- 1No.1 Engineering Co., Ltd., CCCC First Highway Engineering, Beijing, China
- 2School of Civil and Transportation Engineering, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China
Limestone tailings, a significant solid waste generated during cement manufacturing, face challenges of low recycling efficiency and limited engineering application, representing an underutilized resource. This study systematically evaluated the viability of substituting natural aggregates with limestone tailings in base course composites. Four replacement ratios (0%, 20%, 40%, 60%) were investigated through an integrated experimental approach. A comprehensive assessment framework was established, encompassing mechanical tests (compressive and flexural strength), durability evaluations (drying shrinkage, thermal shrinkage, freeze-thaw resistance, erosion stability), XRD phase analysis, and SEM microstructural imaging. Results indicate that limestone tailings micro-particles exhibit a nucleation effect, and their alkaline components, such as calcium oxide, promote cement hydration. Mixture performance exhibited an initial improvement followed by a decline as the tailings content increased. At a 20% cement-tailings content, the composite demonstrated optimal performance: a 10% increase in 90-day compressive strength, a freeze-thaw resistance coefficient exceeding 80%, enhanced resistance to drying and thermal shrinkage, and superior erosion stability compared to the control group mixture. This study demonstrates that partial replacement of natural aggregates with limestone tailings (specifically at 20%) conserves natural resources and enhances key road performance characteristics. The findings provide crucial evidence supporting the resource utilization of limestone tailings in sustainable road construction.
1 Introduction
Cement production consumes a substantial amount of limestone, with an average of approximately 0.8 tons of limestone required to produce 1 ton of cement (Xiang et al., 2018; Bilen, 2021; Mugambi et al., 2024; Pacheco-Menor et al., 2025; Adediran et al., 2025). However, significant variations in the contents of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide within limestone ores mean that many argillaceous limestone deposits are unsuitable for cement production, leading to the accumulation of large quantities of argillaceous limestone tailings. These tailings are primarily managed through stockpiling and backfilling, which not only results in considerable resource wastage but also poses environmental risks to the surrounding areas (Bederina et al., 2013; Liu H. et al., 2024; Feng et al., 2024).
At present, reducing carbon dioxide emissions associated with the production of cement-based materials has become a top priority. These practices include the implementation of energy-saving interventions, the use of renewable energy, and the conversion of fuels. In addition, researchers are trying to improve the efficiency of building materials and promote the reuse and recycling of waste (Griffiths et al., 2023; He et al., 2025). The existing research on industrial solid waste, such as steel slag, has been very thorough. Li et al. (2025) discussed the application of all aspects of steel slag treated by microbial-induced mineral carbonation in engineering construction. Helping the engineering community move towards more circular and environmentally friendly research and development. Similarly, various utilization methods of limestone tailings are gradually being developed (Nguyen et al., 2025; Su et al., 2024). Wang et al. (2022) developed a limestone tailings-based cementitious material using limestone tailings, flue gas desulfurization gypsum, blast furnace slag, cement clinker, and sodium hydroxide as raw materials. The effects of different components on the compressive strength of the binder were analyzed using response surface methodology, and the optimal mix design was determined to be: 9.97% cement clinker, 6% desulfurized gypsum, 50% limestone tailings powder, 34.03% blast furnace slag, and 3% sodium hydroxide. The results demonstrated that the optimized binder could be effectively used as a filling material in karst caves, achieving an approximate 90% utilization rate of limestone tailings. Sakulich et al. (2009) studied the effect of limestone tailings as fine aggregate on the properties of alkali-activated steel slag concrete and compressive strength of concrete up to 65 MPa. Xiang et al. (2018) studied the effect of limestone powder on the geopolymer of slag fly ash, and the results showed that the main function of limestone was a physical modification, but chemical modification could not be ignored. The additional nucleation sites provided by limestone powder slightly accelerated the geopolymerization reaction. Furthermore, limestone powder increased the content of both chemically bound and physically adsorbed water. Therefore, limestone powder is a promising mineral additive, and its beneficial effect on the properties of alkali-activated materials is primarily attributed to its physical filler role (Perez-Cortes and Ivan Escalante-Garcia, 2020; Moseson et al., 2012).
Besides, the accelerated expansion of road infrastructure has precipitated two critical environmental challenges: intensified exploitation of natural mineral aggregates and substantial ecological burden (Gu et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2024; Tong et al., 2021; Andryanti et al., 2024). Liu et al. (2023) investigate the effects of tailings content on the mechanical properties and durability of concrete under dry–wet cycling and negative temperature conditions, where tailings replace river sand at rates of 0%, 10%, 20%, and 30%. The results show that the tailings have excellent physical and chemical properties, and the performance of concrete can be improved by adding an appropriate amount of tailings. The fine-grained tailings fill the internal voids of the concrete aggregate, optimize the pore structure, improve the density and integrity of the concrete, and make up for the particle size defects of the concrete aggregate. In addition, the active substances in the tailings promote the hydration reaction of cement, resulting in an increase in the formation of hydration products such as C-S-H gel in the cement system. Zhang et al. (2023) studied the mixing of non-metallic tailings and iron tailings. The experimental results show that in the prepared iron tailings-based cementitious mortar, the optimal incorporation rate of graphite ore as a supplementary cementitious material is 4 wt%. After 28 days of hydration, the compressive strength of the best mortar test block is 23.21 MPa, and the flexural strength is 7.76 MPa. Iron tailings were incorporated as aggregate substitutes to formulate composite asphalt binders. Empirical evaluations demonstrated that pavement materials containing iron tailings achieved comparable or marginally superior performance metrics relative to conventional gravel-based mixtures (Velasquez et al., 2009; Romero et al., 2001). Wieszczycka (2018) systematically replaced natural aggregates with processed iron tailings in roadway applications, revealing through standardized performance testing that optimally treated tailings could effectively substitute approximately 80% of virgin aggregates. Rao et al. (2019) conducted experimental investigations on base course materials utilizing pumice-iron tailings composites. Their techno-economic analysis confirmed dual benefits: enhanced utilization of industrial byproducts coupled with a 22%–35% reduction in material production costs compared to traditional base layer formulations. At present, the comprehensive utilization of limestone tailings is still in its infancy, especially the use of limestone tailings for the preparation of road materials is rarely studied.
The purpose of this paper is to present a practical idea for the resource utilization of limestone tailings. Limestone tailings are used to efficiently prepare the base mixture. Firstly, the cement content and compaction test of the mixture were selected, and then the compressive strength, flexural strength, dry shrinkage and temperature shrinkage performance, frost resistance, erosion resistance, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis tests were carried out on the mixture with different dosages of limestone tailings. The influence of different dosages of limestone tailings on the performance of the mixture was studied, and XRD and SEM were used to analyze the influence mechanism to realize the design and utilization of limestone tailings mixture.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
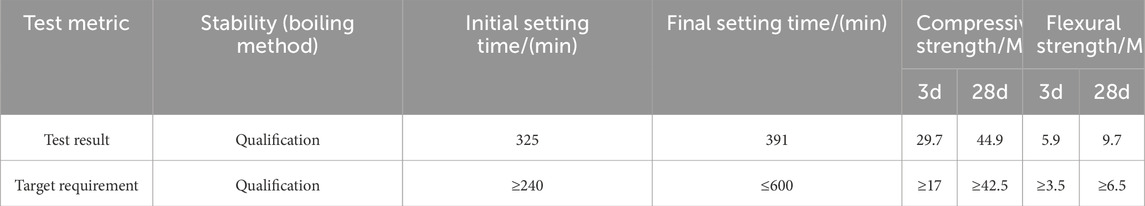
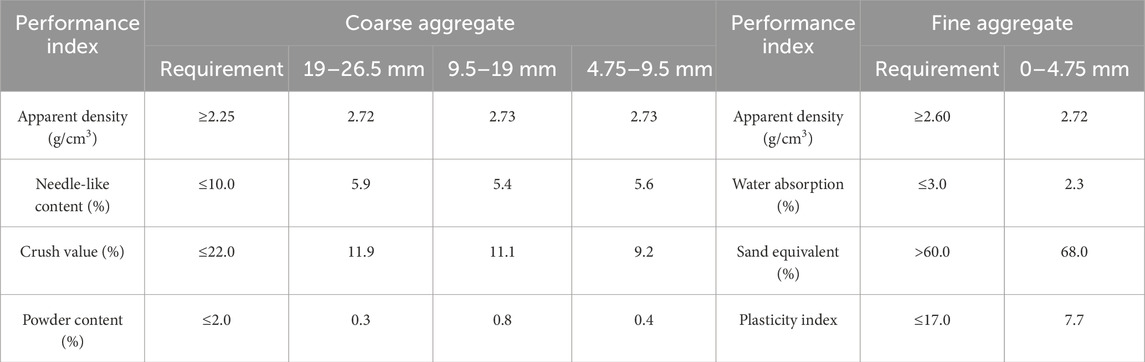
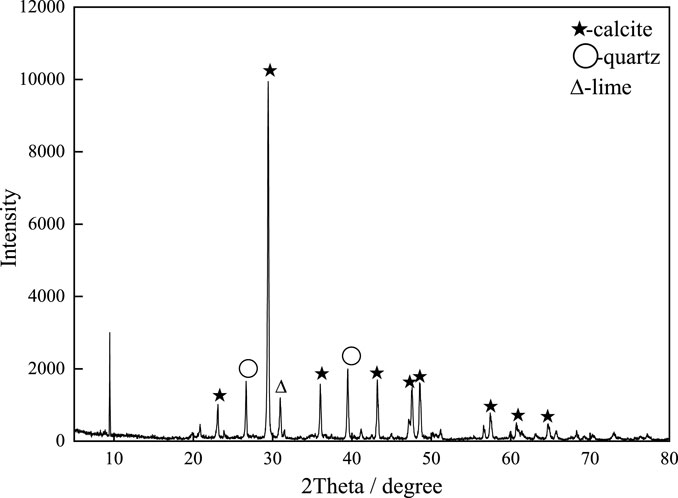
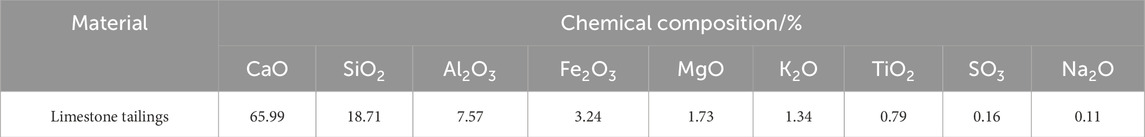
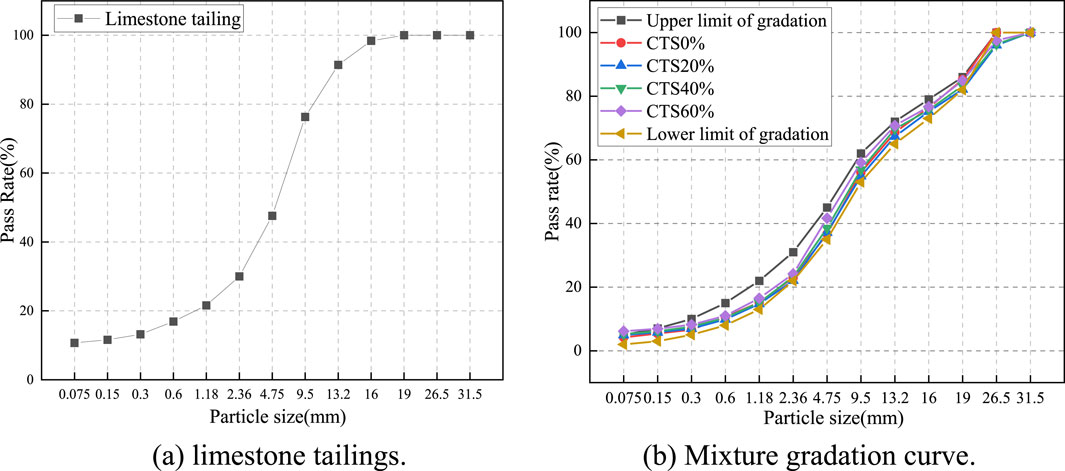
The cement is P.O42.5 cement produced by Gezhouba Yicheng Cement Co., Ltd. The basic performance index test results are shown in Table 1. The test water is local tap water. The natural aggregate is 19–26.5 mm, 9.5–19 mm, 4.75–9.5 mm, and 0–4.75 mm aggregates produced by the stone material field of Jinniushan Forest Farm in Yicheng City. The basic properties are shown in Table 2. The limestone tailings investigated in this study were sourced from the tailings reservoir of Hubei Huaxin Cement (Xiangyang) Co., Ltd. Material characterization was performed using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) and XRD analyses. Figure 1 presents the mineralogical composition, revealing calcite and quartz as predominant crystalline phases. Quantitative chemical analysis (Table 3) demonstrates that silicon dioxide (SiO2) and calcium oxide (CaO) constitute the major components, accounting for 18.71% and 65.99% of the total composition, respectively. Particle size distribution analysis (Figure 2) indicates that 92% of tailings particles fall within the 0.075–4.75 mm range, meeting ASTM C33 specifications for fine aggregates.
2.2 Test Methods
Four formulations of limestone tailings base mixtures were designed with progressive substitution rates of 0%, 20%, 40%, and 60%, designated as CTS0%, CTS20%, CTS40%, and CTS60%, respectively. Limestone tailings base mixtures replacement is the standard is the quality of the aggregate. As illustrated in Figure 2, the aggregate gradation curves conform to ASTM D2940 specifications for dense-graded base materials. Compaction testing revealed distinct compaction characteristics: optimum moisture contents were measured at 4.6%, 4.5%, 4.9%, and 5.4%, while corresponding maximum dry densities decreased progressively from 2.410 g/cm3 to 2.397 g/cm3 with increasing tailings content (2.410, 2.417, 2.401, and 2.397 g/cm3 respectively).
2.2.1 Cement consumption and compaction test
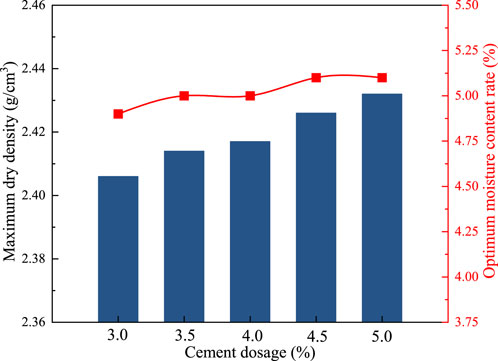
Five groups with varying cement content (3.0%, 3.5%, 4.0%, 4.5%, and 5.0%) were selected for vibration compaction tests to determine the optimum moisture content and maximum dry density for each mix ratio. The optimal cement content was identified based on the analysis of 7-day unconfined compressive strength and a comprehensive performance evaluation. The vibration compaction tests were conducted by T0842-2009 from the Test Methods of Materials Stabilized with Inorganic Binders for Highway Engineering (JTG 3441–2024), to determine each mixture group’s maximum dry density and optimum moisture content.
2.2.2 Unconfined compressive strength and flexural-tensile strength test
Cylindrical specimens with dimensions of φ150 mm × 150 mm were prepared using the optimum moisture content and maximum dry density determined from the compaction tests. Unconfined compressive strength and flexural strength tests were conducted by the JTG 3441–2024, following standards T0805-2024 for compressive strength and T0851-2009 for flexural-tensile strength. The average value of three samples in each group is the strength value.
2.2.3 Drying shrinkage and temperature shrinkage tests
A beam specimen with a size of 100 mm × 100 mm × 400 mm was fabricated for drying shrinkage and temperature shrinkage tests. The specimens were placed in an environment at a temperature of 20°C and relative humidity of 60% after standard curing in the drying shrinkage test, as per the test requirements of the specification. The readings of the dial indicator and the water loss of the test specimen were continuously recorded. The strain gauge method was used in the temperature shrinkage test. After the standard curing, the test specimen was put into an oven at 105°C and heated to constant weight. The temperature shrinkage compensation test specimen was made of a ceramic plate. It was put into the high and low temperature alternating test chamber at 60°C ∼ −15°C. A temperature interval was set every 15°C. The strain gauge data was recorded after keeping 3 h of each temperature interval.
2.2.4 Freeze-thaw cyclic test
Cylindrical specimens with dimensions of φ150 mm × 150 mm were prepared for freeze–thaw cycle testing. After curing under standard conditions for 2 days, the samples were subjected to freeze–thaw testing. For the freeze–thaw test, the specimens were put into the freezer at −18°C for 16 h. Afterward, the samples were removed and immersed in water at 20°C for 8 h. This comprised one complete cycle. Five experiments were performed. The freeze–thaw resistance index (BDR) of the specimens was calculated using the following equation:
Where, BDR is the compressive strength loss of specimens after n freeze–thaw cycles (%); RDC is the compressive strength of specimens after n number of freeze–thaw cycles (MPa); RC is the compressive strength of the control specimen (MPa).
2.2.5 Anti-erosion performance test
Preparation specimens with dimensions of φ 150 mm × 150 mm were prepared for anti-erosion performance testing. Before the test, the specimen was soaked in water for 24 h, so that the pores of the material were filled with water to avoid interfering with the erosion quality results due to the water absorption of the specimen. After weighing, the test piece was placed in the scouring bucket. After the fixation, water was poured into the bucket to be about 5 mm higher than the test piece. The erosion bucket was placed on a vibrating table for fixation, and the relevant parameters of the erosion machine were set: the peak impact force was 0.5 MPa, and the scouring frequency was 10 Hz. After 30 min of washing, the turbid water in the bucket was poured into the metal basin for standing precipitation, and the standing precipitation was 12 h. After standing precipitation, the upper water in the basin was poured out, and the remaining precipitate was placed in the oven, dried, and weighed. The anti-erosion performance of the specimens was calculated using the following equation:
Where P is the erosion mass loss (%); mf is the mass of erosion material (g); m0 is the mass of the specimen (%).
2.2.6 X-ray diffraction analysis
The crystalline phases of the mixture were analyzed using a Rigaku Smartlab high-resolution X-ray diffractometer with Cu-Ka radiation, tube setting of 40 kV and 20 mA, a step size of 0.01°, and a 2ɵ range of 10°–80°. Before the XRD tests, the tested samples were ground into powder with a size lower than 0.075 mm and dried at 60°C for 12 h.
2.2.7 Microstructure analysis
Microstructure analysis was performed to investigate the influence of limestone tailings content on the microstructure of the mixture. A FlexSEM1000 SEM with a 15 kV acceleration voltage was used., Samples for SEM analysis were collected from the compressive strength; they were soaked in ethanol to cease further hydration. Before analysis, a layer of gold particles was sprayed on the observation surface to enhance the electrical conductivity.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Cement consumption and compaction test
Five groups of cement content of 3.0%, 3.5%, 4.0%, 4.5%, and 5.0% were selected for the compaction test, and the optimum water content and maximum dry density of each group of cement content were determined. The test results are shown in Figure 3. At the same time, the φ150 mm × 150 mm cylindrical specimen was prepared according to the test data, and the 7-day unconfined compressive strength test was carried out. The results are shown in Figure 4. According to the comprehensive consideration of construction technology level and construction economy, a 4.5% cement content that meets the requirements of the specification is selected as the best dosage (Jing et al., 2023).
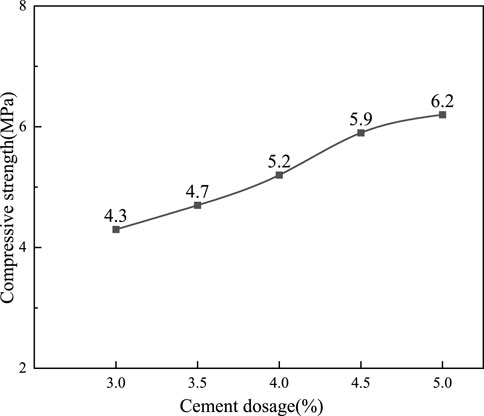
Figure 4. The 7d unconfined compressive strength of the control group with different cement content.
3.2 Unconfined compressive strength and flexural-tensile strength
The unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and flexural-tensile strength of cementitious mixtures incorporating varying dosages of limestone tailings were systematically investigated, with the results presented in Figure 5. As illustrated in the figure, both UCS and flexural strength exhibit a non-linear trend with increasing limestone tailings content: they initially increase, reach a peak, and then gradually decline. This suggests that there is an optimal content range for limestone tailings to enhance mechanical performance. Specifically, the CTS20% achieved the highest unconfined compressive strength of 11.2 MPa, representing an improvement of approximately 9.9% compared to the CTS0% without limestone tailings. However, further increasing the tailings content to 60% led to a reduction in strength, with a UCS value of 10.0 MPa, which is 2.1% lower than that of CTS0%. A similar trend was observed in the flexural strength after 90 days of curing: the CTS20% mixture again displayed the highest strength, outperforming CTS0%, CTS40%, and CTS60% by 2.2%, 2.0%, and 9.2%, respectively. The improvement in mechanical properties at tailings content can be attributed to several factors. First, the fine particles in limestone tailings may serve as nucleation sites, enhancing the hydration process and leading to a denser microstructure. Additionally, the presence of alkaline components such as CaO in the tailings can actively participate in hydration reactions, contributing to strength development. However, when the tailings content exceeds a certain threshold, the dilution effect becomes more pronounced, reducing the overall content of reactive cementitious materials and consequently impairing the strength (Liu Y. S. et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024). Excessive replacement may also disrupt the optimal particle packing, leading to increased porosity and weaker bonding within the matrix. These findings highlight the importance of optimizing the dosage of industrial by-products like limestone tailings to balance mechanical performance and material sustainability in construction applications.
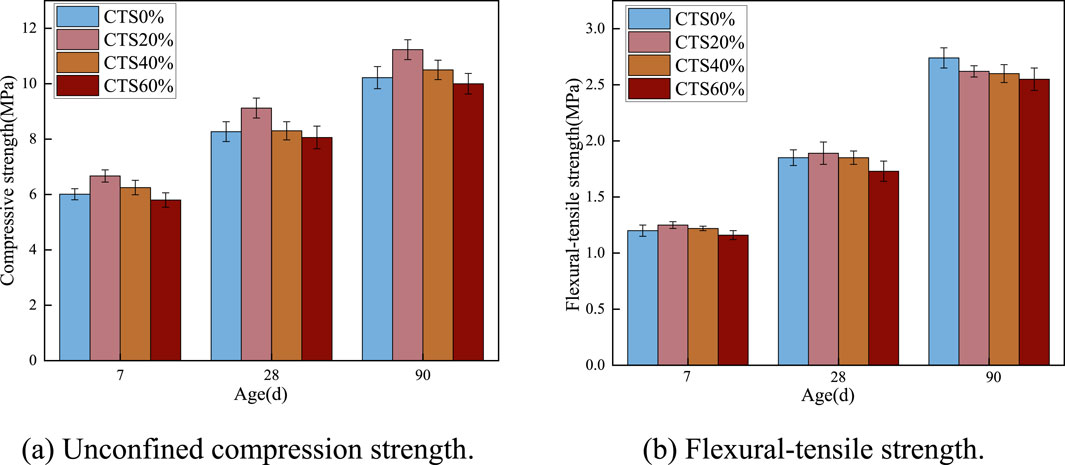
Figure 5. Mechanical properties of limestone tailings base material at different ages. (a) Unconfined compression strength. (b) Flexural-tensile strength.
3.3 Drying shrinkage and temperature shrinkage
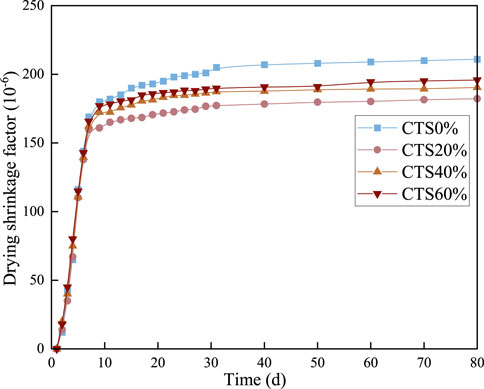
The dry shrinkage coefficients of cementitious mixture specimens incorporating varying contents of limestone tailings were measured at different curing ages, and the results are presented in Figure 6. As shown in the figure, the dry shrinkage coefficient increases progressively with curing time. Notably, a significant rise is observed during the initial 7 days, indicating a rapid shrinkage development in the early curing stage. After approximately 10 days, the rate of increase in shrinkage begins to slow down and gradually levels off, demonstrating a more stable behavior over time. This early-stage shrinkage can be attributed to the intense hydration reactions occurring shortly after mixing. During the initial days, the hydration process consumes a considerable amount of water and generates a dense microstructure, leading to rapid moisture loss and volume reduction. As curing progresses, the hydration reactions become less vigorous due to the depletion of available water and reactive cementitious materials. Consequently, internal structural changes decrease, and the rate of shrinkage stabilizes. Additionally, as internal moisture content continues to decline, both hydration and self-induced expansion diminish, further contributing to the reduced shrinkage rate in the later stages of curing.
Furthermore, the incorporation of limestone tailings appears to influence the shrinkage behavior significantly. With increasing limestone tailings content, the dry shrinkage coefficient of the mixtures generally shows a decreasing trend. Among the tested specimens, the CTS20% exhibited the lowest dry shrinkage coefficient, suggesting an optimal balance between performance and dimensional stability. This reduction in shrinkage can be primarily explained by the alkaline nature of limestone tailings, which promotes slight volumetric expansion during hydration. This expansion partially offsets the shrinkage strain, thus reducing the net shrinkage. Moreover, the nucleation effect of finely divided limestone tailings enhances the early formation of hydration products, leading to a denser microstructure that restrains moisture movement and mitigates shrinkage. However, it is worth noting that excessive limestone tailings content may have the opposite effect. Due to the relatively high specific surface area of the tailings particles, they tend to absorb more free water from the mixture. This can reduce the effective water-to-cement ratio, hinder complete hydration, and create more capillary pores. As a result, the mixture may exhibit increased susceptibility to drying shrinkage at higher tailings content, offsetting the beneficial effects observed at moderate replacement levels. In summary, a moderate addition of limestone tailings, such as 20%, can effectively reduce the dry shrinkage of cementitious mixtures, while excessive dosages may lead to negative effects. Therefore, careful control of the tailings content is essential to optimize dimensional stability and ensure long-term performance (Li et al., 2017).
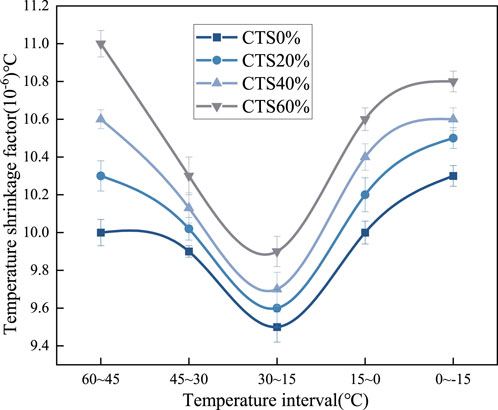
The temperature shrinkage coefficients of cementitious mixtures containing varying limestone tailings content, after 7 days of curing, were measured and are presented in Figure 7. As illustrated, all mixtures exhibited a temperature shrinkage coefficient that followed a parabolic trend concerning temperature variation: the values decreased initially and then increased as the temperature changed. Notably, the minimum temperature shrinkage coefficient for each mixture occurred within the temperature range of 15°C–30°C, indicating a relatively stable thermal response in this interval. This behavior can be attributed to the thermodynamic changes occurring within the mixture as temperature fluctuates (Jing et al., 2023). The thermal response of both the cementitious matrix and the moisture content within the pore structure primarily influences this behavior. The thermal expansion and contraction of both solid and liquid phases are minimal and more balanced, and the rate of moisture movement or phase change (e.g., evaporation or freezing) is limited. This leads to relatively small internal stress changes and a lower overall temperature shrinkage coefficient. However, when the temperature deviates from this moderate range, especially toward lower temperatures, the internal pore water may begin to freeze. Generating internal stress and micro-cracking, which contributes to greater thermal shrinkage deformation upon subsequent temperature decrease. On the other hand, at higher temperatures (above 30°C), increased thermal energy accelerates moisture evaporation from the pore network. The rapid loss of internal water leads to volumetric contraction of the cement matrix. Furthermore, elevated temperatures may cause differential thermal expansion among the various components (cement paste, aggregates, and tailings), generating micro-stress concentrations and contributing to shrinkage deformation. At lower temperatures, a portion of the residual free water within the matrix undergoes phase transition from liquid to solid, which is accompanied by volumetric expansion. This expansion effectively compensates for some of the shrinkage deformation induced by the overall temperature drop, resulting in a lower net shrinkage. However, as the temperature continues to fall outside this optimal range, the compensation effect diminishes, and the mixture exhibits increased thermal contraction. Moreover, the results indicate that the temperature shrinkage coefficient tends to increase with higher limestone tailings content (Chao et al., 2024). This trend suggests that the mixtures become more sensitive to temperature fluctuations as more limestone tailings are incorporated. One possible explanation is that limestone tailings exhibit a higher thermal deformation capacity compared to conventional aggregates (Ji et al., 2023). As a result, their inclusion enhances the overall thermal response of the mixture, leading to greater shrinkage under temperature variation. Despite the slight increase in the temperature shrinkage coefficient with high limestone tailings content, the effect is generally moderate. Importantly, the inclusion of limestone tailings still contributes positively to the mixture performance in terms of cracking resistance. The fine particle size and angular shape of the tailings help improve the internal bonding and restrict micro-crack propagation, which can mitigate temperature-induced cracking. Additionally, the presence of reactive components such as calcium oxide may contribute to the formation of a denser microstructure through secondary hydration, further enhancing the mixture’s structural integrity. In conclusion, while higher limestone tailings content may slightly increase the temperature shrinkage coefficient, the associated improvements in crack resistance and structural compactness make it a viable additive for enhancing pavement material performance, particularly in environments subject to thermal cycling.
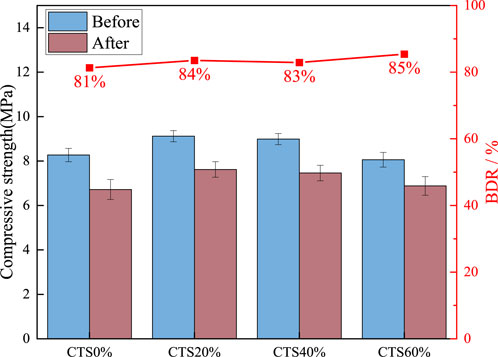
3.4 Freeze-thaw cyclic test
The strength of the 28-day limestone tailings base mixture before and after the freeze-thaw of the curing age is tested, and the results are shown in Figure 8.
As shown in Figure 8, the proportion of limestone tailings increases, and the frost resistance of the mixture is progressively enhanced. The frost resistance coefficients for the mixtures CTS0%, CTS20%, CTS40%, and CTS60% are 81%, 84%, 83%, and 85%, respectively. These results suggest that limestone tailings incorporation can improve the mixture’s resistance to freeze-thaw damage. Freeze-thaw cycling leads to a certain degree of degradation in unconfined compressive strength for all mixtures. This degradation primarily results from the cyclic temperature fluctuations, during which the internal water within the pores of the mixture freezes and thaws repeatedly. When water freezes, it expands in volume, generating internal frost heave pressure. This pressure acts on the pore walls and the internal structure of the material, leading to microcracking, material extrusion, and cumulative damage over repeated cycles (Liu et al., 2025). The mixtures containing limestone tailings exhibit significantly improved durability under freeze-thaw conditions. The BDR of the tailings-containing mixtures is up to 81% higher than that of the CTS0%. This improvement can be attributed to several key factors associated with the physical and thermal properties of limestone tailings. Firstly, limestone tailings consist of finer particles compared to traditional gravel aggregates, which contributes to a denser packing structure and lower porosity in the matrix. The increased specific surface area also enhances interfacial bonding and restricts the movement of free water within the pore network, thus limiting frost-induced damage (Li et al., 2017). Moreover, the presence of soluble salts within the cementitious system introduces osmotic effects during freeze-thaw cycles. As temperature drops, the concentration gradient between the pore solution and ice can generate osmotic pressure. When water in the micropores begins to freeze, the formation of ice crystals draws more liquid toward the freezing front due to this pressure differential. This can result in localized expansion and internal stress buildup. The enhanced microstructure provided by limestone tailings may help to resist these osmotic effects by reducing pore connectivity and limiting moisture migration. In summary, the appropriate incorporation of limestone tailings not only enhances the mechanical properties of the mixture but also improves its resistance to freeze-thaw damage by refining the pore structure, increasing thermal conductivity, and mitigating internal stresses caused by frost heave and osmotic pressure.
3.5 Anti-erosion performance
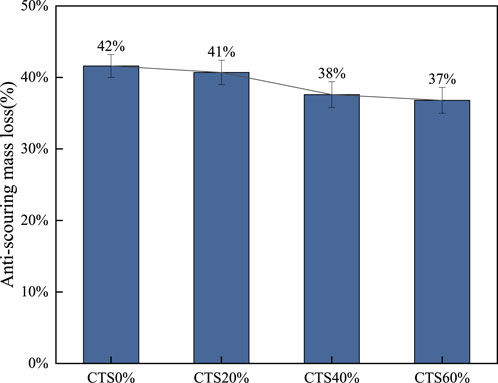
The test shows the change of erosion mass loss of the mixture with different limestone tailings content at 28 days curing age, as shown in Figure 9.
It can be seen from Figure 9 that as the proportion of limestone tailings increases, the erosion-induced mass loss of the specimens gradually decreases, indicating enhanced resistance to hydraulic or mechanical scouring forces. This suggests that the incorporation of limestone tailings positively influences the mixture’s durability against erosive environments. When the limestone tailings content is 0%, 20%, 40%, and 60%, the corresponding mass loss rates under erosion mass loss conditions are 42%, 41%, 38%, and 37%, respectively. These results show a clear downward trend in erosion loss as the tailings content increases. Compared with the CTS0%, the inclusion of limestone tailings effectively reduces the degree of material loss due to scouring. This improvement can be attributed to the presence of fine particles and pozzolanic activity in limestone tailings. Although the pozzolanic activity is relatively low, a small amount of reactive silica and alumina in the tailings can react with calcium hydroxide generated during cement hydration to form additional gel products. This secondary hydration reaction enhances the internal bonding within the matrix and contributes to the densification of the microstructure, reducing the permeability and vulnerability of the mixture to erosive forces. The finer gradation and higher surface area of limestone tailings contribute to better particle packing and improved interfacial transition zones (ITZs) between aggregates and the cementitious matrix. This leads to enhanced cohesion and reduces the risk of particle dislodgement during water flow or scouring conditions. In effect, the compact and well-bonded microstructure acts as a protective barrier, minimizing the penetration and disruptive impact of water or abrasive particles. However, it is also observed that the reduction in mass loss, the frost resistance coefficients of the mixtures with limestone tailings (41%, 38%, and 37% for CTS20%, CTS40%, and CTS60%, respectively) are slightly lower than that of the CTS0% (42%). This suggests a trade-off between frost resistance and scouring resistance at higher limestone tailings content. One possible explanation is that while tailings improve matrix compaction, their higher water absorption and potential to alter pore structure might reduce the mixture’s ability to resist damage caused by freeze-thaw cycles. The addition of limestone tailings significantly improves the anti-scouring performance of the base mixture by refining its microstructure.
3.6 XRD analysis
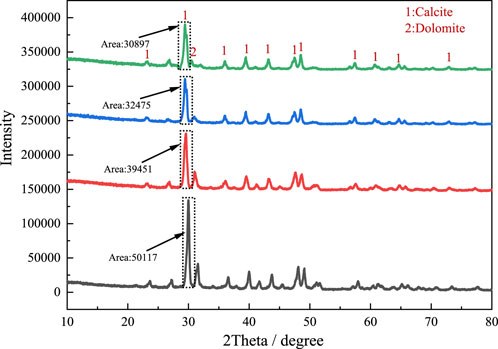
The XRD was used to analyze the crystalline phase composition of the four groups of mixtures cured for 28 days. The test results are shown in Figure 10. By comparing the diffraction patterns of CTS0%, CTS20%, CTS40% and CTS60% four groups of samples, it can be found that at the characteristic peak position of 30°, all groups show the diffraction peak of calcite crystal phase (PDF88-1807), and no newly generated characteristic peak is detected (Liu et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2025). This phenomenon shows that in the range of 20%–60%, the addition of limestone tailings does not cause new chemical reactions, and its physical filling effect dominates, and the components in the tailings do not undergo chemical reactions (Rakhimova et al., 2016). It is worth noting that in the characteristic peak area of calcium carbonate (calcite) near 2θ = 30°, the peak strength of the three groups of samples mixed with tailings decreased by 21.3%, 35.2%, and 38.4%, respectively, compared with the CTS0% group (calculated by Jade software). This regular attenuation may be directly related to the characteristics of tailings materials: XRF composition analysis shows that the total content of SiO2 and Al2O3 in the limestone tailings used is 26.3%, which is significantly higher than that of ordinary limestone raw materials (usually <15%) (Geng et al., 2025), indicating that the proportion of clay minerals (such as kaolinite) is high (Marques et al., 2025). The amorphous structure of clay minerals leads to the weakening of the characteristic peak intensity of calcite crystals in the XRD pattern, which has a significant interference with the quantitative analysis of XRD. The incorporation of tailings does not change the main phase composition of the system, which is conducive to ensuring the volume stability of the material. However, the lack of active components in limestone tailings may affect the long-term strength development (Dietel et al., 2025; Akinbodunse et al., 2024).
3.7 SEM analysis
The microstructure of the mixture with different tailings content at the curing age of 28 days was observed, as shown in Figure 11. It can be seen from Figure 11 that the mixture with different tailings content shows obvious differences in microstructure. It can be seen from Figure 11b that the limestone tailings of low content promotes the formation of hydration products, and the tailings particles have a certain micro-aggregate filling effect, which effectively fills the internal pores of the mixture and forms a denser and more uniform structure, thereby improving the strength of the mixture (Wang et al., 2022; Perez-Cortes and Ivan Escalante-Garcia, 2020; Song et al., 2025). With the increase of tailings content, the microstructure of CTS40% and CTS60% mixtures gradually shows a trend of decreasing overall density and increasing porosity. Excessive micro-particles in the tailings may lead to particle agglomeration, forming a weak interface area and inhibiting the formation of hydration products. In addition, although alkaline components such as calcium oxide in limestone tailings can react to form secondary hydration products, this effect gradually weakens when the content is too high, increasing the inhomogeneity of the microstructure (Elmaasrawy et al., 2025). It can be seen from Figure 11a that the pore structure of the mixture with CTS0% is relatively coarse, and the interface between the aggregate and the cement paste is weak, resulting in the compactness and strength of the overall structure of the mixture being lower than the CTS20%. Therefore, an appropriate amount of limestone tailings can optimize the mixture performance.
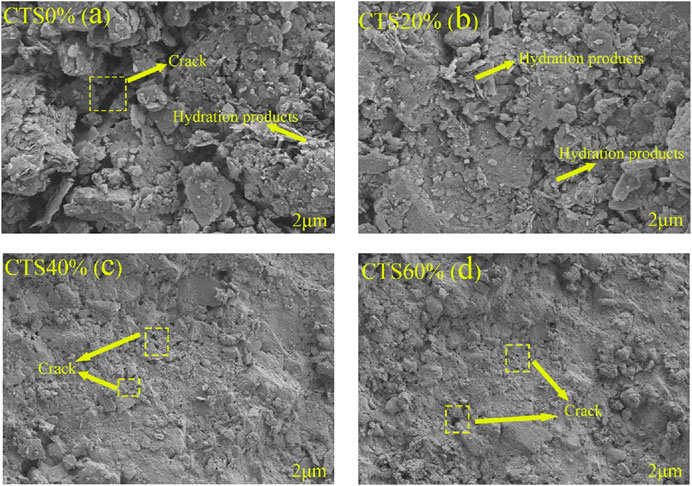

Figure 11. Microstructure of the mixture with different limestone tailings content: (a) CTS0%; (b) CTS20%; (c) CTS40%; (d) CTS60%.
4 Summary and conclusions
In this paper, the performance test and microscopic analysis of base materials with different limestone tailings content were carried out. The unconfined compressive strength and flexural-tensile strength, drying shrinkage and temperature shrinkage, freeze-thaw cyclic, anti-erosion performance, and XRD and SEM analysis are discussed in the paper. From the above analysis, limestone tailings are a promising material with low carbon emission, low energy consumption, and low cost that can be obtained through reasonable design.
1. With the increase of limestone tailings content, the mechanical properties of the mixture increase first and then decrease. The CTS20% achieved the highest compressive strength of 11.2 MPa in 90 days. Limestone tailings have a certain micro-aggregate filling effect, which can improve the strength of the limestone tailings base mixture. After adding limestone tailings, the drying shrinkage performance of the mixture is improved to a certain extent, and the temperature shrinkage coefficient is increased.
2. The appropriate incorporation of limestone tailings material can reduce the strength loss and improve the frost resistance coefficient of the mixture. The alkaline substance contained in the limestone tailings can promote the hydration reaction and enhance the bonding effect of the mixture, thereby improving the anti-erosion performance of the limestone tailings mixture.
3. The crystal phase type of the mixture does not change with the incorporation of limestone tailings, and the incorporation of limestone tailings can produce a micro-aggregate filling effect to effectively fill the internal pores to form a denser and more uniform structure, which improves the performance of the mixture to a certain extent.
4. Future research should explore the use of limestone tailings as aggregate replacement in cement, concrete, and asphalt concrete. Experimental studies are needed to assess mechanical properties and durability under various replacement levels. Additionally, life cycle assessment and economic analysis are also recommended to evaluate sustainability benefits. Extending this approach to practical applications, including field performance and mix design optimization, could promote the resource-efficient use of industrial by-products and enhance the environmental performance of pavement and construction materials.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WL: Supervision, Writing – original draft. CZ: Validation, Writing – original draft, Supervision. CL: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. ZZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZW: Writing – original draft, Validation. QW: Writing – original draft, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study is sponsored by the BUCEA Doctor Graduate Scientific Research Ability Improvement Project (DG2024019), the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC3803403), and the Project of Construction and Support for high-level Innovative Teams of Beijing Municipal Institutions (BPHR20220109).
Conflict of interest
Authors WL, CZ, ZZ, ZW, and QW were employed by No.1 Engineering Co., Ltd.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adediran, A., Rajczakowska, M., Steelandt, A., Novakova, I., Cwirzen, A., and Perumal, P. (2025). Conventional and potential alternative non-conventional raw materials available in nordic countries for low-carbon concrete: a review. J. Build. Eng. 104, 112384. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112384
Akinbodunse, S. J., Ufer, K., Dohrmann, R., and Mikutta, C. (2024). Evaluation of the rietveld method for determining content and chemical composition of inorganic X-ray amorphous materials in soils. Am. Mineral. 109 (12), 2037–2051. doi:10.2138/am-2023-9240
Andryanti, D. M., Tam, M. P., Lee, D.-W., and Park, D.-W. (2024). Impact of cement content in cement bound materials on the reflection cracking performance of asphalt pavements. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 20, e03229. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03229
Bederina, M., Makhloufi, Z., Bounoua, A., Bouziani, T., and Quéneudec, M. (2013). Effect of partial and total replacement of siliceous river sand with limestone crushed sand on the durability of mortars exposed to chemical solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 47, 146–158. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.05.037
Bilen, C. (2021). Limestone grindability in terms of hgi and a new approach for the understanding of grinding energy. Powder Technol. 392, 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2021.06.044
Chao, X. L., Han, C., Shao, C., Wang, C. X., Wen, P. H., and Wang, C. H. (2024). Recent advances in properties and application progress of cement-based materials with iron tailing. Sustainability 16 (23), 10631. doi:10.3390/su162310631
Dietel, J., Ufer, K., Gröger-Trampe, J., Kaufhold, S., and Dohrmann, R. (2025). Interstratified illite-hydroxy-interlayered smectite-a disorder structure model for quantification using rietveld refinement. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. doi:10.1002/jpln.202400024
Elmaasrawy, M., Lan, S. D., Cao, H. Y., Li, S. W., and Gao, X. (2025). Microstructure and durability evaluation of slag-metakaolin-limestone ternary blended alkali activated uhpc. J. Build. Eng. 106, 112674. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112674
Feng, W., Yu, Z., Bao, R., Xiong, J., Yan, K., Liu, R., et al. (2024). Manufacture of tailings-based cementitious materials: insights into tailings activation strategies. Constr. Build. Mater. 439, 137194. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137194
Geng, Z. Y., Yu, W. X., Jiang, M., and Miao, Y. H. (2025). Comparison of microwave sensitivity and performance of asphalt mastic with various steel slag powders. Materials 18 (6), 1348. doi:10.3390/ma18061348
Griffiths, S., Sovacool, B. K., Furszyfer Del Rio, D. D., Foley, A. M., Bazilian, M. D., Kim, J., et al. (2023). Decarbonizing the cement and concrete industry: a systematic review of socio-technical systems, technological innovations, and policy options. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 180, 113291. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2023.113291
Gu, J., Liu, X., and Zhang, Z. (2023). Road base materials prepared by multi-industrial solid wastes in China: a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 373, 130860. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130860
He, D., Cheng, Y., Li, R., and Lin, H. (2025). Preparation and performance optimization of lead–zinc tailing sintered bricks. MATERIALS 18 (6), 1381. doi:10.3390/ma18061381
Ji, X. P., Sun, E. Y., Sun, Y. L., Zhang, X. Y., and Wu, T. D. (2023). Study on crack resistance of cement-stabilized iron tailings. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 24 (2). doi:10.1080/10298436.2022.2124251
Jing, C., Wang, N., Shi, W., Meng, X., and Guo, C. (2023). Experimental study on iron ore tailings sand and municipal solid waste incineration fly ash used in semi-rigid base of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 393, 131981. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131981
Li, J., Hou, Q., Zhang, X., and Zhang, X. (2025). Microbial-induced mineral carbonation: a promising approach for improving carbon sequestration and performance of steel slag for its engineering utilization. Dev. Built Environ. 21, 100615. doi:10.1016/j.dibe.2025.100615
Li, W., Lang, L., Lin, Z., Wang, Z., and Zhang, F. (2017). Characteristics of dry shrinkage and temperature shrinkage of cement-stabilized steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 134, 540–548. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.214
Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Chen, C. L., Huang, Y. F., and Chen, Z. Q. (2024). Research on leaching kinetics and reactivity evaluation of copper tailings as precursor for alkali-activated materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 21, e03663. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03663
Liu, H. B., Zhang, C., Jia, C., and Tao, D. D. (2025). Freeze-thaw cycle characteristics of graphite tailing concrete and steel fiber reinforced-graphite tailing concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 462, 140006. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.140006
Liu, J., Hu, L., Tang, L., Zhang, E. Q., and Ren, J. (2020). Shrinkage behaviour, early hydration and hardened properties of sodium silicate activated slag incorporated with gypsum and cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 248, 118687. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118687
Liu, X., Xu, H., Li, B., Zhang, C., Zhang, Y., Zhao, C., et al. (2023). Investigation of the mechanical properties of iron tailings concrete subjected to dry–wet cycle and negative temperature. Materials 16 (13), 4602. doi:10.3390/ma16134602
Liu, Y. S., Jiang, L. L., Li, J. Q., Zhang, Q. G., Yang, L., and Cao, J. X. (2024). Study on the performance and hydration mechanism of concrete incorporating phosphorus tailings. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 36 (9). doi:10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-17946
Marques, L. M., Mota, S. M., Teixeira, P., Mateus, M., and Pinheiro, C. I. C. (2025). Decarbonisation of cement industry: calcium looping with white mud and limestone as cao-based sorbents for industrial flue gas treatment. Chem. Eng. Process. 213, 110290. doi:10.1016/j.cep.2025.110290
Moseson, A. J., Moseson, D. E., and Barsoum, M. W. (2012). High volume limestone alkali-activated cement developed by design of experiment. Cem. Concr. Compos. 34 (3), 328–336. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.11.004
Mugambi, L. M., Mujombi, S., Mutai, V., Toeri, J. R., Marangu, J. M., and Valentini, L. (2024). Potential of limestone calcined clay cement (Lc3) in soil stabilization for application in roads and pavements construction. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 21, e03706. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03706
Nguyen, V. T., Phan, T. D., Noh, H. W., Lee, S. Y., and Dong, J. K. (2025). Effects of high-volume limestone powder substitution on hydration and mechanical–microstructural development of low-carbon cement pastes: simulation and experiment. Constr. Build. Mater. 471, 140710. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.140710
Pacheco-Menor, M. C., Flores-Colen, I., and de Brito, J. (2025). The use of stone waste as fine aggregate or cement replacement in cement-based mortars: a review. J. Build. Eng. 106, 112503. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112503
Perez-Cortes, P., and Ivan Escalante-Garcia, J. (2020). Alkali activated metakaolin with high limestone contents – statistical modeling of strength and environmental and cost analyses. Cem. Concr. Compos. 106, 103450. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103450
Rakhimova, N. R., Rakhimov, R. Z., Naumkina, N. I., Khuzin, A. F., and Osin, Y. N. (2016). Influence of limestone content, fineness, and composition on the properties and microstructure of alkali-activated slag cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 72, 268–274. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.06.015
Rao, P. S., Gayana, B. C., and Karra, R. C. (2019). Use of iron ore mine tailings in infrastructure projects. Int. J. Min. Min. Eng. 10 (1), 51–67. doi:10.1504/ijmme.2019.098304
Romero, M., Ma Rincón, J., Rawlings, R. D., and Boccaccini, A. R. (2001). Use of vitrified urban incinerator waste as raw material for production of sintered glass-ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 36 (1), 383–395. doi:10.1016/S0025-5408(01)00501-3
Sakulich, A. R., Anderson, E., Schauer, C. L., and Barsoum, M. W. (2009). Influence of Si:Al ratio on the microstructural and mechanical properties of a fine-limestone aggregate alkali-activated slag concrete. Mater. Struct. 43 (7), 1025–1035. doi:10.1617/s11527-009-9563-2
Song, N. X., Huang, Y., Gao, L., Song, J., and Shang, H. S. (2025). Optimization of mix proportions for ultra-high-performance seawater sea-sand engineered cementitious composites (Uhpssecc) incorporated with metakaolin and limestone powder based on central composite design of response surface model. J. Build. Eng. 102, 111984. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.111984
Su, C., Rana, N. M., Zhang, S., and Wang, B. (2024). Environmental pollution and human health risk due to tailings storage facilities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 928, 172437. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172437
Tong, J., Niu, X., Wang, Y., and Lu, Y. (2021). Strength characteristics of iron tailings blended soil as a road base material. Appl. Sci. 11 (16), 7587. doi:10.3390/app11167587
Velasquez, R., Turos, M., Hoon Moon, K., Zanko, L., and Marasteanu, M. (2009). Using recycled taconite as alternative aggregate in asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 23 (9), 3070–3078. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2009.04.003
Wang, Y., Li, Z., Jin, Q., Zhang, M., and Zhou, Z. (2022). High-efficiency utilization of limestone tailings: used as cementitious materials and fine aggregate to prepare karst structure filling material. Constr. Build. Mater. 316, 125841. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125841
Wieszczycka, K. (2018). Wastes generated by mineral extraction industries. Phys. Sci. Rev. 3 (6). doi:10.1515/psr-2018-0026
Wu, W., Fu, Z., and Jiang, W. (2024). Developing a novel sustainable and durable self-luminous pavement material with solar energy absorption capability. Constr. Build. Mater. 445, 137934. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137934
Xiang, J. C., Liu, L. P., Cui, X. M., He, Y., Zheng, G. J., and Shi, C. J. (2018). Effect of limestone on rheological, shrinkage and mechanical properties of alkali - activated slag/fly ash grouting materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 191, 1285–1292. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.209
Xu, H. N., Ji, W. D., Jiang, W. Q., Cui, H. H., and Tan, Y. Q. (2024). Preparation of inorganic binder-stabilised material with iron tailings: strength formation and gradation optimisation. Road. Mater. Pavement Des. 25 (3), 618–636. doi:10.1080/14680629.2023.2212078
Xu, M. C., Hu, L. Y., Zhao, Q., Dong, Z. B., and Mo, L. W. (2025). Effects of fluorite tailings content on formation, properties and fluorine doping preferences of high-silica clinker: experimental study and industrial verification. J. Build. Eng. 106, 112612. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112612
Keywords: road engineering, limestone tailings, base material, mechanical properties, durability performance
Citation: Li W, Zheng C, Liu C, Zhang Z, Wang Z and Wang Q (2025) Study on the performance of cement stabilized limestone tailings blending macadam in pavement base. Front. Mater. 12:1632505. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1632505
Received: 22 May 2025; Accepted: 18 June 2025;
Published: 26 June 2025.
Edited by:
Yu-Fei Wu, RMIT University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Mohammad M. Karimi, Tarbiat Modares University, IranJue Li, Chongqing Jiaotong University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Zheng, Liu, Zhang, Wang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenxu Liu, Y2hlbnh1MjAyMjAyQDEyNi5jb20=
 Wenwei Li1
Wenwei Li1 Chenxu Liu
Chenxu Liu