- 1Department of Stomatology, Xichang People’s Hospital, Xichang, Sichuan, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases and National Center for Stomatology and National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Med-X Center for Materials, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, General Surgery, Xichang People’s Hospital, Xichang, Sichuan, China
Objective: This study aimed to develop a baicalin (BA)-containing storage saline solution and investigate their effects on the physicochemical properties and bioactivity of sandblasted with large grit and acid-etched (SLA) titanium surfaces.
Materials and methods: SLA titanium specimens stored in air and 0.9% NaCl solution were served as controls and stored in three different concentrations of baicalin-containing saline solution were served as experimental groups to investigate the effects of the new storage methods. The specimens were examined for surface microstructure, surface element composition, surface wettability and roughness by field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), water contact angle measurement and laser confocal microscopy, respectively. In addition, the osteoblasts proliferation assay was used to investigate the bioactivity of the SLA titanium surfaces preserved in different conditions.
Results: The micron-scale crystals of different diameters were observed on surfaces stored in three different concentrations of baicalin-containing saline solution. XPS analyses revealed that the amount of titanium dioxide (TiO2) decreased and the carbon (C) increased with the concentration of baicalin increasing. Compared to the control groups, specimens stored in baicalin-containing saline solution exhibited better hydrophilicity. The roughness results showed that specimens stored in 10 µM BA and 100 µM BA solutions displayed lower surface roughness. Moreover, the preservation of specimens in the 100 µM BA solution greatly enhanced the proliferation of osteoblasts.
Conclusion: The storage of SLA titanium materials in baicalin-containing saline solution, especially in the concentration of 100 µM baicalin, could effectively improve the surface properties and make the environment conducive to the proliferation of osteoblasts, which could be a new type of titanium implant storage solution.
1 Introduction
Implant dentures, characterized by their aesthetic benefits, comfort, high chewing efficiency and preservation of adjacent tooth integrity, have gradually become effective treatments for many patients with dentition defects, which are widely accepted worldwide as the third set of teeth for humans. Titanium-based materials are the most widely utilized in implant applications due to their excellent mechanical properties, chemical stability and biocompatibility (Jeng and Chiang, 2020; Li et al., 2021; Li et al., 2020). However, with the widespread application of dental implant technology, implant-related complications have become significant clinical challenges. The establishment of osseointegration in permanent implantation fundamentally depends on interfacial biological activities at the bone-implant interface, and failure in this process may result in osseointegration delay and even the implant failure (Zhang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2018). To this end, domestic and foreign scholars have conducted extensive research on the surface modification of titanium implants to enhance their osteogenic activity and promote osseointegration (Guo et al., 2025).
After fabrication, titanium implants undergo steps such as storage, transportation, and warehousing before entering clinical use. Studies have revealed that the biocompatibility of titanium surfaces diminishes over time, suggesting the occurrence of bioactive aging phenomena in the surfaces (Lee and Ogawa, 2012). To address the challenges of mitigating surface bioactive degradation in titanium implants and augmenting their osteogenic integration capacity, the strategic optimization of post-fabrication storage parameters for titanium biomedical devices has emerged as a critical focus in implantology research. Numerous anti-aging methodologies have been investigated and implemented globally, such as ultraviolet functionalization, saline immersion treatments, plasma treatment, and low vacuum storage (Choi et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2016). Among these, saline solution storage is the most convenient and economical method. Literature studies have demonstrated that prolonged storage in saline solution effectively mitigates carbonaceous deposition on titanium substrates, enhances surface hydrophilicity, and promotes osteoblast adhesion, migration, and proliferation (Ghassemi et al., 2018). In addition, normal saline solution has been used clinically for implant storage, such as the ITI-SLActive hydrophilic implant.
Baicalin is a flavonoid component isolated from the root of the Chinese herb Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (Labiatae), which is considered to exert antioxidation, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anti-apoptotic and other pharmacological activities (Zhu et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2024; Liang et al., 2024). Moreover, numerous studies have confirmed that the baicalin exhibits significant osteoprotective effects, such as increasing bone density, combating osteoporosis, promoting osteoblast differentiation, and inhibiting osteoclast differentiation (Hu et al., 2024; Kunimatsu et al., 2022; Jin et al., 2022). These effects are essential for enhancing implant osseointegration and improving the success rate of implant restoration.
Sandblasted with large grit and acid-etched (SLA), the most prevalent methodology, could generate hierarchically micro-structured topography on titanium surfaces, which has been demonstrated in extensive studies to significantly promote osteogenesis and improve bone-implant integration (Srinivasan et al., 2014; van Velzen et al., 2015; Yeo, 2014). Given the widespread clinical adoption of sandblasted with large grit and acid-etched (SLA) treatment as a well-established titanium surface modification technique, which has been extensively integrated into numerous commercially available implant systems including Straumann, Bego and Ankylos. The SLA titanium surfaces were selected as both control specimens and experimental substrates in this investigation. This approach ensures clinical translatability while systematically evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of the baicalin-containing saline storage solution.
To date, the preservation media employed in studies for hydrated storage of implants predominantly utilize double-distilled water (dd H2O) or saline solution. Existing literature lacks investigations into implant storage methodologies incorporating baicalin. The objective of this study was to establish a cost-effective aqueous preservation protocol. By employing varying concentrations of baicalin-containing saline solutions for the implant storage, we evaluated the impact of this preservation strategy on the surface characteristics and bioactivity of SLA titanium materials. The study also aimed to identify the optimal baicalin concentration for implant storage, which will be a valuable reference for future storage designs.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Specimen preparation
Commercially pure titanium (99.5 wt% purity, China) disks with dimensions of Φ5 mm × 1 mm and Φ10 mm × 1 mm were polished with a series of waterproof silicon carbide (SiC) abrasive paper (#600, #800, #1000, #1200, and #1500). Subsequently, the titanium disks underwent sequential ultrasonic cleaning in distilled water, ethanol, and again in distilled water, each for a duration of 15 min, followed by drying at room temperature for 2 h. The SLA titanium surface was first prepared via sandblasting with large grit Al (OH)3, then etching in HF/HNO3 solution (H2O: HF(0.11 mol/L): HNO3(0.09 mol/L) = 1,000:2:4) for 10 min at room temperature, followed by etching in H2SO4/HCl solution (H2O: HCl (5.8 mol/L):H2SO4 (8.96 mol/L) = 2:1:1) for 45 min at 80°C in a water bath. Following the aforementioned procedures, all SLA specimens were ultrasonically cleaned to remove surface contaminants. Then, the samples were sterilized in an autoclave for 15 min at 121°C prior to use, and finally dried in an oven for 24 h at 65°C.
2.2 Storage solution preparation
Preparation of baicalin-containing storage saline solution: 0.9% NaCl solution (AR, SCR, China) and baicalin (purity≥98%, Macklin, Shanghai, China) were purchased for the storage solution preparation. Firstly, 0.446 g baicalin crystals were accurately weighed and dissolved in 1 L 0.9% NaCl solution. After stirring the solution with a magnetic stirrer for 24 h, 1 mM baicalin containing solution was obtained. Subsequently, the solution was diluted 10-fold and 100-fold with additional 0.9% NaCl solution to prepare storage solutions with concentrations of 100 μM and 10 µM baicalin, respectively. For comparative analysis, the prepared SLA specimens stored in Air and 0.9% NaCl solution were used as control groups. In addition, the prepared SLA specimens were stored in three different concentrations of baicalin-containing saline solution (10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA). All SLA specimens were preserved under ambient temperatures for 4 weeks.
2.3 Surface characterization
The surface morphology of prepared samples, which were stored in different media (Air, 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA) for 4 weeks, was investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, LEO, Germany). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo SCIENTIFIC K-ALPHA, USA) was employed to characterize the surface chemical composition of each sample utilizing a monochromatic Al Kα electrode (15 kV, 150 W, and 45° take-off angle). Survey and high-resolution spectra were acquired using pass energies of 160 and 40 eV, separately. The reference binding energy of each element was obtained from the National Institute of Standards and Technology XPS Online Data base (http://srdata.nist.gov/xps/). Spectra were calibrated by adjusting the binding energy of C 1s to 284.8 eV. The surface wettability of the titanium samples was evaluated based on the static contact angle of one drop of deionized water (5 µL) using an Automatic Contact Angle Meter Model (SL200B, Kino, USA) at room temperature. The roughness of samples was examined by using the laser confocal microscopy (KEYENCE VK-X1,000, Japan). All measurements were performed in triplicate.
2.4 Cell culture
MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells were purchased from the Chinese Academy of Sciences Cell Bank (Shanghai, China). MC3T3-E1 cells were resuspended in vitro and cultured in an α-Minimum Essential Medium (α-MEM, Gibco, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, USA) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco, USA) at 37°C in a cell incubator (95% relative humidity, 5% CO2). The culture medium was routinely changed every 3 days and the cells were passaged at a ratio of 1:4 after reaching 80% cell confluence.
2.5 Cell proliferation assay
To assess cell proliferation, MC3T3-E1 cells (2 × 103 cells/well) were seeded on the prepared titanium surfaces, which were stored in different media for 4 weeks (Air, 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA) in 96-well plates and cultured for 1, 3 and 6 days. In the following days, samples were washed with PBS (phosphate buffer solution) once and then replaced with 100 µL fresh medium and 10 µL Cell Counting Kit 8 (CCK8) regents (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). After incubation at 37°C for 2 h, the medium was transferred into new 96-well plates, and the absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader. All experiment measurements were performed in triplicate.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The software program IBM SPSS Statistics (v22.0; IBM Corp) was used for the statistical analysis. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post-hoc tests. P < 0.05 was set as the threshold for statistical significance.
3 Results
3.1 Surface micromorphology
To assess the influence of different storage conditions (Air, 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA) on the SLA titanium surfaces, we examined the surface microstructure by SEM (Figure 1). The SLA titanium surface exhibited a uniform distribution of micro-pits and spike-like structures when observed at low magnification. In higher magnification examination, sharp edges and micro-pits were observed on the surface. These SEM findings indicated that the various storage conditions employed in this study had no significant impact on the original microstructure of the SLA titanium surfaces. Titanium samples stored in 0.9% NaCl solution and different concentrations of baicalin solution exhibited crystals on their surfaces. In the 0.9% NaCl solution group, the SLA surfaces were characterized by the presence of dense and fine NaCl crystals. When exposed to 10 µM baicalin storage solution, the SLA surfaces exhibited fewer crystals with notable size variation. At a higher concentration of 100 µM baicalin storage, the crystals displayed uniform size and were distributed evenly. In the 1 mM BA group, increased baicalin concentration led to the progressive aggregation of crystals into flake-like structures and covered the surfaces.
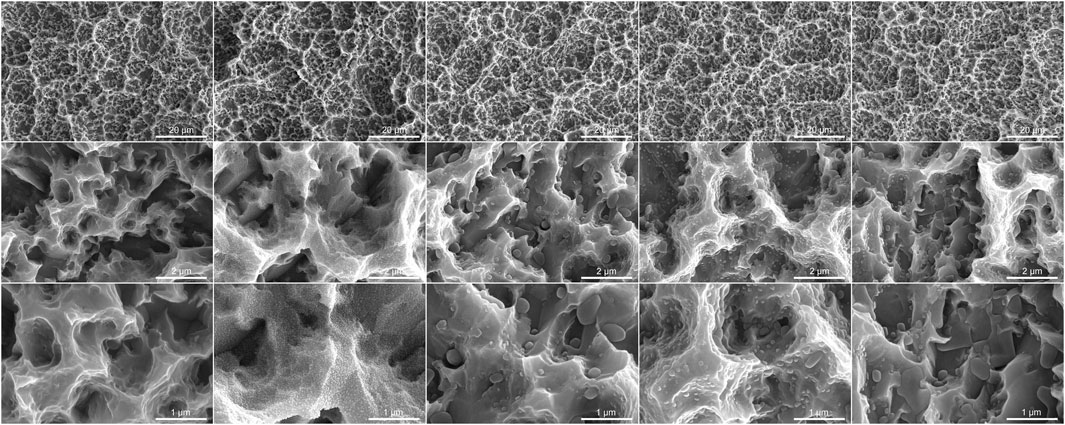
Figure 1. Scanning electron microscopy images of SLA titanium surfaces under different storage conditions for 4 weeks (Magnification 5,000×, 50,000× and 1,000,00×).
3.2 Analysis of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
XPS survey spectra obtained from the SLA titanium surfaces (Figure 2A) showed that carbon (C), titanium (Ti) and oxygen (O) were present on the surfaces stored in different media for 4 weeks (Air, 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA). XPS high-resolution spectra of C 1s, O 1s and Ti 2p on the different titanium surfaces were respectively shown in Figures 2B–D. On the SLA titanium surfaces stored in Air and 0.9% NaCl solution without baicalin, adventitious carbon(C) peaks were most likely attributed to contamination (Liu et al., 2015). Figure 2B showed that the peaks of C 1s for SLA samples were attributed at 284.8 eV. On the SLA titanium surfaces stored in 0.9% NaCl solution, the peaks of C 1s decreased compared with that in other groups. As shown in Figure 2C, in the Air and 0.9% NaCl groups, the peaks of O 1s were attributed at 530.3 eV and 532.3 eV, whereas 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA samples possessed two peaks at 530.3 eV and 532.9 eV, indicating that there were new oxygen-based compounds on the surfaces of the titanium samples. As shown in Figure 2D, two peaks at 464.5 eV and 458.8 eV indicated Ti 2p in all five surfaces. The peaks of C 1s increased gradually, whereas the peaks of Ti 2p and O 1s showed a significantly declining trend as the concentration of baicalin increased in 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA groups. A distinct decrease in both the oxygen and titanium dioxide contents was observed on the three surfaces stored in different baicalin-containing saline solution, and their levels were the lowest in 1 mM BA groups. It may contribute to the baicalin crystals adsorbed on the titanium surface and the adsorption of baicalin crystals on the surface was concentration-dependent.
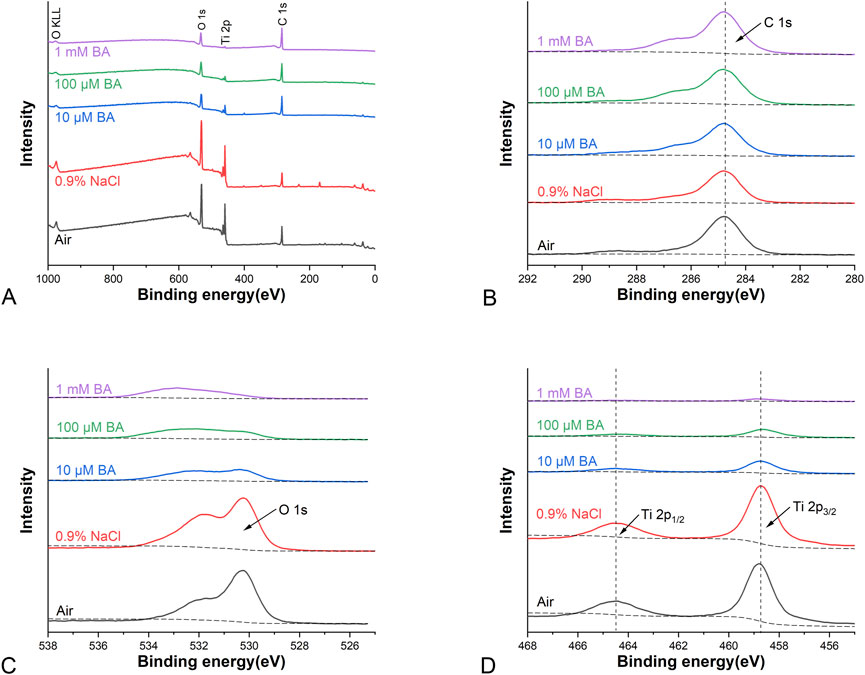
Figure 2. XPS analysis of different titanium surfaces under different storage conditions for 4 weeks [(A) Representative XPS survey spectra analysis; (B) XPS high-resolution spectra analysis of C 1s peaks; (C) XPS high-resolution spectra analysis of O 1s peaks; (D) XPS high-resolution spectra analysis of Ti 2p peaks].
3.3 Surface wettability
Figure 3 showed the water contact angles of the SLA titanium surfaces stored in different media (Air, 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA). The hydrophilicity of the SLA titanium surfaces stored in liquid was significantly higher than that of the titanium surfaces exposed to air. Moreover, the hydrophilicity of the titanium surfaces stored in 0.9% NaCl solution was relatively lower than that of the titanium preserved in the baicalin-containing saline solution. Samples stored in the baicalin-containing saline solution exhibited superhydrophilicity compared with other storage methods, and different concentrations of baicalin does not affect hydrophilicity of the titanium surfaces. The results revealed that the hydrophilic property of the titanium preserved in the baicalin-containing saline solution could be significantly enhanced.
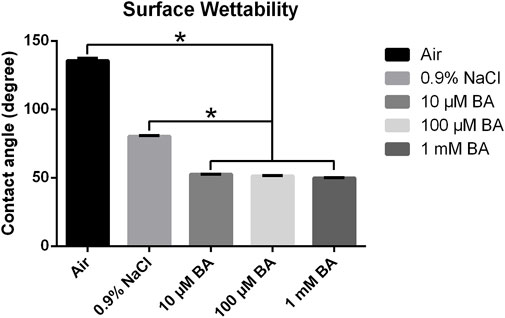
Figure 3. Contact angles of titanium surfaces under different storage conditions for 4 weeks (*P < 0.05).
3.4 Surface roughness
Figures 4, 5 respectively displayed the surface roughness values and three-dimensional surface topography of different specimens stored in different media (Air, 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA). The surface roughness and topography of titanium surfaces stored in 1 mM BA were similar to those stored in air, which were higher than those stored in 0.9% NaCl, 10 µM BA and 100 µM BA. Moreover, there was no significant difference in the samples stored in 0.9% NaCl, 10 µM BA and 100 µM BA.
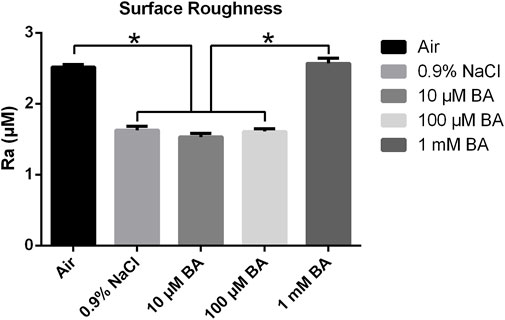
Figure 4. Surface roughness of titanium surfaces under different storage conditions for 4 weeks (*P < 0.05).
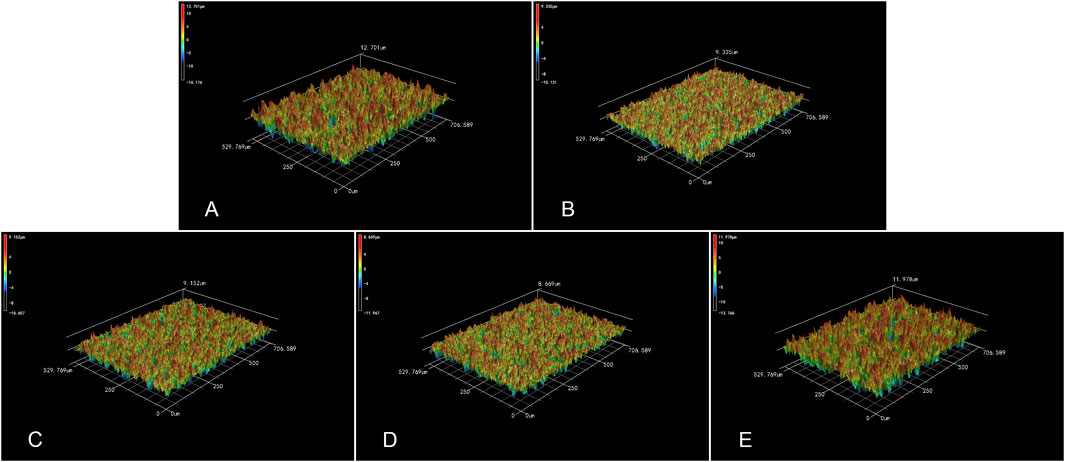
Figure 5. 3D topography of titanium surfaces under different storage conditions for 4 weeks [(A) Air group, (B) 0.9% NaCl group, (C) 10 μM BA group, (D) 100 μM BA group, (E) 1 mM BA group].
3.5 Cell proliferation
The results of proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells grown on titanium surfaces preserved in different storage methods were shown in Figure 6. After 1, 3 and 6 days of culture on the different surfaces, the proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells was examined by the CCK-8 assay. The MC3T3-E1 cells proliferated overtime, indicating excellent cell viabilities on the SLA titanium surfaces. After 1 and 3 days of culture, there was no significant difference in five titanium surfaces. After culturing for 6 days, superior cell proliferation on titanium surfaces stored in 0.9% NaCl, 10 μM BA, 100 µM BA and 1 mM BA were observed in comparison with the titanium surfaces stored in air. Moreover, the cell proliferation in 0.9% NaCl and 1 mM BA groups had no significant differences, which was inferior to the 10 µM BA and 100 µM BA groups, especially the 100 µM BA group. The results revealed that SLA titanium surfaces stored in 100 µM BA solution exhibited the best performance on cell proliferation in all tested surfaces, which could offer more favorable environment for cell proliferation.
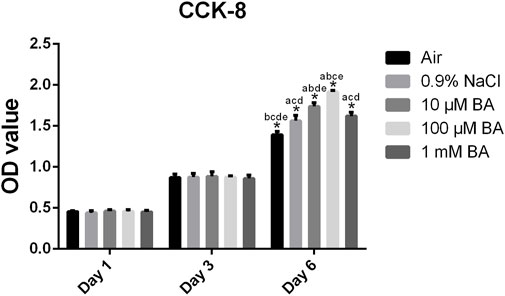
Figure 6. Proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells on SLA titanium surfaces under different storage conditions for 4 weeks was examined via CCK-8 assay after culturing for 1, 3 and 6 days *, P < 0.05; a, P < 0.05 versus Air; b, P < 0.05 versus 0.9% NaCl; c, P < 0.05 versus 10 μM BA; d, P < 0.05 versus 100 μM BA; e, P < 0.05 versus 1 mM BA.
4 Discussion
Numerous studies have shown that the surface physicochemical properties of titanium implants undergo adverse changes during storage, thereby affecting their biocompatibility capability in clinical use. The biocompatibility decrease of aging titanium surfaces may be related to the weakening of surface hydrophilicity, while the newly prepared titanium surfaces are super-hydrophilic, which gradually become hydrophobic over time, and osteoblast adhesion, diffusion, proliferation, and alkaline phosphatase activity all decrease in a time-dependent manner (Minamikawa et al., 2016; Shi et al., 2017). Experimental animal models have demonstrated that titanium implants stored for 4 weeks prior to implantation exhibit peri-implant bone coverage rates below 50% during the initial osseointegration phase when compared to fresh, non-stored implant surfaces (Att et al., 2009).
In this study, the newly fabricated SLA titanium specimens were stored in air and 0.9% NaCl solution as control groups. The experimental groups consisted of SLA titanium surfaces subjected to store in baicalin saline solutions at concentrations of 10 μM, 100 μM, and 1 mM. We evaluated the surface characteristics and bioactivity of SLA titanium specimens preserved in the five conditions for 4 weeks. Our results clearly revealed that titanium preserved in solution reduced hydrocarbon contamination and increased hydrophilicity. Moreover, the baicalin crystals absorbed on the surfaces significantly promoted osteoblast proliferation. Certain concentration of baicalin-containing saline solution could form a favorable titanium surface and improve the bioactivity.
In Figure 1, SEM results demonstrated that the storage methods would not change the initial morphology of SLA titanium surfaces, which was consistent with previous findings (Li et al., 2012). There are studies show that the sandblasted and acid-etched titanium surfaces develop nanostructured morphologies following storage in an aqueous solution, while the titanium surface stored in air-tight containers retain their original surface topography without nanoscale modifications (Shen et al., 2016). The influence of aqueous solution on the surface morphology of biomaterials needs further investigation but the findings indicate that aqueous-phase storage exhibits superior preservation efficacy compared to the gas-barrier-based storage method.
The XPS analysis (Figure 2) showed that peaks of Ti 2p and O 1s gradually declined with the increase in the concentration of baicalin, indicating that baicalin crystals was immobilized onto the titanium surfaces, and surface oxides were covered by the crystals (Xu et al., 2019). In addition, the XPS tests further revealed that specimens preserved in 0.9% NaCl solution exhibited reduced carbon content compared to their air-exposed counterparts. This phenomenon could be attributed to the solution’s ability to prevent airborne hydrocarbons from contacting the titanium surface through liquid-phase isolation effects (Chen et al., 2022). The carbon levels of titanium specimens stored in 10 μM, 100 μM and 1 mM baicalin-containing saline solution increased gradually compared with the 0.9% NaCl solution group, which may contribute to the baicalin crystals adsorbed on the titanium surfaces. The hydrocarbon on titanium surfaces is related to the wettability and the behaviors of osteoblasts (Hayashi et al., 2014).
Hydrophilicity serves as a critical feature which affects the biocompatibility of the titanium surface, as it promotes enhanced protein adsorption and subsequent cell responses (Liddell et al., 2020; Hotchkiss et al., 2016). As shown in Figure 3, the experimental results demonstrated that all three titanium specimens stored in baicalin-containing saline solutions exhibited significantly enhanced hydrophilicity following a 4-week storage period.
Besides hydrophilicity, surface roughness is another important characteristic that affects the cell response and early protein adsorption (Kunrath et al., 2020; Giljean et al., 2011). As shown in Figures 4, 5, the surface roughness of the three titanium surfaces exposed to 0.9% NaCl solution, 10 μM, and 100 µM baicalin-containing saline solution decreased relative to that exposed in the air group, which may be caused by carbon contamination on the titanium surfaces. Moreover, there was no significant difference in the surface roughness of the three SLA surfaces. However, the roughness of the titanium surfaces stored in 1 mM baicalin-containing solution increased probably due to the large amount of baicalin crystals adsorbed onto the titanium surfaces.
Cell proliferation studies were performed to evaluate the bioactivity of titanium surfaces under different storage methods. As shown in Figure 6, the baicalin storage solution significantly promoted the proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells after culturing for 6 days, especially the 100 µM baicalin-containing saline solution.
These results indicated that storage in the baicalin-containing saline solution could effectively reduce the carbon deposition on titanium surfaces and improve the hydrophilicity and roughness. This may be due to the competitive adsorption of the storage solution solutes and hydrocarbons to the titanium surfaces (Chen et al., 2022). We postulated that baicalin crystals may competitively occupy hydrocarbon adsorption sites on titanium surfaces, thereby attenuating hydrocarbon deposition while concurrently enhancing surface hydrophilicity.
Upon completion of the manufacturing process, titanium implants must undergo storage, transportation, and further preservation prior to their clinical application. It has been demonstrated that the biocompatibility of titanium surfaces progressively diminishes over time following various surface treatments (Lavrador et al., 2018), indicating that the surface activity of titanium is subject to an aging phenomenon. This phenomenon is related to carbon contamination on the surface of titanium during preservation. The finished product is typically preserved in an air-permeable sterile vial or pouch for a duration of up to 5 years. As a result of prolonged exposure to ambient air, the majority of implants experience varying levels of carbonaceous contamination and bioactivity degradation over time. Moreover, researches have demonstrated that titanium surfaces exposed to ambient air adsorb airborne hydrocarbons, and the resultant carbon deposition can significantly impair the osteogenic activity of osteoblasts on the titanium surfaces (Chang et al., 2017; Livak and Schmittgen, 2001). Therefore, the choice of storage solution directly influences the surface bioactivity of the implant and is one of the critical factors in ensuring clinical success.
Researches have demonstrated that baicalin can facilitate osteogenic differentiation and exhibit anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the NF-κ B signaling pathway (Qian et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2024). In addition, baicalin acts as an antioxidant and possesses significant antioxidant effect by activating the Nrf2 and MAPK signaling pathway (He et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). Baicalin can scavenge free radicals, such as alkane peroxide and superoxide anion, through decarboxylation in the body to regulate oxidative stress (Liang et al., 2021). Moreover, baicalin has been shown to have important anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and immunomodulatory functions (Paczkowska-Walendowska et al., 2024). Due to these benefits, baicalin can be an excellent candidate as a constituent for implant storage solutions.
In the present study, we investigated that a normal saline solution containing 100 µM baicalin exerts beneficial effects on titanium surfaces and osteoblast proliferation, which provides novel insights and potential directions for clinical implant storage. However, there are several limitations of this study that should be taken into account when interpreting these data. Our research focuses on the effects of baicalin-containing saline solution at different concentrations on the characteristics and bioactivity of SLA titanium materials, with the aim of identifying the optimal baicalin concentration. However, we have not yet delved into the osteogenic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of SLA titanium specimens preserved in different conditions. These aspects will be the key focus of our subsequent studies.
5 Conclusion
To improve the surface properties and bioactivity of titanium materials, we established a new baicalin-containing saline solution to store SLA titanium implants in this study. The results demonstrated that after storing the materials under different conditions for 4 weeks, specimens stored in 100 µM baicalin-containing saline solution exhibited superior surface properties and facilitated the proliferation of osteoblasts, which could be an effective new storage strategy.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
YL: Investigation, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. Y-HY: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XL: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YX: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. C-YB: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. X-SW: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Xichang Science and Technology Plan Project (Project Number: JSYJ-2023-02), Liangshan Prefecture Science and Technology Plan Project (Project Number: 24YYYJ0157), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Number: 82371013).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2025.1618664/full#supplementary-material
References
Att, W., Hori, N., Takeuchi, M., Ouyang, J., Yang, Y., Anpo, M., et al. (2009). Time-dependent degradation of titanium osteoconductivity: an implication of biological aging of implant materials. Biomaterials 30 (29), 5352–5363. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.06.040
Chang, P. C., Chao, Y. C., Hsiao, M. H., Chou, H. S., Jheng, Y. H., Yu, X. H., et al. (2017). Inhibition of periodontitis induction using a stimuli-responsive hydrogel carrying naringin. J. periodontology 88 (2), 190–196. doi:10.1902/jop.2016.160189
Chen, J., Lin, C., Huang, X., and Bian, W. (2024). Baicalin enhances proliferation and reduces inflammatory-oxidative stress effect in H(2)O(2)-induced granulosa cells apoptosis via USP48 protein regulation. BMC complementary Med. Ther. 24 (1), 42. doi:10.1186/s12906-024-04346-z
Chen, W., Zhu, W. Q., Su, S., Liu, Y., and Qiu, J. (2022). Preservation of titanium in a naringin-containing solution to enhance osteogenic and anti-inflammatory activities in vitro. Front. Mater. 9. doi:10.3389/fmats.2022.847497
Choi, S. H., Jeong, W. S., Cha, J. Y., Lee, J. H., Lee, K. J., Yu, H. S., et al. (2017). Effect of the ultraviolet light treatment and storage methods on the biological activity of a titanium implant surface. Dent. Mater. 33 (12), 1426–1435. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2017.09.017
Ghassemi, A., Ishijima, M., Hasegawa, M., Mohammadzadeh Rezaei, N., Nakhaei, K., Sekiya, T., et al. (2018). Biological and physicochemical characteristics of 2 different hydrophilic surfaces created by saline-storage and ultraviolet treatment. Implant Dent. 27 (4), 405–414. doi:10.1097/id.0000000000000773
Giljean, S., Bigerelle, M., Anselme, K., and Haidara, H. (2011). New insights on contact angle/roughness dependence on high surface energy materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 (22), 9631–9638. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.06.088
Guo, C., Ding, T., Cheng, Y., Zheng, J., Fang, X., and Feng, Z. (2025). The rational design, biofunctionalization and biological properties of orthopedic porous titanium implants: a review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13, 1548675. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2025.1548675
Hayashi, R., Ueno, T., Migita, S., Tsutsumi, Y., Doi, H., Ogawa, T., et al. (2014). Hydrocarbon deposition attenuates osteoblast activity on titanium. J. Dent. Res. 93 (7), 698–703. doi:10.1177/0022034514536578
He, P., Wu, Y., Shun, J., Liang, Y., Cheng, M., and Wang, Y. (2017). Baicalin ameliorates liver injury induced by chronic plus binge ethanol feeding by modulating oxidative stress and inflammation via CYP2E1 and NRF2 in mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 4820414. doi:10.1155/2017/4820414
Hotchkiss, K. M., Reddy, G. B., Hyzy, S. L., Schwartz, Z., Boyan, B. D., and Olivares-Navarrete, R. (2016). Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta biomater. 31, 425–434. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2015.12.003
Hu, H., Yao, Y., Liu, F., Luo, L., Liu, J., Wang, X., et al. (2024). Integrated microbiome and metabolomics revealed the protective effect of baicalin on alveolar bone inflammatory resorption in aging. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm. 124, 155233. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155233
Jeng, M. D., and Chiang, C. P. (2020). Autogenous bone grafts and titanium mesh-guided alveolar ridge augmentation for dental implantation. J. Dent. Sci. 15 (3), 243–248. doi:10.1016/j.jds.2020.06.012
Jin, S., Gao, J., Yang, R., Yuan, C., Wang, R., Zou, Q., et al. (2022). A baicalin-loaded coaxial nanofiber scaffold regulated inflammation and osteoclast differentiation for vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 8, 559–572. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.06.028
Kunimatsu, R., Kimura, A., Sakata, S., Tsuka, Y., Yoshimi, Y., Abe, T., et al. (2022). Effects of baicalin on the proliferation and expression of OPG and RANKL in human cementoblast-lineage cells. J. Dent. Sci. 17 (1), 162–169. doi:10.1016/j.jds.2021.05.009
Kunrath, M. F., Dos Santos, R. P., de Oliveira, S. D., Hubler, R., Sesterheim, P., and Teixeira, E. R. (2020). Osteoblastic cell behavior and early bacterial adhesion on macro-micro-and nanostructured titanium surfaces for biomedical implant applications. Int. J. oral and Maxillofac. implants 35 (4), 773–781. doi:10.11607/jomi.8069
Lavrador, P., Gaspar, V. M., and Mano, J. F. (2018). Bioinspired bone therapies using naringin: applications and advances. Drug Discov. today 23 (6), 1293–1304. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2018.05.012
Lee, J. H., and Ogawa, T. (2012). The biological aging of titanium implants. Implant Dent. 21 (5), 415–421. doi:10.1097/id.0b013e31826a51f4
Li, J., Zhou, P., Attarilar, S., and Shi, H. Y. (2021). Innovative surface modification procedures to achieve micro/nano-graded Ti-based biomedical alloys and implants. Coatings 11 (6), 647. doi:10.3390/coatings11060647
Li, J. L., Qin, L., Yang, K., Ma, Z. J., Wang, Y. X., Cheng, L. L., et al. (2020). Materials evolution of bone plates for internal fixation of bone fractures: a review. J. Mater. Sci. and Technol. 36, 190–208. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2019.07.024
Li, S., Ni, J., Liu, X., Zhang, X., Yin, S., Rong, M., et al. (2012). Surface characteristics and biocompatibility of sandblasted and acid-etched titanium surface modified by ultraviolet irradiation: an in vitro study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B, Appl. biomaterials 100 (6), 1587–1598. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.32727
Liang, B., Zhu, Y. C., Lu, J., and Gu, N. (2021). Effects of traditional Chinese medication-based bioactive compounds on cellular and molecular mechanisms of oxidative stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 3617498. doi:10.1155/2021/3617498
Liang, M., Sun, X., Guo, M., Wu, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, J., et al. (2024). Baicalin methyl ester prevents the LPS - induced mice intestinal barrier damage in vivo and in vitro via P65/TNF-α/MLCK/ZO-1 signal pathway. Biomed. and Pharmacother. = Biomedecine and Pharmacother. 180, 117417. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117417
Liddell, R. S., Liu, Z. M., Mendes, V. C., and Davies, J. E. (2020). Relative contributions of implant hydrophilicity and nanotopography to implant anchorage in bone at Early Time Points. Clin. oral implants Res. 31 (1), 49–63. doi:10.1111/clr.13546
Liu, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, X., Chen, Q., and Wu, B. (2015). A strontium-modified titanium surface produced by a new method and its biocompatibility in vitro. PloS one 10 (11), e0140669. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0140669
Livak, K. J., and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods (San Diego, Calif.) 25 (4), 402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Minamikawa, H., Att, W., Ikeda, T., Hirota, M., and Ogawa, T. (2016). Long-term progressive degradation of the biological capability of titanium. Mater. Basel, Switz. 9 (2), 102. doi:10.3390/ma9020102
Paczkowska-Walendowska, M., Koumentakou, I., Lazaridou, M., Bikiaris, D., Miklaszewski, A., Plech, T., et al. (2024). 3D-Printed chitosan-based scaffolds with scutellariae baicalensis extract for dental applications. Pharmaceutics 16 (3), 359. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16030359
Qian, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, L., and Tou, J. (2018). Effects of baicalin on inflammatory reaction, oxidative stress and PKDl and NF-kB protein expressions in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Acta cir. bras. 33 (7), 556–564. doi:10.1590/s0102-865020180070000001
Shen, J. W., Chen, Y., Yang, G. L., Wang, X. X., He, F. M., and Wang, H. M. (2016). Effects of storage medium and UV photofunctionalization on time-related changes of titanium surface characteristics and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B, Appl. biomaterials 104 (5), 932–940. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.33437
Shi, X., Xu, L., Wang, Q., and Xu, L. (2017). Hydrothermal sterilization improves initial osteoblast responses on sandpaper-polished titanium. Mater. Basel, Switz. 10 (7), 812. doi:10.3390/ma10070812
Srinivasan, M., Vazquez, L., Rieder, P., Moraguez, O., Bernard, J. P., and Belser, U. C. (2014). Survival rates of short (6 mm) micro-rough surface implants: a review of literature and meta-analysis. Clin. oral implants Res. 25 (5), 539–545. doi:10.1111/clr.12125
van Velzen, F. J., Ofec, R., Schulten, E. A., and Ten Bruggenkate, C. M. (2015). 10-year survival rate and the incidence of peri-implant disease of 374 titanium dental implants with a SLA surface: a prospective cohort study in 177 fully and partially edentulous patients. Clin. oral implants Res. 26 (10), 1121–1128. doi:10.1111/clr.12499
Wang, C., Wang, S., Yang, Y., Jiang, Z., Deng, Y., Song, S., et al. (2018). Bioinspired, biocompatible and peptide-decorated silk fibroin coatings for enhanced osteogenesis of bioinert implant. J. biomaterials Sci. 29 (13), 1595–1611. doi:10.1080/09205063.2018.1477316
Wang, X., Chang, X., Zhan, H., Zhang, Q., Li, C., Gao, Q., et al. (2020). Curcumin and Baicalin ameliorate ethanol-induced liver oxidative damage via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J. food Biochem. 44 (10), e13425. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13425
Xu, L. N., Shao, S. Y., Zhu, W. Q., Chen, C., Zhang, S. M., and Qiu, J. (2019). Low density lipoprotein adsorption on a titanium surface and its effect on osteoblast behaviors. RSC Adv. 9 (32), 18589–18598. doi:10.1039/c9ra03173a
Yeo, I. S. (2014). Reality of dental implant surface modification: a short literature review. open Biomed. Eng. J. 8, 114–119. doi:10.2174/1874120701408010114
Zhang, Y., Cheng, Z., Liu, Z., Shen, X., Cai, C., Li, M., et al. (2023). Functionally tailored metal-organic framework coatings for mediating Ti implant osseointegration. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger. 10 (29), e2303958. doi:10.1002/advs.202303958
Zhao, Z. F., Cheng, X. F., Yu, M., Shi, W. F., and Zhang, T. (2024). Baicalin plays an anti-osteosarcoma role in vitro and promotes osteogenic differentiation by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Discov. Med. 36 (187), 1648–1656. doi:10.24976/discov.med.202436187.151
Keywords: titanium, baicalin, storage solution, surface characteristics, bioactivity
Citation: Liu Y, Yang Y-h, Liu X, Xiao Y, Bao C-y and Wang X-s (2025) Surface characteristics and bioactivity of titanium preserved in a baicalin-containing saline solution. Front. Mater. 12:1618664. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1618664
Received: 26 April 2025; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 10 June 2025.
Edited by:
Hafedh Dhiflaoui, Tunis University, TunisiaReviewed by:
Bhavani Patel, Medline Industries, LP, United StatesWissem Zayani, Université de Bourgogne, France
Slah Chayoukhi, Tunis University, Tunisia
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Liu, Xiao, Bao and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao-song Wang, eHNfd2FuZzEyNkAxMjYuY29t
 Yao Liu1
Yao Liu1 Chong-yun Bao
Chong-yun Bao Xiao-song Wang
Xiao-song Wang