Abstract
Introduction:
Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) oscillators play a pivotal role in diverse applications such as biosensors and wearable sensors. To optimize their performance and ensure reliability, exploring their periodic properties and pull-in instability during the study of MEMS oscillators with singularity is crucial. The harmonic balance method, a prevalent approach for analyzing nonlinear systems, is selected as the research focus.
Methods:
This study conducts an in-depth theoretical analysis of the harmonic balance method applied to MEMS oscillators. The treatment of singular terms and the selection of approximate solutions within this method are meticulously examined.
Results:
The analysis reveals that the handling of singular terms and the choice of approximate solutions in the harmonic balance method have a significant impact on the accuracy of determining the pull-in condition. Incorrect choices can lead to large errors, while a well-chosen approximate solution can remarkably improve the accuracy of predicting pull-in instability.
Discussion:
The research findings provide valuable insights for enhancing the application of the harmonic balance method in the analysis of MEMS oscillators. These results can serve as references for future studies aiming to further optimize the performance and reliability of MEMS oscillator-based devices.
1 Introduction
Recent years have seen a significant expansion in the field of Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS). This growth can be attributed to the system’s capacity to integrate mechanical and electrical components at a microscopic scale, thereby enabling miniaturized devices with diverse applications across multiple disciplines [1–3].
In the field of mathematics, the development of MEMS has led to significant advancements in advanced modelling and simulation techniques [4–6]. These techniques assist researchers in the creation of complex mathematical models to describe the behavior of MEMS devices, taking into account factors such as micro-scale fluid dynamics, mechanical vibrations and electrical interactions. The development of such models is of paramount importance for the optimization of MEMS device design and performance.
In the domain of nanotechnology, Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) play a pivotal role in the fabrication of nanoscale structures. The integration of nanowires and nanotubes into MEMS sensors has been demonstrated to enhance their sensitivity and selectivity, thereby resulting in highly efficient chemical and biological sensing devices [7, 8].
The field of material science has undergone significant transformations in the wake of MEMS. The demand for specific material properties has driven the development of new materials for MEMS applications. For instance, enhanced piezoelectric materials have been shown to facilitate more efficient energy harvesting and actuation in MEMS devices [9, 10].
MEMS oscillators are of particular importance within the domain of MEMS components [11]. Their utilization is pervasive in energy harvesters [12] and accelerometers [13]. In biosensors, they facilitate precise detection and analysis of biological substances by converting biomolecule-sensor surface interactions into electrical signals. In the context of wearable sensors, they enable uninterrupted monitoring of physiological parameters, including body movements and heart rate.
However, in the research of MEMS oscillators, several aspects require consideration. The periodic property is pivotal in determining the oscillator’s stable operation and frequency characteristics. It is imperative to comprehend the phenomenon of pull-in instability, as its onset can culminate in device failure when the oscillator approaches this state [14, 15]. Additionally, energy conversion efficiency affects power consumption, and temperature stability is vital due to the often varying operating temperatures of MEMS oscillators.
The harmonic balance method is a common technique for analyzing nonlinear systems [16, 17]. This method involves the representation of the response of a nonlinear system as a sum of harmonic functions, thereby providing a relatively simple means by which to analyze complex nonlinear behavior. In the context of MEMS oscillators, this method can occasionally yield analytical solutions, which are valuable for understanding the relationship between system parameters and oscillator performance.
However, it is important to note that the harmonic balance method has limitations when applied to MEMS oscillators. MEMS oscillators exhibit singular terms, which complicates the enhancement of solution accuracy in the vicinity of singularities. Furthermore, the method’s outputs are found to be highly sensitive to harmonic components, necessitating the inclusion of additional components to achieve higher levels of accuracy, which in turn increases the complexity of the calculations. Furthermore, as the applied voltage in MEMS oscillators changes, the system may shift from periodic motion to pull-in instability [18–20], further complicating the analysis.
It is evident that alternative methods, including the homotopy perturbation method [21, 22], the variational iteration method [23, 24], the variational principle [25, 26] and He’s frequency formulation [27, 28], have demonstrated efficacy in addressing singularities. These methods offer different ways to approximate solutions of nonlinear systems and may overcome the limitations of the harmonic balance method in MEMS oscillator analysis. The present study aims to explore the application and limitations of the harmonic balance method in MEMS oscillator analysis and to compare it with alternative methods, thereby providing insights for further research in this field.
2 Harmonic balance methods
The harmonic balance method is a well-established and powerful technique in engineering and physics, serving as a fundamental tool for analyzing nonlinear systems. The underlying principle of this method is based on the representation of the response of a nonlinear system as a sum of harmonic functions.
For a general nonlinear system described by an ordinary differential equation of the form:where f is a nonlinear function. Equation 1 has periodic solution when f/w > 0, and we assume the periodic solution has the following form:where is the frequency, and are coefficients to be determined late.
This method offers several advantages. It provides a relatively straightforward and intuitive way to analyze nonlinear systems. By decomposing the complex nonlinear behavior into individual harmonic components, engineers and researchers can more easily understand and study the fundamental characteristics of nonlinear oscillators. Specifically, it enables the analysis of frequency response and amplitude-related behavior independently. In numerous instances, the harmonic balance method has been shown to yield analytical solutions. These solutions establish explicit relationships between system parameters (e.g., capacitance, stiffness, and applied voltage in MEMS oscillators) and solution characteristics (e.g., amplitude and frequency). This enables a deeper understanding of how changes in these parameters affect the oscillator’s performance. To illustrate this point, consider the analytical expression for the amplitude of a MEMS oscillator in terms of capacitance and applied voltage. This expression can reveal the precise relationship between an increase in voltage and an increase in amplitude.
However, when applied to MEMS oscillators, the harmonic balance method also has some notable drawbacks. Firstly, MEMS oscillators contain singular terms. Conventional numerical techniques frequently employed in the harmonic balance method encounter difficulties in dealing with these singularities, thereby hindering the enhancement of the solution’s accuracy in the vicinity of these points. This can result in substantial errors in the approximation of the oscillator’s behavior. Secondly, the accuracy of the results obtained using the harmonic balance method is highly sensitive to the number of harmonic components considered. Achieving a high level of accuracy in the solution often necessitates the consideration of a substantial number of harmonic components. This not only increases the complexity of the calculation but also makes the computational process more time-consuming. Thirdly, it is important to note that MEMS oscillators exhibit a wide range of dynamical properties. As the voltage increases gradually, the system may transition from periodic motion to pull-in instability. The harmonic balance method may not be able to accurately capture this complex transition behavior, further limiting its effectiveness in analyzing MEMS oscillators.
3 MEMS oscillators
The present paper focuses on a specific MEMS oscillator, the governing equation of which is given [4]:
In this equation, w represents the dimensionless displacement and k is the voltage parameter. This equation is singular, and the presence of this singularity serves to render the problem considerably more complex [29].
In order to apply the harmonic balance method [16, 17], it is necessary to treat with the singular term. To this end, Equation 2 is rewritten in the form:
This transformation is a crucial initial step, as it aligns the equation with the principles of the harmonic balance method, thereby enabling the use of the approximation techniques of this method.
Subsequent to the establishment of the initial conditions of the oscillator, it is assumed that the solution may be expressed in the following form:where A and are unknown for further determination.
Substituting Equation 4 into Equation 3 yields the residual function R:which represents the net force imbalance at each phase (). To satisfy the harmonic balance principle, we evaluate its residual function R at = 0 and , the points corresponding to the oscillator’s equilibrium position and maximum displacement, where the linear stiffness and nonlinear electrostatic forces are most dominant. Setting R = 0 at these locations, we obtain
Equations 5, 6 enforce force balance at critical phases, allowing us to solve for the unknown coefficients A and by projecting the nonlinearity onto the fundamental harmonic component:which provide explicit expressions for the coefficients in terms of the system parameters.
In this study, we will be comparing the approximate solutions obtained using the harmonic balance method with the exact solutions. As demonstrated in Figure 1, the figure reveals a substantial discrepancy between the approximate and exact solutions for different values of k. This discrepancy can be attributed primarily to the selection of the trial solution, as outlined in Equation 4, and the handling of the singularity during the solution process.
FIGURE 1
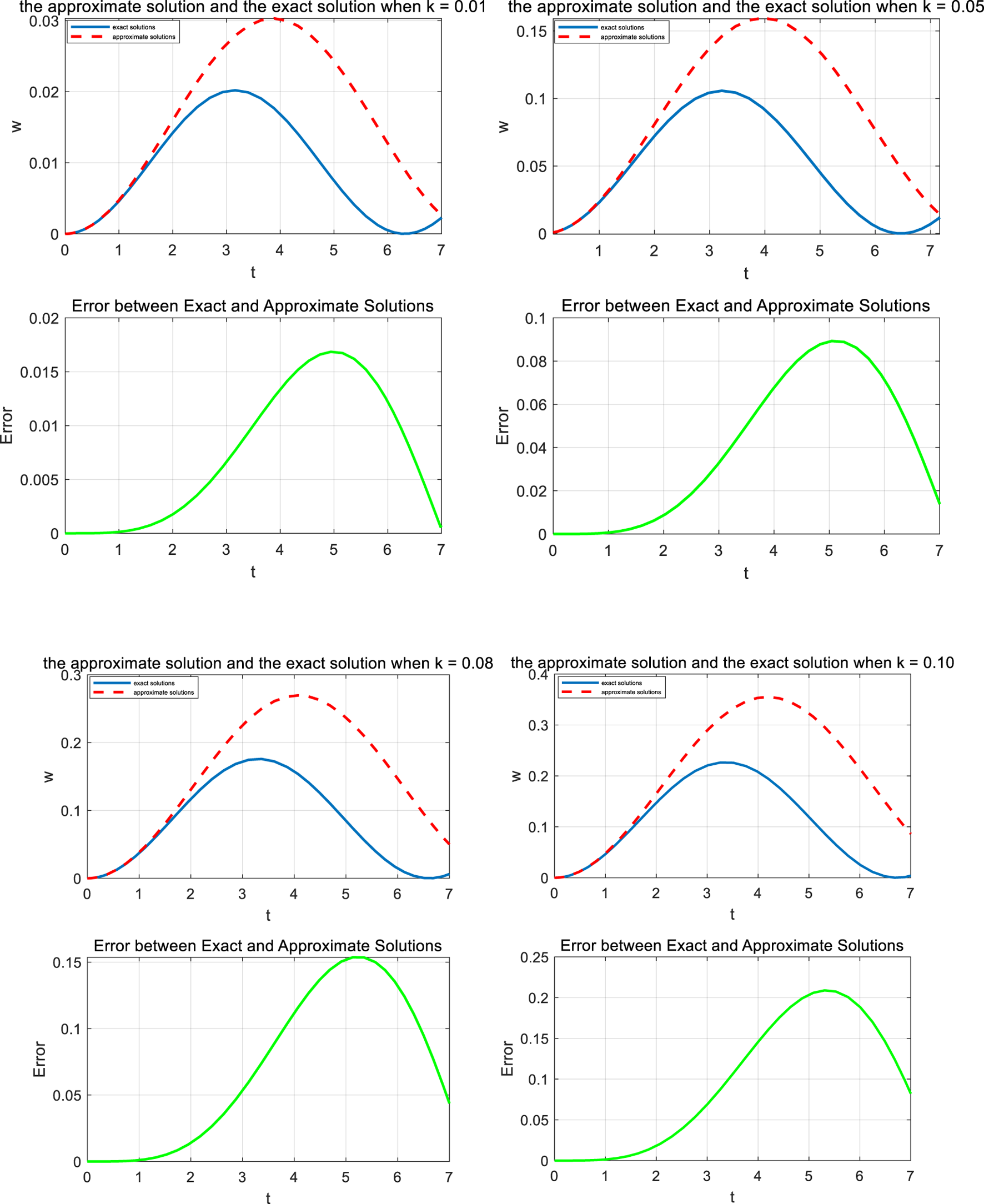
Comparison of the approximate solution of Equation 4 (continued line) with the exact ones (discontinued line) for different values of k.
For the purpose of comparison, an alternative approach to treating the singular term is hereby presented. Utilizing the Taylor series, the following equation can be expressed as:
Substituting Equation 4 into Equation 7 results in the following residual
By a similar operation as above, we have
Equation 8 is equivalent to Equation 5, and Equation 9 can be expressed as follows:
By simultaneously solving Equations 8, 10, we obtain
Based on Equation 11, when A = 1, the pull - in instability emerges and the pull - in voltage is k = 0, a situation that deviates significantly from real - world conditions. Clearly, this method of dealing with the singular term is ineffectual. Given this shortcoming, we shift our focus to selecting an alternative approximate solution in the following form:where B and are unknown for further determination.
The alternative trial solution is proposed to address the limitations of the harmonic approximation of Equation 4, , though it is simple, and meets the initial conditions with a higher harmonic component (), while Equation 12 has lower harmonics with also a simple harmonic component (). This simple modification is critical for improvement of its accuracy.
By a similar operation as above, we obtain the following residual:
We set R = 0 at two location points and , this results in
Figure 2 shows the comparison between the new approximate solution and the exact solutions for different values of k. It is evident that the selection of the trial solution and the treatment of singular terms are pivotal in the harmonic balance method. As discussed in the homotopy perturbation method [30], an initial guess that is well-founded invariably yields an ideal result. The singularity treatment ensures the reliability of the solution process.
FIGURE 2
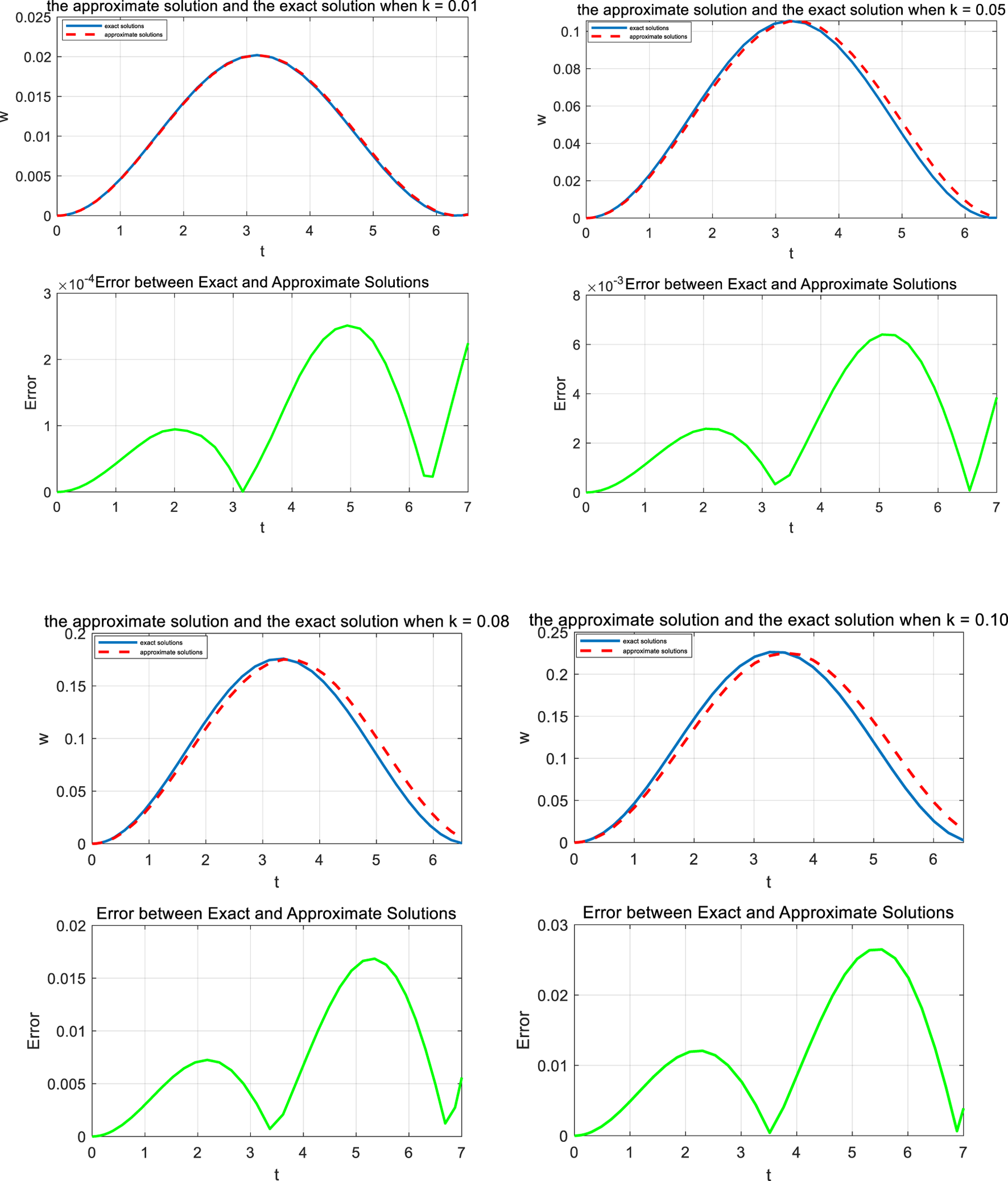
Comparison of the approximate solution of Equation 12 (continued line) with the exact ones (discontinued line) for different values of k.
Pull-in instability occurs when , this results in B = 2/3, and the pull-in voltage k = 2/9, while the exact pull-in voltage is k = 0.20363, the relative error is 9.13%. This error may be acceptable for some engineering applications, but for more precise requirements, further improvement of the analysis method is needed. We can increase the accuracy by considering more harmonic components in the approximate solution or using more advanced numerical techniques to handle the singularities.
To improve the accuracy, the trial solution should include more harmonical components:
In view of the initial conditions, the coefficients in Equation 13 satisfy the following condition
We can choose N location points to determine and , this can greatly improve the accuracy, but it also increases the complexity of the calculation.
4 Discussion and conclusion
The present work makes two distinct contributions to the analysis of MEMS oscillators with singularities. First, unlike traditional approaches that employ homotopy perturbation [31, 32] or variational iteration method [33–35] or numerical methods [36, 37] to address nonlinearity, we demonstrate that the strategic trial function selection in the harmonic balance method can mitigate singularity-induced errors with minimal computational overhead. This offers a design-friendly alternative for rapid parametric analysis, as shown by the 9.13% improvement in pull-in voltage prediction compared to the naive sinusoidal trial solution. The accuracy can be improved if more harmonic components are involved in the trial function. Second, we provide a suitable treatment of the singularity that quantifies the trade-off between trial function complexity and accuracy, a critical gap in prior HBM applications to MEMS. While methods like HPM may achieve higher precision, our approach prioritizes analytical transparency and computational efficiency, making it suitable for preliminary design stages or educational contexts. The insights herein thus expand the utility of HBM in MEMS research and establish a benchmark for future hybrid analytical-numerical methodologies.
Unlike prior studies that rely on complex transformations (e.g., homotopy or series expansions), we demonstrate that simply modifying the trial solution form can significantly reduce singularity-induced errors. This approach retains HBM’s analytical simplicity while improving accuracy, as shown in Figure 2.
In the in - depth study of MEMS oscillators, this paper has presented a detailed comparison between the harmonic balance method and the homotopy perturbation method. MEMS oscillators, with their complex structures and unique operating characteristics, pose significant challenges in the field of analysis.
The harmonic balance method, which is widely applied in engineering and physics, has limitations when used in the analysis of MEMS oscillators. Due to the complexity of MEMS oscillators, the harmonic balance method faces issues such as parameter errors and singularities, which significantly affect the accuracy of the results. Parameter errors stem from various sources. Manufacturing process variations can change the physical dimensions and material properties of oscillator components. For example, minor changes in the thickness of the vibrating structure or the dielectric constant of capacitive elements can notably impact the oscillator’s performance. Environmental factors, especially temperature fluctuations, also play a crucial role. As the temperature changes, the Young’s modulus of the structural materials varies, affecting the oscillator’s stiffness, resonant frequency, and other characteristics. These errors accumulate during the analysis process, making it difficult to accurately predict the behavior of MEMS oscillators.
The homotopy perturbation method shows great potential as an alternative. It can effectively handle the singularities in MEMS oscillators. By leveraging the concept of homotopy, it transforms complex problems into simpler ones, circumventing the difficulties posed by singularities and obtaining more accurate and reliable solutions. This helps in a deeper understanding of the behavior of MEMS oscillators, providing support for optimizing their design and performance. For instance, in the design of high - precision MEMS - based sensors, accurately predicting the oscillator behavior can enhance the sensor’s sensitivity and stability.
However, although the homotopy perturbation method has obvious advantages in dealing with singularities, the harmonic balance method still has its value. The harmonic balance method is intuitive when analyzing the basic characteristics of MEMS oscillators. In some cases, it can yield analytical solutions, facilitating a quick understanding of the relationship between system parameters and oscillator performance. Thus, it can serve as a reference in the initial stage of analysis or when a rough estimate is sufficient.
Looking ahead, this study motivates several avenues for advancing MEMS oscillator analysis. First, refining the harmonic balance method through higher-order trial functions or adaptive singularity modeling could further reduce errors in pull-in voltage predictions, particularly for systems operating near critical gaps. Second, developing hybrid HBM-numerical frameworks—such as using HBM solutions as preconditions for finite element simulations—holds promise for balancing computational efficiency and accuracy in complex geometries. Third, extending the methodology to multi-physics MEMS systems (e.g., thermal or fluid-coupled oscillators [38–40]) will address real-world operational challenges, such as temperature-induced drift. Finally, integrating machine learning [41], AI-powered problem solving [42] and ResNet Neural Network [43] and advanced numerical simulation methods [44] with analytical models could create self-calibrating frameworks that adapt to manufacturing tolerances and experimental data. These advancements will strengthen the harmonic balance method’s utility across precision engineering, nanotechnology, and bio-MEMS applications.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
X-HL: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Data curation. YC: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
SpiegelCABlascoE. 3D printing enables mass production of microcomponents. Nature (2024) 627(8003):276–7. 10.1038/d41586-024-00492-z
2.
NadeemMAinQTAlmakayeelNShaoYBWangSQShutaywiM. Analysis of nanobeam-based microstructure in n/mems system using Van der Waals forces. Facta Universitatis-Series Mech Eng (2024) 22(4):673–88. 10.22190/FUME240904048N
3.
ZhangYNHanYMZhaoXZhaoZPangJ. Applying numerical control to analyze the pull - in stability of MEMS systems. Therm Sci (2024) 28(3A):2171–8. 10.2298/TSCI2403171Z
4.
TianYShaoY. Mini-review on periodic properties of mems oscillators. Front Phys (2024) 12:1498185. 10.3389/fphy.2024.1498185
5.
HeJ-H. Periodic solution of a micro-electromechanical system. Facta Universitatis, Ser Mech Eng (2024) 22(2):187–98. 10.22190/FUME240603034H
6.
ShaoYCuiY. Mathematical approach for rapid determination of pull - in displacement in MEMS devices. Front Phys (2025) 13:1521849. 10.3389/fphy.2025.1521849
7.
NisarAAftuIpurkarNMahaisavariyaBTuantranontA. MEMS - based micropumps in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Sensors Actuators B: Chem (2008) 130(2):917–42. 10.1016/j.snb.2007.10.064
8.
HeJ-HBaiQLuoY-CKuangaliyevaDEllisGYessetovYet alModeling and numerical analysis for MEMS graphene resonator. Front Phys (2025) 13. Article 1551969. 10.3389/fphy.2025.1551969
9.
Trolier-McKinstrySMuraltP. Thin film piezoelectrics for MEMS. J Electroceramics (2004) 12(1 - 2):7–17. 10.1023/b:jecr.0000033998.72845.51
10.
MuraltP. Recent progress in materials issues for piezoelectric MEMS. J Am Ceram Soc (2008) 91(5):1385–96. 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02421.x
11.
TianDAinQAnjumNHeC-HChengB. Fractal N/mems: from pull-in instability to pull-in stability. Fractals (2021) 29:2150030. 10.1142/S0218348X21500304
12.
ZhangJHouXQianSBiXHuDLiuJJet alFlexible multilayer MEMS coils and their application in energy harvesters. Sci China Technol (2024) 67:1282–93. 10.1007/s11431-023-2474-9
13.
LeXLKimKChoaSH. Analysis of temperature stability and change of resonant frequency of a capacitive MEMS accelerometer. Int J Precis Eng Manuf (2022) 23:347–59. 10.1007/s12541-021-00602-1
14.
DengZLaiCZhouJWangY. Design and analysis of a novel low RF MEMS switch with low pull-in voltage and high capacitance ratio. Microsyst Technol (2023) 29:809–21. 10.1007/s00542-023-05459-0
15.
KasambePVBholeKSRaykarNROzaADRameshRBhoirDV. Mechanical modeling, numerical investigation and design of cantilever beam for low pull-in MEMS switch. Int J Interact Des Manuf (2022). 10.1007/s12008-022-01024-7
16.
SharifMNMollaMHUAlimM. A simple modified harmonic balance method for strongly nonlinear oscillator with cubic non-linearity and harmonic restoring force. J Low Frequency Noise, Vibration Active Control (2024) 43(1):250–62. 10.1177/14613484231198958
17.
LuJ-FMaL. Analysis of a fractal modification of attachment oscillator. Therm Sci (2024) 28(3A):2153–63. 10.2298/tsci2403153l
18.
ZhangLGepreelKYuJ. He's frequency formulation for fractal - fractional nonlinear oscillators: a comprehensive analysis. Front Phys (2025) 13. Article 1542758. 10.3389/fphy.2025.1542758
19.
NiuJ-YFengG-Q. A mini-review on ancient mathematics’ modern applications with an emphasis on the old Babylonian mathematics for MEMS systems. Front Phys (2024) 12. Article 1532630. 10.3389/fphy.2024.153263
20.
HeJ-HAn old babylonian algorithm and its modern applications. Symmetry (2024) 16: 1467. 10.3390/sym16111467
21.
FengG. Higher-order homotopy perturbation method for the fractal rotational pendulum oscillator. J Vib Eng Technol (2024) 12:2829–34. 10.1007/s42417-023-01016-1
22.
HeC-HEl‐DibYO. A heuristic review on the homotopy perturbation method for non-conservative oscillators. J Low Frequency Noise, Vibration Active Control (2022) 41(2):572–603. 10.1177/14613484211059264
23.
FengG-QZhangLTangW. Fractal pull - in motion of electrostatic MEMS resonators by the variational iteration method. FRACTALS (2023) 31(9). 10.1142/S0218348X23501220
24.
TebyakinADYakovlevaTVKryskoAV. Stress-strain state analysis of porous elasto-plastic size-dependent plates subjected to hygro-mechanical loads using the variational iterations method. Lobachevskii J Math (2024) 45:2168–83. 10.1134/S1995080224600948
25.
HeC-H. A variational principle for a fractal nano/microelectromechanical (N/mems) system. Int J Numer Methods Heat and Fluid Flow (2022) 33(1):351–9. 10.1108/HFF-03-2022-0191
26.
NiuJ-Y. A remark on a strong minimum condition of a fractal variational principle. Therm Sci (2024) 28(3A):2371–7. 10.2298/tsci2403371n
27.
ZhangJ-GSongQ-RZhangJ-QWangF. Application of He’s frequency formula to nonlinear oscillators with generalized initial conditions. Facta Universitatis, Ser Mech Eng (2023) 21(4):701–12. 10.22190/FUME230909047Z
28.
MohammadianM. Application of He's new frequency - amplitude formulation for the nonlinear oscillators by introducing a new trend for determining the location points. Chin J Phys (2024) 89:1024–40. 10.1016/j.cjph.2024.03.047
29.
HeC-HLiuC. Variational principle for singular waves. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals (2023) 172:113566. 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113566
30.
HeJHHeCHAlsolamiAA. A good initial guess for approximating nonlinear oscillators by the homotopy perturbation method. Facta Universitatis - Ser Mech Eng (2023) 21(1):021–9. 10.22190/fume230108006h
31.
MoussaBYoussoufMAbdoul WassihaNYoussoufP. Homotopy perturbation method to solve Duffing - Van der Pol equation. Adv Differential Equations Control Process (2024) 31(3):299–315. 10.17654/0974324324016
32.
AlshomraniNAMAlharbiWGAlanaziIMAAlyasiLSMAlrefaeiGNMAl’amriSAet alHomotopy perturbation method for solving a nonlinear system for an epidemic. Adv Differential Equations Control Process (2024) 31(3):347–55. 10.17654/0974324324019
33.
YiTShaoYShenYHeJ-H. A variational principle of an electrohydrodynamic fluid. Mod Phys Lett A (2025) 40(04):2450223. 10.1142/S0217732324502237
34.
GuanYZGepreelKAHeJH. Variational formulations for a coupled fractal - fractional KdV system. Fractals (2024) 32(03). 10.1142/S0218348X24500543
35.
TangWAnjumNHeJ-H. Variational iteration method for the nanobeams-based N/MEMS system. MethodsX (2023) 11:102465. 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102465
36.
HanCWangYLLiZY. A high-precision numerical approach to solving space fractional Gray-Scott model. Appl Mathematics Lett (2022) 125:107759. 10.1016/j.aml.2021.107759
37.
CheHYu-LanWZhi-YuanL. Novel patterns in a class of fractional reaction-diffusion models with the Riesz fractional derivative. Mathematics Comput Simulation (2022) 202:149–63. 10.1016/j.matcom.2022.05.037
38.
YangLZhangJXiaJZhangSYangYChuZ. Sound transmission loss of helmholtz resonators with elastic bottom plate. Sound and Vibration (2024) 58:171–83. 10.32604/sv.2024.056968
39.
PangJMaoTTJiaWYJiaXDaiPHuangH. Prediction and analysis of vehicle interior road noise based on mechanism and data series modeling. Sound and Vibration (2024) 58:59–80. 10.32604/sv.2024.046247
40.
YahyaMFDanRMSamsubahaMFRashidZPutraA. Study of axial vibration of a motor - compressor system using operational modal analysis. Sound and Vibration (2023) 57(1):119–31. 10.32604/sv.2023.045029
41.
SuKHWeiJLiMLiHDaWHZhangL. Research on stick - slip vibration suppression method of drill string based on machine learning optimization. Sound and Vibration (2023) 57(1):97–117. 10.32604/sv.2023.043734
42.
HeJH. Transforming frontiers: the next decade of differential equations and control processes. Adv Differential Equations Control Process (2025) 32(1):2589. 10.59400/adecp2589
43.
WuYRLiuXBHuangHBDingWYangM. Multi-objective prediction and optimization of vehicle acoustic package based on ResNet neural Network. Sound and Vibration (2023) 57(1):73–95. 10.32604/sv.2023.044601
44.
ZhangSZhangHLWangYLLiZY. Dynamic properties and numerical simulations of a fractional phytoplankton-zooplankton ecological model. Networks Heterog Media (2025) 20(2):648–669. 10.3934/nhm.2025028
Summary
Keywords
micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS, ), harmonic balance method, periodic solution, pull-in instability, analytical solution
Citation
Lei X-H and Cui Y (2025) Harmonic balance method for MEMS oscillators. Front. Phys. 13:1597421. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1597421
Received
21 March 2025
Accepted
06 June 2025
Published
20 June 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Dragan Marinkovic, University of Novi Sad, Serbia
Reviewed by
Lei Zhao, Yancheng polytechnic college, China
Marcelo Siqueira, Universidade Federal do Amapá, Brazil
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Lei and Cui.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yutong Cui, 1372468047@qq.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.