- 1 School of Nuclear Science and Technology, University of South China, Hengyang, China
- 2 Institute of Applied Electronics, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, China
FLASH radiotherapy (FLASH-RT) has emerged as a significant area of research in the field of radiotherapy in recent years. This innovative technology delivers ultra-high dose rate radiation in a very short time, effectively damaging tumor cells while minimizing the impact on surrounding normal tissues. Currently, the beams that have been proven to achieve the FLASH effect include electrons, protons, and photons. X-ray FLASH-RT exhibits enhanced penetration capabilities and superior cost-effectiveness. However, the detectors currently used for X-ray FLASH-RT dose rate measurement generally exhibit saturation effects and a limited dose linear response range. In this review, we provide a comprehensive summary of the primary devices used to generate ultra-high dose rate X-rays. Additionally, we classify and describe the reported detectors for monitoring the high-dose rate in X-ray FLASH-RT according to three main types: gaseous detectors, scintillators, and semiconductors. This offers researchers valuable insights and a solid reference for selecting and optimizing detectors to achieve more precise and reliable high-dose rate X-ray measurements in X-ray FLASH-RT. Additionally, it provides significant support for the further development and clinical implementation of FLASH-RT technology.
1 Introduction
In 1959, Dewey and Boag [1] conducted a study demonstrating that the effects of oxygen vary when bacteria are exposed to large pulses of radiation. Specifically, under oxygen-rich conditions, bacteria that are initially highly sensitive to radiation exhibit reduced sensitivity following exposure to high doses of radiation. This study represents the first comprehensive report on findings related to ultra-high dose rate research; however, the underlying phenomenon remained unexplained at that time.
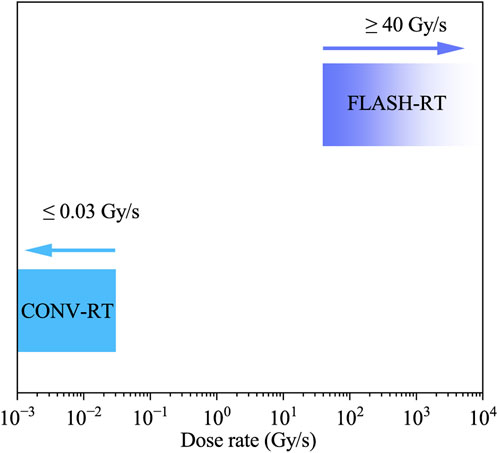
Over the next 50 years, only a limited number of research articles were published on this topic. More recently, advancements in radiation therapy have led to the development of FLASH radiotherapy (FLASH-RT), a novel technique characterized by the delivery of radiation at ultra-high dose rates, typically exceeding 40 Gy/s. In contrast, Conventional Radiotherapy (CONV-RT) delivers radiation at a much lower dose rate of approximately 0.03 Gy/s over a prolonged period.
FLASH-RT is defined by three key parameters: 1) “ultra-high dose rate,” referring to radiation delivery exceeding 40 Gy/s; 2)“high dose,” indicating doses per fraction greater than 10 Gy, significantly exceeding the conventional 1.8–2.0 Gy per fraction; and (3) “short time,” meaning that radiation is delivered in less than 1 s per fraction, as opposed to the several minutes required in conventional radiotherapy.
In 2014, Favaudon et al. [2] conducted a study using a mouse model to investigate the effects of FLASH-RT on the differential responses of normal and tumor tissues. The results demonstrated that FLASH-RT significantly enhanced the differential response between normal and tumor tissues, leading to greater tumor damage while exerting minimal effects on normal tissue. These findings suggest that FLASH-RT holds promise as an effective and safe radiotherapy modality, capable of selectively targeting tumor cells while minimizing damage to normal tissue. This radiobiological advantage distinguishes FLASH-RT from CONV-RT. Unlike CONV-RT, FLASH-RT delivers ultra-high doses in an extremely short time frame, enabling more targeted tumor treatment while reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. As illustrated in Figure 1, this stark contrast in dose rates underlies the therapeutic benefits of FLASH-RT.
The types of radiation beams currently employed in FLASH-RT include electron beams, protons, photons, and heavy ions, each possessing distinct characteristics. The implementation of electron FLASH primarily depends on linear accelerators [3–6] and laser-plasma accelerators [7–10]. However, due to the inherent interaction properties of electrons with matter, controlling the dose distribution of electron beams in the depth direction within the body remains challenging, thereby limiting their therapeutic efficacy for deep-seated tumors [11]. Proton FLASH has been rapidly developed due to its ability to treat deeper tumors due to the Bragg peak effect [12,13]. However, the high cost of proton accelerator limits its widespread clinical application [14].
In 2018, Montay Gruel et al. [15] provided the first evidence that X-rays are capable of inducing the FLASH effect. In this study, whole-brain irradiation was performed with an ultra-high dose rate of 10 Gy (average dose rate 37 Gy/s, slice dose rate 12,000 Gy/s) was conducted. The results demonstrated that this irradiation protocol did not induce memory impairment in mice, mitigated damage to hippocampal cell division, and resulted in reduced reactive astrogliosis. Kilovolt (kV) X-rays generated by synchrotron radiation and X-ray tubes have been employed in clinical X-ray FLASH-RT, but their limited penetration depth, restricts their application to the treatment of shallow tumors [16]. Megavolt (MV) X-rays generated by accelerating electrons to bombard target materials possess high penetration capabilities, rendering them suitable for the treatment of deep-seated tumors. Due to the relatively modest accelerator requirements, this approach presents considerable potential for future advancements in FLASH radiation source development [17].
2 Methodology
In this review, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the current research on FLASH-RT technology and its applications in cancer treatment. The studies included in this review were selected based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, as outlined below.
Figure 2 presents the research trends in FLASH-RT from 2014 to 2024. The data, retrieved from the Web of Science (WOS) database, represent the number of articles published on “ultra-high dose rate” or “FLASH-RT” over this period. Notably, the Google Scholar database, which encompasses non-SCI-indexed and non-English literature, generally returns a greater number of relevant documents than WOS.
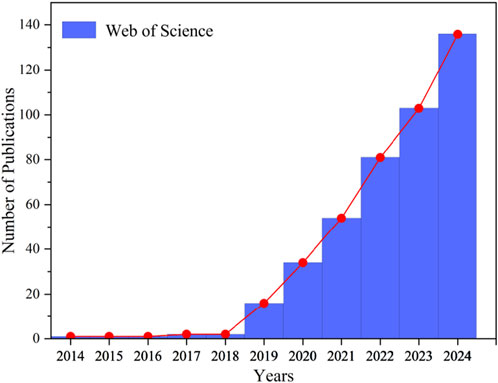
Figure 2. Research trends in FLASH-RT from 2014 to 2024. Articles published between 2014 and 2024 on “ultra-high dose rate” or “FLASH-RT” were retrieved from the Web of Science database.
Figure 2 demonstrates that between 2014 and 2018, research on “ultra-high dose rate” or “FLASH-RT” remained limited. However, in 2019 [18], documented the first reported case of FLASH-RT treatment in a human patient. The patient, suffering from systemic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, had undergone 110 local skin radiotherapy sessions. Given the patient’s poor tolerance to conventional radiotherapy, researchers opted for FLASH-RT as an alternative approach. A skin tumor measuring 3.5 cm in diameter was treated with a specially designed linear accelerator, which delivered a 15 Gy dose within 90 m. As a result, grade 1 dermatitis was observed at 3 weeks, but it quickly disappeared, and the tumor completely responded.
These findings suggest that FLASH-RT is effective in both normal and tumor tissues, further supporting its clinical applicability. This breakthrough is inspiring widespread research on the FLASH effect globally.
3 Device for ultra-high dose rate X-ray FLASH-RT
With the discovery that X-rays can induce the FLASH effect, there has been a growing interest in developing X-ray-based FLASH radiotherapy (FLASH-RT) systems. The key challenge in this field is to achieve ultra-high dose rates while maintaining precise beam control and clinical applicability. In this context, various devices have been explored to generate X-rays suitable for FLASH-RT, including synchrotron radiation sources, linear accelerators, and X-ray tubes.
Synchrotron radiation employs high-energy electron beams that interact with magnetic fields under specific conditions, producing a continuous spectrum of X-rays. In linear accelerators, electrons are accelerated to high energies and then directed onto a target material. The primary mechanism for X-ray production is bremsstrahlung, where the rapid deceleration of electrons as they interact with the target material results in the emission of X-rays. Characteristic X-rays can also be produced, but they are secondary to the bremsstrahlung process. An X-ray tube generates X-rays by accelerating electrons from a heated cathode toward a metal anode, typically tungsten, using a high voltage. Upon collision with the anode, the high-energy electrons are rapidly decelerated, producing X-rays through both Bremsstrahlung (braking radiation) and characteristic radiation (resulting from electron transitions within the target material). These generated X-rays then exit the tube through a window for imaging or analysis.
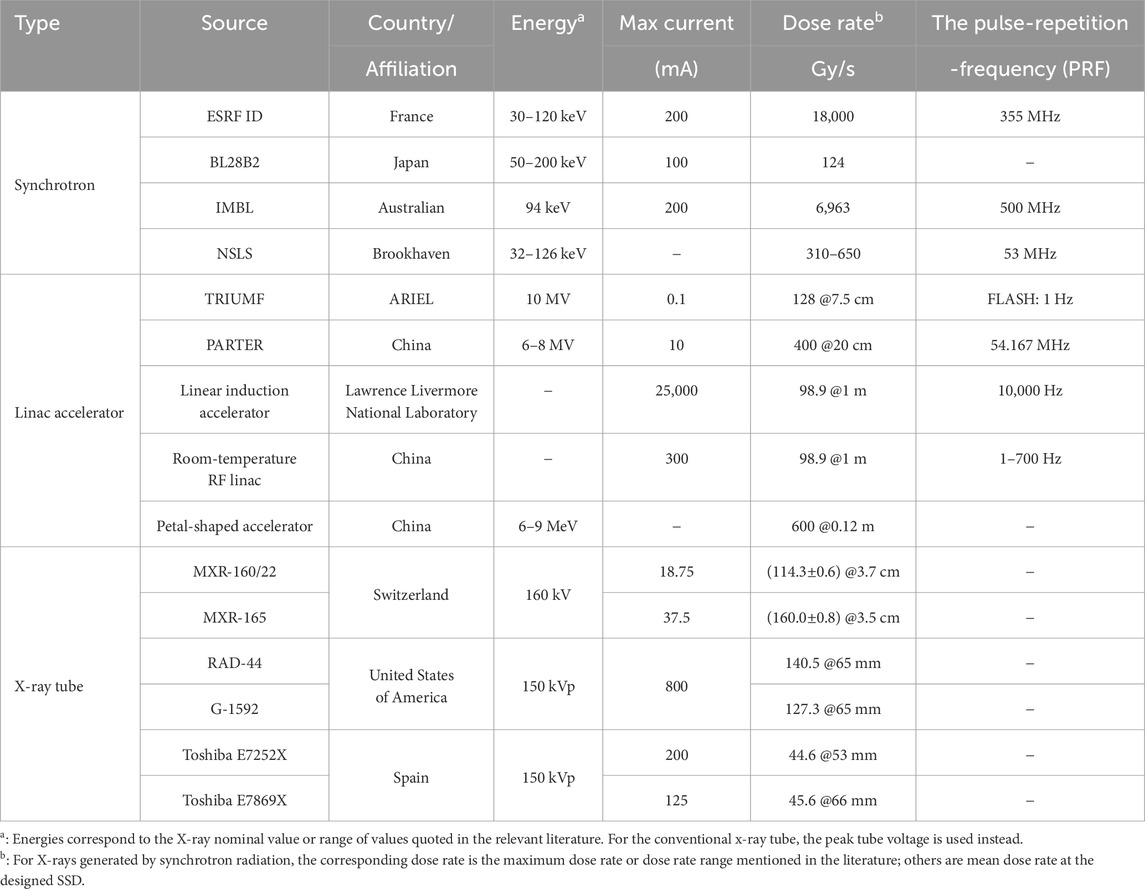
Properly configured conventional X-ray tubes can also fulfill the requirements of FLASH-RT; however, their dose-rate levels are generally lower than those of the other two systems. This subsection provides an overview of the primary devices currently available for generating high-dose-rate X-rays, along with their key characteristics. Table 1 summarizes the devices capable of delivering ultra-high dose rate X-rays.
3.1 Synchrotron radiation
The European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF), situated in Grenoble, France, is renowned as the world’s first high-energy synchrotron radiation source [19]. As a third-generation synchrotron radiation source operating at 6 GeV with a maximum current of 200 mA, the ESRF features the ID17 beamline, specifically dedicated to biomedical research. This beamline is equipped with two experimental stations designed for in vivo and in vitro studies [20]. The X-ray energy produced by the ID17 biomedical beamline, generated by 6 GeV electron bunches circulating at a high frequency of 355 MHz [21], is predominantly distributed within the range of 30 keV–120 keV [22].
In 2018, a study [15] conducted at the ESRF demonstrated, for the first time, that synchrotron X-ray irradiation can induce the FLASH effect. The researchers employed X-rays generated by synchrotron radiation to irradiate the entire brains of mice. During the experiment, the X-ray exposure lasted 0.27 s, resulting in a dose rate of 12,000 Gy/s in a 50
Japan’s third-generation synchrotron radiation facility, the Super Photon Ring with 8 GeV (Spring-8), was established in 1984 and first detected radiation beams in 1997. This facility is specifically designed to support high-precision and high-sensitivity scientific research [23]. The radiation source employed is a broad-spectrum light X-ray bending magnet beam, designated as BL28B2, with an X-ray spectrum ranging from 50–200 keV with a peak around 90 keV. Using an adjustable collimator, the X-ray peak dose rate reached 124 Gy/s and 111 Gy/s for the 100 mm and 20 mm microbeams, respectively [24].
The Imaging and Medicine Beamline (IMBL) at the Australian Synchrotron Radiation Facility functions as a dedicated an X-ray platform for both medical imaging and therapeutic applications [25]. The facility is equipped with a 3 GeV storage ring, an electron beam current of 200 mA, and a pulse repetition rate of 500 MHz [26]. The average energy was measured at 94 keV [27]. Furthermore, the dose rate measured by the PinPoint IC detector in the Al-Al filter configuration at a depth of 15 mm on a water-equivalent plastic phantom was recorded at 6,963 Gy/s, as reported in [28].
The National Synchrotron Light Source at Brookhaven National Laboratory (NSLS) in the United States generates X-rays with a high trigger frequency with a high frequency (53 Hz), with a pulse width of 2 ns. The beam center spacing is 75 or 200
3.2 Linear accelerator
The ARIEL facility in Canada, a significant expansion of TRIUMF’s ISAC facility, is built around a 50 MeV, 10 mA continuous wave electron linear accelerator [30]. This facility is the first X-ray FLASH source in North America and the first globally to achieve a clinically relevant energy of 10 MV, establishing itself as a crucial experimental platform for FLASH radiobiology research [17]. In 2024, TRIUMF successfully developed and characterized the first irradiation platform capable of delivering a 10 MV X-ray beam at an ultra-high dose rate, achieving an average dose rate of 82.6 Gy/s at a depth of 1 cm with a peak beam current of 100
In 2020, Yang Yiwei, a member of our team, collaborated with the research group led by Wu Dai and the team headed by Du Xiaobo from Mianyang Central Hospital. Together, they successfully developed the world’s first high-energy X-ray photon FLASH-RT verification platform, representing a significant milestone in this field. This achievement represents important progress in the realm of FLASH-RT technology. This pioneering platform, known as the “Platform for Advanced Radiotherapy Research (PARTER)”, represents the first successful validation of the high-energy X-ray FLASH effect. It incorporates a superconducting electron accelerator integrated with a terahertz free electron laser system at the China Academy of Engineering Physics, capable of delivering an electron beam energy of 6–8 MeV [31]. The facility achieves a maximum average current exceeding 6 mA, with the electron macro-pulse comprising millions of micro-pulses, each lasting approximately 3–5 ps, and a repetition rate of 54.167 MHz. At a source-to-surface distance (SSD) of 20 cm, the maximum average dose rate reaches approximately 400 Gy/s [32].
In 2021, Sampayan et al. [33] explored the feasibility of using the linear induction accelerator in FLASH-RT. The Experimental Test Accelerator-II accelerated an electron beam to 6.5 MeV, which subsequently impinged on a tantalum (Ta) target, producing induced X-ray radiation. At a source-to-skin distance of 1 m, the recorded surface dose rate was 98.9 Gy/s.
In 2024, the Department of Engineering Physics at Tsinghua University developed an ultra-high dose rate, high-energy X-ray radiation platform based on an S-band (2.856 GHz) backward traveling wave electron linear accelerator. This platform is designed to investigate the feasibility of developing a compact and cost-effective clinical FLASH-RT system that can be accommodated in standard hospital treatment rooms. The linear accelerator generates an 11 MeV electron beam with a pulse current of 300 mA, resulting in an average beam power of 29 kW. The conversion system is capable of sustaining the high beam power for a maximum irradiation for the maximum duration of 0.75 s. When employing a planar filter, the maximum average dose rate measured at different SSD exhibits significant variation: exceeding 80 Gy/s at an SSD of 50 cm and surpassing 45 Gy/s at an SSD of 67.9 cm. All measurements were performed at a depth of 2.1 cm in a water phantom [34].
The petal-shaped electron irradiation accelerator offers several advantages, including stable performance, rapid beam adjustment, high beam power, and the ability to simultaneously provide multiple energy options [35]. Recently, researchers have increasingly focused on the petal-shaped accelerator for the implementation of FLASH-RT. In 2024, the China Academy of Engineering Physics reported achieving an average dose rate exceeding 600 Gy/s at a distance of 0.12 m using X-ray equipment designed based on high-power petal cyclotron technology [36]. The Institute of Modern Physics of China is also actively engaged in a similar design. These developments highlights a potential trend in the future advancement of FLASH-RT technology.
3.3 X-ray tube
A study by Bazalova-Carter et al. in 2019 investigated the feasibility of using conventional high-power X-ray tubes MXR-160/22 and MXR-165, in FLASH-RT experiments [16]. The simulation results revealed that the 160 kV MXR-160/22 and MXR-165 X-ray tubes achieved dose rates of (114.3
In 2021, Rezaee et al. introdeced a novel self-shielded X-ray irradiation box system [37]. This system incorporates two high-capacity radiographic and fluoroscopic X-ray sources utilizing rotating anode technology, namely, the RAD-44 and G-1592 models. These X-ray tubes can operate in radiographic or fluoroscopic mode. They deliver radiation doses in the form of single or multiple pulses at a peak voltage of 150 kV. Moreover, they are configured in a parallel-opposing arrangement. The researchers used the GEANT4 Monte Carlo simulation platform to evaluate the dosimetric characteristics of these X-ray sources. They assessed the performance under both FLASH and conventional dose-rate irradiation conditions. The dose and dose rate of a single RAD-94 X-ray source were experimentally validated in a solid water phantom using Gafchromic film, and simulation results were compared to experimental data to confirm the validity of the Monte Carlo code and model. The study’s findings demonstrated that the system is capable of delivering doses exceeding 50 Gy at ultra-high dose rates ranging from 40 to 240 Gy/s with a 20 mm thick water-equivalent medium. Furthermore, the system achieves a uniform depth dose rate variation of
In 2023, Espinosa-Rodriguez et al. introduced a novel small animal X-ray irradiator [38]. This irradiator is based on a conventional imaging X-ray tube designed for preclinical research and is housed within a shielded cabinet, making it cost-effective and suitable for integration into existing laboratory environments. The study focused on analyzing of two conventional 150 kVp X-ray tubes, with the dose rate and dose uniformity being evaluated using Gafchromic film. Monte Carlo simulations were used to model the irradiator, allowing for the determination of the tube’s efficiency and dose rate, both with and without additional filters. At 150 kVp and a distance of 20 cm, the conventional dose rates ranged from 0.5 to 1 Gy/min without additional filters. By maximizing the tube power and positioning the sample in close proximity to the source, FLASH irradiation could be achieved, resulting in dose rates exceeding 40 Gy/s and a 10 Gy dose delivery. The study demonstrated that a Toshiba E7252X X-ray tube could deliver a dose rate of 44.6 Gy/s for a single 6 Gy fraction at a distance of 53 mm from the source, while a Toshiba E7869X X-ray tube could deliver a dose rate of 45.6 Gy/s for the same fraction at a distance of 60 mm. The researchers are currently developing a new prototype using a 50 kW high voltage generator from SEDECAL, coupled with energy storage capabilities and a custom-designed X-ray tube and generator assembly. This advancement will allow the exit window to be positioned within 3 cm of the focal point, facilitating dose rates exceeding 100 Gy/s.
4 Dosimetry
In FLASH-RT, achieving ultra-high dose rates is a critical factor for its effectiveness. However, this presents significant challenges for dosimetry, as existing detectors may not be capable of accurately measuring the rapidly delivered radiation doses. To ensure precise dose delivery and effective treatment, dosimetries used in FLASH-RT must fulfill specific requirements. These include the ability to respond quickly to high dose rates (on the order of 40 Gy/s or higher), minimal energy dependence, and high accuracy across a broad dose range. Additionally, dosimetry should be capable of operating in the presence of high radiation flux without significant damage or degradation of their performance.
Despite advances in detector technology, existing dosimetries often face limitations when employed in FLASH environments. Traditional dosimetries, such as ionization chambers, scintillation detectors, and thermoluminescent dosimetries, may not be fast enough to capture the brief pulses of radiation delivered in FLASH-RT. Furthermore, many of these detectors exhibit energy and dose rate dependencies that limit their accuracy and reliability in ultra-high dose rate scenarios. As a result, there is an urgent need for the development of specialized detectors capable of addressing these challenges while ensuring precise, real-time dose measurement during FLASH treatment.
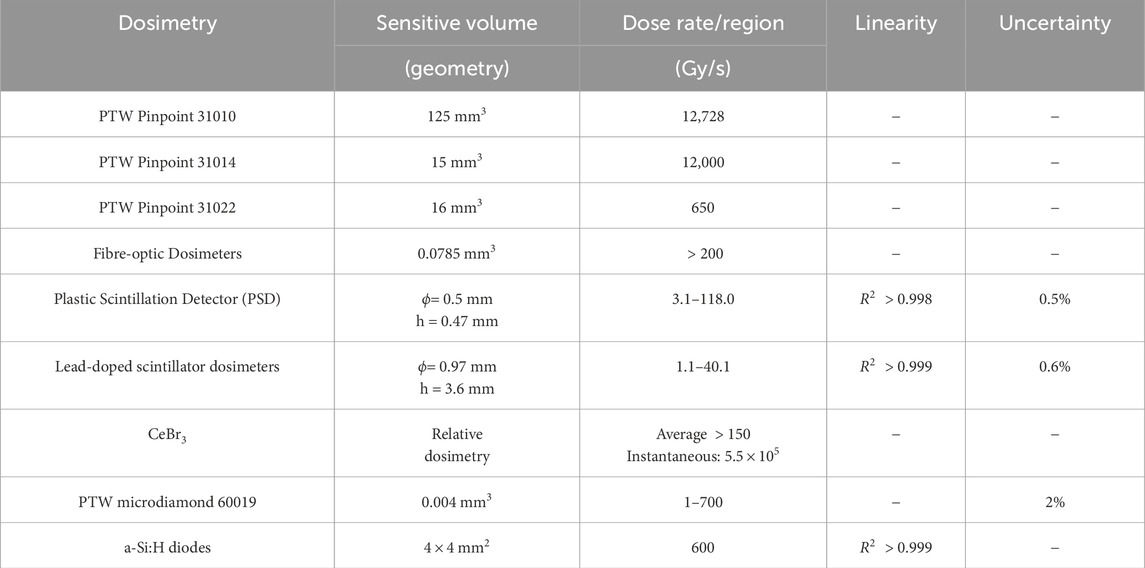
To address these challenges, detectors employed for ultra-high dose rate X-ray measurement can be classified into three categories based on their working medium and detection mechanism: gaseous detectors, scintillation detectors, and semiconductor detectors. This section will provide an overview of the research advancements in each of these detector types, focusing on their performance, advantages, and limitations in ultra-high dose rate X-ray measurements. The detectors that have been used for ultra-high dose rate X-ray dose measurements are summarized in Table 2.
4.1 Gaseous detectors
Gaseous detectors function based on a well - defined principle. Upon irradiation, ionization of the gaseous medium within the detector forms ion pairs. These ion pairs then migrate within the electric field of the detector’s sensitive volume, giving rise to detectable signals.
In 2011, Prezado et al. [39] assessed the dosimetric characteristics of microbeam radiation therapy (MBRT) at the ESRF ID17 beamline. The PTW Semiflex 31010 ionization chamber, which is made of 99.98% pure aluminum and has a sensitive volume of 125
The PTW Pinpoint 31014 ionization chamber, which uses aluminum as the central electrode, has a sensitive volume of 15
The PTW Pinpoint 31022 ionization chamber, featuring a ventilated cylindrical design and a center of electrode made of 99.98% pure aluminum [43], has a radius of 1.45 mm, a length of 2.9 mm, and a sensitive volume of 16
4.2 Scintillation detectors
In radiation therapy, scintillation detectors are commonly employed due to their resistance to radiation damage and insensitivity to temperature variations. These detectors detect radiation by utilizing the flashes generated by ionizing radiation in materials [44]. Scintillator optical fibers have drawn considerable attention due to their advantages such as water-isotropy, radiation hardness, and energy independence [45,46].
In 2019, Archer James et al. [47] conducted a study characterizing a novel dosimetry, the plastic scintillator fiber optic detectors (FODs), at the Australian Synchrotron. This detector utilizes BC-400 plastic scintillator, which exhibits favorable properties including water equivalence, radiation hardness, and energy independence, making it well-suited for dose monitoring in microbeam radiation therapy. The plastic scintillator fiber optic detector consists of a BC-400 plastic scintillator with a thickness of
Cecchi Daniel D et al. [48] utilizd an MRX-160/22 X-ray tube from Comet (Flamatt, Switzerland) and characterized it using a Hyperscint PSD probe. The core component of the probe is a polystyrene scintillator with a diameter of 0.5 mm and a length of 0.47 mm. This scintillator is embedded in a PMMA optical fiber and positioned 5 mm from the beryllium window in the X-ray tube. The beryllium window serves to separate the internal and external and environments of the tube, maintaining the vacuum state while allowing the transmission of X-ray. The study found that at a tube voltage of 80 kVp, the dose rate measured by the PSD exhibited a linear respond
The fiber optic sensor developed by O’Keeffe et al., utilizing the inorganic scintillating material cerium-doped dysprosium oxide
Alexander et al. [55] utilized an MRX-160/22 (Comet, Flamatt, Switzerland) X-ray tube to generate X-rays and investigated four plastic scintillator dosimeters with different compositions. These included BCF-10, a pure plastic scintillator primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen, as well as plastic scintillators doped with 0.5%, 1.4%, and 5% lead. The results showed that plastic scintillators containing 5% lead were capable of absorbing higher dose rates and exhibited independence of dose rate range of 1.1–40.1 Gy/s. Furthermore, the dose measured by the 5% lead-doped scintillation detector closely matched the water simulation results, with an error margin within 0.6%. These lead-doped scintillators demonstrated minimal dependence on dose rate and hold promise as accurate real-time dosimeters for measuring FLASH-RT X-ray beams.
Simultaneously, one of our team members, Yang et al. [32] employed
4.3 Semiconductor detectors
Semiconductor detectors operate by utilizing the interaction between radiation and semiconductors to generate free electrons and holes. These charge carriers are driven by an external electric field, generating current pulses. The electrical signals are then processed and analyzed to extract information on radiation energy.
Livingstone et al. [56,57] investigated the potential of the PTW microdiamond 60019 synthetic single-crystal diamond detector for dosimetry in synchrotron radiation and microbeam radiotherapy. Designed specifically for small-field dosimetry, the detector features a cylindrical active volume of 0.004
Matthew et al. [28] explored the suitability of hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) diodes for dose measurement and beam monitoring in ultra-high dose rate X-ray environments, specifically focusing on X-rays generated by synchrotron radiation facilities. The a-Si:H diode used in the study features a planar barrier structure with an electron-selective contact layer (either
Each diode consists of four
5 Future outlook
When measuring dose rates under ultra-high dose rate X-ray conditions, the performance of various detectors varies significantly. Ionization chambers, such as PTW Semiflex 31010 [39,40], PTW Pinpoint 31014 [41,42], and PTW Pinpoint 31022 [32,43] are commonly used for the such measurements. These ionization chambers, typically featuring a small-volume design with an aluminum central electrode, are prone to ion recombination effects due to the ultra-high dose rates delivered in extremely short time frames. As a results, correction factors must be applied, limiting their utility in ultra-high dose rate X-ray measurements [58,59]. In contrast, detectors that coupling scintillating materials with optical fibers exhibit a good linear response under X-ray FLASH-RT conditions. However, their linearity at higher dose rates needs further validation. Challenges such as PDD (percent depth dose) deviation, angular dependence, and the Cherenkov effect remain to be addressed. Optimized designs and correction methodologies tailored for clinical applications are essential [60]. Semiconductor detectors, such as the PTW microdiamond 60019 synthetic single-crystal diamond detectors and hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) diodes, demonstrate an excellent linear response in ultra-high dose rate X-ray environments. However, saturation effects may occur when operating beyond a certain dose rate range.
In high dose rate measurements for electron, proton, and X-ray FLASH, detectors typically encounter challenges, including ion recombination effects and saturation effects. To accurately capture dose fluctuations over short time, detector must have fast response, linear dose response, high sensitivity, and accuracy [61–63]. Insight from existing research on electron, proton, and heavy-ion FLASH environments can be leveraged to drive advancements in detector performance under ultra-high dose rate X-ray conditions.
5.1 Gaseous detectors
In the study of electron FLASH dose measurement, both Gómez et al. [64] and Liu K. et al. [34] focused on the development and optimization of ultra-thin parallel-plate ionization chambers. Gómez et al. enhanced charge collection efficiency (99%) and improved the precision of ion recombination correction factors at ultra-high dose rates by employing small electrode spacing (0.27 mm and 0.25 mm) and non-tissue-equivalent materials. Similarly, Liu K. et al. Increased the sensitivity of their design to ultra-high dose rate beams by further reducing the electrode spacing to 0.1 mm and optimizing the bias voltage, thus enabling accurate detection of transient dose rate fluctuations. In proton FLASH dosimetry, Lourenco et al. [65] validated the accuracy of a small-gap ionization chamber for ultra-fast proton beam scanning radiotherapy. In carbon ion FLASH therapy, Xinle Lang et al. [66] developed a low-pressure ionization chamber utilizing nitrogen, which demonstrated excellent dose linearity under various pressure conditions and proved effective for real-time dose monitoring.
Previous studies have demonstrated that reducing the electrode gap, increasing the bias voltage, and employing a low-pressure ionization chamber can substantially improve the performance of gaseous detectors under ultra-high dose rate conditions. These approaches improve both the response speed and measurement precision of the detector. Future research could focus on developing new electrode materials to enhance stability and radiation resistance. Additionally, it can focus on optimizing the ionization chamber structure, such as further reducing the electrode gap and improving the electric field distribution. However, there are still challenges in fabricating detectors with high repeatability and even thinner electrodes.
5.2 Scintillation detectors
In 2022, Vanreusel et al. [67] conducted an initial investigation into the performance of point detectors made from various scintillating materials, including
In 2022, Matteo Morrocchi et al. [68] evaluated the potential of scintillators for high dose rate FLASH-RT. Their study demonstrated that both the plastic scintillator EJ212 and the LYSO detectors exhibited excellent performance under ultra-high dose rates. In 2024, Vanreusel et al. [69] introduced the ImageDosis system, which integrates a scientific camera with a 12% doped
Moreover, Baikalov et al. [70] characterized the Hyperscint RP-FLASH system (MedScint, Quebec City, Canada). This system integrates a plastic scintillator probe with a cooled two-dimensional electrical detector array, enabling real-time, millisecond-scale dose measurements across a dose rate range of 1.8–1,341 Gy/s.
Current research demonstrate that scintillator-fiber coupled detectors perform exceptionally well in electron, proton, and high-energy X-ray FLASH applications. In electron FLASH studies, the implementation of point detectors has introduced a novel approach to dose measurement in ultra-high dose rate high-energy X-ray FLASH. By utilizing diverse scintillating materials and optimizing system designs, scintillation detectors can achieve a remarkable linear response and high spatial resolution under ultra-high dose rate conditions. Future research should concentrate on developing new scintillating materials, improving system design, and enhancing the real-time response capability and measurement accuracy of detectors.
5.3 Semiconductor detectors
The study by Kranzer et al. [71] demonstrated that the microDiamond detector T60019 shows a nonlinear response and saturation behavior at ultra-high dose rates. However, its linear range can be extended by adjusting the sensitivity and series resistance. Rahman et al. [72] found that the commercial SNC 1118 detector exhibited good linear response and long-term stability in a 10 MeV ultra-high dose rate electron beam environment. This was particularly evident in the dose rate range of 30–180 Gy/s. SiC detectors with PIN structure also display high temporal resolution and good linear response in ultra-high dose rate electron beam environments [73–75]. Meanwhile, thin silicon sensors have demonstrated the feasibility of monitoring in high dose rate environments [76,77].
Based on these findings, future research should focus on optimizing detector designs to enhance performance in ultra-high dose rat environments. For instance, the linear response range can be extended, and nonlinear and saturation effects can be minimized by adjusting sensitivity and series resistance. Additionally, the development of detectors with higher temporal resolution is crucial. In particular, optimizing the PIN structure of SiC detectors could meet the requirements of fast pulse measurements. The successful application of these detectors in electron and proton FLASH offers a promising direction for advancing ultra-high dose rate X-ray measurement.
6 Conclusion
FLASH-RT exhibits significant potential in cancer treatment, effectively destroying tumor cells while minimizing damage to surrounding normal tissues. Since the first human patient underwent FLASH-RT in 2019, research and clinical trials in this field have rapidly expanded worldwide.
Ultra-high dose rate X-rays have demonstrated efficacy in treating deep-seated tumors while offering improved cost-effectiveness. This article reviews the current technologies for generating ultra-high dose rate X-rays, summarizes suitable detectors for X-ray dose rate measurement, and discusses existing issues and challenges.
The primary challenges in ultra-high dose rate X-ray dosimetry include ion recombination and saturation effects in detectors. Future research on gaseous detectors will emphasize the development of novel electrode materials and the optimization of ionization chamber designs. However, challenges persist in fabricating detectors with high repeatability and ultra-thin electrodes. Scintillator-fiber coupled detectors have demonstrated promising performance in FLASH applications, with ongoing efforts directed toward developing novel scintillating materials, improving system design, and enhancing real-time response and measurement accuracy. Research on SiC detectors prioritizes design optimization to extend the linear response range, minimize nonlinear and saturation effects, and enhance temporal resolution through PIN structure refinement.
The technology surrounding FLASH-RT is expected to continue attracting attention in cancer treatment and to see wider clinical application. Future research should focus on optimizing equipment and technology to enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. Additionally, it is crucial to strengthen research on dose rate measurement and to develop more accurate and reliable detectors to ensure safety and effectiveness during treatment. We believe that, with ongoing research, FLASH-RT will provide more effective and safer treatment options for cancer patients, significantly contributing to the advancement of cancer care and potentially transforming the overall landscape of cancer treatment.
Author contributions
LT: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SF: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. YY: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. BZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No. 2024RC3205), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Contracts No. 2024JJ2044), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos 12375296 and 12375318).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the member of the Chinese Engineering Academy Xiao-Ping Ouyang for inspiration and professional support in this radiation detectors review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Dewey DL, Boag JW. Modification of the oxygen effect when bacteria are given large pulses of radiation. Nature (1959) 183:1450–1. doi:10.1038/1831450a0
2. Favaudon V, Caplier L, Monceau V, Pouzoulet F, Sayarath M, Fouillade C, et al. Ultrahigh dose-rate flash irradiation increases the differential response between normal and tumor tissue in mice. Sci translational Med (2014) 6:245ra93. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3008973
3. Jaccard M, Durán MT, Petersson K, Germond JF, Liger P, Vozenin MC, et al. High dose - per - pulse electron beam dosimetry: commissioning of the oriatron ert6 prototype linear accelerator for preclinical use. Med Phys (2018) 45:863–74. doi:10.1002/mp.12713
4. Vozenin MC, De Fornel P, Petersson K, Favaudon V, Jaccard M, Germond JF, et al. The advantage of flash radiotherapy confirmed in mini - pig and cat - cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res (2018) 25:35–42. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-17-3375CCR-17-3375
5. Lempart M, Blad B, Adrian G, Bäck S, Knöös T, Ceberg C, et al. Modifying a clinical linear accelerator for delivery of ultra - high dose rate irradiation. Radiother Oncol (2019) 139:40–5. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.01.031
6. Montay Gruel P, Petersson K, Jaccard M, Boivin G, Germond JF, Petit B, et al. Irradiation in a flash: unique sparing of memory in mice after whole brain irradiation with dose rates above 100gy/s. Radiother Oncol (2017) 124:365–9. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2017.05.003
7. Bazalova Carter M, Liu M, Palma B, Dunning M, McCormick D, Hemsing E, et al. Comparison of film measurements and Monte Carlo simulations of dose delivered with very high - energy electron beams in a polystyrene phantom. Med Phys (2015) 42:1606–13. doi:10.1118/1.4914371
8. Jaroszynski DA, Bingham R, Brunetti E, Ersfeld B, Gallacher J, van der Geer B, et al. Radiation sources based on laser–plasma interactions. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci (2006) 364:689–710. doi:10.1098/rsta.2005.1732
9. Lundh O, Rechatin C, Faure J, Ben Ismaïl A, Lim J, De Wagter C, et al. Comparison of measured with calculated dose distribution from a 120 - mev electron beam from a laser - plasma accelerator. Med Phys (2012) 39:3501–8. doi:10.1118/1.4719962
10. Kokurewicz K, Brunetti E, Welsh GH, Wiggins SM, Boyd M, Sorensen A, et al. Focused very high - energy electron beams as a novel radiotherapy modality for producing high - dose volumetric elements. Sci Rep (2019) 9:10837. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-46630-w
11. Yang Y, Shi C, Chen CC, Tsai P, Kang M, Huang S, et al. A 2d strip ionization chamber array with high spatiotemporal resolution for proton pencil beam scanning flash radiotherapy. Med Phys (2022) 49:5464–75. doi:10.1002/mp.15706
12. Van Marlen P, Dahele M, Folkerts M, Abel E, Slotman BJ, Verbakel WFAR. Bringing flash to the clinic: treatment planning considerations for ultrahigh dose - rate proton beams. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2019) 106:621–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.11.011
13. Christensen JB, Togno M, Nesteruk KP, Psoroulas S, Meer D, Weber DC, et al. al 2 o 3: c optically stimulated luminescence dosimeters (oslds) for ultra - high dose rate proton dosimetry. Phys Med Biol (2021) 66:085003. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/abe554
14. Tan Y, Zhou S, Haefner J, Chen Q, Mazur TR, Darafsheh A, et al. Simulation study of a novel small animal flash irradiator (safi) with integrated inverse - geometry ct based on circularly distributed kv x - ray sources. Sci Rep (2023) 13:20181. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-47421-0
15. Montay Gruel P, Bouchet A, Jaccard M, Patin D, Serduc R, Aim W, et al. X - rays can trigger the flash effect: ultra - high dose - rate synchrotron light source prevents normal brain injury after whole brain irradiation in mice. Radiother Oncol (2018) 129:582–8. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2018.08.016
16. Bazalova Carter M, Esplen N. On the capabilities of conventional x-ray tubes to deliver ultra-high (flash) dose rates. Med Phys (2019) 46:5690–5. doi:10.1002/mp.13858
17. Esplen N, Egoriti L, Planche T, Rädel S, Koay HW, Humphries B, et al. Dosimetric characterization of a novel uhdr megavoltage x - ray source for flash radiobiological experiments. Sci Rep (2024) 14:822. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-50412-w
18. Bourhis J, Sozzi WJ, Jorge PG, Gaide O, Bailat C, Duclos F, et al. Treatment of a first patient with flash - radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol (2019) 139:18–22. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2019.06.019
19. Buras B, Materlik G. The european synchrotron radiation facility: an overview. Nucl Instrum Meth A (1986) 246:21–31. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(86)90038-0
20. Bravin A. The biomedical programs at the id17 beamline of the european synchrotron radiation facility. In: Brilliant light in life and materials sciences, NATO advanced studies institute, series B: Physics and biophysics. Netherlands: Springer (2007). p. 225–39.
21. Serduc R, Vérant P, Vial JC, Farion R, Rocas L, Rémy C, et al. In vivo two - photon microscopy study of short - term effects of microbeam irradiation on normal mouse brain microvasculature. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2005) 64:1519–27. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.11.047
22. Fernandez Palomo C, Nikitaki Z, Djonov V, Georgakilas AG, Martin OA. Non - targeted effects of synchrotron radiation: lessons from experiments at the australian and european synchrotrons. Appl Sci (2022) 12:2079. doi:10.3390/app12042079
23. Shimomura O, Tsuji K, Hamaya N. The spring - 8 project and the high pressure group in Japan. High Press Res (1992) 8:703–10. doi:10.1080/08957959208206323
24. Uyama A, Kondoh T, Nariyama N, Umetani K, Fukumoto M, Shinohara K, et al. A narrow microbeam is more effective for tumor growth suppression than a wide microbeam: an in vivo study using implanted human glioma cells. J Synchrotron Radiat (2011) 18:671–8. doi:10.1107/S090904951101185X
25. Stevenson AW, Crosbie JC, Hall CJ, Häusermann D, Livingstone J, Lye JE. Quantitative characterization of the x - ray beam at the australian synchrotron imaging and medical beamline (imbl). J Synchrotron Radiat (2017) 24:110–41. doi:10.1107/S1600577516015563
26. Dowd R, LeBlanc G, Zingre K. Commissioning and operation of the 500mhz storage ring rf system for the australian synchrotron. Nucl Instrum Meth A (2008) 592:224–9. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2008.04.037
27. Archer J, Li E, Petasecca M, Stevenson A, Livingstone J, Di Puglia A, et al. Synchrotron x - ray microbeam dosimetry with a 20 micrometre resolution scintillator fibre - optic dosimeter. J Synchrotron Radiat (2018) 25:826–32. doi:10.1107/S1600577518003016
28. Large MJ, Bizzarri M, Calcagnile L, Caprai M, Caricato AP, Catalano R, et al. Hydrogenated amorphous silicon high flux x - ray detectors for synchrotron microbeam radiation therapy. Phys Med Biol (2023) 68:135010. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/acdb43
29. Slatkin DN, Spanne P, Dilmanian FA, Gebbers JO, Laissue JA. Subacute neuropathological effects of microplanar beams of x - rays from a synchrotron wiggler. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1995) 92:8783–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.19.8783
30. Koveshnikov A, Bylinskii I, Hodgson G, Koscielniak S, Nagimov R, Yosifov D. Integration and commissioning of the ariumf e - linac cryogenic system at triumf. Phys Proced (2015) 67:857–62. doi:10.1016/j.phpro.2015.06.144
31. Gao F, Yang YW, Zhu HY, Wang JX, Xiao DX, Zhou Z, et al. First demonstration of the flash effect with ultrahigh dose - rate high - energy x - rays. Radiother Oncol (2022) 166:44–50. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2021.11.004
32. Yang YW, Wang JX, Gao F, Liu Z, Dai TZ, Zhang HW, et al. Flash radiotherapy using high - energy x - rays: current status of parter platform in flash research. Radiother Oncol (2023) 109967:109967. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2023.109967
33. Sampayan SE, Sampayan KC, Caporaso GJ, Chen YJ, Falabella S, Hawkins SA, et al. Megavolt bremsstrahlung measurements from linear induction accelerators demonstrate possible use as a flash radiotherapy source to reduce acute toxicity. Sci Rep (2021) 11:17104. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95807-9
34. Liu FC, Shi JR, Zha H, Li GH, Li A, Gu WH, et al. Development of a compact linear accelerator to generate ultrahigh dose rate high-energy x-rays for flash radiotherapy applications. Med Phys (2023) 50:1680–98. doi:10.1002/mp.16199
35. Pottier J. A new type of rf electron accelerator: the rhodotron. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B (1989) 40:943–5. doi:10.1016/0168-583X(89)90512-0
36. Liao SQ, He XZ, Yang L, Tang R, Wei T, Zhang Z, et al. Study on the design of x - ray flash - rt equipment with high power petal accelerator. China Med Equipment (2024) 12(28):21–3. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-8270.2024.01.004
37. Rezaee M, Iordachita I, Wong JW. Ultrahigh dose - rate (flash) x - ray irradiator for pre - clinical laboratory research. Phys Med Biol (2021) 66:095006. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/abf2fa
38. Espinosa Rodriguez A, Villa Abaunza A, Diaz N, Pérez Díaz M, Sánchez Parcerisa D, Udías J, et al. Design of an x - ray irradiator based on a standard imaging x - ray tube with flash dose - rate capabilities for preclinical research. Radiat Phys Chem (2023) 206:110760. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2023.110760
39. Prezado Y, Martinez Rovira I, Thengumpallil S, Deman P. Dosimetry protocol for the preclinical trials in white - beam minibeam radiation therapy. Med Phys (2011) 38:5012–20. doi:10.1118/1.3608908
40. Klimanov VA, Kirpichev YS, Serikbekova ZK, Belousov AV, Krusanov GA, Walwyn Salas G, et al. Monte - carlo calculation of output correction factors for ionization chambers, solid - state detectors, and ebt3 film in small fields of high - energy photons. J Appl Clin Med Phys (2022) 24:e13753. doi:10.1002/acm2.13753
41. Muir BR, Rogers DW. The central electrode correction factor for high - z electrodes in small ionization chambers. Med Phys (2011) 38:1081–8. doi:10.1118/1.3532818
42. Agostinelli S, Garelli S, Piergentili M, Foppiano F. Response to high - energy photons of ptw31014 pinpoint ion chamber with a central aluminum electrode. Med Phys (2008) 35:3293–301. doi:10.1118/1.2940190
43. Silvestre Patallo I, Carter R, Maughan D, Nisbet A, Schettino G, Subiel A. Evaluation of a micro ionization chamber for dosimetric measurements in image - guided preclinical irradiation platforms. Phys Med Biol (2021) 66:245012. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ac3b35
44. Beaulieu L, Beddar S. Review of plastic and liquid scintillation dosimetry for photon, electron, and proton therapy. Phys Med Biol (2016) 61:R305–43. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/61/20/R305
45. Beddar AS, Mackie TR, Attix FH. Water - equivalent plastic scintillation detectors for high - energy beam dosimetry: I. physical characteristics and theoretical consideration. Phys Med Biol (1992) 37:1883–900. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/37/10/006
46. Beddar AS, Mackie TR, Attix FH. Water - equivalent plastic scintillation detectors for high - energy beam dosimetry: ii. properties and measurements. Phys Med Biol (1992) 37:1901–13. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/37/10/007
47. Archer J, Li E, Davis J, Cameron M, Rosenfeld A, Lerch M. High spatial resolution scintillator dosimetry of synchrotron microbeams. Sci Rep (2019) 9:6873. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-43349-6
48. Cecchi DD, Therriault Proulx F, Lambert Girard S, Hart A, Macdonald A, Pfleger M, et al. Characterization of an x-ray tube-based ultrahigh dose-rate system for in vitro irradiations. Med Phys (2021) 48:7399–409. doi:10.1002/mp.15234
49. O’Keeffe S, Grattan M, Hounsell A, McCarthy D, Woulfe P, Cronin J, et al. Radiotherapy dosimetry based on plastic optical fibre sensors. In: Proceedings of the fifth European Workshop on optical fibre sensors (krakow, Poland), 18 (2013).
50. Alharbi M, Gillespie S, Woulfe P, McCavana P, O’Keeffe S, Foley M. Dosimetric characterization of an inorganic optical fiber sensor for external beam radiation therapy. IEEE Sensors J (2018) 19:2140–7. doi:10.1109/jsen.2018.28854092018.2885409
51. Alharbi M, Martyn M, O’Keeffe S, Therriault Proulx F, Beaulieu L, Foley M. Benchmarking a novel inorganic scintillation detector for applications in radiation therapy. Phys Med (2019) 68:124–31. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2019.11.018
52. Byrne K, Alharbi M, Esplen N, Woulfe P, O’Keeffe S, Bazalova Carter M, et al. Initial evaluation of the performance of novel inorganic scintillating detectors for small animal irradiation dosimetry. IEEE Sens J (2020) 20:4704–12. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2020.2964989
53. Shaharuddin S, Hart A, Cecchi D, Bazalova Carter M, Foley M. Real - time dosimetry of ultrahigh dose - rate x - ray beams using scintillation detectors. In: 2021 IEEE sensors. Sydney, Australia (2021). p. 1–4.
54. Shaharuddin S, Hart A, Bazalova Carter M, Beaulieu L, Giguere C, Kleefeld C, et al. Evaluation of scintillation detectors for ultrahigh dose - rate x - ray beam dosimetry. SPIE PHOTONICS EUROPE (Strasbourg, France) (2022) 170–7. doi:10.1117/12.2621591
55. Hart A, Cecchi D, Giguère C, Larose F, Therriault Proulx F, Esplen N, et al. Lead - doped scintillator dosimeters for detection of ultrahigh dose - rate x - rays. Phys Med Biol (2022) 67:105007. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ac69a5
56. Livingstone J, Stevenson AW, Butler DJ, Häusermann D, Adam JF. Characterization of a synthetic single crystal diamond detector for dosimetry in spatially fractionated synchrotron x - ray fields. Med Phys (2016) 43:4283–93. doi:10.1118/1.4953833
57. Brualla González L, Gómez F, Pombar M, Pardo Montero J. Dose rate dependence of the ptw 60019 microdiamond detector in high dose - per - pulse pulsed beams. Phys Med Biol (2016) 61:N11–N19. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/61/.1/N11
58. Cella L, Liuzzi R, Salvatore M. The Italian affair: the employment of parallel - plate ionization chambers for dose measurements in high dose - per - pulse iort electron beams. Med Phys (2010) 37:2918–24. doi:10.1118/1.3432601
59. Kokurewicz K, Schüller A, Brunetti E, Subiel A, Kranzer R, Hackel T, et al. Dosimetry for new radiation therapy approaches using high energy electron accelerators. Front Phys (2020) 8:568302. doi:10.3389/fphy.2020.568302
60. Ding L, Wu Q, Wang Q, Li Y, Perks RM, Zhao L. Advances on inorganic scintillator - based optic fiber dosimeters. EJNMMI Phys (2020) 7:60. doi:10.1186/s40658-020-00327-6
61. Huang S, Yang YJ, Wei SY, Kang ML, Tsai PF, Chen CC, et al. Implementation of novel measurement-based patient-specific qa for pencil beam scanning proton flash radiotherapy. Med Phys (2023) 50:4533–45. doi:10.1002/mp.16458
62. Kanouta E, Poulsen PR, Kertzscher G, Sitarz MK, Sørensen BS, Johansen JG. Time-resolved dose rate measurements in pencil beam scanning proton flash therapy with a fiber-coupled scintillator detector system. Med Phys (2022) 50:2450–62. doi:10.1002/mp.16156
63. Ashraf MR, Rahman M, Zhang RX, Williams BB, Gladstone DJ, Pogue BW, et al. Dosimetry for flash radiotherapy: a review of tools and the role of radioluminescence and cherenkov emission. Front Phys (2020) 8:328. doi:10.3389/fphy.2020.00328
64. Gómez F, Gonzalez Castaño DM, Fernández NG, Pardo Montero J, Schüller A, Gasparini A, et al. Development of an ultra-thin parallel plate ionization chamber for dosimetry in flash radiotherapy. Med Phys (2022) 49:4705–14. doi:10.1002/mp.15668
65. Lourenço A, Subiel A, Lee N, Flynn S, Cotterill J, Shipley D, et al. Absolute dosimetry for flash proton pencil beam scanning radiotherapy. Sci Rep (2023) 13:2054. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-28192-0
66. Lang XL, Hu ZG, Zhao ZL, Zhou K, Xu ZG, Li M, et al. Preliminary study of low - pressure ionization chamber for online dose monitoring in flash carbon ion radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol (2024) 69:025008. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ad13d0
67. Vanreusel V, Gasparini A, Galante F, Mariani G, Pacitti M, Cociorb M, et al. Point scintillator dosimetry in ultra - high dose rate electron “flash” radiation therapy: a first characterization. Phys Med (2022) 103:127–37. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2022.10.005
68. Morrocchi M, Pensavalle JH, Ciarrocchi E, Di Martino F, Felici G, Galante F, et al. Experimental characterization and Monte Carlo simulation of scintillator detectors in online electron flash radiotherapy dosimetry. JINST (2022) 17:P09005. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/17/09/P09005
69. Vanreusel V, Heinrich S, De Kerf T, Leblans P, Vandenbroucke D, Vanlanduit S, et al. A dose rate independent 2d ce - doped yag scintillating dosimetry system for time resolved beam monitoring in ultra - high dose rate electron “flash” radiation therapy. Sens Actuator A Phys (2024) 371:115313. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2024.115313
70. Baikalov A, Tho D, Liu K, Bartzsch S, Beddar S, Schüler E. Characterization of a time - resolved, real - time scintillation dosimetry system for ultra - high dose rate radiation therapy applications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2024) 121(5):1372–83. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.11.092
71. Kranzer R, Schüller A, Bourgouin A, Hackel T, Poppinga D, Lapp M, et al. Response of diamond detectors in ultra - high dose - per - pulse electron beams for dosimetry at flash radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol (2022) 67:075002. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ac594e
72. Rahman M, Kozelka J, Hildreth J, Schönfeld A, Sloop AM, Ashraf MR, et al. Characterization of a diode dosimeter for uhdr flash radiotherapy. Med Phys (2023) 50:5875–83. doi:10.1002/mp.16474
73. Jones AR. The application of some direct current properties of silicon junction detectors to γ-ray dosimetry. Phys Med Biol (1963) 8:451–9. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/8/4/307
74. Romano F, Milluzzo G, Martino F, D’Oca M, Felici G, Galante F, et al. First characterization of novel silicon carbide detectors with ultra - high dose rate electron beams for flash radiotherapy. Appl Sci (2023) 13:2986. doi:10.3390/app13052986
75. Okpuwe C, Amato A, D’Amico I, De Liso V, De Napoli M, Di Martino F, et al. Silicon carbide detectors for dosimetry and monitoring of ultra - high dose rate beams. JINST (2024) 19:C03064. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/19/03/C03064
76. Medina E, Ferro A, Abujami M, Camperi A, Vignali M, Data E, et al. First experimental validation of silicon - based sensors for monitoring ultra - high dose rate electron beams. Front Phys (2024) 12. doi:10.3389/fphy.2024.1258832
Keywords: FLASH-RT, x-ray, dosimetry, gaseous detectors, scintillators, semiconductors
Citation: Tao L, Feng S, Yang Y and Zheng B (2025) Dosimetry characteristics of ultra-high dose rate X-ray: a short review. Front. Phys. 13:1576227. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1576227
Received: 13 February 2025; Accepted: 09 April 2025;
Published: 02 May 2025.
Edited by:
Ana Luisa Silva, University of Aveiro, PortugalReviewed by:
Andrea Ciavatti, University of Bologna, ItalyEdgardo Bonzi, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba., Argentina
Copyright © 2025 Tao, Feng, Yang and Zheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Song Feng, ZmVuZ3M5MTE1QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Yiwei Yang, d2luZmllbGQxOTIwQDEyNi5jb20=; Bo Zheng, emhlbmdiQHVzYy5lZHUuY24=
 Luyan Tao1
Luyan Tao1 Song Feng
Song Feng