- 1Chengdu Women's and Children's Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Nutrition, Chengdu Women's and Children's Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 3National Center of Technology Innovation for Dairy, Hohhot, China
- 4Baoxing Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Yaan, China
- 5Department of Child Health Care, Xindu Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Chengdu, China
- 6School of Exercise and Nutritional Sciences, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA, United States
A Correction on
Effect of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis YLGB-1496 on common diseases in pediatrics: a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial
by Zhang, X., Chen, K., Lan, H., Chen, H., Chen, H., Yang, P., He, N., Hung, W., Zeng, Z., and Liu, C. (2025). Front. Nutr. 12:1585504. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1585504
In the published article, there was an error in Table 2, “Comparison of the days of common symptoms in infants and young children during the intervention period” as published.
The positions of “IG” and “CG” in the column headings were erroneously swapped. Similarly, “44 0.89” and “99 2.2” in the “Fever” row were incorrectly switched.
The corrected Table 2 appears below.
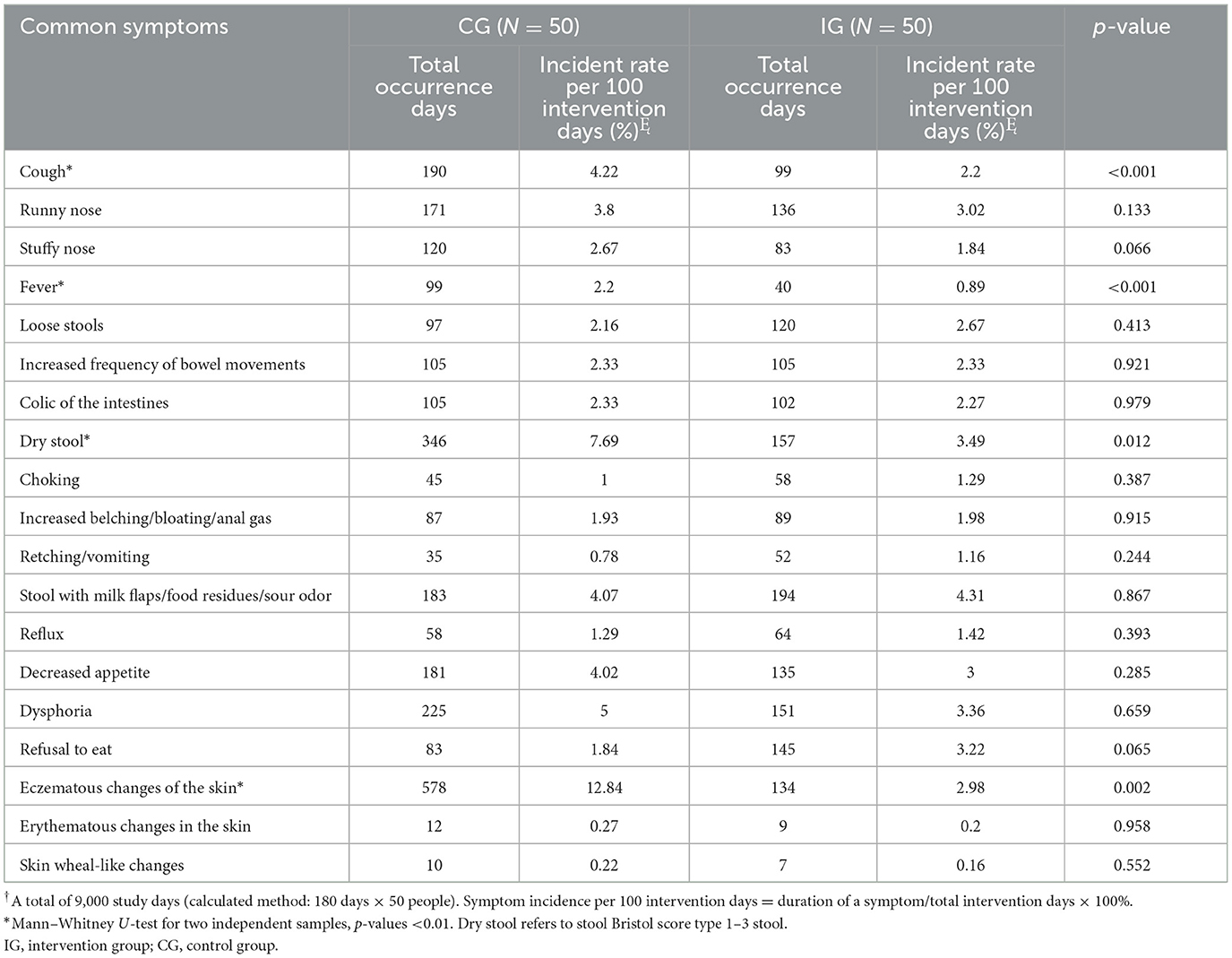
Table 2. Comparison of the days of common symptoms in infants and young children during the intervention period.
The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: probiotics, short chain fatty acids, children, gut microbiota, upper respiratory tract infection
Citation: Zhang X, Chen K, Lan H, Chen H, Chen H, Yang P, He N, Hung W, Zeng Z and Liu C (2025) Correction: Effect of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis YLGB-1496 on common diseases in pediatrics: a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Front. Nutr. 12:1661669. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1661669
Received: 08 July 2025; Accepted: 22 July 2025;
Published: 04 August 2025.
Edited and reviewed by: Michael J. Barratt, Washington University in St. Louis, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Chen, Lan, Chen, Chen, Yang, He, Hung, Zeng and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ke Chen, a2VjaGVuQHVlc3RjLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors share first authorship
 Xi Zhang
Xi Zhang Ke Chen
Ke Chen Hanglian Lan
Hanglian Lan Haixia Chen4
Haixia Chen4 Nianyang He
Nianyang He Changqi Liu
Changqi Liu