- 1School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 2Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
The decline in estrogen levels among menopausal women can trigger multisystem dysfunction, significantly increasing the risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, cognitive impairment, and genitourinary syndrome (GSM). As plant-derived weak estrogen analogs, phytoestrogens demonstrate menopause-related protective potential in preclinical studies by selectively activating ERα, ERβ, and GPER receptor targets to modulate downstream signaling pathways. Current clinical trials indicate their value as an alternative strategy to menopausal hormone therapy (MHT, previously referred to as HRT) for managing menopause-related disorders. Although heterogeneity exists across study outcomes, specific formulations have shown clear efficacy. Future well-designed, large-scale studies are warranted to validate their clinical translational potential.
Introduction
The menopausal transition, driven by progressive ovarian follicular depletion and declining sex hormone production, represents a critical phase in female reproductive aging (1). Characteristic symptoms—including hot flushes, night sweats, mood disturbances, vaginal dryness, and diminished quality of sex life—primarily arise from hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause, culminating in menopause, defined as 12 months of amenorrhea (2, 3). Beyond these, the decline in estrogen and progesterone levels may disrupt multiple physiological systems—affecting metabolism, cognition, the urogenital tract, and skeletal integrity—thereby increasing the long-term risk of age-related symptoms such as cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and cognitive impairment.
Estrogen plays a crucial role not only in regulating female reproductive function but also in neuroprotection, metabolic homeostasis, vascular regulation, and immune modulation through its widely distributed receptors (4). Consequently, estrogen deficiency has been associated with progressive, menopause-related issues in some women. Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is a primary intervention for managing menopausal symptoms, though its risk profile necessitates careful consideration. Early Women's Health Initiative (WHI) findings associated oral combined estrogen–progestogen with elevated risks of breast cancer and thromboembolism, but these results were primarily observed in older women (mean age 63) initiating therapy >10 years post-menopause (5, 6). Specifically, the ESTHER trial demonstrated transdermal estrogen's lower venous thrombosis risk compared to oral formulations (7), while the ELITE study revealed reduced atherosclerosis progression only when MHT initiation occurred within 6 years post-menopause (8). Nurses' Health Study data further indicate substantially increased breast cancer risk with prolonged use exceeding 10 years, contrasting sharply with the minimal risk observed in short-term therapy (9). MHT may carry adverse risks in some populations, and given the conflicting evidence, alternative treatments could offer safer options.
Phytoestrogens represent a diverse group of naturally derived non-steroidal plant compounds. Characterized by multiple hydroxyl-substituted aromatic rings, these molecules share a structural resemblance to endogenous estrogens, allowing them to interact with estrogen receptors and elicit estrogen-like or antagonistic biological responses (10). The major categories of phytoestrogens include isoflavones, lignans, coumestans, and resveratrol-like compounds (11). Isoflavones are predominantly found in leguminous plants, such as soybeans, chickpeas, and red clover. Lignans are abundant in flaxseeds, sesame seeds, whole grains, and certain vegetables. Coumestans are rich in sprouted plants, while resveratrol is primarily derived from grapes, peanuts, and related sources (12).
The route of administration of phytoestrogens, as a potential alternative therapy for managing menopausal symptoms, directly influences their bioavailability, efficacy, and safety. Oral administration via tablets, capsules, or beverages is the most common route. However, it is associated with significant first-pass metabolism, a slower onset of action, complex dose–response relationships, and potential antagonistic effects on estrogen receptors at high doses (13, 14). Vaginal local administration for specific symptoms offers advantages such as precise targeting, lower systemic absorption, and a faster onset of action. Nevertheless, it is largely ineffective for systemic symptoms such as hot flushes (15).
Phytoestrogens, primarily isoflavones from soy and red clover, are predominantly marketed in most countries as over-the-counter (OTC) dietary supplements or functional foods. In the United States, they are regulated as dietary supplements; the FDA does not require pre-market approval (16). In the European Union, they are generally managed under the food supplement pathway, and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has conducted safety assessments (17). Canada regulates them as Natural Health Products (NHPs), requiring product licensing and mandatory label warnings (18). Under Japan's Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) framework, a daily upper intake limit of 30 mg/day for soy isoflavones and specific labeling standards are established (19). Authoritative clinical guidelines do not recommend isoflavones for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms. To date, no prescription drug containing phytoestrogens as the active ingredient has been approved for menopausal symptoms through the medicinal product pathways of either the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) (20).
In addition, preclinical studies suggest that phytoestrogens may exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties. However, clinical evidence remains limited. They are being investigated as potential adjunctive approaches for alleviating menopausal symptoms, reducing osteoporosis risk, and modulating outcomes in hormone-related cancers (21). Given the discordance with current clinical guidelines, this review critically examines the mechanistic basis for phytoestrogens' purported anti-aging effects, evaluates their theoretical potential in managing menopausal conditions, and analyzes translational barriers to evidence-based clinical implementation.
Molecular mechanisms related to phytoestrogen receptors
Following typical oral intake, phytoestrogens primarily exert their biological effects by binding to specific receptors. This article summarizes the mechanisms of action and signaling pathways of phytoestrogens, with a focus on ERα/ERβ (estrogen receptor alpha/beta) nuclear receptors and the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) membrane receptor as the principal targets. Table 1 provides a concise summary of these representative findings.

Table 1. Representative phytoestrogens, their receptor targets, signaling pathways, and reported biological effects.
Nuclear estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ
Phytoestrogens competitively bind to estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ against endogenous estrogens, mediating their effects via classical signaling pathways. Many exhibit higher affinity for ERβ, and this ERβ selectivity contributes to their tissue-specific actions (22, 23). Owing to their predominant dose-dependent relative binding and transactivation preference for ERβ over ERα (24), phytoestrogens may elicit tissue-specific biological responses, including estrogenic-like actions in ERβ-enriched tissues such as bone and vasculature, and modulation of ERα-mediated proliferative signaling in organs, including the breast (25). This receptor selectivity has been proposed to contribute to a more favorable safety profile relative to synthetic estrogens; however, robust clinical evidence confirming reductions in estrogen-sensitive pathologies remains limited. Their efficacy in achieving acute therapeutic endpoints—particularly vasomotor symptom relief—generally appears lower than that of high-potency synthetic estrogen analogs such as ethinyl estradiol (26).
ERβ is expressed at higher levels than ERα in certain tissues, including bone, the cardiovascular system, and specific regions of the central nervous system. This comparison refers only to relative receptor abundance within these tissues and does not imply the diminished functional importance of ERα. In experimental models, ERβ activation can promote apoptosis via mechanisms such as caspase-3 activation, p38/MAPK phosphorylation, and PARP cleavage, suggesting a potential role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and suppressing tumorigenesis (27). However, ERβ signaling exhibits context-dependent effects, and under certain physiological or pathological conditions, its activation may contribute to adverse outcomes (28). In ovariectomized (OVX) osteoporotic rats—a model of postmenopausal bone loss—genistein promotes bone formation and suppresses inflammation via ERβ-mediated MAPK/PI3K signaling cascades (29). In Aβ-treated SH-SY5Y neuronal models of Alzheimer's disease, curcumin demonstrates neuroprotective effects in experimental models by modulating the NF-κB pathway via ERβ, reducing BACE1 expression and Aβ production. Despite curcumin's significant mechanistic promise, its clinical utility is severely limited by low bioavailability and poor absorption, impeding therapeutic translation (30).
Some phytoestrogens may enhance estrogenic signaling in part by upregulating estrogen receptor expression, as shown in selected cellular and animal models. In mouse Neuro-2A neuroblastoma cells, isoflavones increase ERα protein; ERα knockdown reduces isoflavone-induced neurite outgrowth and ER target gene expression, indicating enhanced ERα-mediated signaling (31). Similarly, S-equol upregulates ERβ protein in diabetic osteoporotic rats and osteoblast cells, potentiating bone estrogen signaling (32). In Aβ-induced neuronal apoptosis models, quercetin elevates ERα protein, activating the MAPK/ERK pathway, and inhibiting apoptosis (33). Collectively, data from these models indicate a potential capacity of phytoestrogens to enhance nuclear receptor signaling by upregulating ERα/ERβ protein expression, modulating downstream growth, and survival functions.
GPER membrane receptor
Distinct from classical nuclear receptor pathways, phytoestrogens can also mediate rapid non-genomic effects through the membrane-bound G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), activating downstream signaling cascades including cAMP, Ca2+, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K. Unlike the slower genomic pathways of nuclear ERs, GPER activation typically elicits rapid non-genomic signaling within seconds to minutes, driving transient cellular responses such as ion flux changes or kinase activation. These initial events may subsequently modulate gene expression through secondary messengers (34).
In broiler chickens and primary hepatocytes, genistein promotes glucose uptake via the GPER-cAMP/PKA-AMPK axis, enhancing GLUT2-mediated transport (35). Piceatannol activates GPER-PKA in estrogen-deficient models (OVX mice and 3T3-L1 adipocytes), inducing phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and thereby reducing lipid accumulation (36). Puerarin has been reported to modulate the GPER–Ca2+–SIRT1–AMPK axis, thereby inhibiting hepatic lipogenesis and enhancing lipolysis, which ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis in obese mice and HepG2 cells (37). Regarding cardiovascular protection, 17β-estradiol (E2) predominantly signals through GPER–PI3K to induce vasoprotective effects, whereas phytoestrogens (e.g., daidzein and genistein) exhibit preferential activation of the GPER–PKA pathway to promote vasodilation; however, cross-activation of multiple downstream cascades likely occurs for both E2 and phytoestrogens (38). In ovariectomized mice fed a high-fat diet, kaempferol-induced GPER protein expression upregulation attenuates markers of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/Nrf2. This protection—validated in ox-LDL-injured human aortic endothelial cells—is blocked by GPER silencing, confirming target specificity (39).
In the nervous system, S-equol promotes cerebellar neuron migration in vitro via GPER-ERK1/2 (40). Genistein activation of GPER/PGC-1α confers neuroprotection in OVX mice with cerebral I/R injury, suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation (41). In ischemic rats, icaritin modulates GPER-ERK-NF-κB signaling to suppress harmful microglial activation, shifting them from damaging inflammatory (M1) to protective reparative (M2) states, thereby reducing neuroinflammation (42).
Evidence suggests that GPER can interact with classical ER pathways through context-dependent mechanisms. Its activation induces Src-dependent EGFR phosphorylation, amplifying ERK1/2 signaling, while ERα upregulates EGFR protein levels—creating a feedback loop (43). In certain tumor cells, ERα-dependent estrogenic effects require the concomitant presence of GPER, suggesting a functional interdependence between the two receptors (44). However, direct experimental evidence demonstrating molecular cross-talk between GPER and classical nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα/ERβ) in postmenopausal tissues remains limited and warrants further investigation.
Phytoestrogen interventions in menopause-associated conditions
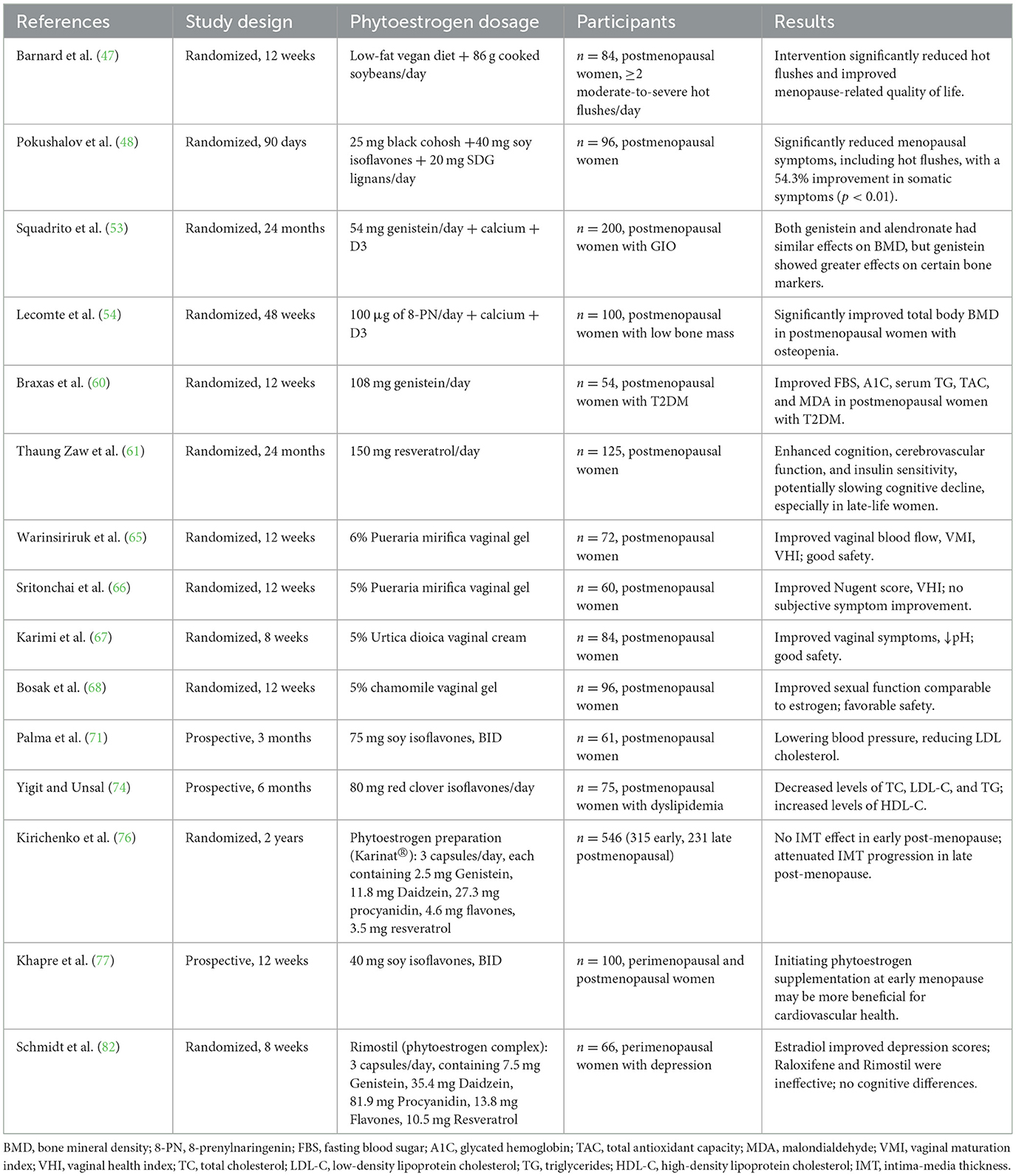
Based on the mechanistic insights described earlier, several recent clinical trials have been conducted to assess the anti-aging and symptom-modulating effects of phytoestrogens in postmenopausal women. Table 2 summarizes these studies, which were selected for inclusion in this review.
Hot flushes
Vasomotor symptoms, particularly hot flushes, arise from estrogen deprivation–induced hypersensitivity in hypothalamic thermoregulatory centers—key mediators of temperature homeostasis—coupled with heightened sympathetic activity. MHT is an effective therapy for hot flushes (45), whereas phytoestrogen efficacy remains inconclusive with inconsistent clinical outcomes. Notably, non-hormonal agents such as the neurokinin-3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant have emerged as evidence-based alternatives for vasomotor symptom management (46).
Plant-based diets with soy supplementation reduced hot flush frequency in postmenopausal women, with one study reporting symptom remission in approximately 50% of participants (47). Trials combining black cohosh, soy isoflavones, and SDG lignans also yielded favorable outcomes. Authors attribute the primary effect to black cohosh, which does not directly bind to estrogen receptors, suggesting a mechanism independent of classical estrogen receptor pathways (48).
Current evidence predominantly derives from complex mixtures, with scarce high-quality trials on single phytoestrogen monomers. Future research must prioritize dose–response relationships and molecular mechanisms of individual compounds to enable evidence-based personalized therapy.
Osteoporosis
The decline in estrogen during menopause accelerates bone resorption and increases osteoporosis risk (49). Phytoestrogens exert anti-osteoporotic effects through receptor-mediated signaling and mitochondrial pathways. For example, glabrene downregulates tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) to inhibit osteoclasts, upregulates osteoprotegerin (OPG) and osteocalcin, and activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling to promote osteogenic genes such as Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) and Osterix (Osx), restoring bone metabolic balance (50). Beyond classical ER-dependent mechanisms, genistein activates estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), upregulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) to promote mitochondrial biogenesis. It also enhances sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) expression, which activates PTEN-induced kinase 1/Parkin (PINK1/Parkin)-dependent mitophagy, reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS), delaying bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMMSC) senescence, and maintaining bone metabolic homeostasis (51).
In a clinical trial conducted in 2018, soy isoflavones were found to reduce bone resorption markers, but their effect on improving bone mineral density (BMD) was minimal (52). However, recent studies have shown that genistein monotherapy may increase lumbar and femoral BMD in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, effects that seem comparable to alendronate (53). Recent studies have also indicated that supplementation with 8-PN standardized hop extract may improve BMD in postmenopausal women with osteopenia, with a positive trend in BMD increase compared to baseline (54).
Overall, clinical evidence suggests phytoestrogens mitigate bone resorption in postmenopausal women, with genistein showing notable efficacy. However, improvements in BMD remain modest, and marked heterogeneity exists among phytoestrogens in both biological activity and clinical outcomes.
Diabetes mellitus
Estrogen regulates glucose and lipid metabolism by enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake. After menopause, estrogen decline increases type 2 diabetes in women (55). Estrogen metabolism also accelerates in diabetic women due to hepatic upregulation of SULT1E1 and ABCG2, promoting estrogen inactivation and excretion (56). Phytoestrogens may improve glucose metabolism via estrogen receptor modulation and direct effects on metabolic pathways. Genistein activates PKA and ERK1/2, promoting β-cell proliferation and improving insulin resistance (57). Coumestrol attenuates insulin resistance by modulating sphingolipid metabolism, inhibiting ceramide synthesis, and upregulating SIRT1 to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation (58, 59).
Some studies suggest phytoestrogens improve glucose metabolism in postmenopausal women, but results remain inconsistent. A double-blind trial in diabetic postmenopausal women showed genistein reduced fasting glucose, HbA1c, triglycerides, and improved antioxidant capacity, insulin sensitivity, and HDL cholesterol (60). A 24-month crossover trial reported that low-dose resveratrol reduced fasting insulin and HOMA-IR, suggesting improved insulin sensitivity (61).
Phytoestrogens may improve diabetes-related parameters in postmenopausal women via estrogen-like activity and glucose-lipid metabolic modulation. However, clinical evidence remains heterogeneous, highlighting the need for large, well-designed prospective trials to confirm their therapeutic value.
Urogenital disorders
Estrogen maintains vaginal elasticity, moisture, and mucosal integrity (62). After menopause, declining estrogen results in epithelial thinning, pH elevation, and disrupted barriers, increasing UTI and GSM risk (63). Estrogen therapy can temporarily alleviate symptoms of vaginal atrophy, and topical phytoestrogen preparations demonstrate unique value.
Experimental evidence suggests phytoestrogens enhance urogenital defense via antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and circulatory-promoting actions (64). A systematic review suggests vaginal phytoestrogen formulations outperform oral forms in alleviating vaginal atrophy, incontinence, and sexual dysfunction (15). Clinical trials demonstrate that locally applied phytoestrogen gels/creams—including 6% Pueraria mirifica gel, 4% soy isoflavone gel, 5% Urtica dioica (stinging nettle) cream, and 5% chamomile gel—improve vaginal atrophy symptoms, increase Vaginal Health Index scores, enhance epithelial maturation and microvascular perfusion, restore Lactobacillus-dominant microbiota, and improve sexual function (65–68). Notably, 5% chamomile gel demonstrated efficacy comparable to estrogen therapy in improving sexual function (67). In contrast, oral phytoestrogens show minimal efficacy for urogenital symptoms and cannot substitute local therapy (69).
Overall, clinical evidence supports locally applied phytoestrogens for alleviating vaginal atrophy, restoring microbiota, and improving sexual function in postmenopausal women. Despite promising results, standardized formulations and long-term data remain limited.
Cardiovascular disease
Estrogen protects the cardiovascular system by promoting nitric oxide (NO) generation, regulating lipid profiles, and suppressing inflammation. Menopause-induced estrogen decline increases CVD risks, including atherosclerosis, hypertension, and arrhythmias (70). Phytoestrogens, by binding to estrogen receptors, may mimic these protective effects.
Despite promising in vitro and animal results, clinical data remain inconsistent. Studies report mixed outcomes, including lowered blood pressure and LDL (71), improved lipid profiles and endothelial function in meta-analyses, yet also increased carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT), suggesting potential atherosclerosis risk (72).
Research outcomes for isoflavones are conflicting. While some studies suggest that isoflavones have individualized effects on cardiovascular risk factors associated with menopause (73), others report improvements in lipid profiles (74, 75). These discrepancies likely arise from variations in plant source, resulting in isoflavone metabolic profiles and population-specific metabolic heterogeneity.
Cardioprotective effects of phytoestrogens appear time-dependent and vary significantly, influenced by menopausal stage (76), genetics, and comorbidities. The latest research suggests that initiating phytoestrogen supplementation during the early stages of menopause (such as the perimenopausal and early postmenopausal periods) may be more beneficial for cardiovascular health (77). Large, long-term trials are needed to confirm their safety and mechanisms.
Cognitive disorders
Phytoestrogens exert neuroprotective effects against cognitive impairment through multiple mechanisms, including: activation of the ERβ-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway to promote neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity (78); modulation of the PI3K/Akt-Nrf2 axis to enhance antioxidant capacity, reducing oxidative damage and apoptosis (79); and regulation of the AMPK-PGC1α pathway to improve mitochondrial biogenesis and maintain energy metabolism homeostasis (80). Notably, emerging preclinical evidence suggests that even suboptimal dietary phytoestrogen exposure—in gonadally intact models (adult male mice)—may compromise hippocampal plasticity and remote memory consolidation (81). While this novel perspective underscores the necessity of maintaining adequate levels, its translational implications for postmenopausal cognition require careful interpretation due to fundamental differences in the hormonal milieu between intact males and estrogen-deficient states.
Clinical evidence for the cognitive benefits of phytoestrogens is limited. Resveratrol enhanced cognition, perfusion, and metabolic status over 24 months in older women (61). A randomized trial for perimenopausal depression (PMD) found that phytoestrogens (Rimostil), transdermal estradiol, and raloxifene failed to demonstrate statistically significant improvements vs. placebo. These findings collectively indicate minimal clinical efficacy of estrogenic therapies in PMD management (82). Despite methodological rigor, these negative outcomes—potentially influenced by the short 8-week duration—highlight the need to explore alternative interventions for this complex neuroendocrine condition.
Moreover, specific monomers such as genistein and daidzein show promise as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) in cognitive trials, particularly for AD (83). S-equol's blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability further supports its potential, though comparative clinical data remain sparse (84).
Selected studies met the following criteria: (1) primary focus on postmenopausal/peri-menopausal women; (2) intervention with defined phytoestrogen compounds or standardized phytoestrogen-rich extracts; (3) reporting outcomes relevant to menopausal health (vasomotor, bone, metabolic, urogenital, cognitive, and quality of life); and (4) clinical trial design (RCT or prospective cohort with ≥8 weeks duration) published between 2019 and 2025. The excluded criteria included: animal studies, reviews, non-primary data, studies on premenopausal women, or interventions where phytoestrogen effects could not be isolated.
Bioavailability challenges and interindividual variability
The absorption and metabolism of phytoestrogens in the human body are influenced by multiple factors, with gut microbiota playing a central role. Phytoestrogen precursors predominantly exist in glycosidic forms, and their hydrolysis into aglycones by gut microbiota is essential for systemic absorption (85). Furthermore, gut microbiota biotransform specific phytoestrogens—including isoflavones, lignans, and ellagitannins—into metabolites with greater biological activity and bioavailability, such as equol, enterolignans, and urolithins (86).
Substantial inter-individual variability exists in these processes. A well-documented example is equol production: 50%−70% of Asian populations are equol producers compared with only 20%−30% of Western populations, largely reflecting gut microbiota composition (80). Such ethnic differences contribute to heterogeneity in phytoestrogen bioavailability and clinical outcomes, particularly in interventions involving soy isoflavones. Beyond ethnicity, other determinants—including genetic background, age, sex, health status, and diet—further shape individual differences in absorption and metabolism (86). In addition, the food matrix and the form of intake significantly influence absorption kinetics (87). Compared with purified extracts, phytoestrogens ingested within whole foods display distinct absorption efficiency and plasma concentrations, as food components such as protein and fiber can modulate their release and interact with the gut microbiota (88).
The critical role of bioavailability in determining the physiological impact of phytoestrogens necessitates careful consideration when evaluating their therapeutic potential for menopausal symptoms. While mechanistic studies often highlight the promising biological effects of compounds such as curcumin, its clinical translation is significantly hampered by its inherently low bioavailability (89). Furthermore, heterogeneity in clinical trial outcomes assessing phytoestrogens for menopausal symptom relief can be partly attributed to substantial variations in bioavailability (90). This variation stems from the diverse formulations used (complex mixtures vs. isolated compounds, capsules vs. whole foods) and significant inter-individual differences among participants, including gut microbiota composition, which profoundly influences absorption and metabolic activation (91). Consequently, inconsistent bioavailability complicates the interpretation of efficacy data and hinders robust comparisons between studies. To enhance the reliability and clinical relevance of future research, methodological refinements are essential. These include the standardized use of well-characterized monomeric compounds with defined pharmacokinetic profiles and the strategic stratification of participant populations based on key determinants of bioavailability, such as enterotype or metabolic phenotypes.
Discussion
Phytoestrogens modulate estrogen signaling through multi-receptor targeting, offering a multi-target strategy for addressing menopause-related dysfunction. In osteoporosis, they bind to ERs, inhibit the RANKL-RANK pathway, suppress osteoclast activity, and activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to improve bone density and structure (92). In diabetes, the targets extend to the PPAR and AMPK pathways, enhancing insulin sensitivity, promoting cholesterol transport, and reducing inflammation (93). Different phytoestrogens vary in receptor affinity and activity, leading to diverse effects. Although mechanistic complexity increases, this model provides potential for systemic, multi-pathway regulation.
Given the potential of phytoestrogens to improve menopausal health, further studies on their mechanisms and efficacy are needed. Current clinical evidence on hot flushes and cardiovascular benefits remains inconsistent (94). First, most positive outcomes are based on multi-component formulations or plant-based dietary interventions, whose synergistic effects may surpass those of standardized single-compound preparations. Evidence for the efficacy of phytoestrogen monomers remains limited, with significant heterogeneity among studies (94). Second, substantial individual differences in the metabolism and bioavailability of phytoestrogens exist, heavily influenced by gut microbiota composition. The proportion of S-equol producers is considerably higher among East Asian women compared to Western populations, which may partially explain inter-population differences in clinical outcomes (95). Third, factors such as chemical structure, dosage form, and food interactions can affect oral absorption rates, resulting in variable plasma concentrations and treatment effects (96). Fourth, different phytoestrogens possess varying affinities and activation capacities for ER subtypes (ERα, ERβ), and some effects are dose-dependent, yet the optimal therapeutic window remains undefined. In addition, population heterogeneity—including menopausal stage, baseline comorbidities, and genetic background—may significantly influence intervention outcomes and should be carefully addressed in future study designs.
Phytoestrogens hold multi-target value in managing menopausal symptoms. Local formulations with puerarin, soy isoflavones, and nettle show good safety and efficacy (15). Genistein displays effects comparable to alendronate in GIOP via ERβ/ERRα and mitochondrial pathways (53). S-equol and resveratrol show promise in cognitive protection by improving cerebral blood flow and reducing β-amyloid (61). Composite plant-based interventions also effectively alleviate vasomotor symptoms, with strong clinical feasibility (47, 97).
Phytoestrogens offer a natural multi-target option in menopausal care. Challenges include heterogeneity, low bioavailability, and individual variability. Future research should focus on standardized monomer studies and precision interventions to optimize safety and efficacy as MHT alternatives.
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XQ: Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – review & editing. YY: Writing – review & editing. ZW: Writing – review & editing. XZ: Writing – review & editing. QG: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the following funding sources: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81803991), the 2024 Jiangsu Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Project (Grant No. MS2024143), and the 2022 Jiangsu Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Plan Project (Grant No. MS2022149).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Santoro N, Randolph JF. Reproductive hormones and the menopause transition. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. (2011) 38:455–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2011.05.004
2. Harlow SD, Gass M, Hall JE, Lobo R, Maki P, Rebar RW, et al. Executive summary of the stages of reproductive aging workshop + 10. Menopause. (2012) 19:387–95. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e31824d8f40
3. Brady SS, Shan L, Markland AD, Huling JD, Arguedas A, Fok CS, et al. Trajectories of depressive symptoms over 20 years and subsequent lower urinary tract symptoms and impact among women. Menopause. (2023) 30:723–31. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002193
4. Stuenkel CA. Menopausal hormone therapy and the role of estrogen. Clin Obstet Gynecol. (2021) 64:757–71. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000648
5. Chaikittisilpa S, Orprayoon N, Vallibhakara O, Vallibhakara SA-O, Tanmahasamut P, Somboonporn W, et al. Summary of the 2023 Thai menopause society clinical practice guideline on menopausal hormone therapy. J Menopausal Med. (2024) 30:24. doi: 10.6118/jmm.24006
6. Zhang G-Q, Chen J-L, Luo Y, Mathur MB, Anagnostis P, Nurmatov U, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and women's health: an umbrella review. PLoS Med. (2021) 18:e1003731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003731
7. Canonico M, Oger E, Plu-Bureau GV, Conard J, Meyer G, LéVesque H, et al. Hormone therapy and venous thromboembolism among postmenopausal women. Circulation. (2007) 115:840–5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.642280
8. Miller VM, Taylor HS, Naftolin F, Manson JE, Gleason CE, Brinton EA, et al. Lessons from KEEPS: the Kronos early estrogen prevention study. Climacteric. (2021) 24:139–45. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2020.1804545
9. Chen WY. Postmenopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: current status and unanswered questions. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. (2011) 40:509–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2011.05.006
10. Alfonso R, Damiani GR, Romano I, Trojano G, Vimercati A, Di Gennaro D, et al. Non-hormonal options for managing menopause symptoms: a narrative review. Italian J Gynaecol Obstet. (2024) 36:571–87. doi: 10.36129/jog.2024.172
11. Patra S, Gorai S, Pal S, Ghosh K, Pradhan S, Chakrabarti S. A review on phytoestrogens: current status and future direction. Phytother Res. (2023) 37:3097–120. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7861
12. Estrada-Camarena E, López-Rubalcava C, Valdés- B, Sustaita, Azpilcueta-Morales GS, María E, et al. Use of phytoestrogens for the treatment of psychiatric symptoms associated with menopause transition. In:Rodriguez-Landa JF and Cueto-Escobedo, , editors. A Multidisciplinary Look at Menopause. Rijeka: InTech (2017) 81–109.
13. Yang Z, Kulkarni K, Zhu W, Hu M. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of genistein: mechanistic studies on its ADME. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. (2012) 12:1264–80. doi: 10.2174/187152012803833107
14. Soyata A, Hasanah AN, Rusdiana T. Isoflavones in soybean as a daily nutrient: the mechanisms of action and how they alter the pharmacokinetics of drugs. Turk J Pharm Sci. (2021) 18:799–810. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2020.79106
15. Abdi F, Rahnemaei FA, Roozbeh N, Pakzad R. Impact of phytoestrogens on treatment of urogenital menopause symptoms: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2021) 261:222–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2021.03.039
16. Bailey RL. Current regulatory guidelines and resources to support research of dietary supplements in the United States. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 60:298–309. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1524364
17. Risk assessment for peri- and post-menopausal women taking food supplements containing isolated isoflavones. EFSA J. (2015) 13:4246. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4246
18. Ng JY, Luong M. Evaluation of the Canadian natural health product regulatory framework in academic research: a scoping review. Eur J Integr Med. (2020) 37:101159. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101159
19. Uehara M. Isoflavone metabolism and bone-sparing effects of daidzein-metabolites. J Clin Biochem Nutr. (2013) 52:193–201. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.13-2
20. Goodman NF, Cobin RH, Ginzburg SB, Katz IA, Woode DE, Camacho PM, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and treatment of menopause. Endocr Pract. (2011) 17:1–25. doi: 10.4158/EP.17.S6.1
21. Petrine JCP, Bianco-Borges BD. The influence of phytoestrogens on different physiological and pathological processes: an overview. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:180–97. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6816
22. Mbachu OC, Howell C, Simmler C, Garcia GRM, Skowron KJ, Dong H, et al. SAR study on estrogen receptor α/β Activity of (Iso)flavonoids: importance of prenylation, C-Ring (Un)saturation, and hydroxyl substituents. J Agric Food Chemist. (2020) 68:10651–63. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03526
23. Park S, Sim K-S, Heo W, Kim J-H, Park S, Sim K-S, et al. Protective effects of coumestrol on metabolic dysfunction and its estrogen receptor-mediated action in ovariectomized mice. Nutrients. (2023) 15:954. doi: 10.3390/nu15040954
24. Jiang Y, Gong P, Madak-Erdogan Z, Martin T, Jeyakumar M, Carlson K, et al. Mechanisms enforcing the estrogen receptor β selectivity of botanical estrogens. FASEB J. (2013) 27:4406–18. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-234617
25. Lecomte S, Demay F, Ferrière F, Pakdel F. Phytochemicals targeting estrogen receptors: beneficial rather than adverse effects? Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:1381. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071381
26. Villaseca P. Non-estrogen conventional and phytochemical treatments for vasomotor symptoms: what needs to be known for practice. Climacteric. (2012) 15:115–24. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2011.624214
27. Wang X, Ha D, Yoshitake R, Chan YS, Sadava D, Chen S, et al. Exploring the biological activity and mechanism of xenoestrogens and phytoestrogens in cancers: emerging methods and concepts. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:8798. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168798
28. Leung Y-K, Lam H-M, Wu S, Song D, Levin L, Cheng L, et al. Estrogen receptor β2 and β5 are associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer, and promote cancer cell migration and invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer. (2010) 17:675–89. doi: 10.1677/ERC-09-0294
29. Cepeda SB, Cutini PH, Valle MI, Campelo AE, Massheimer VL, Sandoval MJ. Bone action of the phytoestrogen genistein under hypoestrogenism and obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2024) 594:112388. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2024.112388
30. Huang P, Zheng N, Zhou H-b, Huang J, Huang P, Zheng N, et al. Curcumin inhibits BACE1 expression through the interaction between ERβ and NFκB signaling pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Mol Cell Biochem. (2019) 463:1. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03638-0
31. Ariyani W, Amano I, Koibuchi N, Ariyani W, Amano I, Koibuchi N. Isoflavones mediate dendritogenesis mainly through estrogen receptor α. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:9011. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109011
32. Xu Z, Xu J, Li S, Cui H, Zhang G, Ni X, et al. S-Equol enhances osteoblastic bone formation and prevents bone loss through OPG/RANKL via the PI3K/Akt pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Front Nutr. (2022) 9 :986192. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.986192
33. Liu L, Liu Y, Zhen Y, Guo T, Wang C, Shen L, et al. Quercetin inhibits cytotoxicity of PC12 cells induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 via stimulating estrogen receptor α, activating ERK1/2, and inhibiting apoptosis. Open Life Sci. (2022) 17:230–42. doi: 10.1515/biol-2021-0014
34. Arterburn JB, Prossnitz ER. G Protein–coupled estrogen receptor GPER: molecular pharmacology and therapeutic applications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2023) 63:295–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-031122-121944
35. Li Q, Yang Y, Wang H, Jiang Z, Ma H. Genistein accelerates glucose catabolism via activation the GPER-mediated cAMP/PKA-AMPK signaling pathway in broiler chickens. Life Sci. (2022) 303:120676. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120676
36. Arisawa K, Matsuoka A, Ozawa N, Ishikawa T, Ichi I, Fujiwara Y, et al. GPER/PKA-dependent enhancement of hormone-sensitive lipase phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by piceatannol. Nutrients. (2024) 16:38. doi: 10.3390/nu16010038
37. Pham TH, Lee GH, Jin SW, Lee SY, Han EH, Kim ND, et al. Puerarin attenuates hepatic steatosis via G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor-mediated calcium and SIRT1 signaling pathways. Phytother Res. (2022) 36:3601–18. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7526
38. V C-S, P S, W M, MV D, JC C, A Z, et al. 17-β-estradiol and phytoestrogens elicit NO production and vasodilatation through PI3K, PKA and EGF receptors pathways, evidencing functional selectivity. Eur J. Pharmacol. (2024) 975:176636. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176636
39. Feng Z, Wang C, Jin Y, Meng Q, Wu J, Sun H. Kaempferol-induced GPER upregulation attenuates atherosclerosis via the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 pathway. Pharm Biol. (2021) 59:1106–16. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1961823
40. Ariyani W, Miyazaki W, Koibuchi N, Ariyani W, Miyazaki W, Koibuchi N, et al. Novel Mechanism of S-equol action in neurons and astrocytes: the possible involvement of GPR30/GPER1. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5178. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205178
41. Wang S, Zhang Z, Wang J, Ma L, Zhao J, Wang J, et al. Neuronal GPER participates in genistein-mediated neuroprotection in ischemic stroke by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in ovariectomized female mice. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:8. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02894-4
42. Yu Z, Su G, Zhang L, Liu G, Zhou Y, Fang S, et al. Icaritin inhibits neuroinflammation in a rat cerebral ischemia model by regulating microglial polarization through the GPER–ERK–NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med. (2022) 28 :142. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00573-7
43. Albini A, Rosano C, Angelini G, Amaro A, Esposito A, Maramotti S, et al. Exogenous hormonal regulation in breast cancer cells by phytoestrogens and endocrine disruptors. Curr Med Chem. (2014) 21:1129–45. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666131129124640
44. Prossnitz ER, Barton M. Estrogen biology: new insights into GPER function and clinical opportunities. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2014) 389:71–83. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.02.002
45. Maclennan A, Broadbent J, Lester S, Moore V. Oral oestrogen and combined oestrogen/progestogen therapy versus placebo for hot flushes. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. (2004) 2004:CD002978. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002978.pub2
46. Akhtar SMM, Ali A, Khan MS, Khan V, Fareed A, Saleem SZ, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant for vasomotor symptoms in postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Gynecol Obstet. (2024) 166:969–83. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.15467
47. Barnard ND, Kahleova H, Holtz DN, Znayenko-Miller T, Sutton M, Holubkov R, et al. A dietary intervention for vasomotor symptoms of menopause: a randomized, controlled trial. Menopause. (2023) 30:80–7. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002080
48. Pokushalov E, Ponomarenko A, Garcia C, Kasimova L, Pak I, Shrainer E, et al. Assessing the combined effects of Black Cohosh, Soy Isoflavones, and SDG Lignans on menopausal symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Nutr. (2025) 64:138. doi: 10.1007/s00394-025-03588-y
49. Cheng C-H, Chen L-R, Chen K-H. Osteoporosis due to hormone imbalance: an overview of the effects of estrogen deficiency and glucocorticoid overuse on bone turnover. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1376. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031376
50. Liu J, Deng X, Liang X, Li L. The phytoestrogen glabrene prevents osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats through upregulation of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2021) 35:e2265. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22653
51. Li M, Yu Y, Xue K, Li J, Son G, Wang J, et al. Genistein mitigates senescence of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via ERRα-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy in ovariectomized rats. Redox Biol. (2023) 61:102649. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102649
52. Tiţ DM, Bungău S, Iovan C, Cseppento DCN, Endres L, Sava C, et al. Effects of the hormone replacement therapy and of soy isoflavones on bone resorption in postmenopause. J Clin Med. (2018) 7:297. doi: 10.3390/jcm7100297
53. Squadrito F, Imbalzano E, Rottura M, Arcoraci V, Pallio G, Catalano A, et al. Effects of genistein aglycone in glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: a randomized clinical trial in comparison with alendronate. Biomed Parmacother. (2023) 163:114821. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114821
54. Lecomte M, Tomassi D, Rizzoli R, Tenon M, Berton T, Harney S, et al. Effect of a hop extract standardized in 8-prenylnaringenin on bone health and gut microbiome in postmenopausal women with osteopenia: a one-year randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2688. doi: 10.3390/nu15122688
55. Zhu J, Zhou Y, Jin B, Shu J. Role of estrogen in the regulation of central and peripheral energy homeostasis: from a menopausal perspective. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. (2023) 14:20420188231199359. doi: 10.1177/20420188231199359
56. Fashe M, Yi M, Sueyoshi T, Negishi M. Sex-specific expression mechanism of hepatic estrogen inactivating enzyme and transporters in diabetic women. Biochem Pharmacol. (2021) 190:114662. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114662
57. Romani AMP. The controversy on the beneficial effect of phytoestrogens in diabetic treatment in postmenopausal women. Biochem Pharmacol. (2021) 190:114619. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114619
58. Zywno H, Bzdega W, Kolakowski A, Kurzyna P, Harasim-Symbor E, Sztolsztener K, et al. The influence of coumestrol on sphingolipid signaling pathway and insulin resistance development in primary rat hepatocytes. Biomolecules. (2021) 11:268. doi: 10.3390/biom11020268
59. Xu Y, Zhang Y, Liang H, Liu X. Coumestrol mitigates retinal cell inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in a rat model of diabetic retinopathy via activation of SIRT1. Aging. (2021) 13:5342–57. doi: 10.18632/aging.202467
60. Braxas H, Rafraf M, Karimi Hasanabad S, Asghari Jafarabadi M. Effectiveness of genistein supplementation on metabolic factors and antioxidant status in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Canad J Diabetes. (2019) 43:490–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2019.04.007
61. Thaung Zaw JJ, Howe PR, Wong RH. Long-term effects of resveratrol on cognition, cerebrovascular function and cardio-metabolic markers in postmenopausal women: a 24-month randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:820–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.08.025
62. Tomczyk K, Chmaj-Wierzchowska K, Wszołek K, Wilczak M. New possibilities for hormonal vaginal treatment in menopausal women. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:4740. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144740
63. Besong C, Philippeaux S, Bham A, Gustinvil N, Castine A, Varrassi G, et al. Managing menopause: the evolving role of estrogens, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and phytoestrogens in balancing hormonal fluctuations. Cureus. (2024) 16:e70440. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70440
64. He M, Yin Y, Yu G, Zhou H. Phytoestrogens: pharmacological potential and therapeutic insights for urinary tract infections. Phytother Res. (2025) 39:1261–76. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8429
65. Warinsiriruk P, Tantitham C, Cherdshewasart W, Shobeiri SA, Manonai J. Effects of Pueraria mirifica on vaginal artery vascularization in postmenopausal women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Maturitas. (2022) 160:4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2022.01.005
66. Sritonchai C, Manonai J, Sophonsritsuk A, Cherdshewasart W. Comparison of the effects of Pueraria mirifica gel and of placebo gel on the vaginal microenvironment of postmenopausal women with Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM). Maturitas. (2020) 140:49–54. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.06.005
67. Karimi FZ, Nazari N, Rakhshandeh H, Mazloum SR. The effect of nettle vaginal cream on subjective symptoms of vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2023) 285:41–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2023.03.037
68. Bosak Z, Iravani M, Moghimipour E, Haghighizadeh MH, Jelodarian P. Effect of chamomile vaginal gel on the sexual function in postmenopausal women: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Sex Med. (2022) 19:983–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2022.03.536
69. Cuccu I, Golia D'Augè T, Firulli I, De Angelis E, Buzzaccarini G, D'Oria O, et al. Update on genitourinary syndrome of menopause: a scoping review of a tailored treatment-based approach. Life. (2024) 14:1504. doi: 10.3390/life14111504
70. Nappi RE, Chedraui P, Lambrinoudaki I, Simoncini T. Menopause: a cardiometabolic transition. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2022) 10:442–56. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00076-6
71. Palma F, Fontanesi F, Neri I, Xholli A, Facchinetti F, Cagnacci A. Blood pressure and cardiovascular risk factors in women treated for climacteric symptoms with acupuncture, phytoestrogens, or hormones. Menopause. (2020) 27:1060–5. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001626
72. Wolters M, Dejanovic GM, Asllanaj E, Günther K, Pohlabeln H, Bramer WM, et al. Effects of phytoestrogen supplementation on intermediate cardiovascular disease risk factors among postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Menopause. (2020) 27:1081–92. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001566
73. Leonard LM, Choi MS, Cross T-WL. Maximizing the estrogenic potential of soy isoflavones through the gut microbiome: implication for cardiometabolic health in postmenopausal women. Nutrients. (2022) 14:553. doi: 10.3390/nu14030553
74. Yigit E, Unsal S. Isoflavones obtained from red clover improve both dyslipidemia and menopausal symptoms in menopausal women: a prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial. Climacteric. (2024) 27:548–54. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2024.2393121
75. Yang S, Zeng Q, Huang X, Liang Z, Hu H. Effect of isoflavones on blood lipid alterations in postmenopausal females: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Adv Nutr. (2023) 14:1633–43. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.09.008
76. Kirichenko TV, Myasoedova VA, Ravani AL, Sobenin IA, Orekhova VA, Romanenko EB, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis progression in postmenopausal women receiving a mixed phytoestrogen regimen: plausible parallels with kronos early estrogen replacement study. Biology. (2020) 9:48. doi: 10.3390/biology9030048
77. Khapre S, Deshmukh U, Jain S. The impact of soy isoflavone supplementation on the menopausal symptoms in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. J Midlife Health. (2022) 13:175–84. doi: 10.4103/jmh.jmh_190_21
78. Yoo DY, Jung S, Kang JS, Baek JH, Park KH, Lee DH, et al. Isoflavone-enriched soybean leaves (Glycine Max) alleviate cognitive impairment induced by ovariectomy and modulate PI3K/Akt signaling in the hippocampus of C57BL6 mice. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4753. doi: 10.3390/nu14224753
79. Sugimoto M, Ko R, Goshima H, Koike A, Shibano M, Fujimori K. Formononetin attenuates H2O2-induced cell death through decreasing ROS level by PI3K/Akt-Nrf2-activated antioxidant gene expression and suppressing MAPK-regulated apoptosis in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells. NeuroToxicology. (2021) 85:186–200. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2021.05.014
80. Ito S, Sasaki H, Gotow T, Suetake I, Nagai K. Soy isoflavone daidzein protects Neuro2a cells from NO stress via activation of AMPK-PGC1α pathway followed by mitochondrial enhancement. PharmaNutrition. (2023) 24:100337. doi: 10.1016/j.phanu.2023.100337
81. Çalişkan G, Raza SA, Demiray YE, Kul E, Sandhu KV, Stork O. Depletion of dietary phytoestrogens reduces hippocampal plasticity and contextual fear memory stability in adult male mouse. Nutr Neurosci. (2021) 24:951–62. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1698826
82. Schmidt PJ, Wei SM, Martinez PE, Dor RRB, Guerrieri GM, Palladino PP, et al. The short-term effects of estradiol, raloxifene, and a phytoestrogen in women with perimenopausal depression. Menopause. (2021) 28:369–83. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001724
83. Wang Y, Hernandez G, Mack WJ, Schneider LS, Yin F, Brinton RD. Retrospective analysis of phytoSERM for management of menopause-associated vasomotor symptoms and cognitive decline: a pilot study on pharmacogenomic effects of mitochondrial haplogroup and APOE genotype on therapeutic efficacy. Menopause. (2020) 27:57–65. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001418
84. Sekikawa A, Wharton W, Butts B, Veliky CV, Garfein J, Li J, et al. Potential protective mechanisms of S-equol, a metabolite of soy isoflavone by the gut microbiome, on cognitive decline and dementia. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:11921. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911921
85. Landete JM, Arqués J, Medina M, Gaya P, De Las Rivas B, Muñoz R. Bioactivation of phytoestrogens: intestinal bacteria and health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2016) 56:1826–43. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2013.789823
86. Gaya P, Medina M, Sánchez-Jiménez A, Landete J. Phytoestrogen metabolism by adult human gut microbiota. Molecules. (2016) 21:1034. doi: 10.3390/molecules21081034
87. Viggiani MT, Polimeno L, Di Leo A, Barone M. Phytoestrogens: dietary intake, bioavailability, and protective mechanisms against colorectal neoproliferative lesions. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1709. doi: 10.3390/nu11081709
88. Domínguez-López I, Yago-Aragón M, Salas-Huetos A, Tresserra-Rimbau A, Hurtado-Barroso S. Effects of dietary phytoestrogens on hormones throughout a human lifespan: a review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2456. doi: 10.3390/nu12082456
89. Bučević Popović V, Karahmet Farhat E, Banjari I, Jeličić Kadić A, Puljak L. Bioavailability of oral curcumin in systematic reviews: a methodological study. Pharmaceuticals. (2024) 17:164. doi: 10.3390/ph17020164
90. Chen MN, Lin CC, Liu CF. Efficacy of phytoestrogens for menopausal symptoms: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Climacteric. (2015) 18:260–9. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2014.966241
91. Oh YJ, Nam K, Kim Y, Lee SY, Kim HS, Kang JI, et al. Effect of a nutritionally balanced diet comprising whole grains and vegetables alone or in combination with probiotic supplementation on the gut microbiota. Prev Nutr Food Sci. (2021) 26:121–31. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2021.26.2.121
92. Gencel VB, Benjamin MM, Bahou SN, Khalil RA. Vascular effects of phytoestrogens and alternative menopausal hormone therapy in cardiovascular disease. Mini Rev Med Chem. (2012) 12:149–74. doi: 10.2174/138955712798995020
93. Jungbauer A, Medjakovic S. Phytoestrogens and the metabolic syndrome. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2014) 139:277–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.12.009
94. Franco OH, Chowdhury R, Troup J, Voortman T, Kunutsor S, Kavousi M, et al. Plant-based therapies and menopausal symptoms. JAMA. (2016) 315:2554–63. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.8012
95. Liang S, Zhang H, Mo Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Cao H, et al. Urinary equol and equol-predicting microbial species are favorably associated with cardiometabolic risk markers in Chinese adults. J Am Heart Assoc. (2024) 13:e034126. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.034126
96. Setchell KD, Brzezinski A, Brown NM, Desai PB, Melhem M, Meredith T, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a slow-release formulation of soybean isoflavones in healthy postmenopausal women. J Agric Food Chem. (2005) 53:1938–44. doi: 10.1021/jf0488099
Keywords: phytoestrogens, menopause management, estrogen receptors, plant-derived therapeutics, clinical translation
Citation: Li Y, Huang F, Qian X, Liu C, Yao Y, Wang Z, Zhu X and Guo Q (2025) Exploring the anti-aging potential of phytoestrogens: focus on molecular mechanisms and menopausal symptom modulation. Front. Nutr. 12:1651367. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1651367
Received: 23 June 2025; Accepted: 04 September 2025;
Published: 25 September 2025.
Edited by:
Karolina Wojtunik-Kulesza, Medical University of Lublin, PolandReviewed by:
Magdalena Żabińska,, University of Gdansk, PolandCeline Camon, Albany Medical College, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, Huang, Qian, Liu, Yao, Wang, Zhu and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qi Guo, Z3VvcWk2MDhAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Yuchen Li
Yuchen Li Feng Huang
Feng Huang Xin Qian1
Xin Qian1 Qi Guo
Qi Guo