- 1Division of Psychology and Language Sciences, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- 2Department of Psychology, University of Westminster, London, United Kingdom
- 3Department of Spanish Language, Linguistics and Literary Theory, University of Seville, Seville, Spain
Language has been argued to arise, both ontogenetically and phylogenetically, from specific patterns of brain wiring. We argue that it can further be shown that core features of language processing emerge from particular phasal and cross-frequency coupling properties of neural oscillations; what has been referred to as the language ‘oscillome.’ It is expected that basic aspects of the language oscillome result from genetic guidance, what we will here call the language ‘oscillogenome,’ for which we will put forward a list of candidate genes. We have considered genes for altered brain rhythmicity in conditions involving language deficits: autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia, specific language impairment and dyslexia. These selected genes map on to aspects of brain function, particularly on to neurotransmitter function. We stress that caution should be adopted in the construction of any oscillogenome, given the range of potential roles particular localized frequency bands have in cognition. Our aim is to propose a set of genome-to-language linking hypotheses that, given testing, would grant explanatory power to brain rhythms with respect to language processing and evolution.
Introduction
Which genes help regulate mental processes? This is surely one of the most pivotal questions in contemporary neurobiology. In their foreword to a recent volume on birdsong and biolinguistics, Berwick and Chomsky (2015) discuss the potential for one particular gene, FOXP2, to contribute to debates about the evolution of our most complex mental capacity, language, commenting that ‘[h]ow far one can drive this genomic work upward into neuronal assemblies – ultimately, the dissection of the underlying circuitry responsible for vocal production – remains to be seen.’
The present paper is aimed to serve as the next step in this biolinguistic approach to language, documenting the genes implicated in oscillatory activity (that is, the way in which neurons synchronize their activity at different scales across the brain in order – putatively – to enhance information transfer) during language processing as a means of establishing genome-oscillome linking hypotheses. As is standard in candidate-gene approach studies, we have examined cognitive conditions entailing both language deficits and oscillatory anomalies (that is, oscillatory behavior differing from neurotypicals) as a way to identify promising candidates. We have focused on schizophrenia (SZ) and autism spectrum disorders (ASD), which entail language impairment mostly at the syntax-semantics interface, or linguistic phenomena that result from interactions between principles of syntactic organization and principles of semantic interpretation (though DSM-V does not include language impairments as core symptoms of autism), and also specific language impairment (SLI) and developmental dyslexia (DD), which entail language impairment mostly at the syntax-phonology interface, or linguistic phenomena that are the product of interactions between principles of syntactic and phonological organization. Both interfaces account for our faculty of language according to standard generative models of language (Hauser et al., 2002; Berwick et al., 2013). For a proposal of how to explain these deficits in oscillatory terms, see Benítez-Burraco and Murphy (2016), Murphy and Benítez-Burraco (2016a,b), Jiménez-Bravo et al. (2017) and Murphy (2018b). At the core of these proposals is the assumption that particular computational and representational properties can be attributed to neural oscillations; that is, a certain degree of processing power not found at other neurophysiological states. This continues a very broad line of research in oscillations (Ding et al., 2016; Meyer, 2017; Meyer and Gumbert, 2018), and also a more specific current which has drawn the following conclusions: computational operations of language can be decomposed into generic processes (Murphy, 2015a); these generic processes interact in dynamic ways and can be implemented via neural oscillations (Murphy, 2015b); these oscillations implement a multiplexing algorithm for the combination and interpretation of linguistic representations (Murphy, 2016a); this multiplexing algorithm appears to be species-specific (Murphy, 2016b); it may have arisen via domestication (Murphy, 2018a); and it is likely implemented via migrating oscillations (Murphy, 2018b). The long-standing conclusions concerning the species-specificity of language therefore come full circle through a human-specific oscillatory code. This approach does not neglect the achievements of the fMRI enterprise, but intends to go beyond this mapping approach and seek an explanatory account of language processing in the brain, as claimed by many neurolinguists (e.g., Poeppel, 2012). What we have argued is that, in effect, although most of the nerve tracks and regions which differ in these pathological conditions are implicated in language processing, neural oscillations provide a more reliable explanatory level of the language deficits exhibited by the affected populations. Moving beyond this now requires an examination of the genes involved in oscillatory behavior.
More broadly, the genetic basis of neural oscillations likely stems from regulatory genes controlling the brain’s neurochemistry (Begleiter and Porjesz, 2006). Oscillations represent highly heritable traits, with heritability rates ranging from 75 to 90% for individual frequency bands (Van Beijsterveldt et al., 1996) to 30–60% for more complex measures, like amplitude fluctuations of oscillations or phase locking related to response inhibition (Linkenkaer-Hansen et al., 2007; Müller et al., 2017). Specifically, the contribution of genes to language-related cerebral oscillatory changes has been estimated at approximately 50% (Araki et al., 2016). Why oscillations are more proximal to gene function (in particular, regulatory function) is a question at the heart of the present contribution. Moreover, oscillations are an interesting combination of being less complex but more proximal to gene function than standard cognitive or diagnostic labels. In what follows, we first provide a functional characterization of candidate genes for the language oscillogenome, with a focus on their biological significance and functions. We then discuss the contribution of these genes to language processing, and sketch genome-to-oscillome-to-language links. With this aim, we will consider the brain areas in which they are expressed, the brain rhythms they have been related to, and the role of these areas and rhythms in language processing. Our goal is to understand how these genes contribute to language processing and how mutations in these genes result in language impairments, with a focus on normal or abnormal oscillatory activity. We conclude with a brief discussion concerning future perspectives for finding links between genes, brain rhythms, and language.
Searching for Language Oscillogenome Candidates
Methodological Concerns
In order to achieve our objective of drafting the language oscillogenome, we first gathered via systematic literature review and database searches a list of potential candidates. We selected genes that (i) are associated with language disorders (DD and SLI) or with language dysfunction in broader cognitive disorders entailing language deficits (SZ and ASD), and (ii) are known to play a role in brain rhythmicity and/or are candidates for conditions entailing brain dysrhythmias, like epilepsy. As noted above, we have chosen these four clinical conditions for three main reasons. Firstly, in our previous work (Benítez-Burraco and Murphy, 2016; Murphy and Benítez-Burraco, 2016a,b; Jiménez-Bravo et al., 2017), we have provided characterizations of their linguistic profile in terms of an abnormal suite of brain rhythms and we have advanced some promising gene-oscillations-language links. Secondly, language impairment in these conditions relate to core aspects of language, in particular, to the interface between syntax and semantics, and between syntax and phonology. Thirdly, we have already proposed a list of candidate genes for the oscillopathic profile of language dysfunction in these conditions.
For SZ we have mostly relied on the Schizophrenia Database (SZDB)1. We have considered 679 candidates based on different source of evidence: candidates resulting from genome-wide association studies (GWAs), genes affected by copy number variant (CNV), genes identified by convergent functional genomics, and genes identified by linkage and association studies. Within these genes, we have identified those that have been found to play a role in language development, and to also play some known role in brain rhythmicity, as discussed in Murphy and Benítez-Burraco (2016a,b). For ASD we have relied mostly on the SFARI database2, which currently includes 881 genes related to the disorder, based on different levels of evidence (genes bearing rare single variants, disruptions/mutations, or small deletions/duplications; candidates resulting from genetic association studies, particularly, GWAs; genes resulting from functional approaches; and genes with CNV associated with ASD). Within these genes, we have equally focused on those highlighted in Benítez-Burraco and Murphy (2016) and Murphy and Benítez-Burraco (2016b) as important for language development and evolution. For DD, we have mostly relied on the last updated list of candidates for this condition, as provided by Paracchini et al. (2016), which includes genes resulting from candidate association studies, GWAs, quantitative GWAs, CNV studies, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) analyses, although we have also surveyed the literature via PubMed3 looking for additional candidates. As before, we selected among these genes those with a known role in brain oscillations. Finally, for SLI, we have mostly relied on the literature review provided by Chen et al. (2017) and on the literature survey and results provided by Pettigrew et al. (2016), which contain candidates resulting from linkage analyses, GWA studies, and NGS analyses. As with DD, we surveyed the literature via PubMed looking for other candidates for this condition. Among these genes, we selected, as noted, those with a stablished role in brain rhythmicity.
Candidate Genes for the Language Oscillogenome
Our list of potential candidates for the language oscillogenome is shown in Table 1.
We expected that the 48 genes we highlight here as part of the shared signature of abnormal brain oscillations associated with language deficits exhibit some kind of functional relationship, and map on to particular regulatory pathways, cell types or functions, or facets of brain development and function of relevance for language and the etiopathogenesis of language impairment in the clinical conditions we have mentioned. Accordingly, we used String 10.54 for examining potential functional links among the proteins encoded by our candidates. String 10.5 is a predictive tool of direct/physical and indirect/functional associations between proteins that are derived from four sources: genomic context, high-throughput experiments (that is, parallel research on different levels of biological complexity, from genes to cell function, usually involving automation equipment, to address biological questions of interest), conserved coexpression, and the knowledge previously gained from text mining (Szklarczyk et al., 2015). In order to uncover potential clusters within our network, a MCL clustering algorithm (inflation parameter = 2) was applied to the distance matrix obtained from the String global scores. The MCL algorithm was used because it is remarkably robust with respect to graph alterations and provides better extractions of complexes from interaction networks (Brohée and van Helden, 2006). As shown in Figure 1, our network comprises several clusters of interest. Also, several proteins (NRG1, ERBB4, PDGFRB, EGR1, APOE, AKT1, MAPK14, PTEN, DISC1, SIRT1, PLAUR, SRPX2, and S100B) are found strongly interconnected; they belong to the same cluster and the confidence values of most of the edges are high (0.700) or at the highest (0.900). Hence, we expect them to be key, core components of the regulatory network involved in different steps of neural development and function important for language processing, particularly in brain oscillatory activity. The specific physical and functional associations between the proteins encoded by the candidate genes as revealed by the String toolbox are spelled out below, together with their involvement in the oscillatory behavior of the brain important for language processing.
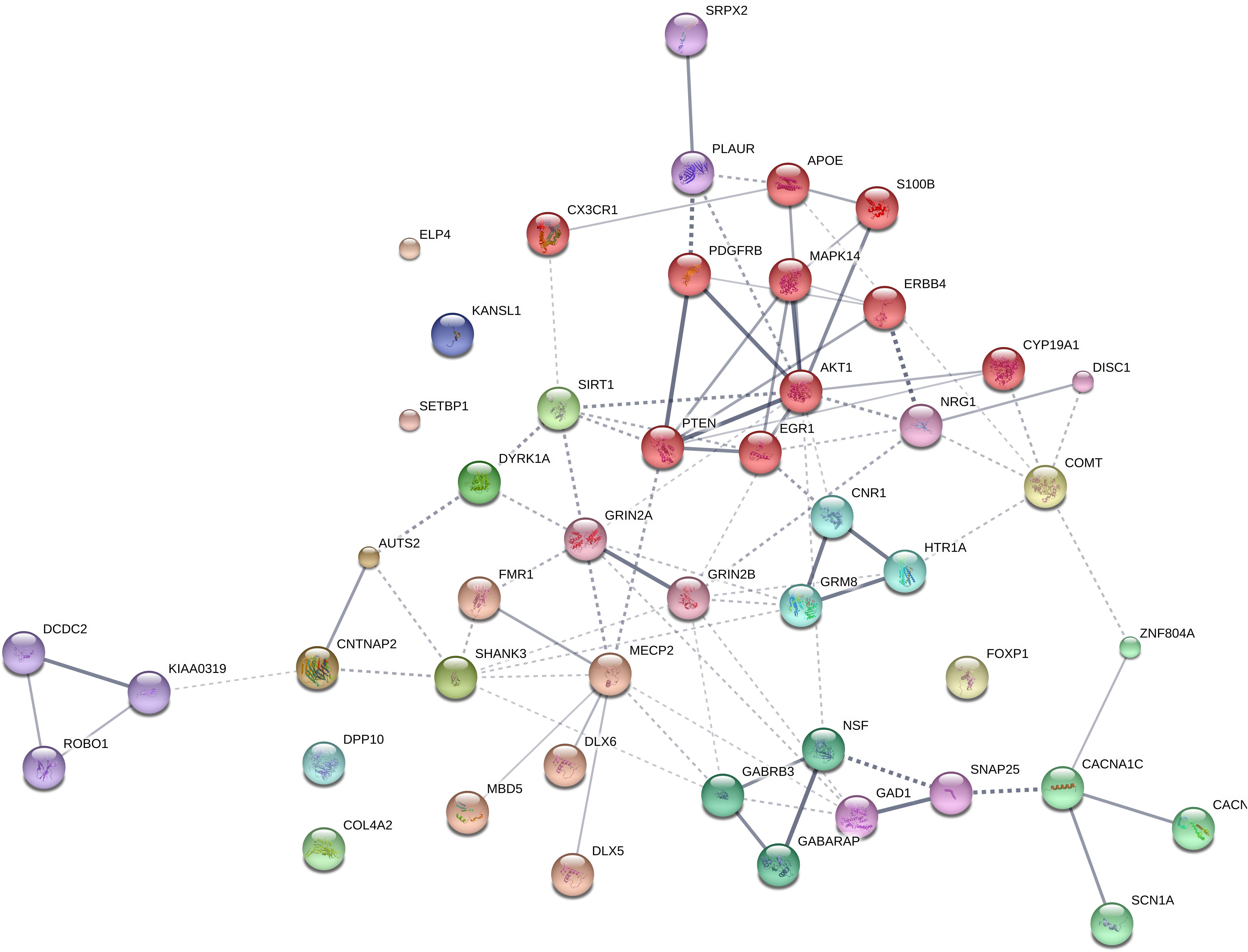
FIGURE 1. Protein interaction network. The diagram shows the network of known and predicted interactions among proteins encoded by genes proposed as candidates for the language oscillogenome (Table 1). The network was drawn with String (version 10.0; Szklarczyk et al., 2015) license-free software (string-db.org/), using the confidence visualization. It contains 48 nodes and 86 edges, with an average node degree of 3.58 and an average local clustering coefficient of 0.384. Colored nodes symbolize proteins included in the query (small nodes are for proteins with unknown 3D structure, while large nodes are for those with known structures). The line thickness of the edges indicates the strength of data support. The medium confidence value was 0.0400 [a 40% probability that a predicted link exists between two enzymes in the same metabolic map in the KEGG database: (genome.jp/kegg/pathway.html)]. Each protein cluster is represented with a different color of the nodes. Inter-cluster edges are represented by dashed-lines. As discussed in the main text, the MCL clustering algorithm was used, selecting the inflation parameter of 2. The input to the algorithm is the distance matrix obtained from the String global scores. The inflation parameter is indirectly related to the precision of the clustering (the higher the inflation, the more clusters one obtains). The diagram only represents the potential connectivity between the involved proteins, which has to be mapped onto particular biochemical networks, signaling pathways, cellular properties, aspects of neuronal function, or cell-types of interest (see the main text for details and Table 2 for a GO analysis).
Functional Characterization of the Candidate Genes for the Language Oscillogenome
NRG1
NRG1 is a membrane glycoprotein that mediates cell-cell signaling and contributes to the regulation of neural proliferation in the subventricular zone (Ghashghaei et al., 2006), thalamocortical axon pathfinding (López-Bendito et al., 2006), and glutamatergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the thalamus and the striatum (Newell et al., 2013). NRG1 and its receptor ERBB4 regulate the migration of GABAergic interneurons from ganglionic eminences to cortex (Li et al., 2012). Additionally, they play a key role in synchronizing neural oscillations in the cortex. Specifically, they enhance the synchrony of pyramidal neurons via presynaptic interneurons, increase the synchrony between pairs of fast-spiking interneurons and non-fast-spiking interneurons in prefrontal cortex, and enhance kainate-induced gamma oscillations in vivo (Hou et al., 2014). Likewise, they are involved in hippocampal gamma oscillations (Kawata et al., 2017). A risk allele of NRG1 (rs35753505) has been found to correlate with semantic (but not lexical) verbal fluency in SZ, and with a decreased activation in the right middle temporal gyri and the anterior cingulate gyrus, as well as the left inferior frontal gyrus of schizophrenic patients (Kircher et al., 2009). The same risk polymorphism is implicated in enhanced memory, IQ scores and linguistic abilities in patients with bipolar disorder (Rolstad et al., 2015). A second risk allele of NRG1 correlates with a reduction of the left superior temporal gyrus volumes in schizophrenics (Tosato et al., 2012). Risk polymorphisms of the gene are also implicated in enhanced memory, IQ scores and linguistic abilities in patients with bipolar disorder (Rolstad et al., 2015). Nrg1(+/-) mice exhibit decreased social activity which mimic the social deficits observed in autistic patients (Ehrlichman et al., 2009).
AKT1, S100B, and APOE
Epistatic interactions between Nrg1 and Akt1 have been found to regulate aspects of behavioral phenotypes and social functions in genetic mouse models of SZ; specifically, double mutant mice exhibit impaired episodic-like memory and impaired sociability, as well as reduced ultrasonic vocalization calls (Huang et al., 2015). Likewise, epistatic interactions between SZ-risk polymorphisms of AKT1 and COMT (discussed below) are relevant for human medial temporal lobe structure and memory function (Tan et al., 2012a). Functional polymorphisms of AKT1 have been related to the dopaminergic signaling in the prefrontal-striatal circuits responsible for the manipulative component of working memory (Tan et al., 2012b). Specifically, an AKT1 allele has been associated with verbal learning and memory (Pietiläinen et al., 2009). Genetic deletion of Akt1 in mice impairs hippocampal long-term potentiation and affects spatial learning, suggesting that AKT1 contributes to regulating hippocampal neuroplasticity and cognition (Balu et al., 2012). Specifically, female Akt1(-/-) mice exhibit increased hippocampal oscillation power in the theta, alpha, beta, and gamma frequency ranges (Chang et al., 2016). Likewise, reduced Akt1 expression in mutant Akt1(+/-) and Akt1(-/-) mice results in increased reduction in theta suppression and gamma synchrony after ketamine administration (Featherstone et al., 2013). AKT1 also regulates GABAergic neuron differentiation and GABAAR expression, important for hippocampus-dependent cognitive functions (Chang et al., 2016). AKT1 interacts with S100B to promote neuronal cell proliferation (Arcuri et al., 2005). S100b knockout mice show a reduced γ band (30–80 Hz) response in the hippocampus after seizure induction with kainic acid (Sakatani et al., 2008). Subjects with medial temporal epilepsy show altered expressions of S100B (Lu et al., 2010). Overall, this is suggestive of some role for S100B-related pathways in the modulation of brain oscillations in specific conditions. S100B encodes a calcium-binding protein involved in neurite extension and axonal proliferation, ultimately being involved in synaptic plasticity and learning. Phosphorylation of Akt is enhanced by APOE (specifically, APOE3) (Okoro et al., 2016), whereas APOE interacts with S100B during astrocytic activation/inhibition (Mori et al., 2005). APOE encodes a component of the Reelin signaling pathway, which has been involved in verbal memory deficits in SZ (Verbrugghe et al., 2012; Li et al., 2015). APOE is the most significant genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer Disease [and thus, for the progressive decline in memory, executive function, and language, observed in this condition (Huynh et al., 2017)]. It has been suggested that APOE is also a candidate for primary progressive aphasia (see Rogalski et al., 2013 for discussion). Interestingly, APOE has been related to some of the metabolic changes that allowed bigger brains (and eventually, enhanced cognitive capacities) to emerge in our clade (Bufill and Carbonell, 2006). In addition, the allele 𝜖4 of the gene (consistently related to a higher risk for developing late onset Alzheimer’s disease) differentially affects low and high frequency bands (particularly, alpha, theta, and delta) in several areas of the brain, plausibly accounting for the reduced cognitive abilities of the carriers (Canuet et al., 2012; Cuesta et al., 2015; Liang et al., 2017).
DISC1
Signaling by NRG1 has been found to increase the expression of an isoform of DISC1, encoded by a robust SZ candidate, during neurodevelopment (Seshadri et al., 2010). DISC1, a protein containing multiple coiled coil motifs and located in the nucleus, cytoplasm and mitochondria, is involved in cortical development, callosal formation, and neurite outgrowth (Brandon and Sawa, 2011; Osbun et al., 2011). DISC1 has been associated with verbal reasoning in the general population (Thomson et al., 2014) and with category fluency in people with bipolar disorder (Palo et al., 2007) and schizophrenia (Nicodemus et al., 2014). Importantly, DISC1 is regulated by FOXP2, a transcription factor encoded by the ‘language (speech) gene’ par excellence (Walker et al., 2012). θ-induced long-term potentiation is altered in the hippocampal area CA1 of transgenic mice expressing a truncated version of Disc1 (Booth et al., 2014). Moreover, the inhibitory effect of DISC1 on NRG1-induced ERBB4 activation and signaling affects the interneuron-pyramidal neuron circuit (Seshadri et al., 2015).
CACNA1C, CACNA1I, COMT, and ZNF804A
Several other candidates for SZ are predicted to be functionally linked to DISC1 and/or NRG1, including CACNA1C, CACNA1I, COMT, and ZNF804A. All of these are known to impact oscillatory patterns. CACNA1I and CACNA1C encode different subunits of calcium channels. CACNA1C encodes the alpha 1C subunit of the Cav1.2 voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel, which contributes to β and γ wave generation (Kumar et al., 2015). Risk alleles of the gene correlate with lower performance scores in semantic verbal fluency tasks in schizophrenics (Krug et al., 2010). Pathogenic variants of CACNA1C have been identified in subjects with intellectual disability, executive dysfunction, hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and/or ASD, as well as forms of childhood-onset epilepsy (Damaj et al., 2015). CACNA1I has been related to changes in sleep spindles in schizophrenics, a form of oscillation that constrains aspects of thalamocortical crosstalk, impacting on memory consolidation and learning (Manoach et al., 2015). Likewise, low voltage α has been associated with low activity levels in COMT, a catechol-O-methyltransferase that catalyzes the O-methylation of neurotransmitters like dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine (Enoch et al., 2003). COMT has been regularly associated with language performance and processing, and language acquisition, particularly with verbal fluency (Krug et al., 2009; Soeiro-De-Souza et al., 2013; Sugiura et al., 2017), but also with reading abilities (Landi et al., 2013). Finally, ZNF804A, a zinc finger binding protein, modulates hippocampal γ oscillations and thus the coordination of hippocampal and prefrontal distributed networks (Cousijn et al., 2015). It also contributes to cortical functioning and neural connectivity, because of its known role in growth cone function and neurite elongation (Hinna et al., 2015). SZ risk polymorphisms of ZNF804A result in lower performance scores in reading and spelling tasks (Becker et al., 2012), but also in task evaluating category fluency during semantic processing (Nicodemus et al., 2014). ASNP within intron 2 of the gene has been found to be associated with ASD subjects that are verbally deficient (Anitha et al., 2012).
ERBB4 and PDGFRB
Concerning ERBB4, this gene has been related to intellectual disability and speech delay (Kasnauskiene et al., 2013). ERBB4 is predicted to interact with PDGFRB, and putative homologs of these two genes have been found to interact in other species, particularly in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans (Figure 1). In human cells, a direct interaction of PDGFRB and one of the functional isoforms of ERBB4 has been recently documented (Sundvall et al., 2010). PDGFRB encodes the β subunit of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor, which plays an important role in central nervous system development. In mice, the knockout of Pdgfrb results in reduced auditory phase-locked γ, which correlates with anatomical, physiological, and behavioral anomalies that are also found in schizophrenics, including decreased GABAergic compactness in the medial prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala, deficient spatial memory and impaired social behavior (Nguyen et al., 2011; Nakamura et al., 2015).
PTEN
ERBB4 is also a functional partner of PTEN, a phosphatase that preferentially dephosphorylates phosphoinositide substrates. Both proteins collaborate in protrusion formation in rhombic lip cells (Sakakibara and Horwitz, 2006). Functional interactions are predicted as well between PTEN and PDGFRB (Figure 1). PTEN is a candidate for a subtype of ASD with macrocephaly which is usually present in conjunction with epilepsy (or paroxysmal EEG) (Buxbaum et al., 2007; Marchese et al., 2014). The gene is highlighted as a candidate for language deficits in ASD, because patients with PTEN-associated ASD show a delay in language development, characterized by poor processing speed and working memory (Naqvi et al., 2000; Tilot et al., 2015). PTEN is a major negative regulator of the mTOR signaling pathway, important for synaptic plasticity and neuronal cytoarchitecture (see Tilot et al., 2015 for review). The knockdown of Pten in mouse primary neuron cultures affects the expression of genes involved in neurogenesis, synaptic activity, and long-term potentiation (Lanz et al., 2013). In mice, the deletion of Pten in adult hippocampal neural stem cells increases proliferation and differentiation of stem cells toward hypertrophied neurons with abnormal polarity, causes seizures and macrocephaly, and impairs social behavior (Amiri et al., 2012). Social dysfunction in mouse models of neural Pten loss includes repetitive behavior, impaired emotional learning (in females) and increased anxiety (in males) (Page et al., 2009; Clipperton-Allen and Page, 2014), but also seizures and epileptiform features (Ogawa et al., 2007). Interestingly, Pten deletion in mice ultimately yields deviant circuit formation in the dentate gyrus, responsible for excitation flow through the hippocampus (Pun et al., 2012), potentially impairing procedural memory capacities relevant to language.
MAPK14, SIRT1, DYRK1A, and GAD1
PTEN is a strong partner of MAPK14, a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase which is also functionally related to ERBB4 and PDGFRB (Figure 1). In glioma cells, the downregulation of MAPK14 correlates with the upregulation of PTEN, resulting in the inhibition of cell migration in vitro (Dasari et al., 2010). The inhibition of MAPK14 activity suppresses hippocampal-dependent associative and spatial memory deficits in mouse models of synaptic dysfunction (Roy et al., 2015). Mice with a single copy disruption of Mapk14 show protection against kainate-induced seizures (Namiki et al., 2007). Another partner of PTEN is SIRT1, a deacetylase of the sirtuin family, which negatively regulates neurogenesis and neural differentiation, contributes to axon formation and elongation, and plays a role in memory formation (Gao et al., 2010; Li et al., 2013; Saharan et al., 2013). Sirt1 prevents seizures and seizure-induced damage in the hippocampus of rat models of epilepsy via miR activity (Wang et al., 2016). The gene is also highly expressed in the cochlea and the auditory cortex (Xiong et al., 2014). SIRT1 phosphorylation and activation by DYRK1A, a dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase, promotes cell survival (Guo et al., 2010). DYRK1A is located within the Down Syndrome Critical Region within chromosome 21. In mice, Dyrk1a has proven to contribute to the balance between cortical and thalamic neurons (Guedj et al., 2012). Dyrk1a overexpression affects the expression of genes encoding GABAergic and glutamatergic related proteins, shifts the excitation/inhibition balance toward inhibition, and impacts on pathways involved in synaptogenesis and synaptic plasticity (Souchet et al., 2014), supporting a role of this gene in learning and memory (Hämmerle et al., 2003). DYRK1A has been related as well to lack of speech, mental retardation and microcephaly (Van Bon et al., 2011; Courcet et al., 2012). In mice, the upregulation of Dyrk1a also results in the upregulation of Gad1 (Souchet et al., 2014), which encodes a glutamic acid decarboxylase that catalyzes the production of GABA, with a specific role in the development of GABAergic neurons in the hippocampus (Pleasure et al., 2000). GAD1 has been related to the pathophysiology of SZ, but also to working memory deficits, because of its impact on prefrontal white matter structure (Lett et al., 2016). GAD1 is a target of FOXP2 (Konopka et al., 2009). Risk alleles of the gene impact as well on long-interval cortical inhibition (LICI) in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics, as shown by transcranial magnetic stimulation with electroencephalography (TMS-EEG); this suggests that the gene contributes to GABAergic inhibitory neurotransmission (Lett et al., 2016). Male Gad1 (+/-) mice exhibit impaired social behavior (Sandhu et al., 2014).
DLX5, DLX6, and MECP2
GAD1 interacts with DLX5 and DLX6, two genes that encode homeobox transcription factors important for GABAergic interneuron development (Cobos et al., 2006; Ghanem et al., 2008; Poitras et al., 2010). Accordingly, in the developing ventral forebrain, the non-coding RNA Evf2 controls transcription of Gad1, Dlx5, and Dlx6 through cis- and trans-acting mechanisms; Evf2 mouse mutants exhibit reduced synaptic inhibition (Bond et al., 2009). Dlx5 and Foxp2 are expressed in the same intercalated cell masses of the amygdala in non-human primates and in rats, and in nearly the same neuronal populations of the striatum (Kaoru et al., 2010). DLX5 and DLX6 are core components of the gene network accounting for aspects of the evolution of our ability to learn and use languages. Heterozygous mice for Dlx5/6 exhibit reduced cognitive flexibility which appears to emerge from abnormal GABAergic interneurons and γ rhythms, particularly in fast-spiking interneurons (Cho et al., 2015), potentially contributing to the irregular long-lasting prefrontal and central γ in ASD, but also to SZ symptoms. Evf2 also recruits Mecp2 to DNA regulatory elements in the Dlx5/6 intergenic region (Bond et al., 2009), whereas DLX5 has been reported to be modulated by MECP2 (Miyano et al., 2008). MECP2 is the principal candidate for Rett syndrome, a neurodegenerative disease involving autistic behavior, motor problems, and language loss (Uchino et al., 2001; Veenstra-VanderWeele and Cook, 2004). MECP2 is a chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA and mediates transcriptional repression, and that is critically needed for normal function of GABA-releasing neurons (Chao et al., 2010). In mice, the loss of Mecp2 from GABAergic interneurons results in auditory event-related potential deficits (Goffin et al., 2014). In response to auditory stimulation, Mecp2+/- mice recapitulate select γ and β band abnormalities and specific latency differences found in ASD subjects (Liao et al., 2012).
EGR1, PLAUR, SRPX2, ELP4, and FOXP2
Another strong partner of PTEN (but also of MAPK14, PDGFRB, ERBB4 and NRG1) is EGR1, a transcription factor that contributes to neural plasticity and memory consolidation (Veyrac et al., 2014). EGR1 is found induced in human epileptic foci and its expression levels correlate with the frequency, amplitude and area of the interictal spikes, a hallmark of epileptic neocortex (Rakhade et al., 2007). EGR1 is a target of FOXP2 (Konopka et al., 2009). In turn, EGR1 downregulates PLAUR (Matsunoshita et al., 2011), which encodes the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and which is also a target of FOXP2 (Roll et al., 2010). Mice lacking Plaur have significantly fewer neocortical GABAergic interneurons, which are vital for oscillatory processes (Bae et al., 2010), and exhibit nearly complete loss in parvalbumin-containing interneurons during brain development, which is associated with increased susceptibility to spontaneous seizures and with impaired social interactions (Bruneau and Szepetowski, 2011). PLAUR is an effector of SRPX2, a protein with three sushi repeats motifs which is another of FOXP2 targets (Royer-Zemmour et al., 2008) and a candidate for rolandic epilepsy and speech dyspraxia (Roll et al., 2006). One distinctive feature of this benign type of epilepsy with an onset in childhood is the presence of abnormal centrotemporal sharp waves, an endophenotype of rolandic epilepsies that has been associated with ELP4 (Strug et al., 2009). ELP4 encodes one component of the elongator protein complex, involved in RNA transcription and tRNA modification, and important for cell mobility and migration, particularly during the development of the cerebral cortex (Creppe et al., 2009). Interestingly, the locus of ELP4 has been linked to speech sound disorder (SSD) (Pal et al., 2010). Microdeletions of ELP4 have also been associated with ASD and linguistic deficits (Addis et al., 2015).
CNR1, HTR1A, GRM8, GRIN2A, GRIN2B, and SHANK3
EGR1 expression is induced by CNR1 (Bouaboula et al., 1995). Genomic studies have highlighted CNR1 as an important gene for brain anomalies and metabolic changes in SZ (Yu et al., 2013; Suárez-Pinilla et al., 2015), for striatal response to happy faces in a Caucasian cohort of ASD individuals (Chakrabarti et al., 2006), and for cases of total absence of expressive speech (Poot et al., 2009). CNR1 encodes the cannabinoid-1 receptor, which modulates θ and γ rhythms in different brain areas, such as the hippocampus, with an impact on sensory gating function in limbic circuitry (Hajós et al., 2008). CNR1-positive GABAergic interneurons play an important role in the response to auditory cues, as well as in other aspects of behavior (Brown et al., 2014). CNR1 is functionally linked to several other genes encoding a subset of related proteins that also appears as a core component of our network (Figure 1), including HTR1A, GRM8, GRIN2A, GRIN2B, and SHANK3. Interestingly, most of these genes encode neurotransmitter receptors.
Beginning with HTR1A, this encodes the receptor 1A of serotonin and contributes to the modulation of hippocampal γ, influencing cognitive functions linked to serotonin, such as learning and working memory (Johnston et al., 2014). Interestingly, the serotonin-1A receptor exhibits a lateralized distribution in the language areas, being the receptor binding 1.8–2.9% higher in right language areas and 2–3.6% higher in left auditory regions (Fink et al., 2009). GRIN2A and GRIN2B encode two components of the subunit NR2 of the NMDA receptor channel, involved in long-term potentiation, a physiological process underlying memory and learning. GRIN2A is reduced in fast-firing interneurons of schizophrenics, which contribute decisively to γ oscillation formation: a blockade of NR2A-containing receptors increases γ power and reduces the modulation of γ by low frequencies (Kocsis, 2012). Language regression and speech impairments have also been found to result from GRIN2A mutations (Carvill et al., 2013; Lesca et al., 2013). The gene is also a candidate for rolandic epilepsies (Dimassi et al., 2014). Speech problems found in patients with mutations in GRIN2A include imprecise articulation, problems with pitch and prosody, and low performance on vowel duration and repetition of monosyllables and trisyllables, which are commonly diagnosed as dysarthria or dyspraxia (Turner et al., 2015). GRIN2B plays a key role in normal neuronal development and in learning and memory. Besides its involvement in SZ, ASD, and SLI, mutations in GRIN2B have been found in subjects with intellectual disability associated with behavioral problems and EEG anomalies, and in patients with epileptic encephalopathies which co-occur with impairment of motor and cognitive functions (Freunscht et al., 2013; Hu et al., 2016; Smigiel et al., 2016). Finally, GRM8 encodes a protein with a glutamate, GABA-B-like receptor activity. Partial duplications of the gene have been associated to developmental delay and intellectual disability (DECIPHER patients 338209 and 289333). Several SNPs of the GRM8 have been found to be associated with θ power in subjects with alcohol dependence, which suggests that variation in GRM8 may modulate θ rhythms during information processing (Chen et al., 2009).
In several organisms, GRIN2B interacts with SHANK3, a postsynaptic scaffolding protein that seems to be important for the maintenance of the adequate balance between neuronal excitation and inhibition. Knockdown of Shank3 in mouse primary neuron cultures affects the expression of genes involved in long-term potentiation and synaptic activity (Lanz et al., 2013). Cultured cortical neuron networks lacking Shank3 show reduced excitation and inhibition behaviors (Lu et al., 2016). Specifically, mice lacking the exon 9 of the gene exhibit reduced excitatory transmission in the hippocampal CA1 region and increased frequency of spontaneous inhibitory synaptic events in pyramidal neurons, which result in mildly impaired spatial memory (Lee et al., 2015). Knocked out mice for the gene exhibit abnormal social interaction and repetitive grooming behavior (Peça et al., 2011). SHANK3 has been linked as well to some of the distinctive symptoms of Phelan-McDermid syndrome (also known as 22q13 deletion syndrome), including intellectual disability, delayed or absent speech, autistic features, seizures and abnormal EEG profiles (Soorya et al., 2013; Holder and Quach, 2016).
ATP13A4, CNTNAP2, and AUTS2
Besides CNVs in GRIN2A and SHANK3, CNVs in genes related to SLI and DD have been found as well in patients with continuous spike and waves during slow-wave sleep syndrome and Landau–Kleffner syndrome, including ATP13A4 and CNTNAP2 (Lesca et al., 2012). The latter encodes a protein associated with K+ voltage-gated channels in pyramidal cells of the temporal cortex largely innervated by GABAergic interneurons (Inda et al., 2006). CNTNAP2 additionally affects language development in non-pathological populations (see Whalley et al., 2011; Whitehouse et al., 2011; Kos et al., 2012). This effect is seemingly due to its role in dendritic arborization and spine development (Anderson et al., 2012), and in the regulation of cerebral morphology and brain connectivity (Scott-Van Zeeland et al., 2010; Tan et al., 2010; Dennis et al., 2011). Homozygous mutations or compound heterozygous CNVs of CNTNAP2 are associated with speech and language regression and epilepsy (Strauss et al., 2006; Marchese et al., 2016; Smogavec et al., 2016). Interestingly, mice and rats with homozygous deletions of Cntnap2 exhibit reduced spectral power in the α (9–12 Hz) range during wake (Thomas et al., 2017). In mice, Cntnap2 is regulated by Auts2, a protein with a suggested role in cytoskeletal regulation (Oksenberg et al., 2014). AUTS2 displays the strongest signal of a selective sweep in anatomically modern humans compared to Neanderthals (Green et al., 2010; Oksenberg et al., 2013) and is a strong candidate for several neurodevelopmental disorders (see Oksenberg and Ahituv, 2013 for review). Specifically, CNVs of the gene have been found in patients with language delay and seizures (Nagamani et al., 2013), and the gene has been cited as a candidate for epilepsy (Mefford et al., 2010). Interestingly, AUTS2 has also been associated with differential processing speeds (Luciano et al., 2011).
GABA Signaling: GABRB3, GABARAP, NSF, and SNAP25
As noted above, the dysfunction of GABA signaling contributes to ASD-like stereotypes, Rett syndrome phenotypes, and SZ (Chao et al., 2010; Fazzari et al., 2010). Abnormal changes in the GABA catabolism give rise to brain and behavioral disturbances that recapitulate the symptoms of ASD, including language impairment (Gibson et al., 1997; Pearl et al., 2003). The fact that our list of candidates for the language oscillogenome includes several receptors for GABA reinforces the view that GABA signaling is crucial for the oscillatory signature of language. As shown in Figure 1, a third subnetwork includes GABRB3, GABARAP and two interactors; NSF and SNAP25. GABRB3 encodes the β-3 subunit of the GABA receptor A (Cook et al., 1998; Shao et al., 2003). Besides its known association with ASD, the gene has been associated as well with childhood absence epilepsy (Urak et al., 2006). Null mutations of Gabrb3 in mice result in cleft palate and epilepsy (Homanics et al., 1997), whereas heterozygous deletion also encompassing Ube3a and Atp10a, recapitulates Angelman syndrome, a neurobehavioral disorder involving absence of language (Jiang et al., 2010). Differences in the expression level of the GABRB3 have been related to changes in the firing of hippocampal pyramidal neurons and the activity of fast networks (Heistek et al., 2010). More generally, genetic variation in GABAA receptor properties have been linked to differences in β and γ oscillations, which likely impact network dynamics and cognition (Porjesz et al., 2002). GABARAP is a candidate for dyslexia and encodes a GABAA receptor-associated protein involved in the clustering of neurotransmitter receptors, but also in inhibitory neural transmission. Gabarap knockout mice exhibit abnormal paroxysmal sharp waves in the hippocampus (Nakajima et al., 2012). Estrogen depletion resulting from the inhibition of the dyslexia candidate CYP19A1, a member of the cytochrome P450 family that catalyzes the formation of aromatic C18 estrogens from C19 androgens, affects GABA synthesis and gives rise to increased spine density and decreased threshold for hippocampal seizures (Zhou et al., 2007). Regarding NSF and SNAP25 (the former a candidate for dyslexia and the latter a candidate for SZ, ASD, and dyslexia), both are needed for neurotransmitter release and synaptic function. NSF encodes a protein involved in vesicle-mediated transport in the Golgi apparatus, whereas SNAP25 contributes to the formation of the soluble NSF attachment protein receptor complex. In mice, reduced levels of Snap25 seems to be related to more frequent spikes, diffuse network hyperexcitability, and epileptiform discharges, as well as to cognitive deficits and social impairment (Corradini et al., 2014; Braida et al., 2015).
FMR1, ROBO1, KIAA0319, and DCDC2
Downregulation of GABA receptors has been linked as well to altered expression of FMR1. Specifically, reduced levels of GABRβ3 and of FMRP have been found in the vermis of adult subjects with ASD (Fatemi et al., 2011), as well as in the hippocampus of En2(-/-) mice model of ASD (Provenzano et al., 2015). FMRP, a polyribosome-associated RNA-binding protein, is encoded by FMRP1, the main candidate for Fragile X syndrome, a condition involving language deficits and frequent features of ASD (Kaufmann et al., 2004; Smith et al., 2012). Low levels of FMRP have been found as well in schizophrenic patients with low IQs (Kovács et al., 2013). Fmr1-knockout mice exhibit enhanced mGluR5 signaling, which results in altered neocortical rhythmic activity because of changes in neocortical excitatory circuitry (Hays et al., 2011). These mice also exhibit abnormal patterns of coupling between θ and γ oscillations in perisomatic and dendritic hippocampal CA1 local field potentials, resulting in abnormally weak changes during tasks involving cognitive challenge (Radwan et al., 2016). Also, inhibitory dysfunctions in layer II/III of the somatosensory cortex has been found in Fmr1 knockout mice, in particular, a reduced activation of low-threshold-spiking interneurons and reductions in synchronized synaptic inhibition and coordinated spike synchrony in pyramidal neurons in response to mGluR agonists (Paluszkiewicz et al., 2011).
FMR1 has been suggested to fit with ROBO1, KIAA0319, S100B, and DCDC2, among others, into a theoretical gene network important for neurite outgrowth and neuronal migration (Poelmans et al., 2011). All these genes are candidates for DD according to results from association studies, GWA analyses, and CNVs studies (Paracchini et al., 2016), and all have been related to abnormal patterns of brain oscillations or seizures when mutated – hence their candidacy for the oscillogenome. Accordingly, they seem to us to be promising candidates for the oscillatory signature of language. Rare variants in the intergenic region between DCDC2 and KIAA0319, and in one intron of DCDC2, which encodes a doublecortin domain-containing protein (locus DYX2) have been associated with differences between dyslexic and control children in a late mismatch negativity around 300–700 ms originating in right central-parietal areas when discriminating between complex auditory stimuli, such as syllables and words (Czamara et al., 2011). The protein encoded by ROBO1 is a membrane receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily which contributes to regulate interaural interaction in auditory pathways (Lamminmäki et al., 2012). ROBO1 is targeted by miR-218, which is found downregulated in the hippocampus of people suffering from medial temporal lobe epilepsy (Kaalund et al., 2014).
Other Candidates of Interest
The remainder of our candidate genes are not clearly functionally interconnected in the core interacting network (Figure 1), although all of them play relevant roles in brain oscillations and are candidates for the basis of language impairments (see Table 1). This is why we still regard them as important components of the language oscillogenome. FOXP1, which encodes a forkhead box transcription factor, is co-expressed with FOXP2 in some areas of the brain and the protein FOXP1 forms heterodimers with the FOXP2 protein. FOXP1 haplo-insufficiency has been found in patients with epileptiform discharges, severe speech delay, and delayed gross motor skills (Carr et al., 2010). Cx3cr1 knockout mice show deficient synaptic pruning, weak synaptic transmission, decreased functional brain connectivity, and social and behavioral features that resemble those found in ASD patients (Zhan et al., 2014). Interestingly, these mice also exhibit reduced θ-driven connections between prefrontal cortex and dorsolateral hippocampus relative to wild-type littermates (Zhan, 2015). CX3CR1 encodes a receptor for fractalkine, a chemokine and transmembrane protein important for cell adhesion and migration. Specifically, CX3CR1 has been involved in the crosstalk between the microglia and the neural stem/progenitor cells during adult hippocampal neurogenesis, which is important for memory, learning and cognition (de Miranda et al., 2017), to the extent that CX3CR1 deficiency results in impairment of hippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity (Rogers et al., 2011). As with other proteins associated with ion channels, like CNTNAP2, DPP10 is of interest due to its binding capacity to K+ channels and its ability to modify their expression and biophysical properties (Djurovic et al., 2010). Rare mutations in DPP10 have been associated with ASD (Marshall et al., 2008). Interestingly, the transcription start site of the gene is hypermethylated in the neurons of the prefrontal cortex of humans compared to extant primates, and regulatory sequences at DPP10 carry elevated nucleotide substitution rates and regulatory motifs absent in archaic hominins, with signals of recent selective pressures and adaptive fixations in modern populations (Shulha et al., 2012). This reinforces the view that this gene might have contributed to cognitive abilities and disorders that are unique to humans. MBD5 encodes a protein with a methyl-CpG-binding domain which binds to methylated DNA. MBD5 haplo-insufficiency has been associated with epilepsy, severe speech delay, mental retardation, and ASD-features (Williams et al., 2010; Talkowski et al., 2011). The gene encodes a methyl-CpG-binding protein. SETBP1, which encodes a SET binding protein, is a candidate for Schinzel-Giedion syndrome, which entails severe developmental delay and occasional epilepsy (Ko et al., 2013; Miyake et al., 2015). Mutations on the gene also result in social and behavioral problems (Coe et al., 2014). As a candidate for SLI, GWAs studies have associated SETBP1 to the complexity of linguistic output (Kornilov et al., 2016). Microdeletions causing the disruption of the gene impact mostly on expressive abilities, whereas receptive language is quite preserved, to the extent that some patients are able to communicate using gestures and mimics (Filges et al., 2011; Marseglia et al., 2012). The C-terminal portion of COL4A2 arrests cell proliferation and migration; mutations in DD-candidate COL4A2 have been found in patients suffering from epilepsy and severe developmental delay (Giorgio et al., 2015; Smigiel et al., 2016). SCN1A encodes the large α subunit of the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.1, which plays a key role in the generation and propagation of action potentials. Mutations in SCN1A have been found in people with ASD (Weiss et al., 2003; O’Roak et al., 2011), but mostly in patients with epilepsy (Schutte et al., 2016). The gene is also associated with Dravet syndrome, a condition characterized by cerebellar signs and a deficit in expressive language with relatively spared comprehension, resulting from motor speech problems which affect to motor planning and executing (Battaglia et al., 2013; Turner et al., 2017). In mice, the downregulation of Scn1a disturbs hippocampal θ oscillations and impairs spatial memory (Bender et al., 2013). Finally, KANSL1, which encodes a putative transcriptional regulator involved in the acetylation of nucleosomal histone H4, plays a role in gene transcription regulation and chromatin organization as part of the NSL1 complex. KANSL1 is a candidate for Koolen-de Vrries syndrome, which entails epilepsy and developmental delay with moderate intellectual disability, which impacts mostly on expressive language abilities (Koolen et al., 2016).
Enrichment Analysis of the Candidate Genes for the Language Oscillogenome
After having completed this survey, we then performed Gene Ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis for outlining the functional profile of our set of genes of interest. GO enrichment analysis identifies groups of genes that function together, reducing the thousands of molecular differences between two particular biological states to a smaller number of differences in specific biological functions, thus providing a biological interpretation of the attested molecular changes. With that aim, we used the String algorithm. The functional enrichment of our candidates for the language oscillogenome (Table 2) points to the fact that most of these genes act in signaling pathways found to be of significance for language processing via its oscillatory implementation, particularly through dopaminergic, GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. The top-scoring biological processes (resulting from functional annotations) include the regulation of cognitive process of particular relevance for language, including learning and memory. Lastly, regarding the cellular localization of the proteins, gene ontology (GO) annotations also performed using String algorithm suggest that the majority of them are found in the plasma membrane, inside the neuron projection components, confirming their role as regulators of neuronal interconnection. In the next section, we discuss how the role played by these genes may underlie most of the oscillatory aspects of brain function that are important for language production and comprehension.
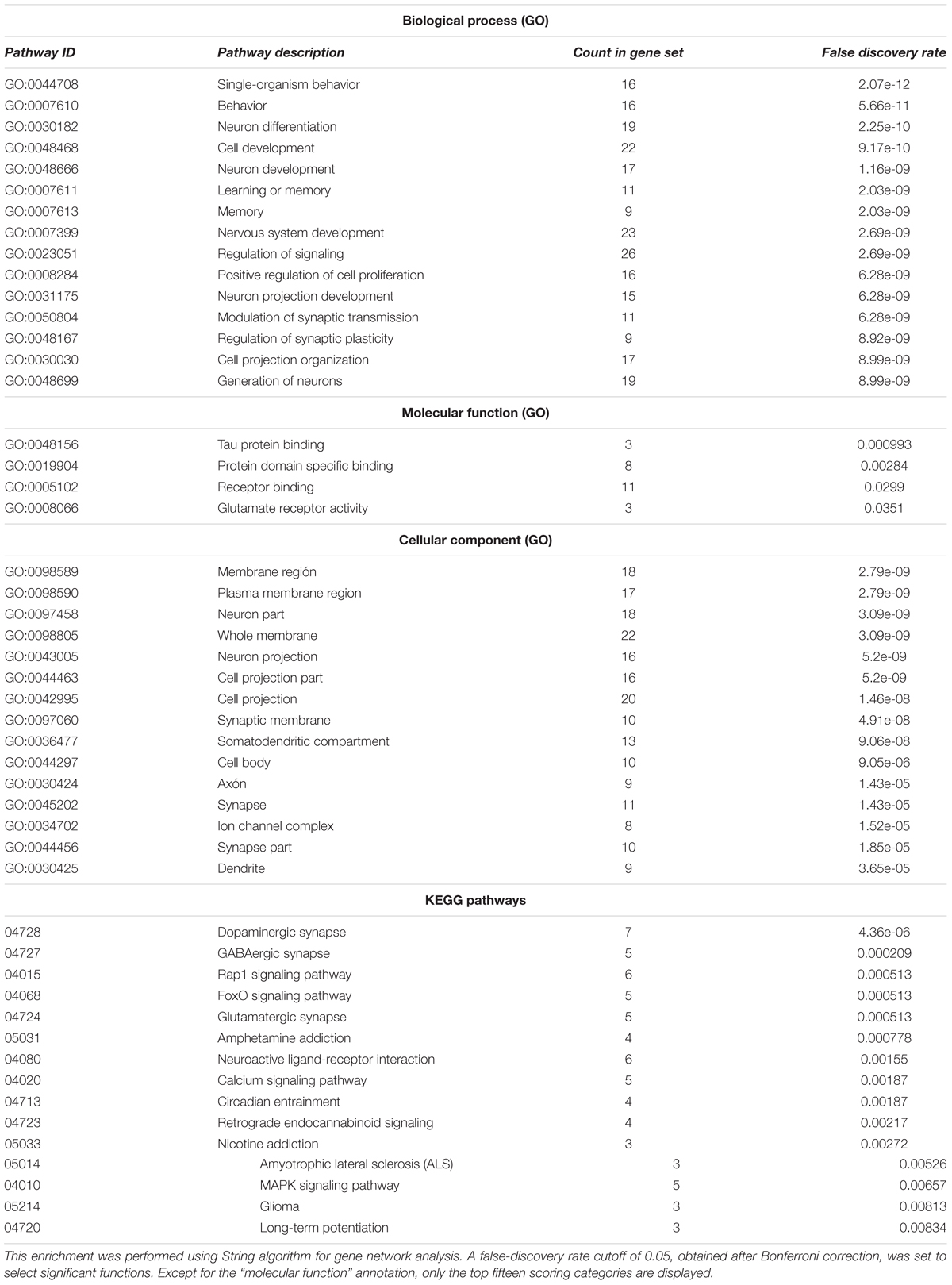
TABLE 2. Functional enrichment of the entire set of candidates for the oscillogenome according to Gene Ontology (GO) consortium annotations.
In order to check the language-specificity of our network, we compared the functional annotations of our network with the results of the functional enrichment analysis carried out over the set of candidates for the four conditions considered here (SZ, ASD, DD, and SLI). Because the String algorithm did not provide significant results for DD and SLI, we instead relied on Enrichr5. Enrichr performs an enrichment analysis of gene sets (that is, groups of genes contributing to the same biological function) using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure (see Chen et al., 2013; Kuleshov et al., 2016 for details). The results are shown in Table 3.
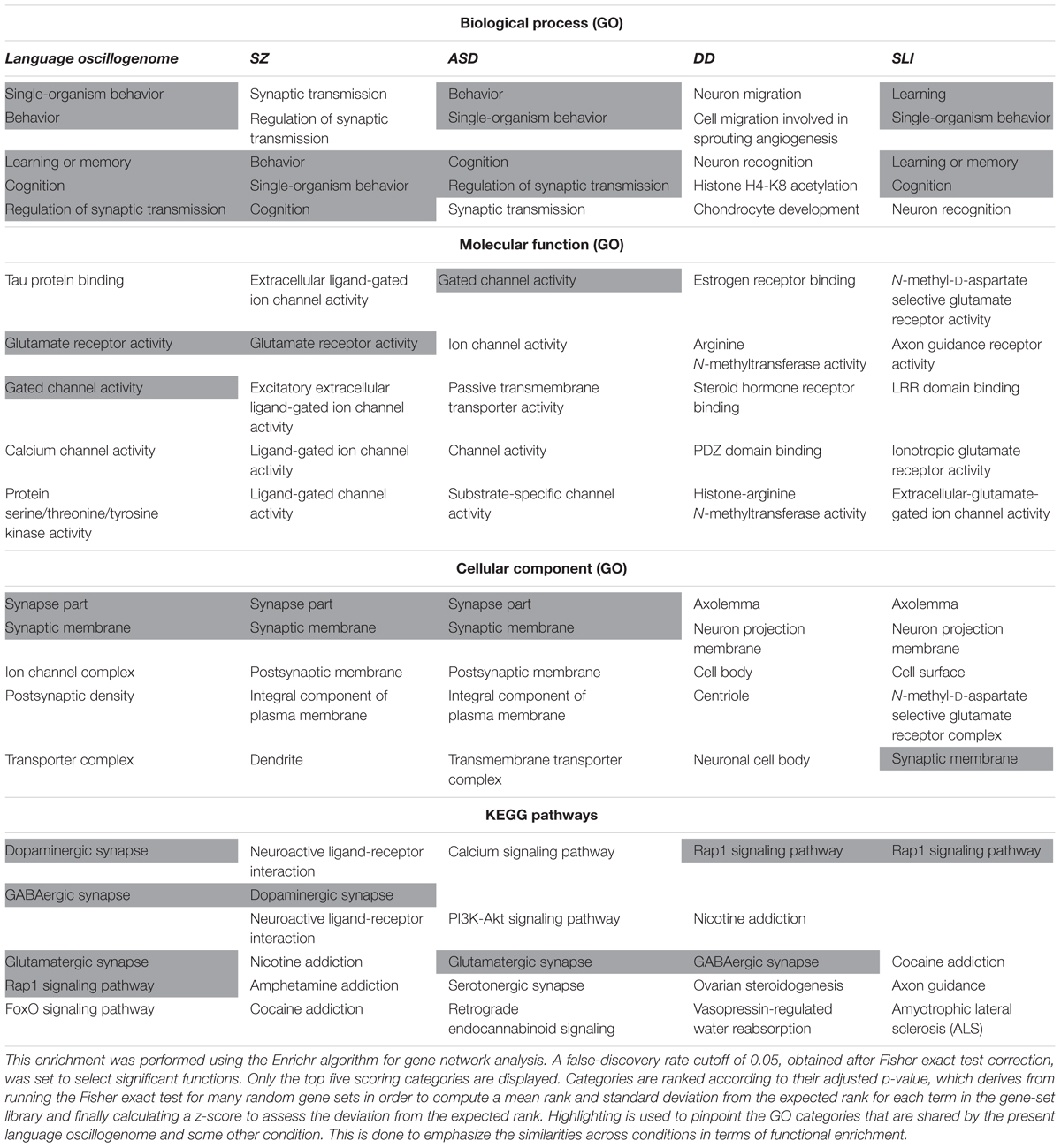
TABLE 3. Comparison of the functional enrichment of candidates for the oscillogenome SZ, ASD, DD, and SLI.
As expected, the top-scoring biological processes resulting from the GO analyses are quite similar across groups, supporting the view that although learning and memory are key aspects of language acquisition and processing, their impairment can result in different cognitive disorders. Regarding the cellular components in which our candidates for the language oscillogenome are preferentially found, they are specifically involved in ion channel formation and function, contrary to candidates for SZ, ASD, DD, or SLI, reinforcing the view that our candidates are important for aspects of brain rhythmicity. In particular, we believe that the extent to which our oscillogenome candidates are language-specific (a claim we do not want to make strongly here, given the role of the above genes in a range of cognitive processes) mostly relies on some of the pathways to which they contribute, particularly, those related to neurotransmitter homeostasis in the brain. Accordingly, they are components of the dopaminergic signaling pathway, which is usually highlighted as being important for motor behavior and vocal learning (Kameda et al., 2011). More importantly, they contribute as well to GABAergic signaling, which is relevant for the maintenance of our species-specific cognitive profile (Long et al., 2013). As discussed in detail in Boeckx and Benítez-Burraco (2014a), some of the key changes that contributed to the emergence of our ability to learn and use languages (usually referred to as our language-readiness) involved GABAergic signaling. Among them we wish to highlight the evolutionary changes in the core candidate for globularization of the human skull/brain, namely, RUNX2, also involved in the development of hippocampal GABAergic neurons (Pleasure et al., 2000), and the generation of an extra source of GABAergic neurons resulting from the expansion of dorsal thalamic structures (Striedter, 2005; Rakic, 2009; Geschwind and Rakic, 2013). Importantly, as reasoned in Murphy and Benítez-Burraco (2016b), hippocampal θ waves, which are produced by slow pulses of GABAergic inhibition (Vertes and Kocsis, 1997), are involved in the extraction of language feature-sets from long-term memory. Additionally, we expect that the language-specificity of our network (again, to the extent that this degree of specificity can be maintained) relies as well on the role played by our candidates in FOXO and RAP1 pathways, contrary to the genes related to broader cognitive conditions like SZ and ASD. Regarding the FOXO signaling pathway, we have already discussed the relevance of FOXP1 and FOXP2. We also wish to highlight FOXO1, which is a target of the two core candidates for the evolutionary changes that prompted the emergence of our language-readiness, namely, RUNX2 (Kuhlwilm et al., 2013) and FOXP2 (Vernes et al., 2011) (see Boeckx and Benítez-Burraco, 2014a,b; Benítez-Burraco and Boeckx, 2015 for details). Additionally, FOXO1 upregulates RELN (Daly et al., 2004), a candidate for ASD and for lissencephaly with language loss (Hong et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2014), and is phosphorylated by DYRK1A (Huang and Tindall, 2007). Regarding the RAP1 signaling pathway, it is important for regulating MAPK activity and for promoting GABA(B) receptor surface expression (Zhang et al., 2015). As shown in Table 3, candidates for clinical conditions affecting language only are enriched in components of this pathway.
In order to further delve into the language-specificity of our network, we also used Enrichr to generate the expression grids of our candidates for the oscillogenome across the brain regions profiled by the Allen Brain Atlas6. Figure 2 compares the grids for up- and downregulated genes in the brain, with the grids for SZ, ASD, DD, and SLI. Overall, our candidates are mostly upregulated in the medial septal nucleus, which innervates the hippocampal formation and which plays a key role in the generation of θ waves (Pignatelli et al., 2012). They are also highly upregulated in the thalamus (specifically, in the sensory-motor cortex, but also in the stria terminalis, which serves as a major output pathway of the amygdala), the insula (in the ventral and the dorsal parts of the agranular insular area and in the superficial stratum of insular cortex), and in the striatum (in the septopallidal area, the striatal septum and the pallidal septum). They are significantly downregulated in several parts of the cerebellum, including the cerebellar cortex and the vermis. Candidates for SLI are mostly upregulated in the basal forebrain and the hindbrain, whereas they are mostly downregulated in different areas of the cortex, including the retrosplenial, frontal and parietal cortices. We think that this might contribute to conferring a degree of specificity to our language-related set of candidates compared to other candidates for language dysfunction. As discussed in detail in Boeckx and Benítez-Burraco (2014a) and Murphy (2015b), the thalamus may have played a central role in the evolutionary changes resulting in our language-readiness. The thalamus acts as a relay device for most of the brain areas involved in language processing, particularly, between the cortex and the basal ganglia (Lieberman, 2008; Theyel et al., 2009), and it is crucially involved in aspects of the syntax-semantics interface (Wahl et al., 2008; David et al., 2011), although it remains to be seen which particular subnuclei are involved in syntax (see Klostermann et al., 2013). Importantly for our hypothesis, the thalamus controls the oscillations generated in the cortex (Theyel et al., 2009; Saalmann et al., 2012). Specifically, thalamic input allows for an enrichment of oscillatory activity in different frequency bands (Singer, 2013; Uhlhaas et al., 2013; Cannon et al., 2014), and it is thalamic GABAergic neurons that crucially contribute to restricting cortical activity, by providing low-frequency oscillations that are capable of embedding higher-frequency oscillations across distant brain areas (Whitman et al., 2013). This embedding plays a key role in aspects of language processing (see Murphy, 2015b, 2016b, 2018b for details). Regarding the striatum, it is crucially involved in vocal learning, as part of the cortico-thalamic-striatal circuits responsible for motor planning and procedural learning (for details, see Boeckx and Benítez-Burraco, 2014b).
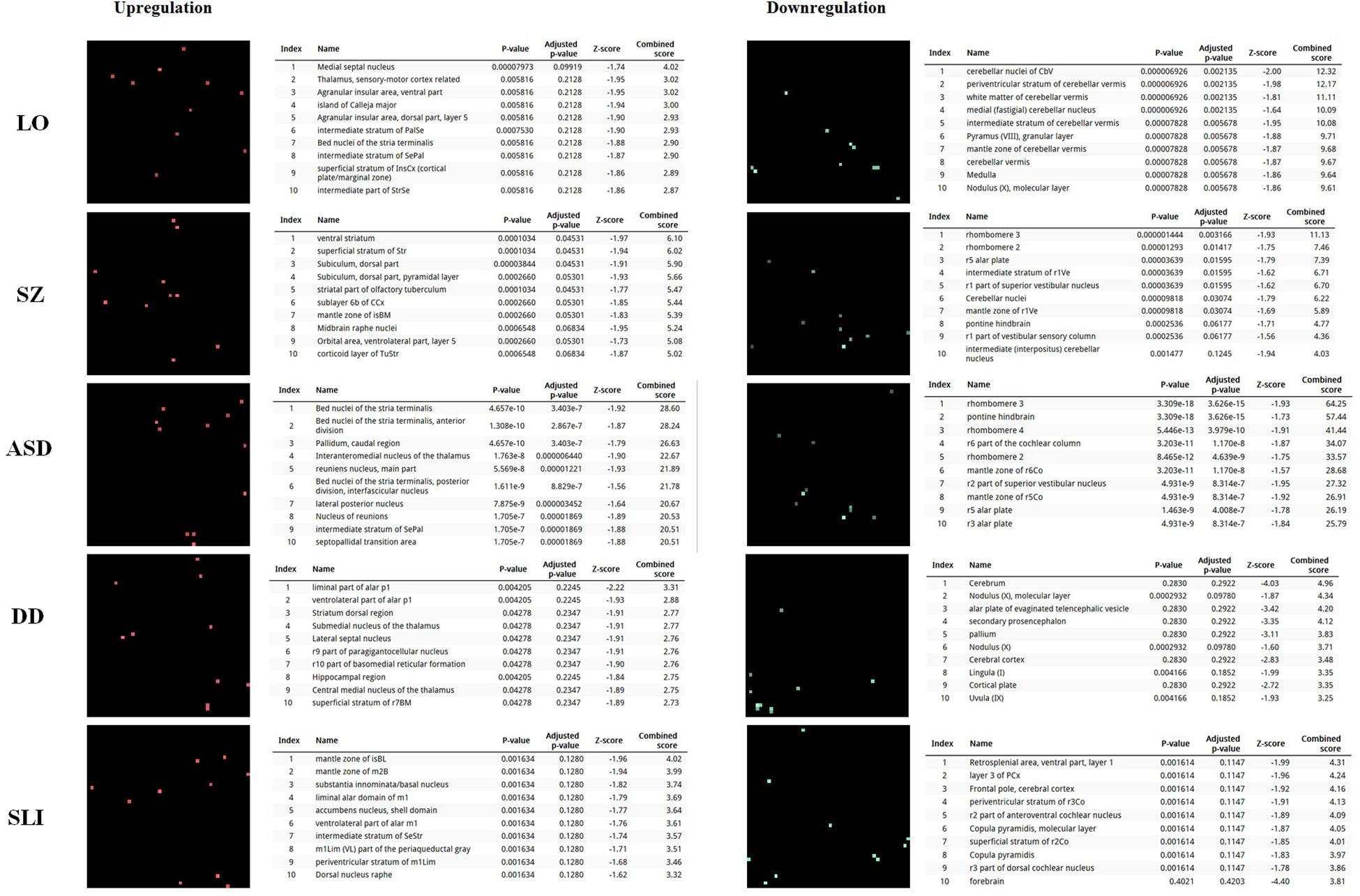
FIGURE 2. Expression profiles in the brain of the set of genes considered in this study. Expression grids were generated with Enrichr. Brain regions where genes are most upregulated are displayed in red, whereas region in which genes are most downregulated are shown in green (the more light the color, the more up- or downregulated a gene is). The tables contain the most up- or downregulated genes according to the Combined Score. The acronyms for the brain regions are from the Allen Brain Atlas and can be checked at developingmouse.brain-map.org/docs/Legend_2010_03.pdf.
Lastly, we have also examined the brain expression profiles of our candidates across development, in order to know whether they are down- or upregulated during the time window when changes in the brain wiring and function, important for language acquisition, take place. Specifically, we wish to know whether changes in the expression levels of our candidates in particular areas of the brain (and presumably, in their regulatory function regarding brain oscillations) can be related to some of the developmental stages of language acquisition by children. As shown in Figures 3, 4, some of these genes exhibit expression peaks in different brain areas between 0 and 5 years of age, like APOE, CX3CR1, CYP19A1, and PDGFRB. Conversely, others are significantly downregulated after birth, like COL4A2, DLX5, GRIN2B, ROBO1, or SETBP1. Because of their involvement in specific aspects of the oscillomic model of language processing (see below), we expect this will help refine our view of how the child develops new components of their linguistic competence over time. Interestingly, several of our candidates exhibit dissimilar expression trends in different brain areas. For instance, after birth, CACNA1L is upregulated in the striatum and downregulated in the thalamus. Likewise, CX3CR1 is downregulated in the cerebellum and upregulated in the cortex, the thalamus, and the striatum. Because of the involvement of the thalamus in our model of language processing and language evolution, it is also of interest that the expression profile of CYP19A1 involves this area, with a sharp peak during childhood. Also of interest is HTR1A, with shows consecutive expression peaks across development: It is highly expressed in the embryonic cortex and the embryonic hippocampus (with a second peak during adolescence), it is upregulated in the cerebellum around birth, and it is upregulated in the amygdala in young children. We expect that these patterns of expression can help explain the observed changes in brain activity during language processing across developmental stages, and ultimately account for some of the changes in the linguistic abilities of the child.
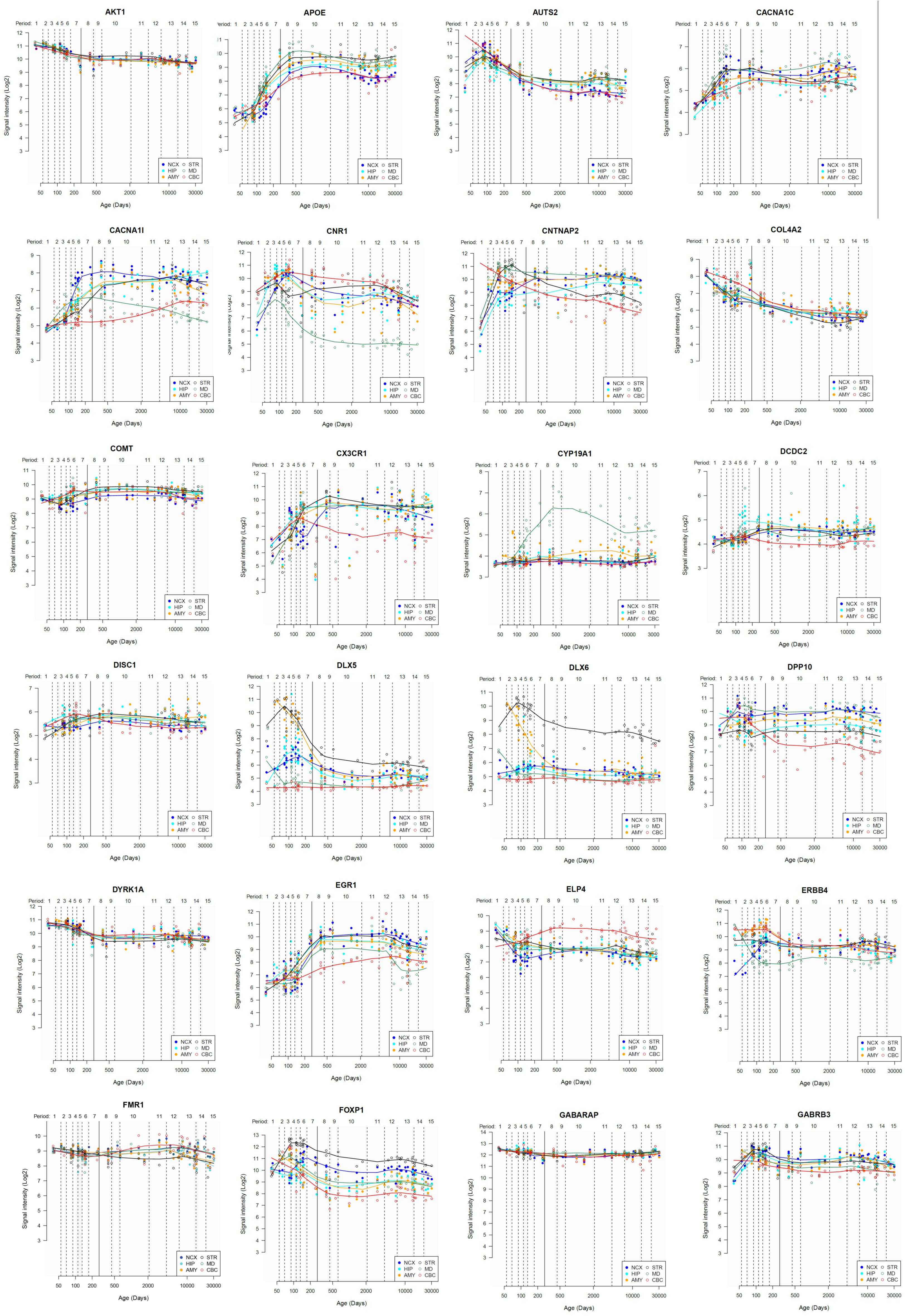
FIGURE 3. Individual brain expression profiles across development of the set of genes considered in this study (1–24). The expression data are from the Human Brain Transcriptome Database (hbatlas.org/). Six different brain regions are considered: the cerebellar cortex (CBC), the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus (MD), the striatum (STR), the amygdala (AMY), the hippocampus (HIP), and 11 areas of neocortex (NCX). Data for SHANK3 were not available.
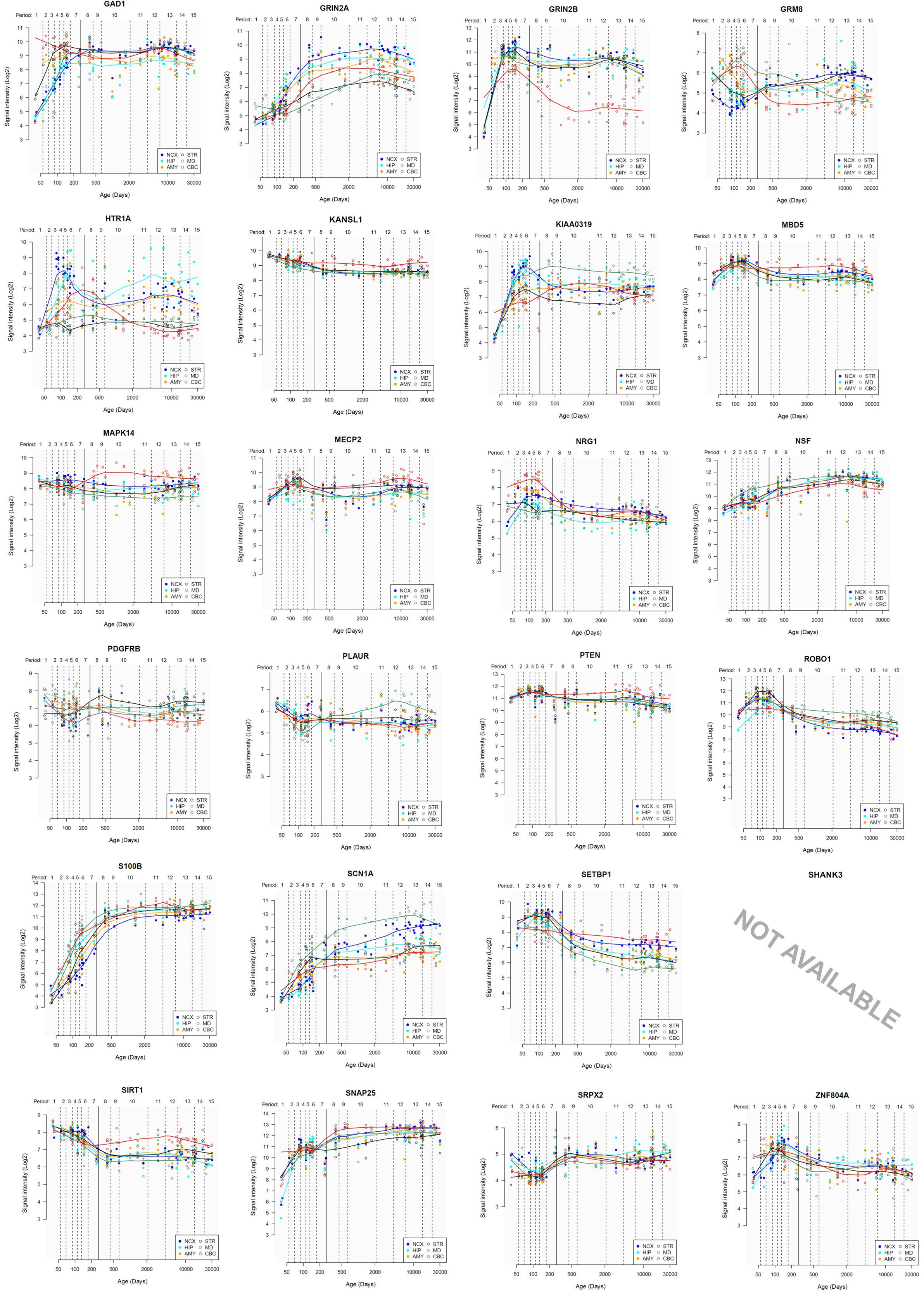
FIGURE 4. Individual brain expression profiles across development of the set of genes considered in this study (25–48).
Linking Candidates for the Language Oscillogenome to Language Processing
A General Framework From Linking Genes to Brain Oscillation to Language Processing
Having documented the most likely candidates which could constitute a robust, testable draft of the language oscillogenome, we now turn to the neurocomputational implementation of language processing, and how an abnormal genetic profile can in turn give rise to abnormal oscillatory signatures. The core feature of our oscillogenomic approach is a rich level of cross-disciplinary integration.
As Anderson (2016, p. 6) says of the relationship between evolutionary psychology and neuroscience, ‘function in the brain depends upon, at least: a neural network, an underlying genetic network, and an overlaid chemical gradient. Each of these elements is only partially understood, and their dynamic interactions even less so.’ By attempting to draw relations between genes, oscillations and linguistic computations we hope that we can shed some light on the nature of these interactions, and ultimately on the neurobiological nature of language. As noted earlier, the interpretation and construction of linguistic phrases requires a range of particular cross-frequency couplings across certain regions (Murphy, 2018b). Genes are expected to contribute decisively to the emergence of this global neuronal workspace, yielding specific patterns of long-distance connections among distributed neurons and, as a result, specific oscillatory signatures of language.
It should be stressed that most of the forms of oscillatory behavior we will review here are far from unique to language, but it is our contention that a range of domain-general oscillatory processes conspire to generate language uniquely, and that their disruption leads to the forms of language deficits found in the conditions currently under discussion. Likewise, it should also be stressed that our present proposals about the structure of the oscillogenome may relate not necessarily to language, but to more general cognitive processes. This would still shed some light of the genetic basis of cognitive processes relevant to, and possibly related to language, but there nevertheless remains the possibility that the specific candidate genes proposed here are more centrally involved in language-external processes (e.g., working memory, attention, speech processing). Lastly, it is also worth noting that recent trends in oscillation research have pointed to the relevance of non-sinusoidal neural oscillations. Though traditional spectral analysis techniques typically assume oscillations to be sinusoidal, Cole and Voytek (2017) explore new measures exposing the non-sinusoidal properties of motor cortical β. They note that, far from being a nuisance, non-sinusoidal oscillations may provide computational properties differing in important ways from sinusoidal waves. As it stands, the research and experimental work we rely on here approaches brain dynamics from the more traditional perspective, and it may well be the case that our oscillogenome is therefore missing crucial pieces of the language system’s neurocomputational basis.
That said, we should not expect univocal links between any of our candidates, particular brain areas involved in language processing as revealed by fMRI experiments, and concrete facets of language, like agreement or binding. Genes do not function in this manner (nor do brain structures). As noted, candidates for the language oscillogenome are involved in broader aspects of brain function, like ion transport or neurotransmitter homeostasis, and of cognition, like working memory. This does not by any means discount the possibility that neural oscillations can be grounded in a coherent neurolinguistic framework. To that end, we accept that the specificity of language, like many other aspects of human cognition, does not rely on the purportedly linguistic nature of its biological components, but on the way domain-general components interact (de Waal and Ferrari, 2010). As noted by Parikshak et al. (2015): ‘Understanding the role of specific genetic variants in the brain involves dissecting a functional hierarchy that encompasses molecular pathways, diverse cell types, neural circuits and, ultimately, cognition and behavior.’ It is within this complex network of interactions where oscillations are expected to play a major role, although we acknowledge that the real challenge is to infer causality in such networks (see Civelek and Lusis, 2013; Chen et al., 2014 on genes and molecular networks). All this is particularly evident for complex pathological conditions like language disorders, which seemingly result from the alteration of many of the genes expressed in the brain (this is the ‘omnigenic’ view of complex disorders; Boyle et al., 2017). To put it differently, rather than focusing on the genes that may account exclusively for the phenotypes with more severe linguistic compromise (some genes like this might exist, but only in cases of rare mutations of high penetrance), it seems more efficacious to examine whole-brain transcriptomic profiles and global changes in brain activity patterns to distinguish among disorders with a complex etiology. At present no global analysis like that is available. We therefore need to rely on the available literature, even if this is currently fragmentary and centered around specific phenotypes (that may be seen as tangential to language), specific brain areas (perhaps not the most consistently related to language) and specific genes (that might be not the strongest candidates for language impairment). Providing just a fragment of a bigger picture, we believe that this approach can lead to novel insights.
In Murphy (2016b), an ‘oscillomic’ model was proposed through which linguistic representations are itemized via γ nesting within parahippocampal θ cycles. It is known that hippocampal neurons are involved in the interpretation of acoustic features (Kumar et al., 2014) and semantic combinatorics (Piai et al., 2016) and so, in synchrony with auditory cortices, θ power in this region presumably plays a major role in the sound-meaning interface. This complex would then be nested within the phase of left-cortical δ, attributing to the set a phrasal identity. Certain of these γ clusters would then slow to β to be maintained in memory. This process of phrasal construction is assumed in Murphy (2015b) to be the only human-specific linguistic computation. Ewerdwalbesloh et al. (2016) show that holding visually constructed objects in memory (as opposed to ‘whole,’ presented object) results in greater fronto-parietal θ synchronization. Since the maintenance of constructed objects in fronto-parietal circuits is vital for language, it was hypothesized in Murphy (2016b) that the language system might recruit this (possibly generic) neural code for computationally analogous purposes. In brief, a lexicalisation process generated by a θ-γ code would interact with a phrasal construction process of δ phase-entrainment. This is a more computationally explicit framework than predictive coding models (e.g., Kessler et al., 2016), going beyond simple procedures like ‘what’ and ‘where’ computations into set-theoretic notions more in line with contemporary linguistic theory.
What are the reasons to believe that oscillations have any causal-explanatory power with respect to language? Vosskuhl et al. (2015) used transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) to decrease participant’s θ such that the θ:γ ratio was altered and a larger number of γ cycles could be nested within θ. This carefully controlled study demonstrated that this manipulation increased working memory performance. Although this study does not directly speak to syntactic combinatorics, given the reliance the language system has on working memory we can infer that the θ-γ code is causally related to linguistic representation construction.
Other experimental evidence for the role of this neural code in language comes from a number of places, such as the finding that left-cortical δ entrains to hierarchical linguistic structures from syllables to sentences (Ding et al., 2016). In addition, the roles ascribed here to particular oscillations and oscillatory interactions are supported by the broader (often domain-general) roles argued for by Ketz et al. (2015); namely, that θ is implicated in recollective memory, β in executive control, and α in sensory information gating. In addition, α decreases at right fronto-temporal sites occur when syllables are temporally expected (Wilsch et al., 2015). Such expectancy effects appear in other linguistic domains, with increased semantic predictability leading to reduced parieto-occipital α (Wöstmann et al., 2015). Finally, a verbal generation task by Wojtecki et al. (2016) resulted in 6–12 Hz power increases and enhanced θ-α coherence between the subthalamic nucleus and frontal sites as a function of successful task performance. Despite the relative paucity of experimental work, the role of α in semantic and phonological prediction seems clear – in particular given this rhythm’s function in coordinating the representations constructed by θ-γ coupling (as reviewed in Murphy, 2016b).
Relevant Links Between Genes, Brain Oscillation, and Aspects of Language Processing
Language impairments in ASD at the syntax-semantics interface most often involve difficulties with relative clauses, wh-questions, raising and passives (Perovic et al., 2007; Perovic and Janke, 2013; Wada, 2015). Increased γ power has also been found for individuals with autism (Rojas et al., 2008; Kikuchi et al., 2013), likely going some way to explain their abnormal linguistic comprehension given the model discussed in Murphy (2016b), with Kikuchi et al. (2013) finding in addition reduced cross-cortical θ, α, and β. Bangel et al. (2014) discovered lower β power during a number estimation task in individuals with ASD, and broader rhythmic abnormalities have been found. These findings may be (partly) explained through what we have reviewed above; namely, that low voltage α has been associated with low activity levels in COMT (Enoch et al., 2003). As mentioned, ZNF804A, HTR1A, and GRIN2B modulate hippocampal γ oscillations (Cousijn et al., 2015) with ZNF804A additionally contributing to cortical functioning and neural connectivity, and so these genes may play a role in the etiopathogenesis of the ASD γ profile. We also noted that knockout of Pdgfrb results in reduced auditory phase-locked γ oscillations, which may be a primary cause of similar oscillatory effects in ASD and SZ. We also reviewed how θ-induced long-term potentiation is altered in hippocampal area CA1 of transgenic mice expressing a truncated version of Disc1 (Booth et al., 2014).
The ASD oscillome also appears to frequently involve reduced θ during tasks necessitating inter-regional synchronization (Doesburg et al., 2013). The reduced θ in the ASD population (also documented by Kikuchi et al., 2013) may therefore arise from these or related hippocampal ensembles, which would in turn contribute to working memory deficits, impacting semantic processing.
Abnormally long-lasting prefrontal and central γ is exhibited by individuals with ASD during processing semantic incongruities (Braeutigam et al., 2008), which potentially reflects the execution of a general search mechanism (high γ) to replace the normal rhythmic processes (low γ) to extract and compare representations. As noted, heterozygous mice for Dlx5/6 exhibit reduced cognitive flexibility which appears to emerge from abnormal GABAergic interneurons and γ rhythms (Cho et al., 2015), and it is possible that this is the correct oscillogenomic model to account for this abnormal γ profile.
Autism spectrum disorders patients with abnormal levels of MECP2 show an abnormal γ response in auditory stimulus discrimination tasks (Peters et al., 2015). Similarly, in response to auditory stimulation mice with a heterozygous loss of Mecp2 function display increased latency of cortically sourced components, and also display γ and β abnormalities associated with ASD and SZ (Liao et al., 2012). Picture-naming tasks also lead to lower left inferior frontal γ and β power in ASD subjects relative to neurotypical controls (Buard et al., 2013), and rhythmic connectivity between auditory and language cortices is also abnormal (Jochaut et al., 2015); results potentially explicable via this oscillogenomic account. In particular, Jochaut et al. (2015) discovered that speech processing results in severely impaired θ-γ coupling in ASD, a finding which may relate to the knockout of Pdgfrb resulting in reduced auditory phase-locked γ. In addition, we noted that Fmr1 knockout mice exhibit enhanced mGluR5 signaling, resulting in altered neocortical rhythmic activity (Hays et al., 2011). Since these mice exhibit abnormal patterns of coupling between hippocampal θ and γ (Radwan et al., 2016), this provides another strong oscillogenomic candidate for θ-γ coupling disruptions.
A study of lexical decision in SZ also exposed lower left-temporal and left-frontal α and β power (Xu et al., 2013) – a rhythmic profile also found in Uhlhaas et al. (2008) and Moran and Hong (2011). A sentence presentation task by Xu et al. (2012) revealed reduced θ at occipital and right frontal lobe sites. As noted, the cannabinoid-1 receptor encoded by CNR1 modulates θ and γ rhythms in several brain areas (Hajós et al., 2008) and so may be involved in these abnormalities. Relatedly, a blockade of NR2A-containing receptors increases γ power and reduces low-frequency γ modulation; we have previously documented unusually fast γ in SZ and ASD patients (Murphy and Benítez-Burraco, 2016b), and so this may be part of the underling oscillogenomic basis. Decomposing the P300 event-related component into its constituent θ and δ rhythms, Jones et al. (2004) report significant linkage and linkage disequilibrium between frontal θ band and a single nucleotide polymorphism from the cholinergic muscarinic receptor gene (CHRM2) on chromosome 7. Due to the likely role of this gene in higher cognition (Gosso et al., 2007), this makes it a strong candidate gene for cognitive deficits in SZ.
Knockout of Ppargc1a in mice decreases the spread of activation in hippocampal CA1 and limits pyramidal cell spiking, giving rise also to unusual modulations of kainate-induced γ oscillations (Bartley et al., 2015). PPARGC1A deficiency in ASD may consequently lead to direct oscillatory alterations at this frequency band. We also noted an association between GRM8 and θ power, suggesting that variations in GRM8 may modulate θ rhythms during information processing, potentially opening it up as a candidate gene for ASD, SZ, and DD, given the abnormal θ modulations documented in these disorders.
With respect to the oscillatory basis of linguistic prosody, we noted that speech problems found in patients with mutations in GRIN2A include imprecise articulation and problems with pitch and prosody – archetypal problems documented in DD. Other research indicates that individuals with DD cannot achieve correct phonological representations, and that these problems arise from impaired phase-locking to slower modulations in the speech signal (below 10 Hz, particularly around 2 Hz), impacting syllabic parsing (Hämäläinen et al., 2012; see also Lehongre et al., 2011). Due to its relevance in the P300 component, the cholinergic muscarinic receptor gene CHRM2 is a possible candidate for these δ abnormalities (Callaway, 1983). Soltész et al. (2013) observed weaker entrainment in right auditory cortex of dyslexic patients during the processing of tone streams delivered at 2 Hz. The authors suggested a connection between reading performance and anticipatory δ phase-synchronization. Abnormal δ rhythms in auditory cortex have been found in dyslexics during the processing of speech sounds too (Molinaro et al., 2016).
It has also been suggested that increased anterior β is strongly reflective of dysphonetic dyslexics (with grapheme-to-phoneme conversion difficulties) whereas increased posterior β are typically found in dyseidetic children (with problems accessing the visual lexicon) (Flynn et al., 1992). These findings are compatible with the model proposed in Murphy (2015b, 2018b) and discussed above, since anterior β is here assumed to be involved in the maintenance of the existing ‘cognitive set,’ with abnormal β impairing the ability of dysphonetic dyslexics to hold one linguistic representation in memory and compare/convert it into another.
Relative to neurotypicals, dyslexics additionally display stronger high γ phase-synchronization in left auditory cortex, possibly indicating the wealth of spectrotemporal information reaching this region, compromising the θ-related auditory buffering capacity along with verbal working memory (Lehongre et al., 2011). This would in turn impair the feature-set combinatorial capacities of dyslexics, with both θ and γ, and their cross-frequency coupling, being abnormal, and so the potential candidate genes discussed above for ASD and SZ (e.g., GRM8) are also possible candidates for dyslexia. More broadly, since oscillations are generated in distinct cortical layers (Giraud and Poeppel, 2012), they might be affected by neuronal migration defects in dyslexia (Giraud and Ramus, 2013).
Turning to SLI, Bishop et al. (2010) explored the discrimination of non-linguistic sounds in a group of 32 patients, comparing them to syllables in an oddball paradigm. Healthy controls exhibited event-related desynchronization in δ, θ, and α during the presentation of oddballs, but SLI patients did not, pointing to a low-level auditory perceptual impairment in SLI. Further studies are needed in order to develop a more fine-grained picture of the perceptual and computational properties of SLI language comprehension, but we can nevertheless conclude that the candidate genes discussed above for these frequency bands remain potential candidates for the SLI oscillogenome.
Comparing the language deficits observed in dyslexia and SLI on the one hand with those observed in ASD and SZ on the other, it seems clear that they both exhibit δ abnormalities of distinct neurocomputational properties. In dyslexia, entrainment to the speech envelope (phonology) is impaired due to abnormal δ (leading to problems with slow-rate speech processing; Goswami et al., 2013), whereas in ASD and schizophrenia it appears that patients cannot properly exploit the δ-related processes of phrasal construction and identification. The δ rhythm therefore seems to act as a syntax-phonology interface but also a syntax-semantics interface, depending on which other regions are impaired in the particular disorder, such as the right supramarginal gyrus (Cutini et al., 2016) and left inferior frontal gyrus (Molinaro et al., 2016) in dyslexics.
Linking Genes to Brain Oscillations to Language Processing: Concluding Remarks
Because many of the computational roles we have ascribed to oscillations are notably generic (with the exception of language-specific δ-driven phrasal construction), this genericity of neurocognitive function can potentially map on to the Generalist Genes Hypothesis (Plomin and Kovas, 2005; Kovas and Plomin, 2006), such that the genes we have here claimed to be relevant to specific linguistic deficits (be it syntactic, phonological, and so on) are also likely implicated in other cognitive capacities, by virtue of the generic computational roles of, for instance, the θ-γ code or α inhibition.
There are alternative accounts to the one presented here which downplay (or simply reject) the existence of any causal-explanatory role for oscillations in language. For instance, Goucha et al. (2017) claim that ‘those (oscillatory) mechanisms seem to already be in place in other species. For example, despite the crucial brain expansion that took place in primates and especially humans compared to other mammals, the rhythmical hierarchy of oscillations is mainly kept unchanged’. While it may be true that this hierarchy has ‘mainly’ been kept unchanged – as indeed recent neuroethological work by Kikuchi et al. (2017) attempts to show – thus far there have been no neuroethological experiments using the kind of stimuli which would allow researchers to compare the oscillatory basis of putatively human-specific computations (like phrase-structure building) to the neural responses of non-human primates attempting to interpret or parse identical structures. Kikuchi et al. (2017) expose humans and monkeys to artificial grammars; not only does this not guarantee that the human subjects would recruit their language systems, but even if it did Kikuchi et al. (2017)’s data analysis did not investigate the kind of cross-frequency couplings over the particular regions and rhythms claimed here to be responsible for phrase-structure building. For instance, Kikuchi et al. (2017) only examine coupling between low frequencies and γ (see their Figure 4), and not coupling between low frequencies such as δ, θ, and β (or indeed other forms of cross-frequency coupling). The authors found that ‘learned ordering relationships modulate the observed form of neural oscillatory coupling in (humans and monkeys),’ but this is a far cry from interpreting or generating hierarchically structured expressions. Indeed, further testing the model outlined here could involve not only refining Kikuchi et al. (2017)’s study to involve a broader class of stimuli and analyses, but it could also involve using MEG and EEG to investigate the oscillatory responses in people with autism and schizophrenia during language comprehension, going some way to lend more direct, experimental forms of support.
As a way of modeling what we have discussed here, Figure 5 outlines a general schema with some specific examples taken from this section. The bridge between the three levels described here remains very much open, but we hope that our framework will play a reflective role in theoretically grounding emerging findings in genetics and neural dynamics within a broader understanding of language processing and evolution.
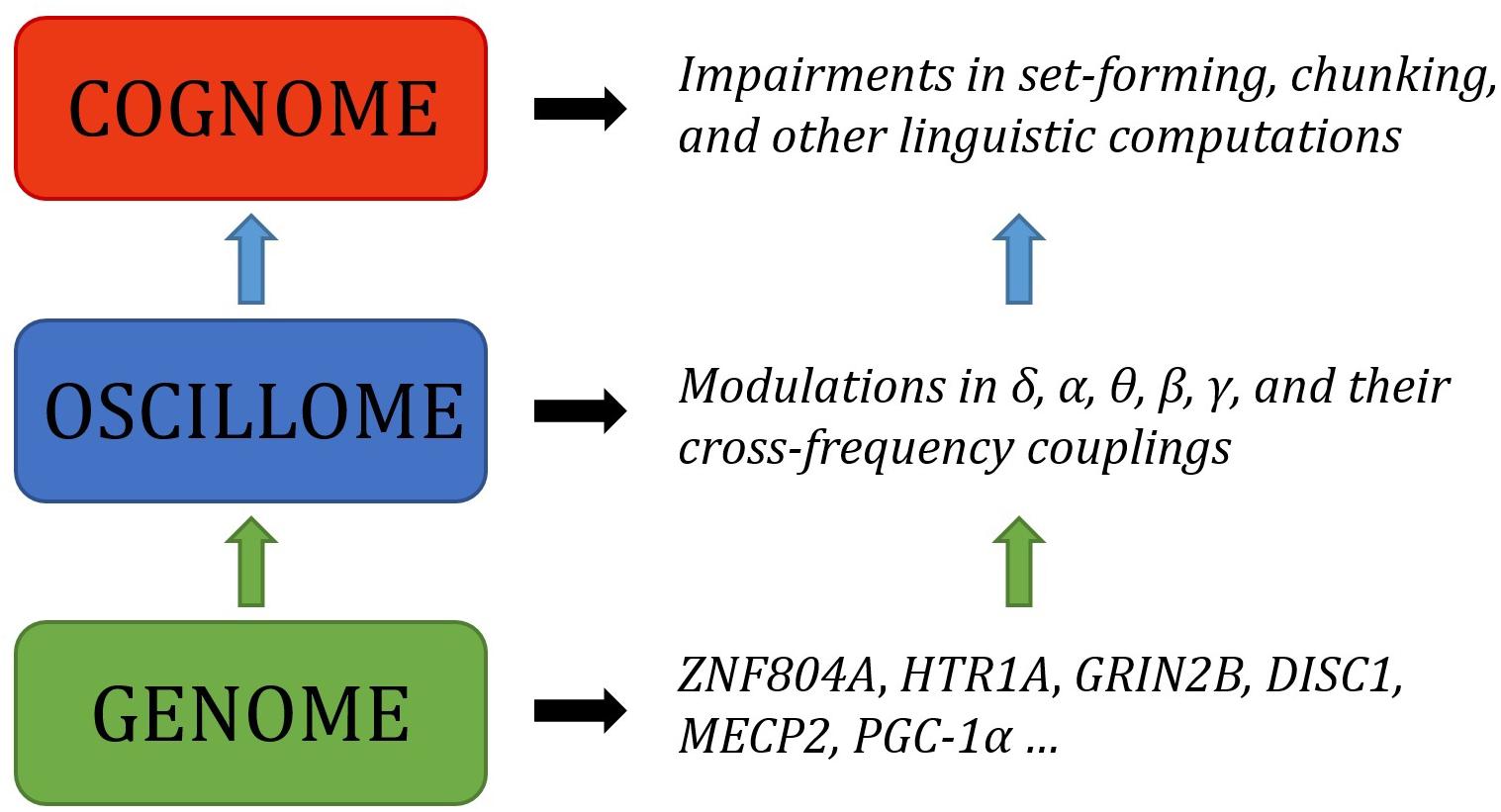
FIGURE 5. Outline of a putative oscillogenomic model for the human faculty of language. ASD, SZ, SLI, and DD have been used as guiding ‘oscillopathies,’ whereas linguistic theory has been employed as a guide for the neurocomputational basis of language. The genome is expected to modulate frequency bands and their interactions at the level of the oscillome, which in turn impacts computational operations at the ‘cognome,’ that is, the basic cognitive operations underlying language, to use a term of Poeppel (2012). For instance, as noted in the text, knockout of Ppargc1a in mice decreases the spread of activation in hippocampal CA1 and limits pyramidal cell spiking, leading to unusual modulations of kainate-induced γ. PPARGC1A deficiency in ASD may consequently lead to direct oscillatory alterations at this frequency band; a hypothesis pending experimental confirmation.
As we hope to have shown, contemporary sequencing technologies have greatly expanded the set of genes associated with cognitive conditions entailing language deficits. The polygenism seen in these diseases is somewhat commensurable with the polygenism expected for language, which is necessary to properly characterize if we want to understand how language unfolds in the brain and develops in the child. Neuroimaging studies from a number of distinct domains suggest that the brain processes language via the coupling of oscillations which enable complex interactions between local and distant brain areas. Nevertheless, it remains imperative to bridge the gap between genes, brain development and function, and language (Figure 6). There are also a number of potentially fruitful avenues to follow with respect to testing some of the core claims made here. For instance, if a given population (e.g., individuals with dyslexia) are known to exhibit particular genetic disruptions which are relevant to the generation of certain brain rhythms (e.g., δ), then this population could undergo M/EEG testing to determine if the linguistic capacities discussed here (e.g., phonological processing) are indeed disrupted in the manner predicted.
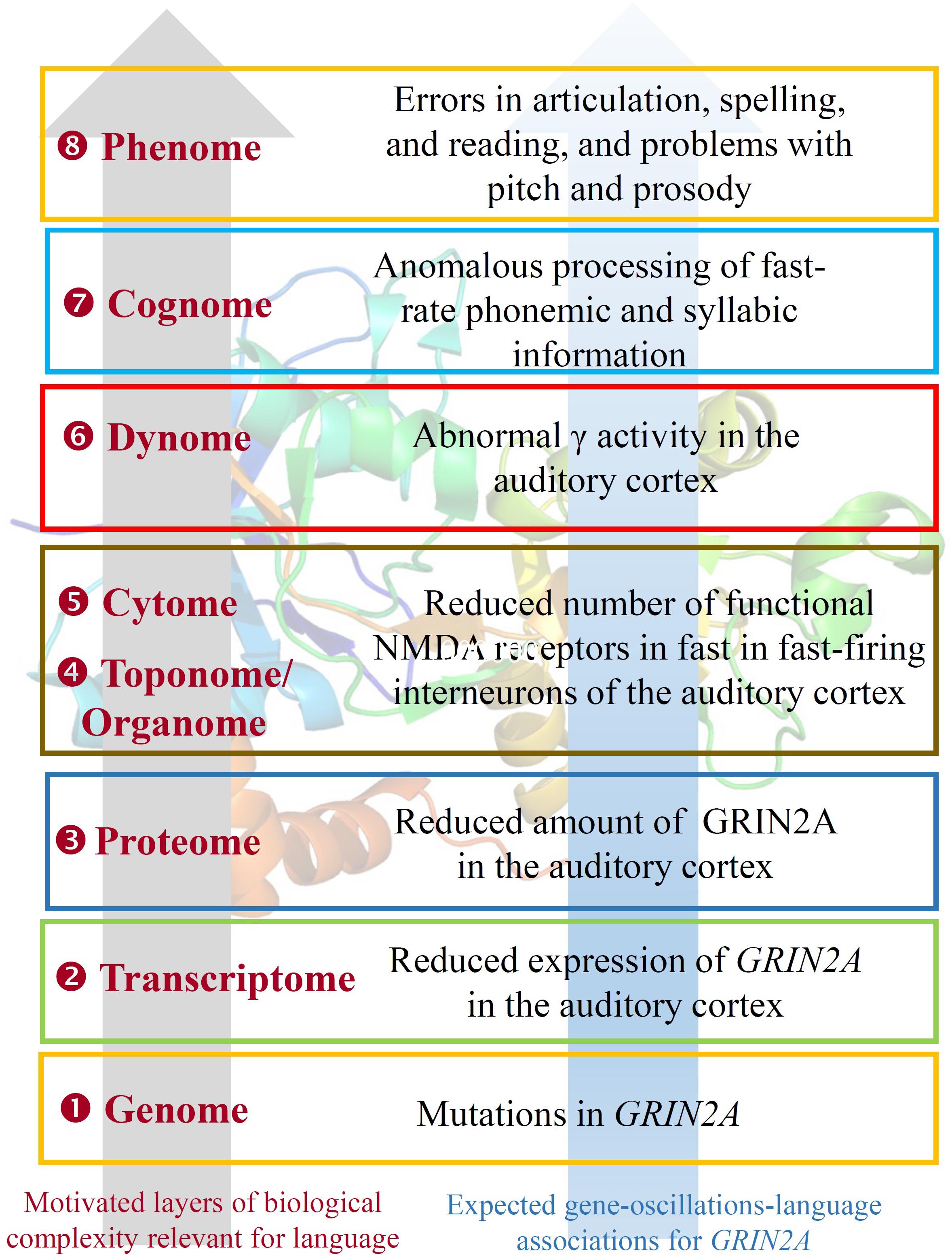
FIGURE 6. GRIN2A as an example of the observed (and expected) bridging links across the different levels of the biological analysis of language. As highlighted in the text, mutations in the gene give rise to different forms of epilepsy-aphasias, like Landau–Kleffner syndrome, continuous spike and waves during slow-wave sleep syndrome, and rolandic epilepsies. GRIN2A expression is found in several brain areas; a noteworthy upregulation of the gene is observed during late embryonic development. GRIN2A encodes the subunit 2A of the NMDA receptor, which plays a key role in long-term potentiation, a physiological process important for memory and learning. This role seemingly results in part from its effect on γ oscillation formation and modulation. As also noted in the text, GRIN2A levels are reduced in fast-firing interneurons of people with schizophrenia. As also discussed, mutations in GRIN2A result in errors in articulation, and in problems with pitch and prosody, which pertain to linguistic prosody, and which can be tracked to the abnormal γ activity, which is crucial for the correct processing of fast-rate phonemic and syllabic information. The 3D structure of GRIN2A, inserted as the background of the picture, is from the RSCB Protein Data Bank (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do). Here, ‘genome’ refers to the set of genes related to brain rhythms that are relevant for language, ‘transcriptome,’ to their RNA products, and ‘proteome’ to the proteins they encode. ‘Toponome’ refers to the whole set of codes of proteins and other biomolecules found in the cells surface, whereas ‘Organome’ refers to the set of cell signaling molecules involved in cell and organ crosstalk. ‘Cytome’ refers to the collection of different cell types of the organism. ‘Connectome’ refers to the wiring of brain areas involved in language processing. ‘Dynome’ refers to the brain dynamics underlying (and supporting) this processing, in the line of Kopell et al. (2014) and Murphy (2015b). ‘Cognome’ refers to the basic cognitive operations underlying language (and in this case, speech processing), in the line of Poeppel (2012). Finally, ‘phenome’ refers to the discrete, language-specific activities (in this case, phonological and phonetic aspects of speech).
Conclusion
Our main conclusion is that the functions of the genes discussed here crucially match aspects of the language oscillome. We have argued that the molecular findings appear to align with the experimental oscillatory results, which in turn align with components of the language cognitive phenotype. These findings only afford tenuous causal-explanatory power to the present genome-oscillome-language linking hypotheses, and further experimental oscillatory and genetic research is required to strengthen the viability of the current gene set and increase the number of candidate genes. Lastly, we expect that our approach will help us gain a better understanding of the complex etiopathogenesis of cognitive conditions entailing problems with language, which should help in turn to design better therapeutic approaches to the diseases (see Wilkinson and Murphy, 2016) aimed to ameliorate the symptoms and improve the abilities of the affected populations.
Author Contributions
EM and AB-B wrote Sections “Introduction and Conclusion.” AB-B wrote Section “Searching for Language Oscillogenome Candidates.” EM wrote “Linking Candidates for the Language Oscillogenome to Language Processing”.
Funding
This work was supported by an Economic and Social Research Council scholarship (1474910) to EM, and by funds from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness [Grant Number FFI2016-78034-C2-2-P (AEI/FEDER, UE)] to AB-B.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
- ^szdb.org
- ^sfari.org
- ^ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed
- ^string-db.org
- ^amp.pharm.mssm.edu/Enrichr
- ^brain-map.org
References
Addis, L., Ahn, J. W., Dobson, R., Dixit, A., Ogilvie, C. M., Pinto, D., et al. (2015). Microdeletions of ELP4 are associated with language impairment, autism spectrum disorder, and mental retardation. Hum. Mutat. 36, 842–850. doi: 10.1002/humu.22816
Amiri, A., Cho, W., Zhou, J., Birnbaum, S. G., Sinton, C. M., McKay, R. M., et al. (2012). Pten deletion in adult hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells causes cellular abnormalities and alters neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 32, 5880–5890. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5462-11.2012
Anderson, G. R., Galfin, T., Xu, W., Aoto, J., Malenka, R. C., and Südhof, T. C. (2012). Candidate autism gene screen identifies critical role for cell-adhesion molecule CASPR2 in dendritic arborization and spine development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 18120–18125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216398109
Anderson, M. L. (2016). Précis of after phrenology: neural reuse and the interactive brain. Behav. Brain Sci. 39:e120. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X15000631
Anitha, A., Nakamura, K., Thanseem, I., Yamada, K., Iwayama, Y., Toyota, T., et al. (2012). Brain region-specific altered expression and association of mitochondria-related genes in autism. Mol. Autism 3:12. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-3-12
Araki, T., Hirata, M., Yanagisawa, T., Sugata, H., Onishi, M., Watanabe, Y., et al. (2016). Language-related cerebral oscillatory changes are influenced equally by genetic and environmental factors. Neuroimage 142, 241–247. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.066
Arcuri, C., Bianchi, R., Brozzi, F., and Donato, R. (2005). S100B increases proliferation in PC12 neuronal cells and reduces their responsiveness to nerve growth factor via Akt activation. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 4402–4414. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406440200
Bae, M. H., Bissonette, G. B., Mars, W. M., Michalopoulos, G. K., Achim, C. L., Depireux, D. A., et al. (2010). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) modulates GABAergic inhibition and seizure susceptibility. Exp. Neurol. 221, 129–135. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.10.011
Balu, D. T., Carlson, G. C., Talbot, K., Kazi, H., Hill-Smith, T. E., Easton, R. M., et al. (2012). Akt1 deficiency in schizophrenia and impairment of hippocampal plasticity and function. Hippocampus 22, 230–240. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20887
Bangel, K. A., Batty, M., Ye, A. X., Meaux, E., Taylor, M. J., and Doesburg, S. M. (2014). Reduced beta band connectivity during number estimation in autism. NeuroImage. Clin. 16, 202–213. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.08.020
Bartley, A. F., Lucas, E. K., Brady, L. J., Li, Q., Hablitz, J. J., Cowell, R. M., et al. (2015). Interneuron transcriptional dysregulation causes frequency-dependent alterations in the balance of inhibition and excitation in hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 35, 15276–15290. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1834-15.2015
Battaglia, D., Chieffo, D., Siracusano, R., Waure, C. D., Brogna, C., Ranalli, D., et al. (2013). Cognitive decline in Dravet syndrome: is there a cerebellar role? Epilepsy Res. 106, 211–221. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.03.012
Becker, J., Czamara, D., Hoffmann, P., Landerl, K., Blomert, L., Brandeis, D., et al. (2012). Evidence for the involvement of ZNF804A in cognitive processes of relevance to reading and spelling. Transl. Psychiatry 2:e136. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.62
Begleiter, H., and Porjesz, B. (2006). Genetics of human brain oscillations. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 60, 162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2005.12.013
Bender, S., Tang, Y., Lindroth, A. M., Hovestadt, V., Jones, D. T. W., Kool, M., et al. (2013). Reduced H3K27me3 and DNA hypomethylation are major drivers of gene expression in K27M mutant pediatric high-grade gliomas. Cancer Cell 24, 660–672. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.10.006
Benítez-Burraco, A., and Boeckx, C. (2015). Possible functional links among brain- and skull-related genes selected in modern humans. Front. Psychol. 6:794. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00794
Benítez-Burraco, A., and Murphy, E. (2016). The oscillopathic nature of language deficits in autism: from genes to language evolution. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 10:120. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00120
Berwick, R. C., and Chomsky, N. (2015). “Foreword: A bird’s-eye view of human language and evolution,” in Birdsong, Speech, and Language: Exploring the Evolution of Mind and Brain, eds J. J. Bolhuis and M. Everaert (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press), 9–12.
Berwick, R. C., Friederici, A., Chomsky, N., and Bolhuis, J. J. (2013). Evolution, brain, and the nature of language. Trends Cog. Sci. 17, 89–98. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2012.12.002
Bishop, D. V. M., Hardimann, M. J., and Barry, J. G. (2010). Lower-frequency event-related desynchronization: a signature of late mismatch responses to sounds, which is reduced or absent in children with specific language impairment. J. Neurosci. 30, 15578–15584. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2217-10.2010
Boeckx, C., and Benítez-Burraco, A. (2014a). The shape of the human language-ready brain. Front. Psychol. 5:282. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00282
Boeckx, C., and Benítez-Burraco, A. (2014b). Globularity and language-readiness: Generating new predictions by expanding the set of genes of interest. Front. Psychol. 5:1324. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01324
Bond, A. M., Vangompel, M. J., Sametsky, E. A., Clark, M. F., Savage, J. C., Disterhoft, J. F., et al. (2009). Balanced gene regulation by an embryonic brain ncRNA is critical for adult hippocampal GABA circuitry. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 1020–1027. doi: 10.1038/nn.2371
Booth, C. A., Brown, J. T., and Randall, A. D. (2014). Neurophysiological modification of CA1 pyramidal neurons in a transgenic mouse expressing a truncated form of disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1. Eur. J. Neurosci. 39, 1074–1090. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12549
Bouaboula, M., Bourrié, B., Rinaldi-Carmona, M., Shire, D., Le Fur, G., and Casellas, P. (1995). Stimulation of cannabinoid receptor CB1 induces krox-24 expression in human astrocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13973–13980. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.13973
Boyle, E. A., Li, Y. I., and Pritchard, J. K. (2017). An expanded view of complex traits: from polygenic to omnigenic. Cell 169, 1177–1186. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.038
Braeutigam, S., Swithenby, S. J., and Bailey, A. J. (2008). Contextual integration the unusual way: a magnetoencephalographic study of responses to semantic violation in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Eur. J. Neurosci. 27, 1026–1036. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06064.x
Braida, D., Guerini, F. R., Ponzoni, L., Corradini, I., De Astis, S., Pattini, L., et al. (2015). Association between SNAP-25 gene polymorphisms and cognition in autism: functional consequences and potential therapeutic strategies. Transl. Psychiatry 5:e500. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.136
Brandon, N. J., and Sawa, A. (2011). Linking neurodevelopmental and synaptic theories of mental illness through DISC1. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 707–722. doi: 10.1038/nrn3120
Brohée, S., and van Helden, J. (2006). Evaluation of clustering algorithms for protein-protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 7:488. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-488
Brown, J. A., Horváth, S., Garbett, K. A., Schmidt, M. J., Everheart, M., Gellért, L., et al. (2014). The role of cannabinoid 1 receptor expressing interneurons in behavior. Neurobiol. Dis. 63, 210–221. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.11.001
Bruneau, N., and Szepetowski, P. (2011). The role of the urokinase receptor in epilepsy, in disorders of language, cognition, communication and behavior, and in the central nervous system. Curr. Pharm. Des. 17, 1914–1923. doi: 10.2174/138161211796718198
Buard, I., Rogers, S. J., Hepbum, S., Kronberg, E., and Rojas, D. C. (2013). Altered oscillation patterns and connectivity during picture naming in autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7:742. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00742
Bufill, E., and Carbonell, E. (2006). Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and neuronal plasticity. Am. J. Human Biol. 18, 556–558. doi: 10.1002/ajhb.20516
Buxbaum, J. D., Cai, G., Chaste, P., Nygren, G., Goldsmith, J., Reichert, J., et al. (2007). Mutation screening of the PTEN gene in patients with autism spectrum disorders and macrocephaly. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 144B, 484–491. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30493
Callaway, E. (1983). The pharmacology of human information processing. Psychopharmacologia 20, 359–370.
Cannon, J., McCarthy, M. M., Lee, S., Lee, J., Börgers, C., Whittington, M. A., et al. (2014). Neurosystems: brain rhythms and cognitive processing. Eur. J. Neurosci. 39, 705–719. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12453
Canuet, L., Tellado, I., Couceiro, V., Fraile, C., Fernandez-Novoa, L., Ishii, R., et al. (2012). Resting-state network disruption and APOE genotype in Alzheimer’s disease: a lagged functional connectivity study. PLoS One 7:e46289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046289
Carr, C. W., Moreno-De-Luca, D., Parker, C., Zimmerman, H. H., Ledbetter, N., Martin, C. L., et al. (2010). Chiari I malformation, delayed gross motor skills, severe speech delay, and epileptiform discharges in a child with FOXP1 haploinsufficiency. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 1216–1220. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.96
Carvill, G. L., Heavin, S. B., Yendle, S. C., McMahon, J. M., O’Roak, B. J., Cook, J., et al. (2013). Targeted resequencing in epileptic encephalopathies identifies de novo mutations in CHD2 and SYNGAP1. Nat. Genet. 45, 825–830. doi: 10.1038/ng.2646
Chakrabarti, B., Kent, L., Suckling, J., Bullmore, E., and Baron-Cohen, S. (2006). Variations in the human cannabinoid receptor (CNR1) gene modulate striatal responses to happy faces. Eur. J. Neurosci. 23, 1944–1948. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04697.x
Chang, C. Y., Chen, Y. W., Wang, T. W., and Lai, W. S. (2016). Akting up in the GABA hypothesis of schizophrenia: Akt1 deficiency modulates GABAergic functions and hippocampus-dependent functions. Sci. Rep. 6:33095. doi: 10.1038/srep33095
Chao, H. T., Chen, H., Samaco, R. C., Xue, M., Chahrour, M., Yoo, J., et al. (2010). Dysfunction in GABA signalling mediates autism-like stereotypies and Rett syndrome phenotypes. Nature 468, 263–269. doi: 10.1038/nature09582
Chen, A. C. H., Tang, Y., Rangaswamy, M., Wang, J. C., Almasy, L., Foroud, T., et al. (2009). Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in a glutamate receptor gene (GRM8) with theta power of event-related oscillations and alcohol dependence. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 150B, 359–368. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30818
Chen, E. Y., Tan, C. M., Kou, Y., Duan, Q., Wang, Z., Meirelles, G. V., et al. (2013). Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics 14:128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-128
Chen, J. C., Alvarez, M. J., Talos, F., Dhruv, H., Rieckhof, G. E., Iyer, A., et al. (2014). Identification of causal genetic drivers of human disease through systems-level analysis of regulatory networks. Cell 159, 402–414. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.021
Chen, X. S., Reader, R. H., Hoischen, A., Veltman, J. A., Simpson, N. H., Francks, C., et al. (2017). Next-generation sequencing identifies novel gene variants and pathways involved in specific language impairment. Sci. Rep. 7:46105. doi: 10.1038/srep46105
Cho, K. K., Hoch, R., Lee, A. T., Patel, T., Rubenstein, J. L., and Sohal, V. S. (2015). Gamma rhythms link prefrontal interneuron dysfunction with cognitive inflexibility in Dlx5/6(+/-) mice. Neuron 85, 1332–1343. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.019
Civelek, M., and Lusis, A. J. (2013). Systems genetics approaches to understand complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 34–48. doi: 10.1038/nrg3575
Clipperton-Allen, A. E., and Page, D. T. (2014). Pten haploinsufficient mice show broad brain overgrowth but selective impairments in autism-relevant behavioral tests. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23, 3490–3505. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu057
Cobos, I., Long, J. E., Thwin, M. T., and Rubenstein, J. L. (2006). Cellular patterns of transcription factor expression in developing cortical interneurons. Cereb. Cortex 16, 82–88. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhk003
Coe, B. P., Witherspoon, K., Rosenfeld, J. A., van Bon, B. W., Vulto-van Silfhout, A. T., Bosco, P., et al. (2014). Refining analyses of copy number variation identifies specific genes associated with developmental delay. Nat. Genet. 46, 1063–1071. doi: 10.1038/ng.3092
Cole, S. R., and Voytek, B. (2017). Brain oscillations and the importance of waveform shape. Trends Cogn. Sci. 21, 137–149. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2016.12.008
Cook, E. H. Jr., Courchesne, R. Y., Cox, N. J., Lord, C., Gonen, D., Guter, S. J., et al. (1998). Linkage-disequilibrium mapping of autistic disorder, with 15q11-13 markers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62, 1077–1083. doi: 10.1086/301832
Corradini, I., Donzelli, A., Antonucci, F., Welzl, H., Loos, M., Martucci, R., et al. (2014). Epileptiform activity and cognitive deficits in SNAP-25+/- mice are normalized by antiepileptic drugs. Cereb. Cortex 24, 364–376. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs316
Courcet, J. B., Faivre, L., Malzac, P., Masurel-Paulet, A., López, E., Callier, P., et al. (2012). The DYRK1A gene is a cause of syndromic intellectual disability with severe microcephaly and epilepsy. J. Med. Genet. 49, 731–736. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101251
Cousijn, H., Tunbridge, E. M., Rolinski, M., Wallis, G., Colclough, G. L., Woolrich, M. W., et al. (2015). Modulation of hippocampal theta and hippocampal-prefrontal cortex function by a schizophrenia risk gene. Hum. Brain Mapp. 36, 2387–2395. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22778
Creppe, C., Malinouskaya, L., Volvert, M. L., Gillard, M., Close, P., Malaise, O., et al. (2009). Elongator controls the migration and differentiation of cortical neurons through acetylation of alpha-tubulin. Cell 136, 551–564. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.043
Cuesta, P., Garcés, P., Castellanos, N. P., López, M. E., Aurtenetxe, S., Bajo, R., et al. (2015). Influence of the APOE ε4 allele and mild cognitive impairment diagnosis in the disruption of the MEG resting state functional connectivity in sources space. J. Alzheimers Dis. 44, 493–505. doi: 10.3233/JAD-141872
Cutini, S., Szûcs, D., Mead, N., Huss, M., and Goswami, U. (2016). Atypical right hemisphere response to slow temporal modulations in children with developmental dyslexia. Neuroimage 143, 40–49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.08.012
Czamara, D., Bruder, J., Becker, J., Bartling, J., Hoffmann, P., Ludwig, K. U., et al. (2011). Association of a rare variant with mismatch negativity in a region between KIAA0319 and DCDC2 in Dyslexia. Behav. Genet. 41, 110–119. doi: 10.1007/s10519-010-9413-6
Daly, C., Wong, V., Burova, E., Wei, Y., Zabski, S., Griffiths, J., et al. (2004). Angiopoietin-1 modulates endothelial cell function and gene expression via the transcription factor FKHR (FOXO1). Genes Dev. 18, 1060–1071. doi: 10.1101/gad.1189704
Damaj, L., Lupien-Meilleur, A., Lortie, A., Riou,É, Ospina, L. H., Gagnon, L., et al. (2015). CACNA1A haploinsufficiency causes cognitive impairment, autism and epileptic encephalopathy with mild cerebellar symptoms. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 23, 1505–1512. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.21
Dasari, V. R., Kaur, K., Velpula, K. K., Gujrati, M., Fassett, D., Klopfenstein, J. D., et al. (2010). Upregulation of PTEN in glioma cells by cord blood mesenchymal stem cells inhibits migration via downregulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. PLoS One 5:e10350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010350
David, O., Maess, B., Eckstein, K., and Friederici, A. D. (2011). Dynamic causal modeling of subcortical connectivity of language. J. Neurosci. 31, 2712–2717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3433-10.2011
de Miranda, A. S., Zhang, C. J., Katsumoto, A., and Teixeira, A. L. (2017). Hippocampal adult neurogenesis: Does the immune system matter? J. Neurol Sci. 372, 482–495. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.10.052
de Waal, F., and Ferrari, P. F. (2010). Towards a bottom-up perspective on animal and human cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 14, 201–207. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.03.003
Dennis, E. L., Jahanshad, N., Rudie, J. D., Brown, J. A., Johnson, K., McMahon, K. L., et al. (2011). Altered structural brain connectivity in healthy carriers of the autism risk gene, CNTNAP2. Brain Connect. 1, 447–459. doi: 10.1089/brain.2011.0064
Dimassi, S., Labalme, A., Lesca, G., Rudolf, G., Bruneau, N., Hirsch, E., et al. (2014). A subset of genomic alterations detected in rolandic epilepsies contains candidate or known epilepsy genes including GRIN2A and PRRT2. Epilepsia 55, 370–378. doi: 10.1111/epi.12502
Ding, N., Melloni, L., Zhang, H., Tian, X., and Poeppel, D. (2016). Cortical tracking of hierarchical linguistic structures in connected speech. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 158–164. doi: 10.1038/nn.4186
Djurovic, S., Gustafsson, O., Mattingsdal, M., Athanasiu, L., Bjella, T., Tesli, M., et al. (2010). A genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in Norwegian individuals, followed by replication in Icelandic sample. J. Affect. Disord. 126, 312–316. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2010.04.007
Doesburg, S. M., Vidal, J., and Taylor, M. J. (2013). Reduced theta connectivity during set-shifting in children with autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7:785. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00785
Ehrlichman, R. S., Luminais, S. N., White, S. L., Rudnickm, N. D., Mam, N., Dowm, H. C., et al. (2009). Neuregulin 1 transgenic mice display reduced mismatch negativity, contextual fear conditioning and social interactions. Brain Res. 1294, 116–127. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.065
Enoch, M. A., Xu, K., Ferro, E., Harris, C. R., and Goldman, D. (2003). Genetic origins of anxiety in women: a role for a functional catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism. Psychiatric Genet. 13, 33–41. doi: 10.1097/00041444-200303000-00006
Ewerdwalbesloh, J. A., Palva, S., Rösler, F., and Khader, P. H. (2016). Neural correlates of maintaining generated images in visual working memory. Hum. Brain Mapp. 37, 4349–4362. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23313
Fatemi, S. H., Folsom, T. D., Kneeland, R. E., and Liesch, S. B. (2011). Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 upregulation in children with autism is associated with underexpression of both Fragile X mental retardation protein and GABAA receptor beta 3 in adults with autism. Anat. Rec. 294, 1635–1645. doi: 10.1002/ar.21299
Fazzari, P., Paternain, A. V., Valiente, M., Pla, R., Luján, R., Lloyd, K., et al. (2010). Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling. Nature 464, 1376–1380. doi: 10.1038/nature08928
Featherstone, R. E., Tatard-Leitman, V. M., Suh, J. D., Lin, R., Lucki, I., and Siegel, S. J. (2013). Electrophysiological and behavioral responses to ketamine in mice with reduced Akt1 expression. Psychopharmacology 227, 639–649. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-2997-9
Filges, I., Shimojima, K., Okamoto, N., Röthlisberger, B., Weber, P., Huber, A. R., et al. (2011). Reduced expression by SETBP1 haploinsufficiency causes developmental and expressive language delay indicating a phenotype distinct from Schinzel-Giedion syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 48, 117–122. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2010.084582
Fink, M., Wadsak, W., Savli, M., Stein, P., Moser, U., Hahn, A., et al. (2009). Lateralization of the serotonin-1A receptor distribution in language areas revealed by PET. Neuroimage 45, 598–605. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.033
Flynn, J. M., Deering, W., Goldstein, M., and Rahbar, M. H. (1992). Electrophysiological correlates of dyslexic subtypes. J. Learn. Disabil. 25, 133–141. doi: 10.1177/002221949202500207
Freunscht, I., Popp, B., Blank, R., Endele, S., Moog, U., Petri, H., et al. (2013). Behavioral phenotype in five individuals with de novo mutations within the GRIN2B gene. Behav. Brain Funct. 9:20. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-9-20
Gao, J., Wang, W. Y., Mao, Y. W., Gräff, J., Guan, J. S., Pan, L., et al. (2010). A novel pathway regulates memory and plasticity via SIRT1 and miR-134. Nature 466, 1105–1109. doi: 10.1038/nature09271
Geschwind, D. H., and Rakic, P. (2013). Cortical evolution: judge the brain by its cover. Neuron 80, 633–647. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.045
Ghanem, N., Yu, M., Poitras, L., Rubenstein, J. L., and Ekker, M. (2008). Characterization of a distinct subpopulation of striatal projection neurons expressing the Dlx genes in the basal ganglia through the activity of the I56ii enhancer. Dev. Biol. 322, 415–424. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.07.029
Ghashghaei, H. T., Weber, J., Pevny, L., Schmid, R., Schwab, M. H., Lloyd, K. C., et al. (2006). The role of neuregulin-ErbB4 interactions on the proliferation and organization of cells in the subventricular zone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 1930–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510410103
Gibson, K. M., Christensen, E., Jakobs, C., Fowler, B., Clarke, M. A., Hammersen, G., et al. (1997). The clinical phenotype of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (4-hydroxybutyric aciduria): case reports of 23 new patients. Pediatrics 99, 567–574. doi: 10.1542/peds.99.4.567
Giorgio, E., Vaula, G., Bosco, G., Giacone, S., Mancini, C., Calcia, A., et al. (2015). Two families with novel missense mutations in COL4A1: when diagnosis can be missed. J. Neurol Sci. 352, 99–104. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.03.042
Giraud, A.-L., and Poeppel, D. (2012). Cortical oscillations and speech processing: emerging computational principles and operations. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 511–517. doi: 10.1038/nn.3063
Giraud, A.-L., and Ramus, F. (2013). Neurogenetics and auditory processing in developmental dyslexia. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol 23, 37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.09.003
Goffin, D., Brodkin, E. S., Blendy, J. A., Siegel, S. J., and Zhou, Z. (2014). Cellular origins of auditory event-related potential deficits in Rett syndrome. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 804–806. doi: 10.1038/nn.3710
Gosso, F. M., de Geus, E. J. C., Polderman, T. J. C., Boomsma, D. I., Posthuma, D., and Heutink, P. (2007). Exploring the functional role of the CHRM2 gene in human cognition: results from a dense genotyping and brain expression study. BMC Med. Genet. 8:66. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-66
Goswami, U., Mead, N., Fosker, T., Huss, M., Barnes, L., and Leong, V. (2013). Impaired perception of syllable stress in children with dyslexia: a longitudinal study. J. Mem. Lang. 69, 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jml.2013.03.001
Goucha, T., Zaccarella, E., and Friederici, A. D. (2017). A revival of the homo loquens as a builder of labeled structures: neurocognitive considerations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 81(Pt B), 213–224. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.01.036
Green, R. E., Krause, J., Briggs, A. W., Maricic, T., Stenzel, U., Kircher, M., et al. (2010). A draft sequence of the neandertal genome. Science 328, 710–722. doi: 10.1126/science.1188021
Guedj, F., Pereira, P. L., Najas, S., Barallobre, M. J., Chabert, C., Souchet, B., et al. (2012). DYRK1A: a master regulatory protein controlling brain growth. Neurobiol. Dis. 46, 190–203. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.01.007
Guo, X., Williams, J. G., Schug, T. T., and Li, X. (2010). DYRK1A and DYRK3 promote cell survival through phosphorylation and activation of SIRT1. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 13223–13232. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102574
Hajós, M., Hoffmann, W. E., and Kocsis, B. (2008). Activation of cannabinoid-1 receptors disrupts sensory gating and neuronal oscillation: relevance to schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 63, 1075–1083. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.12.005
Hämäläinen, J. A., Rupp, A., Soltész, F., Szücs, D., and Goswami, U. (2012). Reduced phase locking to slow amplitude modulation in adults with dyslexia: an MEG study. NeuroImage 59, 2952–2961. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.075
Hämmerle, B., Carnicero, A., Elizalde, C., Ceron, J., Martínez, S., and Tejedor, F. J. (2003). Expression patterns and subcellular localization of the Down syndrome candidate protein MNB/DYRK1A suggest a role in late neuronal differentiation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 17, 2277–2286. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02665.x
Hauser, M. D., Chomsky, N., and Fitch, W. T. (2002). The Faculty of Language: What is it, who has it, and how did it evolve? Science 298, 1569–1579.
Hays, S. A., Huber, K. M., and Gibson, J. R. (2011). Altered neocortical rhythmic activity states in Fmr1 KO mice are due to enhanced mGluR5 signaling and involve changes in excitatory circuitry. J. Neurosci. 31, 14223–14234. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3157-11.2011
Heistek, T. S., Timmerman, A. J., Spijker, S., Brussaard, A. B., and Mansvelder, H. D. (2010). GABAergic synapse properties may explain genetic variation in hippocampal network oscillations in mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 4:18. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2010.00018
Hinna, K. H., Rich, K., Fex-Svenningsen,Å, and Benedikz, E. (2015). The rat homolog of the schizophrenia susceptibility gene ZNF804A is highly expressed during brain development, particularly in growth cones. PLoS One 10:e0132456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132456
Holder, J. L. Jr., and Quach, M. M. (2016). The spectrum of epilepsy and electroencephalographic abnormalities due to SHANK3 loss-of-function mutations. Epilepsia 57, 1651–1659. doi: 10.1111/epi.13506
Homanics, G. E., DeLorey, T. M., Firestone, L. L., Quinlan, J. J., Handforth, A., Harrison, N. L., et al. (1997). Mice devoid of gamma-aminobutyrate type A receptor beta3 subunit have epilepsy, cleft palate, and hypersensitive behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 4143–4148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4143
Hong, S. E., Shugart, Y. Y., Huang, D. T., Shahwan, S. A., Grant, P. E., Hourihane, J. O., et al. (2000). Autosomal recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia is associated with human RELN mutations. Nat. Genet 26, 93–96. doi: 10.1038/79246
Hou, X. J., Ni, K. M., Yang, J. M., and Li, X. M. (2014). Neuregulin 1/ErbB4 enhances synchronized oscillations of prefrontal cortex neurons via inhibitory synapses. Neuroscience 261, 107–117. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.040
Hu, C., Chen, W., Myers, S. J., Yuan, H., and Traynelis, S. F. (2016). Human GRIN2B variants in neurodevelopmental disorders. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 132, 115–121. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2016.10.002
Huang, C. H., Pei, J. C., Luo, D. Z., Chen, C., Chen, Y. W., and Lai, W. S. (2015). Investigation of gene effects and epistatic interactions between Akt1 and neuregulin 1 in the regulation of behavioral phenotypes and social functions in genetic mouse models of schizophrenia. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 8:455. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00455
Huang, H., and Tindall, D. J. (2007). Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2479–2487. doi: 10.1242/jcs.001222
Huynh, T. V., Davis, A. A., Ulrich, J. D., and Holtzman, D. M. (2017). Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease: the influence of apolipoprotein E on amyloid-β and other amyloidogenic proteins. J. Lipid Res. 58, 824–836. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R075481
Inda, M. C., DeFelipe, J., and Muñoz, A. (2006). Voltage-gated ion channels in the axon initial segment of human cortical pyramidal cells and their relationship with chandelier cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 2920–2925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511197103
Jiang, Y. H., Pan, Y., Zhu, L., Landa, L., Yoo, J., Spencer, C., et al. (2010). Altered ultrasonic vocalization and impaired learning and memory in Angelman syndrome mouse model with a large maternal deletion from Ube3a to Gabrb3. PLoS One 5:e12278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012278
Jiménez-Bravo, M., Marrero, V., and Benítez-Burraco, A. (2017). An oscillopathic approach to developmental dyslexia: from genes to speech processing. Behav. Brain Res. 329, 84–95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.03.048
Jochaut, D., Lehongre, K., Saitovitch, A., Devauchelle, A.-D., Olasagasti, I., Chabane, N., et al. (2015). Atypical coordination of cortical oscillations in response to speech in autism. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9:171. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00171
Johnston, A., McBain, C. J., and Fisahn, A. (2014). 5-Hydroxytryptamine1A receptor-activation hyperpolarizes pyramidal cells and suppresses hippocampal gamma oscillations via Kir3 channel activation. J. Physiol. 592, 4187–4199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.279083
Jones, K. A., Porjesz, B., Almasy, L., Bierut, L., Goate, A., Wang, J. C., et al. (2004). Linkage and linkage disequilibrium of evoked EEG oscillations with CHRM2 receptor gene polymorphisms: implications for human brain dynamics and cognition. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 53, 75–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2004.02.004
Kaalund, S. S., Venø, M. T., Bak, M., Møller, R. S., Laursen, H., Madsen, F., et al. (2014). Aberrant expression of miR-218 and miR-204 in human mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis-Convergence on axonal guidance. Epilepsia 55, 2017–2027. doi: 10.1111/epi.12839
Kameda, Y., Saitoh, T., and Fujimura, T. (2011). Hes1 regulates the number and anterior-posterior patterning of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons at the mid/hindbrain boundary (isthmus). Dev. Biol. 358, 91–101. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.016
Kaoru, T., Liu, F. C., Ishida, M., Oishi, T., Hayashi, M., Kitagawa, M., et al. (2010). Molecular characterization of the intercalated cell masses of the amygdala: implications for the relationship with the striatum. Neuroscience 166, 220–230. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.004
Kasnauskiene, J., Ciuladaite, Z., Preiksaitiene, E., Utkus, A., Peciulyte, A., and Kuèinskas, V. (2013). A new single gene deletion on 2q34: ERBB4 is associated with intellectual disability. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 161A, 1487–1490. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35911
Kaufmann, W. E., Cortell, R., Kau, A. S., Bukelis, I., Tierney, E., Gray, R. M., et al. (2004). Autism spectrum disorder in fragile X syndrome: communication, social interaction, and specific behaviors. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 129, 225–234. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30229
Kawata, M., Morikawa, S., Shiosaka, S., and Tamura, H. (2017). Ablation of neuropsin-neuregulin 1 signaling imbalances ErbB4 inhibitory networks and disrupts hippocampal gamma oscillation. Transl. Psychiatry 7:e1052. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.20
Kessler, K., Seymour, R. A., and Rippon, G. (2016). Brain oscillations and connectivity in autism spectrum disorders (ASD): new approaches to methodology, measurement and modelling. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 71, 601–620. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.10.002
Ketz, N. A., Jensen, O., and O’Reilly, R. C. (2015). Thalamic pathways underlying prefrontal cortex–medial temporal lobe oscillatory interactions. Trends Neurosci. 38, 3–12. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2014.09.007
Kikuchi, M., Shitamichi, K., Yoshimura, Y., Ueno, S., Hiraishi, H., and Hirosawa, T. (2013). Altered brain connectivity in 3-to 7-year-old children with autism spectrum disorder. NeuroImage. Clin. 2, 394–401. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.03.003
Kikuchi, Y., Attaheri, A., Wilson, B., Rhone, A. E., Nourski, K. V., Gander, P. E., et al. (2017). Sequence learning modulates neural responses and oscillatory coupling in human and monkey auditory cortex. PLoS Biol. 15:e2000219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000219
Kircher, T., Krug, A., Markov, V., Whitney, C., Krach, S., Zerres, K., et al. (2009). Genetic variation in the schizophrenia-risk gene neuregulin 1 correlates with brain activation and impaired speech production in a verbal fluency task in healthy individuals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30, 3406–3416. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20761
Klostermann, F., Krugel, L. K., and Ehlen, F. (2013). Functional roles of the thalamus for language capacities. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 7:32. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2013.00032
Ko, J. M., Lim, B. C., Kim, K. J., Hwang, Y. S., Ryu, H. W., Lee, J. H., et al. (2013). Distinct neurological features in a patient with Schinzel-Giedion syndrome caused by a recurrent SETBP1 mutation. Childs Nerv. Syst 29, 525–529. doi: 10.1007/s00381-013-2047-2
Kocsis, B. (2012). Differential role of NR2A and NR2B subunits in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist-induced aberrant cortical gamma oscillations. Biol. Psychiatry 71, 987–995. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.10.002
Konopka, G., Bomar, J. M., Winden, K., Coppola, G., Jonsson, Z. O., Gao, F., et al. (2009). Human-specific transcriptional regulation of CNS development genes by FOXP2. Nature 462, 213–217. doi: 10.1038/nature08549
Koolen, D. A., Pfundt, R., Linda, K., Beunders, G., Veenstra-Knol, H. E., Conta, J. H., et al. (2016). The Koolen-de Vries syndrome: a phenotypic comparison of patients with a 17q21.31 microdeletion versus a KANSL1 sequence variant. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 24, 652–659. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.178
Kopell, N. J., Gritton, H. J., Whittington, M. A., and Kramer, M. A. (2014). Beyond the connectome: the dynome. Neuron 83, 1319–1328. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.016
Kornilov, S. A., Rakhlin, N., Koposov, R., Lee, M., Yrigollen, C., Caglayan, A. O., et al. (2016). Genome-wide association and exome sequencing study of language disorder in an isolated population. Pediatrics 137:e20152469. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-2469
Kos, M., van den Brink, D., Snijders, T. M., Rijpkema, M., Franke, B., Fernandez, G., et al. (2012). CNTNAP2 and language processing in healthy individuals as measured with ERPs. PLoS One 7:e46995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046995
Kovács, T., Kelemen, O., and Kéri, S. (2013). Decreased fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) is associated with lower IQ and earlier illness onset in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 210, 690–693. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2012.12.022
Kovas, Y., and Plomin, R. (2006). Generalist genes: implications for cognitive sciences. Trends Cogn. Sci. 10, 198–203. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2006.03.001
Krug, A., Markov, V., Sheldrick, A., Krach, S., Jansen, A., Zerres, K., et al. (2009). The effect of the COMT val(158)met polymorphism on neural correlates of semantic verbal fluency. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 259, 459–465. doi: 10.1007/s00406-009-0010-8
Krug, A., Nieratschker, V., Markov, V., Krach, S., Jansen, A., Zerres, K., et al. (2010). Effect of CACNA1C rs1006737 on neural correlates of verbal fluency in healthy individuals. Neuroimage 49, 1831–1836. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.028
Kuhlwilm, M., Davierwala, A., and Pääbo, S. (2013). Identification of putative target genes of the transcription factor RUNX2. PLoS One 8:e83218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083218
Kuleshov, M. V., Jones, M. R., Rouillard, A. D., Fernandez, N. F., Duan, Q., Wang, Z., et al. (2016). Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W90–W97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377
Kumar, D., Dedic, N., Flachskamm, C., Voulé, S., Deussing, J. M., and Kimura, M. (2015). Cacna1c (Cav1.2) modulates electroencephalographic rhythm and rapid eye movement sleep recovery. Sleep 38, 1371–1380. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4972
Kumar, S., Bonnici, H. M., Teki, S., Agus, T. R., Pressnitzer, D., Maguire, E. A., et al. (2014). Representations of specific acoustic patterns in the auditory cortex and hippocampus. Proc. R. Soc. B 281:20141000. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.1000
Lamminmäki, S., Massinen, S., Nopola-Hemmi, J., Kere, J., and Hari, R. (2012). Human ROBO1 regulates interaural interaction in auditory pathways. J. Neurosci. 32, 966–971. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4007-11.2012
Landi, N., Frost, S. J., Mencl, W. E., Preston, J. L., Jacobsen, L. K., Lee, M., et al. (2013). The COMT Val/Met polymorphism is associated with reading-related skills and consistent patterns of functional neural activation. Dev. Sci. 16, 13–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2012.01180.x
Lanz, T. A., Guilmette, E., Gosink, M. M., Fischer, J. E., Fitzgerald, L. W., Stephenson, D. T., et al. (2013). Transcriptomic analysis of genetically defined autism candidate genes reveals common mechanisms of action. Mol. Autism 4:45. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-4-45
Lee, J., Chung, C., Ha, S., Lee, D., Kim, D. Y., Kim, H., et al. (2015). Shank3-mutant mice lacking exon 9 show altered excitation/inhibition balance, enhanced rearing, and spatial memory deficit. Front. Cell Neurosci. 9:94. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00094
Lehongre, K., Ramus, F., Villiermet, N., Schwartz, D., and Giraud, A.-L. (2011). Altered low-gamma sampling in auditory cortex accounts for the three main facets of dyslexia. Neuron 72, 1080–1090. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.002
Lesca, G., Rudolf, G., Bruneau, N., Lozovaya, N., Labalme, A., Boutry-Kryza, N., et al. (2013). GRIN2A mutations in acquired epileptic aphasia and related childhood focal epilepsies and encephalopathies with speech and language dysfunction. Nat. Genet. 45, 1061–1066. doi: 10.1038/ng.2726
Lesca, G., Rudolf, G., Labalme, A., Hirsch, E., Arzimanoglou, A., Genton, P., et al. (2012). Epileptic encephalopathies of the Landau-Kleffner and continuous spike and waves during slow-wave sleep types: genomic dissection makes the link with autism. Epilepsia 53, 1526–1538. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03559.x
Lett, T. A., Kennedy, J. L., Radhu, N., Dominguez, L. G., Chakravarty, M. M., Nazeri, A., et al. (2016). Prefrontal white matter structure mediates the influence of GAD1 on working memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 41, 2224–2231. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.14
Li, H., Chou, S. J., Hamasaki, T., Pérez-García, C. G., and O’Leary, D. D. (2012). Neuregulin repellent signaling via ErbB4 restricts GABAergic interneurons to migratory paths from ganglionic eminence to cortical destinations. Neural Dev. 7:10. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-10
Li, W., Guo, X., and Xiao, S. (2015). Evaluating the relationship between reelin gene variants (rs7341475 and rs262355) and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 609, 42–47. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.014
Li, X. H., Chen, C., Tu, Y., Sun, H. T., Zhao, M. L., Cheng, S. X., et al. (2013). Sirt1 promotes axonogenesis by deacetylation of Akt and inactivation of GSK3. Mol. Neurobiol. 48, 490–499. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8437-3
Liang, Y., Li, Z., Wei, J., Li, C., Zhang, X., and Neuroimaging Initiative, A. D. (2017). Frequency specific effects of ApoE ε4 allele on resting-state networks in nondemented elders. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017:9823501. doi: 10.1155/2017/9823501
Liao, W., Gandal, M. J., Ehrlichman, R. S., Siegel, S. J., and Carlson, G. C. (2012). MeCP2+/- mouse model of RTT reproduces auditory phenotypes associated with Rett syndrome and replicate select EEG endophenotypes of autism spectrum disorder. Neurobiol. Dis. 46, 88–92. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.048
Lieberman, D. E. (2008). Speculations about the selective basis for modern human craniofacial form. Evol. Anthropol. 17, 55–68. doi: 10.1002/evan.20154
Linkenkaer-Hansen, K., Smit, D. J., Barkil, A., van Beijsterveldt, T. E., Brussaard, A. B., Boomsma, D. I., et al. (2007). Genetic contributions to long-range temporal correlations in ongoing oscillations. J. Neurosci. 27, 13882–13889. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3083-07.2007
Long, Q., Qiu, B., Wang, K., Yang, J., Jia, C., Xin, W., et al. (2013). Genetically engineered bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve functional outcome in a rat model of epilepsy. Brain. Res. 1532, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.07.020
López-Bendito, G., Cautinat, A., Sánchez, J. A., Bielle, F., Flames, N., Garratt, A. N., et al. (2006). Tangential neuronal migration controls axon guidance: a role for neuregulin-1 in thalamocortical axon navigation. Cell 125, 127–142. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.042
Lu, C., Chen, Q., Zhou, T., Bozic, D., Fu, Z., Pan, J. Q., et al. (2016). Micro-electrode array recordings reveal reductions in both excitation and inhibition in cultured cortical neuron networks lacking Shank3. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 159–168. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.173
Lu, C., Li, J., Sun, W., Feng, L., Li, L., Liu, A., et al. (2010). Elevated plasma S100B concentration is associated with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy in Han Chinese: A case–control study. Neurosci. Lett. 484, 139–142. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.036
Luciano, M., Hansell, N. K., Lahti, J., Davies, G., Medland, S. E., Räikkönen, K., et al. (2011). Whole genome association scan for genetic polymorphisms influencing information processing speed. Biol. Psychol. 86, 193–202. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.11.008
Manoach, D. S., Pan, J. Q., Purcell, S. M., and Stickgold, R. (2015). Reduced sleep spindles in schizophrenia: a treatable endophenotype that links risk genes to impaired cognition? Biol. Psychiatry 80, 599–608. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.10.003
Marchese, M., Conti, V., Valvo, G., Moro, F., Muratori, F., Tancredi, R., et al. (2014). Autism-epilepsy phenotype with macrocephaly suggests PTEN, but not GLIALCAM, genetic screening. BMC Med. Genet. 15:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-15-26
Marchese, M., Valvo, G., Moro, F., Sicca, F., and Santorelli, F. M. (2016). Targeted gene resequencing (astrochip) to explore the tripartite synapse in autism-epilepsy phenotype with macrocephaly. Neuromol. Med. 18, 69–80. doi: 10.1007/s12017-015-8378-2
Marseglia, G., Scordo, M. R., Pescucci, C., Nannetti, G., Biagini, E., Scandurra, V., et al. (2012). 372 kb microdeletion in 18q12.3 causing SETBP1 haploinsufficiency associated with mild mental retardation and expressive speech impairment. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 55, 216–221. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.01.005
Marshall, C. R., Noor, A., Vincent, J. B., Lionel, A. C., Feuk, L., Skaug, J., et al. (2008). Structural variation of chromosomes in autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 477–488. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.009
Matsunoshita, Y., Ijiri, K., Ishidou, Y., Nagano, S., Yamamoto, T., Nagao, H., et al. (2011). Suppression of osteosarcoma cell invasion by chemotherapy is mediated by urokinase plasminogen activator activity via up-regulation of EGR1. PLoS One 6:e16234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016234
Mefford, H. C., Muhle, H., Ostertag, P., von Spiczak, S., Buysse, K., Baker, C., et al. (2010). Genome-wide copy number variation in epilepsy: novel susceptibility loci in idiopathic generalized and focal epilepsies. PLoS Genet. 6:e1000962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000962
Meyer, L. (2017). The neural oscillations of speech processing and language comprehension: state of the art and emerging mechanisms. Eur. J. Neurosci. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13748 [Epub ahead of print].
Meyer, L., and Gumbert, M. (2018). Synchronization of electrophysiological responses with speech benefits syntactic information processing. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 11, 1–9. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01236
Miyake, F., Kuroda, Y., Naruto, T., Ohashi, I., Takano, K., and Kurosawa, K. (2015). West syndrome in a patient with Schinzel-Giedion syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 30, 932–936. doi: 10.1177/0883073814541468
Miyano, M., Horike, S., Cai, S., Oshimura, M., and Kohwi-Shigematsu, T. (2008). DLX5 expression is monoallelic and Dlx5 is up-regulated in the Mecp2-null frontal cortex. J. Cell Mol. Med. 12, 1188–1191. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00377.x
Molinaro, N., Lizarazu, M., Lallier, M., Bourguignon, M., and Carreiras, M. (2016). Out-of-synchrony speech entrainment in developmental dyslexia. Hum. Brain Mapp. 37, 2767–2783. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23206
Moran, L. V., and Hong, L. E. (2011). High vs low frequency neural oscillations in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 37, 659–663. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr056
Mori, T., Town, T., Tan, J., Tateishi, N., and Asano, T. (2005). Modulation of astrocytic activation by arundic acid (ONO-2506) mitigates detrimental effects of the apolipoprotein E4 isoform after permanent focal ischemia in apolipoprotein E knock-in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 25, 748–762. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600063
Müller, V., Anokhin, A. P., and Lindenberger, U. (2017). Genetic influences on phase synchrony of brain oscillations supporting response inhibition. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 115, 125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.06.001
Murphy, E. (2015a). Labels, cognomes and cyclic computation: an ethological perspective. Front. Psychol. 6:715. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00715
Murphy, E. (2015b). The brain dynamics of linguistic computation. Front. Psychol. 6:1515. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01515
Murphy, E. (2016b). A theta-gamma neural code for feature set composition with phase-entrained delta nestings. UCL Work. Pap. Linguist. 28, 1–23.
Murphy, E. (2018a). “A domesticated code: on the emergence of the oscillatory basis of phrase structure,” in The Evolution of Language: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference (Evolang 12), eds C. Cuskley, M. Flaherty, L. McCrohon, H. Little, A. Ravignani, and T. Verhoef (Torun: Nicolaus Copernicus University), 335–338. doi: 10.12775/3991-1.081
Murphy, E. (2018b). “Interfaces (travelling oscillations) + recursion (delta-theta code) = language,” in The Talking Species: Perspectives on the Evolutionary, Neuronal and Cultural Foundations of Language, eds E. Luef and M. Manuela (Graz: Unipress Graz Verlag).
Murphy, E., and Benítez-Burraco, A. (2016a). Bridging the gap between genes and language deficits in schizophrenia: an oscillopathic approach. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 10:422. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00422
Murphy, E., and Benítez-Burraco, A. (2016b). Language deficits in schizophrenia and autism as related oscillatory connectomophathies: an evolutionary account. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 83, 742–764. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.07.029
Nagamani, S. C., Erez, A., Ben-Zeev, B., Frydman, M., Winter, S., Zeller, R., et al. (2013). Detection of copy-number variation in AUTS2 gene by targeted exonic array CGH in patients with developmental delay and autistic spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 21, 343–346. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.157
Nakajima, K., Yin, X., Takei, Y., Seog, D.-H., Homma, N., and Hirokawa, N. (2012). Molecular motor KIF5A is essential for GABAA receptor transport, and KIF5A deletion causes epilepsy. Neuron 76, 945–961. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.012
Nakamura, T., Matsumoto, J., Takamura, Y., Ishii, Y., Sasahara, M., Ono, T., et al. (2015). Relationships among parvalbumin-immunoreactive neuron density, phase-locked gamma oscillations, and autistic/schizophrenic symptoms in PDGFR-β knock-out and control mice. PLoS One 10:e0119258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119258
Namiki, K., Nakamura, A., Furuya, M., Mizuhashi, S., Matsuo, Y., Tokuhara, N., et al. (2007). Involvement of p38alpha in kainate-induced seizure and neuronal cell damage. J. Recept. Signal. Transduct. Res. 27, 99–111. doi: 10.1080/10799890701357855
Naqvi, S., Cole, T. Y., and Graham, J. M. Jr. (2000). Cole-Hughes macrocephaly syndrome and associated autistic manifestations. Am. J. Med. Genet 94, 149–152. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(20000911)94:2<149::AID-AJMG7>3.0.CO;2-
Newell, K. A., Karl, T., and Huang, X. F. (2013). A neuregulin. 1 transmembrane domain mutation causes imbalanced glutamatergic and dopaminergic receptor expression in mice. Neuroscience 248, 670–680. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.06.037
Nguyen, P. T., Nakamura, T., Hori, E., Urakawa, S., Uwano, T., Zhao, J., et al. (2011). Cognitive and socio-emotional deficits in platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β gene knockout mice. PLoS One 6:e18004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018004
Nicodemus, K. K., Elvevåg, B., Foltz, P. W., Rosenstein, M., Diaz-Asper, C., and Weinberger, D. R. (2014). Category fluency, latent semantic analysis and schizophrenia: a candidate gene approach. Cortex 55, 182–191. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2013.12.004
Ogawa, S., Kwon, C.-H., Zhou, J., Koovakkattu, D., Parada, L. F., and Sinton, C. (2007). A seizure-prone phenotype is associated with altered free-running rhythm in Pten mutant mice. Brain Res. 1168, 112–123. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.074
Okoro, E. U., Guo, Z., and Yang, H. (2016). Akt isoform-dependent regulation of ATP-Binding cassette A1 expression by apolipoprotein E. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 477, 123–128. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.031
Oksenberg, N., and Ahituv, N. (2013). The role of AUTS2 in neurodevelopment and human evolution. Trends Genet. 29, 600–608. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.08.001
Oksenberg, N., Haliburton, G. D., Eckalbar, W. L., Oren, I., Nishizaki, S., Murphy, K., et al. (2014). Genome-wide distribution of Auts2 binding localizes with active neurodevelopmental genes. Transl. Psychiatry 4:e431. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.78
Oksenberg, N., Stevison, L., Wall, J. D., and Ahituv, N. (2013). Function and regulation of AUTS2, a gene implicated in autism and human evolution. PLoS Genet. 9:e1003221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003221
O’Roak, B. J., Deriziotis, P., Lee, C., Vives, L., Schwartz, J. J., Girirajan, S., et al. (2011). Exome sequencing in sporadic autism spectrum disorders identifies severe de novo mutations. Nat. Genet. 43, 585–589. doi: 10.1038/ng.835
Osbun, N., Li, J., O’Driscoll, M. C., Strominger, Z., Wakahiro, M., Rider, E., et al. (2011). Genetic and functional analyses identify DISC1 as a novel callosal agenesis candidate gene. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 155A, 1865–1876. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34081
Page, D. T., Kuti, O. J., Prestia, C., and Sur, M. (2009). Haploinsufficiency for Pten and serotonin transporter cooperatively influences brain size and social behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 1989–1994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804428106
Pal, D. K., Li, W., Clarke, T., Lieberman, P., and Strug, L. J. (2010). Pleiotropic effects of the 11p13 locus on developmental verbal dyspraxia and EEG centrotemporal sharp waves. Genes Brain Behav. 9, 1004–1012. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00648.x
Palo, O. M., Antila, M., Silander, K., Hennah, W., Kilpinen, H., Soronen, P., et al. (2007). Association of distinct allelic haplotypes of DISC1 with psychotic and bipolar spectrum disorders and with underlying cognitive impairments. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 2517–2528. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm207
Paluszkiewicz, S. M., Olmos-Serrano, J. L., Corbin, J. G., and Huntsman, M. M. (2011). Impaired inhibitory control of cortical synchronization in fragile X syndrome. J. Neurophysiol. 106, 2264–2272. doi: 10.1152/jn.00421.2011
Paracchini, S., Diaz, R., and Stein, J. (2016). “Advances in dyslexia genetics—new insights into the role of brain asymmetries,” in Advances in Genetics, Vol. 96, eds T. Friedmann, J. C. Dunlap, and S. F. Goodwin (London: Academic Press), 53–97. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.08.003
Parikshak, N. N., Gandal, M. J., and Geschwind, D. H. (2015). Systems biology and gene networks in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 16, 441–458. doi: 10.1038/nrg3934
Pearl, P. L., Novotny, E. J., Acosta, M. T., Jakobs, C., and Gibson, K. M. (2003). Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency in children and adults. Ann. Neurol. 54(Suppl. 6), S73–S80. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000059549.70717.80
Peça, J., Feliciano, C., Ting, J. T., Wang, W., Wells, M. F., Venkatraman, T. N., et al. (2011). Shank3 mutant mice display autistic-like behaviours and striatal dysfunction. Nature 472, 437–442. doi: 10.1038/nature09965
Perovic, A., and Janke, V. (2013). Issues in the acquisition of binding, control and raising in high-functioning children with autism. UCL Work. Pap. Linguist. 25, 131–143.
Perovic, A., Modyanova, N., and Wexler, K. (2007). Knowledge of c-command and A-movement in children and adolescents with autism and with Asperger syndrome. Paper Presented at GALA 2007: Generative Approaches to Language Acquisition, Barcelona.
Peters, S. U., Gordon, R. L., and Key, A. P. (2015). Induced gamma oscillations differentiate familiar and novel voices in children with MECP2 duplication and Rett syndromes. J. Child Neurol. 30, 145–152. doi: 10.1177/0883073814530503
Pettigrew, K. A., Frinton, E., Nudel, R., Chan, M. T., Thompson, P., Hayiou-Thomas, M. E., et al. (2016). Further evidence for a parent-of-origin effect at the NOP9 locus on language-related phenotypes. J. Neurodev. Disord. 8:24. doi: 10.1186/s11689-016-9157-6
Piai, V., Anderson, K. L., Lin, J. J., Dewar, C., Parvizi, J., Dronkers, N. F., et al. (2016). Direct brain recordings reveal hippocampal rhythm underpinnings of language processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 11366–11371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603312113
Pietiläinen, O. P., Paunio, T., Loukola, A., Tuulio-Henriksson, A., Kieseppä, T., Thompson, P., et al. (2009). Association of AKT1 with verbal learning, verbal memory, and regional cortical gray matter density in twins. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 150B, 683–692. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30890
Pignatelli, M., Beyeler, A., and Leinekugel, X. (2012). Neural circuits underlying the generation of theta oscillations. J. Physiol. Paris 106, 81–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2011.09.007
Pleasure, S. J., Anderson, S., Hevner, R., Bagri, A., Marin, O., Lowenstein, D. H., et al. (2000). Cell migration from the ganglionic eminences is required for the development of hippocampal GABAergic interneurons. Neuron 28, 727–740. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00149-5
Plomin, R., and Kovas, Y. (2005). Generalist genes and learning disabilities. Psychol. Bull. 131, 592–617. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.131.4.592
Poelmans, G., Buitelaar, J. K., Pauls, D. L., and Franke, B. (2011). A theoretical molecular network for dyslexia: integrating available genetic findings. Mol. Psychiatry 16, 365–382. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.105
Poeppel, D. (2012). The maps problem and the mapping problem: Two challenges for a cognitive neuroscience of speech and language. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 29, 34–55. doi: 10.1080/02643294.2012.710600
Poitras, L., Yu, M., Lesage-Pelletier, C., Macdonald, R. B., Gagné, J. P., Hatch, G., et al. (2010). An SNP in an ultraconserved regulatory element affects Dlx5/Dlx6 regulation in the forebrain. Development 137, 3089–3097. doi: 10.1242/dev.051052
Poot, M., van’t Slot, R., Leupert, R., Beyer, V., Passarge, E., and Haaf, T. (2009). Three de novo losses and one insertion within a pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 in a patient with complete absence of expressive speech and reduced pain perception. Med. Genet. 52, 27–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2008.11.002
Porjesz, B., Almasy, L., Edenberg, H. J., Wang, K., Chorlian, D. B., Foroud, T., et al. (2002). Linkage disequilibrium between the beta frequency of the human EEG and a GABAA receptor gene locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052716399
Provenzano, G., Sgadò, P., Genovesi, S., Zunino, G., Casarosa, S., and Bozzi, Y. (2015). Hippocampal dysregulation of FMRP/mGluR5 signaling in engrailed-2 knockout mice: a model of autism spectrum disorders. Neuroreport 26, 1101–1105. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000477
Pun, R. Y., Rolle, I. J., Lasarge, C. L., Hosford, B. E., Rosen, J. M., Uhl, J. D., et al. (2012). Excessive activation of mTOR in postnatally generated granule cells is sufficient to cause epilepsy. Neuron 75, 1022–1034. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.002
Radwan, B., Dvorak, D., and Fenton, A. A. (2016). Impaired cognitive discrimination and discoordination of coupled theta-gamma oscillations in Fmr1 knockout mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 88, 125–138. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.01.003
Rakhade, S. N., Shah, A. K., Agarwal, R., Yao, B., Asano, E., and Loeb, J. A. (2007). Activity-dependent gene expression correlates with interictal spiking in human neocortical epilepsy. Epilepsia 48(Suppl. 5), 86–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01294.x
Rakic, P. (2009). Evolution of the neocortex: a perspective from developmental biology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 724–735. doi: 10.1038/nrn2719
Rogalski, E., Weintraub, S., and Mesulam, M. M. (2013). Are there susceptibility factors for primary progressive aphasia? Brain Lang. 127, 135–138. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2013.02.004
Rogers, J. T., Morganti, J. M., Bachstetter, A. D., Hudson, C. E., Peters, M. M., Grimmig, B. A., et al. (2011). CX3CR1 deficiency leads to impairment of hippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 31, 16241–16250. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3667-11.2011
Rojas, D. C., Maharajh, K., Teale, P., and Rogers, S. J. (2008). Reduced neural synchronization of gamma-band MEG oscillations in first-degree relatives of children with autism. BMC Psychiatry 8:66. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-8-66
Roll, P., Rudolf, G., Pereira, S., Royer, B., Scheffer, I. E., Massacrier, A., et al. (2006). SRPX2 mutations in disorders of language cortex and cognition. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 1195–1207. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl035
Roll, P., Vernes, S. C., Bruneau, N., Cillario, J., Ponsole-Lenfant, M., Massacrier, A., et al. (2010). Molecular networks implicated in speech-related disorders: FOXP2 regulates the SRPX2/uPAR complex. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 4848–4860. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq415
Rolstad, S., Pålsson, E., Ekman, C. J., Eriksson, E., Sellgren, C., and Landén, M. (2015). Polymorphisms of dopamine pathway genes NRG1 and LMX1A are associated with cognitive performance in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 17, 859–868. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12347
Roy, S. M., Grum-Tokars, V. L., Schavocky, J. P., Saeed, F., Staniszewski, A., Teich, A. F., et al. (2015). Targeting human central nervous system protein kinases: An isoform selective p38αMAPK inhibitor that attenuates disease progression in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6, 666–680. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00002
Royer-Zemmour, B., Ponsole-Lenfant, M., Gara, H., Roll, P., Lévêque, C., Massacrier, A., et al. (2008). Epileptic and developmental disorders of the speech cortex: ligand/receptor interaction of wild-type and mutant SRPX2 with the plasminogen activator receptor uPAR. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17, 3617–3630. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn256
Saalmann, Y. B., Pinsk, M. A., Wang, L., Li, X., and Kastner, S. (2012). The pulvinar regulates information transmission between cortical areas based on attention demands. Science 337, 753–756. doi: 10.1126/science.1223082
Saharan, S., Jhaveri, D. J., and Bartlett, P. F. (2013). SIRT1 regulates the neurogenic potential of neural precursors in the adult subventricular zone and hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 91, 642–659. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23199
Sakakibara, A., and Horwitz, A. F. (2006). Mechanism of polarized protrusion formation on neuronal precursors migrating in the developing chicken cerebellum. J. Cell Sci. 119, 3583–3592. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03080
Sakatani, S., Seto-Ohshima, A., Shinohara, Y., Yamamoto, Y., Yamamoto, H., Itohara, S., et al. (2008). Neural-activity-dependent release of s100b from astrocytes enhances kainate-induced gamma oscillations in vivo. J. Neurosci. 28, 10928–10936. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3693-08.2008
Sandhu, K. V., Lang, D., Müller, B., Nullmeier, S., Yanagawa, Y., Schwegler, H., et al. (2014). Glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 haplodeficiency impairs social behavior in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 13, 439–450. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12131
Schutte, S. S., Schutte, R. J., Barragan, E. V., and O’Dowd, D. K. (2016). Model systems for studying cellular mechanisms of SCN1A-related epilepsy. J. Neurophysiol. 115, 1755–1766. doi: 10.1152/jn.00824.2015
Scott-Van Zeeland, A. A., Abrahams, B. S., Alvarez-Retuerto, A. I., Sonnenblick, L. I., Rudie, J. D., Ghahremani, D., et al. (2010). Altered functional connectivity in frontal lobe circuits is associated with variation in the autism risk gene CNTNAP2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2:56ra80. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001344
Seshadri, S., Faust, T., Ishizuka, K., Delevich, K., Chung, Y., Kim, S. H., et al. (2015). Interneuronal DISC1 regulates NRG1-ErbB4 signalling and excitatory-inhibitory synapse formation in the mature cortex. Nat. Commun. 6:10118. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10118
Seshadri, S., Kamiya, A., Yokota, Y., Prikulis, I., Kano, S., Hayashi-Takagi, A., et al. (2010). Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 expression is regulated by beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme-1-neuregulin cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 5622–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909284107
Shao, Y., Cuccaro, M. L., Hauser, E. R., Raiford, K. L., Menold, M. M., Wolpert, C. M., et al. (2003). Fine mapping of autistic disorder to chromosome 15q11-q13 by use of phenotypic subtypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 539–548. doi: 10.1086/367846
Shulha, H. P., Crisci, J. L., Reshetov, D., Tushir, J. S., Cheung, I., Bharadwaj, R., et al. (2012). Human-specific histone methylation signatures at transcription start sites in prefrontal neurons. PLoS Biol. 10:e1001427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001427
Singer, W. (2013). Cortical dynamics revisited. Trends Cogn. Sci. 17, 616–626. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2013.09.006
Smigiel, R., Cabala, M., Jakubiak, A., Kodera, H., Sasiadek, M. J., Matsumoto, N., et al. (2016). Novel COL4A1 mutation in an infant with severe dysmorphic syndrome with schizencephaly, periventricular calcifications, and cataract resembling congenital infection. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 106, 304–307. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23488
Smith, L. E., Barker, E. T., Seltzer, M. M., Abbeduto, L., and Greenberg, J. S. (2012). Behavioral phenotype of fragile X syndrome in adolescence and adulthood. Am. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 117, 1–17. doi: 10.1352/1944-7558-117.1.1
Smogavec, M., Cleall, A., Hoyer, J., Lederer, D., Nassogne, M. C., Palmer, E. E., et al. (2016). Eight further individuals with intellectual disability and epilepsy carrying bi-allelic CNTNAP2 aberrations allow delineation of the mutational and phenotypic spectrum. J. Med. Genet. 53, 820–827. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103880
Soeiro-De-Souza, M. G., Bio, D. S., David, D. P., Missio, G., Lima, B., Fernandes, F., et al. (2013). Gender effects of the COMT Val 158 Met genotype on verbal fluency in healthy adults. Mol. Med. Rep. 8, 837–844. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1564
Soltész, F., Szücs, D., Leong, V., White, S., Goswami, U., Ziegler, J., et al. (2013). Differential entrainment of neuroelectric delta oscillations in developmental dyslexia. PLoS One 8:e76608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076608
Soorya, L., Kolevzon, A., Zweifach, J., Lim, T., Dobry, Y., Schwartz, L., et al. (2013). Prospective investigation of autism and genotype-phenotype correlations in 22q13 deletion syndrome and SHANK3 deficiency. Mol. Autism 4:18. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-4-18
Souchet, B., Guedj, F., Sahún, I., Duchon, A., Daubigney, F., Badel, A., et al. (2014). Excitation/inhibition balance and learning are modified by Dyrk1a gene dosage. Neurobiol. Dis. 69, 65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.04.016
Strauss, K. A., Puffenberger, E. G., Huentelman, M. J., Gottlieb, S., Dobrin, S. E., Parod, J. M., et al. (2006). Recessive symptomatic focal epilepsy and mutant contactin-associated protein-like 2. N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 1370–1377. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052773
Strug, L. J., Clarke, T., Chiang, T., Chien, M., Baskurt, Z., Li, W., et al. (2009). Centrotemporal sharp wave EEG trait in rolandic epilepsy maps to Elongator Protein Complex 4 (ELP4). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 17, 1171–1181. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.267
Suárez-Pinilla, P., Roiz-Santiañez, R., Ortiz-García de la Foz, V., Guest, P. C., Ayesa-Arriola, R., Córdova-Palomera, A., et al. (2015). Brain structural and clinical changes after first episode psychosis: focus on cannabinoid receptor 1 polymorphisms. Psychiatry Res. 233, 112–119. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.05.005
Sugiura, L., Toyota, T., Matsuba-Kurita, H., Iwayama, Y., Mazuka, R., Yoshikawa, T., et al. (2017). Age-dependent effects of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT) gene Val158Met polymorphism on language function in developing children. Cereb. Cortex 27, 104–116. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw371
Sundvall, M., Veikkolainen, V., Kurppa, K., Salah, Z., Tvorogov, D., van Zoelen, E. J., et al. (2010). Cell death or survival promoted by alternative isoforms of ErbB4. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 4275–4286. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0332
Szklarczyk, D., Franceschini, A., Wyder, S., Forslund, K., Heller, D., Huerta-Cepas, J., et al. (2015). STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D447–D452. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1003
Talkowski, M. E., Mullegama, S. V., Rosenfeld, J. A., van Bon, B. W., Shen, Y., Repnikova, E. A., et al. (2011). Assessment of 2q23.1 microdeletion syndrome implicates MBD5 as a single causal locus of intellectual disability, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 89, 551–563. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.09.011
Tan, G. C., Doke, T. F., Ashburner, J., Wood, N. W., and Frackowiak, R. S. (2010). Normal variation in fronto-occipital circuitry and cerebellar structure with an autism-associated polymorphism of CNTNAP2. Neuroimage 53, 1030–1042. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.018
Tan, H. Y., Chen, A. G., Chen, Q., Browne, L. B., Verchinski, B., Kolachana, B., et al. (2012a). Epistatic interactions of AKT1 on human medial temporal lobe biology and pharmacogenetic implications. Mol. Psychiatry 17, 1007–1016. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.91
Tan, H. Y., Chen, A. G., Kolachana, B., Apud, J. A., Mattay, V. S., Callicott, J. H., et al. (2012b). Effective connectivity of AKT1-mediated dopaminergic working memory networks and pharmacogenetics of anti-dopaminergic treatment. Brain 135, 1436–1445. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws068
Theyel, B., Llano, D., and Sherman, S. (2009). The corticothalamocortical circuit drives higher-order cortex in the mouse. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 84–88. doi: 10.1038/nn.2449
Thomas, A. M., Schwartz, M. D., Saxe, M. D., and Kilduff, T. S. (2017). CNTNAP2 knockout rats and mice exhibit epileptiform activity and abnormal sleep-wake physiology. Sleep 40:zsw026. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw026
Thomson, P. A., Parla, J. S., McRae, A. F., Kramer, M., Ramakrishnan, K., Yao, J., et al. (2014). 708 common and 2010 rare DISC1 locus variants identified in 1542 subjects: analysis for association with psychiatric disorder and cognitive traits. Mol. Psychiatry 19, 668–675. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.68
Tilot, A. K., Frazier, T. W. I. I., and Eng, C. (2015). Balancing proliferation and connectivity in PTEN-associated autism spectrum disorder. Neurotherapeutics 12, 609–619. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0356-8
Tosato, S., Bellani, M., Bonetto, C., Ruggeri, M., Perlini, C., Lasalvia, A., et al. (2012). Is neuregulin 1 involved in determining cerebral volumes in schizophrenia? Preliminary results showing a decrease in superior temporal gyrus volume. Neuropsychobiology 65, 119–125. doi: 10.1159/000330584
Turner, S. J., Brown, A., Arpone, M., Anderson, V., Morgan, A. T., and Scheffer, I. E. (2017). Dysarthria and broader motor speech deficits in Dravet syndrome. Neurology 88, 743–749. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003635
Turner, S. J., Mayes, A. K., Verhoeven, A., Mandelstam, S. A., Morgan, A. T., and Scheffer, I. E. (2015). GRIN2A: an aptly named gene for speech dysfunction. Neurology 84, 586–593. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001228
Uchino, J., Suzuki, M., Hoshino, K., Nomura, Y., and Segawa, M. (2001). Development of language in Rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 23, S233–S235. doi: 10.1016/S0387-7604(01)00367-9
Uhlhaas, P. J., Haenschel, C., Nikolic, D., and Singer, W. (2008). The role of oscillations and synchrony in cortical networks and their putative relevance for the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 34, 927–943. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn062
Uhlhaas, P. J., Roux, F., and Singer, W. (2013). Thalamocortical synchronization and cognition: implications for schizophrenia? Neuron 77, 997–999. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.033
Urak, L., Feucht, M., Fathi, N., Hornik, K., and Fuchs, K. (2006). A GABRB3 promoter haplotype associated with childhood absence epilepsy impairs transcriptional activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 2533–2541. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl174
Van Beijsterveldt, C. E., Molenaar, P. C., de Geus, E. J., and Boomsma, D. I. (1996). Heritability of human brain functioning as assessed by electroencephalography. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 562–573.
Van Bon, B. W., Balciuniene, J., Fruhman, G., Nagamani, S. C., Broome, D. L., Cameron, E., et al. (2011). The phenotype. of. recurrent. 10q22q23 deletions and duplications. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 19, 400–408. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.211
Veenstra-VanderWeele, J., and Cook, E. H. (2004). Molecular genetics of autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 9, 819–832. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001505
Verbrugghe, P., Bouwer, S., Wiltshire, S., Carter, K., Chandler, D., Cooper, M., et al. (2012). Impact of the Reelin signaling cascade (ligands-receptors-adaptor complex) on cognition in schizophrenia. Am. J. Med. Genet B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 159B, 392–404. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32042
Vernes, S. C., Oliver, P. L., Spiteri, E., Lockstone, H. E., Puliyadi, R., Taylor, J. M., et al. (2011). Foxp2 regulates gene networks implicated in neurite outgrowth in the developing brain. PLoS Genet. 7:e1002145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002145
Vertes, R. P., and Kocsis, B. (1997). Brainstem-diencephalo-septohippocampal systems controlling the theta rhythm of the hippocampus. Neuroscience 81, 893–926.
Veyrac, A., Besnard, A., Caboche, J., Davis, S., and Laroche, S. (2014). The transcription factor Zif268/Egr1, brain plasticity, and memory. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 122, 89–129. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420170-5.00004-0
Vosskuhl, J., Huster, R. J., and Herrmann, C. S. (2015). Increase in short-term memory capacity induced by down-regulating individual theta frequency via transcranial alternating current stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9:257. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00257
Wada, R. (2015). Clinician Recasts and Production of Complex Syntax by Children with and without Specific Language Impairment. Master of science thesis, Utah State University, Logan, UT.
Wahl, M., Marzinzik, F., Friederici, A. D., Hahne, A., Kupsch, A., Schneider, G. H., et al. (2008). The human thalamus processes syntactic and semantic language violations. Neuron 59, 695–707. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.07.011
Walker, R. M., Hill, A. E., Newman, A. C., Hamilton, G., Torrance, H. S., Anderson, S. M., et al. (2012). The DISC1 promoter: characterization and regulation by FOXP2. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 2862–2872. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds111
Wang, D., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, G., Wei, M., Hu, Y., et al. (2016). Targeting of microRNA-199a-5p protects against pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus and seizure damage via SIRT1-p53 cascade. Epilepsia 57, 706–716. doi: 10.1111/epi.13348
Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., and Graves, D. T. (2014). FOXO transcription factors: their clinical significance and regulation. Biomed Res. Int. 2014:925350. doi: 10.1155/2014/925350
Weiss, L. A., Escayg, A., Kearney, J. A., Trudeau, M., MacDonald, B. T., Mori, M., et al. (2003). Sodium channels SCN1A, SCN2A and SCN3A in familial autism. Mol. Psychiatry 8, 186–194. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001241
Whalley, H. C., O’Connell, G., Sussmann, J. E., Peel, A., Stanfield, A. C., Hayiou-Thomas, M. E., et al. (2011). Genetic variation in CNTNAP2 alters brain function during linguistic processing in healthy individuals. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 156B, 941–948. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31241
Whitehouse, A. J., Bishop, D. V., Ang, Q. W., Pennell, C. E., and Fisher, S. E. (2011). CNTNAP2 variants affect early language development in the general population. Genes Brain Behav. 10, 451–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2011.00684.x
Whitman, J. C., Ward, L. M., and Woodward, T. S. (2013). Patterns of cortical oscillations organize neural activity into whole-brain functional networks evident in the fMRI BOLD signal. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7:80. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00080
Wilkinson, C., and Murphy, E. (2016). Joint interventions in autism spectrum disorder: relating oscillopathies and syntactic deficits. UCL Work. Pap. Linguist. 28, 1–7.
Williams, S. R., Mullegama, S. V., Rosenfeld, J. A., Dagli, A. I., Hatchwell, E., Allen, W. P., et al. (2010). Haploinsufficiency of MBD5 associated with a syndrome involving microcephaly, intellectual disabilities, severe speech impairment, and seizures. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 18, 436–441. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.199
Wilsch, A., Henry, M. J., Herrmann, B., Maess, B., and Obleser, J. (2015). Alpha oscillatory dynamics index temporal expectation benefits in working memory. Cereb. Cortex 25, 1938–1946. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu004
Wojtecki, L., Elben, S., Vesper, J., and Schnitzler, A. (2016). The rhythm of the executive gate of speech: subthalamic low-frequency oscillations increase during verbal generation. Eur. J. Neurosci. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13429
Wöstmann, M., Herrmann, B., Wilsch, A., and Obleser, J. (2015). Neural alpha dynamics in younger and older listeners reflect acoustic challenges and predictive benefits. J. Neurosci. 35, 1458–1467. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3250-14.2015
Xiong, H., Dai, M., Ou, Y., Pang, J., Yang, H., Huang, Q., et al. (2014). SIRT1 expression in the cochlea and auditory cortex of a mouse model of age-related hearing loss. Exp. Gerontol. 51, 8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.12.006
Xu, T., Stephane, M., and Parhi, K. K. (2012). Selection of abnormal neural oscillation patterns associated with sentence-level language disorder in schizophrenia. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2012, 4923–4926. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347098
Xu, T., Stephane, M., and Parhi, K. K. (2013). Multidimensional analysis of the abnormal neural oscillations associated with lexical processing in schizophrenia. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 44, 135–143. doi: 10.1177/1550059412465078
Yu, W., De Hert, M., Moons, T., Claes, S. J., Correll, C. U., and van Winkel, R. (2013). CNR1 gene and risk of the metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psycopharmacol. 33, 186–192. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e318283925e
Zhan, Y. (2015). Theta frequency prefrontal-hippocampal driving relationship during free exploration in mice. Neuroscience 300, 554–565. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.05.063
Zhan, Y., Paolicelli, R. C., Sforazzini, F., Weinhard, L., Bolasco, G., Pagani, F., et al. (2014). Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 400–406. doi: 10.1038/nn.3641
Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., Huang, S., Sun, Q., Wang, Y., Hu, Y., et al. (2015). GABAB receptor promotes its own surface expression by recruiting a Rap1-dependent signaling cascade. J. Cell Sci. 128, 2302–2313. doi: 10.1242/jcs.167056
Keywords: autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia, specific language impairment, dyslexia, neural oscillations, candidate genes, language deficits
Citation: Murphy E and Benítez-Burraco A (2018) Toward the Language Oscillogenome. Front. Psychol. 9:1999. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01999
Received: 03 April 2018; Accepted: 28 September 2018;
Published: 23 October 2018.
Edited by:
Jon Andoni Dunabeitia, Nebrija University, SpainReviewed by:
Laura V. Sánchez-Vincitore, Universidad Iberoamericana, Dominican RepublicMathieu Declerck, Aix-Marseille Université, France
Copyright © 2018 Murphy and Benítez-Burraco. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Elliot Murphy, ZWxsaW90bXVycGh5OTFAZ21haWwuY29t
 Elliot Murphy
Elliot Murphy Antonio Benítez-Burraco
Antonio Benítez-Burraco