- 1Department of Food Science and Human Nutrition, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
- 2Department of Physiology, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
- 3Department of Health Sciences, University of York, York, United Kingdom
- 4Department of Human Nutrition and Dietetics, NUST School of Health Sciences, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Sector H-12, Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Olive leaf has strong antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially modulating gut microbiota composition. This may help address small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), a gastrointestinal (GI) problem causing malabsorption and potential complications.
Objective: This study aimed to observe the effect of olive leaf tea (OLT) on GI symptoms, body composition, and the hydrogen/methane breath test among patients suffering from SIBO.
Methods: A total of 49 SIBO individuals, confirmed after a glucose breath test (GBT), were divided randomly into two groups. The treatment group (n = 25) took OLT (1.7 g leaf powder/250 mL water) twice/day for 2 months, and the control group (n = 24) was given no tea. After the intervention, GBT was conducted, and symptoms were assessed through the GI symptom rating scale (GSRS) and symptomatic questionnaire, and body composition parameters were assessed. The area under the curve, chi-square, independent, and paired sample t-tests were performed for data analysis.
Results: In the intervention group, there was a significant decrease observed in GSRS score (from 19 to 6.8), symptomatic score (4.1 to 1.7), H2/CH4 peak (20.8–5.7 ppm), mean H2 (p = 0.0041) and mean H2 + CH4 production (p = 0.0043), with 88% GBT normalization rate (p = 0.001), as compared to the control group. A significant decrease in weight, TBW, BMR, and muscle mass was also documented (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: This study concludes that OLT consumption might have therapeutic benefits against SIBO by alleviating symptoms and normalizing GBT, but does not significantly improve body composition parameters.
1 Introduction
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is a GI problem that can be described as colonization of opportunistic or pathogenic bacteria in the small intestine (1). SIBO remained undiscovered or misdiagnosed for many years because its clinical symptoms overlap with other diseases such as celiac disease, Helicobacter pylori, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBS). The treatment of SIBO is challenging, especially in non-symptomatic patients. Therefore, SIBO remains untreated until it causes much damage to the small intestine and presents with further complications (2). Manifestations of SIBO mainly include abdominal pain, distension, bloating, cramping, flatulence, diarrhea, and constipation (2). Risk factors for SIBO include older age, excessive use of PPIs and antibiotics, hypo-chlorhydria, motility disorder, and IBS (3).
Researchers were unable to provide a definitive estimate of SIBO prevalence in the general population. A few studies reported 2.5–22% prevalence in healthy individuals (4), 4.42% in healthy adults in Lahore, Pakistan (5), 31.5% in suspected patients with GI distress, 36.4% in patients with IBS (6), 20% in asymptomatic patients, 50–60% in patients with pancreatitis, 60% in patients with gastroparesis, 9–55% in patients with celiac disease, and 59% in patients with diverticulitis (5).
SIBO has two subtypes, which are classified based on the ratio of gasses produced by the microorganisms residing in the small intestine. Hydrogen-dominant SIBO patients often present with diarrhea, and methane-dominant ones experience decreased bowel transit time, slow basal metabolic rate, and delayed gastric emptying (7). The gut of a healthy person harbors Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes in a balanced ratio, accounting for 90% of the gut microbiome. A comparative analysis of SIBO patients revealed a higher abundance of Firmicutes. Common bacteria that contaminate the gut in SIBO include Escherichia coli, Enterococcus spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (8).
There are three recommended approaches to manage or cure SIBO. First, addressing the underlying cause; second, eradicating bacterial overgrowth; and third, overcoming nutritional deficiencies. Antibiotics are considered the mainstay therapy for SIBO. Taking antibiotics alone increases the chances of recurrence of symptoms, side effects, and causes antibiotic resistance. Herbal therapy is considered as effective as Rifaximin (an antibiotic used to treat IBS with diarrhea) in treating SIBO. Approximately 57% of SIBO patients who did not respond to antibiotics showed a positive response to herbal therapy (9). Therefore, this is the need of the hour to uncover functional foods that may have the potential to manage or treat SIBO.
Olive trees (Olea europaea L.), belonging to the Oleaceae family, grow in places with a Mediterranean atmosphere and are well-adapted to arid conditions. They are dark green and oblong with tapered ends (10). They tend to have a mild bitter taste, attributed to their compound oleuropein. The historical use of olive oil and leaves as natural healers is extensively documented in religious texts. Olive leaves infusion contains antioxidants, including oleuropein, quercetin, fatty acids (oleic acid and oleanolic acid), and the most potent antioxidant hydroxytyrosol and its derivatives. The phenolic content of olive leaves is higher than extra virgin olive oil and olive fruit (11). The olive leaves’ biophenols exhibit strong antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, also flourish the healthy gut microbiota, and decrease the likelihood of bowel-related disorders (12). Ascribed to this, olive leaves may prove beneficial in managing health problems related to bacterial contamination and inflammation. The current study was designed to assess the impact of OLT on intestinal health, GI symptoms, the concentration of H2 and CH4 gasses in exhaled breath, and to analyze the OLT impact on the body composition parameters of SIBO patients.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design
The study was conducted as a randomized controlled trial. The selection of a 2-month (~ 9 weeks) intervention time was based on a previous 10-week clinical study evaluating the therapeutic potential of an antimicrobial herbal blend against SIBO. A trial investigating the effects of the same OLT on hematological parameters also used a 6–12-week duration, and a significant increase in hematocrit was observed in 6 weeks. The methodology of the study consisted of five phases. Phase 1: processing and preparation of Olive Leaf Tea (OLT), Phase 2: screening to identify SIBO suspected individuals, Phase 3: confirmation of SIBO through the hydrogen breath test using a breath analyzer, Phase 4: provision of intervention, and Phase 5: final assessment after intervention.
2.2 Olive leaf tea (OLT) processing and preparation
Fresh olive leaves were purchased from the district Chakwal, Pakistan, harvested in the morning, during September, the non-blooming season, to ensure maximum phytochemical content. The leaves were sorted, rinsed with clean water, and dried at 45°C in the hot air oven (POL-EKO APARATURA® Model: SLN53) until the moisture content was reduced to 12% or less (Figure 1), measured using a Halogen Moisture Analyzer (13). The leaves were crushed and then incorporated into airtight tea packets. No sugar or sweetener was added during the packaging and brewing process of tea. The OLT was evaluated for sensory evaluation by a semi-trained panel. The judges were asked to rate the provided OLT for its aroma, flavor, and color, and overall acceptability on a 9-point hedonic scale ranging from (1 = dislike extremely) and (9 = like extremely).
2.3 Screening and recruitment of participants for intervention
Study participants were recruited via circulated questionnaires across different university campuses. This screening symptomatic questionnaire was developed based on Erdogan et al. (2) with minor modifications. In the questionnaire, individuals were asked to rate the intensity, frequency, and duration of their nine GI symptoms (bloating, burping, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, feeling of satiety, constipation, abdominal pain, and indigestion) using a 3-point Likert scale. Individuals with a mean score ≥4 were considered suspected of SIBO and were further referred to GBT for confirmation. Participants were also asked to indicate foods that initiate or trigger their GI symptoms.
2.4 Confirmatory hydrogen and methane breath test
The participants were instructed to avoid antibiotic use 1 month prior, laxative and PPI use 1 week prior, and fermentable carbohydrate and dairy diet 1–2 days before the test. The 8–10 h of fasting were recommended before the test, while participants can drink water. It was advised to avoid smoking 2 h before the test and to rinse the mouth with antiseptic mouthwash before the test. The breath test was done at the time of screening using a QuinTron breath analyzer (Model SC, QuinTron Instrument Company, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA) following instructions given in the manual. The calibration of the analyzer was performed using 20 mL of Quin gas with standard concentrations of H2 = 154 ppm, CH4 = 74 ppm, and CO2 = 6.1%.
On the test day, the baseline reading of the breath sample was taken empty stomach, and then 50 g of glucose dissolved in 250 mL of water was given to participants orally. Breath samples were taken every 15 min for 2 h, and the concentration of gasses in the breath sample was measured. Individuals having at least a 12 ppm rise in H2 and/or a ≥ 10 ppm rise in CH4 from the baseline reading or the lowest preceding value were diagnosed as positive for SIBO (6).
2.4.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The adults aged 18 years or older and with a mean symptomatic score ≥4 and positive GBT were included in the study. The participants who were hospitalized, diabetic, with chronic medical problems like stroke, coronary obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cancer, with a history of GI surgeries except for cholecystectomy, hysterectomy, and appendectomy, and who were taking antibiotics in the last month were excluded from the study.
2.4.2 Assessment of body composition parameters
Body composition was assessed using the InBody Analyzer 270. Recommendations were to avoid exercise 6–12 h before the test and to stay hydrated and remove socks, metal objects, and heavy clothing (jacket) before the test.
The InBody report provides information about total body water, muscle content, basal metabolic rate, and obesity degree (waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, body mass index, and percent body fat), etc. BMI categories were classified according to Asian-Pacific recommendations as “underweight” (< 18.5 kg/m2), “normal” (18.5–22.9 kg/m2), “overweight” (23–24.9 kg/m2), and “obese” (25–29.9 kg/m2), and morbid obese (≥30 kg/m2).
2.4.3 Assessment of GI symptoms
Patients filled a self-administered validated Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) questionnaire consisting of 15 items categorized into five syndromes: abdominal pain, dyspepsia, indigestion, diarrhea, and constipation. Each category has 3 sub-dimensions, i.e., intensity (none, mild, moderate, and severe), frequency (none, 1–2 times/month, once a week, and >1 time/week), and duration (none, <10 min, 10–30 min, and >30 min). These dimensions were assessed using a 4-point Likert scale (0 = no symptoms; 1 = mild discomfort; 2 = moderate discomfort; 3 = severe discomfort). The total GSRS score was 45, and the mean GSRS was 9.
2.5 Provision of intervention
After written agreement, 50 participants with positive BT results were randomly assigned to two groups, with 25 participants in each group: treatment (n = 25) and control (n = 25). This grouping was performed using the online Research Randomizer software. One participant from the control group left during the study duration.
The intervention group was instructed to take OLT twice a day for 2 months. The participants were instructed to immerse 1.7 g of leaf powder (2 tsp) in hot water for 7–10 min for a better infusion (14). Participants were asked to document their OLT intake daily, as well as any negative effects they may have encountered. The control group did not receive OLT or any other intervention.
2.6 Final assessment
At the end of the 2-month study period, the final readings of GBT and body composition analysis of both intervention and control groups were taken. The participants were also requested to fill out the GSRS questionnaire and the 9-symptoms questionnaire to analyze any improvement in the severity of their GI symptoms.
2.7 Statistical analysis
SPSS (version 23; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical data analysis. The comparison between baseline and termination point readings of mean symptomatic score, GSRS score, GBT normalization rate, and body composition variables was carried out using a paired sample t-test. An independent sample t-test was applied to compare the above parameters between the control and intervention groups. Mean H2 and CH4 gas concentrations in the breath sample were calculated using IUAC. The age, gender, and BMI were correlated with SIBO using a Pearson chi-square test. For all analyses, a significance level of p < 0.05 was applied.
3 Results
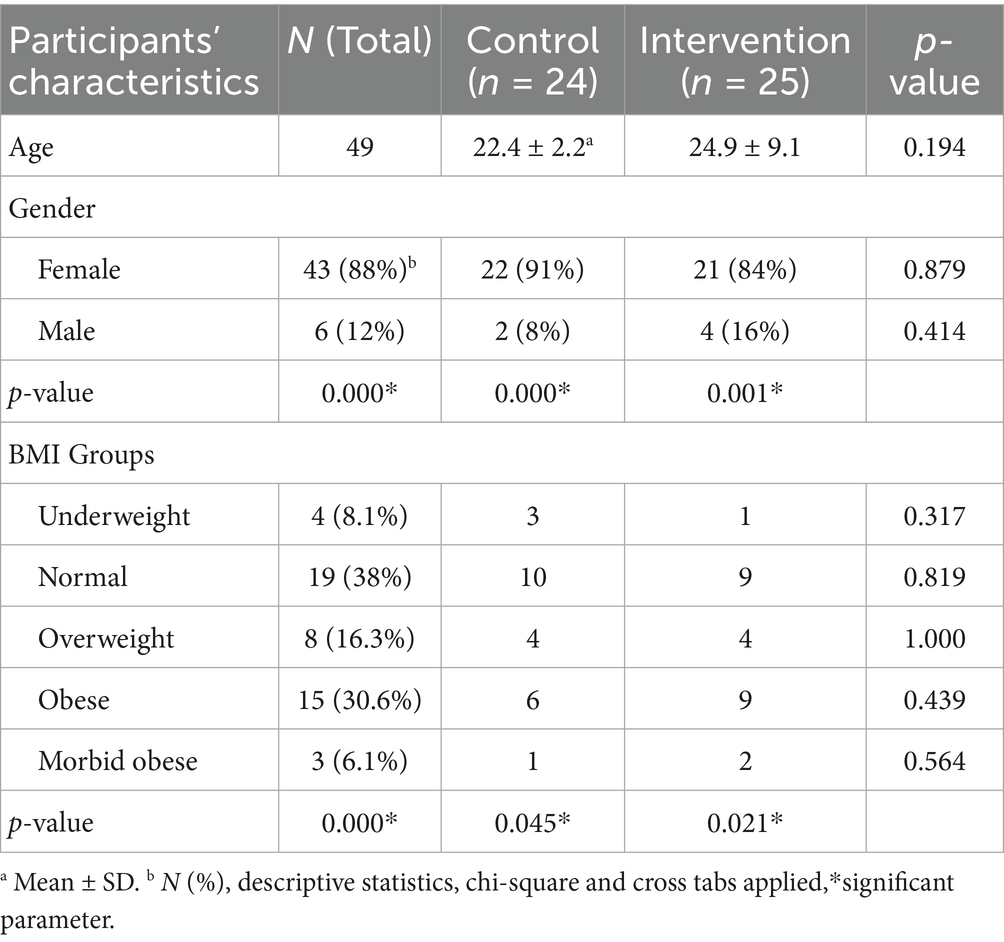
This study includes 49 individuals diagnosed with SIBO, with 43 women and 6 men. Table 1 provides a comparison of the demographic characteristics between the control and treatment groups. The age distribution was almost similar across all SIBO groups, with a predominant representation of females in each group. Out of 49 total participants, the majority of the participants belonged to the normal BMI category (38%), followed by the obese (30.6%). The prevalence of morbidly obese patients was low, with 8% reported in the intervention group and 4.2% in the control group.
The sensory evaluation results, on a 9-point hedonic scale, show that the OLT secured very good results with a mean score of 7 ± 1.2 (like extremely, 11.5%; like very much, 31%, and moderately like 27%) while none of the judges disliked the product.
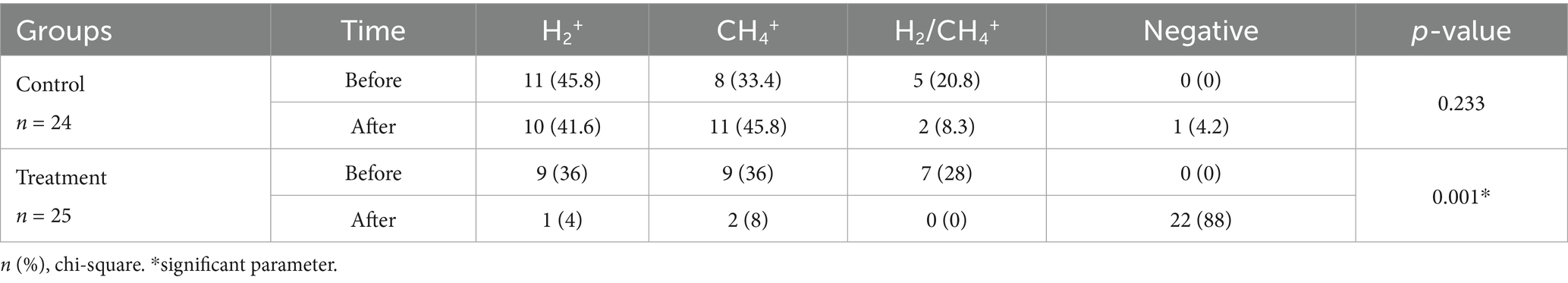
Table 2 shows the prevalence of SIBO subtypes (H2 positive, CH4 positive, and H2/CH4 positive) in the control and treatment groups, and also the effectiveness of OLT intervention in reducing SIBO. The majority, 40.8% (20/49) of patients in both groups at baseline, were H2+ producers, and 34.6% (17/49) were CH4 producers, whereas 24.4% (12/49) of the participants were both H2 and CH4 producers. After 2 months of intervention, methane-dominant SIBO patients decreased from 36 to 8% in the intervention group, while increasing from 33.4 to 45.8% in the control group. In the treatment group, 88% of SIBO patients showed negative hydrogen and methane breath tests, while only 4.2% showed negative HBT in the control group.
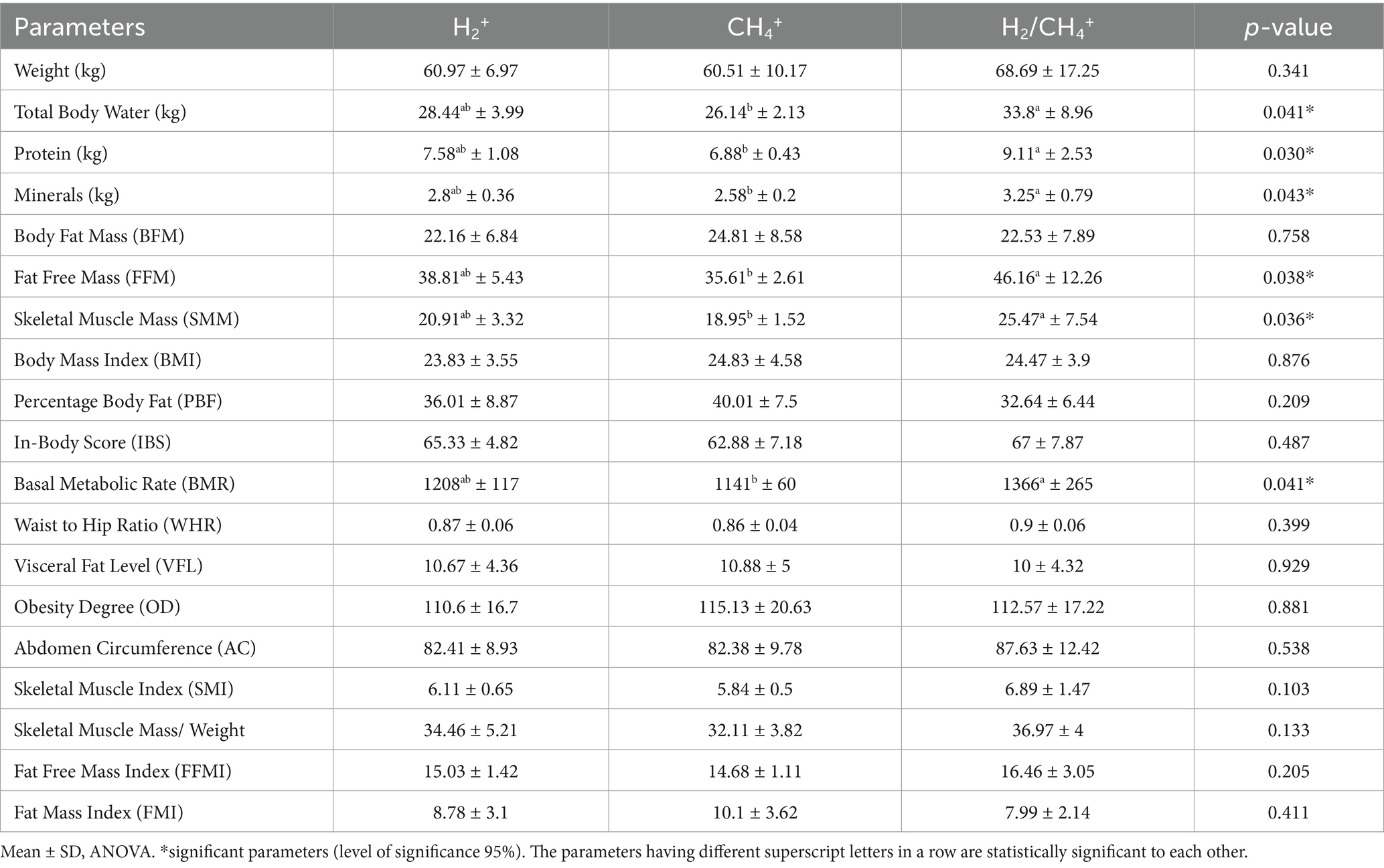
The comparison of the three subtypes of SIBO based on the mean production of H2 and CH4 gasses is shown in Table 3. The total body protein, bone minerals, fat-free mass (FFM), skeletal muscle mass (SMM), and basal metabolic rate (BMR) were significantly deficient in CH4 producers. The SMM, FFM, total body water (TBW), and BMR in the H2+/CH4+-dominant patients were substantially higher than other groups (p = 0.036, p = 0.038, p = 0.041, and p = 0.041, respectively).
The high fat percentage is directly correlated with increased concentrations of exhaled CH4, but the difference did not reach the significance level. Similarities were seen in three groups regarding visceral fat level and degree of obesity; however, there was a trend toward higher total body protein (kg) (p = 0.030), bone minerals (p = 0.043), and weight (p = 0.341) observed in the H2+/CH4+-group.
Table 4 presents the parameters that show significant changes during the study period. Notably, the treatment group exhibited a decreasing trend in TBW. Although a decrease in BMI (p = 0.376) and obesity degree (p = 0.475) has been noticed with regular consumption of OLT, these differences did not reach statistical significance. This post-intervention decrease in body weight and BMI, and BMR may be attributed to a significant decrease in TBW, FFM (p = 0.024), SMM (p = 0.013), and skeletal muscle index (SMI) (p = 0.000) in the treatment group. Conversely, the control group showed a statistically significant increase in TBW, FFM, SMM, BMR, FFMI, and SMI.
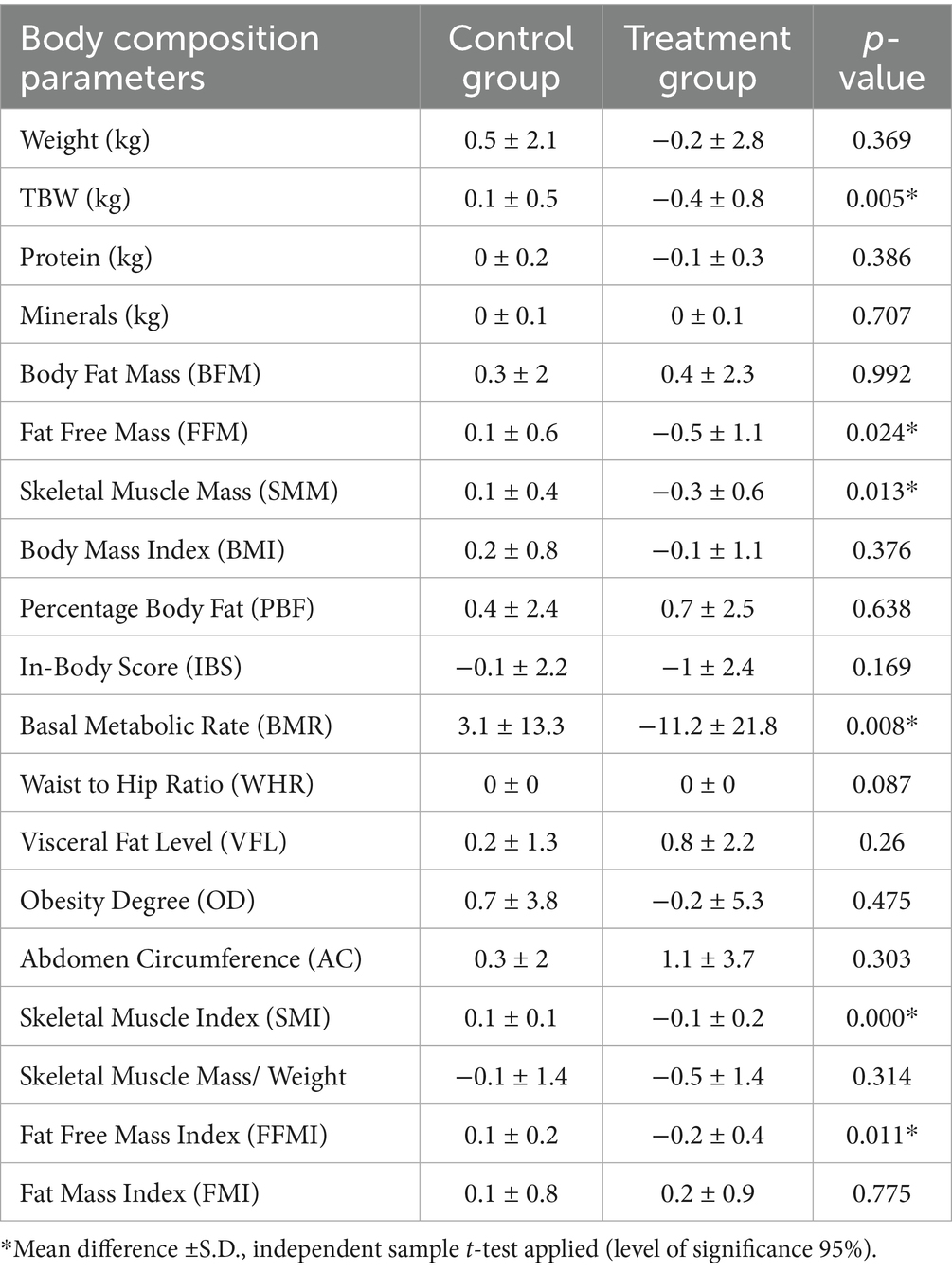
Table 4. Change in body composition parameters between control and treatment groups after Intervention of OLT for 2 months.
Table 5 presents the comparison of baseline and post-study breath test readings among the three SIBO subtypes based on the median production of H2 and CH4 gasses, illustrated as the incremental area under the curve (IAUC) (ppm/min), measured during the 90-min breath test after glucose administration. In the control group, the concentration of methane showed a significant rise after 2 months. However, in mixed-type SIBO, a significant increase has been observed in the median production of hydrogen and methane gasses (p = 0.931). After 2 months of OLT intervention, a significant decrease was observed in the concentration of H2 and CH4 gasses in mixed (H2/CH4) SIBO type (p = 0.043). The level of exhaled H2 gas in the H2-dominant group also showed a considerable decline (p = 0.041). Methane gas production in the intervention group also decreased compared to the baseline, but this decline did not reach a significant level (p = 0.877).
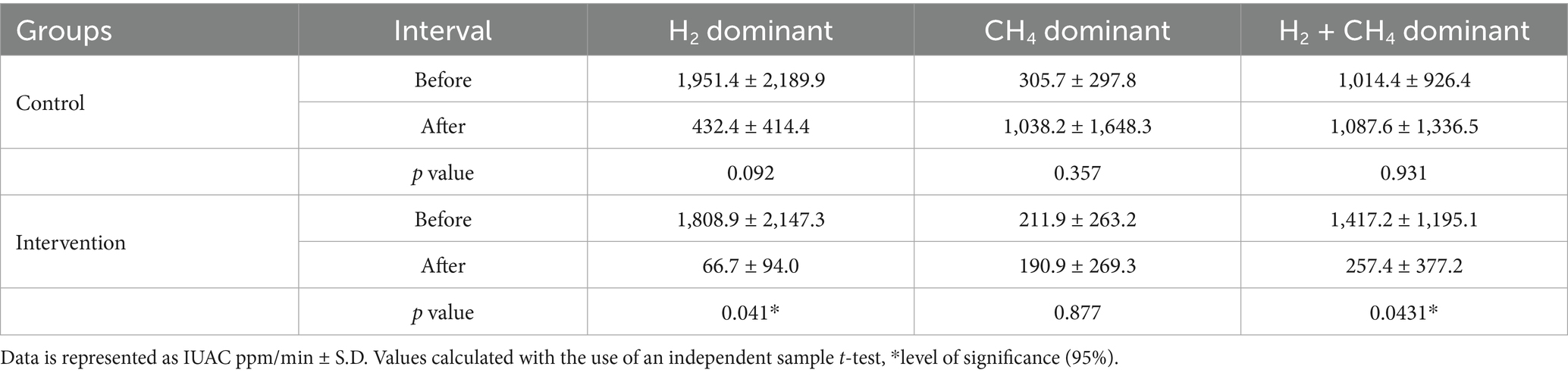
Table 5. Within and between groups comparison of mean hydrogen and methane gas as area under the curve (ppm/min) in H2 and CH4 type SIBO.
Figure 2 shows the peak hydrogen and methane production in subjects calculated during 90-min breath testing. In the control group, the peak mean of H2/CH4 was 19.7 at baseline and 14.6 at the end of the study, with no significant difference in mean peak (p = 0.404). In the treatment group, the hydrogen and methane peak production showed a notable decline (p = 0.004) from baseline in 2 months. The mean rise in hydrogen and methane (ppm) observed was 20.8 at baseline and decreased to 5.7 after the intervention of OLT.
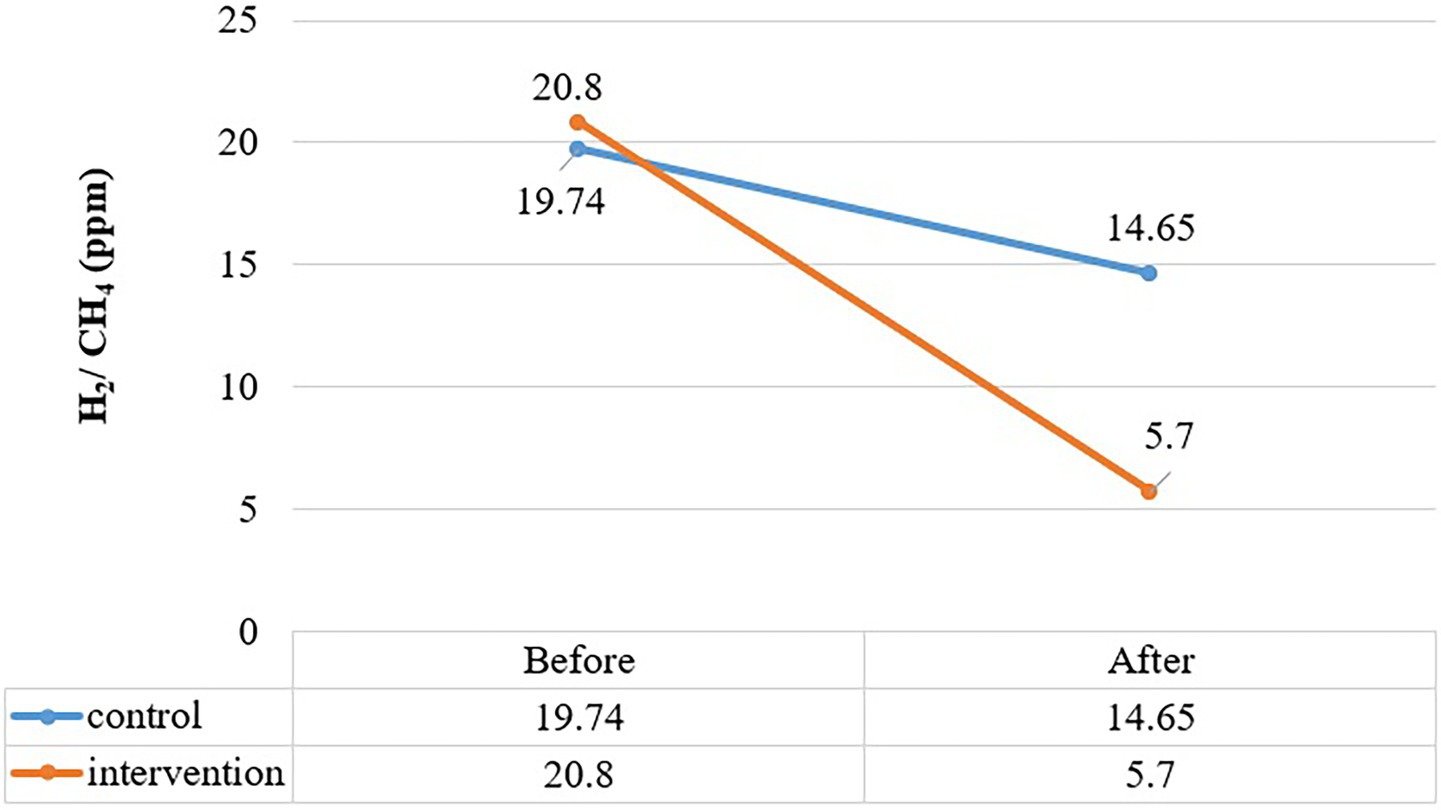
Figure 2. Comparition of peak rise in H2 and CH2 (ppm) between control and treatment group at baseline and end intervention.
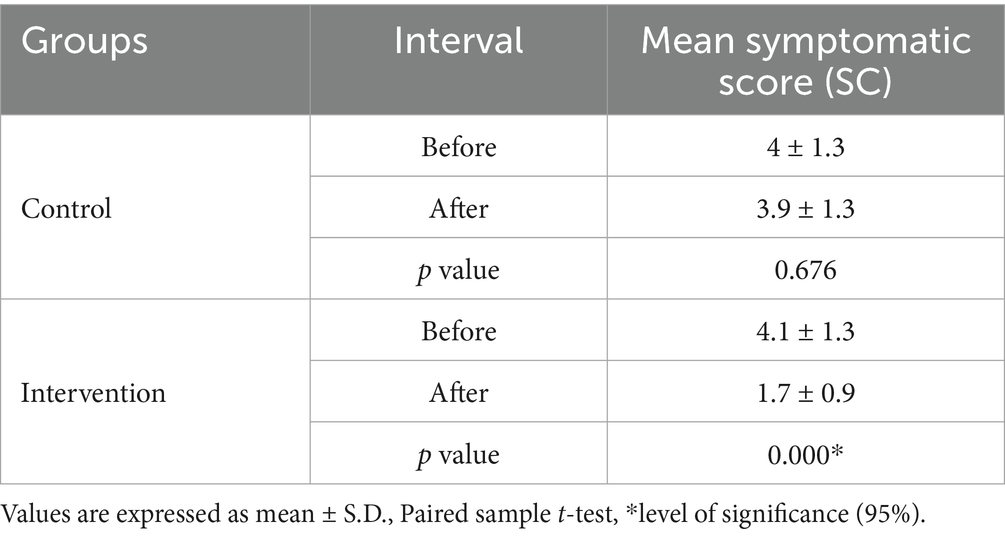
Table 6 reveals additional insights about symptomatic score variation within each group, showing a significant decrease in the mean score of the intervention group (p = 0.000). In the control group, the average symptom score of both intervals (before and after) was comparable, indicating non-significant divergence (p = 0.676).
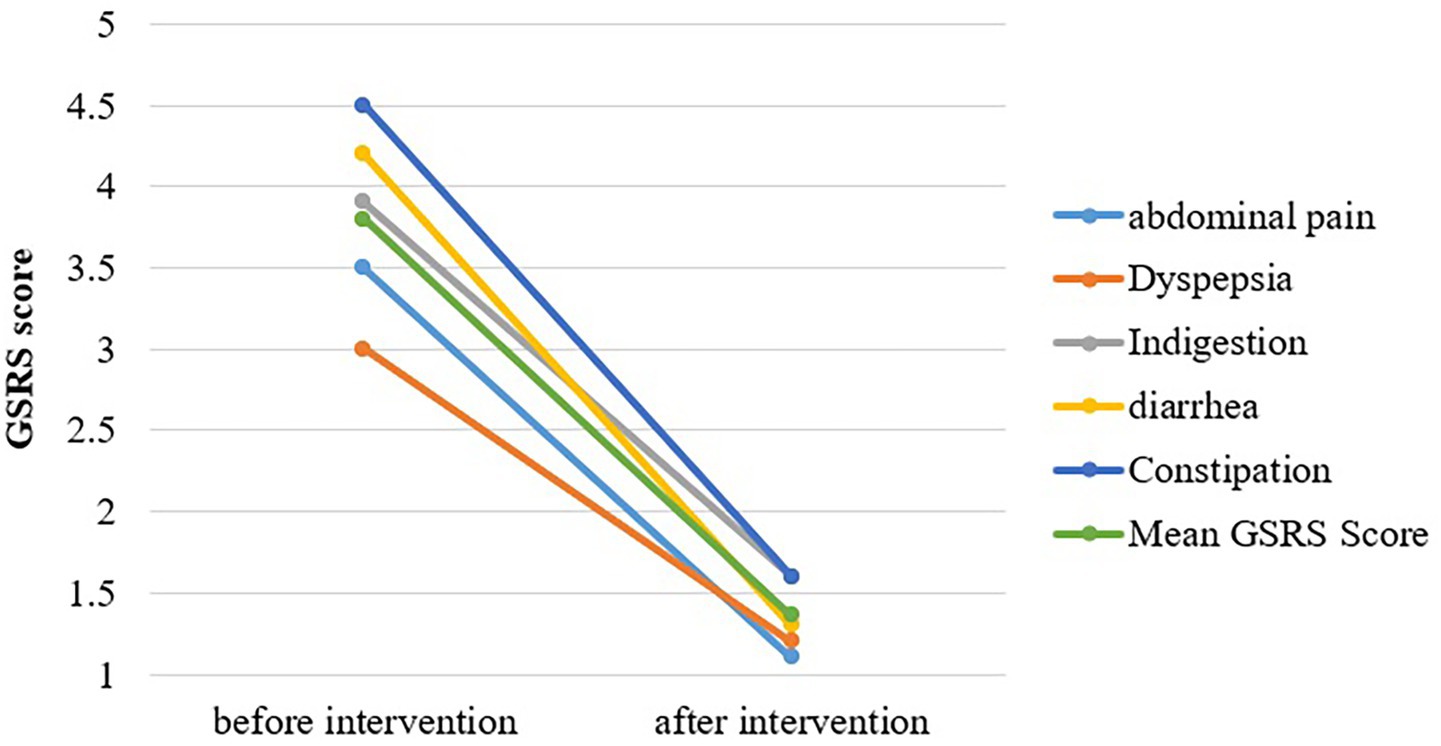
Figure 3 shows the mean of significantly heightened GI symptoms in SIBO patients. Scores for each of the five sub-dimensions of GSRS were significantly reduced after OLT intervention. The intensity of abdominal pain, hunger pains, and nausea was markedly reduced, with the mean difference being 2.4 ± 2 (p = 0.000). The severity of dyspepsia syndrome, including heartburn and acid reflux, reduced from a mean symptomatic score of 3.0 at baseline to 1.2 after intervention (p < 0.05). A considerable improvement in the abdominal distension and bloating of SIBO patients was observed with the highest mean difference of 3 (p = 0.000). The values of indigestion syndrome recorded at the termination point of intervention were quite lower than the baseline values, with a mean score of 4.2 and 1.3, respectively. The mean score of diarrhea syndrome falls from 4.2 (baseline) to 1.3 (post-study), with a level of significance <0.05. The intensity and frequency of constipation were largely reduced with a mean difference of 2.9 (p = 0.000).
4 Discussion
This randomized controlled trial has been conducted to observe the effectiveness of OLT intervention in normalizing hydrogen and methane concentration in GBT and in reducing GI symptoms related to SIBO, such as bloating, constipation, and abdominal pain. The effect of the intervention on the composition of different body compartments in participants was also studied.
4.1 Association between SIBO types and body composition variables
The results of the current study showed that most participants (53%) had a normal BMI. The link between abdominal obesity and positive GBT is also reported by Kim, Park, Paik, Kang, Jo, and Lee (15). According to another study finding targeting obese and overweight individuals, 20% of the obese patients had a positive breath test for methane (16). The pathophysiological mechanism behind SIBO and obesity can be explained by alterations in the gut microbiota composition, which may disrupt the production of appetite hormones, energy balance, and insulin secretion, potentially leading to the development of obesity (17). Our study did not reveal any significant difference in the BMI of different types of SIBO patients. Contrarily, other studies showed that the H2+/CH4+group exhibited high BMI according to Mathur, Amichai, Chua, Mirocha, Barlow, and Pimentel (18), and methane-positive patients had higher BMI (45.2 kg/m2) compared to methane-negative individuals (38.5 kg/m2) (16).
It was observed that CH4 producers had notably lower TBW and total protein levels compared to other groups. However, contrasting results were found in another study where the CH4+ group had higher water content than the H2+ and H2+/CH4+ groups, although this difference was not statistically significant (19). Similarly, in a separate study, the CH4+ group showed the highest SMM and body protein compared to the H2+ and H2+/CH4+ groups, but this discrepancy also lacked statistical significance. This may be explained by the fact that skeletal muscle contains a significant amount of water, and changes in hydration levels directly impact SMM and body protein. In our study, the decrease in TBW in the CH4+ group coincided with reduced body protein and SMM.
The results of a similar study showed that methane producers had a higher %BF than hydrogen producers (18), which comply with our study, in which the CH4+ group was observed to have the highest BFM and % body fat, but this variation was not significant. Interestingly, a study led by Wielgosz-Grochowska, Domanski, and Drywień (19) produced contrasting results to the aforementioned studies, suggesting no significant difference in the percentage of body fat between SIBO subgroups, but a trend toward a higher percentage BF was observed in the H2+ group in the present study.
Our study depicts that OLT results lead to a decrease in BMR. This observation may be linked to the fact that a substantial proportion of SIBO patients in both groups were H2 dominant (37%) or H2/CH4 dominant (29%), having a high BMR, leading to weight loss. Consequently, after intervention of OLT, the SIBO participants experienced a significant change in BMR, which may potentially contribute to more effective weight management and energy metabolism.
InBody analysis report of SIBO patients in a study conducted by Wielgosz-Grochowska, Domanski, and Drywień (19) showed similarities in bone mineral mass across all SIBO types, with the methane-dominant group showing the highest mineral content compared to other groups. Contrarily, our study revealed the highest bone mass in the H2+ group, followed by the H2/CH4 group, with the methane group showing the least concentration of bone minerals. Another study finding revealed that SIBO is associated with low bone mineral density, suggesting SIBO might be the reason behind unexplained osteopenia (20).
4.2 The GI symptoms assessed by the mean SC and GSRS questionnaire
Many functional foods and plants with therapeutic properties manage gut-related disorders and symptoms. The results of this study support the hypothesis that herbal therapy addressed the GI symptoms better than antibiotic therapy. The frequency and intensity of the GI symptoms, GI discomfort (p < 0.001), and overall GSAS (GERD Symptom Assessment Scale) score are considerably improved by taking O. europaea leaves extract (21). Comparative analysis with our study showed that the GI symptoms of SIBO patients were reduced significantly after OLT intervention. While 7-day rifaximin (antibiotic) therapy (22) only decreases the intensity of diarrhea, rumbling sounds in the stomach, and lethargy, no improvement is reported in the severity of anorexia, abdominal pain, and nausea.
Better outcomes were observed in SIBO patients taking broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy combined with probiotic therapy (Lactol) in the rehabilitation phase, with significant alleviation in symptoms of abdominal pain, flatulence, burping, loose stools, and fecal urgency (23). In contrast, OLT turned out to be more effective than above mentioned antibiotics in decreasing the severity of documented symptoms.
In our study, the intensity, frequency, and duration of constipation syndrome have significantly reduced after OLT intervention (p = 0.000) compared to the control group. Comparatively, a trial has been conducted to check the effect of an herbal mix (ginger, ginseng, and Japanese pepper) to treat functional constipation. Both ginger and olive leaf contain polyphenols, flavonoids, and terpenes, which exhibit antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Moreover, olive leaf and ginseng also share some bioactive components, including polysaccharides, saponins, sterols, and polyphenols. The herbal mix was found to increase peristaltic contractions and colon transit activity (24).
The OLT consumption for 2 months resulted in 87.5% GBT normalization rates, which is comparatively higher than the elemental diet, 80–85% (25). The antibiotic therapy combined with probiotic therapy (Lactol) has a higher GBT normalization rate (93.3%) than taking antibiotics (66.7%) (23) and probiotics alone (55%) (26).
5 Conclusion
The findings of this investigation have unveiled the therapeutic benefits of OLT against SIBO by alleviating the intrusiveness, frequency, and duration of GI symptoms. The efficacy of OLT is underscored by its ability to normalize GBT results by decreasing H2 and CH4 concentrations during the breath test. Nevertheless, the body composition parameters did not show much improvement throughout the study period. The intervention group experienced a decrease in TBW, which ultimately affects BMR, % muscle mass, and % fat mass, although BFM and BMD did not change. It is noteworthy that H2+/CH4+ SIBO patients have higher levels of protein, bone minerals, muscle mass, and BMR compared to H2+ and CH4+ groups alone. Beyond its therapeutic aspect, this study also presents evidence that SIBO is associated with an increased risk of obesity.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Human Bio-Ethical Committee, UVAS, Lahore, Pakistan. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WA: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ST: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AA: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. SI: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
All the authors are very thankful to the participants involved in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rezaie, A, Pimentel, M, and Rao, SS. How to test and treat small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: an evidence-based approach. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. (2016) 18:8. doi: 10.1007/s11894-015-0482-9
2. Erdogan, A, Rao, SSC, Gulley, D, Jacobs, C, Lee, Y, and Badger, C. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: duodenal aspiration vs glucose breath test. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2015) 27:481–9. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12516
3. Elphick, DA, Chew, TS, Higham, SE, Bird, N, Ahmad, A, and Sanders, DS. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in symptomatic older people: can it be diagnosed earlier? Gerontology. (2005) 51:396–401. doi: 10.1159/000088704
4. Skrzydło-Radomańska, B, and Cukrowska, BJJ o CM. How to recognize and treat small intestinal bacterial overgrowth? J Clin Med. (2022) 11:6017. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206017
5. Sheeza, I, Iqbal, S, Rabbani, I, and Ali, MA. Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in people with gastrointestinal signs and symptoms using glucose breath test. Act Sci Nutr Health. (2021) 5:127–37.
6. Onana Ndong, P, Boutallaka, H, Marine-Barjoan, E, Ouizeman, D, Mroue, R, Anty, R, et al. Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): correlating H2 or CH4 production with severity of IBS. JGH Open. (2023) 7:311–20. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12899
7. Gandhi, A, Shah, A, Jones, MP, Koloski, N, Talley, NJ, Morrison, M, et al. Methane-positive small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1933313. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1933313
8. Sachdev, AH, and Pimentel, M. Gastrointestinal bacterial overgrowth: pathogenesis and clinical significance. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. (2013) 4:223–31. doi: 10.1177/2040622313496126
9. Ren, X, Di, Z, Zhang, Z, Fu, B, Wang, Y, Huang, C, et al. Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO): a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. (2020) 99:e23737. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000023737
10. Baldoni, L, and Belaj, A. Olive In: J Vollmann and I Rajcan, editors. Oil crops. New York, NY: Springer (2010). 397–421.
11. Rocchetti, G, Callegari, LM, Senizza, A, Giuberti, G, Ruzzolini, J, Romani, A, et al. Oleuropein from olive leaf extracts and extra-virgin olive oil provides distinctive phenolic profiles and modulation of microbiota in the large intestine. Food Chem. (2022) 380:132187. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132187
12. Farràs, M, Martinez-Gili, L, Portune, K, Arranz, S, Frost, G, Tondo, M, et al. Modulation of the gut microbiota by olive oil phenolic compounds: implications for lipid metabolism, immune system, and obesity. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2200. doi: 10.3390/nu12082200
13. Cör Andrejč, D, Butinar, B, Knez, Ž, Tomažič, K, and Knez Marevci, M. The effect of drying methods and extraction techniques on Oleuropein content in olive leaves. Plants. (2022) 11:865. doi: 10.3390/plants11070865
14. Ramírez, EM, Brenes, M, Romero, C, and Medina, E. Olive leaf processing for infusion purposes. Foods. (2023) 12:591. doi: 10.3390/foods12030591
15. Kim, DB, Park, CS, Paik, CN, Kang, YJ, Jo, IH, and Lee, JM. Relationship between untreated obstructive sleep apnea and breath hydrogen and methane after glucose load. Saudi J Gastroenterol. (2022) 28:355–61. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_134_22
16. Basseri, RJ, Basseri, B, Pimentel, M, Chong, K, Youdim, A, Low, K, et al. Intestinal methane production in obese individuals is associated with a higher body mass index. Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2012) 8:22–8.
17. Yao, Q, Yu, Z, Meng, Q, Chen, J, Liu, Y, Song, W, et al. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in obesity and its related diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. (2023) 212:115546. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115546
18. Mathur, R, Amichai, M, Chua, KS, Mirocha, J, Barlow, GM, and Pimentel, M. Methane and hydrogen positivity on breath test is associated with greater body mass index and body fat. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 98:E698–702. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3144
19. Wielgosz-Grochowska, JP, Domanski, N, and Drywień, ME. Influence of body composition and specific anthropometric parameters on SIBO type. Nutrients. (2023) 15:4035. doi: 10.3390/nu15184035
20. Stotzer, PO, Johansson, C, Mellström, D, Lindstedt, G, and Kilander, AF. Bone mineral density in patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Hepato-Gastroenterology. (2003) 50:1415–8.
21. Malfa, GA, Di Giacomo, C, Cardia, L, Sorbara, EE, Mannucci, C, and Calapai, G. A standardized extract of Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) mill and Olea europaea L. improves gastrointestinal discomfort: a double-blinded randomized-controlled study. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:3756–68. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7074
22. Di Stefano, M, Malservisi, S, Veneto, G, Ferrieri, A, and Corazza, GR. Rifaximin versus chlortetracycline in the short-term treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2000) 14:551–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00751.x
23. Khalighi, AR, Khalighi, MR, Behdani, R, Jamali, J, Khosravi, A, Kouhestani, S, et al. Evaluating the efficacy of probiotic on treatment in patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)--a pilot study. Indian J Med Res. (2014) 140:604–8.
24. Kubota, K, Mase, A, Matsushima, H, Fujitsuka, N, Yamamoto, M, Morine, Y, et al. Daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, promotes colonic transit by inducing a propulsive movement pattern. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2019) 31:e13689. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13689
25. Pimentel, M, Constantino, T, Kong, Y, Bajwa, M, Rezaei, A, and Park, S. A 14-day elemental diet is highly effective in normalizing the lactulose breath test. Dig Dis Sci. (2004) 49:73–7. doi: 10.1023/b:ddas.0000011605.43979.e1
26. García-Collinot, G, Madrigal-Santillán, EO, Martínez-Bencomo, MA, Carranza-Muleiro, RA, Jara, LJ, Vera-Lastra, O, et al. Effectiveness of Saccharomyces boulardii and metronidazole for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65:1134–43. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05830-0
Keywords: gastrointestinal symptoms, hydrogen breath test, olive leaf tea, SIBO, gut microbiota
Citation: Zafar A, Ahmed W, Tahir SK, Ahmad AMR and Iqbal S (2025) Therapeutic effects of olive leaf tea (Olea europaea L.) on gastrointestinal symptoms and body composition in adults with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Front. Nutr. 12:1659500. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1659500
Edited by:
Karolina Wojtunik-Kulesza, Medical University of Lublin, PolandReviewed by:
Iraíldo Francisco Soares, Universidade Federal do Piauí (UFPI), BrazilM. Rezaul Karim, Jahangirnagar University, Bangladesh
Copyright © 2025 Zafar, Ahmed, Tahir, Ahmad and Iqbal. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdul Momin Rizwan Ahmad, YWJkdWwubW9taW5AeW9yay5hYy51aw==; Sanaullah Iqbal, c2FuYXVsbGFoLmlxYmFsQHV2YXMuZWR1LnBr
 Ayesha Zafar1
Ayesha Zafar1 Waqas Ahmed
Waqas Ahmed Sajid Khan Tahir
Sajid Khan Tahir Abdul Momin Rizwan Ahmad
Abdul Momin Rizwan Ahmad Sanaullah Iqbal
Sanaullah Iqbal