- School of Information Engineering, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China
Holmium:YAG(Ho:YAG) is still recognized as the gold standard for lithotripsy due to its advantages of high efficiency, safety, wide indications and high compatibility with minimally invasive techniques. However, it still faces challenges such as calculi retropulsion and heat generation risk in clinical applications. With its unique structure and physical properties, thulium fiber laser (TFL) boasts advantages such as higher performance efficiency, superior stability, and an increased energy conversion rate. These features endow TFL with broad application prospects in the treatment for urological calculi, and it is anticipated to become for calculi fragmentation in the future. This article will analyze the performance characteristics of Ho:YAG and TFL, and explore their characteristics and advantages in urolithiasis surgery, in order to provide guidance and inspiration for clinical practice.
1 Introduction
Urological calculi, as a high-risk disease worldwide, is affected by geographical, climatic and lifestyle factors. The incidence for urological calculi is between 2% and 5%, and shows an overall upward trend [1, 2]. With continuous advancements in endoscopy and laser technology, laser lithotripsy has emerged as the dominant treatment for urolithiasis due to its efficiency and safety. Early laser lithotripsy methods employed lasers with respective drawbacks, including significant thermal damage with non-pulsed carbon dioxide lasers [3], limited types of treatable calculis with pulsed dye lasers [4], and poor precision with neodymium lasers [5]. By the end of the 20th century, holmium laser (Ho:YAG), leveraging its exceptional water absorption characteristics and photothermal effect, achieved efficient treatment of various types of calculis through pulsed mode and rapidly became the gold standard for lithotripsy [6]. However, in clinical applications, Ho:YAG lasers still face limitations such as calculi displacement, risk of thermal damage, and restricted manipulation in the inferior calyx or narrow ureter. In recent years, thulium fiber laser (TFL) has demonstrated potential to replace Ho:YAG lasers due to its unique operating wavelength and system architecture advantages, offering higher lithotripsy efficiency and lower retropulsion among other characteristics [7, 8]. This article will focus on the performance characteristics of Ho:YAG and TFL, comparing and analyzing their application advantages in endoscopic surgery for urinary calculi, aiming to provide valuable references for clinical practice.
2 Mechanism of laser lithotripsy
The main mechanisms of laser lithotripsy are photothermal decomposition and photomechanical mechanisms [9–12]. Photothermal mechanism refers to the heat accumulation from the optical fiber to melt the calculi. Photomechanical mechanism is to excite bubbles in water through optical fibers, resulting in the cracking of calculis. In addition to these two mechanisms mentioned, TFL also includes the “micro-explosion” mechanism [13]. Mechanistically, during laser-tissue interaction, photonic energy absorption by intrinsic aqueous components within urinary calculi induces rapid vaporization, generating localized high-pressure zones. Concurrently, the thermal conductivity discrepancy between the hydrated matrix and lithogenic structure propagates dynamic pressure gradients, preferentially inducing microfractures within structurally vulnerable regions to achieve controlled lithotripsy. However, in practice, it is found that the above two mechanisms are not enough to explain all the phenomena in the process of lithotripsy. Cecchetti et al. [14] proposed the ‘plasma’ theory of Ho:YAG. The core of the theory is that due to the large absorption coefficient in water, the water at the end of the fiber quickly absorbs the energy, produces thermal ionization and forms a plasma. Once a plasma is formed, it strongly absorbs the incident laser, and the plasma itself supersedes the incident laser.In addition, there is a ‘Moses effect’ [15] in the calculi process, which is to modulate the pulse energy into two sets of independent pulses through pulse energy modulation technology to achieve accurate crushed calculi. The first group of low-energy short pulses generates micro-vapor bubbles, which separates the water around the end of the fiber, so that the calculis are directly exposed to the end of the fiber, forming a ‘channel’ with low water density between the calculis, that is the Moses effect. The second group of high-energy long pulses transmitted through this ‘channel’ will form a blasting force on the surface of the calculi, which greatly reduces the energy loss caused by absorption in water, and can produce a non-contact calculi effect at a longer distance.
3 Modes of lithotripsy
Lithotripsy technology is mainly divided into three modes: fragmentation [16], dusting [17] and popcorn-like mode [18]. The fragmentation adopts high pulse energy and low frequency (0.6 ∼ 2.0 J, 4.0 ∼ 6.0 Hz) and short pulse width parameters to crush high hardness calculis into grabable fragments and take them out through baskets. The dusting crushes the soft calculis into pieces (≤2 mm) by low-energy high-frequency (0.2 ∼ 0.5 J, 15 ∼ 60 Hz) and long-pulse width parameters, pieces are excreted by the patient himself. Although the use of instruments is reduced, the intraoperative dust may affect the visual field (which can be improved by negative pressure suction). The popcorn-like is aimed at residual calculis, and the eddy current effect is formed by non-contact excitation with medium energy (such as 1 J), medium and high frequency (10∼15 Hz) and medium pulse width parameters to further decompose the debris. The three form a complementary calculis scheme through differentiated energy configuration and operation strategy, taking into account the efficiency and safety of calculi removal. The specific mode to be adopted requires assessment by the physician after considering various aspects of the patient’s calculi condition, as well as their physical status and urinary tract anatomy.
4 Ho:YAG
Holmium:YAG laser is a versatile high-energy pulsed laser with a specific wavelength of 2,100 nm, capable of being delivered through a flexible optical fiber. It generates localized instantaneous high temperatures, inducing rapid vaporization of water within the calculi to form a plasma. This plasma subsequently expands rapidly and collapses, emitting intense supersonic shockwaves with sufficient pressure to initiate physicochemical reactions in the calculi, effectively fragmenting calculis of various compositions. Due to its superior performance, the holmium:YAG laser has found widespread application in the field of urology.
In the early days, Ho:YAG was designed with a single cavity, the output power was less than 30 W, and the pulse energy and frequency were limited (0.8 ∼ 1.2 J, 4 ∼ 10 Hz), forming a classic fragmented mode [6]. Subsequently, Ho:YAG realized high-power lithotripsy through a multi-cavity system. The emergence of the latest Moses effect mode Ho:YAG (Lumenis™) has a power of up to 120 W and a frequency of up to 80 Hz, and the lithotripsy efficiency is significantly improved [19].
Since it was first reported in 1995 for the treatment for urological calculi [20], it has rapidly become the gold standard for intracavitary lithotripsy due to its full-component adaptability (high-hardness calculis such as cystine and calcium oxalate monohydrate can be efficiently treated), precision and low invasiveness (wavelength 2,100 nm is highly absorbed in water, tissue penetration depth is only 0.4 μm, perforation rate <0.1%) and versatility (simultaneous realization of lithotripsy, hemostasis and soft tissue cutting). With the ME pulse modulation technology, the energy loss is reduced by 60%, the non-contact lithotripsy distance is extended to 1 ∼ 2 mm, the shock wave transmission efficiency is increased by 30%, and the calculi retropulsion rate is reduced by 50 times. In complex cases (such as staghorn calculis, incarcerated calculis) [21], the calculi-free rate of single operation is as high as 88%∼98%. Multi-mode parameter configuration covers fragmentation (0.6 ∼ 2.0 J/4 ∼ 6 Hz), dusting (0.2 ∼ 0.5 J/15 ∼ 60 Hz) and popcorn-like (1 J/10 ∼ 15 Hz), combined with ultra-fine fiber (50∼1000 μm) to adapt to the narrow anatomical structure, significantly reducing the risk of ureteral stenosis.In terms of technical iteration, the fourth generation Ho:YAG system (such as Lumenis Pulse P120H) [22] has a power of 120 W and a frequency of 80 Hz, and the calculi efficiency is 2 times higher than the traditional mode, while the cost of domestic equipment (such as JRH-I type) is reduced by 30%, which promotes the popularization rate of primary hospitals by 50%. Based on high efficiency, minimally invasive, multi-scene adaptation and 30 years of evidence-based support, the comprehensive advantages of Ho:YAG in lithotripsy efficiency, tissue protection and operation freedom make it irreplaceable in the existing technical system.
However, studies have shown that Ho:YAG has limits such as significant heat generation, easy to cause calculi retropulsion, and difficulty in completely dusting calculis [23]. Although the latter two can be improved to a certain extent by parameter regulation and precise operation, the tissue damage caused by the thermal effect mechanism is still an unavoidable problem. In particular, the application of high-power high-frequency lasers further aggravates people’s concerns about the thermal effect of intracavity calculi. In addition, the Ho:YAG output energy mode is a multi-mode output beam. When the core diameter of the fiber is small, the beam can not be gathered together, and can only be used on the fiber with a core diameter of ≥200 μm, which may lead to complications such as ureteral stenosis caused by heat generation after surgery, and the “blizzard” effect during lithotripsy is easy to affect the visual field [19]. The special demand for high-power Ho:YAG for more efficient condensing device and voltage energy supply leads to the fact that the production size of the laser generator cannot be portable. At the same time, the power supply of the operating room requires special lines, which leads to the reduction of the efficiency of the operating room in the central hospital with a large amount of surgery, which poses a challenge to the wide clinical application.
5 TFL
As a new type of laser, TFL uses a semiconductor laser as a pump source, a thulium-doped fiber as a working medium, and an emission wavelength of 1940 mm. It has the advantages of higher calculi burning rate, higher irrigation rate, smaller calculi, smaller retropulsion, and air cooling. It has broad application prospects in the field of lithotripsy, and is expected to replace Ho:YAG as a new gold standard in the field for lithotripsy [10, 11].
Compared with Ho:YAG, TFL offers numerous advantages: its 1940 nm wavelength boasts a water absorption coefficient four times that of holmium laser, enabling faster calculi ablation and efficient lithotripsy; its extremely shallow penetration, half that of Ho:YAG, ensures superior thermal safety; it supports high-frequency low-energy pulses, accelerating calculi dusting, particularly suitable for flexible ureteroscopy with a 30%–50% increase in lithotripsy speed; the small shockwaves generated by high-frequency pulses significantly reduce calculi retropulsion, lowering the risk of intraoperative calculi escape; the use of a 50 μm fine fiber enhances lithotripsy efficiency, is ideal for narrow areas, and paves the way for next-generation small ureteroscopes, with minimal reverse thrust facilitating high-flow perfusion for dust clearance, heat dissipation, dust storm avoidance, visibility improvement, and prevention of thermal injury; its pulse frequency exceeds 2,000 Hz, over 20 times that of Ho:YAG; the entire system supports water-free operation, high photoelectric efficiency, all-fiber coupling, and significant volume reduction, garnering increasing attention. These advantages underscore the immense potential of TFL in urological lithotripsy.
In 2005, Fried [24] first reported the in vitro lithotripsy test of TFL. The results showed that TFL could effectively treat calculis with different hardness in pulse mode, and the lithotripsy speed was significantly higher than that of Ho:YAG at that time. Through experiments, Hardy et al. [25] found that under the premise of maintaining the same laser parameters, the degree of dusting of TFL is higher than that of Ho:YAG. Blackmon et al. [26] compared the calculi effect of TFL and Ho:YAG lasers at the same pulse energy (70 mJ). The results show that the calculi efficiency of TFL is 5∼10 times that of Ho:YAG under the same pulse energy. Hardy [27] verified that using low pulse energy and high frequency TFL can produce smaller calculi fragments, which is convenient for patients to discharge.Enikeev [28] first reported the clinical application of TFL percutaneous nephrolithotomy. It can be seen that TFL is superior to Ho:YAG in terms of lithotripsy rate and powdering degree under the same parameters. Cumpanas et al [29]. investigated the impact of irrigation fluid temperature on TFL ablation of urinary calculi, finding that increasing temperature can enhance ablation rates for non-uric acid (non-UA) calculis (Figure 1), yet this effect is less significant than adjusting laser energy, which remains a crucial factor.
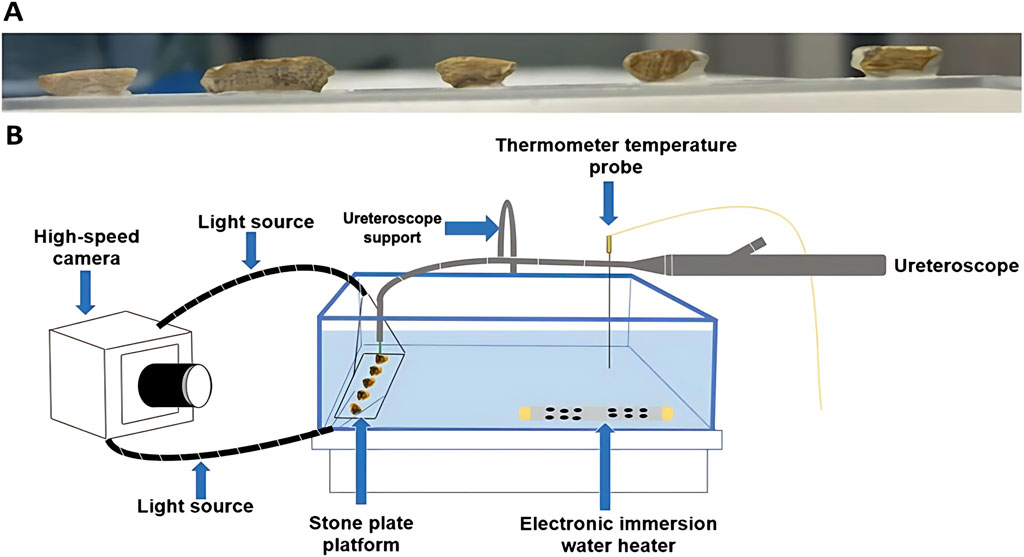
Figure 1. Stone surface preparation (A) and experimental set-up (B). Reprinted with permission from [29]. Copyright © 2025, The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer-Verlag London Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
TFL showed significant advantages in inhibiting calculi retropulsion. Blackmon et al. [30] found that when the TFL pulse energy was 35 mJ and the frequency was lower than 150 Hz, the calculi repelling distance was stable below 2 mm, while the Ho:YAG could cause retropulsion even at 0.2 J at the same energy. Ventimiglia [31] and Enikeev’s [32, 33] studies have confirmed that compared with Ho:YAG and TFL under the same energy, frequency and average power conditions, the calculi retropulsion caused by TFL is less obvious than that of Ho:YAG with different pulse widths, and the resulting more efficient lithotripsy rate and clearer surgical field of vision.
As a new type of calculi technology, the heat generation risk and mechanism of TFL are still controversial. Studies [34–36] have shown that when TFL and Ho:YAG (Ho:YAG) use the same parameters, there is no significant difference in the temperature rise of the lavage fluid between the two [37]. However, in the high-frequency mode [38], TFL has more significant heat accumulation due to shortened pulse interval, and the upper limit of frequency should be limited to 500 Hz to control the tissue temperature <43°C. In the dusting mode [39], although the temperature rise rate of TFL is higher than that of Ho:YAG (peak temperature <45°C), the photothermal effect caused by its short pulse may lead to carbonation of the calculi structure and increase the risk of ureteral stenosis.Christopher et al. [40] conducted a comparison of the thermal dose and temperature profiles of Ho:YAG versus TFL in a kidney mode. Using a 3D-printed model, they observed that the thermal dose delivered by TFL was typically higher than that of Ho:YAG.
TFL shows significant advantages in small fiber applications: compared with Ho:YAG, the loss of fiber tip is higher under the same parameters. TFL can stably couple ultrafine fiber due to the characteristics of near single-mode Gaussian beam and smaller core, so as to avoid the micro-hole ablation damage caused by Ho:YAG due to multimode beam. The small fiber increases the energy density, so that the dusting efficiency of the TFL 150 μm fiber is 3 times that of the Ho:YAG 272 μm fiber, and the calculi particles are finer (≤0.5 mm). At the same time, the irrigation rate [41] of 50 μm ultrafine fiber in 3.6Fr channel reached 28.3 mL/min (duty cycle 90.2%), which was 2.1 times higher than that of 272 μm fiber, reducing the risk of intraoperative temperature rise and shortening the operation time. TFL breaks through the physical limitations of Ho:YAG, supports 50 μm ultra-fine fiber, promotes the miniaturization of ureteroscopy, achieves greater curvature and multi-functional integration, and provides a technical basis for high-frequency dusty lithotripsy.
The clinical application of TFL still faces multiple challenges. First, the ablation efficiency of high-density hard calculis is limited, which is manifested by prolonged lithotripsy time and high energy density, which is easy to cause carbonization of fiber tip. Secondly, there is a significant risk of heat accumulation in the ultra-high frequency mode (>500 Hz) (depending on high irrigation flow such as>50 mL/min), but the relevant clinical evidence is still insufficient. Third, the occasional abnormal ‘explosion flash’ phenomenon [43] may cause mechanical damage to the lens, and its mechanism and solution need to be explored urgently. In addition, although the ultra-fine optical fiber enhances the calculi efficiency by increasing the energy density, it brings problems such as high-precision positioning requirements, accelerated fiber carbonization, and rising use costs. At present, TFL research is still limited by the clinical evidence. Large-scale controlled trials are needed to systematically evaluate its efficacy and safety, and promote the establishment of technical optimization and clinical application specifications.
6 Conclusion
In summary, Ho:YAG and TFL offer complementary strengths in urinary calculi management. Ho:YAG, with its high-energy pulsed mode, is optimal for fragmenting large-volume or high-density calculi, while TFL’s high-frequency thermal ablation excels in precise dusting and navigation within confined anatomical spaces. A comparative analysis of their technical and clinical performance is summarized as Table 1.
Ho:YAG and TFL are the two mainstream technologies in the field of laser treatment for urological calculi. Ho:YAG, with its mature and stable performance and the pulse optimization ability of Moses technology, has become the clinical gold standard through precise energy control and shallow penetration force, especially in the rapid crushing of larger volume or higher hardness calculis. Due to its unique fiber structure and near-single-mode Gaussian beam characteristics, TFL achieves better dusting effect, lower calculi retropulsion rate and higher rrigation rate with higher energy density, ultra-high frequency pulse and ultra-fine fiber compatibility. Its huge frequency reserve and process innovation potential provide a direction for technical iteration. The future technology may combine the deep controllability of Ho:YAG with the fine dusting ability of TFL to achieve efficient in situ calculi, low cost, no heat generation [40], and promote the urinary calculi into the era of precision and intelligence.
Author contributions
S-PH: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. Y-GW: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Tianjin Science and Technology Plan Project [Grant No. 24YDTPJC00780], Open Project of Hebei Province Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Technology and Equipment [Grant No. HBKL-ALTE2024009].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chen Z, Prosperi M, Bird VY. Prevalence of kidney stones in the USA: the national health and nutrition evaluation survey. J Clin Urol (2019) 12(4):296–302. doi:10.1177/2051415818813820
2. Dong C, Song C, He Z, Liao W, Song Q, Xiong Y, et al. An overview of global research landscape in etiology of urolithiasis based on bibliometric analysis. Urolithiasis (2023) 51(1):71. doi:10.1007/s00240-023-01447-1
3. Rosemberg SK. Clinical experience with carbon dioxide laser in renal surgery. Urology (1985) 25(2):115–8. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(85)90524-2
4. Watson G, Murray S, Dretler SP, Parrish JA. The pulsed dye laser for fragmenting urinary calculi. The J Urol (1987) 138(1):195–8. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43043-6
5. Hofmann R, Hartung R, Schmidt-Kloiber H, Reichel E. First clinical experience with a Q-switched neodymium: YAG laser for urinary calculi. The J Urol (1989) 141(2):275–9. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(17)40739-7
6. Fried NM, Irby PB. Advances in laser technology and fibre-optic delivery systems in lithotripsy. Nat Rev Urol (2018) 15(9):563–73. doi:10.1038/s41585-018-0035-8
7. Geavlete P, Multescu R, Geavlete B. Re: comparison of the ablation rates, fissures and fragments produced with 150 μm and 272 μm laser fibers with superpulsed thulium fiber laser: an in vitro study. Eur Urol (2021) 79(5):704–5. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.024
8. The European Association of Urology (EAU) Urolithiasis Guidelines Panel. EAU guidelines on urolithiasis. Arnhem: EAU Guidelines Office (2022).
9. Traxer O, Keller EX. Thulium fiber laser: the new player for kidney stone treatment? A comparison with Holmium: YAG laser. World J Urol (2020) 38:1883–94. doi:10.1007/s00345-019-02654-5
10. Gu R, Li Z, Lei C, Li S, Wang D, Wang X. Thulium-doped fiber laser and its application in urinary lithotripsy. J Med Biol Eng (2023) 43(4):351–61. doi:10.1007/s40846-023-00813-z
11. Lekarev V, Dymov A, Vinarov A, Sorokin N, Minaev V, Minaev N, et al. Mechanism of lithotripsy by superpulse thulium fiber laser and its clinical efficiency. Appl Sci (2020) 10(21):7480. doi:10.3390/app10217480
12. Chan KF, Joshua Pfefer T, Teichman JMH, Welch AJ. A perspective on laser lithotripsy: the fragmentation processes. J Endourology (2001) 15(3):257–73. doi:10.1089/089277901750161737
13. Hardy LA, Irby PB, Fried NM. Scanning electron microscopy of real and artificial kidney stones before and after Thulium fiber laser ablation in air and water. Therapeutics and Diagnostics in Urology 2018. SPIE (2018) 10468:26–36. doi:10.1117/12.2285069
14. Cecchetti W, Cerruto MA, Bianco MD, Milani C, Zattoni F. A four-year experience with Holmium-YAG laser: parameters of use. Urologia J (2007) 74(3):155–9. doi:10.1177/039156030707400306
15. Aldoukhi AH, Black KM, Ghani KR. Emerging laser techniques for the management of stones. Urol Clin (2019) 46(2):193–205. doi:10.1016/j.ucl.2018.12.005
16. Blackmon RL, Irby PB, Fried NM. Holmium: YAG (λ= 2,120 nm) versus thulium fiber (λ= 1,908 nm) laser lithotripsy. Lasers Surg Med The Official J Am Soc Laser Med Surg (2010) 42(3):232–6. doi:10.1002/lsm.20893
17. Panthier F, Traxer O, Yonneau L, Lebret T, Berthe L, Illoul L, et al. Evaluation of a free 3D software for kidney stones’ surgical planning:“kidney stone calculator” a pilot study. World J Urol (2021) 39:3607–14. doi:10.1007/s00345-021-03671-z
18. Weiss B, Shah O. Evaluation of dusting versus basketing—can new technologies improve stone-free rates? Nat Rev Urol (2016) 13(12):726–33. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2016.172
19. Martov AG, Ergakov DV, Guseynov M, Andronov AS, Plekhanova OA. Clinical comparison of super pulse thulium fiber laser and high-power holmium laser for ureteral stone management. J Endourology (2021) 35(6):795–800. doi:10.1089/end.2020.0581
20. Matsuoka K, Iida S, Nakanami M, Koga H, Shimada A, Mihara T, et al. Holmium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser for endoscopic lithotripsy. Urology (1995) 45(6):947–52. doi:10.1016/s0090-4295(99)80113-7
21. Gross AJ, Netsch C. Editorial comment on: Thermal response to high-power holmium laser lithotripsy by Aldoukhi et al. J Endourology (2017) 31(12):1313. doi:10.1089/end.2017.0809
22. Elhilali MM, Badaan S, Ibrahim A, Andonian S. Use of the Moses technology to improve holmium laser lithotripsy outcomes: a preclinical study. J Endourology (2017) 31(6):598–604. doi:10.1089/end.2017.0050
23. Jones P, Beisland C, Ulvik Ø. Current status of thulium fibre laser lithotripsy: an up-to-date review. BJU Int (2021) 128(5):531–8. doi:10.1111/bju.15551
24. Fried NM. Thulium fiber laser lithotripsy: an in vitro analysis of stone fragmentation using a modulated 110-watt Thulium fiber laser at 1.94 µm. Lasers Surg Med The Official J Am Soc Laser Med Surg (2005) 37(1):53–8. doi:10.1002/lsm.20196
25. Hardy LA, Wilson CR, Irby PB, Fried NM. Thulium fiber laser lithotripsy in an in vitro ureter model. J Biomed Opt (2014) 19(12):128001. doi:10.1117/1.jbo.19.12.128001
26. Blackmon RL, Irby PB, Fried NM. Comparison of holmium: YAG and thulium fiber laser lithotripsy: ablation thresholds, ablation rates, and retropulsion effects. J Biomed Opt (2011) 16(7):071403–071403-5. doi:10.1117/1.3564884
27. Hardy LA, Vinnichenko V, Fried NM. High power holmium:YAG versus thulium fiber laser treatment of kidney stones in dusting mode: ablation rate and fragment size studies. Laserssurg Med (2019) 51(6):522–30.
28. Enikeev D, Taratkin M, Klimov R, Alyaev Y, Rapoport L, Gazimiev M, et al. Thulium-fiber laser for lithotripsy: first clinical experience in percutaneous nephrolithotomy. World J Urol (2020) 38:3069–74. doi:10.1007/s00345-020-03134-x
29. Cumpanas AD, Katta N, Vu TN, Wu YX, Gorgen ARH, Hernandez MC, et al. Warm irrigation fluid effect on Thulium fiber laser (TFL) ablation of uroliths. Lasers Med Sci (2025) 40(1):112–0. doi:10.1007/s10103-024-04253-2
30. Blackmon RL, Irby PB, Fried NM. Enhanced thulium fiber laser lithotripsy using micro-pulse train modulation. J Biomed Opt (2012) 17(2):028002. doi:10.1117/1.jbo.17.2.028002
31. Ventimiglia E, Doizi S, Kovalenko A, Andreeva V, Traxer O. Effectof temporal pulse shape on urinary stone phantom retropulsion rate and ablation efficiency using holmium:YAG and super-pulse thulium fibre lasers. BJUInt (2020) 126(1):1 59–67. doi:10.1111/bju.15079
32. Enikeev D, Taratkin M, Klimov R, Inoyatov J, Azilgareeva C, Ali S, et al. Superpulsed thulium fiber laser for stone dusting: in search of a perfect ablation regimen—a prospective single-center study. J Endourology (2020) 34(11):1175–9. doi:10.1089/end.2020.0519
33. Enikeev D, Grigoryan V, Fokin I, Morozov A, Taratkin M, Klimov R, et al. Endoscopiclithotripsy with a super pulsed thulium-fiber laser forureteral stones: a single-center experience. Int Jurol (2021) 28(3):261–5. doi:10.1111/iju.14443
34. Martov A, Adilkhanov M, Andronov A, Altshuler G, Yaroslavsky I, Kovalenko A, et al. Treatment of urolithiasis with Thulium Fiber Laser in fragmentation mode using optimized pulse sequences. J Endourology (2024) 38(10):1097–103. doi:10.1089/end.2023.0689
35. Gul T, Laymon M, Alrayashi M, Abdelkareem M, Salah M. Successful treatment of staghorn stones with flexible ureteroscopy and thulium fiber laser (TFL) lithotripsy: initial experience with 32 cases. Urolithiasis (2024) 52(1):102. doi:10.1007/s00240-024-01598-9
36. Wang C, Li Y, Yang Y, Chen J, Li Z, Song G, et al. Thulium laser enucleation of the prostate plus thulium fiber laser therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia combined with bladder stones. Videosurgery other Miniinvasive Tech (2024) 19(3):370–6. doi:10.20452/wiitm.2024.17897
37. Belle JD, Chen R, Srikureja N, Amasyali AS, Keheila M, Baldwin DD. Doesthe novel thulium fiber laser have a higher risk ofurothelial thermal injury than the conventional holmiumlaser in an in vitro study? J Endourology (2022) 36(9):1249–54. doi:10.1089/end.2021.0842
38. Wanderling C, Saxton A, Phan D, Doersch KM, Shepard L, Schuler N, et al. Getting hot in here! Comparison of Holmium vs. thulium laser in an anatomic hydrogel kidney model. Urolithiasis (2024) 52(1):49. doi:10.1007/s00240-024-01541-y
39. Blackmon RL, HutchensTC HLA, Wilson CR, Irby PB, Fried NM. Thulium fiber laser ablation of kidney stones using a 50-μm-core silica optical fiber. Opt Eng (2015) 54(1):011004. doi:10.1117/1.oe.54.1.011004
40. Su B, Hu W, Xiao B, Ding T, Liu Y, Li J. Needle-perc-assisted endoscopic surgery for patients with complex renal stones: technique and outcomes. Urolithiasis (2022) 50(3):349–55. doi:10.1007/s00240-021-01299-7
Keywords: urological calculi, laser lithotripsy, holmium:YAG, thulium fiber laser, mechanism of laser lithotripsy
Citation: Hou S-P and Wang Y-G (2025) Application status of holmium and thulium fiber laser for urological calculi. Front. Phys. 13:1590456. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1590456
Received: 09 March 2025; Accepted: 03 June 2025;
Published: 12 June 2025.
Edited by:
Tonglei Cheng, Northeastern University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qi Qin, Xingtai University, ChinaRuiliang Xu, Changchun University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Hou and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shu-Ping Hou, aG91c2h1cGluZ0B0amN1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Shu-Ping Hou
Shu-Ping Hou Yu-Guo Wang
Yu-Guo Wang