- 1School of Public Health, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2School of Public Health and Emergency Management, Chongqing Medical and Pharmaceutical College, Chongqing, China
- 3Chongqing Public Health Medical Center, Chongqing, China
- 4West China School of Public Health and West China Fourth Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Introduction: In many countries, especially large developing nations like China, hierarchical healthcare systems face persistent structural challenges such as unbalanced resource allocation and inefficient referral networks. To capture the impact of individual behavior on the evolution of healthcare system structures, this study develops an agent-based modeling (ABM) approach to simulate the dynamic formation of inter-hospital referral networks.
Methods: The model introduces a strategic game-theoretic mechanism among patients, where each agent makes referral decisions based on multiple factors, including medical benefits, commuting costs, and limited information, under resource constraints. Through these decentralized decisions, a directed and weighted referral network emerges, reflecting realistic behavioral patterns. Based on the simulated network, topological analysis is performed to identify key hospitals and design targeted resource allocation strategies.
Results: We simulate the dynamic formation process and obtain a stable referral network structure. The results show that tertiary hospitals exhibit high centrality, indicating a structural “Matthew effect.” Furthermore, the observed community division pattern may correspond to actual administrative regions or the organizational frameworks of medical alliances. In addition, compared to simply strengthening core hospitals, the referral bottleneck mitigation strategy can reduce patient loss while decreasing the overall referral frequency within the system.
Discussion: The study reveals structural imbalances in China's referral network, characterized by a “siphoning effect” toward tertiary hospitals and underutilized secondary institutions. Our findings demonstrate that bottleneck mitigation strategies outperform core-hospital strengthening in reducing both patient loss and referral frequency. To address these issues, we propose a multi-level reform framework encompassing operational capacity-building, institutional payment reforms, and strategic medical consortium optimization. This integrated approach aims to transform the top-heavy healthcare structure into an efficient, hierarchical system with equitable resource distribution.
1 Introduction
In many countries, particularly in large developing nations such as China, the hierarchical healthcare system has faced long-standing structural challenges [1]. With the continued advancement of healthcare system reform in China, the development of hierarchical diagnosis and treatment (HDT) systems and medical consortia (MCs) has been elevated to a national strategic priority. The Healthy China 2030 Planning Outline (State Council, 2016) [2] explicitly calls for the improvement of the HDT system and the optimization of the referral process. This was further reinforced by the Guidelines on Promoting the Construction and Development of Medical Consortia (General Office of the State Council, 2017, No. 32), which emphasized the establishment of clearly defined and accountable referral collaboration networks. In 2023, the National Health Commission issued a new policy that aims to improve referral precision through digital health technologies, underscoring the urgency of optimizing referral networks.
Despite these policy efforts, two prominent challenges remain in practice: unbalanced resource allocation and inefficient referral network structures. Official reports and national surveys consistently [3] indicate that tertiary hospitals continue to bear a disproportionate share of referral demands, while primary care institutions are significantly underutilized [4, 5], reflecting a persistent “siphoning effect” within the healthcare system. These findings suggest substantial redundancy and poor coordination within existing referral systems. As the core mechanism for implementing hierarchical medical services, referral pathways are critical to improving systemic efficiency. However, in the context of uneven regional resource distribution and limited inter-hospital coordination, patient referral behaviors often involve unnecessary detours and suboptimal decisions, leading to diminished diagnostic efficiency and resource effectiveness. Therefore, there is an urgent need to construct and analyze inter-hospital referral network models to uncover their structural features and flow patterns. This analysis provides a critical foundation for enhancing network efficiency and optimizing the allocation of regional healthcare resources.
International research on patient referral networks (also known as patients-sharing networks) has focused primarily on three domains. At first, the structural characteristics of such networks have been widely explored through social network analysis (SNA) [6, 7]. Scholars have used metrics such as centrality, density, and modularity to reveal collaboration and referral patterns between hospitals and physicians, and to examine how the topology of network affects healthcare efficiency and care coordination [8]. Secondly, multiple studies have investigated the impact of network structure on clinical and economic outcomes [9–11]. For example, hospitals with high centrality in referral networks are often associated with lower readmission rates but increased healthcare expenditures [12]. Third, increasing attention has been paid to the resilience of the healthcare system [13–16], particularly in the context of public health emergencies. Scholars have employed approaches such as complex network theory and system dynamics to investigate how referral networks respond to external shocks (e.g., pandemics) and how structural features like redundancy, node centrality, and resource elasticity contribute to system robustness and recovery. In contrast, research in China remains relatively nascent. Most existing studies [17] rely on static analysis of empirical referral data and lack mechanism-based simulation models. There is limited exploration of the evolutionary dynamics, resilience, or optimization of regional healthcare networks. In addition, comprehensive simulation frameworks for policy experimentation and evaluation are still underdeveloped. Against this backdrop, the present study addresses the following core questions.
1. How can a referral network model be constructed to capture the directional, weighted, and dynamic nature of inter-hospital patient transfers?
2. Based on the emergent network structure, how can the main hospitals be identified to improve system efficiency and resource allocation?
3. How can network analysis and simulation be used to evaluate targeted policy interventions, such as strengthening specific types of hospitals or optimizing regional referral corridors, thus offering theoretical support for healthcare coordination and policy design?
The study aims to construct a dynamic evolutionary model of inter-hospital referral networks using an agent-based modeling (ABM) approach [18], incorporating game-theoretic decision-making mechanisms. By simulating patient behavior under realistic constraints, the model enables the emergence of referral networks driven by micro-level interactions. Based on the resulting network, we evaluate and compare multiple resource allocation strategies to identify more effective configurations to reduce patient loss and optimize systemic efficiency. In Section 2, we present the modeling framework, including the construction of the initial network, the simulation of its dynamic evolution, and the application of the weight thresholding method. Subsequently, we obtain a stable network, followed by a comprehensive topological analysis in Section 3. In addition, we examine whether the structural patterns of the network may reflect the underlying institutional or geographic groupings, thereby offering new insights into the organization of regional referral systems. Meanwhile, we identify critical nodes within the network and propose four differentiated resource allocation strategies. Finally, we conclude the paper by summarizing the key findings and offering practical policy recommendations in Section 4.
2 Model description
Based on the agent-based modeling (ABM) approach, this study developed a dynamic evolutionary model of inter-hospital patient referral networks within regional healthcare systems. Unlike conventional models that rely on predefined referral relationships between hospitals, the network structure in this framework emerges endogenously through the simulated medical-seeking and referral behaviors of individual patients. This design aims to more accurately capture the underlying mechanisms and evolutionary dynamics of regional referral networks. During the simulation, patients are modeled as rational agents with strategic intent, whose referral decisions are not random but rather optimized by evaluating real-world constraints such as economic affordability, commuting convenience, and medical accessibility. These decisions are further shaped by the spatial distribution of healthcare resources and the behavioral patterns of other agents, thereby constituting a dynamic, non-cooperative evolutionary game [19].
As the simulation unfolds, referral interactions among patients lead to continuous updates in the weighted, directed edges between hospitals. Over time, the referral patterns stabilize, giving rise to a macro-level network structure driven by micro-level game-theoretic interactions [20]. Hospitals, as critical nodes in the healthcare system, directly influence the flow and distribution of patients through their service capacities and visit limits. The referral pathways chosen by patients collectively form a substantive collaborative structure within the network, revealing the operational dynamics and systemic efficiencies of the regional healthcare system. By integrating evolutionary game theory with agent-based simulation, this model offers a robust theoretical and methodological foundation for analyzing referral mechanisms, detecting critical bottlenecks, and ultimately designing and evaluating optimized resource allocation strategies.
To address the complexities of hospital referral behavior, a structured modeling approach is adopted to simulate and analyze the evolution of the referral network. In the first step, an initial network is established based on hospital characteristics and referral relationships, incorporating both node characteristics and weighted edges. In the second step, a dynamic simulation of patient referrals is performed over time, allowing the network structure to evolve and stabilize. In the third step, weight thresholding is applied to identify key connections, resulting in a significant network structure.
2.1 Initial network
At first, the initial network is constructed as a fully connected directed and weighted network. The basic structure consists of nodes and edges, where the nodes represent hospitals of various grades, and the directed edges denote patient referral relationships between hospitals. The direction of an edge indicates the directionality of the referral path, while the weight of an edge quantifies the cumulative number of historical patient referrals between hospitals, thus reflecting the strength of the referral relationship.
To ensure that the model accurately captures the operational characteristics of the real-world healthcare system, three key attributes are assigned to each hospital node. (i) Hospital grade: According to the hierarchical hospital management system in China, hospitals are classified into three grades: primary (Grade 1), secondary (Grade 2), and tertiary hospitals (Grade 3), based on comprehensive considerations such as institutional scale, medical expertise, equipment conditions, research capacity, and administrative efficiency. These are denoted by
(ii) Geographic location: The study region is conceptualized as a two-dimensional plane, where the geographical location of each hospital is represented by randomly generated coordinates
2.2 Temporal evolution
Secondly, during the temporal evolution of the model, a total of
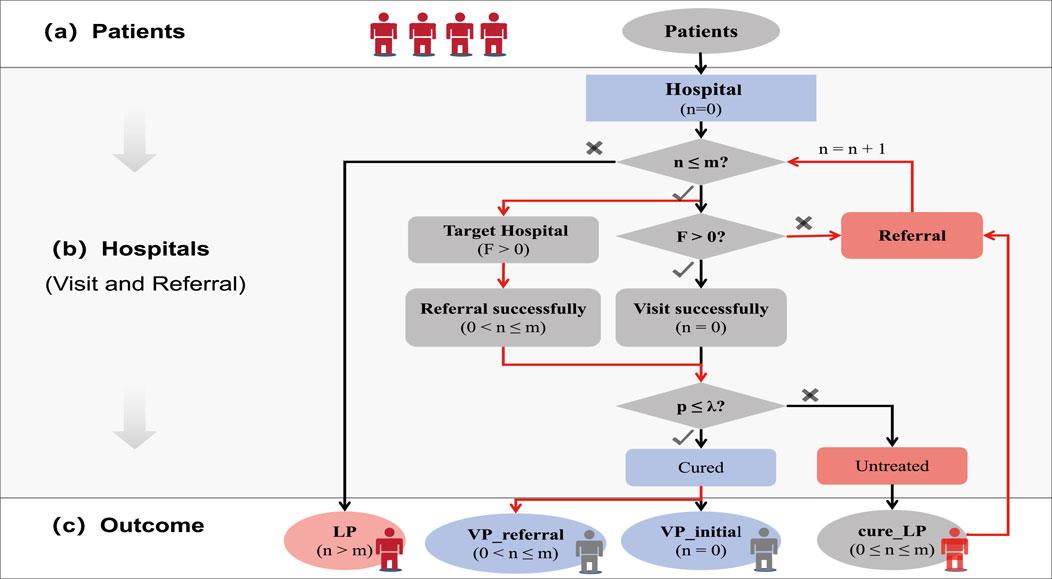
Figure 1. Illustration of the patient referral process. The referral process consists of three stages: (a) patients arrive in the healthcare system; (b) patients visit hospitals for treatment and may be referred to other hospitals when necessary; (c) here are four types of medical outcomes.
Based on a comprehensive review of the relevant literature [21–25], this study identifies three primary factors that jointly influence the selection of referral target hospitals: the historical volume of referrals received by the target hospital, the geographical distance between hospitals [26] and the grade of the target hospital [27]. They represent key dimensions in patient decision making, including the accessibility, capability, and attractiveness of referral target hospitals. (i) Referral based on historical referral volume [28]: Hospitals with a higher number of historical referrals from the current hospital (with a higher edge weight
where
(ii) Referral based on distance: Hospitals located closer to the current hospital (with a shorter geographical distance
where
(iii) Referral based on hospital grade: Hospitals of higher grade (where the grade difference
where
where
When
To fully incorporate the three factors into a unified decision mechanism while ensuring normalization of referral probabilities, we integrate Equations 1, 2 and Equation 4 to derive the overall referral probability::
where
As timestep progresses, the number of patients referred between hospitals accumulates and the corresponding edge weights in the network increase. This dynamic process gradually leads to the emergence of a relatively stable, directed, and weighted referral network. Throughout the evolution process, the model continuously produces a series of statistical indicators to evaluate the operational characteristics of the referral network and the efficiency of the allocation of healthcare resources.
2.3 Weight thresholding
To extract key referral structures, weight thresholding [29] is applied to filter the most significant referral connections within the network. Specifically, a quantile-based filtering method is used, in which only the top 5% of the edges, ranked by their referral weights, are retained to construct the core referral network. To assess the stability of the network structure, we employ topological distance and weight distance as indicators to measure the consistency between two network structures [30]. Topological distance evaluates the structural difference between two directed networks with the same node set. It is computed by checking, for every possible ordered node pair
Here,
if the relative error exceeds a predefined threshold
To ensure symmetry, the process is repeated by swapping the roles of the reference and comparison networks, and the final distance is taken as the average of the two directions.
Topological distance measures whether edges exist consistently, while weight distance measures whether edge weights are consistent where edges are present. If both the topological distance and the weight distance are below a predefined threshold (set at 10%), the two networks are considered to exhibit high structural consistency, indicating a stable network structure. Subsequently, the topological characteristics of this stable network are systematically analyzed using complex network theory.
3 Result
In this section, the study adopts a three-stage research framework of Modeling, Analysis, and Optimization. Firstly, a significant and stable inter-hospital referral network is constructed. Secondly, a topological analysis is conducted from two dimensions, nodes and community structures based on which referral and resource allocation strategies are proposed. Finally, simulation experiments are performed to evaluate patient loss in different scenarios of the resource allocation strategy.
3.1 Stable network structure
To obtain a stable and significant structure of the inter-hospital referral network, different time steps (
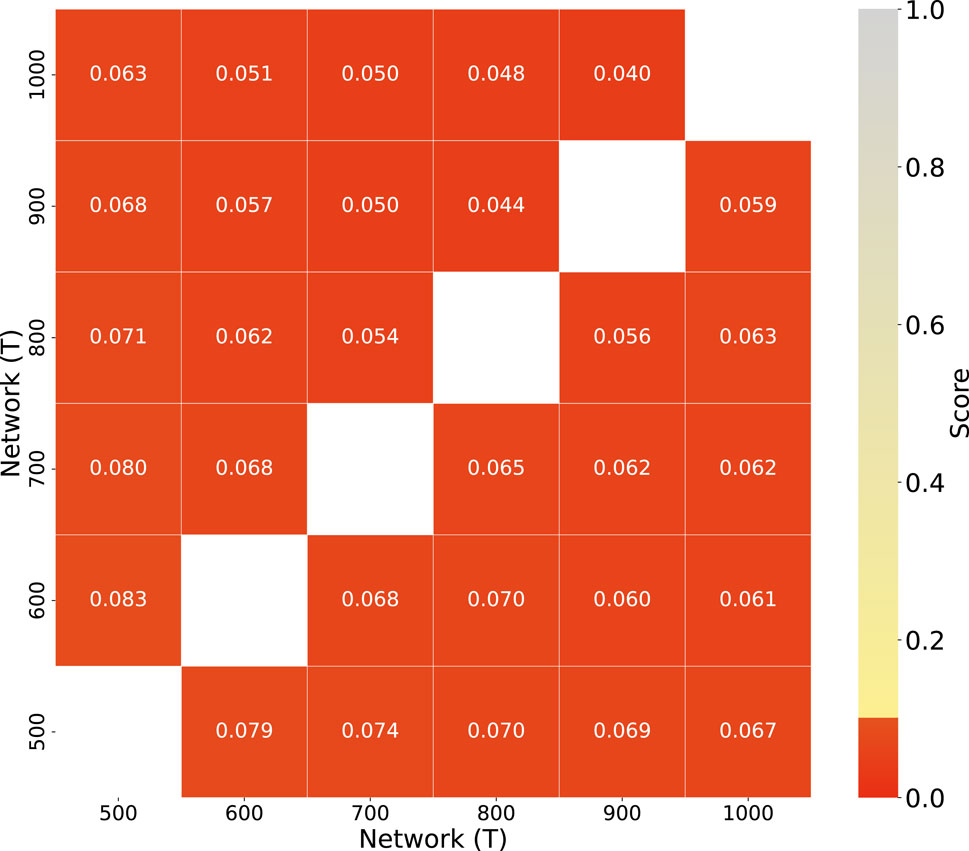
Figure 2. Comparison of network structures at different timesteps(T). This is to obtain a stable network structure. The upper triangle shows topological distances, the lower triangle shows weighted distances, and red boxes denote highly similar simulation result pairs, where the dissimilarity score is less than 0.1.
3.2 Topology analysis
A topological analysis was performed on the inter-hospital referral network, with a particular focus on key network metrics such as average degree, out-degree, and in-degree. In addition, the initial consultation service area (initial-area) and referral service area (referral-area) were systematically computed for hospitals at each grade. The results revealed that tertiary hospitals exhibited a significantly higher centrality within the network, with degree values substantially exceeding those of primary and secondary hospitals (as seen in Figure 3). Specifically, primary hospitals were found to have the highest out-degree, while tertiary hospitals had the highest in-degree. This pattern can be attributed to the limited treatment capacity of grassroots institutions and the common preference of patients for higher-level hospitals that offer superior medical services, both for direct consultations and for referrals. Regarding the service range, the initial consultation area refers to the average geographic distance from the site of the onset of the patients to the hospital where they were successfully cured during their first visit. This distance was found to be approximately 7 km and did not vary significantly between hospital grades, aligning with the ”proximity principle,” that is, patients tend to seek medical care at the nearest hospital. In contrast, the average distance in-degree, which represents the mean distance of referral from all referring hospitals that refer to a given hospital, reflects the area of referral service (as seen in Figure 3). It was observed that the referral service area of primary hospitals was nearly zero, while that of secondary hospitals was approximately 24 km, and that of tertiary hospitals extended to around 90 km. This outcome further supports the trend for patients to gravitate toward higher-level hospitals for treatment. Notably, the number of lost patients (LP) increased with hospital grades (as seen in Figure 3). This outcome can be attributed to the Matthew effect observed in tertiary hospitals. As higher-level institutions, tertiary hospitals initially possess greater medical resources, technical expertise, and reputational advantages. These advantages attract a disproportionate number of referrals from both primary and secondary hospitals. Over time, such advantages accumulate and reinforce their centrality within the referral network—a typical manifestation of the Matthew effect, where ”the rich get richer” [31]. Consequently, patient flows become increasingly concentrated in these few high-level hospitals. When referral demand exceeds their service capacity, a significant number of patients cannot be admitted or treated in time, leading to increased patient loss. This phenomenon underscores how cumulative advantage, while enhancing institutional prominence, can also generate systemic imbalances and bottlenecks in resource allocation within the healthcare network [32].
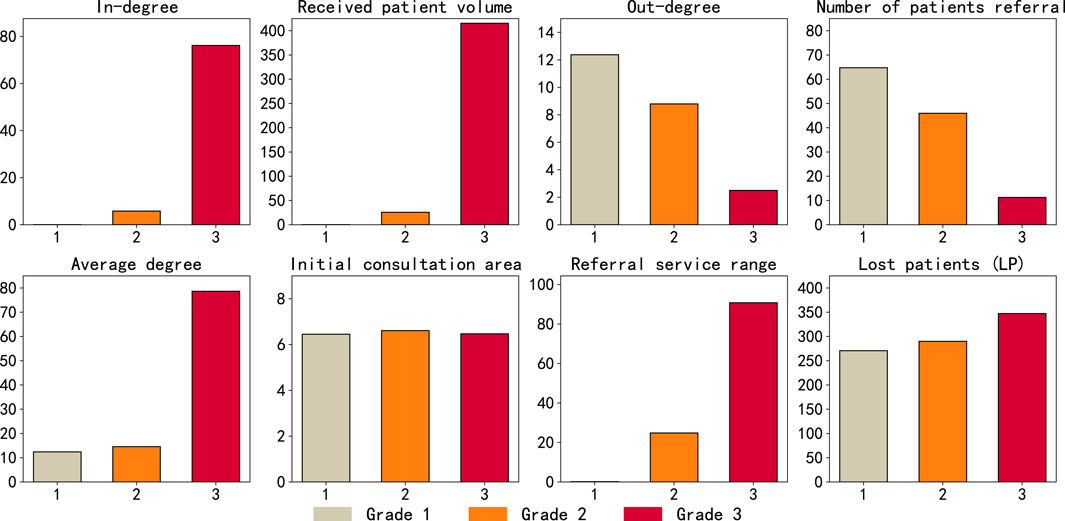
Figure 3. Topology analysis of referral network. The x-axis represents hospital grades, and each chart title corresponds to the metric on the y-axis.
Further analysis was performed using the Louvain algorithm to detect the community structure of the referral network. The results indicated that the network could be divided into five distinct communities (as seen in Figure 4). Each community exhibited a structure characterized by a central tertiary hospital, with primary-level hospitals radiating outward. This pattern of community division may correspond to actual administrative regions [1, 33, 34] or organizational frameworks of medical alliances. It reflects the practical integration of healthcare resources within specific regions. (i) Community structure and potential mapping to administrative regions: regional healthcare networks, collaborative relationships among hospitals are often influenced by administrative jurisdictions, such as the three-tier provincial–municipal–county healthcare system. The detected communities may reflect geographical or administrative boundaries—for example, medical institutions within the same prefecture-level city or county are more likely to form close cooperative ties and thus belong to the same community. If the nodes within a community are evenly distributed across different hospital tiers (i.e., including tertiary, secondary, and primary hospitals), this may correspond to a regionally integrated tiered healthcare delivery network, where core hospitals (typically tertiary) maintain stable referral relationships with subordinate institutions. (ii) Community structure and association with healthcare alliances: If a community is centered around one or two tertiary hospitals and includes several secondary and primary hospitals, it may reflect a medical consortium structure, such as a county-level healthcare community or a regional medical alliance. In a tightly integrated healthcare community, for example, county-level hospitals (secondary) form collaborative clusters with township health centers (primary). In contrast, loosely integrated medical alliances may span multiple regions, forming connections between tertiary hospitals and a subset of lower-level institutions. If a community includes hospitals from multiple administrative regions but exhibits strong internal connectivity, it may reflect a specialty-based alliance or a telemedicine collaborative network, such as a provincial oncology alliance or an inter-regional internet hospital partnership.
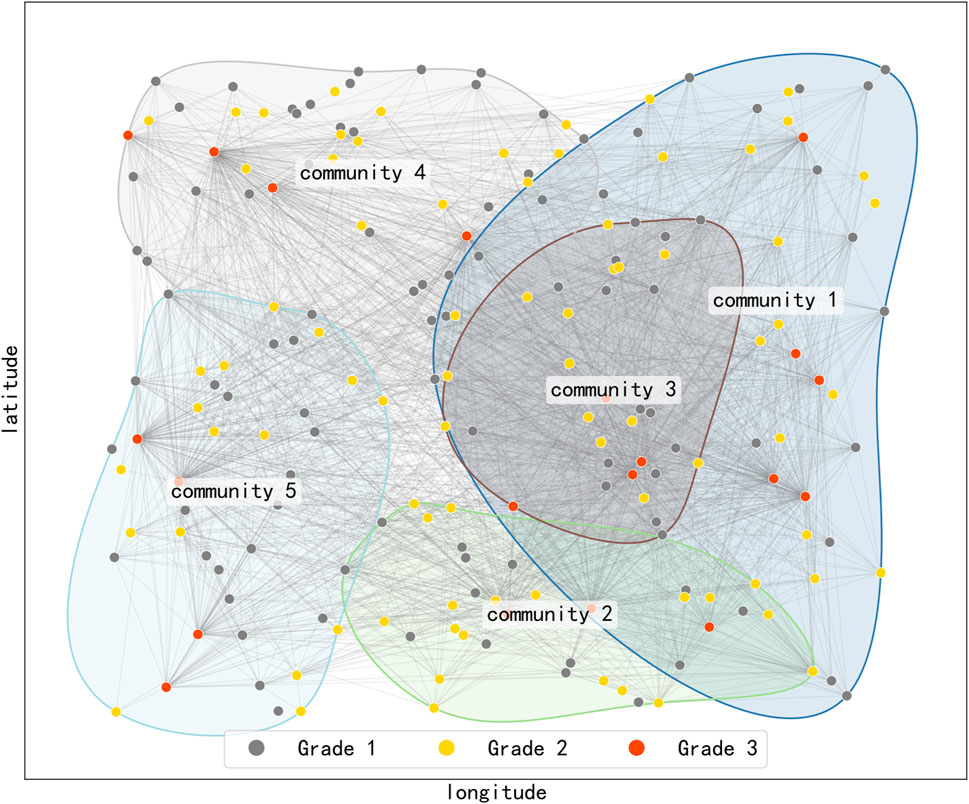
Figure 4. Community structure of the referral network. Node colors represent hospital grades (gray for Grade 1, yellow for Grade II, and red for Grade III). Node positions represent the geographic locations of hospitals in a two-dimensional plane. Nodes belonging to the same community are encircled. This pattern of community division may correspond to actual administrative regions or organizational frameworks of medical alliances.
From the perspective of complex network theory, the formation of community structures is jointly driven by homophily and preferential attachment. Hospitals of the same level may form modular structures due to policy initiatives (e.g., the promotion of healthcare alliances), while core hospitals attract more connections due to their resource advantages. If inter-community connections are sparse, it is advisable to enhance cross-regional medical collaboration, for instance, by promoting remote consultations or bidirectional referral mechanisms to optimize resource flows. Conversely, if a community lacks representation from lower-tier institutions, it may indicate a structural gap in the tiered healthcare delivery system, necessitating efforts to improve vertical integration and coordination between hospitals of different levels.
3.3 Resource allocation strategy
To optimize the allocation of medical resources and alleviate the pressure on tertiary hospitals, this study systematically identified key node characteristics within the referral network by analyzing critical network metrics such as average degree, in-degree, out-degree, and PageRank (as seen in Figure 5). The analysis revealed a high degree of consistency in node rankings based on degree centrality, in-degree, and PageRank, with the highest-ranking nodes predominantly concentrated in tertiary hospitals (represented as red nodes). In contrast, nodes with high out-degree were primarily located in primary and secondary hospitals. These findings provide important insights [35] for the formulation of targeted resource allocation strategies.
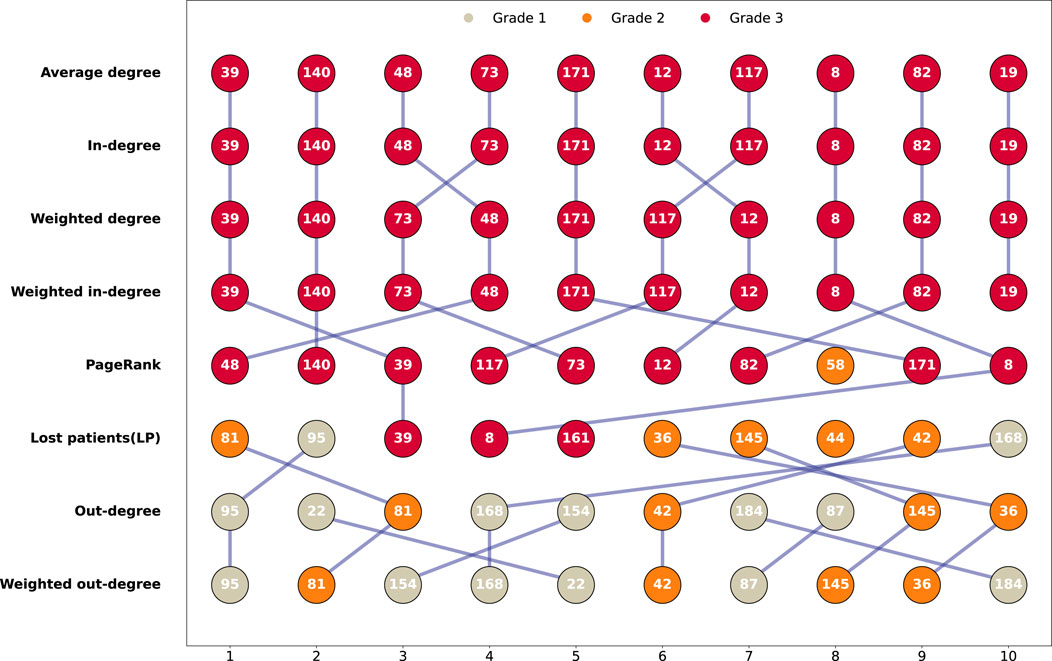
Figure 5. Comparison of top5% nodes across key network metrics. This is conducted to identify and compare the key nodes within the network. Node colors represent hospital grades (gray for Grade 1, yellow for Grade 2, and red for Grade 3). Blue lines connect nodes that appear in the rankings of adjacent metrics to highlight the same node across these metrics.
Based on these findings, four differentiated resource allocation strategies were proposed:
Each strategy was evaluated through ten simulation runs of the referral process under a stable network structure. Key performance indicators, including the number of lost patients (LP) and the total number of referrals, were systematically analyzed to assess the effectiveness of each strategy. This set of strategies integrates both the topological features of the referral network and the practical demands of the healthcare system, thereby providing a robust scientific basis for optimizing medical resource allocation.
The results indicate that the core hospital enhancement strategy is more effective in reducing the number of lost patients. However, it also leads to a noticeable increase in referral frequency (as seen in Figure 6). Furthermore, among all resource allocation strategies, the largest volume of referrals was observed from primary to tertiary hospitals, accounting for approximately 37% of all referrals. This was followed by primary to secondary hospital referrals (approximately 25%), secondary to tertiary hospital referrals (around 18%), and referrals between secondary hospitals, which accounted for 11% (By calculating the weight of the connecting edges between nodes of each grade). This referral pattern closely mirrors the major challenges currently facing China’s hierarchical healthcare system. Although national policy promotes a “primary care first, two-way referral” framework, in practice, primary hospitals often function merely as transitional nodes due to limited diagnostic capabilities, insufficient medical equipment, and a lack of patient trust. In addition, secondary hospitals frequently lack the necessary service capacity, clearly defined referral pathways, and incentive mechanisms to effectively assume their intermediary role. The relatively low level of patient trust in secondary hospitals further exacerbates the issue, resulting in a tendency for patients to bypass secondary care and seek treatment directly at tertiary hospitals. This behavior not only intensifies the burden on tertiary hospitals but also deviates from the fundamental objective of hierarchical diagnosis and treatment, which aims to achieve rational patient distribution across levels of care. When evaluated from the dual perspectives of reducing patient loss and minimizing referral volume, the referral bottleneck mitigation strategy emerges as the most favorable approach. While its performance in reducing the number of lost patients is comparable to that of the core hospital enhancement strategy, the difference is relatively minor. More importantly, this strategy substantially decreases the number of referrals, reflecting greater efficiency in patient flow and more effective utilization of system resources. By reinforcing the capacity of hospitals that experience the highest patient attrition rates, the strategy helps alleviate referral bottlenecks, strengthens the functional role of lower-tier institutions, and contributes to the realization of a more balanced and sustainable hierarchical healthcare system.
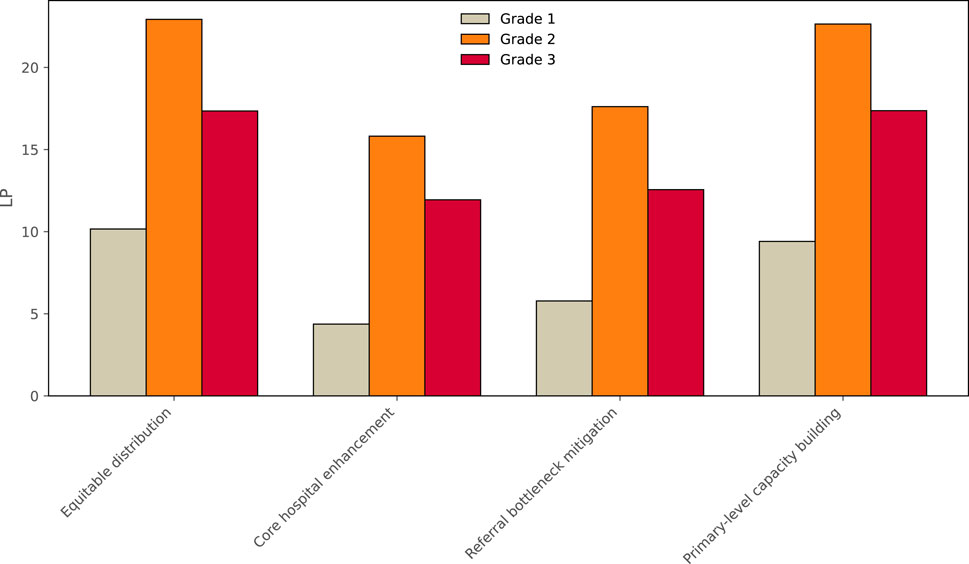
Figure 6. Lost patients (LP) per hospital at different grades under different allocation strategies. This aims to compare the performance of different strategies and identify the optimal resource allocation strategy.
4 Conclusion
This study systematically analyzes the referral network characteristics within China’s hierarchical healthcare system and reveals underlying structural contradictions in current healthcare resource allocation. The findings indicate a pronounced three-tier differentiation in the referral network. Due to limited diagnostic capabilities and low patient trust, primary medical institutions effectively function as referral conduits, rather than as providers of first-contact care. Data analysis shows that as many as 37% of patients are directly referred from primary to tertiary hospitals, while the intermediary role of secondary hospitals remains underutilized, accounting for only 18% of total referrals. This phenomenon of cross-level referrals has led to a continued concentration of high-quality medical resources in tertiary hospitals, resulting in a typical “siphoning effect”. Consequently, not only does this increase the burden on tertiary hospitals, but it also contributes to a growing number of lost patients (LP), which escalates with hospital grade.
Further topological analysis of the network reveals that tertiary hospitals exhibit strong centrality, with significantly higher in-degree values than hospitals of other levels. This asymmetric network structure reflects the persistent “Matthew effect” within China’s healthcare system, whereby institutions that are already resource-rich continue to attract more patients and resources. Additionally, community structure analysis using the Louvain algorithm identified five distinct network communities, offering new insights into regional patterns of medical collaboration. Although the correspondence between these network communities and actual medical alliance organizations requires further validation, this network-based approach provides a valuable perspective for understanding the modular structure of referral systems. Importantly, the study highlights that strategies focused solely on strengthening core hospitals, while effective in reducing patient loss, may exacerbate structural imbalances in the healthcare system. In contrast, the referral bottleneck mitigation strategy not only effectively controls the number of lost patients but also significantly reduces the overall number of referrals, demonstrating superior comprehensive performance.
Based on the study’s findings, a systematic and tiered reform framework is proposed to optimize the hierarchical healthcare system. At the operational level, it is recommended that efforts focus on enhancing the specialty service capacity of secondary hospitals by promoting a “one hospital, one specialty” development model. This should be accompanied by the establishment of standardized referral procedures, including the development of intelligent referral platforms and the appointment of referral coordination officers, to ensure seamless patient transitions between different levels of medical institutions. At the institutional level, urgent reform of the medical insurance payment system is required. A hybrid reimbursement mechanism combining diagnosis-related group (DRG)-based payments and referral-based financial incentives should be implemented, with additional reimbursements provided for cases that successfully follow tiered referral pathways. Simultaneously, a scientific referral performance evaluation system should be established, incorporating both the volume and quality of referrals into hospital performance assessments. This would enable the identification of referral bottlenecks and allow for timely adjustment of resource allocation. At the strategic level, it is suggested that the layout of medical consortia based on regional healthcare demand, aiming to build a grid-based service network led by tertiary hospitals, supported by secondary hospitals, and underpinned by primary care institutions. The internal coordination of such consortia should be strengthened through mechanisms such as telemedicine collaboration, flexible workforce mobility, and mutual recognition of diagnostic results. These three levels of reform must be advanced in parallel and function in a mutually reinforcing manner: operational capacity-building lays the foundation for institutional implementation, institutional innovation drives strategic transformation, and strategic optimization provides direction for operational improvement. Through such a comprehensive and integrated reform, it is expected that the current “top-heavy” referral structure can be fundamentally transformed, leading to the establishment of a well-defined, efficient, and hierarchical medical service system, and ultimately realizing the rational allocation of high-quality healthcare resources and the equitable accessibility of health services for all.
Despite the contributions of this study, several limitations remain: (i) Limitations in data validation: Due to constraints in accessing real-world medical referral data, most model parameters were derived from existing literature and theoretical assumptions, rather than empirical calibration. This may affect the generalizability of the findings. (ii) Complexity of dynamic interactions: The study primarily focuses on the macro-level patterns of inter-hospital referrals, without modeling micro-level interactions between patients and physicians, such as the influence of medical advice or patient satisfaction on referral decisions.
Building upon the findings and addressing the limitations of the present study, future research may pursue the following directions: (i) Multidimensional data integration: By incorporating real-world data such as electronic medical records and insurance claims, more decision variables (e.g., specialty capacity, treatment costs) can be introduced to improve the model’s realism and accuracy. (ii) Heterogeneous behavioral modeling: Future models should account for individual differences among patients (e.g., socioeconomic status, health literacy) and variations in physician referral preferences to construct more granular and realistic decision-making frameworks. (iii) Coupling with multi-level health systems: The referral network model could be integrated with public health emergency response systems to explore strategies to enhance system resilience under external shocks, such as pandemics or natural disasters. This study employs computational experiments to reveal the structural patterns and evolutionary mechanisms of medical referral networks, providing both theoretical foundations and methodological tools to optimize hierarchical healthcare systems. Future research will emphasize data-driven approaches and model refinement to further enhance the relevance of policy and practical applicability of the results.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
TY: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Software. JF: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Software. WG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JQ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. BD: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XZ: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Formal analysis, Visualization. WD: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. WW: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFC2307405), 2025 Medical Scientific Research Project (Grant No. 2025WSJK004) of Chongqing Municipal Health Commission, Chongqing Medical and Pharmaceutical College University-level Research Project, Project Number: ygzrc2024109, and the Chongqing PostGraduate Student Scientific Research and Innovation Project (No. CYS240326).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Li X, Krumholz HM, Yip W, Cheng KK, De Maeseneer J, Meng Q, et al. Quality of primary health care in China: challenges and recommendations. The Lancet (2020) 395:1802–12. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30122-7
3. Liu Y, Kong Q, Yuan S, Van de Klundert J. Factors influencing the choice of health system access level in China: a systematic review. The Lancet (2018) 392:S39. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32668-0
4. Yip W, Fu H, Chen AT, Zhai T, Jian W, Xu R, et al. 10 years of health-care reform in China: progress and gaps in universal health coverage. The Lancet (2019) 394:1192–204. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32136-1
5. Kruk ME, Gage AD, Arsenault C, Jordan K, Leslie HH, Roder-DeWan S, et al. High-quality health systems in the sustainable development goals era: time for a revolution. The Lancet Glob Health (2018) 6:e1196–252. doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(18)30386-3
6. Linde S. The formation of physician patient sharing networks in medicare: exploring the effect of hospital affiliation. Health Econ (2019) 28:1435–48. doi:10.1002/hec.3936
7. Lee BY, McGlone SM, Song Y, Avery TR, Eubank S, Chang C-C, et al. Social network analysis of patient sharing among hospitals in Orange county, California. Am J Public Health (2011) 101:707–13. doi:10.2105/ajph.2010.202754
8. Lee HK, Li J, Musa AJ, Bain PA, Nelson K. Modeling and analysis of patient transitions in community hospitals: a systems approach. IEEE Trans Syst Man, Cybernetics: Syst (2017) 50:686–99. doi:10.1109/tsmc.2017.2723559
9. Carson MB, Scholtens DM, Frailey CN, Gravenor SJ, Kricke GE, Soulakis ND. An outcome-weighted network model for characterizing collaboration. PloS one (2016) 11:e0163861. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163861
10. Barnett ML, Christakis NA, O’Malley J, Onnela J-P, Keating NL, Landon BE. Physician patient-sharing networks and the cost and intensity of care in us hospitals. Med Care (2012) 50:152–60. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31822dcef7
11. Bergmark RW, Jin G, Semco RS, Santolini M, Olsen MA, Dhand A. Association of hospital centrality in inter-hospital patient-sharing networks with patient mortality and length of stay. Plos one (2023) 18:e0281871. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0281871
12. Geissler KH, Lubin B, Ericson KMM. The association between patient sharing network structure and healthcare costs. Plos one (2020) 15:e0234990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0234990
13. Kaleta M, Lasser J, Dervic E, Yang L, Sorger J, Lo Sardo DR, et al. Stress-testing the resilience of the Austrian healthcare system using agent-based simulation. Nat Commun (2022) 13:4259. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31766-7
14. Lo Sardo DR, Thurner S, Sorger J, Duftschmid G, Endel G, Klimek P. Quantification of the resilience of primary care networks by stress testing the health care system. Proc Natl Acad Sci (2019) 116:23930–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.1904826116
15. Landon BE, Keating NL, Onnela J-P, Zaslavsky AM, Christakis NA, O’Malley AJ. Patient-sharing networks of physicians and health care utilization and spending among medicare beneficiaries. JAMA Intern Med (2018) 178:66–73. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.5034
16. Yang T, Gu W, Deng L, Liu A, Wu Q, Zhang Z, et al. A cascade model for the robustness of patient-sharing networks. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals (2025) 191:115827. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2024.115827
17. Hu H, Zhang Y, Zhu D, Guan X, Shi L. Physician patient-sharing relationships and healthcare costs and utilization in China: social network analysis based on health insurance data. Postgrad Med (2021) 133:798–806. doi:10.1080/00325481.2021.1944650
18. Macal CM, North MJ. Tutorial on agent-based modeling and simulation. In: Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, 2005. IEEE (2005). p. 14.
19. Li D, Du J, Sun M, Han D. How conformity psychology and benefits affect individuals’ green behaviours from the perspective of a complex network. J Clean Prod (2020) 248:119215. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119215
20. Li D, Ma J, Han D, Sun M, Tian L, Stanley HE. The co-evolution of networks and prisoner’s dilemma game by considering sensitivity and visibility. Scientific Rep (2017) 7:45237. doi:10.1038/srep45237
21. Omotosho A, Adegbola O, Adebo A. A patient-based hospital referral decision support system. Int J Computer Appl (2016) 115:38–43. doi:10.5120/ijca2016912459
22. Sanjaya GY, Lazuardi L, Hasanbasri M, Kusnanto H. Using hospital claim data to develop referral decision support systems: improving patient flow from the primary care. Proced Computer Sci (2019) 161:441–8. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.143
23. Demiral DG, Özen Ü. Exploring inter-hospital emergency patient referral network. Socio-Economic Plann Sci (2023) 90:101713. doi:10.1016/j.seps.2023.101713
24. Iwashyna TJ, Christie JD, Kahn JM, Asch DA. Uncharted paths: hospital networks in critical care. Chest (2009) 135:827–33. doi:10.1378/chest.08-1052
25. Song Z, Sequist TD, Barnett ML. Patient referrals: a linchpin for increasing the value of care. Jama (2014) 312:597–8. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.7878
26. Kobayashi S, Fujioka T, Tanaka Y, Inoue M, Niho Y, Miyoshi A. A geographical information system using the google map api for guidance to referral hospitals. J Med Syst (2010) 34:1157–60. doi:10.1007/s10916-009-9335-0
27. Xiao Y, Chen X, Li Q, Jia P, Li L, Chen Z. Towards healthy China 2030: modeling health care accessibility with patient referral. Social Sci and Med (2021) 276:113834. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113834
28. Westra D, Angeli F, Jatautaitė E, Carree M, Ruwaard D. Understanding specialist sharing: a mixed-method exploration in an increasingly price-competitive hospital market. Social Sci and Med (2016) 162:133–42. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.06.019
29. Yan X, Jeub LG, Flammini A, Radicchi F, Fortunato S. Weight thresholding on complex networks. Phys Rev E (2018) 98:042304. doi:10.1103/physreve.98.042304
30. Donnat C, Holmes S. Tracking network dynamics: a survey using graph distances. The Ann Appl Stat (2018) 12:971–1012. doi:10.1214/18-aoas1176
31. Merton RK. The matthew effect in science: the reward and communication systems of science are considered. Science (1968) 159:56–63. doi:10.1126/science.159.3810.56
32. Hu K, Shi L, Tao Y, Perc M. Cumulative advantage is a double-edge sword for cooperation. Europhysics Lett (2023) 142:21001. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/acc7c4
33. Shen Y, Sun Z. Estimating the spatial correlation and convergence of china’s healthcare resources allocation: evidence from the yangtze river delta region. Arch Public Health (2022) 80:207. doi:10.1186/s13690-022-00958-4
34. Tang C, Dong X, Lian Y, Tang D. Do chinese hospital services constitute an oligopoly? evidence of the rich-club phenomenon in a patient referral network. Future Generation Computer Syst (2020) 105:492–501. doi:10.1016/j.future.2019.12.001
Keywords: healthcare system, referral, agent-based modeling, inter-hospital referral networks, network analysis
Citation: Yang T, Fan J, Gu W, Qin J, Deng B, Zhao X, Deng W and Wang W (2025) Modeling the evolution of inter-hospital referral networks: an agent-based modeling approach. Front. Phys. 13:1659506. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1659506
Received: 04 July 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 28 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dun Han, Jiangsu University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhidan Zhao, Shantou University, ChinaChangwei Huang, Guangxi University, China
Kesheng Xu, Jiangsu University School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, China
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Fan , Gu , Qin , Deng , Zhao , Deng and Wang . This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenwen Deng, NDQyMTczMzg3QHFxLmNvbQ==; Wei Wang, d3d6cWJjQGNxbXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Tao Yang1†
Tao Yang1† Bing Deng
Bing Deng  Wenwen Deng
Wenwen Deng  Wei Wang
Wei Wang