- 1Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Medical Physics and Technology, Institute of Health and Medical Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 2University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 3School of Biomedical Engineering, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 4Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, China
Exploring suitable saturable absorber materials for the 2.79 μm waveband is always a focus in passive Q-switching laser technology. Pure water exhibits excellent fluidity, high chemical stability, and outstanding thermal properties; notably, its recovery capability suggests it could serve as an effective saturable absorber. This study validates the feasibility of saturable absorption with absorption darkening at 2.79 μm, analyzing the saturation absorption mechanism of water and the origin of absorption darkening. By designing a device to control the thickness of micron-scale water layers, controllable outputs of Q-switched single pulses and multipulses with microsecond intervals were achieved in a 2.79 μm Er, Cr: YSGG laser. With a water layer thickness of 7 μm and a repetition rate of 20 Hz, the maximum energy of the multi-pulse output reached 0.78 mJ, and the shortest single-pulse width was 286 ns. This provides a reference for the application of pure water as a saturable absorber and for the study of other hydroxyl-based saturable absorber materials.
1 Introduction
The 2.79 μm wavelength is in the vicinity of the strong absorption peaks of water and hydroxyapatite [1, 2], and is widely used in biomedical [3]. The extremely high absorption at this wavelength can increase the ablation rate and reduce the thermal damage to surrounding tissues, thereby achieving better clinical ablation outcomes. In addition to laser wavelength, pulse width and energy are also important parameters that affect ablation efficiency. In terms of thermal effects, when the laser pulse width is shorter than the thermal relaxation time of the tissue, the thermal damage to surrounding tissues is minimized. Conversely, if the pulse width is longer than the thermal relaxation time, heat of the sequential pulses will accumulate and conduct to surrounding tissues, causing significant temperature increases and irreversible damage to healthy tissues. In terms of ablation efficiency, at lower pulse energy levels, an increase in the energy per pulse enhances the ablation rate; however, at higher energy levels, excessively high pulse energy can induce melting, carbonization, and the ejection of plasma smoke from the ablated tissue, thereby impeding laser absorption and resulting in pronounced saturation effects. Dividing a high-energy pulse into multiple sub-pulses with microsecond intervals can not only prevent thermal damage but also enhance the ablation rate [4]. Moreover, the narrower the pulse width of each sub-pulse, the higher the ablation efficiency. Studies have shown that [5], under the same inter-pulse interval, sub-pulses with a 20 μs pulse width achieve a 48% higher ablation rate compared to those with a 50 μs pulse width. In addition, the cumulative energy of multiple microsecond-spaced sub-pulses can more effectively disrupt tissue structure, thereby improving both ablation depth and uniformity. Additionally, compared with pulse trains generated by conventional electronic modulation [5], the sub-pulse trains produced by pure-water Q-switching significantly reduce the interval between pulses. This enables subsequent sub-pulses to continue ablation before the thermal effects induced by the preceding pulses have fully dissipated. Such sub-pulse trains, operating at microsecond intervals, not only avoid saturation effects caused by excessively high-energy single pulses, but also improve ablation efficiency by minimizing the delay between successive pulses [4, 6]. In femtosecond laser-induced self-organized micro-nanofabrication, sub-pulse bursts also exhibit unique advantages. Studies have demonstrated that using pulse bursts to fabricate periodic nanogratings not only leads to more well-ordered nanostructures but also enables active modulation of the period and depth of laser-induced periodic surface structures by adjusting the number of sub-pulses [7].
Taking dental hard tissues as an example, the pulse widths of the normal mode currently used in clinical applications are on the order of tens to even hundreds of microseconds, which is far longer than the 24.4 μs thermal relaxation time of dental tissue. Consequently, spray cooling is required during clinical treatment to avoid thermal damage to the surrounding tissue [8]. However, the cooling water mist also causes fluctuations and attenuation of the laser energy, thus affecting the ablation efficiency. Therefore, in practical applications, a shorter pulse width and a high repetition rate are preferred to reduce thermal effects during ablation and improve its efficiency. Developing efficient Q-switching techniques in this waveband to shorten the pulse width and generate multiple sub-pulses, with the aim of minimizing thermal damage to the ablated tissue and enhancing ablation efficiency, has consequently become a promising research direction.
Due to the limitations imposed by the absorption characteristics and damage thresholds of optoelectronic materials in the 3 μm waveband, the search for high-performance materials and devices in this wavelength range has consistently been a formidable challenge in mid-infrared laser technology [9–12]. Among laser Q-switching techniques, passive Q-switching has garnered widespread attention due to its simple structure, the absence of external modulators, ease of miniaturization, and robustness against electromagnetic interference. In recent years, various types of saturable absorber materials suitable for passive Q-switching in the 2.79 μm spectral region have been identified, such as MoS2 [13], topological insulator Bi2Te3 nanosheets [14], Fe: ZnSe [15], graphene [16], and black phosphorus [17]. Although solid-state saturable absorbers can achieve Q-switched output in the mid-infrared wavelength range, these solid-state materials generally have low damage thresholds, making it challenging to obtain high-pulse-energy Q-switched output. Additionally, solid-state saturable absorber materials cannot dynamically adjust their thickness during operation to modify intracavity losses and Q-switched pulse characteristics. In contrast, liquid-phase saturable absorbers offer adjustable thickness, typically possess higher thermal conductivity and damage thresholds, and thus, the investigation of liquid-phase saturable absorbers suitable for the mid-infrared wavelength range has become a focus of research.
Water, a common liquid material in nature, is not only readily purified and obtained but also exhibits excellent thermal diffusivity and remarkable molecular and physicochemical properties. The strength of the H+ and OH− bonds in water plays a significant role in its structure. The stretching and bending vibrations of hydrogen bonds can lead to substantial changes in vibrational density frequencies, which in turn alter the spectroscopic characteristics of water [18, 19]. Under the influence of intense laser fields in the 3 μm waveband and varying temperatures, water exhibits significant saturable absorption characteristics, making it suitable for passive Q-switching applications in this wavelength region [20]. K. L. Vodop’yanov et al. investigated the saturable absorption properties of pure water using a 2.94 μm Er: YAG laser and achieved stable passively Q-switched single-pulse laser output with a pulse width of 120 ns and a single-pulse energy of 20 mJ when the thickness of the pure water solution was approximately 0.5–1 μm [20]. Subsequently, K. L. Vodop’yanov et al. [21] observed that the transmittance of water at 2.94 μm monotonically increases with the accumulation of laser energy deposition, as well as a temperature-dependent variation in water’s optical absorption coefficient [22], thereby initiating theoretical studies on water-based saturable absorbers. Graener et al. [23] experimentally determined that bleaching of water induced by the saturation of absorption transitions is short-lived (on the order of 8 ps), whereas bleaching induced by thermal effects is long-lived (on the order of several hundred nanoseconds). Based on this thermal effect theory, Shori et al. [24] developed a dynamic saturable absorption (DSA) model to accurately predict the absorption coefficient
Hydrogen bonds in water molecules play a pivotal role in the process of saturated absorption. When the hydrogen bonds in water undergo rapid vibrations, heat rapidly accumulates within the system, leading to an increase in temperature. The elevated temperature intensifies the thermal motion of water molecules, making it more frequent and vigorous. This enhanced motion destabilizes the hydrogen bonds, causing them to break more easily. Consequently, the average lifetime of hydrogen bonds shortens, and the overall hydrogen bond strength decreases.
Moreover, nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) are critical in modulating both the stretching and bending vibrational modes of hydrogen bonds [18]. With increasing temperature, the quantum kinetic energy of hydrogen atoms increases, leading to greater delocalization along the hydrogen bond direction. This enhanced delocalization facilitates dynamic reorganization of the hydrogen bond network, enabling global redistribution of energy and further weakening hydrogen bond interactions. In the mid-infrared region, the ∼1 μm absorption band corresponds to the fundamental bending mode, whereas the ∼3 μm band corresponds to the fundamental stretching mode of hydrogen bonds. A temperature increase of 10°C results in an ∼8% broadening of the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the 2.94 μm absorption band and an approximate 3% reduction in its peak absorption. Pressure also contributes to modulating the absorption characteristics.
In summary, elevated temperatures reduce hydrogen bond strength, thereby altering the water absorption spectrum and causing a blue shift of the mid-infrared absorption peaks. The absorption peak initially located at 2.94 μm shifts toward shorter wavelengths, with a stronger absorption peak emerging near 2.79 μm. In this region, the absorption coefficient forms a characteristic concave plateau, commonly referred to as a “dark region” [21]. As the input laser energy increases further, the temperature rise causes the absorption peak to shift beyond 2.79 μm, and water’s absorption coefficient at this wavelength drops significantly. A stable absorption plateau emerges, and bleaching eventually occurs.
This non-monotonic behavior where the absorption coefficient initially increases, then decreases, and finally stabilizes with increasing laser energy is in stark contrast to conventional saturated absorption phenomena, where the absorption coefficient typically decreases monotonically. This makes laser heating and the 2.79 μm band particularly suitable for mid-infrared Q-switching applications around 3 μm.
Unlike the behavior at the 2.94 μm band, the presence of the absorption dark region enhances water’s absorption efficiency in the 2.79 μm spectral range, some studies suggest that this increase may even surpass the absorption at 2.94 μm [25, 26]. It has been demonstrated that the pure water based saturable absorber can be used to realize passively Q-switching in an Er doped fiber laser [27]. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no report on the feasibility of pure water as saturable absorber with absorption darkening at 2.79 μm. Therefore, we try to employ pure water as saturable absorption to investigate the Q-switching characteristics at 2.79 μm.
To address the demand for short-pulse laser applications in biomedical fields at 2.79 μm wavelength and to investigate whether the absorption darkening effect of water in this band can achieve saturable absorption, a mechanically tunable structure with a micron-scale water layer thickness was designed in this work. Experimental validation confirms the feasibility of using pure water as a saturable absorber for an Er, Cr: YSGG solid-state laser. Furthermore, the study analyzes the formation mechanism of the absorption darkening effect at 2.79 μm and the underlying saturable absorption process. The findings aim to provide a reference for the application of water as a saturable absorber and for the development of other hydroxyl-based saturable absorber materials.
2 Experimental setup
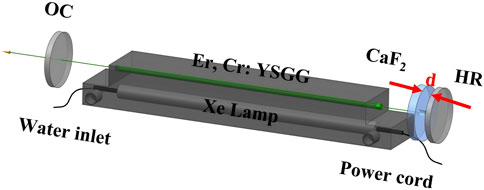
The experimental setup is shown in Figure 1. The Er, Cr: YSGG rod has a diameter of 3 mm and a length of 70 mm, with a Cr3+ concentration of 3 at.% and an Er3+ concentration of 30 at.%. Both ends of the crystal rod are anti-reflection (AR) coated at 2.79 μm. The resonator adopts a plane-parallel cavity, with a geometric cavity length of 248 mm. The high-reflective (HR) mirror has a reflectance of higher than 99% at 2.79 μm, and the output coupler (OC) has a reflectance of 70% at 2.79 μm. The saturable absorber solution is sandwiched between an uncoated CaF2 mirror and the HR mirror. The thickness of the solution is denoted as d, and the CaF2 mirror is mounted on a three-dimensional translation stage, allowing horizontal displacement to precisely control the solution thickness. To prevent slight deformations of the CaF2 mirror and the HR mirror caused by pressure changes in the irradiated liquid during Q-switching which could compromise the alignment conditions of the laser oscillation cavity we incorporated spacers into the mirror mounts for stabilization. Since the thickness of the solution is on the micron scale, a microscope, a micrometer screw gauge, and the three-dimensional translation stage are used to obtain accurate thickness measurements. The saturable absorber solution used in the experiment is ultrapure water with a purity of 99.999%. To verify the strong absorption characteristics of pure water at 2.79 μm, a PE Lambda-950 UV/VIS/NIR spectrophotometer was employed to measure the absorption spectrum of pure water in this wavelength range, showing excellent consistency with previously reported results [28]. The laser is pumped by a xenon lamp, with a discharge pulse width of 250 μs and a pulse repetition rate of 20 Hz. To ensure the safe and stable operation of the laser, deionized water is used for cooling, maintained at a temperature of (293.0 ± 0.1) K and a flow rate of 20 L/min. During the experiment, the laser was firstly operated in normal mode. Then, pure water was injected into the structure using a syringe. The thickness d was gradually reduced until Q-switched pulses was observed.
3 Experimental results and discussion
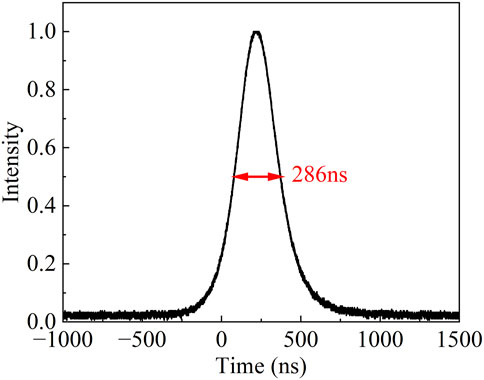
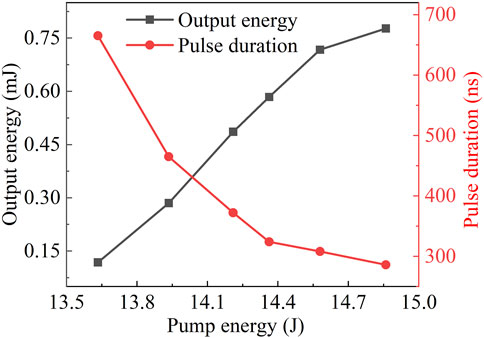
In the experiment, the repetition rate was set to 20 Hz, with a fixed pump energy of 13.63 J. By adjusting the thickness of the pure water layer, a stable Q-switched single-pulse output was obtained when the water thickness was approximately 7 μm. Under these conditions, the generated Q-switched pulse width was 665 ns, with a single-pulse energy of 0.12 mJ. When the pump energy was increased to 14.86 J, a Q-switched pulse sequence with nearly uniform pulse spacing was obtained, a Q-switched output with a main pulse width of 286 ns and a total pulse energy of 0.78 mJ was achieved. The corresponding normalized main pulse waveform is shown in Figure 2. Figure 3 illustrates the curves of the total output energy of the multi-pulse Q-switched pulses and the pulse width of the first pulse. As the pump energy increases, the pulse width continuously decreases, which is a typical characteristic of Q-switched lasers. Due to the power limitations of the power supply, further increases in pump energy were not available. At this power level, the damage threshold of the pure water solution was not reached, and the output energy did not exhibit saturation (as illustrated in Figure 3), indicating the potential for further energy enhancement.
Compared to solid-phase saturable absorbers, the thickness of liquid-phase saturable absorbers can be dynamically adjusted, making it easier to achieve Q-switched output with specific pulse widths. Additionally, pure water, as a liquid-phase saturable absorber, generally has a higher damage threshold than solid-phase absorbers. Its good thermal conductivity, the presence of only OH bonds between molecules, and its high fluidity contribute to the ability to achieve higher energy in Q-switched laser output.
In the experiment, we also observed the occurrence of multiple sub-pulses under a single pump pulse at high pump energies. The number of sub-pulses increased as the pump energy increased. Figure 4a,b,c show the normalized sub-pulse waveforms under pump energies of 14.2 J, 14.36 J, and 14.86 J, respectively. The measured intervals between the sub-pulses range from 3.392 to 5.592 μs, and this fluctuation is attributed to gain non-uniformity caused by the flashlamp pump in the temporal domain.
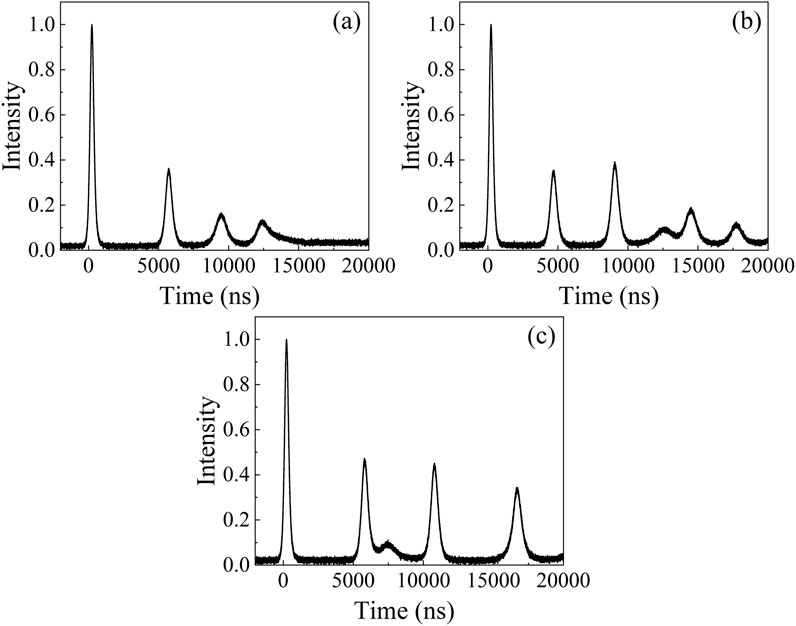
Figure 4. Q-switched temporal profiles with pump energies of 14.2 J (a), 14.36 J (b), and 14.86 J (c), respectively.
The primary cause of sub-pulse generation lies in the significant disparity between the pump pulse duration and the relaxation time of saturated absorption in pure water. Specifically, the pump pulse duration (∼250 μs) greatly exceeds the relaxation time of the saturable absorber, which is on the order of hundreds of nanoseconds. After the generation of the Q-switched main pulse, the saturable absorber undergoes recovery. However, since the pump remains active, the absorber can become bleached again, leading to the generation of a secondary pulse.
If the pump pulse is sufficiently long and has high energy, the main pulse may not be capable of depleting all excited ions from the upper laser level. A substantial number of remaining excited ions can give rise to multiple subsequent pulses. The temporal spacing between sub-pulses is primarily governed by the relaxation time of the saturable absorption process, while the influence of pump intensity is secondary but non-negligible.
In our experiments, we observed that the intensity of sub-pulses is approximately 40% that of the main pulse. We hypothesize that this reduction in intensity is attributable to the presence of an absorption “dark region”. The absorption peak of water shifts with changes in temperature. At room temperature, the absorption coefficient of pure water at 2.79 μm is 4,863 cm-1. As the temperature increases, the absorption coefficient initially rises to a peak value of 13,300 cm-1, then decreases to 3,340 cm-1 (assuming it is consistent with the saturated absorption coefficient at 2.94 μm). During the recovery phase after saturation, the absorption coefficient firstly increases from 3,340 to 13,300 cm-1. If the pump continues, and the temperature drops to the absorption peak value, the absorption coefficient increases again. Compared to the first pulse, this reduces the absorption process in the dark zone, thus shortening the accumulation time of ions in the excited state. Consequently, the peak of subsequent pulses will be lower than that of the first pulse. As the system reaches dynamic equilibrium between the gain and temperature recovery after saturation, the absorption coefficient of subsequent pulses decreases from the equilibrium point to the saturation level, leading to nearly identical peak values for the subsequent pulses.
It is evident that the saturable absorption characteristics arising from the darkening produce a nanosecond giant pulse followed by a sub-pulse sequence with an intensity approximately 40% of the main pulse. The resulting nanosecond pulse train with microsecond time intervals offers unique advantages in applications such as laser ablation, laser cutting, and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). In biological tissue ablation, the nanosecond pulse width can enhance ablation efficiency, reduce thermal damage, and create ablation pits with better tissue morphology, which is beneficial for subsequent repair treatments [29]. Moreover, this nanosecond-interval sub-pulse train can greatly improve material removal rates in laser processing by controlling the pulse interval, reducing re-deposition, and minimizing the heat-affected zone [30]. In applications like LIBS [31], this pulse structure can further increase the energy utilization for cutting, reduce thermal damage to surrounding areas, and improve the signal-to-noise ratio in spectral detection.
4 Conclusion
Pure water is not only easy to prepare, but also exhibits excellent fluidity, high chemical stability, and outstanding thermal and optical properties. Its remarkable saturable absorption characteristics have garnered considerable attention. This study experimentally verifies the feasibility of pure water as a saturable absorber in Q-switching laser at the 2.79 μm and analyzes the formation mechanism of the absorption darkening and the saturable absorption mechanism of water in this waveband. The experimental results show that pure water can achieve stable saturable absorption in the absorption darkening zone, and controlled single pulses and microsecond interval multipulses in Q-switched Er, Cr: YSGG laser are realized by precisely adjusting the thickness of water layer. The high damage threshold, good thermal conductivity of water, and pulse output controllability demonstrate that it is an excellent liquid-phase saturable absorber with broad application prospects in the laser field. This study clarifies the issue of water’s absorption darkening in this wavelength region and provides a reference for the future application of 2.79 μm water saturable absorption Q-switched solid-state lasers and research on saturable absorber materials based on hydroxyl groups. Compared to the pulse trains with microsecond intervals obtained through traditional electrical modulation, the pulse trains generated by this method have shorter time intervals, even down to the nanosecond level. The pulse width of each sub-pulse is also in the nanosecond range, offering unique advantages in improving ablation efficiency, quality, and signal-to-noise ratio in applications such as laser ablation, laser processing, and LIBS.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YW: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Data curation, Validation, Investigation, Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Software, Supervision. LH: Writing – review and editing, Supervision. HK: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Writing – review and editing, Supervision. TC: Writing – review and editing, Supervision. LW: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review and editing. HJ: Visualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. National Key Research and Development Program of China (2024YFB3613302).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Burikov S, Dolenko T, Patsaeva S, Starokurov Y, Yuzhakov V. Raman and IR spectroscopy research on hydrogen bonding in water-ethanol systems. Mol Phys (2010) 108:2427–36. doi:10.1080/00268976.2010.516277
2. Wei C, Zhu X, Norwood RA, Song F, Peyghambarian N. Numerical investigation on high power mid-infrared supercontinuum fiber lasers pumped at 3 μm. Opt Express (2013) 21:29488. doi:10.1364/oe.21.029488
3. Amiri IS, Sahoo SK, Palai G, Tripathy SK. Generation of ‘16’ type of biomedical laser using a single photonic structure: a new paradigm to operation in medical science. Optik (2019) 197:163227. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163227
4. Baraba A, Nathanson D, Matijevic J, Gabric D, Miletic I. Ablative potential of Er:YAG laser in dentin: quantum versus variable square pulse. Photomed Laser Surg (2016) 34:215–20. doi:10.1089/pho.2015.4078
5. Jiang J, Wei M, Xiong Z, Wu X, Cheng T, Jiang H. Observation of dentin ablation using an Er: YAG laser in a sub-pulse sequence mode. Chin J Lasers (2021) 48:0107001. doi:10.3788/CJL202148.0107001
6. Akin M, Veli I, Erdur EA, Aksakalli S, Uysal T. Different pulse modes of Er:YAG laser irradiation: effects on bond strength achieved with self-etching primers. J Orofac Orthop Fortschritte Kieferorthopädie (2016) 77:151–9. doi:10.1007/s00056-016-0019-3
7. Shi L, Yan J, Zhang S, Niu P, Geng J, Steinmeyer G. Burst laser-driven plasmonic photochemical nanolithography of silicon with active structural modulation. Ultrafast Sci (2025) 5:0084. doi:10.34133/ultrafastscience.0084
8. Skorczakowski M, Swiderski J, Pichola W, Nyga P, Zajac A, Maciejewska M, et al. Mid-infrared Q-switched Er: YAG laser for medical applications. Laser Phys Lett (2010) 7:498–504. doi:10.1002/lapl.201010019
9. Wang L, Wang J, Yang J, Wu X, Sun D, Yin S, et al. 2.79 μm high peak power LGS electro-optically Q-switched Cr, Er: YSGG laser. Opt Lett (2013) 38:2150–2. doi:10.1364/ol.38.002150
10. Yang J, Wang L, Wu X, Cheng T, Jiang H. High peak power Q-switched Er: YAG laser with two polarizers and its ablation performance for hard dental tissues. Opt Express (2014) 22:15686–96. doi:10.1364/oe.22.015686
11. Huang L, Wang P, Wang Y, Cheng T, Wang L, Jiang H. Mid-infrared 2.79 μm band Er, Cr: Y3Sc2Ga3O12 laser transmission anti-bending low-loss anti-resonant hollow-core fiber. Photonics (2024) 11:432. doi:10.3390/photonics11050432
12. Cui Q, Wei M, Xiong Z, Hu S, Jiang J, Wang L, et al. 100-300 Hz repetition-rate acousto-optic Q-switched 2.79 μm Er: YSGG laser side-pumped by laser-diode. Infrared Phys Technol (2019) 98:256–9. doi:10.1016/j.infrared.2019.03.029
13. Wang S, Tang Y, Yang J, Zhong H, Fan D. MoS2 Q-switched 2.8 µm Er: ZBLAN fiber laser. Laser Phys (2019) 29:025101. doi:10.1088/1555-6611/aaf642
14. Tang P, Wu M, Wang Q, Miao L, Huang B, Liu J, et al. 2.8-μm pulsed Er3+: ZBLAN fiber laser modulated by topological insulator. IEEE Photon Technol. Lett. (2016) 28:1573–6. doi:10.1109/LPT.2016.2555989
15. Xiong Z, Jiang L, Cheng T, Jiang H. 100 Hz repetition-rate 2.794 μm Cr, Er: YSGG passively Q-switched laser with Fe2+: ZnSe saturable absorber. Infrared Phys Technol (2022) 122:104087. doi:10.1016/j.infrared.2022.104087
16. Li C, Liu J, Jiang S, Xu S, Ma W, Wang J, et al. 2.8 μm passively Q-switched Er: CaF2 diode-pumped laser. Opt Mater Express (2016) 6:1570. doi:10.1364/ome.6.001570
17. Qin Z, Xie G, Ma J, Yuan P, Qian L. 2.8 μm all-fiber Q-switched and mode-locked lasers with black phosphorus. Photon Res (2018) 6:1074. doi:10.1364/prj.6.001074
18. Flór M, Wilkins DM, De La Puente M, Laage D, Cassone G, Hassanali A, et al. Dissecting the hydrogen bond network of water: charge transfer and nuclear quantum effects. Science (2024) 386:eads4369. doi:10.1126/science.ads4369
19. Bratos S, Leicknam J-C, Pommeret S, Gallot G. Laser spectroscopic visualization of hydrogen bond motions in liquid water. J Mol Struct (2004) 708:197–203. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2004.06.036
20. Vodop’yanov KL, Kulevskiǐ L, Pashinin P, Prokhorov A. Water and ethanol as bleachable radiation absorbers in an yttrium-erbium-aluminum garnet laser (λ = 2.94 μm). J Exp Theor Phys (1982) 55:1049–51.
21. Vodop’yanov L. Bleaching of water by intense light at the maximum of the λ ∼ 3 μm absorption band. J Exp Theor Phys (1990) 70:114–21.
22. Vodopyanov KL. Saturation studies of H2O and HDO near 3400 cm−1 using intense picosecond laser pulses. J Chem Phys (1991) 94:5389–93. doi:10.1063/1.460500
23. Graener H, Seifert G, Laubereau A. New spectroscopy of water using tunable picosecond pulses in the infrared. Phys Rev Lett (1991) 66:2092–5. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.66.2092
24. Shori RK, Walston AA, Stafsudd OM, Fried D, Walsh JT. Quantification and modeling of the dynamic changes in the absorption coefficient of water at λ = 2.94 μm. IEEE J Sel Top Quan Electron. (2001) 7:959–70. doi:10.1109/2944.983300
25. Vogel A, Venugopalan V. Mechanisms of pulsed laser ablation of biological tissues. Chem Rev (2003) 103:577–644. doi:10.1021/cr010379n
26. Sahoo MK, Rani MT, Patnaik D, Palai G. Detection of water content in biological tissues using a He-Ne laser and a one-dimensional (1-D) photonic waveguide. LASERS Eng (2023) 56:37–48.
27. Xian T, Zhan L, Gao L, Zhang W, Zhang W. Passively Q-switched fiber lasers based on pure water as the saturable absorber. Opt Lett (2019) 44:863. doi:10.1364/ol.44.000863
28. Zolotarev VM, Mikhailov BA, Alperovitch LI, Popova SI. Dispersion and absorption of liquid water in infra-red and radio-frequency regions. Opt Commun (1970) 1:301–2. doi:10.1016/0030-4018(70)90115-x
29. Xiong Z, Liu L, Hou Y, Tu S, Shi Q, Wu H. Effects of nanosecond- and microsecond-pulse Er, Cr: YSGG laser on the morphology and pulp temperature of dentin in dental restoration debonding. Lasers Med Sci (2025) 40:15. doi:10.1007/s10103-024-04279-6
30. Forsman AC, Banks PS, Perry MD, Campbell EM, Dodell AL, Armas MS. Double-pulse machining as a technique for the enhancement of material removal rates in laser machining of metals. J Appl Phys (2005) 98:033302. doi:10.1063/1.1996834
Keywords: solid state laser, Q-switched, Er,Cr:YSGG laser, saturable absorber, mid infrared
Citation: Wang Y, Huang L, Kong H, Zhang Y, Cheng T, Wang L and Jiang H (2025) Passively Q-switched 2.79-μm Er, Cr: YSGG laser based on pure water saturable absorber. Front. Phys. 13:1618958. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1618958
Received: 27 April 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 08 July 2025.
Edited by:
Rumao Tao, China Academy of Engineering Physics, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Huang, Kong, Zhang, Cheng, Wang and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Wang, bHdhbmdAYWlvZm0uYWMuY24=; Haihe Jiang, aGppYW5nQGhmY2FzLmFjLmNu
 Yinze Wang1,2
Yinze Wang1,2 Tingqing Cheng
Tingqing Cheng Haihe Jiang
Haihe Jiang