- China Tobacco Guangxi Industrial Co., Ltd., Nanning, China
Video surveillance is crucial for various applications, including unmanned aerial vehicle operations, flight safety monitoring, social security management, industrial safety, and criminal detection. The large volume of video data generated in these areas requires efficient processing techniques. However, traditional video compression and encoding methods are often complex and time-consuming, which can hinder the real-time performance needed for effective surveillance systems. To address this challenge, we propose a novel fast coding algorithm optimized for video surveillance applications. Our approach employs frame difference analysis to classify coding units (CUs) into three distinct categories: background CUs (BCs), motion CUs (MCs), and undetermined CUs. For both BCs and MCs, the algorithm examines the probability distribution of potential coding modes and depths, subsequently skipping unlikely combinations to enhance processing efficiency. The remaining candidates are then processed using a decision tree model, which enables accelerated mode and depth selection through early termination. Experimental results show that our method significantly accelerates encoding speed while maintaining almost identical coding efficiency, making it particularly effective for real-time surveillance applications.
1 Introduction
As smart cities continue to develop, urban monitoring systems are increasingly integrated with various technologies, such as public security systems, unmanned aerial vehicles, flight safety mechanisms, traffic management systems, and urban planning systems, to improve overall urban security. In the public security sector, high-definition, wireless, remote, and real-time surveillance capabilities are essential for optimizing operations. Video surveillance, which meets these requirements, plays a key role in ensuring public safety and is a primary tool for crime prevention. It continuously monitors the safety of residents and supports law enforcement agencies in crime detection and suspect tracking. More broadly, video surveillance is a critical component of Cyber-Physical-Social Systems (CPSS), where physical systems (such as surveillance cameras), cyber systems (including data processing, cloud storage, and analytics), and social systems (encompassing human interaction and response) are integrated to improve urban safety, security, and management. However, the substantial volume of video data produced by surveillance systems poses significant transmission challenges, and the requirement to store this data for future reference entails considerable costs, primarily due to the necessity of round-the-clock monitoring.
One effective way to address the challenges of handling large video data volumes is through video compression. However, this process is complex and can negatively impact the real-time performance required by video surveillance systems. Therefore, it is crucial to develop fast coding algorithms specifically tailored for video surveillance applications. In this paper, we first analyze the unique characteristics of video surveillance and then propose a fast video coding algorithm optimized for these applications. Our approach employs frame difference analysis to classify CUs into three distinct categories: BCs, MCs, and undetermined CUs. For both BCs and MCs, the algorithm examines the probability distribution of potential coding modes and depths, subsequently skipping unlikely combinations to enhance processing efficiency. The remaining candidates are then processed using a decision tree model, which enables accelerated mode and depth selection through early termination.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides a review of related work. Section 3 offers a comprehensive overview of the proposed algorithm. Section 4 discusses video surveillance features. Section 5 introduces fast decision methods designed to improve coding speed. Sections 6, 7 present the experimental results and draw conclusions, respectively.
2 Related work
Given the pervasive utilization of video surveillance in daily life, a considerable body of research has been dedicated to exploring various aspects of its application, as outlined below:
To enhance coding efficiency in surveillance video encoding, several innovative methodologies have been introduced. A dynamic texture synthesis approach leveraging a spatiotemporal generative adversarial network (GAN) has been proposed [1], aiming to optimize the process. Wang et al. [2] have devised a background modeling and referencing strategy specifically for surveillance video captured by moving cameras within the framework of high-efficiency video coding (HEVC), thereby achieving bitrate reduction. References [3, 4] have formulated a model that relates the bit rate and distortion metrics to video content and codec control parameters to sustain a desired rate-distortion performance. Furthermore, Gong et al. [5] have introduced an advanced quantization parameter cascading technique, tailored for surveillance video coding, which seeks to uplift coding efficiency through the precise selection and determination of encoding quantization parameters (QPs). These initiatives collectively aim to augment coding efficiency in the realm of surveillance video.
In their research, Zhou et al. [6] integrate feature learning, sparse representation, and dictionary learning to formulate a novel neural network designed for anomaly detection. In parallel, Zhao et al. [7] leverage distinctive features extracted from the HEVC compressed domain to enhance video surveillance purposes, facilitating the efficient segmentation and classification of dynamic objects. Both methodologies aim to advance coding efficiency while concurrently improving the detection, segmentation, and classification of moving objects.
Currently, the availability of fast coding algorithms specifically tailored for video surveillance is relatively limited. Research on video surveillance in CPSS has focused on integrating machine learning and edge computing to efficiently process large volumes of data in real-time. Huang and Lu [8] highlighted key challenges in CPSS, including data security, heterogeneity, and system integration. These concerns are increasingly relevant in the context of intelligent video systems and large-scale video data processing within CPSS. These advancements are crucial for applications in smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and urban security, where timely data processing and decision-making are essential. To enhance the speed of video coding, several prevalent techniques are employed: 1) the prediction of possible coding depths predicated on correlation, accompanied by the exclusion of unlikely depths; 2) the prediction of possible coding depth based on texture feature and exclusion of unlikely depth; and 3) the prediction of probable directional modes (DMs) through the utilization of Hadamard values.
In general, coding units (CUs) that are spatially or temporally adjacent exhibit a high degree of similarity, which allows for predictive coding methodologies utilizing correlated CUs. As discussed in Ref. [9], depths of spatially adjacent CUs are employed to estimate the depth of the current CU, while excluding less probable coding depths to enhance coding speed. Similarly, Ref. [10] employs weighted averages of spatially adjacent CUs to predict potential depths of the current CU and disregards unlikely depths to improve coding speed. Ref. [11] utilizes both temporal and spatially adjacent CUs for predicting feasible coding depths, systematically excluding less probable depths to optimize coding speed. In Ref. [12], the coding depth of pertinent CUs, along with the offline Bayes theorem, serves as the foundation for predicting the coding depths of the current CU. References [13, 14] integrate the coding depths of related CUs with an online Naive Bayes theorem, accounting for degree of correlation, to predict possible coding depths. Nonetheless, given that the correlation degree among adjacent CUs may vary, relying solely on correlation without accounting for its degree can hinder the ability to achieve optimal predictive results. Therefore, literatures [15, 16] advocate for considering both the coding depths of adjacent CUs and their correlation degree to more accurately predict coding depths, thereby excluding less likely coding depths and significantly improving coding speed. Liu et al. [17] proposed a fast inter-frame HEVC coding approach leveraging Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network technology [18]. introduced a HEVC fast CU partition decision method based on Support Vector Machine (SVM). Furthermore, Wang et al. [19] addressed the high complexity issue of CU partitioning in the HEVC/H.265 video coding standard by proposing a fast CU partitioning algorithm that combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and texture classification. Huang et al. [20] proposed a deep learning-based method to accelerate Versatile Video Coding (VVC) intra prediction by training separate models for split and directional modes across different CU sizes. A lightweight network further enables early termination.
It has been identified that the selection process for coding depths is closely correlated to the texture properties of the current coding units (CUs). Numerous studies have explored predictive models for predicting the possible coding depths of CUs based on their textural attributes. For instance, Ref. [21] investigates the textural characteristics of CUs to inform depth predictions. Reference [22] focuses on CU selection by assessing texture complexity. In Ref. [23], global and local edge complexity across various directions are computed to ascertain the necessity for further subdivision. Similarly, Ref. [24] employs a weighted support vector machine to predict coding depth selection by evaluating texture complexity, directional complexity, sub-block complexity, and quantization parameters. Reference [25] also employs a weighted support vector machine, incorporating the current CUs’ texture and other attributes, alongside information from adjacent CUs, to predict coding depth selection. Additionally, Refs. [26, 27] utilize deep learning techniques to predict coding depth selection, leveraging texture features and pertinent coding information or quantization parameters of CUs. Furthermore, literature [28, 29] integrates texture features with data from adjacent CUs to predict potential coding information.
The Hadamard value is an effective metric for assessing predictive accuracy, and is therefore frequently utilized to predict likely DMs and to exclude improbable ones. Studies indicate that optimal DMs are typically found among those with the smallest Hadamard values, leading to the selection of only the top few DMs for encoding purposes. L. Zhao et al. [30] proposed a fast mode decision algorithm specifically for intra-prediction in HEVC. This algorithm aims to expedite the encoding process by reducing the number of prediction modes involved in rate-distortion optimization. To expedite coding speed, literature [31] recommends dismissing unlikely DMs from consideration. Furthermore, Ref. [32] suggests evaluating the disparity between the Hadamard values of the smallest and next smallest DMs. A significant difference implies that only the DM with the lowest Hadamard value and its immediate left and right neighbors should be chosen. Conversely, if the difference is negligible, additional DMs may be considered.
Although the algorithm mentioned above shows promise in speeding up coding, it does not fully consider the unique features of video surveillance, which limits its effectiveness for such applications. Surveillance videos often contain a large portion of BCs, which is generally simpler than the more complex foreground. To develop an effective coding algorithm, it is crucial to analyze the characteristics of both the background and foreground areas. In this paper, we first identify and define the background and foreground regions within surveillance videos and examine their distribution patterns. Based on these insights, we propose an optimized coding algorithm tailored to video surveillance needs.
3 The overview of the proposed algorithm framework
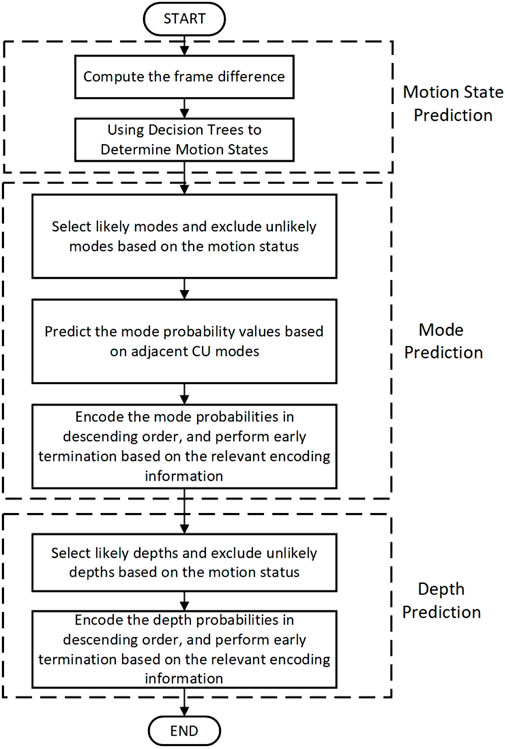
The objective of the proposed fast video encoding framework is to enhance encoding speed while maintaining high encoding efficiency. To achieve this goal, we introduce three key strategies: motion state prediction, fast mode selection strategy, and fast depth selection strategy. The flowchart of the overall algorithm is presented in Figure 1.
First, the judgment of BCs and MCs is performed by using the frame difference method to compute the pixel difference between consecutive frames. This information is then processed using a decision tree to classify and determine the motion state. The identified motion state helps optimize the mode selection process. For the Fast Mode Selection Strategy, the coding mode distribution law is applied to determine the most likely modes. These modes are then encoded in descending order of probability. Early termination is employed during the encoding process, based on the relevant encoding information, to enhance computational efficiency. The Fast Depth Selection Strategy follows a similar approach, where depth values are selected based on their likelihood derived from the motion state. The distribution law for depth coding is applied, and early termination is used to optimize depth encoding.
The proposed strategies are designed to significantly reduce the computational complexity of video encoding, while maintaining high video quality and compression efficiency.
4 Judgment of BCs and MCs
To precisely ascertain the MCs and BCs, we employ the frame difference technique to compute the pixel difference value. This computed value serves as the basis for prediction via a decision tree, as illustrated below.
4.1 Using the frame difference method to obtain the pixel difference value
The frame difference method is a useful technique for detecting moving objects within both background and foreground regions [33]. This approach entails comparing two successive frames in a video sequence and executing a difference operation between them. It proves especially effective when dealing with multiple moving objects, even when the camera itself is in motion. In scenarios where there is unusual movement of objects within the monitored scene, noticeable discrepancies between frames will manifest. By subtracting one frame from the other, the absolute value of the pixel difference can be calculated to ascertain whether it surpasses a predefined threshold, thereby confirming motion within the video. Let f (i,j) and f0 (i,j) denote the pixel values at coordinates (i, j) in the current and preceding frames, respectively; the absolute pixel difference is then determined as follows:
In Equation 1, when
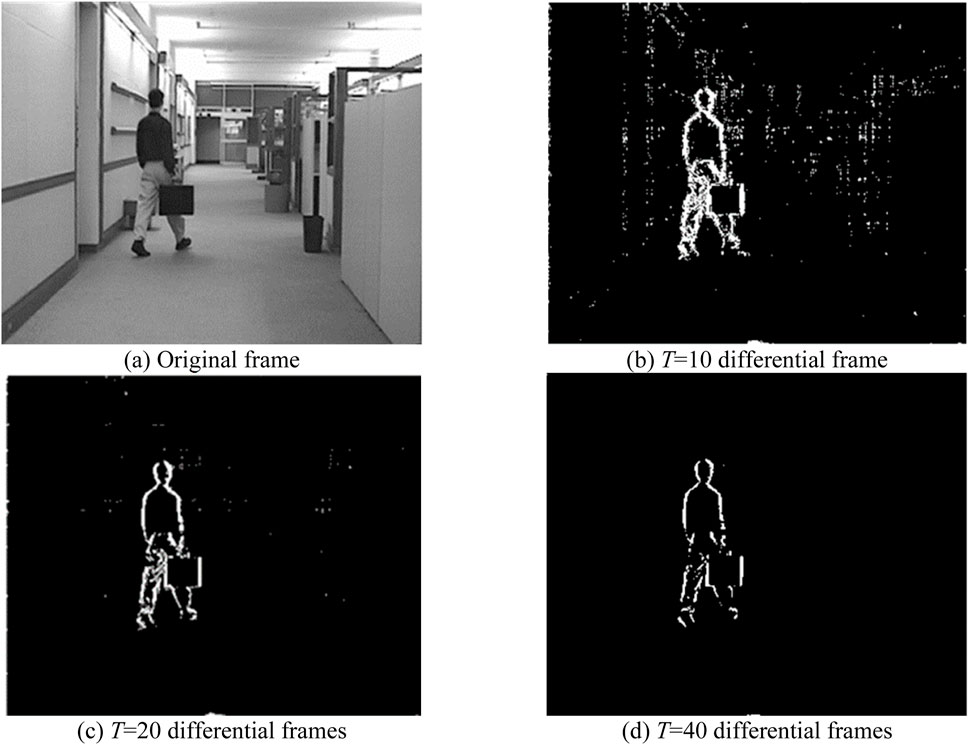

Figure 2. Original frame and differential frame of hall sequence. (A) Original frame. (B) T = 10 differential frame. (C) T = 20 differential frames. (D) T = 40 differential frames.
In Figures 2B–D, the black regions represent BCs, while the white regions denote MCs. Utilizing the aforementioned method, we can distinguish between BCs and MCs within surveillance video. Analysis of Figures 2B–D reveals notable differences among the three differential frames. Figure 2B exhibits an excess of MCs due to the misclassification of some BCs as MCs. Figure 2C more accurately identifies MCs and BCs. Conversely, Figure 2D displays an insufficient number of MCs, resulting from misclassification of certain MCs as BCs. This observation implies that, with an excessively high threshold value T some MCs may be erroneously categorized as BCs. Conversely, an overly low threshold T can lead to the incorrect classification of BCs as MCs. Thus, determining the optimal threshold T is pivotal to addressing this issue effectively.
At present, the threshold value T is predominantly determined through empirical experimentation. Given the variability inherent in video sequences, applying a uniform threshold value T across all sequences often fails to yield optimal outcomes. Machine learning techniques have found extensive application in video coding, leveraging large datasets for training and prediction to accurately forecast a broad spectrum of video sequences. Within the realm of machine learning, decision trees are employed for prediction owing to their straightforward predictive process and commendable accuracy [34]. Using decision trees in video surveillance can accelerate the process by efficiently predicting coding modes and depths based on content features. This reduces computational complexity and improves compression efficiency, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
4.2 Use decision tree to judge the motion state
The aforementioned method enables the determination of a pixel’s motion state. During the video coding process, it is necessary to divide each frame into coding units (CUs), which are then individually encoded. Consequently, assessing the motion state of these CUs becomes essential. The frame difference technique entails subtracting corresponding coding blocks from two consecutive frames and analyzing the resultant differences, as detailed below:
In Equation 2,
By Equation 2, we can calculate the pixel difference value for corresponding CUs across two consecutive frames. Given the numerous pixel differences present within CUs, predictive analysis can be performed using their expected values. For an M × N coding block, the corresponding expected value is:
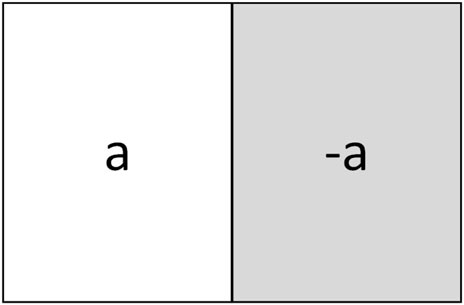
Although the expected value provides an overview of the general state, it may not accurately predict motion status in certain scenarios, as illustrated in Figure 3.
In Figure 3, a represents any number within the range [0-255]. S Due to the use of complementary numbers in different colored sections, their expected value results in 0. Relying solely on this expected value would lead to the incorrect classification of these pixels as BCs when they are, in fact, MCs. To address this issue, we employ the variance of the pixel difference to enhance prediction accuracy. The variance is computed as follows:
The expected
To develop the corresponding decision tree model, suitable training data must be acquired. For this purpose, we have selected CIF format sequences such as “bridge_close” and “hall_objects”, in addition to 720p format sequences like “FourPeople” and “vidyo3”. These sequences can include different motion states, various textures, and essentially represent the characteristics of video surveillance. Incorporating sequences of varying resolutions within the training dataset enhances the model’s adaptability, thereby enabling accurate predictions across videos with different resolutions.
Currently, VVC and HEVC are the two most prevalent standards in video coding. VVC offers remarkable coding efficiency but is accompanied by substantial coding complexity. Conversely, HEVC, while not matching VVC’s efficiency, benefits from reduced coding complexity. Considering the trade-off between coding efficiency and complexity, HEVC was selected for encoding surveillance videos. Utilizing common test conditions, the quantization parameter was set at 22, 27, 32, and 37, with configurations employing Low Delay P (LDP) to encode these video sequences, thereby generating the requisite training and prediction data.
The first 10 frames of each video sequence are encoded, and the resulting encoding information is used as the dataset. The dataset is partitioned, with 80% allocated for training and 20% reserved for validation. To ensure the reliability of our prediction results, a 90% confidence level has been established [34]. If a CU’s confidence level reaches or exceeds this threshold, indicating either a motion or background state, it is classified accordingly as a MC or BC. Conversely, should the confidence level fall short of 90%, the motion state of the CU cannot be conclusively determined. This approach allows us to effectively categorize MCs, BCs, and CUs with indeterminate motion states.
5 Fast mode selection strategy
Initially, the distribution of coding modes for MCs, BCs, and uncertain CUs was derived through experimental analysis, allowing for the exclusion of improbable coding modes. Subsequently, the probability of coding modes for the current CUs is computed based on the coding modes of adjacent CUs, with these probabilities assessed in descending order. Finally, early termination is implemented through a decision tree, as detailed below.
5.1 Coding mode distribution law
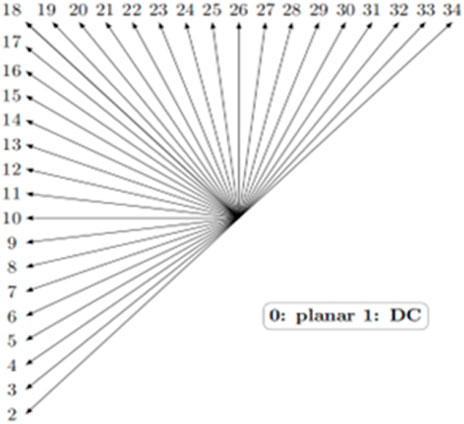
HEVC encompasses both intra and inter coding modes. Intra-mode coding employs 35 DMs, as illustrated in Figure 4. These comprise the Planar (DM0), DC (DM1), and 33 additional DMs. Intra-mode prediction involves two main processes: rough mode decision (RMD) and rate distortion optimization (RDO). During RMD, all 35 DMs are evaluated, and the N DMs with the lowest Hadamard values are selected. Subsequently, RDO utilizes a rate-distortion optimization process to choose the DM that achieves the smallest rate-distortion from these N DMs. The size of the N value is contingent upon the size of the CUs: for 64 × 64, 32 × 32, and 16 × 16 CUs, N is 3; for 8 × 8 and 4 × 4 CUs, N is 8.
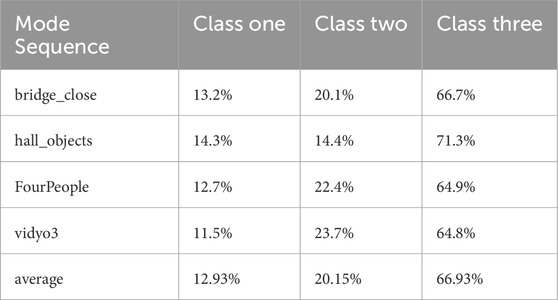
The Inter modes include: 2N × 2N, 2N × N, N×2N, N × N, 2N × nU, 2N × nU, nL × 2N and nR × 2N, as shown in Figure 5. 2N × 2N includes Merge mode, Inter2N × 2N mode and Intra mode. The corresponding encoding modes are: 2N × N, N × 2N, N × N, 2N × nU, 2N × nU, nL × 2N and nR × 2N are Inter2N × N, InterN × 2N, InterN × N, Inter2N × nU, Inter2N × nU, InternL × 2N and InternR × 2N, respectively. Merge and Inter2N × 2N are typically applied to BCs. The Inter2N × N and InterN × 2N are often suitable for predicting very slow-moving CUs. Other modes are generally appropriate for CUs exhibiting complex motion. We categorize Merge and Inter2N × 2N mode as Class One, InterN × 2N and Inter2N × N mode as Class Two, and the remaining modes as Class Three.
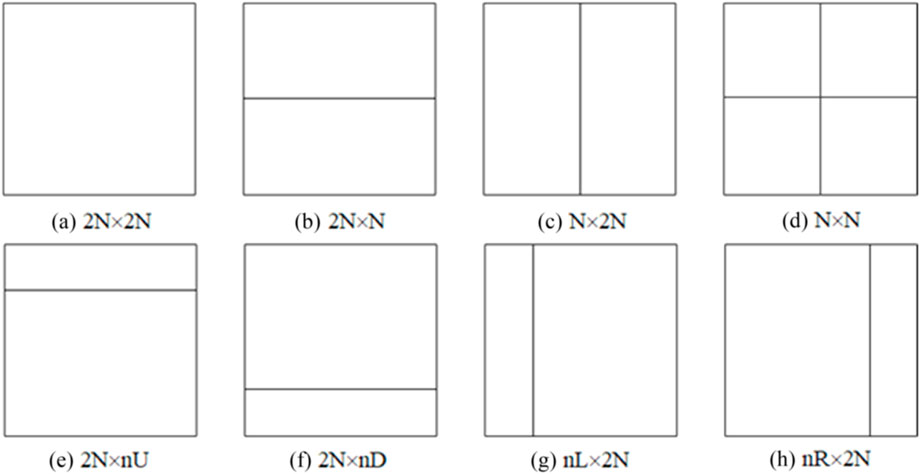
Figure 5. 8 inter-modes in HEVC. (a) 2N × 2N. (b) 2N × N. (c) N × 2N. (d) N × N. (e) 2N × nU. (f) 2N × nD. (g) nL × 2N. (h) nR × 2N.
Applying the test conditions outlined in Section 3, each sequence is encoded with 100 frames, resulting in the mode distributions for BCs and MCs, as depicted in Tables 1, 2, respectively.
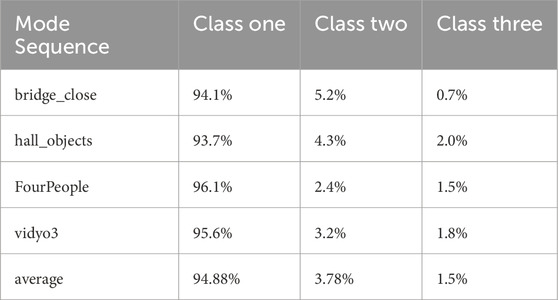
Table 1 reveals that 94.88% of the BCs utilize the encoding mode from Class One, while the proportions for Class Two and Class Three are negligible. Therefore, it is appropriate 5to exclusively employ the Class One mode for encoding these BCs.
Table 2 indicates that 12.93% of MCs employ the Class One coding mode, whereas 20.15% and 66.93% utilize the Class Two and Class Three modes, respectively. It is crucial to acknowledge that, despite its minority usage, the Class One mode should not be overlooked. This is due to the fact that for MCs located within the central area of a moving object, optimal matching can be achieved without necessitating subdivision, whereas MCs positioned along the edges require further subdivision. Additionally, the mode distribution for uncertain CUs does not display any distinctive characteristics.
Through data analysis, it has been established that the Class One coding mode is suitable for BCs, allowing other coding modes to be skipped. However, for MCs and uncertain CUs, it is not feasible to straightforwardly exclude the less probable coding modes, as the distribution of these modes is not distinctly apparent.
5.2 The order of possibility of coding mode
Given the extensive array of coding modes available in HEVC, the likelihood of adopting each mode varies significantly. Hence, it is imperative to evaluate the probabilities of each mode to enhance performance, rather than indiscriminately encoding all modes. To optimize this process, we should first determine the likelihood of each coding mode, then encode them in descending order of probability. The mode selection process can be terminated early based on coding performance metrics. The probabilities of the current CU’s coding modes can be calculated with reference to the coding modes utilized by adjacent CUs.
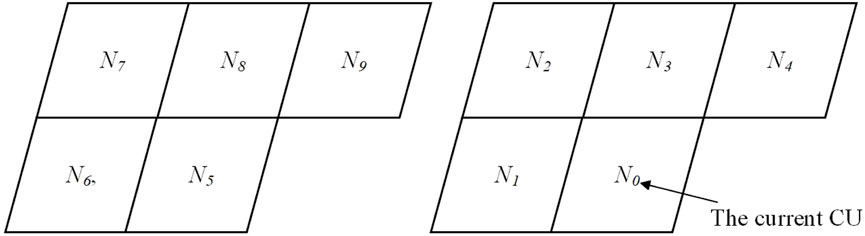
As shown in Figure 6, N0 is the current CUs, N1, N2, N3 and N4 are adjacent CUs, and N4, N5, N6, N7 and N8 are CUs corresponding to the previous frame. Let the encoding mode values of the CUs N0, N1, N2, N3, N4, N5, N6, N7, N8 and N9 be
Since N0 is surrounded by 9 adjacent CUs, each with 9 coding modes, there are 99 possible values to consider. The extensive number of possible values presents a challenge in calculating a probability value for each one. To overcome this, we utilize a Naive Bayes distribution for computation [12]. The Naive Bayes distribution assumes that each adjacent CU is independently considered, allowing Equation 6 to be reformulated as follows:
Using the test conditions in Section 3, each sequence is encoded with 100 frames. Experimental procedures allow us to determine P
5.3 The coding mode is terminated early
The probability values for each mode are derived from the adjacent CUs and encoded in descending order of probability. To enhance encoding speed, a decision tree is employed to facilitate early termination of mode selection. A pivotal aspect of this process is the selection of eigenvalues. For prediction purposes, the following eigenvalues have been selected.
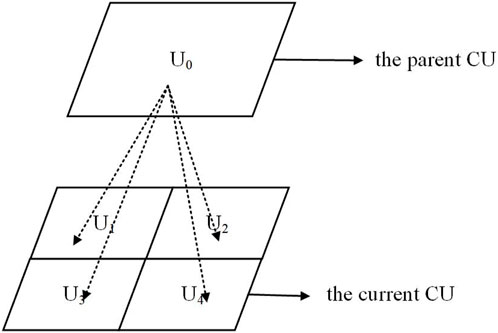
5.3.1 Coding patterns of parental CUs
Since the sub-CUs are derived from the division by parent CUs, as shown in Figure 7,
5.3.2 The probability value of the current coding mode
The probabilities of the coding modes are closely related to the mode selection. The greater the probability of a coding mode, the greater the possibility of selecting this mode as the optimal mode; and vice versa. Therefore, we choose the probability of a coding mode as the feature value.
5.3.3 Texture complexity of CUs
The texture complexity of the CUs is also closely related to the mode of the CUs. CUs with relatively simple textures are more likely to use class one and class two. Thus, texture complexity can be used as a feature value for coding mode selection. The texture complexity can be calculated from the variance of the CUs pixels.
5.3.4 Rate-distortion value
When a certain mode is encoded, the corresponding rate-distortion value is calculated. A lower rate-distortion value suggests a favorable prediction, indicating that the mode is likely to be optimal. Conversely, a higher rate-distortion value implies a less effective prediction, suggesting that the mode may not be optimal.
Using the above four eigenvalues, a decision tree is employed to facilitate early termination of mode selection. If a mode’s confidence level is 90% or higher, it is considered optimal, and the selection process is terminated. Otherwise, the next coding mode is selected, following the order of descending probabilities.
6 Fast depth selection strategy
We first conducted experiments to derive the distributions of coding depths for MCs, BCs, and uncertain CUs, and uncertain CUs, subsequently excluding improbable coding depths. Following this, a decision tree was employed to facilitate early termination of depth selection, as outlined below.
6.1 Coding depth distribution law
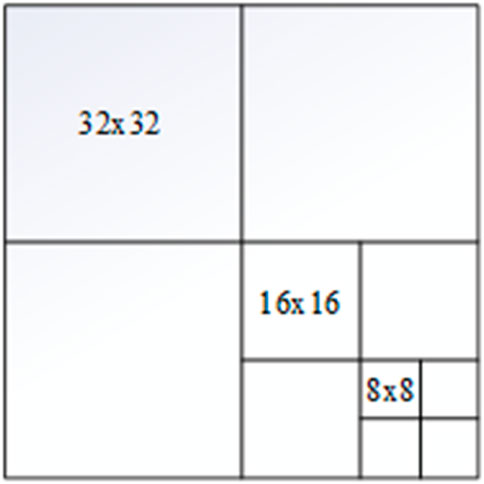
Similar to HEVC, SHVC segments each image frame into multiple 64 × 64 Coding Tree Units (CTUs). Each CTU encompasses four coding depths: depths 0, 1, 2, and 3, corresponding to CUs sized at 64 × 64, 32 × 32, 16 × 16, and 8 × 8, respectively. In the CTU coding process, a 64 × 64 CU is initially subdivided into four 32 × 32 CUs; each 32 × 32 CU is further partitioned into four 16 × 16 CUs; and each 16 × 16 CU is divided into four 8 × 8 CUs. This procedure allows for the examination of all coding depths, enabling the selection of the optimal coding depth. Figure 8 illustrates an example of coding depths within a CU.
The selection of coding depth is intrinsically linked to the motion state of CUs. BCs typically utilize smaller coding depths, such as depth 0, whereas MCs generally require larger coding depths, like depths 2 and 3. Consequently, analyzing the distribution of coding depths in relation to the motion state allows for the omission of unlikely coding depths, thereby significantly enhancing coding speed.
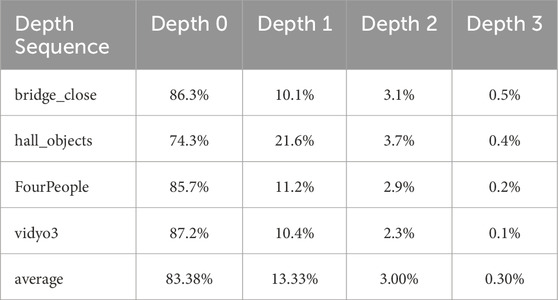
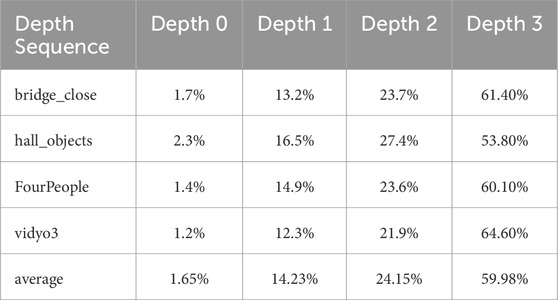
Using the test conditions in Section 3, each sequence is encoded using 100 frames. Experimental results reveal the coding depth distributions for BCs and MCs, which are detailed in Table 3, 4, respectively.
From Table 3, we can see that an average of 83.38% of the BCs use the coding depths of depth 0, an average of 13.33% of the BCs use the coding depths of depth 1, and the proportion of other depths is very small, so we can only use depth 0. and depth 1 to check.
From Table 4, we can see that an average of 1.65% of the MCs use depth 0, an average of 14.23% of the MCs use depth 1, and an average of 24.15% of the MCs use depth 2, with an average of 59.98% of the MCs use depth 3. Since the ratio of depth 0 is small, we can skip the depth directly. Experiments show that the depth distribution of uncertain CUs has no obvious characteristics.
6.2 Early termination of coding depth
By analyzing the distribution of coding depths, we can efficiently exclude improbable coding depths for both BCs and MCs. For the remaining depths, a decision tree is employed to facilitate early termination of depth selection. The following eigenvalues have been selected for predictive purposes.
6.2.1 Size of CUs
The dimensional attributes of CUs are significantly correlated with the selection of coding depths. Generally, larger CUs have a higher probability of being skipped, while the likelihood of early termination increases as well. Therefore, the size of CUs is chosen as a critical eigenvalue for prediction.
6.2.2 Texture complexity of CUs
The texture of the CUs is also closely related to the depth selection. CUs with simpler textures are more likely to use smaller coding depths. Therefore, we select texture complexity as an eigenvalue for encoding depth selection. Texture complexity is assessed through the variance of pixel values within the CUs.
6.2.3 Coding mode
The coding modes are closely related to depth selection [35]. When a simple coding mode is applied at a particular coding depth, the likelihood of early termination for that depth increases, whereas a more complex mode reduces this probability. As such, coding mode is selected as a feature value for consideration in depth selection.
6.2.4 Coding depths of relevant CUs
The relevant CUs are generally similar, so we can use the coding depths of the relevant CUs to determine whether to early terminate depth selection. We first compute the average coding depth of the adjacent CUs and utilize this mean as a feature value for prediction.
6.2.5 Quantization parameters (QPs)
The QP is closely related to depth selection [21]. A larger QP often correlates with the selection of a smaller coding depth as optimal, while smaller QPs typically align with greater coding depths. Therefore, QPs are chosen as key eigenvalues in the depth selection process.
The decision tree employs the aforementioned five eigenvalues to facilitate early termination of depth selection. If the confidence level for terminating a coding depth exceeds or reaches 90%, this depth is considered optimal, thereby terminating further coding at subsequent depths.
7 Experimental results and analysis
To evaluate the efficacy of our proposed algorithm, we utilized HEVC reference software (HM16.7) on a server equipped with an Intel 2.4 GHz CPU and 60 GB of memory. As previously mentioned, according to the common SHM test conditions (CSTC) [36] guidelines, quantization parameters of 22, 27, 32, and 37 were employed, and configurations utilized the LDP to encode video sequences. To assess the algorithm’s general applicability, we selected seven video surveillance sequences filmed in various settings, including classrooms, playgrounds, roads, meeting rooms, laboratories, canteens, and dormitories. These sequences are denoted respectively as classroom, playground, road, meeting room, laboratory, playground, canteen, dormitory.
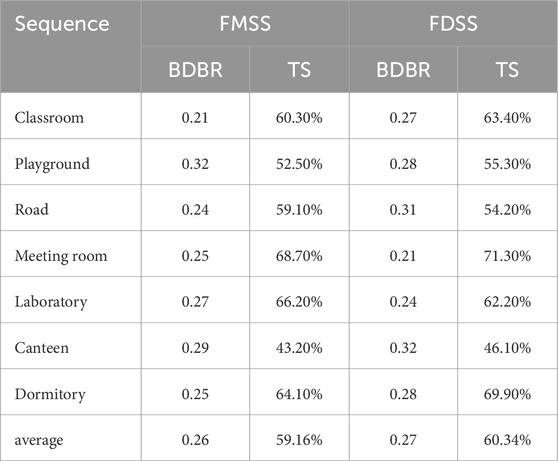
Since the proposed algorithm comprises a Fast Mode Selection Strategy (FMSS) and a Fast Depth Selection Strategy (FDSS), these two strategies were tested independently. Experimental performance was evaluated in terms of coding efficiency and coding time savings. Coding efficiency is assessed using BDBR, where a positive BDBR indicates increased bit rate saving at identical quality, while a negative BDBR signifies a loss in bit rate savings. “TS” denotes the percentage of coding time savings. The impacts on coding efficiency and the enhancements in coding speed for these two strategies are detailed in Table 5.
From Table 5, we find that the average coding efficiency losses in “FMSS” and “FDSS” are 0.26 and 0.27, respectively. Correspondingly, the average coding speed improvements in “FMSS” and “FDSS” are 59.16% and 60.34%, respectively. Obviously, the performance metrics for coding efficiency loss and speed enhancement are strikingly similar between FMSS and FDSS. This similarity arises from the design of the proposed algorithm, which is predicated on assessing motion status. For MCs, the encoding procedures in both FMSS and FDSS are complex and time-intensive, whereas for BCs, these processes are significantly simplified, requiring minimal coding time.
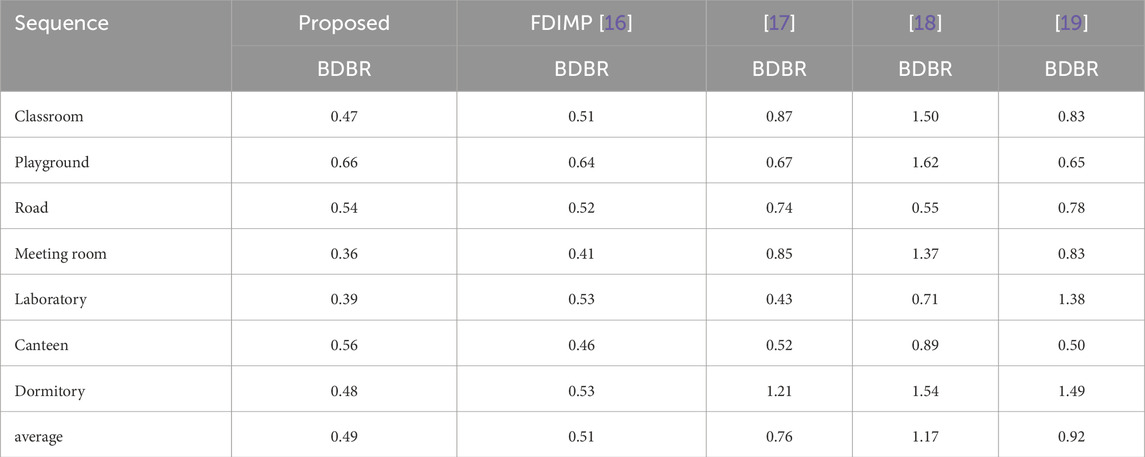
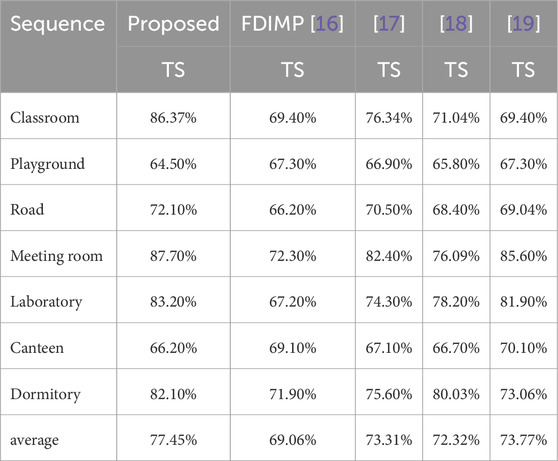
To further demonstrate the performance of our proposed algorithm, we combine “FMSS” and “FDSS” with our proposed method and compare it with FDIMP [16]. Given the limited number of algorithms focused on enhancing video coding efficiency in the context of video surveillance, we also included comparisons with the methods described in [17, 18], and [19]. The comparisons of BDBR and TS between our algorithm and those referenced in [16–18], and [19] are presented in Tables 6, 7, respectively.
As shown in Tables 6, 7, the BDBR and TS of the algorithm proposed in this paper are 0.49% and 77.45%, respectively. In comparison, FDIMP [16] has a BDBR and TS of 0.51% and 69.06% [17], has a BDBR and TS of 0.76% and 73.31% [18], has a BDBR and TS of 1.17% and 72.32%, and [19] has a BDBR and TS of 0.92% and 73.77%. Compared to these algorithms, our algorithm shows an average BDBR improvement of 0.02, 0.27, 0.68, and 0.43, and an average TS improvement of 8.39%, 4.14%, 5.13%, and 3.68%, respectively. Thus, our algorithm demonstrates significantly faster encoding speed and slightly better coding efficiency savings compared to these algorithms. However, it should be noted that the proposed algorithm performs poorly for certain sequences, such as Playground and Canteen. This is attributed to the fact that our algorithm is specifically optimized for surveillance video sequences, which typically contain a large amount of background content. When a sequence involves extensive background, the algorithm performs excellently; however, its performance may be less advantageous in sequences with limited background. Therefore, the proposed algorithm is particularly suitable for surveillance video sequences with significant background elements.
8 Conclusion
This paper presents a fast video coding algorithm designed for surveillance applications. By improving real-time efficiency, the algorithm is particularly beneficial for CPSS, where timely data processing and decision-making are crucial for ensuring urban safety and security. The proposed algorithm uses frame difference analysis to classify CUs into three categories: BCs, MCs, and undetermined CUs. For BCs and MCs, the algorithm analyzes the probability distribution of coding modes and depths, efficiently discarding unlikely combinations. A decision tree is then used to process the remaining candidates, enabling early termination of the mode selection process and thus improving encoding speed. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly accelerates computational performance with only minimal loss in coding quality. The algorithm proves particularly effective for surveillance videos with mostly static backgrounds. However, the method has certain limitations, such as reduced performance in areas with less background content. Future work will explore using deep learning techniques to address these issues. Additionally, we plan to extend the framework to handle surveillance videos with significant motion content.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
BX: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Author BX was employed by China Tobacco Guangxi Industrial Co., Ltd.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yang K, Liu D, Chen Z, Wu F, Li W. Spatiotemporal generative adversarial network-based dynamic texture synthesis for surveillance video coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2022) 32(1):359–73. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2021.3061153
2. Wang G, Li B, Zhang Y, Yang J. Background modeling and referencing for moving cameras-captured surveillance video coding in HEVC. IEEE Trans Multimedia (2018) 20(11):2921–34. doi:10.1109/tmm.2018.2829163
3. Cai Q, Chen Z, Wu D, Huang B. Real-time constant objective quality video coding strategy in high efficiency video coding. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (2020) 30(7):2215–28.
4. Guo H, Zhu C, Chen J, Luo L, Huo Y, Liu Y. Distortion propagation factor estimation for VVC low-delay hierarchical coding. IEEE Trans Broadcasting (2025) 71(2):492–505. doi:10.1109/tbc.2024.3519909
5. Gong Y, Yang K, Liu Y, Lim KP, Ling N, Wu HR. Quantization parameter cascading for surveillance video coding considering all inter reference frames. IEEE Trans Image Process (2021) 30:5692–707. doi:10.1109/tip.2021.3087413
6. Zhou T, Du J, Zhu H, Peng X, Liu Y, Goh RSM. AnomalyNet: an anomaly detection network for video surveillance. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security (2019) 14(10):2537–50. doi:10.1109/tifs.2019.2900907
7. Zhao L, He Z, Cao W, Zhao D. Real-time moving object segmentation and classification from HEVC compressed surveillance video. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2016) 28(6):1346–57. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2016.2645616
8. Huang Y, Lu X. Editorial: security, governance, and challenges of the new generation of cyber-physical-social systems. Front Phys (2024) 12:1–2. doi:10.3389/fphy.2024.1464919
9. Shen L, Liu Z, Zhang X, Zhao W, Zhang Z. An effective CU size decision method for HEVC encoders. IEEE Trans Multimedia (2013) 15(2):465–70. doi:10.1109/tmm.2012.2231060
10. Shen L, Zhang Z, An P. Fast CU size decision and mode decision algorithm for HEVC intra coding. IEEE Trans Consumer Electronics (2013) 59(1):207–13. doi:10.1109/tce.2013.6490261
11. Shen L, Zhang Z, Liu Z. Adaptive inter-mode decision for HEVC jointly utilizing inter-level and spatiotemporal correlations. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (2014) 24(10):1709–22.
12. Tohidypour HR, Pourazad MT, Nasiopoulos P. Probabilistic approach for predicting the size of coding units in the quad-tree structure of the quality and spatial scalable HEVC. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (2016) 18(2):182–95.
13. Tohidypour HR, Bashashati H, Pourazad MT, Nasiopoulos P. Online-learning-based mode prediction method for quality scalable extension of the high efficiency video coding (HEVC) standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2017) 27(10):2204–15. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2016.2576738
14. Kuang W, Chan YL, Tsang SH, Siu WC. Online-learning-based bayesian decision rule for fast intra mode and CU partitioning algorithm in HEVC screen content coding. IEEE Trans Image Process (2020) 29:170–85. doi:10.1109/tip.2019.2924810
15. Wang D, Zhu C, Sun Y, Dufaux F, Huang Y. Efficient multi-strategy intra prediction for quality scalable high efficiency video coding. IEEE Trans Image Process (2019) 28(4):2063–74. doi:10.1109/tip.2017.2740161
16. Wang D, Sun Y, Zhu C, Li W, Dufaux F. Fast depth and inter mode prediction for quality scalable high efficiency video coding. IEEE Trans Multimedia (2020) 22(4):833–45. doi:10.1109/tmm.2019.2937240
17. Liu C. Fast HEVC inter-frame coding based on LSTM neural network technology. J Vis Commun Image Representation (2024) 98:104056–10. doi:10.1016/j.jvcir.2024.104056
18. Bobade R, Vaidya Y, Metkar S. Fast coding unit partition decision in inter prediction mode for HEVC using CNN-LSTM approach. In: International conference on communication and computational technologies. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore (2023). p. 301–12.
19. Wang T, Wei G, Li H, Bui T, Zeng Q, Wang R. Fast CU partition algorithm for intra frame coding based on joint texture classification and CNN. Sensors (2023) 23(18):7923. doi:10.3390/s23187923
20. Huang Y, Yu J, Wang D, Lu X, Dufaux F, Guo H, et al. Learning-based fast splitting and directional mode decision for VVC intra prediction. IEEE Trans Broadcasting (2024) 70(2):681–92. doi:10.1109/tbc.2024.3360729
21. Lei J, Li D, Pan Z, Sun Z, Kwong S, Hou C. Fast intra prediction based on content property analysis for low complexity HEVC-based screen content coding. IEEE Trans Broadcasting (2017) 63(1):48–58. doi:10.1109/tbc.2016.2623241
22. Liu X, Liu Y, Wang P, Lai CF, Chao HC. An adaptive mode decision algorithm based on video texture characteristics for HEVC intra prediction. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2017) 27(8):1737–48. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2016.2556278
23. Min B, Cheung RCC. A fast CU size decision algorithm for the HEVC intra encoder. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (2015) 25(5):892–896.
24. Liu X, Li Y, Liu D, Wang P, Yang LT. An adaptive CU size decision algorithm for HEVC intra prediction based on complexity classification using machine learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2019) 29(1):144–55. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2017.2777903
25. Zhang Y, Pan Z, Li Z, Wang N, Jiang X, Kwong G, et al. Effective data driven coding unit size decision approaches for HEVC INTRA coding. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (2018) 28(11):3208–3222.
26. Xu M, Li T, Wang Z, Deng X, Yang R, Guan Z. Reducing complexity of HEVC: a deep learning approach. IEEE Trans Image Process (2018) 27(10):5044–59. doi:10.1109/tip.2018.2847035
27. Kim K, Ro WW. Fast CU depth decision for HEVC using neural networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2019) 29(5):1462–73. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2018.2839113
28. Shen L, Feng G. Content-based adaptive SHVC mode decision algorithm. IEEE Trans Multimedia (2019) 21(11):2714–25. doi:10.1109/tmm.2019.2909859
29. Shen L, Feng G, An P. SHVC CU processing aided by a feedforward neural network. IEEE Trans Ind Inform (2019) 15(11):5803–15. doi:10.1109/tii.2019.2911708
30. Zhao L, Zhang L, Ma S, Zhao D. Fast mode decision algorithm for intra prediction in HEVC. In: 2011 visual communications and image processing VCIP. Tainan, Taiwan: IEEE (2011). p. 1–4.
31. Zhang H, Ma Z. Fast intra mode decision for high efficiency video coding (HEVC). IEEE Transactions on circuits and systems for video technology (2014) 24(4):660–8.
32. Yan S, Hong L, He W, Wang Q. Group-based fast mode decision algorithm for intra prediction in HEVC. In: 2012 eighth international conference on signal image technology and internet based systems (2012). p. 225–9.
33. Haritaoglu I, Harwood D, Davis LS. W/sup 4/: real-time surveillance of people and their activities. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intelligence (2000) 22(8):809–30. doi:10.1109/34.868683
34. Yang H, Shen L, Dong X, Ding Q, An P, Jiang G. Low-complexity CTU partition structure decision and fast intra mode decision for versatile video coding. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2020) 30(6):1668–82. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2019.2904198
35. Correa G, Assuncao PA, Agostini LV, da Silva Cruz LA. Fast HEVC encoding decisions using data mining. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technology (2015). 25(4):660–73. doi:10.1109/tcsvt.2014.2363753
Keywords: video surveillance, frame difference method, coding mode, coding depth, decision tree
Citation: Xie B (2025) A fast video coding algorithm using data mining for video surveillance. Front. Phys. 13:1633909. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1633909
Received: 23 May 2025; Accepted: 21 July 2025;
Published: 05 August 2025.
Edited by:
Yuanyuan Huang, Chengdu University of Information Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Dayong Wang, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, ChinaHongwei Guo, Honghe University, China
Copyright © 2025 Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bingyue Xie, Mzc1OTc0NTk3QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Bingyue Xie
Bingyue Xie