- 1Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
- 2Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
- 3University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Introduction: Efficient implementation of X-ray ghost imaging (XGI) with megapixel-level field-of-view and spatial resolution of few microns is key towards practical applications of XGI, but such implementation remains constrained by the time-consuming data acquisition and low-quality reconstruction for megapixel images under insufficient overall sampling rates.
Methods: We propose an efficient implementation scheme based on synthetic aperture X-ray ghost imaging (SAXGI), in which only one set of prior-recorded reference images is needed for ghost imaging of multiple objects.
Results: Experimental results demonstrated that images of three different objects, including tungsten fiber, resolution chart and small fish, can be successfully reconstructed with the same set of prior-recorded references, which implicates that the efficiency of data acquisition can be improved significantly. Taking advantage of SAXGI, image size of 2040 × 1440 pixels and system resolution of 10 μm was achieved. Results of a small fish show that comparable image quality is achieved with a sampling rate of 27.6%, which means that the radiation dose is reduced to about 1/4 of a conventional radiography. Furthermore, an extreme sampling rate down to 0.5% is enough to make out the skeleton of the fish, which further demonstrates high robustness and the low-dose potential of the proposed method for X-ray imaging.
Conclusions: In conclusion, the proposed method with a prior-recorded reference is applicable for XGI of multiple samples and the data acquisition efficiency is greatly improved. Through further hardware improvement of the imaging system, SAXGI with a prior-recorded reference is anticipated to provide an efficient solution for megapixel X-ray ghost imaging.
1 Introduction
X-ray ghost imaging (XGI), known as a non-local imaging method, is promising in simultaneously attaining high resolution and large field-of-view (FOV) with radiation dose lower than that of conventional radiology, which is a pivotal aim among research fields including biomedicine [1], material science [2], brain connectomics [3], etc. In a typical setup of the optical path for ghost imaging [4], a randomly intensity-modulated light beam is split into two identical beams, serving as illumination beams for the object and reference arms respectively. The light beam traversing the object arm is directed through the object into a bucket detector devoid of spatial resolution, while the beam in the reference arm propagates an equivalent distance, directly illuminating a planar detector capable of spatial resolution. The reconstructed image, through the correlation between the object and reference signals, resolves the resolution-FOV dichotomy inherent in local imaging, thereby facilitating the possibility of imaging that compromises neither resolution nor FOV with no substantial demand for full sampling dose as that of conventional radiology.
With the ongoing advancements in high-performance X-ray source capabilities, new methodology in X-ray imaging [5–12] and diversified methods for X-ray ghost imaging have been developed in past few decades [13–22]. With respect to experimental setup for ghost imaging, three strategies prevail in X-ray regime: actual beam-splitting strategy, “virtual” or equivalent beam-splitting strategy, and computational strategy [23]. XGI via the actual beam-splitting strategy, as it is, has two distinctive beams at any given time during the experiments to acquire object and reference signals [24–30]. Such strategy is intuitive in consistence with the typical setup and has the potential of dynamic X-ray ghost imaging. However, its validity is established when the two distinctive beams have truly identical intensity distributions, which is often not the case as expected [31]. Virtual beam-splitting strategy bypasses this problem by assuming that a single beam at distinctive moments can be considered as identical “beams” [32–37]. XGI via virtual beam-splitting strategy records object and reference signals at different moments, with the object being moved into and out of the optical path repeatedly, and such strategy suffers from time-inefficiency and low precision in mechanical alignment. Computational XGI abolishes the experimental recording of the reference signals to achieve efficient data acquisition by applying known masks as the light field modulator [38–43]. However, accurate calibration of X-ray masks is constrained by technical limitations, which makes it arduous to implement megapixel XGI via computational strategy.
We aim to achieve timely efficient while readily available X-ray ghost imaging with megapixel FOV and micron-level resolution at relatively low radiation cost, which is yet impractical through computational strategy due to the limitation of accurate mask calibration, and inefficient via virtual beam-splitting strategy in its repeated acquisition of reference signals for different objects. Here we propose an efficient XGI implementation scheme as a compromise between computational strategy and virtual beam-splitting strategy, which only requires recording high-resolution images in the reference arm once to achieve megapixel imaging of multiple objects. In this way, efficient data acquisition for megapixel XGI is achieved with readily available masks. Firstly, we introduces principles of the implementation scheme, which is based on synthetic aperture X-ray ghost imaging (SAXGI) [44] to achieve megapixel imaging with less measurement. Three types of objects are employed to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method for ghost imaging of multiple objects with the same set of prior-recorded references. Finally, conclusion and related discussion are brought out.
2 Principle and method
2.1 SAXGI with prior-recorded reference
Basic experimental setup for ghost imaging consists of two light paths: the object arm and the reference arm, incorporating a bucket detector
Let the bucket detector array used on the object arm be denoted as
Here, the two-dimensional array of bucket detectors on the object arm, denoted as
where
To reduce the number of measurements, i.e., lower the sampling rate of the bucket detector array units, the TVAL3 algorithm [45, 46] for reconstruction can be employed. Unlike conventional correlation-based ghost imaging reconstruction methods that typically require sufficient sampling densities, TVAL3 enables significant reduction in sampling requirements while faithfully recovering image details. The TVAL3 reconstruction algorithm for synthetic aperture ghost imaging is formulated as Equations 4–6:
Here, the optimization objective
Building on the fundamental principles of synthetic aperture ghost imaging, we developed a novel experimental setup with a prior-recorded reference, depicted in Figure 1. According to virtual beam-splitting strategies, the object in question
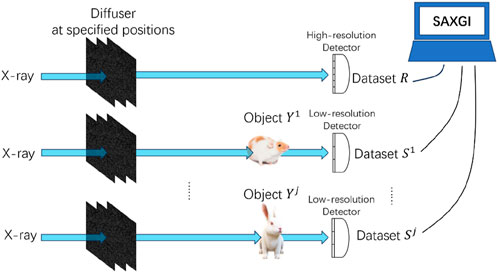
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the proposed experimental setup with a prior-recorded reference based on Synthetic Aperture X-ray Ghost Imaging (SAXGI). With the random scattering medium positioned at different specified locations
In the process of collecting data for multiple objects, provided that the positions of the random scattering medium precisely match between the two arms, it is possible to utilize a single set of reference arm data for different object reconstructions. Initially, the zeroth dataset is recorded prior to other detection--this is when no object is present in the optical path, and the modulated light field are recorded by a high-resolution detector with the diffuser at specified positions
In the optical path of SAXGI with prior-recorded reference, both the high-resolution detector and the low-resolution detector, i.e., the bucket detector array, are required not only to be precisely located at corresponding spatial positions but also to have certain matching in terms of pixel size. Specifically, the pixel size
so that a pixel
2.2 Experimental setup
In this experiment, we utilized a customized detector capable of achieving arbitrary pixel number binning to collect signals. Signal of the reference arm was recorded using the high-resolution mode without binning, while for recording signal of the object arm, the detector was binned according to specific requirements. Since the detector’s position remained unchanged while recording signals from both the object and reference arm signals, high-precision registration between the two arms’ signals was ensured. The detector model used was the Hamamatsu C15440-20UP01, with a pixel array of 2304 × 2304 and a pixel size of 6.5 μm × 6.5 μm, corresponding to a FOV of 14.976 mm × 14.976 mm. With a frame rate of 89.1 fps, the detector ensures rapid acquisition of signals from the object arm. During the acquisition of the object signal, pixel binning was performed by merging pixels from left to right, top to bottom, in square regions of
Based on existing numerical simulation results [44], selecting a pixel binning value of
We conducted the experiments at the BL13HB beamline of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility [48], with a photograph of the experimental setup shown in Figure 3. The experimental apparatus primarily consists of three components: motorized positioning systems for the diffuser (sandpaper), for the objects, and for the customized Hamamatsu detector respectively. Before the experiment, it is crucial to adjust the optical path to ensure the collimation of sandpaper, objects, and the detector along the X-ray beam. The motorized positioning stage for sandpaper scanning in X direction is a Kohzu XA16F-L2101, with a movement range of ±50 mm, a micro-step resolution of 0.5 μm, repeatability accuracy of ≤±0.5 μm, horizontal straightness of ≤4 μm/100 mm, and vertical straightness of ≤2 μm/100 mm. The motorized positioning stage for sandpaper scanning in Z direction is a Kohzu ZA16sA-32F01, with a movement range of
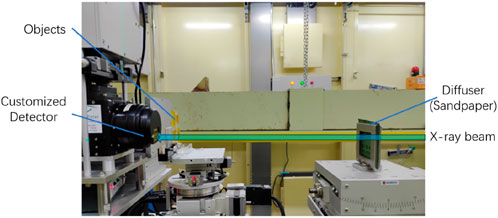
Figure 3. Photograph of the experimental setup, primarily composed of three main parts: a motorized positioning stage for random scattering medium (sandpaper), a motorized positioning stage for objects, and the customized Hamamatsu detector. The detector can achieve binning directly through electronic control without the need to change its position.
During the experimental process, we followed the aforementioned experimental scheme. Firstly, a set of high-resolution randomly modulated reference patterns, of the region of interest (ROI)
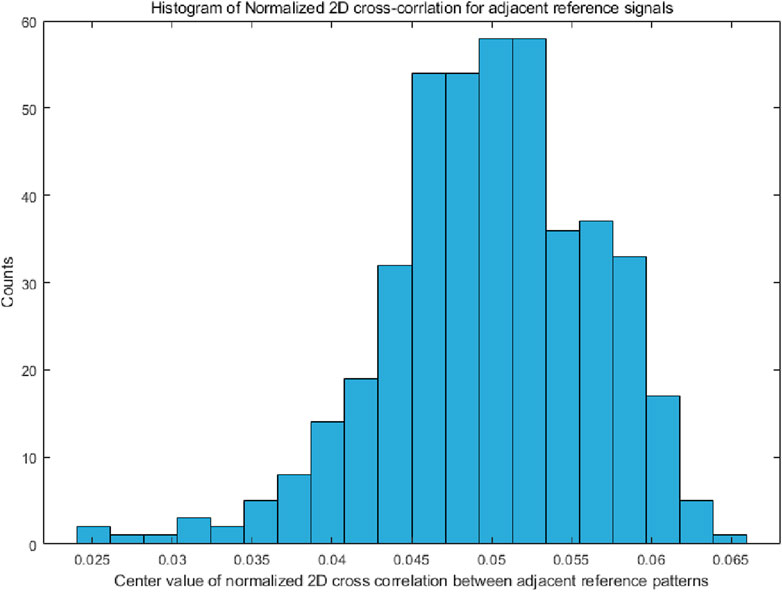
Figure 4. Histogram of the center value for the normalized 2-dimensional cross-correlation between adjacent reference patterns.
The prior-recorded references were then followed by the sequential capture of low-resolution images of the object arm, namely, a small fish (Poecilia reticulata), tungsten wire, and a resolution chart. Considering the impact of the detector’s dynamic range and background noise, a pixel binning of
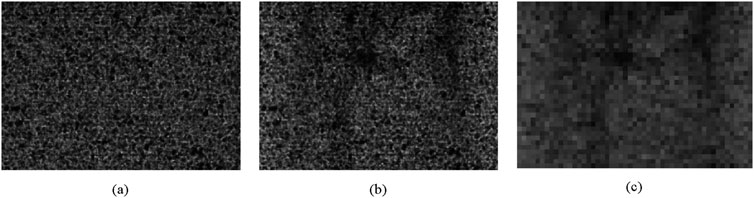
Figure 5. Typical images obtained from SAXGI data acquisition and subsequent processing, scaled to the same size for ease of comparison. (a) Reference signal with randomly modulated light field, with 2040 × 1440 pixels and an effective pixel size of 3.25 μm; (b) Object signal directly acquired with 4 × 4 binned detector, with 510 × 360 pixels and an effective pixel size of 13 μm; (c) Object signal used for SAXGI reconstruction, with 51 × 36 pixels and an effective pixel size of 130 μm.
3 Results and analysis
To validate SAXGI with prior recorded reference, we selected three test objects: tungsten wire, a resolution target, and a small fish, representing strong absorption objects, regular objects, and complex biological objects respectively. This was done to evaluate the performance of our scheme for different types of objects. We first collected a set of high-resolution images from the reference arm by scanning the sandpaper, then adjusted the detector to a 4 × 4 binning mode and sequentially acquired the object signals of the three objects at positions with their correspondent modulated light field. Subsequently, the same set of reference signals was used in reconstruction with the object signals for different objects. Recording the reference arm signal once to achieve SAXGI reconstruction for three different objects, in principle, verifies the feasibility of the efficient implementation of the proposed scheme for imaging multiple objects with a single reference scanning.
3.1 Sample with strong absorption
A tungsten wire object, approximately 20 μm in diameter, almost entirely absorbs 15 keV X-rays and can be considered a simple binary object. This setup allows us to assess the feasibility of imaging strongly absorbing objects with the proposed approach. Reconstruction results are displayed in Figure 6, with Figure 6a providing the target image of the tungsten wire. Figure 6b depicts the 40-binned image from the bucket detector array of the object arm, revealing that the object’s fine details are indiscernible. Figure 6c showcases the SAXGI reconstruction result, clearly revealing the tungsten wire’s details, including bends and closely spaced wire configurations. Furthermore, the weak absorption tape used to fasten the object is also revealed in the reconstructed image. Compared to the target image shown in Figure 6a, here Figure 6c recaptures all the structural details of the tungsten wire object, albeit with slightly reduced contrast. According to the definition of sampling rate
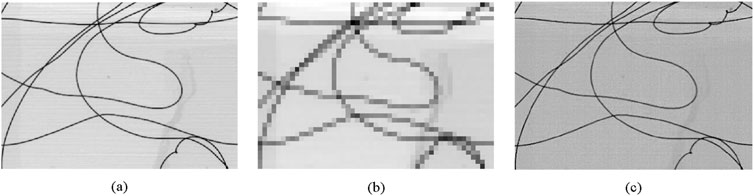
Figure 6. SAXGI with prior-recorded reference of a strong absorption tungsten wire object, where (a) the target image with
3.2 Resolution chart
Compared to the tungsten wire, the resolution chart represents a periodic structure object with relatively low absorption, thereby allowing the testing of the signal-to-noise ratio impact on imaging results within the proposed imaging system. Moreover, the spatial structure information of the resolution chart is more abundant, containing grating structures with periods ranging from 15.0 μm to 0.4 μm, which effectively tests the ability of the proposed method in resolving different spatial frequencies.
Figure 7 presents the SAXGI reconstruction for a resolution chart, where Figure 7a is the high-resolution target image of the resolution chart. Figure 7b shows the 40-binned image from the bucket detector array in the object arm, in which all the periodic structures are indiscernible. From the SAXGI reconstruction shown in Figure 7c, the unit with a period of 15 μm is clearly resolved, and the unit with a period of 10 μm is discernible, indicating that the spatial resolution is 10 μm. Due to noise, units with smaller periods are completely indistinguishable. Since individual pixels cannot resolve discrete objects, we conclude that 10 μm, corresponding to approximately 3 effective pixels of 3.25 μm in the reference arm, represents the best achievable spatial resolution of this system. Given the object’s inherently low contrast, the influence of noise is fully manifested in the reconstructed image of Figure 7c, where the primary source of noise could be the registration error between the low-resolution signal of the object arm and the high-resolution image of the reference arm. Scattering of X-rays by the resolution chart itself and its substrate material may also contribute to the significant noises.
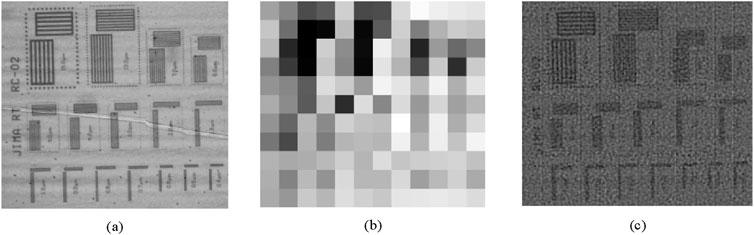
Figure 7. SAXGI with prior-recorded reference of a resolution chart, where (a) the target image with
3.3 Biological specimen
Tungsten wire object with strong absorption and resolution chart object with relatively weakly absorption and periodic structure are both artificial, and the capability to image actual complex objects is a key test of the utility of the method proposed in the paper. A small Poecilia reticulata fish was chosen as the test object to focus on the quality of SAXGI reconstruction to distinguish its skeletal distribution compared to traditional projection imaging. Figure 8 presents the reconstruction results for the small fish object, with Figure 8a showing the high-resolution projection image of the object, with an image size of 2040 × 1440. Figure 8b displays the 40-binned image from the bucket detector array of the object arm, illustrating that the details of the fish’s skeleton are difficult to be discerned. Figure 8c is SAXGI reconstruction result, which clearly resolves the complex skeletal distribution of the small fish. To further compare with the projection image, Figure 8d provides the grayscale distribution profiles at positions marked by the blue and red lines in Figures 8a,c respectively. It can be observed that in areas where the object signal is strong, corresponding to low relative grayscale areas in the absorption image, the SAXGI reconstruction matches well with the projection image. This demonstrates superior reconstruction capabilities of our method for regions with higher SNR. In other areas where the absorption signal is weak, corresponding to high relative grayscale areas, the intensity distribution trends of the two images are consistent, but the ghost imaging reconstruction shows significant random fluctuations in intensity. This indicates that the SAXGI reconstructed images exhibit noticeable noise, leading to reduced imaging contrast in areas where the object signal is weak.
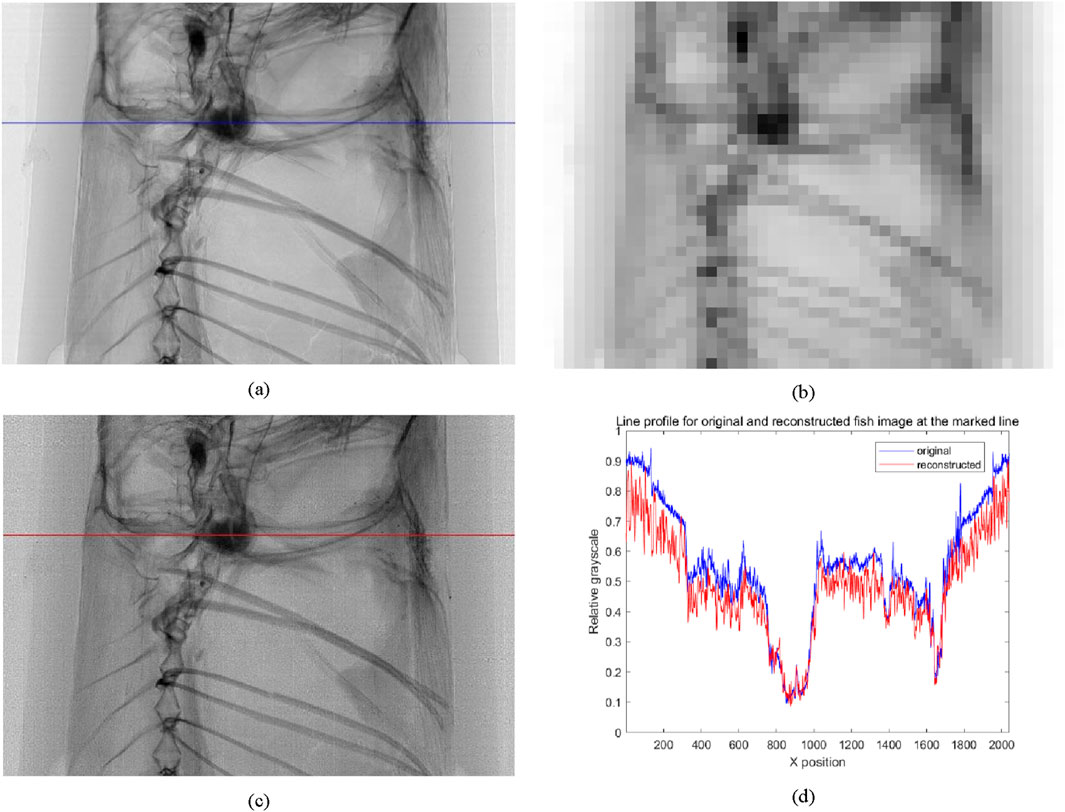
Figure 8. SAXGI with prior-recorded reference of a Poecilia reticulata fish, where (a) the high-resolution projection image with
Images reconstructed via SAXGI method exhibit irregular fluctuations compared to the original images, which could, on the one hand, originate from the residuals of the modulated speckle patterns and, on the other hand, be related to the spatial misalignment between blocks during segmented reconstruction. These factors, combined with other noise influences, result in the deteriorated signal-to-noise ratio of the SAXGI reconstructed images compared to traditional methods. Imperfect matching between the sandpaper scanning in the object and reference arms during multiple measurements could be a significant cause.
Recording the reference signal priorly and then sequentially collecting the object signals for three different objects, the proposed method is capable of reconstructing with high fidelity the structure details of the objects. These results indicate that the implementation scheme with a prior-recorded reference proposed in the paper can achieve ghost imaging of different objects. Data collection process in the proposed scheme is similar to traditional imaging methods and may favor the widespread application of X-ray ghost imaging.
3.4 Potential of low dose radiology
One potential advantage of SAXGI is the capability to achieve imaging at a low sampling rate, which implicates low radiation dose. The experimental results mentioned above were reconstructed using all 441 measurements. With a sampling rate of 27.6%, combined with compressed sensing algorithms such as TVAL3, satisfactory reconstruction results are achieved. Then, reconstructions will be conducted with fewer measurements to validate the performance of the proposed implementation scheme at even lower sampling rates. The reconstruction of the small fish skeletal structure with reduced sampling rates is shown in Figure 9, where Figure 9a is a full FOV projection image of
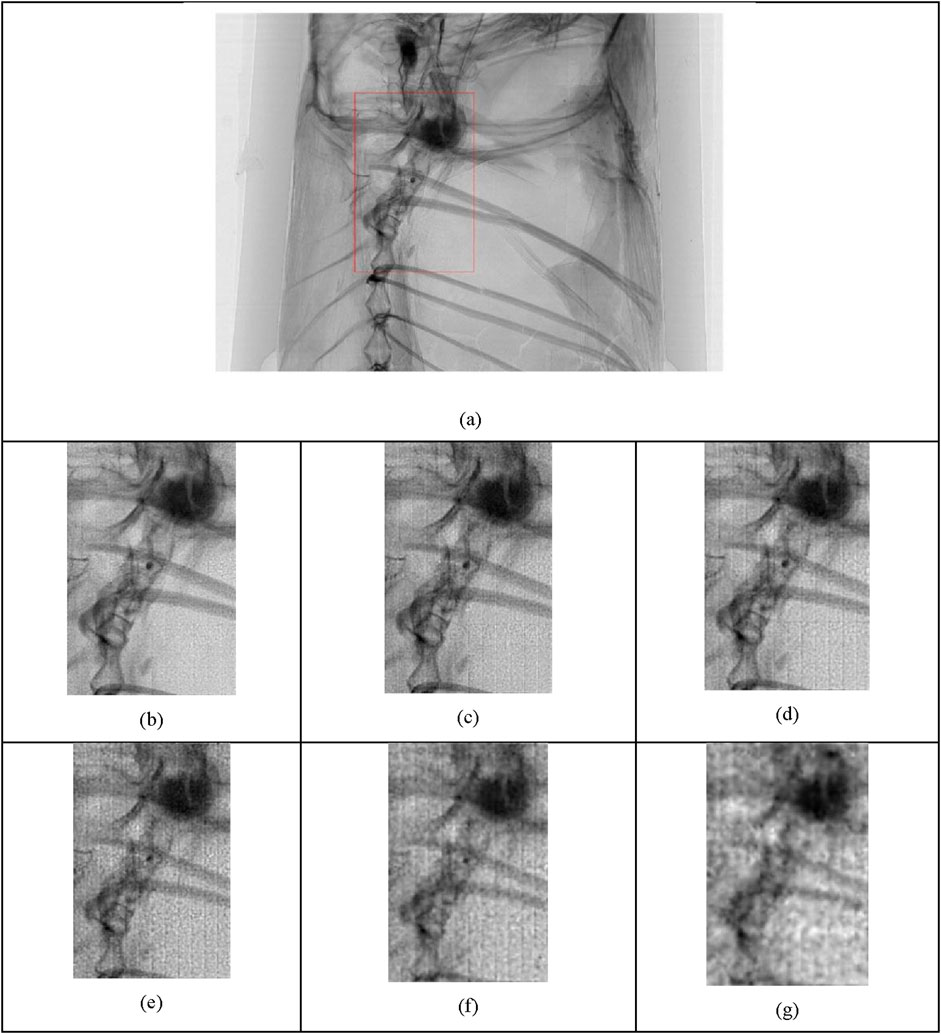
Figure 9. Reconstruction results of a Poecilia reticulata fish at low sampling rates, with an area of 480 × 720 concentrated. (a) High-resolution projection image, image size 2040 × 1440, with the concentrated 480 × 720 area highlighted in a red box; (b) Sampling rate of 27.6%, corresponding to 441 measurements; (c) Sampling rate of 12.5%, corresponding to 200 measurements; (d) Sampling rate of 6.3%, corresponding to 100 measurements; (e) Sampling rate of 3.1%, corresponding to 50 measurements; (f) Sampling rate of 1.25%, corresponding to 20 measurements; (g) Sampling rate of 0.5%, corresponding to 8 measurements.
From Figure 9, it is evident that as the sampling rate decreases, the block effect (see Section 4.1) in the reconstructed images becomes more pronounced, and the impact of noise is more significant. However, even at a sampling rate of 1.3% with 20 measurements used for reconstruction, the main structure of the small fish remains clearly discernible. Even when the number of measurements is reduced to 8, corresponding to a sampling rate of 0.5%, the skeletal outline can still be made out. This indicates that the proposed implementation scheme for SAXGI with a prior-recorded is quite robust, and able to reconstruct object information even at very low sampling rates. In practical applications, an appropriate sampling rate can be selected by compromising the image SNR and radiation dose. By optimizing experimental conditions, especially the scanning precision of the scattering medium, SNR of the reconstructed images at low sampling rates is expected to be improved significantly.
4 Discussion
4.1 Block effect
In the images reconstructed by SAXGI with prior-recorded reference proposed in this article, grid-like boundaries with discontinuous light and dark areas can be observed. This phenomenon, known as the block effect, mainly originates from two sources: (1) Errors caused by the accuracy of the motorized positioning stage during data acquisition. In our experimental scheme, it is necessary to first record the reference at a series of specified positions of the sandpaper, and then collect the object signals at the corresponding positions. Since the motorized positioning stage for sandpaper is not equipped with a closed-loop control system incorporating a grating ruler, its inherent displacement accuracy can lead to certain positioning errors. Moreover, the back-and-forth movement of the sandpaper during scanning contributes to significant positioning errors due to the backlash of the positioning stage. These scanning errors can lead to mismatches between the object and reference arm, resulting in the residual of the sandpaper speckle patterns in the reconstructed images, which affects the imaging contrast. (2) Errors caused by SAXGI reconstruction algorithm. In the reconstruction process of SAXGI, the image is reconstructed based on the signals from the pixel units of the bucket detector array, with the overall imaging FOV composed of blocks formed by the two-dimensional spatial distribution of reconstructed units. Mismatches in spatial positions of object and reference arm signals during data collection, as well as differences in detection sensitivity and quantum efficiency among bucket detector units, can lead to reduced SNR within blocks. Particularly, reconstruction differences between adjacent blocks can cause an abnormal increase in contrast at block edges, resulting in grid-like boundaries.
In the experimental scheme via virtual beam-splitting strategies, the sandpaper did not move during the collection of corresponding object and reference signals, resulting in no spatial registration issues between the object and reference arm signals, and thus no apparent block effect was observed in the reconstruction results of (44), namely, Figure 5d in (44). Numerical simulations also did not reveal the impact of the block effect, as evidenced in Figure 3d in (44), indicating that the SAXGI method itself may not be the main cause of the block effect. Therefore, it can be concluded that in SAXGI with prior-recorded reference proposed in the paper, the block effect mainly arises from the mismatch between the positions of the sandpaper in the object and reference arms during data acquisition.
To further demonstrate that the registration error is the main cause of block effect, we intentionally introduced pixel-level mismatch into our reconstruction process for the tungsten wire to obtain Figure 10. In Figure 10a, one constant leftward pixel mismatch of the diffuser with respect to the detector is introduced, and subsequently evident vertical stripes darker on the left edge and brighter on the right appears, compared to Figure 6c. As a comparison, the reconstruction result Figure 7c also shows block effect mainly as vertical stripes with bright-dark edges, indicating a systematic rightward mismatch in the data acquisition. Similarly in Figure 10b, one upward pixel mismatch of the diffuser with respect to the detector caused horizontal stripes darker on the upper edge and brighter on the lower. These results indicate that registration errors result in block effect as directional boundary artifacts. Note that for this demonstration specifically, since we adopted the experiment data with unknown and non-uniform registration error, stripes in Figure 10 are not as uniform as expected.
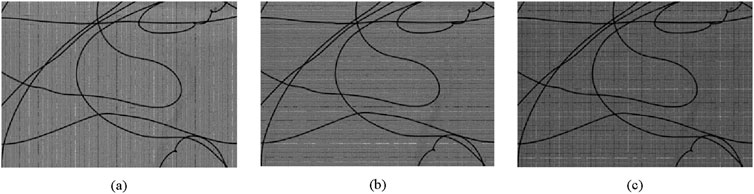
Figure 10. Reconstruction results of tungsten wire when displacement is introduced, with other reconstruction conditions the same as in Figure 6c, where here (a) one constant leftward pixel mismatch of the diffuser with respect to the detector is incorporated; (b) one constant upward pixel mismatch of the diffuser with respect to the detector is incorporated; (c) one constant leftward as well as one constant upward pixel mismatch of the diffuser with respect to the detector is incorporated.
With one leftward as well as one upward pixel mismatch of the diffuser with respect to the detector in Figure 10c, stripes in vertical and horizontal directions combine into evident block effect. Experimentally, the intensity variations at image boundaries observed are predominantly non-deterministic, implying that registration errors are not uniform but exhibit random fluctuations. Such omnidirectional perturbations at boundaries prevent the formation of deterministic textures.
By further improving the scanning accuracy of the motorized positioning stage, adding a closed-loop control system with a grating ruler, and refining the existing TVAL3 algorithm during the reconstruction process by considering the relationships between bucket detector units, it is hoped that the impact of the block effect can be effectively eliminated, thereby improving the SNR of the reconstructed images by the proposed method.
4.2 Quantitative evaluation
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) [49] are commonly utilized indicators for assessing image quality. However, as shown in Tables 1, 2, for the reconstruction outcomes of this experiment, these two indicators do not seem to yield consistent results. Accordingly, we introduced the perceptual loss function from the VGG19 deep learning network [50] as an evaluation metric of the image quality. This criterion utilizes a pretrained deep learning network to extract the features of the image at various depth layers, assessing the similarity between two images by comparing the differences in these feature layers, and the perceptual loss function is formulated in Equation 8:
within this context,
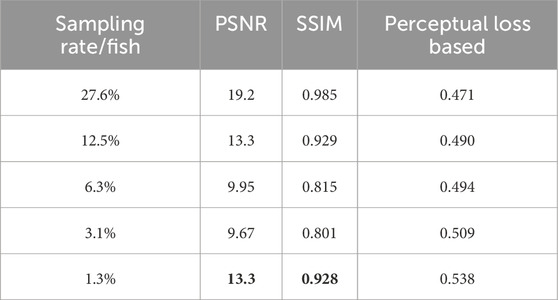
Table 1. Quantitative evaluation of the reconstructed images of fish at different sampling rates, with the bold values being anomalies contrary to expected performance.
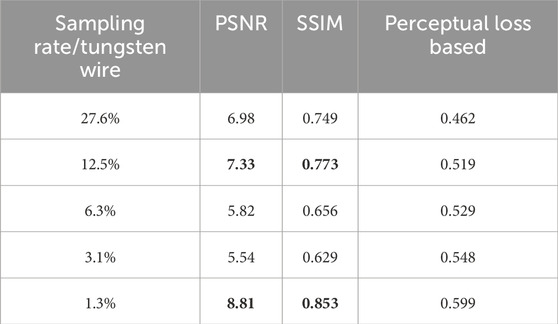
Table 2. Quantitative evaluation of the reconstructed images of tungsten wire at different sampling rates, with the bold values being anomalies contrary to expected performance.
In this study, when performing calculations, the overall network layers
where
Tables 1, 2 present various quantitative metrics between SAXGI reconstructed images and target images of traditional projection at different sampling rates for a fish and tungsten wire respectively.
As the sampling rate decreases, the image quality deteriorates. Therefore, the corresponding PSNR and SSIM values should decrease, and the perceptual loss should increase. The bold values highlighted in Tables 1, 2 denote the anomalies in PSNR and SSIM values with decreasing sampling rates, contrary to the expected performance, indicating that these two commonly used metrics may not provide a consistent assessment of image reconstruction. In contrast, the evaluation metric based on perceptual loss from deep learning offers a consistent assessment.
The discrepancy that PSNR/SSIM occasionally fail to reliably assess reconstruction quality may originate from speckle noise artifacts and dynamic range constraints. On the one hand, speckle intensity fluctuations undetectable by PSNR/SSIM, which lack multi-scale sensitivity, induce metric instability, whereas convolutional neural networks effectively decouple diagnostically irrelevant speckle patterns from structural features. On the other hand, SSIM’s luminance term tends to become unreliable due to dynamic range constraints imposed by mandatory contrast adjustment in TVAL3-reconstructed images for visualization when outlier intensities occur.
While perceptual-loss-based metrics demonstrate enhanced correlation with human visual perception, its utility for science imaging is constrained by subjective parameter selection and case-specific optimization tendencies. Perceptual loss function itself is not an objective evaluation metric, and its effectiveness depends on the selection of network type, weights for different feature layers, norms, and other variables, which detracts from its universality as an image evaluation metric. Establishing a concept of normalization for perception loss is challenging, so it only has relative significance and cannot compare the degradation levels of different images. However, test results indicate that this metric can provide a consistent evaluation of the relative quality differences when assessing the reconstruction quality of SAXGI at different sampling rates.
5 Conclusion
Aiming at efficient implementation of megapixel X-ray ghost imaging, we developed an experimental scheme that achieves X-ray ghost imaging of multiple objects, requiring only once acquisition of the signals in the reference arm. By prior-recording and reusing the same set of high-resolution reference images, the data acquisition efficiency has been significantly improved compared to that of the strategies available, reducing the data acquisition time from 6 h to 40 min. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed scheme can achieve high-quality image reconstruction with a size of 2040 × 1440 pixels. According to the successful reconstruction of the fish skeleton with only 8 measurements, corresponding to a sampling rate of 0.5%, the potential of low dose radiology for the developed method is verified experimentally. Imaging results with a resolution chart demonstrate that a spatial resolution of 10 μm is achieved, comparable to the resolution defined by the effective pixel size of 3.25 μm in the reference arm. By optimizing the scanning speed and positioning control of the random light field modulator, the image acquisition efficiency and the signal-to-noise ratio of the reconstructed images are anticipated to be further improved. With appropriate modifications, the developed experimental scheme is expected to extend the field of view in nano-resolution imaging. In addition, with the development of a dedicated X-ray detector which can switch automatically between high efficiency mode for object arm and high-resolution mode for reference arm, the proposed experimental scheme can be implemented more efficiently.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
JT: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Resources, Data curation, Visualization. HZ: Investigation, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Supervision, Project administration. CZ: Validation, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. NZ: Validation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation. JW: Writing – review and editing, Software, Formal Analysis. HG: Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Funding acquisition, Software. TX: Supervision, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2022YFA1603601, 2021YFF0601203, 2021YFA1600703 and National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 12205361.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to staff members at BL13HB and BL09B of SSRF for their kind help in experiments, including Yan-Ling Xue, Guo-Hao Du, Zhong-Liang Li, along with other members.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Pan A, Zuo C, Yao B. High-resolution and large field-of-view Fourier ptychographic microscopy and its applications in biomedicine. Rep Prog Phys (2020) 83(9):096101. doi:10.1088/1361-6633/aba6f0
2. Das S, Pashminehazar R, Sharma S, Weber S, Sheppard TL. New dimensions in catalysis research with hard X-ray tomography. Chem Ingenieur Technik (2022) 94(11):1591–610. doi:10.1002/cite.202200082
4. Pittman TB, Shih YH, Strekalov DV, Sergienko AV. Optical imaging by means of two-photon quantum entanglement. Phys Rev A (1995) 52(5):R3429–32. doi:10.1103/physreva.52.r3429
5. Yu F, Du K, Ju X, Wang F, Li K, Chen C, et al. Dynamic X-ray speckle-tracking imaging with high-accuracy phase retrieval based on deep learning. IUCrJ (2024) 11(1):73–81. doi:10.1107/s2052252523010114
6. Wang F, Li K, Xu M, Ju X, Xiao T. Move contrast X-ray imaging and its applications. Nucl Instr Methods Phys Res Section A: Acc Spectrometers, Detectors Associated Equipment (2023) 1055:168560. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2023.168560
7. Xu M, Li K, Xue Y, Wang F, Liu Z, Song Z, et al. Water refilling along vessels at initial stage of willow cuttage revealed by move contrast CT. Front Phys (2023) 11. doi:10.3389/fphy.2023.1174387
8. Ju X-L, Deng B, Li K, Yu F-C, Zhang H-P, Xu M-W, et al. Calibrating the linearity between grayscale and element content for X-ray KES imaging of alloys. Nucl Sci Tech (2022) 33(1):1. doi:10.1007/s41365-022-00986-3
9. Choi S, Park E-Y, Park S, Kim JH, Kim C. Synchrotron X-ray induced acoustic imaging. Scientific Rep (2021) 11(1):4047. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-83604-3
10. Luo H, Lou Y, He K, Jiang Z. Coupling in-situ synchrotron X-ray radiography and FT-IR spectroscopy reveal thermally-induced subsurface microstructure evolution of solid propellants. Combustion Flame (2023) 249:112609. doi:10.1016/j.combustflame.2022.112609
11. Brombal L, Arfelli F, Brun F, Di Trapani V, Endrizzi M, Menk R, et al. Edge-illumination spectral phase-contrast tomography. Phys Med and Biol (2024) 69:075027. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ad3328
12. Xu M, Li K, Xue Y, Wang F, Liu Z, Xiao T. Measurement of mass force field driving water refilling of cuttage. Scientific Rep (2024) 14(1):8947. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-59716-x
13. Kingston AM, Myers GR, Pelliccia D, Svalbe ID, Paganin DM. X-ray ghost-tomography: artefacts, dose distribution, and mask considerations. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging (2019) 5(1):136–49. doi:10.1109/tci.2018.2880337
14. Schori A, Borodin D, Tamasaku K, Shwartz S. Ghost imaging with paired x-ray photons. Phys Rev A (2018) 97(6):JTh2A.7. doi:10.1364/cleo_at.2018.jth2a.7
15. Yu H, Lu R, Han S, Xie H, Du G, Xiao T, et al. Fourier-Transform ghost imaging with hard X rays. Phys Rev Lett (2016) 117(11):113901. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.117.113901
16. He Y-H, Zhang A-X, Li M-F, Huang Y-Y, Quan B-G, Li D-Z, et al. High-resolution sub-sampling incoherent x-ray imaging with a single-pixel detector. APL Phontonics (2020) 5(5):056102. doi:10.1063/1.5140322
17. Zhang H, Li K, Zhao C, Tang J, Xiao T. Efficient implementation of x-ray ghost imaging based on a modified compressive sensing algorithm. Chin Phys B (2022) 31(6):064202. doi:10.1088/1674-1056/ac48f7
18. Zhang H, Du K, Zhao C, Tang J, Si S, Jia W, et al. Optimizing the ordering of the Hadamard masks of ghost imaging suitable for the efficient face reconstruction using the max-projection method. Scientific Rep (2023) 13(1):22702. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-48453-2
19. Tan Z, Yu H, Zhu R, Lu R, Han S, Xue C, et al. Single-exposure Fourier-transform ghost imaging based on spatial correlation. Phys Rev A (2022) 106(5):053521. doi:10.1103/physreva.106.053521
20. Ratner D, Cryan JP, Lane TJ, Li S, Stupakov G. Pump-probe ghost imaging with SASE FELs. Phys Rev X (2019) 9(1):011045. doi:10.1103/physrevx.9.011045
21. Driver T, Li S, Champenois EG, Duris J, Ratner D, Lane TJ, et al. Attosecond transient absorption spooktroscopy: a ghost imaging approach to ultrafast absorption spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys (2020) 22(5):2704–12. doi:10.1039/c9cp03951a
22. Li K, Laksman J, Mazza T, Doumy G, Koulentianos D, Picchiotti A, et al. Ghost-imaging-enhanced noninvasive spectral characterization of stochastic x-ray free-electron-laser pulses. Commun Phys (2022) 5(1):191. doi:10.1038/s42005-022-00962-8
23. Shapiro JH. Computational ghost imaging. Phys Rev A (2008) 78(6):061802. doi:10.1103/physreva.78.061802
24. Zhang H-P, Zhao C-Z, Ju X-L, Tang J, Xiao T-Q. Improving quality of crystal diffraction based X-ray ghost imaging through iterative reconstruction algorithm. Acta Phys Sin (2022) 71(7):074201. doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211978
25. Zhao C-Z, Si S-Y, Zhang H-P, Xue L, Li Z-L, Xiao T-Q. Beam splitting characteristics of crystal X-ray Laue diffraction. Acta Phys Sin (2022) 71(4):046101. doi:10.7498/aps.71.20211674
26. CZ Zhao, SY Si, QS Diao, Z Hong, ZL Li, and TQ Xiao. Development of stress-free Laue diffraction crystal for x-ray beam splitting. Proc. SPIE 13069, International Conference on Optical and Photonic Engineering (icOPEN 2023), February 15, 2024 (2024). doi:10.1117/12.3021665
27. Pelliccia D, Rack A, Scheel M, Cantelli V, Paganin DM. Experimental X-ray ghost imaging. Phys Rev Lett (2016) 117(11):113902. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.117.113902
28. Schori A, Shwartz S. X-ray ghost imaging with a laboratory source. Opt Express (2017) 25(13):14822. doi:10.1364/oe.25.014822
29. Pelliccia D, Olbinado MP, Rack A, Kingston AM, Myers GR, Paganin DM. Towards a practical implementation of X-ray ghost imaging with synchrotron light. IUCrJ (2018) 5(4):428–38. doi:10.1107/s205225251800711x
30. Zhao C-Z, Zhang H-P, Tang J, Zhao N-X, Li Z-L, Xiao T-Q. X-ray ghost imaging with a specially developed beam splitter. J Synchrotron Radiat (2024) 31(6):1525–33. doi:10.1107/s1600577524008038
31. Zhao C-Z, Si S-Y, Zhang H-P, Xue L, Li Z-L, Xiao T-Q. Intensity correlation properties of x-ray beams split with Laue diffraction. Chin Phys B (2024) 33(1):014102. doi:10.1088/1674-1056/acf206
32. Zhang A-X, He Y-H, Wu L-A, Chen L-M, Wang B-B. Tabletop x-ray ghost imaging with ultra-low radiation. Optica (2018) 5(4):374–7. doi:10.1364/optica.5.000374
33. Sefi O, Klein Y, Strizhevsky E, Dolbnya IP, Shwartz S. X-ray imaging of fast dynamics with single-pixel detector. Opt Express (2020) 28(17):24568. doi:10.1364/oe.396497
34. Li H, Hou W, Ye Z, Yuan T, Shao S, Xiong J, et al. Resolution-enhanced x-ray ghost imaging with polycapillary optics. Appl Phys Lett (2023) 123(14):141101. doi:10.1063/5.0168704
35. Li H, Ye Z, Yuan T, Hua L, Zhong Y, Hu J, et al. Magnified x ray ghost imaging with tapered polycapillary optics free of the penumbra effect. Opt Lett (2024) 49(2):274–7. doi:10.1364/ol.506276
36. Zhao N, Tang J, Zhao C, Wu J, Zhang H, Guo H, et al. Synthetic aperture X-ray ghost imaging with sub-micron pixel resolution. Opt Express (2025) 33(1):972–82. doi:10.1364/oe.547730
37. Zhao N, Tang J, Zhao C, Wu J, Zhang H, Guo H, et al. Global ghost imaging. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B(2025). doi:10.1364/JOSAB.546265
38. Ceddia D, Paganin DM. Random-matrix bases, ghost imaging, and x-ray phase contrast computational ghost imaging. Phys Rev A (2018) 97(6):062119. doi:10.1103/physreva.97.062119
39. Olbinado MP, Paganin DM, Cheng Y, Rack A. X-ray phase-contrast ghost imaging using a single-pixel camera. Optica (2021) 8(12):1538–44. doi:10.1364/optica.437481
40. He Y-H, Zhang A-X, Yu W-K, Chen L-M, Wu L-A. Energy-selective X-ray ghost imaging. Chin Phys Lett (2020) 37(4):044208. doi:10.1088/0256-307x/37/4/044208
41. Y-H He, A-X Zhang, Y-Y Huang, W-K Yu, L-M Chen, and L-A Wu, editors. Spectroscopic X-ray ghost imaging. 14th pacific rim conference on lasers and electro-optics (CLEO PR 2020). Sydney: Optica Publishing Group (2020).
42. Klein Y, Sefi O, Schwartz H, Shwartz S. Chemical element mapping by x-ray computational ghost fluorescence. Optica (2022) 9(1):63–70. doi:10.1364/optica.441682
43. Klein Y, Schori A, Dolbnya IP, Sawhney K, Shwartz S. X-ray computational ghost imaging with single-pixel detector. Opt Express (2019) 27(3):3284. doi:10.1364/oe.27.003284
44. Zhang H, Li K, Wang F, Yu H, Zhao C, Du G, et al. Megapixel X-ray ghost imaging with a binned detector in the object arm. Chin Opt Lett (2022) 20(3):033401. doi:10.3788/col202220.033401
45. Li C, Yin W, Jiang H, Zhang Y. An efficient augmented Lagrangian method with applications to total variation minimization. Comput Optimization Appl (2013) 56(3):507–30. doi:10.1007/s10589-013-9576-1
46. Li C. An efficient algorithm for total variation regularization with applications to the single pixel camera and compressive sensing [Master]. Houston, Texas, USA: Rice University (2010).
47. Zhang H. Investigation on megapixel X-ray ghost imaging with low radiation dose [Doctor]. Shanghai, China: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics (2023).
48. Xie H-L, Deng B, Du G-H, Fu Y-N, Guo H, Xue Y-L, et al. Methodology development and application of X-ray imaging beamline at SSRF. Nucl Sci Tech (2020) 31(10):102. doi:10.1007/s41365-020-00805-7
49. Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process (2004) 13(4):600–12. doi:10.1109/tip.2003.819861
Keywords: X-ray ghost imaging, TV regularization, synthetic aperture imaging, radiology with low radiation dose, computational imaging
Citation: Tang J, Zhang H, Zhao C, Zhao N, Wu J, Guo H and Xiao T (2025) Megapixel X-ray ghost imaging with a prior-recorded reference. Front. Phys. 13:1615591. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1615591
Received: 21 April 2025; Accepted: 30 May 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Yongyuan Jiang, Harbin Institute of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Tang, Zhang, Zhao, Zhao, Wu, Guo and Xiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tiqiao Xiao, dHF4aWFvQHNhcmkuYWMuY24=; Haipeng Zhang, emhhbmdocEBzYXJpLmFjLmNu
 Jie Tang
Jie Tang Haipeng Zhang2*
Haipeng Zhang2* Tiqiao Xiao
Tiqiao Xiao