- 1School of Computer Science, Sichuan University Jinjiang College, Meishan, China
- 2Network and Data Security Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
This paper introduces a quantum-secure scheme for conducting privacy-preserving maximum value determination, allowing the parties to ascertain the highest value from their confidential inputs while keeping non-maximum data private. Participants first transform their private inputs into binary representations and then apply local operations to encode these values into quantum states. These encoded states are transmitted to a semi-trusted intermediary, which computes the maximum through quantum–mechanical interactions. The protocol is designed to ensure confidentiality against potential external threats, including quantum attack strategies such as intercept-resend, entangle-measure, and Trojan horse attacks, while also preventing any disclosure of inputs between the participants. The framework is practical, utilizing entangled Bell states as carriers of information, leveraging quantum state manipulations for secure encoding, and employing quantum measurements for result extraction. Empirical results obtained from simulations using IBM Quantum Composer demonstrate the operational feasibility of the scheme. A correctness analysis indicates that if the participants accurately submit their respective inputs and adhere strictly to the protocol, the semi-trusted intermediary will reliably reveal the maximum value to both parties. Additionally, fairness is ensured through the intermediary’s role in disclosing the maximum value simultaneously to both parties, preventing any unfair advantage.
1 Introduction
Recent advancements in quantum communication [1, 2] and computation [3, 4] have catalyzed transformative developments in cryptography and data processing. Quantum cryptography [5, 6], for instance, exploits quantum mechanical principles to achieve unprecedented security in information exchange, while quantum machine learning [7, 8] merges quantum computational power with classical algorithms to enhance analytical capabilities.
However, the rapid evolution of quantum computing jeopardizes classical cryptographic frameworks reliant on mathematical hardness assumptions, such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography. Shor’s algorithm [9], capable of factoring large integers exponentially faster than classical methods, directly threatens public-key encryption. Similarly, Grover’s algorithm [10] diminishes the effective security of symmetric-key systems by accelerating unstructured search tasks.
Quantum cryptography emerges as a robust countermeasure, offering protocols like BB84 [11] that ensure information–theoretic security [12] by detecting eavesdropping through quantum-state disturbances. This capability stems from fundamental principles like the no-cloning theorem and wavefunction collapse, which prevents undetected interception of quantum transmissions. Beyond secure communication, quantum cryptography enables functionalities such as quantum key distribution (QKD) [13, 14], quantum secure direct communication (QSDC) [15, 16], quantum key agreement (QKA) [17, 18], quantum private comparison (QPC) [19–27], and quantum private set intersection (QPSI) [28].
Secure multiparty computation (MPC) represents a critical area within modern cryptography, enabling multiple distrustful parties to jointly compute a function without disclosing their private inputs [29]. MPC has applications in various fields, including privacy-preserving data analysis [30–32], secure voting systems [33, 34], and deep learning [35–37]. This concept of MPC was pioneered by Andrew Yao through his foundational work on the Millionaires’ problem [38], where two parties aim to determine who possesses greater wealth without revealing their actual financial amounts. Yao’s formulation established the theoretical basis for numerous MPC protocols, illustrating how collaborative computation can be achieved while preserving data confidentiality. A natural extension of this problem involves privately determining the maximum value among multiple inputs, where participants seek to identify the largest value without exposing their individual data. Classical approaches to this task rely on private comparison protocols [39–43], which compute the maximum value using traditional cryptographic methods. However, these methods depend on unproven computational assumptions, rendering them susceptible to quantum-based attacks. The advent of quantum computing, with its capacity to efficiently solve problems like integer factorization and discrete logarithms, poses a significant threat to the security of classical cryptographic systems.
The computation of maximum values holds significant importance in privacy-sensitive applications, such as sealed-bid auctions [44], electronic voting [45], and federated learning [46]. Although quantum algorithms [47, 48] have been developed to efficiently identify maximum and minimum values within a dataset, they lack mechanisms to protect the privacy of individual inputs during computation. To date, no established quantum scheme that specifically addresses the privacy-preserving computation of the maximum value between two private inputs exists.
To bridge this gap, this paper introduces a novel quantum-based scheme designed to determine the maximum value while safeguarding the privacy of non-maximum inputs. By leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, the proposed scheme allows two users to collaboratively compute the maximum value without disclosing their private data. Security analyses confirm that the scheme is resilient to both external and internal attacks. Furthermore, the scheme employs single-photon operators, including Pauli operators and the Ry rotation operator, alongside Bell states as quantum resources. It utilizes single-photon operations and Bell measurements, making it feasible to implement with current quantum technologies. The practicality of the scheme is validated through simulations conducted on the IBM Quantum Cloud Platform.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 provides the necessary background on unitary operations and encoding techniques. Sections 3 and 4 detail the proposed scheme and its simulation, respectively. Section 5 presents an analysis of the scheme’s correctness, security, fairness, and qubit efficiency. Section 6 provides the conclusions of the paper.
2 Preliminaries
The Ry rotation operator around the y-axis in the Bloch sphere [49] can be represented by
This operator can be considered an encryption operator used to convert a quantum state into an unknown quantum state, and the encryption key is
Three operations are as follows:
•I Gate:
•X Gate:
•Z Gate:
The three local operations written in a matrix form are as follows:
Four Bell states are two-qubit entangled states, which can be written as
We suppose that a third party (TP) prepares a Bell state in
3 The proposed scheme
Consider a scenario involving two parties, Alice and Bob, each possessing private inputs A and B, respectively, where the upper bound of these values is N. Their objective is to determine the maximum value between A and B with the assistance of a semi-honest TP, such as a quantum server, while ensuring the privacy of non-maximum inputs. The proposed privacy-preserving maximum value determination scheme must satisfy the following requirements:
Correctness: If Alice and Bob honestly submit their respective inputs A and B and adhere to the protocol, the semi-honest TP will accurately disclose the maximum value to both parties.
Fairness: The protocol must ensure that no party gains an unfair advantage over the other. Each participant should receive the computation outcome without concerns of manipulation or bias.
Privacy: Except for the maximum value, no party should gain any information about the non-maximum inputs, even in the presence of internal or external eavesdroppers.
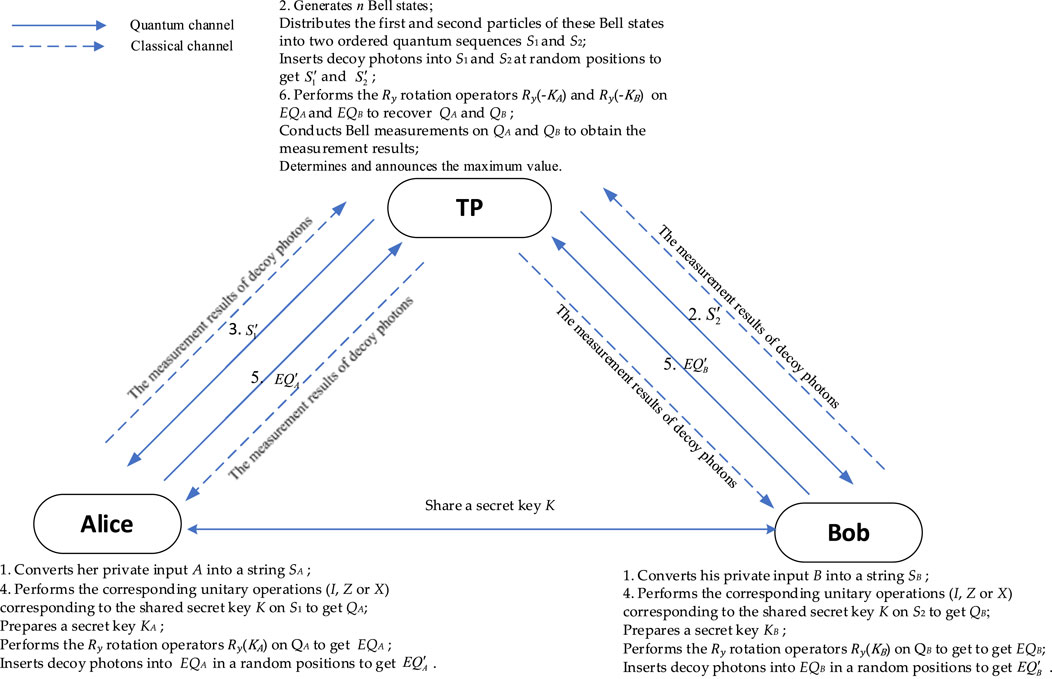
The scheme operates under the honest-but-curious model, where participants follow the protocol but may attempt to infer private information from the execution. The semi-honest TP is equipped with quantum capabilities and is responsible for preparing quantum resources, such as generating Bell states, and performing Bell measurements. Alice and Bob, also possessing quantum capabilities, perform basic single-photon operations and prepare decoy photons for eavesdropping detection. We assume that the protocol operates over an ideal channel with no noise [51]. However, in practical scenarios, quantum error-correcting codes [52, 53] can be implemented to detect and correct errors induced by noise. Additionally, Alice and Bob share a secret key
Step 1. Alice and Bob convert their private inputs A and B into N-bit strings
Step 2. TP generates N Bell states in
Step 3. Upon receiving
Step 4. Alice (Bob) recovers
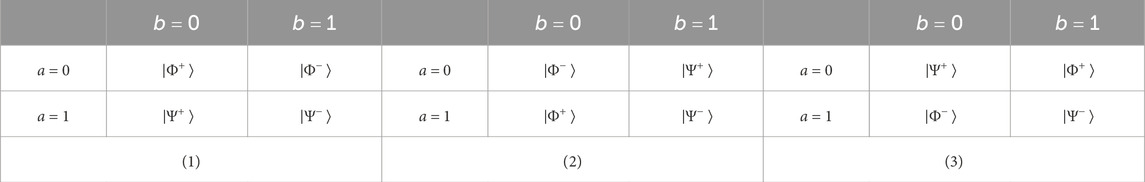
(1) Alice (Bob) chooses one of the three encoding rules in Table 1 based on the shared secret key
•If
•If
•If
(2) Alice applies the unitary operations corresponding to the chosen encoding rule in (1) to the received sequence
(3) Alice prepares a secret key
(4) Alice (Bob) prepares
(5) Alice (Bob) records the inserted positions of these decoy particles and sends
Step 5. After receiving
Step 6. TP recovers
(1) TP applies the Ry rotation operators
(2) TP conducts Bell measurements on
(3) If the first occurrence of the j-th position of the measurement result is
(4) TP announces the maximum value to Alice and Bob.
4 Simulation
Considering a case that Alice and Bob have their private inputs A = 3 and B = 1, respectively, the upper bound of the values A and B is 3 (since the available qubits in IBM Quantum Composer are seven). They intend to determine the maximum value of their inputs with the assistance of a TP while ensuring the privacy of non-maximum inputs. We assume that the secret key shared between Alice and Bob via a QKD protocol is
As described in our scheme, Alice and Bob convert their private inputs A and B into two 3-bit strings
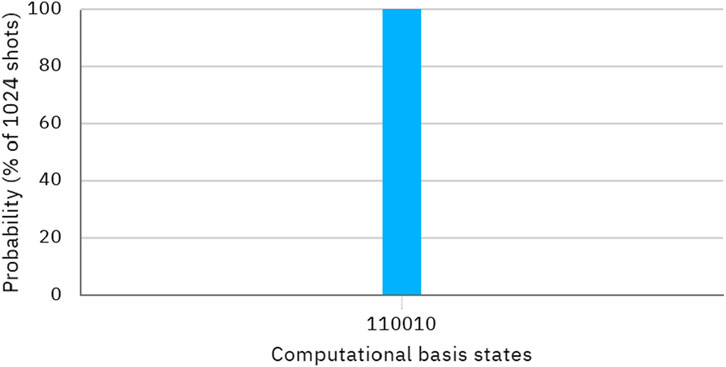
We simulate this scenario using IBM Quantum Composer, concentrating on the quantum operations while excluding eavesdropping detection, as this is a separate process within quantum communication protocols. The quantum circuit designed to determine the maximum value between inputs A and B is illustrated in Figure 2. Additionally, Figure 3 presents a histogram displaying the probability of measuring each state.
According to the results depicted in Figure 3, the final measurement results, from right to left, are 10, 00, and 11, corresponding to
5 Analysis
5.1 Correctness
Alice and Bob each have private inputs A and B. They convert these inputs into two N-bit strings
For instance, we assume that the upper bound of the values A and B is 6, where
When designing the privacy-preserving maximum value determination scheme, we only need to find the starting position of the first occurrence such that both
Therefore, our scheme is correct, provided that Alice and Bob honestly submit their respective sets A and B and adhere to the protocol. Ultimately, the semi-honest third party will disclose the maximum value to both Alice and Bob.
5.2 Security
In our scheme, except for the maximum value, no party learns any information about the other non-maximum inputs, even when facing threats from anyone within the group of participants or from outside eavesdroppers. Therefore, the proposed scheme must satisfy the following security requirements:
(1) Any attempt by an eavesdropper to gain information about the private inputs would be detectable, even if the eavesdropper possesses quantum capabilities and can perform various quantum-attack strategies.
(2) The semi-honest third party has no viable means of obtaining the private inputs, except for the maximum value.
(3) Alice cannot access Bob’s private inputs unless the maximum value corresponds to Bob’s private inputs.
(4) Bob cannot access Alice’s private inputs unless the maximum value determined by the protocol matches Alice’s private inputs.
Theorem 1. Any attempt by an eavesdropper to gain information about the private inputs would be failed, even if the eavesdropper possesses quantum capabilities and perform various quantum-attack strategies.
Proof. In quantum communication, the presence of an outsider eavesdropper, commonly referred to as Eve, poses a significant risk. Eve may apply various quantum-based attacks, including intercept-resend [54, 55], direct-measure [56], entangle-measure [57] and quantum Trojan horse attacks [58], to attempt obtaining the private inputs. To counter these eavesdropping strategies, the participants use the decoy-state method. This technique involves sending additional decoy states along with the actual quantum states. Because of the decoy-state method, Eve’s various quantum-attack strategies (intercept-resend, measure-resend, direct-measure, and entangle-measurement) are rendered ineffective. Alice and Bob can reliably detect any eavesdropping attempts through discrepancies in the statistical properties of the decoy states. This ensures security of their communication.
5.2.1 Case I: the intercept-resend attack
In this scenario, Eve intercepts the quantum particles sent from TP to the participants. She stores these intercepted particles for future use. After storing the intercepted quantum states, Eve prepares her own single particles, which she sends to the participants in place of the original particles. After the participants perform their operations on the particles sent by Eve, Eve intercepts the quantum particles sent back to the TP and measures these particles to extract secret information, while returning her previously stored particles to the TP. Upon receiving the quantum particles, the participants and TP initiate eavesdropping detection. The TP discloses the positions and measurement bases of the decoy particles used during communication. Since Eve does not know the specific states of these particles, there is a 50% probability that the participants will obtain an incorrect result when measuring the particles sent by Eve. For example, if the original decoy photon is in the state ∣1⟩, but Eve prepares a particle in the state ∣+⟩, the measurement performed by the participants on Eve’s particle has a 50% chance of yielding an incorrect result. The probability that Eve can pass the detection is given by
where
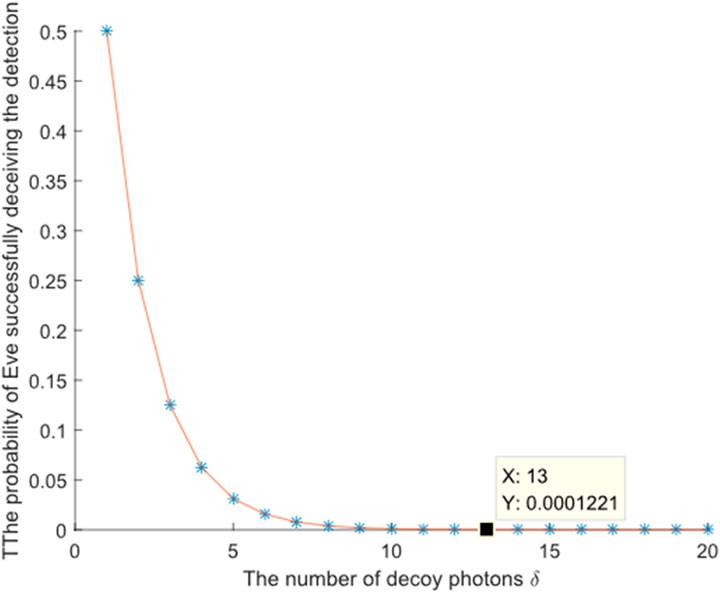
Figure 4. The relationship between the number of decoy photons and the probability of Eve successfully deceiving the detection.
When
5.2.2 Case II: the direct-measure attack
After performing the intercept-resend attack to obtain the positions of the decoy particles, Eve can discard the decoy particles in
5.2.3 Case III: the entangle-measure attack
Eve may also attempt an entangle-measure attack by entangling her auxiliary quantum particles
The coefficients must satisfy normalization conditions:
Substituting the results in Equation 5 into Equations 1–4, the results are given in the following equations:
According to Equations 6–9, Eve’s auxiliary particles remain independent from the target particles For Eve to avoid introducing errors during eavesdropping detection. This lack of entanglement indicates that there is no quantum correlation between Eve’s measurements and the target particles, and Eve cannot gain information about the target particles by measuring her auxiliary particles. As a result of this independence and lack of entanglement, Eve’s attempts to conduct an entanglement attack are ineffective.
5.2.4 Case IV: the Trojan horse attacks
Trojan horse attacks, including the delay-photon attack and invisible photon attack [59], mainly occur in the bidirectional quantum channel that is used for transmission of quantum sequence. Since the quantum sequences transmitted in our scheme are TP–Alice/Bob–TP, our scheme is vulnerable to these attacks. The implementation of a wavelength quantum filter and a photon number splitter [60] significantly enhances the security of the two-way quantum protocol against Trojan horse attacks. By ensuring that only legitimate quantum states are transmitted, the protocol maintains its privacy.
Therefore, any attempt by an eavesdropper to gain information about the private inputs would fail, even if the eavesdropper possesses quantum capabilities and can perform various quantum-attack strategies.
Theorem 2. The semi-honest third party has no viable means of obtaining the private inputs, except for the maximum value.
Proof. In the proposed quantum scheme, a semi-honest TP might attempt to gain information about Alice’s and Bob’s private inputs by preparing single photons instead of the intended Bell states. However, the protocol incorporates mechanisms that ensure security even in the presence of such attacks. In our scheme, TP prepares 2N single photons, distributing N photons to Alice and N to Bob. This setup allows the TP to potentially manipulate the quantum states being transmitted. When Alice and Bob apply their respective unitary operations, based on the secret key K, to encode their inputs into states
Theorem 3. Alice cannot access Bob’s private inputs unless the maximum value corresponds to Bob’s private inputs.
Proof. In the proposed quantum scheme, Alice may attempt an intercept-resend attack to gain access to Bob’s private inputs by intercepting
Therefore, Bob’s private inputs are inaccessible to Alice unless the maximum value corresponds to Bob’s private inputs.
Theorem 4. Bob cannot access Alice’s private inputs unless the maximum value determined by the protocol matches Alice’s private inputs.
Proof. In the proposed quantum scheme, both Alice and Bob have identical roles. If Bob attempts to access private inputs, he may try to execute an intercept-resend attack by intercepting the quantum sequence
5.3 Fairness
Fairness is a critical aspect of any secure computation protocol. In the proposed scheme, the involvement of the third party plays a pivotal role in ensuring that both Alice and Bob have equal access to the maximum value. After measuring the quantum sequence, the third party publishes the results and ensures that both Alice and Bob receive this information simultaneously, thereby preventing any one party from gaining an undue advantage over the other. Consequently, fairness in the proposed scheme is assured through the third party’s role in simultaneously publishing the maximum value for both participants.
5.4 Qubit efficiency
The qubit efficiency, an important indicator for measuring the utilization rate of qubits, can be defined by
where q represents the qubit efficiency, c denotes the upper bound of the input values, and t denotes the number of qubits consumed during the process of determining the maximum value, excluding those designated for eavesdropping detection during the transmission of quantum sequence. In our scheme, N Bell states all in
6 Conclusion
In this work, we introduce a privacy-preserving scheme for determining the maximum value between private inputs while safeguarding the confidentiality of non-maximum values. The proposed scheme employs Bell states as quantum resources, Pauli operators for encoding inputs, the Ry rotation operator for encryption, and Bell measurements to extract the results. This design ensures compatibility with existing quantum technologies, and its practical feasibility has been validated through simulations conducted on the IBM Quantum Cloud Platform. A correctness analysis confirms that if Alice and Bob faithfully provide their respective inputs A and B and strictly follow the protocol, the semi-honest TP will accurately reveal the maximum value to both parties. Security analysis further demonstrates that, beyond the maximum value, no participant or external eavesdropper can gain access to information about the non-maximum inputs, even under adversarial conditions. Fairness is guaranteed by the TP’s role in simultaneously disclosing the maximum value to Alice and Bob, ensuring that neither party gains an unfair advantage. However, it is worth noting that the scheme assumes honest participation. If one party acts rationally, for example, by submitting a false input, the integrity of the other party’s input could be compromised. To address this limitation, future research will explore quantum schemes involving rational participants who may exhibit selfish behavior, aiming to enhance robustness and fairness in such scenarios.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MH: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization, and Supervision. YW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the Open Fund of Network and Data Security Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Grant No. NDS2024-1) and the Gongga Plan for the “Double World-class Project.”
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chen YA, Zhang Q, Chen TY, Cai WQ, Liao SK, Zhang J, et al. An integrated space-to-ground quantum communication network over 4,600 kilometres. Nature (2021) 589(7841):214–9. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-03093-8
2. Pan JW, Simon C, Brukner Č, Zeilinger A. Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature (2001) 410(6832):1067–70. doi:10.1038/35074041
3. Graham TM, Song Y, Scott J, Poole C, Phuttitarn L, Jooya K, et al. Multi-qubit entanglement and algorithms on a neutral-atom quantum computer. Nature (2022) 604(7906):457–62. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04603-6
4. Daley AJ, Bloch I, Kokail C, Flannigan S, Pearson N, Troyer M, et al. Practical quantum advantage in quantum simulation. Nature (2022) 607(7920):667–76. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04940-6
5. Portmann C, Renner R. Security in quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys (2022) 94(2):025008. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.94.025008
6. Mehic M, Michalek L, Dervisevic E, Burdiak P, Plakalovic M, Rozhon J, et al. Quantum cryptography in 5G networks: a comprehensive overview. IEEE Commun Surv & Tutorials (2023) 26:302–46. doi:10.1109/comst.2023.3309051
7. Huang X, Zhang S, Lin C, Xia J. Quantum fuzzy support vector machine for binary classification. Comput Syst Sci Eng (2023) 45(3):2783–94. doi:10.32604/csse.2023.032190
8. Cerezo M, Verdon G, Huang HY, Cincio L, Coles PJ. Challenges and opportunities in quantum machine learning. Nat Comput Sci (2022) 2(9):567–76. doi:10.1038/s43588-022-00311-3
9. Shor PW. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev (1999) 41(2):303–32. doi:10.1137/s0036144598347011
10. Grover LK. Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys Rev Lett (1997) 79(2):325–8. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.79.325
11. Bennett CH, Brassard G. Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor Comput Sci (2014) 560:7–11. doi:10.1016/j.tcs.2014.05.025
12. Luo Y, Li Q, Mao HK. Distributed information-theoretical secure protocols for quantum key distribution networks against malicious nodes. J Opt Commun Networking (2024) 16(10):956–68. doi:10.1364/jocn.530575
13. Zhang W, van Leent T, Redeker K, Garthoff R, Schwonnek R, Fertig F, et al. A device-independent quantum key distribution system for distant users. Nature (2022) 607(7920):687–91. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04891-y
14. Nadlinger DP, Drmota P, Nichol BC, Araneda G, Main D, Srinivas R, et al. Experimental quantum key distribution certified by Bell's theorem. Nature (2022) 607(7920):682–6. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04941-5
15. Huang X, Zhang S, Chang Y, Yang F, Hou M, Cheng W. Quantum secure direct communication based on quantum homomorphic encryption. Mod Phys Lett A (2021) 36(37):2150263. doi:10.1142/s0217732321502631
16. Sheng YB, Zhou L, Long GL. One-step quantum secure direct communication. Sci Bull (2022) 67(4):367–74. doi:10.1016/j.scib.2021.11.002
17. Huang X, Zhang SB, Chang Y, Qiu C, Liu DM, Hou M. Quantum key agreement protocol based on quantum search algorithm. Int J Theor Phys (2021) 60:838–47. doi:10.1007/s10773-020-04703-x
18. Lin S, Zhang X, Guo GD, Wang LL, Liu XF. Multiparty quantum key agreement. Phys Rev A (2021) 104(4):042421. doi:10.1103/physreva.104.042421
19. Wang B, Liu SQ, Gong LH. Semi-quantum private comparison protocol of size relation with d-dimensional GHZ states. Chin Phys B (2022) 31(1):010302. doi:10.1088/1674-1056/ac1413
20. Gong LH, Li ML, Cao H, Wang B. Novel semi-quantum private comparison protocol with Bell states. Laser Phys Lett (2024) 21(5):055209. doi:10.1088/1612-202x/ad3a54
21. Wang B, Gong LH, Liu SQ. Multi-party semi-quantum private comparison protocol of size relation based on two-dimensional Bell states. Chin Phys B (2024) 33(11):110303. doi:10.1088/1674-1056/ad73ae
22. Zhou NR, Chen ZY, Liu YY, Gong L. Multi-party semi-quantum private comparison protocol of size relation with d-level GHZ states. Adv Quan Tech (2024) 8:2400530. doi:10.1002/qute.202400530
23. Huang X, Zhang SB, Chang Y, Hou M, Cheng W. Efficient quantum private comparison based on entanglement swapping of bell states. Int J Theor Phys (2021) 60:3783–96. doi:10.1007/s10773-021-04915-9
24. Hou M, Wu Y. Single-photon-based quantum secure protocol for the socialist millionaires’ problem. Front Phys (2024) 12:1364140. doi:10.3389/fphy.2024.1364140
25. Huang X, Zhang SB, Cheng W. Quantum private comparison based on GHZ-type states[C]//2021 IEEE AFRICON. IEEE (2021). p. 1–4.
26. Hou M, Wu Y, Zhang S. New quantum private comparison using four-particle cluster state. Entropy (2024) 26(6):512. doi:10.3390/e26060512
27. Lian JY, Ye TY, Ye CQ. Circular semiquantum private comparison protocol for equality without a preshared key based on χ-type states. Phys Rev Appl (2025) 23(4):044006. doi:10.1103/physrevapplied.23.044006
28. Huang X, Zhang W, Zhang S. Quantum multi-party private set intersection using single photons. Physica A: Stat Mech its Appl (2024) 649:129974. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2024.129974
29. Tamilselvi P, Lathika V, Jayachitra S, Arunkumar S, Balasubramani M, Kalaichelvi V. Secure multi-party computation for collaborative data analysis in network security[C]. In: 2024 international conference on intelligent and innovative technologies in computing, electrical and electronics (IITCEE). IEEE (2024). p. 1–5.
30. Liu J, Tian Y, Zhou Y, Xiao Y, Ansari N. Privacy preserving distributed data mining based on secure multi-party computation. Computer Commun (2020) 153:208–16. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.014
31. Sahinbas K, Catak FO. Secure multi-party computation-based privacy-preserving data analysis in healthcare IoT systems[M]//Interpretable Cognitive Internet of Things for Healthcare. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2023). p. 57–72.
32. Naidu PS, Kharat R, Tekade R, Mendhe P, Magade V. E-voting system using visual cryptography and secure multi-party computation[C]. In: 2016 international conference on computing communication control and automation (ICCUBEA). IEEE (2016). p. 1–4.
33. Pu H, Cui Z, Liu T. An electronic voting scheme using secure multi-party computation based on secret sharing. Int J Netw Security (2021) 23(6):997–1004. doi:10.6633/IJNS.202111_23(6).06
34. Zhang Q, Xin C, Wu H. Privacy-preserving deep learning based on multiparty secure computation: a survey. IEEE Internet Things J (2021) 8(13):10412–29. doi:10.1109/jiot.2021.3058638
35. Tran AT, Luong TD, Karnjana J, Huynh VN. An efficient approach for privacy preserving decentralized deep learning models based on secure multi-party computation. Neurocomputing (2021) 422:245–62. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2020.10.014
36. Huang Y, Yu J, Wang D, Lu X, Dufaux F, Guo H, et al. Learning-based fast splitting and directional mode decision for VVC intra prediction. IEEE Trans Broadcasting (2024) 2(1):681–92. doi:10.1109/tbc.2024.3360729
38. Yao AC. Protocols for secure computations. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE symposium on foundations of computer science. Washington, DC, USA: FOCS’ 82 (1982). p. 160.
39. Hou M, Sun SY, Zhang W. Quantum private comparison for the socialist millionaire problem. Front Phys (2024) 12:1408446. doi:10.3389/fphy.2024.1408446
40. Huang X, Zhang WF, Zhang SB. Efficient multiparty quantum private comparison protocol based on single photons and rotation encryption. Quan Inf Process (2023) 22(7):272. doi:10.1007/s11128-023-04027-9
41. Hou M, Wu Y, Zhang S. Efficient quantum private comparison based on GHZ states. Entropy (2024) 26(5):413. doi:10.3390/e26050413
42. Huang X, Zhang S, Xia J. Efficient quantum private comparison using locally indistinguishable orthogonal product states[C]. In: International conference on artificial intelligence and security. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2022). p. 260–73.
43. Hou M, Wu Y. New quantum private comparison using bell states. Entropy (2024) 26(8):682. doi:10.3390/e26080682
44. Shi RH. Quantum sealed-bid auction without a trusted third party. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Regular Pap (2021) 68(10):4221–31. doi:10.1109/tcsi.2021.3103857
45. Qiu C, Zhang S, Chang Y, Huang X, Chen H. Electronic voting scheme based on a quantum ring signature. Int J Theor Phys (2021) 60:1550–5. doi:10.1007/s10773-021-04777-1
46. Wen J, Zhang Z, Lan Y, Cui Z, Cai J, Zhang W. A survey on federated learning: challenges and applications. Int J Machine Learn Cybernetics (2023) 14(2):513–35. doi:10.1007/s13042-022-01647-y
47. Ahuja A, Kapoor S. A quantum algorithm for finding the maximum. arXiv preprint quant-ph/9911082. (1999).
48. Durr C, Hoyer P. A quantum algorithm for finding the minimum. arXiv preprint quant-ph/9607014. (1996).
49. Huang X, Zhang W, Zhang S. Practical quantum protocols for blind millionaires’ problem based on rotation encryption and swap test. Physica A: Stat Mech its Appl (2024) 637(10.1):129614. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2024.129614
50. Christensen RB, Popovski P. Private product computation using quantum entanglement. IEEE Trans Quan Eng (2024) 4:1–9. doi:10.1109/tqe.2023.3320052
51. Chen Y, Situ H, Huang Q, Zhang C. A novel quantum private set intersection scheme with a semi-honest third party. Quan Inf Process (2023) 22(12):429. doi:10.1007/s11128-023-04195-8
52. Huang Y, Chen J, Feng C, Chen R. Some families of asymmetric quantum MDS codes constructed from constacyclic codes. Int J Theor Phys (2018) 57:453–64. doi:10.1007/s10773-017-3578-1
53. Beale SJ, Wallman JJ, Gutiérrez M, Brown KR, Laflamme R. Quantum error correction decoheres noise. Phys Rev Lett (2018) 121(19):190501. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.121.190501
54. Hou M, Wu Y. Two-party quantum private comparison protocol for direct secret comparison. Mathematics (2025) 13(2):326. doi:10.3390/math13020326
55. Li J, Che F, Wang Z, Fu A. Efficient quantum private comparison without sharing a key. Entropy (2023) 25(11):1552. doi:10.3390/e25111552
56. Hou M, Wu Y. Efficient quantum private comparison with unitary operations. Mathematics (2024) 12(22):3541. doi:10.3390/math12223541
57. Huang X, Chang Y, Cheng W, Hou M, Zhang SB. Quantum private comparison of arbitrary single qubit states based on swap test. Chin Phys B (2022) 31(4):040303. doi:10.1088/1674-1056/ac4103
58. Gisin N, Fasel S, Kraus B, Zbinden H, Ribordy G. Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys Rev A—Atomic, Mol Opt Phys (2006) 73(2):022320. doi:10.1103/physreva.73.022320
59. Deng FG, Li XH, Zhou HY, Zhang Z. Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys Rev A—Atomic, Mol Opt Phys (2005) 72(4):044302. doi:10.1103/physreva.72.044302
Keywords: privacy-preserving, maximum value determination, local operations, fairness, security
Citation: Hou M and Wu Y (2025) Privacy-preserving maximum value determination scheme. Front. Phys. 13:1592890. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1592890
Received: 13 March 2025; Accepted: 04 July 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Yuanyuan Huang, Chengdu University of Information Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Bing Wang, Nanchang University, ChinaP. Muthulakshmi, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Hou and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Hou, aG91bWluQHNjdWpqLmVkdS5jbg==
 Min Hou
Min Hou Yue Wu1
Yue Wu1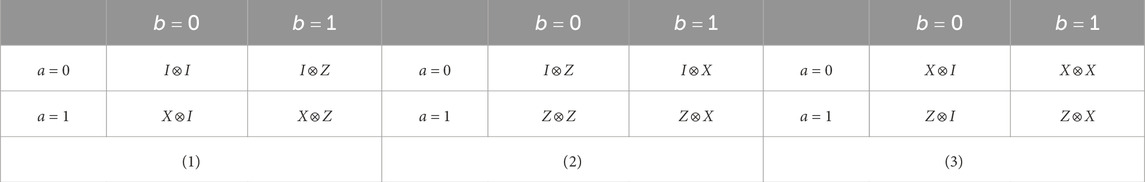
![Quantum circuit diagram with six qubits labeled q[0] to q[5]. It features Hadamard (H) gates, controlled gates, and Ry rotation gates with different angles. Measurements are shown in gray blocks.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1592890/fphy-13-1592890-HTML/image_m/fphy-13-1592890-g002.jpg)