- 1Center for Advanced Laser Technology, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China
- 2Hebei Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Technology and Equipment, Tianjin, China
Real-time detection of trace gas concentrations has a wide range of applications in industrial processes and monitoring and various complex environments. Quartz-Enhanced Photoacoustic Spectroscopy (QEPAS) features high sensitivity and selectivity for the detection of single or multiple gases. It is immune to environmental noise and also boasts advantages such as miniaturization capability, ease of integration, and low cost. However, this technology also faces challenges such as limited laser source performance and the need to optimize quartz tuning fork (QTF) structural parameters. This paper reviews the current research progress in QEPAS, elaborating on its fundamental principle as well as the contributions from both laser source improvements (e.g., power, tuning range, and size) and QTF optimization (e.g., frequency, structure, and coating) to enhanced sensitivity. In addition, this paper systematically evaluates current research on auxiliary enhancement strategies, including relaxant selection, optical path and waveguide optimization, and dual-spectrum fusion. Finally, it summarizes existing technologies and proposes future prospects based on current technical bottlenecks.
1 Introduction
Trace gas detection technology is directly related to key fields like environmental monitoring, industrial safety, and medical diagnosis. For example, in air pollutant monitoring, nitric oxide (NO) is not only an acid rain precursor causing stratospheric ozone depletion, but also a precursor of the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide [1]. Additionally, methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6) are the most important environmental markers for identifying and tracking oil-gas pipeline leaks and wildfires [2]. Therefore, developing sensors to monitor NO, CH4, and C2H6 concentrations is crucial for improving environmental quality. In medical diagnosis, to address issues with existing transcutaneous carbon dioxide (CO2) detectors, such as frequent calibration needs and susceptibility to water vapor interference, a non-invasive skin respiration detection method based on QEPAS technology has been proposed. This method provides a more portable, stable, and chemical reagent-free diagnostic solution for clinical practice [3]. As such, enhancing detection sensitivity is paramount for the further development of these applications. However, conventional gas detection techniques, including electrochemical and polymer-based sensors, as well as absorption spectroscopy, are often limited by inherent shortcomings such as poor long-term stability, short service life, and limited capability for simultaneous multi-component detection [4]. In contrast, Photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS) boasts advantages including zero background interference, high sensitivity, and rapid response [5]. Nevertheless, its reliance on a low quality-factor(Q) (<100) microphone as the core detector causes poor signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and a bulky form factor, which severely hinders its practical deployment. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (QEPAS) employs a high-Q quartz tuning fork (QTF) as an acoustic transducer to replace conventional microphones; such QTFs typically have ∼100,000 Q in vacuum and ∼10,000 under standard atmospheric pressure. The acoustic quadruple characteristic of the QTF makes it sensitive only to symmetrical pressure waves, which significantly boosts environmental noise immunity. Furthermore, the small volume of the QTF results in a sampling volume of <1.3 mm3, ensuring that sensors based on QEPAS are smaller than traditional gas sensors [6], and maintain structural compactness, making QEPAS widely applicable for trace gas detection across various scenarios [7].
However, as trace gas detection advances toward ppb-level sensitivity [8], simultaneous multi-component analysis [9], and enhanced adaptability to harsh environments [10], QEPAS faces increasing constraints from laser source and QTF performance. Regarding laser source bottlenecks, current devices generally have relatively low output power, which limits signal enhancement [11]. As shown in Table 1, commercial near-infrared distributed feedback (NIR-DFB) lasers typically output several watts, while high-sensitivity detection requires watt-level power (>1 W). Additionally, a single laser can hardly cover the absorption spectra of multiple gas simultaneously [12]. Although mid-infrared (MIR) lasers offer higher power and broader spectral coverage, they typically suffer from large physical dimensions and high power consumption, which hinders system miniaturization [13]. For QTF performance bottlenecks, high resonant frequency (f0) conflicts with low relaxation rate gas detection [14]. When the resonant frequency of QTF is reduced, the sensing performance of QEPAS can be significantly improved [15, 16]. Moreover, lower frequency reduces Q value [17, 18]. Furthermore, narrow inter-prong spacing complicates optical alignment, causes significant signal attenuation, and limits the integration of high-power [19]. Besides, QTF piezoelectric conversion efficiency is also affected by circuit impedance and structural coatings [20], and the signal intensity of the detection structure is limited, making it difficult to extend to multi-component measurement [21]. Beyond laser source and QTF limitations, QEPAS has other prominent bottlenecks. Conventional vertical optical-path design has low light-utilization efficiency [22]. Furthermore, the system mostly operates independently, lacks multi-technology integration, and needs to account for additional effects from relaxants [23].
In this review, we systematically summarize the principle of QEPAS, its core components, and the research progress in laser source performance enhancement and QTF structural innovation. Additionally, from the perspective of multi-technology integration, we review performance improvements enabled by technologies such as relaxants, optimized optical paths and waveguide structures, and integrated dual-spectral detection. Finally, we summarize the existing technologies and in light of current technical bottlenecks, such as limitations in simultaneous multi-gas detection and interference from environmental factors, propose potential future development directions, including the development of new laser sources, continuous optimization of QTF design, and improvements in system integration.
2 Analysis of the principle and core components based on QEPAS detection
QEPAS is a highly sensitive gas detection method based on the photoacoustic effect. Its principle is to focus the tunable laser beam onto the gap of the QTF fork, and the laser wavelength is modulated near the absorption peak of the target gas, and the modulation frequency matches the fundamental frequency vibration mode of the QTF. After absorbing the modulated light, the gas converts energy into thermal energy through non-radiative relaxation, which causes thermal expansion and generates periodic pressure waves. Thanks to the high-Q of the QTF, this pressure wave is amplified by the mechanical resonance of the QTF. Subsequently, the piezoelectric effect of the QTF is utilized to convert the pressure wave into an electrical signal, whose amplitude is proportional to the gas concentration [24].
In trace gas detection based on QEPAS, the role of the laser source is crucial. Its main function is to periodically change light intensity or wavelength at a frequency matching the resonant frequency of the QTF through current modulation, generating laser light whose central wavelength is precisely aligned with the absorption line of the target gas [25]. As the core transducing element of QEPAS technology, the QTF replaces the microphone used in traditional PAS. It converts the vibration caused by sound waves generated when the target gas absorbs laser light into an electrical signal through the piezoelectric effect [26]. Its high f0, high Q, and extremely narrow frequency response band (less than 4 Hz) endow it with high detection sensitivity and excellent immunity to environmental noise. Besides, compared with the large photoacoustic cell in PAS, acoustic energy is accumulated in the sharply resonating QTF, resulting in a significant reduction in the size constraints of the gas cell [27, 28].
3 Optimization based on QEPAS detection
3.1 Improvement of the laser source
The selection of the laser source is crucial to the detection sensitivity and scenario adaptability. In recent years, the optimization of laser sources has shown a multi-dimensional development trend, particularly in terms of improved laser power, expanded wavelength tuning range, and system miniaturization.
In terms of power improvement, as shown in Equation 1:
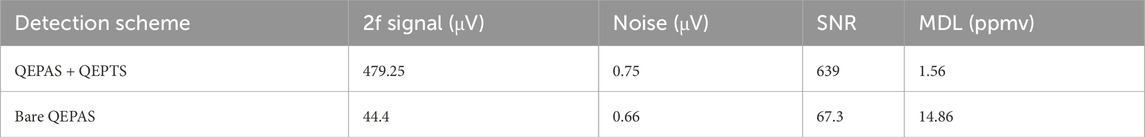
where α is the absorption coefficient, P is the optical power, Q is the Q-factor of QTF, f0 is the QTF resonance frequency. The QEPAS signal amplitude (S) is proportional to the optical power P (see Equation 1), meaning that the gas detection sensitivity of the sensor can be enhanced by increasing the power of the laser source [29]. When detecting ppb-level H2S gas, measuring trace concentrations using NIR-DFB lasers is more challenging compared to MIR lasers. This is mainly because the fundamental frequency absorption band of MIR is at least one order of magnitude stronger in transition than the overtone absorption band of NIR [30]. Increasing laser power is an effective way to compensate for the weak intensity of overtone vibrational transitions [31]. This enhancement can be realized by combining the QEPAS sensor with an erbium-doped fiber-amplified 1,582 nm distributed feedback (DFB) laser. Then, under atmospheric pressure and room temperature conditions, with 1.4 W optical excitation power and an averaging time of 67 s, the H2S detection sensitivity reaches 142 ppbv [30]. In addition to using an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) to amplify the power from a NIR-DFB laser, an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) based on Q-switching technology can also achieve relatively high laser power. Bi et al. coupled the QTF into the laser cavity, utilizing the high power density and round-trip characteristics inside the cavity, as well as the fact that the intracavity power is significantly greater than the output power [32], to enhance the QEPAS signal. Finally,the system exhibits excellent linear response (R2 = 0.99918) over a C2H2 concentration range of 10–100 ppmv, with a minimum detection limit (MDL) of 101 pptv at an integration time of 20 ms [33].
The wavelength tuning range of the laser source also has an important impact. Quantum cascade laser (QCL) offers broader wavelength tunability compared to NIR-DFB lasers. However, their tunable range remains relatively narrow, which limits its effectiveness in multi-gas detection applications. Based on the high power and wide tuning characteristics of solid-state lasers [34], Qiao et al. employed a single-mode solid-state laser with a yttrium aluminum perovskite (YAP) crystal as the gain medium, as shown in Figure 1A. They placed an etalon inside the laser cavity and adjusted its angle to enable single longitudinal mode (SLM) output for the target gas. As a result, the laser covers H2O and NH3 with a wide tuning range of 9.44 nm, and the measured values are 57.3 ppm and 11.2 ppm respectively. In addition, when detecting mixed gases, common NIR and MIR lasers are unable to distinguish them due to the complex overlap of their spectra. By contrast, THz lasers produce distinct fingerprint-like absorption spectra, as their gas absorption is dominated by molecular rotational energy level transitions, thereby significantly improving detection sensitivity. It achieves 30 ppm within 3 s and drops to 13 ppm at a 30-s integration time, demonstrating sensitivity several times higher than that of NIR and MIR lasers [35]. Besides, in fiber lasers based on fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs), multi-gas detection can be achieved by adjusting the Bragg wavelength to produce different central wavelengths that align with the absorption lines of target gases [33].
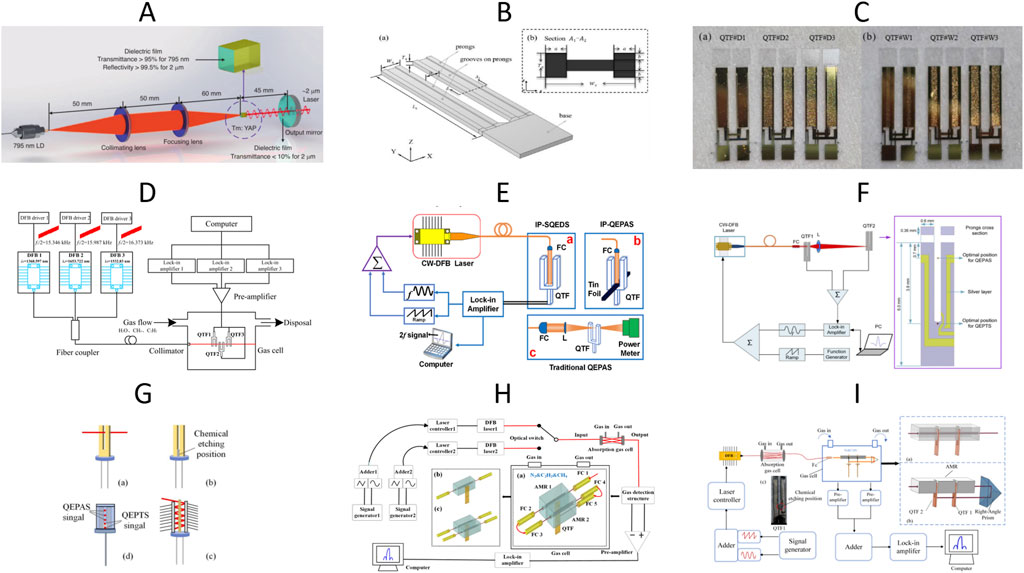
Figure 1. (A) Schematic diagram of solid-state laser under free operation mode. LD, laser diode. Reproduced with permission from [34]. (B) Schematic of the QTF with microgrooves, (a) structure of QTF and (b) cross sectionof QTF. Reproduced with permission from [40]. (C) Schematic of two sets of QTFs, (a) QTF with different groove depths and (b) QTF with different groove widths. Reproduced with permission from [40]. (D) Schematic of the multi-QEPAS sensor system with three QTFs for simultaneous detection of H2O, CH4, and C2H2. Reproduced with permission from [42]. (E) Schematic diagrams of the three experimental configurations: (a) IP-SQEDS; (b) IP-QEPAS, where a tin foil is used to block the laser from reaching the QTF base, thus eliminating the LITES contribution; (c) Traditional QEPAS. Reproduced with permission from [46]. (F) Schematic of the QEPA-PTS sensor. Reproduced with permission from [49]. (G) Different schematic diagrams and principle diagrams of QTF: (a) Bare QTF, (b) Chemical etching of the tuning fork to remove the bottom silver layer, (c) Multiple chemical etching to excite QTF, (d) The positions where QEPAS and QEPTS signals are excited. Reproduced with permission from [50]. (H) Schematic diagrams of QEPAS and LITES: (a) Dual-spectroscopy gas detection structure. (b) Single-excitation QEPAS signal gas detection structure. (c) Dual-excitation QEPAS signal gas detection structure. Reproduced with permission from [51]. (I) Schematic of the dual-spectroscopy sensor integrating QEPAS and LITES. Reproduced with permission from [47].
To summarize, for ppb-level sensitivity and multi-component detection, selecting among NIR-DFB, MIR-QCL and THz lasers requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as absorption line strength, tuning range, output power and compactness. MIR-QCLs can provide high-power laser sources, and their absorption line strength is at least one order of magnitude stronger than that of NIR-DFB lasers. However, their high cost, high power consumption, and size constraints limit their scope of application. In contrast, NIR-DFB lasers feature smaller volume, lower cost, and higher maturity, making them easier to integrate into compact QEPAS systems [29]. THz lasers have ultra-high absorption line strength and excellent spectral selectivity (avoiding hydrocarbon interference) for specific molecules (e.g., H2S) but suffer from poor beam quality, severe divergence (causing low SNR) and reliance on cryogenic cooling (increasing sensor volume, complexity and cost). In practical scenarios, a comprehensive consideration of the above aspects is necessary when selecting the appropriate laser.
3.2 Improvement of the QTF
As QEPAS’ core transduction component, QTF converts the acoustic vibrations from gas molecule stimulated emission into electrical signals via the piezoelectric effect, and standard-frequency QTFs with high f0 and high Q can effectively suppress environmental noise [36]. However, a relatively high f0 hinders slow-relaxation gas detection, while lowering f0 also reduces Q. Furthermore, factors including the QTF prong spacing, equivalent circuit resistance, micro-resonator groove geometry, and surface coating must be considered.
For slow-relaxation gases (e.g., NO, CO, CO2, CH4) or high density and mass (e.g., SF6), standard-frequency QTFs have low electroacoustic conversion efficiency, significantly limited vibrational response and hindered capture of thermoacoustic signals from gas molecules resulting in signal loss [37]. Therefore, f0 should be reduced. Lowering f0 helps the QTF better match these gases’ thermoacoustic signal time scale (e.g., adapting to the prolonged energy release of slow-relaxation gases), reduces mechanical resistance from high-density gases, improves capture of weak signals lost by standard-frequency QTFs, and thus greatly enhances system performance [38, 39]. However, this reduction impairs Q, attenuating detection signals and degrading sensor performance [36]. Additionally, standard QTFs have only 300 μm prong spacing. Consequently, during strict beam alignment, this narrow prong spacing easily causes part of the laser beam to strike the QTF, resulting in unwanted non-zero background noise. Yet, increasing prong spacing raises f0, which contradicts the objective of reducing it [37]. According to the Euler-Bernoulli equation:
where W, L, E, and ρ denote the prong width, prong length, Young’s modulus, and density of quartz, respectively, and:
where T represents the QTF thickness. The specific meanings of W, L, and T can be referred to as shown in Figure 1B. The highest Q (≈16,000) is achieved at f0 = 15 kHz. With L = 9.4 mm, W = 2 mm, and T = 0.25 mm held constant, the prong spacing was ultimately set to 800 μm to facilitate optical alignment (Combining Equations 2, 3) [36].
The resistance R in the equivalent circuit is another key parameter of the QTF, as it determines the value of the piezoelectric current generated when a voltage excitation is applied at f0. When the QTF is equivalent to an RLC series circuit, as shown in Equation 4:
where C denotes the QTF capacitance, if f0 and Q are kept constant, increasing C enables a reduction in R, thereby increasing the piezoelectric current and enhancing the piezoelectric effect. Additionally, by fixing L and W, C is increased by reducing the spacing between the positive and negative electrodes. Concurrently, rectangular grooves are fabricated on the surface of the prongs, and a central electrode is deposited on the surface of these grooves. This design achieves a 30% reduction in R without affecting the Q [36]. Furthermore, by comparing the effects of groove depth and groove width, it is found that increasing the groove depth impairs charge generation, thereby degrading the gas measurement performance. In contrast, while increasing the groove width initially suppresses charge generation, it begins to enhance charge generation once a certain threshold is reached [40]. Moreover, compared with the prongs with a rectangular cross-section of a standard QTF, T-shaped prongs can increase the intensity of the stress field, thereby enhancing the generation of piezoelectric charges [41]. Figure 1C shows the T-shaped microgroove QTF with grooves of different depths and widths. As a result, Compared with the standard frequency QTF, after adopting the T-shaped prongs and optimizing the grooves, the signal peak value and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) are increased by 234% and 577% respectively [40].
In addition to modifying the structural parameters of a single QTF, as shown in Figure 1D, Zhang et al. achieved the detection of three types of gases by increasing the number of QTFs and using three QTFs with different f0. Moreover, they also proposed a multi-QTF theoretical model and verified that QTFs with different f0 can operate simultaneously, and multi-gas detection can be achieved by aligning more QTFs [42].
Additionally, improvements can also be made based on the piezoelectric effect. By depositing gold thin films with a thickness of 600 nm on both sides of the QTF, the piezoelectric charge collection efficiency is enhanced, and ambient electromagnetic noise is reduced [43].
3.3 Other improvement methods
To further enhance sensitivity and anti-interference capability, QEPAS improvements have shifted from single-parameter optimization to multi-dimensional collaborative innovation, with key advancements including relaxants’ introduction, optical path and waveguide optimization, and integrated dual-spectrum detection.
With standard-frequency QTFs, carbon monoxide (CO) exhibits slow energy relaxation after MIR-band excitation, making its QEPAS signal highly susceptible to ambient gases like water vapor (H2O) and oxygen (O2). H2O, as an efficient relaxation catalyst, significantly accelerates CO’s energy release, enhancing its QEPAS signal. Conversely, O2 competitively inhibits CO’s energy release, reducing signal amplitude. Therefore, to obtain the actual CO concentration, it must compensate for the inhibitory effect of O2 through a calibration curve [44]. However, water’s role as a relaxation promoter is not entirely beneficial, as H2O concentration variations can introduce acoustic cross-sensitivity. One solution is to correct real-time signal deviation by measuring sample gas humidity through independent humidity sensing [45].
In traditional detection, the laser incident perpendicular to the QTF plane limits effective interaction between gas molecules and the excitation source [46]. Moreover, in Laser-Induced Thermoelastic Spectroscopy (LITES), the laser first irradiates the QTF’s coating and then transmits to the quartz. However, the coating is a highly reflective silver layer for electrical conductivity, resulting in a low variation in light absorption by the quartz and consequently reducing the QTF sensitivity [47]. Usually, only tuning fork prongs surfaces are coated with silver, not gaps [46]. Therefore, to improve laser absorption efficiency and enhance the photothermal signal intensity [47], an in-plane detection technology (IP-QEPAS) is adopted, which changes laser incidence from perpendicular to parallel to the QTF plane (see Figures 1B–E). Compared with traditional QEPAS, the signal of IP-QEPAS is enhanced by more than 40 times [46]. Additionally, Melchiorre et al. utilized silicon nitride optical waveguides, leveraging their low propagation loss and high refractive index contrast for efficient optical transmission. The optical waveguide is S-shaped, which prevents optical path interference from scattered light incident on the QTF prongs and provides ample space for potential integration of lasers directly bonded to the chip [48].
In integrating dual-spectrum detection, most current trace gas sensors detect QEPAS, QEPTS, or LITES signals separately, lacking multi-signal fusion. As shown in Figure 1F, Hu et al. employed quartz-enhanced photoacoustic photothermal spectroscopy (QEPA-PTS). The laser first generates the QEPAS signal on QTF1, and then injects it into QTF2. Compared to the 2f signals from single-QTF QEPAS and QEPTS systems, the QEPA-PTS system demonstrates signal intensities 10.2 and 1.1 times greater, respectively [49]. Despite its advantages, this method still has limited laser utilization efficiency. To address this, as shown in Figure 1G, Zhao et al. placed two plane mirrors on both sides of the QTF. The laser, incident at a specific angle, reflects multiple times between prongs to repeatedly excite QEPAS and QEPTS signals. This simple optical path structure enables dual-spectroscopy integrated detection and multiple excitations using a single QTF. As shown in Table 2, compared with the bare QEPAS, the signal intensity has increased by 11.1 times, and the SNR has significantly improved [50]. Based on LITES and QEPAS detections (see Figure 1I), a dual-QTF configuration is employed where chemical etching removes the silver layers on both sides of QTF1’s base to enhance laser absorption, ensuring the beam passes through QTF1 before hitting QTF2. Furthermore, a right-angle prism reflects the laser, enabling the superposition of two excited QEPAS signals and two excited LITES signals under single-beam excitation for signal enhancement [47]. Additionally, a single QTF can detect QEPAS and LITES signals simultaneously. As shown in Figure 1H, off-beam acoustic microresonators (AMRs) on both sides of the QTF enhance the QEPAS signal. With multiple fiber collimators, the final laser beam is directed to the QTF sidewall to excite the LITES signal, achieving superposition of two QEPAS and one LITES signal. As shown in Table 3 and Table 4, when detecting CH4 or C2H2, compared with the QEPAS and LITES signals detected separately, the dual-spectroscopy signal significantly improves in terms of signal strength and SNR, while the noise change is very small [51].
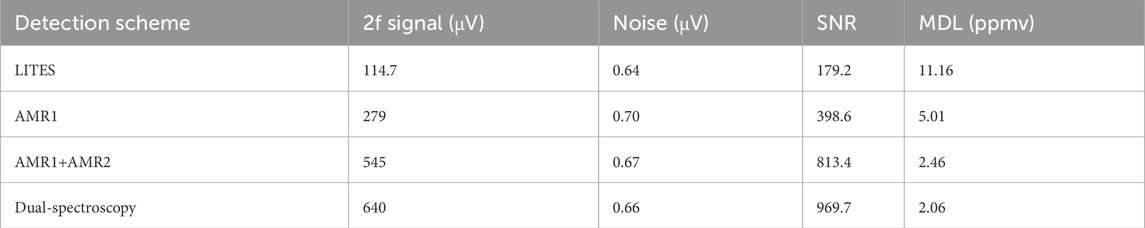
Table 3. Comparison of dual-spectrum detection using QEPAS and LITES with QEPAS-only detection in CH4 sensing.
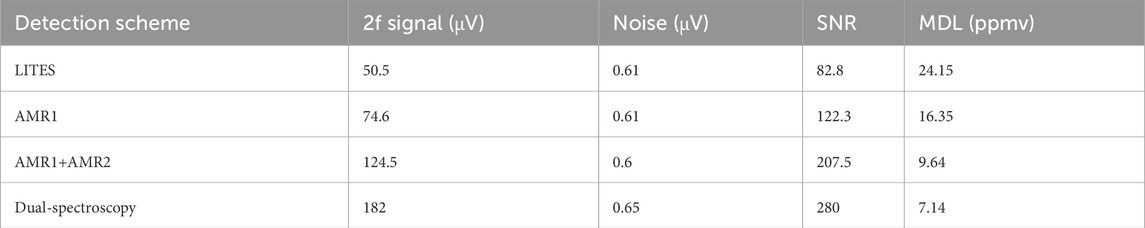
Table 4. Comparison of dual-spectrum detection using QEPAS and LITES with QEPAS-only detection in C2H2 sensing.
4 Summary and outlook
Trace gas detection holds profound significance for fields such as environmental protection, industrial safety, and medical diagnosis. QEPAS shows great potential for trace gas detection due to its high sensitivity, strong anti-interference, and compact structure. This paper systematically reviews research progress in QEPAS.
It elaborates on the fundamental principles and core components, and analyzes the key roles of light sources, QTFs, and auxiliary methods in enhancing detection performance. It focuses on the effects of optimizing laser parameters (e.g., laser power, wavelength tuning) and QTF properties (e.g., frequency, geometry) on enhancing detection sensitivity. In addition, it also summarizes the effects of relaxant addition, optical path and optical waveguide optimization, and dual-spectral detection.
In the future, the development of new light sources with wide tuning ranges and high power will enable coverage of multi-gas absorption lines while enhancing signals, supporting on-site multi-component (e.g., CH4, C2H2) leak detection in industrial settings. Additionally, the miniaturized and arrayed design of QTFs is expected to realize real-time breath analysis (e.g., CO2, NH3) and multi-component simultaneous detection functions in the field of medical testing.
Author contributions
E-QC: Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. GW: Resources, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. Y-FL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YY: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review and editing. YW: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the 173 Project Technical Fund [Grant number: 2022-JCJQ-JJ-0416]; the Central Government Guides Local Funds for Scientific and Technological Development [Grant number: 236Z1813G]; the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province [Grant number: F2024202086, F2024202083]; the Science Research Project of Hebei Education Department [Grant number: BJK2024048]; the Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars of Shijiazhuang [Grant number: 241791207A]; the Science and Technology Cooperation Special Project of Shijiazhuang [SJZZXA24007].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Li B, Menduni G, Giglio M, Patimisco P, Sampaolo A, Zifarelli A, et al. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (Qepas) and beat frequency-qepas techniques for air pollutants detection: a comparison in terms of sensitivity and acquisition time. Photoacoustics (2023) 31:100479. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2023.100479
2. Menduni G, Sgobba F, Dello Russo S, Ranieri AC, Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, et al. Fiber-coupled quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy system for methane and ethane monitoring in the near-infrared spectral range. Molecules (2020) 25(23):5607. doi:10.3390/molecules25235607
3. Li B, Wu HP, Feng CF, Jia ST, Dong L. Noninvasive skin respiration (Co2) measurement based on quartz- enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Anal Chem (2023) 95(14):6138–44. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00536
4. Luo P, Harrist J, Menduni G, Mesdour R, StMichel N, Sampaolo A. Simultaneous detection of methane, ethane, and propane by qepas sensors for on-Site hydrocarbon characterization and production monitoring. Acs Omega (2022) 7(4):3395–406. doi:10.1021/acsomega.1c05645
5. Weigl S, Feldmeier F, Bierl R, Matysik F-M. Photoacoustic detection of acetone in N2 and synthetic air using a high power Uv led. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical (2020) 316:128109. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2020.128109
6. Chen YJ, Liang TT, Qiao SD, Ma YF. A miniaturized 3d-Printed quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy sensor for methane detection with a high-power diode laser. Sensors (2023) 23(8):4034. doi:10.3390/s23084034
7. Lu JC, Wu Q, Zhou CQ, Zheng J, Liu W, Shao J. Compact, highly sensitive, rapid continuous measurement of carbon dioxide released from fruits and vegetables based on qepas and tdlas dual spectrum multiplexing technology. Opt Lasers Eng (2025) 191:109027. doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2025.109027
8. Lin C, Zhang XL, Yan XY, Cai Y, Li WJ. Part-per-billion (Ppb)-Level acetylene sensor employing optical quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (Qepas) with an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (Edfa) and a fiber-optic fabry-perot interferometer. Anal Lett (2025) 58(13):2233–48. doi:10.1080/00032719.2024.2403020
9. Zhuang RB, He JF, Lin HY, Luo HJ, Lin LQ, Wang LH, et al. Conductance-photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and concurrent sensing of hydrogen and hydrocarbons. Photoacoustics (2025) 45:100752. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2025.100752
10. Twomey CF, Biagi G, Ruth AA, Giglio M, Spagnolo V, O'Faolain L, et al. Evanescent wave quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy employing a side-polished fiber for methane sensing. Photoacoustics (2024) 36:100586. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2024.100586
11. Liang TT, Qiao SD, Chen YJ, He Y, Ma YF. High-sensitivity methane detection based on qepas and H-Qepas technologies combined with a self-designed 8.7 khz quartz tuning fork. Photoacoustics (2024) 36:100592. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2024.100592
12. Zifarelli A, De Palo R, Patimisco P, Giglio M, Sampaolo A, Blaser S, et al. Multi-gas quartz-enhanced photoacoustic sensor for environmental monitoring exploiting a vernier effect-based quantum Cascade laser. Photoacoustics (2022) 28:100401. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100401
13. Bonilla-Manrique OE, Gonzalez-Banfi AP, Pérez JV, Dessena G. Photoacoustic spectroscopy combined with a multipass circular cell to detect low concentrations of ammonia. Appl Sciences-Basel (2025) 15(12):6727. doi:10.3390/app15126727
14. Pan YF, Lu P, Cheng L, Li ZY, Liu DC, Zhao JB, et al. Miniaturized and highly-sensitive fiber-optic photoacoustic gas sensor based on an integrated tuning fork by mechanical processing with dual-prong differential measurement. Photoacoustics (2023) 34:100573. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2023.100573
15. Ma Y, Sun X, Sun H, He Y, Qiao S. An ultra-highly sensitive lites sensor based on multi-pass cell with ultra-dense spot pattern designed by multi-objective algorithm. PhotoniX (2025) 6(1):26. doi:10.1186/s43074-025-00187-2
16. Shunda Q, Ziting L, Ying H, Xiyang Z, Yufei M. Calibration-free measurement of absolute gas concentration and temperature via light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy. Adv Photon (2025) 7(6):066007. doi:10.1117/1.AP.7.6.066007
17. Wang JP, Wu HP, Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, Spagnolo V, Jia ST, et al. Quartz-enhanced multiheterodyne resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy. Light-Science and Appl (2024) 13(1):77. doi:10.1038/s41377-024-01425-1
18. Yin XK, Dong L, Wu HP, Gao M, Zhang L, Zhang XS, et al. Compact qepas humidity sensor in Sf6 buffer gas for high-voltage gas power systems. Photoacoustics (2022) 25:100319. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2021.100319
19. Wu YX, Tiehua M, Liu CH, Fan YS, Shi S, Guo SJ, et al. High-sensitivity dynamic detection of dissolved acetylene in transformer oil based on high-power quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy sensing system. Photonics (2025) 12(7):713. doi:10.3390/photonics12070713
20. Shi JQ, Zhao J, Zhang HB, Fu YL, Qin L, Zhao YY, et al. Signal enhancement of the gas detection based on quartz-enhanced photothermal spectroscopy technology. Opt Express (2024) 32(16):27176–87. doi:10.1364/oe.521916
21. Zhao YY, Zhang HB, Qin L, Shi JQ, Wang ZL. Two-component intra-cavity photoacoustic spectroscopy sensor using Y-Shaped photoacoustic cell with two resonant cavities. Infrared Phys and Technology (2024) 138:105199. doi:10.1016/j.infrared.2024.105199
22. Ma Y, Qiao S, Patimisco P, Sampaolo A, Wang Y, Tittel FK, et al. In-Plane quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett (2020) 116(6):061101. doi:10.1063/1.5142330
23. Pangerl J, Mueller M, Rueck T, Weigl S, Bierl R. Characterizing a sensitive compact mid-infrared photoacoustic sensor for methane, ethane and acetylene detection considering changing ambient parameters and bulk composition (N2, O2 and H2o). Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical (2022) 352:130962. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2021.130962
24. Breitegger P, Schweighofer B, Wegleiter H, Knoll M, Lang B, Bergmann A. Towards low-cost qepas sensors for nitrogen dioxide detection. Photoacoustics (2020) 18:100169. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100169
25. Starecki T, Wieczorek PZ. A high sensitivity preamplifier for quartz tuning forks in qepas (Quartz enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy) applications. Sensors (2017) 17(11):2528. doi:10.3390/s17112528
26. Wu H, Dong L, Yin X, Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, Ma W, et al. Atmospheric Ch4 measurement near a landfill using an Icl-based qepas sensor with V-T relaxation self-calibration. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical (2019) 297:126753. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2019.126753
27. Lin C, Liao Y, Fang F. Trace gas detection system based on all-optical quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc (2019) 73(11):1327–33. doi:10.1177/0003702819866468
28. Xie Y, Xiong H, Feng S, Pan N, Li C, Liu Y, et al. Sensitivity improvement of quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy using the stochastic resonance method. Photoacoustics (2025) 43:100707. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2025.100707
29. Ma YF, Tong Y, He Y, Yu X, Tittel FK. High-power dfb diode laser-based Co-Qepas sensor: optimization and performance. Sensors (2018) 18(1):122. doi:10.3390/s18010122
30. Wu H, Dong L, Zheng H, Liu X, Yin X, Ma W, et al. Enhanced near-infrared qepas sensor for sub-ppm level H2s detection by means of a fiber amplified 1582 Nm dfb laser. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical (2015) 221:666–72. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.049
31. Wu H, Dong L, Liu X, Zheng H, Yin X, Ma W, et al. Fiber-amplifier-enhanced qepas sensor for simultaneous trace gas detection of Nh3 and H2s. Sensors (2015) 15(10):26743–55. doi:10.3390/s151026743
32. Bi S, Qian S, Tian C, Zhang Q, Yu Y, Wang Z. Trace gas detection system based on photoacoustic and photothermal spectroscopy using ring fiber laser and quartz tuning fork. Ieee Sensors J (2023) 23(9):9229–36. doi:10.1109/jsen.2023.3244027
33. Zhang Q, Chang J, Cong Z, Bong Y, Wang Z, Wang F, et al. Pptv-level intra-cavity qepas sensor for acetylene detection using a high power Q-Switched fiber laser. Ieee Sensors J (2019) 19(15):6181–6. doi:10.1109/jsen.2019.2910665
34. Qiao S, He Y, Sun H, Patimisco P, Sampaolo A, Spagnolo V, et al. Ultra-highly sensitive dual gases detection based on photoacoustic spectroscopy by exploiting a long-wave, high-power, wide-tunable, single-longitudinal-mode solid-state laser. Light-Science and Appl (2024) 13(1):100. doi:10.1038/s41377-024-01459-5
35. Spagnolo V, Patimisco P, Pennetta R, Sampaolo A, Scamarcio G, Vitiello MS, et al. THz quartz-enhanced photoacoustic sensor for H_2S trace gas detection. Opt Express (2015) 23(6):7574–82. doi:10.1364/oe.23.007574
36. Li S, Wu H, Cui R, Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, Spagnolo V, et al. Piezo-enhanced acoustic detection module for mid-infrared trace gas sensing using a grooved quartz tuning fork. Opt Express (2019) 27(24):35267–78. doi:10.1364/oe.27.035267
37. Sun B, Li Y, Gao Z, Zhang M. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for Sf6 gas matrix based on a T-Shaped quartz tuning fork. Front Phys (2025) 13:1569734. doi:10.3389/fphy.2025.1569734
38. Sun H, He Y, Qiao S, Liu Y, Ma Y. Highly sensitive and real-simultaneous Ch4/C2H2 dual-gas lites sensor based on lissajous pattern multi-pass cell. Opto-Electronic Sci (2024) 3(11):240013–1--10. doi:10.29026/oes.2024.240013
39. Sun H, Qiao S, He Y, Sun X, Ma Y. Parts-per-quadrillion level gas molecule detection: co-lites sensing. Light: Sci and Appl (2025) 14(1):180. doi:10.1038/s41377-025-01864-4
40. Wang Y, Zheng S, Shao D, Fang F, Tao Y, Lin S, et al. Effect of microgroove structure on the performance of qtfs utilized for gas sensing. IEEE Trans Instrumentation Meas (2025) 74:1–11. doi:10.1109/TIM.2025.3566796
41. Hayden J, Giglio M, Sampaolo A, Spagnolo V, Lendl B. Mid-infrared intracavity quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy with Pptv-Level sensitivity using a T-Shaped custom tuning fork. Photoacoustics (2022) 25:100330. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100330
42. Zhang Q, Chang J, Cong Z, Sun J, Wang Z. Qepas sensor for simultaneous measurements of H2o, Ch4, and C2h2 using different qtfs. Ieee Photon J (2018) 10(6):1–8. doi:10.1109/jphot.2018.2880187
43. Zheng H, Liu Y, Lin H, Liu B, Gu X, Li D, et al. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy employing pilot line manufactured custom tuning forks. Photoacoustics (2020) 17:100158. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2019.100158
44. Sgobba F, Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, Giglio M, Menduni G, Ranieri AC, et al. Compact and portable quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy sensor for carbon monoxide environmental monitoring in urban areas. Photoacoustics (2022) 25:100318. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2021.100318
45. Waclawek JP, Moser H, Lendl B. Compact quantum Cascade laser based quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy sensor system for detection of carbon disulfide. Opt Express (2016) 24(6):6559–71. doi:10.1364/oe.24.006559
46. Liang T, Qiao S, Lang Z, Ma Y. Highly sensitive trace gas detection based on in-Plane single-quartz-enhanced dual spectroscopy. Sensors (2022) 22(3):1035. doi:10.3390/s22031035
47. Zhang X, Bi S, Zhang Z, Liu X, Qin L, Shi J, et al. A quartz-enhanced dual-spectroscopy gas sensor based on dual quartz tuning forks. Opt Lasers Eng (2025) 193:109049. doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2025.109049
48. Melchiorre L, Thottoli A, Vorobev AS, Menduni G, Sampaolo A, Magno G, et al. Study and characterization of silicon nitride optical waveguide coupling with a quartz tuning fork for the development of integrated sensing platforms. Sensors (2025) 25(12):3663. doi:10.3390/s25123663
49. Hu Y, Qiao S, He Y, Lang Z, Ma Y. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic-photothermal spectroscopy for trace gas sensing. Opt Express (2021) 29(4):5121–7. doi:10.1364/oe.418256
50. Zhao J, Zhang H, Fu Y, Qin L, Shi J, Zhao Y, et al. Integrated multiexcitation dual-spectroscopy detection technique based on qepts and qepas. Ieee Sensors J (2024) 24(10):16130–6. doi:10.1109/jsen.2024.3381300
Keywords: trace gas, quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy, laser source, quartz tuning fork, gas detection
Citation: Chang E-Q, Wang G, Li Y-F, Yu Y, Wang Y and Lu Z (2025) Study on research progress of quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for trace gas detection. Front. Phys. 13:1709349. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1709349
Received: 20 September 2025; Accepted: 17 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Huadan Zheng, Jinan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zongliang Wang, Liaocheng University, ChinaHanxu Ma, Harbin Institute of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Chang, Wang, Li, Yu, Wang and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gong Wang, d2FuZ2dvbmdAaGVidXQuZWR1LmNu; Yun-Fei Li, eWZsaUBoZWJ1dC5lZHUuY24=
 En-Qi Chang
En-Qi Chang Gong Wang
Gong Wang Yun-Fei Li
Yun-Fei Li Yu Yu
Yu Yu Yulei Wang
Yulei Wang Zhiwei Lu1,2
Zhiwei Lu1,2