- 1Laboratory Implantation, Placentation, Pregnancy and Endometriosis Research group (POPPYe), Department of Development and Regeneration, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 2Laboratory of Ion Channel Research, Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Leuven, Belgium
- 3VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain and Disease Research, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- 4Vancouver Prostate Centre, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 5Department of Urologic Sciences, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 6Centre for Aging SMART, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 7Center for Research on Pandemic Resilience, Faculty of Life Sciences and Institute of Public Health, Universidad Andres Bello, Santiago, Chile
- 8Millennium Institute on Immunology and Immunotherapy, Santiago, Chile
Cobalt-chromium alloys are widely used in orthopedic implants due to their excellent toughness, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. However, cobalt ions released as consequence of corrosion or wear, trigger cytokine secretion and promote inflammation and pain in periprosthetic tissues. Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are a family of voltage-dependent Ca2+ permeable channels involved in various physiological and pathological processes. Because of their permeability and modulation by divalent cations, we studied how TRP channels’ activity is influenced by cobalt ions. We used primary human synovial fibroblasts and through qPCR we found relevant expression of TRPC1, TRPC4, TRPV2, TRPV4, TRPM4 and TRPM7 mRNA in synovial fibroblasts. Next, we exposed synovial fibroblasts to cobalt ions and/or selective pharmacology of TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels. We observed that TRPV2 and TRPV4 are sensitized by cobalt exposure, increasing intracellular calcium in synovial fibroblasts. Furthermore, exposure to TRPV2 and TRPV4 antagonists inhibited the basal long-term intracellular calcium increase, and reduced the secretion of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-a, and VEGF-a triggered by cobalt exposure. However, the sole activation of TRPV2 and TRPV4 did not trigger secretion or expression of these cytokines. Our findings demonstrate for the first time that metal ions released from orthopedic implants, can modulate the function of TRP channels and may contribute to the pathogenesis of fibrosis and inflammation associated with biomedical implants. Notably, we propose a molecular mechanism in which TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels are potentially involved in mediating inflammatory and fibrotic responses in peri-implant tissues. However, further studies are necessary to elucidate the regulatory role of cytosolic calcium in the development of adverse local tissue reactions.
1 Introduction
For 60 years, cobalt-chromium alloys have been the most common metal alloy for orthopedic implants. Their robustness and wear resistance allow outstanding mechanical performance (Szczęsny et al., 2022), while its biocompatibility provides a long-term solution for millions of patients world-wide (Whitehouse et al., 2024). However, the emergence of adverse local tissue reactions to hip implants has led to a high number of revision surgeries and pushed the search for more biocompatible options, such as zirconium and ceramic, whose use has dramatically increased in recent years (National Joint Registry, 2017). Although their use in hip implants has been reduced, cobalt-chromium remain to be the most used alloy in orthopedic implants for knee, elbows, and ankle replacements, and are highly used in coronary and ureteral stents, as well as dental prosthetics. As such, understanding the mechanisms of cell and tissue damage observed in adverse local tissue reactions is critical to elucidate the processes that underlie inflammation and fibrosis generated by cobalt-chromium alloys, to improve treatment strategies and the development of new biomedical materials.
Despite titanium alloys present the highest biocompatibility, bone integration, and acceptable mechanical properties for use in orthopedic implants (Ad et al., 2024), they do not perform well under wear or sliding contact as is the case of hip or knee articulations (Marin and Lanzutti, 2023). Hence, cobalt–chromium alloys are the predominant choice for articulating surfaces. Their high chromium content promotes the formation of a passive oxide layer, which confers excellent corrosion resistance (Mani et al., 2024); however, this passive film can be disrupted by mechanical wear at modular junctions such as taper connections (Jacobs et al., 2014; Eltit et al., 2019). Surface damage initiates fretting–corrosion cycles, characterized by alternating phases of mechanical wear and passive film reformation, ultimately leading to progressive metal ion release. In the femoral head–neck articulation, this crevice corrosion contributes to elevated release of metal ions and particles, which can subsequently be detected in patients’ serum and peri-implant tissues (Vendittoli et al., 2011; Hart et al., 2012).
Adverse local tissue reactions to cobalt chromium alloys are clinically characterized by swelling and pain that is only resolved by the removal of the metal implants (Pandit et al., 2008; Murray et al., 2011). While the etiological factor is the release of cobalt in form of particles or soluble ions (Co2+) (Eltit et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2022; Urish et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020; Samelko et al., 2016), their pathogenesis is still not fully understood. A hypoxia-mimicking effect of Co2+ and increased oxidative stress have been widely described in a variety of cell models (Salloum et al., 2021; Caicedo et al., 2010; Salloum et al., 2018), triggering cytokine secretion and cell death (VanOs et al., 2014; Hallab and Jacobs, 2017; Kanaji et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2022). Studies in human synovial fibroblasts have shown that Co2+ triggers mitophagy and a cytokine storm, which in chronic doses generate cell senescence and cell death (Grant et al., 2024; Eltit et al., 2021a). These cellular events induce physiological events like pain, swelling, chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis (Ricciardi et al., 2016; Eltit et al., 2021b; Eltit et al., 2017). Open questions as how Co2+ enter the cells and the molecular mechanisms that trigger the cytokine storm are currently unresolved.
Transient receptor potential (TRP) are voltage-dependent cation channels located in the cell membrane, that sense a variety of cellular and environmental signals (Vriens et al., 2004a; Zhang et al., 2023). Mammals express 28 different TRP channels that are classified into 7 subfamilies according to their aminoacidic sequence (TRPA, TRPC, TRPM, TRPML, TRPN, TRPP, and TRPV). TRP channels respond to different physical or chemical stimuli such as heat, cold, stress, tension, hormones, oxidative stress, pH, chemicals, or divalent cations (mostly Zn2+and Mg2+) (Jimenez et al., 2020; Persoons et al., 2021; Held et al., 2021). The activation of TRP channels cause the influx of extracellular cations like Mg2+ and Ca2+, which can trigger a variety of intracellular events such as chemo-electrical transmission, gene expression, protein phosphorylation, protein secretion, among many others (Held et al., 2015; Held et al., 2016). These events result in a myriad of physiological and pathological responses (Jimenez et al., 2020; Gatica et al., 2019; Kecskes et al., 2023; Held and Tóth, 2021; Van Hoeymissen et al., 2020). In synovial tissues a variety of TRP channels have been identified, which multiple functions presumably include proprioception in the joints (Matta et al., 2023; Kochukov et al., 2006).
Here we hypothesize that TRP channels in synovial fibroblasts are sensitive to Co2+ and could trigger inflammatory changes observed in adverse local tissue reactions to metal implants. To perform this study, primary human synovial fibroblasts were stimulated by Co2+ in microfluorimetric experiments. Our results show for first time that TRP channel activity could be modulated by metals used in implant alloys. Consequently, this channel modulation results in increased secretion of inflammatory cytokines suggesting that this could be a pathway that causes inflammation and fibrosis in periprosthetic tissues. Because of pharmacological blockers of TRP channels, our study shows possible therapeutic alternatives for preventing fibrosis and inflammation triggered by metal implants.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patients and cells
All procedures were performed under the ethics approval from the University of British Columbia (H14-03050). Synovial tissue samples from patients undergoing primary hip replacement surgery due to osteoarthritis were obtained (demographics of patients in supplementary table SI). The specimens were preserved in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (Life Technologies; Burlington, ON) with 1% penicillin/streptomycin on ice for no more than 1 h. The specimens were mechanically disrupted into ∼1 mm pieces, digested with 0.1% collagenase I (Life Technologies; Burlington, ON) in DMEM with 2% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco) for 90 min at 37 °C under agitation. The digested tissue was filtered using 40 μm grids (Falcon, Corning Inc.; NY), and the obtained suspension was seeded in 10 cm petri dishes. Adherent cells were washed after 12 h and cultured with DMEM 5% glucose, 10% FBS (Life Technologies; Burlington, ON), and 2% penicillin/streptomycin. The purity of fibroblasts in culture was confirmed by immunofluorescent stain of the alpha smooth muscle actin (αSMA). At passage 3, the cells were seeded to perform the experiments described below.
2.2 qPCR for TRP channels in synovial fibroblasts
RNA expression of TRP channels in human primary synovial cells was investigated by qPCR. RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Netherlands) was used for RNA extraction following the manufacturers’ instructions. RNA concentration and quality were determined via the Nanodrop method (Isogen Life Science, Belgium) and Experion RNA Analysis kit (Bio-Rad, Belgium). cDNA was generated from 1 µg of RNA using the First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (GE Healthcare, Belgium). RT-qPCR was performed on triplicate cDNA samples using specific TaqMan gene expression assays (supplementary Table SII) (Life Technologies, Belgium) in the StepOne PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Belgium).
2.3 Microfluorimetric imaging
We activated and inhibited TRPV2 and TRPV4 using the agonists and antagonists listed in Supplementary Table SIII. Briefly, as agonist for TRPV2 we used Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (De Petrocellis et al., 2011) or Cannabidiol (CBD) (De et al., 2012), and for TRPV4 we used the compound GSK1016790A (De Clercq et al., 2015); as antagonists for TRPV2 we used Loratadine (Van den Eynde et al., 2022), and for TRPV4 we used the compound GSK2193874 (Arredondo Zamarripa et al., 2017). Exposure times to cobalt chloride (CoCl2), agonists, and/or antagonists for each condition are provided in the Results section.
To evaluate the activation of TRP channels, we measured total intracellular calcium ions (Ca2+) by using FURA-2 a.m. reaction and high-speed camera protocol as previously described (De Clercq et al., 2017). Briefly, the fibroblasts were incubated with 2 µM Fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester for 30 min at 37 °C. After alternating illumination at 340 and 380 nm using a Lambda XL illuminator (Sutter instruments, Novato, United States), the fluorescent signal was recorded using an Orca Flash 4.0 camera (Hamamatsu Photonics Belgium, Mont-Saint-Guibert, Belgium) on a Nikon Eclipse Ti fluorescence microscope (Nikon Benelux, Brussels, Belgium). We calculated the absolute calcium ions concentrations from the (F340/F380) ratio after correction for the individual background, using the Grynkiewicz equation (Grynkiewicz et al., 1985) The KD of Fura-2 and the isocoefficient α were assumed as described previously (Vriens et al., 2011).
Ionomycin (2 μM, Sigma) was applied at the end of every experiment as positive control. All the experiments were performed in technical triplicates and if not indicated differently, in cells obtained from minimally 3 different patients (biological triplicates). The standard imaging solution (Bath solution) contained in mM: 150 NaCl, 10 HEPES, 2 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2 and 10 Glucose (pH 7.4 with NaOH). For recordings in 0 mM calcium, the CaCl2 was omitted from the solution.
2.4 Cytokine secretion
Culture media from fibroblasts was collected following 24 h of exposure to Co2+ and/or agonist and antagonists of TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels. Cytokine secretion was quantified as previously described (Eltit et al., 2021b). Briefly, after centrifugation, 100 μL aliquots of synovial fluid supernatant were separated and stored at −20 C until analyzed. The concentration of 48 cytokines, chemokines and growth factors associated with inflammation, necrosis, or fibrosis, were quantified, using the Bio-Plex Suspension Array System (48 plex-Eve Technologies, Calgary, AB). The obtained values of cytokine concentration were not normally distributed; thus, we perform Log(10) transformation of the values and confirmed the normal by Shapiro-Wilk test. Then a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey post-hoc and Benjamini-Hochberg correction was used to determine the factors differentially detected between groups.
3 Results
3.1 Cobalt increases the intracellular calcium concentration in synovial fibroblasts
To test our hypothesis that cobalt-induced inflammation is related to the activity of calcium permeable ion channels in synovial fibroblasts, we investigated the direct effect of Co2+ stimulation on the cytosolic calcium levels of synovial fibroblasts. Primary hip synovial fibroblasts of 3 independent patients were exposed to 0.1 mM CoCl2 during microfluorimetric calcium measurements (Figure 1). Stimulation by 0.1 mM CoCl2 produced no effect on the cytosolic calcium levels in a calcium free extracellular medium. In contrast, in the presence of 2 mM calcium in the extracellular medium, application of 0.1 mM CoCl2 induced a robust and transient increase in intracellular calcium concentration (Figure 1A). These results demonstrate that Co2+ triggers calcium intake, and that the source of that calcium is extracellular.
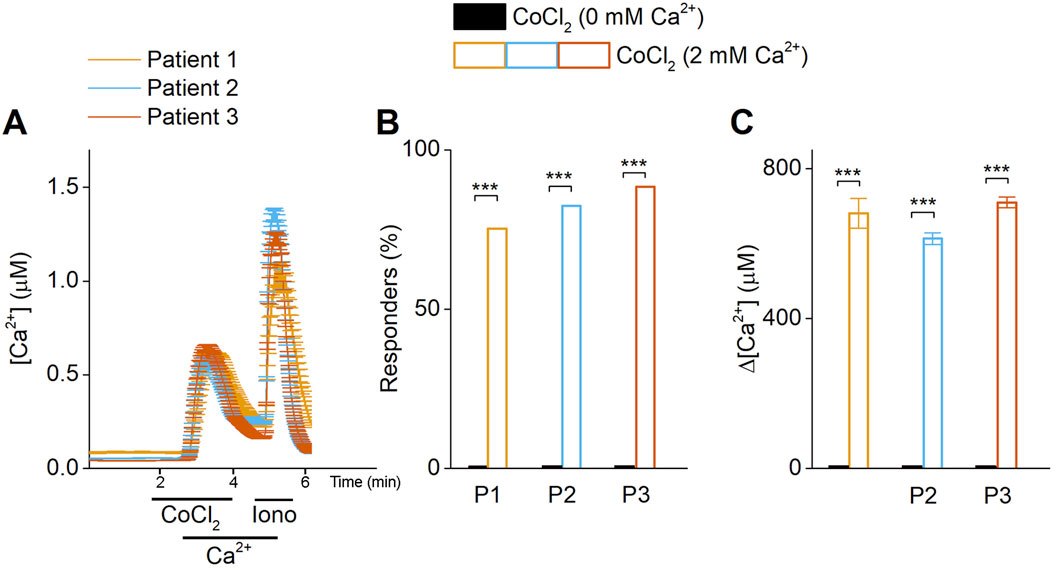
Figure 1. Co2+ triggers calcium flux from the extracellular compartment. (A) Time course of Ca2+ imaging measurements in synovial fibroblasts. At basal conditions and after the exposure of cobalt (CoCl2, 0.1 mM) in calcium-free media, intracellular calcium is not increased. The introduction of calcium (Ca2+) triggers the intracellular calcium increase, demonstrating that calcium influx is due to extracellular influx. (B) Percentage of responder cells, obtained from 3 different patients. (C) Intracellular calcium peak after cobalt exposure.
3.2 TRP channels are expressed in synovial fibroblasts
The previous results demonstrate the presence of a calcium flux into synovial fibroblasts from the extracellular environment. Therefore, we investigated the RNA expression levels of TRP channels in human synovial fibroblasts by qRT-PCR. RNA-expression levels of TRPC1, TRPC4, TRPV2, TRPV4, TRPM4, and TRPM7 were detected in synovial fibroblast in standard culture conditions (Figure 2). Interestingly, the expression of TRPC4, TRPV2, TRPV4 and TRPM4 channels significantly decreased in synovial cells exposed to different doses of Co2+ (0.1 and 0.5 mM CoCl2) while TRPA1 shows an increase in expression at 0.1 mM of Co2+.
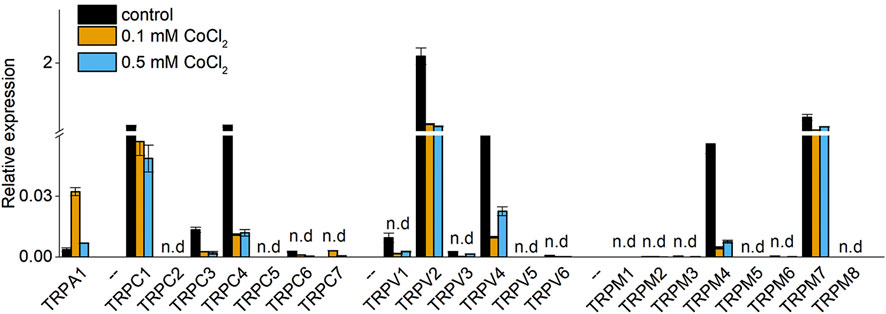
Figure 2. Relative expression of TRP channels in synovial fibroblasts in absence (Control), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM CoCl2. Bars represent mean + - Std. deviation observed in 3 different patients.
3.3 Cobalt sensitizes TRPV2 and TRPV4 in synovial fibroblasts
Following the change in RNA expression of TRP channels induced by Co2+ exposure and the existence of selective pharmacology, we investigated the functional expression of TRPV2 and TRPV4 in synovial fibroblasts.
Stimulation with the TRPV2 selective agonist THC (50 µM) (De Petrocellis et al., 2011) induced an influx in fluorescence in synovial fibroblasts. Interestingly, 24 h preincubation with CoCl2 at 0.1 and 0.5 mM induced an increase in basal calcium concentration compared to the non-exposed controls (Figures 3A,B). Although, preincubation by CoCl2 does not significantly increase the number of responding cells (Figure 3C), it produces a significant increase in the fluorescence amplitude after THC-stimulation compared to non-treated cells (Figures 3A,D). These findings demonstrate that Co2+ modulates TRPV2 channel activity, leading to increased intracellular calcium concentrations both at baseline and following specific TRPV2 stimulation.
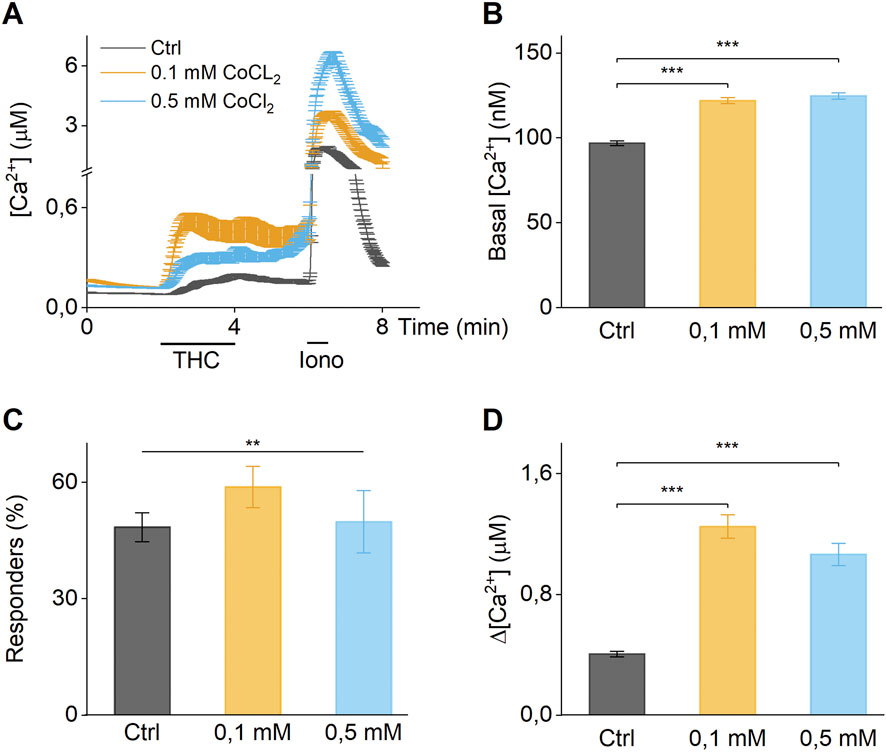
Figure 3. Co2+ increase activity of TRPV2. (A) Time course of calcium imaging measurements in synovial fibroblasts in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. The application of the selective TRPV2 agonist THC shows increased response in cells exposed to cobalt. (B) Basal intracellular calcium concentration of cells in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. (C) Percentage of responder cells to THC stimuli in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM cobalt chloride. (D) Differential calcium concentration of peak after THC stimulation v/s basal concentration in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. (A) Data of cells from a single patient, (B–D) Biological triplicates.
Similar results were obtained after stimulation by the TRPV4 agonist (GSK1016790A) (Thorneloe et al., 2008) (Figure 4). Preincubation with 0.1 and 0.5 mM CoCl2 significantly increased the amplitude of calcium influx (Figures 4A,D). The number of GSK1016790-responding cells was increased when exposed to 0.1 mM of CoCl2, compared to control (Figure 4C). These results demonstrates that TRPV4 channel activity is modulated by the presence of extracellular Co2+, resulting in elevated basal calcium content and increased calcium amplitudes upon stimulation by a selective agonist.
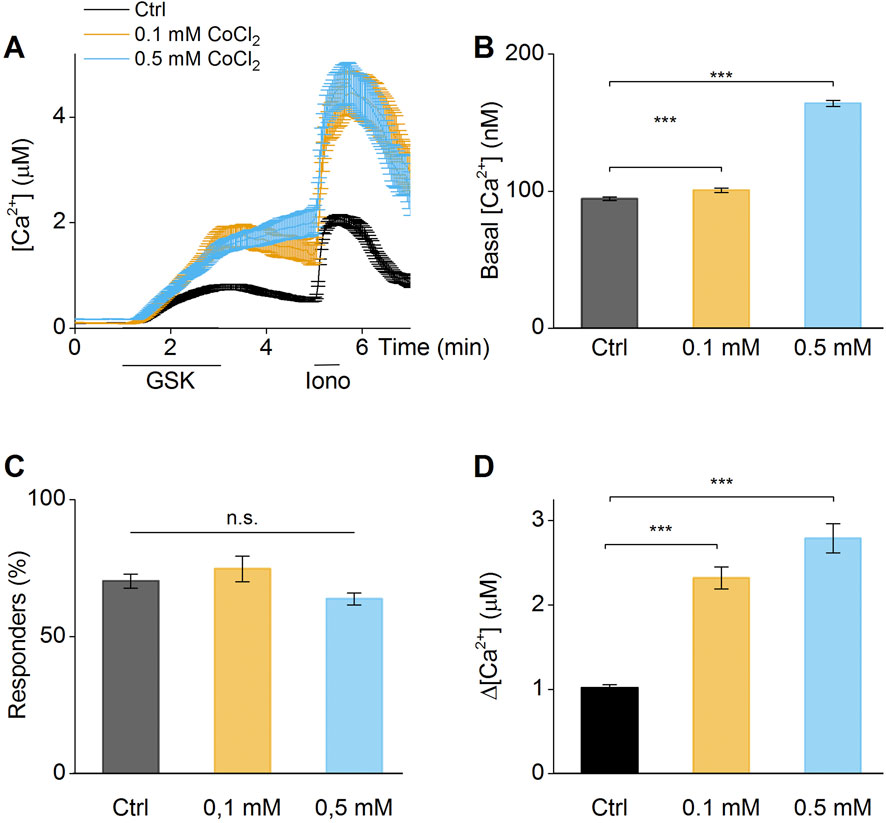
Figure 4. Co2+increase activity of TRPV4. (A) Time course of calcium imaging measurements in synovial fibroblasts in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. The application of the selective TRPV4 agonist (GSK1016790A) shows increased response in cells exposed to cobalt. (B) Basal intracellular calcium concentration of cells in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. (C) Percentage of responder cells to GSK1016790A stimuli in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. (D) Differential calcium concentration of peak after GSK1016790A stimulation v/s basal concentration in absence (Ctrl), 0.1 mM or 0.5 mM Co2+. (A) Data of cells from a single patient, (B–D) Biological triplicates.
3.4 Pharmacological block of TRPV2 can alleviate effects of long-term CoCl2 exposure
Next, we wanted to test whether pharmacological inhibition of Co2+ sensitive TRP channels TRPV2 and TRPV4 could alleviate Co2+-induced increases in intracellular calcium. Therefore, we focused on TRPV2, which exhibited a more pronounced channel sensitization as shown in our experiments above. TRPV2 was reported to be blocked by the antihistaminic drug loratadine (Van den Eynde et al., 2022). In fact, 10 μM loratadine significantly reduced the amount of responsive synovial fibroblast cells (Figures 5A,B) as well as the amplitude in intracellular calcium increases (Figures 5A,C) upon THC application. Notably, the same concentration of loratadine reduced the Co2+-induced increases in basal calcium concentrations of synovial fibroblasts to a level close to the basal calcium concentrations of non-treated fibroblast cells, while direct long-term loratadine incubation did not affect basal calcium levels (Figures 5D,E). Interestingly, this effect could not be explained by a block of the transient increases of intracellular calcium induced by the application of Co2+ (Figures 5F,G). This lack of blocking capability of the cobalt-induced transient calcium influx was also observed after TRPV4 blocking (Supplementary Figure S1). These results show that TRPV2 has a potential role in the increased intracellular calcium concentration induced by Co2+. However, other mechanisms (like ion channels/receptors) will also be involved in the transient calcium increase induced by cobalt exposure.
![This image consists of six graphs labeled A to G, analyzing calcium concentration ([Ca²⁺]i) changes under various conditions. Graph A shows time-course of [Ca²⁺]i with Loratadine and THC. Graph B compares responder percentages for Loratadine with THC versus THC alone. Graph C shows [Ca²⁺]i change for these conditions. Graph D displays [Ca²⁺]i over time with controls and CoCl₂ conditions. Graph E summarizes [Ca²⁺]i levels with different treatments. Graph F presents time-course of [Ca²⁺]i with Loratadine and CoCl₂. Graph G compares [Ca²⁺]i changes for Loratadine with CoCl₂ versus CoCl₂ alone. Statistical significance is indicated by asterisks.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1653364/fmats-12-1653364-HTML/image_m/fmats-12-1653364-g005.jpg)
Figure 5. TRPV2 inhibition decreases basal calcium intracellular concentration but is not capable of reducing the cobalt-induced transient calcium increase. (A) Time course of calcium imaging measurements in synovial fibroblasts from a single patient. The application of the selective TRPV2 antagonist (Loratadine) shows decreased response in cells exposed to the selective agonist THC. (B) Responder cells to THC in presence or absence of Loratadine. (C) Amplitude of response to THC in presence or absence of Loratadine. (D) Basal calcium concentration after long term exposure to cobalt chloride in presence or absence of loratadine. (E) Differences in basal calcium concentration after long term exposure. (F) Time course of calcium imaging measurements in synovial fibroblasts from a single patient. The application of the selective TRPV2 antagonist (Loratadine) cannot block the transient calcium increase triggered by cobalt chloride. (G) Differential calcium concentration of peak after Loratadine + cobalt chloride and after removal of loratadine. Charts correspond to biological triplicates.
3.5 Inhibition of TRPV2 and TRPV4 activity reduces secretion of inflammatory cytokines after cobalt exposure in synovial fibroblasts
To investigate the potential involvement of TRPV2 and TRPV4 in the secretion of cytokines induced by cobalt incubation, cytokine release experiments were performed in the presence of selective pharmacology of TRPV2 (loratadine) (Van den Eynde et al., 2022) and TRPV4 (GSK2193874) (Arredondo Zamarripa et al., 2017) (Figure 6). In the presence of the TRPV2 antagonist loratadine, the IL-6 secretion was reduced by 50%, the secretion of IL-8 and VEGF by 30% while the secretion of TNF-α was not affected (Figure 6). In addition, incubation with the TRPV4 antagonist, GSK2193874, resulted in the significant reduction of IL-6 secretion (∼25%) while no significant reduction was observed of other cytokines (Figure 6). The combined effect of TRPV2 and TRPV4 antagonists significantly reduce the secretion of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and VEGF-α, in rates between 30%–50% (Figure 5). In conclusion, these results demonstrated that the cobalt-induced modulation of both TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels resulted in an altered secretion of cytokines that potentially could trigger inflammation in periprosthetic human tissues.
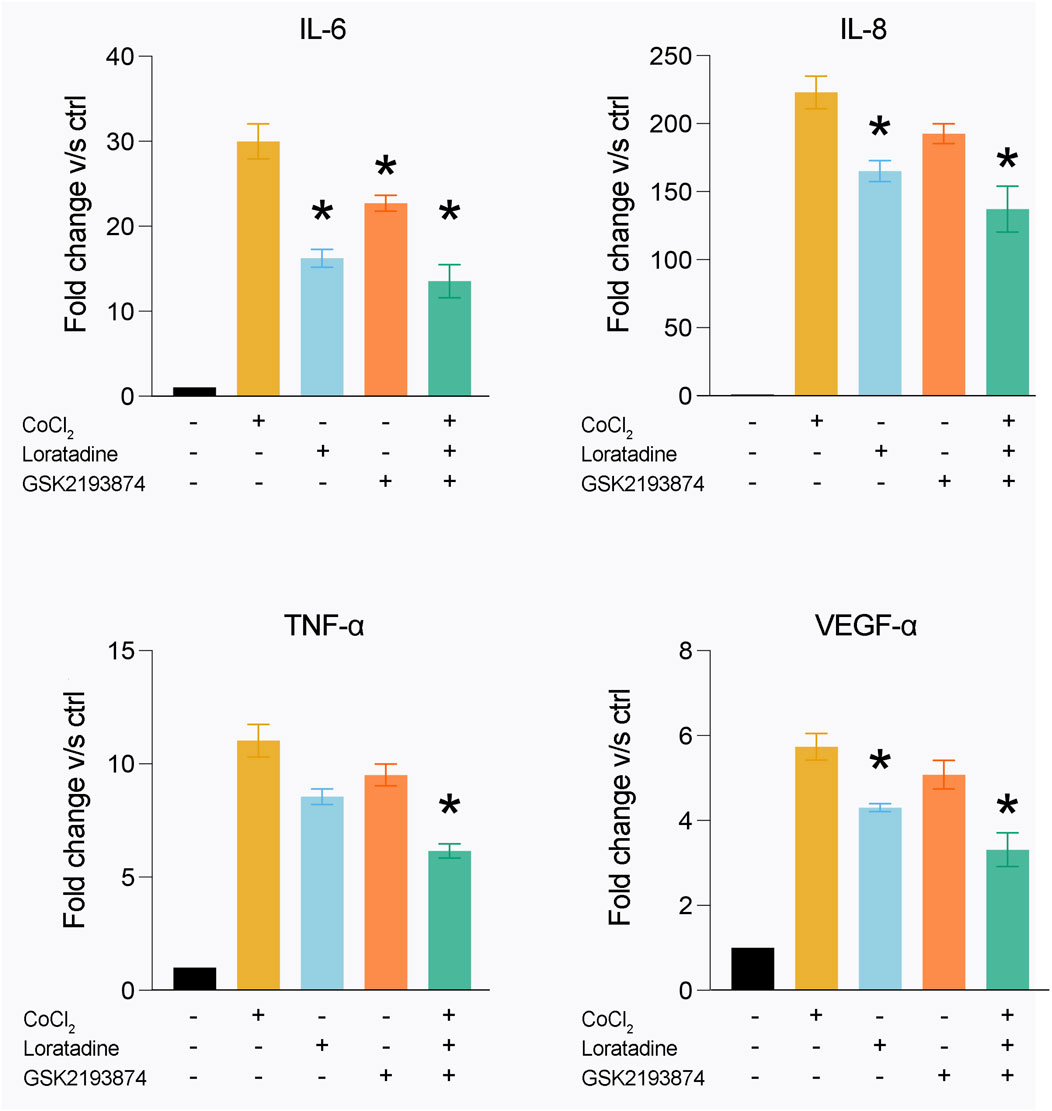
Figure 6. Inhibition of TRPV2 and TRPV4 activity decrease cytokine secretion after cobalt exposure. After 24 h of exposure to 0.1 mM of cobalt, the secretion of IL-6, IL-8, TNF- α and VEGF- α is increased. By using the specific TRPV2 antagonist Loratadine, there is decrease in the secretion of IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF- α, while the exposure to the specific TRPV4 antagonist GSK2193874 produce a decreased secretion of IL-6. Combining both antagonists showed an additive effect, reducing the secretion of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α and VEGF-α. The plots represent the mean +SEM of fibroblasts obtained from 6 patients.
3.6 TRPV2 and TRPV4 activation do not trigger cytokine expression or secretion
We next evaluated whether activation of TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels alone could trigger cytokine secretion. We stimulated synovial fibroblasts with the specific agonist for TRPV2 (CBD) (De et al., 2012) and TRPV4 (GSK1016790A) (De Clercq et al., 2015), either alone or in combination with CoCl2. We did not observe significant changes in cytokine secretion following stimulation with either agonist, in both cobalt-exposed and unexposed cells (Supplementary Figure S2). We also found no changes in cytokine gene expression under the same conditions (Supplementary Figure S3). These results are not due to reduced cell viability, as we confirmed sustained viability after long-term exposure to various concentrations of CoCl2 (Supplementary Figure S4). Together, these findings suggest that TRPV2 and TRPV4 activity contributes to cobalt-induced cytokine secretion, but this effect does not result from their canonical calcium channel activity alone.
4 Discussion
Cobalt alloys remain one of the most common materials used in medical implants. Its’ mechanical robustness, and low corrosion rates allows long-term solutions with minimal deleterious effects. The arise of adverse local tissue reactions to cobalt-based implants, due to the release of Co2+ as consequence of wear and corrosion, generated concerns about possible mechanisms of cell damage induced by Co2+ that may affect peri-implant tissues. In this study, we demonstrate for the first time how Co2+ ions modulate the activity of calcium permeable ion channels in the plasma membrane of human cells. We demonstrate that Co2+ enhances the activity of TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels in human synovial fibroblasts, resulting in increased intracellular calcium influx, which results in increased secretion of inflammatory cytokines.
Cobalt is the most abundant element in alloys for biomedical implants, that also contain 28% of chromium, 8% molybdenum and 1%–2% of trace elements. Its biocompatibility is due mostly to a dense and stable passive layer of ∼4 nm thickness composed of chromium oxide. This superficial passive layer, prevent corrosion of the alloys (Wang et al., 2019). For those reasons cobalt-chromium alloys are considered bioinert. However, the mechanical disruption of this passive layer exposes other elements, such as cobalt and molybdenum that are subject to corrosion (Wang et al., 2022). Cobalt, chromium and molybdenum are then solubilized, until a new passive layer is formed by oxidation of chromium atoms (Wang et al., 2020). The ions released by the corrosion process follow different paths. While Cr3+ forms stable oxides and phosphates which precipitate in the extracellular environment (Hart et al., 2010; Di Laura et al., 2017) Co2+ remains in solution, contacting cells and affecting their metabolism and function (Hallab and Jacobs, 2009; Hallab et al., 2005). In this study, we demonstrate how Co2+ affect the channel activity of TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels resulting in an increased intracellular calcium content, affecting the secretion of cytokines.
TRPV2 and TRPV4 belong to the vanilloid subfamily of TRP channels and are involved in sensing osmolarity and mechanical stimuli (Doñate-Macián et al., 2019; Sato et al., 2013; Perálvarez-Marín et al., 2013). Since calcium signaling is critical for the response and adaptation of tendons and ligaments to mechanical forces (Wall et al., 2016), their presence in hip synovial fibroblasts might be related to these functions. TRPV2 is activated by mechanical stretching, and by chemicals such as cannabinoids (Vriens et al., 2009). TRPV4 is activated by osmotic changes (increasing its activity under hypotonic conditions), moderate temperatures (24–38 °C), shear stress, flavonoids, and organic chemical crystals (Vriens et al., 2004b; Lan et al., 2021; Garcia-Elias et al., 2014). To the best our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating that Co2+ modulates TRPV2 and TRPV4 channel activity and has an agonist function over these channels (and acts as an agonist for these channels).
We observed that Co2+ induces a transient calcium increase in synovial fibroblasts. This transient effect could be due to osmotic change, electrochemical changes, or other non-specific effects (Garcia-Elias et al., 2014). The fact that specific antagonists of TRPV2 and TRPV4 could not inhibit the transient response to Co2+, reinforces the idea of non-specific effect of Co2+ in the transient calcium increase. Furthermore, this transient effect could be related to other TRP channels or intracellular store depletion. However, the fact that long-term exposure to Co2+ triggers an increased response to specific TRPV2 and TRPV4 agonists (observed as increased calcium intake) reveals that Co2+ specifically sensitizes the channel activity of TRPV2 and TRPV4. Furthermore, the long-term effect of the TRPV2 antagonist loratadine, in reducing the basal level of calcium in cobalt-exposed cells, suggests that this sensitization of TRPV2 and TRPV4 has a cellular effect that could be observed over time. Twenty-four-hour inhibition of TRPV2 and TRPV4 reduced cobalt-induced cytokine secretion, supporting a long-term effect of these channels, and potentially explaining the prolonged effects of low-concentration Co2+ observed clinically.
Activation of TRPV2 and TRPV4 induced a robust a calcium influx that could trigger a myriad of intracellular signaling events. Previous studies demonstrated that Co2+ exposure activates the transcription factors Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) (Eltit et al., 2021a; Samelko et al., 2013; Nyga et al., 2015). NF-kB is the transcription factor for the expression of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8; while HIF-1α is directly related with the expression of VEGF-α. In the present study, we describe that TRPV2 and TRPV4 are sensitized by Co2+, enhancing the calcium signaling after. The inhibition of TRPV2 and TRPV4 reduces the secretion of IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF-α. However, the fact that cytokine secretion does not occur after TRPV2 or TRPV4 activation suggests that the activity of both channels is not directly related to NF-κB and HIF-1α activation, and that a mechanism independent of the canonical activity of TRPV2 and TRPV4 is involved.
The secretion of cytokines by synovial fibroblasts after Co2+ exposure has demonstrated the activation of endothelial cells and the migration of monocytic cells (Eltit et al., 2021a), which can be associated with the inflammation, necrosis, and fibrosis surrounding failed orthopedic implants (Murray et al., 2011; Ricciardi et al., 2016; Kurmis et al., 2019; Grammatopoulos et al., 2013). The long-term effects of cobalt ions on synovial fibroblasts were elegantly demonstrated by Xu et al. (2020) (Xu et al., 2020). In their study, synovial fibroblasts extracted from patients with failed metal-on-metal implants exhibited increased collagen secretion, resistance to apoptosis, and enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokine release. Remarkably, these alterations persisted after cell extraction and culture in cobalt-free medium, suggesting that long-term cobalt exposure may induce stable, imprinted changes in synovial fibroblasts. This imprinted inflammation phenotype has been previously demonstrated in models of dermatitis in human dermal fibroblasts (Sharma et al., 2018). Moreover, due to the availability of inhibitors such as loratadine (TRPV2) and GSK2193874 (TRPV4), adverse reactions to metal implants could potentially be treated pharmacologically. In addition, material-based strategies are also critical for mitigating Co2+ release. Alloy optimization can enhance passive film stability and reduce dissolution (Metikoš-Huković et al., 2006), while surface engineering techniques, such as ceramic or diamond-like carbon coatings, have been attempted to minimize wear and corrosion at modular junctions (Roy et al., 2024; Fernandez-Fairen, 2022). Advances in manufacturing, like additive processing and nanostructured alloys, may further improve resistance to fretting-corrosion (Zhang et al., 2024). These material-based solutions may reduce cobalt exposure which activates the mentioned biological responses.
As main limitation of our work, we restricted our analysis to TRPV2 and TRPV4, while other TRP channels are expressed in synovial fibroblasts. Important expression is achieved by TRPC1, TRPC4 TRPM4and TRPM7 and they can also be sensitized by cobalt chloride. Among those, TRPM4 and TRPC4 dramatically drop their expression in presence of cobalt, and TRPM7 and TRPC1 are among the most expressed in this cell type. Importantly, there exists other calcium channels like Piezo1, which responds to mechanical stimuli (Hennes et al., 2019), and has been described in synovial cells (He et al., 2024). Furthermore, Piezo1 has been shown to signal through NFκB (Yu et al., 2025), triggering inflammation and pain in osteoarthritis (Li et al., 2024). Weather mechanosensitive channels like Piezo1 are sensitized by Co stimulation, is matter of investigation.
Another limitation is that we conducted our experiments in concentrations of Co2+ that are higher than what is has been described in peri-implant fluids or tissues (Langton et al., 2019; Lehtovirta et al., 2018), and the time of exposure of the cells is limited to days compared to the years of exposure of peri-implant tissues. As well, our results correspond to in-vitro observations, and patients or animal models are needed to understand the effect of the cobalt-mediated activation of TRPV2 and TRPV4 in the complex peri-implant tissue environment. To test the role of TRPV2 and TRPV4 in mediating cell permeability to implant-derived cations, further work is needed, including patch clamp experiments, or specific TRP channel knock out cell lines among other techniques. Finally, while we performed experiments with pharmacology of TRPV2 and TRPV4, showed high expression in synovial fibroblasts and could potentially also contribute to inflammation and pain in periprosthetic tissues. However, other TRP channels, plasma membrane channels, receptors and intracellular receptors could also be involved in the altered cytosolic calcium levels associated to cobalt incubation. Finally, TRPV2 and TRPV4, which we studied using pharmacological experiments, are highly expressed in synovial fibroblasts and could potentially contribute to inflammation and pain in periprosthetic tissues. However, other TRP channels, plasma membrane channels, receptors, and intracellular receptors could also be involved in the altered cytosolic calcium levels associated with cobalt incubation.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by University of British Columbia (H14-03050). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
KH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Software, Formal Analysis. SK: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. JN: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. RM: Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. FS: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. MC: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Resources. JV: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Resources, Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Formal Analysis, Methodology. FE: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Software, Data curation, Resources, Funding acquisition, Validation, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was possible thanks to the generous donation of Harry Redmond. This project has received funding from the Research Foundation–Flanders (G.084515N, G.0B1819N, and G.0A6719N to JV) and the Research Council of the KU Leuven (C14/24/152). FE holds a Young Investigator Award from the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all patients that participate in this study. We gratefully thank Nicole Robinson for her experimental help in this project. We also thank Simon Cheung, form the Department of Pathology of Vancouver General Hospital, and Enrico Galang from UBC Hospital and for their collaboration in the sample collection and processing.
The authors acknowledge that that the land on which part of this work was performed is the unceded territory of the Coast Salish Peoples, including the territories of the xwməθkwəy'əm (Musqueam), Skwxwú7mesh (Squamish), Stó:lō and Səl'ílwətaʔ/Selilwitulh (Tsleil- Waututh) Nations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2025.1653364/full#supplementary-material
References
Ad, S., Spa, P., Naveen, J., Khan, T., and Khahro, S. H. (2024). Advancement in biomedical implant materials—a mini review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12, 1400918. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2024.1400918
Arredondo Zamarripa, D., Noguez Imm, R., Bautista Cortés, A. M., Vázquez Ruíz, O., Bernardini, M., Fiorio Pla, A., et al. (2017). Dual contribution of TRPV4 antagonism in the regulatory effect of vasoinhibins on blood-retinal barrier permeability: diabetic milieu makes a difference. Sci. Rep. 7, 13094. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-13621-8
Caicedo, M. S., Pennekamp, P. H., McAllister, K., Jacobs, J. J., and Hallab, N. J. (2010). Soluble ions more than particulate cobalt-alloy implant debris induce monocyte costimulatory molecule expression and release of proinflammatory cytokines critical to metal-induced lymphocyte reactivity. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 93A (4), 1312–1321. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32627
De Clercq, K., Held, K., Van Bree, R., Meuleman, C., Peeraer, K., Tomassetti, C., et al. (2015). Functional expression of transient receptor potential channels in human endometrial stromal cells during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. Hum. Reprod. 30 (6), 1421–1436. doi:10.1093/humrep/dev068
De Clercq, K., Van Den Eynde, C., Hennes, A., Van Bree, R., Voets, T., and Vriens, J. (2017). The functional expression of transient receptor potential channels in the mouse endometrium. Hum. Reprod. 32, 615–630. doi:10.1093/humrep/dew344
De Petrocellis, L., Orlando, P., Moriello, A. S., Aviello, G., Stott, C., Izzo, A. A., et al. (2012). Cannabinoid actions at TRPV channels: effects on TRPV3 and TRPV4 and their potential relevance to gastrointestinal inflammation. Acta Physiol. 204 (2), 255–266. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02338.x
De Petrocellis, L., Ligresti, A., Moriello, A. S., Allarà, M., Bisogno, T., Petrosino, S., et al. (2011). Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 163 (7), 1479–1494. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01166.x
Di Laura, A., Quinn, P. D., Panagiotopoulou, V. C., Hothi, H. S., Henckel, J., Powell, J. J., et al. (2017). The chemical form of metal species released from corroded taper junctions of hip implants: synchrotron analysis of patient tissue. Sci. Rep. 7, 10952. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11225-w
Doñate-Macián, P., Enrich-Bengoa, J., Dégano, I. R., Quintana, D. G., and Perálvarez-Marín, A. (2019). Trafficking of stretch-regulated TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels inferred through interactomics. Biomolecules 9 (12), 791. doi:10.3390/biom9120791
Eltit, F., Assiri, A., Garbuz, D., Duncan, C., Masri, B., Greidanus, N., et al. (2017). Adverse reactions to metal on polyethylene implants: highly destructive lesions related to elevated concentration of cobalt and chromium in synovial fluid. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 105 (7), 1876–1886. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.36057
Eltit, F., Wang, Q., and Wang, R. (2019). Mechanisms of adverse local tissue reactions to hip implants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7, 176. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2019.00176
Eltit, F., Noble, J., Sharma, M., Benam, N., Haegert, A., Bell, R. H., et al. (2021a). Cobalt ions induce metabolic stress in synovial fibroblasts and secretion of cytokines/chemokines that may be diagnostic markers for adverse local tissue reactions to hip implants. Acta Biomater. 131, 581–594. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2021.06.039
Eltit, F., Mohammad, N., Medina, I., Haegert, A., Duncan, C. P., Garbuz, D. S., et al. (2021b). Perivascular lymphocytic aggregates in hip prosthesis-associated adverse local tissue reactions demonstrate Th1 and Th2 activity and exhausted CD8+ cell responses. J. Orthop. Res. 39 (12), 2581–2594. doi:10.1002/jor.24998
Fernandez-Fairen, M. (2022). CORR insights®: insights into imprinting: how is the phenomenon of tribocorrosion at head-neck taper interfaces related to corrosion, fretting, and implant design parameters? Clin. Orthop. 480 (8), 1601–1603. doi:10.1097/CORR.0000000000002267
Garcia-Elias, A., Mrkonjić, S., Jung, C., Pardo-Pastor, C., Vicente, R., and Valverde, M. A. (2014). The TRPV4 channel. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 222, 293–319. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_12
Gatica, S., Eltit, F., Santibanez, J. F., Varela, D., Cabello-Verrugio, C., and Simon, F. (2019). Expression suppression and activity inhibition of TRPM7 regulate cytokine production and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome during endotoxemia: a new target for sepsis. Curr. Mol. Med. 19 (8), 547–559. doi:10.2174/1566524019666190709181726
Grammatopoulos, G., Pandit, H., Kamali, A., Maggiani, F., Glyn-Jones, S., Gill, H. S., et al. (2013). The correlation of wear with histological features after failed hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg-Am 95 (12), e81–10. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00775
Grant, M. P., Alatassi, R., Diab, M. O., Abushal, M., Epure, L. M., Huk, O. L., et al. (2024). Cobalt ions induce a cellular senescence secretory phenotype in human synovial fibroblast-like cells that may be an early event in the development of adverse local tissue reactions to hip implants. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 6 (3), 100490. doi:10.1016/j.ocarto.2024.100490
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., and Tsien, R. Y. (1985). A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 260 (6), 3440–3450. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)83641-4
Hallab, N. J., and Jacobs, J. J. (2009). Biologic effects of implant debris. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 67 (2), 182–188.
Hallab, N. J., and Jacobs, J. J. (2017). Chemokines associated with pathologic responses to orthopedic implant debris. Front. Endocrinol. 8, 5. doi:10.3389/fendo.2017.00005
Hallab, N. J., Anderson, S., Caicedo, M., Brasher, A., Mikecz, K., and Jacobs, J. J. (2005). Effects of soluble metals on human peri-implant cells. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 74A (1), 124–140. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.30345
Hart, A. J., Quinn, P. D., Sampson, B., Sandison, A., Atkinson, K. D., Skinner, J. A., et al. (2010). The chemical form of metallic debris in tissues surrounding metal-on-metal hips with unexplained failure. Acta Biomater. 6 (11), 4439–4446. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.006
Hart, A. J., Quinn, P. D., Lali, F., Sampson, B., Skinner, J. A., Powell, J. J., et al. (2012). Cobalt from metal-on-metal hip replacements may be the clinically relevant active agent responsible for periprosthetic tissue reactions. Acta Biomater. 8 (10), 3865–3873. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.05.003
He, D., Liu, X., Yang, W., Guan, T., and Wang, G. (2024). The role of mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 in knee osteoarthritis inflammation. Channels 18 (1), 2393088. doi:10.1080/19336950.2024.2393088
Held, K., and Tóth, B. I. (2021). TRPM3 in brain (Patho)Physiology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 635659. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.635659
Held, K., Voets, T., and Vriens, J. (2015). TRPM3 in temperature sensing and beyond. Temp. Multidiscip. Biomed. J. 2 (2), 201–213. doi:10.4161/23328940.2014.988524
Held, K., Voets, T., and Vriens, J. (2016). Signature and pathophysiology of non-canonical pores in voltage-dependent cation channels. Rev. Physiology, Biochem. Pharmacol. 170, 67–99. doi:10.1007/112_2015_5003
Held, K., Lambrechts, P., Voets, T., and Bultynck, G. (2021). I scream for ice cream – TRPC5 as cold sensor in teeth. Cell Calcium 97, 102419. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2021.102419
Hennes, A., Held, K., Boretto, M., De Clercq, K., Van den Eynde, C., Vanhie, A., et al. (2019). Functional expression of the mechanosensitive PIEZO1 channel in primary endometrial epithelial cells and endometrial organoids. Sci. Rep. 9, 1779. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-38376-8
Jacobs, J. J., Cooper, H. J., Urban, R. M., Wixson, R. L., and Della Valle, C. J. (2014). What do we know about taper corrosion in total hip arthroplasty? J. Arthroplasty 29 (4), 668–669. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2014.02.014
Jimenez, I., Prado, Y., Marchant, F., Otero, C., Eltit, F., Cabello-Verrugio, C., et al. (2020). TRPM channels in human diseases. Cells 9 (12), 2604. doi:10.3390/cells9122604
Kanaji, A., Orhue, V., Caicedo, M. S., Virdi, A. S., Sumner, D. R., Hallab, N. J., et al. (2014). Cytotoxic effects of cobalt and nickel ions on osteocytes in vitro. J. Orthop. Surg. 9, 91. doi:10.1186/s13018-014-0091-6
Kecskes, M., Peigneur, S., and Held, K. (2023). Editorial: contribution of ion channels to neuropathologies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1179663. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1179663
Kochukov, M. Y., McNearney, T. A., Fu, Y., and Westlund, K. N. (2006). Thermosensitive TRP ion channels mediate cytosolic calcium response in human synoviocytes. Am. J. Physiol-Cell Physiol. 291 (3), C424–C432. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00553.2005
Kurmis, A. P., Herman, A., McIntyre, A. R., Masri, B. A., and Garbuz, D. S. (2019). Pseudotumors and high-grade aseptic lymphocyte-dominated vasculitis-associated lesions around total knee replacements identified at aseptic revision surgery: findings of a large-scale histologic review. J. Arthroplasty 34 (10), 2434–2438. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.025
Lan, Z., Chen, L., Feng, J., Xie, Z., Liu, Z., Wang, F., et al. (2021). Mechanosensitive TRPV4 is required for crystal-induced inflammation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80 (12), 1604–1614. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220295
Langton, D. J., Natu, S., Harrington, C. F., Bowsher, J. G., and Nargol, A. V. F. (2019). Is the synovial fluid cobalt-to-chromium ratio related to the serum partitioning of metal debris following metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty? Bone Jt. Res. 8 (3), 146–155. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.83.BJR-2018-0049.R1
Lehtovirta, L., Reito, A., Parkkinen, J., Peräniemi, S., Vepsäläinen, J., and Eskelinen, A. (2018). Association between periprosthetic tissue metal content, whole blood and synovial fluid metal ion levels and histopathological findings in patients with failed metal-on-metal hip replacement. PLoS ONE 13 (5), e0197614. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0197614
Li, Z., Hao, L., Chen, S., Fu, W., Zhang, H., Yin, Z., et al. (2024). Forkhead box C1 promotes the pathology of osteoarthritis in subchondral bone osteoblasts via the Piezo1/YAP axis. Cell Signal 124, 111463. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111463
Liu, Z., Liu, H., Vowden, R., Hughes, L., Qi, D., Francis, W., et al. (2022). Combination of cobalt, chromium and titanium nanoparticles increases cytotoxicity in vitro and pro-inflammatory cytokines in vivo. J. Orthop. Transl. 38, 203–212. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2022.10.013
Mani, G., Porter, D., Collins, S., Schatz, T., Ornberg, A., and Shulfer, R. (2024). A review on manufacturing processes of cobalt-chromium alloy implants and its impact on corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater Res. B Appl. Biomater. 112 (6), e35431. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.35431
Marin, E., and Lanzutti, A. (2023). Biomedical applications of titanium alloys: a comprehensive review. Materials 17 (1), 114. doi:10.3390/ma17010114
Matta, C., Takács, R., Ducza, L., Ebeid, R. A., Choi, H., and Mobasheri, A. (2023). Ion channels involved in inflammation and pain in osteoarthritis and related musculoskeletal disorders. Am. J. Physiol-Cell Physiol. 325 (1), C257–C271. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00040.2023
Metikoš-Huković, M., Pilić, Z., Babić, R., and Omanović, D. (2006). Influence of alloying elements on the corrosion stability of CoCrMo implant alloy in Hank’s solution. Acta Biomater. 2 (6), 693–700. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2006.06.002
Murray, D. W., Grammatopoulos, G., Gundle, R., Gibbons, C. L. M. H., Whitwell, D., Taylor, A., et al. (2011). Hip resurfacing and pseudotumour. HIP Int. 21 (3), 279–283. doi:10.5301/hip.2011.8405
National Joint Registry (2017). National joint registry for England, Wales northern Ireland and the Isle of Man. 523 14th annual report. National Joint Registry.
Nyga, A., Hart, A., and Tetley, T. D. (2015). Importance of the HIF pathway in cobalt nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation in human macrophages. Nanotoxicology 9 (7), 905–917. doi:10.3109/17435390.2014.991430
Pandit, H., Glyn-Jones, S., McLardy-Smith, P., Gundle, R., Whitwell, D., Gibbons, C. L. M., et al. (2008). Pseudotumours associated with metal-on-metal hip resurfacings. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 90-B (7), 847–851. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.90B7.20213
Perálvarez-Marín, A., Doñate-Macian, P., and Gaudet, R. (2013). What do we know about the transient receptor Potential Vanilloid 2 (TRPV2) ion channel? FEBS J. 280 (21), 5471–5487. doi:10.1111/febs.12302
Persoons, E., Kerselaers, S., Voets, T., Vriens, J., and Held, K. (2021). Partial agonistic actions of sex hormone steroids on TRPM3 function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (24), 13652. doi:10.3390/ijms222413652
Ricciardi, B. F., Nocon, A. A., Jerabek, S. A., Wilner, G., Kaplowitz, E., Goldring, S. R., et al. (2016). Histopathological characterization of corrosion product associated adverse local tissue reaction in hip implants: a study of 285 cases. BMC Clin. Pathol. 16, 3. doi:10.1186/s12907-016-0025-9
Roy, A., Bennett, A., and Pruitt, L. (2024). Feasibility of using diamond-like carbon films in total joint replacements: a review. J. Mater Sci. Mater Med. 35 (1), 47. doi:10.1007/s10856-024-06814-x
Salloum, Z., Lehoux, E. A., Harper, M. E., and Catelas, I. (2018). Effects of cobalt and chromium ions on oxidative stress and energy metabolism in macrophages in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 36 (12), 3178–3187. doi:10.1002/jor.24130
Salloum, Z., Lehoux, E. A., Harper, M. E., and Catelas, I. (2021). Effects of cobalt and chromium ions on glycolytic flux and the stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in macrophages in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 39 (1), 112–120. doi:10.1002/jor.24758
Samelko, L., Caicedo, M. S., Lim, S. J., Della-Valle, C., Jacobs, J., and Hallab, N. J. (2013). Cobalt-Alloy implant debris induce HIF-1α hypoxia associated responses: a mechanism for metal-specific orthopedic implant failure. PLoS ONE 8 (6), e67127. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067127
Samelko, L., Landgraeber, S., McAllister, K., Jacobs, J., and Hallab, N. J. (2016). Cobalt alloy implant debris induces inflammation and bone loss primarily through danger signaling, not TLR4 activation: implications for DAMP-ening implant related inflammation. PLoS ONE 11 (7), e0160141. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0160141
Sato, M., Sobhan, U., Tsumura, M., Kuroda, H., Soya, M., Masamura, A., et al. (2013). Hypotonic-induced stretching of plasma membrane activates transient receptor potential Vanilloid channels and sodium–calcium exchangers in mouse odontoblasts. J. Endod. 39 (6), 779–787. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2013.01.012
Sharma, M., Levenson, C., Browning, J. C., Becker, E. M., Clements, I., Castella, P., et al. (2018). East Indian sandalwood oil is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor: a new therapeutic option in the treatment of inflammatory skin disease. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 200. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00200
Szczęsny, G., Kopec, M., Politis, D. J., Kowalewski, Z. L., Łazarski, A., and Szolc, T. (2022). A review on biomaterials for orthopaedic surgery and traumatology: from past to present. Materials 15 (10), 3622. doi:10.3390/ma15103622
Thorneloe, K. S., Sulpizio, A. C., Lin, Z., Figueroa, D. J., Clouse, A. K., McCafferty, G. P., et al. (2008). N-((1 S)-1-{[4-((2 S)-2-{[(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)sulfonyl]amino}-3-hydroxypropanoyl)-1-piperazinyl]carbonyl}-3-methylbutyl)-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide (GSK1016790A), a Novel and Potent Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 Channel Agonist Induces Urinary Bladder Contraction and Hyperactivity: Part I. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 326 (2), 432–442. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.139295
Urish, K. L., Giori, N. J., Lemons, J. E., Mihalko, W. M., and Hallab, N. (2019). Trunnion corrosion in total hip arthroplasty – basic concepts. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 50 (3), 281–288. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2019.02.001
Van den Eynde, C., Held, K., Ciprietti, M., De Clercq, K., Kerselaers, S., Marchand, A., et al. (2022). Loratadine, an antihistaminic drug, suppresses the proliferation of endometrial stromal cells by inhibition of TRPV2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 928, 175086. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175086
Van Hoeymissen, E., Held, K., Nogueira Freitas, A. C., Janssens, A., Voets, T., and Vriens, J. (2020). Gain of channel function and modified gating properties in TRPM3 mutants causing intellectual disability and epilepsy. eLife 9, e57190. doi:10.7554/eLife.57190
VanOs, R., Lildhar, L. L., Lehoux, E. A., Beaulé, P. E., and Catelas, I. (2014). In vitro macrophage response to nanometer-size chromium oxide particles. J. Biomed. Mater Res. B Appl. Biomater. 102 (1), 149–159. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.32991
Vendittoli, P. A., Amzica, T., Roy, A. G., Lusignan, D., Girard, J., and Lavigne, M. (2011). Metal ion release with large-diameter metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplasty 26 (2), 282–288. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.12.013
Vriens, J., Owsianik, G., Voets, T., Droogmans, G., and Nilius, B. (2004a). Invertebrate TRP proteins as functional models for mammalian channels. Pflüg Arch. 449 (3), 213–226. doi:10.1007/s00424-004-1314-1
Vriens, J., Watanabe, H., Janssens, A., Droogmans, G., Voets, T., and Nilius, B. (2004b). Cell swelling, heat, and chemical agonists use distinct pathways for the activation of the cation channel TRPV4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (1), 396–401. doi:10.1073/pnas.0303329101
Vriens, J., Appendino, G., and Nilius, B. (2009). Pharmacology of Vanilloid transient receptor potential cation channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 75 (6), 1262–1279. doi:10.1124/mol.109.055624
Vriens, J., Owsianik, G., Hofmann, T., Philipp, S., Stab, J., Chen, X., et al. (2011). TRPM3 is a nociceptor channel involved in the detection of noxious heat. Neuron 70 (3), 482–494. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.051
Wall, M. E., Dyment, N. A., Bodle, J., Volmer, J., Loboa, E., Cederlund, A., et al. (2016). Cell signaling in tenocytes: response to load and ligands in health and disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 920, 79–95. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-33943-6_7
Wang, Q., Eltit, F., and Wang, R. (2019). “Corrosion of orthopedic implants,” in Encyclopedia of biomedical engineering (Elsevier), 65–85. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801238-3.99863-5
Wang, Q., Eltit, F., Garbuz, D., Duncan, C., Masri, B., Greidanus, N., et al. (2020). CoCrMo metal release in metal-on-highly crosslinked polyethylene hip implants. J. Biomed. Mater Res. B Appl. Biomater. 108 (4), 1213–1228. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.34470
Wang, Q., Eltit, F., Feng, R., Garbuz, D., Duncan, C., Masri, B. A., et al. (2022). Nature of fretting corrosion products in CoCrMo hip implants from in vivo study to in vitro simulation. Materialia 22, 101433. doi:10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101433
Whitehouse, M. R., Patel, R., French, J. M. R., Beswick, A. D., Navvuga, P., Marques, E. M. R., et al. (2024). The association of bearing surface materials with the risk of revision following primary total hip replacement: a cohort analysis of 1,026,481 hip replacements from the National Joint Registry. PLOS Med. 21 (11), e1004478. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1004478
Xu, J., Yang, J., Chen, J., Zhang, X., Wu, Y., Hart, A., et al. (2020). Activation of synovial fibroblasts from patients at revision of their metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. Part Fibre Toxicol. 17, 42. doi:10.1186/s12989-020-00374-y
Yu, L., Tian, D., Su, Z., Zhang, L., Jie, L., Guo, S., et al. (2025). Mechanical stress overload promotes NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated osteoarthritis synovitis and fibrosis through Piezo1. Cell Signal 132, 111786. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111786
Zhang, M., Ma, Y., Ye, X., Zhang, N., Pan, L., and Wang, B. (2023). TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8, 261. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01464-x
Keywords: cobalt cell damage, hip arthroplasty, metabolic stress, calcium signaling, ALTRs, hip pseudotumors
Citation: Held K, Koobor S, Nieckarz J, Mousavizadeh R, Simon F, Cox ME, Vriens J and Eltit F (2025) Cobalt ions sensitize TRPV2 and TRPV4 channels in synovial fibroblasts, leading to cytokine secretion. Front. Mater. 12:1653364. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1653364
Received: 24 June 2025; Accepted: 07 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Jong Seto, University of California, San Francisco, United StatesReviewed by:
Ziqian Xiang, Shandong University, ChinaSakshi Schmid, EPFL, Switzerland
Ezra Omar Sarmiento, University of California, Irvine, United States
Copyright © 2025 Held, Koobor, Nieckarz, Mousavizadeh, Simon, Cox, Vriens and Eltit. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Felipe Eltit, ZmVsaXBlZWx0aXRAZ21haWwuY29t; Katharina Held, a2F0aHplODhAZ21haWwuY29t; Sara Koobor, c2tvb2hib3JAcHJvc3RhdGVjZW50cmUuY29t
 Katharina Held
Katharina Held Sara Koobor4,5*
Sara Koobor4,5* Felipe Simon
Felipe Simon Michael E. Cox
Michael E. Cox Joris Vriens
Joris Vriens Felipe Eltit
Felipe Eltit