- 1Institute of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, China
- 2Qingdao Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
Introduction: Root canal therapy (RCT) is the most common treatment for pulpitis or pulp necrosis. However, in immature permanent teeth, loss of pulp vitality hampers root development and apical closure, resulting in thin and fragile dentin walls. Regenerative endodontic treatment (RET) has emerged as a promising approach to restore pulp vitality and promote root maturation. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α), a key chemokine, has shown significant potential in enhancing the migration and odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Methods: To protect the bioactivity of SDF-1α during delivery and achieve controlled release, we fabricated core-shell structured SDF-1α/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres using electrospinning technology. The morphology, release profile, and biocompatibility of the microspheres were characterized, and their effects on hDPSC migration and differentiation were evaluated in vitro.
Results: The core-shell microspheres demonstrated uniform particle size, excellent biocompatibility, and sustained-release behavior. SDF-1α released during the first two weeks significantly promoted the migration of hDPSCs, confirming the preservation of its bioactivity. Furthermore, the microspheres continuously induced the odontogenic and angiogenic differentiation of hDPSCs without requiring repeated administration.
Discussion: These findings suggest that the sustained-release SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres effectively maintain growth factor activity, support long-term therapeutic outcomes, and enhance the efficiency of RET. Their ability to promote hDPSC migration and differentiation positions them as a promising scaffold component for future pulp regeneration applications.
1 Introduction
Root canal therapy (RCT) is the most commonly used clinical treatment for pulpitis or necrosis (Taha et al., 2023), removing infected and necrotic pulp tissue, bacteria, and other harmful agents. In mature permanent teeth, the loss of nutritional support from pulp tissue following RCT can reduce the resistance of the remaining dentin. For immature permanent teeth, the loss of pulp vitality inhibits root development and apical closure, resulting in thin and fragile dentin walls (Krastl et al., 2021). Therefore, numerous studies have focused on regenerative endodontic treatment (RET) to restore tooth vitality and promote root development (Panda et al., 2022).
Dental stem cells, scaffolds, and growth factors are essential components of RET (Li et al., 2023). Stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) has recently been shown to promote odontogenic differentiation in human dental pulp cells (Liu et al., 2021) and plays a crucial role in recruiting, migrating, and differentiating stem/progenitor cells, including hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells (Liu et al., 2014). However, the half-life of SDF-1α in a 37°C aqueous environment is short, and its bioactivity must be protected during drug delivery to be effective. Thus, an appropriate sustained-release carrier is required to enhance the efficacy of bioactive factors. Studies on various properties of scale scaffolds have introduced new directions for the sustained release of bioactive factors (Zhang X. et al., 2023). As a tissue engineering scaffold, poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) provides a three-dimensional space for cell adhesion. It simulates a suitable environment by enhancing cell attachment, contact, and spreading, thereby influencing cellular proliferation and differentiation capabilities (Vahidi et al., 2024). Due to its good biocompatibility and biodegradability, PLGA has been widely studied in tissue engineering. The injectability of PLGA microspheres makes them ideal materials for dentin-pulp complex regeneration (C Silva et al., 2015). PLGA microspheres are currently the most commonly used polymer materials in drug delivery systems, mainly for research on sustained-release drug carriers (Ruan et al., 2022). The coaxial electrospray method enables the one-step fabrication of microspheres loaded with drugs. It offers advantages such as monodispersity, reproducibility, and controllable microsphere size, making it highly promising in controlled drug release. Therefore, we hypothesize that PLGA could be a biocompatible sustained-release scaffold for regenerative endodontic treatment.
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs), as a key source of stem cells for pulp regeneration (Sui et al., 2019), possess strong proliferative capacity and multidirectional differentiation potential (Zhai et al., 2019). Compared to other types of stem cells, DPSCs are more likely to form pulp-like tissues (Siddiqui et al., 2022) and have been widely applied in regenerative medicine. Growth factors are critical signaling molecules that guide stem cells in the process of tissue regeneration. SDF-1α, a member of the CXC chemokine subfamily, plays a crucial role in the recruitment, migration, and differentiation of stem/progenitor cells such as hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells (Ito et al., 2021). SDF-1α has been shown to promote odontogenic differentiation in human dental pulp cells (Li Z. et al., 2021). However, how SDF-1α can exert its effects over an extended period in regenerative endodontic treatment remains unresolved. This study aims to develop PLGA microspheres loaded with SDF-1α and investigate their impact on the proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) in vitro to explore the potential application of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres in pulp regeneration therapy.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
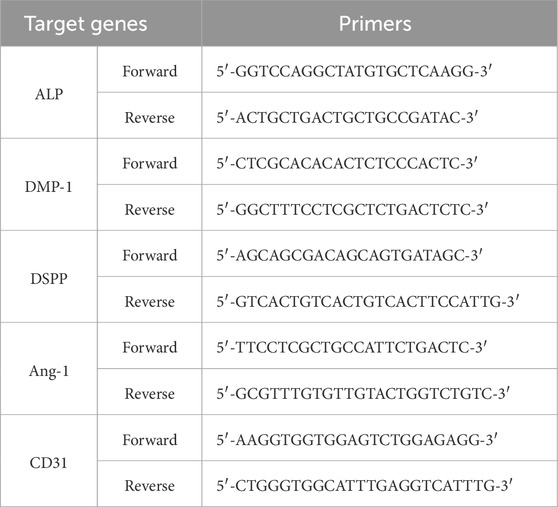
The following reagents were used: PLGA (50:50, Mw: 30000) was purchased from Shenzhen Maiqi Biomaterials Co. Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) was purchased from Shanghai Darui Fine Chemical Co. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) was purchased from PeproTech Co., Ltd. (New Jersey, United States). The ELISA kit was purchased from Wuhan Boster Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). Cell Counting Kit8 (CCK-8) kit was purchased from GLPBIO Co., Ltd. (Montclair, CA, United States). Anti-CD34, anti-CD45, anti-CD90, and anti-CD105 were purchased from Abcam (Shanghai, China). TRIzol kit was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd. (St. Louis, Missouri, United States). SYBR PreMix Ex TaqTMII, PrimeScriptTM RT kits were purchased from Takara Biotech Co., Ltd. (Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan). Primers were designed and synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2 Preparation and characterization of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres
A 4% concentration of PLGA solution was used as the shell solution, and 25, 50, and 100 ng/mL SDF-1α was used as the core solution. The low-loading (L), medium-loading (M), and high-loading (H) groups were prepared, respectively. The flow rates were set to 1 mL/h for the shell and 0.2 mL/h for the core, allowing spray deposition onto aluminum foil to form SDF-1α/PLGA particles. The electrospinning process was conducted at a voltage of 20 kV, with a collecting distance of 15 cm, under ambient conditions of 25°C room temperature and 40% humidity.
The aluminum foil with collected microspheres was cut into 1 cm × 1 cm samples for gold sputtering, and their morphology was observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The diameters of 100 randomly selected microspheres were measured using ImageJ software. Diameter data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 10, and a diameter distribution graph was plotted.
A drop of the microspheres suspension was placed onto a copper grid. After solvent evaporation, the structure of the microspheres was observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) at an operating voltage of 100 kV.
2.3 Drug loading efficiency and encapsulation efficiency
A 20 mg sample of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres lyophilized powder was dissolved in 2 mL of dichloromethane and 5 mL of PBS buffer. The mixture was thoroughly mixed using a vortex shaker to extract SDF-1α into the aqueous phase. The solution was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 20 min to ensure complete separation of the aqueous and organic phases. The SDF-1α concentration in the aqueous phase was determined using an ELISA kit, and the following formulas were used for calculations:
here,
2.4 In vitro release of sustained release microspheres
Fifty milligrams of microspheres from each group (L, M, H) were placed in 5 mL of PBS and incubated in a thermostatic shaker at 37°C with a constant shaking rate of 120 rpm. At specific time points within 15 days, 100 μL of the solution was withdrawn and replaced with 100 μL of fresh PBS. The concentration of SDF-1α in the collected samples was measured using an ELISA kit. The cumulative release rate was calculated, and the cumulative drug release curve was plotted using GraphPad Prism 10.
2.5 Isolation and culture of hDPSCs
Freshly extracted third molars were collected from three patients aged 18 to 23 who underwent extraction due to impacted teeth at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Qingdao Stomatological Hospital. All patients provided informed consent. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Qingdao Stomatological Hospital (2023KQYX039). Informed consent was obtained from all patients and their families, and all procedures were conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. The freshly extracted teeth were split open, and the pulp tissue was carefully removed and cut into small pieces measuring 1.0 mm × 1.0 mm × 1.0 mm. The tissue fragments were evenly distributed at the bottom of culture flasks, followed by the addition of DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin antibiotics. The flasks were initially inverted and placed in a cell incubator. After overnight incubation, the flasks were returned upright, and the culture medium was replaced every 3 days. When the cells growing out from the tissue fragments reached 80%–90% confluency, they were passaged. Cells between passages 3 and 4 were used for subsequent experiments.
2.6 Identification of hDPSCs
Flow cytometry was used to analyze the surface markers CD90, CD105, CD34, and CD45 on the isolated cells. The cell concentration was adjusted to 1 × 107 cells/mL. For each group, 100 μL of the cell suspension was collected and incubated separately with the following antibodies: anti-human CD90, anti-human CD105, anti-human CD34, and anti-human CD45. The cells were incubated in the dark at 4°C for 30 min.
After incubation, the cells were washed and resuspended in an appropriate buffer. The samples were then subjected to flow cytometry analysis to determine the positive expression rates of the surface markers.
2.7 Assessment of microsphere biocompatibility
The L, M, and H groups of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres were sterilized with UV light for 12 h before the preparation of the microspheres suspension. After sterilization, the microspheres were subjected to extraction, centrifugation, and filtration to obtain a sterile extract solution.
Cells were seeded into a 96-well plate at a density of 5 × 103 cells/well. Once cell adhesion was achieved, the culture medium was replaced with the microsphere extract. Cells were cultured for 1, 3, and 5 days. At each time point, the plate was removed from the incubator, and the CCK-8 reagent was added following the manufacturer’s instructions. After a 2-h incubation, the optical density (OD) of each well was measured at 450 nm using an 800TS microplate reader.
Additionally, hDPSCs were co-cultured with SDF-1α at various concentration gradients (0 ng/mL, 25 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL). The OD values were similarly measured on days 1, 3, and 5 to evaluate cell proliferation under different SDF-1α concentrations.
2.8 Determination of core layer solution concentration
Cells were seeded into 6-well plates at a density of 1 × 105 cells per well. Three experimental groups were established. Once the cells reached full confluency, a straight scratch (wound) was created vertically across the bottom of the well using a sterile pipette tip. The cells were washed with PBS to remove any cell debris, and the medium was replaced with serum-free α-MEM to halt cell proliferation and focus on migration.
The cells were incubated for 24 h, after which images of the wound area were captured. The wound healing process was observed by analyzing the scratch images, and the average distance between the edges of the scratch was measured using ImageJ software. The measurements were repeated three times for each group to ensure accuracy and reproducibility.
2.9 Effect of microspheres on the migration of hDPSCs
At the 2-week time point, the supernatants of the three groups (L/M/H) of SDF-1α/PLGA microsphere suspensions at a concentration of 20 mg/mL were collected and used as the lower chamber solution in the Transwell assay. Cells were seeded into the upper chamber of a Transwell insert at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well. The lower chamber was filled with either the microspheres supernatant or an SDF-1α solution to serve as a chemoattractant.
After 24 h of incubation, the Transwell inserts were removed, and the upper chamber was washed with PBS to remove non-migrated cells. Cells that had migrated to the lower side of the membrane were fixed and stained. Quantitative analysis of the migrated cells was conducted using ImageJ software to assess cell migration efficiency.
2.10 Effect of microspheres on the differentiation of hDPSCs
hDPSCs were seeded in 6-well plates, and each well was treated with the corresponding group’s microsphere extract (L/M/H group extracts collected every 3 days). The culture medium was refreshed every 3 days, and the cells were maintained for 2 weeks. On day 14, total RNA was extracted from treated cells using TRIzol reagent, and the RNA concentration was measured with a microvolume spectrophotometer. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using a reverse transcription kit from the extracted RNA. RT-qPCR was performed for each sample using GAPDH as an internal control. The relative expression levels of target genes were calculated using the 2^-ΔΔCt method. The primer sequences used for target gene amplification are listed in Table 1.
2.11 Statistical analysis
All data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (x ± SD), and statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9.0 software. A t-test was used to compare differences between two groups, while one-way ANOVA was employed to analyze differences among three or more groups. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three measurements per group. Differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres
We successfully prepared SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres with a shell concentration of 4% using a fixed receiving distance, injection voltage, and core solution concentration. The morphology and structure of the microspheres were thoroughly analyzed using SEM and TEM. SEM observations revealed that the surface of the prepared microspheres was smooth and evenly dispersed, with no fiber-like connections between particles (Figure 1A). This surface property is critical for drug delivery systems, as smooth surfaces reduce nonspecific adsorption in vivo, enhancing biocompatibility (Amani et al., 2024). The uniform distribution of microspheres indicates the stability of the preparation process and proper control of process parameters, ensuring consistency and reproducibility of the microspheres.
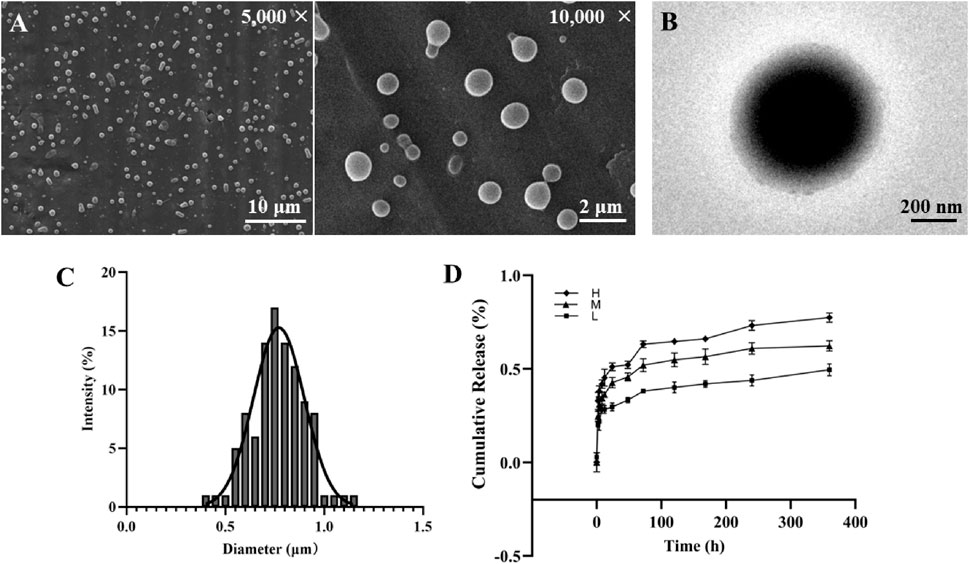
Figure 1. Construction and surface morphology of SDF-1α/PLGA Microspheres. (A) SEM images of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres. Scale bar = 10/2 μm. (B) TEM images of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres. Scale bar = 200 μm. (C) Diameter distribution of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres. (D) The cumulative drug release profiles of PLGA microspheres with different SDF-1α loading amounts.
The average particle size of the microspheres, measured using ImageJ software, was approximately 0.77 μm, with a relatively narrow size distribution (Figure 1C). Particle size plays a vital role in determining the distribution, metabolism, and excretion pathways of the microspheres in the body, directly influencing drug efficacy and safety. Microspheres of micron-scale size offer favorable circulation time and targeting ability in vivo (Kapate et al., 2021), making them highly advantageous for drug delivery applications. Furthermore, uniform particle size helps regulate drug release rates, ensuring stable drug concentrations within the body.
TEM analysis confirmed the presence of a distinct core-shell structure in the prepared microspheres, with the shell-to-core thickness ratio measured at 24.1% ± 0.59% (Figure 1B). The design of the core-shell structure enables the encapsulation of drugs or growth factors within the microspheres, providing sustained release. The shell layer protects the active components from external environmental factors, prolonging their efficacy in vivo (Yuan et al., 2024). Additionally, the thickness of the shell can be precisely controlled by adjusting the PLGA concentration and solution flow rate to meet different therapeutic needs. This core-shell architecture offers a flexible drug loading and release mechanism, allowing the delivery of various bioactive molecules. As a result, these microspheres exhibit significant potential for applications in drug delivery systems across multiple therapeutic areas.
3.2 In Vitro drug release profile of sustained release microspheres
The PLGA microspheres loaded with different concentrations of SDF-1α exhibited the following DL and encapsulation efficiency EE: the low-loading group showed a DL of 4.02% ± 0.85% and an EE of 89.71% ± 4.78%; the medium-loading group exhibited a DL of 6.75% ± 0.96% and an EE of 81.77% ± 5.20%; while the high-loading group reached a DL of 9.31% ± 1.11%, the EE decreased to 70.24% ± 6.52%. Overall, the microsphere system demonstrated favorable drug-loading capacity and encapsulation efficiency. At the medium drug concentration, drug loss during preparation was minimal, balancing a high drug content with microsphere stability. Although the high-loading group achieved greater drug loading, the reduced encapsulation efficiency suggests that excess drug may not be fully incorporated within the microsphere matrix. Conversely, the low-loading group had the highest encapsulation efficiency despite a lower drug content, making it more suitable for sustained-release applications where drug stability is critical. A high encapsulation efficiency indicates that most of the drug was successfully entrapped within the microspheres, which is particularly important for controlled-release systems (Li et al., 2024). Therefore, microspheres with varying drug-loading levels can be selectively chosen based on specific therapeutic needs. Among them, the medium-loading formulation offers a favorable balance between drug utilization and sustained-release performance, showing strong potential for clinical application.
The sustained release curves of each group of microspheres (L, M, H, 50 mg) are shown in Figure 1D. During the initial 24 h, the three groups released 29.67%, 42.67%, and 51.07% of SDF-1α, respectively, indicating a significant initial burst release. This burst release is typically due to drug molecules attached to or near the surface of the microspheres (Schutzman et al., 2023). Over the following 7 days, the release rate slowed down, with cumulative release reaching 41.93%, 56.33%, and 66.03%, respectively. Subsequently, the release rate further decreased, exhibiting a sustained slow-release profile. By day 15, the cumulative release reached 49.57%, 62.33%, and 77.43%. Both diffusion and degradation mechanisms generally govern the release of drugs from SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres. The initial burst release is primarily due to diffusion, while the subsequent sustained release is closely related to the degradation of PLGA (Bode et al., 2019). The results from this study demonstrate that the microspheres can provide stable drug release over an extended period, which is highly advantageous for regenerative medicine applications that require long-term factor supply (Wang et al., 2022). In addition, as the drug loading increases, the release rate at each time point also rises, indicating that the release rate can be modulated by adjusting the drug loading.
SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres, with their combination of burst and sustained release, hold potential for various clinical applications. The rapid initial drug release can quickly achieve therapeutic concentrations to address acute symptoms or infections, while the subsequent slow release ensures sustained therapeutic effects, reducing dosing frequency and improving patient compliance (Zhou et al., 2024). For example, in dental pulp regeneration, the initial release of growth factors can rapidly stimulate cell proliferation, while the sustained release supports cell differentiation and tissue maturation. This release behavior provides new strategies and tools for regenerative medicine and other therapies requiring long-term drug supply. Future studies will further advance the clinical application of these microsphere systems to meet diverse therapeutic needs (Dhamecha et al., 2019).
3.3 Culture and identification of hDPSCs
In this study, dental pulp tissue fragments were minced and cultured using the tissue explant adherence method. By the 10th day, a large number of cells were observed radially arranged around the tissue fragments. When hDPSCs were passaged to the third generation, the cells were evenly distributed within the culture flask, exhibiting a spindle-shaped morphology, and were in contact with each other, displaying a typical fibroblast-like whorled pattern.
To verify the purity of the obtained cells, flow cytometry analysis was performed (Figure 2A). The results showed high expression of mesenchymal stem cell surface markers, with CD90 at 99.68% and CD105 at 99.69%, while hematopoietic cell markers CD34 and CD45 were expressed at very low levels (0.57% and 0.22%, respectively). These findings confirm that the extracted cells were high-purity hDPSCs, effectively excluding contamination from hematopoietic stem cells (Zhou et al., 2023).
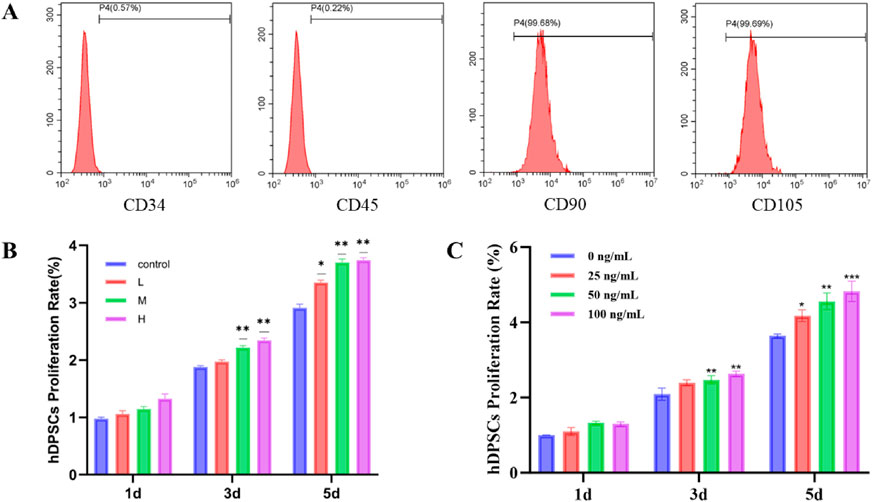
Figure 2. (A) Identification of hDPSCs surface antigen by flow cytometry. The expression rates of CD90, CD105, CD34 and CD45 were 99.68%, 99.69%, 0.57% and 0.22%, respectively. (B) The effect of PLGA microspheres with different SDF-1α loading amounts on the viability of hDPSCs. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05. (C) Effect of different concentrations of SDF-1α on the viability of hDPSCs. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 vs. 0 ng/mL group.
The high expression of CD90 and CD105 is not only characteristic of mesenchymal stem cells but is also closely associated with their proliferation and multipotent differentiation potential (Kang et al., 2024). These attributes further validate the unique advantages of hDPSCs as an ideal cell model for regenerative medicine research (Li et al., 2022).
3.4 Effect of different concentrations of microspheres on the proliferative activity of hDPSCs
The proliferation of hDPSCs at different time points (1 day, 3 days, and 5 days) was assessed through co-culture using the CCK-8 assay. A control group and treatment groups using 20 mg/mL extract solutions from SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres with different loading levels (L/M/H) were established. As shown in Figure 2B, on the first day of co-culture, there were no significant differences among the four groups (P > 0.05), indicating that the short-term release of SDF-1α had not yet produced a noticeable proliferative effect and that the microspheres had no immediate impact on the cells (Zhao et al., 2023). By Day 3, the OD values in the M and H groups were significantly higher than in the control group (P < 0.05, P < 0.01), while the L group showed a slight increase without statistical significance, suggesting that medium and high loading concentrations had begun to exert biological effects. Furthermore, none of the treatment groups inhibited cell proliferation, confirming the excellent biocompatibility of PLGA, which did not trigger cellular stress responses (Liu et al., 2023). By Day 5, the proliferative effect became more pronounced. The H group showed the highest OD value, followed by the M group, while the L group also displayed an upward trend. All three groups were significantly higher than the control (P < 0.05). The difference between the H and M groups was not significant, indicating that a concentration of 50 ng/mg may already approach the saturation threshold for proliferation-promoting effects. Additionally, PLGA materials themselves may have a supportive role in cell proliferation, possibly due to their degradation products facilitating cellular metabolism (Barough et al., 2024). PLGA microspheres with varying SDF-1α loading levels demonstrated good biocompatibility. A medium loading level (50 ng/mg) was sufficient to significantly enhance cell activity, while a higher loading level (100 ng/mg) showed a further increasing trend but with no significant difference, suggesting a plateau in the dose-response relationship. These results indicate that SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres possess favorable pro-growth properties and are suitable carriers for sustained delivery of bioactive factors in dental pulp regeneration therapy.
3.5 Effect of different concentrations of SDF-1α on the proliferative activity of hDPSCs
Using the CCK-8 assay at various time points (1 day, 3 days, and 5 days), we observed significant effects of SDF-1α concentrations on the proliferation rates of hDPSCs (Figure 2C). The results indicated a clear concentration-dependent relationship, with the proliferation rates of hDPSCs showing a marked increase as the concentration of SDF-1α increased. In the treatment groups of 25 ng/mL and 50 ng/mL, the proliferation rates gradually elevated, demonstrating statistical significance compared to the control group (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001). This suggests that an appropriate concentration of SDF-1α can effectively promote the proliferation of hDPSCs (Saravanan et al., 2019).
Furthermore, the results also indicated that SDF-1α has a time-dependent effect on promoting cell proliferation. At the 1-day culture time point, there were no substantial differences in the proliferation rates among the groups, and all groups exhibited relatively low proliferation rates. This may be attributed to the cells not fully adapting to the SDF-1α environment in a short period or the initial phase of cell proliferation being relatively slow. As the culture time extended, the proliferation rates in the 25 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, and 100 ng/mL SDF-1α groups were significantly higher than those in the control group, particularly at the 3-day and 5-day marks, which showed even more pronounced differences. This phenomenon aligns with previous research findings (Meng et al., 2021). SDF-1α, also known as CXCL12, is a chemokine that primarily promotes cell proliferation and migration by binding to its receptor CXCR4, thereby activating intracellular signaling pathways. Existing studies have demonstrated that SDF-1α enhances cell survival by promoting proliferation and regulating cellular metabolism and growth states (Chen et al., 2022). In dental pulp stem cells, SDF-1α enhances the potential for cell proliferation by facilitating cell cycle progression and regulating the expression of associated growth factors.
3.6 Effects of different concentrations of SDF-1α on the migration of hDPSCs
To investigate the impact of SDF-1α on the migration ability of hDPSCs, a cell scratch wound healing assay was conducted to assess changes in cell migration (Figures 3A,B). The experimental groups were treated with 25 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, and 100 ng/mL SDF-1α, while the control group received no cytokine addition. The results of the scratch wound healing assay revealed that different concentrations of SDF-1α significantly influenced the migration capabilities of hDPSCs. The control group exhibited the shortest cell migration distance. The results indicated that the promoting effect of 25 ng/mL SDF-1α on cell migration was relatively limited. However, as the concentration increased to 50 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL, the migration ability was significantly enhanced (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001), which may be attributed to stronger chemotactic signals activating more CXCR4 receptors and downstream signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 (Li J. et al., 2021). These pathways play a crucial role in cytoskeletal reorganization and the expression of adhesion molecules, thereby enhancing cell motility and directional migration. Notably, when the concentration reached 100 ng/mL, there was no significant difference in migration ability compared to the 50 ng/mL group, suggesting that the chemotactic effect may have reached saturation at 50 ng/mL, with receptor binding approaching its maximum capacity (Kim et al., 2023). Therefore, this experiment utilized 50 ng/mL as the optimal concentration of SDF-1α for the assays. Furthermore, this study confirmed the promoting effect of SDF-1α on the migration of hDPSCs, providing strong support for its application in dental pulp regeneration therapies.
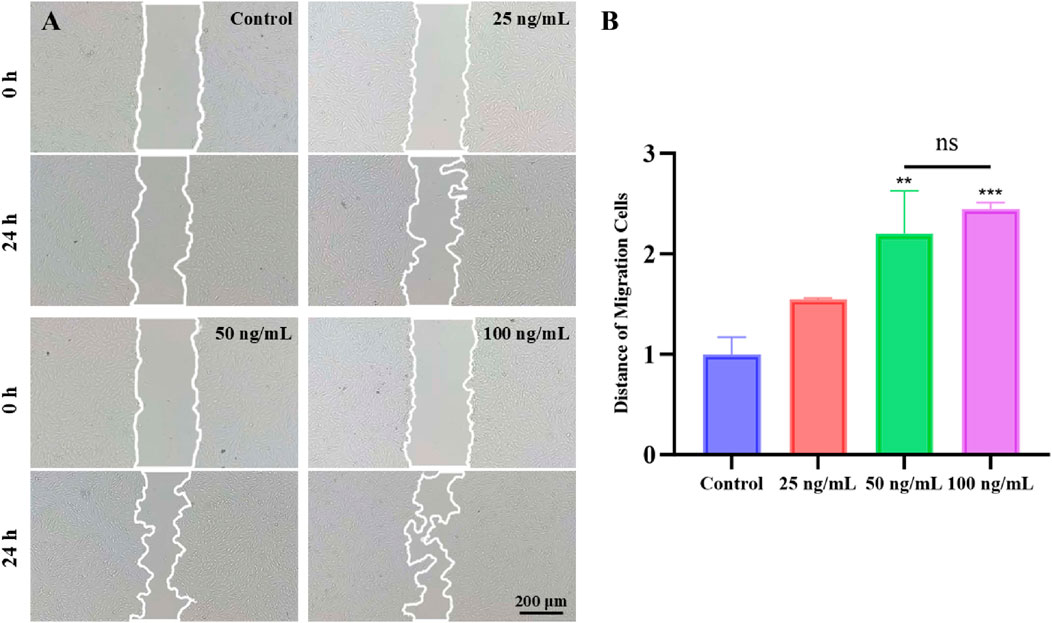
Figure 3. Scratch assay assessing the migration of hDPSCs stimulated by different concentrations of SDF-1α (0, 25, 50, and 100 ng/mL). (A) Representative images of scratch closure at 0 h and 24 h in each group. Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of wound closure percentage after 24 h; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 vs. 0 ng/mL group.
3.7 Effect of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres on the migration of hDPSCs
To evaluate the effect of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres on hDPSC migration, we used the Transwell assay. As shown in Figures 4A,B, the number of migrating cells in the L group was similar to that of the control group, indicating a limited chemotactic ability. In contrast, the M group showed a significant increase in cell migration, suggesting that the released SDF-1α was sufficient to activate the CXCR4-mediated chemotactic pathway. Although the H group exhibited a slightly higher number of migrating cells than the M group, the difference was not statistically significant, indicating that the chemotactic effect may have reached saturation at around 50 ng/mg, and further increasing the loading did not significantly enhance migration.
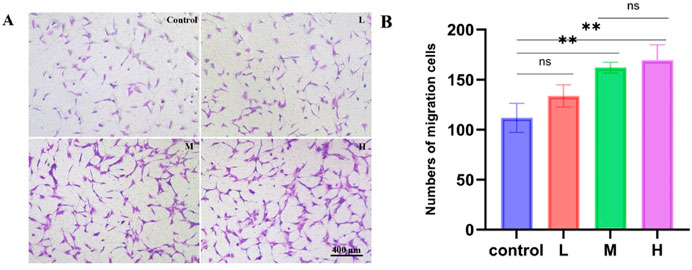
Figure 4. Chemotactic effects of PLGA microspheres loaded with low, medium, and high doses of SDF-1α on hDPSCs. (A) Representative images of hDPSCs migrating through Transwell membranes in each group; scale bar = 400 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of migrated cell numbers, showing enhanced chemotaxis in the M and H groups; **P < 0.01 vs. control group.
Moreover, the sustained-release solution from both the M and H groups at the 2-week time point was still able to promote hDPSCs proliferation significantly, confirming that the SDF-1α released from the microspheres at this stage retained its biological activity.
These findings validate the effectiveness of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres as a drug carrier, capable of stably releasing SDF-1α over an extended period while preserving its bioactivity. This has significant clinical implications for the regeneration of dental pulp tissue. The application of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres not only provides a mechanism for the sustained release of growth factors but also protects SDF-1α from rapid degradation, ensuring its effective concentration is maintained during the treatment period (Mullin et al., 2024). Such a sustained release system is critical for regenerative medicine strategies that require prolonged factor support (Subbiah and Guldberg, 2019).
In summary, this study demonstrates the effectiveness of SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres in promoting the migration of hDPSCs and highlights the potential of this sustained-release system for applications in regenerative medicine. Future research could further explore the application of this system across various cell types and tissue regeneration contexts and optimize its release characteristics to enhance therapeutic outcomes. Combined with other biomaterials, SDF-1α/PLGA microspheres have the potential to play a broader role in the field of regenerative medicine.
3.8 The promotive effect of microspheres on the differentiation of hDPSCs
We co-cultured hDPSCs with sustained-release solutions of PLGA microspheres loaded with different concentrations of SDF-1α, changing the medium every 3 days for a total of 14 days, to evaluate their effects on DPSC differentiation. RT-PCR results (Figures 5A–E) showed that all experimental groups exhibited higher expression levels of the five differentiation marker genes compared to the blank control group. The M and H groups significantly upregulated odontogenic genes such as ALP, DMP-1, and DSPP, indicating enhanced potential for odontoblastic differentiation. The marked increase in Ang-1 and CD31 expression also suggested that the material promoted endothelial differentiation, contributing to vascularization during dental pulp regeneration. Although the expression levels in the H group were slightly higher than those in the M group, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05), implying that the chemotactic and differentiation effects reached a plateau at the medium loading concentration (50 ng/mg). While the L group did not show significant upregulation, it still exhibited a certain degree of inductive effect compared to the blank control, reflecting the dose-dependent biological activity of SDF-1α.
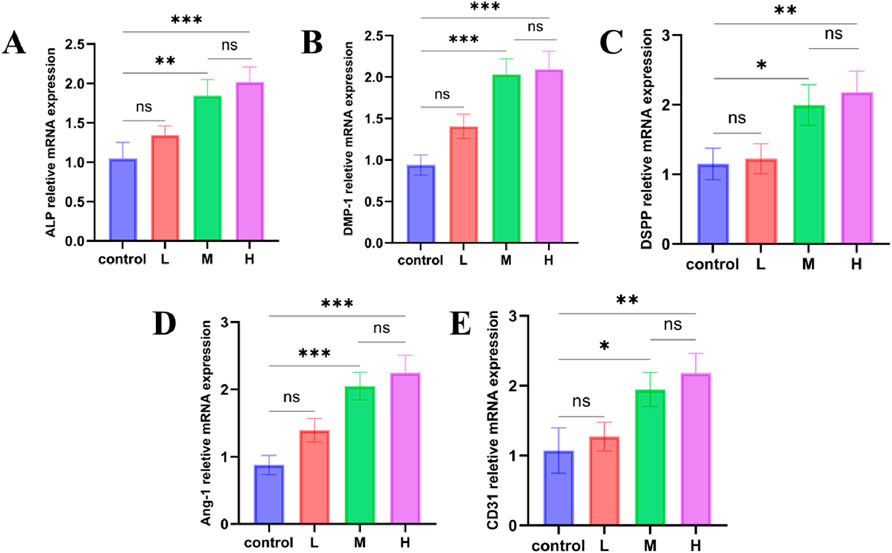
Figure 5. RT-qPCR analysis of odontogenic and angiogenic gene expression in hDPSCs after 14-day induction by extracts from PLGA microspheres loaded with low, medium, and high doses of SDF-1α. (A–C) Relative mRNA expression levels of odontogenic markers ALP, DMP-1, and DSPP; (D–E) Expression levels of angiogenic markers Ang-1 and CD31; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05 vs. control group.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP-1), and dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) are important markers for osteogenesis, dentin generation and mineralization. ALP is an early marker of osteoblast differentiation, reflecting the transition of cells to an osteoblastic phenotype (Kim et al., 2022). DMP-1 plays a crucial role in dentin formation by regulating the formation of the mineralized matrix. DSPP is a key factor in tooth mineralization, primarily expressed during the process of dentinogenesis. Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) and CD31 are critical indicators for assessing angiogenesis. Ang-1 plays a crucial role in vascular maturation and stabilization, while CD31, a marker of endothelial cells, is involved in the differentiation and junction formation of vascular endothelial cells.
The results showed that the expression of Ang-1 and CD31 was significantly upregulated in the SDF-1α/PLGA group, indicating that this system effectively promotes angiogenesis. The role of SDF-1α in neovascularization has been widely recognized, supporting the regenerative process by enhancing angiogenesis (Zhang Y. et al., 2023). Enhanced angiogenic capacity not only improves the nutritional supply to the regenerated tissue but also facilitates the integration and functional recovery of the regenerated tissue (Wu et al., 2017). Overall, the PLGA microspheres loaded with SDF-1α effectively promoted the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells by providing sustained release of the growth factor. Compared to traditional single-layer PLGA microspheres or other carriers, such as hydrogels and liposomes, the core–shell microspheres prepared by coaxial electrospray in this study demonstrate more stable and sustained release. Unlike single-layer microspheres, which often have a significant initial burst release and loss of drug activity, the core–shell structure protects SDF-1α, ensuring sustained release for over 30 days and better control of bioactivity. Additionally, the electrospray method produces uniform particles and is suitable for encapsulating thermosensitive substances, offering good process control and clinical potential. This novel sustained release system holds great potential in regenerative medicine, offering new strategies for tissue regeneration (Yu et al., 2022).
4 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study successfully developed novel core-shell structured SDF-1α/PLGA sustained-release microspheres using electrospinning technology, specifically designed for the unique environment of the oral cavity. These microspheres exhibit an excellent drug loading capacity, high encapsulation efficiency, good biocompatibility, and a drug release performance that lasts for at least 2 weeks. The outstanding sustained release properties enable the microspheres to continuously promote the migration of hDPSCs without repeated dosing and effectively enhance their odontogenic and angiogenic differentiation over an extended period. Therefore, SDF-1α/PLGA coaxial electrospun sustained release microspheres possess the potential not only for development as materials for dental pulp regeneration therapy but also for applications in other areas of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Future studies will focus on further optimizing the release performance of the microspheres and conducting in vivo validation in animal models to assess their safety and therapeutic efficacy in pulp regeneration comprehensively. In addition, we will explore their clinical feasibility and translational potential in dental applications to facilitate the transition from laboratory research to clinical practice.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Qingdao Stomatological Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
WF: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. CL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. QA: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. SS: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. YW: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. GL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review and editing. DS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Qingdao Natural Science Foundation (23-2-1-165-zyyd-jch), Qingdao Key Health Discipline Development Fund (2025-2027), Qingdao Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases (22-3-7-lczx-7-nsh), and Shandong Provincial Key Medical and Health Discipline of Oral Medicine (2025-2027).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Amani, H., Alipour, M., Shahriari, E., and Taboas, J. M. (2024). Immunomodulatory biomaterials: tailoring surface properties to mitigate foreign body reaction and enhance tissue regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (29), 2401253. doi:10.1002/adhm.202401253
Barough, M. S., Seyfoori, A., Askari, E., Mahdavi, M., Sarrami Forooshani, R., Sadeghi, B., et al. (2024). Gemcitabine-loaded injectable hydrogel for localized breast cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34 (41), 2403910. doi:10.1002/adfm.202403910
Bode, C., Kranz, H., Fivez, A., Siepmann, F., and Siepmann, J. (2019). Often neglected: PLGA/PLA swelling orchestrates drug release: HME implants. J. Control. Release 306, 97–107. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.05.039
Chen, W., Wu, P., Yu, F., Luo, G., Qing, L., and Tang, J. (2022). HIF-1α regulates bone homeostasis and angiogenesis, participating in the occurrence of bone metabolic diseases. Cells 11 (22), 3552. doi:10.3390/cells11223552
C Silva, A., M Lopes, C., Ms Lobo, J., and H Amaral, M. (2015). Delivery systems for biopharmaceuticals. Part I: nanoparticles and microparticles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 16 (11), 940–954. doi:10.2174/1389201016666150731112532
Dhamecha, D., Movsas, R., Sano, U., and Menon, J. U. (2019). Applications of alginate microspheres in therapeutics delivery and cell culture: past, present and future. Int. J. Pharm. 569, 118627. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118627
Ito, S., Sato, T., and Maeta, T. (2021). Role and therapeutic targeting of SDF-1α/CXCR4 axis in multiple myeloma. Cancers 13 (8), 1793. doi:10.3390/cancers13081793
Kang, Q. M., Wang, J., Chen, S. M., Song, S. R., and Yu, S. C. (2024). Glioma-associated mesenchymal stem cells. Brain 147 (3), 755–765. doi:10.1093/brain/awad360
Kapate, N., Clegg, J. R., and Mitragotri, S. (2021). Non-spherical micro-and nanoparticles for drug delivery: progress over 15 years. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 177, 113807. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2021.05.017
Kim, J. M., Yang, Y. S., Hong, J., Chaugule, S., Chun, H., van Der Meulen, M. C., et al. (2022). Biphasic regulation of osteoblast development via the ERK MAPK–mTOR pathway. Elife 11, e78069. doi:10.7554/elife.78069
Kim, Y. H., Kim, S., Ju, H. J., Han, M. J., Park, Y., Kim, E., et al. (2023). In-situ wound healing by SDF-1-mimic peptide-loaded click crosslinked hyaluronic acid scaffold. J. Control. Release 364, 420–434. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.10.047
Krastl, G., Weiger, R., Filippi, A., Van Waes, H., Ebeleseder, K., Ree, M., et al. (2021). Endodontic management of traumatized permanent teeth: a comprehensive review. Int. Endod. J. 54 (8), 1221–1245. doi:10.1111/iej.13508
Li, J., Chen, H., Zhang, D., Xie, J., and Zhou, X. (2021b). The role of stromal cell-derived factor 1 on cartilage development and disease. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 29 (3), 313–322. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2020.10.010
Li, J., Zheng, L., Daraqel, B., Liu, J., and Hu, Y. (2023). The efficacy of concentrated growth factor and platelet-rich fibrin as scaffolds in regenerative endodontic treatment applied to immature permanent teeth: a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 23 (1), 482. doi:10.1186/s12903-023-03164-y
Li, Q., Ma, C., Jing, Y., and Liu, X. (2024). Multifunctional nanofibrous hollow microspheres for enhanced periodontal bone regeneration. Adv. Sci. 11, 2402335. doi:10.1002/advs.202402335
Li, Y., Duan, X., Chen, Y., Liu, B., and Chen, G. (2022). Dental stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as promising therapeutic agents in the treatment of diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 14 (1), 2. doi:10.1038/s41368-021-00152-2
Li, Z., Liu, L., Wang, L., and Song, D. (2021a). The effects and potential applications of concentrated growth factor in dentin–pulp complex regeneration. Stem cell Res. and Ther. 12 (1), 357. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02446-y
Liu, K., Yu, S., Ye, L., and Gao, B. (2021). The regenerative potential of bFGF in dental pulp repair and regeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 680209. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.680209
Liu, Y., Guo, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Mo, X., and Wu, T. (2023). Progress in electrospun fibers for manipulating cell behaviors. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5 (4), 1241–1272. doi:10.1007/s42765-023-00281-9
Liu, Y. S., Ou, M. E., Liu, H., Gu, M., Lv, L. W., Fan, C., et al. (2014). The effect of simvastatin on chemotactic capability of SDF-1α and the promotion of bone regeneration. Biomaterials 35 (15), 4489–4498. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.02.025
Meng, Z., Feng, G., Hu, X., Yang, L., Yang, X., and Jin, Q. (2021). SDF factor-1α promotes the migration, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 30 (2), 106–117. doi:10.1089/scd.2020.0165
Mullin, J. A., Rahmani, E., Kiick, K. L., and Sullivan, M. O. (2024). Growth factors and growth factor gene therapies for treating chronic wounds. Bioeng. and Transl. Med. 9 (3), e10642. doi:10.1002/btm2.10642
Panda, P., Mishra, L., Govind, S., Panda, S., and Lapinska, B. (2022). Clinical outcome and comparison of regenerative and apexification intervention in young immature necrotic teeth—a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 11 (13), 3909. doi:10.3390/jcm11133909
Ruan, L., Su, M., Qin, X., Ruan, Q., Lang, W., Wu, M., et al. (2022). Progress in the application of sustained-release drug microspheres in tissue engineering. Mater. Today Bio 16, 100394. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100394
Saravanan, S., Vimalraj, S., Thanikaivelan, P., Banudevi, S., and Manivasagam, G. (2019). A review on injectable chitosan/beta glycerophosphate hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 121, 38–54. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.014
Schutzman, R., Shi, N. Q., Olsen, K. F., Ackermann, R., Tang, J., Liu, Y. Y., et al. (2023). Mechanistic evaluation of the initial burst release of leuprolide from spray-dried PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 361, 297–313. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.016
Siddiqui, Z., Acevedo-Jake, A. M., Griffith, A., Kadincesme, N., Dabek, K., Hindi, D., et al. (2022). Cells and material-based strategies for regenerative endodontics. Bioact. Mater. 14, 234–249. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.11.015
Subbiah, R., and Guldberg, R. E. (2019). Materials science and design principles of growth factor delivery systems in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8 (1), 1801000. doi:10.1002/adhm.201801000
Sui, B., Chen, C., Kou, X., Li, B., Xuan, K., Shi, S., et al. (2019). Pulp stem cell–mediated functional pulp regeneration. J. Dent. Res. 98 (1), 27–35. doi:10.1177/0022034518808754
Taha, N. A., Abuzaid, A. M., and Khader, Y. S. (2023). A randomized controlled clinical trial of pulpotomy versus root canal therapy in mature teeth with irreversible pulpitis: outcome, quality of life, and patients’ satisfaction. J. Endod. 49 (6), 624–631.e2. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2023.04.001
Vahidi, M., Rizkalla, A. S., and Mequanint, K. (2024). Extracellular matrix-surrogate advanced functional composite biomaterials for tissue repair and regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (27), 2401218. doi:10.1002/adhm.202401218
Wang, Y., Guo, Q., Wang, W., Wang, Y., Fang, K., Wan, Q., et al. (2022). Potential use of bioactive nanofibrous dural substitutes with controlled release of IGF-1 for neuroprotection after traumatic brain injury. Nanoscale 14 (48), 18217–18230. doi:10.1039/d2nr06081g
Wu, T., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Sun, B., Guo, X., Morsi, Y., et al. (2017). Development of dynamic liquid and conjugated electrospun poly (L-lactide-co-caprolactone)/collagen nanoyarns for regulating vascular smooth muscle cells growth. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 13 (3), 303–312. doi:10.1166/jbn.2017.2352
Yu, C., Wang, T., Diao, H., Liu, N., Zhang, Y., Jiang, H., et al. (2022). Photothermal-triggered structural change of nanofiber scaffold integrating with graded mineralization to promote tendon–bone healing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4 (4), 908–922. doi:10.1007/s42765-022-00154-7
Yuan, K., Chen, Q., Qin, M., Gao, S., Wang, Q., Gao, S., et al. (2024). Micro/nano encapsulated phase change materials: preparation, principle, and emerging advances in medical field. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2314487. doi:10.1002/adfm.202314487
Zhai, Q., Dong, Z., Wang, W., Li, B., and Jin, Y. (2019). Dental stem cell and dental tissue regeneration. Front. Med. 13, 152–159. doi:10.1007/s11684-018-0628-x
Zhang, X., Guo, M., Guo, Q., Liu, N., Wang, Y., and Wu, T. (2023a). Modulating axonal growth and neural stem cell migration with the use of uniaxially aligned nanofiber yarns welded with NGF-loaded microparticles. Mater. Today Adv. 17, 100343. doi:10.1016/j.mtadv.2023.100343
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. Y., Pan, Z. W., Li, Q. Q., Sun, L. H., Li, X., et al. (2023b). GDF11 promotes wound healing in diabetic mice via stimulating HIF-1ɑ-VEGF/SDF-1ɑ-mediated endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and neovascularization. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 44 (5), 999–1013. doi:10.1038/s41401-022-01013-2
Zhao, X., Ni, S., Song, Y., and Hu, K. (2023). Intranasal delivery of Borneol/R8dGR peptide modified PLGA nanoparticles co-loaded with curcumin and cisplatin alleviate hypoxia in pediatric brainstem glioma which improves the synergistic therapy. J. Control. Release 362, 121–137. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.08.048
Zhou, F., Chen, M., Qian, Y., Yuan, K., Han, X., Wang, W., et al. (2024). Enhancing endogenous hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritic joints with an anti-inflammatory supramolecular nanofiber hydrogel delivering HAS2 lentivirus. Small 20, 2400542. doi:10.1002/smll.202400542
Keywords: SDF-1α, microspheres, sustained release, dental pulp regeneration, human dental pulp stem cells
Citation: Feng W, Li C, An Q, Shi S, Wang Y, Lu G and Sun D (2025) Preparation of SDF-1α-loaded electrospun coaxial microspheres and their study on promoting migration and differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Front. Mater. 12:1568591. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1568591
Received: 30 January 2025; Accepted: 13 June 2025;
Published: 30 June 2025.
Edited by:
Ceren Karaman, Akdeniz University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Debanjan Sarkar, University at Buffalo, United StatesDawei Li, Jiangnan University, China
Copyright © 2025 Feng, Li, An, Shi, Wang, Lu and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guanfan Lu, NDA2MzA3NzZAcXEuY29t; Degang Sun, c3VuZGVnYW5nMDgwMUAxNjMuY29t
 Wenjie Feng1
Wenjie Feng1 Yuanfei Wang
Yuanfei Wang Degang Sun
Degang Sun