–128).
Lutein belongs to the xanthophyll subclass of carotenoids, distinguished by the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups. These polar groups affect their orientation within biological membranes, with lutein spanning the lipid bilayer perpendicular to the membrane surface (129, 130). This specific membrane organization enables lutein to efficiently intercept lipid peroxyl radicals before they initiate chain reactions, particularly protecting the polyunsaturated fatty acid-rich membranes of developing oocytes and sperm cells (131–133). Research indicates that lutein's membrane-stabilizing effects contribute significantly to maintaining mitochondrial integrity under oxidative challenge—a critical factor for energy-intensive reproductive processes (134).
Unlike some antioxidants with restricted tissue distribution, carotenoids effectively cross both the blood-testis and blood-follicle barriers, providing direct protection to gametes (135). Their strong lipophilicity also facilitates accumulation in steroidogenic tissues, where they protect steroid-synthesizing enzymes from oxidative damage, potentially preserving hormonal balance essential for reproductive function (136–138).
3.3 Other active components: organosulfur compounds
Beyond polyphenols and carotenoids, several other phytochemical classes demonstrate significant antioxidant activity relevant to reproductive health. Organosulfur compounds, predominantly found in Allium species (garlic, onions) and cruciferous vegetables, represent a structurally diverse group including allicin, diallyl sulfides, and isothiocyanates (139–141). These compounds feature reactive sulfur-containing functional groups that provide unique biochemical properties extending beyond conventional antioxidant mechanisms.
Allicin (diallyl thiosulfinate), formed when garlic is crushed through the enzymatic action of alliinase on alliin, contains a reactive thiosulfinate group that interacts with thiol-containing proteins. This interaction affects multiple redox-sensitive enzymes and transcription factors (142–144). Rather than acting primarily as direct radical scavengers, organosulfur compounds function as indirect antioxidants by potently inducing phase II detoxification enzymes through the Nrf2 pathway. Additionally, they upregulate thioredoxin and glutathione systems—critical components of cellular redox homeostasis in reproductive tissues (145–147).
S-allylcysteine and S-allylmercaptocysteine, water-soluble organosulfur derivatives found in aged garlic extracts, demonstrate particular efficacy in reproductive protection. These compounds preserve mitochondrial function under oxidative challenge, inhibit lipid peroxidation cascades, and modulate inflammatory prostaglandin production (148–151). Studies indicate they maintain sperm membrane integrity and motility when exposed to oxidative insults, suggesting specific applications in male fertility preservation (149, 150, 152).
3.4 Bioavailability and action targets
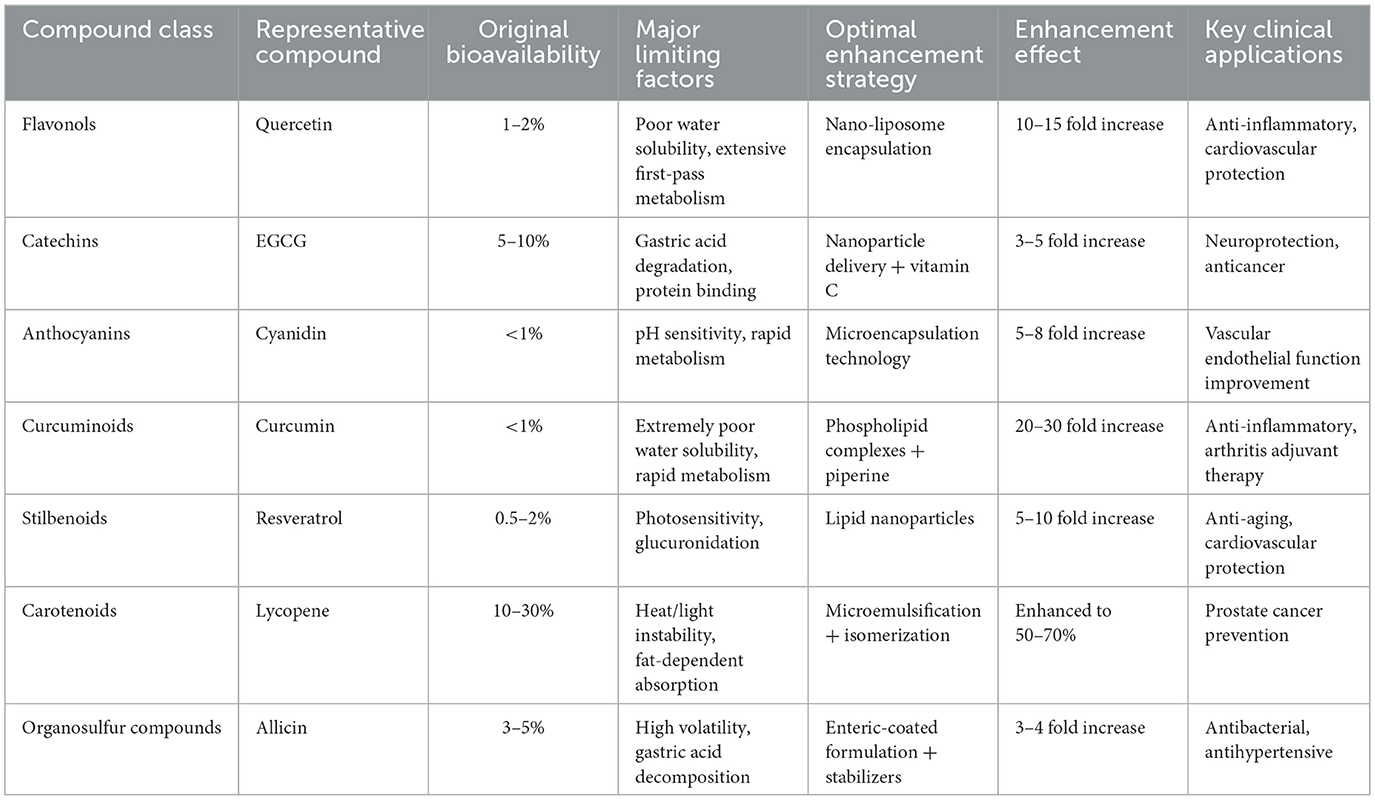
The therapeutic potential of plant-derived antioxidants faces a significant challenge: their limited bioavailability (91, 153, 154). The very chemical properties that make polyphenols and carotenoids such effective antioxidants—their aromatic rings, extensive conjugation, and hydroxyl groups—also contribute to poor water solubility, limited absorption, extensive first-pass metabolism, and rapid elimination. Most compounds demonstrate systemic bioavailability below 10% when administered in conventional forms, substantially limiting their biological effects (91, 153, 155–157).
Bioavailability varies considerably between compounds and depends on multiple factors including molecular size, lipophilicity, solubility, pKa, and matrix effects (158, 159). Carotenoids illustrate how food processing dramatically influences absorption—cooking tomatoes in oil increases lycopene bioavailability by up to fivefold compared to raw consumption, as heat disrupts cellular structures while lipids facilitate incorporation into mixed micelles necessary for intestinal uptake (158, 160, 161). For polyphenols like anthocyanins, intact glycosides are absorbed differently than their aglycone counterparts, with transporter-mediated uptake playing a crucial role (162, 163).
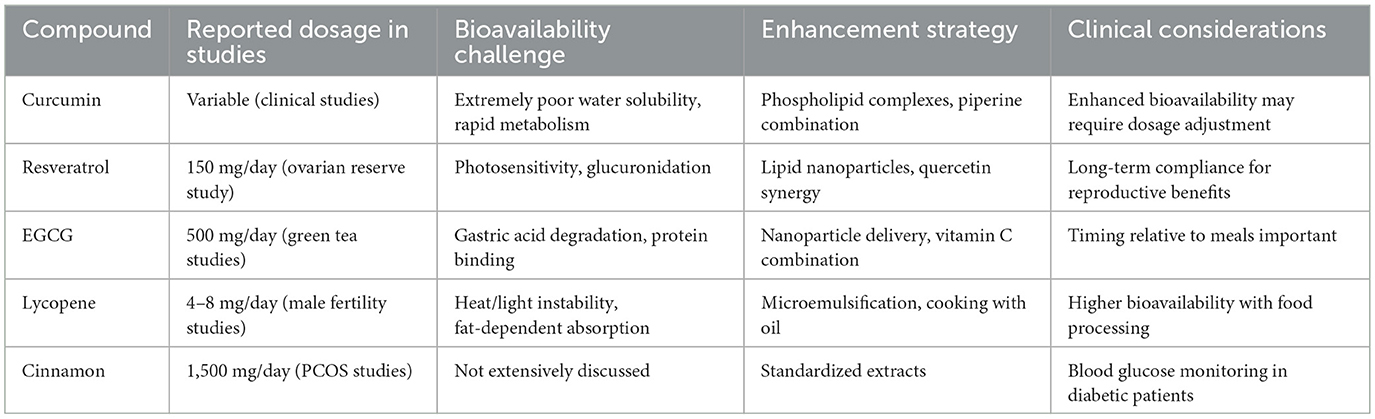
Compounds including curcumin and resveratrol face particularly profound bioavailability challenges. Despite demonstrated efficacy in vitro, curcumin's poor aqueous solubility, chemical instability at physiological pH, and extensive metabolism result in barely detectable plasma concentrations after oral administration (164–167). Similarly, resveratrol undergoes extensive sulfation and glucuronidation, with free resveratrol representing less than 1% of total plasma resveratrol after oral dosing (168–171).
To address these limitations, several innovative delivery strategies have emerged. Nanoencapsulation techniques using liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, or polymeric micelles dramatically improve water dispersibility while protecting compounds from premature degradation (172–174). Phospholipid complexation enhances membrane transport and tissue distribution by improving amphipathic properties (175). Formulation with absorption enhancers like piperine inhibits conjugating enzymes and efflux transporters, significantly increasing bioavailability. For instance, piperine co-administration increases curcumin bioavailability by up to 2,000%, though the clinical significance of this enhancement in humans requires further validation (176, 177).
The molecular targets of plant-derived antioxidants extend far beyond direct radical scavenging, revealing sophisticated mechanisms that explain their effects on reproductive health. Many compounds modulate key transcription factors that serve as master regulators of cellular redox status. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation by polyphenols and curcumin triggers coordinated upregulation of dozens of cytoprotective enzymes, creating persistent protection that outlasts the compound's presence. Simultaneously, inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) suppresses inflammatory cascades that would otherwise amplify oxidative damage (178–181).
Plant antioxidants also demonstrate remarkable specificity for critical reproductive targets. Epigallocatechin gallate and resveratrol modulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity, improving insulin sensitivity crucial for hormonal balance in polycystic ovary syndrome (182–184). Flavonoids and carotenoids directly influence mitochondrial function—the energy and ROS production centers within reproductive cells—by stabilizing membranes, improving electron transport efficiency, and activating mitochondrial antioxidant systems. These targeted effects explain why plant-derived compounds often show reproductive benefits that exceed what would be predicted from their direct radical scavenging capacity alone (183). Table 2 summarizes the bioavailability challenges faced by major plant antioxidant classes and the corresponding enhancement strategies that have proven most effective in improving their therapeutic potential.
3.5 Integrated antioxidant mechanisms and signaling pathway regulation
Plant-derived antioxidants protect reproductive function through an integrated network of mechanisms that extend beyond simple ROS neutralization. The coordinated regulation of multiple signaling pathways generates synergistic protective effects, addressing the multifactorial nature of reproductive oxidative stress through the engagement of diverse cellular defense systems.
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1–Nuclear factor erythroid 2–Antioxidant Response Element pathway (Keap1–Nrf2–ARE) is a master regulator of cellular antioxidant responses and a primary target for many plant compounds (185–187). Under basal conditions, Nrf2 remains sequestered in the cytoplasm by Keap1 (64, 186, 187). Plant antioxidants can modify cysteine residues in Keap1, causing conformational changes that release Nrf2 and allow its nuclear translocation (186–188). Once in the nucleus, Nrf2 binds to antioxidant response elements and activates cytoprotective genes such as glutathione synthase, thioredoxin reductase, and heme oxygenase-1(64). This cascade amplifies antioxidant defenses and enhances resilience against oxidative insults in reproductive tissues.
The nuclear factor kappa B pathway (NF-κB ) represents another crucial target. Aberrant NF-κB activation drives pro-inflammatory cytokine production that exacerbates oxidative stress in reproductive pathologies (189, 190). Plant compounds such as curcumin, resveratrol, and EGCG inhibit NF-κB signaling by preventing IκB phosphorylation, blocking nuclear translocation, and suppressing DNA binding activity (16, 181, 189, 191). These anti-inflammatory actions directly complement antioxidant defenses, disrupting the feed-forward loop between inflammation and oxidative stress that underpins many reproductive disorders (16, 192).
Mitochondrial protection is equally significant for reproductive cells with high energy demands. Plant antioxidants activate SIRT1 and PGC-1α to promote mitochondrial biogenesis (193, 194), enhance the activity of mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes (193), improve electron transport chain efficiency (194), and regulate mitochondrial membrane permeability (194). Such preservation of mitochondrial integrity ensures sustained ATP production and reduces ROS overgeneration, processes that are critical for oocyte maturation and sperm motility.
Finally, metabolic regulation provides an additional protective layer, particularly in conditions such as PCOS and diabetic erectile dysfunction (ED) (195, 196). Plant compounds activate AMPK signaling, enhance glucose utilization, and regulate lipid metabolism (195). By addressing systemic metabolic dysregulation, these actions indirectly alleviate reproductive oxidative stress while reinforcing direct antioxidant effects.
Collectively, these mechanisms demonstrate how antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, mitochondrial, and metabolic pathways converge to safeguard reproductive health. Their simultaneous engagement distinguishes plant-derived antioxidants from conventional single-target drugs and helps explain their efficacy across diverse reproductive pathologies, as illustrated in Figure 5 and summarized in Table 3.
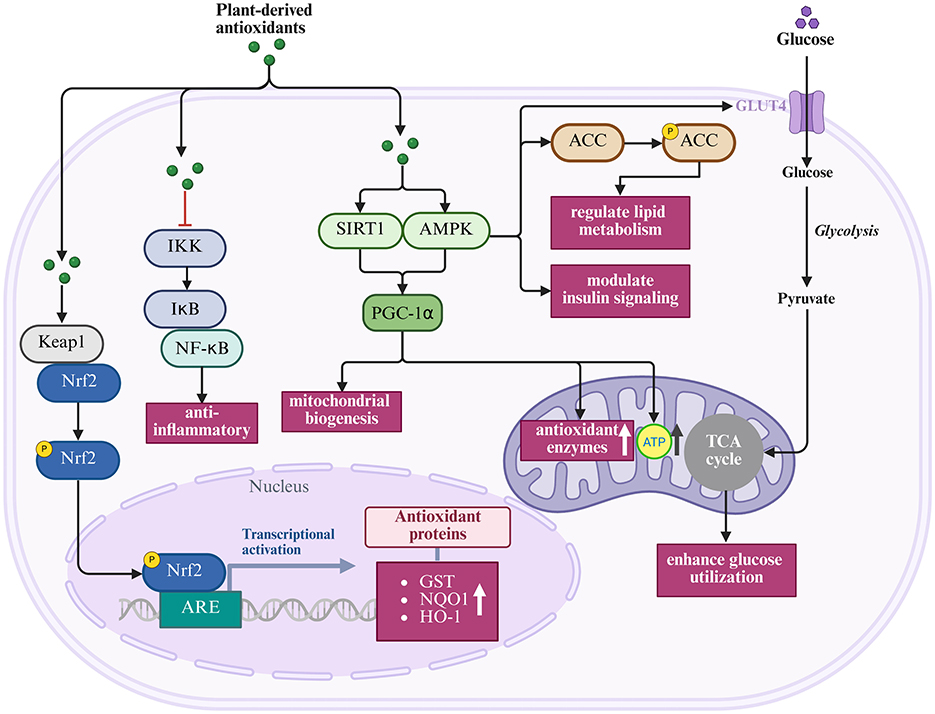
Figure 5. Integrated pathways regulated by plant-derived antioxidants (Created with BioRender.com).
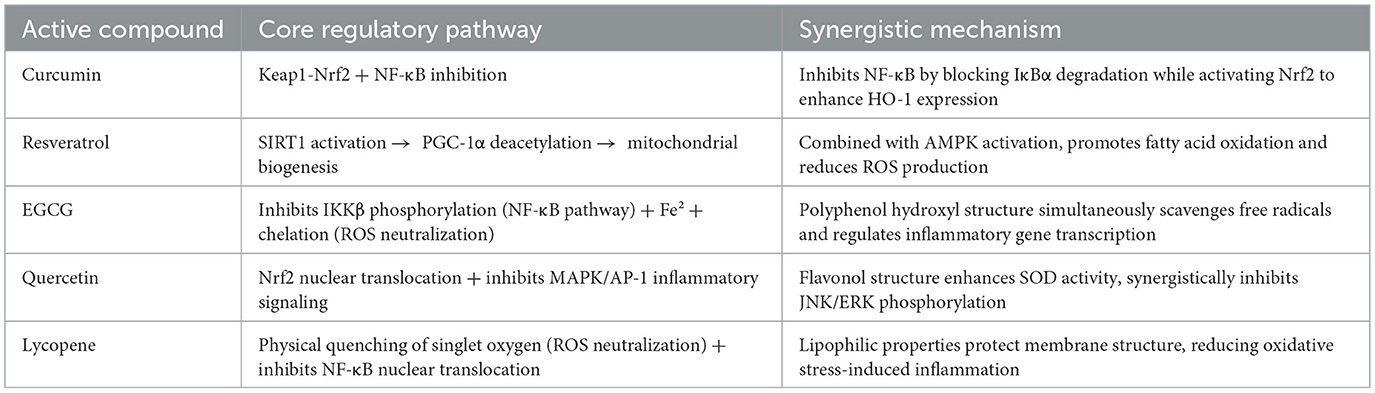
Table 3. Core regulatory pathways and synergistic mechanisms of major plant antioxidants in reproductive health.
4 Plant antioxidant interventions in reproductive diseases: clinical evidence and therapeutic strategies
Plant antioxidant interventions have shown promising therapeutic potential across major reproductive disorders, with clinical evidence supporting their efficacy in treating fertility issues, inflammatory conditions, and metabolic dysfunction.
4.1 Interventions in fertility disorders
Oxidative stress represents a major contributing factor to both male and female infertility, making plant-derived antioxidants attractive therapeutic candidates with growing clinical evidence.
4.1.1 Evidence-based approaches for male infertility
Oxidative stress represents a major contributing factor to male infertility, with studies indicating its involvement in 30%−80% of idiopathic infertility cases (197). Plant-derived antioxidants have demonstrated significant potential in addressing sperm oxidative damage and improving male fertility parameters through targeted interventions with strong clinical evidence (198–200).
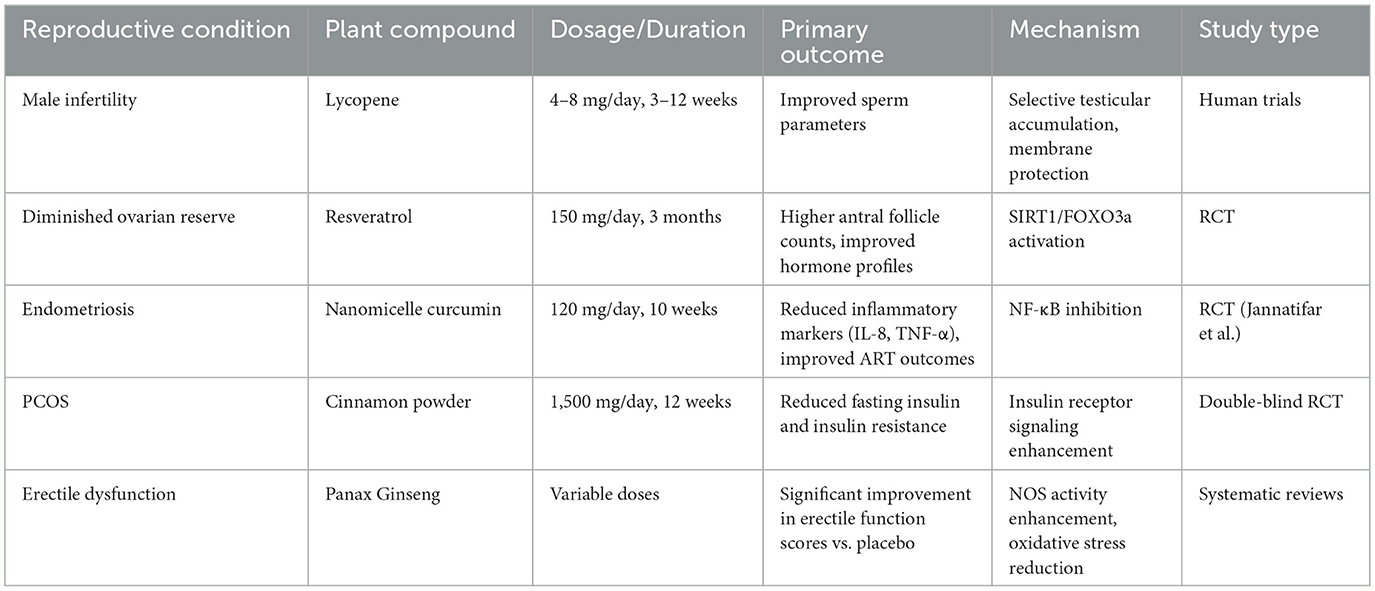
Lycopene has emerged as one of the most well-studied plant antioxidants for male fertility. Human trials reported that lycopene supplementation (4–8 mg daily for 3–12 weeks) significantly improved sperm parameters (116). Mechanistically, lycopene's selective accumulation in the testes (reaching concentrations 10-fold higher than serum levels) enables direct protection of developing sperm cells from oxidative damage (201).
Coenzyme Q10, though not strictly a plant compound but available in various plant sources, has demonstrated consistent benefits in male infertility treatment (202, 203). A meta-analysis including eight randomized controlled trials with a total of 877 male participants showed that CoQ10 supplementation significantly increased total sperm count, sperm motility, and progressive motility, and also improved the rate of normal sperm morphology (203). These improvements correlate with decreased oxidative stress markers in seminal plasma and reduced sperm DNA fragmentation, confirming the antioxidant mechanism underlying the clinical benefits (204).
Green tea catechins represent another promising intervention. Studies have shown that the addition of green tea extract during sperm cryopreservation can significantly improve sperm motility and DNA integrity (205–207). The combined antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of green tea catechins appear particularly beneficial for men with elevated seminal inflammatory markers (208, 209).
Combination approaches may offer enhanced therapeutic potential compared to single-compound interventions. Evidence suggests that the combination of Serenoa repens (saw palmetto) with lycopene and selenium shows greater efficacy than Serenoa alone in reducing prostate inflammation. While this combination theoretically may improve sperm quality through multiple pathways, clinical studies are still needed to verify its specific effects on fertility parameters (210). This potential synergistic effect likely results from complementary mechanisms targeting different aspects of oxidative damage protection.
Practical clinical considerations for male infertility management include initiating antioxidant therapy for at least 3 months (corresponding to the spermatogenic cycle); higher doses may be required for men with severe oxidative stress or inflammatory conditions; regular monitoring of seminal oxidative stress markers to assess treatment response; combining plant antioxidants with lifestyle modifications for optimal results; and considering individualized approaches based on specific infertility factors.
4.1.2 Botanical interventions for female fertility enhancement
Female reproductive function demonstrates particular vulnerability to oxidative damage, with both oocyte quality and ovarian reserve showing sensitivity to redox imbalances. The clinical application of plant antioxidants in female fertility has yielded promising results, though evidence levels vary across different compounds and conditions.
Resveratrol has shown remarkable potential in improving ovarian function and oocyte quality (211). In clinical research, resveratrol supplementation (150 mg/day for 3 months) significantly improved ovarian response in women with diminished ovarian reserve undergoing assisted reproduction, resulting in higher antral follicle counts and improved hormone profiles (212). The ability of resveratrol to activate SIRT1/FOXO3a pathways appears particularly beneficial for preserving follicular reserve and enhancing mitochondrial function in aging oocytes (213, 214).
Curcumin demonstrates significant potential for women with endometriosis-related infertility. A randomized clinical trial by Jannatifar et al. (215) investigated the effect of nanomicelle curcumin (120 mg/day for 10 weeks) in women with stage III/IV endometriosis undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART). The study showed that nanomicelle curcumin supplementation significantly reduced inflammatory markers (IL-8 and TNF-α) and oxidative stress biomarkers (MDA) in follicular fluid, while increasing antioxidant enzyme levels (TAC, CAT, and SOD). These biochemical improvements translated to enhanced ART outcomes, including increased number of mature oocytes, improved fertilization rates, and higher quality embryos. This correlates with reduced oxidative stress biomarkers in follicular fluid and normalized inflammatory markers (215).
Clinical application guidelines for female fertility include individualized selection of plant antioxidants based on specific fertility issues (216); initiating treatment at least 3 months before conception attempts for optimal effect (217); regular monitoring of ovarian reserve markers to assess response; careful consideration of dosage, as excessive antioxidant supplementation may paradoxically impair normal reproductive processes by disrupting physiological ROS signaling essential for fertilization and embryo development; and special attention to formulation quality and bioavailability enhancement (183, 216). Additionally, the timing of intervention appears critical, with benefits maximized when treatment begins well before assisted reproductive procedures.
4.2 Plant antioxidants in inflammation-related reproductive system diseases
Inflammatory conditions of the reproductive system, particularly endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), represent significant clinical challenges with substantial oxidative stress components. Plant antioxidants have emerged as promising non-hormonal management options with favorable side effect profiles in these conditions.
Curcumin has demonstrated particular efficacy in endometriosis management (218, 219). The latest randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that nanocurcumin (80 mg/day) combined with dienogest for 8 weeks significantly improved dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, chronic pelvic pain, and dyschezia in endometriosis patients, while enhancing quality of life and sexual function index (except for orgasm domain) (218). These clinical benefits correspond with curcumin's ability to inhibit endometriotic implant growth and invasiveness through multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of NF-κB activation, reduction of inflammatory cytokine production, decreased angiogenic factor expression, and induction of apoptosis in ectopic endometrial cells (219, 220). In endometriosis mouse models, curcumin treatment significantly reduced implanted endometrial lesions, attributed to inhibition of NF-κB translocation and reduction of angiogenic mediators (220).
Green tea polyphenols complement curcumin's effects in endometriosis management (221). Research indicates that EGCG can inhibit endometrial implant proliferation and adhesion while inducing apoptosis in ectopic tissue (221). Animal studies report that green tea extract reduced both the number and size of endometriosis lesions through antiangiogenic and antioxidant effects, suggesting effective disease progression control through simultaneous targeting of multiple pathological processes (221, 222).
Resveratrol represents another promising intervention, demonstrating powerful anti-inflammatory and antiangiogenic properties in endometriosis models (223). By inhibiting COX-2 and reducing prostaglandin synthesis, resveratrol mitigates inflammatory cytokine release. In an experiment, oral resveratrol administration to nude mice with human endometriosis implants significantly reduced lesion number and volume through blockade of NF-κB activation and disruption of the inflammatory microenvironment required for lesion maintenance (224).
For pelvic inflammatory disease, plant antioxidants serve as valuable adjuncts to antibiotic therapy (225). According to NHANES data, PID affects approximately 2.5 million women of reproductive age in the United States, and while antibiotic treatment can alleviate symptoms, poor obstetric outcomes and high recurrence rates persist. Studies indicate that antioxidant supplementation during and after antibiotic treatment can reduce residual oxidative damage, improve recovery rates, and potentially decrease the risk of post-inflammatory sequelae such as tubal factor infertility (226). This approach addresses the oxidative stress and inflammatory cascade that continue even after pathogen eradication. For example, a study on asiatic acid (AA) demonstrated that AA significantly inhibits oxidative stress, reduces cytokine and chemokine production, and decreases inflammatory cascade through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway, similar to mechanisms observed with other plant antioxidants such as curcumin and resveratrol in suppressing NF-κB activation. Complementary and alternative medicine as an adjunctive therapy to Western medicine has shown significant efficacy in PID treatment through dual mechanisms of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions, providing new strategies for improving patient outcomes (227).
In male reproductive tract inflammation, particularly prostatitis and epididymitis, plant antioxidants have also shown promising therapeutic potentia. Chronic prostatitis, affecting up to 50% of men during their lifetime, presents significant therapeutic challenges with substantial oxidative stress components. Recent studies have demonstrated that plant-derived antioxidants effectively modulate inflammatory pathways in male reproductive tissues (228). For instance, lycopene has shown remarkable therapeutic effects in epididymitis through multiple mechanisms: significantly reducing inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α), enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD, GSH-PX, and CAT), and inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (229). Similarly, curcumin has demonstrated efficacy in prostatitis management by suppressing NF-κB activation and reducing pro-inflammatory mediators, while quercetin has been clinically proven to improve symptoms in chronic prostatitis patients (230). These plant-based compounds not only complement antibiotic therapy but also address the persistent oxidative stress and inflammatory cascade that continue after infection resolution, potentially reducing long-term complications such as infertility and chronic pelvic pain syndrome in male patients.
4.3 Plant antioxidants in metabolic reproductive disorders
Metabolic reproductive disorders such as PCOS and erectile dysfunction require comprehensive approaches that simultaneously address oxidative stress and underlying metabolic imbalances.
4.3.1 Multi-target approach in polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) represents a complex endocrine-metabolic disorder characterized by a vicious cycle between insulin resistance and oxidative stress (16, 231, 232). Plant antioxidants offer unique therapeutic potential through multi-target regulation of these interlinked pathological processes.
Cinnamon extract demonstrates remarkable efficacy in PCOS management (16). In a study of 80 women with PCOS, daily administration of 1,500 mg cinnamon powder capsules for 12 weeks significantly reduced fasting insulin and insulin resistance. Another double-blind randomized controlled trial showed that 3 g/day of cinnamon extract significantly decreased fasting blood glucose (p = 0.001) and glycosylated hemoglobin (p = 0.023) (16). These improvements are attributed to cinnamon's ability to enhance insulin receptor signaling and its polyphenols acting as insulin mimetics (233). Additionally, cinnamon's antioxidants alleviate systemic oxidative stress, evidenced by significantly reduced serum MDA levels in cinnamon-treated PCOS patients (234).
Green tea catechins similarly demonstrate capacity to improve PCOS metabolic and endocrine states. Clinical trials in overweight PCOS women found that green tea extract (rich in EGCG) 500 mg/day for 12 weeks led to significantly reduced free testosterone and fasting insulin levels compared to baseline (235). Decreased free testosterone indicates alleviated hyperandrogenemia, partly attributed to improved insulin sensitivity (235). Green tea polyphenols not only increase antioxidant defenses but also possess anti-androgenic effects; by reducing ovarian oxidative stress, EGCG may help restore more normal hormonal balance and promote ovulation (235).
Curcumin's anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects effectively counter low-grade inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in PCOS (236, 237). In rodent models of PCOS, curcumin supplementation restored estrous cycles and reduced ovarian oxidative stress markers, improving oocyte quality and ovulation rates (238). Human research, though preliminary, shows encouraging results: PCOS patients taking curcumin (1,500 mg/day) for 12 weeks significantly lowered fasting blood glucose and insulin levels (237). Additionally, curcumin reduced oxidative stress biomarkers and increased total antioxidant capacity (236). These results align with curcumin's known ability to activate AMPK (enhancing insulin signaling) and upregulate Nrf2-dependent antioxidants, thereby breaking the insulin resistance-oxidative stress cycle (239).
Resveratrol also demonstrates significant metabolic and endocrine benefits in PCOS. In a double-blind trial, PCOS women taking resveratrol (1,500 mg/day) for 3 months showed 23% reduced total testosterone and 22% reduced dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels, while the placebo group showed no significant changes (240). This significant androgen level reduction suggests resveratrol directly improves ovarian steroidogenesis, possibly through reducing ovarian theca cell hyperresponsiveness. Resveratrol-treated patients also showed improved insulin sensitivity and mild weight reduction, though not all parameters reached statistical significance (240).
Clinical implementation considerations for PCOS include the importance of individualized approaches based on PCOS phenotype; the value of combining multiple plant antioxidants to address different aspects of this heterogeneous syndrome; and the need for sufficient treatment duration (minimum 12 weeks) to achieve measurable improvements in metabolic and reproductive parameters.
4.3.2 Therapeutic strategies for erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) represents a common complication with complex pathophysiology involving endothelial dysfunction and reduced nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability (241). Metabolic diseases such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity contribute to ED through shared mechanisms (242–244). Plant antioxidants offer promising therapeutic options by targeting these fundamental mechanisms.
Panax Ginseng and its active components ginsenosides have attracted attention for their potential to improve erectile function (245, 246). Studies indicate that ginsenosides possess antioxidant properties that can enhance nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity in cavernosal endothelial cells, reducing oxidative stress damage to vascular endothelium, thereby promoting NO-mediated smooth muscle relaxation and improving erectile function (245, 246). Systematic reviews of multiple clinical trials have shown that compared to placebo, ginseng preparations can significantly improve erectile function scores in ED patients, which is consistent with their antioxidant and NO-promoting mechanisms of action, despite some heterogeneity in study design and preparations used (247–249).
Pycnogenol® (French maritime pine bark extract) is a standardized extract rich in powerful antioxidants including proanthocyanidins, catechins, and phenolic acids that directly target endothelial dysfunction associated with ED (250). Research confirms that Pycnogenol® enhances endothelial NO production by increasing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity and protects the generated NO from degradation by scavenging superoxide anion radicals, thereby improving its bioavailability (250). Its powerful antioxidant capacity helps reduce vascular oxidative stress. Clinical trials, particularly those combining Pycnogenol® with the NO precursor L-arginine, report significant improvements in men's erectile function scores, an effect attributed to synergistically enhanced NO bioavailability and vascular endothelial protection (251).
Pomegranate (Punica granatum) is rich in potent polyphenolic antioxidants such as punicalagins and ellagic acid that effectively combat oxidative stress (252, 253). Preclinical studies and some clinical evidence suggest that pomegranate and its extracts can promote cardiovascular health by improving endothelial function and reducing oxidative stress levels (253, 254). Research indicates that pomegranate juice can enhance NO bioavailability by protecting NO from oxidative destruction and possibly upregulating eNOS expression (255). Although large-scale clinical evidence for ED is limited, a preliminary study observed improvements in erectile function scores in some men with mild to moderate ED after consuming pomegranate juice, suggesting the need for larger controlled trials for verification (256). The core mechanism for its potential vascular benefits (relevant to ED) is believed to be the reduction of systemic and vascular oxidative stress, thus protecting the NO signaling pathway critical for erectile response (253, 254).
Green tea catechins, particularly EGCG, show broad prospects for alleviating ED. In animal studies, EGCG supplementation preserved cavernosal smooth muscle content and improved erectile responses (257). One study found that rats receiving EGCG (with sildenafil) showed significantly increased eNOS expression and cyclic guanosine monophosphate levels in cavernosal tissues, with reduced MDA (lipid peroxidation marker) levels, compared to untreated groups (258). This indicates that EGCG enhances NO signaling and reduces oxidative damage in penile tissues (257). Researchers concluded that EGCG serves as a “cavernosal antioxidant,” potentially offering useful adjunctive therapy to PDE5 inhibitors for patients (258).
Curcumin, despite its broad antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, faces bioavailability challenges in ED treatment (259, 260). Recent innovations using topically applied curcumin-loaded nanoparticles found significantly improved erectile function parameters (261). This provides evidence that curcumin can protect erectile function by improving penile endothelial function and reducing fibrosis and oxidative damage. Studies have shown that administration of curcumin or its water-soluble conjugate led to enhancement of erectile function in diabetes induced-erectile dysfunction by stimulating increased synthesis of endothelial NOS and neuronal NOS (262, 263).
Clinical application considerations include the potential for plant antioxidants as adjunctive therapy alongside conventional PDE5 inhibitors; the importance of early intervention, ideally at the first signs of metabolic complications; and the value of addressing both metabolic control and oxidative stress simultaneously for optimal outcomes. Comprehensive treatment approaches combining lifestyle modifications with targeted antioxidant supplementation may provide the most effective strategy for improving erectile function, especially in cases where ED is driven by metabolic disorders and oxidative stress. Table 4 consolidates the clinical evidence for plant antioxidants across various reproductive disorders, including dosage regimens, primary outcomes, and underlying mechanisms demonstrated in human studies.
5 Bioavailability enhancement strategies and functional food development
5.1 Formulation strategies for enhanced bioavailability
A key challenge limiting the clinical efficacy of plant antioxidants lies in their generally poor bioavailability. Novel formulation technologies have emerged to address this critical issue, significantly enhancing the therapeutic potential of these compounds in reproductive health applications.
Nanoencapsulation techniques represent a major advancement in plant antioxidant delivery (264, 265). Liposomal encapsulation markedly enhances the bioavailability of compounds like curcumin and resveratrol, with some studies reporting up to a five-fold increase in blood concentrations (266–268). Nanoemulsion technology can enhance the solubility and cellular uptake of lipophilic compounds such as lycopene and carotenoids, and may promote their distribution in biological fluids and improve in vivo bioavailability (269, 270). Solid lipid nanoparticles offer additional advantages of controlled release profiles and enhanced stability during gastrointestinal transit, which proves particularly valuable for compounds prone to degradation in acidic environments (271–273).
Phospholipid complexation substantially improves the pharmacokinetic profiles of many plant antioxidants (274, 275). Through the formation of amphipathic complexes with phospholipids, EGCG demonstrates enhanced membrane permeability and improved bioavailability (276). Animal pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that phospholipid-complexed curcumin exhibits approximately a fivefold increase in plasma concentration compared to standard curcumin formulations (277). This technology particularly benefits reproductive applications where penetration of blood-testis and blood-follicle barriers proves crucial for therapeutic efficacy.
Enzyme inhibition strategies represent another effective approach to enhancing bioavailability. Piperine, a major component of black pepper, inhibits UDP-glucuronosyltransferase and hepatic arylhydrocarbon hydroxylase, thereby reducing the first-pass metabolism of compounds such as curcumin. Clinical studies have demonstrated that co-administration of piperine (20 mg) with curcumin can increase curcumin's bioavailability by up to 2,000%, although this widely cited figure remains subject to debate regarding its actual therapeutic impact in clinical settings (278). Similarly, certain flavonoids like quercetin have been reported to inhibit metabolizing enzymes when co-administered with specific compounds, potentially prolonging their half-lives and enhancing therapeutic efficacy (279).
Chemical modification approaches, while more complex, offer significant potential. Developing water-soluble derivatives of lycopene and other carotenoids has shown promise in preclinical studies, with these modified compounds maintaining antioxidant activity while exhibiting superior absorption characteristics. Similarly, synthesizing pro-drug forms of plant polyphenols that undergo enzymatic activation in target tissues can enhance tissue-specific delivery and reduce systemic side effects.
Implementation considerations for clinical practice include recognizing that different plant antioxidants benefit from different enhancement technologies; considering potential interactions between delivery systems and the antioxidant mechanisms of the compounds; and acknowledging that enhanced bioavailability may necessitate dosage adjustments to maintain optimal safety profiles. Table 5 provides practical guidance on clinical dosing and bioavailability considerations for the major plant antioxidants discussed, facilitating evidence-based implementation in reproductive health practice.
5.2 Functional food development for reproductive health
Translating plant antioxidant research into accessible functional food products represents an important strategy for reproductive health protection. Functional food development requires specific design principles, with formulations incorporating complementary antioxidants in physiologically relevant ratios. For instance, combining lycopene, selenium, and zinc has demonstrated synergistic effects in improving male fertility (280). Matrix selection significantly impacts stability and bioavailability—lipid matrices enhance absorption of lipophilic antioxidants, while protein matrices support sustained release of polyphenolic compounds (281). Processing parameters must be optimized to maintain bioactivity while ensuring safety and shelf life, with techniques such as microencapsulation and freeze-drying widely applied (281). Sensory characteristics determine consumer acceptance, with taste and texture influencing long-term compliance—particularly important for reproductive interventions requiring extended periods (282, 283).
Fortified beverages represent widely applied functional food formats. Green tea beverages have demonstrated significant effects on male sperm parameters, including enhanced motility and DNA integrity protection (206, 284, 285). Pomegranate juice has shown improvements in mild erectile dysfunction, with mechanisms linked to enhanced nitric oxide bioavailability (286, 287). While convenient, beverages have limited carrier capacity for lipophilic compounds, which can be addressed through emulsifiers or nanoemulsion technologies (288–291).
Stability control represents a key challenge, addressed through co-antioxidants, microencapsulation techniques, and appropriate packaging systems (292–295). Quality control and standardization ensure safety and efficacy, including toxicological analysis and monitoring batch-to-batch variation. Regulatory frameworks vary between regions, with the US FDA allowing relatively relaxed structure-function claims, while EFSA requires health claims based on substantial clinical evidence (296–298).
In conclusion, functional food development for reproductive health has established systematic frameworks encompassing formulation design, carrier selection, and stability control. By optimizing these factors, the bioavailability and stability of plant antioxidants can be enhanced, providing practical pathways for application in reproductive health protection. Table 6 outlines potential functional food development applications based on the evidence presented, illustrating how plant antioxidants can be translated into practical interventions for reproductive health promotion.
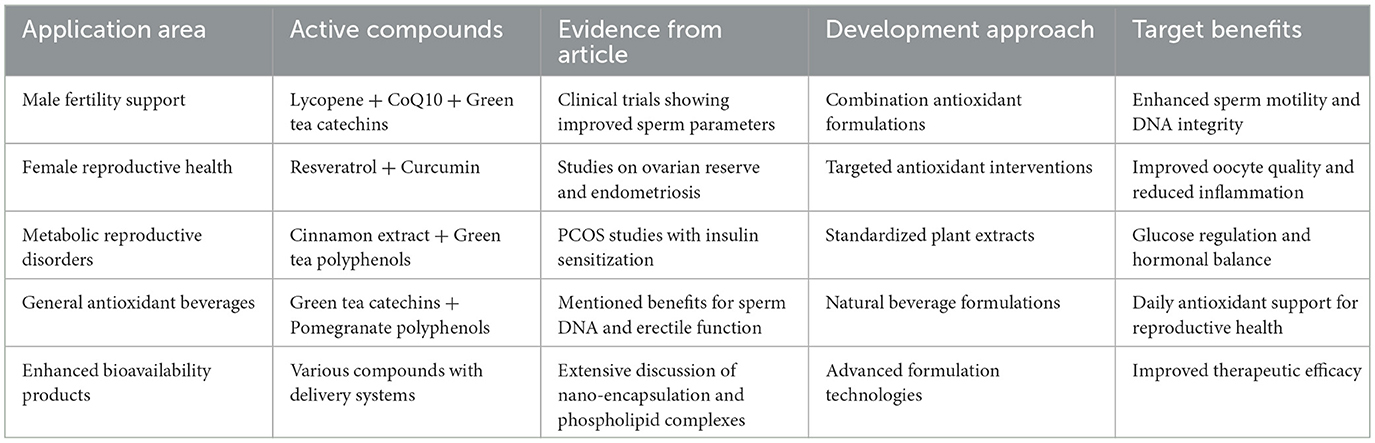
Table 6. Functional food development applications for reproductive health based on evidence from research studies.
6 Future perspectives and conclusions
This review systematically explored the regulatory effects of bioactive components from plant-based foods on reproductive system oxidative stress and their protective mechanisms. By integrating the latest research advances, we examined the relationship between oxidative stress and reproductive dysfunction, analyzed how plant-derived antioxidants protect against inflammation-related and metabolism-related reproductive diseases, and evaluated their application in treating male and female infertility. From a food science perspective, we highlighted the sources, bioavailability, and optimal delivery methods of these bioactive compounds, providing a comprehensive framework for translating laboratory findings into practical dietary strategies and functional food development for reproductive health protection.
Future research should elucidate the tissue-specific mechanisms of plant active components in reproductive tissues; develop bioavailability enhancement technologies to overcome the limitations of low bioavailability; evaluate the synergistic effects of multiple plant active components to optimize combination strategies; and conduct standardized long-term clinical studies to establish optimal intervention protocols for different reproductive disorders. Emerging advanced techniques, such as single-cell RNA sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and integrative metabolomics, offer powerful tools to address these questions. Single-cell and spatial approaches enable the dissection of tissue- and cell-type–specific gene expression patterns within reproductive organs, while high-resolution metabolomics combined with bioinformatics pipelines allows the identification of metabolic signatures that couple with these transcriptional programs (299). Such integrated multi-omics strategies will provide a concrete framework to link plant-derived antioxidant interventions with tissue-specific molecular pathways, thereby advancing precision reproductive medicine. Additionally, integration with functional genomics and bioinformatics will promote the development of personalized antioxidant intervention strategies.
Another critical future direction involves the establishment of uniform dosage standards for plant extracts in clinical trials. Variability in plant origin, cultivation conditions, harvest time, and processing methods often leads to inconsistencies in bioactive compound concentrations, thereby complicating dose–response evaluation. To overcome these uncertainties, standardized extraction protocols, chemical fingerprinting, and quantification of key bioactive components should be routinely applied. In addition, adherence to good manufacturing practice guidelines and the development of internationally recognized reference standards will be essential to ensure reproducibility and comparability across studies. Such measures will facilitate the reliable translation of plant-based bioactives into clinical and functional food applications.
It should also be noted that plant-derived antioxidants may exert dose-dependent biphasic effects, exhibiting potential pro-oxidant activity under specific concentrations or redox conditions. Moreover, prolonged or high-dose use could pose risks of unknown toxicity or adverse interactions, particularly when combined with pharmaceuticals or other dietary supplements. Therefore, future clinical research should incorporate rigorous dose–response studies, long-term safety evaluations, and systematic monitoring of potential drug–nutrient and nutrient–nutrient interactions to ensure both efficacy and safety in translational applications.
In addition, the future translation of these findings into clinical and functional food applications will require rigorous safety evaluation and compliance with regulatory frameworks to ensure both efficacy and consumer protection. Overall, plant-derived bioactive substances regulate reproductive system oxidative stress through multi-pathway protective mechanisms, providing significant interventions from inflammation inhibition to metabolic improvement. Combined with functional food development, these compounds hold strong potential to deliver safe, effective, and sustainable solutions for reproductive health challenges.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. TZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. EZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation. CB: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. QL: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Supervision. KW: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft, Software, Validation. SW: Writing – review & editing, Software, Writing – original draft, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by the grants of: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82174431); The National Celebrated Traditional Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Studio of S-BW (Project No: CJJ2023062).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The author(s) confirm that generative AI tools were employed in the preparation of this manuscript. Specifically, generative AI (Claude 3.7 Sonnet by Anthropic) was used to assist in drafting the abstract and refining selected sections of the main text. All AI-generated content has been thoroughly reviewed, edited, and verified by the author(s) to ensure accuracy, originality, and scientific integrity. The author(s) take full responsibility for the content of the manuscript, including all statements produced or enhanced by generative AI.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ombelet W. WHO fact sheet on infertility gives hope to millions of infertile couples worldwide. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. (2020) 12:249–51.
3. Kazandi M, Gunday O, Mermer TK, Erturk N, Ozkinay E. The status of depression and anxiety in infertile Turkish couples. Iran J Reprod Med. (2011) 9:99.
4. Cui C, Wang L, Wang X. Effects of self-esteem on the associations between infertility-related stress and psychological distress among infertile Chinese women: a cross-sectional study. Psychol Res Behav Manage. (2021) 14:1245–55. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S326994
5. Ombelet W, Cooke I, Dyer S, Serour G, Devroey P. Infertility and the provision of infertility medical services in developing countries. Hum Reprod Update. (2008) 14:605–21. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmn042
6. Lee MC, Chien PS, Zhou Y, Yu T. Prevalence and help-seeking for infertility in a population with a low fertility rate. PLoS ONE. (2024) 19:e0306572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306572
7. Wang Y, Kong F, Fu Y, Qiao J. How can China tackle its declining fertility rate? BMJ. (2024) 386:e078635. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-078635
8. Pavlova SA, Plokhotnikova AI, Sarlova AB, Katsyna AR, Troian NA. Impact of climate change, environmental pollution, and nutrition on women's reproductive health. VF Snegirev Archiv Obstet Gynecol. (2024) 11:245–54. doi: 10.17816/aog627079
9. Itziou A, Balis V, Lakioti E, Karayannis V, Tsanaktsidis C. Environmental pollution and oxidative stress: health effects during pregnancy: a review. Appl Sci. (2024) 14:9884. doi: 10.3390/app14219884
10. Ono M, Dai Y, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H, Daikoku T, Ando H, et al. Influence of lifestyle and the circadian clock on reproduction. Reprod Med Biol. (2025) 24:e12641. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12641
11. Meli R, Monnolo A, Annunziata C, Pirozzi C, Ferrante MC. Oxidative stress and BPA toxicity: an antioxidant approach for male and female reproductive dysfunction. Antioxidants. (2020) 9:405. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050405
12. Jomova K, Raptova R, Alomar SY, Alwasel SH, Nepovimova E, Kuca K, et al. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Arch Toxicol. (2023) 97:2499–574. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9
13. Walke G, Gaurkar SS, Prasad R, Lohakare T, Wanjari M. The impact of oxidative stress on male reproductive function: exploring the role of antioxidant supplementation. Cureus. (2023) 15:e42583. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42583
14. Zhang X, Wu XQ, Lu S, Guo YL, Ma X. Deficit of mitochondria-derived ATP during oxidative stress impairs mouse MII oocyte spindles. Cell Res. (2006) 16:841–50. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310095
15. Huang Y, Cui Y, Huang J, Xinyuan H, Zihang W, Luo T, et al. Proanthocyanidins protects 3-NPA-induced ovarian function decline by activating SESTRIN2-NRF2-mediated oxidative stress in mice. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:25643. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76743-w
16. Rudnicka E, Duszewska AM, Kucharski M, Tyczyński P, Smolarczyk R. Oxidative stress and reproductive function: oxidative stress in polycystic ovary syndrome. Reproduction. (2022) 164:F145–54. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0152
17. Mackay A, Taylor S, Glass B. Inequity of access: scoping the barriers to assisted reproductive technologies. Pharmacy. (2023) 11:17. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy11010017
18. Bahamondes L, Makuch MY. Infertility care and the introduction of new reproductive technologies in poor resource settings. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2014) 12:87. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-87
19. Coussa A, Hasan H, Barber T. Impact of contraception and IVF hormones on metabolic, endocrine, and inflammatory status. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2020) 37:1267–72. doi: 10.1007/s10815-020-01756-z
20. Sunderam S, Kissin DM, Zhang Y, Jewett A, Boulet SL, Warner L, et al. Assisted reproductive technology surveillance - United States 2018. MMWR Surveill Summ. (2022) 71:1–19. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7104a1
21. Njagi P, Groot W, Arsenijevic J, Dyer S, Mburu G, Kiarie J. Financial costs of assisted reproductive technology for patients in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Human Reprod Open. (2023) 2023:hoad007. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoad007
22. Hoffman JR, Delaney MA, Valdes CT, Herrera D, Washington SL, Aghajanova L, et al. Disparities in fertility knowledge among women from low and high resource settings presenting for fertility care in two United States metropolitan centers. Fertil Res Pract. (2020) 6:15. doi: 10.1186/s40738-020-00084-1
23. Hossain MS, Wazed MA, Asha S, Amin MR, Shimul IM. Dietary phytochemicals in health and disease: mechanisms, clinical evidence, and applications-a comprehensive review. Food Sci Nutr. (2025) 13:e70101. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70101
24. Muscolo A, Mariateresa O, Giulio T, Mariateresa R. Oxidative stress: the role of antioxidant phytochemicals in the prevention and treatment of diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:3264. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063264
25. Rajashekar CB. Dual role of plant phenolic compounds as antioxidants and prooxidants. Am J Plant Sci. (2023) 14:15–28. doi: 10.4236/ajps.2023.141002
26. Nigar S, Shimul IM, Hossain MS, Sultana R, Asha S, Huq AKO. Comparative analysis on phytonutrient properties of different fig varieties (Ficus spp). Food Chem Adv. (2025) 6:100878. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2024.100878
27. Silva E, Almeida H, Castro JP. (In)Fertility and oxidative stress: new insights into novel redox mechanisms controlling fundamental reproductive processes. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:4674896. doi: 10.1155/2020/4674896
28. Joó JG, Sulyok E, Bódis J, Kornya L. Disrupted balance of the oxidant-antioxidant system in the pathophysiology of female reproduction: oxidative stress and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Curr Issues Mol Biol. (2023) 45:8091–111. doi: 10.3390/cimb45100511
29. Lu J, Wang Z, Cao J, Chen Y, Dong Y. A novel and compact review on the role of oxidative stress in female reproduction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2018) 16:80. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0391-5
30. Shaw GA. Mitochondria as the target for disease related hormonal dysregulation. Brain Behav Immun Health. (2021) 18:100350. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100350
31. Jaita G, Kodithuwakku SP. Editorial: cytoprotective role of mitochondria in reproduction. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1448126. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1448126
32. Alahmar AT. Role of oxidative stress in male infertility: an updated review. J Hum Reprod Sci. (2019) 12:4–18. doi: 10.4103/jhrs.JHRS_150_18
33. Nguyen M, Sabry R, Davis OS, Favetta LA. Effects of BPA, BPS, and BPF on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme expression in bovine oocytes and spermatozoa. Genes. (2022) 13:142. doi: 10.3390/genes13010142
34. Wang C, He C, Xu S, Gao Y, Wang K, Liang M, et al. Bisphenol A triggers apoptosis in mouse pre-antral follicle granulosa cells via oxidative stress. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:20. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01322-y
35. Hale A, Moldovan GL. Novel insights into the role of bisphenol A (BPA) in genomic instability. NAR Cancer. (2024) 6: zcae038. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae038
36. Matuszczak E, Komarowska MD, Debek W, Hermanowicz A. The impact of bisphenol A on fertility, reproductive system, and development: a review of the literature. Int J Endocrinol. (2019) 2019:4068717. doi: 10.1155/2019/4068717
37. Drevet JR, Aitken RJ. Oxidation of sperm nucleus in mammals: a physiological necessity to some extent with adverse impacts on oocyte and offspring. Antioxidants. (2020) 9:95. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020095
38. Rashki Ghaleno L, Alizadeh A, Drevet JR, Shahverdi A, Valojerdi MR. Oxidation of sperm DNA and male infertility. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:97. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010097
39. Sengupta P, Pinggera GM, Calogero AE, Agarwal A. Oxidative stress affects sperm health and fertility-Time to apply facts learned at the bench to help the patient: lessons for busy clinicians. Reprod Med Biol. (2024) 23:e12598. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12598
40. Iommiello VM, Albani E, Di Rosa A, Marras A, Menduni F, Morreale G, et al. Ejaculate oxidative stress is related with sperm DNA fragmentation and round cells. Int J Endocrinol. (2015) 2015:321901. doi: 10.1155/2015/321901
41. Kurkowska W, Bogacz A, Janiszewska M, Gabryś E, Tiszler M, Bellanti F, et al. Oxidative stress is associated with reduced sperm motility in normal semen. Am J Mens Health. (2020) 14:1557988320939731. doi: 10.1177/1557988320939731
42. Agarwal A, Maldonado Rosas I, Anagnostopoulou C, Cannarella R, Boitrelle F, Munoz LV, et al. Oxidative stress and assisted reproduction: a comprehensive review of its pathophysiological role and strategies for optimizing embryo culture environment. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:477. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030477
43. Al-Saleh I, Coskun S, Al-Rouqi R, Al-Rajudi T, Eltabache C, Abduljabbar M, et al. Oxidative stress and DNA damage status in couples undergoing in vitro fertilization treatment. Reprod Fertil. (2021) 2:117–39. doi: 10.1530/RAF-20-0062
44. Musicki B, Lagoda G, Goetz T, La Favor JD, Burnett AL. Transnitrosylation: a factor in nitric oxide-mediated penile erection. J Sex Med. (2016) 13:808–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.03.003
45. Odetayo AF, Olayaki LA. Omega 3 fatty acid improves sexual and erectile function in BPF-treated rats by upregulating NO/cGMP signaling and steroidogenic enzymes activities. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:18060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45344-4
46. Davies R, Minhas S, Jayasena CN. The role of seminal reactive oxygen species assessment in the setting of infertility and early pregnancy loss. World J Urol. (2023) 41:3257–65. doi: 10.1007/s00345-023-04472-2
47. Wang Y, Fu X, Li H. Mechanisms of oxidative stress-induced sperm dysfunction. Front Endocrinol. (2025) 16:1520835. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1520835
48. Wang X, Zhang Y, Hou Y, Jiang H, Kuang T, Li R, et al. Mechanistic insights into Salidroside's mitochondrial protection via AMPK/Sirt1/HIF-1α pathway in hypoxic HT22 cells. J Vis Exp. (2025) 218. doi: 10.3791/66923
49. Dutta S, Majzoub A, Agarwal A. Oxidative stress and sperm function: a systematic review on evaluation and management. Arab J Urol. (2019) 17:87–97. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1599624
50. Milkovic L, Cipak Gasparovic A, Cindric M, Mouthuy PA, Zarkovic N. Short overview of ROS as cell function regulators and their implications in therapy concepts. Cells. (2019) 8:793. doi: 10.3390/cells8080793
51. Nowicka-Bauer K, Nixon B. Molecular changes induced by oxidative stress that impair human sperm motility. Antioxidants. (2020) 9:134. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020134
52. Agarwal A, Virk G, Ong C, du Plessis SS. Effect of oxidative stress on male reproduction. World J Mens Health. (2014) 32:1–17. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.1.1
53. Liang J, Gao Y, Feng Z, Zhang B, Na Z, Li D. Reactive oxygen species and ovarian diseases: antioxidant strategies. Redox Biol. (2023) 62:102659. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102659
54. Agarwal A, Durairajanayagam D, Du Plessis SS. Utility of antioxidants during assisted reproductive techniques: an evidence based review. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2014) 12:112. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-112
55. Krylatov AV, Maslov LN, Voronkov NS, Boshchenko AA, Popov SV, Gomez L, et al. Reactive oxygen species as intracellular signaling molecules in the cardiovascular system. Curr Cardiol Rev. (2018) 14:290–300. doi: 10.2174/1573403X14666180702152436
56. Musicki B, Burnett AL. eNOS function and dysfunction in the penis. Exp Biol Med. (2006) 231:154–65. doi: 10.1177/153537020623100205
57. Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V, Ye Q, Wu D, Liu Y, et al. ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2016) 2016:4350965. doi: 10.1155/2016/4350965
58. Takata T, Araki S, Tsuchiya Y, Watanabe Y. Oxidative stress orchestrates MAPK and nitric-oxide synthase signal. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8750. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228750
59. Jalmi SK, Sinha AK. ROS mediated MAPK signaling in abiotic and biotic stress- striking similarities and differences. Front Plant Sci. (2015) 6:769. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00769
60. Liu S, Pi J, Zhang Q. Signal amplification in the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE antioxidant response pathway. Redox Biol. (2022) 54:102389. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102389
61. Raghunath A, Sundarraj K, Nagarajan R, Arfuso F, Bian J, Kumar AP, et al. Antioxidant response elements: discovery, classes, regulation and potential applications. Redox Biol. (2018) 17:297–314. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.05.002
62. Keum YS. Regulation of Nrf2-mediated phase II detoxification and anti-oxidant genes. Biomol Ther. (2012) 20:144–51. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2012.20.2.144
63. Sykiotis GP. Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:828. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060828
64. Tu W, Wang H, Li S, Liu Q, Sha H. The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis. (2019) 10:637–51. doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.0513
65. Darbandi M, Darbandi S, Agarwal A, Sengupta P, Durairajanayagam D, Henkel R, et al. Reactive oxygen species and male reproductive hormones. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2018) 16:87. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0406-2
66. O'Flaherty C, Scarlata E. Oxidative stress and reproductive function: the protection of mammalian spermatozoa against oxidative stress. Reproduction. (2022) 164:F67–78. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0200
67. Tvrdá E, Benko F, Duračka M. Oxidative stress as an underlying mechanism of bacteria-inflicted damage to male gametes. Oxygen. (2022). doi: 10.3390/oxygen2040036
68. Kuchakulla M, Masterson T, Arora H, Kulandavelu S, Ramasamy R. Effect of nitroso-redox imbalance on male reproduction. Transl Androl Urol. (2018) 7:968–77. doi: 10.21037/tau.2018.08.14
69. Rizzo A, Roscino MT, Binetti F, Sciorsci RL. Roles of reactive oxygen species in female reproduction. Reprod Domest Anim. (2012) 47:344–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2011.01891.x
70. Sharma R K, Agarwal A. Role of reactive oxygen species in gynecologic diseases. Reprod Med Biol. (2004) 3:177–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0578.2004.00068.x
71. Wang L, Yang S, Ma X, Yang L, Ma J, Zhao X, et al. Bibliometric and visual analysis on oxidative stress in gynecological and reproductive diseases: a systematic review. Medicine. (2024) 103:e37815. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037815
72. Amini MA, Karimi M, Talebi SS, Piri H, Karimi J. The association of oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species modulator 1 (ROMO1) with infertility: a mini review. Chonnam Med J. (2022) 58:91–5. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2022.58.3.91
73. Kim S M, Hwang K A, Choi K C. Potential roles of reactive oxygen species derived from chemical substances involved in cancer development in the female reproductive system. BMB Rep. (2018) 51:557–62. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.11.056
74. Ghezzi P. Environmental risk factors and their footprints in vivo - A proposal for the classification of oxidative stress biomarkers. Redox Biol. (2020) 34:101442. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101442
75. Walters JLH, De Iuliis GN, Nixon B, Bromfield EG. Oxidative stress in the male germline: a review of novel strategies to reduce 4-hydroxynonenal production. Antioxidants. (2018) 7:132. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100132
76. Mottola F, Palmieri I, Carannante M, Barretta A, Roychoudhury S, Rocco L. Oxidative stress biomarkers in male infertility: established methodologies and future perspectives. Genes. (2024) 15:539. doi: 10.3390/genes15050539
77. Debbarh H, Jamil M, Jelloul H, Kabit A, Ennaji M, Louanjli N, et al. Evaluation of oxidative and nitrosative stress markers related to inflammation in the cumulus cells and follicular fluid of women undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a prospective study. Int J Fertil Steril. (2024) 18:108–14. doi: 10.22074/ijfs.2023.559526.1342
78. Ijiri TW, Mahbub Hasan AK, Sato K. Protein-tyrosine kinase signaling in the biological functions associated with sperm. J Signal Transduct. (2012) 2012:181560. doi: 10.1155/2012/181560
79. Ng JY, Boelen L, Wong JW. Bioinformatics analysis reveals biophysical and evolutionary insights into the 3-nitrotyrosine post-translational modification in the human proteome. Open Biol. (2013) 3:120148. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120148
80. Georgadaki K, Khoury N, Spandidos DA, Zoumpourlis V. The molecular basis of fertilization (Review). Int J Mol Med. (2016) 38:979–86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2723
81. Siu KK, Serrão VHB, Ziyyat A, Lee JE. The cell biology of fertilization: gamete attachment and fusion. J Cell Biol. (2021) 220:e202102146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202102146
82. Schmidt CM, Blount JD, Bennett NC. Reproduction is associated with a tissue-dependent reduction of oxidative stress in eusocial female Damaraland mole-rats (Fukomys damarensis). PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e103286. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103286
83. Ziomkiewicz A, Sancilio A, Galbarczyk A, Klimek M, Jasienska G, Bribiescas RG. Evidence for the cost of reproduction in humans: high lifetime reproductive effort is associated with greater oxidative stress in post-menopausal women. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0145753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145753
84. Bisht S, Dada R. Yoga: impact on sperm genome and epigenome - clinical consequences. Ann Neurosci. (2019) 26:49–51. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.260202
85. Nishihara T, Matsumoto K, Hosoi Y, Morimoto Y. Evaluation of antioxidant status and oxidative stress markers in follicular fluid for human in vitro fertilization outcome. Reprod Med Biol. (2018) 17:481–6. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12229
86. Zec I, Goldštajn MŠ, Kuna K, Mikuš M, Stabile G, Bianco B, et al. Oxidative homeostasis in follicular fluid and reproductive outcomes - from bench to bedside. Prz Menopauzalny. (2022) 21:276–84. doi: 10.5114/pm.2022.124019
87. Olszak-Wasik K, Bednarska-Czerwińska A, Olejek A, Tukiendorf A. From “Every Day” hormonal to oxidative stress biomarkers in blood and follicular fluid, to embryo quality and pregnancy success? Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2019) 2019:1092415. doi: 10.1155/2019/1092415
88. Panche AN, Diwan AD, Chandra SR. Flavonoids: an overview. J Nutr Sci. (2016) 5:e47. doi: 10.1017/jns.2016.41
89. Quideau S, Deffieux D, Douat-Casassus C, Pouységu L. Plant polyphenols: chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. (2011) 50:586–621. doi: 10.1002/anie.201000044
90. Vuolo M, Lima V, Maróstica Junior M. Chapter 2-Phenolic Compounds: Structure, Classification, and Antioxidant Power (MRSBT-BC Campos [Z]). Woodhead Publishing (2019). doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-814774-0.00002-5
91. D'Archivio M, Filesi C, Varì R, Scazzocchio B, Masella R. Bioavailability of the polyphenols: status and controversies. Int J Mol Sci. (2010) 11:1321–42. doi: 10.3390/ijms11041321
92. Chen J, Yang J, Ma L, Li J, Shahzad N, Kim CK. Structure-antioxidant activity relationship of methoxy, phenolic hydroxyl, and carboxylic acid groups of phenolic acids. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:2611. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59451-z
93. Yamauchi M, Kitamura Y, Nagano H, Kawatsu J, Gotoh H. DPPH measurements and structure-activity relationship studies on the antioxidant capacity of phenols. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:309. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030309
94. Scarano A, Laddomada B, Blando F, De Santis S, Verna G, Chieppa M, et al. The chelating ability of plant polyphenols can affect iron homeostasis and gut microbiota. Antioxidants. (2023) 12:630. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030630
95. Hassanpour SH, Doroudi A. Review of the antioxidant potential of flavonoids as a subgroup of polyphenols and partial substitute for synthetic antioxidants. Avicenna J Phytomed. (2023) 13:354–76. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2023.21774
96. Zeb A. Concept, mechanism, and applications of phenolic antioxidants in foods. J Food Biochem. (2020) 44:e13394. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13394
97. Lv QZ, Long JT, Gong ZF, Nong KY, Liang XM, Qin T, et al. Current state of knowledge on the antioxidant effects and mechanisms of action of polyphenolic compounds. Nat Prod Commun. (2021) 16: 1934578X211027745. doi: 10.1177/1934578X211027745
98. Tamafo Fouegue AD, Ghogomu JN, Bikélé Mama D, Nkungli NK, Younang E. Structural and antioxidant properties of compounds obtained from Fe(2+) chelation by Juglone and two of its derivatives: DFT, QTAIM, and NBO studies. Bioinorg Chem Appl. (2016) 2016:8636409. doi: 10.1155/2016/8636409
99. Crascì L, Lauro MR, Puglisi G, Panico A. Natural antioxidant polyphenols on inflammation management: anti-glycation activity vs metalloproteinases inhibition. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 58:893–904. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1229657
100. Lakey-Beitia J, Burillo AM, La Penna G, Hegde ML, Rao KS. Polyphenols as potential metal chelation compounds against Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. (2021) 82:S335–57. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200185
101. Qi G, Mi Y, Fan R, Li R, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Tea polyphenols ameliorate hydrogen peroxide- and constant darkness-triggered oxidative stress via modulating the Keap1/Nrf2 transcriptional signaling pathway in HepG2 cells and mice liver. RSC Adv. (2017) 7:32198–208. doi: 10.1039/C7RA05000C
102. Zhou Y, Jiang Z, Lu H, Xu Z, Tong R, Shi J, et al. Recent advances of natural polyphenols activators for Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Chem Biodivers. (2019) 16:e1900400. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201900400
103. Wang D, Wang T, Li Z, Guo Y, Granato D. Green tea polyphenols upregulate the Nrf2 signaling pathway and suppress oxidative stress and inflammation markers in D-galactose-induced liver aging in mice. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:836112. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.836112
104. Scapagnini G, Vasto S, Abraham NG, Caruso C, Zella D, Fabio G. Modulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by food polyphenols: a nutritional neuroprotective strategy for cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurobiol. (2011) 44:192–201. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8181-5
105. Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y, Blachier F, Tossou MC, Rahu N. Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2016) 2016:7432797. doi: 10.1155/2016/7432797
106. Yahfoufi N, Alsadi N, Jambi M, Matar C. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1618. doi: 10.3390/nu10111618
107. Qi S, Feng Z, Li Q, Qi Z, Zhang Y. Myricitrin modulates NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS production to inhibit endotoxin-mediated inflammation by blocking the JAK/STAT1 and NOX2/p47(phox) pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:9738745. doi: 10.1155/2017/9738745
108. Zuo X, Tian C, Zhao N, Ren W, Meng Y, Jin X, et al. Tea polyphenols alleviate high fat and high glucose-induced endothelial hyperpermeability by attenuating ROS production via NADPH oxidase pathway. BMC Res Notes. (2014) 7:120. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-120
109. Ho CC, Chen YC, Tsai MH, Tsai HT, Weng CY, Yet SF, et al. Ambient particulate matter induces vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic changes via NOX1/ROS/NF-κB dependent and independent pathways: protective effects of polyphenols. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:782. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050782
110. Yun MR, Park HM, Seo KW, Lee SJ, Im DS, Kim CD. 5-Lipoxygenase plays an essential role in 4-HNE-enhanced ROS production in murine macrophages via activation of NADPH oxidase. Free Radic Res. (2010) 44:742–50. doi: 10.3109/10715761003758122
111. González-Peña MA, Ortega-Regules AE, Anaya de Parrodi C, Lozada-Ramírez JD. Chemistry, occurrence, properties, applications, and encapsulation of carotenoids-a review. Plants. (2023) 12:313. doi: 10.3390/plants12020313
112. Różanowska MB, Czuba-Pelech B, Landrum JT, Różanowski B. Comparison of antioxidant properties of dehydrolutein with lutein and zeaxanthin, and their effects on cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells. Antioxidants. (2021) 10:753. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050753
113. Terao J. Revisiting carotenoids as dietary antioxidants for human health and disease prevention. Food Funct. (2023) 14:7799–824. doi: 10.1039/D3FO02330C
114. Ismail RF, Hamed M, Sayed AE-DH. Lycopene supplementation: effects on oxidative stress, sex hormones, gonads and thyroid tissue in tilapia Oreochromis niloticus during Harness® exposure. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1237159. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1237159
115. Babaei A, Asadpour R, Mansouri K, Sabrivand A, Kazemi-Darabadi S. Lycopene protects sperm from oxidative stress in the experimental Varicocele model. Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 9:6806–17. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2632
116. Durairajanayagam D, Agarwal A, Ong C, Prashast P. Lycopene and male infertility. Asian J Androl. (2014) 16:420–5. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.126384
117. Ardawi MSM, Badawoud MH, Hassan SM, Ardawi AMS, Rouzi AA, Qari MH, et al. Lycopene nanoparticles promotes osteoblastogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2021) 25:6894–907. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202111_27238
118. Gong X, Marisiddaiah R, Zaripheh S, Wiener D, Rubin LP. Mitochondrial β-carotene 9′, 10′ oxygenase modulates prostate cancer growth via NF-κB inhibition: a lycopene-independent function. Mol Cancer Res. (2016) 14:966–75. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0075
119. Bowen P, Chen L, Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis M, Duncan C, Sharifi R, Ghosh L, et al. Tomato sauce supplementation and prostate cancer: lycopene accumulation and modulation of biomarkers of carcinogenesis. Exp Biol Med. (2002) 227:886–93. doi: 10.1177/153537020222701008
120. Patel HR. Does oral lycopene reduce benign prostate enlargement/hyperplasia (BPE/BPH). Oncol Cancer Case Rep. (2016) 1:2. doi: 10.4172/2471-8556.1000108
121. Vakili S, Samare-Najaf M, Karimi A, Jahromi BN, Mohit M, Hashempur MH. Lycopene in male infertility. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 398:4817–35. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03520-x
122. Van Breemen RB, Pajkovic N. Multitargeted therapy of cancer by lycopene. Cancer Lett. (2008) 269:339–51. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.05.016
123. Zhang Y, Liu Y, Lv Q. DFT study on the quenching mechanism of singlet oxygen by lycopene. RSC Adv. (2016) 6:98498–505. doi: 10.1039/C6RA19639J
124. Di Mascio P, Kaiser S, Sies H. Lycopene as the most efficient biological carotenoid singlet oxygen quencher. Arch Biochem Biophys. (1989) 274:532–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90467-0
125. Pirayesh Islamian J, Mehrali H. Lycopene as a carotenoid provides radioprotectant and antioxidant effects by quenching radiation-induced free radical singlet oxygen: an overview. Cell J. (2015) 16:386–91. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2015.485
126. Heymann T, Heinz P, Glomb MA. Lycopene inhibits the isomerization of β-carotene during quenching of singlet oxygen and free radicals. J Agric Food Chem. (2015) 63:3279–87. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00377
127. Ramel F, Birtic S, Cuiné S, Triantaphylidès C, Ravanat JL, Havaux M. Chemical quenching of singlet oxygen by carotenoids in plants. Plant Physiol. (2012) 158:1267–78. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.182394
128. Elango P, Asmathulla S. “A systematic review on lycopene and its beneficial effects”. Biomed Pharmacol J. (2017) 10:2113–20. doi: 10.13005/bpj/1335
129. Grudzinski W, Nierzwicki L, Welc R, Reszczynska E, Luchowski R, Czub J, et al. Localization and orientation of xanthophylls in a lipid bilayer. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:9619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10183-7
130. Widomska J, Subczynski WK, Welc-Stanowska R, Luchowski R. An overview of lutein in the lipid membrane. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12948. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612948
131. Welc-Stanowska R, Pietras R, Mielecki B, Sarewicz M, Luchowski R, Widomska J, et al. How do xanthophylls protect lipid membranes from oxidative damage? J Phys Chem Lett. (2023) 14:7440–4. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c01374
132. Neelam K, Goenadi CJ, Lun K, Yip CC, Au Eong KG. Putative protective role of lutein and zeaxanthin in diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. (2017) 101:551–8. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-309814
133. Kumar P, Banik SP, Ohia SE, Moriyama H, Chakraborty S, Wang CK, et al. Current insights on the photoprotective mechanism of the macular carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin: safety, efficacy and bio-delivery. J Am Nutr Assoc. (2024) 43:505–18. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2024.2319090
134. Chucair AJ, Rotstein NP, Sangiovanni JP, During A, Chew EY, Politi LE. Lutein and zeaxanthin protect photoreceptors from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress: relation with docosahexaenoic acid. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2007) 48:5168–77. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0037
135. Schweigert FJ, Steinhagen B, Raila J, Siemann A, Peet D, Buscher U. Concentrations of carotenoids, retinol and alpha-tocopherol in plasma and follicular fluid of women undergoing IVF. Hum Reprod. (2003) 18:1259–64. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deg249
136. Bohn T, Bonet ML, Borel P, Keijer J, Landrier JF, Milisav I, et al. Mechanistic aspects of carotenoid health benefits – where are we now? Nutr Res Rev. (2021) 34:276–302. doi: 10.1017/S0954422421000147
137. Pasquariello R, Anipchenko P, Pennarossa G, Crociati M, Zerani M, Brevini TA, et al. Carotenoids in female and male reproduction. Phytochemistry. (2022) 204:113459. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113459
138. Zhuang C, Yuan J, Du Y, Zeng J, Sun Y, Wu Y, et al. Effects of oral carotenoids on oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in the recent 20 years. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:754707. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.754707
139. Jafari F, Khalilzadeh S, Nejatbakhsh F, Naderie M. Therapeutic effects of garlic (Allium sativum) on female reproductive system: a systematic review. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e22555. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22555
140. Tocmo R, Liang D, Lin Y, Huang D. Chemical and biochemical mechanisms underlying the cardioprotective roles of dietary organopolysulfides. Front Nutr. (2015) 2:1. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2015.00001
141. Park S, Kim HW, Joo Lee C, Kim Y, Sung J. Profiles of volatile sulfur compounds in various vegetables consumed in Korea using HS-SPME-GC/MS technique. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1409008. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1409008
142. Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC, Nwachukwu ID, Slusarenko AJ. Allicin: chemistry and biological properties. Molecules. (2014) 19:12591–618. doi: 10.3390/molecules190812591
143. Rabinkov A, Miron T, Konstantinovski L, Wilchek M, Mirelman D, Weiner L. The mode of action of allicin: trapping of radicals and interaction with thiol containing proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1998) 1379:233–44. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4165(97)00104-9
144. Gruhlke MCH. Thiol-Modification as Important Mode of Action for Allicin from Garlic (Allium sativum). Proceedings (2019). doi: 10.3390/proceedings2019011027
145. Li X J, Liu T, Wang Y. Allicin ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Nat Med. (2024) 78:53–67. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01745-3
146. Song X, Yue Z, Nie L, Zhao P, Zhu K, Wang Q. Biological functions of diallyl disulfide, a garlic-derived natural organic sulfur compound. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:5103626. doi: 10.1155/2021/5103626
147. Sun F, Xu K, Zhou J, Zhang W, Duan G, Lei M. Allicin protects against LPS-induced cardiomyocyte injury by activating Nrf2-HO-1 and inhibiting NLRP3 pathways. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2023) 23:410. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03442-1
148. Orozco-Ibarra M, Muñoz-Sánchez J, Zavala-Medina ME, Pineda B, Magaña-Maldonado R, Vázquez-Contreras E, et al. Aged garlic extract and S-allylcysteine prevent apoptotic cell death in a chemical hypoxia model. Biol Res. (2016) 49:7. doi: 10.1186/s40659-016-0067-6
149. Colín-González AL, Santana RA, Silva-Islas CA, Chánez-Cárdenas ME, Santamaría A, Maldonado PD. The antioxidant mechanisms underlying the aged garlic extract- and S-allylcysteine-induced protection. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2012) 2012:907162. doi: 10.1155/2012/907162
150. Takemura S, Ichikawa H, Naito Y, Takagi T, Yoshikawa T, Minamiyama Y. S-allyl cysteine ameliorates the quality of sperm and provides protection from age-related sperm dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2014) 55:155–61. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.14-39
151. Ohtani M, Nishimura T. Sulfur-containing amino acids in aged garlic extract inhibit inflammation in human gingival epithelial cells by suppressing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and IL-6 secretion. Biomed Rep. (2020) 12:99–108. doi: 10.3892/br.2019.1269
152. Agarwal A, Leisegang K, Majzoub A, Henkel R, Finelli R, Panner Selvam MK, et al. Utility of antioxidants in the treatment of male infertility: clinical guidelines based on a systematic review and analysis of evidence. World J Mens Health. (2021) 39:233–90. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.200196
153. Abourashed EA. Bioavailability of plant-derived antioxidants. Antioxidants. (2013) 2:309–25. doi: 10.3390/antiox2040309
154. Żyżelewicz D, Oracz J. Bioavailability and bioactivity of plant antioxidants. Antioxidants. (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122336
155. Aqil F, Munagala R, Jeyabalan J, Vadhanam MV. Bioavailability of phytochemicals and its enhancement by drug delivery systems. Cancer Lett. (2013) 334:133–41. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.02.032
156. Hu M. Commentary: bioavailability of flavonoids and polyphenols: call to arms. Mol Pharm. (2007) 4:803–6. doi: 10.1021/mp7001363
157. Miao Y, Wang X, Zhao X, Hu Y, Liu X, Deng D. Co-assembly strategies of natural plant compounds for improving their bioavailability. Food Med Homol. (2025) 2:9420022. doi: 10.26599/FMH.2025.9420022
158. Wu K, Kwon SH, Zhou X, Fuller C, Wang X, Vadgama J, et al. Overcoming challenges in small-molecule drug bioavailability: a review of key factors and approaches. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:13121. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313121
159. Matsui T. Polyphenols-absorption and occurrence in the body system. Food Sci Technol Res. (2022) 28:13–33. doi: 10.3136/fstr.FSTR-D-21-00264
160. van het Hof KH, de Boer BC, Tijburg LB, Lucius BR, Zijp I, West CE, et al. Carotenoid bioavailability in humans from tomatoes processed in different ways determined from the carotenoid response in the triglyceride-rich lipoprotein fraction of plasma after a single consumption and in plasma after four days of consumption. J Nutr. (2000) 130:1189–96. doi: 10.1093/jn/130.5.1189
161. Fielding JM, Rowley KG, Cooper P, O'Dea K. Increases in plasma lycopene concentration after consumption of tomatoes cooked with olive oil. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2005) 14:131–6.
162. Kay CD. Aspects of anthocyanin absorption, metabolism and pharmacokinetics in humans. Nutr Res Rev. (2006) 19:137–46. doi: 10.1079/NRR2005116
163. Xue H, Sang Y, Gao Y, Zeng Y, Liao J, Tan J. Research progress on absorption, metabolism, and biological activities of anthocyanins in berries: a review. Antioxidants. (2022) 12:3. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010003
164. Prasad S, Tyagi AK, Aggarwal BB. Recent developments in delivery, bioavailability, absorption and metabolism of curcumin: the golden pigment from golden spice. Cancer Res Treat. (2014) 46:2–18. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.46.1.2
165. Kroon MA, Berbee JK, Majait S, Swart NE, Kemper EM, Tellingen OV, et al. Plasma concentrations of curcumin in individuals using curcumin with adjuvants or lipid formulated curcumin supplements: a real world cohort. medRxiv. [preprint] (2023). doi: 10.1101/2023.03.23.23287619
166. Kroon MAGM, Berbee JK, Majait S, Swart EL, van Tellingen O, van Laarhoven HWM, et al. Non-therapeutic plasma levels in individuals utilizing curcumin supplements in daily life. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1267035. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1267035
168. Yu X, Jia Y, Ren F. Multidimensional biological activities of resveratrol and its prospects and challenges in the health field. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:2024. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1408651
169. Iannitti RG, Floridi A, Lazzarini A, Tantucci A, Russo R, Ragonese F, et al. Resveratrol supported on magnesium dihydroxide (Resv@MDH) represents an oral formulation of resveratrol with better gastric absorption and bioavailability respect to pure resveratrol. Front Nutr. (2020) 7:2020. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.570047
170. Radeva L, Yoncheva K. Resveratrol—a promising therapeutic agent with problematic properties. Pharmaceutics. (2025) 17:134. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010134
171. Kapetanovic IM, Muzzio M, Huang Z, Thompson TN, McCormick DL. Pharmacokinetics, oral bioavailability, and metabolic profile of resveratrol and its dimethylether analog, pterostilbene, in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2011) 68:593–601. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1525-4
172. Nisar M F, Wan C. Nanotechnology-based delivery systems for enhanced bioavailability of antioxidant compounds in fruits and vegetables. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci J. (2025) 13(Special Issue Phytonutrients June 2025):1–15. doi: 10.12944/CRNFSJ.13.Special-Issue-July.01
173. Lu H, Zhang S, Wang J, Chen Q. A review on polymer and lipid-based nanocarriers and its application to nano-pharmaceutical and food-based systems. Front Nutr. (2021) 8:783831. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.783831
174. Yakubu J, Pandey AV. Innovative delivery systems for curcumin: exploring nanosized and conventional formulations. Pharmaceutics. (2024) 16:637. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050637
175. Drescher S, van Hoogevest P. The phospholipid research center: current research in phospholipids and their use in drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. (2020) 12:1235. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121235
176. Tripathi AK, Ray AK, Mishra SK. Molecular and pharmacological aspects of piperine as a potential molecule for disease prevention and management: evidence from clinical trials. Beni Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. (2022) 11:16. doi: 10.1186/s43088-022-00196-1
177. Pratti VL, Thomas M, Bhoite R, Satyavrat V. Investigating bioavailability of curcumin and piperine combination in comparison to turmeric rhizomes: an in vitro study. J Exp Pharmacol. (2024) 37–47. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S427818
178. Park JY, Sohn HY, Koh YH, Jo C. Curcumin activates Nrf2 through PKCδ-mediated p62 phosphorylation at Ser351. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:8430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87225-8
179. Liu Z, Dou W, Zheng Y, Wen Q, Qin M, Wang X, et al. Curcumin upregulates Nrf2 nuclear translocation and protects rat hepatic stellate cells against oxidative stress. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 13:1717–24. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4690
180. Karunaweera N, Raju R, Gyengesi E, Münch G. Plant polyphenols as inhibitors of NF-κB induced cytokine production-a potential anti-inflammatory treatment for Alzheimer's disease? Front Mol Neurosci. (2015) 8:24. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00024
181. Jobin C, Bradham CA, Russo MP, Brenner DA, Sartor RB, Juma B, et al. Curcumin blocks cytokine-mediated NF-κB activation and proinflammatory gene expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-κB kinase activity. J Immunol. (1999) 163:3474–83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.163.6.3474
182. Floyd ZE, Wang ZQ, Kilroy G, Cefalu WT. Modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma stability and transcriptional activity in adipocytes by resveratrol. Metabolism. (2008) 57(7 Suppl 1):S32–8. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.04.006
183. Vašková J, Klepcová Z, Špaková I, Urdzík P, Štofilová J, Bertková I, et al. The importance of natural antioxidants in female reproduction. Antioxidants. (2023) 12:907. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040907
184. Enayati A, Ghojoghnejad M, Roufogalis BD, Maollem SA, Sahebkar A. Impact of phytochemicals on PPAR receptors: implications for disease treatments. PPAR Res. (2022) 2022:4714914. doi: 10.1155/2022/4714914
185. Stefanson AL, Bakovic M. Dietary regulation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway: focus on plant-derived compounds and trace minerals. Nutrients. (2014) 6:3777–801. doi: 10.3390/nu6093777
186. Baird L, Yamamoto M. The molecular mechanisms regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway. Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 40:e00099-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00099-20
187. Khan MZ, Li L, Zhan Y, Binjiang H, Liu X, Kou X, et al. Targeting Nrf2/KEAP1 signaling pathway using bioactive compounds to combat mastitis. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:2025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1425901
188. Mozaheb N, Arefian E, Amoozegar MA. Designing a whole cell bioreporter to show antioxidant activities of agents that work by promotion of the KEAP1–NRF2 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:3248. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39011-w
189. Mamun AA, Shao C, Geng P, Wang S, Xiao J. Polyphenols targeting NF-κB pathway in neurological disorders: what we know so far? Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:1332–55. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.90982
190. Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2017) 2:17023. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
191. Giordano A, Tommonaro G. Curcumin and cancer. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2376. doi: 10.3390/nu11102376
192. Manokaran K, Bhat P, Nayak D, Baskaran R, Paramasivam P, Ahmed SF, et al. Oxidative stress and female reproductive disorder: a review. Asian Pac J Reprod. (2022) 11:107–16. doi: 10.4103/2305-0500.346088
193. Wang SJ, Zhao XH, Chen W, Bo N, Wang XJ, Chi ZF, et al. Sirtuin 1 activation enhances the PGC-1α/mitochondrial antioxidant system pathway in status epilepticus. Mol Med Rep. (2015) 11:521–6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2724
194. Zhou Y, Wang S, Li Y, Yu S, Zhao Y. SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling promotes mitochondrial functional recovery and reduces apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Front Mol Neurosci. (2018) 10:2017. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00443
195. Li M, Ding L, Cao L, Zhang Z, Li X, Li Z, et al. Natural products targeting AMPK signaling pathway therapy, diabetes mellitus and its complications. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:2025. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1534634
196. Rehman R, Baig M, Alam F. Editorial: oxidative stress, metabolic dysfunction and subfertility. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:2023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1247585
197. Agarwal A, Parekh N, Panner Selvam MK, Henkel R, Shah R, Homa ST, et al. Male oxidative stress infertility (MOSI): proposed terminology and clinical practice guidelines for management of idiopathic male infertility. World J Mens Health. (2019) 37:296–312. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.190055
198. Kumbhare SD, Ukey S S, Gogle DP. Antioxidant activity of Flemingia praecox and Mucuna pruriens and their implications for male fertility improvement. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:19360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46705-9
199. Gaznee A, Kohli A, Kumar R. Role of antioxidants of natural herbs in management of male infertility. J Res Appl Sci Biotechnol. (2023) 2:55–80. doi: 10.55544/jrasb.2.1.9
200. Purushothaman B, Lokesh K, Harini V, Veerammal l, Sharma S. Antioxidants' use in the treatment of male infertility, systemic review and analysis of evidence –based clinical guidelines. Int J Pharm Res Appli. (2024) 9:250–74. doi: 10.35629/4494-0905250274
201. Babaei A, Asadpour R, Mansouri K, Sabrivand A, Kazemi-Darabadi S. Lycopene improves testicular damage and sperm quality in experimentally induced varicocele: relationship with apoptosis, hypoxia, and hyperthermia. Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 10:1469–80. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2762
202. Lafuente R, González-Comadrán M, Solà I, López G, Brassesco M, Carreras R, et al. Coenzyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. (2013) 30:1147–56. doi: 10.1007/s10815-013-0047-5
203. Akhigbe TM, Fidelis FB, Adekunle AO, Ashonibare VJ, Akorede BA, Shuaibu MS, et al. Does coenzyme Q10 improve semen quality and circulating testosterone level? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1497930. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1497930
204. Alahmar AT, Sengupta P, Dutta S, Calogero AE. Coenzyme Q10, oxidative stress markers, and sperm DNA damage in men with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratospermia. Clin Exp Reprod Med. (2021) 48:150–5. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2020.04084
205. Alqawasmeh OA, Zhao M, Chan CP, Leung MB, Chow KC, Agarwal N, et al. Green tea extract as a cryoprotectant additive to preserve the motility and DNA integrity of human spermatozoa. Asian J Androl. (2021) 23:150–6. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_58_20
206. Allah AAA, Ibrahim EA, Ibrahim ES, Mahmoud NF, Afify MM. Thiocyclam-induced reproductive toxicity, oxidative stress and genomic DNA damage in testicular tissues of rats: protective effects of green tea extract. J Environ Anal Toxicol. (2018) 8:566. doi: 10.4172/2161-0525.1000566
207. Mustofa I, Susilowati S, Wurlina W, Hernawati T, Oktanella Y. Green tea extract increases the quality and reduced DNA mutation of post-thawed Kacang buck sperm. Heliyon. (2021) 7:e06372. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06372
208. Reygaert WC. Green tea catechins: their use in treating and preventing infectious diseases. Biomed Res Int. (2018) 2018:9105261. doi: 10.1155/2018/9105261
209. Szulińska M, Stepień M, Kregielska-Narożna M, Suliburska J, Skrypnik D, Bak-Sosnowska M, et al. Effects of green tea supplementation on inflammation markers, antioxidant status and blood pressure in NaCl-induced hypertensive rat model. Food Nutr Res. (2017) 61:1295525. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1295525
210. Cannarella R, Calogero AE, Condorelli RA, Giacone F, Mongioi' LM, La Vignera S. Non-hormonal treatment for male infertility: the potential role of Serenoa repens, selenium and lycopene. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:3112–20. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17595
211. Bertoldo A, Pizzol D, Yon DK, Callegari M, Gobbo V, Cuccurese P, et al. Resveratrol and female fertility: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:12792. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312792
212. Conforti A, Iorio GG, Di Girolamo R, Rovetto MY, Picarelli S, Cariati F, et al. The impact of resveratrol on the outcome of the in vitro fertilization: an exploratory randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:81. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01391-7
213. Nishigaki A, Tsubokura H, Tsuzuki-Nakao T, Okada H. Hypoxia: role of SIRT1 and the protective effect of resveratrol in ovarian function. Reprod Med Biol. (2022) 21:e12428. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12428
214. Zhou J, Xue Z, He HN, Liu X, Yin SY, Wu DY, et al. Resveratrol delays postovulatory aging of mouse oocytes through activating mitophagy. Aging. (2019) 11:11504. doi: 10.18632/aging.102551
215. Jannatifar R, Asa E, Cheraghi E, Verdi A. Nanomicelle curcumin improves oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, and assisted reproductive techniques outcomes in endometriosis cases: a randomized clinical trial. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03958-7
216. Tesarik J. Towards personalized antioxidant use in female infertility: need for more molecular and clinical studies. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:1933. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121933
217. Shang Y, Song N, He R, Wu M. Antioxidants and fertility in women with ovarian aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Nutr. (2024) 15:100273. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2024.100273
218. Sargazi-Taghazi M, Ghaznavi H, Sheervalilou R, Razavi M, Sepidarkish M. Add-on effect of curcumin to dienogest in patients with endometriosis: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Phytomedicine. (2025) 141:156715. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156715
219. Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y. Curcumin and endometriosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:2440. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072440
220. Ding J, Mei S, Cheng W, Ni Z, Yu C. Curcumin treats endometriosis in mice by the HIF signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. (2022) 14:2184–98.
221. Kamal DAM, Salamt N, Zaid SSM, Mokhtar MH. Beneficial effects of green tea catechins on female reproductive disorders: a review. Molecules. (2021) 26:2675. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092675
222. Wang CC, Xu H, Man GC, Zhang T, Chu KO, Chu CY, et al. Prodrug of green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (Pro-EGCG) as a potent anti-angiogenesis agent for endometriosis in mice. Angiogenesis. (2013) 16:59–69. doi: 10.1007/s10456-012-9299-4
223. Dull AM, Moga MA, Dimienescu OG, Sechel G, Burtea V, Anastasiu CV. Therapeutic approaches of resveratrol on endometriosis via anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic pathways. Molecules. (2019) 24:667. doi: 10.3390/molecules24040667
224. Bruner-Tran KL, Osteen KG, Taylor HS, Sokalska A, Haines K, Duleba AJ. Resveratrol inhibits development of experimental endometriosis in vivo and reduces endometrial stromal cell invasiveness in vitro. Biol Reprod. (2011) 84:106–12. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.086744
225. Zhong HZ, Yan PJ, Gao QF, Wu J, Ji XL, Wei SB. Therapeutic potential of botanical drugs and their metabolites in the treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:2025. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545917
226. Wang D, Jiang Y, Feng J, Gao J, Yu J, Zhao J, et al. Evidence for the use of complementary and alternative medicine for pelvic inflammatory disease: a literature review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:1364297. doi: 10.1155/2022/1364297
227. Kong D, Fu P, Zhang Q, Ma X, Jiang P. Protective effects of Asiatic acid against pelvic inflammatory disease in rats. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 17:4687–92. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7498
228. Yang C H, Sohn D W, Cho Y-H. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Lycopene on Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis Rat Model. Korean J Urol. (2006) 47:1348–53. doi: 10.4111/kju.2006.47.12.1348
229. Li Y, Zhu J, Zhao X, Sun Y, Xu F, Xu S, et al. Oral lycopene administration attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating plasma lipids in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced epididymitis. J Inflamm Res. (2022) 15:6517–31. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S380785
230. Teiten MH, Gaascht F, Eifes S, Dicato M, Diederich M. Chemopreventive potential of curcumin in prostate cancer. Genes Nutr. (2010) 5:61–74. doi: 10.1007/s12263-009-0152-3
231. Bhattacharya K, Dey R, Sen D, Paul N, Basak AK, Purkait MP, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome and its management: In view of oxidative stress. Biomol Concepts. (2024) 15:38. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2022-0038
232. Liu Y, Ling N, Zhang B, Chen C, Mo X, Cai J, et al. Flavonoid-rich mulberry leaf extract modulate lipid metabolism, antioxidant capacity, and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obesity: potential roles of FGF21 and SOCS2. Food Med Homol. (2024) 1:9420016. doi: 10.26599/FMH.2024.9420016
233. Wahyuningtyas R, Sa'adi A. Cinnamon extract effects on insulin resistance, metabolic factors, and menstrual cyclicity of women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. F1000Res. (2021) 10: 523. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.52383.1
234. Borzoei A, Rafraf M, Niromanesh S, Farzadi L, Narimani F, Doostan F. Effects of cinnamon supplementation on antioxidant status and serum lipids in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Tradit Complement Med. (2018) 8:128–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.04.008
235. Maleki V, Taheri E, Varshosaz P, Tabrizi FPF, Moludi J, Jafari-Vayghan H, et al. A comprehensive insight into effects of green tea extract in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2021) 19:147. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00831-z
236. Mohammadi S, Karimzadeh Bardei L, Hojati V, Ghorbani AG, Nabiuni M. Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin on insulin resistance index, levels of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and liver histology in polycystic ovary syndrome-induced rats. Cell J. (2017) 19:425–33. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2017.4415
237. Jamilian M, Foroozanfard F, Kavossian E, Aghadavod E, Shafabakhsh R, Hoseini A, et al. Effects of curcumin on body weight, glycemic control and serum lipids in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2020) 36:128–33. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.01.005
238. Zhang W, Peng C, Xu L, Zhao Y, Huang C, Lu L. The therapeutic effects of curcumin on polycystic ovary syndrome by upregulating PPAR-γ expression and reducing oxidative stress in a rat model. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1494852. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1494852
239. Akter T, Zahan MS, Nawal N, Rahman MH, Tanjum TN, Arafat KI, et al. Potentials of curcumin against polycystic ovary syndrome: Pharmacological insights and therapeutic promises. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e16957. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16957
240. Banaszewska B, Wrotyńska-Barczyńska J, Spaczynski RZ, Pawelczyk L, Duleba AJ. Effects of resveratrol on polycystic ovary syndrome: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2016) 101:4322–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1858
241. Musicki B, Burnett AL. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetic erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. (2007) 19:129–38. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901494
242. Defeudis G, Mazzilli R, Tenuta M, Rossini G, Zamponi V, Olana S, et al. Erectile dysfunction and diabetes: a melting pot of circumstances and treatments. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. (2022) 38:e3494. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3494
243. Corona G, Mannucci E, Forti G, Maggi M. Hypogonadism, ED, metabolic syndrome and obesity: a pathological link supporting cardiovascular diseases. Int J Androl. (2009) 32:587–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2008.00951.x
244. Meng X, Rao K, Chen J. Editorial: metabolic factors in erectile dysfunction. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1344191. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1344191
245. Ying A, Yu QT, Guo L, Zhang WS, Liu JF, Li Y, et al. Structural-activity relationship of ginsenosides from steamed ginseng in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Am J Chin Med. (2018) 46:137–55. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X18500088
246. Leung KW, Wong AS. Ginseng and male reproductive function. Spermatogenesis. (2013) 3:e26391. doi: 10.4161/spmg.26391
247. Tahvilian R, Golesorkhi MA, Parhoudeh F, Heydarpour F, Hosseini H, Baghshahi H, et al. The effect of the combination of ginseng, tribulus terrestris, and L-arginine on the sexual performance of men with erectile dysfunction: a randomized, double-blind, parallel, and placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Pharmacopuncture. (2024) 27:82–90. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2024.27.2.82
248. Lee HW, Lee MS, Kim TH, Alraek T, Zaslawski C, Kim JW, et al. Ginseng for erectile dysfunction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2021) 4:Cd012654. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012654.pub2
249. Jang DJ, Lee MS, Shin BC, Lee YC, Ernst E. Red ginseng for treating erectile dysfunction: a systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2008) 66:444–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03236.x
250. Tian Y, Zhou Q, Li W, Liu M, Li Q, Chen Q. Efficacy of L-arginine and Pycnogenol® in the treatment of male erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1211720. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1211720
251. Stanislavov R, Nikolova V. Treatment of erectile dysfunction with pycnogenol and L-arginine. J Sex Marital Ther. (2003) 29:207–13. doi: 10.1080/00926230390155104
252. Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Sumi D, de Nigris F, Napoli C. Pomegranate juice protects nitric oxide against oxidative destruction and enhances the biological actions of nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide. (2006) 15:93–102. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2006.03.001
253. Delgado NTB, Rouver WN, Dos Santos RL. Protective effects of pomegranate in endothelial dysfunction. Curr Pharm Des. (2020) 26:3684–99. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200406152147
254. Wang D, Özen C, Abu-Reidah IM, Chigurupati S, Patra JK, Horbanczuk JO, et al. Vasculoprotective effects of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:2018. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00544
255. de Nigris F, Williams-Ignarro S, Lerman LO, Crimi E, Botti C, Mansueto G, et al. Beneficial effects of pomegranate juice on oxidation-sensitive genes and endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity at sites of perturbed shear stress. Proc Nat Acad Sci. (2005) 102:4896–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500998102
256. Forest CP, Padma-Nathan H, Liker HR. Efficacy and safety of pomegranate juice on improvement of erectile dysfunction in male patients with mild to moderate erectile dysfunction: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover study. Int J Impot Res. (2007) 19:564–7. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901570
257. Chen D, Zhang KQ, Li B, Sun DQ, Zhang H, Fu Q. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates erectile function in aged rats via regulation of PRMT1/DDAH/ADMA/NOS metabolism pathway. Asian J Androl. (2017) 19:291–7. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.178486
258. Mostafa T, Sabry D, Abdelaal AM, Mostafa I, Taymour M. Cavernous antioxidant effect of green tea, epigallocatechin-3-gallate with/without sildenafil citrate intake in aged diabetic rats. Andrologia. (2013) 45:272–7. doi: 10.1111/and.12005
259. Jiang Y, Xing S, Ni D, Yang B, Kai J, Wang T, et al. Curcumin attenuates ferroptosis and ameliorates erectile function in diabetic rats by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Andrologia. (2023) 2023:7236816. doi: 10.1155/2023/7236816
260. Yang L, Ren Z, Liu Z, Peng Z, Song P, Zhou J, et al. Curcumin slow-release membrane promotes erectile function and penile rehabilitation in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. (2022) 16:836–49. doi: 10.1002/term.3334
261. Draganski A, Tar MT, Villegas G, Friedman JM, Davies KP. Topically applied curcumin-loaded nanoparticles treat erectile dysfunction in a rat model of type-2 diabetes. J Sex Med. (2018) 15:645–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2018.03.009
262. Abdel Aziz MT, Motawi T, Rezq A, Mostafa T, Fouad HH, Ahmed HH, et al. Effects of a water-soluble curcumin protein conjugate vs. pure curcumin in a diabetic model of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. (2012) 9:1815–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02741.x
263. Abdel Aziz MT, Rezq AM, Atta HM, Fouad H, Zaahkouk AM, Ahmed HH, et al. Molecular signalling of a novel curcumin derivative versus Tadalafil in erectile dysfunction. Andrologia. (2015) 47:616–25. doi: 10.1111/and.12309
264. Jia W, Zhou L, Li L, Zhou P, Shen Z. Nano-based drug delivery of polyphenolic compounds for cancer treatment: progress, opportunities, and challenges. Pharmaceuticals. (2023) 16:101. doi: 10.3390/ph16010101
265. Jadhav MSR, Kale MSH, Rathod MSB, Kohale NB. Novel drug delivery systems for delivery of herbal medicine. Int J Adv Res Sci Commun Technol. (2023) 3:302–14. doi: 10.48175/IJARSCT-8698
266. Xiong L, Wei Y, Si H, Li Z, Wen J, Liu F, et al. Development of the curcumin analog CA7 liposome and its evaluation for efficacy against cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. (2024) 19:13411–28. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S493074
267. Huang M, Liang C, Tan C, Huang S, Ying R, Wang Y, et al. Liposome co-encapsulation as a strategy for the delivery of curcumin and resveratrol. Food Funct. (2019) 10:6447–58. doi: 10.1039/C9FO01338E
268. Narayanan NK, Nargi D, Randolph C, Narayanan BA. Liposome encapsulation of curcumin and resveratrol in combination reduces prostate cancer incidence in PTEN knockout mice. Int J Cancer. (2009) 125:1–8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24336
269. Zare M, Norouzi Roshan Z, Assadpour E, Jafari SM. Improving the cancer prevention/treatment role of carotenoids through various nano-delivery systems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 61:522–34. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1738999
270. Fan Y, Gao L, Yi J, Zhang Y, Yokoyama W. Development of β-carotene-loaded organogel-based nanoemulsion with improved in vitro and in vivo bioaccessibility. J Agric Food Chem. (2017) 65:6188–94. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02125
271. Pant N C, Juyal V. Enhancing oral bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs through solid lipid nanoparticles: recent advancements. Asian Pac J Health Sci. (2022) 9:10–15. doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2022.9.1.03
272. Harde H, Das M, Jain S. Solid lipid nanoparticles: an oral bioavailability enhancer vehicle. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. (2011) 8:1407–24. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2011.604311
273. Munir M, Zaman M, Waqar MA, Khan MA, Alvi MN. Solid lipid nanoparticles: a versatile approach for controlled release and targeted drug delivery. J Liposome Res. (2024) 34:335–48. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2023.2268711
274. Chandrakar R, Vyas A, Kumar N, Sahu U, Jain V. Phyto-phospholipid complex vesicles: a revolutionary approach for enhancing bioavailability and optimizing therapeutic potential in herbal medicine. J Ravishankar Univ Part B. (2024) 37:80–95. doi: 10.52228/JRUB.2024-37-2-8
275. Bhattacharyya S, Ahammed SM, Saha BP, Mukherjee PK. The gallic acid-phospholipid complex improved the antioxidant potential of gallic acid by enhancing its bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech. (2013) 14:1025–33. doi: 10.1208/s12249-013-9991-8
276. Shariare M H, Afnan K, Iqbal F, A Altamimi M, Ahamad SR, S Aldughaim M, et al. Development and optimization of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) nano phytosome using design of experiment (DoE) and their in vivo anti-inflammatory Studies. Molecules. (2020) 25:5433. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225453
277. Javandoost A, Afshari A, Saberi-Karimian M, Sahebkar A, Safarian H, Moammeri M, et al. The effects of curcumin and a modified curcumin formulation on serum cholesteryl ester transfer Protein concentrations in patients with metabolic syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Avicenna J Phytomed. (2018) 8:330–7.
278. Volak LP, Ghirmai S, Cashman JR, Court MH. Curcuminoids inhibit multiple human cytochromes P450, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, and sulfotransferase enzymes, whereas piperine is a relatively selective CYP3A4 inhibitor. Drug Metab Dispos. (2008) 36:1594–605. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.020552
279. Choi J-S, Piao Y-J, Kang KW. Effects of quercetin on the bioavailability of doxorubicin in rats: Role of CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibition by quercetin. Arch Pharm Res. (2011) 34:607–13. doi: 10.1007/s12272-011-0411-x
280. Dimitriadis F, Borgmann H, Struck JP, Salem J, Kuru TH. Antioxidant supplementation on male fertility-a systematic review. Antioxidants. (2023) 12:836. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040836
281. Mehrdadi S. Lipid-based nanoparticles as oral drug delivery systems: overcoming poor gastrointestinal absorption and enhancing bioavailability of peptide and protein therapeutics. Adv Pharm Bull. (2024) 14:48–66. doi: 10.34172/apb.2024.016
282. Kayode OT, Kolawole IO, Afolabi OA, Ohanaka NJ, Iyobhebhe ME. Reproductive health-promoting effects of functional foods. Func Foods Health Dis. (2023) 13:448. doi: 10.31989/ffhd.v13i9.1130
283. Moin A, Zaid M, Moin M, Giuffrè AM. Consumer acceptance and sensory properties of wheat- millet composite biscuits fortified with Moringa oleifera and Camellia sinensis leaves powder. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci J. (2024) 12:683–95. doi: 10.12944/CRNFSJ.12.2.16
284. Azizi MSP, Mehranjani S. The effect of green tea extract on the sperm parameters and histological changes of testis in rats exposed to para-nonylphenol. Int J Reprod Biomed. (2019) 17:717–26. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v17i10.5290
285. Han C, Liu C, Geng J, Tang Y, Li Y, Wang Y, et al. Black and green tea supplements ameliorate male infertility in a murine model of obesity. J Med Food. (2020) 23:1303–11. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2020.4784
286. Gur S, Rezk BM, Abd Elmageed ZY, Kadowitz PJ, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJG. Characterisation of pomegranate juice effects on human corpus cavernosum. Andrologia. (2017) 49:1–7. doi: 10.1111/and.12712
287. Azadzoi KM, Schulman RN, Aviram M, Siroky MB. Oxidative stress in arteriogenic erectile dysfunction: prophylactic role of antioxidants. J Urol. (2005) 174:386–93. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000161209.39959.67
288. Hasanah YM, Raharjo S, Pranoto Y, Ningrum A. Aplikasi Nano-Size Lipid Carrier (NLC) Minyak Bekatul (RBO) Pada Minuman Sari Buah Apel Dan Jeruk Komersial. J Nutr Coll. (2024) 13:38–48. doi: 10.14710/jnc.v13i1.41713
289. Baghel P, Roy A, Verma S, Satapathy T, Bahadur S. Amelioration of lipophilic compounds in regards to bioavailability as self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Future J Pharm Sci. (2020) 6:21. doi: 10.1186/s43094-020-00042-0
290. Nasr Esfahani F, Karimi S, Jalilian Z, Alavi M, Aziz B, Alhagh Charkhat Gorgich E, et al. Functionalized and theranostic lipidic and tocosomal drug delivery systems: potentials and limitations in cancer photodynamic therapy. Adv Pharm Bull. (2024) 14:524–36. doi: 10.34172/apb.2024.038
291. Raikos V, Hayward N, Hayes H, Meroni E, Ranawana V. Optimising the ratio of long- to short-chain triglycerides of the lipid phase to enhance physical stability and bioaccessibility of lycopene-loaded beverage emulsions. Int J Food Sci Technol. (2018) 54:1355–62. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14024
292. Rodriguez ES, Julio LM, Henning C, Diehl BW, Tomás MC, Ixtaina VY. Effect of natural antioxidants on the physicochemical properties and stability of freeze-dried microencapsulated chia seed oil. J Sci Food Agric. (2019) 99:1682–90. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9355
293. Díaz-Maroto MC, Pérez-Coello MS, Cabezudo MD. The effect of Laurus nobilis L. essential oil and different packaging systems on the photo-oxidative stability of Chemlal extra-virgin olive oil. J Food Sci Technol. (2018) 55:4212–22. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3357-x
294. Bińkowska W, Szpicer A, Stelmasiak A, Wojtasik-Kalinowska I, Półtorak A. Microencapsulation of polyphenols and their application in food technology. Appl Sci. (2024) 14:11954. doi: 10.3390/app142411954
295. Baghi F, Gharsallaoui A, Dumas E, Ghnimi S. Advancements in biodegradable active films for food packaging: effects of nano/microcapsule incorporation. Foods. (2022) 11:760. doi: 10.3390/foods11050760
296. Yao S, Zhang J, Wang D, Hou J, Yang W, Da J, et al. Discriminatory components retracing strategy for monitoring the preparation procedure of Chinese patent medicines by fingerprint and chemometric analysis. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0121366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121366
297. Brody T. Food and dietary supplement package labeling-guidance from FDA's warning letters and title 21 of the code of federal regulations. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. (2016) 15:92–129. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12172
298. Turner RE, Degnan FH, Archer DL. Label claims for foods and supplements: a review of the regulations. Nutr Clin Pract. (2005) 20:21–32. doi: 10.1177/011542650502000121
Keywords: food bioactive compounds, antioxidant active ingredients, phytochemicals, functional foods, anti-inflammation, reproductive health
Citation: Liu X, Zeng T, Zhang E, Bin C, Liu Q, Wu K, Luo Y and Wei S (2025) Plant-based bioactives and oxidative stress in reproduction: anti-inflammatory and metabolic protection mechanisms. Front. Nutr. 12:1650347. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1650347
Received: 19 June 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 09 October 2025.
Edited by:
William Kwame Amakye, South China University of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Liu, Zeng, Zhang, Bin, Liu, Wu, Luo and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shaobin Wei, d2Vpc2hhb2JpbjU2MjBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡These authors share first authorship
 Xue Liu
Xue Liu Tongtong Zeng
Tongtong Zeng Enfeng Zhang
Enfeng Zhang Chengli Bin
Chengli Bin Qun Liu1
Qun Liu1 Shaobin Wei
Shaobin Wei