- 1Center for Advanced Laser Technology, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China
- 2Hebei Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Technology and Equipment, Tianjin, China
AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (DUV-LEDs), as a novel solid-state ultraviolet light source, compared with the traditional ones, have competitive advantages over traditional UV sources such as mercury (Hg) pollution free, low energy consumption, small size, and tunable wavelengths. They hold broad prospects for development in critical fields including air purification, water disinfection, biosensing, and communications. Enhancing the electro-optical conversion efficiency of DUV-LEDs is essential for achieving large-scale commercial applications in disinfection and sterilization. Improving the device’s relatively low light extraction efficiency (LEE) has proven to be an effective strategy for boosting electro-optical efficiency and overcoming technical barriers. In this review, the fundamental configurations of the AlGaN DUV-LEDs and the regulatory logic of optical polarization characteristics on LEE are summarized. The detailed discussions include the recent research advances in improving the LEE of the DUV-LEDs via optical polarization—specifically by adjusting quantum well structures, optimizing polarization-dependent light propagation paths, and incorporating additional reflection/diffraction structures. Furthermore, it outlines the challenges and development prospects for improving LEE at the optical polarization level.
1 Introduction
Deep ultraviolet light (DUV, wavelength range approximately 200–280 nm) plays a pivotal role in semiconductor manufacturing, public health, food safety, and other fields. (A-8) [1]With the implementation of the Minamata Convention, traditional UV light sources have gradually been phased out due to their potential environmental pollution. Compared to conventional UV sources, AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (DUV-LEDs), as a novel solid-state UV light source, have competitive advantages such as mercury-free pollution, low energy consumption, small size, and tunable wavelength. They represent the future development trend for deep ultraviolet light sources. These LEDs hold broad prospects in key fields including air purification [2], water disinfection [3], biosensing [4], medical treatment [5] and communications [6],representing one of the primary development directions in the field of III-nitride wide-bandgap semiconductor optoelectronics [7].
Despite these advantages, the widespread adoption of DUV-LEDs is still hindered by their relatively low electro-optical conversion efficiency. Recent studies have introduced innovative device architectures to address these challenges. Incorporating a Si-doped n-AlGaN tunneling layer on the p-side of a 254 nm LED can enhance IQE to 62% and improve output power by 34%, by promoting hole injection via quantum tunneling [8]. Similarly, the use of an N-polar AlGaN tunnel junction (TJ) in a 284 nm UV-B LED leads to an exceptional IQE of 93% with nearly zero efficiency droop, along with a sixfold increase in light output power [9].Another key factor contributing to this situation is the device’s low light extraction efficiency (LEE) [10]. Consequently, enhancing LEE through optical polarization control has become a key strategy for improving the overall electro-optical conversion efficiency of deep ultraviolet LEDs.
In this review, the fundamental configurations of DUV-LEDs and the regulatory logic of optical polarization characteristics on light extraction efficiency are summarized. The detailed discussions include the recent research advances in enhancing the LEE of the DUV-LEDs via optical polarization—specifically by adjusting quantum well structures, optimizing polarization-dependent light propagation paths, and incorporating additional reflection/diffraction structures. Furthermore, we also discuss challenges and development prospects for DUV-LEDs based on AlGaN in terms of quantum well valence band structure control and improvement of device structure integration.
2 Optical polarization characteristics of deep ultraviolet LEDs and their correlation mechanism with light extraction efficiency
2.1 Fundamental polarization characteristics of AlGaN materials
The root cause of low LEE in DUV LEDs stems from the inherent physical properties of AlGaN materials and devices. The basic configuration of a DUV LED is depicted in the figure. This structure begins with AlN and AlN/AlGaN buffer layers as the starting layers, followed by functional layers sequentially composed of n-AlGaN, multiple-quantum wells (MQWs), and p-type regions. The n-AlGaN layer provides electrons and forms an ohmic contact with the n-type electrode, while the MQW restricts carriers and facilitates electron-hole recombination. The p-type region comprises a p-type electron blocking layer (p-EBL) to suppress electron leakage, p-AlGaN for hole provision, and p-GaN, which also serves as the ohmic contact layer to the p-type electrode.
During device operation, three processes occur internally, which are current injection, electro-optical conversion, and light extraction. Due to the refractive index differences among the layers of materials, during the light emission process after electro-optical conversion, the light rays will undergo refraction and total reflection at different interfaces, thus altering their propagation paths. Apart from a small portion of ultraviolet light being effectively drawn out of the device, most of the light is eventually consumed within the device, thereby limiting the LEE. The key scientific issues restricting the improvement of the LEE of DUV-LEDs can be further classified into three categories, namely, the problem of light polarization, the problem of total reflection, and the problem of light extraction. Among them, the issue of light polarization is that high Al composition AlGaN quantum wells mainly emit in the transverse magnetic (TM) mode, which exits laterally, resulting in significant light loss. This review primarily focuses on exploring ways to improve the vLEE by optimizing light polarization.
2.2 Control logic of polarization characteristics on light extraction efficiency
To optimize LEE at the level of optical polarization, the polarization degree of quantum wells must be enhanced. The polarization degree of QWs is closely related to their band structure. In wurtzite-structured AlGaN materials, the valence band comprises heavy hole (HH), light hole (LH), and crystal field split-off hole (CH) subbands due to the effects of crystal field and spin-orbit coupling.
Deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes generate light mainly through the recombination of electrons and holes between the conduction band and valence bands. Due to the asymmetric P-orbitals in the valence band, electron transitions to different valence subbands produce photons with distinct polarizations [11]. Transitions from the conduction band to the HH subband dominate transverse electric (TE) polarization (electric field perpendicular to the c-axis), as the orbital overlap favors in-plane dipole oscillation. Transitions to the CH subband dominate transverse magnetic (TM) polarization (electric field parallel to the c-axis), resulting in in-plane propagation of light.
This polarization dependence is directly reflected in experimental spectra (Figure 1). For example, Figure 1a compares the in-plane TE/TM emission spectra of two AlGaN QW samples: Sample A (low in-plane compressive stress, DOP = 41.5%) exhibits comparable TE and TM intensities, while Sample E (high in-plane compressive stress, DOP = 61.9%) shows a significant enhancement in TE intensity relative to TM—this is because compressive stress further stabilizes the HH subband above the CH subband, promoting TE-polarized transitions. Similarly, Figure 1b demonstrates that staggered QW structures (with step-function Al content distribution) enhance the quantum confinement of HH states, leading to a DOP increase from 20.8% to 40.2% via strengthened TE-polarized emission.
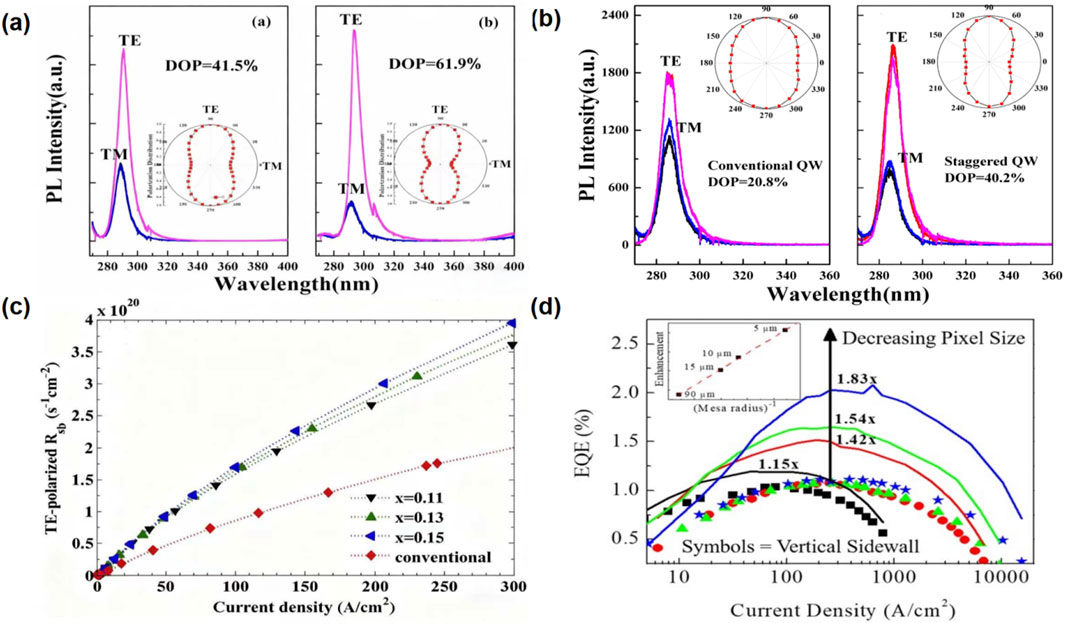
Figure 1. (a) TE and TM polarized in-plane emission spectra for sample A and sample E from ref.11. Copyright (2023) Elsevier. (b) TE and TM polarized PL spectra of conventional Al0.37Ga0.63N or Al0.55Ga0.45N and staggered Al0.33Ga0.67N or Al0.45Ga0.55Nor Al0.55Ga0.45N QWs from ref.13. Copyright (2023) Elsevier. (c) The total spontaneous emission rate (Rsp) for TE polarization as a function of current density from ref.15. Copyright (2023) Elsevier. (d) Comparison of External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) between Vertical Sidewall and Bare-Slanted Sidewall AlGaN DUV Micropixel LEDs and Analysis of Pixel Size Dependence (from [23] Copyright (2023) Elsevier).
To better describe the polarization characteristics of AlGaN, researchers introduced the concept of degree of polarization (DOP), defined as follows:
where I⊥ and I∥ represent the emission intensities of TE light and TM light from the quantum well, respectively.
The TE mode shows a higher level of extraction efficiency,which means extracting polarization from the TM mode poses greater challenges than from the TE mode. For DUV LEDs, the TM mode’s LEE is no more than one-tenth of the TE mode’s [10]. Therefore, enhancing the LEE of AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet LEDs can be achieved by increasing the LEE of the TM mode or by increasing the proportion of TE mode light in the emitted light. The following sections describe methods to enhance LEE through optical polarization by adjusting quantum well structures, optimizing polarized light propagation paths, and incorporating additional reflective/diffractive structures.
3 Methods to enhance light extraction efficiency via optical polarization
3.1 Modulating quantum well valence band structure
Modulating the valence band structure of quantum wells to enhance the polarization is a key strategy for improving LEE in DUV-LEDs.
Specifically, quantum well structural design can be optimized directly through methods such as adjusting quantum well dimensions, applying compressive stress, or introducing insertion layers. These approaches refine the valence band structure and transition characteristics of QWs. Additionally, the valence band environment of quantum wells can be indirectly controlled by designing the electron-blocking layer (EBL), hole source layer (HSL), and waveguide, thereby increasing quantum well polarization.
An underlying n-AlGaN layer exerts compressive stress on the AlGaN MQWs, and this stress application induces valence band ordering. As a result, the HH subband is positioned above the CH subband in k-space, which helps facilitate the generation of TE-polarized light [12]. The c-plane Al0.37Ga0.63N or Al0.5Ga0.5N quantum well exhibits strong TE-polarized emission, displaying distinct polarization characteristics under different in-plane compressive strains. As the in-plane compressive strain on the AlN template increases, the polarization degree rises from 41.5% to 61.9%, enhancing the proportion of TE-polarized light [13]. Figure 1a shows the room - temperature in - plane TE and TM polarized emission spectra of Sample A (with a low in - plane compressive stress and a DOP of 41.5%) and Sample E (with a high in - plane compressive stress and a DOP of 61.9%). Compared to planar DUV MQWs, AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet MQWs featuring strain-modulated nanostructures exhibit a threefold increase in photoluminescence (PL) intensity, with the DOP rising from −0.43 to −0.16 [14].
Ultraviolet light-emitting devices employing staggered AlGaN quantum well structures enhance the quantum confinement effect while avoiding degradation in AlGaN layer crystal quality caused by quantum confinement variations (reduced well width) or growth orientation, thus significantly boosting TE-polarized emission intensity and improving optical output efficiency [15]. Figure 1b presents the integrated intensity distribution of edge emission from both conventional and staggered QWs relative to the prism edge. MOCVD-grown staggered quantum well structures with step-function Al content distribution can enhance TE-polarized radiation, achieving an increase in the degree of polarization (DOP) from 20.8% to 40.2% [16].
A heterostructure insertion layer can be introduced to modulate polarization characteristics. By adjusting the composition of the insertion layer to alter band alignment, this approach enables rearrangement of valence band subbands and optimization of electron-hole wave function overlap. Compared with conventional structures, inserting an InxAl1-xN layer between the barrier layer and the well layer leads to larger electron-hole wavefunction separation in TM-polarization-dominated transitions. For InxAl1-xN insertion layer structures with x values of 0.11, 0.13, and 0.15, the total spontaneous emission rate of TE-polarized light increases by 76%–105% when the current density falls in the range of 2–300 A cm(−2), thus enabling TE polarization to become the predominant emission mode [17]. Figure 1c shows the dependence of the TE-polarized Rsp on current density for the InxAl1-xN insertion layer structures.
Additionally, the designs of EBL, HSL, and waveguides exert a significant influence on the polarization state of QWs. By implementing gradient designs in the AlN composition of these three structures, the polarization charge of the guide can be induced, thereby indirectly regulating the valence band environment of the QWs. AlN composition gradient design can be applied to the p-EBL and p-HSL structures, and polarization bulk charges can be introduced into both p-EBL and p-HSL (p-type dual polarization). These two measures work together to shield the polarization-induced electric field and increase the hole energy, enabling the realization of a DUV LED with high IQE (55.65%) in the 237 nm band [18]. While suppressing electron leakage, they enhance hole injection, ensure electron-HH band recombination in the QWs, and improve the proportion of TE-polarized emission. As for the waveguide (WG), a graded AlN composition AlxGa1-xN WG layer in the DUV NW-LD induces bulk polarization charges, which compensate the effect of the polarization-induced electric field, suppress optical field leakage, and increase carrier injection efficiency. The optical confinement factor (OCF) is enhanced by 82% (from 17.3% to 33.5%), indirectly consolidating the dominant position of TE polarization [19].
3.2 Optimizing polarized light propagation pathways
The LEE of LEDs increases with enhanced sidewall light emission. Regulating the propagation pathways of polarized light to extract TM-polarized light represents a crucial approach to addressing low light extraction efficiency caused by low quantum well polarization. Specifically, geometric design of LED sidewalls or reduction of the active region size can optimize light propagation pathways.
Geometric design of LED sidewalls can adjust the reflection of TM-polarized light, making it easier to enter the light-emitting cone [20, 21]. The dimensions and shape of the LED sidewalls significantly influence light extraction in deep ultraviolet LEDs. As the circumference of the sloped sidewall structure increases, LEE increases [22]. Additionally, increasing the sidewall area facilitates light extraction. A interrupted mesa structure can enhance the sidewall area. A high-power DUV-LED featuring a 46.9° sloped sidewall structure with n-electrode holes and an interrupted mesa structure exhibits a 250% increase in sidewall area, significantly optimizing device performance. At a 250 mA operating current, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) and wall plug efficiency (WPE) reached 9.19% and 7.13%, respectively, representing improvements of 9.6% and 4.4% [23]. The chip sidewall geometry (CSG) also influences the performance of deep ultraviolet LEDs. The DUV LEDs with the CSG structure have sloped epitaxial sidewalls that can capture more photons than near-horizontal structures, providing more possible pathways for photon escape to increase the LEE of the LEDs [24]. Controlling the sloped sidewall angle is critical. Due to two scattering mechanisms present in sloped sidewalls, the optimal angle for deep ultraviolet LEDs decreases as chip size increases. The optimal sidewall inclination angle should be controlled between 25° and 65° [25]. The sidewall angle is determined by the etch selectivity ratio of the mask material, and a higher etch selectivity ratio leads to the formation of a larger sidewall angle [26].
Reducing the active area size—such as by adopting truncated micro-pixel designs or micro-array structures on chips—to optimize the perimeter-to-area ratio, thereby shortening the propagation path of TM-polarized light and minimizing internal losses. When the chip size of an AlGaN deep ultraviolet LED is reduced from 90 μm to 5 μm, the LEE increases by 1.8 times due to the reduced re-absorption of sideways-travelling photons. [27]. Figure 1d presents the EQE of devices with vertical and slanted sidewalls prior to Al2O3/Al coating, revealing that the slanted sidewall devices exhibit a significant pixel size-dependent enhancement in EQE. A larger perimeter-to-area ratio (P/A ratio) of the p-electrode-covered platform area in DUV µ-LEDs significantly enhances LEE, with this effect becoming more pronounced as µ-LED dimensions further shrink. Measurements of the EQE for DUV µ-LED structures with circular, pentagonal, and quadrilateral shapes at different P/A ratios confirmed this conclusion, with the quadrilateral µ-LED exhibiting the highest EQE. [28]. In addition, dividing a single large-sized active region into an array of multiple independent micro-units is an effective approach. Lee et al. designed a 5 × 5 array of microrings featuring sloped sidewalls on the outer periphery and a p-GaN-free inner periphery for DUV LEDs, which were used in conjunction with MgF2/Al omnidirectional reflectors. Compared to the reference LED, the micro-ring array deep ultraviolet LED exhibits a light output power 70% higher than the reference [29].
3.3 Designing additional reflective or diffractive structures
The LEE of deep ultraviolet LEDs is constrained by the lateral propagation characteristics of TM-polarized light and total internal reflection losses. Designing additional reflective or diffractive structures can enhance the extraction of polarized light. The following sections explore two main categories: reflective structures and diffractive structures.
Reflective structures rely on artificially designed highly reflective interfaces to redirect light confined within the device toward the light emission cone, minimizing absorption losses. Based on their reflection mechanisms, these structures can be categorized into omnidirectional reflectors and distributed Bragg reflectors.
Zhang et al. proposed a method for full-space omnidirectional reflectors. By coating the top and sidewalls of the chip with highly UV-reflective aluminum (Al), light propagating to these surfaces is reflected into the light emission cone, simultaneously improving LEE for both TE and TM polarization [30]. Researchers further applied Al reflectors in DUV LED packaging, which significantly enhanced the LEE. [31] also proposes an aluminum-based sidewall reflector structure, which optimizes the diameter and tilt angle of the sidewall. For 285-nm DUV-LEDs, this optimization enhances the light power output by 18.38% at a working current of 100 mA [32].
On the basis of the omnidirectional reflector, suitable passivation layers and metals can be deposited on the sloped sidewalls to enhance the propagation of TM-polarized light. Using MgF2/Al reflectors on the sloped sidewalls of the truncated cone structure effectively enhances the reflection of deep ultraviolet light by the sloped sidewalls [33]. Building upon this foundation, a remote cavity structure with sloped sidewalls can be adopted. This design eliminates the sidewall metal reflectors and relocates them to the top of the device. The cavity structure effectively minimizes light absorption by the sidewall metal, thereby increasing the output of DUV-LEDs by over 40% [34].
In addition to omnidirectional reflectors (ODR), deep ultraviolet nanoporous distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs) can be designed. The MQWs grown in these structures exhibit greater compressive strain, thereby enhancing TE mode emission. Owing to their reflective characteristics, the LEE of both TE and TM modes is enhanced [35]. Moreover, integrating embedded porous AlGaN reflectors during epitaxial growth can improve LEE in deep ultraviolet optoelectronic devices. Compared to conventional AlGaN/AlN DBR structures, porous AlGaN/n-AlGaN DBR structures fabricated via EC wet etching exhibit shorter epitaxial growth time, lower compressive strain, and higher reflectivity [36].
The core principle of diffractive structures lies in utilizing Bragg diffraction from periodic subwavelength structures to convert guided modes confined within the device into vertical radiation modes. The addition of nanowire structures to AlN photonic crystals suppresses guided-mode emission, enhances diffraction of TM-polarized light, and increases the vertical luminous efficiency of DUV LEDs to 79.4%, while improving the top-surface LEE of nanowire light-emitting diodes [37].
4 Conclusion
AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes, as novel solid-state light sources replacing mercury lamps, require enhanced light extraction efficiency to achieve high-performance devices. In this review, we systematically elucidate the optical polarization characteristics of DUV LEDs and their correlation with LEE from an optical polarization perspective. We also summarize polarization control methods for promoting LEE through three approaches: quantum well valence band structure tuning, optimized propagation paths for polarized light, and enhanced reflection/diffraction of polarized light. Furthermore,we outline recent research progress in improving LEE for AlGaN-based DUV LEDs.
However, numerous challenges persist in enhancing LEE for DUV LEDs based on AlGaN materials through optical polarization optimization. On one hand, precise control over the valence band structure of QWs is needed to enhance polarization while avoiding adverse effects on internal quantum efficiency. On the other hand, how to enhance device integration and promote active region miniaturization to align with industry trends. With breakthroughs in these key technologies, DUV-LEDs optimized for optical polarization will demonstrate broader application prospects in fields such as sterilization and environmental monitoring, driving further advancement in deep ultraviolet optoelectronics.
Author contributions
D-XZ: Writing – original draft. GW: Writing – review and editing. Y-FL: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the 173 Project Technical Fund (Grant No. 2022-JCJQ-JJ-0416), the Central Government Guides Local Funds for Scientific and Technological Development (Grant No. 236Z1813G), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant Nos. F2024202086 and F2024202083), the Science Research Project of Hebei Education Department (Grant No. BJK2024048), the Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars of Shijiazhuang (Grant No. 241791207A), and the Science and Technology Cooperation Special Project of Shijiazhuang (Grant No. SJZZXA24007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lang J, Xu F, Wang J, Zhang L, Fang X, Zhang Z, et al. Progress in performance of algan-based ultraviolet light emitting diodes. Adv Electron Mater (2024) 11(1):2300840. doi:10.1002/aelm.202300840
2. Hsu T-C, Teng Y-T, Yeh Y-W, Fan X, Chu K-H, Lin S-H, et al. Perspectives on uvc led: its progress and application. Photonics (2021) 8(6):196. doi:10.3390/photonics8060196
3. Feng L-Y, Lu H-M, Zhu Y-F, Chen Y-Y, Yu T-J, Wang J-P. Intelligent optimization design of electron barrier layer for algan-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Acta Physica Sinica (2023) 72(4):048502. doi:10.7498/aps.72.20222004
4. Won W-S, Tran LG, Park W-T, Kim K-K, Shin CS, Kim N, et al. Uv-Leds for the disinfection and bio-sensing applications. Int J Precision Eng Manufacturing (2018) 19(12):1901–15. doi:10.1007/s12541-018-0218-5
5. Kneissl M, Seong T-Y, Han J, Amano H. The emergence and prospects of deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode technologies. Nat Photon (2019) 13(4):233–44. doi:10.1038/s41566-019-0359-9
6. Ren Z, Yu H, Liu Z, Wang D, Xing C, Zhang H, et al. Band engineering of iii-nitride-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes: a review. J Phys D: Appl Phys (2020) 53(7):073002. doi:10.1088/1361-6463/ab4d7b
7. Peng K, Lai S, Shen M, Li S, Zheng L, Dai Y, et al. Algan-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with varied thickness of sidewall passivation Via atomic layer deposition. IEEE Trans Electron Devices (2023) 70(11):5727–31. doi:10.1109/ted.2023.3316633
8. Sharif MN, Khan MA, Wali Q, Ayub K, Rani M, Wang F, et al. Tunnelling assisted by Si-Doped N-Algan layer on the P-Side of 254 nm duv led. Opt Quan Electronics (2023) 55(9):785. doi:10.1007/s11082-023-04895-6
9. Rahman HU, Ayub K, Sharif N, Khan MA, Wang F, Liu Y. Advantages of algan tunnel junction in N-Polar 284 Nm Ultraviolet-B light emitting diode. ECS J Solid State Sci Technology (2024) 13(6):065005. doi:10.1149/2162-8777/ad52c2
10. Ryu H-Y, Choi I-G, Choi H-S, Shim J-I. Investigation of light extraction efficiency in algan deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express (2013) 6(6):062101. doi:10.7567/apex.6.062101
11. Wang X, Jiang K, Sun X, Zhang Z-H, Chen Y, Wang B, et al. Valence subbands profile regulation in algan quantum well based on K·P theory. Physica Scripta (2023) 98(3):035103. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/acb860
12. Long H, Wang S, Dai J, Wu F, Zhang J, Chen J, et al. Internal strain induced significant enhancement of deep ultraviolet light extraction efficiency for algan multiple quantum Wells grown by mocvd. Opt Express (2018) 26(2):680. doi:10.1364/oe.26.000680
13. Zhang S, Zhang Y, Tang N, Wang W, Chen X, Fu L, et al. Compressive strain induced enhancement of transverse-electric polarized ultraviolet light emission for algan quantum Wells. Superlattices and Microstructures (2021) 150:106749. doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2020.106749
14. Xu H, Long H, Jiang J, Sheikhi M, Li L, Guo W, et al. Strain modulated nanostructure patterned algan-based deep ultraviolet multiple-quantum-wells for polarization control and light extraction efficiency enhancement. Nanotechnology (2019) 30(43):435202. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/ab3208
15. Wang W, Lu H, Fu L, He C, Wang M, Tang N, et al. Enhancement of optical polarization degree of algan quantum Wells by using staggered structure. Opt Express (2016) 24(16):18176. doi:10.1364/oe.24.018176
16. Yang GF, Xie F, Dong KX, Chen P, Xue JJ, Zhi T, et al. Design of deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with staggered algan quantum Wells. Physica E: Low-dimensional Syst Nanostructures (2014) 62:55–8. doi:10.1016/j.physe.2014.04.014
17. Li Y, Zhu Y, Wang M, Deng H, Yin H. Enhanced Te-Polarized emission of algan-based deep-ultraviolet light emitting diodes by using an inaln insertion layer. Jpn J Appl Phys (2019) 58(11):114001. doi:10.7567/1347-4065/ab47a8
18. Xing Z, Zhang A, Qu Y, Wang F, Sharif MN, Liou JJ, et al. Increasing the hole energy by the P-Type dual polarization for high internal quantum efficiency of 237 nm-Band deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Opt Eng (2024) 63(02). doi:10.1117/1.Oe.63.2.027103
19. Nawaz SM, Niass MI, Wang Y, Xing Z, Wang F, Liu Y. Enhancement of the optoelectronic characteristics of deep ultraviolet nanowire laser diodes by induction of bulk polarization charge with graded aln composition in Alxga1-Xn waveguide. Superlattices and Microstructures (2020) 145:106643. doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2020.106643
20. Chen Q, Zhang H, Dai J, Zhang S, Wang S, He J, et al. Enhanced the optical power of algan-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diode by optimizing Mesa sidewall angle. IEEE Photon J (2018) 10(4):1–7. doi:10.1109/jphot.2018.2850038
21. Tian M, Yu H, Memon MH, Xing Z, Huang C, Jia H, et al. Enhanced light extraction of the deep-ultraviolet micro-led Via rational design of chip sidewall. Opt Lett (2021) 46(19):4809. doi:10.1364/ol.441285
22. Wierer JJ, Allerman AA, Montaño I, Moseley MW. Influence of optical polarization on the improvement of light extraction efficiency from reflective scattering structures in algan ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett (2014) 105(6):061106. doi:10.1063/1.4892974
23. Xu H, Liu Z, Guo W, Sun J, Fang A, Liu J. Enhancing the performance of high-power duv-leds with sloped sidewall by introducing N-Electrode holes and interrupted Mesa. Opt Express (2025) 33(8):17253. doi:10.1364/oe.553503
24. Peng K-W, Tseng M-C, Lin S-H, Lai S, Shen M-C, Wuu D-S, et al. Sidewall geometric effect on the performance of algan-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Opt Express (2022) 30(26):47792. doi:10.1364/oe.475219
25. Wang L, Jia T, Liu Z, Chu C, Tian K, Zhang Y, et al. On the origin of the enhanced light extraction efficiency of duv led by using inclined sidewalls. Opt Lett (2024) 49(11):3275. doi:10.1364/ol.526100
26. Xu H, Liu Z, Liu N, Wang B, Zhang T, Guo W, et al. A novel intermittent Mesa structure with an Rh reflective layer and sloped sidewalls for high-power duv leds. Opt Commun (2025) 591:132105. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2025.132105
27. Floyd R, Gaevski M, Hussain K, Mamun A, Chandrashekhar MVS, Simin G, et al. Enhanced light extraction efficiency of micropixel geometry algan duv light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express (2021) 14(8):084002. doi:10.35848/1882-0786/ac0fb8
28. Xiao S, Yu H, Memon MH, Jia H, Luo Y, Wang R, et al. In-Depth investigation of deep ultraviolet microled geometry for enhanced performance. IEEE Electron Device Lett (2023) 44(9):1520–3. doi:10.1109/led.2023.3294819
29. Fayisa GB, Lee JW, Kim J, Kim Y-I, Park Y, Kim JK. Enhanced light extraction efficiency of micro-ring array algan deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Jpn J Appl Phys (2017) 56(9):092101. doi:10.7567/jjap.56.092101
30. Zhang S, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Xu L, Chen Q, et al. Optical polarization characteristics and light extraction behavior of deep-ultraviolet led flip-chip with full-spatial omnidirectional reflector system. Opt Express (2019) 27(20):A1601. doi:10.1364/oe.27.0a1601
31. Liu X, Mou Y, Wang H, Liang R, Wang X, Peng Y, et al. Enhanced light extraction of deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes by using optimized aluminum reflector. Appl Opt (2018) 57(25):7325. doi:10.1364/ao.57.007325
32. Pai Y-M, Lin C-H, Lee C-F, Lin C-P, Chen C-H, Kuo H-C, et al. Enhancing the light-extraction efficiency of algan-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes by optimizing the diameter and tilt of the aluminum sidewall. Crystals (2018) 8(11):420. doi:10.3390/cryst8110420
33. Lee JW, Park JH, Kim DY, Schubert EF, Kim J, Lee J, et al. Arrays of truncated cone algan deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes facilitating efficient outcoupling of in-Plane emission. ACS Photon (2016) 3(11):2030–4. doi:10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00572
34. Zhang J, Chang L, Zheng Y, Chu C, Tian K, Fan C, et al. Integrating remote reflector and air cavity into inclined sidewalls to enhance the light extraction efficiency for algan-based Duv leds. Opt Express (2020) 28(11):17035. doi:10.1364/oe.393166
35. Shan M, Guo C, Zhao Y, Chen Q, Deng L, Zheng Z, et al. Nanoporous algan distributed bragg reflectors for deep ultraviolet emission. ACS Appl Nano Mater (2022) 5(7):10081–9. doi:10.1021/acsanm.2c02689
36. Wu C-J, Kuo C-Y, Wang C-J, Chang W-E, Tsai C-L, Lin C-F, et al. Deep-Uv porous algan distributed bragg reflectors for deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. ACS Appl Nano Mater (2020) 3(1):399–402. doi:10.1021/acsanm.9b02034
Keywords: AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes, light extraction efficiency, optical polarization, quantum well structure, reflective/diffractive structure
Citation: Zhu D-X, Wang G and Li Y-F (2025) Advances in enhancing the light extraction efficiency of AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes via optical polarization. Front. Phys. 13:1718751. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1718751
Received: 04 October 2025; Accepted: 30 October 2025;
Published: 11 November 2025.
Edited by:
Youyou Hu, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Nawaz Khattak, RIKEN, JapanCopyright © 2025 Zhu, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gong Wang, d2FuZ2dvbmdAaGVidXQuZWR1LmNu; Yun-Fei Li, eWZsaUBoZWJ1dC5lZHUuY24=
 Dong-Xu Zhu1,2
Dong-Xu Zhu1,2 Gong Wang
Gong Wang Yun-Fei Li
Yun-Fei Li