- 1Department of Automotive and Marine Engineering Technology, Public Authority for Applied Education and Training, Adailiyah, Kuwait
- 2Faculty of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering Technology, Universiti Malaysia Pahang Al-Sultan, Abdullah, Pahang, Malaysia
- 3Centre for Sustainable Materials and Surface Metamorphosis, Chennai Institute of Technology, Chennai, India
- 4Centre for Research in Advanced Fluid and Processes, University Malaysia Pahang Al-Sultan Abdullah, Pekan, Pahang, Malaysia
- 5Centre for Advanced Mechanical and Green Technology, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, Multimedia University, Melaka, Malaysia
- 6Department of Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Prague, Czechia
- 7Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
- 8Centre of Smart System and Innovative Design, Faculty of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka, Melaka, Malaysia
- 9School of Engineering, University Southern Queensland, Toowoomba, QLD, Australia
This study explores the development and optimization of a novel nano lubricant by incorporating graphene-cellulose nanoparticles into SAE 10W-40 engine oil to enhance its thermophysical and tribological performance. The nano lubricants were prepared with varying concentrations (0.01%, 0.03%, and 0.05% by volume) and subjected to a comprehensive evaluation of their thermal conductivity, dynamic viscosity, and tribological properties under operational conditions. The thermal conductivity analysis demonstrated that the inclusion of graphene-cellulose nanoparticles improved heat transfer capabilities, particularly at higher concentrations, while maintaining stability over a wide temperature range (30°C–90°C). The dynamic viscosity measurements revealed a synergistic effect of graphene and cellulose, enhancing dispersion stability and lubrication characteristics, with optimal performance achieved at 0.03% concentration. Tribological testing confirmed a significant reduction in the coefficient of friction, achieving a value as low as 0.0406, demonstrating improved wear resistance. Response Surface Methodology was employed to optimize the input parameters, providing insights into the interactions between concentration, load, speed, and temperature. The findings highlight the potential of graphene-cellulose nanocomposites as sustainable, high-performance additives for automotive lubricants, paving the way for energy-efficient and durable applications in the automotive and industrial sectors.
1 Introduction
Lubricants are used for various purposes, including lubrication, cooling, and sealing (Chen et al., 2020; Ouyang et al., 2022). It sticks to moving surface areas, generating fluid films that split the surfaces of the moving surfaces (Ajimotokan, 2024). Wear particles and heat are carried away from the system by moving components (Kadirgama et al., 2012). Lubricants are widely manufactured and contain a variety of additives and base oils. Biological, synthetic, and mineral oils are the most common classifications of base oils (Rasheed et al., 2016). Lignin is a complex biopolymer that originated from a variety of biological materials, including wood, herbaceous plants, grasses, crops and their by-products, and from bacterial, algal, and animal origins (Popa, 2018; Srivastava et al., 2021). This biomacromolecule displays features and properties that are closely related to its biological source, the stage of development and maturity, the applied pretreatment, and the processing conditions and chemical reactions (Tardy et al., 2021). Volatile lignocellulosic biomass often requires enzymatic treatment to degrade its extractives, lignin, and hemicellulose (Lu et al., 2021). Trache et al. (2020a) provided an in-depth overview of the various pretreatment and processing approaches that are typically utilized for pure cellulose extraction from lignocellulosic feedstocks.
The semi-crystalline structure of cellulose consists of crystalline domains with a high degree of order and relatively disordered amorphous regions (Salem et al., 2023). This biopolymer can be found in various polymorphic states, and its structural configurations can be modified via targeted chemical reactions or thermal processing (Mittal et al., 2018). Cellulose, when reduced to nanoscale dimensions, becomes cellulose nanomaterials; which are also referred to as nanocellulose (NC) and has exceptional physical, chemical, biological, magnetic, electrical, and optical properties (Xue et al., 2017; Tan et al., 2022; Heise et al., 2021; Thomas et al., 2018). Leveraging nanoscale structure, these properties are much improved over conventional bulk cellulose. A theoretical synthesis of nanocellulose using a top-down hydrolysis process can be achieved using a series of sequential stages, that is, pretreatment processes on lignocellulosic biomass (Pradhan et al., 2022). First mechanically separate coarse particles, oils, and surface dust from raw materials using crushing, screening, washing, and cooking (Achaw and Danso-Boateng, 2021). After that, various treatment processes such as chemical, physical, physicochemical, and biological methods are used to remove the extractives, hemicellulose, and lignin. This is followed by a cleaving and size fractionation step based on methods that utilize heat, pressure, or shear force to split up the basic cellulose fibrils or microfibrils into nanoscale fibers (Achaw and Danso-Boateng, 2021).
One of the most common ways to increase the quality of nanocellulose is by implementing filtration, solvent removal, dialysis, sonication, centrifugation, surface modification, stabilization, and drying (Low et al., 2022). NC exhibits good functional properties including renewability, environmental benignancy, suitability for biological application, non-toxic, versatile hydrogen bond forming, crystallinity tuning, resistance to chemicals, adjustable aspect ratio, low coefficient of thermal expansion, surface reactivity, low density (1.6 g/cm3), high specific surface area (100–200 of m2/g), high tensile strength (7.5–7.7 GPa) and elastic modulus (130–150 GPa) (Trache et al., 2020b; Ray, 2023; Shrestha, 2019; Zhan, 2019). This unique polysaccharide has attracted considerable interest in research for over 20 years and has been examined in a variety of applications due to its impressive properties (Yu et al., 2018). These are in the fields of sensors and biosensors, energy harvesting devices, oil and gas drilling and cementing, papermaking, filtration, decontamination, adsorption, separation, wood adhesives, Pickering emulsifiers, medical applications, and nanocomposites. Nanocellulose (NC) is generally divided into two categories, cellulose nano-objects (e.g., cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), bacterial nanocellulose (BC)) and cellulose nanostructured materials (e.g., microcrystalline cellulose, cellulose microfibrils), according to isolation approach, morphology, and size (Kargarzadeh et al., 2017; Trache et al., 2020c; Solhi et al., 2023).
Nanofibers have some important advantages over nanostructured materials like more narrow particle size distribution, higher specific surface area, amphiphilic behavior, enhanced barrier properties, and higher crystallinity (Lim, 2017; Samylingam et al., 2024a). These traits endow them with the capacity to develop robust self-assembled structures (hydrogels, films, etc.) with long-term kinetic stability. Besides the previously mentioned nanofibres, many individual nanomaterials of different types of cellulose components came into the literature in the past years: amorphous nanocellulose, cellulose nanoyarn, and cellulose nanoplatelets (Amjad et al., 2022). In recent years, in-depth reviews with extensive discussions regarding NC-based materials have been reported, providing detailed insights on the sources of nanocellulose, its extraction methods, structural modification, possible applications, and merits (Norizan et al., 2022; Choudhary et al., 2023; Xiao et al., 2023).
Recently discovered by Novoselov et al. (2004), graphene displays many ideal features such as high mechanical strength and electrical conductivity and a small molecular barrier. This groundbreaking two-dimensional (2D) material thus has a sheet-like structure of a honeycomb or hexagonal lattice of sp2 hybridized carbon atoms that are closely packed and covalently bonded in a flat plane (Smith et al., 2019). Graphene is a single atomic sheet obtained from graphite and is an all-carbon allotrope in which each atom almost completely interacts with its surrounding atoms by a three-dimensional electronic cloud stretching out, with a standard length of C–C bond of 0.142 nm. Graphene is considered the building block of all carbon allotropes and is the “mother” of the graphitic family of all dimensions (Novoselov et al., 2004). Nanoindentation of freestanding graphene monolayer membranes, performed with an atomic force microscope, has been used to explore the elastic properties and intrinsic breaking strength of this material, clearly demonstrating extraordinary material properties (Lee et al., 2008; Agius Anastasi, 2021).
Graphene force-displacement response reveals nonlinear elastic stress-strain behavior with values of second-order and third-order elastic stiffness were 340 and 690 N/m, respectively (Hu and Lu, 2014). The breaking strength (42 N/m) corresponds to the intrinsic strength of an ideal defect-free graphene sheet. These values correspond to Young’s modulus of E = 1.0 terapascals, the elastic stiffness of the third order of D = -2.0 terapascals, and the intrinsic strength of bulk graphite of int = 130 gigapascals (Lee et al., 2008; Ranjbartoreh et al., 2011; Thakre et al., 2021; Cahangirov et al., 2016). These results validate graphene as the strongest material ever measured, and demonstrate that nanoscale materials with atomic perfection can deform well into the non-linear elastic continuum (Lee et al., 2008). Due to these extraordinary characteristics, considerable research attention has been attributed to the inclusion of graphene into polymers for the synthesis of advanced polymer-based nanocomposites (Smith et al., 2019). As an ex-situ solution approach, one simple way to fabricate GnPs-filled poly(propylene) polymer nanocomposites can be divided into different loadings. The polymer PNCs show remarkable enhancements in thermal stability, as well as enhanced crystallinity (Li et al., 2011).
Using pristine graphene is highly challenging owing to its bottom-up production methods being complex, poor solubility and strongly aggregated in solution due to strong van der Waals interactions (Smith et al., 2019). Due to the superb mechanical properties and ultra-smooth atomic surface of graphene, it is an outstanding additive for improving anti-wear performance (Xiao et al., 2022). Graphene, a promising tribology-enhancing additive, has been the subject of thorough investigations in base greases. Graphene was synthesized using a physical exfoliation method for inclusion into lithium-based greases, and its tribological characterization and critical loads for different graphene-based greases were performed (Fu et al., 2019; Kadirgama, 2022).
More recently, several investigations have focused on exploiting the properties of graphene to improve the tribological behavior and thermal conductivity of different greases and carbon-polymer composites (Manu et al., 2021; Jayalakshmy and Mishra, 2019; Prashanth et al., 2024). The preeminence of graphene in this context has led to much greater interest in its properties with researchers exploring specific applications like frictional performance and heat transfer. However, a significant gap still exists, where the investigations have not yet adequately correlated the tribological character of the grease with its thermal conductivity (Fu et al., 2019). At higher temperatures, GO undergoes thermal treatment in which oxygen-containing functional groups decompose into gases such as CO and CO2 (Akbi et al., 2024). The fast gas generation enables the exfoliation of the single GO nanosheets. For example, GO can be reduced into reduced graphene oxide (RGO) through high-temperature annealing under oxygen-free conditions or nonconventional approaches (e.g., microwaving GO powders or intense light source) to induce a fast GO film reduction (Singh et al., 2016; Pei and Cheng, 2012). Which promotes the GO effective reduction and functional properties improvement.
Reduction agents are often introduced to reduce graphene oxide (GO) solutions chemically by popular methods. Photocatalytic processes have also been used to synthesize rGO. Smith et al. (2019) successfully achieved the reduction of GO using ultraviolet (UV) irradiation in the presence of a titanium dioxide (TiO2) catalyst. Herein, graphene oxide suspended within an ethanol solvent is reduced by accepting electrons from UV-irradiated TiO2 suspensions. The decrease also resulted in a significant change via color evolution from brownish to black in the suspension affirming the absorption of graphene oxide. The direct contact between the TiO2 particles and the graphene sheets is the key point in preventing the aggregation of exfoliated sheets. When deposited as solid films on borosilicate glass coated with gold-sputtered terminations, they show an order of magnitude decrease in lateral resistance after the photocatalytic reduction with TiO2 (Williams et al., 2008).
GO can also be effectively reduced by electrochemical reduction without requiring chemical-reducing agents. It involves only electron rearrangement between the GO and the electrodes in a classic electrochemical cell (Sundararaman et al., 2022). Numerous environmentally friendly (“green”) reducing agents, including ascorbic acid, sugars, amino acids, and even microorganisms have been successfully used in recent years to produce reduced graphene oxide (rGO) (Rai et al., 2020).
The novelty of this study lies in the synergistic integration of graphene and cellulose as nano-lubricant additives, leveraging their complementary properties to enhance both the thermophysical and tribological performance of engine oil. While graphene’s exceptional thermal conductivity and mechanical strength have been widely studied, its propensity to aggregate at higher concentrations often limits its practical application. Similarly, cellulose’s inherent renewability and stabilizing properties have made it a promising additive, but its full potential in hybrid formulations remains underexplored. This research bridges these gaps by developing a graphene-cellulose hybrid nano lubricant that combines the thermal and tribological advantages of graphene with the stabilization and dispersion-enhancing characteristics of cellulose. The systematic investigation of their combined effects on thermal conductivity, dynamic viscosity, and tribological behavior under real-world conditions provides a comprehensive understanding of this novel formulation. By optimizing the concentration and operational parameters through advanced statistical methods, this study offers a groundbreaking approach to improving energy efficiency, wear resistance, and durability in automotive lubrication systems.
2 Methodology
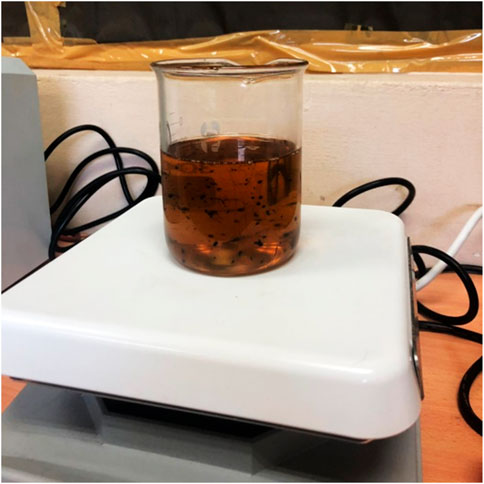
The sample preparation starts with weight measurements. The ratio is arrived for the importance of optimizing the nanoparticle particle used in the analysis. The mass of graphene was calculated with the values of 0.132 g and 0.2201 g for 0.03% (V/V) and 0.05% (V/V) concentration, respectively. The mass of cellulose was also repeated with the same calculation with the value of 0.03, 0.09, and 0.15 g for 0.01% (V/V), 0.03% (V/V), and 0.05% (V/V) concentration, respectively. The base oil of 10W-40 engine oil was added with nanoparticles in a beaker and then mixed using a magnetic stirrer at a constant speed at room temperature for 30 min, as shown in Figure 1.
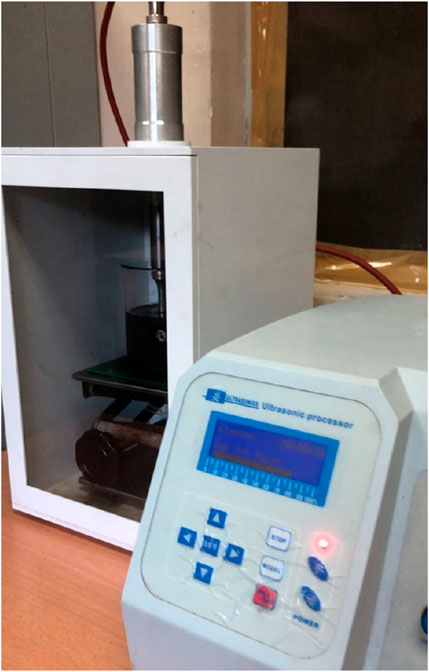
After mixing the lubricant with a magnetic stirrer the nano-lubricant solution, sonication was performed using a probe sonicator as shown in Figure 2. A sonicator is a very effective laboratory instrument used to produce ultrasonic electric signals that will be passed to a transducer. The unit that responds dynamically to electric current is the transducer, which contains piezoelectric crystals that convert the electric signals into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations are enhanced and retained along the journey within the sonicator before reaching the probe at 30 min. The probe then moves rapidly up and down, transferring the ultrasonic vibrations directly to the solution, thus allowing the effective dispersion of nanoparticles (Kabir et al., 2007). A stability test was done with sedimentation observation for 1 month.
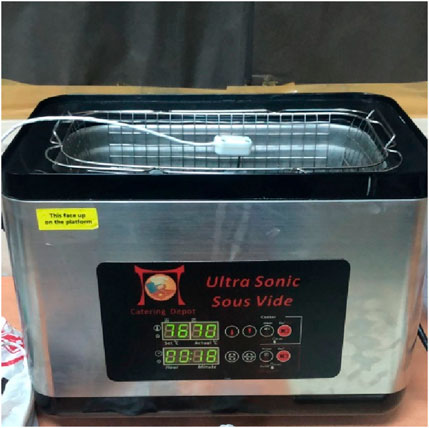
The thermal conductivity of the graphene cellulose nano lubricant samples was measured using a Tempos thermal properties analyzer (METER group). This probe works with the principle of a transient hot wire technique. The thermal conductivity measurement used the KS-3 sensor (60 mm long, 1.3 mm diameter) as shown in Figure 3. An ultrasonic Sous Vide Heated water bath with a heating power of 500 W was used for controlling the temperature within ±1 °C as shown in Figure 4. The ultrasonic cavitation effect can help with thermal conduction and circulation, resulting in even temperature distribution inside the tank and accurate temperature readings. The thermal conductivity of the graphene cellulose nano lubricant solutions was investigated at six different temperatures of 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 °C. This approach is now widely recognized as the most exact and dependable way of determining the thermal conductivity of fluids over a large temperature and pressure range. Nanofluids are projected to have better heat transfer capabilities than traditional heat transfer fluids. According to one concept, the suspended particles are expected to boost nanofluids’ thermal conductivity significantly. The thermal conductivity of nanofluid is well understood to be substantially influenced by the volume fraction size and characteristics of nanoparticles (Nallusamy, 2016).
For lubricating testing, the viscosity of the lubricant is an important indicator. A Brookfield DV-I prime viscometer was used to run the viscosity testing as shown in Figure 5. A rotational viscometer with a spindle submerged in the nano lubricant sample is used. The nano lubricant was poured into the chamber test and coupled to the rheometer in a 25 mL amount. The chamber and water jacket were then carefully connected to the rheometer spring, with the deflection of the spring being within 2–3 percent. A circulating water bath was used to heat the nano lubricant sample until it reached the desired temperature. The dynamic viscosity measurements were carried out at 30–80°C. The current viscosity measurement was performed using Rheocalc software. The viscosity of the sample was determined by altering the spindle rotation speed (de Castro et al., 2016).
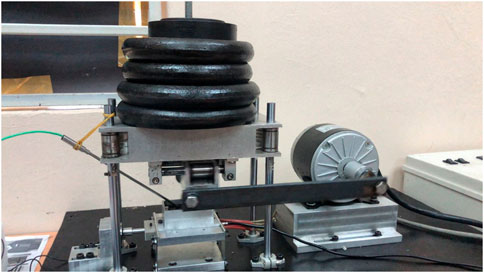
The tribological testing characteristics are experimented with using a modified frequency reciprocating friction machine. The tribological test rig’s main parts are the electric motor, heating element, shaft, lubrication bath, applied load, computing system device, and Arduino. A load cell, tachometer, and k-type thermocouple are the sensors utilized in this experiment. Figure 6 displays the tribology test rig’s configuration and Figure 7 depicts a schematic of the friction pairs. The instruments works as per ASTM G77-17. The wear test was conducted under lubricated sliding conditions against the outer surface of the specimen (aluminum 6061) for 30 min at two conditions (low speed and high load) and (high speed and low load). Normal loads are applied to the device by hanging weights on the bearing lever. The load of choice ranged from 4 to 10 kg. During testing, low engine-speed intervals (200 rpm–500 rpm) were chosen because these conditions cause the most friction in engines, especially during the first movement and at the top dead center (TDC). The internal combustion engine’s working temperature range was 30°C–90°C, and each specimen was operated for 30 min.
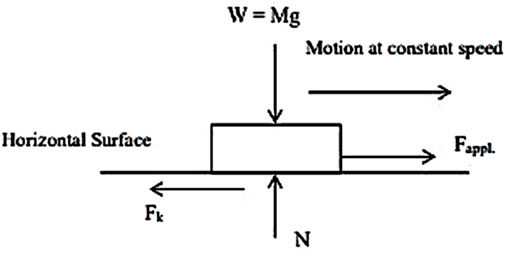
Figure 7. Coefficient of friction evaluation (Sakinah et al., 2016).
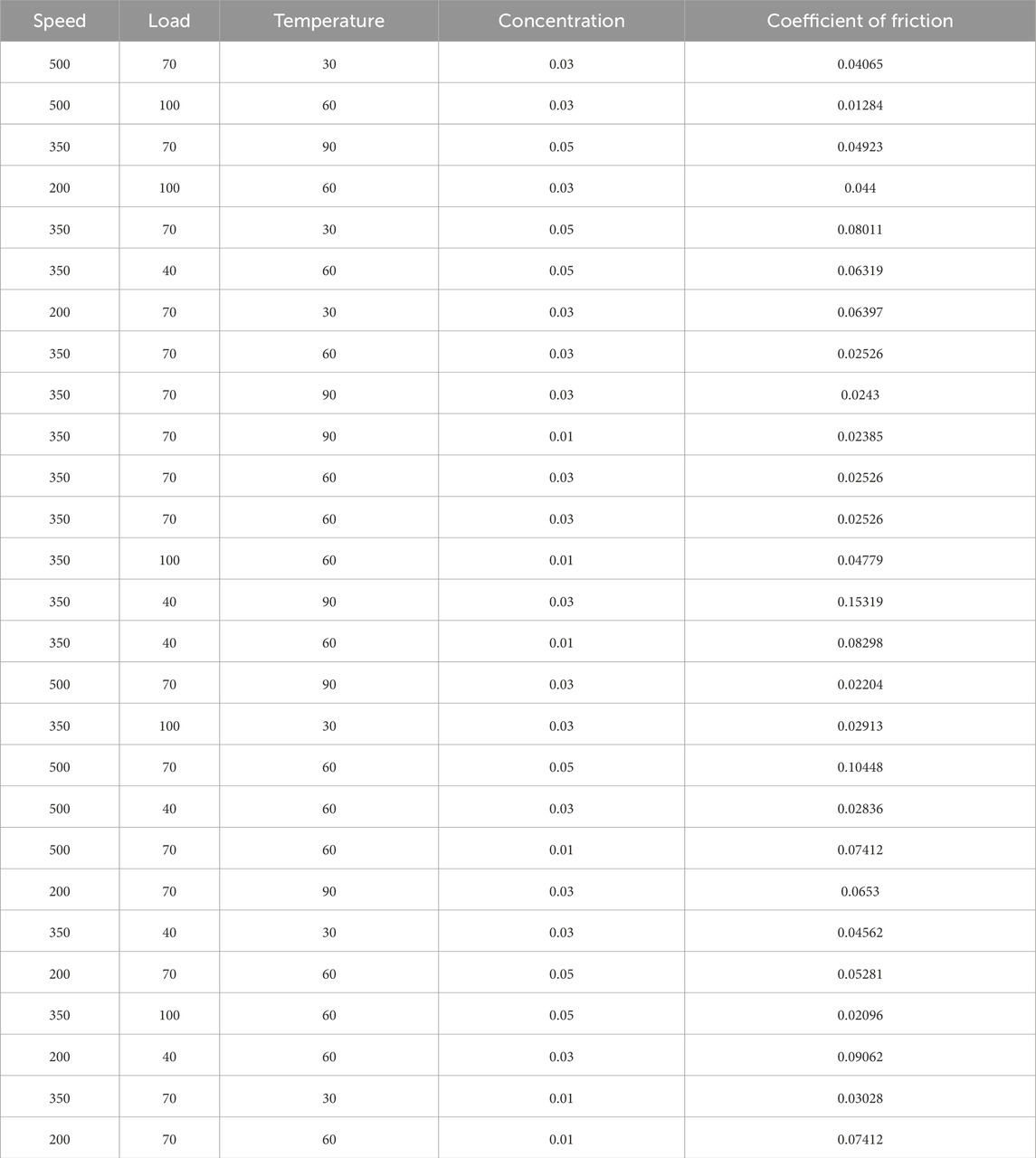
Several input variables significantly influence the coefficient of friction (COF), including nano lubricant load, speed, temperature, and concentration. However, investigating the effect of each parameter individually on COF can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. To address this, the current study employs the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) to analyze the combined impact of these parameters on COF. RSM provides a robust mathematical and statistical framework to evaluate the relationships between independent variables (input parameters) and dependent variables (output responses) (Kadirgama et al., 2018; Kadirgama et al., 2009; Sandanamsamy et al., 2023). In this study, the input parameters considered are load, speed, temperature, and nano lubricant concentration, while COF is the dependent variables. Using RSM, the levels of the input factors were systematically varied to determine the optimal values of COF. This approach allows for the efficient assessment of interactions between input parameters, thereby providing deeper insights into their combined effects on the tribological properties of nano lubricants (Ahmed et al., 2022). The methodology incorporates both linear and non-linear relationships through interaction and quadratic terms to capture complex behaviors. To statistically validate the model and quantify the relationships, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed. This analysis evaluates the significance of each model term by calculating F-values and p-values. A p-value threshold of 0.05 was used to determine statistical significance, ensuring the reliability of the model. The ANOVA analysis not only assesses the individual impact of input variables but also explores their interactions, offering a comprehensive understanding of the system dynamics (Gonaygunta et al., 2023). The Box-Behnken design within RSM was employed for the experimental setup. This design uses a three-level framework—low (−1), high (+1), and center (0)—to systematically vary the input parameters: load (L), speed (S), temperature (T), and volume concentration (C). These levels enable the evaluation of both main effects and interaction effects, minimizing experimental effort while maximizing the information gained. The study conducted a total of 27 experiments based on the Box-Behnken design to examine the influence of these variables on COF. Each experiment was carefully designed to assess the main effects and interactions among the input parameters, ensuring a comprehensive analysis of the tribological responses. The experimental results and corresponding design matrix are presented in Table 1, providing a detailed summary of the trial layout and the observed outcomes. In this analysis, the cumulative effects of load, speed, temperature, and nano lubricant concentration were explored to identify the optimal operating conditions for minimizing COF. The interaction between these parameters revealed non-linear trends, emphasizing the importance of considering their combined effects rather than isolating individual factors. By using RSM, this study not only reduced the time required for experimental investigations but also enhanced the understanding of how key parameters influence tribological performance. These findings will be discussed in greater detail in the subsequent sections, where the optimal conditions and their implications for nano lubricant performance are elaborated.
3 Results and discussion
Visual sedimentation analysis was performed to investigate the stability of graphene-cellulose-based nano lubricants. This approach has been based on taking photographs of the nano lubricant samples at regular time intervals to assess their dispersion stability and the behavior of the nanoparticles in the suspension as a function of time. For this experiment, the graphene-cellulose nano lubricants were prepared and housed in transparent test tubes. Extensive effort was made to ensure that external disturbances (e.g., footsteps, vibrational disturbances, influx of air at different temperatures) were minimized during the stage when the samples were left undisturbed. To observe the stability and sedimentation states, samples were monitored visually and documented photographically over 5 weeks. The dispersion of the nano lubricants at the end of the first week was, in great part, homogeneous and no sedimentation was observed at the bottom of the test tubes. This initial stage is presented in Figure 8 for the nano lubricants. The results is compared to the baseline 10w40 to show the advantages and synergistic mechanism of the composite nanoscale additive. The homogeneous distribution of the graphene-cellulose nanoparticles suggests that the nanoparticles were successfully stabilized by the base fluid to avoid fast aggregation or sedimentation (Dimic-Misic et al., 2021). The initial stability is an important feature since it indicates the effectiveness of surfactants or dispersants used to formulate the nano lubricants (Ashraf et al., 2022). At the end of the 5-week observation period, slight graphene-cellulose nanoparticles were noted at the bottom of the test tubes, as presented in Figure 9. The measured sedimentation was low, suggesting that nano lubricants maintained relatively high stability during this period (Sethurajaperumal et al., 2024).
These findings underscore the potential of graphene-cellulose composites to retain suspension over long periods due to synergistic interactions and the unique properties of the cellulose matrix, which could improve the downstream dispersion of graphene nanoparticles (Tiong et al., 2023). Just minimal sedimentation after 5 weeks indicates that the nano lubricant formation counteracts nanoparticle aggregation. These characteristics pave the way for excellent stability due to the physical and chemical properties of graphene and cellulose (Trache et al., 2020c). With extremely high surface area and functional groups, graphene plays a role in steric stabilization, while cellulose, a natural polymer, provides steric and electrostatic repulsion to prevent the nanoparticles from agglomerating and sedimentation in the system (Li et al., 2021). Compared to conventional nanofluids, graphene-based nano lubricants exhibited superior suspension stability, consistent with the stability results reported earlier in (Le Ba et al., 2020; Dhanola and Gajrani, 2023; Ilyas et al., 2021; Samylingam et al., 2024b). This sedimentation at 5 weeks is a natural process observed in all colloids, including nanoparticles, due to the force of gravity which acts in the opposite direction to the Brownian motion, causing the particles to settle to the bottom (Kadirgama et al., 2021). Despite the limited sedimentation assessed here, it sustains the potential of graphene-cellulose composites for long-lasting usage in lubrication systems as one of the main requisites is stability.
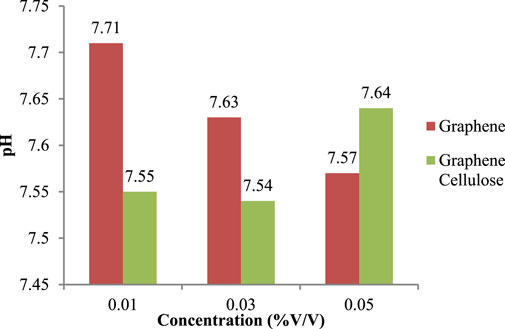
pH trend of the graphene-based and graphene-cellulose nano lubricants with various concentrations of 0.01%, 0.03%, and 0.05% (v/v) are shown in Figure 10. Both nano lubricant formulations seem to show a trend of increasing acid or basic nature with concentration, and, one can see, that both nano lubricant formulations show different behaviors such as chemical stability and dispersion of nanoparticles in base fluid. These data were represented as the pH of graphene nano lubricants in red bars and graphene-cellulose nano lubricants in green bars. At the lowest concentration of 0.01% (v/v), the graphene nano lubricant has a relatively higher pH of 7.71 than graphene-cellulose nano lubricants of 7.55. This indicates that graphene alone is more basic than the other materials at lower concentrations, possibly due to the presence of surface functional groups or interactions with the surrounding medium (Nebol’Sin et al., 2020). In contrast to graphene, which is surface active, cellulosic materials are not surface active, and thus, may neutralize or ameliorate the surface activity of graphene, yielding a lower pH at a lower concentration (Trache et al., 2020c). At the same time, both nano lubricants show a decrease in pH with increasing concentration to 0.03% (v/v). The pH value stands at 7.63 for the graphene nano lubricant, while falls slightly to 7.54 for the graphene-cellulose nano lubricant. This trend means that the trend of the attracted or affinity will occur more at higher concentrations as the interactions between the nanoparticles become stronger and will lower the pH (Abarca-Cabrera et al., 2021). Such behavior may be due to the stacking of the graphene sheets together or the microstructures that “reengineer” the chemical properties of the dispersion.
At 0.03% (v/v) concentration, the decrease in pH is only slight for graphene-cellulose, which showcases the capacity of cellulose to yield near-neutral conditions even in this situation, emphasizing its ability to serve as a stabilizer in nano lubricant formulations. In particular, at the maximum concentration of 0.05% (v/v), the pH of the graphene nano lubricant increases slightly up to 7.57, while the pH of the graphene-cellulose nano lubricant is 7.64, which is significantly increased. The trend reversal observed in graphene-cellulose nano lubricants in concentrated forms indicates a potential role played by cellulose in enhancing the stability and homogeneity of the nano lubricant (Hisham et al., 2024). Graphene interacts with cellulose molecules, which may inhibit the clustering of nanoparticles to ensure more homogenous dissemination along with an alkaline environment. In addition, at this concentration, the increased pH values indicate improved compatibility of graphene-cellulose nano lubricants with the base fluid, thus it can be used in applications that require chemical stability (Oprea and Voicu, 2020). Upon critical analysis of these findings, the superiority of graphene-cellulose nano lubricants compared to pure graphene nano lubricants based on pH stability over diverse concentrations is evident. Such pH changes at low concentration levels could present problems for the long-term stability of graphene nano lubricants, affecting sedimentation properties or performance (Dhanola and Gajrani, 2023).
3.1 Thermal conductivity
The figures compare the coefficients of thermal conductivity for graphene and graphene-cellulose nano lubricants in three concentrations (0.01%, 0.03%, and 0.05% v/v). Figures 11, 12 represent data for pure graphene nano lubricants and graphene-cellulose nano lubricants respectively. Overall, the behavior of both formulations is concentration-dependent, though critical differences arise between the thermal performance of the two types of formulation. The graphene and graphene-cellulose also exhibited high thermal conductivity coefficients at the lowest concentration (0.01% v/v) approximately 0.11 W/m·K and approximately 0.10 W/m·K respectively, which implied that at lower concentrations the high intrinsic thermal conductivity of graphene dominated the performance with little external agents interference, such as cellulose (Ma et al., 2021). Nevertheless, both systems display a marked drop in thermal conductivity at 0.03% v/v, suggesting aggregation or diminished colloidal stability of the particles (Grasberger et al., 2024).
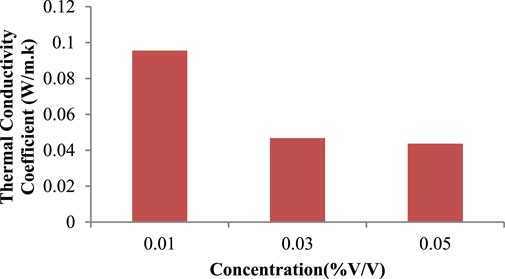
Figure 11. Thermal conductivity of 10W-40 engine oil with different concentrations of graphene graph.
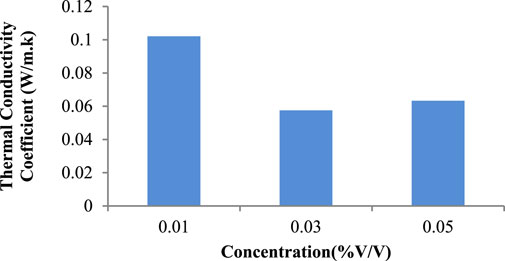
Figure 12. Thermal conductivity of 10W-40 engine oil with different concentrations of graphene cellulose graph.
The thermal conductivities of graphene decrease steeply to 0.06 W/m·K, while the thermal conductivities of graphene-cellulose remain stable at 0.07 W/m·K indicating that cellulose played a critical role, preventing the agglomeration of graphene nanoparticles possibly through steric hindrance and better dispersion of nanoparticles (Chanda and Bajwa, 2021; Aramfard et al., 2022). The stabilizing effect of cellulose appeared more potent at higher concentrations, suggesting that this polymer may serve as an effective dispersion aid in nano lubricant formulations (Liu et al., 2022). At higher concentrations (0.05% v/v), the performance of the graphene-cellulose nano lubricants also exceeds that of pure graphene, obtaining a thermal conductance coefficient of 0.08 W/m·K, compared to the 0.07 W/m·K of the same standalone material, indicating that cellulose significantly improves the performance of the thermal transport pathways via a more homogeneous dispersion even at increased particle load (Li et al., 2024). On the other hand, the graphene nano lubricant may be experiencing over-clustering of nanoparticles at this concentration, so the excellent intrinsic properties of graphene exceed the advantages derived from the high thermal conductivity of the nano lubricant (Marlinda et al., 2023; Samykano et al., 2021). As graphene concentration increases, despite the superior thermal properties of graphene at low concentrations, its propensity to self-aggregate becomes increasingly detrimental to its thermal performance. Conversely, graphene-cellulose nano lubricants exhibit more uniform and beneficial thermal performance in all concentrations, bolstering the benefit of hybrid formulations (Wambu and Huang, 2024). This balanceis especially important for industrial applications where consistent thermal conductivity is required for functional heat transfer.
3.2 Viscosity
Focusing on the flow characteristics, the dynamic viscosity profiles of graphene and graphene−cellulose nano lubricants are compared in the two figures at concentrations of 0.01%, 0.03%, and 0.05% v/v, thus providing crucial information regarding their flow properties at successive nanoparticle fractions. Figure 13 is hydrogenated graphene nano lubricants], and Figure 14 is graphene-cellulose nano lubricants. For graphene nano lubricants, the dynamic viscosity is highest at 0.01% concentration (0.5557 cP), reduces drastically (0.5143 cP) at 0.03%, before increasing sharply (0.5643 cP) at 0.05%. This non-linear trend means that at lower concentrations, graphene nanoparticles are well-dispersed, which is likely to enhance or contribute to the viscosity increment. Yet at 0.03% aggregation is likely to take place which will weaken the effective particle-fluid interaction causing lower viscosity. At 0.05%, the increased viscosity was likely due to enhanced particle-particle interactions or the formation of a network that restricts the flow of the fluid. This behavior illustrates graphene’s tendency to agglomerate or form clusters under specific conditions that can influence the flow dynamics (Zeinedini and Shokrieh, 2024). The graphene-cellulose nano lubricants, on the other hand, show a more uniform trend of dynamic viscosity.
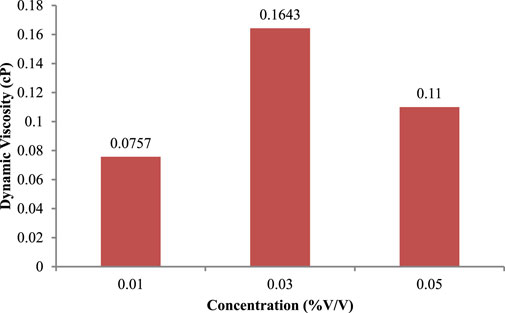
Figure 13. Average dynamic viscosity of engine oil 10W-40 with different concentrations of graphene.
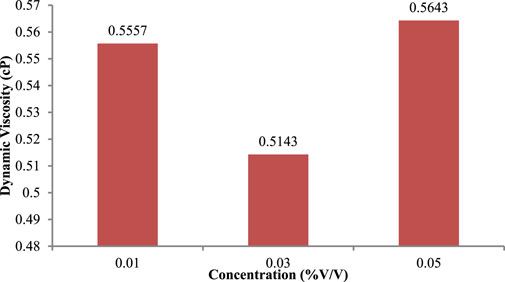
Figure 14. Average dynamic viscosity of engine oil 10W-40 with different concentrations of graphene cellulose.
From 0.01% it was 0.0757 cP, going one point higher, 0.03% it was 0.1643 cP, and one point lower 0.05% viscosity at this point was already low, only 0.11 cP. This behavior illustrates the stabilizing role of cellulose in the dispersion. At a cellulose concentration of 0.03%, cellulose probably helps particle stabilization to increase viscosity due to the interaction of more nanoparticles with the fluid (Guo et al., 2023). Interestingly, the viscosity declines sharply up to 0.05% and the reduction is significant with just 0.05% indicating that this is the ideal quantity for cellulose to prevent the particle clustering while still ensuring less networks thus basal solution viscosities (Li et al., 2021; Ramachandran et al., 2018). At 0.01% and 0.05% concentrations, the graphene nano lubricants exhibited greater viscosity values than the graphene-cellulose formulations, but the opposite trend is shown for the 0.03% concentration (graphene-cellulose formulations exhibited higher viscosity). This reversal effect suggests a key role of cellulose in controlling the rheological properties of the nano lubricant. Cellulose not only stabilizes the nanoparticles but also can reduce aggregation of nanoparticles as well and thereby provide a more uniform interaction between the fluid and the particles (Li et al., 2021). This stability also becomes more apparent at 0.03%, when comparing effective viscosity enhancement of the composites, with graphene-cellulose proving far superior to graphene. In the practical approach, the 0.03% graphene-cellulose nano lubricants show a higher viscosity compared to where viscosity is a function of lubrication, and if the lubricant has high viscosity and the surface of the wear of the sample shows, better lubrication properties and load-carrying capacity (Wang et al., 2022). On the other hand, the non-linear trend of graphene nano lubricants may restrict its application in the field of stable and predictable viscosity behavior.
3.3 ANOVA analysis for COF
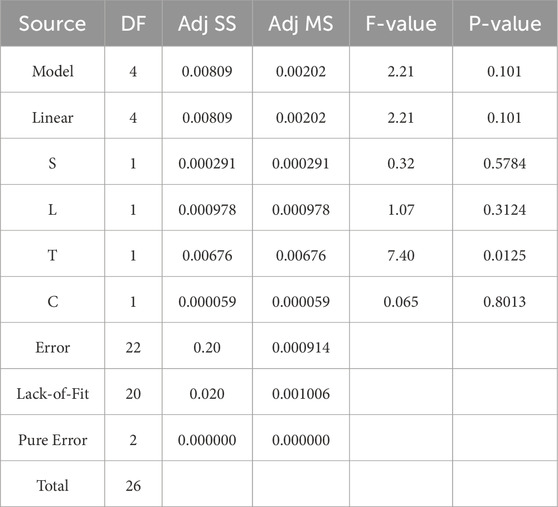
Statistical tools including Fisher’s F-test, probability (P-value), and the coefficient of determination (R-squared) were used to determine the adequacy and importance of a fitted model, which can be developed by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Response model was analyzed using variance analysis (ANOVA). The statistical data for the coefficient of friction (COF) of graphene-cellulose nano lubricants by a linear model is presented in Table 2. Key statistical indicators can be useful for confirming the validity of a model to predict thermal conductivity or other outputs such as COF. In the case of one-way ANOVA, the F-value greater than 1 and P-value less than 0.05 are important factors that indicate the goodness of fit of the model. The F-test results show that the required statistical levels of accuracy and reliability are achieved in this study. That high F-value means the variance attributed to the model is much greater than the variance associated with random noise, and that a P-value below 0.05 asserts that the observed effects have statistical significance.
In addition, the coefficient of determination R-squared (R2) and adjusted R-squared R2-adj were employed to assess the goodness of fit for the model. The results for the graphene-cellulose nano lubricant were an R2 value of 0.2869 and R2-adj of 0.1572 (cf. Tab. 4.19). R2 indicates the fraction of the variance in the response variable (COF) that can be explained by the input parameters (load, speed, temperature, and concentration) in our model. On the other hand, the adjusted R2, adjusts R2 for the number of predictors in the model and is more reliable in the case of multiple variable models (Sharma et al., 2021). Generally speaking, both the R2 as well as the R2-adj values which are assessed in this study do not prove to be excessively high. However, their proximity to each other speaks to a relatively good degree of reliability in terms of the predictive capacity of the model. It is also important to note the relatively low value of R2 = 0.2869 which indicates the fact the model used is insufficient to describe the whole system or that other important system variables have not been included in the analysis (Yang et al., 2024). The small difference between R2 and R2-adj indicates that the model is not overfitting, and it is a reasonable approximation of the relationship between input and output variables. This consistency suggests it may be a sufficiently robust model to be used for predicting future COF results, although the accuracy of the model can be improved.
Overall, a model should have both a high R2 and R2-adj to exhibit strong predictive capability. Nevertheless, the results of this study show that the RSM model can be used and is reliable to predict COF concerning nano lubricants based on graphene-cellulose. In the future, similar work can extend to cover multiple other variables or use a non-linear model to improve accuracy and explanatory power.
4 Conclusion
The thermal conductivity value reflects the amount of heat energy transferred across a temperature gradient, with higher thermal conductivity indicating more efficient energy transfer. Based on experimental data and calculations, the thermal conductivity of graphene-cellulose nano lubricant is lower than that of graphene nano lubricant. This indicates that graphene-cellulose nano lubricant has inferior heat transfer capabilities compared to other nano lubricants. Dynamic viscosity, which measures a fluid’s internal resistance to flow under an applied force, generates friction and heat. A higher dynamic viscosity results in increased heat production. The dynamic viscosity of graphene-cellulose nano lubricant is higher than that of graphene nano lubricant, suggesting it produces more heat when used as a lubricant. The tribological performance of graphene-cellulose nano lubricant was optimized using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Under optimal conditions, the coefficient of friction (COF) achieved the highest desirability with a recorded value of 0.0778.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JA: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AE: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. KK: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LS: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. NA: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. CK: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. DR: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. WH: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AV: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SS: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. BY: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The author would like to thank Universiti Malaysia Pahang Al-Sultan Abdullah for providing financial support under grant no. UIC230821 and RDU232409.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Universiti Malaysia Pahang Al-Sultan Abdullah for providing financial support under grant no. UIC230821 and RDU232409.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abarca-Cabrera, L., Fraga-García, P., and Berensmeier, S. (2021). Bio-nano interactions: binding proteins, polysaccharides, lipids and nucleic acids onto magnetic nanoparticles. Biomater. Res. 25 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s40824-021-00212-y
Achaw, O.-W., and Danso-Boateng, E. (2021). Chemical and process industries. Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Agius Anastasi, A. (2021). Nanoindentation of Graphene Membranes Using Atomic Force Microscopy and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, PhD Dissertation, University of Malta.
Ahmed, F., Khanam, A., Samylingam, L., Aslfattahi, N., and Saidur, R. (2022). Assessment of thermo-hydraulic performance of MXene-based nanofluid as coolant in a dimpled channel: a numerical approach. J. Therm. Analysis Calorim. 147 (22), 12669–12692. doi:10.1007/s10973-022-11376-7
Ajimotokan, H. A. (2024). “Lubricants and materials for tribological applications,” in Principles and applications of tribology (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 47–72.
Akbi, H., Rafai, S., Mekki, A., Touidjine, S., and Hamouche, M. A. (2024). Correlating heat treatment conditions with the physicochemical properties of thermally reduced graphene oxide-based materials: a comprehensive review. Univ. J. Carbon Res. 2, 1–43. doi:10.37256/2220244853
Amjad, A., Anjang Ab Rahman, A., Awais, H., Zainol Abidin, M. S., and Khan, J. (2022). A review investigating the influence of nanofiller addition on the mechanical, thermal and water absorption properties of cellulosic fibre reinforced polymer composite. J. Indust. Text. 51 (1_Suppl. l), 65S–100S. doi:10.1177/15280837211057580
Aramfard, M., Kaynan, O., Hosseini, E., Zakertabrizi, M., Pérez, L. M., and Asadi, A. (2022). Aqueous dispersion of carbon nanomaterials with cellulose nanocrystals: an investigation of molecular interactions. Small 18 (37), 2202216. doi:10.1002/smll.202202216
Ashraf, A., Shafi, W. K., Ul Haq, M. I., and Raina, A. (2022). Dispersion stability of nano additives in lubricating oils–an overview of mechanisms, theories and methodologies. Tribol. Mater., Surf. Interf. 16 (1), 34–56. doi:10.1080/17515831.2021.1981720
Cahangirov, S., Sahin, H., Le Lay, G., and Rubio, A. (2016). Introduction to the physics of silicene and other 2D materials, 930. Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Chanda, S., and Bajwa, D. S. (2021). A review of current physical techniques for dispersion of cellulose nanomaterials in polymer matrices. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 60 (1), 325–341. doi:10.1515/rams-2021-0023
Chen, Y., Jha, S., Raut, A., Zhang, W., and Liang, H. (2020). Performance characteristics of lubricants in electric and hybrid vehicles: a review of current and future needs. Front. Mech. Eng. 6, 571464. doi:10.3389/fmech.2020.571464
Choudhary, N., Singh, S., Bhardwaj, S., Gupta, S., Nandi, U., Chandra, R., et al. (2023). Recent advancements in nanocellulose-based supercapacitors for energy storage devices: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 7, 100416. doi:10.1016/j.carpta.2023.100416
de Castro, C. S. C., do Espírito Santo Filho, D. M., Siqueira, J. R. R., Barbosa, A. P. F., da Costa Rodrigues, C. R., Cabral, M. L., et al. (2016). Evaluation of the metrological performance of two kinds of rotational viscometers by means of viscosity reference materials. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 138, 292–297. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2015.12.003
Dhanola, A., and Gajrani, K. K. (2023). Novel insights into graphene-based sustainable liquid lubricant additives: a comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 386, 122523. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2023.122523
Dimic-Misic, K., Buffiere, J., Imani, M., Nieminen, K., Sixta, H., and Gane, P. (2021). Improved stabilisation of graphite nanoflake dispersions using hydrothermally-produced nanocellulose. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 610, 125668. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125668
Fu, H., Yan, G., Li, M., Wang, H., Chen, Y., Yan, C., et al. (2019). Graphene as a nanofiller for enhancing the tribological properties and thermal conductivity of base grease. RSC Adv. 9 (72), 42481–42488. doi:10.1039/c9ra09201c
Gonaygunta, H., Meduri, S. S., Podicheti, S., and Nadella, G. S. (2023). The impact of virtual reality on social interaction and relationship via statistical analysis. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Sustain. Dev. 5 (2), 1–20.
Grasberger, K. F., Lund, F. W., Simonsen, A. C., Hammershøj, M., Fischer, P., and Corredig, M. (2024). Role of the pea protein aggregation state on their interfacial properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 658, 156–166. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2023.12.068
Guo, D., Yuan, T., Sun, Q., Yan, Z., Kong, Z., Zhong, L., et al. (2023). Cellulose nanofibrils as rheology modifier and fluid loss additive in water-based drilling fluids: rheological properties, rheological modeling, and filtration mechanisms. Indust. Crops Prod. 193, 116253. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116253
Heise, K., Kontturi, E., Allahverdiyeva, Y., Tammelin, T., Linder, M. B., Ikkala, O., et al. (2021). Nanocellulose: recent fundamental advances and emerging biological and biomimicking applications. Adv. Mater. 33 (3), 2004349. doi:10.1002/adma.202004349
Hisham, S., Kadirgama, K., Alotaibi, J. G., Alajmi, A. E., Ramasamy, D., Sazali, N., et al. (2024). Enhancing stability and tribological applications using hybrid nanocellulose-copper (II) oxide (CNC-CuO) nanolubricant: an approach towards environmental sustainability. Tribol. Int. 194, 109506. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2024.109506
Hu, Z., and Lu, X. (2014). “Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes and graphene,” in Carbon nanotubes and graphene (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 165–200.
Ilyas, S. U., Ridha, S., Sardar, S., Estellé, P., Kumar, A., and Pendyala, R. (2021). Rheological behavior of stabilized diamond-graphene nanoplatelets hybrid nanosuspensions in mineral oil. J. Mol. Liq. 328, 115509. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115509
Jayalakshmy, M., and Mishra, R. K. (2019). “Applications of carbon-based nanofiller-incorporated rubber composites in the fields of tire engineering, flexible electronics and EMI shielding,” in Carbon-based nanofillers and their rubber nanocomposites (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 441–472.
Kabir, M. E., Saha, M., and Jeelani, S. (2007). Effect of ultrasound sonication in carbon nanofibers/polyurethane foam composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 459 (1-2), 111–116. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2007.01.031
Kadirgama, G. (2022). Graphene nanoplatelets–cellulose nanocrystals in engine oil for automotive applications. Green Mater. 11 87–95. doi:10.1680/jgrma.21.00061
Kadirgama, K., Anamalai, K., Ramachandran, K., Ramasamy, D., Samykano, M., Kottasamy, A., et al. (2018). Thermal analysis of SUS 304 stainless steel using ethylene glycol/nanocellulose-based nanofluid coolant. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97, 2061–2076. doi:10.1007/s00170-018-2061-3
Kadirgama, K., Noor, M., and Rahman, M. (2012). Optimization of surface roughness in end milling using potential support vector machine. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 37, 2269–2275. doi:10.1007/s13369-012-0314-2
Kadirgama, K., Noor, M. M., Rahman, M. M., Rejab, M. R. M., Haron, C. H. C., and Abou-El-Hossein, K. A. (2009). Surface roughness prediction model of 6061-T6 aluminium alloy machining using statistical method. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 25 (2), 250–256.
Kadirgama, K., Samylingam, L., Aslfattahi, N., Samykano, M., Ramasamy, D., and Saidur, R. (2021). “Experimental investigation on the optical and stability of aqueous ethylene glycol/mxene as a promising nanofluid for solar energy harvesting,” in IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (IOP Publishing).
Kargarzadeh, H., Ahmad, I., Thomas, S., and Dufresne, A. (2017). Handbook of nanocellulose and cellulose nanocomposites. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons.
Le Ba, T., Mahian, O., Wongwises, S., and Szilágyi, I. M. (2020). Review on the recent progress in the preparation and stability of graphene-based nanofluids. J. Therm. Analysis Calorim. 142, 1145–1172. doi:10.1007/s10973-020-09365-9
Lee, C., Wei, X., Kysar, J. W., and Hone, J. (2008). Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321 (5887), 385–388. doi:10.1126/science.1157996
Li, M., Wang, F., Ouyang, S., Liu, Y., Hu, Z., Wu, Y., et al. (2024). A comprehensive review on preparation and functional application of the wood aerogel with natural cellulose framework. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 275, 133340. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133340
Li, M. C., Wu, Q., Moon, R. J., Hubbe, M. A., and Bortner, M. J. (2021). Rheological aspects of cellulose nanomaterials: governing factors and emerging applications. Adv. Mater. 33 (21), 2006052. doi:10.1002/adma.202006052
Li, Y., Zhu, J., Wei, S., Ryu, J., Sun, L., and Guo, Z. (2011). Poly (propylene)/graphene nanoplatelet nanocomposites: melt rheological behavior and thermal, electrical, and electronic properties. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 212 (18), 1951–1959. doi:10.1002/macp.201100263
Lim, C. T. (2017). Nanofiber technology: current status and emerging developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 70, 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.03.002
Liu, Z., Zhu, G., Dai, J., Zhu, Y., and Lin, N. (2022). Cellulose nanocrystals as sustainable additives in water-based cutting fluids. Carbohydr. Polym. 298, 120139. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120139
Low, Z. L., Low, D. Y. S., Tang, S. Y., Manickam, S., Tan, K. W., Ban, Z. H., et al. (2022). Ultrasonic cavitation: an effective cleaner and greener intensification technology in the extraction and surface modification of nanocellulose. Ultrason. Sonochem. 90, 106176. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106176
Lu, Y., He, Q., Fan, G., Cheng, Q., and Song, G. (2021). Extraction and modification of hemicellulose from lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Green Process. Synthesis 10 (1), 779–804. doi:10.1515/gps-2021-0065
Ma, H., Gao, B., Wang, M., Yuan, Z., Shen, J., Zhao, J., et al. (2021). Strategies for enhancing thermal conductivity of polymer-based thermal interface materials: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 1064–1086. doi:10.1007/s10853-020-05279-x
Manu, B. R., Gupta, A., and Jayatissa, A. H. (2021). Tribological properties of 2D materials and composites—a review of recent advances. Materials 14 (7), 1630. doi:10.3390/ma14071630
Marlinda, A. R., Thien, G. S. H., Shahid, M., Ling, T. Y., Hashem, A., Chan, K.-Y., et al. (2023). Graphene as a lubricant additive for reducing friction and wear in its liquid-based form. Lubricants 11 (1), 29. doi:10.3390/lubricants11010029
Mittal, H., Ray, S. S., Kaith, B. S., Bhatia, J. K., Sharma, J., Alhassan, S. M., et al. (2018). Recent progress in the structural modification of chitosan for applications in diversified biomedical fields. Eur. Polym. J. 109, 402–434. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.10.013
Nallusamy, S. (2016). “Thermal conductivity analysis and characterization of copper oxide nanofluids through different techniques,” in Journal of Nano Research 40, 105–112.
Nebol’Sin, V., Galstyan, V., and Silina, Y. (2020). Graphene oxide and its chemical nature: multi-stage interactions between the oxygen and graphene. Surfaces Interfaces 21, 100763. doi:10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100763
Norizan, M. N., Shazleen, S. S., Alias, A. H., Sabaruddin, F. A., Asyraf, M. R. M., Zainudin, E. S., et al. (2022). Nanocellulose-based nanocomposites for sustainable applications: a review. Nanomaterials 12 (19), 3483. doi:10.3390/nano12193483
Novoselov, K. S., Geim, A. K., Morozov, S. V., Dubonos, S. V., Zhang, Y., and Jiang, D., (2004). Room-temperature electric field effect and carrier-type inversion in graphene films. arXiv. arXiv preprint cond-mat/0410631.
Oprea, M., and Voicu, S. I. (2020). Cellulose composites with graphene for tissue engineering applications. Materials 13 (23), 5347. doi:10.3390/ma13235347
Ouyang, J.-H., Li, Y.-F., Zhang, Y.-Z., Wang, Y.-M., and Wang, Y.-J. (2022). High-temperature solid lubricants and self-lubricating composites: a critical review. Lubricants 10 (8), 177. doi:10.3390/lubricants10080177
Pei, S., and Cheng, H.-M. (2012). The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 50 (9), 3210–3228. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2011.11.010
Popa, V. I. (2018). “Biomass for fuels and biomaterials,” in Biomass as renewable raw material to obtain bioproducts of high-tech value (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 1–37.
Pradhan, D., Jaiswal, A. K., and Jaiswal, S. (2022). Emerging technologies for the production of nanocellulose from lignocellulosic biomass. Carbohydr. Polym. 285, 119258. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119258
Prashanth, G., Gadewar, M., Lalithamba, H., Rao, S., Rashmi, K., Yatish, K., et al. (2024). Synthesis, and applications of carbon-integrated polymer composites and foams: a concise review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 166, 112614. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2024.112614
Rai, V. K., Mahata, S., Kashyap, H., Singh, M., and Rai, A. (2020). Bio-reduction of graphene oxide: catalytic applications of (reduced) GO in organic synthesis. Curr. Org. Synth. 17 (3), 164–191. doi:10.2174/1570179417666200115110403
Ramachandran, K., Kadirgama, K., Ramasamy, D., Samykano, M., Samylingam, L., Tarlochan, F., et al. (2018). Evaluation of specific heat capacity and density for cellulose nanocrystal-based nanofluid. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 51 (2), 169–186.
Ranjbartoreh, A. R., Wang, B., Shen, X., and Wang, G. (2011). Advanced mechanical properties of graphene paper. J. Appl. Phys. 109 (1). doi:10.1063/1.3528213
Rasheed, A., Khalid, M., Javeed, A., Rashmi, W., Gupta, T., and Chan, A. (2016). Heat transfer and tribological performance of graphene nanolubricant in an internal combustion engine. Tribol. Int. 103, 504–515. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2016.08.007
Ray, U. (2023). Mechanics and thermal transport modeling in nanocellulose and cellulose-based materials. College Park: University of Maryland.
Sakinah, M., Amirruddin, A., Kadirgama, K., Ramasamy, D., Rahman, M., and Noor, M. (2016). The application of response surface methodology in the investigation of the tribological behavior of palm cooking oil blended in engine oil. Adv. Tribol. 2016 (1), 1–11. doi:10.1155/2016/6545904
Salem, K. S., Kasera, N. K., Rahman, M. A., Jameel, H., Habibi, Y., Eichhorn, S. J., et al. (2023). Comparison and assessment of methods for cellulose crystallinity determination. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 6417–6446. doi:10.1039/d2cs00569g
Samykano, M., Kananathan, J., Kadirgama, K., Amirruddin, A., Ramasamy, D., and Samylingam, L. (2021). Characterisation, performance and optimisation of nanocellulose metalworking fluid (MWF) for green machining process. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 18 (4), 9188–9207. doi:10.15282/ijame.18.4.2021.04.0707
Samylingam, L., Aslfattahi, N., Kok, C. K., Kadirgama, K., Sazali, N., Liew, K. W., et al. (2024a). Enhancing lubrication efficiency and wear resistance in mechanical systems through the application of nanofluids: a comprehensive review. J. Adv. Res. Micro Nano Eng. 16 (1), 1–18. doi:10.37934/armne.16.1.118
Samylingam, L., Aslfattahi, N., Kok, C. K., Kadirgama, K., Sazali, N., Schmirler, M., et al. (2024b). Green engineering with nanofluids: elevating energy efficiency and sustainability. J. Adv. Res. Micro Nano Eng. 16 (1), 19–34. doi:10.37934/armne.16.1.1934
Sandanamsamy, L., Harun, W., Ishak, I., Romlay, F., Kadirgama, K., Ramasamy, D., et al. (2023). A comprehensive review on fused deposition modelling of polylactic acid. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 8 (5), 775–799. doi:10.1007/s40964-022-00356-w
Sethurajaperumal, A., Srivastava, S., Ganesh, G., Sundara, R., and Varrla, E. (2024). Natural surfactant stabilized aqueous MoS2 nano-lubricants for reducing friction and wear. Chem. Eng. J. 496, 154080. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.154080
Sharma, P. N., Shmueli, G., Sarstedt, M., Danks, N., and Ray, S. (2021). Prediction-oriented model selection in partial least squares path modeling. Decis. Sci. 52 (3), 567–607. doi:10.1111/deci.12329
Shrestha, S. (2019). Effect of nanocellulose reinforcement on the properties of polymer composites. West Lafayette, IN: Purdue University.
Singh, R. K., Kumar, R., and Singh, D. P. (2016). Graphene oxide: strategies for synthesis, reduction and frontier applications. Rsc Adv. 6 (69), 64993–65011. doi:10.1039/c6ra07626b
Smith, A. T., LaChance, A. M., Zeng, S., Liu, B., and Sun, L. (2019). Synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide and their nanocomposites. Nano Mater. Sci. 1 (1), 31–47. doi:10.1016/j.nanoms.2019.02.004
Solhi, L., Guccini, V., Heise, K., Solala, I., Niinivaara, E., Xu, W., et al. (2023). Understanding nanocellulose–water interactions: turning a detriment into an asset. Chem. Rev. 123 (5), 1925–2015. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00611
Srivastava, N., Shrivastav, A., Singh, R., Abohashrh, M., Srivastava, K., Irfan, S., et al. (2021). Advances in the structural composition of biomass: fundamental and bioenergy applications. J. Renew. Mater. 9 (4), 615–636. doi:10.32604/jrm.2021.014374
Sundararaman, R., Vigil-Fowler, D., and Schwarz, K. (2022). Improving the accuracy of atomistic simulations of the electrochemical interface. Chem. Rev. 122 (12), 10651–10674. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00800
Tan, K., Samylingam, L., Aslfattahi, N., Johan, M. R., and Saidur, R. (2022). Investigation of improved optical and conductivity properties of poly (methyl methacrylate)–MXenes (PMMA–MXenes) nanocomposite thin films for optoelectronic applications. Open Chem. 20 (1), 1416–1431. doi:10.1515/chem-2022-0221
Tardy, B. L., Mattos, B. D., Otoni, C. G., Beaumont, M., Majoinen, J., Kämäräinen, T., et al. (2021). Deconstruction and reassembly of renewable polymers and biocolloids into next generation structured materials. Chem. Rev. 121 (22), 14088–14188. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01333
Thakre, K. G., Barai, D. P., and Bhanvase, B. A. (2021). A review of graphene-TiO2 and graphene-ZnO nanocomposite photocatalysts for wastewater treatment. Water Environ. Res. 93 (11), 2414–2460. doi:10.1002/wer.1623
Thomas, B., Raj, M. C., Joy, J., Moores, A., Drisko, G. L., Sanchez, C., et al. (2018). Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications. Chem. Rev. 118 (24), 11575–11625. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00627
Tiong, A. C. Y., Tan, I. S., Foo, H. C. Y., Lam, M. K., Mahmud, H. B., Lee, K. T., et al. (2023). Study on the synergism of cellulose nanocrystals and janus graphene oxide for enhanced oil recovery. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 221, 111242. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2022.111242
Trache, D., Tarchoun, A. F., Derradji, M., Hamidon, T. S., Masruchin, N., Brosse, N., et al. (2020b). Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced applications. Front. Chem. 8, 392. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00392
Trache, D., Tarchoun, A. F., Derradji, M., Mehelli, O., Hussin, M. H., and Bessa, W. (2020a). “Cellulose fibers and nanocrystals: preparation, characterization, and surface modification,” in Functionalized nanomaterials I (CRC Press), 171–190.
Trache, D., Thakur, V. K., and Boukherroub, R. (2020c). Cellulose nanocrystals/graphene hybrids—a promising new class of materials for advanced applications. Nanomaterials 10 (8), 1523. doi:10.3390/nano10081523
Wambu, E. W., and Huang, J. (2024). Chemistry of Graphene: Synthesis, Reactivity, Applications and Toxicities. BoD–Books on Demand.
Wang, Y., Azam, A., Zhang, G., Dorgham, A., Liu, Y., Wilson, M. C., et al. (2022). Understanding the mechanism of load-carrying capacity between parallel rough surfaces through a deterministic mixed lubrication model. Lubricants 10 (1), 12. doi:10.3390/lubricants10010012
Williams, G., Seger, B., and Kamat, P. V. (2008). TiO2-graphene nanocomposites. UV-assisted photocatalytic reduction of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2 (7), 1487–1491. doi:10.1021/nn800251f
Xiao, N., Chen, Y., Lin, H., Zhang, F., and Yang, K. (2022). Multidimensional nanoadditives in tribology. Appl. Mater. Today 29, 101641. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101641
Xiao, W., Sun, R., Hu, S., Meng, C., Xie, B., Yi, M., et al. (2023). Recent advances and future perspective on lignocellulose-based materials as adsorbents in diverse water treatment applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 253, 126984. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126984
Xue, Y., Mou, Z., and Xiao, H. (2017). Nanocellulose as a sustainable biomass material: structure, properties, present status and future prospects in biomedical applications. Nanoscale 9 (39), 14758–14781. doi:10.1039/c7nr04994c
Yang, H., Sun, Z., Han, P., and Ma, M. (2024). Data-driven prediction of ship fuel oil consumption based on machine learning models considering meteorological factors. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 238 (3), 483–502. doi:10.1177/14750902231210047
Yu, Y., Shen, M., Song, Q., and Xie, J. (2018). Biological activities and pharmaceutical applications of polysaccharide from natural resources: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 183, 91–101. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.009
Zeinedini, A., and Shokrieh, M. M. (2024). Agglomeration phenomenon in graphene/polymer nanocomposites: reasons, roles, and remedies. Appl. Phys. Rev. 11 (4). doi:10.1063/5.0223785
Keywords: tribology, graphene, nanocellulose, engine oil, thermophysical properties
Citation: Alotaibi JG, Eid Alajmi A, Kadirgama K, Samylingam L, Aslfattahi N, Kok CK, Ramasamy D, Harun WSW, Veerendra AS, Sivaraos S and Yousif BF (2025) Enhancing engine oil performance with graphene-cellulose nanoparticles: insights into thermophysical properties and tribological behavior. Front. Mater. 12:1549117. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1549117
Received: 20 December 2024; Accepted: 15 April 2025;
Published: 06 May 2025.
Edited by:
Mauro Zarrelli, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyReviewed by:
Claudia Cirillo, University of Salerno, ItalySathickbasha K, B. S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science And Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Alotaibi, Eid Alajmi, Kadirgama, Samylingam, Aslfattahi, Kok, Ramasamy, Harun, Veerendra, Sivaraos and Yousif. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: L. Samylingam, bGluZ2VudGhpcmFuQG1tdS5lZHUubXk=; Subramaniam Sivaraos, c2l2YXJhb0B1dGVtLmVkdS5teQ==
 Jasem Ghanem Alotaibi
Jasem Ghanem Alotaibi Ayedh Eid Alajmi1
Ayedh Eid Alajmi1 L. Samylingam
L. Samylingam Navid Aslfattahi
Navid Aslfattahi W. S. W. Harun
W. S. W. Harun A. S. Veerendra
A. S. Veerendra Subramonian Sivaraos
Subramonian Sivaraos Belal F. Yousif
Belal F. Yousif