- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, India
- 2Department of Botany and Plant Physiology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, India
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of bioactive-based edible coatings on the shelf life of tomatoes. Bioactive compounds were extracted from rice and wheat straw. Different concentrations of phenolic extracts (0.2–1.0 g/mL) were blended with 1% chitosan and applied to fresh tomatoes stored at 28 °C and 74%−84% relative humidity (RH) for 30 days. Periodic evaluations revealed that tomatoes coated with 1.0 g/mL extract of rice and wheat straw coatings were highly effective in maintaining tomato quality as compared to controls. Tomatoes coated with 1.0 g/mL extract of wheat straw exhibited the most favorable results, including delayed weight loss (1.29%), slowed ripening, reduced pH levels, and lower lycopene (2.79 mg/100 g) and beta-carotene (0.62 mg/100 g) contents as compared to those coated with coatings containing rice straw extracts. Additionally, wheat straw extract-coated tomatoes had the lowest disease incidence (2%) after 30 days, as compared to 100% incidence in control samples. Overall, using edible coatings enriched with rice and wheat straw extracts presents a promising approach to extending the shelf life of tomatoes while preserving their nutritional value, inhibiting microbial growth, and offering a more sustainable and eco-friendlier alternative to conventional packaging methods.
Highlights
• Wheat straw extract (1.0 g/mL) coating reduced weight loss to 1.29 % and minimized ripening in tomatoes during 30 days of storage.
• Coated tomatoes retained lower lycopene (2.79 mg/100 g) and beta-carotene (0.62 mg/100 g), indicating better nutritional preservation.
• Edible coatings enriched with bioactive compounds from rice and wheat straw extracts were successfully developed, offering an eco-friendly solution for extending the shelf life of tomatoes.
• Tomatoes coated with a higher concentration of bioactive extracts showed significantly lower disease occurrence and severity compared to control samples.
1 Introduction
Currently, agriculture faces the dual challenge of meeting the increasing global demand for food production while adopting sustainable practices to minimize waste generated from agricultural activities. Over the past 50 years, the global population has increased from 3.7 billion to 7.9 billion and is projected to reach 8.6 billion by 2030, 9.8 billion by 2050, and 11.2 billion by 2100, according to a United Nations report (1). This rapid population growth has driven the need for increased agricultural output, which, in turn, has resulted in the generation of sustainable amounts of agricultural waste (2). Such waste contains valuable polyphenolic compounds, including flavonoids, tannins, phenolic acids, and anthocyanins, which offer potential for reuse in sustainable technologies such as edible coatings and films. Utilizing these compounds presents a promising solution for extending the shelf life and maintaining the quality of fruits and vegetables during postharvest storage. In recent times, consumers have become more worried about their food habits, rejecting products with additives and giving preference to fresh ones. Therefore, there is a dire need to develop a biodegradable edible coating for prolonging the shelf life of fruits and vegetables and preserving the nutritional quality of the fruit by minimizing the degradation of vitamins and antioxidants, potentially making them a sustainable alternative to traditional packaging methods.
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is one of the most widely cultivated and significant crops, ranking second only to potatoes in annual global production (3). Despite being a rich source of vitamins and antioxidants, tomatoes are highly perishable, with a typical shelf life of 4 to 8 days at room temperature. Their rapid spoilage is primarily due to pathogenic infections, leading to significant postharvest losses (4, 5). Traditional packaging materials, such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride, have been widely used to mitigate these losses (6). However, these non-biodegradable materials pose significant environmental challenges, prompting increased interest in sustainable alternatives (7). Recently, biodegradable packaging materials have gained attention for their eco-friendly characteristics (8, 9). Edible coatings, composed of materials classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), offer a promising solution for extending the shelf life of perishable produce (10). Among these, edible films, primarily composed of proteins or polysaccharides, have emerged as a promising solution, with polysaccharide-based packaging materials receiving particular focus (11–13). Among polysaccharide-based coatings, chitosan stands out for its favorable properties, including film-forming ability, biodegradability, antimicrobial activity, and antioxidant capacity (14, 15). However, its limitations, such as water sensitivity and poor mechanical strength, necessitate the incorporation of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and compatible plasticizers to overcome this limitation by increasing the free volume and molecular mobility within the amorphous polymer matrix, thereby reducing intermolecular hydrogen bonding interactions and improving film flexibility (16, 17).
Agricultural wastes such as rice straw and wheat straw are rich in phenolic compounds with antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Utilizing these extracts in chitosan-based films can reduce respiration rates, limit oxidative damage, and inhibit microbial growth, making them highly effective for extending the shelf life of tomatoes (18). Considering the present issue of the short shelf life of tomato fruits, this study aimed to develop and evaluate chitosan-based edible coatings enriched with phenolic extracts from agricultural waste to improve the postharvest quality and shelf life of Hisar Arun tomatoes, providing a sustainable alternative to conventional preservation methods. The objective of this study was to analyze the physiochemical (physiological loss, color, firmness, pH, and titrable acidity) and nutritional (ascorbic acid, lycopene, and β-carotene content) parameters of tomato during different intervals of storage.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Materials
Agricultural waste, such as rice straw and wheat straw, was collected from fields of CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, Haryana, India. All chemicals used in the study were of analytical grade and purchased from Thermo Scientific (Rockford, IL, USA). Fresh fruits of tomato (Hisar Arun) at the light red stage of ripening were procured from the farm of the Department of Vegetable Sciences, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar (Haryana) at 11:00 a.m. and transported in perforated plastic crates under ambient field temperature conditions (~30 °C).
2.2 Methods
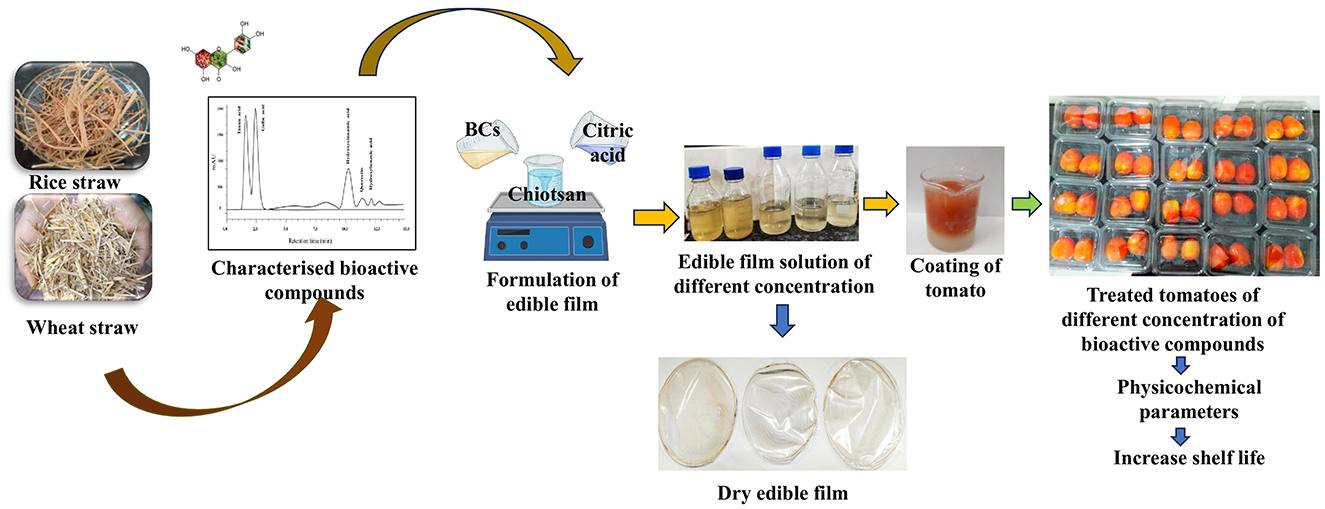
Dried powder of rice and wheat straw was pretreated with NaOH (1.5%) and 5% H2SO4 at 90 °C with continuous stirring for 2 h as described by Kim and Han (78). Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) (Vibra CellTM VCX750, Sonics & Materials, Inc., Newtown, CT, USA) was used for extraction of bioactive compounds from pretreated rice and wheat straw using 80% methanol as a solvent under ultrasonic field conditions at 40 °C for 55 min (maintaining the sample in an ice bath to prevent heating), using 750 W power, 20 kHz frequency, and 50% sonication amplitude. The solvent was further removed using a rotary evaporator (86, 89). The extracted bioactive compounds were dehydrated using anhydrous sodium sulfate and stored at 4 °C until further use.
2.2.1 Preparation bioactive compound-based coating solution
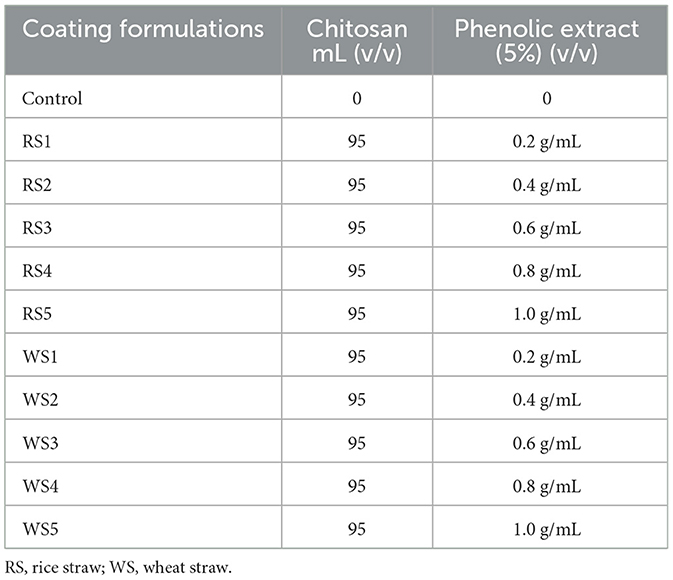
To prepare the chitosan solution, 1% chitosan was dissolved in a 0.5% aqueous citric acid solution to enhance solubility. The solution was homogenized at 10,000 rpm for 10 min and stirred continuously for 60 min at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C) using a magnetic stirrer (Accumax, Neuation, iStir HP 10M). Next, 5 mL of rice straw (RS) and wheat straw (WS) extracts, with concentrations of 0.2 g/mL, 0.4 g/mL, 0.6 g/mL, 0.8 g/mL, and 1.0 g/mL (Table 1), along with 1 % glycerol as a plasticizer, were added to the prepared chitosan solution. This mixture was stirred for another 60 min at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C). The resulting solution was then used to prepare an edible coating.
2.2.2 Coating of bioactive-based film on Hisar Arun tomatoes
Uniform-sized tomatoes were selected for coating. Initially, tomatoes were rinsed with sodium hypochlorite solution (50 ppm) for 1 min; excess sodium hypochlorite was removed by rinsing with distilled water. The fruits were coated using the immersion method as described by Mhd Haniffa et al. (19). A total of 10 formulations were prepared using rice and wheat straw extracts at concentrations of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 g/mL, along with an uncoated control (C), all maintained at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C). Three tomatoes per sample were used, and each treatment was conducted in three replications during the experiment. Fresh tomatoes were dipped into the coating solution for 1 min, allowed to drain, and air-dried at room temperature to remove excess coating. This process was repeated three times. The tomatoes were then allowed to dry at 25 °C, forming a thin-film coating (Figure 1). After drying, they were placed in polypropylene plastic covers and stored at room temperature. The coated tomatoes were weighed and stored at 25 ± 2 °C and 75 ± 5% relative humidity (RH) for 30 days.
2.3 Effect of coating on physicochemical parameters of tomatoes during the storage period
Various physicochemical parameters were analyzed during storage at 25 ± 2 °C and 75 ± 5% RH. Fruit weight loss, color, firmness, pH, and titrable acidity were analyzed at intervals, specifically on days 0, 7, 15, and 30. In addition, the incidence and severity of diseases were assessed on days 15 and 30 of storage to monitor the development of postharvest diseases.
2.3.1 Weight loss
Tomato samples (three fruit per replication) were weighed at day 0 and the end of days 7, 15, and 30 of storage. The difference between the initial and final weight of the fruit was considered as total weight loss during the storage interval and calculated as percentages on a fresh weight basis by the standard (74) method. The results were reported as a weight loss percentage using the following formula:
2.3.2 Change in fruit firmness
The firmness of Hisar Arun tomatoes was evaluated using a handheld fruit pressure tester penetrometer (model BGS - 25 Make Biogen Scientific), equipped with a cylindrical plunger of 8 mm diameter and a firmness scale of 13 kg cm−2. To ensure accurate measurements, firmness was assessed on both sides of the equatorial region of each fruit. A total of three tomatoes were tested, with four random measurements taken on each tomato. The firmness of two tomatoes per treatment was measured, and it was expressed in kg cm−2. The average of these measurements was recorded and expressed in units of kg cm?2.
2.3.3 Change in color and hue angle
The change in color of treated and untreated tomato samples was evaluated using a high-quality colorimeter (BCM-200). The L*, a*, b* color spaces were employed to evaluate the impact of coatings on color change. The following parameters were recorded: L* value (lightness), ranging from 0 (black) to 100 (white); an a* value ranging from negative (green) to positive (red); and b* value ranging from negative (blue) to positive (yellow). The color of tomatoes on day 0 was used as the reference point, and subsequent color changes were compared to this baseline. To ensure accurate and representative color measurements, multiple surface readings were taken from each sample by randomly repositioning the tomato fruits (20). To obtain the real color change during storage, a* and b* values were evaluated to calculate the hue angle value using the following equation (21):
where Hue0 = 0 represents purple red, 900 represents yellow, 1800 represents green–blue, 2700 represents blue.
2.3.4 Change in pH
Initially, the fresh tomatoes were juiced using an electric juicer, and then the resulting liquid was filtered through filter paper to remove any solids. The pH of the filtered tomato juice was then measured using a digital pH meter (Eutech, pH 700, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at storage intervals of 0, 7, 15, and 30 days to monitor changes over time. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate.
2.3.5 Change in titrable acidity
The change in total acidity of tomato pulp during storage was determined using titration with 0.1 N NaOH, according to the method described by Ranganna (22). A total of 5 g of fruit pulp was macerated in 5 mL of distilled water, and the mixture was diluted to 100 mL with distilled water. The solution was thoroughly shaken and filtered through Whatman No. 1 filter paper to remove any solids. An aliquot of 20 mL filtrate was titrated with 0.1 N NaOH using 1% phenolphthalein as the indicator, and the endpoint was noted by the appearance of a stable pink color. The acidity of the sample was calculated based on the volume of NaOH used and expressed as a percentage (%).
2.4 Effect of coating on the composition of bioactive compounds of tomatoes during storage
2.4.1 Change in lycopene content
One gram of fresh tomato fruit was extracted twice with 10 mL of an acetone:n-hexane mixture (4:6 ratio). To facilitate extraction, the mixture was allowed to stand in an ice bath for 10 min, followed by centrifugation at 1,370 × g for 10 min. The supernatant was then separated using a separating funnel. The absorbance of the hydrophobic fraction was measured spectrophotometrically at wavelengths of 663, 645, 505, and 453 nm using a UV Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific™ GENESYS™ series, 180), with acetone as a blank (72). Three replicates were performed for each fruit sample. The lycopene concentration was quantified using the equation proposed by Nagata and Yamashita (23):
2.4.2 Change in β-carotene contents
The concentration of beta-carotene was determined using a colorimetric assay developed by Biswas et al. (24). A total of 500 mg of dried fresh tomato fruits was extracted twice with 5 mL of chilled acetone. The mixture was allowed to stand in an ice bath for 15 min with shaking and then mixed vigorously for 10 min. Subsequently, the mixture was centrifuged at 1,370 × g for 10 min. The resulting supernatants were collected and filtered using Whatman No. 1 filter paper, and their absorbance was measured at wavelengths 663, 645, 505, and 453 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific™ GENESYS™ series, 180). Each sample was analyzed in triplicate. The beta-carotene content was calculated using the following equation:
2.4.3 Change in ascorbic acid
The ascorbic acid content was determined using the method of Mukherjee and Choudhuri (25), which was based on the reduction of 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine. A 0.1 mL aliquot of the sample was properly diluted and then mixed with 1.9 mL distilled water, 1 mL 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine (2%), and a drop of 10% thiourea. The mixture was thoroughly mixed and kept in a boiling water bath for 15 min. After boiling, the mixture was cooled at room temperature, and the absorbance was measured at 530 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific™ GENESYS™ series, 180). The quantity of ascorbic acid was determined by comparing the absorbance reading to a standard curve of ascorbic acid, using concentrations ranging from 10 to 100 μg.
2.5 Disease incidence (DI)
The proportion of tomatoes affected by diseases is referred to as disease incidence. DI was determined as a percentage of fruit having symptoms of diseases such as dots and rots in each batch of storage (5). The percentage of disease incidence of tomatoes was calculated by using the following formula
2.6 Disease severity
Tomato disease severity (DS) was assessed following the method described by Mohamed et al. (26). The severity scale is used as follows: 0 = 0% (no visible symptoms); 1 = 1%−25% (fruit surface slightly necrotic spots and fungal mycelia); 2 = 26%−50% (fruit covered by necrotic spots and fungal mycelia); 3 = 51%−75% (presence of spore mass); and 4 = >75% (fruit appears soft and decayed).
2.7 Statistical analysis
The experimental data were statistically analyzed using analysis of variance techniques (ANOVA), using Duncan's multiple range test following the completely randomized design (CRD) method with the OPSTAT software available on the CCS HAU homepage (http://www.opstat.somee.com/). To visualize the results, heatmap and contour maps of representative data were constructed using R 2019 [3.3.2 (64-bit)] and Origin 2018 (64-bit) software. These analytical tools facilitated a more precise presentation and interpretation of the data by elucidating underlying patterns and variations within the results (82).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of coating on physiological weight loss of tomatoes
The percentage of weight loss during storage was affected by the maturity stage and biological variances of fruits (5). The different concentrations of extract used in coating treatments significantly affect the loss of weight of tomatoes over the 30 days of storage. Tables 2, 3 show the average weight loss of control and treated tomatoes with different concentrations of rice straw extract and wheat straw extract. After 30 days of storage, the percentage of weight loss was maximum in the control as compared to the treated samples. The minimum weight loss was observed in tomatoes treated with WS5. The RS5-treated sample exhibited physiological losses of 0.43%, 1.09%, and 1.79% at 7, 15, and 30 days of storage, respectively, while the WS5-treated sample showed losses of 0.26%, 1.02%, and 1.29% over the same period. Jiang and Li (27) reported that 2% chitosan coating resulted in minimal weight loss in longan fruit. A notable difference was observed with the coating of rice and wheat straw extract. Das et al. (28) recorded a 3.53% reduction in weight loss in tomatoes coated with rice starch and coconut oil-based edible coating enriched with tea leaf extract compared to the uncoated fruits during storage at 24 °C for 20 days, demonstrating the moisture barrier properties of lipid-based edible coatings.
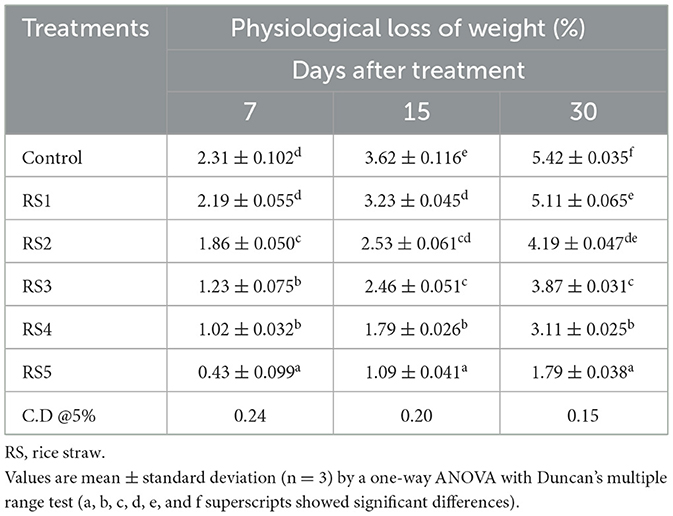
Table 2. Physiological loss of weight (%) of tomato using different concentrations of rice straw extract (RS).
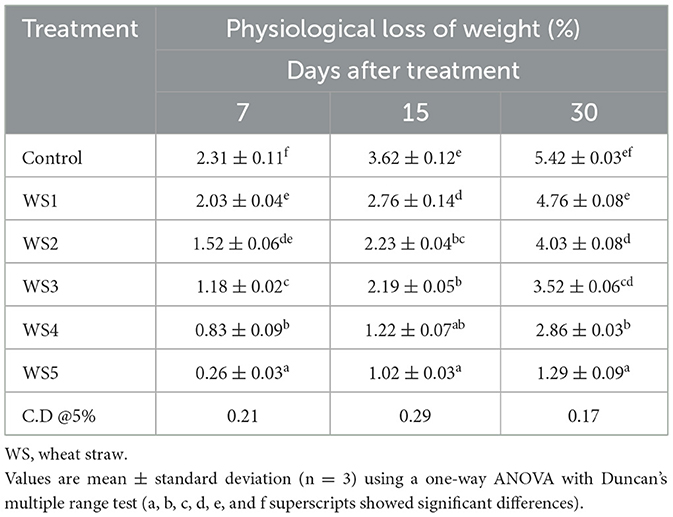
Table 3. Physiological loss of weight (%) of tomato using different concentrations of wheat straw extract (WSE).
Similarly, the color change in the contour map of tomatoes (Figure 2) depicts the change in physiological loss in weight (%) of treated and control samples of tomatoes during the storage period. Initially, on day 0, there was no change in physiological weight as indicated by the dark blue. As the storage period increased, a change in color was observed from blue to red. The red color indicates the maximum reduction in weight.
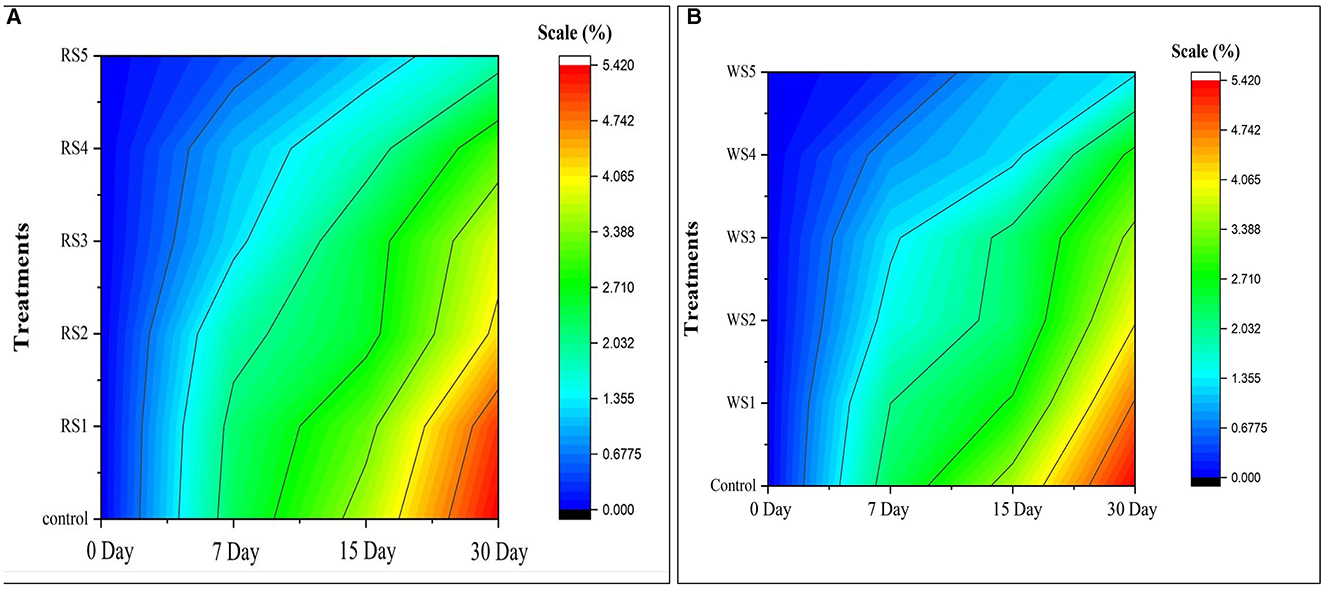
Figure 2. Contour map on physiological loss of weight (%) of control and treated tomatoes with different concentrations of rice straw (A) and wheat straw (B) extract.
The incorporation of chitosan with different concentrations of phenolic extract affects the structural integrity of the coating, potentially increasing the number of pores through which moisture may be more readily lost (29, 30). Weight loss in fresh produce is a critical indicator of postharvest life, as it directly reflects the extent of water loss, respiration, and overall quality degradation. In this study, the storage environment and concentration of extract significantly influenced the transpiration and respiration rates of Hisar Arun tomato fruits, directly impacting their overall quality.
Similar results were observed in previous studies that indicated coatings of biopolymers on pepper (31), beeswax on carrot (80), carvacrol on tomatoes (85), cassava starch and citrus pectin on mango (75), tara gum and lipid on strawberry (83), and whey protein with oregano extract on guava (77) reduce the rate of respiration, delay senescence, and reduce the loss of texture and overall extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables.
3.2 Effect of coating on firmness of tomatoes
On day 0 of storage, control and treated tomatoes exhibited similar firmness values, which gradually decreased over 7, 15, and 30 days, as shown in Figures 3, 4. Tomatoes treated with varying concentrations of RS and WS extract coating solution consistently showed significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher firmness values as compared to the control samples. Out of all the treated tomatoes, WS5-coated tomatoes showed higher firmness values as compared to those coated with RS5. During storage, the fruit firmness gradually decreases due to metabolic and physiological processes, including the activity of the polygalacturonase enzyme, which contributes to cell wall softening (32).
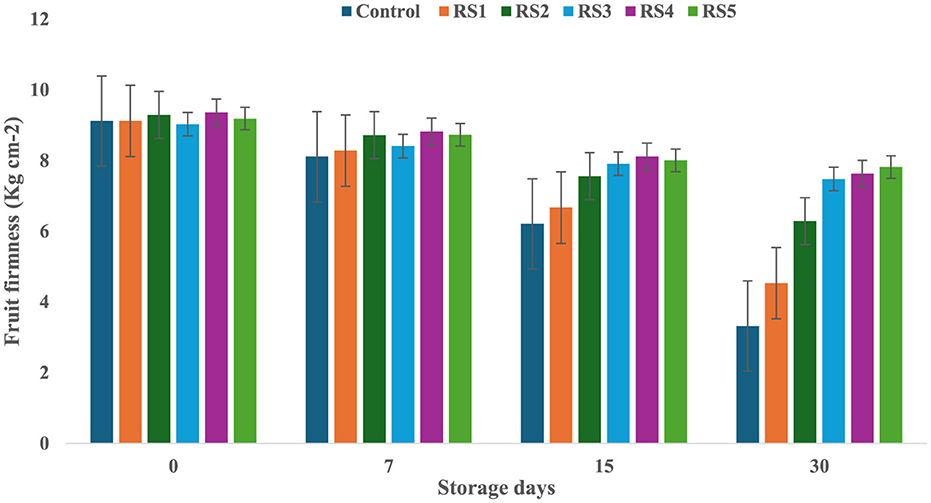
Figure 3. Change in fruit firmness of tomatoes during storage with coating of rice straw (RS) extract in different concentrations and uncoated tomatoes [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
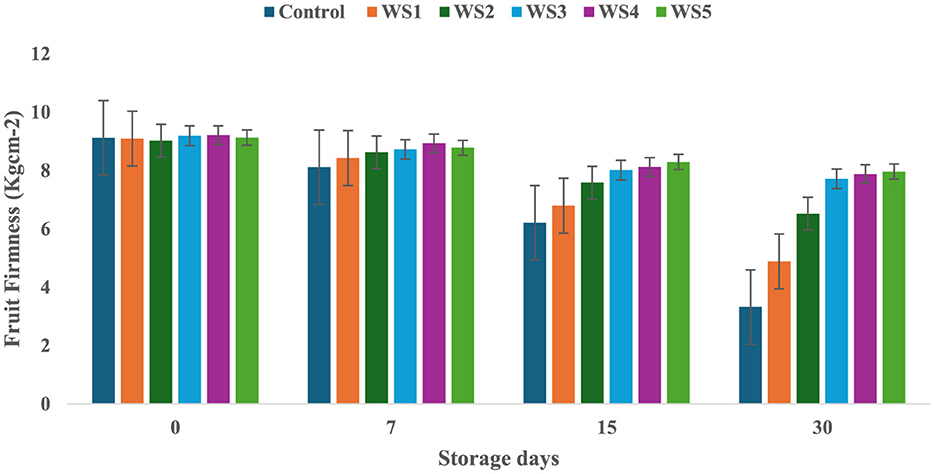
Figure 4. Change in fruit firmness of tomatoes during storage with coating of wheat straw (WS) extract in different concentrations and uncoated tomatoes [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
A similar mechanism for firmness retention was reported by Donjio et al. (88) in tomatoes coated with pineapple peel extract and Arabic gum, which was attributed to the antioxidants present in the pineapple peel extract. In addition, coating materials act as semipermeable barriers that modify the internal atmosphere by reducing oxygen levels and increasing carbon dioxide levels, thereby slowing biochemical reactions and contributing to the preservation of fruit firmness during storage (33). The findings of the present study are consistent with those of Kumar et al. (34), who observed that tomatoes coated with a chitosan–pullulan composite edible coating enriched with pomegranate peel extract maintained higher firmness than the uncoated control during storage at 23 °C for 15 days. The coatings were effective in regulating the respiration rate of the products during postharvest storage, which, in turn, slowed down the ripening process and helped maintain fruit firmness (35). The firmness of fruits is primarily influenced by two key factors: the structural integrity of the cell wall and the turgor pressure within the fruit cells (36). Similarly, the coating of extract of aloe vera and sodium alginate increases the fruit firmness of strawberry during storage (76). A similar study by Tilahun (37) showed that mature green fruits have higher firmness values than those at the fully ripe stage. Fruit firmness typically declines when cell wall integrity is compromised or turgor pressure decreases. In contrast, the minimum water loss was observed in tomatoes treated with RS and WS extracts, i.e., this helped to preserve the cell wall integrity and maintain higher turgor pressure, ultimately leading to improved firmness of fruits (33). By minimizing water loss, the bioactive edible coating played a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of the fruit, resulting in a more stable and firmer texture.
3.3 Effect of coating on pH of tomatoes
The observed variation in pH among the treated and untreated samples of tomatoes could be attributed to differences in metabolic processes and their interactions with the applied coating materials, which may influence the rate of respiration and biochemical activities in the fruit, leading to a change in pH. As shown in Figures 5, 6, a significant (p ≤ 0.05) difference in pH values was observed among the stored tomato samples. The lowest pH values, 5.5 and 5.8, were recorded in WS5- and RS5-treated samples after 30 days of storage, whereas the highest pH value, 6.9, was obtained in the control sample of tomatoes. This suggests that the coating materials had a significant impact on the pH levels of the tomatoes, with the WS5 and RS5 treatments resulting in a more acidic environment.
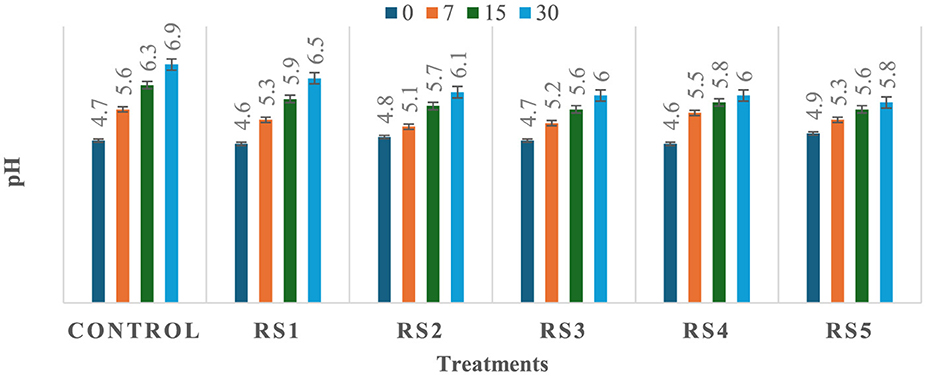
Figure 5. Change in pH of tomatoes during storage with coating of rice straw (RS) extract in different concentrations and uncoated tomatoes [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
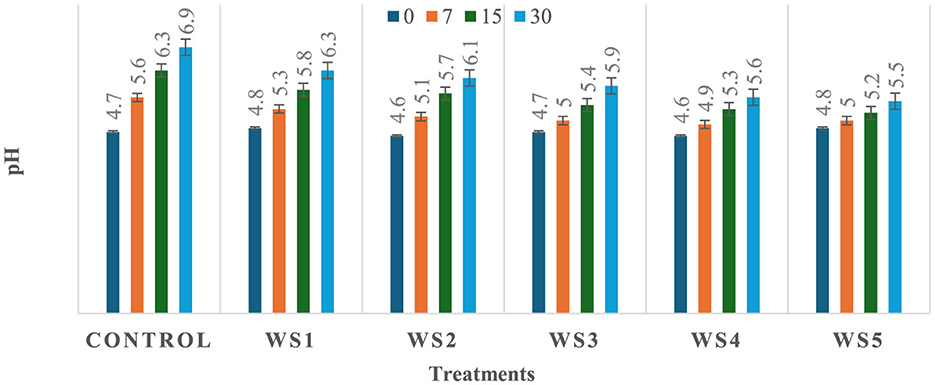
Figure 6. Change in pH of tomatoes during storage with coating of wheat straw (WS) extract in different concentrations and uncoated tomatoes [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
A decrease in pH values may be associated with an increase in the titrable acidity of the tomato fruits, potentially resulting from a lowered respiration rate that slows down the breakdown and consumption of organic acids during storage (27). As a result, the organic acids accumulate, leading to a decrease in pH values and an increase in titrable acidity. Several studies have reported that as tomato fruits transition from the mature-green stage to full ripeness, their pH tends to increase due to the degradation of organic acids during the ripening process (38, 39, 79). Ribeiro-Santos et al. (40) reported a slight increase in pH (from 4.62 to 5.77) in tomatoes coated with cassava starch–chitosan coatings enriched with Lippia sidoides essential oils and pomegranate peel extract during storage at 25 °C for 12 days, compared to the uncoated control. The pH results of the present study are also consistent with those of Firdous et al. (41), who observed a slight increase from 4.98 to 5.00 in tomatoes coated with 80% aloe vera gel and 2% calcium chloride after 30 days of storage. Fruits coated with chitosan have exhibited lower acidity loss, and similar observations were also found in previous studies conducted on strawberry (42, 84), guava and litchi (43), and capsicum (73).
3.4 Change in titrable acidity (TA) of tomatoes during storage
The titrable acidity of tomatoes was significantly affected by the different concentrations of extract during the storage for 30 days. The titrable acidity of the untreated or control sample of tomatoes was significantly (p < 0.05) decreased from 0.62 to 0.30 during the 30 days of storage, but in the treated samples, the titrable acidity was consistently decreased during the storage days. The RS5-treated samples showed a minimum (0.46) decrease in titrable acidity, followed by RS4 (0.41) and RS3 (0.39) (Figure 7). Similarly, the WS5-treated sample showed a minimum (0.45) decrease in titrable acidity, followed by WS4 (0.43) and WS3 (0.40) (Figure 8).
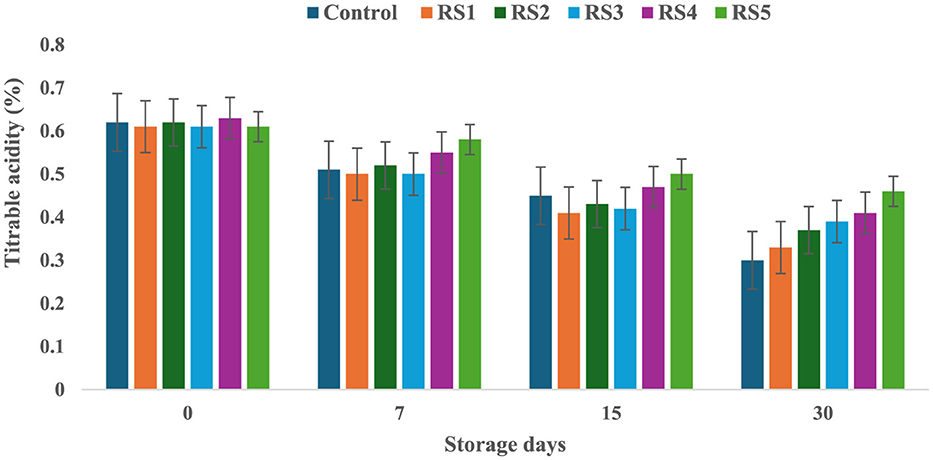
Figure 7. Change in titrable acidity of tomatoes as a function of storage time for coated tomatoes with rice straw (RS) extract in different concentrations (RS1: 0.2, RS2: 0.4, RS3: 0.6, RS4: 0.8, and RS5-1%) and uncoated tomatoes (control) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
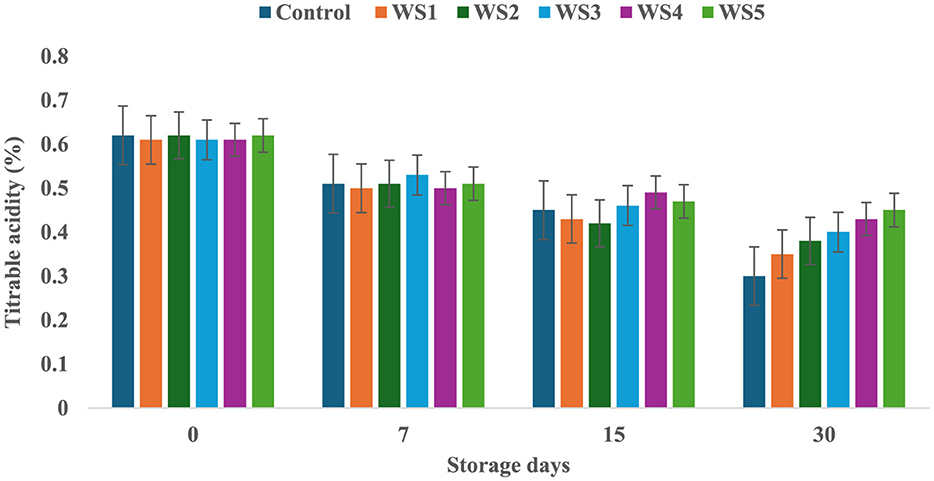
Figure 8. Change in titrable acidity of tomatoes as a function of storage time for coated tomatoes with wheat straw (WS) extract in different concentrations (WS1: 0.2, WS2: 0.4, WS3: 0.6, WS4: 0.8, and WS5: 1%) and uncoated tomatoes (control) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
A higher loss of titrable acidity in tomatoes is often associated with increased respiration and ripening rates, as organic acids are utilized as substrates in the respiration process (44). Adjouman et al. (45) reported a significant delay in titrable acidity (TA) changes in tomatoes coated with cassava starch-based composite edible coatings compared to both uncoated fruits and those coated with commercial Semperfresh™. Moreover, another study by Saliba-Colombani et al. (46) had shown that total sugars were positively correlated to pH and titrable acidity. Additionally, studies have found a positive correlation between total sugars and pH/titrable acidity, indicating that fruits with higher sugar content tend to have more free organic acids and lower hydrogen ion concentrations. This suggests that fruits with higher sugar content may have a more acidic pH. Furthermore, it has been observed that titrable acidity content generally decreases during ripening and storage (47). However, maintaining higher fruit acidity is beneficial, as it can reduce the incidence of fungal infection (48). Similar results were also reported by Tigist et al. (87), who observed a general trend of increasing ascorbic acid content during the early ripening stages, followed by a decline at full ripeness of tomatoes. Likewise, Ali et al. (90) found that papaya fruits coated with chitosan exhibited a slower initial increase in ascorbic acid compared to uncoated fruits.
3.5 Effect of coating on color of tomatoes
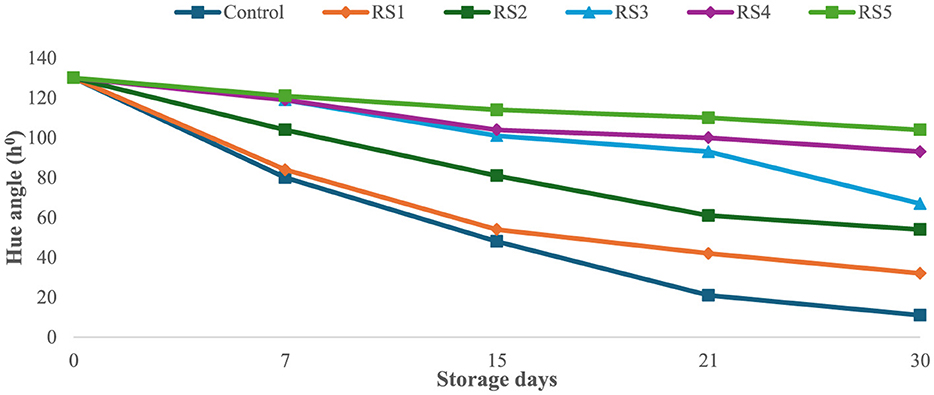
The bioactive coating formed a thin, homogeneous, semipermeable membrane on the surface of the tomato skin, facilitating controlled gas exchange. Throughout the experimental storage period, noticeable changes were observed in the L*, a*, and b* values of all the tomato samples. The L* values remained stable until the ripening stage, indicating that brightness remained constant, while the tomatoes were green. The L* gradually decreased progressively with increasing storage time of untreated and treated tomato samples. However, this decrease was slower for tomatoes treated with 1.0 g/mL phenolic extract of rice straw and wheat straw as compared to untreated samples. After 15 days of storage, tomatoes treated with RS5 and WS5 maintained significantly higher chroma values compared to other treated and control tomatoes, indicating better color retention. However, the color was significantly (p < 0.05) changed in uncoated samples as compared to the treated samples of tomatoes. The values were sharply decreased in the control after the 7th day of storage, as compared to the treated samples of tomatoes. The hue angle remained stable in RS2-, RS3-, RS4-, and RS5-treated samples up to 15 days (Figure 9), followed by a slight decrease thereafter. A similar pattern was observed in tomatoes treated with wheat straw extract (Figure 10). This reduction was attributed to the formation of a thick, continuous coating that covered the epidermal openings and modified the internal atmosphere, leading to elevated carbon dioxide and reduced oxygen levels (49).
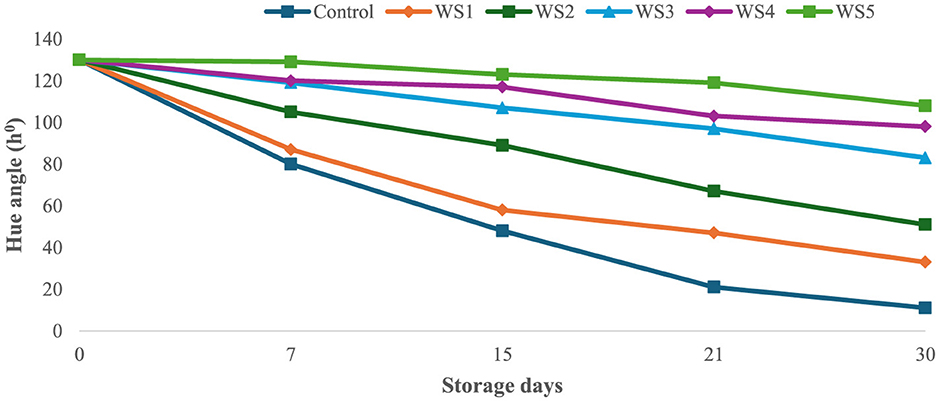
Figure 10. Effect of coating of wheat straw (WS) extract on the hue angle of tomato fruit during storage.
According to Paul et al. (49), tomatoes coated with 2.15% chitosan and 0.05% glycerol exhibited a reduced respiration rate of 21.21 ± 0.06 mg CO2 kg−1 h−1 and a DE of 2.31 ± 0.01 during storage. This reduction was attributed to the formation of a thick and continuous coating that covered the epidermal openings, thereby modifying the internal atmosphere by increasing carbon dioxide levels and reducing oxygen availability.
3.6 Effect of coating on lycopene content of tomatoes during storage
The lycopene content of tomatoes varied with the ripening stages, and similar variations were observed in the experimental setup. Ripeness is characterized by a decline in chlorophyll concentration and a rapid production of red pigment lycopene. On day 30 of storage, the lycopene content of control tomato samples during their ripening stage was 2 mg/100 g. In contrast, the lycopene content of rice straw-coated samples (RS1, RS2, RS3, RS4, and RS5) was 2.67, 2.87, 3.00, 3.01, and 2.81 mg/100 g, respectively. For wheat straw extract-coated samples (WS1, WS2, WS3, WS4, and WS5, the lycopene content was 2.50, 2.89, 2.80, 3.01, and 2.79 mg/100 g, respectively. Both treated and control tomatoes showed a consistent rise in lycopene content until the 15 days of storage, followed by a gradual decline. However, tomatoes treated with wheat straw extract exhibited a steady increase in lycopene content throughout the entire 30-day storage period. The earlier increase in lycopene content in tomato fruits may be due to the faster ripening, which facilitates the accumulation of lycopene. During this process, lycopene integrates into the internal cell membranes, and the conversion of chloroplasts into chromoplasts occurs (81). Figures 11 and 12 illustrate the changes in lycopene content for tomatoes treated with varying concentrations of rice straw and wheat straw extracts over the 30-day storage period.
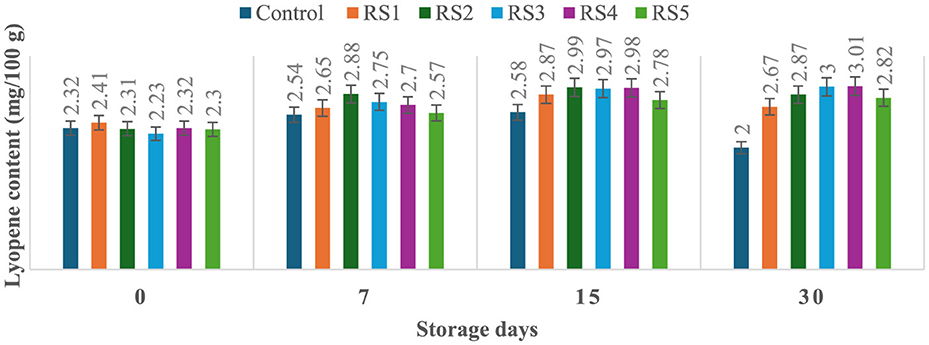
Figure 11. Effect of coating of rice straw extract on lycopene content of tomatoes during storage (RS1: 0.2, RS2: 0.4, RS3: 0.6, RS4: 0.8, and RS5: 1%) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
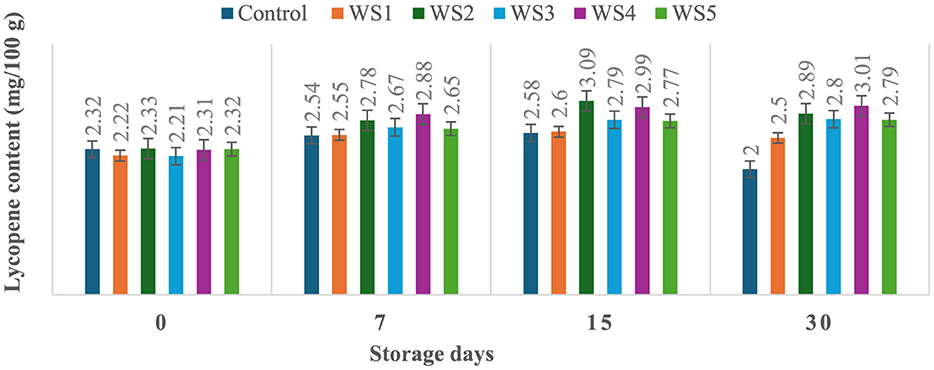
Figure 12. Effect of coating of wheat straw extract on lycopene content of tomatoes during storage (WS1: 0.2, WS2: 0.4, WS3: 0.6, WS4: 0.8, and WS5-1%) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
Javanmardi and Kubota (50) reported that temperature range and respiration rate are the major factors influencing lycopene synthesis in tomatoes during storage. Ali et al. (51) reported that lycopene content generally increased with the storage time in both treated and control fruits. However, tomatoes treated with high concentrations of gum arabic (15% and 20 %) exhibited the lowest lycopene levels, even after 20 days of storage. Furthermore, it has been noted that the rate of transpiration during storage significantly influences lycopene synthesis (50). Coatings reduce respiration by limiting oxygen exposure. After 15 days, lycopene content in red-ripe fruits was 0.95, 0.59, and 0.62 mg/100 g, for control, chitosan, and pectin-coated samples, respectively (52). Ripening-related pigment changes are characterized by the conversion of chloroplasts into chromoplasts, leading to a rapid accumulation of carotenoids, particularly lycopene, and a concurrent decline in chlorophyll content (53). These transformations underline the dynamic changes in tomato pigmentation during ripening and storage.
3.7 Effect of coating on β-carotene content of tomatoes during storage
The production of β-carotene was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher in the untreated or control sample of tomatoes as compared to the treated tomato samples stored for 30 days. Control, RS1-, RS2-, RS3-, RS4-, and RS5-treated samples showed 0.33, 0.34, 0.32, 0.31, 0.36, and 0.31 mg/100 g beta-carotene content on day 0 after coating. For untreated samples of tomatoes, the content was increased to 1.36 mg/100g after 30 days of storage, whereas in treated samples, it consistently was increased to 1.32, 1.03, 0.81, 0.73, and 0.63 for RS1, RS2, RS3, RS4, and RS5, respectively (Figure 13). Similarly, in the WS5-treated tomatoes, minimum beta-carotene content (0.62 mg/100 g) was observed at 30 days of storage, followed by WS4- and WS3-treated tomatoes (Figure 14).
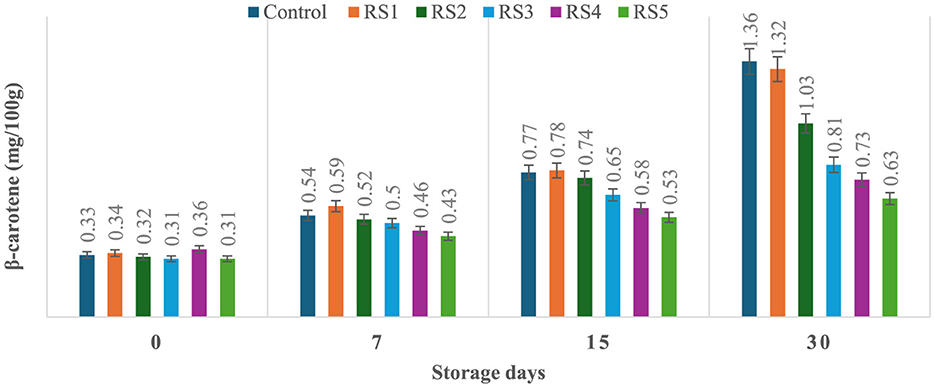
Figure 13. Effect of coating of rice straw extract on β-carotene content of tomatoes during storage (RS1: 0.2, RS2: 0.4, RS3: 0.6, RS4: 0.8, and RS5: 1%) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
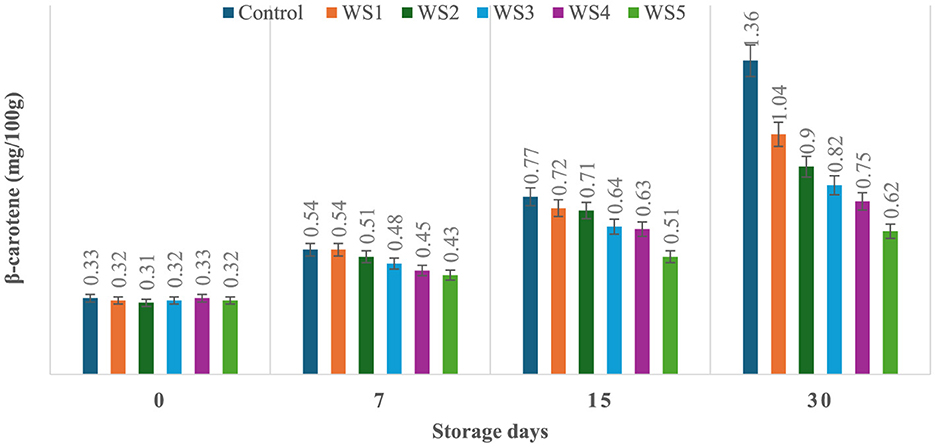
Figure 14. Effect of coating of wheat straw extract on β-carotene content of tomatoes during storage (WS1: 0.2, WS2: 0.4, WS3: 0.6, WS4: 0.8, and WS5: 1%) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
The ripening process in tomatoes is primarily characterized by the production and accumulation of pigments, particularly carotenoids such as lycopene (54, 55). This study proposed that a higher concentration of bioactive compounds in the coating can act as a barrier to ethylene gas and slow down the ripening process. As a result, the control samples might exhibit higher beta-carotene levels than the treated tomato samples.
3.8 Effect of coating on ascorbic acid content of tomatoes during storage
At the start of the experiment, the ascorbic acid content in the control tomato samples was 29.14 mg/100 g, which rapidly decreased to 16.11 mg/100 g after 30 days of storage. In contrast, tomatoes treated with varying concentrations of rice straw and wheat straw extracts exhibited a more gradual reduction in ascorbic acid content over the same period. Figures 15 and 16 illustrate the effect of these bioactive coatings on the ascorbic acid levels of tomatoes during storage. Among the treated samples, the minimum reduction in ascorbic acid content was observed in RS4- and RS5-treated tomatoes, followed by RS3 and RS2. A similar trend was noted in tomatoes treated with wheat straw extract, with higher concentration treatments (WS4 and WS5) showing the most significant retention of ascorbic acid content.
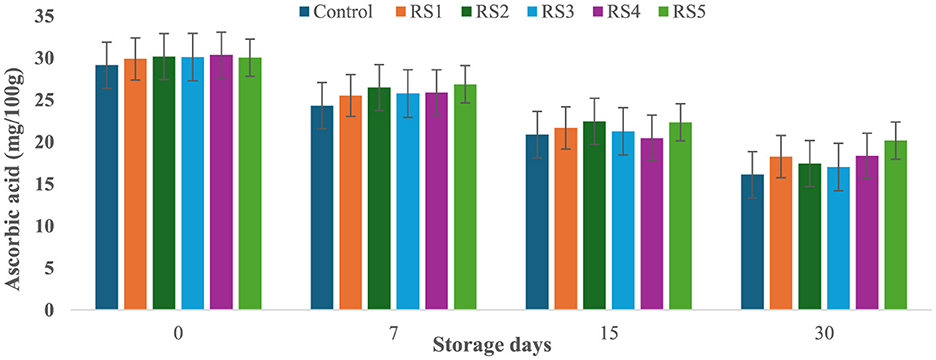
Figure 15. Effect of coating of rice straw extract on ascorbic acid content of tomatoes during storage (RS1: 0.2, RS2: 0.4, RS3: 0.6, RS4: 0.8, and RS5-1%) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
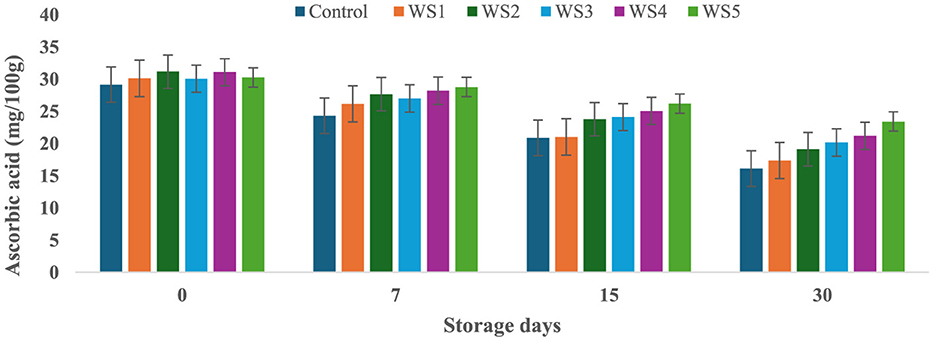
Figure 16. Effect of coating of wheat straw extract on ascorbic acid content of tomatoes during storage (WS1: 0.2, WS2: 0.4, WS3: 0.6, WS4: 0.8, and WS5-1%) [values are mean ± standard deviation (n = 3)].
This demonstrates that the bioactive coatings from rice and wheat straw extracts effectively slow the degradation of ascorbic acid, preserving the nutritional quality of the tomatoes during storage. Bioactive coatings from rice and wheat straw extracts help preserve ascorbic acid in tomatoes by forming semipermeable barriers that reduce oxygen diffusion and respiration, thereby slowing oxidative degradation (52). The phenolic compounds present in these extracts further scavenge reactive oxygen species and inhibit oxidative enzymes, stabilizing the ascorbate pool (33, 71). In addition, reduced transpiration maintains tissue integrity, which contributes to slower vitamin C loss during storage (56, 57). The observed pattern aligns with general trends, where fruits and vegetables experience ascorbic acid depletion with prolonged storage and higher temperatures (58, 59). Similar reductions in ascorbic acid content during storage have been reported in bananas (60), tomatoes (61), and kiwifruit (62).
3.9 Diseases incidence in tomatoes during the storage period
A significant difference was observed in the frequency of disease occurrence in tomato fruits throughout the storage period. The coating application postponed the rate of firmness loss by preserving the integrity of the cell wall. Moreover, the coating could lower the rate of ethylene synthesis and the metabolic pathway of respiration (63). When these circumstances come together, cell walls may be better able to withstand fungal invasion (64). Figures 17A, B illustrate that disease incidence in tomato fruits was significantly influenced by the different coating treatments of rice and wheat straw extract. Coated tomatoes exhibited a marked reduction in disease occurrence compared to untreated control fruits. The control sample of tomatoes showed a 90% incidence of disease after 30 days of storage, while the RS5- and WS5-treated samples showed lowest disease incidence. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the coatings in mitigating disease progression during storage.
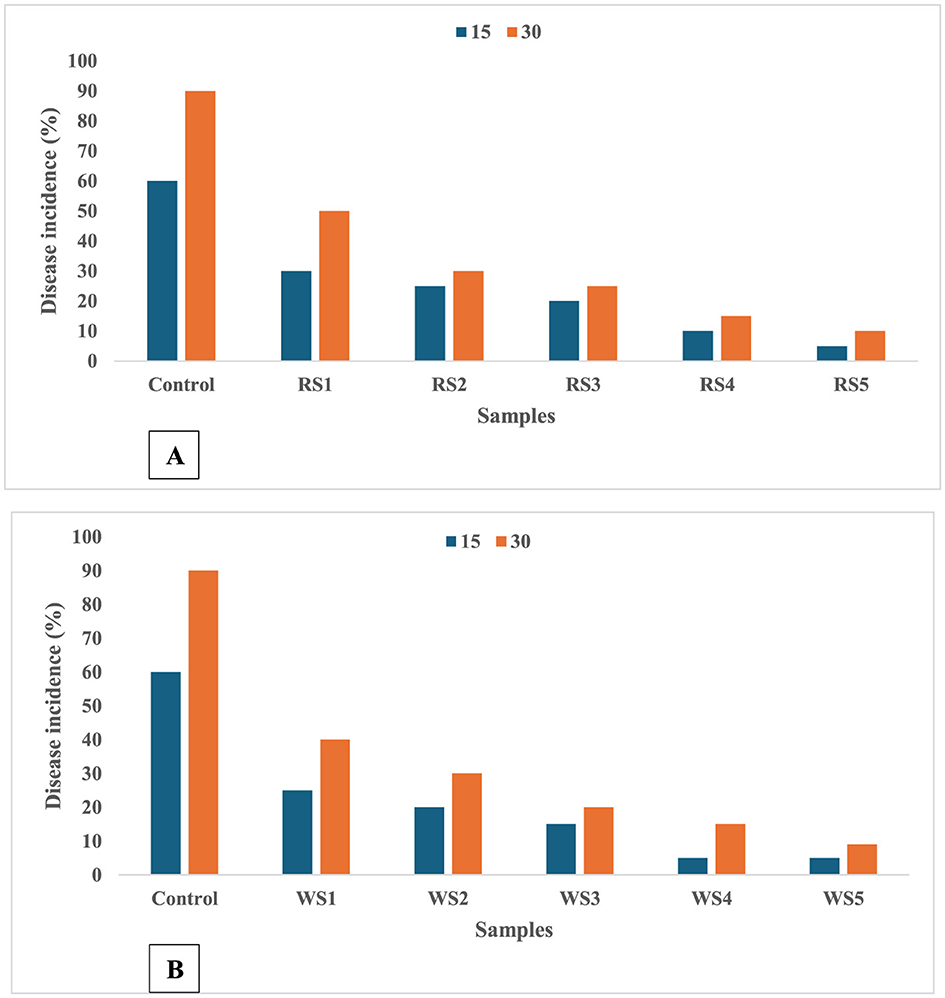
Figure 17. Effect of coating of rice straw (A) and wheat straw (B) extract on disease incidence of tomatoes during storage of 15 and 30 days (RS, rice straw; WS, wheat straw).
3.10 Disease severity in tomatoes during storage
The impact of different coatings on the disease severity of tomatoes during storage of 15 and 30 days is shown in Figure 18. No diseases were observed in the treated tomato sample on the 7th day of storage, whereas the untreated or control samples exhibited rot on the 7th day. On 15 days of storage, control samples showed a disease severity of 2, while tomatoes treated with rice straw extract coatings—RS1, RS2, RS3, RS4, and RS5—exhibited disease severity levels of 2, 1, 1, 1, and 0, respectively. On day 30, tomatoes treated with RS4 and RS3 had disease severity levels of 1 and 0, respectively. Similarly, tomatoes treated with wheat straw extract (WS)—WS1, WS2, WS3, WS4, and WS5—displayed disease severity levels of 3, 3, 3, 2, and 0, respectively.
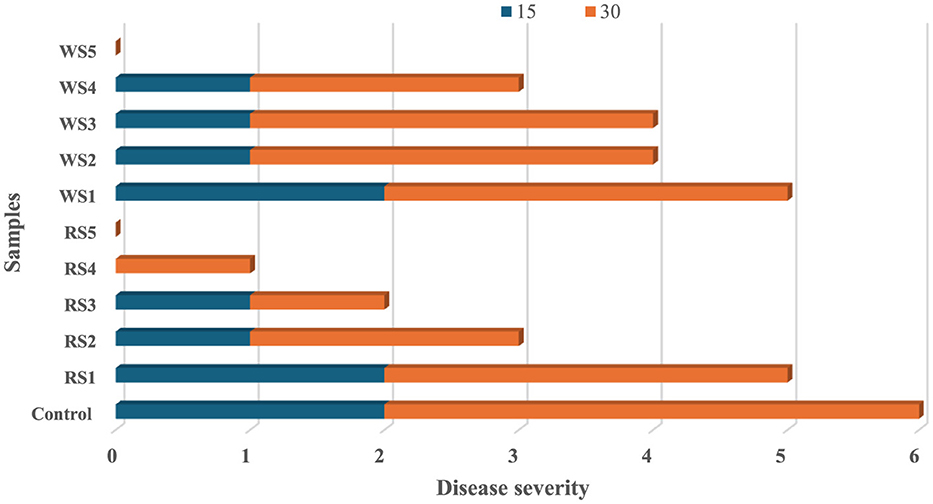
Figure 18. Effect of coating on disease severity of tomatoes during storage of 15 and 30 days (RS, rice straw; WS, wheat straw).
The bioactive coatings significantly enhanced the cellular and tissue integrity of fresh tomatoes, reducing their susceptibility to pathogenic infections (64). This protective effect was particularly evident as the tomatoes approached senescence, a process that the coatings helped to delay.
3.11 Shelf life of tomatoes
After harvesting, the time taken by fruits to begin deteriorating is considered their shelf life (65). The lowest shelf life of 10 days recorded for uncoated fruits was likely due to accelerated physiological changes and metabolic activities, including increased respiration and ethylene biosynthesis during storage, which led to fruit senescence (66, 67). At the senescence stage, fruits become more susceptible to microbial infections because of the loss of cellular and tissue integrity, resulting in rapid deterioration (68). In contrast, fruits coated with formulations of 1.0% extracts of rice and wheat straw exhibited a marked extension of shelf life by 17 and 15 days, respectively, at 25 ± 2 °C and 75 ± 5% RH. This extension can be attributed to the coatings' ability to reduce respiration rate, ethylene production, physiological changes, microbial decay, and senescence. Extending the shelf life of tomatoes offers significant economic benefits by reducing postharvest losses, enabling wider market access, improving retail efficiency, increasing revenue, enhancing consumer satisfaction, and promoting sustainability. Collectively, these advantages contribute to a stronger and more efficient supply chain, benefiting all stakeholders involved (52, 69, 70).
4 Conclusion
This study demonstrated that bioactive coatings enriched with rice and wheat straw extracts significantly influenced the postharvest quality and shelf life of tomatoes. The coatings formed a thin, semipermeable membrane on the tomato surface, effectively reducing weight loss, preserving firmness, and delaying color changes during storage. Tomatoes treated with higher concentrations of RS and WS extracts, particularly RS4, RS5, WS4, and WS5, exhibited improved preservation of physicochemical properties, including ascorbic acid and lycopene content. These bioactive compounds contributed to the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the coatings, which enhanced the cellular and tissue integrity of the fruits and reduced disease incidence and severity during storage. The results also indicated that while the coatings slowed down ripening processes, overconcentration of bioactive compounds could decrease film flexibility, potentially reducing coating efficacy. Despite this, RS5- and WS5-treated tomatoes maintained superior quality compared to control samples, exhibiting reduced disease severity and better retention of chroma and firmness over 30 days of storage. These findings suggest that the application of bioactive coatings derived from agricultural waste extracts (rice straw and wheat straw) offers a sustainable and effective solution for extending the shelf life and maintaining the postharvest quality of fresh tomatoes. This approach not only adds value to agricultural byproducts but also provides an eco-friendly alternative for reducing postharvest losses in fruits. Transforming waste from straw into food packaging can offer two significant advantages: (i) decreased environmental impact and lower disposal costs associated with both plastic packaging and agricultural waste and (ii) extended shelf life for food and reduced food waste. Additional research is needed to evaluate the effectiveness of bioactive packaging in preserving the quality of various food product categories under different storage conditions.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are available on request. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Kamla Malik via a2FtbGFtYWxpazA2QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==.
Author contributions
SY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. KM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft. KS: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. PD: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. DH: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Department of Microbiology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar and ICAR-AICRP-EAAI scheme for providing necessary facilities during the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Kaza S, Yao LC, Bhada-Tata P, Van Woerden F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. Urban Development. Washington, DC: World Bank (2018). doi: 10.1596/978-1-4648-1329-0
2. Yadav S, Malik K, Moore JM, Kamboj BR, Malik S, Malik VK, et al. Valorisation of agri-food waste for bioactive compounds: recent trends and future sustainable challenges. Molecules. (2024) 29:2055. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092055
3. FAOSTAT F. Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations. Statistical database (2020). Available online at: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/
4. Obeng FA, Gyasi PB, Olu-Taiwo M, Ayeh-Kumi FP. Microbial assessment of tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum) sold at some central markets in Ghana. Biomed Res Int. (2018) 2018:6743826. doi: 10.1155/2018/6743826
5. Islam MN, Wang A, Pedersen JS, Sørensen JN, Körner O, Edelenbos M, et al. Online measurement of temperature and relative humidity as marker tools for quality changes in onion bulbs during storage. PLoS ONE. (2019) 14:e0210577. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210577
6. Teasdale A, Jahn M, Bailey S, Feilden A, Taylor G, Corcoran ML, et al. Controlled extraction studies applied to polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene materials: conclusions from the ELSIE controlled extraction pilot study. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. (2015) 16:664–74. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0249-x
7. Zhang W, Ahari H, Zhang Z, Jafari SM. Role of silica (SiO2) nano/micro-particles in the functionality of degradable packaging films/coatings and their application in food preservation. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2023) 133:75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2023.01.009
8. Zhou Y, Xu T, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Lu Z, Lu F, et al. Effect of tea polyphenols on curdlan/chitosan blending film properties and its application to chilled meat preservation. Coatings. (2019) 9:262. doi: 10.3390/coatings9040262
9. Zhao L, Liu Y, Zhao L, Wang Y. Anthocyanin-based pH-sensitive smart packaging films for monitoring food freshness. J Agric Food Res. (2022) 9:100340. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100340
10. Tharanathan RN. Biodegradable films and composite coatings: past, present and future. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2003) 14:71–8. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2244(02)00280-7
11. Manzoor A, Dar AH, Pandey VK, Shams R, Khan S, Panesar PS, et al. Recent insights into polysaccharide-based hydrogels and their potential applications in food sector: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 213:987–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.044
12. Zhu F. Polysaccharide based films and coatings for food packaging: effect of added polyphenols. Food Chem. (2021) 359:129871. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129871
13. Kong I, Degraeve P, Pui LP. Polysaccharide-based edible films incorporated with essential oil nanoemulsions: physico-chemical, mechanical properties and its application in food preservation—A review. Foods. (2022) 11:555. doi: 10.3390/foods11040555
14. Kean T, Thanou M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. (2010) 62:3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.09.004
15. Anraku M, Fujii T, Kondo Y, Kojima E, Hata T, Tabuchi N, et al. Antioxidant properties of high molecular weight dietary chitosan in vitro and in vivo. Carbohydr Polym. (2011) 83:501–5. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.009
16. Aljawish A, Chevalot I, Piffaut B, Rondeau-Mouro C, Girardin M, Jasniewski J, et al. Functionalization of chitosan by laccase-catalyzed oxidation of ferulic acid and ethyl ferulate under heterogeneous reaction conditions. Carbohydr Polym. (2012) 87:537–44. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.08.016
17. Teixeira-Costa BE, Ferreira WH, Goycoolea FM, Murray BS, Andrade CT. Improved Antioxidant and mechanical properties of food packaging films based on chitosan/deep eutectic solvent, containing Açaí-filled microcapsules. Molecules. (2023) 28:1507. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031507
18. Singh SK, Anand A, Verma SK, Siddiqui MA, Mathur A, Saklani S, et al. Analysis of phytochemical and antioxidant potential of Ocimum kilimandscharicum Linn. Int J Curr Med Pharm Res. (2011) 3:40–6.
19. Mhd Haniffa MAC, Ching YC, Abdullah LC, Poh SC, Chuah CH. Review of bionanocomposites coating films and their application. Polymers. (2016) 8:246. doi: 10.3390/polym8070246
20. Cao X, Islam MN, Lu D, Han C, Wang L, Tan M, et al. Effects of barley seedling powder on rheological properties of dough and quality of steamed bread. Food Sci Technol Int. (2023) 10820132231188988. doi: 10.1177/10820132231188988
21. Pék Z, Helyes L, Lugasi A. Color changes and antioxidant content of vine and postharvest-ripened tomato fruits. Hort Science. (2010) 45:466–8. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.45.3.466
22. Ranganna, S. Handbook of Analysis and Quality Control for Fruit and Vegetable Products. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Education. Pvt. Ltd. (2010).
23. Nagata M, Yamashita I. Simple method for simultaneous determination of chlorophyll and carotenoids in tomato fruit. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi. (1992) 39:925–8. doi: 10.3136/nskkk1962.39.925
24. Biswas AK, Sahoo J, Chatli MK. A simple UV-Vis spectrophotometric method for determination of β-carotene content in raw carrot, sweet potato and supplemented chicken meat nuggets. LWT Food Sci Technol. (2011) 44:1809–13. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.03.017
25. Mukherjee SP, Choudhuri MA. Implications of water stress-induced changes in the levels of endogenous ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide in Vigna seedlings. Physiol Plant. (1983) 58:166–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1983.tb04162.x
26. Mohamed NTS, Ding P, Kadir J, Ghazali HM. (2017). Potential of UVC germicidal irradiation in suppressing crown rot disease, retaining postharvest quality and antioxidant capacity of Musa AAA “Berangan” during fruit ripening. Food Sci Nutr. 5, 967–980. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.482
27. Jiang Y, Li Y. Effects of chitosan coating on postharvest life and quality of longan fruit. Food Chem. (2001) 73:139–43. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00246-6
28. Das DK, Dutta H, Mahanta CL. Development of a rice starch-based coating with antioxidant and microbe-barrier properties and study of its effect on tomatoes stored at room temperature. LWT Food Sci Technol. (2013) 50:272–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2012.05.018
29. Jhanani GK, Alsalhi MS, Shanmuganathan R. As assessment of shelf life increasing competence of pectin (Zucchini) based edible coating on tomatoes. Environ Res. (2024) 258:119368. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119368
30. Kundu P, Adhikary NK, Maji S. A critical review on use of edible coating to enhance shelf life of mango. Curr J Appl Sci Technol. (2020) 39:116–28. doi: 10.9734/cjast/2020/v39i2730926
31. Ochoa-Reyes E, Martínez-Vazquez G, Saucedo-Pompa S, Montañez JC, Rojas-Molina R, De Leon-Zapata MA, et al. (2013). Improvement of shelf-life quality of green bell peppers using edible coating formulations. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci. 2:2448–51.
32. Paniagua C, Ric-Varas P, García-Gago JA, López-Casado G, Blanco-Portales R, Muñoz-Blanco J, et al. Elucidating the role of polygalacturonase genes in strawberry fruit softening. J Exp Bot. (2020) 71:7103–17. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa398
33. Ali A, Maqbool M, Ramachandran S, Alderson PG. Gum arabic as a novel edible coating for enhancing shelf-life and improving postharvest quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2010) 58:42–7. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2010.05.005
34. Kumar N, Pratibha N, Trajkovska Petkoska, A. Improved shelf life and quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by using chitosan-pullulan composite edible coating enriched with pomegranate peel extract. ACS Food Sci Technol. (2021) 1:500–10. doi: 10.1021/acsfoodscitech.0c00076
35. Malvano F, Corona O, Pham PL, Cinquanta L, Pollon M, Bambina P, et al. Effect of alginate-based coating charged with hydroxyapatite and quercetin on colour, firmness, sugars and volatile compounds of fresh cut papaya during cold storage. Eur Food Res Technol. (2022) 248:2833–42. doi: 10.1007/s00217-022-04093-w
36. Shackel KA, Greve C, Labavitch JM, Ahmadi H. Cell turgor changes associated with ripening in tomato pericarp tissue. Plant Physiol. (1991) 97:814–6. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.2.814
37. Tilahun AT. Analysis of the effect of maturity stage on the postharvest biochemical quality characteristics of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) fruit. Int J Appl Pharm Sci Res. (2013) 3:180–6.
38. Borji H, Jafarpour GM. A comparison between tomato quality of mature-green and red-ripe stages in soilless culture. Afr J Agric Res. (2012) 7:1601–3. doi: 10.5897/AJAR11.1148
39. Sonti, S. Consumer perception and application of edible coatings on fresh-cut fruits and vegetables. [Master Thesis]. Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, Baton Rouge, LA, United States (2003).
40. Ribeiro-Santos R, Andrade M, Sanches-Silva A, de Melo NR. Essential oils for food application: natural substances with established biological activities. Food Bioprocess Technol. (2018) 11:43–71. doi: 10.1007/s11947-017-1948-6
41. Firdous N, Khan MR, Butt MS, Shahid M. Application of aloevera gel based edible coating to maintain postharvest quality of tomatoes. Pakistan J Agric Sci. (2020) 57. doi: 10.21162/PAKJAS/20.7746
42. Hernandez-Munoz P, Almenar E, Del Valle V, Velez D, Gavara R. Effect of chitosan coating combined with postharvest calcium treatment on strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) quality during refrigerated storage. Food Chem. (2008) 110:428–35. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.020
43. Dong H, Cheng L, Tan J, Zheng K, Jiang Y. Effects of chitosan coating on quality and shelf life of peeled litchi fruit. J Food Eng. (2004) 64:355–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2003.11.003
44. Lurie S, Klein JD. Heat treatment of ripening apples: differential effects on physiology and biochemistry. Physiol Plant. (1990) 78:181–6. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.1990.780203.x
45. Adjouman YD, Nindjin C, Kouassi KN, Tetchi FA, Amani N' GG, Sindic M. Effect of edible coating based on improved cassava starch on post-harvest quality of fresh tomatoes (Solanum Lycopersicum L.). Int J Nutr Sci Food Technol. (2018) 4:1–8.
46. Saliba-Colombani V, Causse M, Langlois D, Philouze J, Buret M. Genetic analysis of organoleptic quality in fresh market tomato. 1 Mapping QTLs for physical and chemical traits. Theor Appl Genet. (2001) 102:259–72. doi: 10.1007/s001220051643
47. Castro LD, Vigneault C, Charles MT, Cortez LA. Effect of cooling delay and cold-chain breakage on Santa Clara tomato, Santa Clara tomato. J Agric Food Environ. (2005) 3:49–54. doi: 10.1234/4.2005.517
48. Mohammed M, Wilson LA, Gomes PI. Postharvest sensory and physiochemical attributes of processing and non processing tomato cultivars. J Food Qual. (1999) 22:167–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4557.1999.tb00549.x
49. Paul SK, Sarkar S, Sethi LN, Ghosh SK. Development of chitosan based optimized edible coating for tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and its characterization. J Food Sci Technol. (2018) 55:2446–56. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3162-6
50. Javanmardi J, Kubota C. Variation of lycopene, antioxidant activity, total soluble solids and weight loss of tomato during postharvest storage. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2006) 41:151–5. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.03.008
51. Ali A, Maqbool M, Alderson PG, Zahid N. Effect of gum arabic as an edible coating on antioxidant capacity of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit during storage. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2013) 76:119–24. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2012.09.011
52. Yadav A, Kumar N, Upadhyay A, Sethi S, Singh A. Edible coating as postharvest management strategy for shelf-life extension of fresh tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.): an overview. J Food Sci. (2022) 87:2256–90. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16145
53. Frusciante L, Carli P, Ercolano MR, Pernice R, Di Matteo A, Fogliano V, et al. Antioxidant nutritional quality of tomato. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2007) 51:609–17. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200600158
54. Pholsin R, Shiekh KA, Jafari S, Kijpatanasilp I, Nan TN, Suppavorasatit I, et al. Impact of pectin edible coating extracted from cacao shell powder on postharvest quality attributes of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) fruit during storage. Food Control. (2024) 155:110023. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.110023
55. Orsi B, Sestari I, Preczenhak AP, de Abreu Vieira AP, Tessmer AP, da Silva Souza MA, et al. Fruits from tomato carotenoid mutants have altered susceptibility to grey mold. Plant Physiol Biochem. (2023) 204:108100. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108100
56. Lakshan ND, Senanayake CM, Liyanage T, Lankanayaka A. Clove essential oil emulsions-loaded arrowroot starch-beeswax-based edible coating extends the shelf life and preserves the postharvest quality of fresh tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) stored at room temperature. Sustain Food Technol. (2024) 2:1052–68. doi: 10.1039/D4FB00033A
57. Mahfoudhi N, Hamdi S. Use of almond gum and gum Arabic as novel edible coating to delay postharvest ripening and to maintain sweet cherry (Prunus avium) quality during storage. J Food Process Preserv. (2015) 39:1499–508. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.12369
58. Lee SK, Kader AA. Preharvest and postharvest factors influencing vitamin C content of horticultural crops. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2000) 20:207–20. doi: 10.1016/S0925-5214(00)00133-2
59. Adisa VA. The influence of molds and some storage factors on the ascorbic acid content of orange and pineapple fruits. Food Chem. (1986) 22:139–46. doi: 10.1016/0308-8146(86)90031-2
60. Chauhan OP, Raju PS, Dasgupta DK, Bawa AS. Modified atmosphere packaging of banana (cv. Pachbale) with ethylene. Am J Food Technol. (2006) 1:179–89. doi: 10.3923/ajft.2006.179.189
61. Pantos CE, Markakis P. Ascorbic acid content of artificially ripened tomatoes. J Food Sci. (1973) 38:550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1973.tb01481.x
62. Agar IT, Massantini R, Hess-Pierce B, Kader AA. Postharvest CO2 and ethylene production and quality maintenance of fresh-cut kiwifruit slices. J Food Sci. (2006) 64:433–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1999.tb15058.x
63. Xue J, Huang L, Zhang S, Sun H, Gao T. Study on the evaluation of carboxymethyl-chitosan concentration and temperature treatment on the quality of “Niuxin” persimmon during cold storage. J Food Process Preserv. (2020) 44:e14560. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.14560
64. Hassan ZH, Lesmayati S, Qomariah R, Hasbianto A. Effects of wax coating applications and storage temperatures on the quality of tangerine citrus (Citrus reticulata) var. Siam Banjar Int Food Res J. (2014) 21:641–8.
65. Osae R, Apaliya MT, Alolga RN, Kwaw E, Otu PNY, Akaba S, et al. Influence of shea butter, bee wax and cassava starch coatings on enzyme inactivation, antioxidant properties, phenolic compounds and quality retention of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruits. Appl Food Res. (2022) 2:100041. doi: 10.1016/j.afres.2022.100041
66. Kumar A, Saini CS. Edible composite bi-layer coating based on whey protein isolate, xanthan gum and clove oil for prolonging shelf life of tomatoes. Measurement. (2021) 2:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.meafoo.2021.100005
67. Peralta-Ruiz Y, Tovar CDG, Sinning-Mangonez A, Coronell EA, Marino MF, Chaves-Lopez C, et al. Reduction of postharvest quality loss and microbiological decay of tomato “Chonto” (Solanum lycopersicum L.) using chitosan-e essential oil-based edible coatings under low-temperature storage. Polymers. (2020) 12:1822. doi: 10.3390/polym12081822
68. Tanada-Palmu PS, Grosso CR. Effect of edible wheat gluten-based films and coatings on refrigerated strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) quality. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2005) 36:199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2004.12.003
69. Iqbal SZ, Waseem M, Zia KM, Iqbal M, Mohammed OA, Amina N, et al. Application of chitosan, zinc oxide nanoparticles, and Aloe vera gel edible coating for the extension in shelf life of tomatoes. Food Packag Shelf Life. (2025) 50:101570. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2025.101570
70. Akhtar M, Akhtar A, Nazir W, Khalid N. Formulation of edible coatings from alfalfa Saponins to enhance the postharvest quality of tomatoes. Prev Nutr Food Sci. (2023) 28:178. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.2.178
71. Abdullah AH, Awad-Allah MA, Abd-Elkarim NA, Ahmed ZF, Taha EM. Carboxymethyl cellulose from banana rachis: a potential edible coating to extend the shelf life of strawberry fruit. Agriculture. (2023) 13:1058. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13051058
72. Aguirre NC, Cabrera FAV. Evaluating the fruit production and quality of cherry tomato (Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme). Rev Fac Nacl Agron Medell. (2012) 65:6599–610.
73. Alpos MA, Bayogan ERV. Effects of chitosan coating on the postharvest quality and antioxidant properties of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Philipp J Sci. (2023) 152:125–39. doi: 10.56899/152.03.13
74. AOAC International. Official methods of analysis of AOAC International (Vol. 17, No. 1-2). Maryland: AOAC International (2000).
75. Estrada Mesa EM, Padilla Reyes F, Márquez Cardozo CJ. Efecto de recubrimientos protectores sobre la calidad del mango (Mangifera indica L.) en poscosecha. Rev UDCA Actual Divul Cient. (2015) 18:181–8. doi: 10.31910/rudca.v18.n1.2015.468
76. García-Figueroa A, Ayala-Aponte A, Sánchez-Tamayo MI. Efecto de recubrimientos comestibles de Aloe vera y alginato de sodio sobre la calidad poscosecha de fresa. Rev UDCA Actual Divul Cient. (2019) 22. doi: 10.31910/rudca.v22.n2.2019.1320
77. González RE, Cervantes YC, Caraballo LDC. Conservación de la guayaba (Psidium guajava L.) en postcosecha mediante un recubrimiento comestible binario. Temas Agrarios. 21:54. (2017). doi: 10.21897/rta.v21i1.891
78. Kim I, Han JI. Optimization of alkaline pretreatment conditions for enhancing glucose yield of rice straw by response surface methodology. Biomass Bioenergy. (2012) 46:210–7. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.08.024
79. Moneruzzaman KM, Hossain ABMS, Sani W, Saifuddin M, Alenazi M. Effect of harvesting and storage conditions on the post-harvest quality of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) cv. Roma VF Aust J Crop Sci. (2009) 3:113–21.
80. Moreno DR. Efecto de dos gomas y tintura de propóleo en el desarrollo de un recubrimiento evaluado en zanahoria (Daucus carota). [Doctoral Dissertation]. Zamorano: Escuela Agrícola Panamericana (2013).
81. Naeem A, Abbas T, Ali TM, Hasnain A. Effect of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of guar gum coating containing spice extracts and its application on tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J Food Meas Charact. (2018) 12:2725–34. doi: 10.1007/s11694-018-9890-5
82. Panse VG, Sukhatme PV. Statistical methods for agricultural workers. New Delhi: Indian Council of Agricultural Research, xvi+-361 (1985).
83. Pavón-Vargas D, Valencia-Chamorro S. Efecto de recubrimientos comestibles compuestos a base de goma tara en la calidad poscosecha de frutilla (Fragaria ananassa). Rev Iberoam Tecnol Postcosecha. (2016) 17:65–70.
84. Petriccione M, Mastrobuoni F, Pasquariello MS, Zampella L, Nobis E, Capriolo G, et al. Effect of chitosan coating on the postharvest quality and antioxidant enzyme system response of strawberry fruit during cold storage. Foods. (2015) 4:501–23. doi: 10.3390/foods4040501
85. Santa Catharina CM, Bretschneider FGB, Piva B, Weber CI, Stadler F, Romio AP, et al. Edible coating containing carvacrol for postharvest microbiological conservation of tomato. Braz J Dev. (2020) 6:4786–94. doi: 10.34117/bjdv6n1-344
86. Soni B, Mahmoud B. Chemical isolation and characterization of different cellulose nanofibers from cotton stalks. Carbohydr Polym. (2015) 134:581–9. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.031
87. Tigist M, Workneh TS, Woldetsadik K. Effects of variety on the quality of tomato stored under ambient conditions. J Food Sci Technol. (2013) 50:477–86. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0378-0
88. Donjio TR, Aghofack Nguemezi J, Anoumaa M, Tafre Phounzong E, Kenfack JO, Fonkou T, et al. (2023). Using response surface methodology to optimize edible coating formulations to delay ripening and preserve postharvest quality of tomatoes. J Food Qual. 2023:1019310. doi: 10.1155/2023/1019310
89. Zahran M, Marei AH. Innovative natural polymer metal nanocomposites and their antimicrobial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. (2019) 136:586–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.114
Keywords: rice straw, wheat straw, bioactive compounds, tomato, edible coating, shelf life
Citation: Yadav S, Malik K, Sharma K, Dhillon P and Harikarthik D (2025) Assessment of chitosan-based edible coatings containing bioactive compounds derived from agricultural residue for improving postharvest quality characteristics of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Front. Nutr. 12:1673029. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1673029
Received: 25 July 2025; Accepted: 26 September 2025;
Published: 03 November 2025.
Edited by:
Astride Franks Kamgang Nzekoue, GOURMEY, FranceReviewed by:
Nimesh Dileesha Lakshan, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Sri LankaNur Karimah Mukhtar, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Yadav, Malik, Sharma, Dhillon and Harikarthik. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kamla Malik, S2FtbGFtYWxpazA2QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Sujeeta Yadav
Sujeeta Yadav Kamla Malik
Kamla Malik Kashish Sharma1
Kashish Sharma1