- 1School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China
- 2Xinjiang Transportation Investment (Group) Co., Ltd., Urumqi, China
- 3Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Arid Desert Highway Engineering Technology for the Transportation Industry, Urumqi, China
- 4Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Green Construction and Smart Traffic Control of Transportation Infrastructure, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China
To address the challenge of obtaining core samples directly from the field for low-temperature crack resistance tests of asphalt mixtures, this study utilizes the not-notched semi-circular bending (NN-SCB) creep test as a novel evaluation method. The feasibility of this method is discussed and validated through both simulation and experimental testing. First, ABAQUS software was employed to model the NN-SCB creep test, with various viscoelastic and creep load parameters analyzed to evaluate the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy in asphalt mixtures with different characteristics. The results indicate that the tensile creep dissipation energy consistently accounts for approximately 31.5% of the total creep dissipation energy across all tested asphalt mixtures, irrespective of their properties. Five types of asphalt mixtures were designed, three of which incorporated Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) as the aggregate base. These mixtures were subjected to both NN-SCB and Thermal Stress Restrained Specimen Test (TSRST) methods. The experimental findings demonstrate that the tensile creep dissipation energy in the NN-SCB test provides a robust and consistent measure of low-temperature crack resistance, with results closely aligning with those from TSRST. Specifically, the tensile creep dissipation energy of mixtures containing 40% RAP showed a significant reduction in low-temperature cracking resistance, with a 41.3% lower creep rate compared to the virgin asphalt mixture. The study confirms the feasibility of using NN-SCB and tensile creep dissipation energy as reliable indices for evaluating the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixtures.
1 Introduction
Low-temperature cracking is a major distress in asphalt pavements in regions with seasonal frost (Aliha et al., 2015; Kliewer et al., 1996; Nian et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2015). This type of cracking usually occurs during cold weather, as ambient temperatures decrease gradually. This decrease in temperature restricts the free contraction of asphalt pavements, generating thermal stress. Cracking occurs when the accumulated thermal stress exceeds the tensile strength of the asphalt mixture. Even as cooling continues, the asphalt mixture retains its viscoelastic properties at low temperatures. This allows part of the thermal stress to relax, reducing further stress accumulation (Al-Qudsi et al., 2020; Dave et al., 2013; Gao et al., 2022; Medeiros et al., 2015). Consequently, the stress relaxation capacity fundamentally determines the material’s resistance to thermal cracking. Therefore, quantitative characterization of stress relaxation behavior provides critical insights for assessing low-temperature cracking resistance. However, experimental challenges arise in stress relaxation testing due to non-instantaneous strain application, imposing rigorous error control protocols (You et al., 2014a; You et al., 2014b). As a result, the stress relaxation performance of asphalt mixtures is usually assessed indirectly by creep testing (Tian et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2021; Wenbiao et al., 2011).
Extensive research efforts have focused on low-temperature creep testing of asphalt mixtures, with the indirect tensile test (IDT) and trabecular bending test (TBT) being the most commonly used methods. The AASHTO T322 standardized protocol specifically prescribes IDT methodology for quantitative assessment of asphalt mixture’s cryogenic cracking resistance (). Building upon the Superpave IDT framework, which includes the IDT residual modulus test, IDT creep test, and IDT failure test, Roque et al. introduced a ratio of creep dissipation energy during the IDT failure test to that during the IDT creep test as an index for assessing the low-temperature performance of asphalt mixtures (Roque et al., 2004). Complementary investigations by Das et al. validated IDT-derived creep rate as a robust predictor of cryogenic performance (Das et al., 2012). Hua et al. quantitatively verified the predictive capability of IDT creep compliance for asphalt pavement cracking initiation (Yin and Gao, 2021). The AASHTO Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide explicitly incorporates IDT-derived creep compliance and splitting strength as critical inputs for determining pavement fracture temperature thresholds (). Test specimens can be obtained either through laboratory fabrication or on-site core drilling, offering versatile solutions for mixture design, performance evaluation, and real-world pavement testing. Nevertheless, IDT implementation necessitates specialized extensometry systems characterized by high operational complexity and substantial capital investment (Jahangiri et al., 2021).
The trabecular bending test (TBT) has been extensively employed to investigate low-temperature creep behavior of asphalt mixtures. Li et al. utilized TBT to characterize creep behavior of polyphosphoric acid-modified asphalt composites under multi-parameter conditions (temperature, load), linking creep rate to crack resistance (Li et al., 2021). Based on TBT data, Liu et al. established a parameter system for crack resistance evaluation, comprising stress relaxation time, creep rate, dissipation energy ratio, and creep rate-stiffness ratio (Liu et al., 2010). Pszczola et al. demonstrated via TBT that the stress field at the specimen base in three-point bending configuration replicates in-service pavement mechanics. Furthermore, this method exhibits operational simplicity and well-defined physical interpretability (Pszczola et al., 2019). However, specimen representativeness challenges constrain TBT’s applicability for evaluating field performance of pavements under cryogenic conditions.
In addition to the IDT and TBT, several other creep testing methods have been proposed by researchers to evaluate the low-temperature cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures. Pszczola et al. conducted tensile creep tests to evaluate low-temperature cracking resistance in asphalt mixtures (Pszczola et al., 2019). Zofka et al. proposed bending beam rheometry (BBR)-compatible specimens matching asphalt mortar dimensions for thermal cracking evaluation (Zofka et al., 2008). Jahangiri et al. introduced the disc tensile creep test for characterizing cryogenic creep behavior of asphalt mixtures (Jahangiri et al., 2021).
An optimal creep testing protocol requires specimens that replicate in-situ stress states and allow dual-source acquisition (laboratory-prepared or field-cored). This ensures the practicality of mixture design, creep performance evaluation, and the detection of low-temperature behavior in actual pavement. However, tensile creep test specimens cannot be obtained from field pavements, limiting the ability to assess the low-temperature crack resistance of in-service roads. Although BBR specimens allow field coring, their limited dimensions and significant result variability remain critical limitations. Despite dual-source availability (lab/in-situ), DCT specimens exhibit microcrack initiation at loading holes, frequently causing premature test termination (Wagoner et al., 2005). The semi-circular specimen used in the asphalt mixture semi-circular bending (SCB) test demonstrates several advantages: it can be sourced widely, either formed in the lab or obtained through on-site core drilling, and consumes less material. Consequently, SCB testing has emerged as a predominant methodology for low-temperature cracking resistance assessment in pavement engineering. Current SCB-based evaluation employs three principal indices: fracture energy (AASHTO, 2013), J integral (Elseifi et al., 2012) and flexibility factor (Ozer et al., 2016). Teshale et al. recommended stress-uniformity zones in notched SCB specimens for cryogenic creep analysis (Teshale et al., 2013). However, the area with uniform stress in the notched specimen primarily experiences compressive stress, which does not align with the actual stress conditions of pavement. Furthermore, the SCB test requires pre-cutting of the specimen, leading to significantly higher creep at the notch compared to other areas, resulting in substantial variability in the experimental results. Liu et al. simulated the NN-SCB using finite element methods, with results showing that the bottom area of the specimen primarily experiences tensile stress (Liu et al., 2008). This stress state closely mirrors that of actual pavement, and the larger tensile region makes it suitable for evaluating the overall creep performance of asphalt mixtures (Yang et al., 2022). Therefore, by isolating the tensile creep dissipation energy in the NN-SCB creep test, it is possible to assess the overall tensile creep performance of the mixture, providing a reliable method for evaluating the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixtures. Sun et al. established a correlation between the relaxation properties of asphalt mastics and their low-temperature crack resistance, and proposed a prediction model based on these properties (Sun, 2023). Qi et al. developed a reliable and time-efficient method to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of toughened epoxy asphalt mixtures using grey theory to correlate influencing factors with performance (Qi et al., 2021).
Traditional asphalt materials are facing significant resource consumption issues. The extraction and processing of virgin asphalt require substantial amounts of energy and natural resources, contributing to environmental degradation. As the demand for asphalt continues to grow in the construction industry, it becomes crucial to explore alternative solutions. Recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) emerges as a promising alternative, with the potential to reduce the reliance on virgin materials and minimize resource depletion. Building on NN-SCB’s unique attributes, this study validates its feasibility as a low-temperature cracking resistance assessment methodology. Phase I involves finite element simulation (ABAQUS) of NN-SCB tests to quantify tensile-to-total creep energy dissipation ratios. Parametric analysis subsequently examines influential factors on these energy dissipation ratios. Phase II develops a novel tensile creep energy quantification method, subsequently applied for low-temperature cracking resistance assessment. Phase III implements NN-SCB testing on five engineered asphalt mixtures. Assessment integrates three metrics: creep rate, total dissipation energy, and tensile-specific dissipation energy. The results are then compared with those obtained from the TSRST to verify the validity of the proposed test method and evaluation index.
2 The simulation of NN-SCB creep test
2.1 NN-SCB creep test model
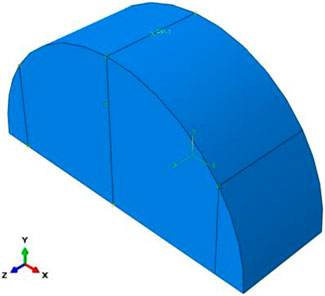
The NN-SCB creep model was established using the ABAQUS finite element method, as shown in Figure 1.
The finite element model geometry was defined with a radius of 75 mm, thickness of 50 mm, and support span of 120 mm. The components were represented using three-dimensional deformable solid elements, with the mesh unit selected as C3D8R. Mesh generation followed a convergence-optimized sizing scheme. Viscoelastic analysis implemented the *VISCO subroutine over a 100-s creep test duration. Constraints were applied in the Uy direction at the support locations, in the Ux direction along the centerline at the bottom of the model, and in the Uz direction at one endpoint of the bottom centerline to prevent sliding. A kinematic coupling constraint (*COUPLING) linked the top centerline nodes to a reference point located at the surface centroid. A concentrated static load was imposed at the reference point through displacement control.
2.2 Percentage calculation of tensile creep dissipated energy
Firstly, the creep stress and creep strain components of each element are extracted from the Abaqus calculation results by Python program, and the creep dissipation energy density of each component is obtained by multiplying the stress component by the corresponding creep strain, as shown in Equation 1.
The creep dissipation energy of each component can be obtained by multiplying the creep dissipation energy density by the unit volume, as shown in Equation 2.
Then, the total dissipation energy of creep test is obtained by summing up all the dissipation energy consumed in the model, as shown in Equation 3. The energy dissipated by all the tensile stress components in the model is summed to obtain the tensile creep dissipation energy, as shown in Equation 4. The percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy to total dissipation energy is shown in Equation 5.
where,
where,
where,
where,
where,
Because the mesh is divided by size control, it can be assumed that the volume of all elements is equal, so Equation 5 can be simplified to Equation 6. It can be seen from Equation 6 that the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy is only related to the stress-strain state, but not to the size of the grid unit (Chen et al., 2021). Since it is assumed that the volume of all elements is equal, the influence of mesh size on the test results needs to be further studied to ensure the accuracy of the subsequent research results. The smaller the mesh size, the more accurate the stress and strain of the simulated element, and the more accurate the calculated percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy (Gong et al., 2019). Therefore, the grid side lengths of 12 mm, 10 mm, 8 mm, and 6 mm are selected to analyze the accuracy of the assumed calculation results, and the appropriate grid unit size is determined.
2.3 Parameters of virtual asphalt mixture
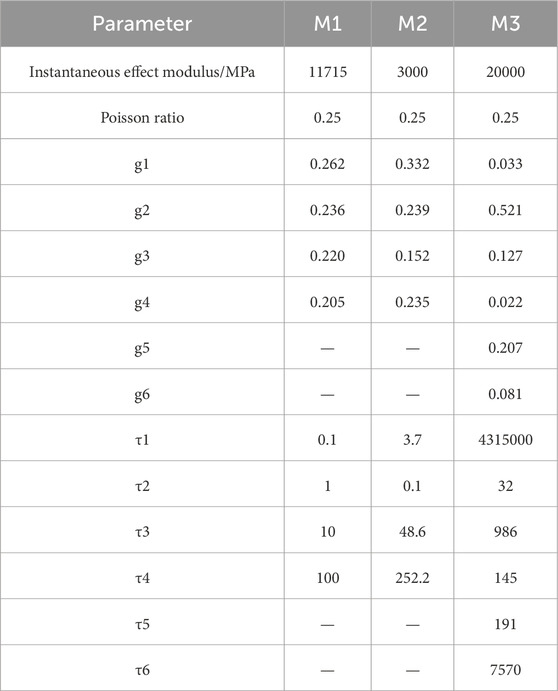
Due to the varying performance of different asphalt mixtures, their modulus, strength, and viscoelastic properties differ. To investigate the effect of mixture properties on tensile creep energy dissipation ratios in NN-SCB, three sets of relaxation modulus parameters and loading magnitudes were varied. The Prony series parameters for each mixture were chosen based on prior studies, ensuring they represent the viscoelastic behavior of the mixtures under low-temperature conditions. These parameters are validated by references such as Zhang et al., 2022 and Li et al., 2018, as shown in Tables 1, 2 (Zhang and Sun, 2022; Li et al., 2018).
3 Materials and experimental methods
In this study, five asphalt mixtures with varying mix proportions were tested for low-temperature cracking resistance using both NN-SCB and TSRST. Three of the asphalt mixture specimens were prepared using RAP as the aggregate base. Comparative analysis of evaluation outcomes validated NN-SCB’s efficacy as a robust low-temperature cracking resistance assessment methodology.
3.1 Materials
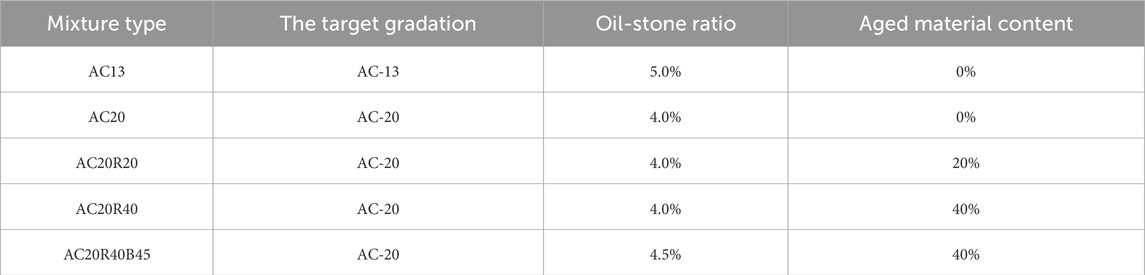
The composition of the five asphalt mixtures is shown in Table 3. Among them, the asphalt is No.70 asphalt, the aggregate is limestone, the old material content represents the mass ratio of the old aggregate to the total aggregate, and the target gradation is the recommended gradation median. All mixtures were formed by the Superpave Gyratory Compactor (SGC) method with a target void ratio of 4%. Experimental protocols strictly followed the Strategic Highway Research Program (SHRP) specifications for mix design and performance testing.
3.2 Method of the test
3.2.1 Method of the NN-SCB
Low-temperature cracking resistance usually occurs during the cold wave period, and the atmospheric temperature is approximately 0 °C, thus the indoor test temperature is set to 0°C. The creep load is 0.2 times the failure load. The reason is that the failure load of the asphalt mixture with large modulus is larger, and the temperature stress generated by the low-temperature shrinkage of the asphalt mixture is also greater. Therefore, selecting a relatively high load ratio improves the differentiation of creep performance among asphalt mixtures. Yang et al. have shown that the longer the creep time is, the greater the dissipated energy is, which is more conducive to distinguishing the low-temperature performance of different asphalt mixtures (Yang et al., 2022). To enhance the discrimination of the test results and pay attention to the efficiency of the test, the test time is 2 h.
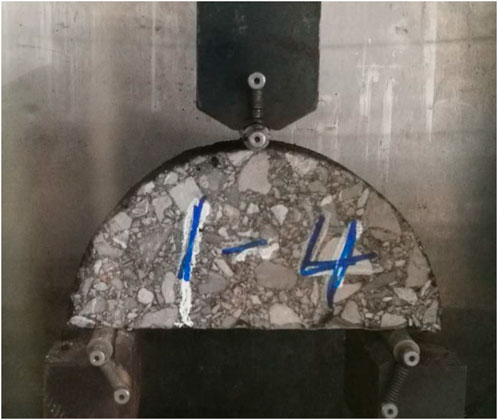
The test specimens were prepared using the SGC method. In order to increase the representativeness of the test results and reduce the variability, the formed specimens were cut into semi-circular specimens with a thickness of 50 mm, as shown in Figure 2.
During the test, the uncut mixture specimens were first placed in a 0°C environment box for 4 h, and then three specimens were randomly selected for failure test. The bearing spacing was 120 mm, and the average value was used as its failure load. Then, the creep test was carried out with 0.2 times the failure load as the creep load, and at least three repeated samples were made for each mixture. The creep rate and total creep dissipation energy are used to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixture. The creep rate represents the change rate of the indenter creep deformation in the last 15 min, as shown in Equation 7. The total creep dissipation energy represents the energy consumed by the specimen during the creep process, as shown in Equation 8.
where, s represents creep rate;
where,
At the same time, the evaluation index of low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixture is proposed by tensile creep dissipation energy. Since the tensile area of the NN-SCB is mainly located at the bottom of the specimen, and the tensile stress in other areas is very small, the calculated total tensile creep dissipation energy is used to represent the tensile dissipation energy in the bottom tensile area. The calculation method of tensile dissipation energy is shown in Equation 9.
3.2.2 Method of the TSRST
The test specimen is formed by the SGC method, and then the Φ50 mm × 160 mm specimen is obtained by drilling and cutting, as shown in Figure 3.
During the test, the bonded specimens need to be kept at 5 °C for 4 h. The initial temperature of the test is 5°C, and the cooling rate is 10°C/h. The test process refers to the AASHTO TP 9 test method (2025). Two sets of parallel tests were carried out for each mixture, and the freezing temperature was used as the evaluation index of low-temperature crack resistance.
4 Analysis and discussion of simulation results
4.1 Calculation accuracy analysis of percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy
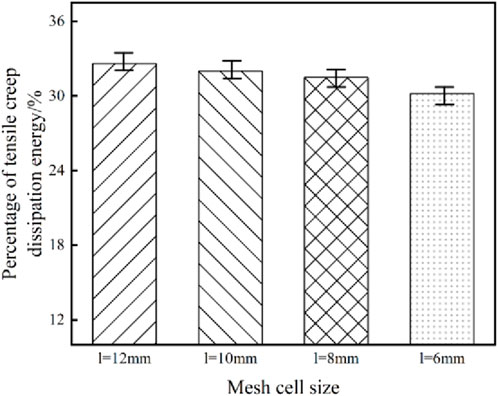
Since the volume of all elements is assumed to be equal when calculating the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy, in order to verify the influence of this assumption on the accuracy of the calculation results, the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy of different mesh size models is analyzed. The analysis results are shown in Figure 4.
The smaller the unit size, the more accurate the calculation results. As the mesh size becomes smaller, the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy gradually becomes smaller, but the magnitude of change is very small. When the unit size is reduced from 12 mm to 6 mm, the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy only changes by 2.4%, which is lower than the accuracy requirement of less than 5% in engineering. Therefore, it can be considered that the proposed calculation method of the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy is feasible and can meet the engineering accuracy requirements. In the subsequent parameter analysis, in order to ensure the calculation efficiency and a certain accuracy, an 8 mm grid cell size is selected for calculation.
4.2 The influence of mixture parameters on the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy
4.2.1 The influence of viscoelastic parameters
The viscoelastic parameters of asphalt mixtures with different viscoelastic properties are different, and the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy under different viscoelastic parameters is shown in Figure 5.
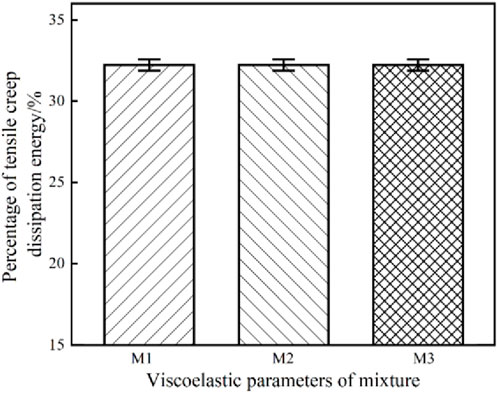
Figure 5. Effect of different viscoelastic parameters on the percentage of energy dissipated by tensile creep.
Comparing the viscoelastic parameters of M1 and M2, it can be found that the relaxation time of the two is similar but the instantaneous modulus is quite different. The calculated results show that the percentage of tensile creep dissipation of the two parameters is basically the same, about 31.5%. Comparing the parameters M1 and M3, it can be found that the instantaneous modulus of the two is similar but the relaxation time is quite different. The calculation results also show that the percentage of tensile creep dissipation of the two parameters is basically the same, about 31.5%. It can be found that the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy of asphalt mixtures with different viscoelastic properties in SCB creep test is the same, accounting for about 31.5% of the total creep dissipation energy.4.2.2 The influence of creep load.
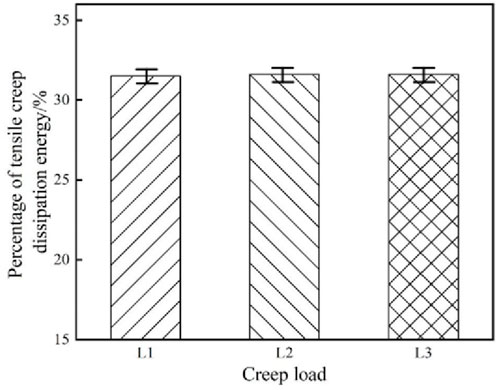
The failure strength of different asphalt mixtures is different. When the same stress ratio is used as the load of NN-SCB, the creep load of different mixtures is also different. The percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy of asphalt mixture under different creep loads is shown in Figure 6.
The percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy under different creep loads is also almost equal, about 31.5%. Therefore, the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy of asphalt mixtures with different strength characteristics in NN-SCB is also the same.
According to the simulation results of NN-SCB under different viscoelastic parameters and creep loads, it can be found that the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy in NN-SCB has nothing to do with the characteristics of asphalt mixture. The tensile creep dissipation energy of NN-SCB of different asphalt mixtures accounts for about 31.5% of the total creep dissipation energy. The coefficient α in Equation 9 is a constant. Therefore, the total creep dissipation energy of NN-SCB can be used to conveniently calculate the tensile creep dissipation energy consumed in the tensile area of the specimen, and then evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of the mixture.
5 Analysis and discussion of practice results
5.1 Results of NN-SCB creep
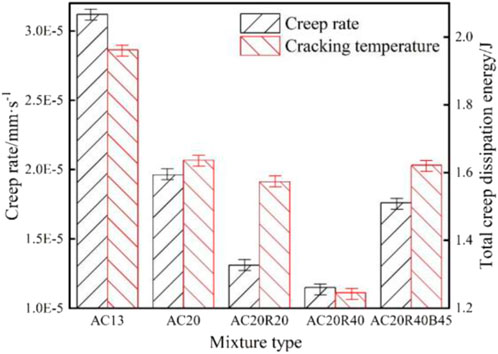
The creep rate of NN-SCB of five asphalt mixtures is shown in Figure 7.
The experimental results demonstrate that AC13 exhibits the highest creep rate, measuring 59.2% higher than AC20, suggesting superior stress relaxation capability in AC13 likely attributed to its higher asphalt content. Incorporation of recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) materials reduces the creep rate of asphalt mixtures. Specifically, AC20R20 and AC20R40 show 33.2% and 41.3% lower creep rates, respectively, compared to AC20. This reduction stems from the inferior creep performance of aged asphalt in RAP relative to virgin asphalt. The creep rate decreases proportionally with increasing RAP content. However, augmenting virgin asphalt content effectively restores the creep performance of recycled mixtures. For instance, AC20R40B45, containing 40% RAP with a 0.5% virgin asphalt additive, achieves a creep rate marginally below that of virgin asphalt mixtures, demonstrating successful performance recovery through binder compensation.The creep rate solely represents the asphalt mixture’s deformation behavior during the creep stability phase, failing to account for the effects of initial creep deformation and applied creep load on overall creep characteristics. To comprehensively evaluate creep performance, this study introduces total creep dissipation energy as an additional assessment parameter. Figure 7 presents comparative data for five asphalt mixtures, revealing that AC13 exhibits the highest creep dissipation energy—40.9% greater than AC20. This discrepancy, less pronounced than the creep rate difference, is attributed to AC20’s superior strength characteristics. Incorporation of reclaimed materials reduces mixture dissipation energy, with AC20R20 and AC20R40 showing 9.4% and 33.3% decreases respectively compared to AC20. Notably, these reductions remain smaller than corresponding creep rate reductions, indicating that while reclaimed materials significantly lower creep rates, enhanced strength facilitates greater energy consumption. The comparable dissipation energy between AC20R40B45 and AC20 demonstrates that optimizing asphalt-aggregate ratio in recycled mixtures can effectively compensate for diminished energy dissipation capacity caused by asphalt aging.
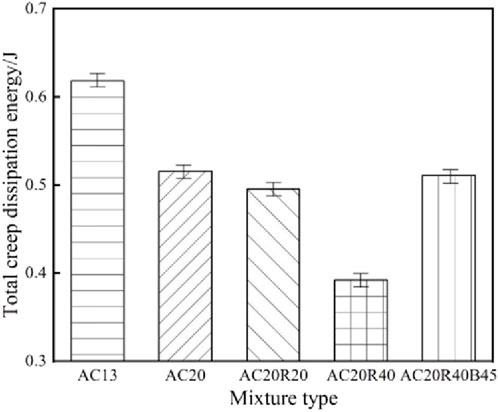
Although the creep rate and total creep dissipation energy can evaluate the creep performance of asphalt mixture, the creep deformation measured in the NN-SCB and the calculated total creep dissipation energy include the compressive creep deformation and compressive creep dissipation energy in the compression zone of the specimen, which is inconsistent with the low-temperature stress characteristics of the actual pavement. Therefore, it is more realistic to calculate the tensile creep dissipation energy of the specimen in the NN-SCB and evaluate the creep performance of the asphalt mixture with the tensile creep dissipation energy. The results of tensile creep dissipation energy calculated by five kinds of asphalt mixtures are shown in Figure 8.
The evaluation results of tensile creep dissipation energy are consistent with the evaluation results of total creep dissipation energy, and also have the characteristics of total creep dissipation energy, that is, the influence of load and deformation on creep performance is considered at the same time, and the physical meaning is more consistent with the field practice.
5.2 Results of TSRST
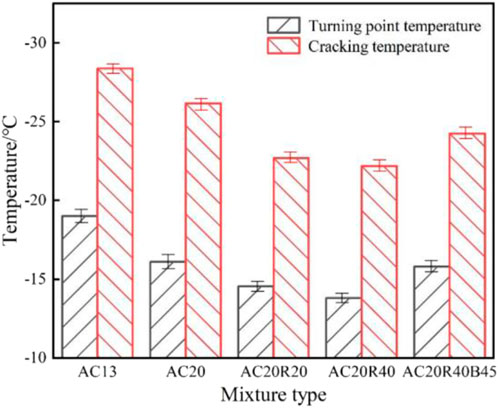
The freezing temperature and turning point temperature of the five asphalt mixtures are shown in Figure 9.
AC13 demonstrates the lowest fracture temperature, indicating superior low-temperature cracking resistance among the tested mixtures. The remaining mixtures exhibit progressively higher fracture temperatures in the order: AC20 < AC20R20B45 < AC20R20 < AC20R40. Comparative analysis of mixtures with equivalent nominal maximum aggregate sizes reveals that incorporating reclaimed materials elevates fracture temperatures and reduces low-temperature crack resistance. This deterioration stems from aged asphalt in recycled components increasing mixture stiffness modulus, thereby amplifying thermal stresses during cooling. Concurrently, aged asphalt exhibits diminished stress relaxation capacity compared to virgin asphalt, resulting in reduced thermal stress dissipation and greater accumulated stress. Consequently, recycled asphalt mixtures display elevated fracture temperatures and compromised low-temperature performance. The comparable fracture temperatures of AC20R40B45 and AC20 demonstrate that optimized asphalt-aggregate ratio adjustment in recycled mixtures effectively counteracts the detrimental effects of aged asphalt on low-temperature cracking resistance.
In addition, after adding the old materials, the turning point temperature of the asphalt mixture increases, and after increasing the amount of new asphalt, the turning point temperature decreases again. The change of the turning point temperature reflects the temperature at which the asphalt mixture changes from viscoelastic to brittle, indicating that the temperature at which the asphalt mixture loses its viscous characteristics after adding the old material increases, which explains the reason why the recycled asphalt mixture accumulates temperature stress faster. At the same time, increasing the amount of new asphalt can reduce the speed of accumulation of temperature stress in asphalt mixture.
5.3 Constractive analysis of results of NN-SCB creep and TSRST
In this study, NN-SCB was used to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixture, and five types of asphalt mixtures were evaluated using creep rate, total creep dissipation energy and tensile creep dissipation energy. In order to select a more reasonable and representative evaluation index, this paper compares the three indexes obtained from the NN-SCB with the freezing temperature obtained from the TSRST. The results show that the evaluation results of low-temperature crack resistance of five types of asphalt mixtures according to the three indexes obtained from NN-SCB are consistent with the results of TSRST. The order of low-temperature crack resistance of these five types of asphalt mixtures is: AC13 > AC20 > AC20R40B45 > AC20R20 > AC20R40. This shows that it is feasible to evaluate the low-temperature performance of asphalt mixture by NN-SCB.However, there are obvious differences in the degree of change of low-temperature crack resistance of different asphalt mixtures reflected by different indexes obtained from NN-SCB.
When the creep rate and total creep dissipation energy are used to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance, the difference of low-temperature crack resistance between different asphalt mixtures is significantly greater than that of the freezing temperature index, which means that the creep rate and total creep dissipation energy may be used to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of the mixture. When the actual low-temperature crack resistance of the mixture is too high or too low, it will have an adverse effect on the actual engineering application. In addition, the physical meaning of creep rate and total creep dissipation energy is not consistent with the actual low-temperature tensile stress state of asphalt pavement. Therefore, these two indicators cannot effectively evaluate the actual low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixture in pavement. When the tensile creep dissipation energy index is used to evaluate the low-temperature performance of asphalt mixture, the change degree of low-temperature crack resistance between different mixtures is very similar to the evaluation result of freezing temperature. At the same time, the tensile creep dissipation energy is more sensitive to the content of the old material in the recycled asphalt, which is very consistent with the change of the low-temperature crack resistance of the actual recycled asphalt pavement with the content of the old material. Therefore, it seems more reasonable to use the tensile creep dissipation energy as an index of the NN-SCB to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of the asphalt mixture.
6 Conclusion
In this study, the NN-SCB is used as a test method to evaluate the low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixture. The main conclusions are summarized as follows:
(1) The creep test model of NN-SCB was established by ABAQUS software, and the influence of different viscoelastic parameters and creep load on the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy in NN-SCB was analyzed. The results show that the percentage of tensile creep dissipation energy in NN-SCB is independent of the properties of asphalt mixture, and the tensile creep dissipation energy accounts for about 31.5% of the total creep dissipation energy.
(2) Combined with the simulation results of NN-SCB, the method of calculating tensile creep dissipation energy by NN-SCB is proposed. It is suggested that the tensile creep dissipation energy of NN-SCB should be used as the evaluation index of low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mixture. Compared with creep rate and total creep dissipation energy, the physical meaning of tensile creep dissipation energy is more clear, and it is closer to the stress form of asphalt pavement at low-temperature.
(3) The low-temperature crack resistance of five asphalt mixtures was evaluated using both NN-SCB and TSRST. The results indicate that the low-temperature crack resistance assessed by tensile creep dissipation energy is consistent with the low-temperature fracture temperature results obtained from TSRST. The low-temperature crack resistance of the five asphalt mixtures follows the order: AC13 > AC20 > AC20R40B45 > AC20R20 > AC20R40. Specifically, the tensile creep dissipation energy of AC13 is 40.9% higher than that of AC20, indicating its superior low-temperature performance.
(4) As the content of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) increases, the creep rate and total creep dissipation energy of the mixtures decrease. For example, the creep rates of AC20R20 and AC20R40 are 33.2% and 41.3% lower, respectively, compared to AC20. However, increasing the content of virgin asphalt effectively restores the creep performance of the recycled mixtures. For instance, AC20R40B45 (containing 40% RAP with 0.5% virgin asphalt) exhibits a creep rate slightly lower than that of the virgin asphalt mixture, indicating that the performance of the recycled mixture can be effectively restored by adding binder materials.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XX: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Formal Analysis, Validation, Methodology, Supervision, Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing. DT: Visualization, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Investigation. ZW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Data curation. NZ: Data curation, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Basic scientific research projects of universities in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (202435120001); Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Special Environment Road Engineering of Hunan Province (kfj230602); Tianchi Doctoral Program Project in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; Youth Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Natural Science Foundation (202435120003); Service Function Enhancement Technology for Apron Areas in Xinjiang Expressway Service Zones, Scientific Research Project of Xinjiang Communications Investment Group (XJJTZKX-FWCG-202312-0523).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge their financial support. In addition, thank you to all the authors in the following references.
Conflict of interest
Author XX was employed by Xinjiang Transportation Investment (Group) Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
AASHTO (2013). Standard method of test for determining the fracture energy of asphalt mixtures using the semicircular bend geometry (SCB), American association of state Highway and transportation. Washington, DC.
Aliha, M. R. M., Fazaeli, H., Aghajani, S., and Moghadas Nejad, F. (2015). Effect of temperature and air void on mixed mode fracture toughness of modified asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 95, 545–555. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.07.165
Al-Qudsi, A., Falchetto, A. C., Wang, D., Buechler, S., Kim, Y. S., and Wistuba, M. P. (2020). Finite element cohesive fracture modeling of asphalt mixture based on the semi-circular bending (SCB) test and self-affine fractal cracks at low temperatures. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 169, 102916. doi:10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102916
AASHTO TP 9 test method (2025). Standard method of test for determining the creep compliance and strength of hot-mix asphalt (HMA) using the indirect tensile test device.
Chen, H., Xu, J., and Luo, R. (2021). Distribution of dissipated pseudo-strain energies and temperature effect on fatigue cracking resistance in asphalt mixtures under destructive tensile loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 305, 124767. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124767
Das, P. K., Tasdemir, Y., and Birgisson, B. (2012). Low temperature cracking performance of WMA with the use of the Superpave indirect tensile test. Constr. Build. Mater. 30, 643–649. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.12.013
Dave, E. V., Buttlar, W. G., Leon, S. E., Behnia, B., and Paulino, G. H. (2013). IlliTC - low-temperature cracking model for asphalt pavements. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 14, 57–78. doi:10.1080/14680629.2013.812838
Elseifi, M. A., Mohammad, L. N., Ying, H., and Cooper, S. (2012). “Aapt, modeling and evaluation of the cracking resistance of asphalt mixtures using the semi-circular bending test at intermediate temperatures,” in Conference of the association-of-asphalt-paving-technologists (AAPT). Austin, TX, 277–302.
Gao, L., Kong, H., Deng, X., and Wang, Z. (2022). Multi-scale finite element simulation of asphalt mixture anti-cracking performance. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 121, 103490. doi:10.1016/j.tafmec.2022.103490
Gong, F., Yan, J., Li, X., and Luo, S. (2019). A peak-strength strain energy storage index for rock burst proneness of rock materials. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 117, 76–89. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.03.020
Jahangiri, B., Karimi, M. M., Giraldo-Londono, O., and Buttlar, W. G. (2021). Characterization of viscoelastic properties of asphalt mixture at low temperatures using DC(T) creep test. Constr. Build. Mater. 298, 123731. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123731
Kliewer, J. E., Zeng, H. Y., and Vinson, T. S. (1996). Aging and low-temperature cracking of asphalt concrete mixture. J. Cold Regions Eng. 10 (3), 134–148. doi:10.1061/(asce)0887-381x(1996)10:3(134)
Li, C., Pan, K., and Wang, L. (2021). Low-temperature cracking performance of asphalt mixture based on stepwise loading bending creep test. J. Central South Univ. Sci. Technol. 52 (7), 2450–2458. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.07.030
Li, L., Li, W., Wang, Z., Dong, M., and Zhang, Y. (2018). Characterizing stress-dependent complex and relaxation moduli of dense graded asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 193, 55–63. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.162
Liu, S., Cao, W., Shang, S., Qi, H., and Fang, J. (2010). Analysis and application of relationships between low-temperature rheological performance parameters of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 24 (4), 471–478. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2009.10.015
Liu, Y., Zhang, X., and Wang, D. (2008). Prediction of fatigue life of asphalt mixture in crack growth stage. Nat. Sci. Ed. 36 (2), 41–47. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.2008.02.008
Medeiros, M. S., Daniel, J. S., and Chehab, G. R. (2015). Framework for low-temperature cracking analysis of asphalt mixtures using a viscoelastic continuum damage model. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 27 (10). doi:10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0001215
Nian, T., Li, P., Mao, Y., Zhang, G., and Liu, Y. (2018). Connections between chemical composition and rheology of aged base asphalt binders during repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 159, 338–350. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.097
Ozer, H., Al-Qadi, I. L., Lambros, J., El-Khatib, A., Singhvi, P., and Doll, B. (2016). Development of the fracture-based flexibility index for asphalt concrete cracking potential using modified semi-circle bending test parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 115, 390–401. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.144
Pszczola, M., Jaczewski, M., and Szydlowski, C. (2019). Assessment of thermal stresses in asphalt mixtures at low temperatures using the tensile creep test and the bending beam creep test. Appl. Sciences-Basel 9 (5), 846. doi:10.3390/app9050846
Qi, L., Xu, R., and He, J. (2021). Research on low-temperature crack resistance of toughened epoxy asphalt mixture. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 63 (1/2), 16. doi:10.1504/ijmpt.2021.117033
Roque, R., Birgisson, B., Drakos, C., and Dietrich, B. (2004). Aapt, Development and field evaluation of energy-based criteria for top-down cracking performance of hot mix asphalt. Tech. Sess. Association-of-Asphalt-Paving-Technologists, 229–260. doi:10.1037/a0024076
Sun, H. (2023). Determination of low-temperature crack resistance of asphalt mastics based on relaxation properties. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 19, e02389. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2023.e02389
Teshale, E. Z., Stolarski, H. K., and Marasteanu, M. O. (2013). Determination of creep compliance of asphalt concrete from notched semi-circular bend (SCB) test. Exp. Mech. 53 (6), 919–928. doi:10.1007/s11340-012-9688-z
Tian, X., Yu, Z., and Jing, B. (2010). Study on asphalt mixture nonlinear viscoelastic model based on stress relaxation test. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 27 (8), 7–11. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2010.08.002
Wagoner, M. P., Buttlar, W. G., and Paulino, G. H. (2005). Disk-shaped compact tension test for asphalt concrete fracture. Exp. Mech. 45 (3), 270–277. doi:10.1177/0014485105053205
Wang, L., Pei, K., and Li, C. (2021). On rheological properties and constitutive relationship of polyphosphoric acid-SBS composite modified asphalt mixture at low temperature. J. Build. Mater. 24 (4), 842–850. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.04.02
Wenbiao, W. U., Xiaoge, T., and Songtao, L. V. (2011). Xuzhihong, time-temperature-aging equivalent relation of asphalt mixture based on relaxation property. J. Build. Mater. 14 (3), 340–344. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2011.03.010
Xu, H., Guo, W., and Tan, Y. (2015). Internal structure evolution of asphalt mixtures during freeze-thaw cycles. Mater. and Des. 86, 436–446. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2015.07.073
Yang, T., Chen, S., Pan, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2022). Investigation of the accuracy of fracture energy in evaluating the low-temperature cracking performance of asphalt mixture. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 34 (9). doi:10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0004353
Yin, H., and Gao, S. (2021). Evaluation of low-temperature cracking resistance of asphalt mixture by indirect tensile creep test. J. Funct. Mater. 52 (9). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.09.020
You, T., Abu Al-Rub, R. K., Masad, E. A., Kassem, E., and Little, D. N. (2014a). Three-dimensional microstructural modeling framework for dense-graded asphalt concrete using a coupled viscoelastic, viscoplastic, and viscodamage model. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 26 (4), 607–621. doi:10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0000860
You, T., Masad, E. A., Abu Al-Rub, R. K., Kassenn, E., and Little, D. N. (2014b). Calibration and validation of a comprehensive constitutive model for asphalt mixtures. Transp. Res. Rec. 2447, 13–22. doi:10.3141/2447-02
Zhang, Y., and Sun, Y. (2022). Fast-acquiring high-quality Prony series parameters of asphalt concrete through viscoelastic continuous spectral models. Materials 15 (3), 716. doi:10.3390/ma15030716
Keywords: asphalt mixture, low-temperature crack resistance, semi-circular bending creep test, tensile dissipation energy, reclaimed asphalt pavement
Citation: Xi X, Tang D, Wang Z and Zhang N (2025) Multi-Scale evaluation of low-temperature performance in asphalt mixtures using not-notched semi-circular bending creep testing. Front. Mater. 12:1624268. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1624268
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 27 May 2025;
Published: 06 June 2025.
Edited by:
Mario Milazzo, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Rui Zhang, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaXuetang Xiong, Foshan University, China
Kefei Liu, Central South University Forestry and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Xi, Tang, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Naitian Zhang, em50QHhqdS5lZHUuY24=
 Xinghao Xi1,2,3
Xinghao Xi1,2,3 Zhenghe Wang
Zhenghe Wang Naitian Zhang
Naitian Zhang