- 1Department of Biotechnology, Era University, Lucknow, India
- 2Department of Food and Nutrition, Era University, Lucknow, India
- 3Department of Biology and Biotechnology, Faculty of Science, American University of Madaba, Amman, Jordan
- 4Institute of Nutrition and Health, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 5Department of General and Clinical Pharmacology, Medical Institute, People’s Friendship University of Russia, Moscow, Russia
Chronic non-communicable diseases including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and autoimmune disorders pose mounting global health and economic challenges. Conventional drugs often focus on symptom management, frequently accompanied by side effects and rarely reversing disease progression. Nutraceuticals bioactive compounds sourced from foods, herbs, and marine organisms, offer a promising alternative due to their inherent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective properties. This review synthesizes current evidence on key nutraceutical classes (e.g., polyphenols, flavonoids, omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, plant alkaloids), elucidating their molecular mechanisms such as oxidative stress mitigation, immune modulation, gene regulation, and signaling pathway interactions and highlighting therapeutic applications across major chronic conditions. Addressing a critical limitation, we analyze advanced delivery technologies (e.g., nano-formulations, encapsulation, liposomes, micro- and hydrogels, co-administered bioenhancers) designed to enhance bioavailability and targeting. We also discuss navigating hurdles such as regulatory inconsistencies, safety concerns, herb–drug interactions, and the need for standardization. To fully incorporate nutraceuticals into modern healthcare, the review emphasizes the imperative for rigorous clinical validation, manufacturing quality control, and long-term safety monitoring. Finally, we propose future directions including personalized nutraceutical strategies, AI-assisted discovery, and global regulatory harmonization positioning nutraceuticals as sustainable and evidence-based adjuncts or alternatives in chronic disease management.
1 Introduction
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), another name for chronic diseases, are long-term ailments that often develop gradually and last a person’s entire life. These encompass a wide range of illnesses, including musculoskeletal disorders like arthritis, diabetes mellitus, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and cardiovascular diseases (such as hypertension and coronary artery disease). The World Health Organization (1) estimates that chronic diseases account for around 74% of deaths worldwide each year, with cardiovascular diseases alone causing more than 17.9 million deaths. These disorders are frequently caused by a confluence of behavioral, physiological, environmental, and genetic variables, and their prevalence is increasing as a result of aging populations, poor diet, stress, and sedentary lifestyles (133). Although there is no denying that traditional pharmaceutical therapies have increased life expectancy and quality of life, they are not without drawbacks. Instead than addressing the underlying causes of chronic diseases, many synthetic medications concentrate on symptom suppression. Furthermore, side effects, drug resistance, and decreased patient compliance are often linked to prolonged prescription usage. In patients with arthritis, for example, long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) may result in renal impairment, cardiovascular risks, and stomach ulcers. Similar to this, even if they are effective, several chemotherapeutic medicines used to treat cancer can have crippling side effects that drastically lower quality of life (2).
Given these drawbacks, natural substances and nutraceuticals are gaining popularity throughout the world as potential supplements or substitutes for traditional treatments. Nutraceuticals, which are food-derived products that offer health or medicinal advantages beyond simple nourishment, contain a variety of bioactive substances, including vitamins, minerals, polyphenols, flavonoids, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant extracts. Among other things, these compounds have been demonstrated to have cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer properties (3). Because of their natural origin, multiple methods of action, and reduced toxicity, nutraceuticals are being more and more integrated into preventative and therapeutic healthcare. Systematic studies that compile the available data, examine bioavailability issues, and indicate potential future paths in the use of nutraceuticals for the treatment of chronic diseases are desperately needed as this field of study grows.
2 Aim of the review
This review systematically investigates the therapeutic potential of natural compounds and nutraceutical formulations in the prevention and management of chronic diseases. In light of the growing global burden of non-communicable diseases and the limitations of long-term pharmacotherapy, the review highlights how bioactive compounds derived from natural sources such as polyphenols, flavonoids, probiotics, and plant-based alkaloids may offer effective adjuncts or alternatives to conventional treatments. Emphasizing their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective properties, the review explores the biological activities, mechanisms of action, and clinical efficacy of these nutraceuticals across a spectrum of chronic conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases. A key focus is on overcoming challenges related to bioavailability and targeted delivery, through advanced formulation strategies such as nanoformulations, encapsulation, and synergistic combinations with other compounds or pharmaceuticals. The review also addresses regulatory frameworks, safety considerations, and standardization issues that currently hinder the broader clinical adoption of nutraceuticals. By synthesizing current scientific evidence and clinical applications, this review aims to guide healthcare professionals, researchers, and policymakers toward the informed integration of evidence-based nutraceuticals into mainstream healthcare, while identifying promising directions for future research.
3 Methodology
This narrative review is based on a comprehensive search of peer-reviewed literature published between 2000 and 2024 in PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. Searches combined controlled vocabulary and free-text keywords using Boolean operators, with terms including “nutraceuticals,” “natural compounds,” “antioxidants,” “polyphenols,” “cancer prevention,” “cardiovascular health,” “diabetes management,” “neuroprotection,” “inflammation,” “autoimmune disorders,” and “nanoformulations.” The initial search yielded (insert number) records; after screening and eligibility assessment, (insert number) articles were included. Eligible studies comprised original research, reviews, meta-analyses, and clinical trials reporting mechanisms, therapeutic outcomes, safety, or formulation strategies. Non-English, unavailable full texts, unrelated topics, and commentaries were excluded. Compounds were selected based on frequency in literature, strength of evidence, and clinical relevance. Preference was given to publications from the last decade (2014–2024), with older landmark studies included when foundational.
4 Overview of nutraceuticals and natural compounds
Utilizing natural substances and nutraceuticals has become a viable strategy for managing chronic illnesses and preserving health in recent years. These compounds, which come from natural extracts, herbs, or food sources, are well-known for their medicinal qualities that go beyond their fundamental nutritional roles. Despite having different definitions, legal contexts, and intended applications, the phrases nutraceuticals, dietary supplements, and functional foods are sometimes used interchangeably. To appreciate their responsibilities in therapeutic and preventative healthcare, it is imperative to comprehend these distinctions. The main differences between these categories are shown in the Table 1 below and Table 2 outlines major categories of nutraceuticals, describing their key health benefits and typical sources, with supporting references for each.
Bioactive substances called nutraceuticals come from a variety of natural sources, including as microbes, plants, and marine life. The most researched and commonly utilized nutraceuticals are those produced from plants, which include substances like terpenoids, polyphenols, flavonoids, and alkaloids. These phytochemicals have strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cardioprotective qualities and are widely distributed in fruits, vegetables, herbs, spices, and whole grains (4). The abundance of omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA), carotenoids like astaxanthin, polysaccharides, and bioactive peptides from fish, algae, and shellfish has led to a rise in interest in marine-derived nutraceuticals. According to Shahidi et al. (5), these substances have been connected to anti-cancer, cognitive function support, and cardiovascular advantages. Probiotics and fermentation metabolites are examples of microbial-derived nutraceuticals that have demonstrated effectiveness in regulating gut microbiota, boosting immunological response, and promoting gastrointestinal health. Usually, they come from strains of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which are frequently found in fermented foods like kimchi and yogurt (6).
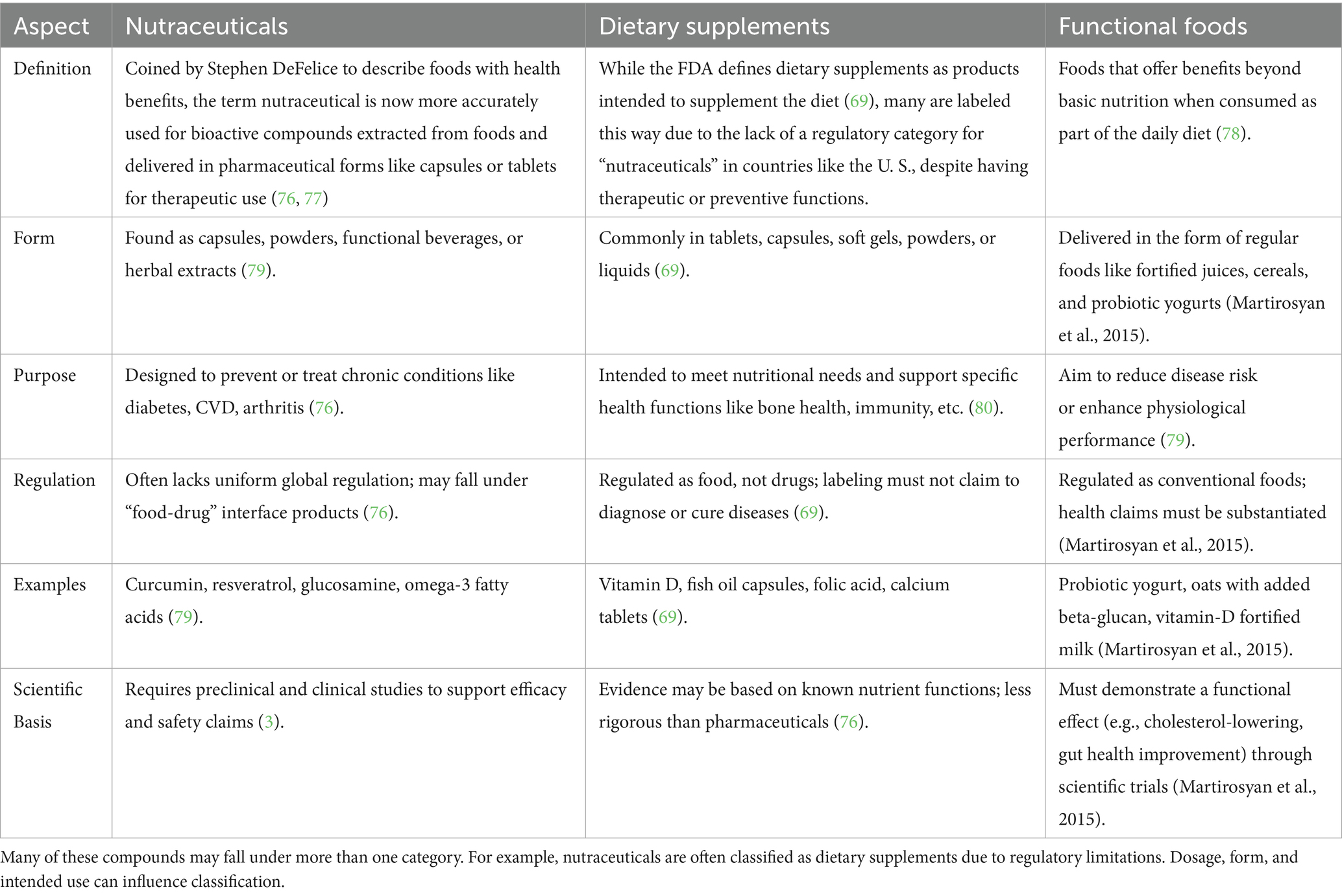
Nutraceuticals are essential to preventative healthcare because they help to preserve physiological balance and lower the risk of chronic diseases before they manifest. For example, by altering metabolic pathways and lowering oxidative stress, consistent consumption of dietary fibers and polyphenols can prevent diseases including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and obesity (7). By focusing on disease-specific molecular pathways, these substances aid in or improve treatment results in therapeutic healthcare. By causing apoptosis and preventing tumor growth, nutraceuticals such as curcumin and resveratrol have demonstrated promise as adjuvant cancer treatments (8). Therefore, including nutraceuticals into dietary and medical procedures presents a viable, low-toxicity, and multipurpose strategy for managing chronic illnesses and enhancing general health (Figure 1). Illustrates the extensive benefits of nutraceuticals by categorizing their impact into two major areas: health promotion and disease prevention. It represents how nutraceuticals bioactive compounds derived from food sources, support various physiological functions and help maintain overall wellness. On the health promotion side, the figure highlights how nutraceuticals contribute to gastrointestinal and renal health, mitochondrial biogenesis, stem cell growth, antioxidant activity, reproductive health, anti-aging effects, and lifespan extension. These benefits demonstrate their role in enhancing bodily functions and preventing premature aging. On the disease prevention side, the figure showcases how nutraceuticals help protect against and manage several chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, obesity, diabetes mellitus, cancer, osteoarthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, oral disorders, and eye conditions. By incorporating nutraceuticals into the diet, individuals may improve their health, boost their body’s natural defenses, and reduce the likelihood of disease development.
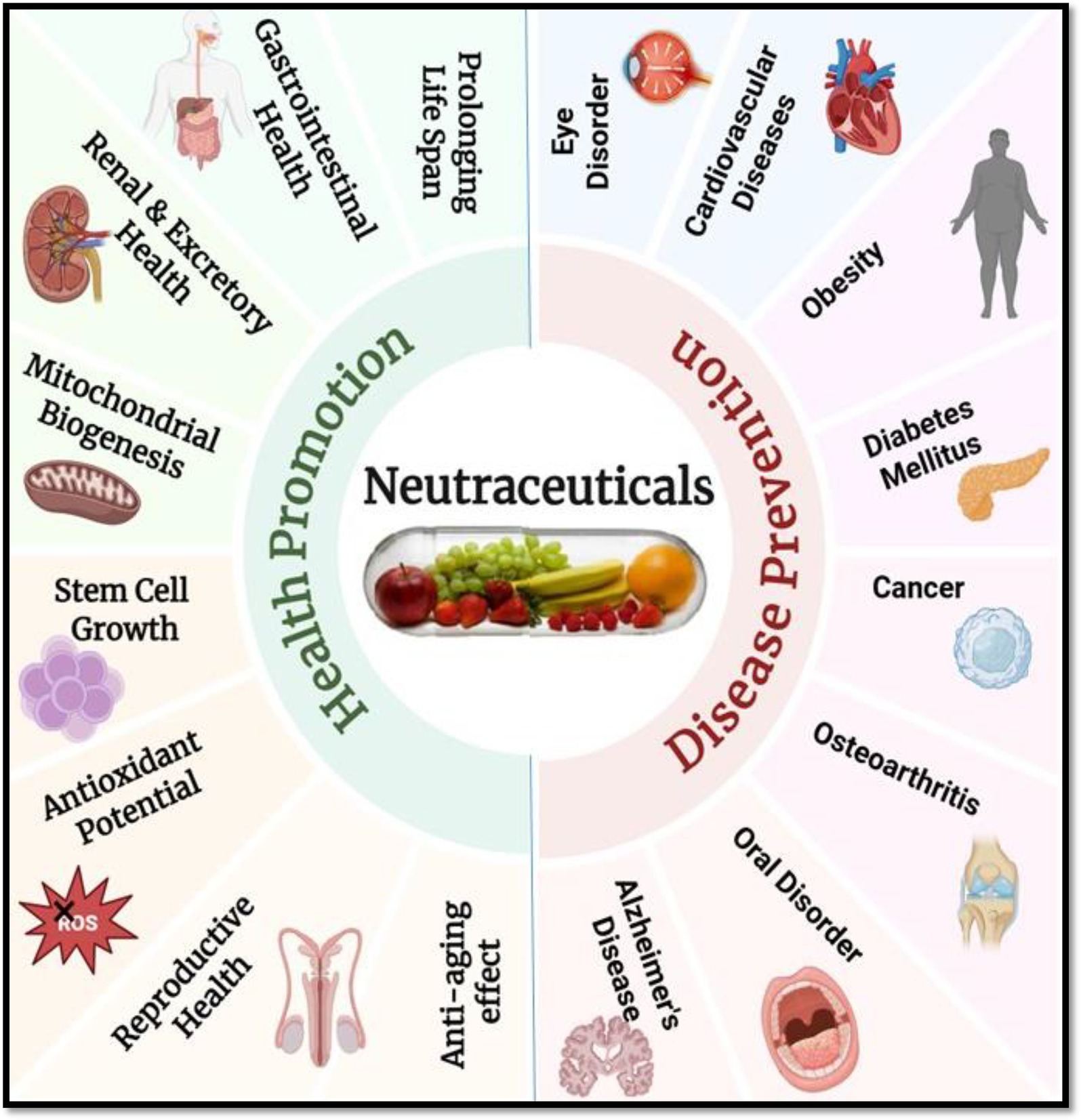
Figure 1. Multifaceted benefits of nutraceuticals in health promotion and disease prevention. Created with BioRender.com.
5 Mechanisms of action
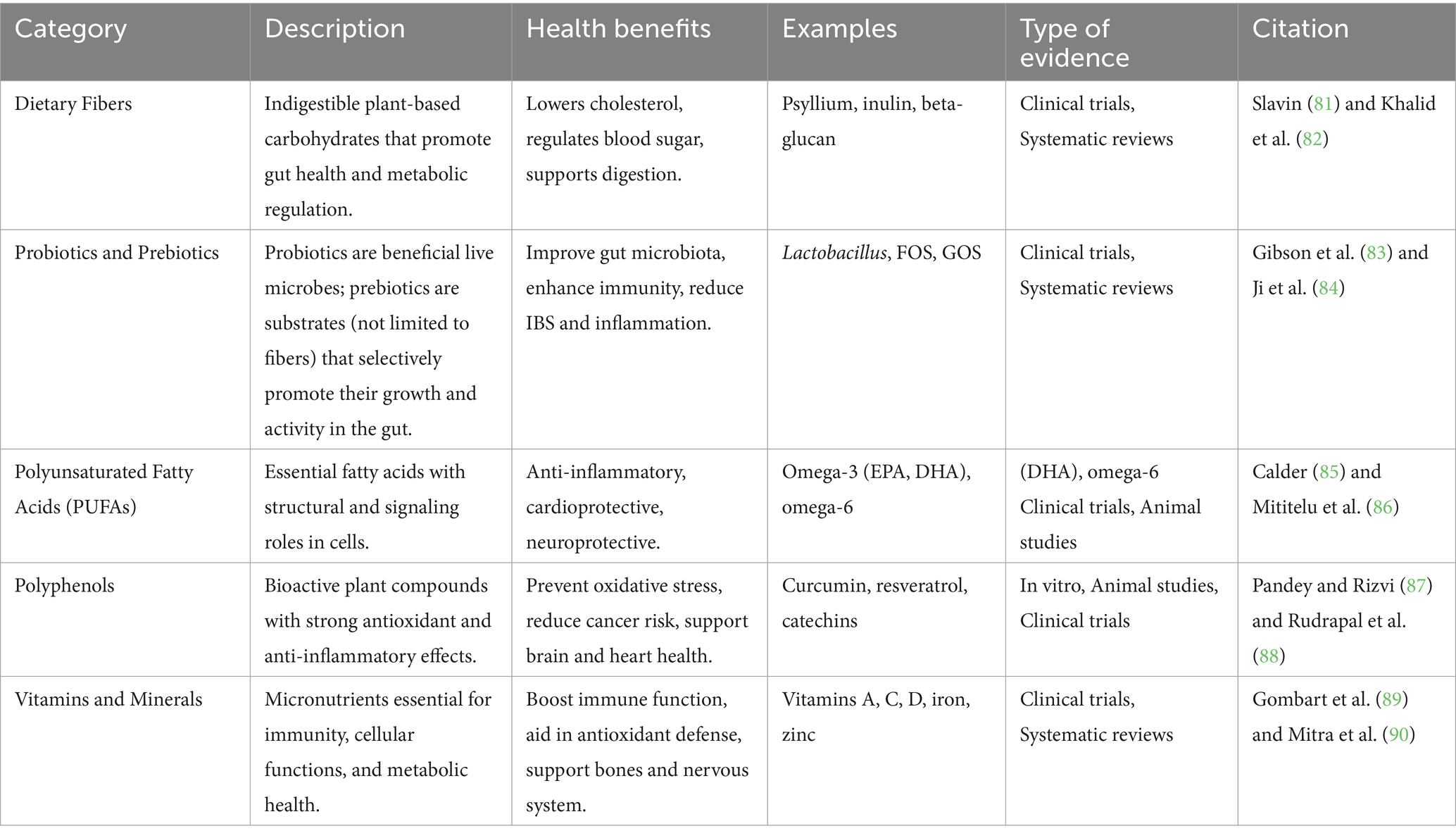
Numerous biological processes, many of which interact with crucial pathways implicated in the development and progression of chronic diseases, allow nutraceuticals to provide their therapeutic advantages. Their antioxidant activity is one of the main processes; substances like polyphenols, carotenoids, and vitamins (like C and E) neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), shielding cells from damage brought on by oxidative stress. According to Pisoschi et al. (9), oxidative stress has a significant role in aging and a number of chronic illnesses, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and cardiovascular disease (Figure 2). Presents a schematic representation of oxidative stress and its pivotal role in cellular damage leading to aging and chronic degenerative diseases. It highlights how reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) produced endogenously or triggered by external factors such as toxins, smoking, and ultraviolet (UV) light, accumulate within cells, inducing widespread oxidative stress. This oxidative burden causes multiple forms of molecular and cellular damage, including: DNA damage, which can lead to mutations and genomic instability; Protein oxidation, impairing structural and enzymatic functions; Membrane damage, disrupting cellular compartmentalization and signaling; Mitochondrial dysfunction, diminishing energy production and amplifying ROS generation; Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, which contributes to protein misfolding and cell stress responses (10). In order to maintain cellular homeostasis, polyphenols like resveratrol and flavonoids like quercetin scavenge free radicals and increase the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. The anti-inflammatory properties of nutraceuticals are another important mechanism. The pathophysiology of conditions including cancer, diabetes, and arthritis is linked to chronic inflammation. Nutraceuticals like gingerols, curcumin, and omega-3 fatty acids block important inflammatory enzymes like COX-2 and iNOS and limit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 (11). Additionally, these substances suppress transcription factors such as NF-κB, which is essential for fostering immunological dysregulation and inflammation (12).
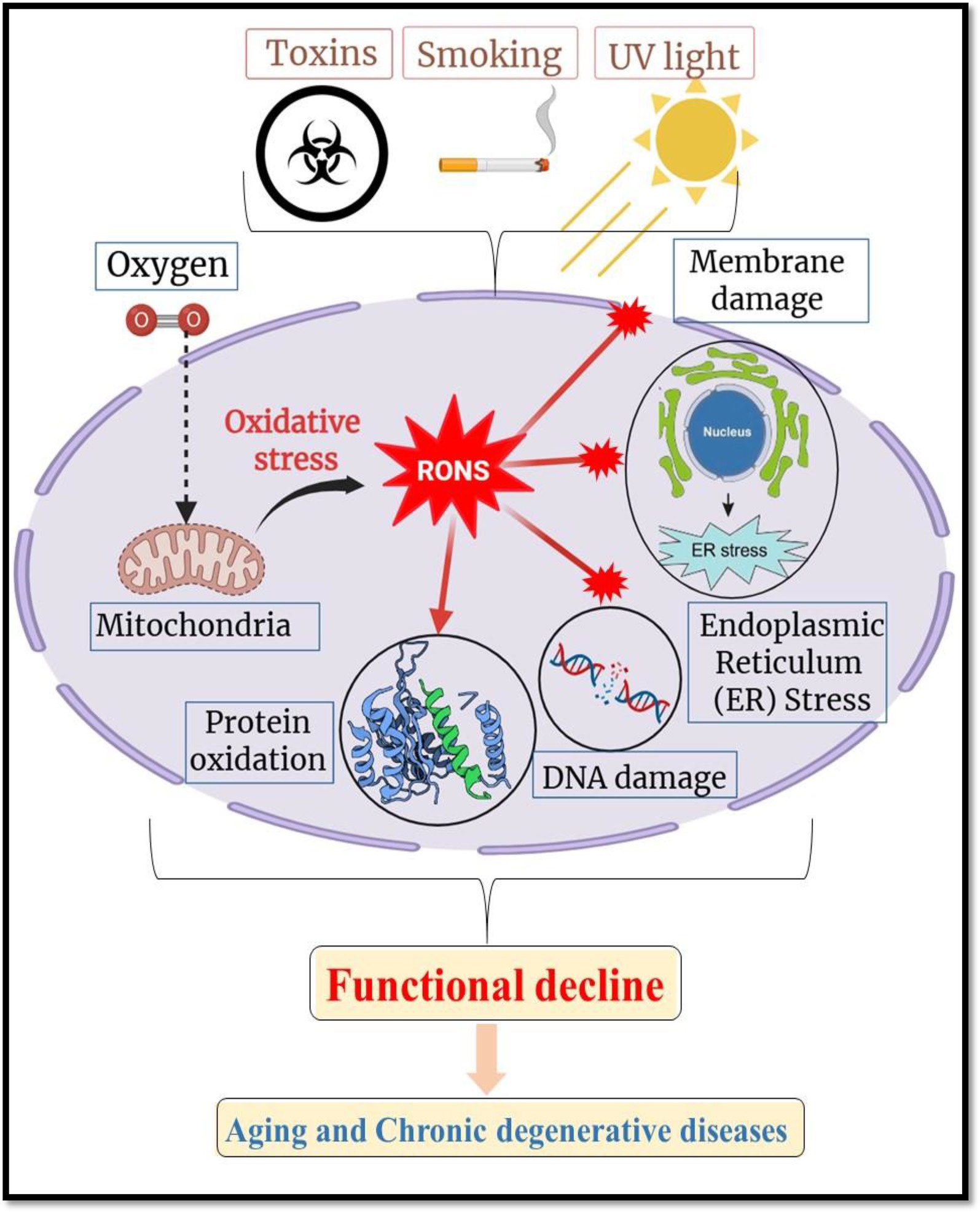
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of oxidative stress and RONS-mediated cellular damage in aging and degenerative diseases. Created with BioRender.com.
Another crucial component of nutraceutical function is immune response modulation. By altering dendritic cell activity, boosting T and B lymphocyte proliferation, and encouraging immunoglobulin production, certain probiotics, vitamins (such as vitamin D), and polysaccharides from mushrooms and algae improve both innate and adaptive immune responses (13). Beta-glucans, for example, have been shown to excite natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages, enhancing host defense against cancers and infections (14). Nutraceuticals also affect epigenetic changes including DNA methylation, histone acetylation, and miRNA expression, as well as the control of gene expression. Because they can change the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and detoxification, nutrients such as sulforaphane, genistein, and folate are intriguing candidates for epigenetic therapy, particularly in the prevention of cancer (15).
Additionally, there is mounting evidence that nutraceuticals play a part in the regulation of gut microbiota. While inhibiting pathogenic species, prebiotics like inulin and polyphenols like catechins encourage the growth of good gut bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. According to Ojeda et al. (16), this microbial balance promotes metabolic health, lowers systemic inflammation, and strengthens the intestinal barrier. Lastly, a lot of nutraceuticals have an impact on signal transduction pathways that control growth, metabolism, inflammation, and cell survival. For instance, resveratrol and curcumin have anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, and insulin-sensitizing properties by modulating pathways such NF-κB, MAPK, AMPK, and PI3K/Akt (17, 18). Nutraceuticals’ tailored modulation of these pathways, which are frequently dysregulated in chronic illnesses, provides a multifaceted treatment strategy with low toxicity.
6 Role of nutraceuticals in specific chronic diseases
6.1 Cardiovascular diseases (CVD)
The top cause of death worldwide is still cardiovascular diseases (CVD), which include hypertension, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke (19). The pathophysiology of CVD is greatly influenced by lifestyle variables such chronic inflammation, poor nutrition, and inactivity (20). By focusing on important risk factors like dyslipidemia, hypertension, and endothelial dysfunction, nutraceuticals present intriguing alternatives to traditional treatments. The cardioprotective benefits of omega-3 fatty acids, especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are mostly found in fish oils, are well established (21). They assist in lowering blood pressure, improving vascular function, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and lowering plasma triglyceride levels (22). By lowering oxidative stress indicators in vascular tissues and downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α, omega-3 PUFAs have anti-inflammatory effects (23). These outcomes help to stabilize pre-existing atherosclerotic plaques and prevent new ones from forming.
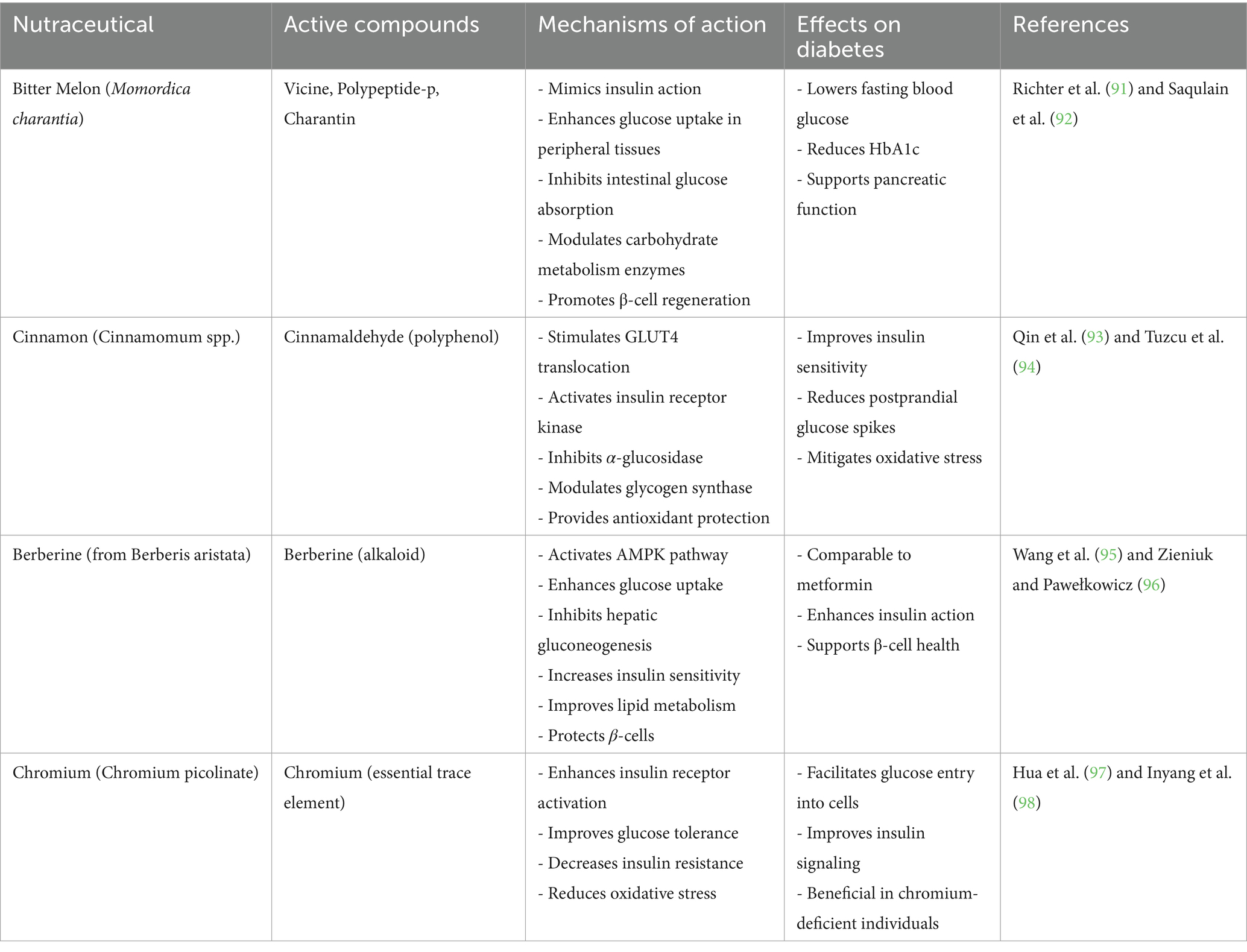
Strong antioxidants and vasodilators, flavonoids are a type of polyphenolic substances that can be found in citrus fruits, tea, berries, and cocoa. By lowering oxidative stress in vascular tissues and raising nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, they enhance endothelial function (24). Diets high in flavonoids have been linked to improved lipid profiles and decreased blood pressure, especially through improvements in HDL cholesterol and decreases in LDL cholesterol (25). They also alter lipid metabolism-related enzyme systems like lipoprotein lipase and HMG-CoA reductase. Naturally found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils, plant sterols and stanols structurally resemble cholesterol and competitively prevent the intestinal absorption of it. Without influencing HDL or triglyceride levels, this lowers serum LDL cholesterol levels (25). When paired with other lifestyle changes, a daily consumption of 2 grams of plant sterols can reduce cardiovascular risk and LDL cholesterol by up to 10% (26). When taken as a whole, these nutraceuticals help to improve endothelial function, blood pressure regulation, and lipid profiles three key areas in the prevention and treatment of CVD. They are useful in integrative cardiometabolic healthcare because their incorporation into dietary plans offers a low-toxicity, natural method of lowering cardiovascular risk (Figure 3). Illustrates the positive effects of nutraceuticals in the prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). It highlights the cardio protective roles of omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA), flavonoids, and plant sterols, each acting on key risk factors associated with CVD, including dyslipidemia, endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension (26).
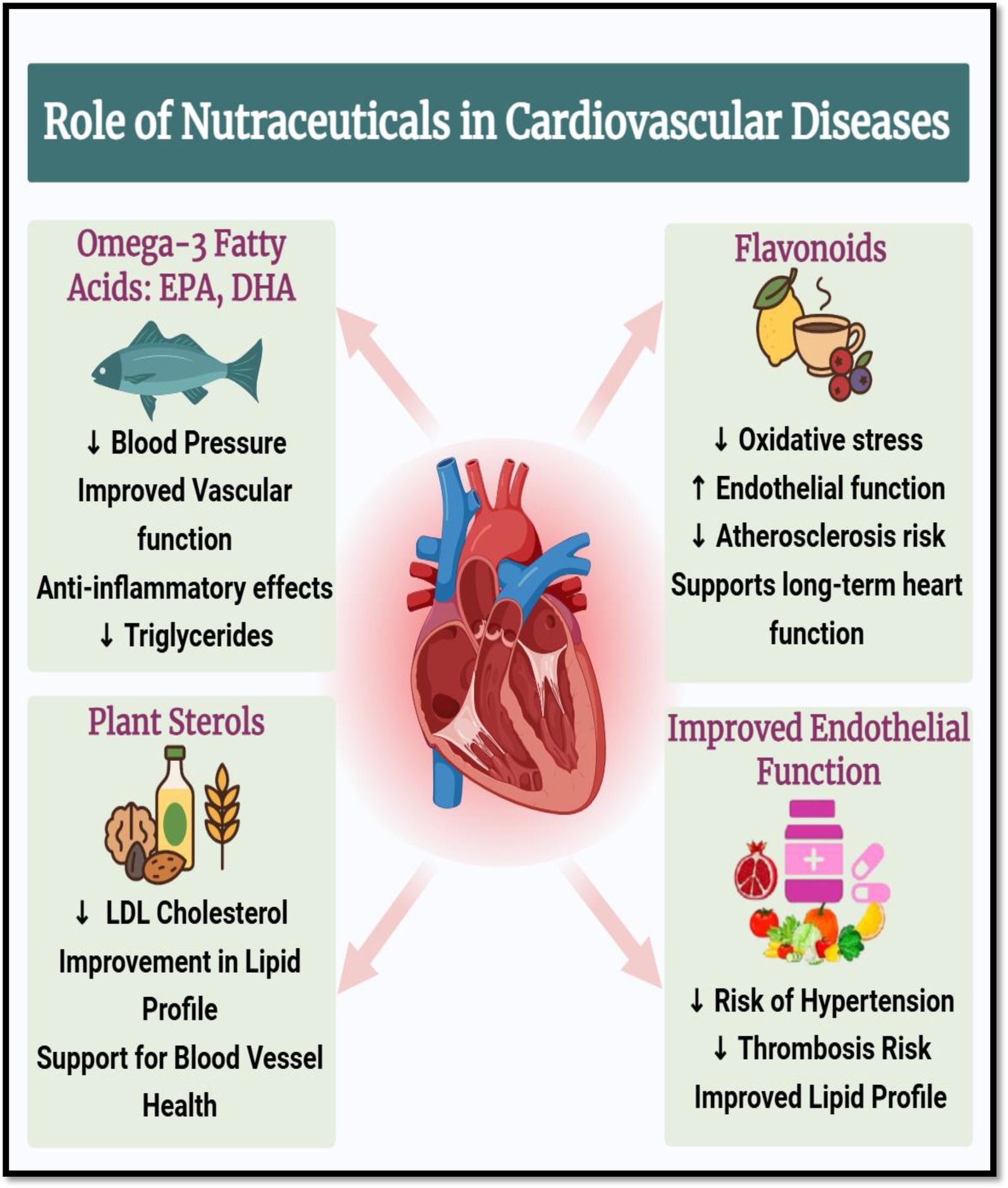
Figure 3. Cardioprotective roles of nutraceuticals in cardiovascular diseases. Created with BioRender.com.
6.2 Diabetes mellitus
The chronic metabolic disease known as diabetes mellitus, and more specifically type 2 diabetes (T2DM), is typified by hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and decreased insulin secretion. The prevalence of diabetes is rising worldwide, which emphasizes the need for complementary therapy in addition to traditional medications. Nutraceuticals have great therapeutic potential for controlling blood sugar levels and preserving pancreatic function because of their capacity to alter several metabolic pathways with few adverse effects. Traditional medicine has long utilized bitter melon (Momordica charantia) for its hypoglycemic properties. It contains bioactive substances including vicine, polypeptide-p, and charantin that act in an insulin-like manner, enhance glucose uptake in peripheral tissues, and reduce intestinal glucose absorption (27). Experimental studies further show that bitter melon alters key carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes and promotes pancreatic β-cell regeneration (28), while both animal and clinical trials demonstrate its ability to lower fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels.
By stimulating GLUT4 translocation in adipose and muscle tissues and activating insulin receptor kinase, cinnamon (Cinnamomum spp.), particularly its polyphenolic component cinnamaldehyde, improves insulin sensitivity and glucose absorption (29). Evidence from both experimental and human studies indicates that cinnamon also reduces postprandial glucose spikes by inhibiting intestinal α-glucosidase and modulating glycogen synthase (30). In addition, its antioxidant properties may help mitigate oxidative stress associated with diabetic complications. Similarly, berberine, an alkaloid isolated from plants such as Berberis aristata, has shown antidiabetic effects comparable to metformin. Preclinical studies demonstrate its ability to enhance glucose utilization, inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis, and increase insulin sensitivity via activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway (31). Clinical evidence further supports its role in improving lipid metabolism and protecting pancreatic β-cells in diabetic patients (32).
The metabolism of fats and carbohydrates also depends heavily on chromium, an essential trace metal (33). In individuals with chromium deficiency, supplementation with chromium picolinate has been shown in clinical trials to enhance insulin receptor activation, improve glucose tolerance, and reduce insulin resistance (34). By improving insulin signaling, chromium facilitates cellular glucose uptake and may reduce oxidative stress in diabetes. Collectively, these nutraceuticals—through mechanisms supported by both preclinical and clinical studies—help preserve pancreatic β-cell function, improve insulin sensitivity, and regulate glucose metabolism, making them promising candidates for integrative approaches in type 2 diabetes prevention and management. Compared to synthetic antidiabetic medications, their inclusion in dietary or supplement regimens may provide supportive glycemic control with fewer side effects (35) (Table 3). highlights key nutraceuticals used in managing T2DM, detailing their active compounds, mechanisms of action, and observed effects on blood glucose control and insulin sensitivity, supported by relevant experimental and clinical evidence.
6.3 Cancer
Uncontrolled cell proliferation, apoptosis evasion, prolonged angiogenesis, and metastasis are the hallmarks of cancer, which continues to rank among the world’s top causes of illness and mortality (36). Despite their effectiveness, traditional cancer therapies like radiation and chemotherapy sometimes cause serious side effects and resistance. Because of their low toxicity, multitargeted methods of action, and ability to improve therapeutic outcomes, nutraceuticals present attractive supplementary strategies. Curcumin, resveratrol, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), and sulforaphane are among the naturally occurring substances whose anti-cancer effects have been well investigated (37). The main polyphenol in turmeric (Curcuma longa), curcumin, has strong anti-cancer properties against a range of cancers. It lowers survival pathways like NF-κB, STAT3, and PI3K/Akt and triggers apoptosis by activating caspases and altering Bcl-2 family proteins. By suppressing VEGF and preventing the growth of endothelial cells, curcumin also has anti-angiogenic properties that reduce tumor vascularization. Additionally, it stops the growth of cancer cells by causing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase (38).
Resveratrol, a stilbene polyphenol found in grapes, berries, and peanuts, targets various signaling pathways implicated in carcinogenesis. It suppresses angiogenesis by lowering the production of VEGF and HIF-1α and encourages apoptosis through p53 activation and mitochondrial failure. By altering cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and their inhibitors, resveratrol also causes cell cycle arrest, especially in the S and G1 phases (39, 40). Its antioxidant qualities also lessen oxidative DNA damage, which is a major factor in tumor growth and mutagenesis. The most prevalent catechin in green tea, EGCG (epigallocatechin-3-gallate), exhibits anticancer properties via a variety of pathways. In cancer cells, it inhibits telomerase activity, causes apoptosis, and decreases angiogenesis. Additionally, EGCG suppresses matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inhibits signaling pathways like Akt and MAPK, which lessens tumor dissemination and invasiveness (17, 18). Its chemopreventive potential is further enhanced by its capacity to scavenge free radicals and bind metal ions (41).
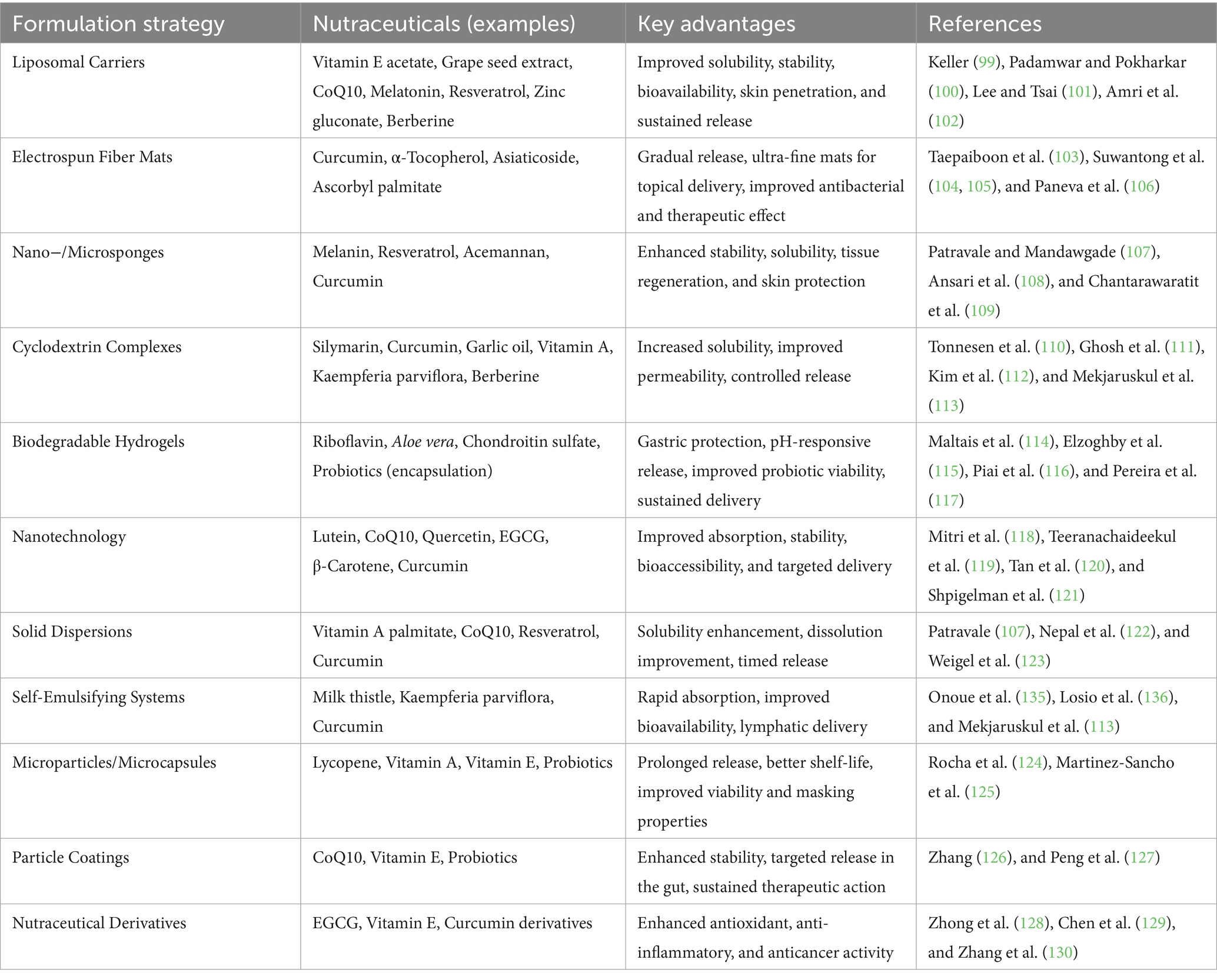
Broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables contain sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate that has been shown to be a potent inducer of phase II detoxification enzymes and a modulator of epigenetic control. It reduces angiogenesis by decreasing VEGF and HIF-1α, causes cell cycle arrest at G2/M, and stimulates apoptosis via mitochondrial mechanisms. Additionally, sulforaphane affects DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), indicating a potential use in epigenetic cancer treatment (42, 43). By causing apoptosis, preventing angiogenesis, and stopping the cell cycle, these nutraceuticals work together to suppress tumor growth and improve the effectiveness of traditional treatments. Their incorporation with chemopreventive measures presents a viable way to lower the risk of cancer and its recurrence (44) (Figure 4). Presents the major hallmarks of cancer, which are fundamental biological traits that allow cancer cells to survive, proliferate, and spread. These hallmarks include sustained proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, activating invasion and metastasis, avoiding immune destruction, tumor-promoting inflammation, genome instability and mutation, and deregulating cellular energetics. Together, these capabilities represent how cancer cells bypass normal cellular controls and thrive in the body. The figure also highlights the potential of anti-cancer nutraceuticals- natural compounds such as curcumin, resveratrol, EGCG, and sulforaphane, in targeting these hallmarks. These dietary components, derived from turmeric, grapes, green tea, and cruciferous vegetables respectively, have shown promise in interfering with various mechanisms of cancer progression, offering a complementary strategy for cancer prevention and therapy (45).
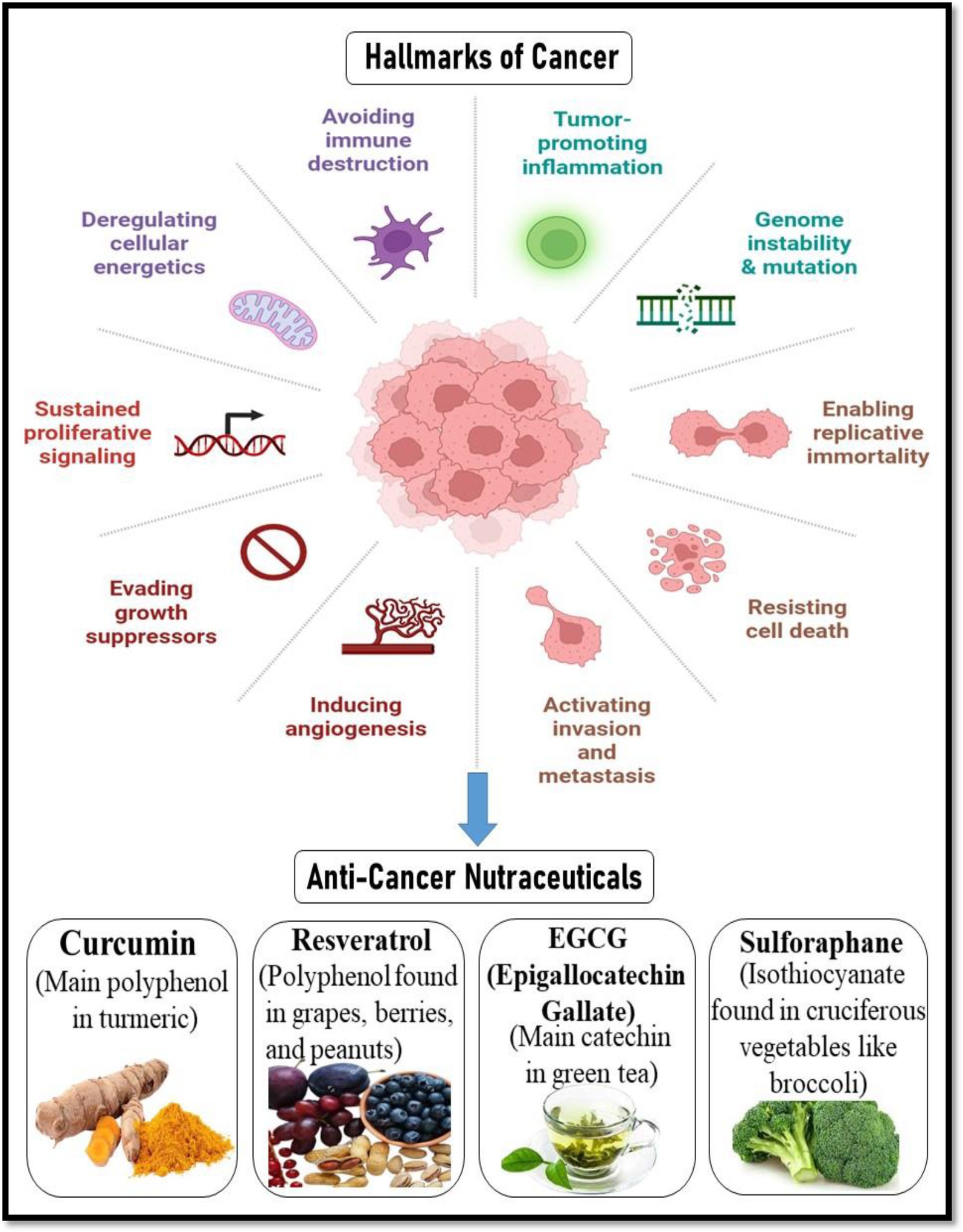
Figure 4. Hallmarks of cancer and the role of anti-cancer nutraceuticals. Created with BioRender.com.
6.4 Neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s)
Nutraceutical formulations and natural compounds have shown promise in combating shared pathogenic pathways in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases including oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, protein aggregation (Aβ, tau, α-synuclein), mitochondrial dysfunction, and synaptic impairment. Notably, curcumin though hampered by poor oral bioavailability and rapid clearance exhibits anti-amyloid, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects; advanced nano- and polymeric delivery systems (liposomes, PLGA/lipid nanoparticles, dendrimers, nanomicelles) significantly enhance its gastrointestinal absorption, plasma half-life, brain penetration (up to ~16 × bioavailability), and therapeutic efficacy in preclinical rodent models, and early clinical work in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s supports improved delivery and safety profile (46). Green-tea–derived EGCG protects against oxidative and inflammatory neurotoxicity, reduces amyloid and α-synuclein aggregation, preserves dopaminergic neurons in MPTP and 6-OHDA models, and activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (47). Flavonoids like quercetin and apigenin confer neuroprotection in vitro and in vivo through antioxidant defense, anti-amyloidogenic effects, synaptic support, and neuroinflammation modulation. Resveratrol modulates NF-κB/JNK/MAPK signaling, SIRT1 activation, and microglial cytokine release, offering neuroinflammatory and anti-amyloid benefits—though clinical outcomes remain mixed and oral bioavailability low (~0.5%), prompting exploration of improved formulations (48). Huperzine A, an alkaloid cholinesterase and NMDA-receptor inhibitor, crosses the blood–brain barrier and has shown cognitive-benefit signals in AD trials, despite methodological limitations of existing studies. Complementing these are omega-3 fatty acids, sulfur-rich sulforaphane, carotenoids, and marine phlorotannins, which together address neuroinflammation, mitochondrial health, and proteostasis. While clinical trials (e.g., curcumin, resveratrol, luteolin, crocin, EGb 761) report some cognitive or biomarker improvements in mild AD, they often suffer from low bioavailability, small cohorts, and inconsistent methodologies. Future progress requires standardized, well-powered RCTs, multi-compound synergistic formulations, and advanced CNS-targeted delivery platforms (e.g., nanoparticles, nanomicelles, NADES), alongside robust pharmacokinetics, dosage optimization, gut–brain axis evaluation, and safety characterization to translate these nutraceuticals into effective adjunctive neurotherapeutic regimens (49).
6.5 Inflammatory and autoimmune disorders
Dysregulated immune responses, chronic inflammation, and compromised immunological tolerance are the causes of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Because traditional immunosuppressive treatments are frequently linked to side effects and an elevated risk of infection, there is growing interest in nutraceuticals as safer, complementary alternatives. By controlling cytokines, T-cell activity, and the composition of the gut microbiota, substances such as probiotics, turmeric, ginger, and boswellia have shown immunomodulatory qualities (50).
Strong anti-inflammatory properties are demonstrated by turmeric (Curcuma longa), especially its active polyphenol curcumin, which inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. One important regulator of inflammation and autoimmunity, the NF-κB signaling pathway, is inhibited. Curcumin also reduces chronic inflammation at the molecular level by downregulating inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Curcumin has also been demonstrated to alter T-cell differentiation, boosting regulatory T-cells (Tregs) and inhibiting Th17 cells to restore immunological balance (51).
Bioactive substances called gingerols and shogaols, which are found in ginger (Zingiber officinale), have been demonstrated to prevent the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators such prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Ginger inhibits the activation of NF-κB and lowers the release of inflammatory cytokines by T-cells and macrophages. Due to its inhibition of the COX and lipoxygenase (LOX) pathways, ginger has been shown in clinical tests to help individuals with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis experience less pain and stiffness (52, 53).
The boswellic acids produced by Boswellia serrata, commonly referred to as Indian frankincense, target the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), which is in charge of leukotriene production. In diseases including RA, asthma, and IBD, this activity helps lower inflammation. Boswellic acids can be used to control autoimmune diseases since they also decrease TNF-α and IL-6 and enhance immunological regulation by reducing CD4 + T-cell proliferation and activation (54). By altering the gut microbiota, probiotics—particularly strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium—have an impact on immunological responses both locally and systemically. They improve intestinal barrier integrity, lower systemic endotoxin burden, and alter dendritic cell and T-cell responses by reestablishing microbial balance (55). According to Ouwehand et al. (56), probiotics are known to reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines and enhance anti-inflammatory markers such as IL-10, which helps to reduce symptoms of autoimmune illnesses and induce remission in IBD. Together, these nutraceuticals provide a multifaceted and all-natural method of treating inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by regulating T-cells, balancing the microbiota, and modulating cytokines. Their inclusion in treatment plans may help maintain long-term immunological health, decrease side effects, and lessen reliance on synthetic immunosuppressants (57).
7 Formulation strategies for enhanced efficacy
The poor bioavailability of nutraceuticals, which is frequently caused by low solubility, instability in the gastrointestinal system, quick metabolism, and poor absorption, is a significant obstacle restricting their clinical application, despite their great therapeutic potential. Advanced formulation techniques have been created to solve these problems and guarantee effective distribution to the intended tissues (58). These include targeted delivery systems, bioavailability enhancers, encapsulating methods, and nano-formulations, all of which are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of nutraceuticals. Liposomes and nanoparticles are examples of nano-formulations that have drawn a lot of interest because of their capacity to increase solubility, shield bioactive substances from deterioration, and promote cellular uptake. The stability and controlled release of nutraceuticals such as curcumin, EGCG, and resveratrol can be improved by liposomes, which are spherical vesicles made of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate both hydrophilic and lipophilic substances (59). Likewise, polymeric and lipid-based nanoparticles enhance pharmacokinetic characteristics by extending systemic circulation and improving gastrointestinal absorption. Additionally, these nanosystems offer surface changes that improve therapeutic specificity by enabling targeting of particular regions (60).
Encapsulation methods, such as hydrogel systems and microencapsulation, are frequently used to shield delicate nutraceuticals from gastrointestinal and environmental deterioration. Encasing bioactive substances in microscopic carriers composed of biopolymers as chitosan, gelatin, or alginate is known as microencapsulation. In addition to protecting the substances from oxidation and pH changes, this method enables regulated release and covers up offensive tastes or odors (61). Probiotics and polyphenols have been encapsulated in hydrogels, which are cross-linked, water-swollen polymeric networks that improve their release at specific intestinal locations and guarantee their passage through the digestive tract. A number of methods for improving bioavailability have been developed in order to overcome first-pass metabolism and limited absorption. Piperine co-administration is one of the most well-known, especially when combined with curcumin. According to Shoba et al. (62, 63), piperine, an alkaloid found in black pepper, increases the plasma concentration of curcumin by up to 2000% by blocking intestinal and hepatic glucuronidation. Emulsification, which involves adding the nutraceutical to oil-in-water emulsions, is another technique that enhances the solubility and absorption of lipophilic substances including fat-soluble vitamins and carotenoids (64).
By guiding the active ingredient to the site of action while reducing systemic exposure and adverse effects, targeted delivery systems are also essential for increasing efficacy. Enzyme-sensitive release mechanisms, pH-responsive carriers, or ligand-functionalized nanoparticles can all do this. For example, nutraceuticals can be delivered directly to cancer cells that overexpress folate receptors using folic acid-conjugated nanoparticles (65). By lowering the necessary dosage and improving therapeutic outcomes, such precision techniques improve treatment efficiency and patient satisfaction. All things considered, these formulation techniques greatly enhance the bioavailability, stability, and therapeutic targeting of nutraceuticals, making them more dependable and potent medicines. These methods should soon be further refined by continuing developments in material science and nanotechnology, allowing for disease-specific and customized nutraceutical delivery (Table 4). Summarizes innovative formulation technologies developed to improve the delivery and effectiveness of nutraceuticals. It outlines various strategies such as liposomes, nanotechnology, hydrogels, and self-emulsifying systems, highlighting their associated nutraceuticals, delivery advantages, and key scientific references (66).
8 Safety, toxicity, and regulatory aspects
Although nutraceuticals are frequently promoted as natural and safe substitutes for medicines, issues with their toxicity, safety, and regulatory monitoring still need to be addressed. The widespread belief that “natural equals safe” is untrue because using nutraceuticals excessively or inappropriately can have negative effects, particularly in susceptible groups or when taken with concomitant drugs. Integrating nutraceuticals into traditional healthcare systems requires ensuring safe dosing, avoiding negative interactions, and following established laws. The main causes of toxicological issues are incorrect dosage, contamination, adulteration, or extended use without monitoring. Even though a lot of nutraceuticals come from food, their bioactive ingredients might have pharmacological effects at greater dosages when they are condensed into supplements. For example, too much consumption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) can accumulate in bodily tissues and cause toxicity. Likewise, in sensitive people, elevated levels of green tea catechins have been linked to liver damage (67). Therefore, it is crucial to establish the safe dosage range for each molecule, which needs to be backed up by toxicological research, including LD50 and NOAEL (No Observed Adverse Effect Level) data.
The possibility of herb-drug interactions, in which specific nutraceuticals may change the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of prescription medications, is a serious safety concern. St. John’s Wort, for instance, can increase cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP3A4, which decreases the effectiveness of medications including immunosuppressants, anticoagulants, and oral contraceptives. Similarly, when combined with anticoagulants like warfarin, substances like ginseng, garlic, and ginkgo biloba may raise the risk of bleeding (68). When mixing nutraceuticals with pharmaceuticals, rigorous screening and clinical guidance are necessary because such interactions may lead to heightened toxicity or therapeutic failure. The legal systems that regulate nutraceuticals differ greatly across the globe. According to the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (134), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (69) (FDA) in the US regulates nutraceuticals as dietary supplements. Although pre-market approval is not necessary for these products, they must refrain from making promises about curing diseases unless they are backed up by proof. Under the Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (Regulation EC No. 1924/2006), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the European Union assesses health claims for functional foods and supplements. In order to promote Ayurvedic-based nutraceuticals with standards for quality and labeling, the AYUSH Ministry and FSSAI, respectively, regulate traditional and health supplements in India. Nonetheless, disparities in classification, labeling requirements, and enforcement practices among nations frequently lead to market misunderstandings and a range of product quality (70).
Furthermore, to guarantee efficacy and reproducibility, clinical validation and standardization of nutraceuticals are necessary. Many products lack thorough human clinical trials and are instead promoted on the basis of preclinical or anecdotal evidence. Different brands and batches may experience different results because to variations in the sourcing of raw materials, extraction techniques, and concentrations of active compounds. Consequently, quality assurance, standardization of active substances, and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential. To assess the clinical efficacy and safety profile of nutraceuticals across populations and disease situations, long-term randomized controlled studies (RCTs) are also required (71). To support clinical translation, the most commonly studied nutraceutical bioactive compounds, their typical dosages (posology), and reported adverse effects are summarized in Table 5. This table provides a quick reference for clinicians and researchers, highlighting evidence-based dosage ranges from clinical studies and known safety concerns, thereby serving as a practical tool for integrating nutraceuticals into clinical practice.
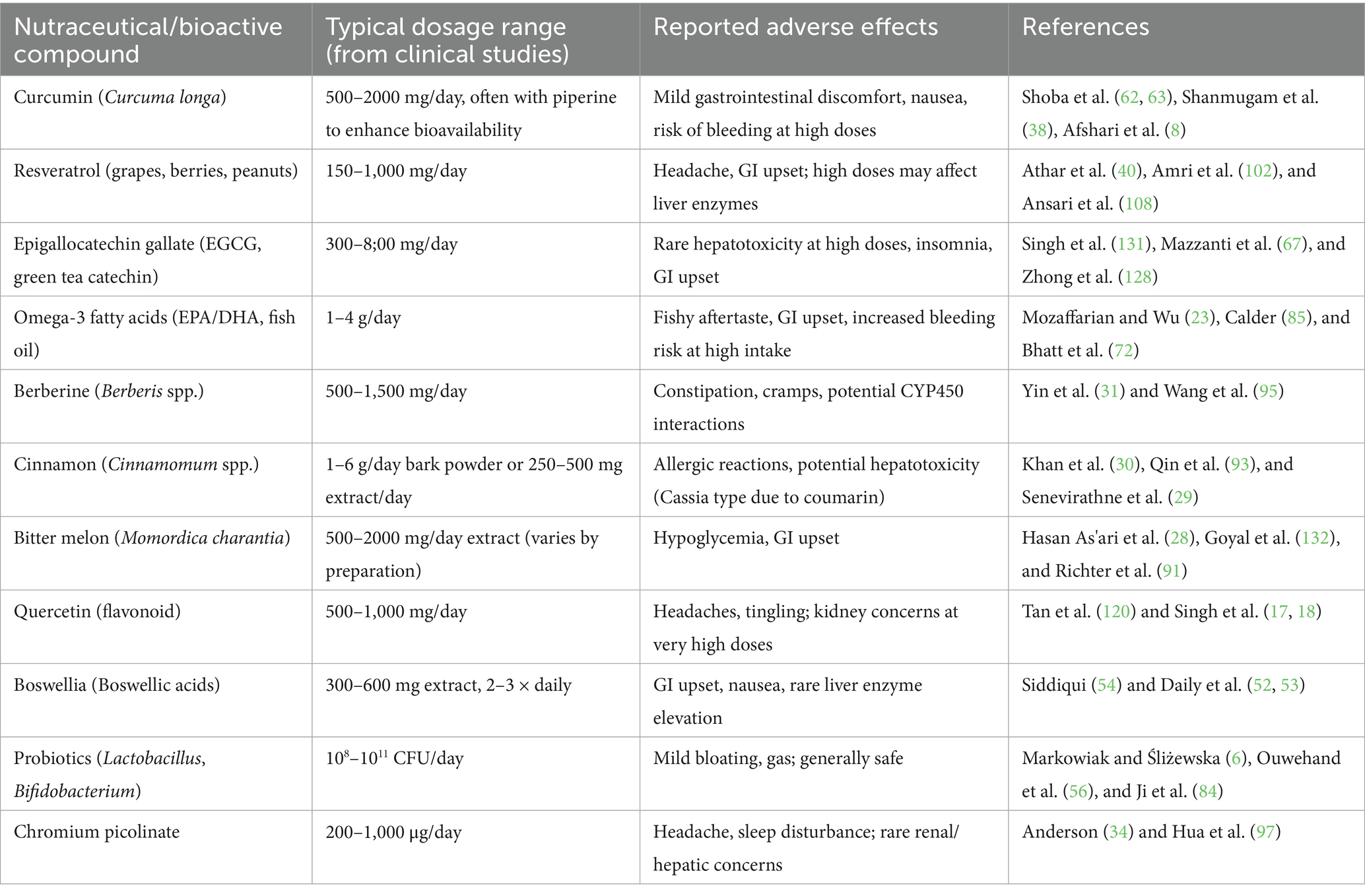
Table 5. Common nutraceutical bioactive compounds with typical dosages and reported adverse effects (based on clinical and preclinical evidence).
9 Clinical evidence and limitations
A growing number of clinical research and meta-analyses examining the effectiveness of nutraceuticals in controlling chronic diseases have been prompted by their therapeutic promise. Numerous of these research back up the usage of nutraceuticals in addition to traditional pharmaceuticals as supplementary therapy. Nevertheless, despite promising results, a number of issues pertaining to study design, standardization, and sample size have hindered the conversion of preclinical outcomes into reliable clinical success. Nutraceuticals have been shown to be useful in improving clinical outcomes in a number of significant clinical trials. For example, omega-3 fatty acids significantly decreased cardiovascular events in high-risk patients with hypertriglyceridemia, according to a double-blind, placebo-controlled research (72). In a similar vein, curcumin has demonstrated promise in reducing the symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis; meta-analyses have showed decreases in inflammatory markers, disease activity, and pain levels when compared to a placebo (52, 53). In a different randomized study, berberine was found to be just as successful as metformin at lowering blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes (31). When compared to conventional pharmaceutical therapies, these investigations highlight the therapeutic equivalency or synergistic impact of specific nutraceuticals.
However, because to variations in research length, formulation types, and patient groups, efficacy results from different trials continue to be inconsistent, particularly when compared to conventional medications. Even if some studies show notable improvements, others are unable to reproduce these advantages in demanding clinical settings. The clinical significance of several nutraceuticals is called into question by placebo-controlled studies that frequently yield moderate or statistically insignificant outcomes (73). Sometimes, rather than hard clinical outcomes like mortality or illness remission, positive outcomes are restricted to surrogate endpoints (such biomarker alterations). The diversity of clinical research presents a significant obstacle. Because of the considerable variations in dosage, duration, administration methods, and outcome measures found in nutraceutical trials, it is challenging to perform meta-analyses and reach generalizable findings. For instance, various studies may utilize different amounts of EGCG in their green tea extracts, which could result in uneven therapeutic benefits. Furthermore, a lot of trials are underpowered because of their short durations or small sample numbers, which restricts their statistical reliability and generalizability to larger populations (74). Another crucial problem is variation in the bioactive content. Nutraceuticals, in contrast to pharmaceutical medications, are frequently made from entire plants or blended extracts, where the concentration and makeup of active ingredients might vary depending on the region of origin, the cultivation practices, and the extraction techniques used. Even the same product may produce varying findings in different experiments if sufficient standardization is not implemented. In addition to impeding repeatability, this inconsistency makes safety assessments and dose–response analyses more difficult (75).
10 Future prospects and research directions
Nutraceuticals have a bright future in healthcare thanks to developments in integrated medicine, tailored nutrition, and biotechnology. Nutraceuticals are anticipated to become increasingly important in reducing the burden of chronic diseases as worldwide awareness of preventative health increases. The creation of individualized nutraceutical regimens based on a person’s genetic composition, microbiome composition, lifestyle, and disease risk profile is one of the main directions. With the help of nutrigenomics and metabolomics, this strategy seeks to maximize therapeutic benefits while reducing side effects. Furthermore, advancements in delivery methods including biosensors, controlled-release platforms, and smart nanocarriers will improve the stability, bioavailability, and focused action of nutraceutical substances. Particularly for substances with limited solubility or fast metabolism, these technologies are probably going to increase patient compliance and efficacy. Combining many nutraceuticals or integrating them with traditional medications in synergistic formulations has the potential to increase therapeutic advantages and more comprehensively treat multifactorial disorders like diabetes, cancer, and neurodegeneration.
Furthermore, by forecasting compound-disease connections, evaluating clinical data, and determining ideal dosage ranges, the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics in nutraceutical research helps speed up discovery. In order to increase worldwide acceptance, guarantee safety, and encourage the evidence-based use of nutraceuticals, regulatory harmonization and quality standardization among nations will also be essential. Large-scale, carefully planned clinical trials must be given top priority in future studies, along with the investigation of new biomarkers for efficacy and the expansion of our knowledge of long-term impacts, mechanisms of action, and population-specific reactions. Nutraceuticals are positioned to become a crucial component of future healthcare strategies as consumer desire and scientific data align, bridging the gap between medicine and nutrition in the search for preventive, tailored, and sustainable health solutions.
11 Conclusion
Through processes like antioxidant activity, inflammatory control, immunological modulation, and metabolic regulation, nutraceuticals and natural substances have become invaluable partners in the prevention and management of chronic diseases. These bioactive substances, which come from a variety of sources such as plants, marine life, and microorganisms, have shown promise in treating complicated illnesses like diabetes, cancer, heart disease, neurological disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Their clinical usefulness and bioavailability have been further improved by advanced formulation techniques such encapsulation technologies and nano-delivery systems. The broad use of nutraceuticals in conventional medicine is hampered by issues with safety, standardization, herb-drug interactions, and inconsistent regulations, despite encouraging preclinical and clinical data. It is still essential to conduct thorough, extensive human studies for clinical validation in order to prove their effectiveness and guarantee reliable treatment results. The future of nutraceutical use will be significantly shaped by the combination of global regulatory frameworks, AI-driven discovery, and customized nutrition.
Author contributions
GF: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Supervision, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SK: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Data curation. VS: Methodology, Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Resources, Writing – review & editing. WA: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Visualization. DL: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YG: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the author(s) used BioRender software for making figures. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
2. O'Reilly, M, Mellotte, G, Ryan, B, and O'Connor, A. Gastrointestinal side effects of cancer treatments. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. (2020) 11:2040622320970354. doi: 10.1177/2040622320970354
3. Daliu, P, Santini, A, and Novellino, E. From pharmaceuticals to nutraceuticals: bridging disease prevention and management. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. (2019) 12:1–7. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1552135
4. Salehi, B, Ata, A, Anil Kumar, N, Sharopov, F, Ramírez-Alarcón, K, Ruiz-Ortega, A, et al. Antidiabetic potential of medicinal plants. Biomolecules. (2019) 9:551. doi: 10.3390/biom9100551
5. Shahidi, F, and Ambigaipalan, P. Functional food ingredients from marine sources. Current opinion in food. Science. (2015) 2:10. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2014.12.009
6. Markowiak, P, and Śliżewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Nutrients. (2017) 9:1021. doi: 10.3390/nu9091021
7. Nasri, H, et al. Nutraceuticals as alternatives for pharmaceuticals. Int J Prev Med. (2014) 5:1487–99.
8. Afshari, AR, Hashemi, M, Gholizadeh Navashenaq, J, Baradaran, B, Sadighparvar, S, Yousefi, B, et al. Curcumin-based nanomedicines for cancer therapy: recent advances and future prospects. J Funct Biomater. (2023) 14:408
9. Pisoschi, AM, and Pop, A. Role of antioxidants in oxidative stress. Eur J Med Chem. (2015) 97:55–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040
10. Li, B, Ming, H, Qin, S, Nice, EC, Dong, J, du, Z, et al. Redox regulation: mechanisms, biology and therapeutic targets in diseases. Sig Transduct Target Ther. (2025) 10:2095. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02095-6
11. Ranzato, E, Martinotti, S, Calabrese, CM, and Calabrese, G. Role of nutraceuticals in cancer therapy. J Food Res. (2014) 3:18. doi: 10.5539/jfr.v3n4p18
12. Calvani, M, Pasha, A, and Favre, C. Nutraceutical boom in cancer: inside the labyrinth of reactive oxygen species. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:1936. doi: 10.3390/ijms21061936
13. Calder, PC. Feeding the immune system. Proc Nutr Soc. (2013) 72:299–309. doi: 10.1017/S0029665113001286
14. Zhu, Z, He, L, Bai, Y, Xia, L, Sun, X, and Qi, C. Yeast β-glucan modulates macrophages and improves antitumor NK-cell responses in cancer. Clin Exp Immunol. (2023) 214:50–60. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad080
15. Hardy, TM, and Tollefsbol, TO. Epigenetic diet and cancer. Epigenomics. (2011) 3:503–18. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.71
16. Ojeda, P, et al. Nutritional modulation of gut microbiota. J Nutr Biochem. (2016) 28:191–200. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.08.013
17. Singh, CK, et al. Resveratrol combinatorial strategies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2013a) 1290:113–21. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12160
18. Singh, CK, Ndiaye, MA, and Ahmad, N. Resveratrol and quercetin in combinatorial cancer therapy: a review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2013b) 1290:113–21.
19. Di Cesare, M, Perel, P, Taylor, S, Kabudula, C, Bixby, H, Gaziano, TA, et al. The heart of the world. Glob Heart. (2024) 19:11. doi: 10.5334/gh.1288
20. Ojeda-Granados, C, Campisi, E, Barchitta, M, and Agodi, A. Genetic, lifestyle and metabolic factors contributing to cardiovascular disease in the Italian population: a literature review. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1379785. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1379785
21. Krupa, KN, Fritz, K, and Parmar, M. Omega-3 fatty acids. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing (2025).
22. Endo, J, and Arita, M. Cardioprotective mechanism of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Cardiol. (2016) 67:22–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2015.08.002
23. Mozaffarian, D, and Wu, JH. Omega-3 and cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2011) 58:2047–67. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.063
24. Zahra, M, Abrahamse, H, and George, BP. Flavonoids: antioxidant powerhouses and their role in nanomedicine. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:922. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080922
25. Hollman, PC, Cassidy, A, Comte, B, Heinonen, M, Richelle, M, Richling, E, et al. Antioxidant effects of polyphenols. J Nutr. (2011) 141:989S–1009S. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.131490
26. Katan, MB, et al. Efficacy of plant stanols and sterols. Mayo Clin Proc. (2003) 78:965–78. doi: 10.4065/78.8.965
27. Goyal, R, Singhal, M, and Jialal, I. Type 2 Diabetes. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing (2025).
28. Hasan As’ari, A, et al. Hypoglycemic trace elements in bitter gourd. Jurnal Ilmiah Aplikasi Isotop dan Radiasi. (2021) 17:5–10. doi: 10.17146/jair.2021.17.1.5965
29. Senevirathne, BS, Jayasinghe, MA, Pavalakumar, D, and Siriwardhana, CG. Ceylon cinnamon: a versatile ingredient for futuristic diabetes management. J Future Foods. (2022) 2:125–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jfutfo.2022.03.010
30. Khan, A, Safdar, M, Ali Khan, MM, Khattak, KN, and Anderson, RA. Cinnamon improves glucose and lipids of people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2003) 26:3215–8. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.12.3215
31. Yin, J, Xing, H, and Ye, J. Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. (2008) 57:712–7. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.01.013
32. Senevirathne, BS, Ediriweera, ERHSS, Tennekoon, KH, Samarakoon, SR, and de Silva, ED. Antidiabetic properties of cinnamon polyphenols – A review. J Diabetes Metab Disord. (2022) 21:167–77.
33. Vincent, JB. New evidence against chromium as an essential trace element. J Nutr. (2017) 147:2212–9. doi: 10.3945/jn.117.255901
34. Anderson, RA. Chromium in the prevention and control of diabetes. Diabetes Metab. (2000) 26:22–7.
35. Dinić, S, Arambašić Jovanović, J, Uskoković, A, Mihailović, M, Grdović, N, Tolić, A, et al. Oxidative stress-mediated beta cell death and dysfunction as a target for diabetes management. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:1006376. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1006376
36. Tufail, M, Hu, JJ, Liang, J, He, C-Y, Wan, W-D, Huang, Y-Q, et al. Hallmarks of cancer resistance. iScience. (2024) 27:109979. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109979
37. Zafar, A, Khatoon, S, Khan, MJ, Abu, J, and Naeem, A. Advancements and limitations in traditional anti-cancer therapies: a comprehensive review of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormonal therapy. Discov Oncol. (2025) 16:607. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02198-8
38. Shanmugam, MK, Rane, G, Kanchi, MM, Arfuso, F, Chinnathambi, A, Zayed, ME, et al. The multifaceted role of curcumin in cancer prevention and treatment. Molecules. (2015) 20:2728–69. doi: 10.3390/molecules20022728
39. Hosseini, SAM, Alaei, E, Doodmani, SM, Rahimzadeh, P, Farahani, N, Alimohammadi, M, et al. Role of resveratrol in the prevention and treatment of urological cancers: new perspectives on multiple molecular targets and signaling pathways. J Funct Foods. (2025) 132:106981. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2025.106981
40. Athar, M, Back, JH, Tang, X, Kim, KH, Kopelovich, L, Bickers, DR, et al. Resveratrol: a review of preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2007) 224:274–83. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.12.025
41. Kciuk, M, Alam, M, Ali, N, Rashid, S, Głowacka, P, Sundaraj, R, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate therapeutic potential in cancer: mechanism of action and clinical implications. Molecules. (2023) 28:5246. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135246
42. Pledgie-Tracy, A, et al. Sulforaphane induces apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. (2007) 6:1013–21. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0494
43. Sita, G, Hrelia, P, Graziosi, A, and Morroni, F. Sulforaphane from cruciferous vegetables: recent advances to improve glioblastoma treatment. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1755. doi: 10.3390/nu10111755
44. Aggarwal, P, Dutta, G, Shaurya, R, Rajendran, V, Thirunavukkarasu, P, Charan, J, et al. Unlocking the potential of nutraceuticals in cancer chemotherapy: a comprehensive review. Cureus. (2025) 17:e89328. doi: 10.7759/cureus.89328
45. Hanahan, D, and Monje, M. Cancer hallmarks intersect with neuroscience in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41:573–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.02.012
46. Nahar, L, Charoensup, R, Kalieva, K, Habibi, E, Guo, M, Wang, D, et al. Natural products in neurodegenerative diseases: recent advances and future outlook. Front Pharmacol. (2025) 16:1529194. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1529194
47. Kelsey, NA, Wilkins, HM, and Linseman, DA. Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules. (2010) 15:7792–814. doi: 10.3390/molecules15117792
48. Satyam, SM, and Bairy, LK. Neuronutraceuticals combating neuroinflammaging: molecular insights and translational challenges-a systematic review. Nutrients. (2022) 14:3029. doi: 10.3390/nu14153029
49. Suvaiv, SK, Hasan, S, et al. Huperzine A: a natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with multifunctional neuroprotective effects. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. (2025) 14:82. doi: 10.1186/s43088-025-00675-1
50. Song, X, Liang, H, Nan, F, Chen, W, Li, J, He, L, et al. Autoimmune diseases: molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. MedComm. (2025) 6:e70262. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70262
51. Chai, YS, et al. Curcumin regulates CD4+ T cells. Biomed Pharmacother. (2020) 125:109946. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109946
53. Daily, JW, Zhang, X, Kim, DS, and Park, S. Efficacy of ginger for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and joint and muscle pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Pain Med. (2015b) 16:2243–55.
54. Siddiqui, MZ. Boswellia serrata: an overview. Indian J Pharm Sci. (2011) 73:255–61. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.93507
55. Ragab, EA, Abd El-Wahab, MF, Doghish, AS, Salama, RM, Eissa, N, and Darwish, SF. The journey of boswellic acids from synthesis to pharmacological activities. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 397:1477–504. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02725-w
56. Ouwehand, AC, Salminen, S, and Isolauri, E. Probiotics: an overview of beneficial effects. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. (2002) 82:279–89. doi: 10.1023/A:1020620607611
57. Guo, N, and Lv, LL. Mechanistic insights into the role of probiotics in modulating immune cells in ulcerative colitis. Immun Inflamm Dis. (2023) 11:e1045. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1045
58. Subramanian, P. Lipid-based Nanocarrier system for the effective delivery of nutraceuticals. Molecules. (2021) 26:5510. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185510
60. Sivadasan, D, Sultan, MH, Madkhali, O, Almoshari, Y, and Thangavel, N. Polymeric lipid hybrid nanoparticles (PLNs) as emerging drug delivery platform-A comprehensive review of their properties, preparation methods, and therapeutic applications. Pharmaceutics. (2021) 13:1291. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081291
61. Dima, C, et al. Bioavailability of bioactives. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. (2020) 19:2862–84. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12623
62. Shoba, G, et al. Piperine’s effect on curcumin pharmacokinetics. Planta Med. (1998a) 64:353–6. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-957450
63. Shoba, G, Joy, D, Joseph, T, Majeed, M, Rajendran, R, and Srinivas, PS. Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers. Planta Med. (1998b) 64:353–6.
64. Teixé-Roig, J, Oms-Oliu, G, Odriozola-Serrano, I, and Martín-Belloso, O. Emulsion-based delivery systems to enhance the functionality of bioactive compounds: towards the use of ingredients from natural, sustainable sources. Foods. (2023) 12:1502. doi: 10.3390/foods12071502
65. Aqil, F, et al. Enhancing phytochemical bioavailability. Cancer Lett. (2013) 334:133–41. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.02.032
66. Puri, V, Nagpal, M, Singh, I, Singh, M, Dhingra, GA, Huanbutta, K, et al. A comprehensive review on nutraceuticals: therapy support and formulation challenges. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4637. doi: 10.3390/nu14214637
67. Mazzanti, G, Menniti-Ippolito, F, Moro, PA, Cassetti, F, Raschetti, R, Santuccio, C, et al. Green tea hepatotoxicity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2009) 65:331–41. doi: 10.1007/s00228-008-0610-7
68. Izzo, AA, and Ernst, E. Herbal medicine interactions. Drugs. (2009) 69:1777–98. doi: 10.2165/11317010-000000000-00000
69. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Dietary supplements. New York, NY: U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2023).
70. Sarma, N, et al. Regulation of nutraceuticals in India. J Ethnopharmacol. (2011) 138:354–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.025
71. Hathcock, JN. Vitamins and minerals: efficacy and safety. Am J Clin Nutr. (1997) 66:427–37. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/66.2.427
72. Bhatt, DL, Steg, PG, Miller, M, Brinton, EA, Jacobson, TA, Ketchum, SB, et al. Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:11–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812792
73. Vickers, AJ. Botanicals in cancer trials. J Soc Integr Oncol. (2007) 5:125–9. doi: 10.2310/7200.2007.011
74. Hasani-Ranjbar, S, et al. Herbal medicines for hyperlipidemia. Curr Pharm Des. (2010) 16:2935–47. doi: 10.2174/138161210793176464
75. Jeet Kaur, R, Dutta, S, Charan, J, Bhardwaj, P, Tandon, A, Yadav, D, et al. Cardiovascular adverse events from COVID-19 vaccines. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:3909–27. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S324349
76. Kalra, EK. Nutraceutical--definition and introduction. AAPS PharmSci. (2003) 5:E25. doi: 10.1208/ps050325
77. Visen, A, Visen, S, Sharma, A, et al. Nutraceuticals as a natural alternative for preventive and proactive health care In: RC Gupta, editor. Functional foods and nutraceuticals in metabolic and non-communicable diseases. 1st ed. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press (2022). 603–18. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819815-5.00040-9
78. Martirosyan, D, and Singh, J. A new definition of functional food by FFC: what makes a new definition unique? Funct Foods Health Dis. (2015) 5:209–23. doi: 10.31989/ffhd.v5i6.183
79. Das, L, Bhaumik, E, Raychaudhuri, U, and Chakraborty, R. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. J Food Sci Technol. (2012) 49:173–83. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0269-4
80. Brower, V. Nutraceuticals: poised for a healthy slice of the healthcare market? Nat Biotechnol. (1998) 16:728–31. doi: 10.1038/nbt0898-728
81. Slavin, J. Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients. (2013) 5:1417–35. doi: 10.3390/nu5041417
82. Khalid, W, Arshad, MS, Jabeen, A, Muhammad Anjum, F, Qaisrani, TB, and Suleria, HAR. Fiber-enriched botanicals: a therapeutic tool against certain metabolic ailments. Food Sci Nutr. (2022) 10:3203–18. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2920
83. Gibson, GR, et al. Expert consensus document: the ISAPP consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 14:491–502. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75
84. Ji, J, Jin, W, Liu, SJ, Jiao, Z, and Li, X. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in health and disease. MedComm. (2023) 4:e420. doi: 10.1002/mco2.420
85. Calder, PC. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2015) 1851:469–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.010
86. Mititelu, M, Lupuliasa, D, Neacșu, SM, Olteanu, G, Busnatu, ȘS, Mihai, A, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and human health: a key to modern nutritional balance in association with polyphenolic compounds from food sources. Foods. (2024) 14:46. doi: 10.3390/foods14010046
87. Pandey, KB, and Rizvi, SI. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2009) 2:270–8. doi: 10.4161/oxim.2.5.9498
88. Rudrapal, M, Khairnar, SJ, Khan, J, Dukhyil, AB, Ansari, MA, Alomary, MN, et al. Dietary polyphenols and their role in oxidative stress-induced human diseases: insights into protective effects, antioxidant potentials and mechanism(s) of action. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:806470. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.806470
89. Gombart, AF, Pierre, A, and Maggini, S. A review of micronutrients and the immune system. Nutrients. (2020) 12:236. doi: 10.3390/nu12010236
90. Mitra, S, Paul, S, Roy, S, Sutradhar, H, Bin Emran, T, Nainu, F, et al. Exploring the immune-boosting functions of vitamins and minerals as nutritional food bioactive compounds: a comprehensive review. Molecules. (2022) 27:555. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020555
91. Richter, E, Geetha, T, Burnett, D, Broderick, TL, and Babu, JR. The effects of Momordica charantia on type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4643. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054643
92. Saqulain, S, Verma, M, Singh, H, Dharmalingam, S, Eldhose, MJ, Srivastav, Y, et al. Therapeutic role of Gymnema sylvestre and Momordica charantia in diabetes management: a detailed review of their mechanisms in insulin resistance, glucose metabolism regulation, and clinical efficacy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Pharm Sci. (2025) 3:1757–68. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.14902101
93. Qin, B, Panickar, KS, and Anderson, RA. Cinnamon: potential role in the prevention of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. (2010) 4:685–93. doi: 10.1177/193229681000400324
94. Tuzcu, Z, Orhan, C, Sahin, N, Juturu, V, and Sahin, K. Cinnamon polyphenol extract inhibits hyperlipidemia and inflammation by modulation of transcription factors in high-fat diet-fed rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:1583098. doi: 10.1155/2017/1583098
95. Wang, H, Zhu, C, Ying, Y, Luo, L, Huang, D, and Luo, Z. Metformin and berberine, two versatile drugs in treatment of common metabolic diseases. Oncotarget. (2017) 9:10135–46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20807
96. Zieniuk, B, and Pawełkowicz, M. Berberine as a bioactive alkaloid: multi-omics perspectives on its role in obesity management. Meta. (2025) 15:467. doi: 10.3390/metabo15070467
97. Hua, Y, Clark, S, Ren, J, and Sreejayan, N. Molecular mechanisms of chromium in alleviating insulin resistance. J Nutr Biochem. (2012) 23:313–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.11.001
98. Inyang, E, Ijeh, II, and Oyedemi, S. Mixed sweeteners supplemented with chromium picolinate (CrPic) improved some diabetes-related markers and complications in a type 2 diabetic rat model. Nutraceuticals. (2024) 4:658–72. doi: 10.3390/nutraceuticals4040036
99. Keller, BC. Liposomes in nutrition. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2001) 12:25–31. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2244(01)00044-9
100. Padamwar, M, and Pokharkar, VB. Development of vitamin loaded topical liposomal formulation using factorial design approach: drug deposition and stability. Int J Pharm. (2006) 320:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.04.001
101. Lee, W, and Tsai, T. Preparation and characterization of liposomal coenzyme Q10 for in vivo topical application. Int J Pharm. (2010) 395:78–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.05.006
102. Amri, A, Chaumeil, JC, Sfar, S, and Charrueau, C. Administration of resveratrol: what formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations? J Control Release. (2012) 158:182–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.09.083
103. Taepaiboon, P, Rungsardthong, U, and Supaphol, P. Vitaminloaded cellulose acetate nanofiber mats as transdermal and dermal therapeutic agents of vitamin A acid and vitamin E. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. (2007) 67:387–97.
104. Suwantong, O, Opanasopit, P, Ruktanonchai, U, and Supaphol, P. Electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats containing curcumin and release characteristic of the herbal substance. Polymer. (2007) 48:7546–57. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2007.11.019
105. Suwantong, O, Ruktanonchai, U, and Supaphol, P. Electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats containing asiaticoside or Centella asiatica crude extract and the release characteristics of asiaticoside. Polymer. (2008) 49:4239–47. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2008.07.020
106. Paneva, D, Manolova, N, Argirova, M, and Rashkov, I. Antibacterial electrospun poly (e-caprolactone)/ascorbyl palmitate nanofibrous materials. Int J Pharm. (2011) 416:346–55.
107. Patravale, VB, and Mandawgade, SD. Novel cosmetic delivery systems: an application update. Int J Cosmet Sci. (2008) 30:19–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2494.2008.00416.x
108. Ansari, KA, Vavia, PR, Trotta, F, and Cavalli, R. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for delivery of resveratrol. In vitro characterisation, stability, cytotoxicity and permeation study. Am Assoc Pharmaceutical Scientists. (2011) 12:279–86.
109. Chantarawaratit, P, Sangvanich, P, Banlunara, W, Soontornvipart, K, and Thunyakitpisal, P. Acemannan sponges stimulate alveolar bone, cementum and periodontal ligament regeneration in a canine class II furcation defect model. J Periodontal Res. (2013) 49:164–78. doi: 10.1111/jre.12090
110. Tonnesen, HH, Masson, M, and Loftsson, T. Studies of curcumin and curcuminoids. XXVII. Cyclodextrin complexation: solubility, chemical and photochemical stability. Int J Pharm. (2002) 244:127–35. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00323-X
111. Ghosh, A, Biswas, S, and Ghosh, T. Preparation and evaluation of silymarin b-cyclodextrin molecular inclusion complexes. J Young Pharm. (2011) 3:205–10.
112. Kim, SO, Youn, JY, Kim, KM, Kang, KC, Pyo, HB, and Lee, SJ. Characterization of an inclusion complex of 7-dehydrocholesterol and cyclodextrin. J Ind Eng Chem. (2010) 16:119–21.
113. Mekjaruskul, C, Yang, Y, Leed, MGD, Sadgrove, MP, Jay, M, and Sripanidkulchai, B. Novel formulation strategies for enhancing oral delivery of methoxyflavones in kaempferia parvoflora by SMEDDS or complexation with 2-hydroxypropylb-cyclodextrin. Int J Pharm. (2013) 445:1–11.
114. Maltais, A, Remondetto, GE, and Subirade, M. Soy protein cold-set hydrogels as controlled delivery devices for nutraceutical compounds. Food Hydrocoll. (2009) 23:1647–53. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.12.006
115. Elzoghby, AO, El-Fotoh, WSA, and Elgindy, NA. Caseinbased formulations as promising controlled release drug delivery systems. J Control Release. (2011) 153:206–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.02.010
116. Piai, JF, Lopes, LC, Fajardo, AR, Rubira, AF, and Muniz, EC. Kinetic study of chondroitin sulphate release from chondroitin sulphate/chitosan complex hydrogel. J Mol Liq. (2010) 156:28–32. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2010.05.017
117. Pereira, R, Mendes, A, and Bartolo, P. Alginate/Aloe vera hydrogel films for biomedical applications. Procedia CIRP. (2013) 5:210–5. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2013.01.042
118. Mitri, K, Shegokar, R, Gohla, S, Anselmi, C, and Muller, RH. Lutein nanocrystals as antioxidant formulation for oral and dermal delivery. Int J Pharm. (2011) 420:141–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.026
119. Teeranachaideekul, V, Souto, EB, Junyaprasert, VB, and Muller, RH. Cetyl-palmitate based NLC for topical delivery of coenzyme Q10- development, physicochemical characterization and in vitro release studies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. (2007) 67:141–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.01.015
120. Tan, B, Liu, Y, Chang, K, Lim, BKW, and Chiu, GNC. Perorally active nanomicellar formulation of quercetin in the treatment of lung cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. (2012) 7:651–61.
121. Shpigelman, A, Israeli, G, and Livney, YD. Thermallyinduced-protein-polyphenol co-assemblies: betaLactoglobulin based nanocomplexes as protective nanovehicles for EGCG. Food Hydrocoll. (2010) 24:735–43. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.03.015
122. Nepal, PR, Han, H, and Choi, H. Enhancement of solubility and dissolution of coenzyme Q10 using solid dispersion formulation. Int J Pharm. (2010) 383:147–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.09.031
123. Weigel, LA, Mauer, LJ, Edgar, KJ, and Taylor, LS. Crystallization of amorphous solid dispersions of resveratrol during preparation and storage–impact of different polymers. J Pharm Sci. (2013) 102:171–84.
124. Rocha, GA, Favaro-Trindade, CS, and Grosso, CRF. Microencapsulation of lycopene by spray drying: characterization, stability and application of microcapsules. Food Bioprod Process. (2012) 90:37–42.
125. Martınez-Sancho, C, Herrero-Vanrell, R, and Negro, S. Vitamin A palmitate and aciclovir biodegradable microspheres for intraocular sustained release. Int J Pharm. (2006) 326:100–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.07.010
126. Zhang, J, and Wang, S. Topical use of coenzyme-Q10-loaded liposomes coated with trimethyl chitosan: tolerance, precorneal retention and anti-cataract effect. Int J Pharm. (2009) 372:66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.01.001
127. Peng, C, Kim, J, and Chauhan, A. Extended delivery of hydrophilic drugs from silicone-hydrogel contact lenses containing vitamin E diffusion barriers. Biomaterials. (2010) 31:4032–47. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.113
128. Zhong, Y, Chiou, Y, Pan, M, and Shahidi, F. Antiinflammatory activity of lipophilic epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) derivatives in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages. Food Chem. (2012) 134:742–8. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.172
129. Chen, W, Park, SK, Yu, W, Xiong, A, Sanders, BG, and Kline, K. Synthesis and screening of novel vitamin E derivatives for anticancer functions. Eur J Med Chem. (2012) 58:72–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.09.045
130. Zhang, Z, Tan, S, and Feng, S. Vitamin E TPGS as a molecular biomaterial for drug delivery. Biomaterials. (2012) 33:4889–906. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.046
131. Singh, BN, et al. EGCG mechanisms and applications. Biochem Pharmacol. (2011) 82:1807–21. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.07.093
132. Goyal, R, Khanna, R, Srivastava, R, et al. Antidiabetic effect of bitter melon: A systematic review. J Integr Med. (2023) 21:1–10.
133. WHO. (2023). Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/global-health-achievements-2023
134. DSHEA. WHO (1994). Available online at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/About/DSHEA_Wording.aspx
135. Onoue, T, Sato, H, Nakamura, T, Noguchi, T, Hidaka, Y, Shirai, N, et al. Deep-sea record of impact approximately unrelated to mass extinction in the Late Triassic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (2012) 109:19134–19139.
136. Losio, MN, Pavoni, E, Bilei, S, Bertasi, B, Bove, D, Capuano, F, et al. Microbiological survey of raw and ready-to-eat leafy green vegetables marketed in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. (2011) 210:88–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.05.026
Glossary
AI - Artificial Intelligence
AMPK - Activated Protein Kinase
CDK - Cyclin-Dependent Kinase
COX-2 - Cyclooxygenase-2
CVD - Cardiovascular Disease
DHA - Docosahexaenoic Acid
DNMT - DNA Methyltransferase
DSHEA - Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act
EGCG - Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate
EPA - Eicosapentaenoic Acid
EFSA - European Food Safety Authority
FDA - Food and Drug Administration
FOS - Fructooligosaccharides
GOS - Galactooligosaccharides
HDAC - Histone Deacetylase
HIF-1α - Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-alpha
IBD - Inflammatory Bowel Disease
IL - Interleukin
iNOS - Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
LOX - Lipoxygenase
MAPK - Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase
MMP - Matrix Metalloproteinase
MS - Multiple Sclerosis
NF-κB - Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells
NK cells - Natural Killer Cells
NCD - Non-Communicable Disease
NOAEL - No Observed Adverse Effect Level
NSAIDs - Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
PUFAs - Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
PI3K/Akt - Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway
RCT - Randomized Controlled Trial
RA - Rheumatoid Arthritis
ROS - Reactive Oxygen Species
SLE - Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
STAT3 - Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3
Th17 - T Helper 17 Cells
T2DM - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
TNF-α - Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
Tregs - Regulatory T Cells
VEGF - Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Keywords: chronic diseases, nutraceuticals, natural compounds, antioxidant, therapeutic potential, functional foods, bioactive compounds, metabolic disorders
Citation: Fatima G, Khan S, Shukla V, Awaida W, Li D and Gushchina YS (2025) Nutraceutical formulations and natural compounds for the management of chronic diseases. Front. Nutr. 12:1682590. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1682590
Edited by:
Vincenzo Piccolo, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyReviewed by:
Yaír Adonaí Sánchez Nuño, University of Guadalajara, MexicoAngela Erna Rossato, University of the Extreme South of Santa Catarina, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Fatima, Khan, Shukla, Awaida, Li and Gushchina. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ghizal Fatima, Z2hpemFsZmF0aW1hOEBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†ORCID: Ghizal Fatima, orcid.org/0000-0001-8516-655X
Sadaf Khan, orcid.org/0009-0000-4650-8385
Vani Shukla, orcid.org/0009-0003-4815-8050
 Ghizal Fatima
Ghizal Fatima Sadaf Khan
Sadaf Khan Vani Shukla
Vani Shukla Wajdy Awaida
Wajdy Awaida Duo Li
Duo Li Yulia Sh Gushchina5
Yulia Sh Gushchina5