- Department of Psychology, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA
Whether lexical selection is by competition is the subject of current debate in studies of monolingual language production. Here, I consider whether extant data from bilinguals can inform this debate. In bilinguals, theories that accept the notion of lexical selection by competition are divided between those positing competition among all lexical nodes vs. those that restrict competition to nodes in the target language only. An alternative view rejects selection by competition altogether, putting the locus of selection in a phonological output buffer, where some potential responses are easier to exclude than others. These theories make contrasting predictions about how quickly bilinguals should name pictures when non-target responses are activated. In Part 1, I establish the empirical facts for which any successful theory must account. In Part 2, I evaluate how well each theory accounts for the data. I argue that the data do not support theories that reject lexical selection by competition, and that although theories where competition for selection is restricted to the target language can be altered to fit the data, doing so would fundamentally undermine the distinctness of their position. Theories where selection is by competition throughout both target and non-target language lexicons must also be modified to account for the data, but these modifications are relatively peripheral to the theoretical impetus of the model. Throughout, I identify areas where our empirical facts are sparse, weak, or absent, and propose additional experiments that should help to further establish how lexical selection works, in both monolinguals and bilinguals.
Introduction
All models of lexical selection start with the same assumption: that our search for words is semantically guided, such that a cohort of semantically related words becomes active, therefore requiring the system to select the appropriate entry from among a number of alternatives. Implicit in this view is the further assumption that the semantic features specified by the speaker will generally point to a single lexical node (lemma) that uniquely matches the speaker’s intended semantic intent. Cases of within-language synonymy (couch/sofa) have been interpreted as the exceptions that prove the rule (e.g., Peterson and Savoy, 1998).
The real world, however, does not fully justify this latter assumption. Given that bilingualism is the global norm, a semantically guided search is not sufficient for most people to specify a single lexical node. Rather, a large body of evidence indicates that in bilinguals, both a target node and its translation may become active, even to the level of phonology (for a review, see Kroll et al., 2006). Nevertheless, bilingual speakers hardly ever produce cross-language intrusions (Poulisse and Bongaerts, 1994). This is sometimes termed the “hard problem” of bilingual lexical access: how do bilinguals manage to select words in the intended language, rather than their semantically equivalent translations? The answer to this question is potentially informative about theories of lexical selection in monolinguals that are currently the subject of heated debate: whether or not there is competition for selection between non-target nodes at the lexical level.
Selection by Competition
The earliest psycholinguistic studies of language production relied mainly on speech errors. However, given that the ultimate goal has been to understand successful language production, the field gradually shifted to tasks such as picture naming, where the timecourse of successful lexical retrieval could be examined. Among the earliest and most robust discoveries in this domain was that picture naming latency could be modulated by presenting a distractor word, either visually (e.g., Lupker, 1979) or auditorily (e.g., Schriefers et al., 1990). Crucially, if the distractor word belonged to the same category as the target picture (e.g., a picture of a dog with the word cat1 written on it), reaction times were slowed significantly more than if the distractor word were unrelated (e.g., a picture of a dog with the word table written on it). This effect came to be known as semantic interference, and eventually led to the entire paradigm being known as picture–word interference. Subsequent studies manipulated the nature of the picture–word relationship as well as the time delay between the onset of the picture and the onset of the word, and found that semantically related distractors yielded the most interference when they were presented slightly before or at the same time as the target word. Phonologically related distractors (e.g., a picture of a dog with the word doll written on it) exerted their maximal effect when presented after the target picture, and yielded facilitation instead of interference. These findings, among others, were interpreted as evidence for two-stage theories of lexical access. According to these theories, semantic features of the to-be-named target picture spread activation to the many lexical nodes that are connected to them. The production system must then choose which of the activated nodes should be selected for production. The distinctive tenet of models where selection is by competition is that the amount of time it takes to select a target node is a function of the activation level of non-target nodes. Thus, anything that increases the activation of non-target nodes during this stage (such as a semantically related distractor word) will make it harder for the system to select the target word, thereby slowing naming times. In contrast, the next stage of lexical access is at the phonological level. Here, activated lemmas spread activation to their associated phonological nodes, which then interface with the motor system for actual production. During this phase, the presentation of a semantically related distractor has little effect, since the target lemma has already been selected. Presenting a phonologically related distractor, however, can speed reaction times, because it will activate some of the same nodes that need to be activated for the picture naming task. These basic findings, among others, are most prominently captured in the Levelt et al. (1999) WEAVER++ model, which has been a strongly dominant model of lexical access. Although the original model assumed strict seriality between the lexical and phonological stages, feed-forward cascaded activation is now widely accepted (Jescheniak and Schriefers, 1998; Peterson and Savoy, 1998; Cutting and Ferreira, 1999; Morsella and Miozzo, 2002; Navarrete and Costa, 2005).
However, this account is not without its challenges. For example, selection by competition predicts that distractors that share more semantic features with a target picture should engender more competition and thus lead to slower reaction times; however, Mahon et al. (2007) found that semantically close distractors yielded less competition than semantically far distractors. In addition, selection by competition predicts that semantic interference should only arise when lexical selection is ongoing. However, Janssen et al. (2008) found semantic interference even when the distractor was presented a full second after the target picture, at which point participants should have had ample time to select the target lemma. Another reported challenge is the finding that uncommon distractor words yield stronger semantic interference than common distractors (Miozzo and Caramazza, 2003). These and other challenges to selection by competition have motivated the resuscitation of non-competitive models of lexical selection. Although these results have not been universally accepted (Vigliocco et al., 2004; Rahman and Melinger, 2009; Hutson et al., 2010; Lee and de Zubicaray, 2010; Rahman and Aristei, 2010; Spalek et al., 2010; Janssen et al., 2011; Mädebach et al., 2011; Roelofs et al., 2011; Starreveld et al., in press), they have inspired a revival of interest in non-competitive theories of selection. Any non-competitive theory will eventually have to account for reaction time results in picture–word interference studies. Recently, the response exclusion hypothesis (REH; Mahon et al., 2007) has emerged as the most promising of these accounts.
Response Exclusion
The distinctive claim of non-competitive theories of lexical access is that the activation level of non-target lemmas does not influence the speed or difficulty of lexical access. Rather, the first lexical node to reach a critical threshold will be the one selected for production. Previous threshold models (e.g., Stemberger, 1985; Dell, 1986) fell out of favor when they struggled to account for the timecourse effects in picture–word interference studies. However, several recent studies suggest that the REH may be able to account for these effects without positing selection by competition (Finkbeiner and Caramazza, 2006; Finkbeiner et al., 2006a; Mahon et al., 2007; Janssen et al., 2008; Dhooge and Hartsuiker, 2010, 2011). It should be noted that Response Exclusion is not itself a full theory of lexical selection, but rather a non-competitive account of chronometric effects in picture–word experiments. Because of the central role that picture–word interference has played in the development of competitive theories, non-competitive theories must offer an explanation.
Three central ideas ground this hypothesis. First, given that humans only have one mouth, it is only possible to speak one word at a time. Selection is therefore, in the limit, forced to happen prior to articulation. But prior to articulation, there is nothing that forces selection in such an obvious way, and indeed the evidence for cascaded activation indicates that speakers activate the phonology of words that they do not eventually name. Thus, the REH posits that competition takes place not at an abstract lexical level, but in a pre-articulatory buffer, where the system needs to decide which set of motor commands to send to the articulators.
The model’s second central tenet is that both visually and auditorily presented distractor words have a privileged relationship with the articulators in a way that pictures do not. That is, reading or hearing a word automatically engages that word’s motor plan, whereas the same is not true for seeing a picture of an object. This means that when a person is confronted with a picture–word stimulus, the distractor word will reach the pre-articulatory buffer before the target picture’s name.
The third and final major claim is that the speed of picture naming is a function of how easily a potential but incorrect response can be dislodged from the pre-articulatory buffer. The more response-relevant features a candidate response shares with the target, the harder it will be to dislodge that response from the buffer, leading to slower reaction times. Conversely, candidate responses that share very little with the target response are easy to exclude, leading to faster reaction times.
The model therefore has a natural explanation for semantic interference effects insofar as a distractor like cat is a potential response that shares features with the target “dog,” and is therefore harder to exclude than a distractor like table, which shares hardly any features with “dog,” and is therefore easy to exclude. The REH also predicts the observed semantic interference even in a delayed naming task (Janssen et al., 2008), which was problematic for models of selection by competition. In addition, the REH can handle the counterintuitive finding that low-frequency distractors slow naming more than high-frequency distractors (Miozzo and Caramazza, 2003); this is because high-frequency distractors are easier to process and can therefore be excluded more quickly.
However, each of these claims has been challenged. The finding that semantically far distractors interfere more than semantically close distractors has proven difficult to replicate (Lee and de Zubicaray, 2010), and is in contradiction with results from Vigliocco et al. (2004). At least two research groups have also failed to replicate semantic interference under delayed naming conditions (Spalek et al., 2010; Mädebach et al., 2011). The distractor frequency effect is easily replicable, but both Rahman and Melinger (2009) and Roelofs et al. (2011) advocate competitive models that they claim can account for the data. Meanwhile, Starreveld et al. (in press) conclude that the REH makes the wrong predictions about the timecourse of the distractor frequency effect and its relationship to semantic interference.
Another challenge for the REH is that semantic interference effects have been observed even without overt naming, in paradigms such as syllable decisions and phoneme monitoring (Hutson et al., 2010) and picture–word interference (Rahman and Aristei, 2010). Finally, neither Aristei et al. (2011) nor Janssen et al. (2011) found the expected ERP signature of response selection.
Discriminating between the Models
The current literature is thus complicated by inconsistent data and multiple explanatory accounts, all of which focus exclusively on monolinguals. One potential way to distinguish the theories is to ask what predictions they make about how lexical selection might operate in bilinguals, and then evaluate the extent to which the data support those predictions. Specifically, the theories make different predictions regarding how bilinguals should name pictures in the context of various within- and between-language distractor words. To assess the degree to which the various theories can account for the data, it is first necessary to outline what the relevant facts are. To that end, Part 1 of this paper reviews the published literature concerning bilingual picture–word interference studies, including quantitative analyses where they are useful. Part 2 then evaluates whether the data are predicted under the theoretical accounts above, and considers the changes that would be necessary to allow the theories to account for the data. Throughout, I identify areas where the empirical evidence is sparse, weak, or absent, and propose additional experiments that should help to further establish how lexical selection works, in both monolinguals and bilinguals.
Part 1: A Meta-Analysis of Picture–Word Studies in Bilinguals
Method
In order to evaluate the above theories, we must first establish the empirical facts. While there are certainly many experimental situations that inform these theories, I focus here on how bilinguals name pictures in the context of various distractor words. The published literature includes a relatively small number of studies of picture naming in bilinguals. However, the studies analyzed below represent data from 419 bilingual participants across 10 different conditions of interest. Across the studies, the bilingual data yield 80 independent observations of group level picture–word “effects” (related minus unrelated).
Table 1 lists the various distractor conditions that are relevant for monolinguals and bilinguals. For clarity and convenience, I adopt a schematic nomenclature to refer to the various types of distractors that might be presented. In each case, the subjects’ task is to name a picture of a dog. Distractors are then classified on the basis of their relationship to the target word, including whether or not they belong to the target language. Translations of non-target language distractors are given in parentheses. These example distractors will then be used throughout the paper to illustrate the conditions tested in various studies and between various pairs of languages.
The bilingual data analyzed below are drawn from Hermans et al. (1998), Costa and Caramazza (1999), Costa et al. (1999), Costa et al. (2003), and Hermans (2004). Older picture–word studies in bilinguals were excluded because they measured response time to entire lists rather than to individual trials, tested children, focused on orthographic effects, and/or did not compute effects relative to an unrelated baseline. Excluded papers include: Ehri and Ryan (1980), Goodman et al. (1985), Mägiste (1984, 1985), Rayner and Springer (1986), and Smith and Kirsner (1982).
One additional study was excluded from quantitative analysis, but is theoretically informative. Knupsky and Amrhein (2007) studied phonological facilitation through translation in bilinguals who named pictures in both their dominant and non-dominant language. Their conditions are directly comparable to those included below, but their naming times are orders of magnitude larger than those observed in any other study. Effects that hover around 20–50 ms in most papers were on the order of several hundred milliseconds, including two conditions reporting facilitation effects of more than 1000 ms. This is presumably because the authors intentionally avoided repeating stimuli during the experiment; each picture–word pair was encountered only once. While these results are meaningful and internally consistent, introducing them into a meta-analysis would yield more confusion than clarity, and thus they are discussed independently.
Unless otherwise noted, the methodology employed for the meta-analysis was as follows. The mean reaction times for each group of subjects were organized by distractor type (e.g., semantically related, phonologically related, unrelated, etc.). The effects of interest were calculated by subtracting reaction times in the unrelated condition from reaction times in each of the related conditions in turn: thus, a positive number indicates interference while a negative number indicates facilitation. Multiple regression was performed on the effects from each relevant group of subjects reported in the above literature. The dependent variable was always a reaction time measure: either raw reaction time, or the size of a particular effect (related minus unrelated). It was important to control for stimulus-onset asynchrony (SOA), which is known to have a strong impact on naming latencies. Because these effects are typically strongest at one SOA and fall off on either side, SOA was treated as a quadratic regressor. However, none of the timecourse effects proved to be relevant for adjudicating between the various models; therefore, those results will not be discussed in detail here.
Whether bilinguals named the pictures in their dominant or non-dominant language was another potential source of variance. The bilinguals in the following analyses were generally proficient in both languages; however, they ranged from late bilinguals having at least 5–6 years of classroom instruction (Costa and Caramazza, 1999; Hermans, 2004) to being extremely proficient and balanced native bilinguals (Costa et al., 1999, 2003), with some in between (Hermans et al., 1998). Proficiency and degree of language dominance have been shown to influence performance in other psycholinguistic paradigms such as cued language switching (e.g., Costa and Santesteban, 2004; Costa et al., 2006). To see whether proficiency influenced behavior in a picture–word context, I examined raw reaction times in the unrelated condition when subjects named pictures in L1 vs. L2. Because the unrelated condition forms the basis of all other effect calculations, it was important to establish whether language dominance influenced naming times. Multiple regression was performed on raw naming times in the unrelated condition, with SOA (continuous) as a quadratic regressor, and target dominance (L1 vs. L2) and distractor dominance (L1 vs. L2) as logistic regressors. Neither target dominance [F(1,37) = 0.03, p = 0.88] nor distractor dominance [F(1,37) = 0.16, p = 0.69] accounted for significant variance (both <1%) suggesting that these subjects are equally skilled at naming pictures in both their languages. Therefore, language dominance will not be considered in the analyses to follow.
It is worth noting that very low-proficiency bilinguals were not tested in any of these papers, and might behave differently. Low-proficiency might mean reduced automaticity of reading an L2 distractor word, for example, in which case one might expect generally weaker effects. Or, if the task is to name in L2, an L1 distractor might exert a disproportionately strong effect. In both cases, it seems likely that proficiency would only modulate the strength of a given effect, not its overall pattern, especially considering that in most cases, the results of interest are calculated with respect to processing an unrelated distractor in the same-language. The stability of patterns in the current data across early/late, balanced/unbalanced, and medium/high proficiency bilinguals is consistent with this view. Furthermore, if we take beginning readers as a model of low-proficiency bilinguals (since they too would be less skilled at processing a written distractor), we find reliable interference even from early stages of reading (Stroop: Comalli et al., 1962; Schiller, 1966; Guttentag and Haith, 1978, 1979; Picture–Word: Rosinsky et al., 1975; Ehri, 1976; Ehri and Wilce, 1977; Rosinsky, 1977). Even children with reading disabilities show large Stroop effects (Das, 1993; Everatt et al., 1997; Faccioli et al., 2008). Therefore, while the performance of low-proficiency bilinguals remains an empirical question, the data discussed below seem likely to generalize to bilinguals with more than a minimal degree of L2 proficiency.
Results
Basic PWI effects (dog, cat, and doll)
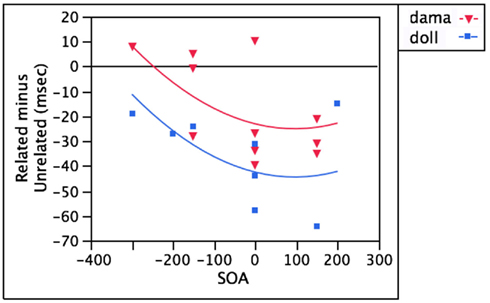
Figure 1 compares the performance of bilinguals to that of monolinguals in the three most basic conditions in the picture–word paradigm: an identity distractor (dog, Figure 1A), a semantically related distractor (cat, Figure 1B), and a phonologically related distractor (doll, Figure 1C). Monolingual data for this comparison were drawn from a thorough but non-exhaustive review of the studies that used these types of distractors. I aimed to include papers whose data made significant contributions to the theoretical issues at stake. The following papers contributed the data for monolingual speakers: Glaser and Düngelhoff (1984), Schriefers et al. (1990), Starreveld and La Heij (1995), Starreveld and La Heij (1996), Jescheniak and Schriefers (1998), Damian and Martin (1999), Cutting and Ferreira (1999), Starreveld (2000), and Damian and Bowers (2003). These papers provide data from 738 participants. As can be seen from Table 1, these distractors have the same relationship to the target for monolinguals and bilinguals; thus, all models predict that the populations should not differ, which proves to be the case.
Figure 1. Monolinguals and bilinguals do not differ in (A) target identity facilitation, (B) semantic interference, or (C) phonological facilitation, with target language distractors. Y-axis in all graphs represents milliseconds.
When the target response is itself presented as a distractor (dog), both monolinguals and bilinguals are faster to say “dog” than in the context of an unrelated distractor like table. The population variable (monolingual vs. bilingual) accounts for no variance (0%) in the size of the target identity facilitation effect [F(1,37) = 0.002, p = 0.96].
When the distractor refers to something that belongs to the same category as the target (cat), both monolinguals and bilinguals are slower to say “dog” than in the presence of an unrelated distractor. Again, population accounts for less than 1% of the variance in this semantic interference effect [F(1,56) = 0.16, p = 0.69].
Finally, when the distractor shares phonology with the target (doll), both monolinguals and bilinguals are faster to say “dog” than in the presence of an unrelated distractor. Population explains only 2% of the variance that SOA does not [F(1,38) = 0.72, p = 0.40].
Having established that bilinguals behave in predictable ways compared to monolinguals, we can now ask how bilinguals behave when the distractors engage (directly or indirectly) various responses in the non-target language.
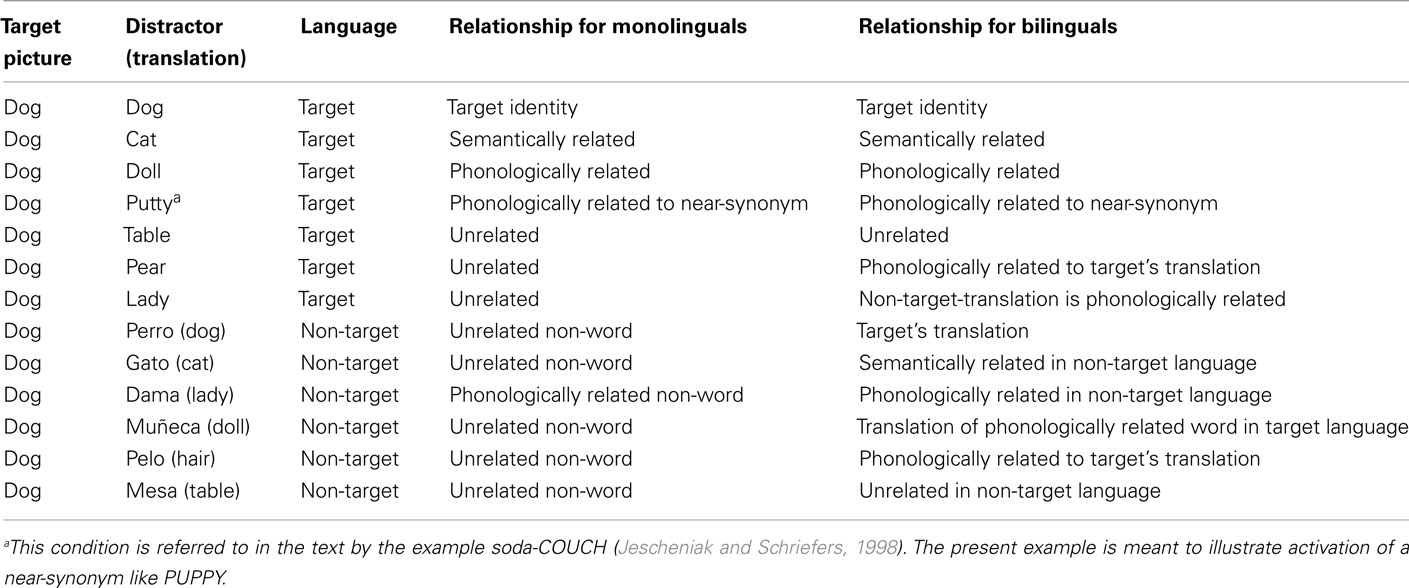
Translation facilitation (perro)
One obvious first step is to ask how bilinguals respond when the distractor word (e.g., perro) is the translation of the target word (e.g., “dog”). Under these conditions, bilinguals are significantly faster to say “dog” than when the distractor is an unrelated word in the non-target language (e.g., mesa). The timecourse of the facilitation is strongest at early SOAs (−200 to −100 ms), waning to non-significance by +200 ms SOA (Costa and Caramazza, 1999; Costa et al., 1999; Hermans, 2004). Interestingly, this facilitation has a similar timecourse to, but is much weaker than, the facilitation observed with the target identity distractor dog, as shown in Figure 2. After controlling for SOA, language membership accounts for an additional 58.2 of the variance, with dog exerting a much stronger facilitatory effect [F(1,13) = 32.04, p < 0.001]. This difference in magnitude combined with the fact that perro’s effect wanes to non-significance before dog’s may reflect direct input-to-output phonological activation that is beneficial from dog but not from perro; however, cascaded activation from within the production system may also contribute.
Semantically related words in the non-target language (gato)
In the case of semantically related words, bilinguals experience semantic interference over a similar timecourse for distractors in both the target language (cat) and non-target language (gato), with the strongest effects between −150 and +150 ms SOA (Hermans et al., 1998; Costa and Caramazza, 1999; Costa et al., 1999, 2003). Figure 3 demonstrates that unlike the case of perro and dog above, a non-target language distractor like gato interferes to the same degree as a target language distractor like cat. After controlling for SOA, adding language as a regressor accounts for less than 1% additional variance [F(1,20) = 0.22, p = 0.64].
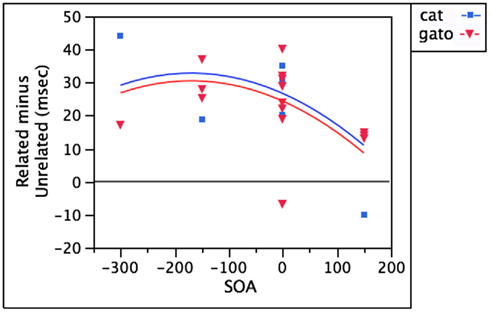
Figure 3. Equivalent semantic interference from target language and non-target language distractors.
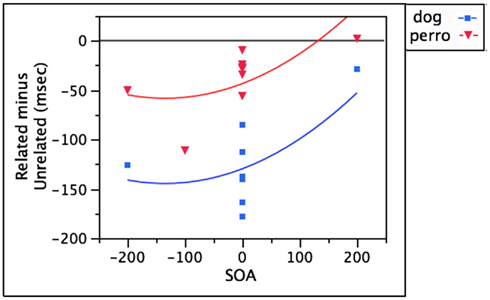
Non-target distractors that share phonology with the target (dama)
As seen above with distractors like doll, words in the non-target language that are directly phonologically related to the target (e.g., dama) should also yield facilitation thanks to the input-to-output connections between the comprehension and production systems. Indeed, facilitatory effects are observed at SOAs ranging from −200 to +200 ms (Hermans et al., 1998; Costa et al., 1999, 2003). As with doll, facilitation from dama is still robust at positive SOAs by which time semantically related distractors no longer interfere.
After controlling for SOA, the distractor’s language membership accounts for an additional 23.1% of the variance, with target language distractors (doll) yielding stronger facilitation [F(1,18) = 6.44, p < 0.05] than non-target language distractors (dama). This additional facilitation cannot be due to target language distractors sharing more segments with the picture name than non-target language distractors; t-tests revealed no significant differences (all p values > 0.3). Because the representation of similar phonemes might differ slightly between languages, it is possible that non-target language distractors like dama are simply less effective phonological primes than target language distractors like doll. These data are illustrated in Figure 4.
In theory, monolinguals too should experience phonological facilitation from distractors like dama, which would be, to them, non-words. However, they would have facilitation from only one source (direct input-to-output mappings) whereas bilinguals might also benefit from activation that cascades down from the lexical node for DAMA (which is absent in monolinguals). While some evidence suggests that monolinguals do experience phonological facilitation from non-words, the stimuli are suboptimal in that visually presented distractors differed in word shape (Posnansky and Rayner, 1977; Rayner and Posnansky, 1978), and auditorily presented distractors contained no information that was inconsistent with the target word (e.g., da rather than dapo; Starreveld, 2000). Given the theoretical importance of assessing how activation at lemma and lexeme levels influences naming times, future studies should test monolinguals and bilinguals using distractors like dama for both groups. The measure to which bilinguals experience more facilitation than monolinguals provides a measure of the contribution of facilitation at the lexical level, over and above direct input-to-output mappings.
Phonological facilitation through translation into non-target language (lady)
Another way to address the contribution of lexical factors to phonological priming is to ask how reaction times would be affected by presenting a distractor like lady, which is the target language translation of dama. Monolinguals would presumably treat lady as a totally unrelated distractor, but it is conceivable that bilinguals might covertly activate the phonology of its translation, dama, and thus show facilitation. The only test of such distractors included in this meta-analysis did not find evidence of such facilitation (Costa et al., 1999; Expt 6). However, Knupsky and Amrhein (2007) did find such evidence in a similar study, as discussed below. This pattern of results suggests that the majority of phonological facilitation is due to sub-lexical sources: direct input-to-output connects that do not rely on accessing a word’s lemma or lexeme. However, it would be premature to rule out any contribution of lexical factors. It is possible that lady does activate its translation, dama, which then cascades activation to its phonological units. The effect may simply be too weak to be easily observable with standard methods, given that dama is significantly less effective at priming “dog” even when directly activated.
Phonological facilitation through translation into target language (muñeca)
This same question can be raised, then, with regard to distractors whose translations are phonologically related to the target: for example, muñeca, whose translation is doll. If the non-target language distractor muñeca activates its translation equivalent, DOLL, then facilitation might be expected, and might be easier to observe than with lady, since doll is a more effective prime for “dog” than dama. The data here are somewhat equivocal. When comparing distractors like muñeca to unrelated distractor words which were never used as potential names in the experiment, both Costa et al., 1999, Expts 5 and 7) and Hermans (2004) failed to find evidence of such facilitation. However, when comparing muñeca against unrelated distractors whose names were potential responses, Hermans found significant phonological facilitation at −100 ms SOA. These data are displayed in Figure 5. Hermans argues that these effects emerge when subjects have reason to access the distractors’ translations. It could also be that −100 ms is simply the best SOA at which to observe these effects.
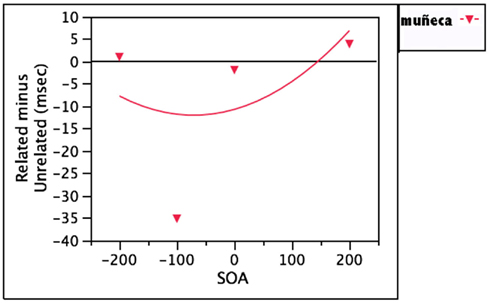
Figure 5. Mixed results for distractors in the non-target language whose translations are phonologically related to the target (muñeca, translates to doll).
Still, the discrepancy between the findings of Costa et al. (1999) and those of Hermans (2004) calls for additional investigation. In a similar study, Knupsky and Amrhein (2007) explored this phonological facilitation through translation in a paradigm designed to minimize stimulus repetition, which characterizes most PWI experiments. Their subjects saw each target item only once, and this is reflected in the much longer reaction times they report. Their results revealed significant facilitation for both lady and muñeca at 0 ms SOA, which was the only SOA tested. Taken together, these results imply that there can be lexical contributions to the phonological facilitation effect, although they seem to exert less of an influence than direct input-to-output activation. However, these effects are clearly less robust than other effects, and care should be taken to avoid overinterpreting them until more data are available.
Phonological neighbors of the target’s translation (pear and pelo)
In monolinguals, interference has been observed when presenting a distractor word that is phonologically related to a near-synonym of the target (Jescheniak and Schriefers, 1998). In their study, presenting soda as a distractor made subjects slower to name “couch” than when a distractor like apple was presented. Their interpretation of these results was that soda activated SOFA, which competed for selection with COUCH. In bilinguals, this then raises the possibility that interference might result if distractors are presented that are phonologically related to the target’s translation (since the translation is, by definition, a near-synonym). According to theories where lexical selection is competitive (e.g., Levelt et al., 1999), the strongest semantic competitor ought to be the lemma that shares the most semantic properties with the target. For a bilingual, that would be the target’s translation (perro, for the target “dog”). Therefore, the question of interest regards the behavior of distractors that are phonologically similar to the target’s translation (perro), whether in the target language (pear), or in the non-target language (pelo). As seen in Figure 6, effects of these distractors tend to be weaker, but that is to be expected for all such mediated effects. When significant, both pear (Hermans et al., 1998) and pelo (Hermans et al., 1998; Costa et al., 2003) have yielded interference. The scattered nature of the observed effects results in a regression where neither SOA nor target-distractor relationship reaches statistical significance. SOA accounts for only 8.4% of the variance (linear and quadratic Fs < 1.1, both ps > 0.3). Whether the distractor is in the target (pear) or non-target (pelo) language accounts for an additional 10.4% of the variance. In general, pelo tends to produce stronger interference than pear, but with only four data points in the latter condition, this tendency does not approach statistical significance [F(1,10) = 1.28, p = 0.28]. Nevertheless, there is no shortage of observations that these distractors slow naming times in bilinguals. The explanation offered by Hermans et al. (1998) is that this interference is due to the distractors activating the lemma for PERRO, and it is generally easier to phonologically activate nodes in the same-language (cf. the increased phonological facilitation for doll over dama).
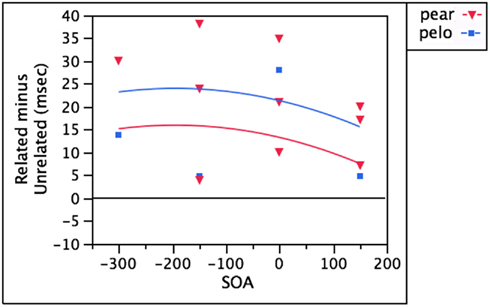
Figure 6. Distractors that are phonologically related to the target’s translation yield interference whether they’re in the target (pear) or non-target (pelo) language.
The data from pear /pelo and perro raise an interesting paradox. Recall that pear /pelo were chosen as distractors because they were theorized to be phonologically related to a semantic competitor of the target (cf. soda-COUCH from Jescheniak and Schriefers, 1998). In this case, that supposed competitor was the translation identity, PERRO. However, when perro itself is presented as a distractor, it yields facilitation, not interference. This puzzle was investigated further by Costa et al. (2008), who found that in a classic Stroop task, distractor words analogous to pelo did not slow reaction times more than unrelated distractor words analogous to mesa. They advise caution when relying on this condition to adjudicate between theories, as it is apparently more robust in some paradigms than others. Nevertheless, the authors also acknowledge that having a small response set, as in Stroop tasks, makes the effect more likely to disappear. Given that natural language production has a very large response set, I would argue that when considering conflicting results from different paradigms, we should more heavily weight those whose task demands more closely approximate natural production: in this case, picture–word studies. Even still, this does not resolve the pelo–perro paradox. The models reviewed below acknowledge this apparent puzzle, but differ in their proposed solutions.
Unrelated distractors in the target vs. non-target language (table vs. mesa)
One final result worth mentioning regards the difference in raw reaction time between unrelated words in the target language (table) and the non-target language (mesa). Some researchers have found evidence that unrelated distractors in the target language yield longer reaction times than unrelated distractors in the non-target language (Costa and Caramazza, 1999; Costa et al., 1999). This finding, termed the “language effect,” has been strongly interpreted by some authors (e.g., Costa et al., 1999; Finkbeiner et al., 2006a). Unlike the effects above, the dependent variable here is not a subtraction measure; instead, raw reaction times are of interest. Therefore, rather than directly comparing reaction times across groups, a more appropriate analysis is to consider the difference between target language and non-target language distractors for each group of subjects that was tested in both conditions. This approach yields 14 pairs of data points, each of which comes from the same population tested on the same items at the same SOA. A paired t-test reveals that unrelated distractors in the target language do yield significantly longer naming times than unrelated distractors in the non-target language [t(13) = 3.22, p < 0.01].
The task facing a model of bilingual lexical access is now clear. Without losing the ability to account for the basic similarities between monolinguals and bilinguals, a successful model of bilingual lexical access must also explain:
1. why perro yields facilitation, but to a lesser extent than dog
2. why gato yields semantic interference that is as strong as cat
3. why dama yields phonological facilitation that is weaker than doll
4. why muñeca produces weak facilitation, but more than lady
5. why pear and pelo yield interference when perro itself facilitates
6. why unrelated target language distractors (table) yield longer RTs than unrelated distractors in the non-target language (mesa).
Part 2: Evaluating the Models
Bilingual Lexical Selection by Lexical Competition between both Languages: The Multilingual Processing Model
Models that adopt the assumption of competition for selection at the lexical level generally share the same basic architecture as the implemented WEAVER++ model (Levelt et al., 1999). Adaptations of this model for bilingual speakers generally posit that lemmas are “tagged” for language membership, and that a speaker’s intention to use a particular language is represented in the pre-verbal message. The challenge for these models is to explain how that pre-verbal intention ensures that the intended lexical node in the target language is more active than its equivalent in the non-target language. At least three such mechanisms have been proposed: (1) positing that the pre-verbal message is semantically specific enough to preferentially activate the lexical node in the target language (Concept Selection Model; La Heij, 2005), (2) reactively inhibiting nodes in the non-target language (Inhibitory Control Model; Green 1986, 1993, 1998), and (3) boosting the activation of all lexical nodes in the target language (Multilingual Processing Model; de Bot, 2004). The viability of the Concept Selection model (La Heij, 2005) has been seriously compromised by persistent evidence that lexical (and sub-lexical) nodes in the unintended language do become active and influence naming times. It is now widely agreed that the solution to bilingual lexical selection is not that easy. Evidence for inhibition, however, is more readily attested. The language switching literature has been the primary focus of evidence in favor of inhibitory accounts. Some studies focus on the finding that bilinguals sometimes take longer to switch from L2 into L1 (e.g., Meuter and Allport, 1999), while others argue that a more reliable sign of inhibition is slower RTs for L1 trials than L2 trials in a switching/mixing context (Gollan and Ferreira, 2009).
Not all researchers accept that these data are indicative of universal features of lexical access in bilinguals. For example, Costa and colleagues demonstrate that switch cost asymmetries are modulated by proficiency (Costa and Santesteban, 2004; Costa et al., 2006). According to such views, inhibition may be involved for some but not all bilinguals, potentially undermining claims that inhibitory processes are a core component of lexical access in bilinguals. Additional arguments against using language switching to index inhibition come researchers arguing that: (1) the findings can be explained without inhibition at all (Roelofs, 1998), and (2) aspects of the results have more to do with task switching than language switching, urging caution when using these tasks to model lexical selection (Finkbeiner et al., 2006b).
It should be noted, however, that evidence suggesting that inhibition plays some role in bilingual language production can be found in other paradigms, including picture naming (Levy et al., 2007) semantic fluency (Linck et al., 2009), semantic competitor priming (Lee and Williams, 2001), and in speaking L3 (for a review, see Cenoz, 2001).
Given the consensus against Concept Selection and the controversy surrounding Inhibitory Control, I will focus instead on a model that has received relatively little attention in the literature: the Multilingual Processing Model (MPM – de Bot, 2004; see also de Bot and Schreuder, 1993).
Like other models in this family, the MPM is largely based on the monolingual research of Levelt and colleagues (Levelt, 1989; Roelofs, 1992; Levelt et al., 1999). As shown in Figure 7, the pre-verbal message contains information about the semantic content of the intended utterance, as well as the language in which it should be spoken. These two types of information flow to separate representations: conceptual information directly and equivalently activates lemmas in both languages, while language intent flows to an external language node, which is connected to both the lemmas and the lexemes (and/or phonemes) belonging to that language. Having this node represented outside of the pre-verbal message accomplishes several functions. Most importantly, as in all models of this type, it solves the hard problem of bilingual lexical access by allowing the speaker’s intention to use a given language to bias the level of activation of all nodes in that language. In addition, by being independently connected to the lexical and phonological levels, it allows for cases in which a speaker selects lemmas from one language and sounds from another, such as when deliberately speaking with a foreign accent. Because each language has its own external node with its own connections to lemmas and lexemes, this model is also easily scaled up to account for people who know three or more languages.
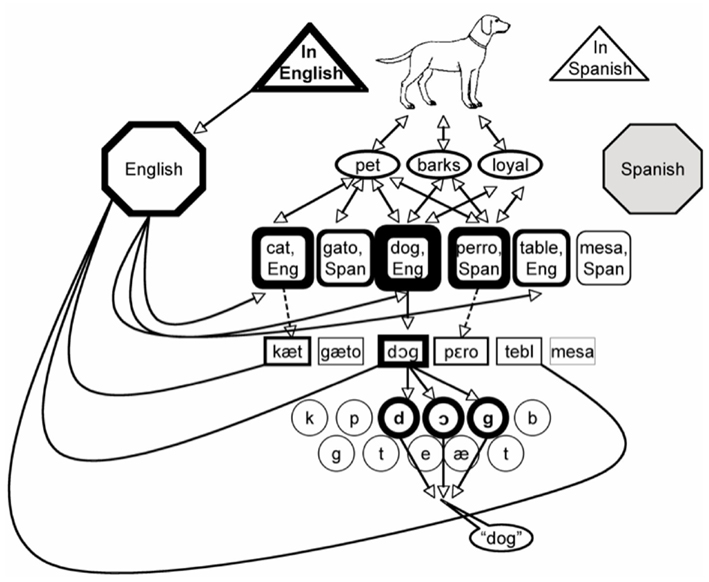
Figure 7. A schematic illustration of de Bot’s (2004) multilingual processing model. When a speaker intends to name in English, Spanish nodes may receive activation and do compete for selection. However, the speaker’s intention biases activation such that target language nodes are always more active than their translations.
The MPM provides a relatively straightforward account of picture naming in bilinguals. Because it shares its basic architecture with WEAVER++, it predicts that bilinguals and monolinguals should not differ in target identity facilitation (dog), semantic interference (cat), and phonological facilitation (doll), as is the case. The more interesting effects are those where bilinguals are predicted to differ from monolinguals.
First, because the MPM allows conceptual activation to flow to lemmas in the non-target language, and because all activated lemmas are considered candidates for selection, the model predicts that distractors like gato should yield interference. More specifically, because conceptual activation flows equally to lemmas in the target and non-target language, CAT and GATO should become equally active. However, activation from the language node should break this tie, making CAT more active than GATO. Is this problematic for the model, given the finding that cat and gato produce the same-size semantic interference effect?
Contrary to the claims of Costa et al. (1999) and Finkbeiner et al. (2006a), the existence of the language node does not predict that the size of the semantic interference effect will be greater for cat than for gato. Recall that the semantic interference effect is computed with respect to an unrelated baseline. It is true that the language node biases the overall level of activation for nodes in the target language, but this applies equally to all nodes in the language, including unrelated distractors like table and mesa. Thus, the baseline increase in activation between target and non-target nodes is factored out when computing the semantic interference effect. The model does predict, however, that a language bias should be detectable in raw reaction times; it should simply take longer to say “dog” in the presence of cat than gato. This comparison appears only five times within subjects in the available literature; thus, a meta-analysis suffers from very low power. Nevertheless, a trend in the predicted direction is observed: speakers needed an average of 23 ms longer to name “dog” in the presence of cat than of gato [t(4) = 2.06, one-tailed p = 0.054].
The “language effect” described above can be better evaluated by examining raw reaction times in the unrelated condition, where more data are available. Because the language node confers a general level of activation to all nodes in the target language, the MPM predicts that unrelated distractors in the target language (e.g., table) should cause a greater delay in naming “dog” than equally unrelated distractors in the non-target language (e.g., mesa). Recall that in a meta-analysis of the 28 relevant data points, a small but significant effect emerged. Distractors like table increased naming time by about 14 ms relative to distractors like mesa [t(13) = 3.22, p < 0.01]. Thus, it appears that the model’s prediction is indeed born out by the data.
The MPM can also account for the small but significant facilitation observed from distractors like muñeca, whose translations (doll) are phonologically similar to the target. If, as monolingual research suggests, distractor words activate their lemmas, a distractor like muñeca will spread some of its activation up through shared conceptual nodes and back down to its translation equivalent lemma, DOLL. Cascaded activation then allows DOLL to pass some of its activation down to the phonological level, where it activates nodes shared by the target response, “dog,” yielding facilitation. This is quite a long path to traverse, however, and so any activation will be much weaker than that induced by doll itself, as is the case. Still, muñeca should yield stronger phonological facilitation than a distractor like lady. In order for lady to differ from an unrelated word, it would have to pass activation from its lemma to its translation (DAMA) which would then pass activation to its lexeme through cascading. However, as established above, dama produces weaker phonological facilitation than doll; thus, its effects are even less likely to be observed. Accordingly, these effects have been difficult to observe, but when significant, they have yielded facilitation (Costa et al., 1999; Hermans, 2004; Knupsky and Amrhein, 2007).
The MPM shares with WEAVER++ the assumption that lexical selection is a competitive process. Therefore, distractors that activate lemmas that share semantic features with the target should increase naming times more than unrelated distractors, regardless of which language they belong to. This was shown to be the case with cat and gato above. The model predicts that distractors like pear and pelo should also cause interference relative to an unrelated baseline. As outlined above, presenting pear or pelo as a distractor activates a cohort of lemmas, which includes PERRO, the target’s translation. Because the lemma for PERRO also receives activation from the conceptual level, it should compete with DOG for selection more than an unrelated distractor. Once again, the data are in accordance with the model’s prediction. Both pear and pelo are found to yield interference when compared to unrelated distractors like table and mesa2.
Perhaps the most central prediction of not just the MPM, but all models in this family, is that when a bilingual intends to name an object, the strongest competitor should be the lemma of its translation equivalent: whereas a lemma like CAT shares many semantic features with the target, the translation equivalent shares all of the target’s semantic features. The fact that successful naming is still achieved can be accounted for by virtue of the language node biasing activation in the target’s favor. However, when the target’s translation (perro) is overtly presented as a distractor, interference ought to be at its strongest, and naming times should be especially slowed relative to an unrelated distractor. Here, however, the data do not appear to support the model. Distractors like perro result in significant facilitation, rather than the predicted interference, although the facilitation is considerably weaker than what is observed with the target name, dog, is presented as a distractor. The reliability of this effect is not in question; since being first observed by Costa and Caramazza (1999), it has been replicated a series of experiments testing both balanced (Costa et al., 1999) and non-balanced bilinguals (Hermans, 2004).
I will argue later that it may be possible for the Multilingual Processing Model to account for facilitation from distractors like perro (see Hermans, 2000). Here, I note only that this discovery was instrumental in motivating alternative accounts of lexical access in bilinguals, including both the language-specific selection model (LSSM) and the REH.
Language-Specific Selection Model: Lexical Selection by Competition within Only the Target Language
One observation that has been noted about the bilingual picture naming data is that distractors in the non-target language yield the same kind of effect as their target language translations. Cat and gato both yield interference, and as has just been noted, dog and perro both yield facilitation. These facts led Costa and colleagues to propose that although nodes in the non-target language may become active, they are simply not considered as candidates for selection (Costa, 2005). According to the Language-Specific Selection Model (LSSM), the speaker’s intention to speak in a particular language is represented as one feature of the pre-verbal message. The LSSM solves the hard problem by preventing nodes in the non-target language from entering into competition for selection, although they may still become activated. Following Roelofs (1992, 1998), the language specified in the pre-verbal message forms the basis of a “response set,” such that only lexical nodes whose language tags belong to the response set will be considered for selection. More formally, only the activation level of nodes in the target language is entered into the denominator of the Luce choice ratio. The LSSM is illustrated in Figure 8.
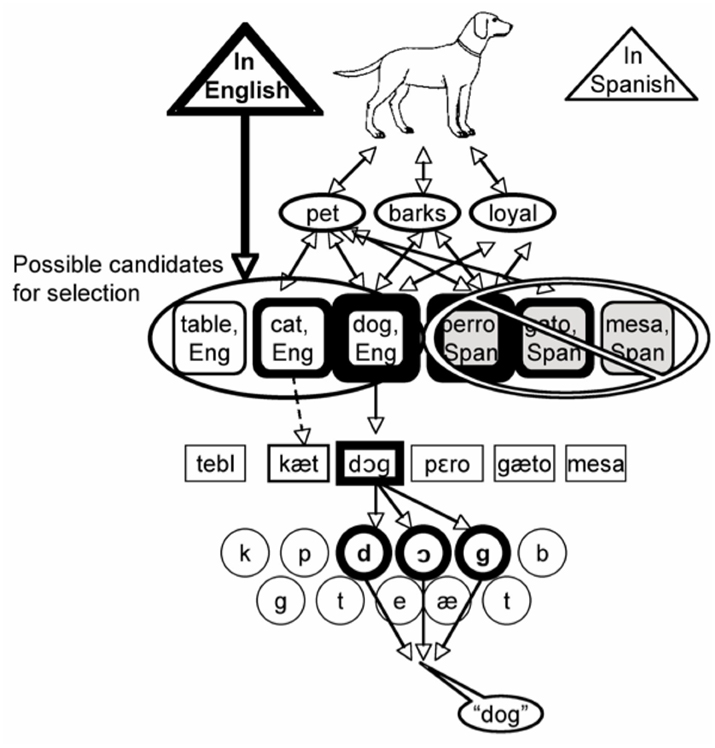
Figure 8. A schematic illustration of the language-specific selection model (Costa, 2005). Lexical candidates in Spanish may become active, but their activation level is not considered during lexical selection. Spanish distractors influence naming times by activating their English translations.
The proposed restriction on selection at the lexical level does not prohibit nodes in the non-target language from receiving or spreading activation. Active lexical nodes in the non-target language are expected to activate their associated phonology to some degree through cascading, and are also expected to activate their translations through shared conceptual features. The fact that these pathways are open allows the LSSM to propose that the semantic interference observed from distractors like gato does not reflect competition for selection between DOG and GATO. Instead, they argue that the interference results from gato activating its translation node, CAT, which then competes with DOG for selection. The chief advantage of this model is that it provides a straightforward explanation of why perro facilitates naming when the MPM and other models in that family incorrectly predict interference. According to this account, perro activates PERRO, which spreads activation to DOG without itself being considered for selection.
One curious feature of the LSSM is the claim that distractors like gato will activate the lemma for CAT just as strongly as cat would (the same goes for perro activating DOG). Costa et al. (2003) were explicit about this “automatic translation” assumption.
…[T]he lexical nodes in the response lexicon are activated to equal degrees regardless of the language in which the distractor is presented… A critical feature of this hypothesis is “automatic translation”: a word distractor is assumed to activate its output lexical representations in the two languages of the bilingual speaker… This hypothesis also assumes that the lexical nodes in the two languages are activated to the same degree. (p. 377)
This assumption was included to explain why cat and gato produced the same degree of interference. Costa and colleagues reasoned that if, as the MPM claims, the lexical node for CAT is more strongly activated by cat than by gato, then cat should yield greater interference than gato. However, I have argued above that this is not the correct prediction. Because semantic interference effects are calculated with respect to an unrelated distractor word in the same language, any baseline increase in activation for the target language over the non-target language is factored out in the subtraction. Therefore, it is at best unnecessary to assume automatic translation. At worst, doing so leads the model to make the wrong prediction about raw reaction times. If distractors automatically activated their translations, then the raw reaction times for saying “dog” in the presence of cat should be the same as saying “dog” in the presence of gato. However, the limited data available indicate that subjects tend to need more time to say “dog” in the presence of cat. A stronger test of this point is to examine picture naming times for unrelated distractors in the target (table) and non-target (mesa) languages. Doing so reveals that bilinguals need more time to say “dog” in the presence of table than in the presence of mesa. These findings constitute a strong argument for discarding the “automatic translation” assumption.
Does discarding this assumption have other consequences for the LSSM? One concern to which Costa et al. (1999) devote attention is the finding that dog confers more facilitation than perro. If both of these distractors were equally effective at activating the lexical node for DOG, it might seem that they should facilitate equally. However, dog also shares phonological information with the target response “dog,” which perro does not; thus, regardless of how strongly distractor words activate their translations, the LSSM can still explain stronger facilitation from dog than from perro.
Discarding the automatic translation assumption becomes more relevant when considering distractors like muñeca. If muñeca activated DOLL as much as doll did, we would expect to see facilitation that was as strong as that produced by doll. To the contrary, Costa et al. (1999) found no facilitation. Rather than questioning the automatic translation assumption, their interpretation was that activation from the lexical level does not contribute to phonological facilitation. This claim forces the LSSM to predict that phonological facilitation should never be observed unless a related distractor is overtly presented. This is at odds with other observations of phonological facilitation through translation (Hermans, 2004; Knupsky and Amrhein, 2007). These authors find that distractors like muñeca do interfere, but weakly: exactly as expected if distractors do activate their translations, but to a lesser extent.
It seems to be the case, then, that when this unmotivated and unnecessary assumption is dropped from Costa’s model, the LSSM can account for all of the data reviewed thus far. However, there remains one class of distractors that is problematic even for this revised version of the model: pear and pelo.
Recall that according to the LSSM, lexical nodes in the non-target language do not enter into competition for selection. Therefore, any distractor that activates the target’s translation should have a facilitatory effect, because the target is not itself a competitor, but does spread activation to its translation, which is the target. In the revised version of the model proposed above, this effect might be small, but if anything, it should be in a facilitatory direction. Unfortunately, the data are at odds with this prediction. As first noticed by Hermans et al. (1998), and subsequently replicated by Costa et al. (2003), distractors like pelo cause significant interference across a wide range of SOAs, from −300 to +150 ms, although at each SOA a combination of significant and null effects have been obtained across experiments. In general, pelo interferes more at earlier SOAs. Significant interference has also been obtained from distractors like pear, which belong to the target language, but are phonologically related to the target’s translation. This effect was only observed at 0 ms SOA (Hermans et al., 1998). These distractors are conceptually unrelated to the target, and therefore should not differ from unrelated distractors like table and mesa, except that they share phonological structure with the target’s translation, perro. If Costa’s model were correct, this should result in facilitation, but instead causes interference. This seems to be at least as problematic for the LSSM as facilitation from perro was for the Multilingual Processing Model. Whether or not either of these models can be fully reconciled to the data is explored below.
Lexical Selection by Competition: Toward a Possible Synthesis
I have just considered two models of bilingual lexical access that both assume that lexical selection is by competition. They differ mainly in whether or not lexical nodes in the non-target language are considered candidates for selection. If the answer is yes, as proposed by de Bot (2004; see also de Bot and Schreuder, 1993; Poulisse, 1997; Green, 1998; La Heij, 2005), then the model must explain why overt presentation of the target’s translation, which ought to be the strongest competitor, yields facilitation rather than interference. If the answer is no, then the model must explain why indirectly activating the target’s translation yields interference rather than facilitation.
Without changing any of the fundamental characteristics of de Bot’s (2004) Multilingual Processing Model, it is possible to explain how the lemmas for DOG and PERRO can compete for selection at the lexical level and yet still have a net facilitatory result from perro as a distractor. As suggested by Hermans (2000), all that must be assumed is that the net facilitatory effect is the sum of three component processes: semantic facilitation from perro to DOG through shared concepts, lexical competition between the lemmas for PERRO and DOG, and more phonological facilitation from dog than from perro. That all three processes play a role is uncontroversial; the question simply concerns their relative contributions. If it is the case that the joint combination of semantic and phonological facilitation outweighs the competition between lemmas, then the MPM successfully handles all the data reviewed in this paper. This is certainly a plausible scenario, but it remains to be determined empirically. Recall that results from the semantic competitor priming paradigm have been interpreted as evidence that lexical inhibition is a much stronger and longer-lasting effect than semantic facilitation (Wheeldon and Monsell, 1994; Lee and Williams, 2001). However, the vast differences between these paradigms hinder the degree to which such straightforward comparisons are informative, and a firm conclusion awaits further research. One key step toward understanding these processes will be quantifying how strongly cascaded activation from the production system figures in phonological facilitation. To answer this question, one could compare the size of the phonological facilitation effect in response to distractors in the non-target language for bilinguals, which would seem like non-words to monolinguals. If the two groups differ, it cannot be due to differences in the phonological properties of the items, since both would have received the same perceptual input. Instead, any observed differences could be attributed to activation flowing through the production system in bilinguals but not monolinguals. Some evidence along these lines comes from the finding that bilinguals – but not monolinguals – are faster at naming pictures whose names in the non-target language are cognates (Costa et al., 2000). Likewise, bilinguals are slower to say that a given phoneme is not present in a picture’s name if that phoneme is present in the picture’s translation (Colomé, 2001). These data demonstrate that lexical nodes in the non-target language do become active at the phonological level through cascaded activation. Such cascaded phonological activation would be present for a distractor like dog but absent for a distractor like perro.
There are two ways to account for the problematic data in Costa’s LSSM. First, if it were the case that lemmas in the non-target language did compete for selection, then the effect of distractors like pear and pelo would fall neatly out of the model. Although such a proposal would enable the model to account for the full range of data (pending the above-proposed solution for perro’s facilitation), it greatly diminishes the model’s distinctiveness, rendering it nearly identical to the MPM. Consequently, Costa et al. (2003) opt for another solution. They suggest that perhaps distractors in the picture–word interference paradigm do not exert their effect only at the lexical level, but also at the sub-lexical level. That is, there may be competition not just among lemmas, but among lexemes as well. Their proposal leaves the details somewhat vague, but the reader is left to presume that – in contrast to the MPM – lexemes are no longer tagged for language membership, and therefore the presence of cross-language competition ceases to be a relevant question. Ultimately, however, this is not very different from the idea that elements in the non-target language do compete for selection, which again undermines the original motivation for the model.
We are left, then, with a certain degree of ambiguity about these results. Although a case can be made that the language non-specific MPM might be able to handle the data without major changes, it is not an empirical certainty. The LSSM might be modified to account for the data, but also depends on some yet-unproven assumptions. It seems worth questioning, then, whether these limitations might be due to some assumption that both models share. One recent proposal takes just such an approach.
Response Exclusion Hypothesis: Bilingual Lexical Selection without Lexical Competition
In contrast to the previous two models, the Response Exclusion Hypothesis (REH) does not posit that competition for selection occurs at the lexical level. It accounts for reaction time effects by proposing a pre-articulatory buffer that considers each potential response as it becomes available. Because distractor words engage the articulatory system in a way that pictures do not, the distractor’s speech plan will be the first to enter the buffer. Response times will therefore be fastest if the first potential response to arrive in the buffer is the target response (“dog”). In all other cases, the prepotent distractor response will first have to be dislodged or “excluded” from the buffer so that the next potential response can be evaluated. This theory finds intuitive appeal in the notion that selection is not logically necessary at the lexical level; in fact, evidence for cascaded activation indicates that non-selected words do become active at the phonological level. However, because humans have only one mouth, they can only speak one word at a time, and so selection must eventually happen prior to articulation. In addition, it is worth remembering that early theories of lexical selection in monolinguals assumed a non-competitive process, and only fell out of favor when they struggled to explain reaction time effects in picture–word experiments (e.g., Stemberger, 1985; Dell, 1986). As noted in the introduction, a number of investigators have recently offered accounts of these effects together with others that are problematic for accounts of selection by competition. However, these interpretations are still a matter of active debate, and an attempt to resolve them is far beyond the scope of this paper. I focus instead on examining how well the REH accounts for data from picture–word studies in bilinguals.
Currently, the only published treatment of bilingual lexical selection under the REH is from Finkbeiner et al. (2006a), who offer an account of several of the key findings above. To avoid the “hard problem” of bilingual access the bilingual version of the REH need only assume that the speaker’s intent to speak the target language allows nodes in that language to accrue activation faster than nodes in the non-target language. Figure 9 presents a schematic illustration of the model.
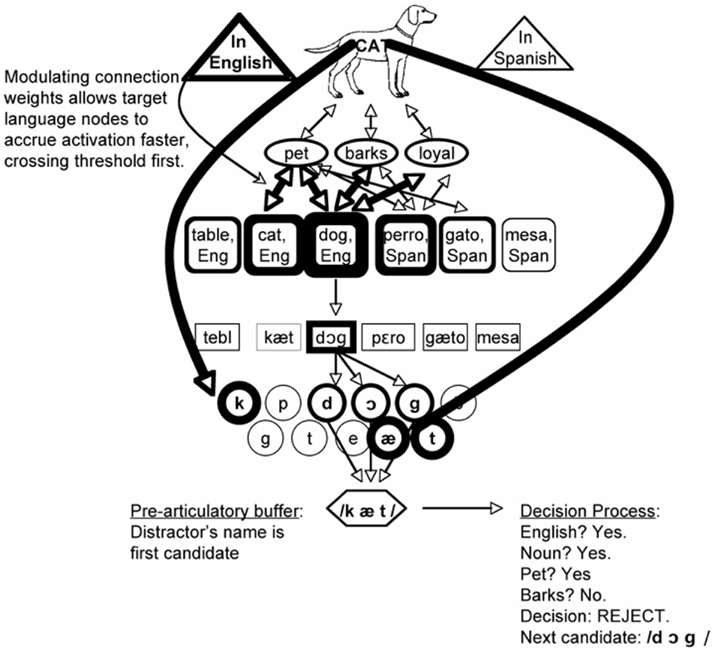
Figure 9. A schematic illustration of the response selection model (Finkbeiner et al., 2006a). Lemma selection is accomplished by a threshold mechanism, rather than by competition. The speaker’s intention to use English allows English lemmas to accrue activation faster. In PWI experiments, a distractor’s name will be the first available response; naming latency is a function of how quickly a potential response can be rejected, allowing the target’s speech plan to be articulated.
The first effect that Finkbeiner et al. (2006a) explore is the “language effect”: that is, why unrelated distractors belonging to the non-target language (mesa) yield faster reaction times than unrelated distractors belonging to the target language (table). According to the REH, one major determinant of how quickly a potential response can be excluded is its response-relevance. Although this construct could benefit from further clarification, the REH only needs to posit that (1) language membership is a response-relevant feature, and (2) response exclusion processes have access to the language membership of potential responses. If we accept those premises, then the REH makes the clear prediction that target language distractors should be harder to exclude than non-target language distractors, successfully accounting for the language effect.
The idea that distractors in the non-target language are easily excluded also allows the REH to predict that translation distractors (perro) will yield facilitation rather than interference, as follows. If selection is by threshold instead of by competition, then anything that increases the activation of the target node will help the target’s response to arrive at the pre-articulatory buffer faster than it otherwise would. Note that many of the things that increase activation of the target are also response-relevant, and therefore hard to exclude. However, a translation distractor (perro) is a special case in which all of the target’s features are activated (yielding semantic priming) while the response itself is not considered relevant, because it belongs to the non-target language. It can therefore be excluded as quickly as an unrelated non-target language distractor like mesa, but semantic priming from featural overlap between DOG and PERRO will end up yielding net facilitation. This neatly accounts for what has been taken to be the most problematic data for models where selection is by competition.
The third and final effect that Finkbeiner et al. (2006a) consider is the observation that distractors like gato yield the same degree of semantic interference as distractors like cat. Their explanation is reminiscent of the account I advanced above for competitive models. Namely, that since semantic interference effects are computed with reference to a same-language unrelated distractor, the effects of language membership cancel themselves out, and similar behavior should be expected from distractors like cat and gato.
However, this account is ultimately problematic for the REH, because it is inconsistent with the account given to explain why perro yields facilitation. Recall that according to the REH, both perro and mesa are response-irrelevant and are thus excluded quickly. However, because perro (and not mesa) activates semantic features shared by the target DOG, facilitation is observed. In order to be coherent, the REH must predict that the same principle should apply to a distractor like gato. Because it belongs to the non-target language, it is response-irrelevant and should be excluded quickly, just like mesa. However, because it shares semantic features with the target, the REH should instead predict facilitation through semantic priming, not interference. Interference is still expected from cat, because CAT shares response-relevant features (language membership, semantic features) with the target DOG. The REH could successfully account for semantic interference from gato if it discarded the idea that semantic overlap from response-irrelevant distractors led to facilitation via semantic priming. However, then it would lose the ability to account for why perro yields facilitation, as well as a number of other facilitative effects in the PWI literature (e.g., Mahon et al., 2007). Alternatively, the REH could say that semantic overlap between targets and distractors only yields priming, such that shared semantic features do not make a potential response harder to exclude from the pre-articulatory buffer. However, this would render the REH incapable of accounting for traditional semantic interference effects. At present, it remains unclear how the REH could account for the fact that distractors like perro yield facilitation while distractors like gato yield interference.
Observations of phonological facilitation might also pose problems for the REH. To the best of my knowledge, the published literature does not contain any accounts of phonological facilitation under the REH – a gap that will be important to fill. Broadly speaking, there are two logical possibilities. If response exclusion processes are sensitive to phonological overlap between the distractor and the target, then it ought to be more difficult to exclude a distractor that shares the target’s phonology. This would predict that a distractor like doll, which is response-relevant and shares the target’s phonology, should yield slower reaction times than a distractor like table. This prediction stands in contrast to the empirical observation of facilitation for phonologically related distractors. (The predictions for distractors like dama, which are phonologically related to the target but not response-relevant, are less clear. Based on the explanation of the language effect for unrelated distractors, the REH might predict that dama should confer more facilitation, since it can be more quickly rejected and yet it confers priming to the target response. This conflicts with the observation that same-language distractors like doll yield stronger facilitation, but one could attribute that to phonological representations being only partially shared between languages.) Alternatively, it is conceivable that response exclusion processes are not sensitive to phonology; under this account, phonological facilitation arises because even excluded responses pass activation on to the motor level; thus, when the target response activates some of the same motor units, the response can be executed faster (Finkbeiner, personal communication). This account does satisfactorily explain phonological facilitation (including its late timecourse), but it seems odd to postulate that response exclusion processes wait to operate until responses are phonologically well-formed, but then do not consider phonological form in deciding which responses to exclude. This is also at odds with evidence from Dhooge and Hartsuiker (2010) who link response exclusion to monitoring, which is believed to be sensitive to phonological form (Postma, 2000). Thus, the REH may be able to account for phonological facilitation, but it is hardly an intuitive consequence of the model’s architecture.
A successful theory must also explain why distractors like muñeca produce weak facilitation. Recall that theories of selection by competition accounted for facilitation from distractors like muñeca because they would be expected to activate their target language translation (DOLL), which shares phonology with the target, DOG. These models made clear predictions that phonological facilitation should be expected. I have just argued that the REH is not as clear in its predictions about phonological facilitation; however, even if the model succeeds in account for facilitation from distractors like doll, then the REH must still explain how a response-irrelevant distractor like muñeca manages to activate its translation (DOLL) so strongly or so quickly that “doll” arrives at the pre-articulatory buffer before “dog” does. This would be the only way for it to prime the motor commands for /da/ such that they are already active by the time “dog” is released for production.
A further challenge is posed by distractors that are semantically unrelated to the target, but might activate the target’s translation (e.g., pear or pelo, which might both activate PERRO). According to the REH, pear and table are equally response-irrelevant and should not differ. The same goes for pelo and mesa. Thus, these distractors should not yield any reliable effects – especially those that are in the non-target language, and should hence be quickly discarded. Even if the REH had a mechanism for distractor words to activate their translations and send them quickly to the pre-articulatory buffer, the outcome to be expected here would be facilitation, since activating PERRO directly is found to be facilitative. However, the data indicate that both target language distractors (pear) and non-target language distractors (pelo) yield interference. There is not, at present, any explanation for these effects under the REH. Note that this difficulty also applies to similar results in monolinguals, such as interference from soda to COUCH (Jescheniak and Schriefers, 1998)3.
In summary, we have seen that the REH succeeds in accounting for only a subset of the empirical data, including the “language effect” and facilitation from distractors like perro. It might also be successful in accounting for phonological facilitation, both within (doll) and between (dama) languages, but the mechanisms by which this would happen would contradict the spirit of the model and have not yet been made explicit. The remainder of the bilingual picture naming data are problematic for the REH. First, it predicts that distractors in the non-target language which share semantic features with the target should yield facilitation. While perro does yield facilitation, gato yields interference. There are ways to modify the REH such that it predicts interference from perro or facilitation from gato; however, these modifications will always end up predicting that perro and gato should behave similarly, whereas the empirical data reveal them to have opposite effects. The REH encounters further difficulty when dealing with mediated effects, including distractors like muñeca (activates DOLL), pear (activates PERRO), and pelo (activates PERRO). Common to all these cases is the necessity that related but non-presented responses would not only become active but in fact arrive in the pre-articulatory buffer ahead of the target response, “dog.” Even if the necessary modifications were made, the theory would still predict interference from muñeca (because “doll” should be hard to exclude when you are trying to say “dog”), and facilitation from pear and pelo, because they activate PERRO, which facilitates through semantic priming. The empirical data, however, indicate precisely the opposite pattern: facilitation from muñeca and interference from pear and pelo.
In view of this evidence, the response selection model fares rather poorly at accounting for bilinguals’ picture naming data, and the phenomena for which it does account may not be particularly problematic for models where selection is by competition at the lexical level. However, it is worth considering a unique and as-yet untested prediction of the REH.
Recall that part of the justification for shifting the locus of competition from the lexical to the phonological level is that there is necessarily competition for production in a bilingual with only one set of articulators. A Spanish–English bilingual simply cannot say both “dog” and a semantic competitor like “gato” at the same time. However, bimodal bilinguals (those who are proficient in both a spoken and a signed language) have two independent sets of articulators. Therefore, the critical test would be to ask bimodal bilinguals to sign the names of pictures in the presence of written or spoken distractor words. The REH predicts that semantically related distractors would yield facilitation, if anything, whereas selection by competition predicts that they should experience interference. Research on language production in bimodal bilinguals is just beginning, and extant evidence leaves both possibilities open. In natural conversation and story retelling, bimodal bilinguals prefer to code-blend, rather than to code-switch; that is, they frequently produce a spoken word and its signed translation (Naughton, 1996; Emmorey et al., 2008). In a more controlled setting, code-blending incurred no costs (in reaction time or error rate) compared to producing English alone or ASL alone (Emmorey et al., under review). This was the case for both early and late ASL–English bilinguals. These findings demonstrate that when bilinguals have more than one set of articulators, they do sometimes choose to produce items in more than one language, which is consistent with the late locus of selection posited by non-competitive theories. On the other hand, it is clear from these same results that there is a very tight coupling of mouth and hand in code-blends for both meaning and timing, and there may be strong limitations on what types of words can be selected in a code-blend without incurring a cost (e.g., translation-equivalents only?). Also, when ASL is the matrix language in natural discourse, English rarely intrudes, suggesting a role of inhibition. These latter findings are more consistent with competitive theories. In sum, this is a young area of research that clearly merits further investigation. Testing picture–word interference in bimodal bilinguals should be a particularly illuminating area to explore.
Discussion
Understanding the dynamics of lexical selection in bilinguals is important for the practical reason that bilinguals constitute a global majority, and for the theoretical reason that bilingualism can and should inform psycholinguistic theories of lexical access. One theoretical issue that is currently controversial concerns whether lexical access is competitive. If so, does competition occur between nodes in all of a speaker’s languages, or only between nodes in the target language? If lexical access is not competitive, does the REH account for the data, or do we need to look elsewhere?
On the basis of the available evidence, I have argued that models of selection by competition can account for the extant data in bilingual picture naming, with minor modification. The most serious challenge to these theories concerns the fact that when a target’s translation is presented as a distractor, reaction times are faster, not slower. However, this can be explained if facilitation from semantic priming (assumed to exist by all theories) outweighs interference from lexical competition. At present, I know of no published work that directly tests this hypothesis; this will be an important gap to fill. One approach could be to isolate the contribution of cascaded activation from the lexical level. A starting point here will be to measure the strength of phonological facilitation for monolinguals and bilinguals on the same set of items, where the distractors are phonologically related words in the non-target language. Bilinguals will have lexical entries for these, whereas monolinguals will not. Therefore, the measure to which phonological facilitation differs between bilinguals and monolinguals can serve as an index of the contribution of cascading activation from the lexical level, independent of direct input-to-output mappings.
I have argued that there is little evidence to justify the assumption that lexical competition for selection is limited to nodes in the target language. One major impetus was to account for the observation that semantically related distractors in the target and non-target language (e.g., cat and gato) interfered to the same degree. However, I have shown here that (a) equal-sized semantic interference effects are predicted by models where competition is not language-specific, (b) that the LSSM’s assumptions about the nature of phonological facilitation are unnecessary, and (c) the model makes the wrong predictions about distractors that indirectly activate the target’s translation (e.g., pear and pelo). Another motivation driving the LSSM was to explain why perro yields facilitation rather than interference. Again, models where selection is by competition throughout both languages may be able to handle this result.
Finally, I considered the REH, and argued that it fails to account for interference from gato, pelo, and pear, nor does it readily predict facilitation from doll, dama, or muñeca. It does account for facilitation from perro and faster reaction times for mesa compared to table, but neither of these findings was necessarily problematic for theories where selection is by competition. The data from bilinguals would therefore seem to argue against the REH, at least in its current instantiation. However, the REH also makes an as-yet untested prediction: that when bimodal bilinguals name picture in a sign language, they should experience either nothing or facilitation from semantically related distractors, since the distractor word would not compete for the manual articulators. Conversely, selection for competition predicts that bimodal bilinguals should experience semantic interference.
It may be objected that my argument here focuses on only a subset of the empirical literature, and that the replicability of some of the effects reviewed here has been questioned. This latter criticism applies chiefly to two types of distractors: pear, which has been tested only twice (Hermans et al., 1998, Expt 1; Knupsky and Amrhein, 2007), and muñeca, which has been tested three times (Costa et al., 1999; Hermans, 2004; Knupsky and Amrhein, 2007) with mixed results. The literature would therefore benefit from additional investigation of these distractor types, including the publication of sufficiently powered failures to replicate. But it is also worth remembering that some effects, especially mediated ones, are predicted by one theory to be small and by another theory to be impossible. In such cases, mixed evidence favors the theory that predicts small effects rather than no effects.
With regard to the former objection, I acknowledge that the scope of the theories I discuss here is far broader than simply the domain of picture naming in the context of various distractors. For example, there is a rich and varied literature on language switching in bilinguals, asking whether switching or mixing costs can inform theories of lexical selection (e.g., Meuter and Allport, 1999; Costa and Santesteban, 2004; Costa et al., 2006; Finkbeiner et al., 2006b; Abutalebi and Green, 2007; Kroll et al., 2008; Gollan and Ferreira, 2009; Garbin et al., 2011). A truly successful theory will be able to integrate data from other paradigms as well. Even within the picture–word studies of monolinguals, manipulations of semantic distance (Vigliocco et al., 2004; Mahon et al., 2007; Lee and de Zubicaray, 2010) and delayed naming (Janssen et al., 2008; Mädebach et al., 2011) have been central to the development of recent theories. It will be important for future studies to test whether similar results are obtained in bilingual speakers. However, one of my aims has been to demonstrate that even the limited data we currently have from picture naming in bilinguals are helpful in constraining theories of lexical access.
Still, one might ask whether the conclusions would be different if we were to examine a broader range of behavioral and neurocognitive data. While other areas of the literature yield mixed results concerning the finer points of the various competitive models (see, for example, Costa and Santesteban, 2004; Finkbeiner et al., 2006b), behavioral and neuroimaging data from other paradigms do generally favor competitive over non-competitive theories of lexical selection. Behavioral evidence from studies of picture naming, language switching, and cognate effects, points to inhibition at work during bilingual lexical selection (for a review, see Kroll et al., 2008). Evidence from cognate naming is particularly relevant to consider because picture–word and language switching studies can be criticized for forcing overt engagement of both languages in a way that natural production may not. Cognate studies avoid this criticism by having the task be ostensibly restricted to one language; thus, any evidence of cross-language activation is presumably a natural part of bilingual lexical access. Under the assumption that lexical selection is competitive, cognate facilitation effects (Costa et al., 2000; Hoshino and Kroll, 2008) support models where competition is not restricted to the target language. However, the REH also predict that bilinguals should name cognates faster than non-cognates, because cognate names can be quickly rejected as belonging to the non-target language, but still activate phonological properties of the intended response. Thus, since both theories can account for some aspects of the behavioral data, it may be helpful to look to neuroimaging and electrophysiological evidence to fill out the picture. Here, the data provide converging evidence for competition during bilingual lexical selection (Verhoef et al., 2009; Riès et al., 2010; Aristei et al., 2011; Hoshino and Thierry, 2011; for reviews of earlier studies, see Abutalebi and Green, 2007; Kroll et al., 2008). Moreover, recent attempts to find neurocognitive support for the REH have been unsuccessful (Hocking et al., 2010; Aristei et al., 2011; Janssen et al., 2011). In fact, the strongest findings in support of non-competitive theories come from picture naming studies in monolinguals (Miozzo and Caramazza, 2003; Finkbeiner and Caramazza, 2006; Mahon et al., 2007; Janssen et al., 2008; Dhooge and Hartsuiker, 2011): the very domain where I have argued that data from bilinguals pose a strong challenge to the REH. It is worth noting once more that the REH is not co-extensive with non-competitive theories of lexical access; other non-competitive theories may yet be developed that fare better. However, in the current absence of alternative accounts, and in the presence of competitive theories with more empirical support, I see little reason to abandon the notion of lexical selection by competition, especially if we pay attention to bilinguals.
Conclusion
In addition to being the global norm, bilinguals afford unique ways of exploring the dynamics of lexical selection. Two currently contested theories (selection by competition vs. response exclusion) make different predictions about how quickly bilinguals should name pictures in the context of various distractors. I have shown that models where selection is by competition across a bilingual’s languages (e.g., the Multilingual Processing Model; Hermans, 2004) do well at accounting for the data, and that results that have previously been considered damaging to these theories are either unproblematic (equal-sized semantic interference from cat and gato, faster RTs to mesa than to table) or manageable with additional assumptions (net facilitation from perro). I have argued that there is little empirical justification for positing that selection for competition needs to be restricted to the target language only, as in the LSSM (Costa, 2005). Finally, I have explored how the REH (Finkbeiner et al., 2006a; Mahon et al., 2007) might account for the full range of picture–word data in bilinguals, and found that it does not meet with much success. Along the way, I have highlighted areas where the empirical evidence is weak, and have suggested several new avenues of investigation that may prove fruitful. Insofar as the goal is to understand how all humans manage to select the right words at the right time, we would do well to keep bilinguals in mind.
Author Note
I thank Tamar Gollan, Victor Ferreira, and Matthew Finkbeiner for helpful discussions, as well as Aimee Knupsky for sharing summary data. Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Matt Hall, Department of Psychology 0109, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Dr., La Jolla, CA 92093-0109, USA, or may be e-mailed tobWF0dGhhbGxAdWNzZC5lZHU=. During the preparation of this manuscript, the author was supported by NIH Grant HD051030 and by NIH Grant 5T32DC000041-19.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
- ^Throughout this paper, distractor words will be underlined, lexical nodes will be CAPITALIZED, distractor translations will be italicized, and potential responses will appear in quotations. English represents any target language; Spanish represents any non-target language.
- ^The fact that pelo leads to stronger competition than pear is likely due to the greater match between phonemes within a language than between languages. Pelo would more strongly activate its neighbor perro, which predicts stronger competition than in the PEAR case.
- ^I thank an anonymous reviewer for offering this observation.
References
Abutalebi, J., and Green, D. (2007). Bilingual language production: the neurocognition of language representation and control. J. Neurolinguistics 20, 242–275.
Aristei, S., Melinger, A., and Abdel Rahman, R. (2011). Electrophysiological chronometry of semantic context effects in language production. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 23, 1567–1586.
Cenoz, J. (2001). “The effect of linguistic distance, L2 status, and age on cross-linguistic influence in third language acquisition,” in Cross-Linguistic Influence in Third Language Acquisition: Psycholinguistic Perspectives, eds J. Cenoz, B. Hufeisen, and U. Jessner (Buffalo, NY: Multilingual Matters Ltd.), 8–20.
Colomé, À. (2001). Lexical activation in bilinguals’ speech production: language-specific or language-independent? J. Mem. Lang. 45, 721–736.
Comalli, P. E. Jr., Wapner, S., and Werner, H. (1962). Interference effects of Stroop color-word test in childhood, adulthood, and aging. J. Genet. Psychol. 100, 47–53.
Costa, A. (2005). “Lexical access in bilingual production,” in Handbook of Bilingualism: Psycholinguistic Approaches, eds J. Kroll, and A. M. B. de Groot (New York: Oxford University Press), 308–325.
Costa, A., Albareda, B., and Santesteban, M. (2008). Assessing the presence of lexical competition across languages: evidence from the Stroop task. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 11, 121–131.
Costa, A., and Caramazza, A. (1999). Is lexical selection in bilingual speech production language-specific? Further evidence from Spanish-English and English-Spanish bilinguals. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 2, 231–244.
Costa, A., Caramazza, A., and Sebastián-Gallés, N. (2000). The cognate facilitation effect: Implications for models of lexical access. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 26, 1283–1296.
Costa, A., Colomé, À., Gómez, O., and Sebastián-Gallés, N. (2003). Another look at cross-language competition in bilingual speech production: Lexical and phonological factors. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 6, 167–179.
Costa, A., Miozzo, M., and Caramazza, A. (1999). Lexical selection in bilinguals: do words in the bilingual’s two languages compete for selection? J. Mem. Lang. 41, 365–397.
Costa, A., and Santesteban, M. (2004). Lexical access in bilingual speech production: evidence from language switching in highly proficient bilinguals and L2 learners. J. Mem. Lang. 50, 491–511.
Costa, A., Santesteban, M., and Ivanova, I. (2006). How do highly proficient bilinguals control their lexicalization process? Inhibitory and language-specific selection mechanisms are both functional. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 32, 1057–1074.
Cutting, J. C., and Ferreira, V. S. (1999). Semantic and phonological information flow in the production lexicon. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 25, 318–344.
Damian, M. F., and Bowers, J. S. (2003). Locus of semantic interference in picture-word interference tasks. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 10, 111–117.
Damian, M. F., and Martin, R. C. (1999). Semantic and phonological codes interact in single word production. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 25, 345–361.
Das, J. P. (1993). Differences in cognitive processes of children with reading disabilities and normal readers. Dev. Disabil. Bull. 21, 46–62.
de Bot, K. (2004). The multilingual lexicon: modeling selection and control. Int. J. Multilingualism 1, 17–32.
de Bot, K., and Schreuder, R. (1993). “Word production and the bilingual lexicon,” in The Bilingual Lexicon, eds R. Schreuder and B. Weltens (Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Company), 191–214.
Dell, G. S. (1986). A spreading-activation theory of retrieval in sentence production. Psychol. Rev. 93, 283–321.
Dhooge, E., and Hartsuiker, R. J. (2010). The distractor frequency effect in picture-word interference: evidence for response exclusion. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 26, 878–891.
Dhooge, E., and Hartsuiker, R. J. (2011). The distractor frequency effect in a delayed picture-word interference task: further evidence for a late locus of distractor exclusion. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 18, 116–122.
Ehri, L. C., and Ryan, E. B. (1980). Performance of bilinguals in a picture-word interference task. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 9, 285–302.
Ehri, L. C., and Wilce, L. S. (1977). Does word training increase or decrease interference in a Stroop task? J. Exp. Child. Psychol. 27, 352–364.
Emmorey, K., Borinstein, H. S., Thompson, R., and Gollan, T. H. (2008). Bimodal bilingualism. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 11, 43–61.
Everatt, J., Warner, J., Miles, T. R., and Thomson, M. E. (1997). The incidence of Stroop interference in dyslexia. Dyslexia 3, 222–228.
Faccioli, C., Peru, A., Rubini, C., and Tassinari, G. (2008). Poor readers but compelled to read: Stroop effects in developmental dyslexia. Child Neuropsychol. 14, 277–283.
Finkbeiner, M., and Caramazza, A. (2006). Now you see it, now you don’t: on turning semantic interference into facilitation in a Stroop-like task. Cortex 42, 790–796.
Finkbeiner, M., Gollan, T., and Caramazza, A. (2006a). Bilingual lexical access: what’s the (hard) problem? Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 9, 153–166.
Finkbeiner, M., Almeida, J., Janssen, N., and Caramazza, A. (2006b). Lexical selection in bilingual speech production does not involve language suppression. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 32, 1075–1089.
Garbin, G., Costa, A., Sanjuan, A., Forn, C., Rodriguez-Pujadas, A., Ventura, N., Belloch, V., Hernandez, M., and Ávila, C. (2011). Neural bases of language switching in high and early proficient bilinguals. Brain Lang. 119, 129–135.
Glaser, W. R., and Düngelhoff, F.-J. (1984). The time course of picture-word interference. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 10, 640–654.
Gollan, T. H., and Ferreira, V. S. (2009). Should I stay or should I switch? A cost–benefit analysis of voluntary language switching in young and aging bilinguals. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 35, 640–655.
Goodman, G. S., Haith, M. M., Guttentag, R. E., and Rao, S. (1985). Automatic processing of word meaning: intralingual and interlingual interference. Child Dev. 56, 103–118.
Green, D. (1986). Control, activation, and resource: a framework and a model for the control of speech in bilinguals. Brain Lang. 27, 210–223.
Green, D. (1993). “Towards a model of L2 comprehension and production,” in The Bilingual Lexicon, eds R. Schreuder and B. Weltens (Philadelphia: John Benjamins Publishing Company), 249–278.
Green, D. (1998). Mental control of the bilingual lexico-semantic system. iling. (Camb. Engl.) 1, 67–81.
Guttentag, R. E., and Haith, M. M. (1978). Automatic processing as a function of age and reading ability. Child Dev. 49, 707–716.
Guttentag, R. E., and Haith, M. M. (1979). A developmental study of automatic word processing in a picture classification task. Child Dev. 50, 894–896.
Hermans, D. (2000). Word Production in a Foreign Language. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Nijmegen, Nijmegen.
Hermans, D. (2004). Between-language identity effects in picture-word interference tasks: a challenge for language-nonspecific or language-specific models of lexical access? Int. J. Biling. 8, 115–125.
Hermans, D., Bongaerts, T., de Bot, K., and Schreuder, R. (1998). Producing words in a foreign language: can speakers prevent interference from their first language? Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 1, 213–229.
Hocking, J., McMahon, K. L., and de Zubicaray, G. I. (2010). Semantic interference in object naming: an fMRI study of the postcue naming paradigm. Neuroimage 50, 796–801.
Hoshino, N., and Kroll, J. F. (2008). Cognate effects in picture naming: does cross-language activation survive a change of script? Cognition 106, 501–511.
Hoshino, N., and Thierry, G. (2011). Language selection in bilingual word production: electrophysiological evidence for cross-language competition. Brain Res. 1371, 100–109.
Hutson, J., Damian, M., and Spalek, K. (2010). “Distractor frequency effects in picture-word tasks with vocal and manual response,” in Poster presented at the Sixth International Workshop on Language Production, Edinburgh.
Janssen, N., Carreiras, M., and Barber, H. A. (2011). Electrophysiological effects of semantic context in picture and word naming. Neuroimage 57, 1243–1250.
Janssen, N., Schirm, W., Mahon, B. Z., and Caramazza, A. (2008). Semantic interference in a delayed naming task: evidence for the response exclusion hypothesis. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1, 249–256.
Jescheniak, J. D., and Schriefers, H. (1998). Discrete versus cascaded processing in lexical access in speech production: further evidence from the co-activation of near-synonyms. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 24, 1256–1274.
Knupsky, A. C., and Amrhein, P. C. (2007). Phonological facilitation through translation in a bilingual picture-naming task. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 10, 211–223.
Kroll, J. F., Bobb, S. C., Misra, M., and Guo, T. (2008). Language selection in bilingual speech: evidence for inhibitory processes. Acta Psychol. (Amst.) 128, 416–430.
Kroll, J. F., Bobb, S. C., and Wodniecka, Z. (2006). Language selectivity is the exception, not the rule: arguments against a fixed locus of language selection in bilingual speech. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 9, 119–135.
La Heij, W. (2005). “Selection processes in monolingual and bilingual lexical access,” in Handbook of bilingualism: Psycholinguistic approaches, eds J. F. Kroll and A. M. De Groot (New York: Oxford University Press), 289–307.
Lee, M. L., and de Zubicaray, G. (2010). “Lexical selection is by competition: a failure to replicate Mahon et al.’s (2007) experiment 7,” in Poster Presented at the Sixth Annual Workshop on Language Production, Edinburgh.
Lee, M.-W., and Williams, J. N. (2001). Lexical access in spoken word production by bilinguals: evidence from the semantic competitor priming paradigm. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 4, 233–248.
Levelt, W. J. M., Roelofs, A., and Meyer, A. S. (1999). A theory of lexical access in speech production. Behav. Brain Sci. 22, 1–75.
Levy, B. J., McVeigh, N. D., Marful, A., and Anderson, M. C. (2007). Inhibiting your native language: the role of retrieval-induced forgetting during second-language acquisition. Psychol. Sci. 18, 29–34.
Linck, J. A., Kroll, J. F., and Sunderman, G. (2009). Losing access to the native language while immersed in a second language: evidence for the role of inhibition and second-language learning. Psychol. Sci. 20, 1507–1515.
Lupker, S. J. (1979). The semantic nature of response competition in the picture-word interference task. Mem. Cogn. 7, 485–495.
Mädebach, A., Oppermann, F., Hantsch, A., Curda, C., and Jescheniak, J. D. (2011). Is there semantic interference in delayed naming? J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 37, 522–538.
Mägiste, E. (1984). Stroop tasks and dichotic translation: the development of interference patterns in bilinguals. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 10, 304–315.
Mägiste, E. (1985). Development of intra- and inter-lingual interference in bilinguals. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 14, 137–154.
Mahon, B. Z., Costa, A., Peterson, R., Vargas, K. A., and Caramazza, A. (2007). Lexical selection is not by competition: a reinterpretation of semantic interference and facilitation effects in the picture-word interference paradigm. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 33, 503–535.
Meuter, R. F. I., and Allport, A. (1999). Bilingual language switching in naming: asymmetrical costs of language selection. J. Mem. Lang. 40, 25–40.
Miozzo, M., and Caramazza, A. (2003). When more is less: a counterintuitive effect of distractor frequency in the picture-word interference paradigm. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 132, 228–252.
Morsella, E., and Miozzo, M. (2002). Evidence for a cascade model of lexical access in speech production. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 28, 555–563.
Naughton, K. (1996). Spontaneous Gesture and Sign: A Study of ASL Signs Co-Occurring with Speech. M. A. thesis, California State University, Northridge.
Navarrete, E., and Costa, A. (2005). Phonological activation of ignored pictures: further evidence for a cascade model of lexical access. J. Mem. Lang. 53, 359–377.
Peterson, R. P., and Savoy, P. (1998). Lexical selection and phonological encoding during language production: evidence for cascaded processing. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 24, 539–557.
Posnansky, C. J., and Rayner, K. (1977). Visual-feature and response components in a picture-word interference task with beginning and skilled readers. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 24, 440–460.
Postma, A. (2000). Detection of errors during speech production: a review of speech monitoring models. Cognition 77, 97–131.
Poulisse, N. (1997). “Language production in bilinguals,” in Tutorials in Bilingualism, eds A. de Groot and J. Kroll (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum), 201–224.
Poulisse, N., and Bongaerts, T. (1994). First language use in second language production. Appl. Linguist. 15, 36–57.
Rahman, R. A., and Aristei, S. (2010). Now you see it… and now again: semantic interference reflects lexical competition in speech production with and without articulation. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 17, 657–661.
Rahman, R. A., and Melinger, A. (2009). Semantic context effects in language production: a swinging lexical network proposal and a review. Lang. Cogn. Process. 24, 713–734.
Rayner, K., and Posnansky, C. J. (1978). Stages of processing in word identification. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 107, 64–80.
Rayner, K., and Springer, C. J. (1986). Graphemic and semantic similarity effects in the picture-word interference task. Br. J. Psychol. 77, 207–222.
Riès, S., Burle, B., and Alario, F.-X. (2010). “Spatio-temporal dynamics of contextual semantic interference in picture naming,” in Poster Presented at the Sixth International Workshop on Language Production, Edinburgh.
Roelofs, A. (1992). A spreading activation theory of lemma retrieval in speaking. Cognition 42, 107–142.
Roelofs, A. (1998). Lemma selection without inhibition of languages in bilingual speakers. Biling. (Camb. Engl.) 1, 94–95.
Roelofs, A., Piai, V., and Schriefers, H. (2011). Selective attention and distractor frequency in naming performance: comment on Dhooge and Hartuisker (2010). J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 37, 1032–1038.
Rosinsky, R. R., Golinkoff, R. M., and Kukish, K. S. (1975). Automatic semantic processing in a picture-word interference task. Child Dev. 46, 247–253.
Schiller, P. H. (1966). Developmental study of color-word interference. J. Exp. Psychol. 72, 105–108.
Schriefers, H., Meyer, A. S., and Levelt, W. J. M. (1990). Exploring the time course of lexical access in language production: picture-word interference studies. J. Mem. Lang. 29, 86–102.
Smith, M. C., and Kirsner, K. (1982). Language and orthography as irrelevant features in colour-word and picture-word Stroop interference. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 34A, 153–170.
Spalek, K., Bohle, H., and Damian, M. F. (2010). “The time-course of picture-word interference and Stroop effects,” in Poster Presented at the Sixth International Workshop on Language Production, Edinburgh.
Starreveld, P. A. (2000). On the interpretation of onsets of auditory context effects in word production. J. Mem. Lang. 42, 497–525.
Starreveld, P. A., and La Heij, W. (1995). Semantic interference, orthographic facilitation, and their interaction in naming tasks. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 21, 686–698.
Starreveld, P. A., and La Heij, W. (1996). Time-course analysis of semantic and orthographic context effects in picture naming. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 22, 896–918.
Starreveld, P. A., La Heij, W., and Verdonschot, R. G. (in press). Time course analysis of the effects of distractor frequency and categorical relatedness in picture naming: an evaluation of the response exclusion account. Lang. Cogn. Process.
Stemberger, J. P. (1985). “An interactive model of language production,” in Progress in the Psychology of Language, ed. A. Ellis (London: Erlbaum), 143–186.
Verhoef, K., Roelofs, A., and Chwilla, D. J. (2009). Role of inhibition in language switching: evidence from event-related brain potentials in picture naming. Cognition 110, 84–99.
Vigliocco, G., Vinson, D. P., Lewis, W., and Garrett, M. F. (2004). Representing the meaning of object and action words: the featural and unitary semantic space hypothesis. Cogn. Psychol. 48, 422–488.
Keywords: bilingual, lexical selection, selection by competition, response exclusion, picture–word interference, multilingual processing model, language-specific selection model, response exclusion hypothesis
Citation: Hall ML (2011) Bilingual picture–word studies constrain theories of lexical selection. Front. Psychology 2:381. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00381
Received: 30 June 2011;
Accepted: 30 November 2011;
Published online: 29 December 2011.
Edited by:
Eduardo Navarrete, Universita di Padova, ItalyReviewed by:
Judith F. Kroll, Penn State University, USAMikel Santesteban, University of the Basque Country, Spain
Ansgar Hantsch, Basque Center on Cognition, Brain and Language, Spain
Copyright: © 2011 Hall. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial License, which permits non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in other forums, provided the original authors and source are credited.
*Correspondence: Matthew L. Hall, Department of Psychology, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Dr, Mail Code 0109, La Jolla, CA, USA. e-mail:bWF0dGhhbGxAdWNzZC5lZHU=