- 1Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Bursa Technical University, Bursa, Türkiye
- 2Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN Unidad Saltillo, Ceramics Engineering Department, Ramos Arizpe, Coahuila, Mexico,
Editorial on the Research Topic
Advancements in multifunctional ceramic and metal matrix composites for sustainable engineering
Multifunctional ceramic and metal matrix composites, featuring innovative designs, can exhibit the desired properties for a wide variety of applications, such as thermal, mechanical, electrical, magnetic, and optical properties. These materials also may have inherent characteristics like stability and resistance to corrosion, thereby offering the potential to resolve a broad spectrum of engineering and technological challenges. Recent developments in the field of nanoscience and nanotechnology have become a significant driving force for CMC and MMC materials, expanding their applications to a broader range of industries, including biomedical, medicine, electronics, aerospace, and defence. In-situ phase-reinforced CMC and MMC designs are one of the promising time, cost, and energy-saving approaches that require further research to apply these innovations and integrate them into sustainable applications. Despite these significant advances, considerable gaps remain to be filled in realizing the full potential of multifunctional composites, particularly in optimizing their properties for specific application desires, novel approaches, and addressing environmental concerns during production and service conditions.
Under this Research Topic, novel developments and state-of-the-art science and technology in the field of CMCs and MMCs are presented, with a special focus on starting raw materials, waste valorization, processing, structural design, properties, and final performance. The primary scope of this study is to address key challenges related to optimizing these composites for a wide variety of applications, integrating in situ and ex-situ phases, and considering the produced CMCs and MMCs’ environmental aspects. By examining these features, the research aims to contribute to the development of novel approaches that yield more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly composite materials.
Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) is an intermetallic compound that is primarily used in high-temperature applications, such as heating elements and resistors. It has a high melting temperature (2030°C) and is characterized by a density of 6.23 g/cm3. Due to the mechanical, physical, and thermal properties of MoSi2, it has attracted significant interest in a wide range of industrial applications. Tapia-López et al. discussed the state of the art of the intermetallic compound MoSi2, including its crystal structure, oxidation behavior, general properties, and applications, as well as the recycling and utilization of MoSi2 as a matrix or reinforcement to produce ceramic and metal matrix composites for various potential applications (Figure 1).
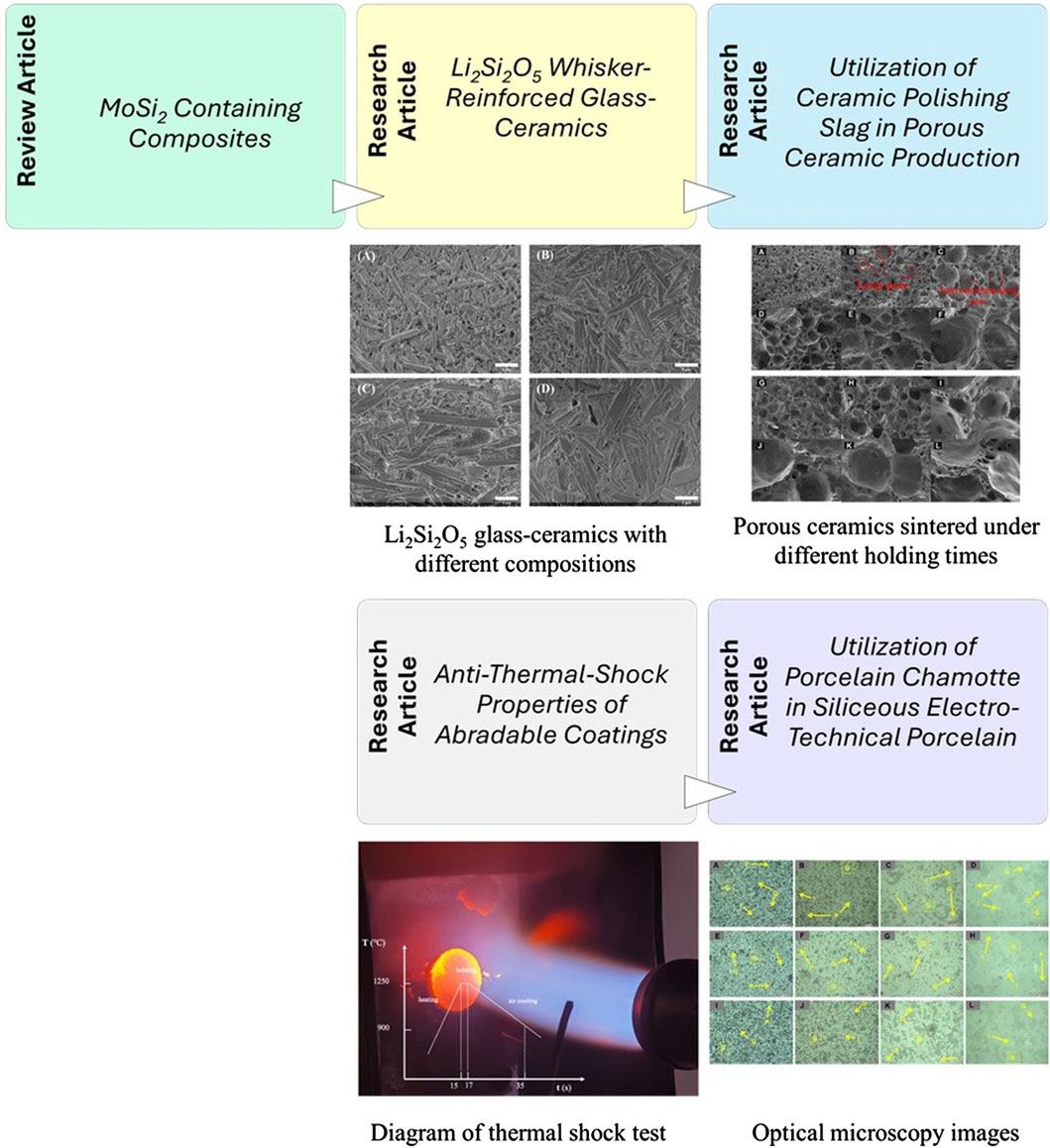
Figure 1. The summary of five papers representing the recent advancements in multifunctional ceramic and metal matrix composites for sustainable engineering
Phase content, microstructural development, and mechanical properties are crucial features that considerably affect the final performance of the material. Yan et al. conducted a systematic study to investigate the effects of varying amounts of Li2Si2O5 whisker reinforcement, synthesized via a facile hydrothermal approach, on the glass-ceramic phase content, microstructural features, and mechanical properties. The crystal growth and toughening mechanisms are discussed in detail to explain how the elongated, rod-like Li2Si2O5 whiskers affect the final performance of the designed glass-ceramic composition. Yan et al. reported that the addition of Li2Si2O5 whiskers directly into glass powders resulted in a bimodal microstructure, consisting of both large, rod-like and fine Li2Si2O5 crystals embedded in the glass matrix. With the increasing amount of Li2Si2O5 whiskers, a slight increase in crystallinity was reported. Additionally, it is noted that the average crystal size increased with the increase in Li2Si2O5 whisker content. Yan et al. concluded that the bimodal crystal size distribution in microstructure development effectively contributed to achieving higher mechanical properties.
Recycling, the reuse of materials, and the transformation of various wastes into new products, are vital industrial-scale and socially accepted approaches to protecting the circular economy and the environment. Fu et al. systematically investigated the utilization of ceramic polishing slag for the production of porous ceramics to determine the effect of holding time on the pore structure of the produced porous ceramics with a high polished slag ratio (60%). The pore structure of the designed samples was investigated using a combination of SEM and X-CT. The final properties of the produced porous ceramics are discussed in detail. As a result of the conducted experimental studies, Fu et al. determined that the optimal properties were achieved at a holding time of 30 min, resulting in a volume density of 0.68 g/cm3, a water absorption of 27.33%, an apparent porosity of 15.49%, and a compressive strength of 13.07 MPa.
Jing et al. investigated the improvement of the anti-thermal-shock properties of abradable coatings containing Sc2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2-CaF2-PHB by developing high-wetness textures on SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites via femtosecond laser processing. Both numerical analysis and experimental verification studies were conducted to ensure a thorough understanding of the performance of the designed coatings in challenging thermal conditions. Jing et al. reported that the developed surface textures significantly influence the anti-thermal-shock properties of the designed abradable coatings by enhancing the contact area and optimizing the interface stress distribution.
Mineral resources, such as high-quality quartz, clay, and feldspar, have been used in the ceramic industry in large amounts for a considerable time. Owing to the high volume consumption of these minerals, many sources are approaching exhaustion. Therefore, it is important to ensure the effective use of waste materials in ceramic products. Clay-based ceramic products, such as porcelain, are potential candidate systems to ensure the effective use of waste materials in ceramic products. Generally, commercial siliceous porcelain insulators contain a high amount of clay (40%–50%), feldspar (35%–45%), and quartz (10%–15%). Rodríguez et al. investigated the effect of substituting traditional binary raw materials (quartz and feldspar) with waste porcelain chamotte in siliceous electro-technical porcelain to manufacture eco-friendly high-voltage porcelain insulators. After characterizing the produced samples, it was determined that using porcelain chamotte in a siliceous electro-technical porcelain composition has been favorable, with outstanding properties.
Author contributions
AK: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MP-C: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: ceramic matrix composites, metal matrix composites, microstructure, recycling, porous ceramics, glass-ceramics
Citation: Kalemtas A and Pech-Canul MI (2025) Editorial: Advancements in multifunctional ceramic and metal matrix composites for sustainable engineering. Front. Mater. 12:1672998. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1672998
Received: 25 July 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 21 August 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Vincenzo M. Sglavo, University of Trento, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Kalemtas and Pech-Canul. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Martin I. Pech-Canul, bWFydGluLnBlY2hAY2ludmVzdGF2LmVkdS5teA==
 Ayse Kalemtas
Ayse Kalemtas Martin I. Pech-Canul
Martin I. Pech-Canul