- 1Guangxi GuiTong Engineering Management Group Co., Ltd., Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 2National Engineering Laboratory of Highway Maintenance Technology, School of Transportation, Changsha University of Science & Technology, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 3Guangxi Beitou Low-altitude Economy Investment Co., Ltd., Nanning, Guangxi, China
The insufficient adhesion between sandstone aggregates and asphalt binders makes the mixture susceptible to fatigue cracking under moisture conditions, limiting the widespread application of sandstone aggregates. Thus, two non-amine anti-stripping agents, XT-1 (XT) and PM-JL-06A (PM), were selected to enhance the adhesion properties of sandstone asphalt mixtures. First, the type and optimal dosage of anti-stripping agents were determined through three indicators and the boiled method test. Then, four point bending strength tests with different loading rates were carried out on the immersion and non-immersion sandstone asphalt mixture, and on this basis, four point bending fatigue test and fatigue residual strength test were carried out. The results show that compared to the XT anti-stripping agent, the PM agent more effectively enhances the adhesion of sandstone–asphalt mixtures, raising the adhesion grade from level 3 to above level 4 at an optimal dosage of 0.4%. Compared with conventional SBS-modified sandstone asphalt mixtures, PM-modified mixtures showed a 5.3% average increase in dynamic load strength under dry conditions and an 8.4% improvement under water immersion conditions. Furthermore, the addition of PM anti-stripping agent increased the fatigue life by 33.8% under dry conditions and 38.9% under water immersion conditions. Notably, PM modification significantly reduced the damage factor and damage sensitivity of the mixture under cyclic loading while substantially decreasing the fatigue strength decay rate.
1 Introduction
Asphalt pavements, as a critical component of road infrastructure, dominate high-grade highway construction in China owing to their advantages of low construction costs, reduced driving noise, and enhanced safety and comfort (Jin et al., 2021; Ma et al., 2016). However, with the rapid development of road construction, the scarcity of high-quality aggregates, such as basalt, limestone, and diabase, along with the high procurement costs, became a particularly prominent issue. Therefore, road engineers gradually focused on seeking alternative materials. Currently, many road engineers have studied the feasibility of using steel slag (Zhao et al., 2024; Lei B. et al., 2025; Lei Z. et al., 2025; Liu et al., 2025), ceramic waste (Sun et al., 2024; Lawanwadeekul, et al., 2025; Meena et al., 2022), blast furnace slag (Mahto and Sinha, 2022; Lei B. et al., 2025; Silva et al., 2023) and sandstone (Zhang et al., 2022; Zaidi et al., 2022; Yang, 2018) as road construction materials, and have achieved a number of re-search findings. Among them, relevant studies (Du et al., 2019; Lei et al., 2024) showed that sandstone aggregates possessed characteristics such as dense texture, high hardness, and strong wear resistance, offering superior mechanical properties compared to the traditionally used limestone and diabase. However, some studies (Fan et al., 2023; Liu and Chen, 2024), showed that sandstone aggregates exhibited defects in adhesion with both matrix asphalt and modified asphalt, resulting in insufficient interfacial bonding strength to meet the technical requirements for surface layers in highways. This, in turn, led to the failure of the mixture’s water stability indicators. If directly used in asphalt pavement construction, it would severely affect the service life of the asphalt pavement. Therefore, it is necessary to take appropriate measures to improve the adhesion between sandstone aggregates and asphalt binder, in order to make full use of local materials.
With the swift rise in traffic volume and axle load, asphalt pavements progressively develop issues like cracking, rutting, disintegration, and surface abrasion under repeated traffic loading (Moreno and Rubio, 2013; Zhang et al., 2021; Ling et al., 2021). Among these pavement types, sandstone asphalt pavement is particularly prone to fatigue cracking under repeated wheel loading. Nevertheless, there has been a notable scarcity of systematic investigations into the fatigue properties of sandstone asphalt mixtures subjected to cyclic loading, and correspondingly, few effective enhancement strategies have been put forward. Currently, direct tension (Jiang et al., 2018), uniaxial compression (Mirzaiyanrajeh et al., 2022), splitting (Ali et al., 2015), and four-point bending fatigue tests (Izadi et al., 2018) are the conventional methods for studying the damage evolution characteristics of asphalt mixtures. These methods are widely used due to their advantages of short test cycles, simple operation, and low cost. Compared with the other three tests, the four-point bending fatigue test simulates pavement loading stress more realistically, and the fatigue crack location remains fixed, improving the rationality of evaluating the performance of non-uniform materials (Meng et al., 2024).
Research methods for fatigue cracking mainly include the phenomenological method (Fan et al., 2022; Ameri et al., 2017), mechanical approximation method (Li et al., 2022), damage mechanics method (Corradini and Cerni, 2020), and energy method. The dam-age mechanics method views fatigue as a dynamic process of continuous accumulation and evolution of internal material damage. When damage develops to a critical state and causes material failure, fatigue fracture occurs. This theory can unify the descriptions of fatigue crack initiation and propagation stages and enable a continuous analysis of the entire fatigue failure process (Yu et al., 2012) making it favored by many researchers. The core of this method lies in selecting damage variables with clear physical meaning and ease of experimental measurement to quantify material damage, and in establishing the quantitative relationship between loading action and material performance degradation through damage evolution equations. Studies have shown that the residual strength of asphalt mixtures during cyclic loading is not only easy to measure but can also directly reflect the performance degradation of pavement materials, demonstrating considerable research potential (Ni et al., 2017). The fatigue residual strength test measures the residual strength of asphalt mixture specimens after different numbers of loading cycles throughout the fatigue life cycle, in order to reflect the strength variation law of asphalt mixture during the fatigue process.
In summary, to enhance the water stability of sandstone asphalt mixtures, PM and XT anti-stripping agents were incorporated into SBS-modified asphalt in this study. The optimal anti-stripping agent type and dosage were determined through three key indices and the boiled method test. Subsequently, four-point bending dynamic strength tests at varying loading rates were conducted on water immersed sandstone asphalt mixtures. Further, four-point bending fatigue tests and fatigue residual strength tests under different stress ratios were performed to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of anti-stripping agents in improving fatigue performance after water damage.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Raw material test
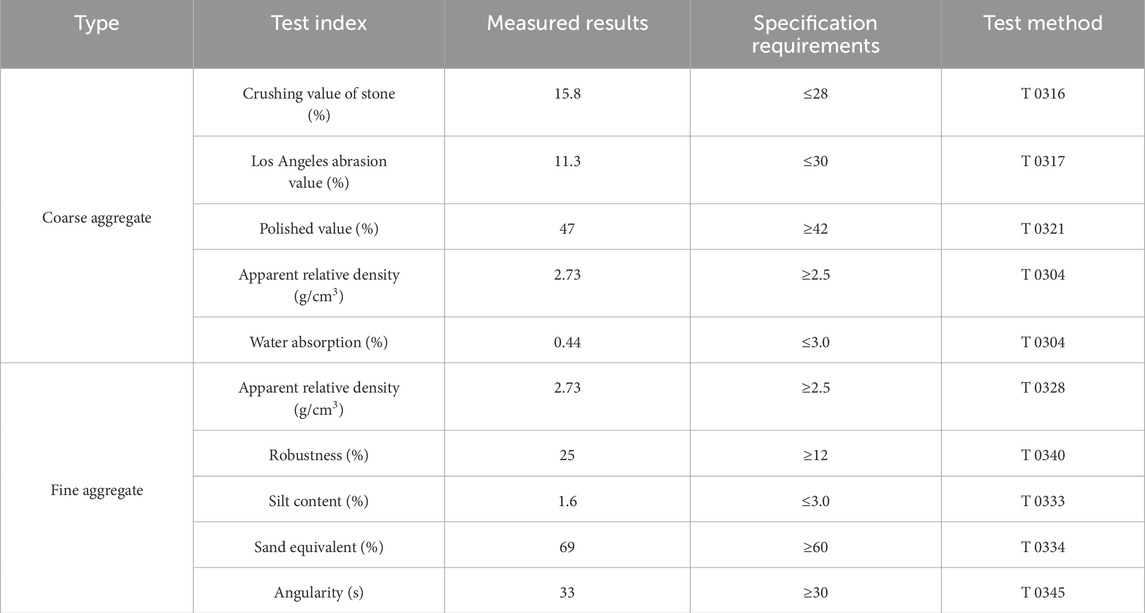
The aggregates used in this study are from the sandstone gravels mined in Taozhi notch project section of cangzhao Expressway in Guangxi. The filler is limestone. Aggregates were collected on-site (Figure 1), and test results are summarized in Tables 1, 2.

Figure 1. Sandstone aggregate collection construction site; (a) Sandstone aggregate collection and crushing; (b) Crushed sandstone aggregate.
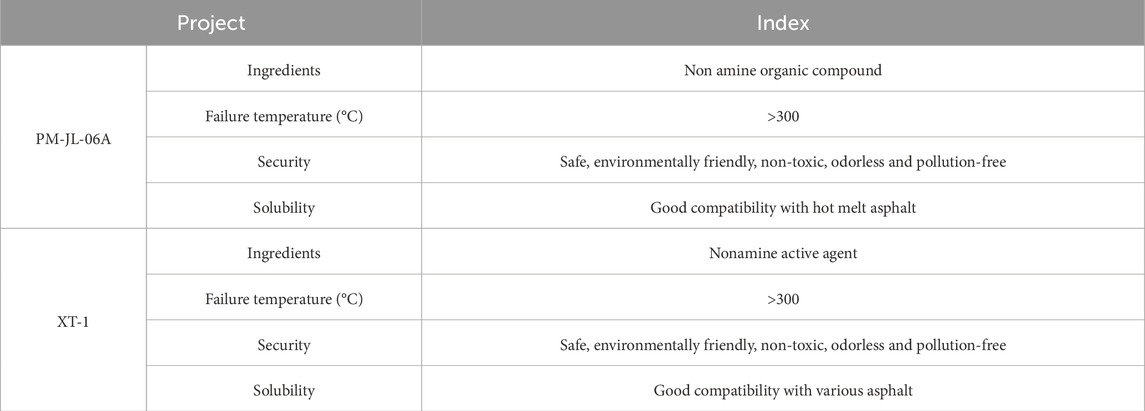
According to existing literature, the selection of anti-stripping agents for asphalt binders primarily considers economic viability, construction feasibility, and gain stability (Nazirizad et al., 2015; Arabani et al., 2014). Lime- and fly ash-based anti-stripping agents often suffer from inconsistent dispersion, resulting in non-uniform adhesion within asphalt mixtures. While nanomaterial additives are cost-prohibitive, amine-based agents suffer from poor thermal stability. Furthermore, many novel anti-stripping agents remain at the laboratory research stage and lack engineering validation. Consequently, non-amine anti-stripping agents emerge as the optimal choice. In this study, the non-amine agents XT-1 (XT)and PM-JL-06A (PM), developed by Littel Company, were selected to enhance the adhesion between sandstone aggregates and asphalt binders. The parameters of these anti-stripping agents are summarized in Table 3.
2.2 Preparation of modified asphalt with anti-stripping agent
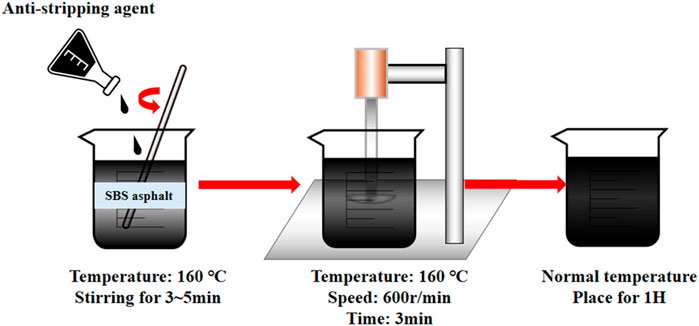
According to the specification for modified additives of asphalt mixture, Asphalt mixture modified additives Part IV Anti-stripping agent JT/T 860.4–2014 (Ministry of Transport of the Peoples Republic of China, 2014), the SBS-modified asphalt is first heated to 160°C in an oven. The anti-stripping agent is then added according to the predetermined dosage. A heating furnace is employed to maintain the mixing temperature at approximately 160°C, and a glass rod is used to thoroughly mix the anti-stripping agent with the asphalt, ensuring uniform heating of the mixture. Subsequently, the mixture is subjected to shearing using a shear machine operating at 600 r/min for 3 min. Following this mechanical mixing, the agitator is deactivated and the mixture is maintained at the processing temperature for 1 h to complete the maturation process. The detailed procedural steps are illustrated in Figure 2.
2.3 Grading design and optimal asphalt-aggregate ratio
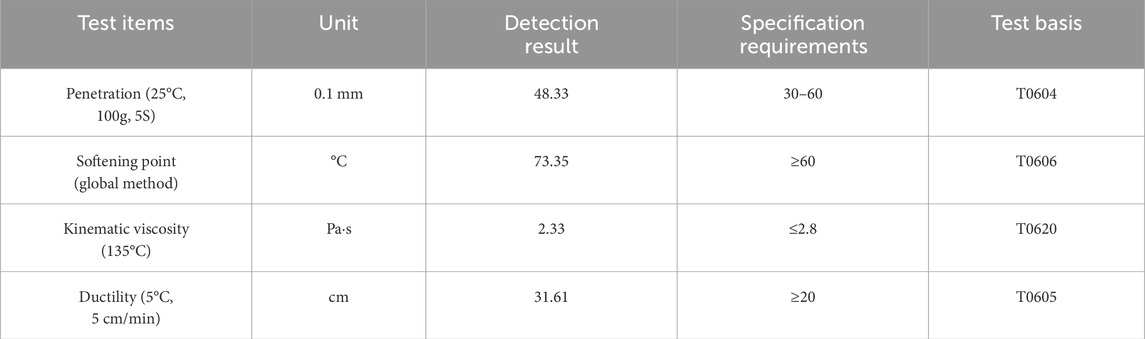
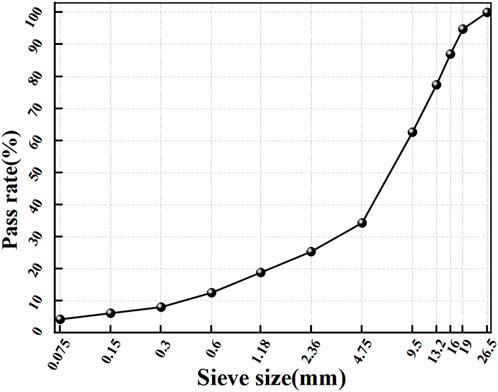
The AC-20 asphalt mixture gradation, commonly employed in the middle surface layer of expressways, was selected as the research subject, with its gradation curve presented in Figure 3. Using the Marshall test method, the optimal asphalt-to-aggregate ratio for the modified asphalt mixture was determined to be 4.8%. The performance parameters corresponding to this optimal ratio are summarized in Table 4.
2.4 Test method
Based on existing literature (Nazirizad et al., 2015; Arabani et al., 2014) and manufacturer-recommended dosage ranges, PM and XT anti-stripping agents (0.1%–0.5% by mass) were blended with SBS-modified asphalt to prepare 10 modified asphalt variants. Following the Standard Test Procedure for Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture of Highway Engineering JTG E20-2011 (Ministry of Transport of the Peoples Republic of China, 2011), conventional tests (penetration, ductility, and softening point) and anti-stripping performance evaluation using the boiling method (T0663-2000) were conducted to determine the optimal anti-stripping agent dosage.
The aggregate used in this study originated from the Taozhi Notch section of the Cangzhao Expressway in Guangxi, China. Given Guangxi’s annual temperature range of 10°C–23°C, a test temperature of 15°C was selected for asphalt mixture fatigue analysis. To simulate water damage effects, four-point bending fatigue specimens were conditioned using the water immersion Marshall test method (T 0709–2011). Specimens were water immersed in a constant-temperature water bath at 15°C for 48 h to replicate prolonged environmental water exposure. Subsequent four-point bending dynamic strength tests were performed at seven loading rates: 0.01 MPa/s, 0.02 MPa/s, 0.05 MPa/s, 0.1 MPa/s, 0.2 MPa/s, and 0.5 MPa/s. Using baseline dynamic strengths at 0.01 MPa/s, 0.05 MPa/s, and 0.2 MPa/s, five stress ratios (0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, and 0.6) were applied to conduct bending fatigue tests and fatigue residual strength evaluations.
When conducting the fatigue residual strength test, it is essential to choose specimens subjected to various cyclic loading times in order to ascertain the residual strength. This step is crucial for elucidating the strength degradation characteristics of asphalt mixtures during the fatigue process. The selection of different cyclical loading times typically adheres to the following principles: 1. To prevent specimen failure before reaching the target duration, the number of cycles should not be excessively high. 2. Adequate intervals between cyclic loading durations must be maintained to ensure the test results comprehensively reflect the strength attenuation pattern. In this study, based on the research findings of Ni et al. (2017) and others, 20%, 50%, 65%, and 80% of fatigue life were selected as the target cyclic loading durations.
2.5 Specimen preparation
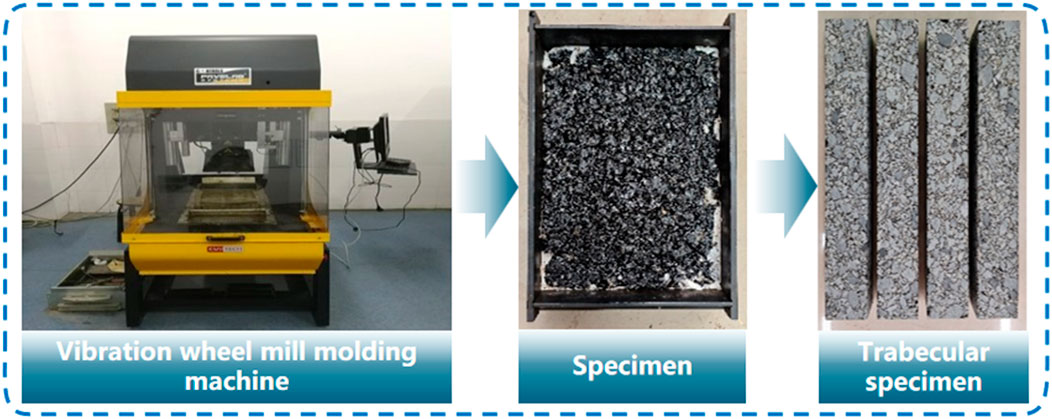
The beam specimen forming process is shown in Figure 4. The quantity of asphalt mixture required is determined based on the specimen size, target void ratio, and maximum theoretical density. After hot mixing, the material is placed into a mold and compacted using a vibrating wheel roller, with the specimen height monitored in real time. Once formed, the slab is allowed to stand at a temperature not exceeding 35°C for 24 h, after which it is cut into four small beam specimens with dimensions of 380 × 63 × 50 mm.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 The optimal dosage of anti-spalling is determined
Through conducting the standard asphalt three index test (ductility, softening point, and penetration) along with the boiling method test, the accurate optimal dosage of XT and PM anti-stripping agents was determined, with the comprehensive test findings visually summarized and presented in Figures 5, 6.
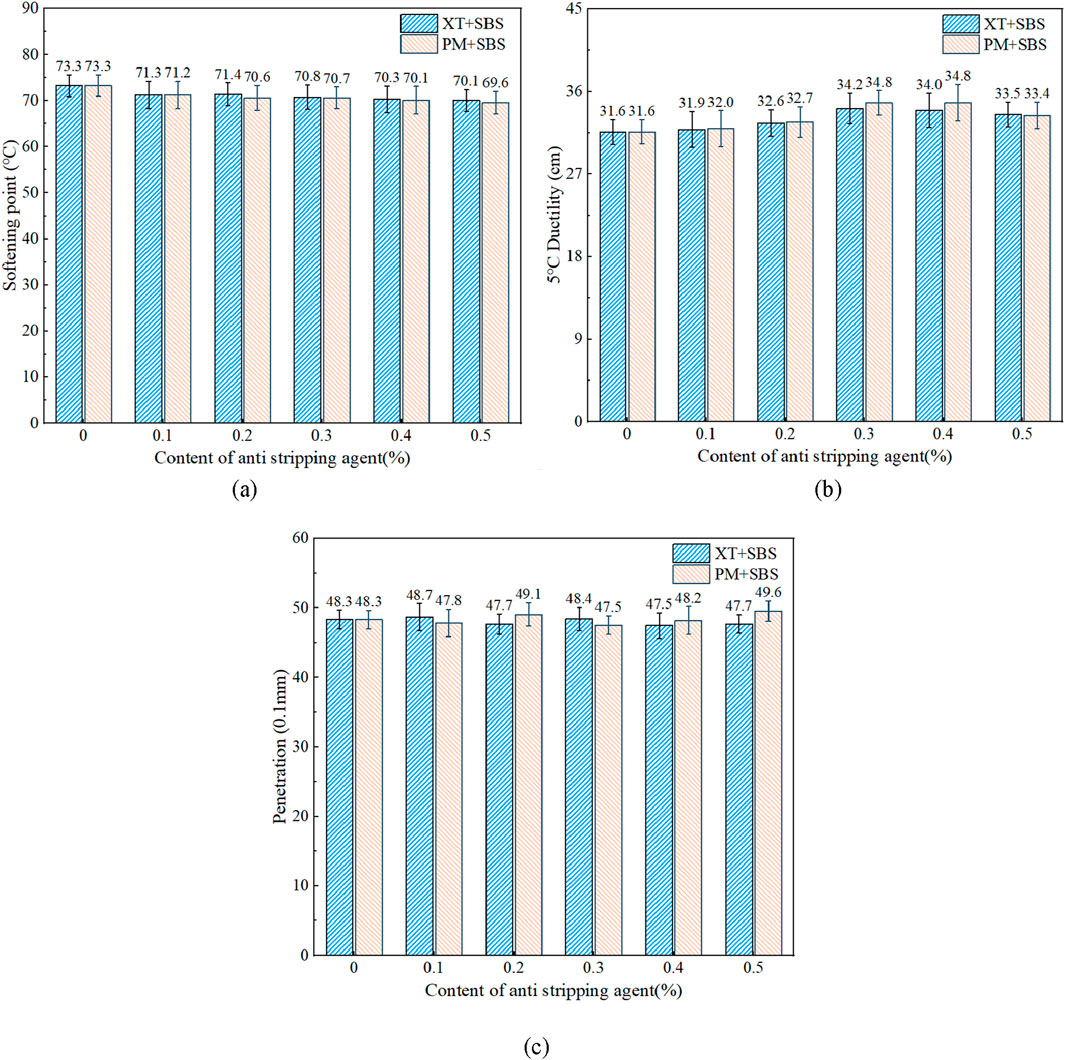
Figure 5. Effect of anti-stripping agent content on three indexes of asphalt; (a) Softening; (b) Ductility; (c) Penetration.
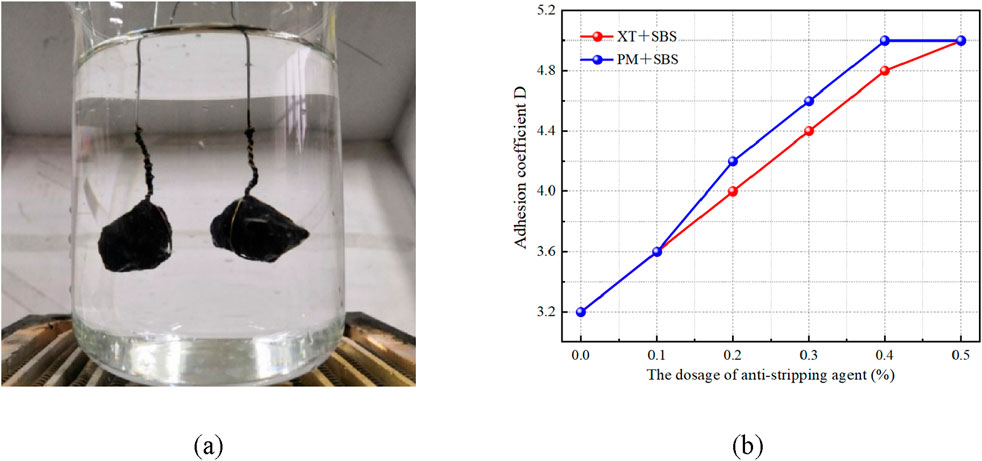
Figure 6. Effect of anti-stripping agent content on asphalt adhesion coefficient; (a) Boiling test; (b) test result.
From Figure 5, it can be observed that the addition of the anti-stripping agent has no significant effect on the softening point and penetration of the two asphalt types. However, the ductility shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. This phenomenon can be explained by the composition and physical behavior of asphalt. The softening point is primarily influenced by the asphaltene content and intermolecular forces, while penetration is associated with the balance between light and heavy components in the asphalt. Since the anti-stripping agent does not alter the proportions of saturates, aromatics, and asphaltenes, it does not significantly affect the softening point or penetration (Lu et al., 2023). In contrast, the observed changes in ductility can be attributed to the influence of agent on the mechanical properties of asphalt. The anti-stripping agent reduces the elastic recovery capacity and resistance to deformation across a wide frequency domain at high temperatures. Consequently, it enhances the flexibility and ductility of asphalt under low-temperature conditions (Shu et al., 2022). Through the evaluation of adhesion by boiling method, it was found that when the content of two anti-stripping agents exceeded 0.2%, the adhesion grade of asphalt and sandstone reached above grade 4. When the content of PM anti-stripping agent and XT anti strip-ping agent is 0.4% and 0.5%, respectively, the adhesion coefficient of asphalt reaches the peak. Compared with XT anti-stripping agent, PM anti-stripping agent has more significant effect on improving the adhesion of asphalt. In conclusion, PM anti strip-ping agent has better effect on improving the overall performance of asphalt, and further research is carried out with the dosage of 0.4% PM anti-stripping agent.
3.2 Dynamic strength characteristics of sandstone asphalt mixture considering the influence of water immersion and loading rate
Under the condition of 15 °C, carry out four point bending dynamic load strength tests at different loading rates for SBS and sandstone asphalt mixture mixed with PM anti-stripping agent after water immersing the test piece in water for 48 h, and use Equation 1 to fit the variation of bending tensile strength value with the loading rate. The results are shown in Figure 7, and the fitting equation under different conditions is shown in Equations 2–5.
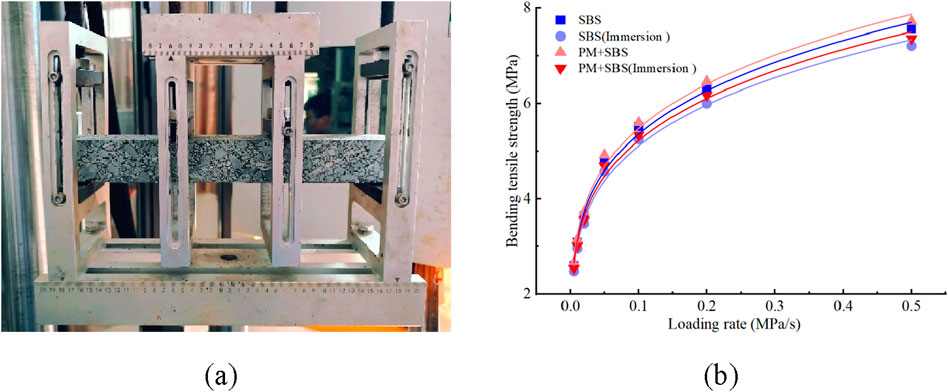
Figure 7. Test results of flexural tensile strength of sandstone asphalt mixture at different temperatures; (a) Four point bending test of sandstone asphalt mixture; (b) Fitting curve of flexural tensile strength of sandstone asphalt mixture.
Where, R is the dynamic load strength, MPa; v is the loading rate, MPa/s; a and b are fitting parameters, a reflect the strength of asphalt mixture, b reflect the sensitivity of asphalt mixture to loading rate.
SBS:
SBS(immersion):
SBS + PM:
SBS + PM(immersion):
Where, RSBS is the dynamic load strength of SBS modified asphalt under non immersed conditions, MPa; RSBS-I is the dynamic load strength of SBS modified asphalt under immersion conditions, MPa; RSBS+PM is the dynamic load strength of SBS + PM asphalt under non immersed conditions, MPa; RSBS+PM-I is the dynamic load strength of SBS + PM asphalt under immersion conditions, MPa;
At 15°C, the dynamic load strength and loading rate of the two kinds of sandstone asphalt mixtures under water immersion and non-water immersion conditions are power functions, and the initial strength growth rate is fast and then slow. Compared with SBS sandstone asphalt mixture, the average dynamic load strength of PM + SBS sandstone asphalt mixture under non-water immersion conditions increased by 5.3%, while the average dynamic load strength under water immersion conditions increased by 8.4%, which indicates that adding PM anti-stripping agent can effectively improve the strength of sandstone, which is mainly due to the improvement of asphalt aggregate interface adhesion and the integrity of the mixture under water immersion conditions.
3.3 Fatigue properties of sandstone asphalt mixture after water immersion
In order to study the effect of adding PM type anti-stripping agent on the fatigue characteristics of sandstone asphalt mixture after water immersion, based on the four point bending strength of 0.01 MPa/s,0.05 MPa/s and 0.2 MPa/s, the stress ratios of 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 and 0.6 were selected to determine the fatigue loading stress, and the four point bending fatigue test of sandstone asphalt mixture at 15°C and loading frequency of 10Hz was carried out, and the test results were fitted by the S-N fatigue equation shown in Equation 6. The results are shown in Figure 8, and the fitting parameters are shown in Table 5.
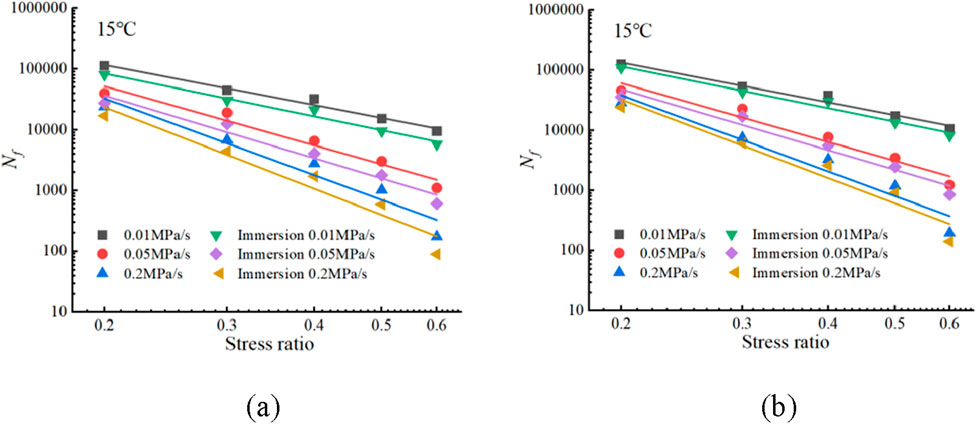
Figure 8. Fatigue life fitting curve based on stress ratio; (a)SBS sandstone asphalt mixture; (b)SBS + PM Sandstone asphalt mixture.
Where, Nf is the fatigue life of the specimen, times; k and n are fitting parameters, which reflect fatigue life and fatigue sensitivity, respectively; t is the stress ratio.
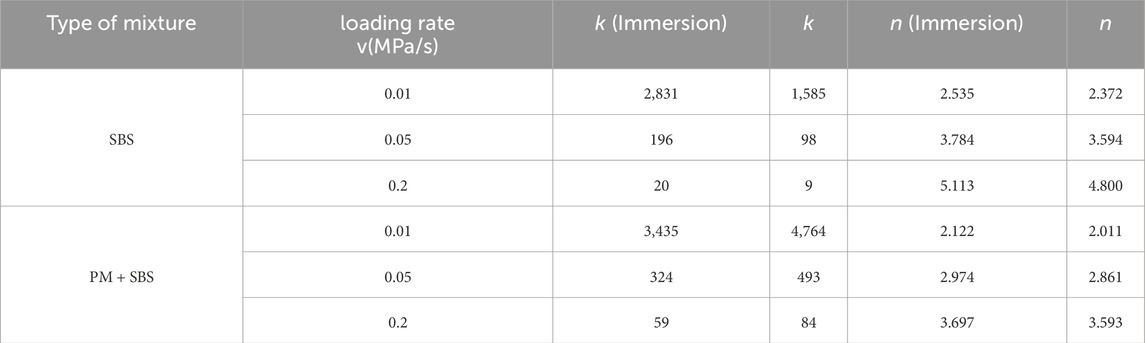
It can be seen from the above that the fatigue life of SBS sandstone asphalt mixture and SBS + PM sandstone asphalt mixture after water immersion test is significantly attenuated compared with that of non-water immersion condition. The fatigue life of the mixture without anti-stripping agent decreased by 25%–48%, while the fatigue life of the mixture with PM anti-stripping agent decreased by 12%–30%. It is worth noting that adding PM type anti-stripping agent can increase the fatigue life of sandstone asphalt mixture under the condition of non-water immersion by 33.8%, and under the condition of water immersion by 38.9%, which indicates that PM type anti-stripping agent can effectively improve the water damage resistance of asphalt mixture.
Parameters k and n in the S-N equation represent fatigue durability and stress sensitivity respectively. It can be seen from Table 7 that compared with SBS sandstone asphalt mixture, the k value of SBS + PM sandstone asphalt mixture under the condition of no soaking is increased by 22.1%, and the n value is reduced by 19.8%; The k value increased by 25.3% and the n value decreased by 23.1% under the condition of water immersion. This shows that PM anti-stripping agent can effectively improve the water damage resistance of sandstone asphalt mixture, and effectively improve the water stability of the mixture by strengthening the interface bonding between asphalt and sandstone aggregate, so as to maintain higher durability of the material under fatigue load; At the same time, the stress sensitivity is reduced, and finally the synergistic improvement of fatigue resistance and water stability is realized.
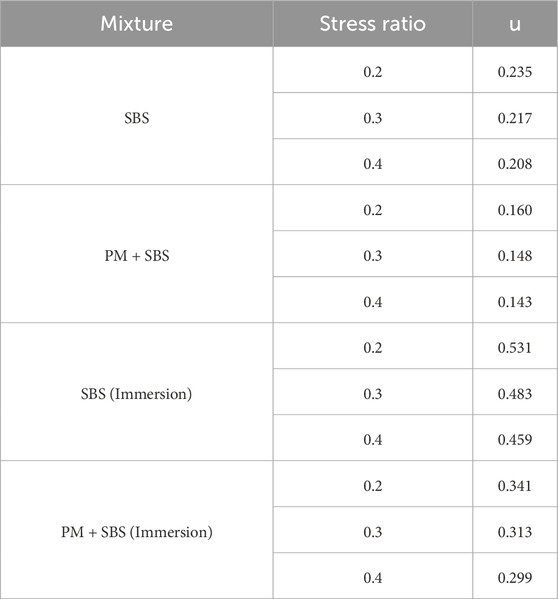
Table 7. Parameters of the fit curve for damage evolution of sandstone asphalt mixture based on residual strength.
3.4 Study on the degradation pattern of residual strength of sandstone asphalt mixtures under the effects of water immersion and cyclic loading
Considering the insufficient fatigue life of sandstone asphalt mixtures under stress ratios of 0.5 and 0.6 for conducting residual strength characterization, this study implemented four-point bending fatigue residual strength tests based on predetermined damage levels corresponding to cyclic loading stages. The experimental protocol was established through systematic analysis of four-point bending fatigue test results obtained at stress ratios of 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4. Specifically, critical loading cycles corresponding to 20%, 50%, 65%, and 80% damage progression thresholds were determined through fatigue life prediction modeling. The resultant residual strength evolution patterns under progressive damage conditions are systematically presented in Table 6, demonstrating significant degradation characteristics associated with accumulated fatigue damage.
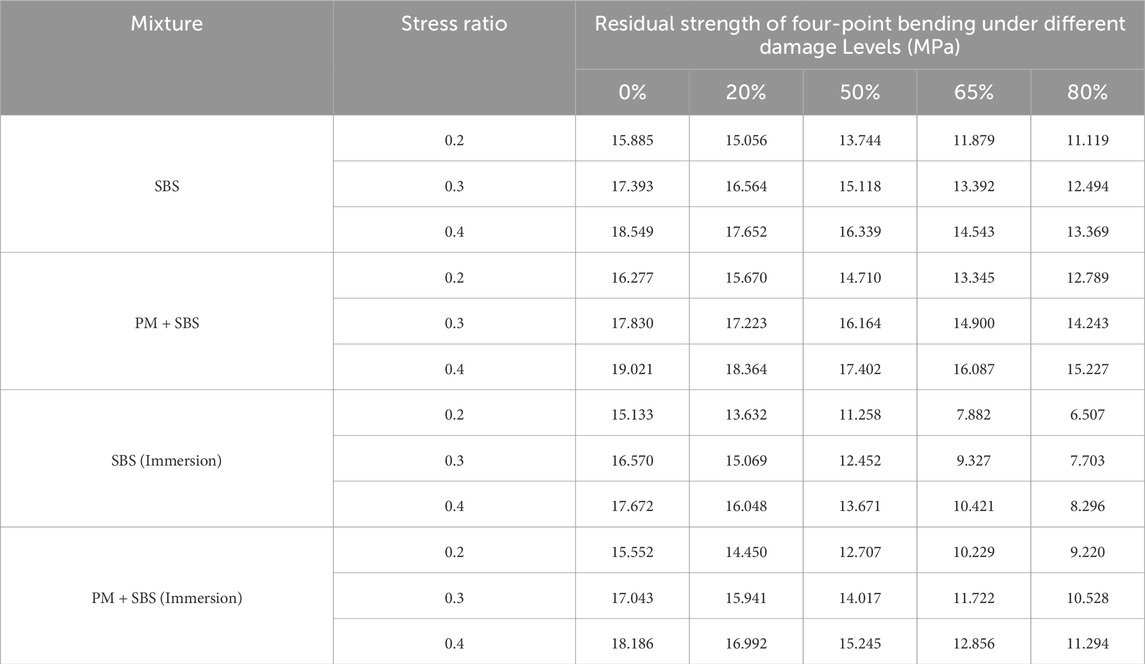
Table 6. Four-point bending residual strength of sandstone asphalt mixture considering the influence of water immersion.
The experimental findings demonstrate that both SBS-modified and SBS + PM-reinforced sandstone asphalt mixtures exhibit pronounced nonlinear residual strength degradation under water immersed and non-water immersed conditions. Notably, these materials share a consistent three-stage degradation progression (incubation, accelerated deterioration, and terminal failure), as evidenced by comparative analysis of fatigue damage evolution pathways:In the initial damage phase (0%–40% damage degree), the intergranular interlocking effect maintains effective stress trans-mission capacity, resulting in a gradual decline of residual strength accompanied by stable microcrack propagation within the composite microstructure. During the intermediate degradation stage (40%–80% damage degree), interfacial debonding evolution and interconnected crack network development induce significant degradation in material stiffness, manifesting as accelerated deterioration characteristics of residual strength. Upon reaching the critical failure threshold (>80% damage degree), percolation damage through the aggregate-matrix interface leads to coalescence of macro-cracks, triggering catastrophic strength reduction and abrupt fracture failure accompanied by structural instability (Zhou et al., 2020).
To elucidate the strength degradation mechanism of sandstone asphalt mixtures under cyclic four-point bending loading, a damage index D is defined as the ratio of residual strength Rx% to initial strength R0 at specified loading cycles. The critical damage threshold is determined when the accumulated loading cycles reach the fatigue life (N=Nf), enabling the division of the fatigue process into two distinct phases: damage accumulation phase and strength failure phase. A fatigue damage evolution equation is subsequently formulated through Equation 7, The evolution curves and fitting parameters are shown in Figure 9 and Table 7, respectively.
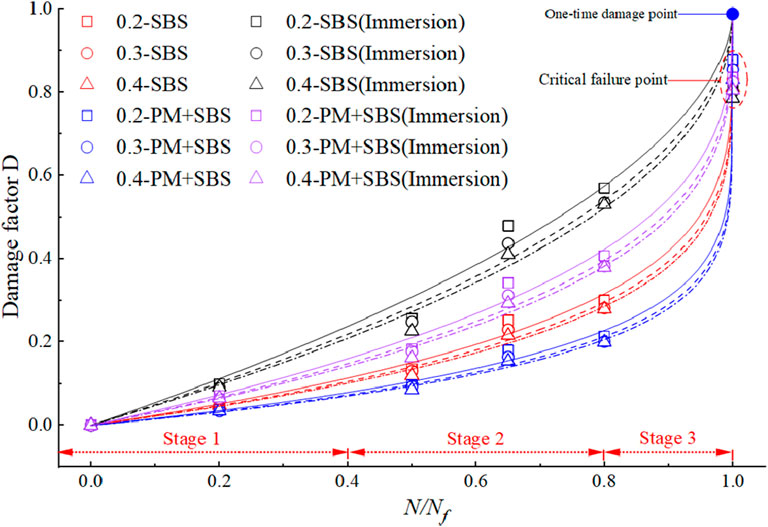
Figure 9. Damage evolution law of residual strength of sandstone asphalt mixture considering the effect of water immersion.
Where, Rx% is the remaining strength value under different damage levels in a four-point bending test.; R0 is the initial intensity value of the four-point bending.; u is the model parameter, Indicating damage sensitivity.
According to the relationship between the fitting curve parameter u and the stress ratio, the damage evolution models of SBS and SBS + PM sandstone asphalt mixtures under water immersion and non-water immersion conditions were established, as shown in Equations 8–11.
SBS:
SBS(Immersion):
SBS + PM:
SBS + PM(Immersion):
Where, RSBS-x% is the residual strength of SBS modified asphalt under x% fatigue life under non immersed conditions, MPa; RSBS-I-x% is the residual strength of SBS modified asphalt under x% fatigue life under immersion conditions, MPa; RSBS+PM-x% is the residual strength of SBS + PM asphalt under x% fatigue life under non immersed conditions, MPa; RSBS+PM-I is the residual strength of SBS + PM asphalt under x% fatigue life under immersion conditions, MPa.
Under non-water immersed conditions, the damage factor of the PM-modified sandstone asphalt mixture demonstrates a marginal reduction compared to the control mixture without anti-stripping agent. When subjected to water immersion, however, the damage factor exhibits a substantial percentage decrease in amplitude. These findings indicate that the PM anti-stripping agent significantly enhances the water stability of sandstone asphalt mixtures and effectively mitigates the degradation of fatigue residual strength under combined hydro-mechanical loading conditions. The u-value serves as an indicator of damage susceptibility during fatigue loading, with higher values corresponding to accelerated decay rates in mixture performance. Comparative analysis reveals that the SBS + PM modified sandstone asphalt mixture shows a 31.6% reduction in u-value under non-water immersed conditions and a 38.7% decrease under water immersed conditions relative to the conventional SBS-modified mixture. This demonstrates that the incorporation of PM-type anti-stripping agent effectively improves the fatigue strength degradation resistance of sandstone asphalt mixtures, thereby enhancing their long-term durability.
4 Conclusion
To address the insufficient moisture stability between sandstone aggregates and asphalt binders, this study incorporated PM-type anti-stripping agent into SBS-modified sandstone asphalt mixtures. The improvement effects of the anti-stripping agent on strength and fatigue performance were systematically investigated through asphalt and mixture tests. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) The experimental results obtained from the three fundamental asphalt indices and boiling water adhesion testing revealed that both XT and PM anti-stripping agents induced no statistically significant alterations in the penetration or softening point characteristics of SBS-modified asphalt. However, they substantially enhanced the ductility performance and adhesion coefficient. Comparative analysis demonstrated that the PM-type anti-stripping agent exhibited superior efficacy in augmenting the interfacial adhesion properties of asphalt relative to its XT counterpart. At an optimal 0.4% PM anti-stripping agent dosage, the SBS-modified asphalt system yielded a marked increase in dynamic viscosity while achieving a superior adhesion classification (Grade ≥4) between the asphalt binder and sandstone aggregates, as quantified through standardized adhesion grading protocols.
(2) The dynamic compressive strength of sandstone asphalt mixtures exhibited a power-law dependence on loading rate under both water immersed and non-water immersed conditions, characterized by an initial rapid increase followed by gradual asymptotic stabilization. Comparative analysis revealed that the PM + SBS composite mixture demonstrated a 5.3% enhancement in dynamic strength relative to the conventional SBS-modified mixture under non-water immersed conditions, with this improvement amplifying to 8.4% under water immersed conditions.
(3) The PM anti-stripping agent effectively enhanced the post-water immersion fatigue performance of sandstone asphalt mixtures. Adding PM agent increased fatigue life by 33.8% in non-water immersed mixtures and 38.9% under water immersion. Compared to the SBS-modified sandstone asphalt mixture, the SBS + PM composite exhibited a 22.1% increase in the fatigue resistance coefficient (k-value) and a 19.8% reduction in the stress sensitivity index (n-value) under non-water immersed conditions. Under water immersed conditions, these enhancements were further amplified, with the (k-value) increasing by 25.3% and the (n-value) decreasing by 23.1%.
(4) Considering the combined effects of water immersion and stress, the damage evolution curves of sandstone asphalt mixtures based on residual strength exhibit a three-phase evolution pattern. Under non-water immersed conditions, the in-corporation of a PM-type anti-stripping agent induces a slight decrease in both damage factor and damage sensitivity index compared to SBS-modified sand-stone asphalt mixtures. In water immersed environments, however, these parameters demonstrate a marked reduction in magnitude, indicating that the water immersion fatigue resistance is significantly enhanced.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
DZ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. ZhZ: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. TH: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. ZH: Software, Writing – review and editing. ZiZ: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. JH: Project administration, Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to thank Hunan Provincial Education Department, Grant No. Guike 23A0246. And authors also thank List of key scientific and technological projects in the transportation industry (resource utilization technology of sandstone in Guangxi high-grade highway pavement engineering, Grant No. Guike 22MS5125). Their assistance is sincerely appreciated.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the reviewers for their review and suggestions, as well as all those who have contributed to this research.
Conflict of interest
Author DZ was employed by Guangxi GuiTong Engineering Management Group Co., Ltd. Author JH was employed by Guangxi Beitou Low-altitude Economy Investment Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ali, Y., Irfan, M., Ahmed, S., Khanzada, S., and Mahmood, T. (2015). Sensitivity analysis of dynamic response and fatigue behaviour of various asphalt concrete mixtures. Fatigue and Fract. Eng. Mater. and Struct. 38, 1181–1193. doi:10.1111/ffe.12297
Ameri, M., Seif, M. R., Abbasi, M., and Khiavi, A. K. (2017). Investigation of fatigue life of asphalt mixtures based on the initial dissipated energy approach. Petroleum Sci. Technol. 35, 107–112. doi:10.1080/10916466.2016.1248777
Arabani, M., Hamedi, G., and Hamedi, G. (2014). Using the surface free energy method to evaluate the effects of liquid antistrip additives on moisture sensitivity in hot mix asphalt. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 15, 66–78. doi:10.1080/10298436.2013.778410
Corradini, A., and Cerni, G. (2020). A new analytical approach for stiffness loss modelling of asphalt mixtures under cyclic indirect tensile loadings. Int. J. Fatigue 135, 105535. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105535
Du, Q., Pan, T., Lv, J., Zhou, J., Ma, Q., and Sun, Q. (2019). Mechanical properties of sandstone cement-stabilized macadam. Applied-Sciences-Basel 9 (17), 3460. doi:10.3390/app9173460
Fan, J., Xu, G., Zhu, Y., and Cai, Z. (2023). Feasibility of siliceous sandstone utilization in porous asphalt mixture. J. Transp. Eng. 149. doi:10.1061/JPEODX.PVENG-1028
Fan, X., Liu, C., Lv, S., Ge, D., and Pan, Q. (2022). Unified fatigue characterization of asphalt mixture under multi-field coupling condition: stress state, frequency, and temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 353, 129027. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129027
Izadi, A., Motamedi, M., Alimi, R., and Nafar, M. (2018). Effect of aging conditions on the fatigue behavior of hot and warm mix asphalt. Constr. and Build. Mater. 188, 119–129. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.119
Jiang, J., Ni, F., Dong, Q., Zhao, Y., and Xu, K. (2018). Fatigue damage model of stone matrix asphalt with polymer modified binder based on tensile strain evolution and residual strength degradation using digital image correlation methods. Measurement 123, 30–38. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.037
Jin, D., Wang, J., You, L., Ge, D., Liu, C., Liu, H., et al. (2021). Waste cathode-ray-tube glass powder modified asphalt materials: preparation and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 314, 127949. doi:10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.127949
Lawanwadeekul, S., Bunma, M., Kattiyawara, K., Sillapapiromsuk, S., and Phonphuak, N. (2025). Upcycling ceramic industrial and local plastic waste into alternative construction materials focusing on performance and material utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 501, 145337. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145337
Lei, B., Yu, L., Chen, J., Meng, Y., Lu, D. L. I. N., Qu, F., et al. (2025a). Sustainable asphalt mixtures reinforced with basic oxygen furnace steel slag: multi-scale analysis of enhanced interfacial bonding. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 22, e04198. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e04198
Lei, J., Zheng, N., Zhao, F., Wang, Y., and Xue, J. (2024). Influence of aggregate types on the long-term skid resistance of porous asphalt mixture based on the laboratory MMLS. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 36. doi:10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-17780
Lei, Z., Qi, W., Zhnag, L., and Zhuorui, Z. (2025b). Preparation and comprehensive performance optimization of green insulation building materials based on blast furnace slag. J. Build. Eng. 106, 112591. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112591
Li, Y., Huang, D., and He, J. (2022). Energy evolution and damage constitutive model of anchored jointed rock masses under static and fatigue loads. Int. J. Fatigue 167, 107313. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107313
Ling, M., Zhang, J., Luis, F., Lubinda, W., and Rober, l. (2021). A mechanistic framework for tensile fatigue resistance of asphalt mixtures. Int. J. Fatigue 151, 106345. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106345
Liu, X., and Chen, S. (2024). Closure to “Investigation of Adhesion Property between Asphalt Binder and Aggregate Using Modified Boiling Methods for Hot and Wet Area”. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 36. doi:10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-17110
Liu, Z., Li, C., Hu, X., and Wang, L. (2025). Finite element simulation of crack propagation behaviour of warm-mix steel slag crumb rubber-modified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 462, 140007. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2025.140007
Lu, Z. Y., Chen, A. Q., Wu, S. P., Li, Y. Y., Zou, Y. X., Zhu, Y. S., et al. (2023). Experimental study on the physicochemical properties of asphalt modified by different anti-stripping agents and their moisture susceptibility with aggregates. Materials 16, 4545. doi:10.3390/ma16134545
Ma, T., Zhang, Y., Zhang, D., Yan, J., and Ye, Q. (2016). Influences by air voids on fatigue life of asphalt mixture based on discrete element method. Constr. Build. Mater. 126, 785–799. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.09.045
Mahto, S., and Sinha, S. (2022). Application of marble dust and ground granulated blast-furnace slag in emulsified asphalt warm mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 370, 133532. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133532
Meena, R., Jain, J., Chouhan, H., Chouhan, H. S., Ramswaroop, M., and Beniwal, A. S. (2022). Impact of waste ceramic tile on resistance to fire and abrasion of self-compacting concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 1. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.12.287
Meng, Y., Liu, D., Rong, H., and Yang, X. (2024). Review and prospect of four-point bending fatigue test of asphalt mixture. J. Road Eng. 4, 446–467. doi:10.1016/j.jreng.2023.05.004
Ministry of Transport of the Peoples Republic of China (2011). Test procedures for bitumen and bituminous mixtures in highway engineering (JTG E20-2011). Beijing: China Communications Press.
Ministry of Transport of the Peoples Republic of China (2014). Asphalt mixture modified additives part IV anti-stripping agent (JT/T 860.4-2014). Beijing: China Communications Press.
Mirzaiyanrajeh, D., Eshan, V., Sias, J., and Garg, N. (2022). Exploration of cracking-related performance-based specification indexes for airfield asphalt mixtures. J. Transp. Eng. 148 (4), 04022057. doi:10.1061/jpeodx.0000401
Moreno, F., and Rubio, M. (2013). Effect of aggregate nature on the fatigue-cracking behavior of asphalt mixes. Mater. and Des. 47, 61–67. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2012.12.048
Nazirizad, M., Kavussi, A., and Abdi, A. (2015). Evaluation of the effects of anti-stripping agents on the performance of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 84, 348–353. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.03.024
Ni, F., Yu, B., Gu, X., and Xu, K. (2017). Characterization of fatigue damage of hot mix asphalt based on residual strength. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 29. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001908
Shu, S. Q., Zhuang, C. Y., Ren, R. B., Xing, B. D., Chen, K., and Li, G. (2022). Effect of different anti-stripping agents on the rheological properties of asphalt. Coatings 12, 1895. doi:10.3390/coatings12121895
Silva, L., Nehring, V., and Paiva, F. (2023). Use of blast furnace slag in cementitious materials for pavements - systematic literature review and eco-efficiency. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 22. doi:10.1016/j.scp.2023.101030
Sun, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, J., Liao, J., Shi, C., and Huang, C. (2024). Mixing design and performance of porous asphalt mixtures containing solid waste. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 21, e03644. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03644
Yang, T. (2018). Study on road performance of sandstone asphalt concrete in Guangxi. Chongqing (China): Chongqing Jiaotong University.
Yu, J., Tsai, B., Zhang, X., and Monismith, C. (2012). Development of asphalt pavement fatigue cracking prediction model based on loading mode transfer function. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 13, 501–517. doi:10.1080/14680629.2012.695240
Zaidi, S., Airey, G., Grenfell, J., Naveed, A., and Ahmed, I. (2022). Moisture susceptibility assessment of hydrated lime modified asphalt mixture and surface energy. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 23, 599–611. doi:10.1080/10298436.2020.1763347
Zhang, E., Yang, Y., and Yang, D. (2022). Moisture stability of hard sandstone asphalt mixture based on APT with MMLS3. Adv. Mater. Sci. and Eng. 2022, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2022/5468264
Zhang, Z., Liu, Q., Wu, Q., Xu, H., and Oeser, M. (2021). Damage evolution of asphalt mixture under freeze-thaw cyclic loading from a mechanical perspective. Int. J. Fatigue 142, 105923. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105923
Zhao, W., Wen, W., Li, H., and H, J. (2024). Research on the performance of asphalt mixture with acid-treated steel slag based on microscopic properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 455, 139134. doi:10.1016/J.CONBUILDMAT.2024.139134
Keywords: sandstone asphalt mixture, anti-stripping agent, adhesion, fatigue residual strength, fatigue damage evolution model
Citation: Zhang D, Zhang Z, Huang T, Huang Z, Zhou Z and Huang J (2025) Study on fatigue characteristics of anti-stripping sandstone asphalt mixture after water immersion. Front. Mater. 12:1634717. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1634717
Received: 25 May 2025; Accepted: 10 July 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Fahmi Zairi, Université de Lille, FranceReviewed by:
Ma Qiang, Hubei University of Technology, ChinaSalam Aletba, Wasit University, Iraq
Meizhao Han, Harbin Institute of Technology, Weihai, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Huang, Huang, Zhou and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tuo Huang, aHRAY3N1c3QuZWR1LmNu
 Dabin Zhang1
Dabin Zhang1 Tuo Huang
Tuo Huang