- 1Department of Periodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Science (SIMATS), Chennai, India
- 2Instituto de Alta Investigacion, Universidad de Tarapacá, Arica, Chile
- 3Toxioclogy, Arba Minch University, Ethiopia
- 4Department of Mechanical Engineering, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai, India
- 5Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Science and Humanities, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur, Tamil Nadu, India
- 6Department of Chemistry, Graphic Era (Deemed to be University), Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
- 7Center for Supramolecular Chemistry and Catalysis and Department of Chemistry, College of Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
The escalating accumulation of toxic wastes and biowastes constitutes a critical environmental crisis that demands immediate and effective solutions. Traditional waste treatment methods, predominantly chemical and physical, are increasingly viewed as unsustainable, burdened by high operational costs and the risk of generating secondary pollutants. Against this backdrop, bioremediation emerges as a crucial and sustainable alternative, utilizing the natural detoxifying capabilities of microorganisms. This review article focuses on the use of fungal and bacterial strategies in bioremediation, emphasizing their vital role in the degradation, stabilization, or detoxification of pollutants. We provide an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms by which fungi and bacteria break down various contaminants, presenting a current snapshot of the field’s state of knowledge. The article highlights recent innovative advancements that improve the effectiveness and expand the applicability of bioremediation technologies. Moreover, it discusses the practical challenges of scaling these solutions to meet global environmental needs and suggests directions for future research and implementation. This synthesis not only underscores the significance of microbial bioremediation in addressing pressing environmental problems but also acts as a call to action for continued innovation in the sustainable management of hazardous wastes.
1 Introduction
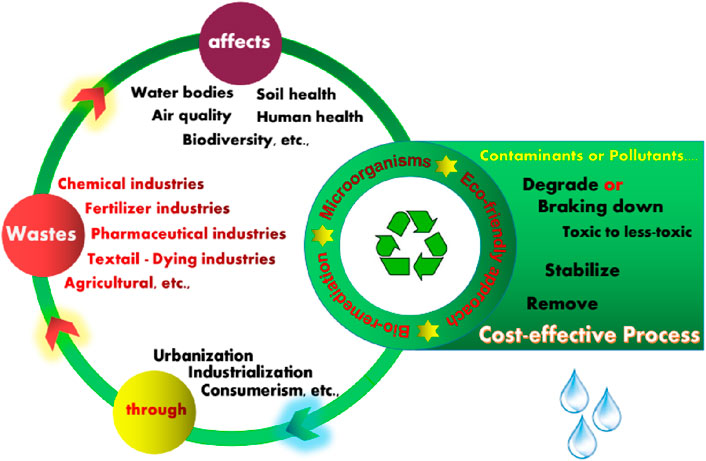
In a world marked by rapid industrial and technological progress, our achievements are shadowed by the escalating generation of toxic waste (ToxicW) and biowaste (BioW). This expansion, highlighted in Khandaker et al. (2022), has led to pressing environmental challenges. Mismanagement and improper disposal of these wastes jeopardize water resources, soil vitality, air quality, human health, and biodiversity. Toxic waste, which includes a spectrum of hazardous substances from heavy metals—such as arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), nickel (Ni), tin (Sn), vanadium (V), and zinc (Zn)—to persistent organic pollutants, carries risks of bioaccumulation, potentially causing long-term ecological and health problems (Vodyanitskii, 2013; Naja and Volesky, 2017). Amidst increasing urbanization, industrialization, and consumerism, the need for innovative and sustainable waste remediation technologies is more critical than ever. This urgency has spurred scientific exploration into natural solutions, notably the potential of microorganisms for bioremediation (BioR) processes, opening new pathways for environmental recovery (Figure 1).
BioR stands out as a sustainable and cost-effective method to tackle environmental pollution through the natural degradative capabilities of fungi and bacteria, offering an advantageous alternative to conventional chemical and physical treatments that can be expensive and generate secondary pollutants. For instance, fungi like Phanerochaete chrysosporium utilize extracellular enzymes to break down complex pollutants such as PAHs and dioxins in contaminated soils, reducing their toxicity. Similarly, bacterial strategies, notably demonstrated during the Exxon Valdez oil spill, involve species like Pseudomonas and Alcanivorax, which degrade oil into less harmful substances using biosurfactants to enhance microbial access to pollutants. Additionally, certain bacteria such as Cupriavidus metallidurans address heavy metal contamination by transforming toxic metals into less harmful precipitates. These examples highlight the effectiveness of microbial bioremediation in transforming hazardous waste to benign forms, with ongoing research promising to broaden their applicability and scalability, further bolstering their role in future environmental remediation efforts (Maheshwari et al., 2014).
This review ambitiously sets out to dissect and thoughtfully scrutinize the application of fungal and bacterial BioR, ToxicW and BioW. By delving into the symbiotic dynamics between these microorganisms and hazardous substances, it aims to shed light on the innovative strides, practical hurdles, and prospective trajectories within the field. Citing sources such as Addagada et al., 2023; Sahu et al., 2023, this analysis leverages a wealth of current literature, illustrative case studies, and empirical data. The overarching goal is to forge a nuanced understanding of how these bioremediation strategies can be fine-tuned and expanded, thus significantly bolstering efforts toward environmental preservation and public health enhancement.
In pursuit of these goals, the review will explore a variety of essential themes, such as the distinct metabolic pathways employed by fungi and bacteria for decomposing diverse pollutants, the factors that impact the efficiency of bioremediation processes, and the cutting-edge methods being crafted to boost the microbial breakdown of more resilient and intricate contaminants (refer to Figure 2). This synthesis of information is designed to provide meaningful perspectives on the evolution of waste management and environmental clean-up, highlighting the pivotal contributions of microbial biotechnologies toward a greener, pollutant-free environment (Sharma, 2020).
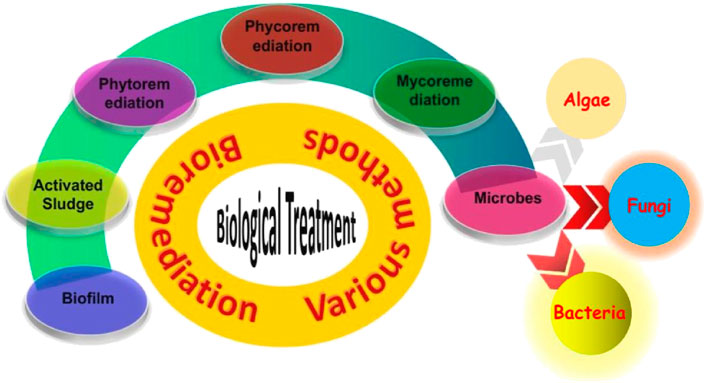
Figure 2. Structure of the review. Highlighting the various approaches, strategies, approaches and techniques adapted for the treatment of toxic and biowaste.
2 Classification and principles of bioremediation
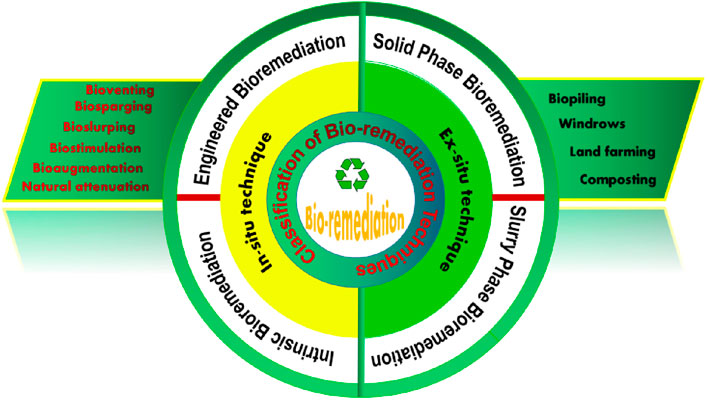
BioR stands out as a crucial strategy for environmental cleanup, using the detoxification abilities of fungi and bacteria to transform pollutants into less harmful substances. This approach addresses pollution from industrial, agricultural, and accidental sources through in situ (on-site) and ex situ (off-site) techniques (Figure 3), including bioventing, biostimulation, and bioaugmentation, tailored to specific pollutants and conditions (Khatun et al., 2024). Microorganisms degrade pollutants through complex mechanisms influenced by oxygen, temperature, pH, and nutrient availability, breaking down compounds into simpler, assimilable forms. Fungi, especially white-rot fungi, excel in decomposing organic pollutants like Poly Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and pesticides with their enzymatic toolkit but have limitations like slower growth and specific environmental needs (Chane et al., 2024; Navina et al., 2024). Bacteria offer rapid degradation of a wide range of pollutants under various conditions and are key to treating oil spills and heavy metals, though they may require assistance for more complex compounds.
Due to their high protein, amino acid, and bioactive content, mushrooms and other members of the fungus class are regarded as edible and are consumed for their nutritional and medicinal benefits (Hamza et al., 2024). This segment explores the strategies and mechanisms underlying fungal BioR, focusing on white-rot fungi and their applications in various environmental contexts.
2.1 Types of bioremediations
Ex-situ and In-situ BioRs are two categories into which BioR approaches can be divided based on the application or process location (Figure 3).
2.2 In-situ bioremediation techniques
In-situ BioR involves treating contaminants at their original location without excavating or removing the contaminated materials. Since the contaminated soil is handled directly at the source of the pollution, it is less expensive than ex-situ BioR methods. Microbes in the contaminated soil improve certain in-situ BioR methods (Kuppusamy et al., 2016; Hussain et al., 2022). Polluted sites containing hydrocarbons, heavy metals, dyes, and chlorinated solvents have been successfully treated using in-situ BioR approaches.
Intrinsic Bioremediation harnesses and amplifies the inherent microbial populations within contaminated zones by supplying nutrients or other enhancements, accelerating the degradation of pollutants. Bioslurping innovatively merges vacuum extraction with bioventing techniques to extract pollutants directly from groundwater while fostering the aerobic decomposition of contaminants. Bioventing actively injects oxygen into subterranean environments, sparking the activation of microbes that methodically break down organic pollutants present in the soil and groundwater (Kakkar and Kumar, 2024). Biosparging injects air or oxygen into groundwater to bolster the efficacy of aerobic microbes, enhancing the breakdown of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Bioaugmentation enriches contaminated sites with specific microbial strains or enzymes to boost the degradation potential, thereby augmenting the native microbial community. Phytoremediation strategically employs various plant species and their associated microbial partners to absorb, dismantle, or sequester contaminants from soil, water, or air, targeting a diverse range of pollutants (Devendrapandi et al., 2024). Mycoremediation utilizes the enzymatic power of fungi, leveraging the complex network of their mycelium to efficiently decompose a broad spectrum of pollutants, including hydrocarbons and heavy metals. Phycoremediation employs algae and other aquatic plants to purify water from pollutants through dynamic processes such as absorption, adsorption, or transformation, demonstrating significant advantages in nutrient removal and wastewater treatment (Barman et al., 2024; Sultana et al., 2024).
These diverse BioR techniques offer effective and sustainable solutions for cleaning up ToxicW sites, with options tailored to specific contaminants and environmental conditions. Further, each BioR technique offers advantages depending on the type and extent of contamination, site characteristics, and regulatory requirements. Integrating both ex-situ and in-situ approaches can provide comprehensive and effective solutions for remediation of ToxicW sites. The integration of fungal and bacterial strengths through consortia presents a synergistic approach, enhancing the degradation of a broader pollutant range and boosting BioR efficiency (Wibowo et al., 2024). This collaborative method underscores the potential of BioR in achieving a cleaner, more sustainable environment by leveraging the complementary capabilities of these microorganisms.
In-situ bioremediation stands out as a cost-efficient method for cleaning up large areas of contamination, effectively reaching spots that might otherwise be inaccessible. This technique is particularly noted for its ability to handle both organic and inorganic pollutants, thereby offering a versatile approach to environmental cleanup. It surpasses conventional pump-and-treat methods by achieving faster rates of remediation, which facilitates the quick restoration of environmental health (Rani et al., 2024). However, in-situ bioremediation is not without its challenges, especially when dealing with low-level pollution. The process heavily relies on the presence and activity of indigenous microorganisms, which can be hindered by the presence of heavy metals. Moreover, the metabolic processes involved can sometimes produce more toxic intermediates than the original pollutants. Additionally, certain stubborn contaminants remain resistant to this form of treatment (Sakhaei et al., 2024). Thus, it is imperative to assess the suitability of in-situ bioremediation on a case-by-case basis to ensure its effectiveness in mitigating environmental pollution.
2.3 Ex-situ methods of bioremediation
Ex-situ bioremediation involves the process of removing contaminated materials from their original sites to treat them in a controlled environment. This method is chosen based on several factors, including the depth and concentration of pollution, the cost of treatment, the type of pollution, and the geographic location of the contaminated site. The treatment can employ either slurry phases that contain bioremediators or solid phases with bioremediators, depending on the specifics of the pollution and the remediation goals (Nano et al., 2003; Wilcox et al., 2024). Techniques such as biopiles, windrows, landfarming, composting, and bioreactors fall under the umbrella of ex-situ bioremediation, each with its distinct approach to facilitating the degradation of pollutants by microorganisms under optimal conditions.
Biopiles and windrows techniques involve piling contaminated soil and periodically turning it to introduce oxygen and enhance microbial degradation. While biopiles mix soil with bulking agents, nutrients, and moisture to create favorable conditions, windrows, arranged in long rows, are more suitable for large-scale projects due to their ease of aeration (Laubach et al., 2024). Landfarming spreads contaminated soil over a large area, incorporating regular tilling to boost microbial activity, making it ideal for treating soil polluted with petroleum hydrocarbons. Composting, on the other hand, is effective for organic pollutants and biodegradable waste, mixing contaminated material with bulking agents and ensuring aerobic conditions for decomposition (Dahiya et al., 2024; Yaashikaa et al., 2024). Lastly, bioreactors, which can operate under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, optimize environmental conditions in engineered systems to treat contaminated water or soil, catering to a broad spectrum of contaminants.
Our innovative ex-situ bioremediation system brings a plethora of advantages to the forefront of environmental cleanup efforts. Harnessing the precision of controlled degradation, our biodegradation system maximizes the efficacy of breaking down pollutants to unprecedented levels. It stands out for its adaptability, efficiently neutralizing a diverse spectrum of contaminants (Alkhanjaf et al., 2024). This innovation not only abbreviates the timeline for treatment processes but also amplifies productivity significantly. As a result, it positions itself as a robust and sustainable powerhouse, propelling forward the pace of environmental clean-up initiatives. Despite its numerous strengths, the system does face hurdles, especially in ex-situ bioremediation scenarios where chlorinated hydrocarbons are involved (Saad et al., 2024). The soil type, particularly impermeable varieties, can impede biodegradation effectiveness. Addressing this challenge may require preparatory treatments to enhance soil receptivity to bioremediation. Such nuances underscore the complexity of environmental remediation and accentuate the necessity for remediation strategies that are both flexible and powerful, capable of adapting to varied ecological conditions.
3 Fungal bioremediation: strategies and mechanisms
Fungi are increasingly recognized for their vast potential in BioR applications, drawing attention due to their ability to originate from a variety of biological wastes, including those from agro-industrial, agricultural, and industrial sources. As eukaryotic organisms within the tree of life, fungi represent a diverse kingdom, yet their classification remains a subject of ongoing debate. The latest taxonomical update delineates fungi into nineteen major phyla, including Aphelidiomycota, Ascomycota, Basidiobolomycota, Basidiomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Calcarisporiellomycota, Caulochytriomycota, Chytridiomycota, Entomophthoromycota, Entorrhizomycota, Glomeromycota, Kickxellomycota, Monoblepharomycota, Mortierellomycota, Mucoromycota, Neocallimastigomycota, Olpidiomycota, Rozellomycota, and Zoopagomycota. While estimates suggest there are between two and four million fungal species, only about one million have been described so far (Coleine et al., 2024; Schreiber et al., 2024). Fungi, which are chemoheterotrophic, inhabit both aquatic and terrestrial environments. However, research has predominantly focused on terrestrial fungi, with less attention given to those in aquatic settings, especially marine ecosystems (Rahimlou et al., 2024). Notably, while the majority of known fungi are aerobic and thrive in oxic conditions, anaerobic varieties have been identified in animal digestive tracts and ocean oxygen minimum zones.
Fungi stand at the forefront of decomposing complex organic matter, with a remarkable proficiency in breaking down substances such as wood, lignin, cellulose, and various other plant-based materials often found in agricultural waste. This capability makes Fungal BioR (Bioremediation) a key player in environmental restoration efforts. What sets certain fungi apart is their extraordinary ability to degrade and eliminate a wide array of pollutants. These microorganisms are adept at transforming a variety of toxins, including hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and organic pollutants, into less harmful substances (Adnane et al., 2024; Navina et al., 2024). This versatility in dealing with contaminants stems from fungi’s ability to attack and metabolize a wide range of compound classes, both inorganic and organic, through their intra- and extracellular enzymatic machinery and their capacity to excrete acids. One notable feature of fungal enzymes is their low substrate selectivity, which, rather than being a drawback, proves advantageous (Hu and Scott, 2024). This characteristic allows the non-specific enzymes to catalyze a variety of reactions, enabling fungi to use a wide array of substances for carbon and energy sources. The biodegradation capabilities of fungi are largely linked to oxidative enzymatic reactions, driven by an assortment of oxidases and peroxidases. Consequently, an oxic environment is typically essential for fungi to prosper, as it facilitates these critical enzymatic processes.
Fungi display a remarkable range of enzymatic activities, segmented into intracellular and extracellular categories. Within the extracellular domain, enzymes such as oxidoreductases specifically laccases and peroxidases (including manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase) are fundamental. Laccases harness oxygen, while peroxidases utilize hydrogen peroxide as their electron acceptor. The generation of hydroxyl radicals, either through quinone cycling by laccases or via peroxide-dependent hydroxylations, is instrumental in the breakdown of pollutants’ cyclic or aliphatic structures, facilitating their transformation into simpler metabolites (Das et al., 2024; Mohamed et al., 2024). These exergonic reactions efficiently dismantle complex pollutant frameworks into manageable metabolite intermediates. On the intracellular front, an array of cytochromes drives a variety of oxidation processes. A notable illustration is Phanerochaete chrysosporium, which possesses an extensive array of 150 Cytochrome P450 genes, showcasing the extensive enzymatic capabilities endemic to fungi (refer to Figure 1; Table 1).
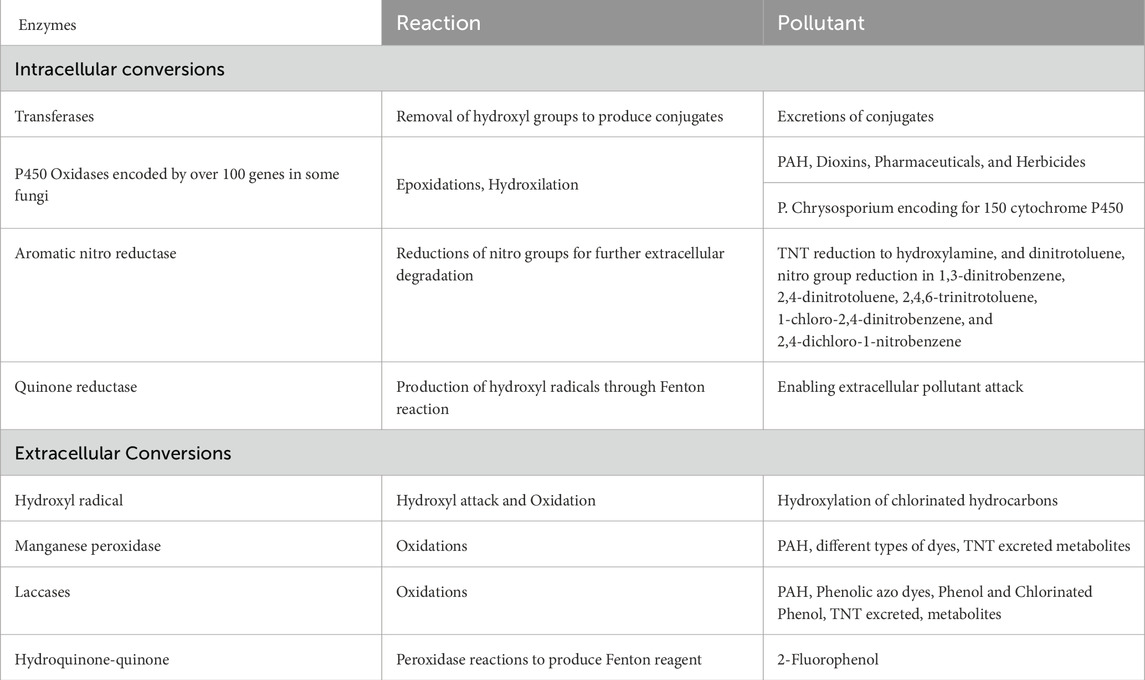
Table 1. Different types of extracellular and intracellular mechanisms observed in different types of enzymes for the degradation of toxic pollutants.
3.1 Mechanistic insights of degradation of PAH pollutants
PAHs constitute a significant class of environmental pollutants, with notable examples including naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene, pyrene, and benzo [a]pyrene. These compounds are ubiquitous in various environments due to their widespread sources, including incomplete combustion of organic matter such as fossil fuels, wood, and tobacco (Paniagua-Michel and Banat, 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). PAHs are of concern due to their persistence, toxicity, and potential carcinogenicity, posing risks to both human health and the environment. Efforts to mitigate PAH pollution involve understanding their sources, transport, transformation, and effective remediation strategies.
Since phenolic compounds are extensively found in industrial effluents and have a negative impact on human health, marine life, and animal life, biodegradation of these compounds is an efficient way to safeguard the environment worldwide. Another byproduct of the breakdown of several benzene conjugate compounds is phenol (Bhatia et al., 2024). After phenol is broken down or converted to catechol by phenol hydrolase, dioxygenases (catechol 1, 2, and three dioxygenases) react with the catechol to produce semialdehyde forms (Hexa-2,4-dienedioic acid and 2-Hydroxy Muconic semialdehyde respectively and finally both yields to Oxaloacetate, its is a metabolic intermediate in many processes). This is connected to the catechol’s ortho-and meta-cleavage. These forms are hydrolyzed to produce pyruvate (is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell) and acetaldehyde after being further oxidized to oxaloacetate (Proietti Tocca et al., 2024). The pathway of the phenol’s breakdown can be completed by metabolizing these end products to its most basic form (Figure 4).
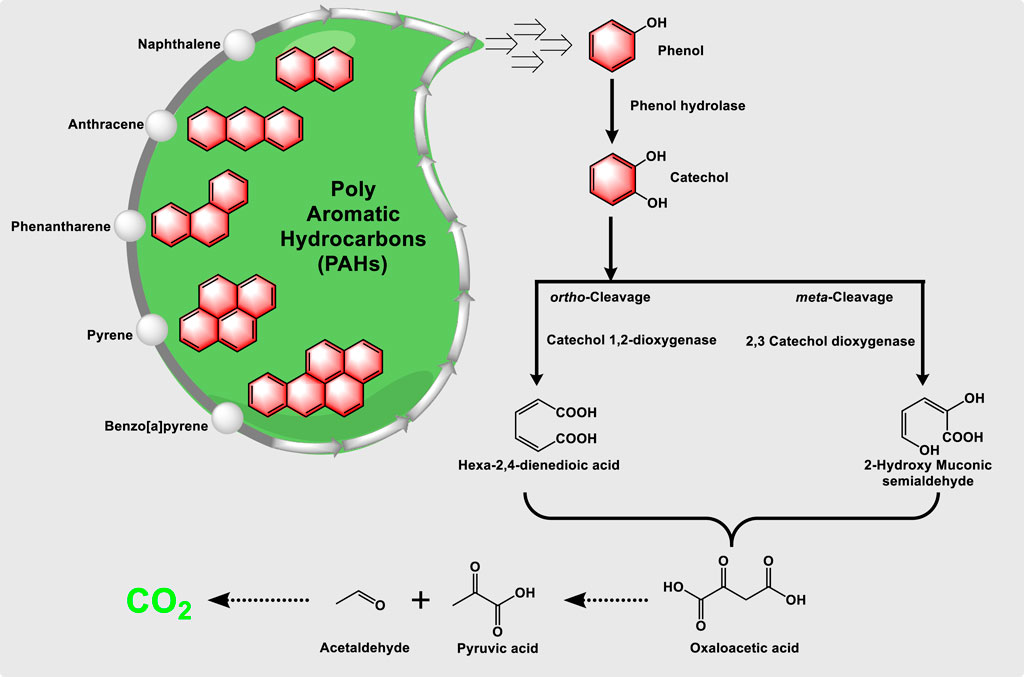
Figure 4. Degradation pathways of benzene conjugate compounds (PAHs) to phenol - Catechol (major degradation product) to simplest form as end-products, as CO2.
Fungal BioR harnesses the unique capabilities of fungi to degrade, transform, or detoxify pollutants through natural metabolic processes. Among the diverse fungal species, white-rot fungi stand out for their exceptional BioR potential, primarily due to their robust enzymatic systems capable of breaking down complex organic pollutants.
3.2 Mechanistic insights of degradation of heavy pollutants
Endophytic bacteria and Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) are key in heavy metal bioremediation. Endophytic bacteria dwell within plant tissues, shielding cells from metal stress. They alter heavy metal availability, reducing toxicity. Pseudomonas, Bacillus, and Rahnella species show notable resistance to Pb, Mn, and Cd. PGPR, including Bacillus, Enterobacter, and Pseudomonas, aid heavy metal-contaminated soil remediation (Karabulut et al., 2024). They enhance plant growth, produce beneficial compounds like phytohormones, and solubilize phosphate. Microorganisms, pervasive in nature, play vital roles in heavy metal bioremediation. They employ diverse mechanisms to combat toxicity, including using contaminants for nutrition and self-defense. Figure 5 depict microorganisms interacting with contaminants through biosorption and biotransformation mechanisms.
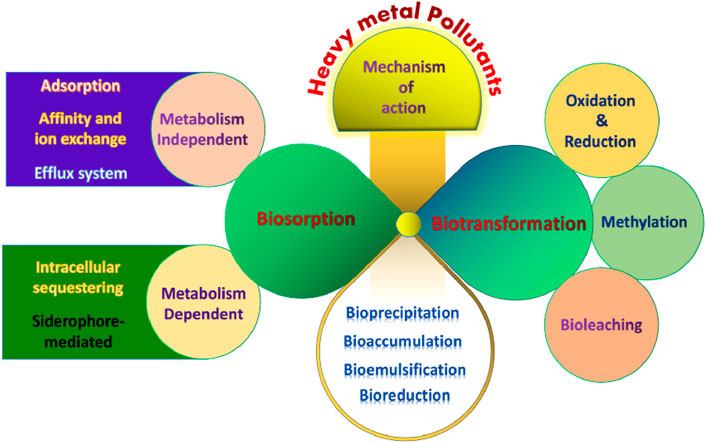
Figure 5. Diagram showing different mechanisms of bioremediation action for the heavy metal detoxification.
3.3 Metabolism-independent biosorption
Whether the cell was living or dead, this sort of biosorption relies on its chemical and physical characteristics. This category includes the following: Adsorption, known as extracellular sequestration, relies on cellular components’ affinity with metal ions in the periplasm (Roy et al., 2024). The extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) associated with bacterial cell walls plays a vital role in metal adsorption, containing polysaccharides, mucopolysaccharides, and proteins, along with functional groups facilitating heavy metal sequestering. Cunninghamella and Saccharomyces cerevisiae demonstrate promising heavy metal binding abilities, particularly in textile wastewater treatment, utilizing ion exchange methods (Yang et al., 2024). Efflux systems act as a crucial defense mechanism against heavy metal toxicity by forming a protective outer layer and expelling metal ions from the cytoplasm to the periplasmic region. Recent reports emphasize transformation and efflux as primary methods of bacterial resistance to heavy metals.
3.4 Metabolism-dependent biosorption
This mechanism involves the metabolic activity of viable microorganisms, contrasting with metabolism-independent biosorption. Bioaccumulation, also known as intracellular sequestering, entails the complexing of metals within the cytoplasm of cells (Jamir et al., 2024). As reported in studies examining Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens strain NRC-R cells using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), chromium accumulation inside the cell was confirmed through EDX analysis. Metal accumulation occurs through attachment to the cell surface, followed by slow penetration into the periplasm and ultimately reaching the cytoplasm, resembling a nutrient uptake process. It has been noted that cysteine-rich proteins play a crucial role in sequestering Zn, Cd, and Cu in Cd-tolerant Pseudomonas putida, while glutathione aids in Cd sequestration by Rhizobium leguminosarum (Chaudhary and Sindhu, 2024). Fungi also contribute significantly to the elimination of inorganic metals, utilizing their rigid cell walls as ligands in the decontamination process.
Siderophore-mediated biosorption, also referred to as chelation, is observed in aerobic soils where certain microorganisms produce siderophores facilitating the utilization of poorly water-soluble metals through an energy-dependent process. Microbacterium flavescens has been found to utilize siderophores for acquiring its iron nutritional requirements, and it employs desferrioxamine-(DF) siderophores to bind with U, Pu, and Fe (Kumar et al., 2024).
Biotransformation is a process that leverages the cellular metabolic activities of microorganisms to catalyze chemical reactions, primarily through redox mechanisms. This involves the alteration of metals’ oxidation states by reducing them, a phenomenon observed with elements like Cr, Se, U, and Hg in natural environments. Microorganisms serve as catalysts for both oxidation and reduction processes (Mushtaq et al., 2024). As oxidizing agents, they release electrons to react with anions in contaminated soil, thereby also aiding in the decontamination of organic compounds under anaerobic conditions. The process is significantly enhanced in the presence of iron (III). Reduction processes can be facilitated either directly, using a bioreactor in a pump and treat system, or indirectly, through soil excavation followed by inoculation with a suitable microbial consortium. An alternative, indirect method involves sulfate-reducing bacteria, which are essential for ecological balance. These bacteria can either reduce sulfate directly or form biofilms, aiding in the reduction process. This indirect approach is preferred for its cost-effectiveness and minimal environmental impact (Lin et al., 2024). The role of sulfate-reducing bacteria, such as Desulfosphorosinus spp. and Clostridium spp., is exemplified in the effective decontamination of uranium, showcasing their significance in bioremediation efforts.
Microbial methylation plays a crucial role in metal remediation, transforming metals like Hg(II), Se, As, and Pb into their volatile methylated forms. This process is facilitated by specific bacteria, including strains of Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Clostridium, and Bacillus, which aids in their removal from environments (Aryal, 2024). Another method, bioleaching, involves microorganisms that secrete compounds to detoxify metals via dissolution or precipitation. For example, some microbes can leach Cd using organic acids, and Citrobacter species can trigger metal phosphate precipitation by producing inorganic phosphate. Furthermore, the technique of plant-microbial remediation, particularly rhizoremediation, underscores the synergy between microorganisms and plants in enhancing bioremediation’s effectiveness and cost-efficiency, crucial for environmental cleanup. Mycorrhizal fungi, which form symbiotic relationships with plants, notably increase contaminant biodegradation and heavy metal biosorption. Research indicates that plants associated with mycorrhizal fungi show a significantly greater uptake of Cd than those without, underlining rhizoremediation’s potential (Fashola et al., 2024; Nkuna and Matambo, 2024). The processes involved in rhizoremediation encompass metal phosphate activation, acidification, organic acid production, chelation, and ion transport, each contributing to the comprehensive approach to environmental remediation.
3.5 Microorganisms responsible for bioremediation
Bioremediation, employing microorganisms to restore ecological balance and eliminate contaminants, aims to stimulate microbial metabolic activity through nutrient or chemical agents. Initially patented in 1981 for petroleum oil degradation by Pseudomonas putida, bioremediation enhances microbial tolerance and physiological activity to remove, destroy, or neutralize contaminants. Microbial consortium diversity influences heavy metal bioremediation efficiency, with indigenous and extraneous microorganisms utilized based on their source. Indigenous microorganisms, present at contamination sites, negate the need for constant monitoring (Joshi et al., 2024; Saravanan et al., 2024). Upon successful bioremediation, soil and water regain their usability, driven by mechanisms including metal ion accumulation, efflux, biotransformation, and methylation. This process underscores nature’s innate capacity for ecological restoration and the pivotal role of microbial communities in environmental sustainability.
3.6 White-rot fungi: nature’s detox agents
White-rot fungi are renowned for their ability to decompose lignin, a complex organic polymer found in wood, making them the only group of organisms capable of fully mineralizing lignin to carbon dioxide and water. This ability is attributed to their unique enzymatic toolkit, which includes lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase, and laccase. These enzymes catalyze the breakdown of a wide range of recalcitrant organic pollutants, such as PAHs, dioxins, and various pesticides, into smaller, less harmful molecules (Chepyala et al., 2024). The enzymatic degradation process initiated by white-rot fungi involves the generation of free radicals, which non-specifically attack and break the chemical bonds of pollutants (Figure 6). This oxidative mechanism allows for the degradation of substances that are resistant to other forms of biodegradation, offering a versatile solution for the treatment of ToxicW and BioW.
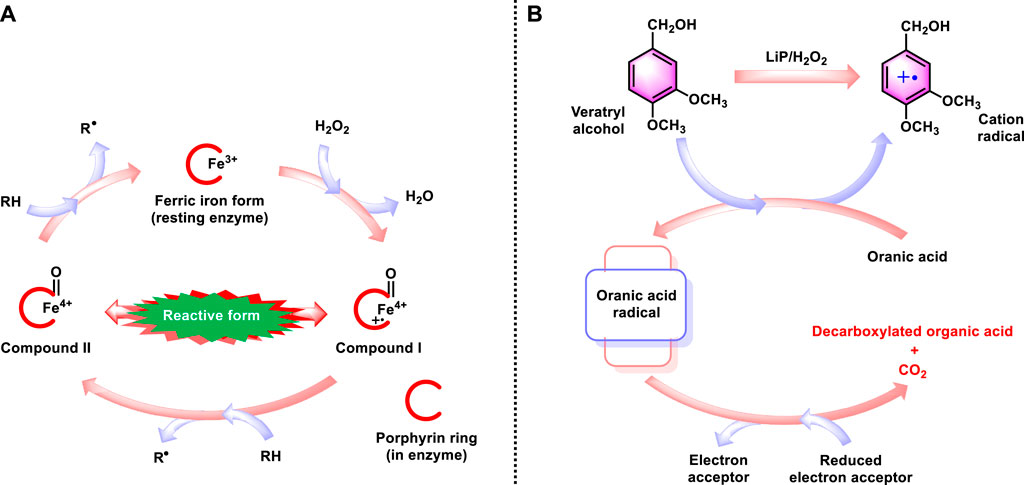
Figure 6. (A) Catalytic cycle for lignin peroxidases. The iron is in heme (protoporphyrin IX). (B) Mechanism for catalyzing reductions using lignin peroxidases. The fungus uses oxalate as the electron donor and EDTA can be used for this purpose. The electron acceptors include molecular oxygen to produce superoxide.
Generally, White rot fungus completely degrade lignin and a wide range of other environmental contaminants (toxic aromatic and non-aromatic hydrocarbons) through a number of different processes (Figure 6). For lignin and environmental contaminants to be metabolized, both oxidative and reductive processes are necessary. A family of peroxidases secreted by the fungi is used to catalyze the direct and indirect oxidation of substances. Reductions utilizing electron donors to produce reductive radicals can also be catalyzed by the peroxidases (Mohamed et al., 2024). TNT and other compounds can also be reduced using a cell-surface membrane potential.
White rot fungus has exceptional biodegradative properties. They can oxidize a wide variety of compounds, as well as different kinds of chemicals. As a result, complicated mixes can be handled, and substances that are typically thought to be very resistant to biodegradation can actually undergo breakdown (Hofrichter et al., 2010). The white rot fungus has a complicated biodegradation pathway. It is therefore necessary to comprehend the underlying mechanisms before applying it.
3.7 Strategies for enhancing fungal bioremediation
To optimize the BioR potential of white-rot fungi, several strategies have been developed. One approach involves the selection and adaptation of fungal strains that exhibit high degradation efficiencies under specific environmental conditions. Genetic engineering and mutation breeding techniques have also been employed to enhance the enzymatic activity and pollutant specificity of these fungi. Additionally, co-cultivation of white-rot fungi with other microbial species can lead to synergistic interactions, potentially increasing the range of pollutants that can be degraded and improving overall BioR efficiency (Stein et al., 2018). The application of fungal consortia, combining multiple fungal species with complementary degradation capabilities, offers another promising strategy for tackling complex mixtures of pollutants.
3.8 Case studies of fungal bioremediation success
Several case studies highlight the successful application of fungal BioR in diverse environmental settings. For instance, the use of white-rot fungi to treat contaminated soil at a former industrial site led to the significant reduction of PAH concentrations, demonstrating the feasibility of using fungi for in situ soil remediation. Another example involves the application of fungal bioreactors for the treatment of wastewater contaminated with synthetic dyes. Through the action of selected fungal strains, these bioreactors were able to degrade the dyes, effectively reducing the chemical and biological oxygen demand of the wastewater. In agricultural contexts, white-rot fungi have been used to degrade pesticide residues in soils, thereby mitigating the environmental impact of agricultural chemicals (Espinosa-Ortiz et al., 2022). These case studies exemplify the versatility and effectiveness of fungal BioR in addressing a wide array of environmental pollutants. In summary, fungal BioR, particularly through the action of white-rot fungi, offers a powerful and versatile approach for the detoxification of ToxicW and BioW. Through the deployment of strategic interventions and the leveraging of fungal enzymatic mechanisms, this BioR method holds significant promise for the sustainable management of contaminated environments.
4 Bacterial bioremediation: Techniques and applications
Bacterial BioR stands as a cornerstone in the field of environmental remediation, offering a biological avenue for the detoxification and degradation of ToxicW and BioW. A wide range of microorganisms are essential to the BioR process, which treats and recovers wastewater and reduces its environmental harm. Due to their ability to digest recalcitrant pollutants, which are typically left untreated by traditional WWT processes, these microorganisms hold great potential as a green technology tool for the WWT industry (Figure 2). The microorganisms receive energy in return, which allows them to grow and multiply. This section delves into the capabilities of bacterial species known for their BioR potential, the metabolic pathways they employ to tackle complex pollutants, and the innovative integration of bacterial and fungal systems to enhance BioR outcomes (Sravan et al., 2024).
Bacteria play a pivotal role in wastewater treatment (WWT) across the globe due to their vast range of enzymatic activities and their abundance in sewage water. These microorganisms exhibit a wide variety of sizes, typically ranging from about 0.5 to 5 μm (μm) and are characterized by several major shapes, including spherical, spiral, straight, and curved forms. Their cellular arrangement can vary based on their shape, presenting as individual cells, in pairs, or connected in chains. Bacteria are primarily categorized into two main types: heterotrophs and autotrophs. Autotrophic bacteria have the ability to utilize inorganic materials for their carbon (C) and energy sources, whereas heterotrophic bacteria, such as Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium, Archromobacter, and Alcaligenes, rely on organic molecules (Mobarak et al., 2024; Naciri et al., 2024). Further differentiation of heterotrophs is made based on their oxygen (O2) requirements, dividing them into three distinct groups.
(i) aerobes (require free O2 for decomposition of organic matter),
(ii) anaerobes (does not require O2 for decomposition), and
(iii) facultative (can perform decomposition of organic material both in oxic and anoxic conditions)
These are the main microorganisms that are present in biological WWT processes, namely, trickling filters and activated sludge processes. According to Eq 1, they catalyze the organic matter’s breakdow
Bacteria serve a crucial role as biocatalysts in the aerobic biodegradation of organic substrates, a process that is both beneficial and autocatalytic. This process varies depending on several factors, including the pH, temperature, and the specific biological process in use. Among these processes, the activated sludge process stands out for utilizing the highest concentration of bacteria. This method is not only straightforward but also cost-effective, making it an excellent option for converting a significant quantity of substrate in aerobic wastewater treatment (WWT) (Ezeorba et al., 2024). Additionally, it is worth noting that aerobic bacteria, which are employed in processes like the activated sludge method, exhibit a significantly faster metabolic rate when compared to their anaerobic counterparts.
In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic bacteria break down organic pollutants in wastewater and obtain energy from substances like nitrates and sulfates, as shown in Eqs 2, 3:
The reduction of organic materials during this anaerobic transformation necessitates a large number of bacteria and a lengthy residence time, and it is metabolically relatively slow. However, this method has a number of benefits, including the following: Because enormous mechanical devices are not needed for aeration, the process is (i) cost-effective; (ii) has a higher yielding performance than the activated sludge process because of the constraints on O2 transfer; and (iii) uses no O2, making it energy-efficient. (iv) Because there is no oxygen present, aerosol production is also prevented; (v) Reductive precipitation is a more effective method of removing heavy metals than oxidative precipitation; (vi) The energy produced can be used to create BioG; and, (vii) There is very little sludge buildup. About ninety-five percent of the organic stuff is converted into a combustible gas, making it a realistic example of waste disposal (Fernández-Domínguez et al., 2024).
Microalgae, encompassing eukaryotic algae and cyanobacteria, represent photosynthetic microorganisms with considerable potential for wastewater BioR. They offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for eliminating nutrients, heavy metals, and various organic pollutants from both municipal and industrial wastewater. The term “phycoremediation” is coined for the technology employing algal species for BioR purposes. Prominent algae taxa utilized in phycoremediation include Tetraselmis sp., Chlorella vulgaris, Chlorella sp., Picochlorum sp., and Scenedesmus sp. Additionally, various cyanobacterial strains such as Anabaena sp., Dolichospermum sp., Hapalosiphon sp., and others are also employed in phycoremediation endeavors (Gong et al., 2024; Lutzu et al., 2024; Mahlangu et al., 2024).
4.1 The potential of bacterial species in bioremediation
Bacteria possess an innate capacity to metabolize a wide spectrum of compounds, making them indispensable allies in BioR efforts. Certain bacterial species are particularly noted for their efficiency in degrading pollutants, including hydrocarbons (found in oil spills), heavy metals, and persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Genetically engineered bacteria have been designed to possess enhanced BioR capabilities, targeting specific contaminants with improved degradation pathways, resistance to toxic conditions, and overall efficiency (Priya et al., 2024). These advancements in microbial biotechnology have opened new avenues for the application of bacterial BioR in various environmental contexts.
4.2 Metabolic pathways in bacterial degradation
The metabolic versatility of bacteria is central to their role in BioR. Through processes such as oxidation, reduction, and methylation, bacteria can transform pollutants into less harmful substances. Oxidation reactions, for example, are critical in the breakdown of hydrocarbons, converting them into water-soluble products that can be further metabolized or mineralized. Heavy metals, on the other hand, may undergo reduction, wherein bacteria convert metals to less toxic forms, aiding in their removal or stabilization within the environment.
These metabolic processes are facilitated by a complex network of enzymes and co-factors within the bacterial cells, enabling the degradation of complex and varied pollutants. The adaptability of bacterial metabolic pathways is further evidenced by their ability to function under a range of environmental conditions, from anaerobic to aerobic, and across diverse pH and temperature ranges (Joshi et al., 2024).
4.3 Synergistic approaches with fungal systems
The integration of bacterial and fungal BioR systems represents a synergistic approach that leverages the strengths of both microbial kingdoms. Such consortia have shown promise in achieving more comprehensive degradation of complex waste mixtures, surpassing the capabilities of individual microbial species. For instance, recent studies have highlighted the success of integrated fungal and bacterial systems in degrading synthetic polymers, pesticides, and heavy metals, showcasing the enhanced efficiency and spectrum of pollutant degradation achievable through microbial collaboration.
These integrated BioR systems capitalize on the complementary metabolic pathways of fungi and bacteria. Fungi, with their extensive enzymatic repertoire, initiate the breakdown of complex molecules, which are then further metabolized by bacteria (Taylor and Bhatnagar, 2024). This sequential degradation process can significantly improve the overall efficiency of BioR projects, offering a potent solution for the treatment of mixed-contaminant waste streams.
In conclusion, bacterial BioR, through its diverse techniques and applications, embodies a crucial strategy in the fight against environmental pollution. The exploration of bacterial species with significant BioR potential, including genetically engineered variants, alongside the understanding of their metabolic pathways, underscores the adaptability and efficiency of bacteria in addressing complex pollutants. The integration of bacterial and fungal systems further amplifies these capabilities, presenting a holistic approach to environmental remediation that promises a cleaner and more sustainable future.
5 Advancements in fungal bioremediation
The field of fungal BioR has seen remarkable advancements, driven by cutting-edge research and technological innovation. These developments have significantly enhanced the efficiency and scope of BioR strategies, offering new solutions for the treatment of ToxicW and BioW. This section explores the synergistic use of fungi and bacteria, the impact of genetic engineering and molecular biology on microbial degradation capabilities, and recent innovations that promise to reshape the landscape of BioR.
5.1 Synergistic use of fungi and bacteria in bioremediation
A notable advancement in the field is the strategic integration of fungal and bacterial systems to form synergistic consortia, capable of degrading complex waste mixtures more comprehensively than either organism could achieve alone. This approach leverages the unique metabolic pathways of fungi and bacteria, allowing for the targeted breakdown of a wide range of pollutants, from synthetic polymers and pesticides to heavy metals. Research has demonstrated the effectiveness of these consortia in various environmental settings, showcasing their potential to significantly improve BioR outcomes.
In bioremediation processes, the collaborative interaction between fungi and bacteria plays a crucial role in enhancing the degradation of contaminants. These microorganisms possess complementary metabolic pathways, which enables them to break down a broader spectrum of pollutants when combined. This synergy not only leads to improved degradation efficiency through mechanisms such as cross-feeding and metabolic cooperation but also increases their resilience to challenging environmental conditions (Singh et al., 2024). Together, fungi and bacteria can withstand extreme pH levels, temperature fluctuations, and high salinity, making them more effective in diverse bioremediation scenarios.
The cooperation extends to their enzymatic capabilities as well. Both fungi and bacteria produce a wide range of enzymes, each capable of targeting different pollutants. This enzymatic diversity allows for the effective degradation of complex contaminant mixtures, leveraging the strengths of each microorganism. Moreover, bacteria’s propensity for biofilm formation creates protective environments that facilitate the growth and function of microbial communities (Qu et al., 2024). Fungi contribute to this process by aiding in biofilm formation and breaking down complex matrices, which enhances the penetration of bacterial consortia into contaminated materials.
The synergistic use of fungi and bacteria in bioremediation, or BioR, strategies is versatile, finding applications across a variety of contaminant types. These include hydrocarbons, heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals, underscoring the broad applicability of these microbial partnerships in addressing environmental pollution. The combination of these microorganisms not only optimizes the biodegradation process but also expands the range of conditions and contaminants that can be effectively treated, showcasing the potential of integrative approaches in environmental cleanup efforts. Yeliang Dai et. al., studied the synergistic mechanism of autochthonous fungal bioaugmentation and ammonium nitrogen biostimulation for enhanced phenanthrene degradation in oil-contaminated soils (Dai et al., 2024). The study provides valuable insights into the synergistic use of autochthonous fungal bioaugmentation and ammonium nitrogen biostimulation for enhanced phenanthrene degradation in oil-contaminated soils. Following bioaugmentation, there was a discernible decline in the biodiversity of soil microorganisms and a weakening of interrelationships among them, which resulted in a degradation of the network structure.
Through DNA stable-isotope probing and microbial network analysis, it was observed that both treatments significantly improved phenanthrene removal, with their combined application yielding the best results. Notably, fungal bioaugmentation facilitated PAH removal via extracellular enzyme secretion but reduced soil microbial diversity and ecological stability. Conversely, nitrogen biostimulation stimulated indigenous soil degrading microbes, including fungi and key bacteria, while maintaining soil ecological diversity.
The combination of both approaches emerged as the most effective strategy, achieving optimal phenanthrene degradation and relatively stable soil biodiversity. These findings shed light on the mechanisms underlying fungal bioaugmentation and nitrogen biostimulation, suggesting their combined use as a viable in situ bioremediation tool for PAH-contaminated soils. Further research in this area could pave the way for more effective and sustainable remediation strategies in contaminated environments.
5.2 Genetic engineering and molecular biology: pushing the boundaries
The application of genetic engineering and molecular biology has been instrumental in advancing fungal BioR. Through genetic modification, scientists have been able to enhance the natural degradation capabilities of fungi, equipping them with the ability to target specific pollutants with increased efficiency. For example, the introduction of genes encoding for specific degradation enzymes into fungal genomes has resulted in strains with heightened abilities to breakdown persistent organic pollutants (POPs) (Singh and Sable, 2024).
In parallel, the development of genetically modified bacteria that express fungal degradation enzymes represents a significant leap forward. This cross-kingdom genetic engineering not only expands the repertoire of degradable substances but also enhances the overall efficiency of BioR processes. These genetically enhanced microorganisms can be tailored to address the specific needs of contaminated sites, offering a more precise and effective approach to BioR.
5.3 Enhancement through nanotechnology
Microbial-assisted nanotechnology enhances wastewater BioR by leveraging the synergistic capabilities of fungi and bacteria with nanomaterials. Nano-sized particles facilitate targeted pollutant degradation, amplifying the efficiency of microbial activity. This integration expands surface area, promoting greater adsorption and catalytic reactions, thus accelerating contaminant removal. Additionally, nanoparticles (NPs) can aid in the immobilization of microorganisms, ensuring their sustained activity over time. Through precise control and manipulation at the nanoscale, this approach optimizes remediation processes, leading to improved water quality outcomes (Figure 7) (Zhai et al., 2024). The microbial-assisted nanotechnology represents a cutting-edge solution for tackling wastewater contamination, offering sustainable and efficient means for environmental restoration.
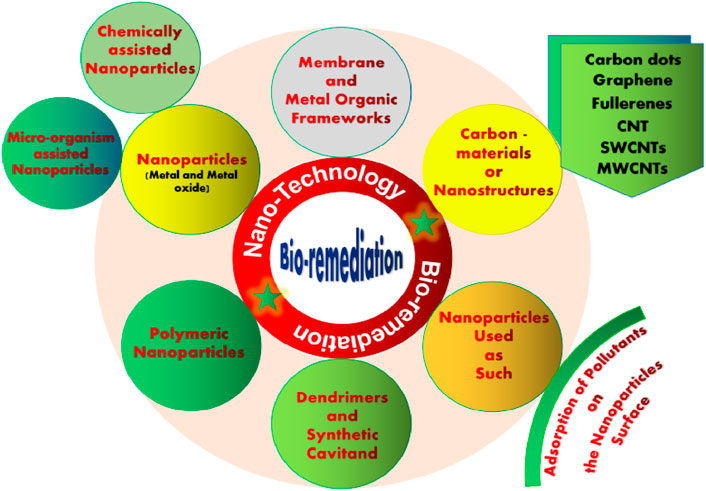
Figure 7. Microbial-assisted nanotechnology for bioremediation of wastewater. MOFs: Metal organic frameworks; MWCNTs: multi-walled carbon nanotubes; SWCNTs: Single-walled carbon nanotubes.
Nanotechnology holds immense promise for WWT, leveraging the unique properties of nanomaterials to address diverse pollutants efficiently. NPs derived from carbon and metal-based materials offer versatile solutions, including filtration, adsorption, and photocatalytic degradation. Microbial involvement enhances nanotechnology’s viability and environmental benefits, circumventing limitations associated with chemically generated nanomaterials.
Bio-fabrication of NPs using microorganisms like bacteria and fungi presents a sustainable approach, exemplified by the synthesis of copper nanoparticles by Escherichia sp. SINT7. These biogenic NPs demonstrate remarkable efficacy in decomposing textile effluents and azo dyes, contributing to pollutant reduction in industrial effluents. Malachite green, direct blue-1, Congo red, and reactive black-5 were reduced at 25 mg/L concentration to 90.55, 88.42, 97.07, and 83.61%, respectively; at 100 mg/L, the reduction was 31.08, 62.32, 83.90, and 76.84%, respectively. By treating industrial effluents, phosphate, chloride ions, and suspended particles have been reduced in processed samples (Gayakwad et al., 2024). The industry can benefit from the efficiency of biogenic nanoparticles to achieve lucrative and sustainable production. Additionally, microbial synthesis of nanoparticles from natural sources, such as Chlorella vulgaris-derived exopolysaccharides, showcases enhanced removal capabilities for heavy metals and nutrients like NH4+ and PO43−.
Furthermore, microorganisms play a pivotal role in enhancing nanotechnology by facilitating the synthesis of nanoparticles with specialized functionalities. For instance, Pseudoalteromonas sp. CF10–13 aids in synthesizing nanoparticles for biodegradation, while demonstrate the endogenic development of iron-sulfur nanoparticles for dye degradation. Synthetic nanoparticles have been shown to remove over 90% of heavy metals, including Zn(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Pb(II), from wastewater. These particles may regenerate in around five cycles.
The use of nanomaterials for the restoration of contaminated soils has expanded as a result of the development of nanotechnology. However, no studies on the relationship between carbon dots and heavy metals (loid)s in phytoremediation have been published as of yet. Carbon dots (CDs) derived from plant waste and environmental toxins offer a sustainable solution for both waste management and nanomaterial synthesis. Their biocompatibility, low toxicity, and tunable optical properties make them promising candidates for applications ranging from bioimaging and drug delivery to environmental sensing and energy storage (Aryamol et al., 2024; Ramasubburayan et al., 2024; Thirumalaivasan et al., 2024). This study looked into how new CDs made from fungal exopolysaccharides affected the development and uptake of Cd in maize plants. The transfer factor and phytoremediation rate of Cd increased by 5.7 and 6.7 times, respectively, as a result of carbon dots. In soils free of cadmium, the amount of dissolved organic carbon increased by 39.9% and 77.9% in response to the presence of carbon dots, respectively. Under the carbon dots and Cd + carbon dots treatments, respectively, soil microbial biomass carbon increased by 54.9% and 24.1% (Sadeghi et al., 2023).
The study delves into the novel application of fungal CDs in phytoremediation, shedding light on their interaction with heavy metals in contaminated soils. Results indicate significant enhancements in maize growth and Cd uptake, with notable improvements in shoot dry weight and chlorophyll content. The presence of carbon dots remarkably increased the transfer factor and phytoremediation rate of Cd, demonstrating their efficacy in soil restoration. Moreover, a boost in soil microbial biomass carbon suggests potential ecological benefits. This underscores the promising role of nanotechnology, particularly fungal CDs, in addressing environmental contamination challenges, offering a sustainable pathway for soil remediation.
Utilizing microbial-assisted nanotechnology, such as MOFs, MWCNTs, and SWCNTs, holds great potential for enhancing the BioR of wastewater. These nanomaterials can efficiently adsorb and degrade pollutants, while microbial activity further aids in the breakdown of contaminants (Saeed et al., 2022). By synergistically combining nanotechnology with microbial processes, we can achieve more efficient and sustainable WWT strategies, mitigating environmental pollution and ensuring water quality for future generations.
This holistic approach not only addresses environmental challenges but also offers cost-effective solutions for industries seeking sustainable production practices. By harnessing the synergy between microorganisms and nanotechnology, we can advance WWT methods, paving the way for cleaner water resources and a more sustainable future.
5.4 Innovative techniques for enhanced bioremediation efficiency
Recent advancements have also focused on improving the practical aspects of fungal BioR, such as the immobilization of fungi for easier recovery and reuse. Innovative immobilization techniques ensure that fungal cells remain active and can be efficiently separated from treated materials, facilitating their application in continuous BioR processes. This not only enhances the sustainability of the approach but also reduces costs associated with the BioR of large-scale environmental pollutants.
Additionally, the development of bioaugmentation techniques, wherein specific microbial strains are introduced into contaminated environments, has proven to be a key advancement. This strategy enhances the natural BioR potential of the site, accelerating the degradation of pollutants and improving the efficacy of the cleanup process (Singh et al., 2020).
The advancements in fungal BioR, driven by synergistic microbial consortia, genetic engineering, and innovative application techniques, represent a significant stride towards more effective and sustainable solutions for the treatment of ToxicW and BioW. As research continues to unfold, these cutting-edge approaches hold the promise of transforming our ability to mitigate environmental pollution, paving the way for cleaner and healthier ecosystems.
6 Biorefineries from bioremediation techniques
Biorefineries represent a nexus of sustainability, integrating multiple bio-based processes to transform waste into valuable products. Leveraging BioR techniques, these facilities remediate environmental pollutants while simultaneously producing bioenergy, Biogas, (BioG), biofuels (BioF), Bioelectricity (BioE), Biofertilizer (BioFz) and other bioproducts (Figure 8). At the core of biorefineries is BioR, employing biological agents to clean up pollutants from soil, water, or air. Microorganisms and plants are utilized to degrade or absorb contaminants, effectively restoring ecosystems (Leong et al., 2021).
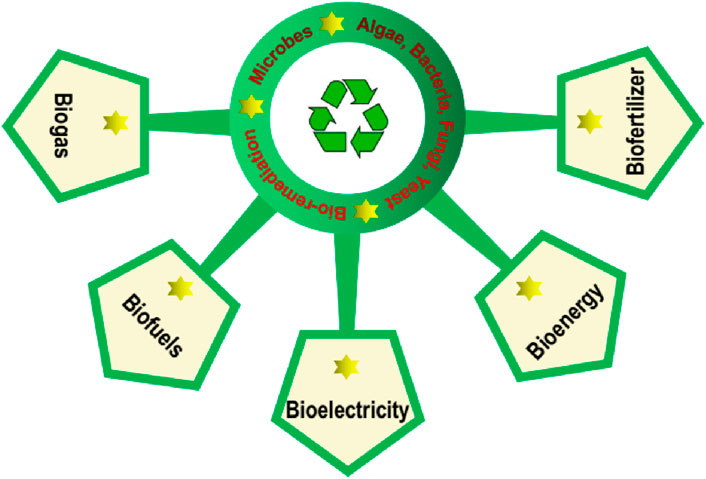
Figure 8. BioRtechniques, these facilities remediate environmental pollutants while simultaneously producing bioenergy, Biogas, (BioG), biofuels (BioF), Bioelectricity (BioE), Biofertilizer (BioFz) and other bioproducts.
In addition to environmental remediation, biorefineries extract energy and valuable compounds from biomass. Through anaerobic digestion, organic waste is converted into BioG, a renewable energy source rich in methane. This BioG can be further processed into BioF for transportation or used to generate BioE through combustion or microbial fuel cells. Moreover, the byproducts of biorefinery processes hold significant value. The nutrient-rich residues from BioG production serve as BioFz, enriching soils and promoting agricultural sustainability.
By integrating BioR, BioG production, BioF generation, BioE generation, and BioF production, biorefineries exemplify a circular economy model, where waste is transformed into valuable resources. These multifaceted facilities play a pivotal role in advancing environmental sustainability and reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels. After harvesting from the alternative culture and treatment system, algal biomass undergoes extraction using various methods including sedimentation, flocculation, centrifugation, and membrane filtration (Pérez et al., 2020). The extracted biomass finds applications as BioFs, BioG, biopolymers, feedstock, or agricultural fertilizer (also known as BioFz), contributing to sustainable resource utilization and waste management.
Biogas (BioG): BioG produced through fungal and bacterial BioR harnesses the natural ability of microorganisms to break down pollutants, offering a sustainable solution for both waste management and renewable energy production. Algal biomass cultivated in WWT ponds presents a valuable resource for BioG production, alongside its potential for lipid extraction. Unlike higher plants, microalgae offer advantages for BioG generation due to their higher production efficiency and independence from land or freshwater constraints (Srivastava et al., 2020; Umar et al., 2024). This dual capability underscores the versatility and sustainability of microalgae as a renewable energy source, contributing to both BioF production and BioG generation while mitigating environmental impacts associated with conventional energy sources.
Biofuels (BioF): BioF, derived from organic matter like plants and algae, offer a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability in energy production. They encompass a range of options including biodiesel, bioethanol, and BioG, playing a vital role in the transition towards cleaner energy sources. Microalgae cultivation, utilizing High Rate Algal Ponds (HRAP) for WWT, offers an affordable and sustainable approach for BioF production. Harvested algae biomass, rich in lipids, undergoes extraction for biodiesel conversion. Sun drying, especially viable in tropical regions, prepares the biomass for extraction. Various methods exist, including Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL), a superior technique avoiding drying and solvent steps (Srivastava et al., 2021). HTL subjects the algal slurry to high temperature and pressure, yielding high-energy oil. This process recovers over 90% of algal lipids, with minimal sulfur emissions and low ash content, producing approximately 0.4 tons of oil per dry algae ton.
Bioelectricity (BioE): BioE generated through fungal and bacterial BioR harnesses microbial metabolism to convert organic pollutants into electrical energy, offering a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to waste management while simultaneously producing renewable power. This innovative process not only addresses environmental concerns but also contributes to the diversification of clean energy sources, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future (Venkata Mohan et al., 2013; Gaur et al., 2024; Umar et al., 2024).
Biofertilizer (BioFz): BioFz produced through fungal and bacterial BioR techniques utilize microbial activity to convert organic waste into nutrient-rich additives, enhancing soil fertility and promoting sustainable agriculture practices. By harnessing the natural processes of microorganisms, BioF offer an eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers, minimizing environmental impact while supporting crop growth and soil health (Anshuman, 2024; Pandiyan et al., 2024). Algal biomass stands out as a promising fertilizer, not only for its moisture retention benefits but also for its controlled release of nutrients essential for plant growth. This characteristic not only promotes healthier soil but also reduces the emission of CO2 associated with chemical fertilizers. Data from studies reveal a stark difference, with 1 kg of algal mass as fertilizer mitigating 0.23 kg CO2EQV emissions compared to the manufacturing of chemical fertilizers, which typically release 3.15 and 1.39 tons of CO2EQV per ton for nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers, respectively. Additionally, microalgal-based WWT systems play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by capturing CO2 during photosynthesis. These systems, such as HRAP and photobioreactors, offer a cost-effective alternative to conventional methods, significantly decreasing CO2 release per unit of treated wastewater (El-Bendary et al., 2024). Overall, the integration of algal biomass in both agriculture and WWT demonstrates its potential in mitigating climate change impacts.
7 Drawbacks and limitations
Fungal and bacterial BioR techniques face drawbacks including slow degradation rates for complex pollutants, limited effectiveness against diverse contaminants, and dependency on optimal environmental conditions. In highly contaminated sites, incomplete remediation may occur, posing risks of secondary contamination. Regulatory hurdles and logistical challenges in accessing remote sites add complexity, while scaling up processes for large waste volumes entails significant costs and technical demands.
Some of the specific points as follows: (1) Slow degradation rates, especially for complex pollutants or large waste volumes, can prolong the remediation process. (2) Specificity of microorganisms may limit their effectiveness against a wide range of contaminants, requiring the use of multiple strains or consortia. (3) BioR efficiency is heavily reliant on optimal environmental conditions such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability. (4) Effectiveness in highly contaminated sites with persistent pollutants or complex matrices may be limited. (5) Inadequate containment measures can lead to the release of potentially toxic metabolites, posing risks of secondary contamination. (6) Regulatory hurdles may arise, especially for genetically modified microorganisms or novel BioR techniques. (7) Accessing and treating contaminated sites, particularly remote or inaccessible areas, can be logistically challenging. and (8) Scaling up BioR processes to treat large volumes of waste can be costly and technically complex, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and resources.
8 Challenges and solutions
The utilization of fungal and bacterial BioR techniques for the treatment of ToxicW and BioW offers a promising path toward sustainable environmental cleanup. However, the application of these biological methods faces several challenges that can limit their effectiveness. This section delves into the obstacles encountered in microbial BioR, the limitations of current technologies, and the innovative solutions being developed to overcome these challenges.
8.1 Overcoming bioavailability and environmental constraints (optimization of bioremediation conditions)
One of the primary challenges in microbial BioR is the bioavailability of pollutants. Many contaminants are tightly bound to soil particles or are present in non-aqueous phase liquids, making them difficult for microorganisms to access. Additionally, environmental conditions such as pH, temperature, and moisture levels can significantly impact the efficiency of BioR processes. These factors can inhibit microbial growth and enzyme activity, reducing the degradation rate of pollutants.
Numerous biotic and abiotic variables, including microbial populations, aeration status, moisture content, temperature, and others, affect the performance criteria. Furthermore, for effective BioR, choosing the right technique is crucial (Grover et al., 2019). To address these issues, strategies such as the addition of surfactants to increase the solubility of hydrophobic compounds and the adjustment of environmental conditions to optimize microbial activity have been explored. Furthermore, advances in bioreactor design have facilitated the control of BioR conditions, enhancing the efficiency of microbial degradation processes (Radhakrishnan et al., 2023).
The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the appropriate microbial population. The ideal moisture content range to be kept is between 50% and 55%. Neither too acidic nor too basic of a pH should exist. These alterations have an impact on the microbiological population. A minimum of 40% organic content is required, and a pH close to neutrality is ideal. The C/N ratio is also crucial and should be less than 50 for quick biodegradation. The ideal temperature is between 65◦C and 70°C. It should be mentioned that applying chemometrics techniques can enhance the effectiveness of the degradation process and aid to optimize the BioR environment. Chemometrics techniques can assist in determining the critical elements, such as temperature, pH, and nutrient concentration, that influence the effectiveness of BioR and can help adjust the circumstances accordingly by analyzing and modeling the link between the input variables and the output variables (Soleimani et al., 2013; Li and Yang, 2021; Pandya and Kumar, 2021). This is done by tracking the development of the biodegradation process through the analysis of the intricate data sets that are produced, including the alterations in microbial populations and metabolite production.
Several chemometric techniques are frequently employed in the optimization of BioR conditions, such as genetic algorithms, artificial neural networks, response surface methodology, design of experiments, and principal component analysis. The use of chemometrics in BioR may provide more effective and affordable ways to carry out BioR plans in a sustainable manner, given the current developments in bioinformatics and data analytics. It is believed that there are two stages to the biodegradation process: the curing stage (second mesophilic phase) and the maturation stage, which includes the thermophilic phase (>45°C) and the mesophilic phase (25–45°C). The procedure is also primarily dependent on the ratio of mixing, as improper mixing inhibits the growth of the target microorganisms. Petroleum pollutants are commonly treated using these two-stage procedures.
8.2 Navigating the complexities of fungal bioremediation
Fungal BioR, while offering unique advantages in the degradation of complex pollutants, faces challenges related to the specific growth conditions and nutrient requirements of fungi. The development of specialized bioreactors and co-cultivation strategies with bacteria have shown promise in creating more adaptable and robust fungal BioR systems. These innovations allow for the cultivation of fungi under controlled conditions, improving their viability and pollutant degradation capabilities.
8.3 Addressing bacterial bioremediation challenges
Bacterial BioR efforts can be hindered by the difficulty in maintaining viable microbial populations in contaminated environments. Additionally, there is concern over the potential transfer of antibiotic resistance genes from genetically modified bacteria to native microbial communities. Advances in encapsulation technologies have emerged as a key solution, protecting introduced bacteria from harsh environmental conditions and minimizing gene transfer risks. Controlled-release systems further ensure the sustained activity of bacterial populations, improving the overall effectiveness of BioR efforts.
8.4 The path forward: Research and innovation
Despite the challenges, ongoing research and technological innovations continue to enhance the capabilities and applications of microbial BioR. The integration of multidisciplinary approaches, ranging from molecular biology to engineering, is crucial for addressing the limitations of current BioR technologies. Continued investment in research is essential for uncovering new strategies and microbial strains with improved BioR potential, paving the way for more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solutions to the management of ToxicW and BioW.
In conclusion, while microbial BioR faces significant challenges, the development of innovative solutions and the deepening understanding of microbial processes offer a promising outlook for overcoming these obstacles. By addressing the limitations and harnessing the full potential of fungal and bacterial BioR techniques, we can advance toward a more sustainable and effective approach to environmental cleanup.
9 Future directions and sustainability considerations
The field of microbial BioR, involving the use of fungal and bacterial techniques for the treatment of ToxicW and BioW, is poised for significant advancements. As we look to the future, the integration of emerging technologies and innovative strategies is expected to address current challenges and enhance the efficacy and sustainability of BioR processes. This section explores potential future directions in microbial BioR and underscores the importance of incorporating these techniques into broader waste management and sustainability frameworks.
9.1 Emerging technologies and strategies
The future of microbial BioR is likely to be shaped by advancements in genetic engineering, nanotechnology, and systems biology. These technologies hold the promise of creating microbial strains with tailored degradation pathways, capable of targeting specific pollutants with unprecedented efficiency. Optimizing consortia compositions, through the strategic combination of fungal and bacterial species, will enhance the range and speed of pollutant degradation. This approach takes advantage of the complementary metabolic pathways of different microorganisms, leading to more comprehensive and effective BioR.
Furthermore, the development of more efficient delivery systems for microbial consortia and the implementation of innovative recovery methods will improve the applicability and sustainability of BioR processes. These advancements will enable the targeted treatment of contaminated sites with minimal environmental disruption and facilitate the recovery and reuse of valuable microbial agents.
9.2 Integration with waste management and sustainability practices
Integrating microbial BioR into broader waste management and sustainability practices is crucial for creating holistic environmental solutions. This integration involves considering BioR as a key component of circular economy models, where the goal is to minimize waste, recover resources, and regenerate natural systems. By linking BioR with waste-to-energy technologies, there is potential not only for pollution mitigation but also for the recovery of resources. Such synergy can transform waste management practices, shifting from mere disposal or cleanup to the generation of renewable energy and the recovery of useful materials.
The incorporation of microbial BioR into sustainability practices also emphasizes the need for interdisciplinary approaches, combining insights from environmental science, engineering, economics, and social sciences. This multidisciplinary perspective will facilitate the development of policies and frameworks that support the adoption and scaling of BioR technologies, ensuring that they contribute effectively to global sustainability goals.
As we advance, the field of microbial BioR is set to play an increasingly critical role in addressing environmental pollution and enhancing sustainability. The future will likely see a focus on optimizing microbial consortia, engineering advanced microbial strains, and developing novel integration strategies with waste management systems. Embracing these innovations and integrating BioR into broader environmental and sustainability practices will be key to unlocking its full potential. By doing so, microbial BioR can contribute significantly to the creation of sustainable, resilient, and clean environments for future generations.
10 Future perspectives and challenges
It would be beneficial to delve deeper into the specific challenges that could hinder the broader application of microbial BioR techniques. For instance, while these methods are promising, they face obstacles such as the scalability of bioremediation processes in diverse environmental conditions, the economic feasibility of large-scale implementations, and potential regulatory hurdles. Moreover, future perspectives could include a discussion on the need for robust frameworks to monitor and control the ecological impacts of deploying genetically engineered microorganisms in open environments. Highlighting the ongoing need for interdisciplinary research that bridges microbiology, environmental science, and engineering could also enrich this section. This approach will not only outline the challenges but also set the stage for addressing them through future research directions.
11 Conclusion
In the conclusion, it is essential to reinforce the significance of fungal and bacterial BioR techniques within the broader context of sustainability and environmental protection. Emphasizing the role of innovative technologies and collaborative efforts in enhancing the efficiency and application range of these bioremediation strategies could provide a more dynamic closure to the review. Additionally, articulating a vision for how these techniques could integrate into existing and future environmental policies would underscore their relevance. A call to action, encouraging global cooperation among scientists, policymakers, and industry leaders to invest in and prioritize microbial BioR as a critical component of the global strategy against pollution, would serve as a powerful ending to the manuscript.
By expanding these sections to address these points, the review can offer a more comprehensive analysis of the potential and limitations of microbial BioR, as well as a clearer roadmap for future research and application in environmental management. This enhancement will not only satisfy the reviewer’s concerns but also increase the impact and relevance of the work in the field of environmental science.
Author contributions
NT: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. LG: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. SK: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing–review and editing. RD: Writing–review and editing. TS: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft. SR: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. SN: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. KK: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abo Alkasem, M. I., Maany, D. A., El-Abd, M. A. E. H., and Ibrahim, A. S. S. (2022). Bioreduction of hexavalent chromium by a novel haloalkaliphilic Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens strain NRC–R isolated from hypersaline soda lakes. 3 Biotech 12, 7. doi:10.1007/s13205-021-03082-2
Addagada, L., Goel, M., Shahid, M. K., Prabhu, S. V., Chand, S., Sahoo, N. K., et al. (2023). Tricks and tracks in resource recovery from wastewater using bio-electrochemical systems (BES): a systematic review on recent advancements and future directions. J. Water Process Eng. 56, 104580. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104580
Adnane, I., Taoumi, H., Elouahabi, K., Lahrech, K., and Oulmekki, A. (2024). Valorization of crop residues and animal wastes: anaerobic co-digestion technology. Heliyon 10, e26440. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26440
Alkhanjaf, A. A. M., Sharma, S., Sharma, M., Kumar, R., Arora, N. K., Kumar, B., et al. (2024). Microbial strategies for copper pollution remediation: mechanistic insights and recent advances. Environ. Pollut. 346, 123588. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123588
Anshuman, K. P. (2024). “Potential use of fungi as biofertilizer in sustainable agriculture,” in Entrepreneurship with microorganisms (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 279–292.
Aryal, M. (2024). Rhizomicrobiome dynamics: a promising path towards environmental contaminant mitigation through bioremediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 112221. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2024.112221
Aryamol, K., Kanagaraj, K., Nangan, S., Haponiuk, J. T., Okhawilai, M., Pandiaraj, S., et al. (2024). Recent advances of carbon pathways for sustainable environment development. Environ. Res. 250, 118513. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2024.118513
Barman, F., Nath, S., Dey, S., Ansari, M. T. A., Kundu, R., and Paul, S. (2024). “Aquatic plant-mediated bioremediation strategies,” in Toxicity of aquatic system and remediation (Boca Raton, Florida, United States: CRC Press), 146–168. doi:10.1201/9781003297901-12
Bhatia, L., Kaladhar, D. S. V. G. K., Sarkar, T., Jha, H., and Kumar, B. (2024). Food wastes phenolic compounds (PCs): overview of contemporary greener extraction technologies, industrial potential, and its integration into circular bioeconomy. Energy, Ecol. Environ., 1–31. doi:10.1007/s40974-024-00321-z
Chane, A. D., Košnář, Z., Hřebečková, T., Jozífek, M., Doležal, P., and Tlustoš, P. (2024). Persistent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal from sewage sludge-amended soil through phytoremediation combined with solid-state ligninolytic fungal cultures. Fungal Biol. 128, 1675–1683. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2024.01.007
Chaudhary, S., and Sindhu, S. S. (2024). “Microbiome-mediated remediation of heavy metals: impact on soil health, crop production, and ecosystem sustainability,” in Microbiome-assisted bioremediation (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 257–312.
Chepyala, S., Bathula, J., and Bodiga, S. (2024). “Myco-degradation of lignocellulosic waste biomass and their applications,” in Valorization of biomass wastes for environmental sustainability: green practices for the rural circular economy (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 269–286. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-52485-1_15
Coleine, C., Kurbessoian, T., Calia, G., Delgado-Baquerizo, M., Cestaro, A., Pindo, M., et al. (2024). Class-wide genomic tendency throughout specific extremes in black fungi. Fungal Divers. 125, 121–138. doi:10.1007/s13225-024-00533-y
Dahiya, P., Behl, M., Kumari, D., Arya, E., Rathour, R. K., Kumar, V., et al. (2024). “Detoxification of contaminated soil to restore its health for sustainable agriculture,” in Advancements in microbial biotechnology for soil health (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 295–322. doi:10.1007/978-981-99-9482-3_13
Dai, Y., Li, J., Wang, S., Cai, X., Zhao, X., Cheng, X., et al. (2024). Unveiling the synergistic mechanism of autochthonous fungal bioaugmentation and ammonium nitrogen biostimulation for enhanced phenanthrene degradation in oil-contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 465, 133293. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.133293
Das, J., Badak, M., and Singh, R. K. (2024). “Sustainable innovations and production strategies of white rot fungi-derived laccase,” in Microbiology-2.0 update for a sustainable future (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 285–306. doi:10.1007/978-981-99-9617-9_13
Devendrapandi, G., Liu, X., Balu, R., Ayyamperumal, R., Valan Arasu, M., Lavanya, M., et al. (2024). Innovative remediation strategies for persistent organic pollutants in soil and water: a comprehensive review. Environ. Res. 249, 118404. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2024.118404
El-Bendary, M. A., Hamed, S. R., Elgamal, N. N., and Gawdat, N. A. (2024). Scope of nanotechnology in agriculture and environment. Nanotoxicology for agricultural and environmental applications. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 3–39. doi:10.1016/B978-0-443-15570-3.00002-8
Espinosa-Ortiz, E. J., Rene, E. R., and Gerlach, R. (2022). Potential use of fungal-bacterial co-cultures for the removal of organic pollutants. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 42, 361–383. doi:10.1080/07388551.2021.1940831
Ezeorba, T. P. C., Okeke, E. S., Mayel, M. H., Nwuche, C. O., and Ezike, T. C. (2024). Recent advances in biotechnological valorization of agro-food wastes (AFW): optimizing integrated approaches for sustainable biorefinery and circular bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 26, 101823. doi:10.1016/j.biteb.2024.101823
Fashola, M. O., Anagun, O. S., Ogun, M. L., Ndimele, P. E., and Babalola, O. O. (2024). “Biotechnological strategies for effective remediation of heavy metals,” in Heavy metal remediation: sustainable nexus approach (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 139–164. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-53688-5_7
Fernández-Domínguez, D., Sourdon, L., Pérémé, M., Guilayn, F., Steyer, J. P., Patureau, D., et al. (2024). Retention time and organic loading rate as anaerobic co-digestion key-factors for better digestate valorization practices: C and N dynamics in soils. Waste Manag. 181, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2024.03.031
Gaur, S., Kaur, M., Kalra, R., Rene, E. R., and Goel, M. (2024). Application of microbial resources in biorefineries: current trend and future prospects. Heliyon 10, e28615. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28615
Gayakwad, K., Ambade, B., Kumar, A., and Gautam, S. (2024). Sustainable solutions: reviewing the future of textile dye contaminant removal with emerging biological treatments. Limnol. Rev. 24, 126–149. doi:10.3390/limnolrev24020007
Gong, X., Shi, W., Zhang, Z., Luo, M., Zhang, B., Wan, S., et al. (2024). Exploring the effects of zeolite, biochar, and diatomite as additives for enhancing heavy metals passivation and eliminating antibiotic resistance genes in composts during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge and green waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 112201. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2024.112201
Grover, R., Burse, S. A., Shankrit, S., Aggarwal, A., Kirty, K., Narta, K., et al. (2019). Myg1 exonuclease couples the nuclear and mitochondrial translational programs through RNA processing. Nucleic acids Res. 47, 5852–5866. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz371
Hamza, A., Mylarapu, A., Krishna, K. V., and Kumar, D. S. (2024). An insight into the nutritional and medicinal value of edible mushrooms: a natural treasury for human health. J. Biotechnol. 381, 86–99. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2023.12.014
Hofrichter, M., Ullrich, R., Pecyna, M. J., Liers, C., and Lundell, T. (2010). New and classic families of secreted fungal heme peroxidases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 87, 871–897. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2633-0
Hu, M., and Scott, C. (2024). Toward the development of a molecular toolkit for the microbial remediation of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 90, e0015724. e00157-24. doi:10.1128/aem.00157-24
Hussain, A., Rehman, F., Rafeeq, H., Waqas, M., Asghar, A., Afsheen, N., et al. (2022). In-situ, Ex-situ, and nano-remediation strategies to treat polluted soil, water, and air–A review. Chemosphere 289, 133252. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133252
Jamir, I., Ezung, L. Y., Merry, L., Tikendra, L., Devi, R. S., and Nongdam, P. (2024). Heavy metals clean up: the application of fungi for biosorption. Geomicrobiol. J. 1-12. doi:10.1080/01490451.2024.2307899
Joshi, S. S., Jadhav, M. P. K., Chourasia, N. K., Jadhav, M. P. J., Pathade, K. N., KR, K., et al. (2024). Bioremediation strategies for soil and water pollution harnessing the power of microorganisms. Migr. Lett. 21, 1–20.
Kakkar, A., and Kumar, S. (2024). “Remediation technologies for petroleum hydrocarbons from the environment,” in Impact of petroleum waste on environmental pollution and its sustainable management through circular economy (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 205–233.
Karabulut, F., Parray, J. A., Shafi, N., and Ikram, M. (2024). “Endophytes: role in maintaining plant health under stress conditions,” in Plant endophytes and secondary metabolites (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 105–132. doi:10.1016/B978-0-443-13365-7.00004-X
Khandaker, S., Bashar, M. M., Islam, A., Hossain, M. T., Teo, S. H., and Awual, M. R. (2022). Sustainable energy generation from textile biowaste and its challenges: a comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 157, 112051. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2021.112051
Khatun, M., Kobir, M. M., Miah, M. A. R., Sarkar, A. K., and Alam, M. A. (2024). Technologies for remediation of heavy metals in environment and ecosystem: a critical overview of comparison study. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 23, 61–80. doi:10.9734/ajee/2024/v23i4540
Kumar, A., Kumar, V., Chawla, M., Thakur, M., Bhardwaj, R., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Bioremediation of mercury contaminated soil and water: a review. Land Degrad. Dev. 35, 1261–1283. doi:10.1002/ldr.4989
Kuppusamy, S., Palanisami, T., Megharaj, M., Venkateswarlu, K., and Naidu, R. (2016). In-situ remediation approaches for the management of contaminated sites: a comprehensive overview. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 236, 1–115. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-20013-2_1
Laubach, J., Flesch, T. K., Ammann, C., Bai, M., Gao, Z., Merbold, L., et al. (2024). Methane emissions from animal agriculture: micrometeorological solutions for challenging measurement situations. Agric. For. Meteorology 350, 109971. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2024.109971
Leong, H. Y., Chang, C. K., Khoo, K. S., Chew, K. W., Chia, S. R., Lim, J. W., et al. (2021). Waste biorefinery towards a sustainable circular bioeconomy: a solution to global issues. Biotechnol. Biofuels 14, 87–15. doi:10.1186/s13068-021-01939-5
Li, J., and Yang, H. (2021). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon improves the anaerobic biodegradation of benz [α] anthracene in sludge via boosting the microbial activity and bioavailability. Pak. J. Zoology 53. doi:10.17582/journal.pjz/20200106160152
Lin, W., Chen, R., Gong, C., Desmond, P., He, X., Nan, J., et al. (2024). Sustained oxidation of Tea-Fe (III)/H2O2 simultaneously achieves sludge reduction and carbamazepine removal: the crucial role of EPS regulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 470, 134182. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134182
Lutzu, G. A., Parsaeimehr, A., Ozbay, G., Ciurli, A., Bacci, L., Rao, A. R., et al. (2024). Microalgae and cyanobacteria role in sustainable agriculture: from wastewater treatment to biofertilizer production. Algae Mediat. Bioremediation Ind. Prospect. 2, 565–618. doi:10.1002/9783527843367.ch29
Maheshwari, R., Singh, U., Singh, P., Singh, N., Jat, B. L., and Rani, B. (2014). To decontaminate wastewater employing bioremediation technologies. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 5, 7–15.
Mahlangu, D., Mphahlele, K., De Paola, F., and Mthombeni, N. H. (2024). Microalgae-mediated biosorption for effective heavy metals removal from wastewater: a review. Water 16, 718. doi:10.3390/w16050718
Mobarak, M. H., Siddiky, A. Y., Islam, M. A., Hossain, A., Rimon, M. I. H., Oliullah, M. S., et al. (2024). Progress and prospects of electrospun nanofibrous membranes for water filtration: a comprehensive review. Desalination 574, 117285. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2023.117285
Mohamed, H. I., Aal, M. H. A., and El-Mahdy, O. M. (2024). “Fungal metabolites and their role in remediation of environmental pollution,” in Fungal secondary metabolites (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 283–315. doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-95241-5.00020-4
Mushtaq, Z., Muzammil, A., Bellitürk, K., Anwar, W., Akhter, A., Khan, H. A. A., et al. (2024). “Role of Rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metal,” in Heavy metal remediation: sustainable nexus approach (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 183–211. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-53688-5_9
Naciri, Y., Ghazzal, M. N., and Paineau, E. (2024). Nanosized tubular clay minerals as inorganic nanoreactors for energy and environmental applications: a review to fill current knowledge gaps. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 326, 103139. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2024.103139
Naja, G. M., and Volesky, B. (2017). “Toxicity and sources of Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr, As, and radionuclides in the environment,” in Handbook of advanced industrial and hazardous wastes management (Boca Raton, Florida, United States: Crc Press), 855–903.
Nano, G., Borroni, A., and Rota, R. (2003). Combined slurry and solid-phase bioremediation of diesel contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 100, 79–94. doi:10.1016/s0304-3894(03)00065-7
Navina, B. K., Velmurugan, N. K., Senthil Kumar, P., Rangasamy, G., Palanivelu, J., Thamarai, P., et al. (2024). Fungal bioremediation approaches for the removal of toxic pollutants: mechanistic understanding for biorefinery applications. Chemosphere 350, 141123. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141123
Nkuna, R., and Matambo, T. S. (2024). Insights into metal tolerance and resistance mechanisms in Trichoderma asperellum unveiled by de novo transcriptome analysis during bioleaching. J. Environ. Manag. 356, 120734. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.120734
Pandiyan, A., Sarsan, S., Durga, G. G. S., and Ravikumar, H. (2024). “Biofertilizers and biopesticides as microbial inoculants in integrated pest management for sustainable agriculture,” in Microbial essentialism (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 485–518. doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-13932-1.00010-6
Pandya, D. K., and Kumar, M. A. (2021). Chemo-metric engineering designs for deciphering the biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 411, 125154. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125154
Paniagua-Michel, J., and Banat, I. M. (2024). Unravelling diatoms’ potential for the bioremediation of oil hydrocarbons in marine environments. Clean. Technol. 6, 93–115. doi:10.3390/cleantechnol6010007
Pérez, V., Pascual, A., Rodrigo, A., Torreiro, M. G., Latorre-Sánchez, M., Lozano, C. C., et al. (2020). “Integrated innovative biorefinery for the transformation of municipal solid waste into biobased products,” in Waste biorefinery (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 41–80. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-818228-4.00002-2
Priya, A., Muruganandam, M., Kumar, A., Senthilkumar, N., Shkir, M., Pandit, B., et al. (2024). Recent advances in microbial-assisted degradation and remediation of xenobiotic contaminants; challenges and future prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 60, 105106. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.105106
Proietti Tocca, G., Agostino, V., Menin, B., Tommasi, T., Fino, D., and Di Caprio, F. (2024). Mixotrophic and heterotrophic growth of microalgae using acetate from different production processes. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technology 23, 93–132. doi:10.1007/s11157-024-09682-7
Qu, Y., Zou, Y., Wang, G., Zhang, Y., and Yu, Q. (2024). Disruption of communication: recent advances in antibiofilm materials with anti-quorum sensing properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16, 13353–13383. doi:10.1021/acsami.4c01428
Radhakrishnan, A., Balaganesh, P., Vasudevan, M., Natarajan, N., Chauhan, A., Arora, J., et al. (2023). Bioremediation of hydrocarbon pollutants: recent promising sustainable approaches, scope, and challenges. Sustainability 15, 5847. doi:10.3390/su15075847
Rahimlou, S., Quandt, C. A., and James, T. Y. (2024). “Metabolic constraints and dependencies between “uncultivable” fungi and their hosts,” in Fungal associations (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 33–57. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-41648-4_2
Ramasubburayan, R., Kanagaraj, K., Gnanasekaran, L., Thirumalaivasan, N., and Senthilkumar, N. (2024). Greener approach supported nitrogen-infused carbon dots for biocompatible cellular markers and fluorescent ink based spray-assisted fingerprint analysis. Waste Biomass Valorization, 1–10. doi:10.1007/s12649-024-02442-2
Rani, M., Yadav, J., Shanker, U., and Wang, C. (2024). Recent updates on remediation approaches of environmentally occurring pollutants using visible light-active nano-photocatalysts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 22258–22283. doi:10.1007/s11356-024-32455-2
Roy, B., Tiwari, A., Khan, S. A., Debnath, A., and Nath, P. C. (2024). “Application of genetically modified microorganisms for effective removal of heavy metals,” in Genetically engineered organisms in bioremediation (Boca Raton, Florida, United States: CRC Press), 136–150. doi:10.1201/9781003188568-9
Saad, N. A., Jabit, N. A., Ismail, S., Ishak, K. E. H. K., Aminuddin, M. I. K. A., Halim, M. S. M., et al. (2024). “Management and treatment methods of acid mine drainage,” in Industrial waste engineering (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 441–507. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-46747-9_10
Sadeghi, J., Lakzian, A., Halajnia, A., and Alikhani, M. (2023). Effects of fungal carbon dots application on growth characteristics and cadmium uptake in maize. Plant Physiology Biochem. 204, 108102. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108102
Saeed, M. U., Hussain, N., Sumrin, A., Shahbaz, A., Noor, S., Bilal, M., et al. (2022). Microbial bioremediation strategies with wastewater treatment potentialities–A review. Sci. total Environ. 818, 151754. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151754
Sahu, S., Kaur, A., Singh, G., and Kumar Arya, S. (2023). Harnessing the potential of microalgae-bacteria interaction for eco-friendly wastewater treatment: a review on new strategies involving machine learning and artificial intelligence. J. Environ. Manag. 346, 119004. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119004
Sakhaei, Z., Daryaee, R., Moosavi, A. A., Carrasco-Marin, F., Betancur, S., Bailón-García, E., et al. (2024). Chemical-assisted biological methods for in situ remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Biotechnol. Emerg. Microbes, 217–261. doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-15397-6.00013-9
Saravanan, A., Thamarai, P., Deivayanai, V. C., Karishma, S., Shaji, A., and Yaashikaa, P. R. (2024). Current strategies on bioremediation of personal care products and detergents: sustainability and life cycle assessment. Chemosphere 354, 141698. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141698
Schreiber, M., Jayakodi, M., Stein, N., and Mascher, M. (2024). Plant pangenomes for crop improvement, biodiversity and evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet., 1–15. doi:10.1038/s41576-024-00691-4
Sharma, I. (2020). “Bioremediation techniques for polluted environment: concept, advantages, limitations, and prospects,” in Trace metals in the environment-new approaches and recent advances (Primorsko-Goranska, Croatia: IntechOpen).
Singh, S., Khan, N. A., Ramadan, R., Shehata, N., Kapoor, D., Dhanjal, D. S., et al. (2024). Environmental fate, toxicological impact, and advanced treatment approaches: atrazine degradation and emphasises on circular economy strategy. Desalination Water Treat. 317, 100201. doi:10.1016/j.dwt.2024.100201
Singh, S., Kumar, V., Datta, S., Dhanjal, D. S., Sharma, K., Samuel, J., et al. (2020). Current advancement and future prospect of biosorbents for bioremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 709, 135895. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135895
Singh, V., and Sable, H. (2024). “Bioremediation of emerging pollutants: a sustainable remediation approach,” in Emerging contaminants (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 335–361.
Soleimani, M., Farhoudi, M., and Christensen, J. H. (2013). Chemometric assessment of enhanced bioremediation of oil contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 254, 372–381. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.004
Sravan, J. S., Matsakas, L., and Sarkar, O. (2024). Advances in biological wastewater treatment processes: focus on low-carbon energy and resource recovery in biorefinery context. Bioengineering 11, 281. doi:10.3390/bioengineering11030281
Srivastava, R. K., Shetti, N. P., Reddy, K. R., and Aminabhavi, T. M. (2020). Sustainable energy from waste organic matters via efficient microbial processes. Sci. total Environ. 722, 137927. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137927
Srivastava, R. K., Shetti, N. P., Reddy, K. R., Kwon, E. E., Nadagouda, M. N., and Aminabhavi, T. M. (2021). Biomass utilization and production of biofuels from carbon neutral materials. Environ. Pollut. 276, 116731. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116731
Stein, H. P., Navajas-Pérez, R., and Aranda, E. (2018). Potential for CRISPR genetic engineering to increase xenobiotic degradation capacities in model fungi. Approaches Bioremediation New Era Environ. Microbiol. Nanobiotechnology, 61–78. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-02369-0_4
Sultana, S., Khan, S., Ranga Rao, A., Haque, M. M., Mahmud, M. Y., and Ravishankar, G. A. (2024). Phycoremediation of aquaculture wastewater by algae. Algae Mediat. Bioremediation Ind. Prospect. 1, 271–294. doi:10.1002/9783527843367.ch13
Taylor, D. L., and Bhatnagar, J. M. (2024). “Fungi in soil: a rich community with diverse functions,” in Soil microbiology, ecology and biochemistry (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 75–129.
Thirumalaivasan, N., Mahapatra, S., Ramanathan, G., Kumar, A., Raja, T., Muthuramamoorthy, M., et al. (2024). Exploring antimicrobial and biocompatible applications of eco-friendly fluorescent carbon dots derived from fast-food packaging waste transformation. Environ. Res. 244, 117888. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117888
Umar, A., Mubeen, M., Ali, I., Iftikhar, Y., Sohail, M. A., Sajid, A., et al. (2024). Harnessing fungal bio-electricity: a promising path to a cleaner environment. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1291904. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1291904
Venkata Mohan, S., Venkateswar Reddy, M., Chandra, R., Venkata Subhash, G., Prathima Devi, M., and Srikanth, S. (2013). Bacteria for bioenergy: a sustainable approach towards renewability. doi:10.1039/9781849737142-00251
Vodyanitskii, Y. N. (2013). Contamination of soils with heavy metals and metalloids and its ecological hazard (analytic review). Eurasian Soil Sci. 46, 793–801. doi:10.1134/s1064229313050153
Wibowo, Y. G., Safitri, H., Khairurrijal, K., Taher, T., Ode Arham, L., Jarwinda, , et al. (2024). Recent advances in acid mine drainage treatment through hybrid technology: comprehensive review of scientific literature. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 21, 100945. doi:10.1016/j.enmm.2024.100945
Wilcox, S. M., Mulligan, C. N., and Neculita, C. M. (2024). Bioprecipitation as a bioremediation strategy for environmental cleanup. Bioremediation for sustainable environmental cleanup. Boca Raton, Florida, United States: CRC Press, 19–39. doi:10.1201/9781003277941-2
Yaashikaa, P., Karishma, S., Kamalesh, R., Vickram, A., and Anbarasu, K. (2024). A systematic review on enhancement strategies in biochar-based remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 355, 141796. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141796
Yang, G., Wei, L., Wang, X., Wu, X., He, Y., Li, G., et al. (2024). Enhancing commercially iron powder electron transport by surface biosulfuration to achieve uranium extraction from uranium ore wastewater. Inorg. Chem. 63, 1378–1387. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c03906
Zhai, Y., Bai, J., Chang, P., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, G., et al. (2024). Microplastics in terrestrial ecosystem: exploring the menace to the soil-plant-microbe interactions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 174, 117667. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2024.117667
Zhang, X., Sun, T., Li, F., Ji, C., and Wu, H. (2024). Risk assessment of trace metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in seawater of typical bays in the Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 200, 116030. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116030
Glossary
Keywords: fungi, bacteria, bioremediation, pollutants, toxic waste, biowaste, detoxification, Lessharmful
Citation: Thirumalaivasan N, Gnanasekaran L, Kumar S, Durvasulu R, Sundaram T, Rajendran S, Nangan S and Kanagaraj K (2024) Utilization of fungal and bacterial bioremediation techniques for the treatment of toxic waste and biowaste. Front. Mater. 11:1416445. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2024.1416445
Received: 12 April 2024; Accepted: 24 May 2024;
Published: 15 July 2024.
Edited by:
Saraschandra Naraginti, Anhui Polytechnic University, ChinaReviewed by:
Jie Li, Hohai University, ChinaThambiraj Selvarathinam, City College of New York (CUNY), United States
Copyright © 2024 Thirumalaivasan, Gnanasekaran, Kumar, Durvasulu, Sundaram, Rajendran, Nangan and Kanagaraj. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Suresh Kumar, c3VyZXNoLmt1bWFyQGFtdS5lZHUuZXQ=; Saravanan Rajendran, c2FyYXZhbmFuMy5yYWpAZ21haWwuY29t; Senthilkumar Nangan, bnNrdW1hcmNoZW1pc3Q5MUBnbWFpbC5jb20=; Kuppusamy Kanagaraj, a2FuYWdhcmFqMTk1QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Natesan Thirumalaivasan1
Natesan Thirumalaivasan1 Saravanan Rajendran
Saravanan Rajendran Senthilkumar Nangan
Senthilkumar Nangan Kuppusamy Kanagaraj
Kuppusamy Kanagaraj