- 1School of Physics and Electronic Information, Huaibei Normal University, Huaibei, China
- 2School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Suzhou University, Suzhou, China
Dense copper oxide nanoribbons arrays are prepared on a copper sheet by using a low-temperature hydrothermal method. The wettability of the surface modified by stearic acid is superhydrophobic, and the water contact angle is 153.6°. It is demonstrated that the reversible transition from superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity is successfully achieved by heat treatment and re-modification, and the whole process can be accomplished in 170 s. Potentiodynamic polarization curves and Nyquist curves show that these superhydrophobic surfaces have good corrosion resistance and superior durability.
Introduction
The superwetting surface has attracted considerable research interest due to its important application in self-cleaning, oil/water separation, corrosion resistance, and so on (Forooshani et al., 2017a; Bagheri et al., 2017; Forooshani et al., 2017b; Bagheri et al., 2018; Forooshani et al., 2019; BaratiDarband et al., 2020; Hatte and Pitchumani, 2021). Generally, a surface with water contact angles (WCAs) greater than 150° and slide angles less than 10° is called the superhydrophobic surface (Taghvaei et al., 2021). A rough structure and surface chemical energy are very significant to the composition of the superhydrophobic surface (Siddiqui et al., 2021a). The preparation of the superhydrophobic surface is generally divided into two steps. The first step is to prepare a rough structure on a solid surface through various methods, and the second step is to modify with low surface energy substances (Yu et al., 2021).
With the rapid development of the smart surface with controlled wetting behavior, reversible superwetting transition between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity has received particular attention (Ding et al., 2018; Wan et al., 2018; Brehm et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020). UV irradiation (Li et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2017; Jiang et al., 2019), pH (Yu et al., 2005; Chen et al., 2017; Cheng et al., 2019), electric field (Idriss et al., 2020), and heat treatment (Wang et al., 2021) are widely reported as external stimuli for achieving wettability transition in many literatures. Among the mentioned external stimuli, UV has been extensively employed, because some photocatalytic materials, such as ZnO, TiO2, and SnO2, can realize wettability transition under UV irradiation (Velayi and Norouzbeigi, 2019). However, these reported methods have many drawbacks, such as long transition time, complex fabrication process, and high costs. For example, Zhou et al. (Zhou et al., 2019) fabricated a superhydrophobic TiO2 film with excellent UV responsibility by anodic oxidation. The superhydrophobic film could be changed into superhydrophilicity within 13 min under UV irradiation. Nevertheless, the transition time from superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity requires 100 h when it was heated at 60°C in the dark. Li et al. (Li et al., 2019a) fabricated the superhydrophobic micro/nano-scale hierarchical structure on brass surfaces by laser ablation. The results revealed that an alternative heating–reheating cycle can lead to a reversible change between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity within 5 h. But the sample preparation process and the instrument used were complicated. In addition, the corrosion performance of reversible superwetting transition is always examined when the surface is superhydrophobic, but few studies have been carried out.
In this study, a superhydrophobic surface composed of copper oxide nanoribbons arrays was successfully fabricated on a copper sheet surface by simple and low-cost solution-immersion methods. The superhydrophobic surface can be achieved by soaking stearic acid. Noteworthy, the reversible transition between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity can be easily achieved by heat treatment and re-modification. In addition, the corrosion current density and impedance spectrum of superwetting surfaces were also studied.
Experimental Procedure
Preparation of a Superhydrophobic Surface Composed of Copper Oxide Nanoribbons Arrays
Copper sheet with a thickness of 0.5 mm was used as a substrate material. First, copper sheets were ultrasonically cleaned with HCl (3 M). Second, the cleaned copper sheets were etched in NH3·H2O (0.03 M) at 20°C for one day in a water bath pot, followed through washing with distilled water and drying with blower. Last, the treated copper sheets were placed in the ethanol solution of stearic acid (0.2 mol L−1) for 2 h in order to obtain superhydrophobic properties.
Reversible Superwetting Transition of Copper Oxide Nanoribbons Arrays
The prepared superhydrophobic samples can be converted into superhydrophilic ones after being heated at 400°C for 150 s in a muffle furnace. The wettability properties reversed into superhydrophobicity just by soaking in the ethanol solution of stearic acid for 10 s.
Sample Characterization
The surface morphology of copper sheet was observed by using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (JEOL JSM-6610LV). The composition of the sample was employed by X-ray diffraction (XRD-600, Japan). The measurement of WCAs was carried out by using a contact angle measuring instrument (JC 2000C1, Shanghai). The standard three-electrode system was used (CHI 760E, Shanghai), in which the samples with an exposed area of 1 cm2 served as the working electrode, the Ag/AgCl was the reference electrode, and graphite was the counter electrode.
Results and Discussion
Structures of Surface and Reversible Wettability
Figure 1A presents the SEM micrographs of the bare copper sheet by ultrasonic cleaning with HCl. It can be confirmed that the surface of copper has only a few scratches and some patchy defects. Figure 1B shows the copper oxide nanoribbons arrays well aligned which are fabricated on a copper sheet. It can be seen from the high magnification image in Figure 1C that nanoribbons are bundled together. Figure 1D shows the cross sections of the copper oxide nanoribbons arrays whose thickness is approximately 5 μm. Figure 2 shows the XRD of patterns of copper oxide nanoribbons arrays prepared on the copper sheet. The diffraction peaks of (002) and (200) correspond to the copper oxide crystals, except two peaks (111) and (200) from the copper sheet. This shows that the micro/nano-scale hierarchical structure on the copper sheet is copper oxide.
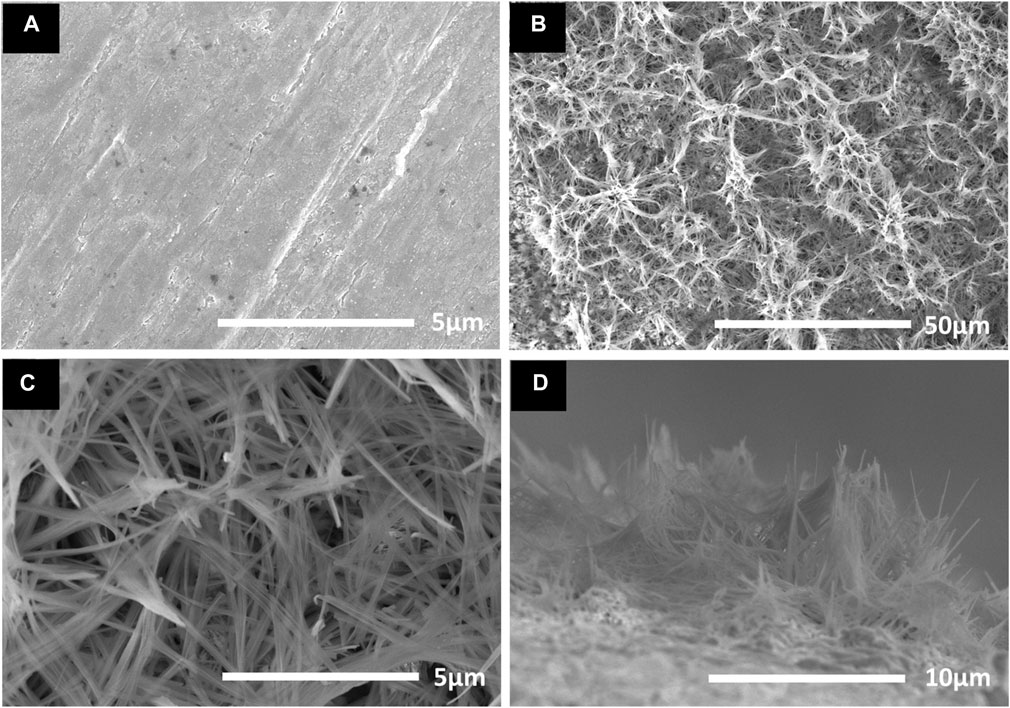
FIGURE 1. SEM micrographs of (A) bare copper, (B) copper oxide nanoribbons arrays, (C) higher magnification image, and (D) cross-sectional image.
Figure 3A shows that the WCA on the modified copper oxide nanoribbons array film is about 153.6°. The formation mechanism of superhydrophobicity can be expressed by Cassie equation (Wenzel, 1936), which is as follows:
where θ* is the WCA on the modified copper oxide nanoribbons arrays film, θ is the WCA on the smooth copper sheet, and f1 is the fraction of solid in contact with the water droplets. It can be estimated from Figure 1 that the value of f1 is about 0.1. The WCA on the smooth copper sheet is about 85°. The theoretical calculation results are in good agreement with the experimental results. After the heat treatment at 400°C in a muffle furnace for 150 s, the wettability of prepared film becomes superhydrophilic and the WCA is about 0°, as shown in Figure 3B. The film can recover its superhydrophobic properties after re-modification with stearic acid for 10 s. This process can be repeated for at least 4 cycles, as shown in Figure 4.
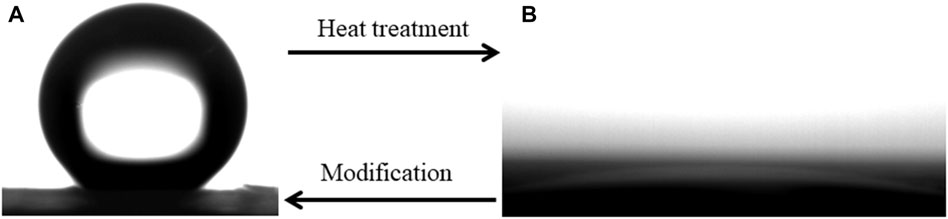
FIGURE 3. Shapes of water droplets on the prepare film (A) superhydrophobic and (B) superhydrophilic under the alternation of heat treatment and re-modification.
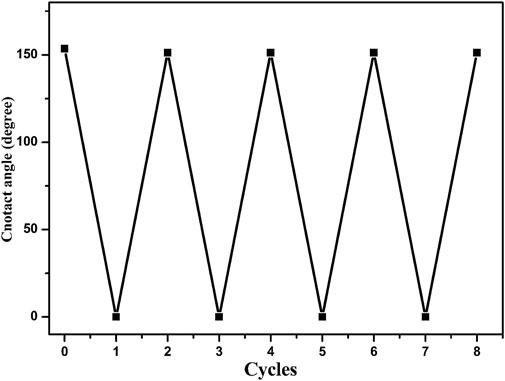
FIGURE 4. The reversible wettability transition between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity under the alternation of heat treatment and re-modification.
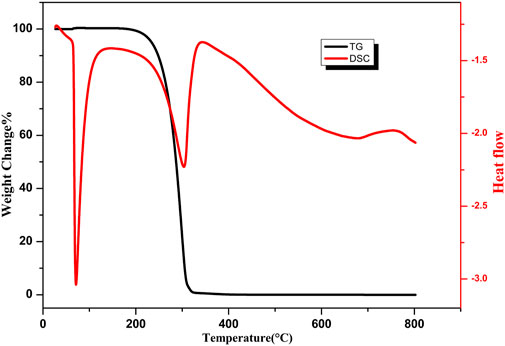
Rough structure and low surface energy organic matter are important factors to obtain the superhydrophobic surface. Stearic acid is a commonly used modifier to obtain a low surface energy (Li H. et al., 2019). Figure 5 shows the Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of copper oxide nanoribbons arrays, copper oxide nanoribbons arrays after modification by stearic acid, and copper oxide nanoribbons arrays after heat treatment. Figure 5A shows the three characteristic absorption peaks of copper oxide. This indicates nanoribbons arrays fabricated on the copper sheet are copper oxide. As shown in Figure 5B, two absorption peaks at 2,918 and 2,850 cm−1 are derived from the stretching vibration of the C–H bond (Meth and Sukenik, 2003). This indicates that stearic acid forms a self-assembled monolayer on the surface of the sample. A new absorption peak appears at 1,585 cm−1 corresponding to -COOH- groups, indicating that stearic acid forms a chemical bond with copper oxide. When copper oxide was heated, Figure 5C depicts that the three peaks that belong to stearic acid in Figure 5B disappear. To explain the disappearance of the absorption peaks, Figure 6 presents results from the thermogravimetric analysis differential scanning calorimetric (TG-DSC) of stearic acid. A distinct endothermal peak appears at near 300°C. This demonstrates that the stearic acid coating on the surface of copper oxide is totally decomposed. Therefore, it can be inferred that the wettability transition from superhydrophobicity to superhydrophilicity is due to the increase of surface energy after the heat treatment. The wettability of the prepared film will turn into superhydrophobic after re-modification, as shown in Figure 3.
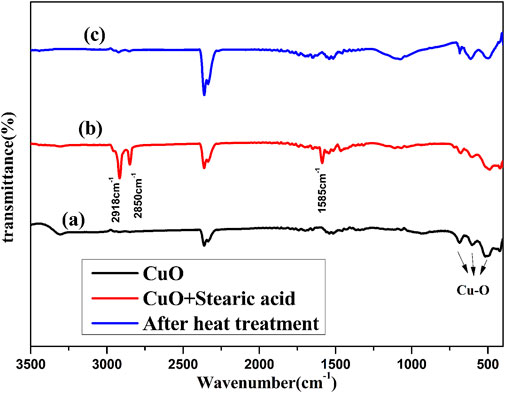
FIGURE 5. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of copper oxide nanoribbons arrays (A), copper oxide nanoribbons arrays after modification by stearic acid (B), and copper oxide nanoribbons arrays after heat treatment (C).
Corrosion Resistance and Mechanism
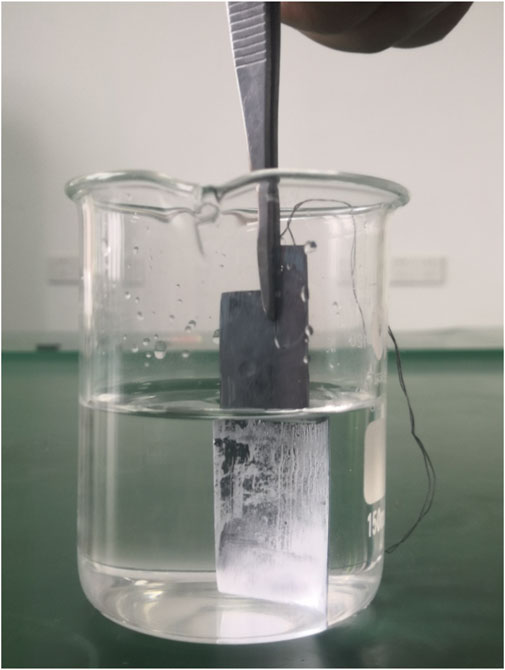
Figure 7 presents the digital graph of prepared film immersed into 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. It can be seen that the surface of the prepared film is relatively bright due to total reflection. Air is a medium with a lower refractive index relative to the sodium chloride solution. The incident ray will all be reflected if the incident angle is greater than a certain critical angle. This suggests that a lot of air is trapped among the rough structure of the prepared film. Meanwhile, this trapped air can protect the copper sheet through blocking the contact of corrosion solution and copper. Thus, this superhydrophobic film can be used to prevent metal corrosion.
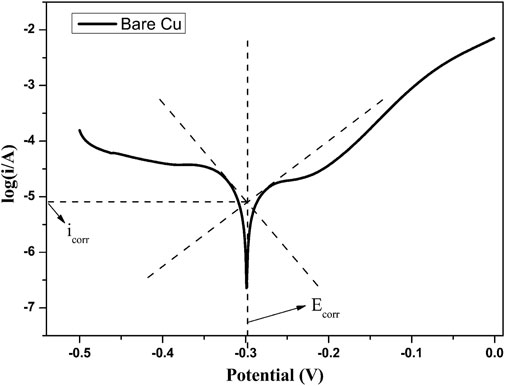
In order to investigate the corrosion resistant property of the prepared film, Figure 8 shows the potentiodynamic polarization curves of a bare copper sheet, superhydrophilic film, and superhydrophobic film. Taking bare copper as an example (Figure 9), the values of Ecorr and icorr can be obtained from Tafel polarization curves. In general, the lower corrosion current and more positive corrosion potential means better corrosion resistance. The corrosion potential of the samples was −0.299, −0.331, and −0.136 V, respectively. The parameters associated with Tafel curves are summarized in Table. 1.
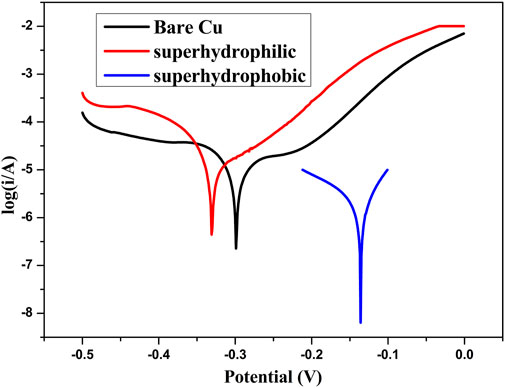
FIGURE 8. Potentiodynamic polarization curves of bare copper, superhydrophilic film, and superhydrophobic film.
The corresponding corrosion inhibition efficiency can be expressed as follows (Li et al., 2019b):
where
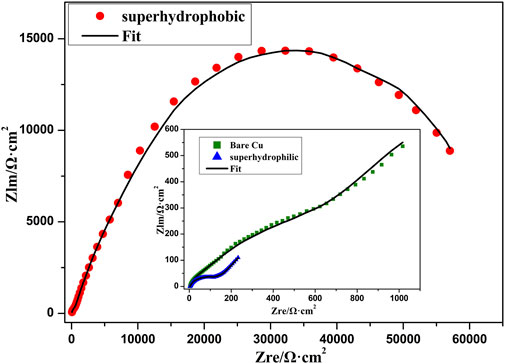
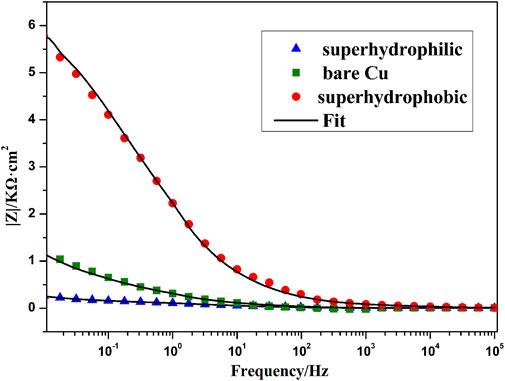
Figure 10 shows the Nyquist plots of bare copper sheet, superhydrophilic film, and superhydrophobic film. The Nyquist plots of bare copper sheet and superhydrophilic film are made up of a circular arc at a high frequency and a straight line at a low frequency. It is well known that the larger arc radius means a larger resistance. In addition, the higher the slopes of Warburg impedance, the faster the electrolyte ion diffusion at the electrode interface. Thus, the bare copper sheet exhibits better corrosion resistance than the superhydrophilic film. The impedance semicircle diameter of superhydrophobic film is about tens of thousands of Ω·cm2, which is consistent with results in Figure 8 and Table 1. In the Bode plot (as shown in Figure 11), the superhydrophobic surface has the largest impedance modulus. An equivalent circuit shown in Figure 12 was proposed to fit the Nyquist plots of three samples. As shown in Figure 12A, the equivalent circuit model representing the electrochemical behavior of the copper sheet and superhydrophilic film, demonstrated by the similar Nyquist plot. Rs, Rp, Rt, W, and CPE represent solution resistance, corrosion layer resistance, charge transfer resistance, diffusion resistance, and double-layer capacitance, respectively (Siddiqui et al., 2021b). The equivalent circuit of superhydrophobic film is presented in Figure 12B. Rf and Cf represent the resistance and capacitance of the air layer, respectively. After fitting, the electrochemical parameters of three samples are shown in Table. 2. It can be seen that the superhydrophobic film has the best corrosion resistance.
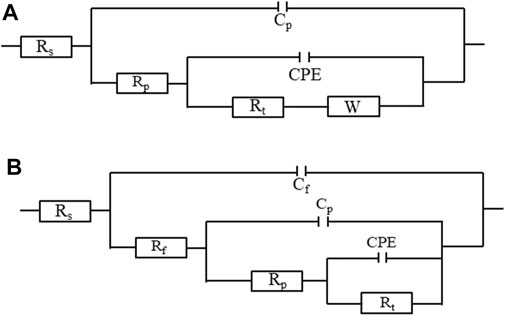
FIGURE 12. The equivalent circuit about cooper substrate, superhydrophilic film (A), and superhydrophobic film (B) after immersion in simulated seawater.
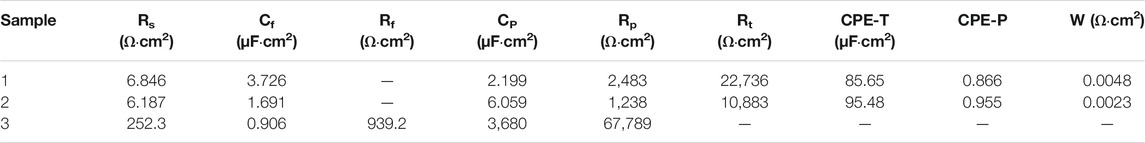
TABLE 2. Corresponding fitted electrochemical parameters of bare copper sheet, superhydrophilic film and superhydrophobic film after immersion in simulated seawater. The three samples are labeled as 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
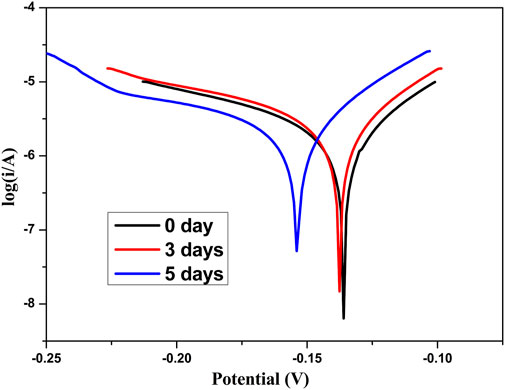
In order to evaluate the actual anticorrosion behavior of the superhydrophobic film, Figure 13 shows the Tafel curves of superhydrophobic film after in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution for 3 and 5 days. The corresponding corrosion current density (icorr) and the corrosion potential (Ecorr) are summarized in Table 3. With the increase of soaking time from 0 to 5 days, the corrosion inhibition efficiency only decreases from 93.24 to 86.94%. This indicates that the air which is trapped in the micro/nano-scale hierarchical structure can slow the chlorine ion attack on metal surfaces. Figure 14 shows the Nyquist plot of the superhydrophobic film after in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution for different times. The impedance semicircle diameters of the superhydrophobic film decrease slowly even after immersion for 5 days.
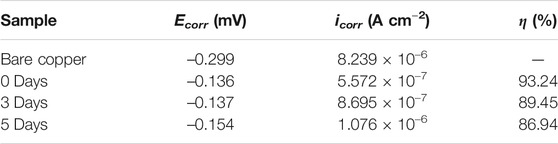
TABLE 3. Potential dynamic results of the superhydrophobic film after immersion in simulated seawater for different times.
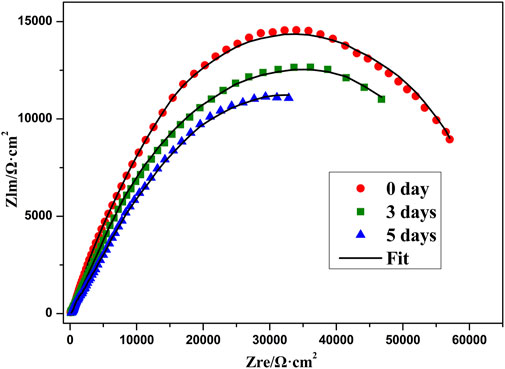
FIGURE 14. Nyquist plot of superhydrophobic film after in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution for different times.
Durability of Superhydrophobic Surface
In practical applications, superhydrophobic surfaces are often exposed to acidic or alkaline environments, so it is essential for superhydrophobic surfaces to have a good stability. The prepared superhydropbhobic surfaces are immersed in solutions of pH = 4 and 10 at different times (Figure 15). The WCA decreased slowly with the increase of immersion time in both alkaline and acidic environments. However, the WCA decreases slowly in alkaline solution in comparison with the acidic solution. This behavior indicates that the superhydrophobic surface is more resistant to the alkaline environment than an acidic one.
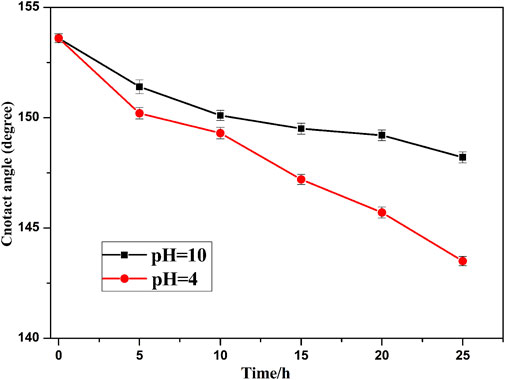
FIGURE 15. The WCA is tested after immersion in solutions of pH = 4 and pH = 10 with different times.
Conclusion
In summary, the copper sheet-based copper oxide nanoribbons arrays are fabricated through a simple low temperature hydrothermal method. The wettability of the prepared film is superhydrophobic after modification by stearic acid with a WCA of 153.6°. In addition, the WCA can reach up to 0° after heat treatment at 400°C for 150 s. The reversible wettability transition between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity can be easily achieved by heat treatment and modification. Meanwhile, the entire transition time requires only 170 s. The electrochemical measurement results illustrate that the superhydrophobic film has higher anticorrosion performance. Even if the superhydrophobic film was immersed in simulated seawater for 5 days, its corrosion inhibition efficiency only decreases from 93.24 to 86.94%. Therefore, this article may provide a useful attempt for corrosion protection.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
TC, YL, XF, XC and QL participated in the discussion and gave useful suggestions. The manuscript was composed by HL and JZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1808085ME140), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11974127 and 51973078), and the Natural Science general Foundation of Anhui Higher Education Institutions of China (KJ2020B09).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bagheri, H., Aliofkhazraei, M., Mojiri Forooshani, H., and Sabour Rouhaghdam, A. (2017). Electrodeposition of the Hierarchical Dual Structured (HDS) Nanocrystalline Ni Surface with High Water Repellency and Self-Cleaning Properties. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 80, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2017.07.023
Bagheri, H., Aliofkhazraei, M., Forooshani, H. M., and Rouhaghdam, A. S. (2018). Facile Fabrication of Uniform Hierarchical Structured (UHS) Nanocomposite Surface with High Water Repellency and Self-Cleaning Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 436, 1134–1146. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.156
Barati Darband, G., Aliofkhazraei, M., Khorsand, S., Sokhanvar, S., and Kaboli, A. (2020). Science and Engineering of Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Review of Corrosion Resistance, Chemical and Mechanical Stability. Arabian J. Chem. 13, 1763–1802. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.01.013
Brehm, M., Scheiger, J. M., Welle, A., and Levkin, P. A. (2020). Reversible Surface Wettability by Silanization. Adv. Mater. Inter. 7, 1902134. doi:10.1002/admi.201902134
Chen, K., Jia, J., Zhao, Y., Lv, K., and Wang, C. (2017). Transparent Smart Surface with pH-Induced Wettability Transition between Superhydrophobicity and Underwater Superoleophobicity. Mater. Des. 135, 69–76. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2017.09.017
Cheng, M., He, H., Zhu, H., Guo, W., Chen, W., Xue, F., et al. (2019). Preparation and Properties of pH-Responsive Reversible-Wettability Biomass Cellulose-Based Material for Controllable Oil/water Separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 203, 246–255. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.051
Ding, R., Li, W., Wang, X., Gui, T., Li, B., Han, P., et al. (2018). A Brief Review of Corrosion Protective Films and Coatings Based on Graphene and Graphene Oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 764, 1039–1055. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.133
Forooshani, H. M., Aliofkhazraei, M., and Rouhaghdam, A. S. (2017). Superhydrophobic Aluminum Surfaces by Mechanical/chemical Combined Method and its Corrosion Behavior. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 72, 220–235. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.014
Forooshani, H. M., Aliofkhazraei, M., and Rouhaghdam, A. S. (2017). Superhydrophobic Copper Surfaces by Shot Peening and Chemical Treatment. Surf. Rev. Lett. 24, 1750093. doi:10.1142/s0218625x17500937
Forooshani, H. M., Aliofkhazraei, M., and Bagheri, H. (2019). Fabrication of Hierarchical Dual Structured (HDS) Nickel Surfaces and Their Corrosion Behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 784, 556–573. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.079
Hatte, S., and Pitchumani, R. (2021). Analytical Model for Drag Reduction on Liquid-Infused Structured Non-wetting Surfaces. Soft Matter 17, 1388–1403. doi:10.1039/d0sm01272f
Idriss, H., Elashnikov, R., Guselnikova, O., Postnikov, P., Kolska, Z., Lyutakov, O., et al. (2020). Reversible Wettability Switching of Piezo-Responsive Nanostructured Polymer Fibers by Electric Field, Chem. Pap. 75, 191–196. doi:10.1007/s11696-020-01290-3
Jiang, C., Liu, W., Yang, M., Liu, C., He, S., Xie, Y., et al. (2019). Robust Multifunctional Superhydrophobic Fabric with UV Induced Reversible Wettability, Photocatalytic Self-Cleaning Property, and Oil-Water Separation via Thiol-Ene Click Chemistry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 463, 34–44. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.197
Li, W., Guo, T., Meng, T., Huang, Y., Li, X., Yan, W., et al. (2013). Enhanced Reversible Wettability Conversion of Micro-nano Hierarchical TiO2/SiO2 Composite Films under UV Irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 283, 12–18. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.085
Li, X., Jiang, Y., Jiang, Z., Li, Y., Wen, C., and Lian, J. (2019a). Reversible Wettability Transition between Superhydrophilicity and Superhydrophobicity through Alternate Heating-Reheating Cycle on Laser-Ablated Brass Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 492, 349–361. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.145
Li, X., Shi, T., Li, B., Chen, X., Zhang, C., Guo, Z., et al. (2019b). Subtractive Manufacturing of Stable Hierarchical Micro-nano Structures on AA5052 Sheet with Enhanced Water Repellence and Durable Corrosion Resistance. Mater. Des. 183, 108152. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108152
Li, H., Lu, H., Liu, S., Li, Q., and Liu, Q. (2019). SiO2 Shell on ZnO Nanoflake Arrays for UV-Durable Superhydrophobicity on Al Substrate. Mater. Res. Bull. 114, 85–89. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.02.022
Meth, S., and Sukenik, C. N. (2003). Siloxane-anchored Thin Films on Silicon Dioxide-Modified Stainless Steel. Thin Solid Films 425, 49–58. doi:10.1016/s0040-6090(02)01296-8
Siddiqui, A. R., Li, W., Wang, F., Ou, J., and Amirfazli, A. (2021). One-step Fabrication of Transparent Superhydrophobic Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 542, 148534. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148534
Siddiqui, A. R., Maurya, R., Katiyar, P. K., and Balani, K. (2021). Superhydrophobic, Self-Cleaning Carbon Nanofiber CVD Coating for Corrosion protection of AISI 1020 Steel and AZ31 Magnesium Alloys. Surf. Coat. Tech. 404, 126421. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126421
Taghvaei, E., Afzali, N., Taghvaei, N., and Moosavi, A. (2021). Mechanically Stable Superhydrophobic Nanostructured Aluminum Mesh with Reduced Water Surface Friction. Nanotechnology 32, 195302. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/abe071
Velayi, E., and Norouzbeigi, R. (2019). Fabrication of Fluorine-free ZnO/CuO Nanocomposite Superantiwetting Surfaces with Reversible Wettability Tuning. Surf. Coat. Technol. 367, 252–261. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.04.007
Wan, Y., Chen, M., Liu, W., Shen, X., Min, Y., and Xu, Q. (2018). The Research on Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surfaces of Pure Copper by Hydrothermal Method and its Corrosion Resistance. Electrochim. Acta 270, 310–318. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2018.03.060
Wang, J., Pei, X., Zhang, J., Liu, S., Li, Y., and Wang, C. (2021). Reversible Switch of Wettability of ZnO@stearic Acid Nanoarray through Alternative Irradiation and Heat-Treatment. Ceramics Int. 47, 9164–9168. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.041
Wenzel, R. N. (1936). Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 28, 988–994. doi:10.1021/ie50320a024
Yang, H., Hu, X., Su, C., Liu, Y., and Chen, R. (2017). Reversibly Photo-Switchable Wettability of Stearic Acid Monolayer Modified Bismuth-Based Micro-/nanomaterials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 31666–31674. doi:10.1039/c7cp05848a
Yu, X., Wang, Z., Jiang, Y., Shi, F., and Zhang, X. (2005). Reversible pH-Responsive Surface: from Superhydrophobicity to Superhydrophilicity. Adv. Mater. 17, 1289–1293. doi:10.1002/adma.200401646
Yu, N., Kiani, S., Xu, M., and Kim, C.-J. C. (2021). Brightness of Microtrench Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Visual Detection of Intermediate Wetting States. Langmuir 37, 1206–1214. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03172
Zhao, X., Wei, J., Li, B., Li, S., Tian, N., Jing, L., et al. (2020). A Self-Healing Superamphiphobic Coating for Efficient Corrosion Protection of Magnesium Alloy. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 575, 140–149. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.097
Keywords: corrosion protection, superhydrophobic surface, reversible transition, copper oxide nanoribbons arrays, hydrothermal method
Citation: Li H, Chen T, Lu Y, Fu X, Chu X, Liu Q and Zhang J (2021) Reversible Superwetting Transition Between Superhydrophilicity and Superhydrophobicity on a Copper Sheet, and Its Corrosion Performance. Front. Mater. 8:710377. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2021.710377
Received: 16 May 2021; Accepted: 05 July 2021;
Published: 12 August 2021.
Edited by:
Her-Hsiung Huang, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Mahmood Aliofkhazraei, Tarbiat Modares University, IranYuri Alexandre Meyer, State University of Campinas, Brazil
Copyright © 2021 Li, Chen, Lu, Fu, Chu, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong Li, bGlob25nZ3JlYXRAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Hong Li
Hong Li Tiange Chen2
Tiange Chen2 Qinzhuang Liu
Qinzhuang Liu