- Department of Psychology, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea
The reverse correlation (RC) method has been widely used, because it allows visualization of mental representations without a priori assumptions about relevant dimensions. We employed the RC method to visualize mental representations of self and examined their relationships with traits related to self-image. For this purpose, 110 participants (70 women) performed a two-image forced choice RC task to generate a classification image of self (self-CI). Participants perceived their self-CIs as bearing a stronger resemblance to themselves than did CIs of others (filler-CIs). Valence ratings of participants who performed the RC task (RC sample) and of 30 independent raters both showed positive correlations with self-esteem, explicit self-evaluation, and extraversion. Moreover, valence ratings of independent raters were negatively correlated with social anxiety symptoms. On the other hand, valence ratings of the RC sample and independent raters were not correlated with depression symptoms, trait anxiety, or social desirability. The results imply that mental representations of self can be properly visualized by using the RC method.
Introduction
Self-image is defined as a subjective perception of oneself, affecting one’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior to a great extent (Coon, 1997). Self-image is commonly known to be in a verbal form. For example, a person with a positive self-image associates words like “Nice,” “Competent,” or “Attractive” with oneself (Amos et al., 1997). It can also be in a visual form, when people conceive images of themselves. Among those images, a facial self-image is claimed to be a fundamental factor of self-identity, self-recognition, and self-awareness, by which one distinguishes oneself from others (Keenan et al., 2000; Lou et al., 2004). However, very little is known about the visual aspect of facial self-image. To understand self-image more thoroughly, we aimed to visualize mental representations of self by using a technique called reverse correlation (RC) and examine their relationships with features relevant to self-image.
The RC method is a data-driven approach to creating visual proxies of mental representations (Mangini and Biederman, 2004; Dotsch and Todorov, 2012; Brinkman et al., 2017). In a typical RC image classification task, a large set of facial stimuli is presented to participants in pairs. These facial stimuli are produced by superimposing random noise patterns on a single base facial image. In each trial, participants select one from a pair of faces that better resembles the target category. By averaging the selected stimuli across many trials, one classification image (CI) is generated (for technical details, see Brinkman et al. (2017), who suggested interpreting a CI as a visual form of the internal representations of interest).
In the field of psychology, the RC method has been widely used to visually identify diagnostic features that are involved in social judgments (Dotsch and Todorov, 2012; Brinkman et al., 2017). For example, it has been used to classify features diagnostic for race: Chinese faces (Dotsch et al., 2008), Moroccan faces (Dotsch et al., 2008, 2011), and Black and White faces (Krosch and Amodio, 2014). It has also been employed to classify features diagnostic for personality traits. Dotsch and Todorov (2012) found that diagnostic facial features that are key to the judgment of trustworthiness were a subtle smile and femininity, and dominance was also related to facial masculinity. In another line of research, the RC method has been employed to examine the associations between the distortion in mental representation and pre-existing knowledge or prejudice. For instance, Dotsch et al. (2008) found that the higher the Dutch participants’ level of implicit prejudice toward Moroccans, independent raters rated the CIs of typical Moroccan faces as more criminal and less trustworthy. Imhoff et al. (2013) also assessed the participant’s mental representation of two occupation groups: male nursery teachers and managers. The CIs of nursery teachers were evaluated as warmer but less competent than those of managers.
An RC task has an important strength of incorporating participants’ spontaneous use of information, because they can freely adopt criteria that are important for their judgments about the stimuli (Brinkman et al., 2017). For example, when asked to select faces that bore a stronger resemblance to themselves, some may place greater weight on the eyes or noses of the presented face, but others may focus on somewhat ambiguous factors, such as emotional impressions or trustworthiness in faces. Some participants may not even be aware of the features they adopt to make such judgments. Because the RC method allows participants to make spontaneous and instinctive decisions, a priori assumptions about related dimensions are not needed to visualize a participant’s self-image. In this vain, Brinkman et al. (2017) suggested that the RC method could be used to visualize how individuals implicitly see themselves.
How people conceive themselves is an important psychological feature, because it can be closely related to personality traits and the patterns of interpersonal relationships. For instance, Epley and Whitchurch (2008) showed that participants who had a more positive sense of self-worth were more likely to recognize an attractively enhanced version of their face as their own than others. Meanwhile, Buhlmann et al. (2008) reported that people with body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) perceived themselves as less attractive compared to how independent raters perceived them. Similarly, patients with social phobia possessed negatively biased self-image rather than a realistic portrayal of how they come across (Clark and Wells, 1995). Moreover, Hirsch et al. (2006) reported that people who were asked to rehearse negative self-image perceived their performance in social situations more poorly than those who were asked to rehearse positive self-image.
Application of the RC method in the dimension of self-image can give additional knowledge by making the ineffable explicit as a form of image which cannot be easily captured by semantic categories (Mangini and Biederman, 2004). The RC task can generate a visual proxy for self-image, whereas traditional assessments of self-image have been focused on verbalized evaluation, such as self-report measures. For example, Amos et al. (1997) measured self-image by directly asking participants to rate themselves on 19 traits using a Likert scale. Though verbal assessments can reveal important aspects of self-image, they would miss out on a visual aspect. This can also be true for indirect measures. For example, Implicit measures assess the association between semantic categories and target (e.g., the Implicit Association Test; Greenwald et al., 1998; Greenwald and Farnham, 2000). These measures can inform automatic attitudes toward self but cannot show how one’s self-image looks like.
Although the RC method has yielded notable findings in the area of social perception, an RC task has not yet been actively used to visualize mental representation of self. In a pioneering study, Imhoff and Dotsch (2013) generated CIs of self, a national in-group (German), and a superordinate group (European). They found that self-image and images of their in-group were independently projected into the visual representation of the superordinate group. However, they examined neither the individual differences in the CIs of self nor its associations with traits relevant to self-image. In fact, to our knowledge, the RC method has not yet been used to examine self-image.
In this study, we aim to visualize mental representations of self by using a reverse-correlation task and examining their relationships with traits related to self-image. Our hypotheses are as follows. First, people would perceive their CIs as bearing a stronger resemblance to themselves than would CIs of others. Second, CI valence rated by self and independent raters would be positively correlated with self-esteem, explicit self-evaluation, and extraversion, but negatively with social anxiety symptoms. Self-esteem is a long-established variable associated with positive self-image (Rosenberg, 1965). According to Oikawa et al. (2012), evaluation of one’s own face and self-esteem are linked at the neural level. Also, previous findings support that socially anxious individuals tend to have negative self-images, as it is known to be a maintaining factor of social anxiety disorder (see for review Ng et al., 2014). We postulated that extraversion (X) of the HEXACO model would be positively correlated with valence ratings of self-CIs, because multiple studies have shown stable associations between extraversion, self-esteem, and the quality of interpersonal relationships (Visser and Pozzebon, 2013; Aghababaei et al., 2016). In addition to the main hypotheses, we explored the relationships between valence ratings of self-CIs and psychological indices, including depression symptoms, trait anxiety, and social desirability.
Methods
Participants and Design
We recruited two separate samples: one that performed the RC task (RC sample) and a sample of independent raters. The RC sample included 110 students (70 women). Each participant in the RC sample produced one self-CI. The mean age of this sample was 22.90 (SDage = 3.09; age-range: 18–34). The RC sample received a gift card equivalent to $13 for their participation. Additionally, 60 participants were recruited as independent raters (30 women; Mage = 25.17, SDage = 3.75; age-range: 19–35) to acquire objective evaluations of the valence of the CIs created by the RC sample. They received $10 for their participation.
We used deception in introducing the aim of the study to blind the participants to the hypotheses and then debriefed them after the experiment. We introduced that the aim of this study is to examine the way of inferring personality traits from artificially generated facial images. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB).
Materials and Procedures
Image-Creation Phase
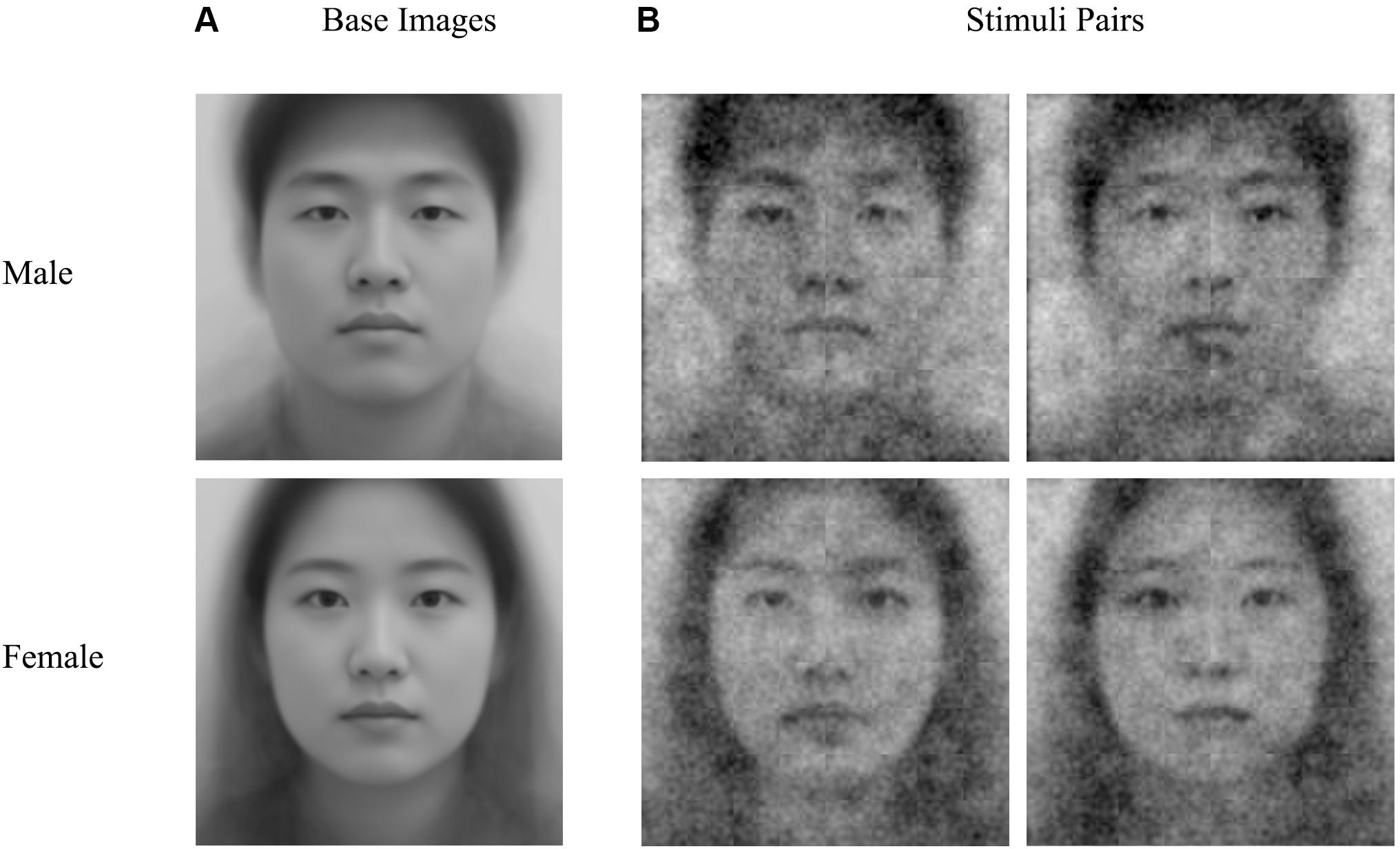
After completing self-report questionnaires, the RC sample performed a two-image forced choice RC task (Dotsch and Todorov, 2012) to generate a classification image of the self. Presented images were a one-base facial image (a morphed composite of 100 faces for each sex) with superimposed random grayscale visual noise (see Figure 1). Every grayscale visual noise was generated by averaging five layers of sinusoid patches. Each patch consisted of different numbers of sinusoid patterns (12, 48, 192, 768, and 3272; see Dotsch and Todorov, 2012 for details).
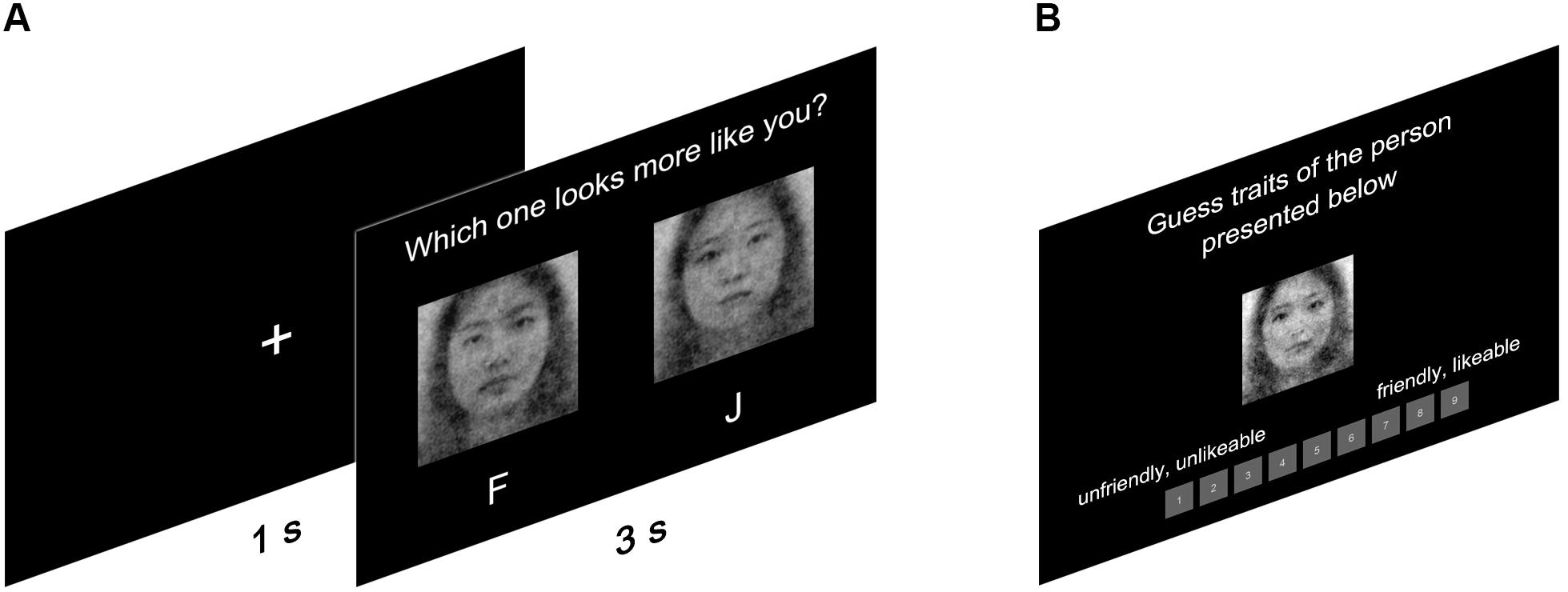
In 300 trials, participants selected one from two facial stimuli that looked more like themselves (see Figure 2A). Female participants only viewed female faces; males only male faces. Stimuli were presented in random order to the participants, who were forced to make a choice within 3 s. The self-CI of a participant was seamlessly generated by the rcicr package (Dotsch, 2016) in R (R Core Team, 2019) upon the completion of the RC task. The rcicr package averages the noise of the selected images and superimposes the averaged noise on the base image to generate a self-CI for each participant (R codes for generating self-CIs can be found in https://github.com/a072826/The_Mirror_of_Mind). To make sure that participants were unaware of the fact that self-CIs were derived from the image selection task, we exclusively used one computer for performing the RC task and the other for generating the self-CIs. Two computers were synchronized with Internet connection so that self-CIs could be created remotely to minimize the risk of being noticed by the participants. The entire procedure of participation was computerized using psychoPy (Peirce et al., 2019).
Image-Rating Phase
Two separate samples rated the CIs generated: the RC sample and the independent rater sample (see Figure 2B). The RC sample rated the CIs that they generated on the valence and on how much it resembled oneself. Also, we presented five filler-CIs with the CI that the participant generated; these filler-CIs for each sex were selected from a pilot study. In the pilot study, 10 men and 10 women (Mage = 25.05, SDage = 3.14; age-range: 20–29) evaluated trustworthiness and dominance with a 9-point Likert scale from 10 CI stimuli. We selected a set of five CI stimuli per sex considering the average of trustworthiness and dominance of each stimulus set to be similar to the total average. The presentation order of six CIs (five filler-CIs and one self-CI) was randomized to reduce experimental biases. We did not inform participants that they were viewing the CI that they had generated.
Resemblance was rated on 9 Likert points ranging from 1 = weaker resemblance to myself to 9 = stronger resemblance to myself. Valence was measured with seven items adapted from 14 self-presentational domains (Leary and Allen, 2011)1. They were presented on 9-point bipolar scales. Seven items were (a) unfriendly, unlikable vs. friendly, likable; (b) incompetent, unintelligent vs. competent, intelligent; (c) irresponsible, undependable vs. responsible, dependable; (d) immoral, unethical vs. moral, ethical; (e) serious, not playful vs. humorous, playful; (f) unattractive, ugly vs. attractive, good-looking; (g) illogical, irrational vs. logical, reasonable. All items were presented in random order. The seven valence items were averaged to calculate one valence rating. All eight items (self-resemblance and valence) were presented in random order. Participants needed to answer all eight items for each CI presented in the middle of the monitor before moving to the next CI.
The independent raters who were blinded to the study hypotheses also rated the valence of the CIs generated by the RC sample with the seven items listed above. We randomly assigned the independent raters into two groups taking sex ratio into account. Each group evaluated 55 images out of 110 self-CIs. The presentation orders of the CI and of the valence items per CI were randomized across the independent raters. After answering all valence items, independent raters evaluated the next CI.
Self-Image Relevant Variables
Rosenberg self-esteem scale (RSE)
We used the RSE (Rosenberg, 1965) to measure self-reported global self-esteem. The RSE consists of 10 5-point Likert-scale items (1 = not very true of me to 5 = very true of me). We used the Korean version of RSE (Lee and Won, 1995).
Social interaction phobia scale (SIPS)
The SIPS was employed to assess social anxiety symptoms (Carleton et al., 2009). The scale consists of 14 5-point Likert-scale items (0 = Not at all characteristic of me to 4 = Extremely characteristic of me). Higher scores indicate a higher degree of social anxiety symptoms. We used the Korean version of the SIPS (Kim et al., 2013).
Explicit self-evaluation
To assess explicit self-evaluation, we asked the RC sample to rate how they evaluate themselves using seven items from 14 self-presentational domains (Leary and Allen, 2011). These seven items were also used for the valence ratings of CIs.
Extraversion
To assess extraversion, we used 10 items from the HEXACO-60 (Ashton and Lee, 2009)2. The HEXACO-60 is scored on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree). The extraversion dimension of the HEXACO-60 consists of four subscales: social self-esteem, social boldness, sociability, and liveliness. We used the Korean version of the HEXACO-60 (Lee and Ashton, 2013).
Control Variables
Center for epidemiological studies depression scale (CES-D)
The CES-D is a 20-item measure to assess depressive symptomatology (Randloff, 1977). The inventory is scored on a 4-point Likert-scale ranging from 0 = rarely or none of the time (less than 1 day) to 3 = most or all of the time (5–7 days) to assess how often participants felt depressed during the past week. Higher scores indicate more depressive symptoms. We used the Korean version of CES-D (Chon et al., 2001).
Taylor manifest anxiety scale (TMAS)
Taylor (1953) developed the Manifest Anxiety Scale (MAS) to measure chronic anxiety symptoms, and Bendig (1956) developed the shortened version of the original scale. The TMAS consists of 20 binary items. We used the Korean version of the TMAS (Lee, 2000).
Marlowe-crowne social desirability scale (MCSDS)
The MCSDS is a self-report scale developed by Crowne and Marlowe (1960) to measure the tendency to appear socially desirable. The MCSDS consists of 33 binary items. We used the Korean version of MCSDS (Lee, 2000).
Results
Resemblance Rating
For raw data, please see Supplementary Material S1. To test whether participants perceived their own CI as bearing a stronger resemblance to themselves than did filler CIs, we performed a one-way (target: self-CI vs. filler-CIs) repeated measure analysis of variance (RM ANOVA) with resemblance rating as a dependent variable. RM ANOVA was performed due to differing numbers of CIs for each target (one vs. five). There was a significant main effect of target, F(1, 109) = 124.38, p < 0.001, ηp2 = 0.53, with a stronger resemblance rating for self-CI (M = 5.89, SD = 1.93, 95% CI = 5.61, 6.17) than for filler-CIs (M = 3.76, SD = 2.00, 95% CI = 3.48, 4.04). The resemblance rating was significantly correlated with valence ratings of the RC sample on their own self-CIs, r = 0.33, p < 0.001. Specifically, resemblance rating was significantly correlated with competency (r = 0.46, p < 0.001), reliability (r = 0.41, p < 0.001), and reasonableness (r = 0.33, p < 0.001) among the seven valence items. Meanwhile, the resemblance rating was significantly correlated neither with the valence ratings of self-CIs evaluated by independent raters (r = −0.02, p = 0.598) nor with the other study variables (|r| s = 0.01 ∼0.13, p = ns), except for the valence ratings evaluated by the RC sample.
Valence Rating
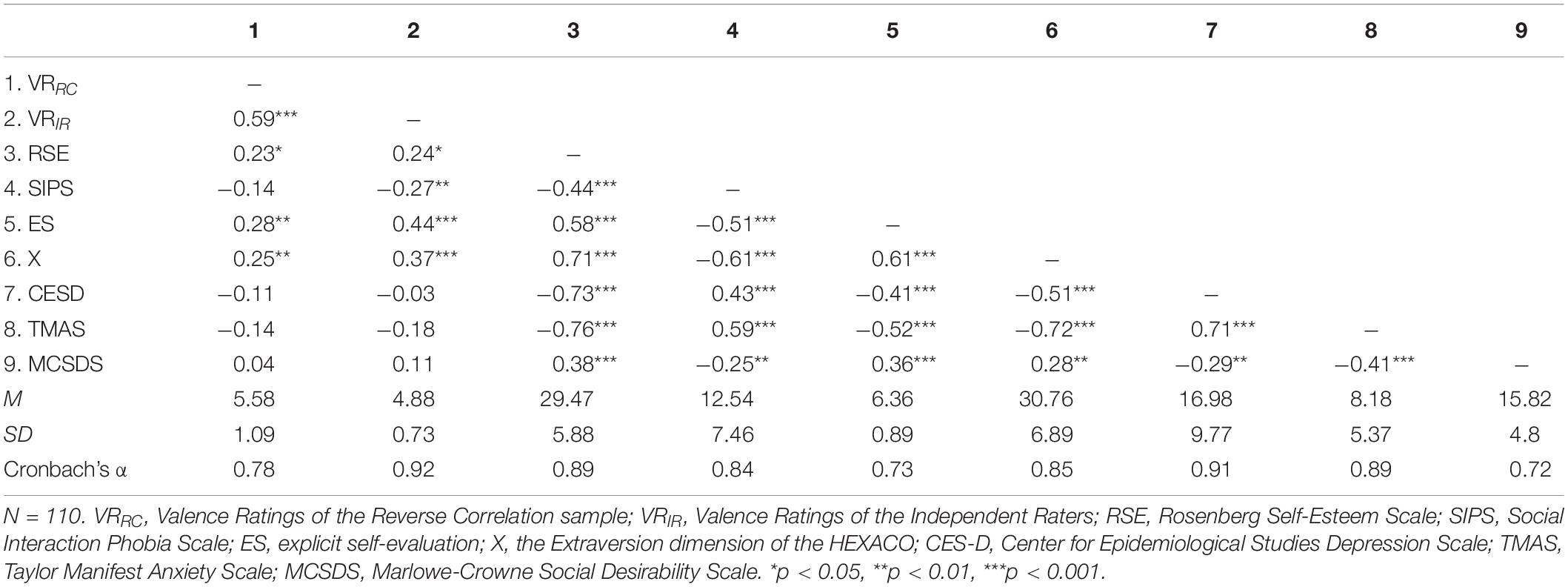
The basic statistics and correlations are shown in Table 1. Reliabilities were acceptable for all measures, with the lowest being 0.72 for MCSDS (Marlowe-Crowne Social Desirability Scale). The valence ratings of self-CIs evaluated by the RC sample and independent raters were positively correlated. For the descriptive purpose, we averaged the resulting self-CIs by high and low groups of self-esteem, social anxiety symptoms, and explicit self-evaluation (see Figure 3). To test the main hypothesis, we investigated the association between the valence ratings of CIs and variables related to self-image. As expected, the valence ratings of the RC sample and independent raters were positively associated with self-esteem, explicit self-evaluation, and extraversion. In addition, the valence ratings of the independent raters were negatively correlated with social anxiety symptoms. Meanwhile, the valence ratings of neither the RC sample nor the independent raters were correlated with depression symptoms, trait anxiety, and social desirability. On the other hand, all of the self-reported measures included in the analysis were significantly correlated to each other, |r| s = 0.28 ∼0.76, p < 0.01.
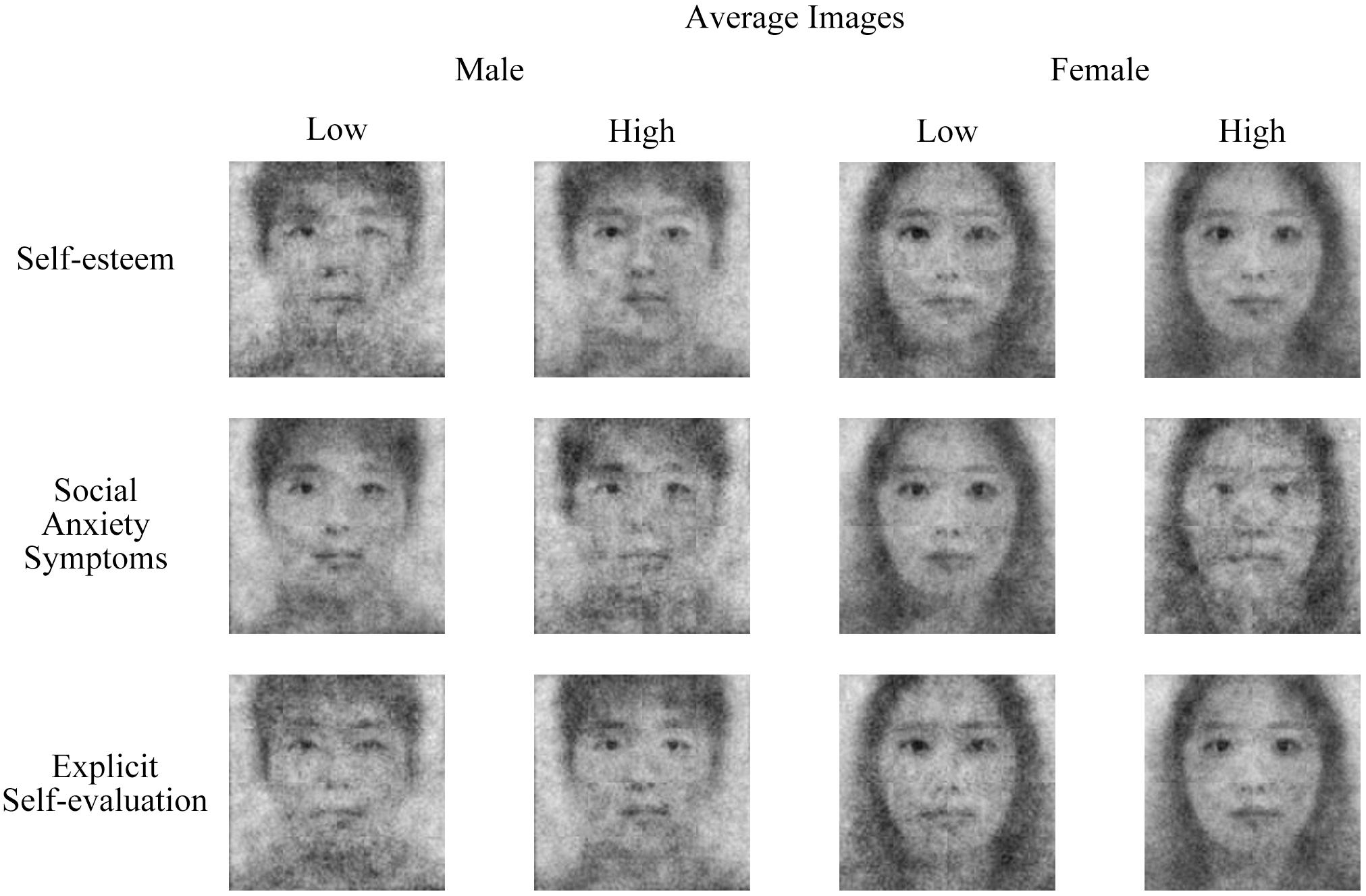

Figure 3. The average self-CIs (classification images of self) by low (−1 SD) and high (+1 SD) groups of self-esteem, social anxiety symptoms, and explicit self-evaluation.
Discussion
Using the RC image classification task (Dotsch and Todorov, 2012), we visualized the mental representation of self. Our data provide evidence that CIs can be regarded as valid proxies of facial self-images. Participants perceived their self-CIs as bearing a stronger resemblance to themselves than did filler CIs, without knowing that the self-CI was an image that they had created via the RC task. Also, in line with our hypothesis, the valence ratings of self-CIs were significantly associated with variables relevant to self-image, including self-esteem, social anxiety symptoms, explicit self-evaluation, and extraversion.
Consistent with the existing literature, our findings suggest that self-image is associated with self-esteem (Rosenberg, 1965; Oikawa et al., 2012) and social anxiety symptoms (Hirsch et al., 2003, 2004). Our findings extend previous research by illustrating that mental representation of self can be visualized through the RC method. It is shown that individuals’ self-images may differ in terms of valence, and this difference can be reliably evaluated across independent raters. Moreover, the data imply that the valence of a mental representation of self pertains to the attitude toward self and the social interaction patterns that one shows.
We also found that the valence ratings of self-CIs were not associated with self-reported depressive symptoms, trait anxiety, or social desirability. On the other hand, all the self-reported variables in this study were correlated with each other. Paulhus (1984) suggested self-deception and impression management as two main contributing factors of self-report bias. These two factors were associated with social desirability. Given the close correlations between social desirability and self-reported measures, it is interesting that the valence ratings of self-CIs did not show significant correlations with social desirability along with depressive symptoms, and trait anxiety. This may imply an advantage of examining self-CIs over self-reported measures, because they allow the researchers to assess participants’ perception of self with less chances of being biased by certain response patterns or social desirability.
It has been reported that distortion in self-perception is a key factor of psychiatric symptoms such as social anxiety disorder (Clark and Wells, 1995; Hirsch et al., 2003, 2004, 2006) or BDD (Buhlmann et al., 2008). Thus, clinicians assess how patients perceive themselves to evaluate the severity of the symptoms and to examine the effectiveness of the therapeutic interventions. Our research suggests the clinical usefulness of using the RC method as a tool to assess how patients see themselves, which may be hard to depict in words.
There may be a concern that participants’ selection of images might be determined solely by the physical resemblance of the presented stimuli. However, we believe that the participants would have considered aspects other than facial resemblance such as emotional impression and trustworthiness in selecting images that looked more like themselves, based on the results of this study and prior research. The valence ratings of self-CIs evaluated by independent raters were not significantly correlated with the resemblance rating, but the valence ratings by independent raters showed significant associations with features related to self-image. On the contrary, the resemblance rating was not correlated with any of the variables related to self-image. The fact that valence ratings by independent raters provided the independent and incremental information about self-image over resemblance rating suggests that participants were less likely to rely exclusively on physical resemblance while performing the RC task. Comparably, previous studies have demonstrated that resemblance judgment was associated with the attitude toward target apart from facial resemblance. For example, women who kept passionate relationships tended to idealize their romantic partners’ facial appearance as more attractive and trustworthy than women who kept less passionate relationships (Gunaydin and DeLong, 2015). Similarly, the more positive automatic attitudes people have toward themselves, the more they select attractively modified images as their actual image (Epley and Whitchurch, 2008).
Limitations
The limitations of this study are as follows. First, because we employed only self-reported measures to measure the validity of self-CIs, variables that were significantly associated with valence ratings of self-CIs were also closely related to self-reported measures. Thus, the incremental validity of self-CI can be further explored in future studies. The result of Epley and Whitchurch (2008) suggests that visual representations of self may be more closely related to implicit measures than to explicit measures. Therefore, future research can include both implicit and self-reported measures to examine the incremental validity of CI ratings. Also, since we did not incorporate the physical appearance of participants into our analyses, our data cannot explicitly demonstrate an advantage of evaluating self-CIs over physical appearance. It remains for future studies to take physical appearance into consideration in examining visualized self-representation more thoroughly. Finally, the sample in this study was limited to young adults; therefore, the results may not be applicable to other ages. Future research with a broader age range is needed to generalize the current findings.
Conclusion
Overall, our results support that mental representations of self can be visualized via the RC method. Participants perceived their self-CIs as bearing a stronger resemblance to themselves than did CIs of others (filler-CIs). The valence ratings of participants (RC sample) and independent raters were associated with variables related to self-image. A remaining issue for future research is about the intrinsic and additional information about self-image that the RC method can provide but that traditional measures and physical appearance cannot.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article is available from the Supplementary Material.
Ethics Statement
The study was approved by the institutional review board at Korea University (KUIRB-2019-0154-01). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
KM and YK conceived and designed the experiment. KM and JK performed the experiment. KM, YK, and HK analyzed the data. KM, SK, and JK wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01149/full#supplementary-material
MATERIAL S1 | Raw data sets of self-report measurements and of the evaluation of participants’ self-CIs in sheet 1 (total_data) and an example data set of the RC task in sheet 2 (RC_data).
Footnotes
- ^ We conducted an exploratory factor analysis to reduce the dimensions of the 14 self-presentational domains based on the ratings of independent raters. Seven items with high factor loadings on the valence (trustworthiness) factor were selected and averaged to calculate valence ratings (factor loadings = 0.94 ∼0.88).
- ^ Participants also answered the other 50 items of the HEXACO-60. However, the other five personality dimensions were not significantly correlated with the valence ratings of self-CIs, |r| s < 0.17.
References
Aghababaei, N., Błachnio, A., Arji, A., Chiniforoushan, M., Tekke, M., and Fazeli Mehrabadi, A. (2016). Honesty–Humility and the HEXACO structure of religiosity and well-being. Curr. Psychol. 35, 421–426. doi: 10.1007/s12144-015-9310-5
Amos, A., Gray, D., Currie, C., and Elton, R. (1997). Healthy or druggy? Self-image, ideal image and smoking behaviour among young people. Soc. Sci. Med. 45, 847–858. doi: 10.1016/S0277-9536(96)00425-X
Ashton, M. C., and Lee, K. (2009). The HEXACO-60: a short measure of the major dimensions of personality. J. Pers. Assess. 91, 340–345. doi: 10.1080/00223890902935878
Bendig, A. W. (1956). The development of a short form of the manifest anxiety scale. J. Consult. Psychol. 20:384. doi: 10.1037/h0045580
Brinkman, L., Todorov, A., and Dotsch, R. (2017). Visualising mental representations: a primer on noise-based reverse correlation in social psychology. Eur. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 28, 333–361. doi: 10.1080/10463283.2017.1381469
Buhlmann, U., Etcoff, N. L., and Wilhelm, S. (2008). Facial attractiveness ratings and perfectionism in body dysmorphic disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. J. Anxiety Disord. 22, 540–547. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.05.004
Carleton, R. N., Collimore, K. C., Asmundson, G. J., McCabe, R. E., Rowa, K., and Antony, M. M. (2009). Refining and validating the social interaction anxiety scale and the social phobia scale. Depress. Anxiety 26, E71–E81. doi: 10.1002/da.20480
Chon, K. K., Choi, S. C., and Yang, B. C. (2001). Integrated Adaptation of CES-D in Korea. Korean J. Health Psychol. 6, 59–76.
Clark, D. M., and Wells, A. (1995). “A cognitive model of social phobia,” in Social Phobia: Diagnosis, Assessment, and Treatment, eds M. Liebowitz and R. G. Heimberg (New York, NY: Guilford Press), 69–93.
Coon, D. (1997). Essentials of Psychology: Exploration and Application. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Crowne, D. P., and Marlowe, D. (1960). A new scale of social desirability independent of psychopathology. J. Consult. Psychol. 24, 349–354. doi: 10.1037/h0047358
Dotsch, R. (2016). rcicr: Reverse correlation image classification toolbox. R package version 0.3.4.1.
Dotsch, R., and Todorov, A. (2012). Reverse correlating social face perception. Soc. Psychol. Pers. Sci. 3, 562–571. doi: 10.1177/1948550611430272
Dotsch, R., Wigboldus, D. H. J., Langner, O., and van Knippenberg, A. (2008). Ethnic Out-Group Faces Are Biased in the Prejudiced Mind. Psychol. Sci. 19, 978–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02186.x
Dotsch, R., Wigboldus, D. H. J., and van Knippenberg, A. (2011). Biased allocation of faces to social categories. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 100, 999–1014. doi: 10.1037/a0023026
Epley, N., and Whitchurch, E. (2008). Mirror, mirror on the wall: enhancement in self-recognition. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 34, 1159–1170. doi: 10.1177/0146167208318601
Greenwald, A. G., and Farnham, S. D. (2000). Using the Implicit Association Test to measure self-esteem and self-concept. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 79, 1022–1038. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.79.6.1022
Greenwald, A. G., McGhee, D. E., and Schwartz, J. L. K. (1998). Measuring individual differences in implicit cognition: the implicit association test. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 74, 1464–1480. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.74.6.1464
Gunaydin, G., and DeLong, J. E. (2015). Reverse correlating love: highly passionate women idealize their partner’s facial appearance. PLoS One 10:e0121094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121094
Hirsch, C. R., Clark, D. M., Mathews, A., and Williams, R. (2003). Self-images play a causal role in social phobia. Behav. Res. Ther. 41, 909–921. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(02)00103-1
Hirsch, C. R., Mathews, A., Clark, D. M., Williams, R., and Morrison, J. A. (2006). The causal role of negative imagery in social anxiety: a test in confident public speakers. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 37, 159–170. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2005.03.003
Hirsch, C. R., Meynen, T., and Clark, D. M. (2004). Negative self-imagery in social anxiety contaminates social interactions. Memory 12, 496–506. doi: 10.1080/09658210444000106
Imhoff, R., and Dotsch, R. (2013). Do we look like me or like Us? Visual projection as self- or ingroup-projection. Soc. Cogn. 31, 806–816. doi: 10.1521/soco.2013.31.6.806
Imhoff, R., Woelki, J., Hanke, S., and Dotsch, R. (2013). Warmth and competence in your face! Visual encoding of stereotype content. Front. Psychol. 4:386. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00386
Keenan, J. P., Wheeler, M. A., Gallup, G. G., and Pascual-Leone, A. (2000). Self-recognition and the right prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 4, 338–344. doi: 10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01521-7
Kim, S., Yoon, H. Y., and Kwon, J. H. (2013). Validation of the Short Form of the Korean Social Interaction Anxiety Scale (K-SIAS) and the Korean Social Phobia Scale (K-SPS). Cogn. Behav. Ther. Korea 13, 511–535.
Krosch, A. R., and Amodio, D. M. (2014). Economic scarcity alters the perception of race. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 9079–9084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404448111
Leary, M. R., and Allen, A. B. (2011). Self-presentational persona: simultaneous management of multiple impressions. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 101, 1033–1049. doi: 10.1037/a0023884
Lee, H., and Won, H. (1995). An exploratory study on the relationship between paranoid tendency, self-concept, and self-consciousness. Korean Psychol. Assoc. Ann. Conf. 1, 277–290.
Lee, K., and Ashton, M. C. (2013). The H Factor of Personality: Why Some People are Manipulative, Self-Entitled, Materialistic, and Exploitive—and Why it Matters for Everyone. Seoul: Moonye Publishing Co., Ltd.
Lee, Y. S. (2000). Ironic Effects of Suppression on Obsessive Thoughts. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Seoul National University, Seoul.
Lou, H. C., Luber, B., Crupain, M., Keenan, J. P., Nowak, M., Kjaer, T. W., et al. (2004). Parietal cortex and representation of the mental Self. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 101, 6827–6832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400049101
Mangini, M., and Biederman, I. (2004). Making the ineffable explicit: estimating the information employed for face classifications. Cogn. Sci. 28, 209–226. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsci.2003.11.004
Ng, A. S., Abbott, M. J., and Hunt, C. (2014). The effect of self-imagery on symptoms and processes in social anxiety: a systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 34, 620–633. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2014.09.003
Oikawa, H., Sugiura, M., Sekiguchi, A., Tsukiura, T., Miyauchi, C. M., Hashimoto, T., et al. (2012). Self-face evaluation and self-esteem in young females: an fMRI study using contrast effect. Neuroimage 59, 3668–3676. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.098
Paulhus, D. L. (1984). Two-component models of socially desirable responding. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 46, 598–609. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.46.3.598
Peirce, J., Gray, J. R., Simpson, S., MacAskill, M., Höchenberger, R., Sogo, H., et al. (2019). PsychoPy2: experiments in behavior made easy. Behav. Res. Methods 51, 195–203. doi: 10.3758/s13428-018-01193-y
R Core Team (2019). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Randloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl. Psychol. Measure. 1, 385–401. doi: 10.1177/014662167700100306
Taylor, J. A. (1953). A personality scale of manifest anxiety. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 48, 285–290. doi: 10.1037/h0056264
Keywords: self-image, self-perception, facial images, visual representations, classification images, self-esteem, social anxiety, extraversion
Citation: Moon K, Kim S, Kim J, Kim H and Ko Y (2020) The Mirror of Mind: Visualizing Mental Representations of Self Through Reverse Correlation. Front. Psychol. 11:1149. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01149
Received: 27 November 2019; Accepted: 05 May 2020;
Published: 12 June 2020.
Edited by:
Frédéric Gosselin, Université de Montréal, CanadaReviewed by:
Takahiro Kawabe, Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, JapanRu-Yuan Zhang, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2020 Moon, Kim, Kim, Kim and Ko. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Young-gun Ko, ZWxpcEBrb3JlYS5hYy5rcg==
 Kibum Moon
Kibum Moon SoJeong Kim
SoJeong Kim Jinwon Kim
Jinwon Kim Hackjin Kim
Hackjin Kim Young-gun Ko
Young-gun Ko