- 1School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China
- 2Ningbo Communications Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China
Silt soil is widely distributed in coastal, river, and lacustrine sedimentary zones, characterized by high water content, low bearing capacity, high compressibility, and low permeability, representing a typical bulk solid waste. Studies have shown that cement and ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) can significantly enhance the strength and durability of stabilized silt. However, potential variations due to groundwater fluctuations, long-term loading, or environmental erosion require further validation. This study comprehensively evaluates cement-slag composite stabilized silt as a sustainable subgrade material through integrated laboratory and field investigations. Laboratory tests analyzed unconfined compressive strength (UCS), seawater erosion resistance, and drying shrinkage characteristics. Field validation involved constructing a test section with embedded sensors to monitor dynamic responses under 50% overloaded truck traffic (simulating 16–33 months of service) and environmental variations. Results indicate that slag incorporation markedly improved the material’s anti-shrinkage performance and short-term erosion resistance. Under coupled heavy traffic loads and natural temperature-humidity fluctuations, the material exhibited standard-compliant dynamic responses, with no observed global damage to the pavement structure or surface fatigue damage under equivalent 16–33-month loading. The research confirms the long-term stability of cement-slag stabilized silt as a subgrade material under complex environmental conditions.
1 Introduction
The construction of various engineering projects in China’s coastal areas generates a large amount of construction silty residues soils annually. This bulk solid waste is characterized by high water content, high porosity, low permeability, and low bearing capacity, classified as poor soft soils (Zhang et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2021). Conventional disposal methods for silt soils, such as surface stockpiling, marine dumping, and pit burial, can cause regional soil and water contamination and may trigger slope sliding accidents (Wang et al., 2025). Therefore, it is imperative to explore novel utilization approaches for this type of silt soil. By solidifying and using silt soils as subgrade material, in-situ resource recycling of silty residues soils can be achieved, offering significant economic and environmental benefits (Liu et al., 2023). Currently, soil stabilization techniques primarily include drainage consolidation and chemical stabilization (Dai et al., 2021; Gao et al., 2023; Shi et al., 2023). While drainage consolidation provides rapid dewatering capability, its reliance on inherent soil strength limits effectiveness in low-cohesion materials like silt soil (Pu et al., 2020). In contrast, chemical stabilization employs inorganic binders such as cement, ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS), lime, and fly ash. Through multiple physicochemical processes like hydration reactions and ion exchange, this method induces multi-scale structural reorganization of the soil matrix, significantly enhancing the mechanical properties of solidified silt soil (Pu et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2024a).
Cement-stabilized silt achieves notable compressive strength, but its high susceptibility to desiccation cracking under moisture loss and aging limits standalone applications (He et al., 2024a). Incorporating inorganic binders effectively addresses cracking issues and further enhances the mechanical properties of stabilized soils (Zhu et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022). In relevant soil solidification research, Ca2+ in lime-based stabilization systems can undergo ion exchange with Na+ and K+ on soil particle surfaces, promoting particle agglomeration, improving compaction characteristics, and enhancing early-stage strength of stabilized silt (Pu et al., 2020). However, subsequent accelerated carbonation may inhibit long-term hydration reactivity (Kim et al., 2024). Fly ash systems through pozzolanic reactions to form low-calcium C-A-S-H gels, while micro-aggregate effect fills soil pores to improve the compactness and strength of solidified soil (Zhu et al., 2021). Nevertheless, they exhibit slow early-strength development, require alkaline activation, and carry risks of alkali-aggregate reactions (Chen et al., 2024a). In contrast, GGBFS contains abundant CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3. Activated by cement hydration products, it generates additional C-S-H gels and ettringite (AFt), demonstrating faster reaction kinetics than fly ash and more significant early-strength enhancement (Liu et al., 2022). In addition, relevant studies have shown that utilizing the maximum dosage of GGBFS in cement-based systems and activating its potential through alkaline activation can enhance the chloride ion (Cl−)-binding capacity of the cement matrix, thereby resisting structural degradation (Kim et al., 2018). Despite demonstrated synergistic effects of inorganic binders in short-term strength development of soil stabilization, the long-term performance of cement-slag stabilized silt, particularly its durability in practical engineering applications, remains to be further validated.
Modern asphalt pavement design protocols prioritize two critical mechanical parameters: tensile strain at the asphalt layer’s base and vertical compressive strain at the subgrade interface. Empirical validation of these metrics typically employs full-scale test and accelerated loading tests (Arraigada et al., 2014; Jiang et al., 2022). It applies controlled and repeatable wheel loads, either instantaneous or continuous, to the actual pavement, and then sensors collect the dynamic responses of the pavement structures to the traffic loads (Garg et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2021; Habbouche et al., 2022). Which simulate vehicular stresses through controlled, repetitive wheel loading. Sensors embedded within pavement layers capture real-time structural responses, enabling precise quantification of stress-strain behavior under operational conditions. Yang et al. (2023) conducted mechanical response analysis of asphalt pavement with the large-sized crushed stone base treated with fly ash and slag powder, and used analysis of variance (ANOVA) to explore e influence of the interaction among various factors and established a strain prediction equation. Ku et al. (2022) measured the spontaneous, drying, and thermal shrinkage of the concrete pavement from the initial pouring stage based on sensors, and the measured drying shrinkage strain range was approximately 54% higher than that measured by the traditional non-stress cylinder method. Kodippily et al. (2020) monitored the influence of moisture and environmental conditions on the mechanical response of the pavement under driving conditions in the Sunshine Coast region of Queensland, Australia for 3 years. As the subgrade material for solid waste recycling, field validation of silt soil mechanical compatibility within multi-layered pavement systems remains underexplored.
In this study, systematically investigated the multi-factor service adaptability of cement-slag stabilized silt subgrade materials. First, optimization proportions of cement-GGBFS binders were determined through laboratory unconfined compressive strength (UCS) tests, seawater erosion tests, and drying shrinkage tests, with environmental sensitivity of the stabilized silt evaluated. Subsequently, a test section of cement-slag stabilized silt subgrade was constructed for pavement structure implementation. The bearing capacity of the stabilized subgrade was verified through settlement monitoring during construction and field performance tests. Finally, combined with field load tests, dynamic responses of the pavement structure under overweight truck loads, temperature and moisture variations under natural winter conditions in southern China were analyzed. The dynamic loading stability and environmental stability of the entire pavement structure were comprehensively examined. This research aims to provide reliable references for understanding the long-term performance and mechanical response of cement-slag stabilized silt subgrade materials.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Raw materials
The soil samples used in the experiment were taken from the silt soil excavated in a project near the Hangzhou Bay Bridge in Ningbo, China. The water content of the original silt soil was as high as 42.7%. It’s natural density (ρ), natural void ratio (e), liquid limit (LL), and plastic limit (PL) were 1.72 g/cm3, 1.15, 15.6%, and 38.9% respectively. The natural organic matter content was approximately 1.92% as described in JGJ/T 233–2011. The particle size distribution was measured by Bettersize 2000 particle size analyzer produced by Dandong Baite Instrument Co., Ltd. (Liaoning, China) and according to the engineering classification method of soil, it belongs to clay with low liquid limit (CL).
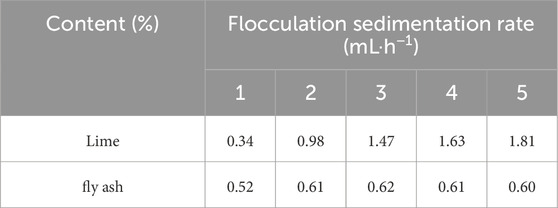
The flocculent and dehydration of the highly water containing silt soil is carried out on the construction site. A glass measuring cylinder with a volume of 1,000 mL was used to measure the sedimentation rate with lime admixture ranging from 0% to 4%, fly ash admixture ranging from 0% to 4%. The results are shown in Table 1. When the lime addition amount is 2%, the peak sedimentation rate of the silt is greater than 1.4 mL/h and continues to increase, while the influence of fly ash is not significant. Then, 2% lime and 5% fly ash were used as flocculants, and pressure filtration dehydration was carried out. After dehydration, the water content of the silt soil is reduced to 21.7%. Its liquid limit and plastic limit are 24.6% and 15.8% respectively, which are significantly lower than those of the original silt soil.
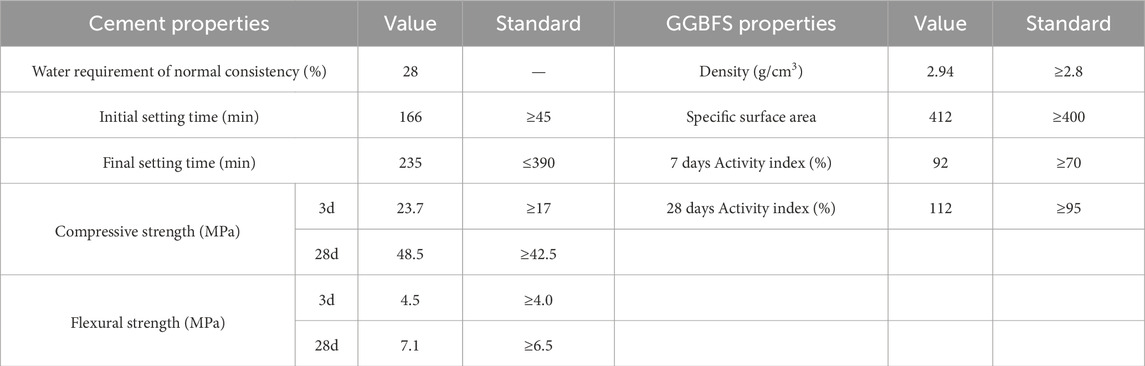
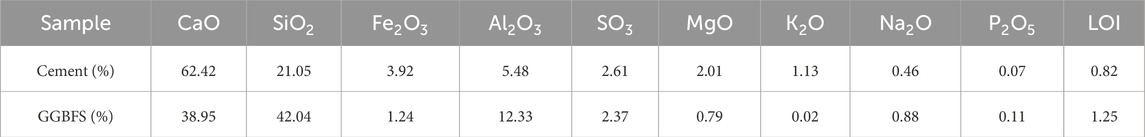
The dehydrated silt soil cannot meet the performance requirements when directly used for subgrade filling. Before paving the dehydrated silt soil, curing agent needs to be added for further solidification to improve its performance. Considering that lime and fly ash already exists in the raw materials, the main curing materials used are P O 42.5 Portland cement and S95 GGBFS. Compared with the standard GB175-2023 and GB/T 18046, the physical indexes of cement and GGBFS are shown in Table 2., chemical composition are shown in Table 3.
2.2 Test scheme
2.2.1 Preparation of solidified silt soil sample
Take the silt soil from the site where dehydration is completed. The samples of composite solidified silt soil with 3%–5% GGBFS and 3%–7% cement are designed. The optimum moisture content was determined based on the T 0804-1994 compaction test method in the JTG 3441-2024 specification, and a compaction degree of 98% was selected according to JTG/T 3610-2019. Add a part of water less than the optimum water content. After thorough mixing, place the samples for 6–8 h. Then add solidified soil and the remaining water, and mix them evenly again. Finally, according to the size requirements of the test specimens, use a press to form samples with a compaction degree of 98% at a speed of 1 mm/min. Cure the samples at room temperature for 12 h, then place them in a standard curing room for 7/28 days. One day before the performance test when the age is reached, keep the samples in water at room temperature of (20 ± 2) °C for 24 h. The prepared solidified silt soil sample is shown in Figure 1.
2.2.2 Unconfined compressive strength test
The objective of this experiment is to explore the influence of different dosages of cement and GGBFS on the strength of samples, optimize the best proportion of cement-GGBFS solidified silt soil, and prepare for subsequent adaptation tests. UCS tests were carried out with cement dosages of 3%, 5%, and 7% and GGBFS dosages of 3%, 4%, and 5%. Cylindrical specimens with a size of Φ50 × 50 mm were molded and cured for 7 days and 28 days. The unconfined compressive strength tests were conducted using a TYE - 2000 type pressure testing machine at a loading rate of 1 mm/min (JTG E50-2009). The unconfined compressive strength of the specimens is calculated according to the following Equation 1:
Where, Rc is the UCS (MPa) at the time of specimen failure, P is the maximum stress (N) when specimen failure, and A is the cross-sectional area (mm2) of the specimen.
2.2.3 Seawater erosion test
There are salts in e moisture of the specific environment in coastal areas (Shu et al., 2024). Whether this has an impact on the strength of cement-slag solidified silt soil still needs further verification. Cylindrical specimens with a size of Φ50 mm × 50 mm and GGBFS contents of 3%, 4%, and 5% were prepared respectively. The cement content was fixed at 5%. After 28 days of curing, seawater from the offshore area of Ningbo (salinity: 3.5%) was used to soak the solidified silt soil specimens. UCS tests were carried out after soaking for 7 days and 28 days. For the control group, specimens under continuous standard curing were used. The water stability coefficient K after anti-erosion was calculated using Equation 2 to measure the water stability performance of cement-slag solidified silt soil (Chen et al., 2024b).
Where, Ys is the UCS of the specimen after soaking in seawater, Y is the UCS of the specimen after standard curing at the same time as the soaking water group.
2.2.4 Drying shrinkage test
During the service life of the pavement, the moisture content of each structural layer keeps changing (Tamrakar and Nazarian, 2021). Therefore, the influence of the change in moisture content under natural temperature and the slag content on the drying shrinkage performance of cement - slag solidified sludge soil was investigated. The study on the slag content aims to prove whether the slag has a regulating effect. The experiment is divided into two parts. The initial moisture content of the sludge soil was adjusted to 15%, 18%, 21% and 24%. The cement - slag content was set at the optimal ratio, and the slag content was 3%, 4%, 5% and 6% of 5% cement under the optimal moisture content. Cubic specimens of 100 × 100 × 400 mm were formed. The curing scheme was that the specimens were bagged and placed in a standard curing room for 7 days, and the drying shrinkage test was carried out. The drying shrinkage strain is calculated using the following Equations 3–5:
Where, Wi is water loss ratio at the i-th measurement (%), δi is the observed drying shrinkage deformation at the i-th measurement (mm), εi is the drying shrinkage strain at the i-th measurement (%), mi is e weighed mass of e standard specimen at the i-th measurement, Xi, j is the dial gauge reading of the j-th indicator during the ith test (mm), l denotes the length of the standard specimen, mp is the oven-dried mass of the standard specimen.
2.2.5 Field settlement and performance test
There are significant differences in the mixing uniformity of materials, compaction degree, and curing compared with laboratory experiments. To further verify the adaptability of cement-GGBFS solidified soil as a subgrade under actual engineering conditions, a test section was built on the under-construction Hang yong double line Expressway in Cixi City, Zhejiang Province, China. To save costs, a combination of 3% cement and 3% slag was adopted. The study area is situated within a subtropical monsoon climate zone, and the predominant landform type of the test section is characterized as a plain area. The test section is situated within the S5 section of the initial phase of the Hangzhou-Ningbo double line project, specifically at K7+465∼K7+565.
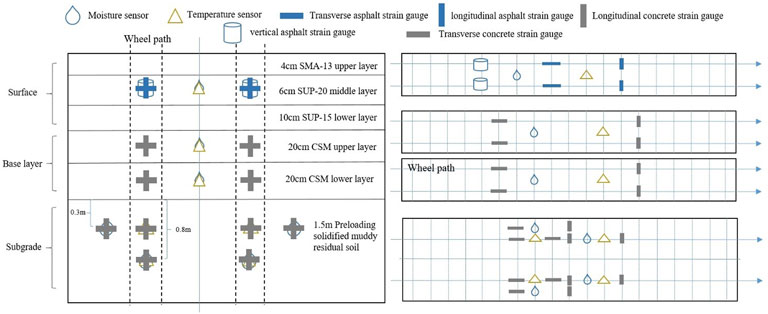
The test section adopts a pavement structure combination form of a 4-cm SMA-13 + 6-cm SUP-20 + 10-cm SUP-25 asphalt mixture surface layer structure, an 18-cm + 20-cm cement-stabilized macadam base structure, and a subgrade filled with 1.5-m pre-compressed solidified silt soil, as well as a 50-cm crushed stone cushion constructed by dividing it into two layers and paving a layer of steel-plastic gorged in the middle. A monitoring system for the pavement structure was developed using PT-100, FDS-100, DH1205, and DH-1204 resistive sensors produced by Jiangsu Donghua Testing Technology Co. Ltd., as well as the corresponding DH5921 acquisition system with 8-channel parallel synchronous sampling. Figure 2 illustrate the schematic diagram of pavement structures and sensor burial point test section.
During the construction of the subgrade in the test section, the mixture is combined in a centralized plant. The top surface width of the subgrade in the test section is 34.5 m, while the bottom surface width is 48 m, and the filling height is 4.4 m. Solidified silt soil is utilized as the subgrade fill, with the slope protection edge soil, capping layer, and isolation layer implemented. The edging soil consists of cohesive material, with the thickness of the edging measuring 0.75 m. A drainage channel is positioned at the foot of the slope, and the slope ratio is 1:1.5.
The solidified silt soil is deposited in four layers, with the thickness of the loose paving ranging from 30 to 40 cm, and A paver or grader is utilized for paving and leveling the solidified soil. During the construction process, field settlement monitoring and performance testing of the subgrade were conducted in accordance with JTG D30-2015 to verify the stability and load-bearing capacity of the pavement.
2.2.6 Field loading test
JTG D50-2017 stipulates that highway and urban road pavement designs adopt a 100 kN single-axle dual-wheel group load as the standard axle load. It requires converting axle loads from different vehicle types into equivalent standard axle load repetitions based on the damage equivalence principle. Overloaded vehicles, following the damage accumulation theory, enable short-term simulation of long-term heavy-traffic pavement performance. The test utilized Shacman Delong M 3000 heavy-duty four-axle trucks with 50% overload (axle configuration type 1,122), as shown in Figure 3. Three trucks operated at speeds of 20–40 km/h while traveling side-by-side in reciprocal lanes.
According to the equivalent axle load conversion principle, 1 month of loading under 50% overloaded truck conditions simulated pavement service conditions equivalent to 19–39 months of standard axle loads. In this study, instantaneous strain data induced by overloaded truck loading, combined with temperature and moisture variations, were collected over 26 days.
The strain response of the pavement structure under overweight truck loading was analyzed using instantaneous strain response amplitude. The strain amplitude calculation method varied based on stress states: for tension-compression cycles, it equaled the summation of peak tensile and compressive strain absolute values (Equation 6); for unidirectional loading, it represented the absolute peak strain value (Equation 7).
Where, Δε denotes the instantaneous strain amplitude, εmax represents the instantaneous maximum tensile strain in tension-compression alternating states, εmin indicates the instantaneous maximum compressive strain in tension-compression alternating states.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Laboratory test
3.1.1 UCS with vary cement-GGFBS contents
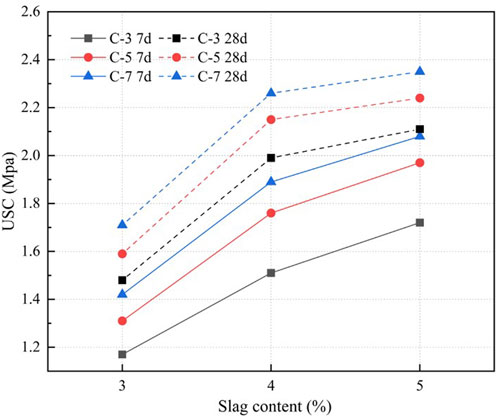
As shown in Figure 4. In cement-stabilized silt samples with C3-S3 formulation, the unconfined compressive strength demonstrates age-dependent development, progressing from 1.17 MPa at 7 days to 1.48 MPa after 28 days of curing. When cement proportion elevates to C5 concentration, a distinct strength enhancement pattern emerges: the 7-day UCS measurements sequentially increase to 1.31 MPa, 1.76 MPa, and 1.97 MPa, while corresponding 28-day values rise to 1.59 MPa, 2.15 MPa, and 2.24 MPa. The C7-C5 composite exhibits further mechanical improvement, attaining 2.08 MPa and 2.35 MPa at 7 and 28 days respectively. Experimental data reveal that GGBFS incorporation substantially modifies material performance, particularly in S5 mixtures where strength parameters reach 1.71 MPa (7-day) and 2.11 MPa (28-day). Strength increment analysis indicates differential growth rates of 0.4 MPa and 0.25 MPa for 3%–4% and 4%–5% GGBFS additions, demonstrating its effective reinforcement capability.
The action mechanisms of the UCS related to cement and GGBFS) have been extensively proven (Kasmi et al., 2017). The hydration of cementitious phases (C3S and C2S) produces C-S-H gel and portlandite (Ca(OH)2), and a small amount of ettringite, which contributing to the initial strength development in stabilized dredged materials (Manso et al., 2013). The latent hydraulic components (CaO - SiO2-Al2O3 system) in GGBFS undergo alkaline activation through portlandite Ca(OH)2 mediation (Han et al., 2022), undergo secondary reactions (Mujtaba et al., 2018), low-calcium C-(A)-S-H gel is formed, exhibiting a denser structure compared to conventional C-S-H, with reduced porosity (Subagdja et al., 2020). Additionally, the Al2O3 in GGBFS reacts with C3A in cement to generate stable monosulfoaluminate (AFm) rather than expansive ettringite (AFt), thereby mitigating the risk of microcracking (Kryvenko et al., 2024), increase the strength of solidified silt (He et al., 2023). The continuously generated cementitious materials fill pores and enhance the structural compactness of the solidified silt soil (Han et al., 2022), which further improves the UCS.
According to local specifications including Zhejiang Province DBJ33/T 1312-2024 and TCECS 737-2020 from China Association for Engineering Construction Standardization, when the cement and GGBFS dosage exceeds 3%, the solidified silt soil demonstrates UCS exceeding 1.2 MPa at both 7-day and 28-day curing periods. The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) values of the solidified silty sludge under this strength level meet the technical requirements for subgrade materials. Considering cost effectiveness in practical construction applications, the subsequent construction section adopts the cement-GGBFS dosage combination of C3-S3.
3.1.2 UCS under seawater erosion
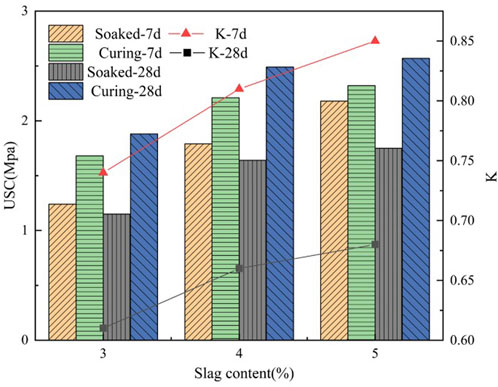
The strength loss of solidified silt soil in the presence of seawater is shown in Figure 5. Submersion in seawater induces marked deterioration in the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of stabilized silt. Strength losses range from 0.3–0.9 MPa at 7 days and 0.8–0.9 MPa at 28 days post-immersion. Short-term exposure (7 days) reveals an inverse correlation between slag powder content and UCS decline, with higher GGBFS proportions mitigating strength reduction. However, this protective effect diminishes over extended immersion periods, as no comparable trend emerges at 28 days. The inclusion of GGBFS demonstrates enhanced short-term resilience against seawater degradation in treated silt. Empirical evidence through K-value analysis confirms this improvement, with 7-day immersion coefficients progressing to 0.74, 0.81, and 0.85, and 28-day values advancing to 0.61, 0.66, and 0.68, respectively. These metrics underscore GGBFS’s capacity to bolster.
When seawater exists in the environment where solidified silt soil is located, ions such as Cl−, Mg2+ and SO42− will undergo ion exchange with C-S-H and Ca(OH)2 in the solidified silt soil, destroy gel network structure and weaken cementation ability (Hou et al., 2025). Although the C-(A)-S-H and AFm phases derived from GGBFS partially fill micropores and enhance initial stability, the continuous invasion of Cl− reacts with C-(A)-S-H to form Friedel’s salt, causing volumetric expansion (Yu et al., 2023). Additionally, ion exchange induces decalcification of C-(A)-S-H, transforming it into non-cementitious substances and initiating microcracks (Qu et al., 2022). Furthermore, the activation of GGBFS relies on Ca(OH)2 generated by cement hydration (Lv et al., 2020). Cl− preferentially reacts with Ca(OH)2 and aluminates to form Friedel’s salt, depleting Ca(OH)2 in the system (Zada Farhan et al., 2022). When Ca(OH)2 is insufficient, Cl− corrosion leads to decalcification of C-S-H, further damaging the structure (He et al., 2024c). Ultimately, this compromises the structural integrity of the solidified silt under prolonged marine exposure.
In coastal engineering practices, tidal actions subject the material to cyclic wetting and drying, causing repeated crystallization and dissolution of salts in the pores of the solidified soil, which accelerates structural degradation and performance deterioration. Incorporating GGBFS into the cement system enhances the matrix’s ability to bind Cl− and SO42−, thereby resisting erosive damage. In conclusion, it’s important to optimize the cement-GGBFS ratio and implement effective drainage structures in pavement design to minimize prolonged seawater exposure of the solidified silt subgrade.
3.2 Drying shrinkage of laboratory test
3.2.1 Drying shrinkage with varying initial moisture conditions
Figures 6A,B illustrate the dehydration and shrinkage behavior of stabilized silt soil across varying initial moisture conditions. The initial drying phase exhibits a linear relationship between moisture loss and shrinkage strain, reaching equilibrium within 10–15 days. The stabilized silt with moisture contents of 15%, 18%, 21%, and 24% demonstrates water loss values of 112–162 g and drying shrinkage strains of 2,258–3,231 με. The hydration reactions of cement and GGBFS require water molecule participation. The initial moisture content directly determines the amount of free water available for both reactions and evaporation, while moisture reduction induces soil shrinkage through capillary tension and surface energy effects (Zhang et al., 2022).
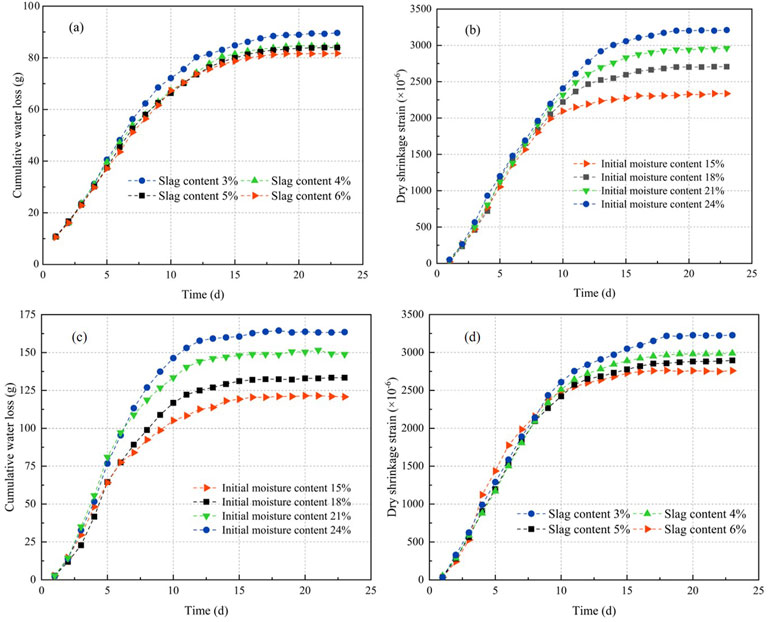
Figure 6. Results of drying shrinkage test: (a) Water loss and (b) dry shrinkage strain at Initial water content; (c) Water loss and (d) dry shrinkage strain at different GGBFS contents.
At excessively high moisture contents, the limited compressible air in specimens and the increased pore structures storing surplus free water result in rapid evaporation of this excess water during drying, leading to greater water loss and shrinkage strain (He and Lu, 2024b). Furthermore, excessive moisture in high-water-content specimens dilutes the cement-GGBFS hydration product matrix, weakens interparticle bonds, and likely creates more open or less stable pore structures (Umar Khan et al., 2021). This forms additional water-saturated pores where enhanced capillary negative pressure elevates overall shrinkage stress. Conversely, insufficient moisture content reduces the degree of cement-GGBFS hydration reactions, resulting in fewer hydration products to effectively fill pores (Aghaeipour and Madhkhan, 2018). Simultaneously, inadequate lubrication between soil particles hinders the compaction rearrangement of dry particles, ultimately generating more voids that also contribute to increased water loss and shrinkage strain (Huang et al., 2024b).
3.2.2 Drying shrinkage with different GGBFS contents
The water loss and drying shrinkage strain of stabilized silty soil with different GGBFS contents are shown in Figures 6C,D. As the GGBFS content increases, the water loss and drying shrinkage strain of the stabilized silty soil gradually decrease, ranging from 80 to 90 g and 2,731–3,689 με, respectively. The addition of GGBFS increases the dosage of the stabilizing agent, and the two-stage hydration reactions consume more water; therefore, the water loss and drying shrinkage strain increase with higher GGBFS incorporation. Additionally, compared to the variation range under different initial moisture contents, the water loss and drying shrinkage strain of the stabilized silty soil are reduced, indicating that the influence of initial moisture content is greater than that of the stabilizing material.
Although the secondary hydration reactions of GGBFS generate more cementitious substances, filling structural pores, converting some interconnected pores into isolated ones, and transforming large pores into finer ones (He and Lu, 2024a), the weight loss caused by moisture reduction due to drying shrinkage gradually decreases. However, the excessive moisture in high-moisture-content specimens affects compaction characteristics (He and Lu, 2024b), retaining more pores. While low-moisture-content specimens reduce pores through hydration product filling, their insufficient hydration degree and weaker cementation result in limited shrinkage inhibition (Eid et al., 2015). Furthermore, unreacted GGBFS may entrain pores containing air, increasing the overall porosity of the soil, which also leads to elevated water loss and drying shrinkage strain (He et al., 2024b). In conclusion, when evaluating the long-term performance of stabilized silty soil, moisture management holds greater operational priority in engineering practices.
3.3 Settlement and performance of field subgrade
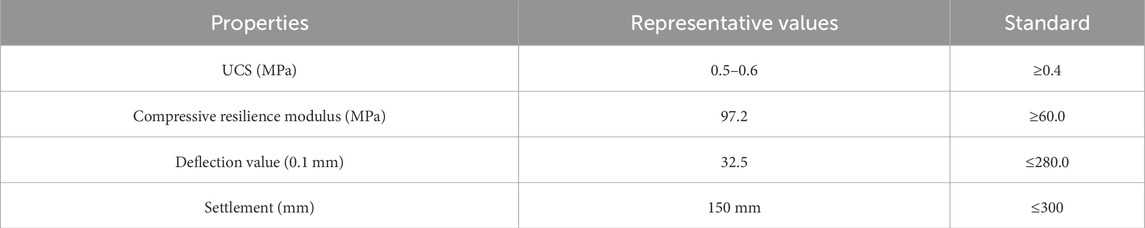
The performance results of the field subgrade are presented in Table 4. It can be observed that, except for the surface layer, the strength of 7-day cured specimens exceeds 0.5 MPa, and that of 28-day cured specimens reaches 0.6 MPa. All tested samples exhibit strengths greater than 0.4 MPa. The unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of the stabilized silty soil obtained from field tests is reduced by approximately half. This can be explained by the following: laboratory specimens achieve 100% compaction density through standard compaction methods, resulting in low porosity and a dense structure for the stabilized silty soil, while standard curing ensures thorough curing reactions. In contrast, field curing is affected by fluctuations in environmental temperature and moisture, and the layered compaction at construction sites cannot achieve the same degree of densification as in the laboratory (Wang et al., 2022). This increases porosity, leading to lower measured field strengths compared to laboratory results. Therefore, stricter control measures are recommended during the actual construction and placement of stabilized silt. Real-time compaction monitoring should be implemented during layered spreading. Immediately after construction, composite geotextile membranes or double-layer permeable non-woven fabrics should be laid, and spraying systems should be used to replenish surface moisture to maintain moisture during the construction period.
Although the UCS exhibited a significant reduction in outdoor conditions compared to indoor tests, the total settlement of the experimental subgrade section remained below the 300 mm limit. The typical deflection value was 32.5 (0.01 mm), far lower than the 280.0 control threshold specified in JTG D30-2015. The average compressive resilience modulus reached 97.2 MPa, markedly exceeding the 60 MPa technical requirement outlined in JTG D50-2017. No uneven settlement was observed during the entire monitoring period, and deflection values gradually stabilized over time, with minimal variation in resilience modulus across different test points. Overall, field test results demonstrate that the stabilized silt subgrade maintains structural integrity and uniform load distribution. These performance metrics validate the engineering stability and satisfactory bearing capacity of the stabilized subgrade under stress conditions.
3.4 Temperature and moisture in field pavement structures
3.4.1 Temperature in pavement structures
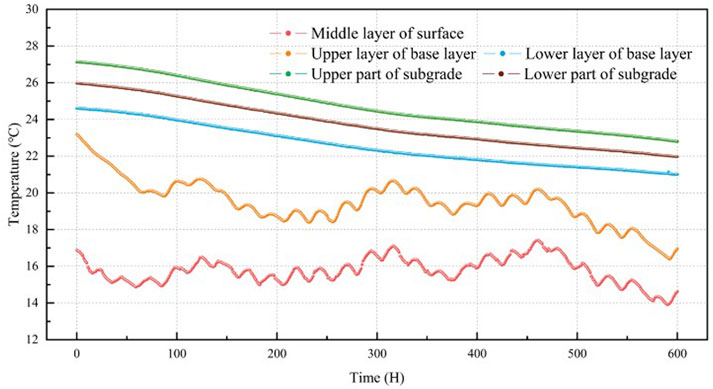
During the monitoring period of this test section, the temperature variations of each layer of the pavement structure are shown in Figure 7. The superficial subgrade stratum exhibited the highest temperatures, succeeded by deeper subgrade regions and the lower base layer, while the upper base and surface course recorded minimal temperature values. Continuous temperature dissipation occurred in the upper subgrade, lower subgrade, and lower base sections, with peak temperatures declining by 5°C (27°C–22°C), 3°C (25°C–22°C), and 3°C (24°C–21°C), respectively. The decrease in e temperature of is pavement structures is related to factors such as the reduction of solar radiation in winter and the heat loss caused by the heat exchange between the pavement structure and the external atmosphere (Cheng et al., 2021). Moreover, this overall decrease in pavement temperature is beneficial to the improvement of the resilient modulus of pavement materials (Abdollahi and Vahedifard, 2022).
Seasonal thermal dynamics significantly influenced surface and upper base layers, which displayed pronounced diurnal fluctuations compared to deeper sections. The lower base and subgrade strata demonstrated minimal responsiveness to ambient temperature shifts, with thermal inertia increasing proportionally to depth (Zhao et al., 2020). This depth-dependent thermal lag was most apparent during initial monitoring phases, diminishing as ambient temperature differentials stabilized. Notably, daily thermal variability within the test structure remained confined to 5°C, starkly contrasting the 55°C diurnal swings (60°C–5°C) reported in recent investigations (Liu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). The temperature stress of the pavement structure was in a relatively stable state.
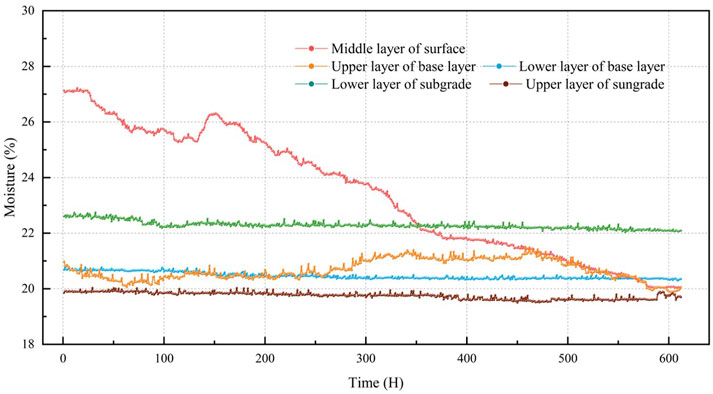
3.4.2 Moisture in pavement structures
During the monitoring period of this test section, the moisture changes of each layer of the pavement structure are shown in Figure 8. As can be seen from figure, the surface layer shows the largest moisture change during the entire monitoring period. The moisture reached 27% in the early stage of monitoring, and then decreased from 27% to 21% in the middle and late stages of monitoring. The moisture change of surface layer is due to the large amount of water replenishment during light rain in the early stage of monitoring. During non-rainy days such as sunny and cloudy days later, the continuous evaporation of water in the natural environment results in the largest moisture change of the surface layer during the entire monitoring period. The upper part of e base course shows the largest moisture change except for the surface layer. It slowly rises from 20.7% to 21.6% in middle and early stages of monitoring and then continuously drops to 20% in the late stage of monitoring. This is related to the water migration between the surface layer and the upper part of the base course in the middle and late stages of monitoring (Hu et al., 2015).
The subgrade exhibits elevated saturation levels, with moisture contents of 20% (upper stratum) and 23% (lower stratum), indicating significant moisture infiltration. Such conditions may compromise load-bearing performance and amplify fracture susceptibility in untreated soils. Stabilized silt soil subgrades and the lower base layer maintained consistent moisture equilibrium throughout the observation period. This stability mitigates pore pressure fluctuations in the base course induced by water migration from underlying strata, thereby reducing risks of differential vertical settlement or lateral deformation in the upper subgrade structure (Pan et al., 2021). In a study by Kodippily and Yeaman (2018), when the moisture in the pavement base course increases and the temperature decreases at the end of the day, a sudden tensile strain will occur in the base course. The moisture data of the test section remains stable within a day, which is beneficial to e stability of the stress of the pavement structures itself. In the short term, the influence of moisture on the strain response behavior of the pavement structures can be considered very small.
3.5 Strain behavior under overweight truck loading
3.5.1 Instantaneous strain
When vehicles travel over pavement structures, the contact between the wheel track and the pavement surface induces strain responses across different structural layers. The strain response curves obtained from this interaction enable the determination of stress conditions and magnitudes within each pavement layer.
Figure 9 shows the representative strain response curves of overweight trucks on different layers and in different directions of the pavement structure. Monitoring data reveal localized strain peaks coinciding with axle passage, where interconnected strain profiles collectively map the composite deformation pattern. In the asphalt layer, vertical sensors predominantly record 70 με compressive strain, while transverse sensors exhibit tensile strain with minimal residual deformation. Axle-specific variations align with load distribution patterns (Ge et al., 2022), showing 20 με for the front axles and 50–60 με for rear axles. Within the base layer, longitudinal sensors display cyclical compression-tension-compression sequences, whereas horizontal instrumentation registers mixed strain modes: 10 με (front axles) and 20 με (rear axles). Transverse tensile stresses in surface and lower base layers correlate with sensor positioning relative to tire edges. This is because when the tire passes through the sensor, the sensor is located outside the tire and at the tire shoulder (Yang et al., 2021; Ye et al., 2021).
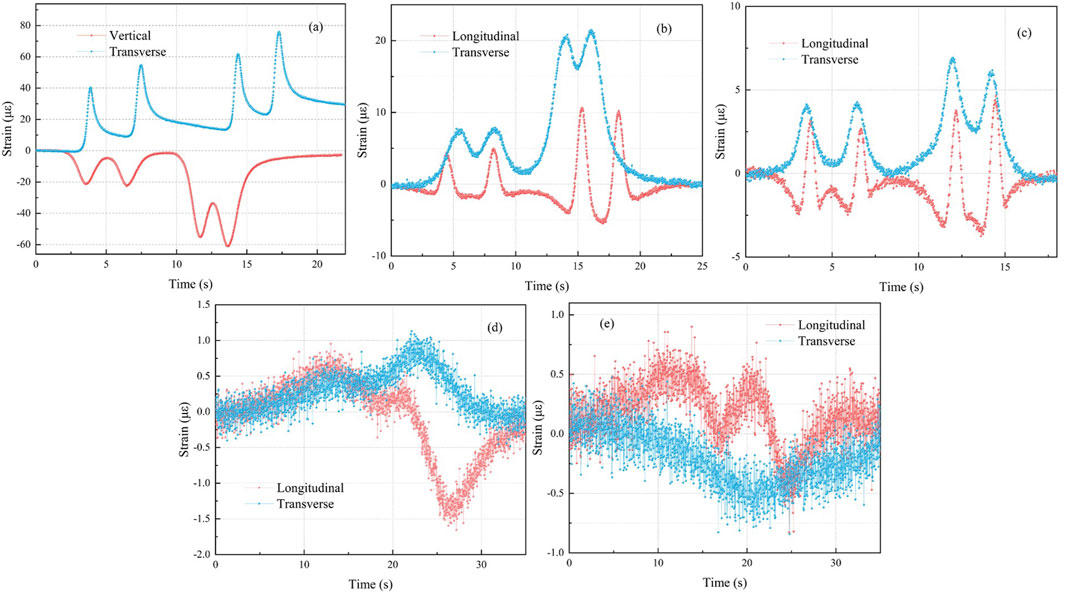
Figure 9. Time-course curves at pavement structures: (a) middle asphalt surface layers and (b) upper parts of base layer and (c) lower parts of base layer and (d) beneath the wheel path at upper part of subgrade and (e) outside the wheel path at upper part of subgrade.
With increasing structural depth, strain amplitudes attenuate exponentially—base layer strains halve surface layer values, while lower base deformations fall below 10 με. Subgrade instrumentation demonstrates alternating tensile-compressive cycles longitudinally, forming oscillatory “up-down” waveforms. Transverse sensors beneath wheel path register compressive stresses (1-2 με at 0.3 m depth), contrasting with tensile strains outside load zones. No measurable deformation occurs at 0.8 m subgrade depth, confirming load dissipation mechanisms.
Current fatigue resistance criteria in pavement design, as outlined by AASHTO and JTG D50-2017, prescribe critical tensile strain limits of 60–150 με for asphalt surface layers and ≤60–80 με for semi-rigid base courses. Field measurements from this investigation recorded tensile strains of 20∼25 με in subgrade layers during load testing. This disparity highlights the negligible mechanical impact of vehicular loads on underlying strata, confirming efficient stress dissipation through upper pavement layers. The observed performance aligns with theoretical load-transfer mechanisms, where composite pavement systems effectively attenuate dynamic stresses before reaching foundational soils. Such empirical validation underscores the test section’s exceptional structural resilience, meeting advanced engineering requirements for heavy-load infrastructure.
3.5.2 Strain changes in long-term driving loading
According to the vehicle loading plan in this paper, a single loading site bears 792–1,320 passes of a single four - axle vehicle per day during the monitoring period. 26-day loading could simulate pavement service conditions equivalent to 16–33 months of standard axle loads. The ranges of strain magnitudes of sensors in each layer of the pavement structure during the monitoring period of the test section are shown in Figure 10, and the appearance of the pavement after the test is shown in Figure 11.
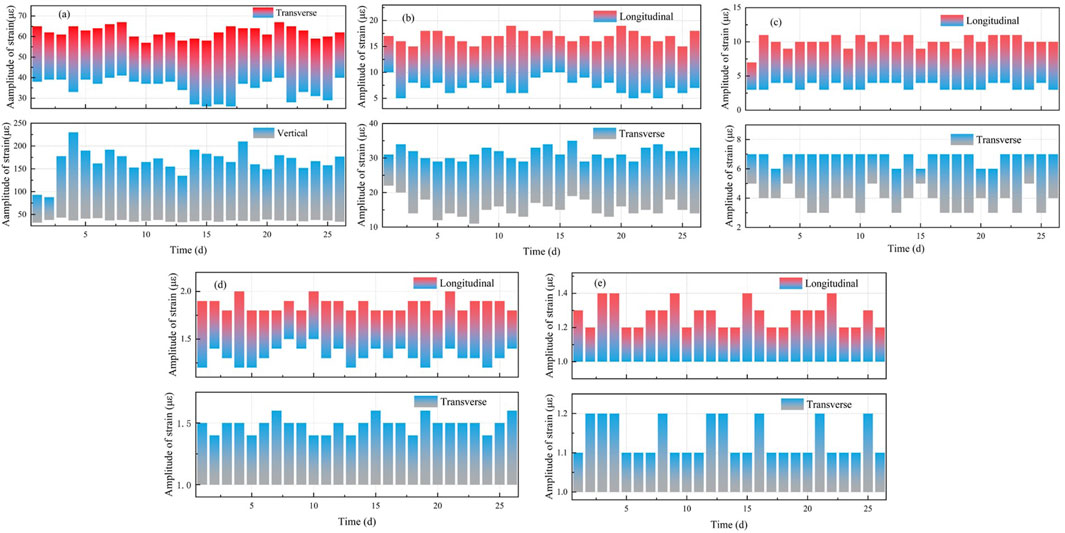
Figure 10. Instantaneous response change at pavement structures: (a) middle asphalt surface layers and (b) upper parts of base layer and (c) lower parts of base layer and (d) beneath the wheel path at upper part of subgrade and (e) outside the wheel path at upper part of subgrade.
Under prolonged service conditions, the asphalt surface layer exhibits pronounced cyclic deformation, with transverse strains oscillating within 20–200 με and vertical strains ranging 35–65 με. Vertical strain magnitudes demonstrate spatial dependency, correlating with localized loading patterns and transient vehicular velocity, as documented in recent studies (Clauß and Wellner, 2023). In contrast, the base layer displays attenuated mechanical responses, with horizontal strains confined to 5–30 με and vertical strains limited to 5–10 με, reflecting enhanced structural uniformity and reduced sensitivity to load positioning. Subgrade instrumentation at 0.3 m depth reveals minimal deformation gradients, measuring 1-2 με beneath wheelpath and 1–1.5 με in adjacent zones. This mechanical stability aligns with the absence of observable structural deterioration-no rutting, cracking, or surface deformation—after cumulative exposure to 30,000 overweight truck passes. The resilience underscores the efficacy of the pavement-subgrade system in mitigating load-induced stresses, validating its compliance with durability standards for high-traffic infrastructure.
4 Summary and conclusion
This study systematically elucidates the engineering applicability and environmental adaptability mechanisms of cement-GGBFS composite stabilized dredged silt as recycled subgrade material through multi-scale experiments and engineering validation, leading to the following main conclusions:
(1) Laboratory and field investigations confirm the engineering feasibility of cement-GGBFS stabilized silt as a sustainable subgrade material. Despite strength reduction in practical applications, the stabilized silt meets critical technical specifications and demonstrates structural compatibility under real load conditions.
(2) The synergistic stabilization with GGBFS enhances mechanical properties and resistance to environmental erosion, offering solutions for strength optimization and degradation mitigation in aggressive service environments, highlighting slag’s dual role in reinforcing strength and alleviating environmental deterioration.
(3) Pavement system exhibits depth-dependent strain decay, aligning with international design standards, and validates its capacity to endure long-term heavy traffic loads without significant fatigue damage.
(4) The stabilized silt demonstrated stability under natural temperature and moisture fluctuations during monitoring, maintaining an equilibrium moisture state to ensure durability under climatic variations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
CZ: Formal Analysis, Validation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. DY: Validation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Formal Analysis. BS: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition. YW: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Project administration. YH: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. HW: Writing – review and editing, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The project presented in this article is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (300102314201), Key R&D project of Shaanxi Province (2024GX-YBXM-423), Science and Technology Innovation 2025 Major Project of Ningbo (2019B10048) and National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (X202410710595).
Conflict of interest
Authors BS, YW, and YH were employed by Ningbo Communications Engineering Construction Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdollahi, M., and Vahedifard, F. (2022). Predicting resilient modulus of unsaturated subgrade soils considering effects of water content, temperature, and hydraulic hysteresis. Int. J. Geomechanics 22(1), 04021259. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002244
Aghaeipour, A., and Madhkhan, M. (2018). Effect of ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) on mechanical properties of roller-compacted concrete pavement. J. Test. Eval. 48 (4), 2786–2802. doi:10.1520/JTE20170786
Arraigada, M., Pugliessi, A., Partl, M. N., and Martinez, F. (2014). Effect of full-size and down-scaled accelerated traffic loading on pavement behavior. Mater. Struct. 47 (8), 1409–1424. doi:10.1617/s11527-014-0319-2
Chen, M., Wu, D., Chen, K., Cheng, P., and Tang, Y. (2024a). The influence of fly ash-based geopolymer on the mechanical properties of OPC-solidified soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 432, 136591. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.136591
Chen, Q., Xie, K., Tao, G., Nimbalkar, S., and Zhang, H. (2024b). Laboratory assessment of impact of nano-SiO2 on different soil types in onshore and offshore environment. Acta Geotech. 19 (8), 5065–5087. doi:10.1007/s11440-023-02067-0
Cheng, H., Jianing, L., Lijun, S., and Liu, L. (2021). Critical position of fatigue damage within asphalt pavement considering temperature and strain distribution. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 22(14), 1773–1784. doi:10.1080/10298436.2020.1724288
Clauß, M., and Wellner, F. (2023). Influence of the load position of heavy vehicles on the service life of asphalt pavements. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 24(2), 2149962. doi:10.1080/10298436.2022.2149962
Dai, C.-X., Zhang, Q.-F., He, S.-H., Zhang, A., Shan, H.-F., and Xia, T.-D. (2021). Variation in micro-pores during dynamic consolidation and compression of soft marine soil. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9 (7), 750. doi:10.3390/jmse9070750
Eid, J., Taibi, S., Fleureau, J. M., and Hattab, M. (2015). Drying, cracks and shrinkage evolution of a natural silt intended for a new earth building material. Impact of reinforcement. Constr. Build. Mater. 86, 120–132. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.03.115
Gao, Q., Ge, J., Zhang, J., Ren, Z., Wu, D., Cheng, G., et al. (2023). Experimental study on the engineering characteristics of modified silt in the Yellow River alluvial plain. Constr. Build. Mater. 398, 132491. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132491
Garg, N., Li, Q., and Brill, D. (2020). Accelerated pavement testing of perpetual pavement test sections under heavy aircraft loading at FAA’s national airport pavement test facility. J. Test. Eval. 48 (1), 107–119. doi:10.1520/JTE20180906
Ge, H., Quezada, J. C., Houerou, V. L., and Chazallon, C. (2022). Multiscale analysis of tire and asphalt pavement interaction via coupling FEM–DEM simulation. Eng. Struct. 256, 113925. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.113925
Habbouche, J., Piratheepan, M., Hajj, E. Y., Bista, S., and Sebaaly, P. E. (2022). Full-scale pavement testing of a high polymer-modified asphalt concrete mixture. J. Test. Eval. 50 (2), 865–888. doi:10.1520/JTE20210283
Han, Y., Qin, Y., Wang, Y., and Zhang, X. (2022). The effect of different ages and water-binder ratios on the mechanical properties of circulating fluidized bed combustion desulfurization slag cement-soil. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 17, e01660. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01660
He, J., Luo, S.-r., Li, W.-j., Kang, D.-y., and Zuo, Z.-w. (2024a). Capillary water absorption and strength of solidified marine soft soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 423, 135729. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135729
He, R., and Lu, N. (2024a). Air void system and freezing-thawing resistance of concrete composite with the incorporation of thermo-expansive polymeric microspheres. Constr. Build. Mater. 419, 135535. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135535
He, R., and Lu, N. (2024b). Hydration, fresh, mechanical, and freeze-thaw properties of cement mortar incorporated with polymeric microspheres. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 7 (3), 92. doi:10.1007/s42114-024-00899-2
He, R., Nantung, T., and Lu, N. (2024b). Unraveling microstructural evolution in air-entrained mortar and paste: insights from MIP and micro-CT tomography amid cyclic freezing-thawing damage. J. Build. Eng. 94, 109922. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.109922
He, R., Nantung, T., Olek, J., and Lu, N. (2023). Field study of the dielectric constant of concrete: a parameter less sensitive to environmental variations than electrical resistivity. J. Build. Eng. 74, 106938. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106938
He, X., Yang, J., Niu, M., Hanif, A., and Li, G. (2024c). Synthesis of CaLiAl-LDHs and its optimization on the properties and chloride binding capacity of eco-friendly marine cement-based repair materials. J. Clean. Prod. 443, 141183. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141183
Hou, W., Ye, F., Yu, Y., Chen, D., Wang, J., Liu, F., et al. (2025). Experimental study on the strength characteristics and seawater degradation resistance of sandy silt solidified with alkali-activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 458, 139610. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.139610
Hu, X., Shen, Z., and Walubita, L. F. (2015). Three-dimensional modelling of multilayered asphalt concrete pavement structures: strain responses and permanent deformation. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 16(3), 727–740. doi:10.1080/14680629.2015.1028968
Huang, B., Liu, J., Tang, W., Li, J., Li, B., and Wei, A. (2024a). Development of composite magnesium oxychloride cement and its application on solidification of dredged sludge. Constr. Build. Mater. 420, 135587. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135587
Huang, C., He, R., Lu, N., and Feng, Y. (2024b). Influence of the colloidal nano silica on the bonding of new-to-old concrete interface. Constr. Build. Mater. 428, 136390. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.136390
Jiang, X., Titi, H., Ma, Y., Polaczyk, P., Zhang, M., Gabrielson, J., et al. (2022). Evaluating the performance of inverted pavement structure using the accelerated pavement test (APT). Constr. Build. Mater. 346, 128489. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128489
Kasmi, A., Abriak, N.-E., Benzerzour, M., and Azrar, H. (2017). Environmental impact and mechanical behavior study of experimental road made with river sediments: recycling of river sediments in road construction. J. Material Cycles Waste Manag. 19 (4), 1405–1414. doi:10.1007/s10163-016-0529-5
Kim, G. M., Adem, J. K., and Park, S. (2024). Reaction and microstructural characteristics of OPC pastes with low-lime calcium silicate cements under carbonation curing. Constr. Build. Mater. 415, 134993. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.134993
Kim, H. G., Atta ur, R., Qudoos, A., and Ryou, J.-S. (2018). Self-healing performance of GGBFS based cementitious mortar with granulated activators exposed to a seawater environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 188, 569–582. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.092
Kodippily, S., John, Y., Theunis, H., and Tighe, S. (2020). Effects of extreme climatic conditions on pavement response. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 21(5), 1413–1425. doi:10.1080/14680629.2018.1552620
Kodippily, S., Yeaman, J., and Henning, T. F. (2018). Evaluating pavement performance through smart monitoring – effects of soil moisture, temperature and traffic. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 19 (1), 71–86. doi:10.1080/14680629.2016.1235507
Kryvenko, P., Sikora, P., Rudenko, I., and Konstantynovskyi, O. (2024). Advances in using seawater in slag-containing cement systems. J. Build. Eng. 96, 110386. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.110386
Ku, J., Roh, S., and Hwang, H. (2022). Monitoring of structural performance of early-age concrete pavement. Sensors Mater. 34 (1), 437. doi:10.18494/sam3761
Liu, X., Zhao, J., and Liu, L. (2023). Advancements in the evolution of engineering characteristics and reinforcement technologies for subgrade silt. Materials 16 (21), 6965. [Online]. doi:10.3390/ma16216965
Liu, Y., Lu, H., Liu, M., Cai, L., Wei, N., and Liu, Y. (2022). Microanalytical characterizations, mechanical strength and water resistance performance of solidified dredged sludge with industrial solid waste and architecture residue soil. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 17, e01492. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01492
Liu, Z., Cui, B., Yang, Q., and Gu, X. (2024). Sensor-based structural health monitoring of asphalt pavements with semi-rigid bases combining accelerated pavement testing and a falling weight deflectometer test. Sensors 24 (3), 994. doi:10.3390/s24030994
Lv, W., Sun, Z., and Su, Z. (2020). Study of seawater mixed one-part alkali activated GGBFS-fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 106, 103484. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103484
Manso, J. M., Ortega-López, V., Polanco, J. A., and Setién, J. (2013). The use of ladle furnace slag in soil stabilization. Constr. Build. Mater. 40, 126–134. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.09.079
Mujtaba, H., Aziz, T., Farooq, K., Sivakugan, N., and Das, B. M. (2018). Improvement in engineering properties of expansive soils using ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Geol. Soc. India 92 (3), 357–362. doi:10.1007/s12594-018-1019-2
Pan, Q.-x., Zheng, C.-c., Lü, S.-t., Qian, G.-p., Zhang, J.-h., Wen, P.-h., et al. (2021). Field measurement of strain response for typical asphalt pavement. J. Central South Univ. 28 (2), 618–632. doi:10.1007/s11771-021-4626-9
Pu, S., Zhu, Z., Song, W., Wan, Y., Wang, H., and Xu, X. (2020). Comparative study of compressibility and deformation properties of silt stabilized with lime, lime, and cement, and SEU-2 binder. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 45 (5), 4125–4139. doi:10.1007/s13369-020-04406-9
Pu, S., Zhu, Z., Wang, H., Song, W., and Wei, R. (2019). Mechanical characteristics and water stability of silt solidified by incorporating lime, lime and cement mixture, and SEU-2 binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 214, 111–120. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.103
Qu, F., Li, W., Guo, Y., Zhang, S., Zhou, J. L., and Wang, K. (2022). Chloride-binding capacity of cement-GGBFS-nanosilica composites under seawater chloride-rich environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 342, 127890. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127890
Shi, Y., Weng, H., Yu, J., and Gong, Y. (2023). Study on modification and mechanism of construction waste to solidified silt. Materials 16 (7), 2780. doi:10.3390/ma16072780
Shu, S., Xue, X., Wang, Q., Li, Y., and Hadkhale, P. (2024). Long-term environmental impact of an artificial island of solidified dredged marine silt. Environ. Geotech. 11 (9), 725–734. doi:10.1680/jenge.22.00066
Subagdja, A., Sofyan, A., and Rusmanto, A. (2020). Compressive strength and permeability of concrete by using GGBFS against seawater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 830 (2), 022045. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/830/2/022045
Tamrakar, P., and Nazarian, S. (2021). Moisture effects on moduli of pavement bases. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 22 (11), 1410–1422. doi:10.1080/10298436.2019.1696460
Umar Khan, M., Nasir, M., Baghabra Al-Amoudi, O. S., and Maslehuddin, M. (2021). Influence of in-situ casting temperature and curing regime on the properties of blended cement concretes under hot climatic conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 272, 121865. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121865
Wang, H., Wang, Z., Yang, W., Jia, H., and You, Z. (2025). Characterization, pollution, and beneficial utilization assessment of dredged sediments from coastal ports in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 211, 117389. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.117389
Wang, S.-j., Jiang, H.-g., Wang, Z.-b., Wang, Y.-j., Li, Y.-x., Geng, X.-y., et al. (2022). Evaluation of heavy roller compaction on a large-thickness layer of subgrade with full-scale field experiments. J. Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A 23 (11), 933–944. doi:10.1631/jzus.A2200201
Wu, X.-T., Qi, Y., Liu, J.-N., and Chen, B. (2021). Solidification effect and mechanism of marine muck treated with ionic soil stabilizer and cement. Minerals 11 (11), 1268. doi:10.3390/min11111268
Yang, H., Zhu, J., Tao, Y., Wang, Z., and Zheng, Q. (2022). Effect of the dry-wet cycle on the performance of marine waste silt solidified by calcium carbide residue and plant ash. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10 (10), 1442. doi:10.3390/jmse10101442
Yang, H.-l., Wang, S.-j., Miao, Y.-h., Wang, L.-b., and Sun, F.-y. (2021). Effects of accelerated loading on the stress response and rutting of pavements. J. Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A 22 (7), 514–527. doi:10.1631/jzus.A2000259
Yang, R., Gan, X., Liu, L., Sun, L., and Yuan, J. (2023). Field measurement and analysis on the mechanical response of asphalt pavement using large-particle-size crushed stone base treated with fly ash and slag powder. Materials 16 (23), 7277. doi:10.3390/ma16237277
Ye, Z., Miao, Y., Zhang, W., and Wang, L. (2021). Effects of random non-uniform load on asphalt pavement dynamic response. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 14 (3), 299–308. doi:10.1007/s42947-020-0147-0
Yu, Z., Long, Y., Wang, H., Nie, R., and Shen, X. (2023). Macro and micro properties of the cement-based material mixed with coral powder and GGBFS under seawater condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 404, 133279. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133279
Zada Farhan, K., Azmi Megat Johari, M., and Demirboğa, R. (2022). Evaluation of properties of steel fiber reinforced GGBFS-based geopolymer composites in aggressive environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 345, 128339. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128339
Zhang, H., Liu, M., Yu, J., Sun, Y., Zhou, P., Song, J., et al. (2022). Mechanical and physical properties of silt-based foamed concrete with different silt types. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 47 (10), 12803–12815. doi:10.1007/s13369-021-06551-1
Zhang, J., Hu, H., Peng, J., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, A. (2024). Enhanced understanding of subgrade soil hydraulic characteristics: effects of wetting–drying cycles and stress states on subgrade water migration. J. Hydrology 635, 131165. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.131165
Zhang, T., Cai, G., and Liu, S. (2017). Application of lignin-based by-product stabilized silty soil in highway subgrade: a field investigation. J. Clean. Prod. 142, 4243–4257. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.002
Zhao, X., Aiqin, S., and Ma, B. (2020). Temperature response of asphalt pavement to low temperatures and large temperature differences. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 21(1), 49–62. doi:10.1080/10298436.2018.1435883
Keywords: cement-slag stabilized silt, drying shrinkage, seawater erosion, pavement structures, dynamic response, temperature and moisture, solid waste utilization
Citation: Zhu C, Yang D, Song B, Wang Y, Hu Y and Wu H (2025) Optimization ratios and multi factor service adaptability of cement-GGBFS stabilized silt in pavement structures. Front. Mater. 12:1597578. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1597578
Received: 21 March 2025; Accepted: 15 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited by:
Bing Bai, Beijing Jiaotong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Mohammad M. Karimi, Tarbiat Modares University, IranChuanqing Fu, Zhejiang University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Yang, Song, Wang, Hu and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenyu Zhu, MjAxODkwNTYxNEBjaGQuZWR1LmNu
 Chenyu Zhu
Chenyu Zhu Dianqiu Yang
Dianqiu Yang Bingquan Song2
Bingquan Song2