Abstract
Introduction:
AnShenDingZhiLing is an effective Chinese herbal formula that is clinically used to treat pediatric attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In terms of the overall prescription, it has shown great efficacy in alleviating ADHD symptoms and holds broad clinical application prospects. However, due to the lack of in vitro and in vivo studies, the chemical components and metabolites of AnShenDingZhiLing remain poorly understood, which also hinders research into the pathogenesis of ADHD.
Methods:
In this study, we established a rapid and efficient method employing the UHPLC-HRMS system and integrated multiple strategies to systematically characterize and identify the chemical profiles and drug metabolites in the biological samples of AnShenDingZhiLing and AnShenDingZhiLing-treated rats.
Results and discussion:
243 compounds (including 60 flavonoids, 50 terpenoids, 24 phenylpropanoids, 18 alkaloids, 18 anthraquinones, 16 phenylethanoid glycosides, 13 phenolic acids, nine xanthones, nine oligosaccharides, eight phthaleins, eight naphthopyrones, four organic acids, four aromatic aldehydes, and two diarylheptanoids) were characterized. Following the administration of AnShenDingZhiLing to rats, a total of 110 compounds related to Chinese herbal medicine ingredients were identified in the plasma and cerebrum samples. The primary metabolic pathways of chemicals derived from AnShenDingZhiLing can be summarized in methylation, demethylation, hydrolysis, hydroxylation, sulfation, and glucuronidation. In summary, through this rapid and accurate analytical method, the comprehensive chemical profiles of AnShenDingZhiLing and its metabolites were characterized. Additionally, in this study, we provide essential analytical thinking and scientific evidence for exploring the material basis of AnShenDingZhiLing efficacy further.
1 Introduction
The incidence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is progressively higher among children and adolescents, and it still has the possibility of affecting the patient’s normal life in adulthood (Li et al., 2024). Pharmacological treatments including methylphenidate and atomoxetine and non-pharmacological treatments including parent training, behavioral therapy, and dietary modifications have been shown to be partially effective. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) shows unique therapeutic benefits in treating numerous diseases. Recently, research workers mainly focused on TCM due to the significant therapeutic efficacy on neurological diseases (Moreira et al., 2023). However, the corresponding targets and efficacy of the TCM ingredients are not very clear due to the diversity of chemical structures and complex material basis. AnShenDingZhiLing (ASDZL) comprises 12 herbal medicines, including Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (Scu), Bupleurum chinense DC. (Bup), Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (Ang), Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) Libosch. ex DC. (Reh), Uncaria rhynchophylla (Miq.) Miq. ex Havil. (Unc), Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S. Irwin and Barneby (Sen), Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl (For), Acorus calamus var. angustatus Besser (Aco), Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. (Alp), Curcuma aromatica Salisb. (Cur), Polygala tenuifolia Willd. (Pol), and Bambusa textilis McClure (Bam). ASDZL has the efficacy of clearing the heart and calming the liver, eliminating phlegm and resuscitation, and soothing and calming the mind (Yaqun et al., 2022). Catalpol, a main constitute in ASDZL, can inhibit neuronal apoptosis, promotes myelination, and enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression by modulating crucial proteins involved in prefrontal cortical maturation. Baicalin derived from Scu ameliorates ADHD symptoms by significantly increasing dopamine levels in the striatum. Saikosaponin A derived from Bup downregulates dopamine transporter levels and increases BDNF expression in the brain. Although there have been correlational studies on catalpol, baicalin, and saikosaponin A (Jichao et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2019), for ASDZL, the intricate material basis is still poorly understood, and the mechanism of action is yet to be clarified. Hence, there is an urgent need to elucidate the overall variety of the chemical profiles of ASDZL (Su et al., 2023).
For TCM, detailed analysis of its chemical composition facilitates the discovery, isolation, and purification of bioactive components. Currently, the development of more diverse analytical techniques has provided innovative methods to elucidate its material basis. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) has been broadly used to characterize the complex components of TCM due to high-efficiency chromatographic separation, high-sensitive mass spectrometry performance, and a large amount of mass spectrum information (Hong et al., 2025). Nevertheless, research workers expended a lot of time and energy to analyze a large number of UHPLC-HRMS raw data. The Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking (GNPS), an open-access platform, facilitates mass spectrometry data analysis and visual annotation of compounds, which is a huge advantage for discovering potential natural products with biological activity. Feature-based molecular networking (FBMN) utilizes the GNPS platform to provide various and reachable applications in comparison with expensive commercial mass spectrometry databases (Wang et al., 2016; Nothias et al., 2020). FBMN integrates abundance mass spectrometry data, alignment tools, and chromatographic behavioral features of natural products (Katajamaa et al., 2006; Pluskal et al., 2010). FBMN can generate molecular networks (MNs) using the GNPS platform. The MN clusters structurally related compounds based on similar spectral information, and these compounds tend to have similar backbones and fragmentation pathways (Chen et al., 2024). GNPS is a powerful tool to discover potential novel natural products and distinguish isomers for TCM (Pakkir Shah et al., 2024).
In this study, the UHPLC-HRMS method was employed to obtain dependable mass spectrometry data of ASDZL. We proposed the integrated strategy that organically combines diagnostic ion filtering (DIF), neutral loss filtering (NLF), and MN strategies (Zhu et al., 2023). First, the DIF, NLF, NRF, and mass spectrometric fragmentation pathways of different compound types were systematically summarized using reference standards and literature reports. In addition, unknown compounds in ASDZL were inferred using FBMN analysis on the online workflow GNPS. A detailed non-targeted chemical analysis of ASDZL was performed by integrating the characteristic structural analysis of the compounds with the MN analysis (Han et al., 2025). Finally, with the reliability and accuracy of the above work being ensured, we focused on the prototype components of ASDZL present in the blood and brain. In vivo metabolic components were extrapolated and predicted using MetabolitePilot™ software and literature reports. This experiment systematically characterized the material chemical basis of ASDZL and utilized the visualization function of MN. The findings not only establish a scientific foundation for subsequent ASDZL studies but also propose a novel analytical approach for processing TCM mass spectrometry data.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental materials
Methanol (MeOH) (HPLC grade) and acetonitrile (ACN) (LC–MS grade) were purchased from Merck Co., Ltd. (Darmstadt, Germany), and formic acid (FA) (LC–MS grade) was obtained from Thermo Fisher Technology Co., Ltd. Ultrapure water purification was carried out using a Milli-Q system (Millipore, Bedford, MA, United States of America). Detailed information on the herbal medicines and reference standards used in this study can be found in the Supplementary Material.
2.2 Preparation of the ASDZL formula
Twelve herbal medicines (Scu, Bup, Ang, Reh, Unc, Sen, For, Aco, Alp, Cur, Pol, and Bam) in the ASDZL formula were mixed in a weight ratio of 5:3:5:5:5:5:5:5:5:3:5:3, and then the herbal mixture was soaked in an 8-fold volume of distilled water for 1 h. The herbal mixture was subsequently decocted twice with distilled water (1 h per extraction). Finally, the solution was collected and concentrated to 0.89 g/mL using a rotary evaporator.
2.3 Animal experiments
Twelve male Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats (180–220 g, SPF grade) were offered by Jiangsu Qinglongshan Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (license no. SCXK-Zhe-20,230,077). The animal experiment protocol was approved by the Animal Ethical Committee of the Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, and all animal treatments were implemented in agreement with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the US National Institutes of Health. The rats were kept standardly in a specified pathogen-free condition (indoor temperature, 23°C ± 3°C; relative humidity, 40%–60%; 12 h light/dark cycle). All rats were allowed free access to food and water ad libitum for 7 days. Animals were randomly allocated to two groups: the blank group (n = 6) and the ASDZL group (n = 6). The rats in the ASDZL group were administered ASDZL (uniformly at 9:00 a.m. and 15:00 p.m.) at 20.16 g/kg, whereas rats in the blank group were administered the same volume of distilled water twice daily. Finally, plasma and cerebrum samples were collected following the final oral administration of ASDZL extract.
2.4 Preparation of ASDZL extract
An amount of 200 µL of ASDZL (0.89 g/mL) solution was accurately pipetted to each 2-mL EP tubes, and then 600 µL of methanol was added. After mixing, the solution was ultrasonically extracted for 30 min. The supernatant was collected after centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. The vacuum centrifugal concentrator (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was employed to evaporate the supernatant, which was transferred to a new tube. The residues were redissolved with 300 µL of methanol. The solvent was vortexed for 3 min and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. Finally, 50 µL of the supernatant was accurately aspirated, and 200 µL of methanol was added. The solution was aspirated in the injection bottle and prepared for UHPLC-HRMS analysis.
2.5 Biological sample preparation
Rat blood samples were acquired in the heparinized centrifuge tubes (1.5 mL) at 1 h and 4 h after the last ASDZL extract administration. Rat plasma was obtained by centrifuging at 4,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. An amount of 600 µL acetonitrile was added to 200 μL of plasma samples to precipitate proteins. Next, the supernatant was obtained by centrifuging at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The appropriate amount of the supernatant was evaporated, and then 300 µL methanol was added to redissolve the residues. Finally, the supernatant was aspirated in the injection bottle and prepared for the analysis after centrifugation.
Similarly, rat cerebrum samples were collected. A total of 300 mg of cerebrum samples was added to each 2-mL EP tubes. Subsequently, 600 µL of physiological saline was added. The mixture was homogenized at 60 Hz for 5 min at 4°C using two zirconia beads. After centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, 300 µL of the brain tissue homogenate was aspirated and mixed with 300 µL acetonitrile to precipitate proteins. The appropriate amount of the supernatant was evaporated, and then the residues were redissolved in 200 µL methanol. Finally, the supernatant was aspirated in the injection bottle and prepared for the analysis after centrifugation.
2.6 UHPLC-HRMS analysis
2.6.1 UHPLC conditions
Liquid chromatography separation was performed on an ExionLC™ 2.0 UHPLC system (AB SCIEX). The column Accucore™ C18 (2.1 × 100 mm, 2.6 µm, Thermo Fisher Scientific™) was employed for the separation of various constituents at 40°C. The mobile phases consisted of water containing 0.1% formic acid (A) and acetonitrile (B). The UHPLC elution procedure was implemented in accordance with the following gradient: 0–2 min, 10% B; 2–28 min, 10%–80% B; 28–30 min, 80% B; 30–30.1 min, 80%–10% B; 30.1–32 min, 10% B. The flow rate was set at 0.4 mL/min. The injection volume was 4 μL.
2.6.2 MS conditions
Mass spectrometric analysis was carried out on the ZenoTOF™ 7600 QTOF mass spectrometer (AB SCIEX, United States of America). Comprehensive mass spectrometric data of the constituents were acquired using the information-dependent acquisition (IDA) mode. The MS1 mass range was set at m/z 100–1,250 and the MS2 mass range was set at m/z 80–1,250 both in the positive and negative ion modes. Dynamic background subtraction (DBS) was turned on to reduce interference. Other parameters were set as follows: curtain gas (CUR), 35 psi; atomizing gas (GS1), 55 psi; auxiliary gas (GS2), 55 psi; accumulation time, 0.05 s; the ESI temperature, 550°C; the ion spray voltage was 5,500 V in the positive ion mode and −5,500 V in the negative ion mode; the collision energy (CE) was 35 V in the positive ion mode and −35 V in the negative ion mode; the de-clustering potential (DP) was 80 V in the positive ion mode and −80 V in the negative ion mode.
2.7 FBMN annotation on GNPS
The GNPS platform provides FBMN for advanced MS data analysis (https://gnps.ucsd.edu). Utilizing the MSConvertGUI software version 3.0, which was from the open-source, cross-platform ProteoWizard (https://proteowizard.sourceforge.io/), the raw data from UHPLC-HRMS were converted to “mzML” format files. The “peak picking” was selected from different filters. Under the vendor algorithm, MS level 1–2 was added. Furthermore, the MS data were imported to MZmine software 4.3.0 (https://github.com/mzmine/mzmine/releases/tag/v4.3.0). For MS data, the mass detection thresholds were set to a noise level of 1,000 for MS1 and 100 for MS2. Chromatogram builder was performed with the following parameters: MS level filter (level = 1); minimum consecutive scans, five; minimum absolute height, 7,000; minimum intensity for consecutive scans, 3,000; m/z tolerance, 0.005 Da or 10.0 ppm. The local minimum feature resolver was implemented with the chromatographic threshold of 90.0%, minimum absolute height of 7,000, peak duration range of 0–1 min, and five minimum scans. The main 13C isotope filter parameters were as follows: m/z tolerance, 0.001 Da or 5.0 ppm; retention time tolerance, 0.01 min; maximum charge of one and monotonic shape check. The join aligner was implemented with m/z of 0.001 Da or 5.0 ppm, weight for m/z of 3, retention time tolerance of 0.1 min, and weight for retention time of one. Then, the feature list rows filter was performed with feature with MS2 scan and the never remove feature with MS2. Finally, the processed feature list was uploaded onto the GNPS online platform through WinSCP software version 6.3.5 (https://winscp.net/eng/download.php). The FBMN parameters were set as follows: precursor ion mass tolerance of 0.02 Da, fragment ion mass tolerance of 0.02 Da, minimum pairs cosine of 0.70, minimum matched fragment ions of six, and library search min matched peaks of six. The data of the FBMN were analyzed by Cytoscape software version 3.10.2 (https://www.cytoscape.org/).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Summary of integration strategy
Given that ASDZL consists of twelve TCMs, identifying its numerous chemical compounds is particularly challenging. Therefore, we developed a fast, effective, and accurate integrated strategy for comprehensive characterization of ASDZL’s chemical constituents. The procedure primarily comprises the following steps: (1) for HRMS ZenoTOF™ 7600, Zeno™ Trap on, the IDA technology mode and DBS can more sensitively obtain accurate MS information. ASDZL data were acquired by using UHPLC-HRMS. Then, the chemical components’ database of ASDZL was established in conjunction with literature reports as well as the TCMSP database, including precise molecular mass, compound names, and major fragment ions. (2) The preprocessed MS data were implemented by FBMN assignment at the online platform, GNPS. The annotated results of MN were carefully analyzed in conjunction with reference standards and literature reports. (3) Key MS information on DIF, NLF, and the fragmentation pathway were summarized for these major types of components. Annotation information of potential components from MN and the reference standards in ASDZL were integrated to characterize the chemical profiles of ASDZL. Subsequently, chromatographic data and MS data were analyzed using PeakView™ software (AB SCIEX). (4) With the reliability and accuracy of the above workflow established, this step focused on identifying the prototypical components absorbed into biological samples. The DIF and NLF strategies were integrated to extrapolate and predict in vivo metabolic components using MetabolitePilot™ software and literature reports. Finally, the metabolic pathways of the predominant chemical constituents in ASDZL were systematically summarized.
3.2 Annotation of components by feature-based molecular networking
The number of components in ASDZL is so large that it is not sufficient to characterize the full chemical profile by literature reports. Hence, the data were processed using MZmine to generate MN through the online platform FBMN, and the MN provided more comprehensive MS information to complement and modify the chemical profile of ASDZL (Heuckeroth et al., 2024). Positive (Supplementary Figure S1) and negative ion mode (Supplementary Figure S2) MN were generated by FBMN. Blue nodes represent unknown compounds, and orange nodes represent annotated compounds. The positive ion mode comprised a total of 610 nodes, 489 clustered nodes, and 121 non-clustered nodes. Among these, 141 molecular nodes were annotated through MS2 spectral comparison with reference spectra in the GNPS database. The negative ion mode comprised a total of 244 nodes, 139 clustered nodes, and 105 non-clustered nodes, and 77 nodes were annotated through MS2 spectral comparison with reference spectra in the GNPS database. In terms of the clustered nodes, 29 of 64 positive FBMN clusters (nodes≥ 2) and 16 of 28 negative FBMN clusters (nodes≥ 2) contained annotated compounds (Li et al., 2023; Qu et al., 2023). With respect to the non-clustered nodes, 14 nodes of positive FBMN and eight nodes of negative FBMN were annotated by the GNPS database. The MS2 fragments and structure type of the annotated nodes are relatively similar in analyzing the clusters that were primarily annotated. Thus, components in the same cluster are likely to have the same diagnostic ions, neutral losses, and fragmentation pathways. Flavonoids, phenylethanoid glycosides, and triterpenoids were annotated in both the positive and negative FBMN clusters, and nodes with red borders were identified as reference standards (Figure 1). Alkaloids and anthraquinones were only annotated in positive FBMN, and organic acids and oligosaccharides were only annotated in negative FBMN. A sufficient number of nodes that share similar MS2 spectral features with the annotated nodes and may be potentially new compounds have still not been annotated. Particularly, in the example of alkaloids isomers, the annotations of isorhynchophylline (compound 94) and rhynchophylline (compound 109) were consistent with those of the reference standards and the literature reports, which suggests that there is a great potential to identify isomers by FBMN workflow. Indeed, the rapid advancement of the UHPLC-HRMS technology coupled with the FBMN strategy has greatly enhanced the scientific analysis of TCMs. As an irreplaceable analytical instrument, UHPLC-HRMS poses challenges due to its large data volume and the inference of isomers. Therefore, we rely on the FBMN strategy to quickly annotate compounds and isomers. However, the FBMN analysis is limited by the GNPS database, resulting in false positives and unannotated compounds (Zhang et al., 2024a). After comparing the other reference standards and screening out the unreasonable redundant nodes and wrong annotations by DIF and NLF strategies, 61 components were finally obtained from the MN. A total of 61 compounds included 21 flavonoids, 11 alkaloids, eight terpenoids, six phenylpropanoids, four anthraquinones, six phenylethanoid glycosides, three oligosaccharides, one phenolic acid, and one organic acid (Supplementary Table S1).
FIGURE 1
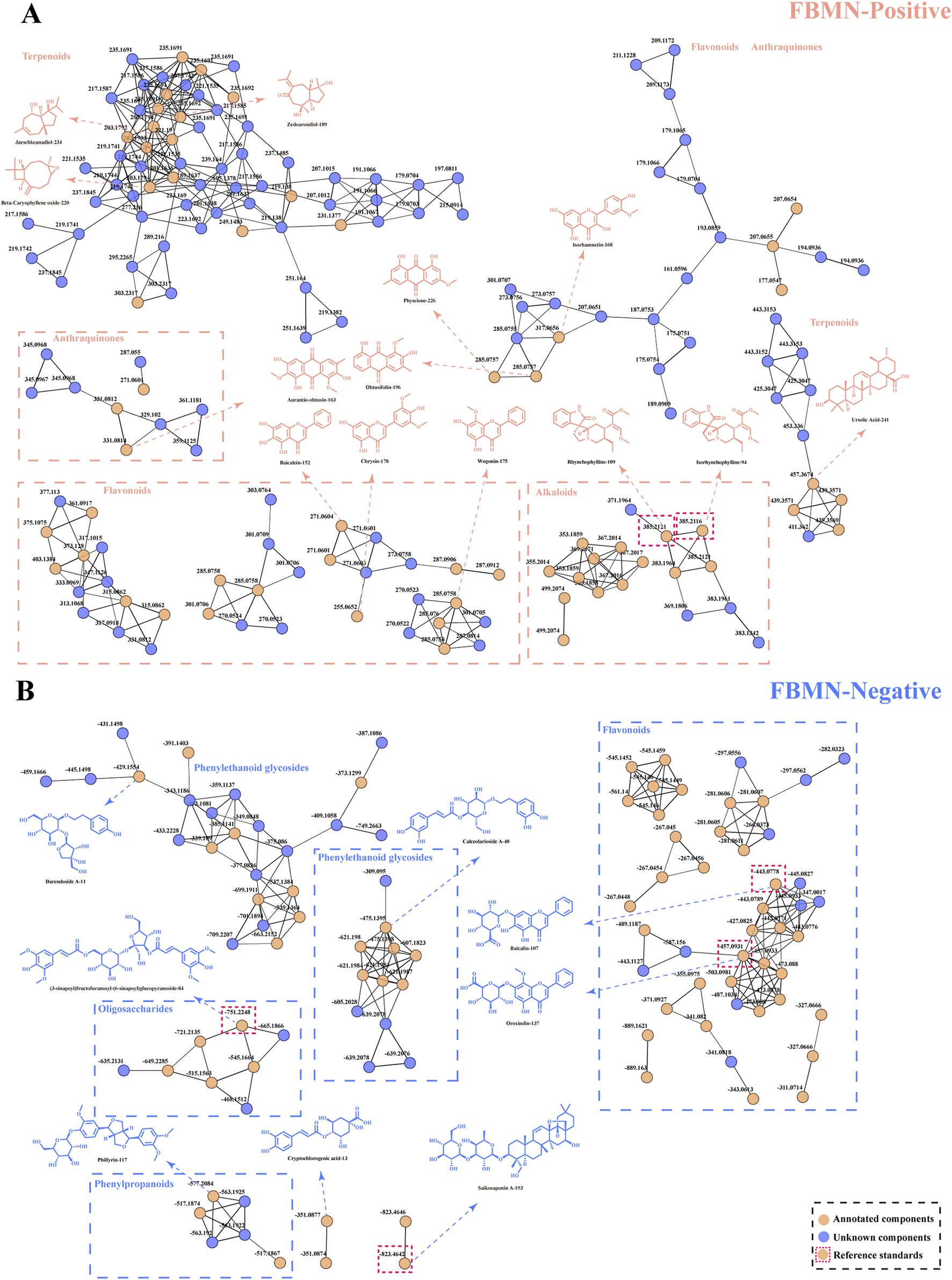
Visual analysis of FBMN in the positive (A) and negative (B) ion modes. Blue nodes represent unknown compounds, and orange nodes represent annotated compounds. Nodes with red borders were identified as reference standards.
3.3 Utilization of DPI and NLF strategies of main structure types
Multiple structure types were identified in ASDZL. Diagnostic ions and neutral losses of flavonoids, terpenoids, anthraquinones, alkaloids, phenylethanoid glycosides, oligosaccharides, xanthones, and phenolic acids were summarized based on the MS information of 11 reference standards and two components from the MN in the positive and negative ion modes (Supplementary Table S2). Diagnostic ions are mainly obtained for retro-Diels–Alder (RDA) cleavage, losses of glycosides, and specialized skeletons. Neutral molecules were mostly glycosides, H2O, and CO (van Dinteren et al., 2021).
3.4 Analysis of components from ASDZL
The UHPLC-HRMS base peak chromatograms (BPCs) of ASDZL could be seen in Figure 2. The BPCs of the reference standards were exhibited in Supplementary Figure S3. The adduct ions were set as follows: positive ion mode: [M + H]+, [M + NH4]+, and [M + H-H2O]+; negative ion mode: [M–H]- and [M + HCOO]-. Chemical constituents of ASDZL and their detailed characteristics are shown in Supplementary Table S3. A total of 243 compounds (including 60 flavonoids, 50 terpenoids, 24 phenylpropanoids, 18 alkaloids, 18 anthraquinones, 16 phenylethanoid glycosides, 13 phenolic acids, nine xanthones, nine oligosaccharides, eight phthaleins, eight naphthopyrones, four organic acids, four aromatic aldehydes, and two diarylheptanoids) were characterized from ASDZL. Among these, 61 compounds were annotated by GNPS database matching, whereas 17 compounds were identified using authentic reference standards. The distribution of these compounds and the types of structure are intuitively illustrated in Figure 3. Organic acids and the components with glycosides exhibit higher polarity and are usually ahead in retention time. However, flavonoids, alkaloids, and triterpenoids have relatively late retention times. In terms of numbers, the main chemical structure types of ASDZL are flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenylpropanoids. Jingning fang is used for the treatment of ADHD. Both Jingning fang and ASDZL contain the same three herbal medicines, namely, Reh, Pol, and Aco. The main compounds of Jingning fang are triterpenoids, oligosaccharides, and phenolic acids, which are also partially present in ASDZL (Yang et al., 2017). All the chemical structures of the constituents in ASDZL are classified in Figure 4. The mass error of 242 compounds was within five, and only compound 55 reached −5.844, but it was confirmed to be 4-hydroxybenzoic acid by accurate MS2 information. Therefore, summarizing the fragmentation pathway of different types of compounds is of great interest in the identification of numerous compounds.
FIGURE 2
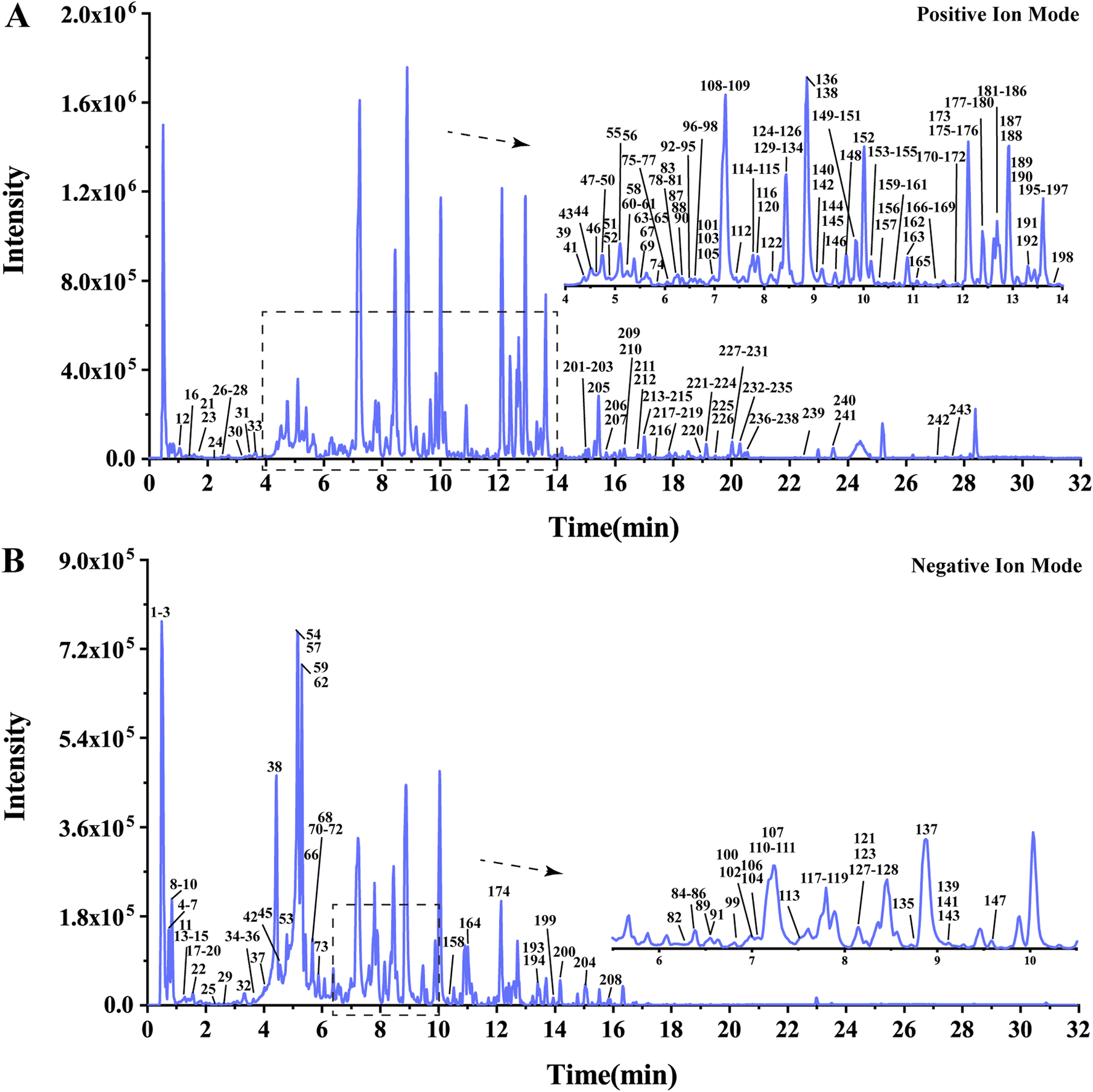
Base peak chromatogram (BPC) of ASDZL in UHPLC-HRMS positive (A) and negative (B) ion modes.
FIGURE 3
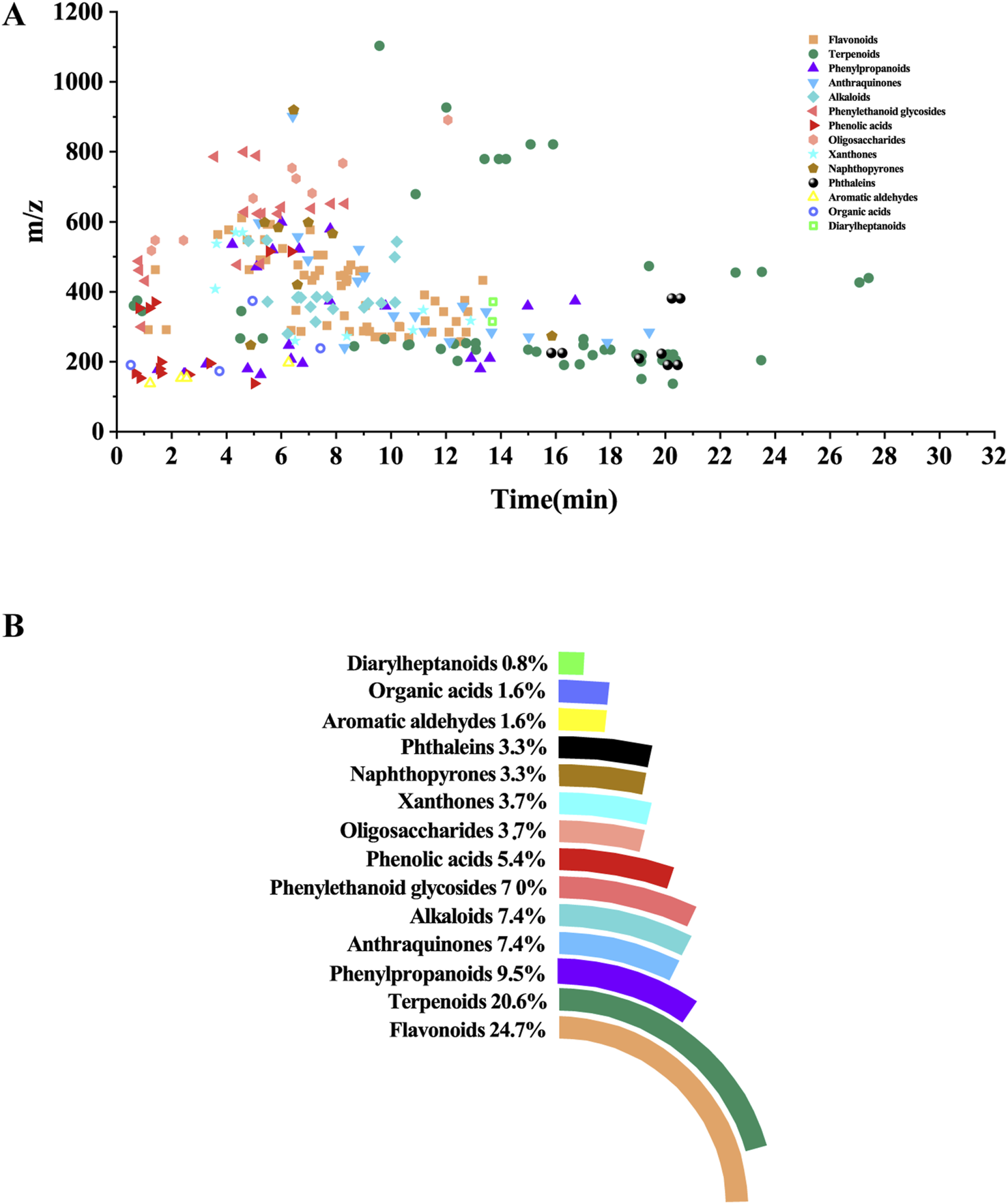
Distribution and chemical structure of 243 components characterized from ASDZL. (A) Distribution of retention time, accurate mass, and chemical structure in the scatterplot. (B) Proportion of 14 chemical structures from donut and pie chart.
FIGURE 4
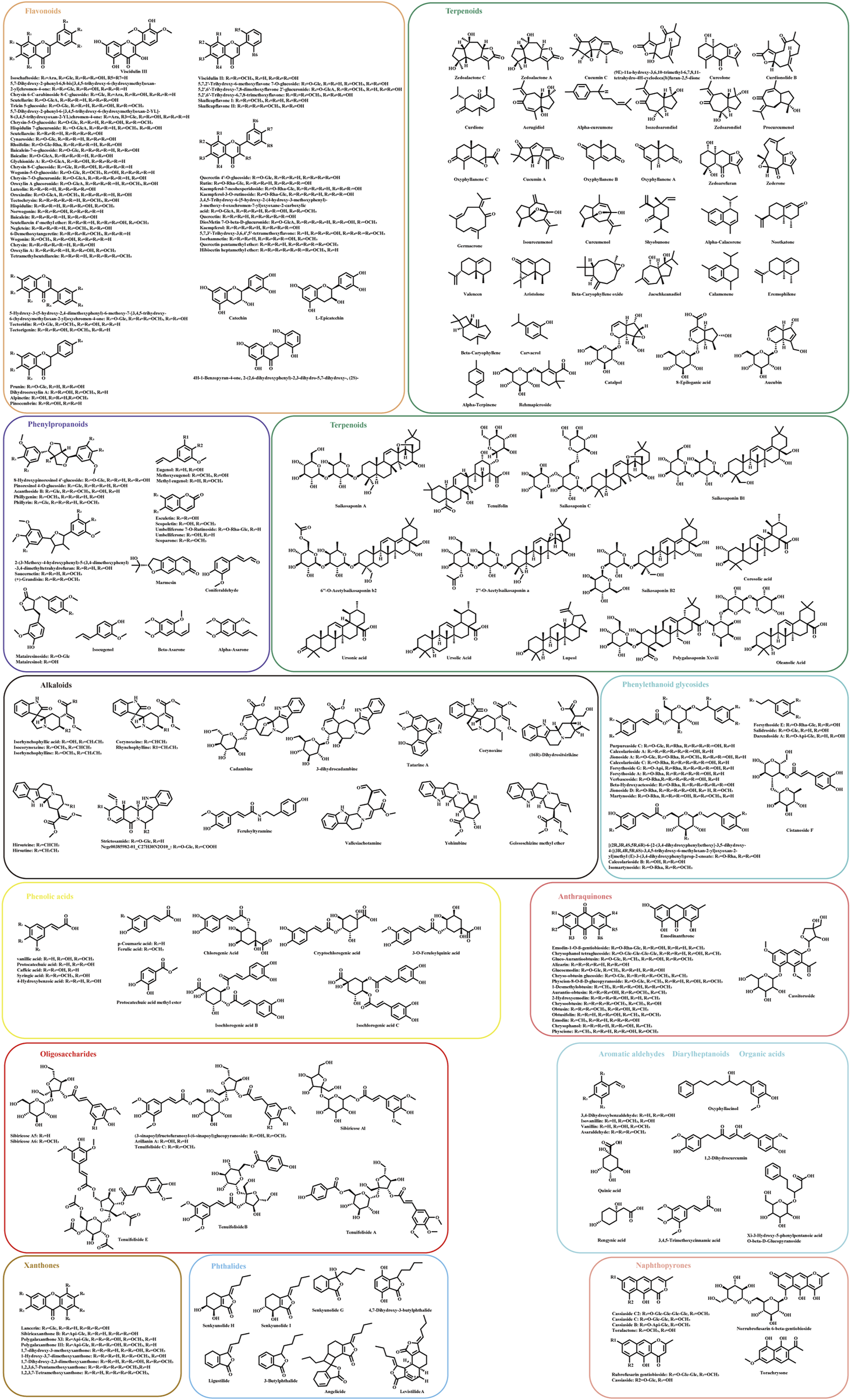
Chemical structural formulas of ASDZL are classified in different types.
3.4.1 Flavonoids analysis
There are 60 compounds of flavonoids in ASDZL, which are mainly from Scu. They mainly include flavonoid glycosides, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonoids, and polymethoxyflavonoids (PMFs) (Zhang et al., 2024b). Due to their structural diversity, flavonoids exhibit significant potential in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (Ramanan et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2021). Flavonoid glycosides generally tend to lose glycosyl moieties during fragmentation pathways. Additionally, the classical RDA cleavages are characteristic fragmentation pathways for flavonoids. Furthermore, hydroxyl, methyl, or methoxy groups are usually attached to the flavonoid ring (A ring), resulting in the losses of the following neutral fragments: CH3 (−15 Da), CH2O (−30 Da), CO (−28 Da), H2O (−18 Da), and O (−16 Da), for example, baicalin (compound 107, tR = 7.23 min), and its chemical formula is C21H18O11 ([M–H]-, m/z 445.0780) (Figure 5A). In the negative MS2 spectrum, the fragmentation ion of m/z 269.0551 [M–H–C6H8O6]- was observed after losing glucuronic acid (GlcA, 176 Da). Continued losses of H2O (−18 Da) and CO (−28 Da) neutral fragments yielded m/z 251.0361 [M–H–C6H8O6–H2O]- and m/z 223.0416 [M–H–C6H8O6–H2O–CO]-, respectively. Because of classical RDA cleavage, fragmentation ions at m/z 169.0667 were also detected in the MS2 spectrum. Fragmentation ions of m/z 269.0551 and m/z 169.0667 can be considered as diagnostic ions. Similarly, the fragment pattern of baicalin is the same as that of baicalein (compound 152, tR = 10.02 min) (Supplementary Figure S4A). In addition, except compound 37, all other flavonoids exhibit characteristic fragment patterns. However, compound 37 was annotated by positive FBMN, and its fragment ions were consistent with the GNPS online library.
FIGURE 5
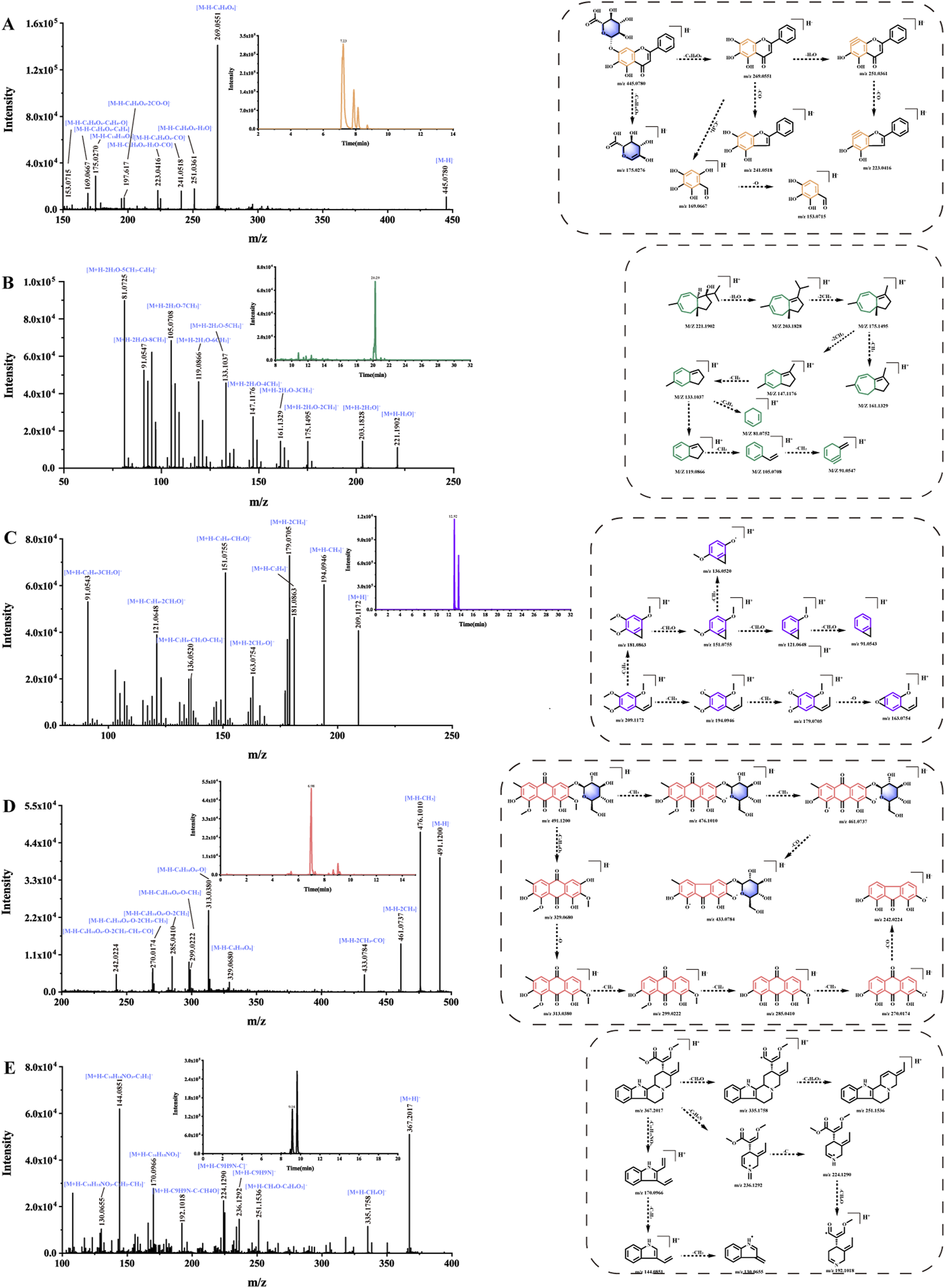
Fragmentation routes of the main components of ASDZL: (A) baicalin, (B) jaeschkeanadiol, (C) β-asarone, (D) geissoschizine methyl ether, and (E) glucoaurantio-obtusin.
3.4.2 Terpenoids analysis
Terpenoid compounds are mainly derived from Cur and Bup. There are six monoterpenes, 31 sesquiterpenes, and 13 triterpenes. Because of the presence of hydroxyl, methyl, and carbonyl groups in the structure of terpenoids, their MS2 spectrum showed the losses of CO (−28 Da), H2O (−18 Da), and CH2 (−14 Da) neutral molecules. In terms of terpenoids, sesquiterpenes are characteristic bioactive components from Cur (Zhao et al., 2023). For instance, under the positive FBMN workflow, jaeschkeanadiol (compound 234, tR = 20.29 min) was annotated. Jaeschkeanadiol (Figure 5B) (C15H24O) yielded a quasi-molecular ion at m/z 203.1828 [M + H–H2O]+. The fragment ions at m/z 175.1495 [M + H–H2O–2CH2]+, m/z 161.1329 [M + H–H2O–3CH2]+, m/z 147.1176 [M + H–H2O–4CH2]+, m/z 133.1037 [M + H–H2O–5CH2]+, m/z 119.0866 [M + H–H2O–6CH2]+, m/z 105.0708 [M + H–H2O–7CH2]+, m/z 91.0547 [M + H–H2O–8CH2]+, and m/z 81.0725 [M + H–H2O–5CH2–C4H4]+ were yielded in its positive MS2 spectrum. The characteristic fragment pattern is due to the continuous losses of CH2 (−14 Da). In summary, 31 compounds exhibiting similar MS2 fragmentation patterns were identified as sesquiterpenes, four of which were further annotated via the FBMN analysis.
For monoterpenes, aucubin (Supplementary Figure S4B) (compound 10, tR = 0.92 min) showed an excimer ion at m/z 345.1188 [M–H]-. In the negative ion MS2 spectrum, the successive losses of neutral fragments CH2O (−30 Da), O (−16 Da), and glucosyl residue (−162 Da) yield fragment ions at m/z 299.1147 [M–H–CH2O–O]- and m/z 137.0609 [M–H–CH2O–O–C6H10O5]-. Then, the fragment ions at m/z 119.0446 [M–H–CH2O–O–C6H10O5–H2O]-, m/z 113.0248 [M–H–CH2O–O–C6H10O5–2C]-, and m/z 101.0247 [M–H–CH2O–O–C6H10O5–2H2O]- referred to successive neutral losses of H2O (−18 Da) and carbon chain C2 (−24 Da). The MS2 spectrum also yielded fragment ions at m/z 179.0565 [M–H–C9H10O3]- and m/z 89.0249 [M–H–2CH2O–O–C6H10O5–H2O]-. Likewise, compounds 2, 4, 10, and 42 generated similar MS2 fragment ions at m/z 179.0565 and m/z 89.0249, which were considered diagnostic ions.
Triterpenoids in ASDZL include oleanane-type pentacyclic triterpenoids and ursane-type tetracyclic triterpenoids, for example, ursolic acid (Supplementary Figure S4C) (compound 241, tR = 23.52 min) from ursane-type tetracyclic triterpenoids, and its formula was C30H48O3 ([M + H]+, m/z 457.3677). In the positive ion mode, fragmentation ions of m/z 439.3579, m/z 411.3607, and m/z 393.3513 were detected owing to successive losses of H2O (−18 Da) and CO2 (−28 Da). According to literature reports, ursolic acid may have three RDA cleavage patterns. In this study, based on characteristic RDA cleavage, fragment ions (diagnostic ions) at m/z 249.1352, m/z 203.1791, and m/z 191.1795 were observed in its MS2 spectrum (Xu et al., 2025). Similarly, compounds 225, 239, 242, and 243 showed similar MS2 fragment patterns. However, compounds 147, 164, 173, 193, 199, 200, 204, and 208, identified as oleanane-type pentacyclic triterpenoids, were prone to losing glycoside units at glycoside (−162 Da) or arabinose (−146 Da) in the negative ion mode.
3.4.3 Phenylpropanoids analysis
In this study, 24 phenylpropanoids were identified in ASDZL. Some phenylpropanoids were observed to lose neutral molecules, including H2O (−18 Da), CO2 (−44 Da), CH3 (−15 Da), CH2O (−30 Da), and CO (−28 Da). β-Asarone (Figure 5C) (compound 188, tR = 12.92 min) exhibited a [M + H]+ quasi-molecular ion at m/z 209.1172. The product ions at m/z 194.0946 [M + H–CH3]+, m/z 181.0836 [M + H–CH2O]+, m/z 179.0705 [M + H–2CH3]+, m/z 163.0754 [M + H–2CH3–O]+, m/z 151.0755 [M + H–2CH2O]+, m/z 136.0520 [M + H–2CH2O–CH3]+, m/z 121.0648 [M + H–3CH2O]+, and m/z 91.0543 [M + H–4CH2O]+ were detected in the positive MS2 spectrum. According to literature reports, in addition to β-asarone, there is also its isomer α-asarone, and β-asarone has a shorter retention time (Wei et al., 2022). Therefore, compound 188 was identified as β-asarone, and compound 195 was identified as α-asarone. In addition, four compounds (38, 55, 72, and 95) showed losses of glucosyl residue (−162 Da) or rutinoside residue (−308 Da) in the MS2 spectrum. The remaining phenylpropanoids exhibited similar neutral losses.
3.4.4 Alkaloids analysis
The alkaloids are predominantly derived from Unc. Because of the lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom, these alkaloids are readily protonated under positive-ion electrospray ionization conditions, leading to enhanced peak symmetry and detection sensitivity. Unc primarily contains monoterpene indole alkaloids, which are divided into tetracyclic and pentacyclic monoterpene indole alkaloids. Indole alkaloids possess complicated structures. According to literature reports, they are generally identified based on the open-ring cleavage of their parent nucleus and the fragments information after the loss of the nitrogen bridge ring neutral molecule (Pan et al., 2015), for example, geissoschizine methyl ether (Figure 5D) (compound 144, tR = 9.16 min) from tetracyclic monoterpene indole alkaloids. The positive ion MS2 spectrum yielded a parent ion at [M + H]+m/z 367.2017. The product ions at m/z 335.1758 and m/z 251.1537 were found owing to neutral losses of CH4O and C4H4O2. The most characteristic fragmentation pathway for monoterpene indole alkaloids was the preferable cleavage of ring C, which produces diagnostic ions. In this way, fragment ions at m/z 236.1292 [M + H–C9H9N]+ and m/z 170.0966 [M + H–C10H15NO3]+ were observed through the cleavage of ring C. Then, the product ions were found at m/z 224.1292 [M + H–C9H9N-C]+, m/z 192.1080 [M + H–C9H9N–C–CH4O]+, m/z 144.0851 [M + H–C10H15NO3–C2H2]+, and m/z 130.0655 [M + H–C10H15NO3–C2H2–CH2]+. Furthermore, nine compounds (94, 96, 108, 109, 115, 140, 144, 148, and 155) were annotated in positive FBMN.
3.4.5 Anthraquinones analysis
Anthraquinones are characteristic bioactive components from Sen. Anthraquinones were prone to losing neutral molecules, including H2O (−18), O (−16 Da), CH3 (−15 Da), and CO (−28 Da). Additionally, anthraquinone glycosides usually presented glycosyl moieties in their MS2 spectrum, for example, glucoaurantio-obtusin (Figure 5E) (compound 100, tR = 6.98 min), whose molecular formula was C23H24O12 ([M–H]-, m/z 491.1200). The fragment ions at m/z 476.1010 [M–H–CH3]-, m/z 461.0737 [M–H–2CH3]-, and m/z 433.0784 [M–H–2CH3–CO]- emerged due to consecutive neutral losses. The fragment ions at m/z 329.0680 were detected due to neutral loss of glucosyl residue (−162 Da). Other product ions at m/z 313.0380, m/z 299.0222, m/z 285.0410, m/z 270.0174, and m/z 242.0224 referred to consecutive neutral losses of O (−16 Da), CH2 (−14 Da), CH3 (−15 Da), and CO (−28 Da). A total of 18 compounds (58, 85, 92, 100, 126, 135, 136, 141, 153, 163, 167, 176, 182, 194, 196, 203, 218, and 226) were identified as anthraquinones owing to similar MS2 fragment behaviors.
3.4.6 Other types of analysis
In addition to the above five main types of compounds, ASDZL also contains 16 phenylethanoid glycosides, 13 phenolic acids, nine xanthones, nine oligosaccharides, eight phthaleins, nine naphthopyrones, four organic acids, four aromatic aldehydes, and two diarylheptanoids. Interestingly, owing to the unique chemical structures of diarylheptanoids, they have been extensively studied. These compounds exhibit significant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects (Sudarshan et al., 2024). Phenylethanoid glycosides are formed by the formation of a glycosidic bond between phenethyl alcohol and β-D-glucopyranose. Forsythoside A (Supplementary Figure S4D) (compound 63, tR = 9.16 min) generated a parent ion at m/z 623.1984 [M–H]-. The fragment ions at m/z 461.1665 and m/z 443.1542 were detected, owing to consecutive neutral losses of glucosyl residue (−162 Da) and H2O (−18 Da). Then, the product ions at m/z 179.0351 [M–H–C20H18O11]-, m/z 179.0351 [M–H–C20H18O11–O]-, and m/z 135.0452 [M–H–C20H18O11–CO2]- were found in the MS2 spectrum. The remaining eight phenylethanoid glycosides showed similar mass fragment patterns. Oligosaccharides are the main characteristic components of Pol. Glucoses or rhamnoses, which are mainly based on sucrose as a common core, are connected by different forms of glycosidic bonds to form oligosaccharides, which then form esters with organic acid components (Zhang et al., 2023). For instance, tenuifoliside C (Supplementary Figure S4E) (compound 124,tR = 8.25 min) generated an excimer ion at m/z 767.2398 [M–H]-. The product ions are generated at m/z 529.1556 [M–H–C12H14O5]-, m/z 341.1987 [M–H–C23H22O8]-, m/z 325.0892 [M–H–C23H22O8–O]-, m/z 295.0818 [M–H–C23H22O8–O–CH2O]-, m/z 265.0721 [M–H–C23H22O8–O–2CH2O]-, m/z 237.0764 [M–H–C23H30O14]-, m/z 223.0617 [M–H–C23H30O14–CH2]-, and m/z 205.0507 [M–H–C23H30O14–CH2–CO]-. Likewise, the remaining eight oligosaccharides showed similar mass fragment patterns.
3.5 Identification of ASDZL-related constituents in vivo
Research shows that when TCMs are taken orally, and their primary metabolic pathways involve hydrolyzation, methylation, oxidation, sulfation, glucuronidation, and reduction reactions (Guo et al., 2022). The identification of ASDZL components in vivo is likely to be compromised by endogenous interference from complex biological matrices. To address this, extracted ion chromatograms (XICs) can be generated from MS data to improve detection sensitivity and simplify data processing. In this study, the mass spectrum analysis was performed in positive and negative ion modes using UHPLC-HRMS. The ASDZL-related constituents in vivo was based on molecular formula, retention time, accurate mass and fragment ions information. The prototype components in the rat plasma and cerebrum samples were identified using the XIC function in PeakView™ software. Subsequently, MetabolitePilot™ software was used to predict potential metabolites. The predicted metabolites were further compared with prototype compounds and data in the literature using the XIC function in PeakView™ software. In addition, these potential metabolites can be screened using DIF and NLF strategies. Finally, based on literature reports and the identified prototypes and metabolites, the metabolic pathways of the main types of chemical components in ASDZL were elucidated. In the negative ion mode, [M–H]− was detected, whereas in the positive ion mode, [M + H]+ was observed. Our analysis showed that 50 constituents were identified from plasma samples, whereas these components were not observed in the blank plasma samples. In addition, 16 compounds were found in the cerebrum samples of the ASDZL-administered rats that were not identified in the blank cerebrum samples (Supplementary Figure S6). A total of 50 prototypes were detected in vivo. In addition, 16 compounds (Supplementary Table S4) were found to be shared in the plasma and cerebrum samples, indicating that a significant portion of TCM components cannot cross the blood–brain barrier to reach the target in the brain. The interaction between complex Chinese herbal medicine constituents and the gut microbiota is a new target. Therefore, the brain–gut axis may serve as a bridge for studying the interaction between TCMs and the brain (Feng et al., 2019; Feng et al., 2023).
3.5.1 Prototype and metabolite components in bio-samples
There were 50 prototypes, four of which were confirmed by reference standards, including ferulic acid, baicalin, rhynchophylline, and oroxindin. The prototypes included 22 flavonoids, 11 terpenoids, four alkaloids, four phenolic acids, four phenylpropanoids, one anthraquinone, one naphthopyrone, one xanthones, one phthalein, and 1 organic acid. Screening analysis of the XIC diagrams of the 50 prototypes revealed that 10 compounds (P5, P17, P22–P26, P33, P35, and P39) had relatively high intensity, as shown in Figure 6. Baicalin, baicalein, oroxindin, and wogonin are characteristic bioactive components from Scu (Zhang et al., 2025). These four compounds have been reported to exhibit significant anti-inflammatory and antiviral activities through in vitro experiments and molecular docking studies (Liu et al., 2023). Baicalin and baicalein also have significant antioxidant capacity. However, the low bioavailability of baicalin and oroxindin limits their application (Pan et al., 2021). After oral administration, baicalin and oroxindin are absorbed in small amounts in the stomach and small intestine. In the colon, baicalin and oroxindin, acting as prodrugs, can be hydrolyzed by microbial β-glucuronidase into their aglycones, baicalein, and wogonin (Wang et al., 2012; Noh et al., 2016). This metabolic conversion enhances their bioavailability, allowing better colonic absorption and generating pharmacological effects. Furthermore, baicalin can alleviate neuroinflammation by inhibiting Toll-like receptor (Guo et al., 2019). Baicalin and baicalein can significantly inhibit the enzymatic action of MAO-B and then alleviate neuronal suppression mediated by astrocytic GABA (Cho et al., 2024). Wogonin attenuates LPS + ATP-induced inflammatory damage by inhibiting the NLRP3/GSDMD pyroptosis pathway and regulating the CD39 purinergic pathway (Wang et al., 2024). Ferulic acid exhibits multiple pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antidepressant, and neuroprotective effects. In addition, its antidepressant and neuroprotective properties have been validated in both in vivo and in vitro studies (Dong and Huang, 2022). Clinical applications of ferulic acid and its derivatives remain limited, mainly due to insufficient understanding of their mechanisms of action. Additional studies are needed to elucidate their molecular targets and signaling pathways. Except ferulic acid, which is a phenolic acid compound, the rest are flavonoid compounds. This indicates that flavonoid compounds are the main biological constituents absorbed following oral administration of ASDZL extract. The BPC diagrams of ASDZL in the plasma and cerebrum samples in the positive ion mode and the negative ion mode are shown in Supplementary Figure S6. The identification results and related mass spectrum information of prototypes and 60 metabolites are shown in Tables 1, 2, including 34 flavonoids, 18 phenolic acids, six phenylpropanoids, one terpenoid, and one anthraquinone.
FIGURE 6
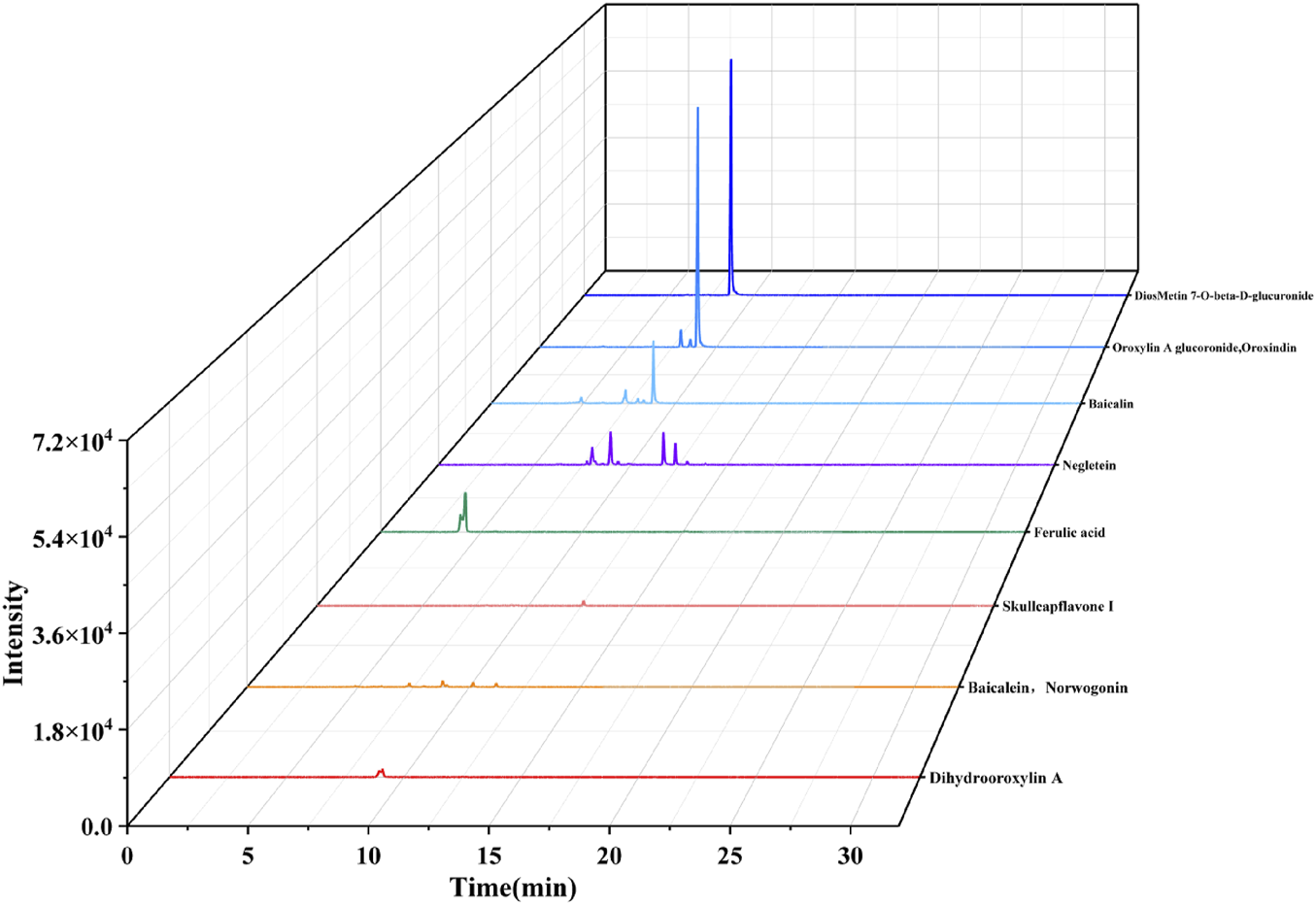
Extraction of ion chromatograms of 10 prototypes with relative high intensity from plasma samples.
TABLE 1
| NO. | RT (min) | Identification | Formula | Selected ion | Theoretical mass (Da) | Measured mass (Da) | Error (ppm) | MS/MS fragments | Plasma | Cerebrum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.77 | 8-Epiloganic acid | C16H24O10 | [M–H]- | 375.1297 | 375.1296 | −0.21 | 213.0770, 169.0885, 151.0760, 125.0610 | + | - |
| P2 | 1.33 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | [M–H]- | 179.0350 | 179.0353 | 1.77 | 135.0458, 89.0394 | + | - |
| P3 | 1.67 | p-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | [M–H]- | 163.0401 | 163.0399 | −1.27 | 119.0510. 93.1455 | + | - |
| P4 | 1.92 | Protocatechuic acid | C7H6O4 | [M–H]- | 153.0193 | 153.0190 | −1.97 | 135.0091, 109.0300, 91.0192 | + | - |
| P5 | 3.86 | Ferulic acid* | C10H10O4 | [M + H]+ | 195.0652 | 195.0652 | 0.06 | 177.0543, 163.0392, 145.0281, 117.0334, 89.0385 | + | + |
| P6 | 4.54 | Zedoalactone C | C15H22O4 | [M + H]+ | 267.1591 | 267.1595 | 1.39 | 249.1497, 231.1370, 213.1273, 203.1432, 185.1320, 147.1160, 133.1010 | + | + |
| P7 | 4.71 | Chrysin 6-C-arabinoside 8-C-glucoside | C26H28O13 | [M + H]+ | 549.1603 | 549.1612 | 1.62 | 495.1340, 465.1200, 363.0874 | + | - |
| P8 | 5.40 | 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-6-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl) oxan-2-YL]-8-(3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-YL) chromen-4-one | C26H28O13 | [M + H]+ | 549.1603 | 549.1598 | −0.79 | 531.1546, 483.1377 | + | - |
| P9 | 5.46 | Zedoalactone A | C15H22O4 | [M + H]+ | 267.1591 | 267.1580 | −4.17 | 249.1479, 231.1374, 213.1290, 185.1377 | + | - |
| P10 | 6.47 | Hispidulin 7-glucuronide | C22H20O12 | [M + H]+ | 477.1028 | 477.1050 | 4.74 | 301.0708, 286.0495 | + | - |
| P11 | 6.74 | Isocorynoxeine | C22H26N2O4 | [M + H]+ | 383.1965 | 383.1959 | −1.70 | 267.1511, 160.0758 | + | - |
| P12 | 6.77 | Corynoxeine | C22H26N2O4 | [M + H]+ | 383.1965 | 383.1968 | 0.81 | 160.0751 | + | - |
| P13 | 7.13 | 3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-[5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-methoxy-4-oxochromen-7-yl] oxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | C23H22O13 | [M–H]- | 505.0988 | 505.0984 | −0.70 | 329.0672, 314.0440, 299.0199 | + | - |
| P14 | 7.18 | 5.2′,6′-Trihydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone 2′-glucuronide | C23H22O13 | [M-H]- | 505.0988 | 505.0986 | −0.36 | 329.0671, 314.0435, 299.0195 | + | - |
| P15 | 7.25 | Cynaroside | C21H20O11 | [M–H]- | 447.0933 | 447.0939 | 1.30 | 271.0608, 256.0383 | + | - |
| P16 | 7.33 | Rhynchophylline* | C22H28N2O4 | [M + H]+ | 385.2122 | 385.2146 | 6.22 | 353.1868, 269.1672, 160.0763 | + | - |
| P17 | 7.34 | Baicalin* | C21H18O11 | [M–H]- | 445.0776 | 445.0777 | 0.22 | 269.0461, 251.0346, 241.0511, 223.0406, 175.0250, 169.0661 | + | + |
| P18 | 7.59 | 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid | C12H14O5 | [M + H]+ | 239.0914 | 239.0914 | −0.19 | 206.0570, 193.0841, 191.0338, 178.0624, 163.0391 | + | - |
| P19 | 7.86 | Viscidulin II | C17H14O7 | [M + H]+ | 331.0812 | 331.0812 | −0.06 | 316.0656, 298.0504, 270.0525, 242.0575 | + | - |
| P20 | 8.32 | Glychionide A | C21H18O11 | [M-H]- | 445.0776 | 445.0783 | 1.59 | 269.0461, 241.0506, 225.0551, 197.0608 | + | - |
| P21 | 8.53 | Chrysin-7-O-glucuronide | C21H18O10 | [M–H]- | 429.0827 | 429.0836 | 1.98 | 253.0509, 175.0267, 113.0245, 99.0082, 85.0304 | + | - |
| P22 | 8.57 | Oroxylin A glucuronide | C22H20O11 | [M–H]- | 459.0933 | 459.0930 | −0.69 | 283.0618, 268.0383 | + | - |
| P23 | 8.64 | DiosMetin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide | C22H20O12 | [M + H]+ | 477.1028 | 477.1040 | 2.60 | 301.0779, 286.0511 | + | + |
| P24 | 8.80 | Norwogonin | C15H10O5 | [M + H]+ | 271.0601 | 271.0611 | 3.85 | 253.0492, 225.0533, 169.0118, 141.0676, 123.0080 | + | + |
| P25 | 8.86 | Dihydrooroxylin A | C16H14O5 | [M + H]+ | 287.0914 | 287.0917 | 1.03 | 183.0292, 168.0050, 140.0095, 131.0487 | + | - |
| P26 | 9.00 | Oroxindin* | C22H20O11 | [M–H]- | 459.0933 | 459.0934 | 0.19 | 283.0626, 268.0384 | + | + |
| P27 | 9.14 | 1-Hydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthone | C15H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 273.0758 | 273.0765 | 2.69 | 255.0747, 227.0673 | + | - |
| P28 | 9.15 | Tectoridin | C22H22O11 | [M–H]- | 461.1089 | 461.1081 | −1.83 | 285.0773, 175.0253, 165.9908, 137.9956 | + | - |
| P29 | 9.25 | Geissoschizine methyl ether | C22H26N2O3 | [M + H]+ | 367.2016 | 367.2023 | 1.79 | 335.1782, 224.1286, 170.0953, 144.0794 | + | - |
| P30 | 9.33 | Curcumin C | C15H16O3 | [M + H]+ | 245.1172 | 245.1167 | −2.10 | 229.0466, 199.0348, 181.0748 | + | - |
| P31 | 10.08 | 5.2′,6′-Trihydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone | C18H16O8 | [M + H]+ | 361.0918 | 361.0906 | −3.41 | 346.0686, 331.0447, 313.0347 | + | - |
| P32 | 10.10 | Curdionolide B | C15H20O3 | [M + H]+ | 249.1485 | 249.1484 | −0.31 | 231.1378, 213.1272, 203.1422, 185.1321, 161.0991, 147.0803 | + | - |
| P33 | 10.18 | Baicalein | C15H10O5 | [M + H]+ | 271.0601 | 271.0605 | 1.33 | 253.0532,225.0542,169.0649,123.0074 | + | + |
| P34 | 10.78 | Curcolone | C15H18O3 | [M + H]+ | 247.1329 | 247.1339 | 4.19 | 229.1234, 211.1103, 201.0803, 183.1171, 143.0845, 129.0206 | + | - |
| P35 | 11.69 | Negletein | C16H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 285.0758 | 285.0763 | 1.77 | 270.0540, 168.0063, 140.0105 | + | - |
| P36 | 11.73 | Curdione | C15H24O2 | [M + H]+ | 237.1849 | 237.1851 | 0.94 | 219.1343, 201.1609, 175.1407, 159.1173, 145.1027 | + | - |
| P37 | 12.31 | β-Asarone | C12H16O3 | [M + H]+ | 209.1172 | 209.1178 | 2.73 | 181.1217, 179.1089, 121.9462, 91.0546 | + | - |
| P38 | 12.32 | Wogonin | C16H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 285.0758 | 285.0765 | 2.71 | 270.0531, 252.0428, 242.0583, 179.0492, 151.0539 | + | + |
| P39 | 12.61 | Skullcapflavone I | C17H14O6 | [M + H]+ | 315.0863 | 315.0868 | 1.50 | 300.0628, 285.0397, 282.0521, 257.0438 | + | + |
| P40 | 12.75 | Methyl eugenol | C11H14O2 | [M + H]+ | 179.1067 | 179.1065 | −0.62 | 151.0753, 121.0622, 107.0481, 91.0536 | + | + |
| P41 | 12.92 | Oroxylin A | C16H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 285.0758 | 285.0758 | 0.22 | 270.0523, 168.0051 | + | + |
| P42 | 13.86 | Obtusifolin | C16H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 285.0758 | 285.0759 | 0.68 | 270.0510, 253.0404, 242.0579, 225.0548, 211.0752 | + | - |
| P43 | 13.95 | α-Asarone | C12H16O3 | [M + H]+ | 209.1172 | 209.1175 | 1.28 | 181.1204, 179.1075, 165.0722, 135.1147, 121.1031, 91.0538 | + | + |
| P44 | 14.32 | Procurcumenol | C15H22O2 | [M + H]+ | 235.1693 | 235.1692 | −0.24 | 217.1569, 189.1635, 175.1105, 161.0956, 133.1003, 119.0846 | + | - |
| P45 | 15.82 | Toralactone | C15H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 273.0758 | 273.0760 | 1.08 | 255.0642, 227.0700, 212.0465, 184.0515 | + | + |
| P46 | 16.55 | Oxyphyllanene B | C12H14O2 | [M + H]+ | 191.1067 | 191.1069 | 1.29 | 173.0934, 163.1087, 145.0981, 131.0888 | + | + |
| P47 | 16.88 | Saucernetin | C22H28O5 | [M + H]+ | 373.2010 | 373.2016 | 1.83 | 235.1309, 217.1207, 202.0976, 179.1057, 165.0887, 151.0754 | + | - |
| P48 | 19.05 | Calamenene | C15H22 | [M + H]+ | 203.1794 | 203.1797 | 1.39 | 203.1121, 147.1136, 133.1025, 119.0916 | + | - |
| P49 | 19.49 | 4,7-Dihydroxy-3-butylphthalide | C12H14O4 | [M + H]+ | 223.0965 | 223.0962 | −1.30 | 207.0318, 191.0009, 149.0235 | + | + |
| P50 | 20.44 | Eremophilene | C15H24 | [M + H]+ | 205.1951 | 205.1953 | 0.94 | 149.0234, 135.1174, 121.1006, 107.0838, 93.0698 | + | + |
Absorbed constituents in plasma samples after oral administration of ASDZL (P50).
Note: P: prototype component; * confirmed by comparing with the reference standards; + means detectable, - means undetectable, RT(min) means retention time(min).
TABLE 2
| NO. | Rt (min) | Identification | Formula | Selected ion | Theoretical mass (Da) | Measured mass (Da) |
Error (ppm) | MS/MS fragments | Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 0.73 | Caffeic acid-2O | C9H8O2 | [M–H]- | 147.0452 | 147.0454 | 1.50 | 145.0497, 103.0576, 89.0246 | Phenolic acids |
| M2 | 0.76 | Ferulic acid+2H | C10H12O4 | [M + H]+ | 197.0808 | 197.0805 | −1.77 | 179.0718, 161.0596, 151.0388, 135.0446, 133.0648, 105.0692, 91.0540 | Phenolic acids |
| M3 | 0.82 | Protocatechuic acid + SO3+CH3 | C8H8O7S | [M–H]- | 246.9918 | 246.9918 | −0.07 | 167.0354, 152.0118, 123.0453, 108.0220 | Phenolic acids |
| M4 | 0.86 | Caffeic acid + SO3+2H | C9H10O7S | [M–H]- | 261.0075 | 261.0074 | −0.25 | 217.0182, 181.0516, 137.0614 | Phenolic acids |
| M5 | 1.00 | Caffeic acid+2H | C9H10O4 | [M–H]- | 181.0506 | 181.0507 | 0.23 | 163.0408, 135.0457, 119.0507 | Phenolic acids |
| M6 | 1.01 | Protocatechuic acid-CO2+SO3 | C6H6O5S | [M–H]- | 188.9863 | 188.9865 | 1.18 | 109.0310, 91.0192 | Phenolic acids |
| M7 | 1.25 | Ferulic acid-CH2 | C9H8O4 | [M + H]+ | 181.0495 | 181.0501 | 3.08 | 163.0391, 145.0274, 141.0728, 135.0449, 117.0344, 105.0701, 89.0382 | Phenolic acids |
| M8 | 1.25 | Caffeic acid + C6H8O6 | C15H16O10 | [M–H]- | 355.0671 | 355.0675 | 1.31 | 179.0358, 135.0457 | Phenolic acids |
| M9 | 1.35 | Caffeic acid + SO3 | C9H8O7S | [M–H]- | 258.9918 | 258.9924 | 2.45 | 179.0354, 135.0456 | Phenolic acids |
| M10 | 1.39 | Caffeic acid + CH2 | C10H10O4 | [M–H]- | 193.0506 | 193.0509 | 1.15 | 178.0255, 134.0379 | Phenolic acids |
| M11 | 1.42 | Ferulic acid + SO3 | C10H10O7S | [M–H]- | 273.0075 | 273.0073 | −0.45 | 193.0512, 178.0279, 149.0615, 134.0380 | Phenolic acids |
| M12 | 1.49 | Caffeic acid + SO3+CH2 | C10H10O7S | [M–H]- | 273.0075 | 273.0073 | −0.54 | 193.0512, 178.0274, 149.0609, 134.0377 | Phenolic acids |
| M13 | 1.62 | Caffeic acid-O | C9H8O3 | [M–H]- | 163.0401 | 163.0399 | −0.90 | 145.8898, 119.0507 | Phenolic acids |
| M14 | 1.67 | Ferulic acid-CH2-O | C9H8O3 | [M–H]- | 163.0401 | 163.0399 | −1.27 | 119.0510, 93.1455 | Phenolic acids |
| M15 | 1.67 | Caffeic acid + SO3-O | C9H8O6S | [M–H]- | 242.9969 | 242.9965 | −1.60 | 163.0410, 119.0508 | Phenolic acids |
| M16 | 1.93 | Ferulic acid + C6H8O6 | C16H18O10 | [M–H]- | 369.0827 | 369.0820 | −2.08 | 193.0510, 178.0271, 134.0377 | Phenolic acids |
| M17 | 2.15 | Zedoalactone C+2H | C15H24O4 | [M + H]+ | 269.1747 | 269.1735 | −4.63 | 251.1648, 233.1556, 215.1459, 203.1461 | Terpenoids |
| M18 | 4.08 | Ferulic acid + CH2+2H | C11H14O4 | [M + H]+ | 211.0965 | 211.0964 | −0.62 | 181.1248, 179.0670, 149.0248, 131.0855, 115.0516, 105.0738, 91.0540 | Phenolic acids |
| M19 | 4.45 | Baicalein-O+2H | C15H12O4 | [M + H]+ | 257.0808 | 257.0801 | −2.81 | 163.0395, 151.1130, 135.0441, 123.0439 | Flavonoids |
| M20 | 6.09 | Oroxindin + O | C22H20O12 | [M + H]+ | 477.1028 | 477.1024 | −0.75 | 301.0705 | Flavonoids |
| M21 | 6.11 | Baicalin + C6H8O6 | C27H26O17 | [M–H]- | 621.1097 | 621.1095 | −0.37 | 445.0774, 269.0457 | Flavonoids |
| M22 | 6.12 | Norwogonin + C6H8O6 | C21H18O11 | [M–H]- | 445.0776 | 445.0755 | −4.85 | 269.0455 | Flavonoids |
| M23 | 6.16 | Glychionide A + C6H8O6 | C27H26O17 | [M–H]- | 621.1097 | 621.1104 | 1.05 | 445.0779, 269.0459 | Flavonoids |
| M24 | 6.19 | Baicalin+2O+2H | C21H20O13 | [M + H]+ | 481.0977 | 481.0975 | −0.27 | 305.0663, 290.0445 | Flavonoids |
| M25 | 6.37 | Oroxindin + C6H8O6 | C28H28O17 | [M + H]+ | 637.1399 | 637.1416 | 2.54 | 461.1085, 285.0757 | Flavonoids |
| M26 | 6.44 | Baicalin + C6H8O6+CH2 | C28H28O17 | [M–H]- | 635.1254 | 635.1253 | −0.17 | 459.0914, 283.0619, 268.0382 | Flavonoids |
| M27 | 6.49 | Ferulic acid-O+2H | C10H12O3 | [M + H]+ | 181.0859 | 181.0866 | 3.62 | 151.0371, 137.0577, 123.0797, 107.0866, 105.0356, 89.0392 | Phenolic acids |
| M28 | 6.77 | Dihydrooroxylin A + C6H8O6 | C22H22O11 | [M + H]+ | 461.1089 | 461.1096 | 1.41 | 285.0786, 270.0537, 252.0435 | Flavonoids |
| M29 | 6.79 | DiosMetin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide + C6H8O6 | C28H28O18 | [M + H]+ | 653.1348 | 653.1369 | 3.20 | 477.1042, 301.0715 | Flavonoids |
| M30 | 7.25 | Tectoridin-CH2 | C21H20O11 | [M–H]- | 447.0933 | 447.0939 | 1.30 | 271.0608, 256.0383 | Flavonoids |
| M31 | 7.33 | Baicalin + CH2+O | C22H20O12 | [M–H]- | 475.0882 | 475.0879 | −0.72 | 299.0570, 284.0351 | Flavonoids |
| M32 | 7.95 | Skullcapflavone I + C6H8O6 | C23H22O12 | [M + H]+ | 491.1184 | 491.1209 | 5.17 | 315.0875, 300.0621, 285.0344 | Flavonoids |
| M33 | 8.02 | Wogonin + C6H8O6 | C22H20O11 | [M–H]- | 459.0933 | 459.0938 | 1.04 | 283.0613, 268.0382 | Flavonoids |
| M34 | 8.06 | Baicalin + CH2 | C22H20O11 | [M–H]- | 459.0933 | 459.0930 | −0.66 | 283.0620, 268.0386 | Flavonoids |
| M35 | 8.24 | Glychionide A + CH2 | C22H20O11 | [M–H]- | 459.0933 | 459.0924 | −1.91 | 283.0615, 268.0380, 240.0427 | Flavonoids |
| M36 | 8.45 | Glychionide A-C6H8O6-O | C15H10O4 | [M + H]+ | 255.0652 | 255.0654 | 0.99 | 199.0734, 181.1005, 153.0183 | Flavonoids |
| M37 | 8.50 | Glychionide A-O | C21H18O10 | [M–H]- | 429.0827 | 429.0811 | −3.71 | 253.0512 | Flavonoids |
| M38 | 8.64 | Baicalein + CH2+O | C16H12O6 | [M + H]+ | 301.0707 | 301.0715 | 2.66 | 286.0472, 183.9997, 155.9957, 127.0066 | Flavonoids |
| M39 | 8.68 | Baicalein+2H | C15H12O5 | [M + H]+ | 273.0758 | 273.0749 | −3.06 | 229.0489, 168.8711 | Flavonoids |
| M40 | 8.69 | Viscidulin II + CH2 | C18H16O7 | [M + H]+ | 345.0965 | 345.0965 | 0.00 | 330.0717, 312.0627, 284.0689, 266.0647 | Flavonoids |
| M41 | 8.71 | Chrysin-7-O-glucuronide-C6H8O6+SO3 | C15H10O7S | [M–H]- | 333.0075 | 333.0088 | 3.95 | 253.0515, 225.0562 | Flavonoids |
| M42 | 9.03 | Norwogonin-O | C15H10O4 | [M + H]+ | 255.0652 | 255.0659 | 2.72 | 227.0705, 209.0576, 199.0745, 181.0635, 153.0697 | Flavonoids |
| M43 | 9.06 | DiosMetin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide-O | C22H20O11 | [M–H]- | 459.0933 | 459.0934 | 0.24 | 283.0620, 268.0387, 175.0253 | Flavonoids |
| M44 | 9.12 | Baicalin-O | C21H18O10 | [M–H]- | 429.0827 | 429.0841 | 3.17 | 253.0509 | Flavonoids |
| M45 | 9.20 | Viscidulin II-O | C17H14O6 | [M + H]+ | 315.0863 | 315.0861 | −0.53 | 300.0435, 285.0328, 269.0952 | Flavonoids |
| M46 | 9.21 | Oroxindin + CH2+O | C23H22O12 | [M + H]+ | 491.1184 | 491.1181 | −0.70 | 315.0863, 300.0624, 285.0403 | Flavonoids |
| M47 | 9.48 | Methyl eugenol-2CH2 | C9H10O2 | [M + H]+ | 151.0754 | 151.0747 | −4.19 | 107.0857, 91.0542 | Phenylpropanoids |
| M48 | 9.57 | DiosMetin 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide + CH2 | C23H22O12 | [M + H]+ | 491.1184 | 491.1193 | 1.83 | 315.0871, 300.0621 | Flavonoids |
| M49 | 9.81 | Oroxylin A + SO3 | C16H12O8S | [M–H]- | 363.0180 | 363.0186 | 1.57 | 283.0615, 268.0381 | Flavonoids |
| M50 | 9.85 | Wogonin + SO3 | C16H12O8S | [M–H]- | 363.0180 | 363.0184 | 1.17 | 283.0620, 268.0386 | Flavonoids |
| M51 | 10.27 | Wogonin + O | C16H12O6 | [M + H]+ | 301.0707 | 301.0713 | 2.27 | 286.0496, 255.1266, 145.0174, 127.0064 | Flavonoids |
| M52 | 10.76 | β-Asarone-2CH2 | C10H12O3 | [M + H]+ | 181.0859 | 181.0864 | 2.71 | 139.0753, 135.0810, 107.0866 | Phenylpropanoids |
| M53 | 11.09 | Methyl eugenol-2CH2 | C10H12O2 | [M + H]+ | 165.0910 | 165.0912 | 1.11 | 137.0958, 121.0648, 119.0853, 107.0492, 91.0543 | Phenylpropanoids |
| M54 | 11.63 | β-Asarone-CH2 | C11H14O3 | [M + H]+ | 195.1016 | 195.1022 | 3.07 | 163.0390, 133.0315, 121.1020, 91.0529 | Phenylpropanoids |
| M55 | 11.88 | α-Asarone-2CH2 | C10H12O3 | [M + H]+ | 181.0859 | 181.0862 | 1.53 | 139.0732, 135.0797, 107.0847 | Phenylpropanoids |
| M56 | 12.42 | Oroxylin A + O | C16H12O6 | [M + H]+ | 301.0707 | 301.0704 | −0.87 | 283.0598, 268.0353, 240.0409, 227.0692 | Flavonoids |
| M57 | 12.53 | Wogonin+2H | C16H14O5 | [M + H]+ | 287.0914 | 287.0920 | 2.23 | 183.0283, 175.0145, 168.0052, 159.0230, 131.0498 | Flavonoids |
| M58 | 14.02 | Methyl eugenol+2H | C11H16O2 | [M + H]+ | 181.1223 | 181.1226 | 1.66 | 123.0801, 91.0548 | Phenylpropanoids |
| M59 | 14.04 | Dihydrooroxylin A + CH2 | C17H16O5 | [M + H]+ | 301.1071 | 301.1072 | 0.59 | 286.9927, 283.0514, 255.1261 | Flavonoids |
| M60 | 19.96 | Obtusifolin + CH2 | C17H14O5 | [M + H]+ | 299.0914 | 299.0914 | 0.16 | 283.0485, 269.0814, 250.9921, 226.0585 | Anthraquinones |
Metabolites in plasma samples after oral administration of ASDZL (60 M).
Note: M: metabolite component.
3.5.2 Metabolites of flavonoid-related components analysis
Flavonoids are the primary components of ASDZL in vivo after oral administration. Flavonoids demonstrate various pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial effects, and are widely applied in active ingredient research and disease treatment (Wang et al., 2018). In this study, 57 flavonoids of prototypes and metabolites were identified in the biological samples. The primary metabolic pathways of flavonoids include methylation, demethylation, hydroxylation, hydroxylation, sulfation, and glucuronidation, for example, compound P17 (C21H18O11, tR = 7.34 min), for which the diagnostic ions m/z 269.0461 and m/z 169.0661 were observed in the negative MS2 spectrum due to the loss of glucuronic acid (GlcA, 176 Da) and RDA cleavage. The fragmentation ion of 251.0346 [M–H–C6H8O6–H2O]- and m/z 223.0406 [M–H–C6H8O6–H2O–CO]- was also detected. Thus, compound P17 was identified as baicalin. Subsequently, M34 (C22H10O11, tR = 7.34 min) in the negative MS2 spectrum yield the parent ion at m/z 459.0930 and the product ion at m/z 283.0620, which were both 14 Da more than P17. M34 was inferred as the methylation metabolite of P17. M21 (C27H26O17, tR = 6.11 min) generated a quasi-molecular ion at m/z 621.1095, which was 176 Da higher than the parent ion of P17, and its product ion at m/z 269.0457 corresponded to P17 in the negative ion mode. Therefore, M21 was the glucuronidation metabolite of P17. Fragment ions at m/z 299.0507 and m/z 284.0351 indicated the loss of CH3 (−15 Da). On the basis of comparing parent ions and fragment ions, we speculated that P17 went through methylation and hydroxylation to produce M31. M44 (C21H18O10, tR = 9.12 min) yielded the parent ion at m/z 429.0841 and the product ion at m/z 253.0509, which were both 16 Da less than P17. Hence, M44 was inferred as the dihydroxylation metabolite of P17. The metabolic pathway of baicalin and baicalein are shown in Figure 7.
FIGURE 7
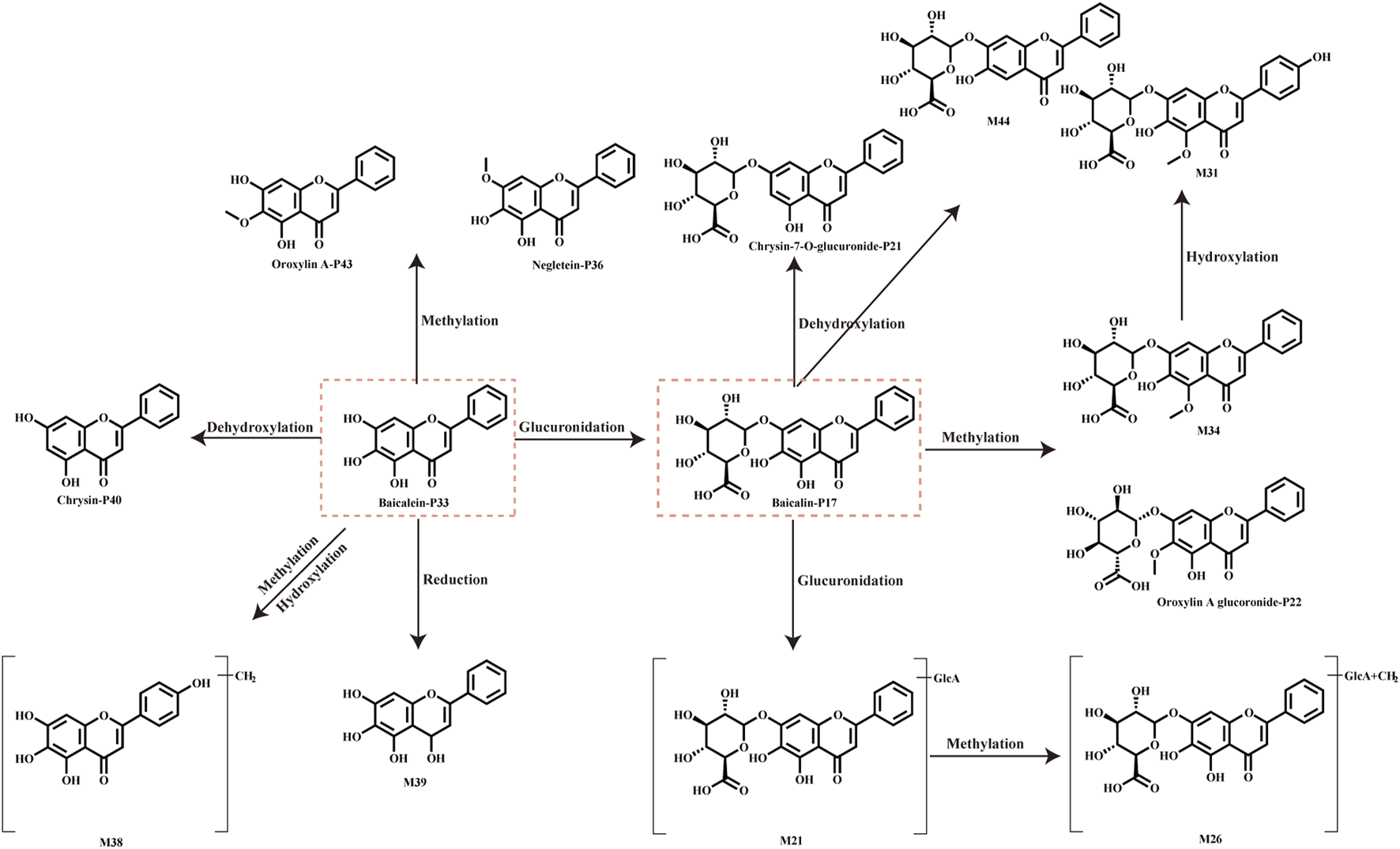
Main metabolic pathways of the flavonoids of baicalin and baicalein.
4 Conclusion
In this study, we integrated multiple strategies to successfully identify 243 components in ASDZL, with 61 components annotated by FBMN. In plasma samples, 50 prototypes and 60 metabolites were identified. The integrated analytical strategy used in this study contributes to the characterization of compounds in ASDZL, enabling further investigation of its pharmacological mechanisms.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw mass spectrometry data generated in this study are available in the Figshare repository under accession number figshare.29975296. The data can be accessed at: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.29975296.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Institutional Welfare and Ethical Committee: No. DW20240507-125. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
TH: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Software, Data curation. DN: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Software. WZ: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. DF: methodology, Writing – original draft, Resources. AK: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Software. YW: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. JS: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Fund (2024GXNSFAA010147) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (82260953, 82474578).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2025.1647159/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Chen T. Massias J. Bertrand S. Guitton Y. Le Bizec B. Dervilly G. (2024). Innovative molecular networking analysis of steroids and characterisation of the urinary steroidome. Sci. Data11 (1), 818. 10.1038/s41597-024-03599-0
2
Cho J. Hong E. B. Kim Y. A.-O. Song J. A.-O. Ju Y. H. Kim H. et al (2024). Baicalin and baicalein from Scutellaria baicalensis georgi alleviate aberrant neuronal suppression mediated by GABA from reactive astrocytes. CNS Neurosci. and Ther.30 (5), e14740. 10.1111/cns.14740
3
Dong X. Huang R. (2022). Ferulic acid: an extraordinarily neuroprotective phenolic acid with anti-depressive properties. Phytomedicine105, 154355. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154355
4
Feng W. Ao H. Peng C. Yan D. (2019). Gut microbiota, a new frontier to understand traditional Chinese medicines. Pharmacol. Res.142, 176–191. 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.02.024
5
Feng W. Yang Z. Liu Y. Chen R. Song Z. Pan G. et al (2023). Gut microbiota: a new target of traditional Chinese medicine for insomnia. Biomed. and Pharmacother.160, 114344. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114344
6
Guo J. Shang Y. Yang X. Li J. He J. Gao X. et al (2022). An online stepwise background subtraction-based ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight tandem mass spectrometry dynamic detection integrated with metabolic molecular network strategy for intelligent characterization of the absorbed chemical-fingerprint of QiangHuoShengShi decoction in vivo. J. Chromatogr. A1675, 463172. 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463172
7
Guo L.-T. Wang S.-Q. Su J. Xu L.-X. Ji Z.-Y. Zhang R.-Y. et al (2019). Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J. Neuroinflammation16 (1), 95. 10.1186/s12974-019-1474-8
8
Han M. Xia H. Xia G. Wei X. Li J. Wu Y. et al (2025). Feature-based molecular networking (FBMN): an efficient booster for discovering novel natural products or metabolites. Acta Pharm. Sin. B15 (4), 2283–2286. 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.02.019
9
Heuckeroth S. Damiani T. Smirnov A. Mokshyna O. Brungs C. Korf A. et al (2024). Reproducible mass spectrometry data processing and compound annotation in MZmine 3. Nat. Protoc.19 (9), 2597–2641. 10.1038/s41596-024-00996-y
10
Hong L.-l. Cui D.-x. Wang H.-d. Jing Q. Li X. Hu Y. et al (2025). Recent advances in traditional Chinese medicine metabolism: sample pre-treatment, MS-oriented analytical strategies and typical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem.189, 118269. 10.1016/j.trac.2025.118269
11
Jichao S. Xinmin H. Xianguo R. Dongqi Y. Rongyi Z. Shuang L. et al (2017). Saikosaponin A alleviates symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder through downregulation of DAT and enhancing BDNF expression in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med.2017 (1), 2695903. 10.1155/2017/2695903
12
Katajamaa M. Miettinen J. Orešič M. (2006). MZmine: toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics22 (5), 634–636. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btk039
13
Li L. Zhu N. Zhang L. Kuja-Halkola R. D’Onofrio B. M. Brikell I. et al (2024). ADHD pharmacotherapy and mortality in individuals with ADHD. Jama331 (10), 850. 10.1001/jama.2024.0851
14
Li X.-L. Guo Z.-F. Wen X.-D. Li M.-N. Yang H. (2023). A molecular networking-assisted automatic database screening strategy for comprehensive annotation of small molecules in complex matrices. J. Chromatogr. A1710, 464417. 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464417
15
Liu S. Ding P. Wu M. Zhu Z. Tao J. Wang J. et al (2023). Screening quality markers (Q-markers) of xiaoer chaige tuire oral liquid by in vitro sequential metabolism and in vivo biopharmaceutical analysis. Phytomedicine116, 154844. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154844
16
Moreira J. Machado M. Dias-Teixeira M. Ferraz R. Delerue-Matos C. Grosso C. (2023). The neuroprotective effect of traditional Chinese medicinal plants—A critical review. Acta Pharm. Sin. B13 (8), 3208–3237. 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.009
17
Noh K. Kang Y. Nepal M. R. Jeong K. S. Oh D. G. Kang M. J. et al (2016). Role of intestinal microbiota in baicalin-induced drug interaction and its pharmacokinetics. Molecules21, 337. 10.3390/molecules21030337
18
Nothias L.-F. Petras D. Schmid R. Dührkop K. Rainer J. Sarvepalli A. et al (2020). Feature-based molecular networking in the GNPS analysis environment. Nat. Methods17 (9), 905–908. 10.1038/s41592-020-0933-6
19
Pakkir Shah A. K. Walter A. Ottosson F. Russo F. Navarro-Diaz M. Boldt J. et al (2024). Statistical analysis of feature-based molecular networking results from non-targeted metabolomics data. Nat. Protoc.20 (1), 92–162. 10.1038/s41596-024-01046-3
20
Pan H. Yang W. Zhang Y. Yang M. Feng R. Wu W. et al (2015). An integrated strategy for the systematic characterization and discovery of new indole alkaloids from Uncaria rhynchophylla by UHPLC/DAD/LTQ-Orbitrap-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.407 (20), 6057–6070. 10.1007/s00216-015-8777-0
21
Pan L. Cho K.-S. Yi I. To C.-H. Chen D. F. Do C.-W. (2021). Baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin: protective effects against ischemia-induced neurodegeneration in the brain and retina. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev.2021 (1), 8377362. 10.1155/2021/8377362
22
Pluskal T. Castillo S. Villar-Briones A. Orešič M. (2010). MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinforma.11 (1), 395. 10.1186/1471-2105-11-395
23
Qu B. Liu Y. Shen A. Guo Z. Yu L. Liu D. et al (2023). Combining multidimensional chromatography-mass spectrometry and feature-based molecular networking methods for the systematic characterization of compounds in the supercritical fluid extract of Tripterygium wilfordii hook F. Analyst148 (1), 61–73. 10.1039/d2an01471h
24
Ramanan M. Sinha S. Sudarshan K. Aidhen I. S. Doble M. (2016). Inhibition of the enzymes in the leukotriene and prostaglandin pathways in inflammation by 3-aryl isocoumarins. Eur. J. Med. Chem.124, 428–434. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.08.066
25
Su Y. Tao L. Zhang X. Sheng X. Li Q. Fei W. et al (2023). Non-targeted characteristic filter analysis combined with in silico prediction strategies to identify the chemical components and in vivo metabolites of dalitong granules by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis222, 115086. 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.115086
26
Sudarshan K. Yarlagadda S. Sengupta S. (2024). Recent advances in the synthesis of diarylheptanoids. Chem. – Asian J.19 (15), e202400380. 10.1002/asia.202400380
27
van Dinteren S. Araya-Cloutier C. de Bruijn W. J. C. Vincken J.-P. (2021). A targeted prenylation analysis by a combination of IT-MS and HR-MS: identification of prenyl number, configuration, and position in different subclasses of (iso)flavonoids. Anal. Chim. Acta1180, 338874. 10.1016/j.aca.2021.338874
28
Wang H. Lan Y. Luo L. Xiao Y. Meng X. Zeng Y. et al (2024). The scutellaria-coptis herb couple and its active small-molecule ingredient wogonoside alleviate cytokine storm by regulating the CD39/NLRP3/GSDMD signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol.329, 118155. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118155
29
Wang M. Carver J. J. Phelan V. V. Sanchez L. M. Garg N. Peng Y. et al (2016). Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with global natural products social molecular networking. Nat. Biotechnol.34 (8), 828–837. 10.1038/nbt.3597
30
Wang T.-y. Li Q. Bi K.-s. (2018). Bioactive flavonoids in medicinal plants: structure, activity and biological fate. Asian J. Pharm. Sci.13 (1), 12–23. 10.1016/j.ajps.2017.08.004
31
Wang X. Cao Y. Chen S. Lin J. Bian J. Huang D. (2021). Anti-inflammation activity of flavones and their structure–activity relationship. J. Agric. Food Chem.69 (26), 7285–7302. 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c02015
32
Wang Y. Yang J. Fau - Li X. Li X Fau - Wang J. Wang J. (2012). The metabolism of baicalin in rat and the biological activities of the metabolites. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med.2012, 1741–1746. 10.1155/2012/404529
33
Wei W. Han Q. Tian S. Wang Y. Zhang H. Wang H. et al (2022). Effective separation of α-asarone and β-asarone in TCM by covalent organic framework modified magnetic solid phase extraction. Microchem. J.175, 107015. 10.1016/j.microc.2021.107015
34
Xu Q. Liu J. Wang X. jiao Y. Zhang Y. Shang X. (2025). Characterization, target isolation of triterpenes in the anti-inflammatory fraction of Salvia rosmarinus via UPLC-orbitrap MS/MS coupled with GNPS. J. Agric. Food Chem.73 (18), 10985–10997. 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c12650
35
Yang C. Yin X. Dong X. Zhang X. You L. Wang W. et al (2017). Determination of the phytochemical composition of jingning Fang and the in vivo pharmacokinetics of its metabolites in rat plasma by UPLC–MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B1067, 71–88. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.09.019
36
Yaqun L. Haixia Y. Yuchen S. Mingxin Z. Manqi L. Yunlong T. et al (2022). An shen ding zhi ling ameliorates the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder via modulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor-related signaling pathways. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med.2022, 1–13. 10.1155/2022/5471586
37
Yuan H. Ni X. Zheng M. Han X. Song Y. Yu M. (2019). Effect of catalpol on behavior and neurodevelopment in an ADHD rat model. Biomed. and Pharmacother.118, 109033. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109033
38
Zhang J. Tan B. Wu H. Han T. Fang D. Cai H. et al (2025). Scutellaria baicalensis extracts restrict intestinal epithelial cell ferroptosis by regulating lipid peroxidation and GPX4/ACSL4 in colitis. Phytomedicine141, 156708. 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156708
39
Zhang J.-j. Mao m. Shao M.-m. Wang M.-c. (2024a). Therapeutic potential of natural flavonoids in pulmonary arterial hypertension: a review. Phytomedicine128, 155535. 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155535
40
Zhang L. Yong Y.-Y. Deng L. Wang J. Law B. Y.-K. Hu M.-L. et al (2023). Therapeutic potential of polygala saponins in neurological diseases. Phytomedicine108, 154483. 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154483
41
Zhang Y. Liao J. Le W. Zhang W. Wu G. (2024b). In-Depth analysis of molecular network based on liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry in natural products: importance of redundant nodes discovery. Anal. Chem.96 (40), 15888–15897. 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c02230
42
Zhao P. Qiu J. Pan C. Tang Y. Chen M. Song H. et al (2023). Potential roles and molecular mechanisms of bioactive ingredients in curcumae rhizoma against breast cancer. Phytomedicine114, 154810. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154810
43
Zhou R. Wang J. Han X. Ma B. Yuan H. Song Y. (2019). Baicalin regulates the dopamine system to control the core symptoms of ADHD. Mol. Brain12 (1), 11. 10.1186/s13041-019-0428-5
44
Zhu H. He L. Wu W. Duan H. Chen J. Xiao Q. et al (2023). A compounds annotation strategy using targeted molecular networking for offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis: Yupingfeng as a case study. J. Chromatogr. A1702, 464045. 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464045
Summary
Keywords
UHPLC-HRMS, feature-based molecular networking, flavonoids, integrated strategies, prototype and metabolite components
Citation
Han T, Ni D, Zhu W, Fang D, Kang A, Wu Y and Sun J (2025) UHPLC-HRMS analysis combined with feature-based molecular networking methods for systematic identification of chemicals in AnShenDingZhiLing and its absorbed metabolites. Front. Chem. 13:1647159. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1647159
Received
14 June 2025
Accepted
10 July 2025
Published
03 September 2025
Volume
13 - 2025
Edited by
Zhao Huan, Jinan University, China
Reviewed by
Kasireddy Sudarshan, Purdue University, United States
Jinchao Wei, University of Macau, China
P. Lin, Jinan University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Han, Ni, Zhu, Fang, Kang, Wu and Sun.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jichao Sun, sunjc@gxtcmu.edu.cn; Yumiao Wu, 17342605289@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.