- 1Department of Chemistry, School of Chemical Engineering and Physical Sciences, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab, India
- 2School of Mechanical Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab, India
- 3FunGlass, Alexandar Dubcek University of Trenčín, Trenčín, Slovakia
The widespread use of the toxic insecticide Thiamethoxam (TMX) poses significant risks to environmental and human health, necessitating effective remediation methods. This study reports the successful synthesis of novel Nickel-doped Lead Sulfide (Ni-PbS) nanoparticles via a straightforward co-precipitation approach for the visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of TMX. Structural analysis confirmed that the Ni-PbS nanoparticles crystallize in a face-centred cubic structure. Morphological examination revealed a flower-like architecture composed of nanosheets. Optical studies showed a narrowed band gap of 2.2 eV, confirming visible-light responsiveness. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) further verified the presence of Pb2+, S2-, and the successful incorporation of Ni2+ into the PbS lattice. The Ni-PbS catalyst demonstrated significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity, achieving 78.93% TMX degradation within 210 min with a rate constant of 0.02225 min−1. Optimal performance was observed at pH 3 and a catalyst loading of 0.5 g/L. The catalyst also exhibited excellent stability and reusability over five consecutive cycles. Scavenger studies revealed that valence band holes (h+) and hydroxyl radicals (•OH) were the dominant reactive species driving the degradation. Overall, this work highlights Ni-PbS as a robust and efficient photocatalyst for the remediation of water contaminated with neonicotinoid insecticides.
1 Introduction
In the contemporary world, the rapid increase in human population has led to excessive use of pesticides and insecticides in agriculture to protect crops and improve yields. Although these chemicals improve agricultural yield, their persistence in the environment poses serious risks to aquatic ecosystems and human health (Díez et al., 2019). These chemicals are non-biodegradable and recalcitrant, limiting the effectiveness of conventional removal methods and causing long-term accumulation in soil and groundwater (Singh et al., 2024).
Among these, TMX, a neonicotinoid insecticide derived from natural toxins, has attracted particular concern. Initially considered relatively safe for crop protection (Žabar et al., 2012), later studies revealed significant risks. TMX induces chronic toxicity in aquatic insects, with Chaoborids larvae showing high sensitivity, leading to ecological imbalance in freshwater systems (Finneg et al., 2017). It has also been implicated in pollinator mortality, with bee populations (Apis mellifera) experiencing high losses when exposed to TMX alone or in combination with fungicides such as tetraconazole (Li et al., 2023). Such mixtures have been shown to increase toxicity synergistically, raising concern over combined pesticide exposures (Finneg et al., 2017). Beyond ecological impacts, chronic human exposure has been linked to developmental and neurological effects. Toxicokinetic studies in rats suggested that TMX can accumulate in lung tissues at concentrations associated with developmental toxicity (Ayare and Gogate; Yi et al., 2023). A review by Qamar et al. further highlighted potential health risks, including skin and eye irritation, asthma, nervous system disorders, and hormonal imbalances leading to reproductive issues (Qamar et al., 2023).
Widespread detection of TMX in surface waters further underscores its environmental significance, with concentrations reported up to 4,315 ng/L globally (Mohamed et al.). In India, TMX is widely applied to crops such as Capsicum annuum L., Vigna unguiculata, and Mangifera indica (Bhattacherjee and Dikshit, 2016). Residue analysis revealed detectable amounts in food products and runoff waters: for example, ∼0.13 mg/kg of TMX on cowpea 5 days after spraying (Reddy and Paul, 2021), and ∼0.08–0.13 mg/kg on mango even after 20 days (Bhattacherjee and Dikshit, 2016). Runoff into waterbodies reached levels ranging from 199 ng/L to 13,264 ng/L (Sahoo and Patra, 2023), with peak concentrations during cropping seasons. Laboratory studies further confirmed the persistence of TMX in Indian soils, with half-lives ranging from 46.3 to 301 days depending on moisture, indicating its high environmental stability (Banerjee et al., 2008).
Several treatment strategies have been developed for TMX contaminated water. Adsorption using activated carbon, magnetic nanocomposites, and modified adsorbents has shown effectiveness, but performance is limited by saturation and regeneration requirements (de et al., 2022; Baskar et al., 2022). Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), including Fenton reaction, ozonation, and electrochemical oxidation, have been successfully applied, though their high cost and energy demand limit large-scale implementation (García-Segura, 2022). Biological methods using bacterial strains such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and P. putida offer environmentally friendly alternatives but exhibit slower degradation rates and require specific reaction conditions (Rani and Shanker, 2018; Singh and Basu, 2020). In contrast, photocatalytic oxidation provides an efficient and sustainable solution, utilizing light energy to mineralize pesticides into harmless products without producing secondary pollutants (Singh and Basu, 2020; Nayak et al., 2024). Semiconductors such as TiO2, ZnO, and g-C3N4 have been widely studied as photocatalysts due to their stability, reusability, and ability to achieve complete degradation (Kourkoumelis et al., 2021; Azim et al., 2018).
To enhance visible-light utilization, strategies such as bandgap engineering, morphology control, and heterojunction construction have been employed (Singh et al., 2020; Ahmad, 2025). Metal sulfides, especially PbS, are attractive candidates because of their narrow bandgap (bulk ∼0.41 eV) and strong absorption in the visible region. Nano structuring and doping can further tune its bandgap up to ∼2.0 eV, improving solar light harvesting (Bayram et al., 2025; Nam et al., 2014). Several PbS-based photocatalysts have already shown activity for degrading organic contaminants. For instance, Ni–PbS synthesized via chemical routes achieved significant degradation of methyl orange (89%) and methylene blue (75%) under visible light ( et al., 2018; et al., 2016), while PbS–clinoptilolite nanocomposites reached 76% degradation of ciprofloxacin ( et al., 2024). Other heterojunction systems, such as WO3/g-C3N4, have also demonstrated high efficiency in pollutant removal (Singh et al., 2019).
In this report, Ni-PbS nanostructures offer a promising yet unexplored strategy for TMX remediation. Ni2+ incorporation not only reduces PbS particle size and tunes the bandgap but also enhances charge separation and reactive oxygen species generation (Horoz et al., 2018). Moreover, the co-precipitation synthesis route provides a simple and scalable approach to prepare such doped sulfide nanoparticles. Previous studies have reported the advantages of Ni doping and PbS-based nanostructures for enhanced photocatalysis. For instance, Ni-modified g-C3N4 photocatalysts exhibited improved charge separation and visible-light activity (She et al., 2019), while PbS nanostructures have been explored for their tunable optical properties and photocatalytic behaviour (Parveen et al., 2018). However, these studies did not address the degradation of TMX, nor did they investigate Ni doping in PbS specifically for environmental remediation.
The novelty and importance of this study can be summarized as follows: Ni-PbS nanoparticles were synthesized through a simple co-precipitation method and, for the first time, applied for TMX degradation under visible light. Ni doping effectively tuned the band gap of PbS and enhanced charge separation, resulting in significantly improved photocatalytic activity and stability compared to pristine PbS. This work therefore establishes Ni-PbS as a green, cost-effective, and sustainable strategy for the removal of TMX from contaminated water.
In contrast, the present work introduces Ni-PbS nanoparticles synthesized via a simple co-precipitation route and applies them, for the first time, to the visible-light-driven degradation of TMX. This dual novelty targeting a highly persistent neonicotinoid pollutant and demonstrating band-gap tuning through Ni incorporation differentiates our study from previous reports and highlights its environmental relevance.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Nickel Sulphate Extra pure hexahydrate (NiSO4.6H2O) (≥99.86%) and Sodium Sulphide hydrate flak (Na2S.xH2O) (≥60.0%) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was purchased from Loba Chemic Pvt. Ltd. Lead acetate trihydrate (CH3COO)2Pb.3H2O (≥99.96%) was purchased from Qualikems fine Chem Pvt. Ltd. All the chemicals were used as received without further purification.
2.2 Synthesis of Ni doped PbS
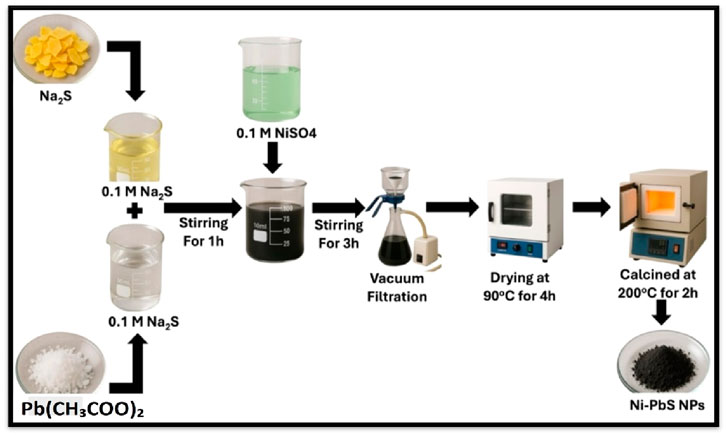
Ni doped PbS catalyst was synthesized by using chemical synthesis route. Initially, 0.1 M lead acetate dissolved in 25 mL water and in other beaker, 0.1 M sodium sulfide was dissolved in 25 mL water. Both the solution was sonicated for 15 min and then mixed both solutions and further stirred for 1 h. Subsequently, a 0.2 M solution of NaOH in 10 mL of water was prepared and added to the mixture. The resulted solution was stirred for 3 h at room temperature. In parallel, a separate solution of 0.1 M NiSO4 was prepared in 50 mL of water and stirring the mixture for 30 min. This NiSO4 solution was then carefully mixed with the previously prepared mixture and stirred for an additional 3 h to facilitate the formation of Ni-PbS. After 3 h reaction period, the resulting solution underwent filtration to isolate the Ni-PbS product. The product was then washed thoroughly with distilled water and dried in a hot air oven for 3–4 h. Finally, the crystals of Ni-PbS were collected and subjected to calcination at 200 °C for 2 h. For the synthesis of PbS, the above process was repeated without the addition of NiSO4. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram for the synthesis of Ni-PbS.
2.3 Characterization techniques
The synthesised particles were analysed by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns recorded by Bruker D8 Advance. The surface morphology was examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images using FE-SEM: JEOL JSM-7610F plus. The adsorbents BET surface area was measured by a BET surface area analyser using Bel, Japan, Inc., Microtec BELSORP MINI-II. The elemental composition of the synthesized nanomaterials was analysed through Energy-Dispersive X-ray System (EDS) carried out in an OXFORD EDS LN2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) for the samples was investigated by by Nexsa G2; Surface Analysis System (Thermo Scientific). The diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) of the samples were recorded using a Jasco V-750 spectrophotometer.
2.4 Photocatalytic degradation
The photocatalytic experiments for the degradation of TMX were done in visible light (CFL lamp, 70W, 125W/m). The stock solution of 5 ppm TMX was prepared in a 1 L water solution. For each experiment, 10 mL of solution was taken with the desired amount of sample and stirred under the light for a fixed treatment time. The absorbance of the treated solution was examined using a UV-visible spectrophotometer at λmax = 250 nm. The degradation efficiency was calculated by the following Equation 1:
Where C0 and C are the initial and final concentrations of the solution.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization results
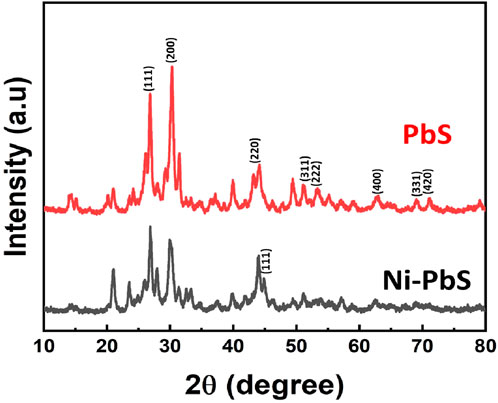
The XRD patterns of the as-synthesised PbS nanoparticles (Figure 2) exhibit broad diffraction peaks typical of nanocrystalline materials, which can be indexed to the face-centred cubic (fcc) phase of PbS. The main peaks appear at 2θ values of ∼24.9°, 26.9°, 30.5°, 40.0°, 45.9°, 50.2°, 62.7°, 71.7°, and 79.2°, corresponding to the (111), (200), (220), (311), (222), (400), (331), and (420) planes, respectively (Salavati-Niasari et al., 2008), in good agreement with standard JCPDS data, confirming the formation of phase-pure PbS. The broadness of these peaks reflects the small crystallite size, which enhances surface-to-volume ratio and benefits photocatalysis. For Ni–PbS, the diffraction pattern retains the fcc structure but shows subtle modifications: an additional signal near the (111) plane and slight peak shifts, without any secondary phases related to Ni or NiO (Ubale, 2012; Mohammed et al., 2018), indicating successful Ni incorporation into the PbS lattice rather than forming separate phases. A notable change is the shift in preferential orientation from the (200) plane in pristine PbS to the (111) plane in Ni–PbS, along with variations in relative peak intensities. These changes, together with shifts toward higher 2θ values, arise from lattice contraction due to substitution of larger Pb2+ ions (∼1.19 Å) with smaller Ni2+ ions (∼0.69 Å). This contraction modifies interplanar spacing, crystallite growth, and electronic structure while preserving the overall fcc framework (Ahmad and Niaz). Such structural tuning by Ni doping is directly linked to enhanced charge separation and improved photocatalytic activity.
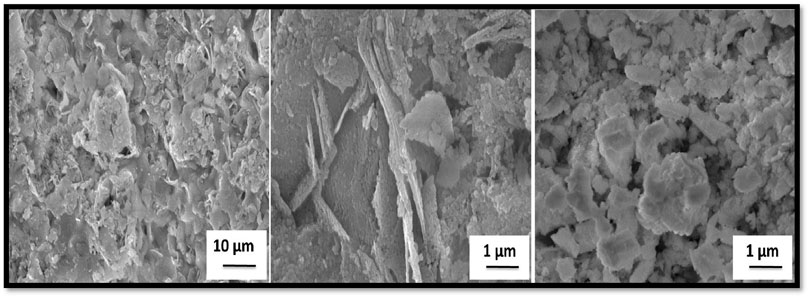
FE-SEM was employed to investigate the microstructural features of the samples, with particular attention to morphology. Figure 3a presents the SEM micrographs of Ni–PbS, which reveal an uneven distribution of particles with varying sizes and shapes. In Figure 3b, taken at the same magnification but from a different region, another dominant morphology is observed. The structure is primarily composed of thin, flat nanoflakes or nanosheets (Kuppan et al., 2014), which tend to agglomerate into larger three-dimensional clusters resembling “flower-like” or “rosette-like” architectures. Such hierarchical self-assembly, frequently reported for wet chemical synthesis methods, generates a material with a significantly enhanced effective surface area (Kumar et al., 2016). This high surface area facilitates greater adsorption of TMX molecules and provides more active sites for photocatalytic reactions. Furthermore, the interconnected flake-like network promotes light harvesting and efficient charge transport, thereby reducing electron–hole recombination. Although this morphology is commonly observed in PbS-based nanostructures, the distinctive aspect of the present work lies in the synergistic role of Ni incorporation. Nickel doping introduces lattice distortions and modifies the electronic structure of PbS, thereby complementing the surface-driven effects of the nanoflake morphology and leading to enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation performance.
Figure 4 illustrates the EDX and mapping of Ni-PbS, which demonstrates the presence of lead, sulphur, and nickel elements in the sample. The weight percentages for Pb, S, and Ni are 83.92%, 7.23%, and 8.85%, respectively. Moreover, all the elements have homogeneous distribution throughout the catalyst surface.
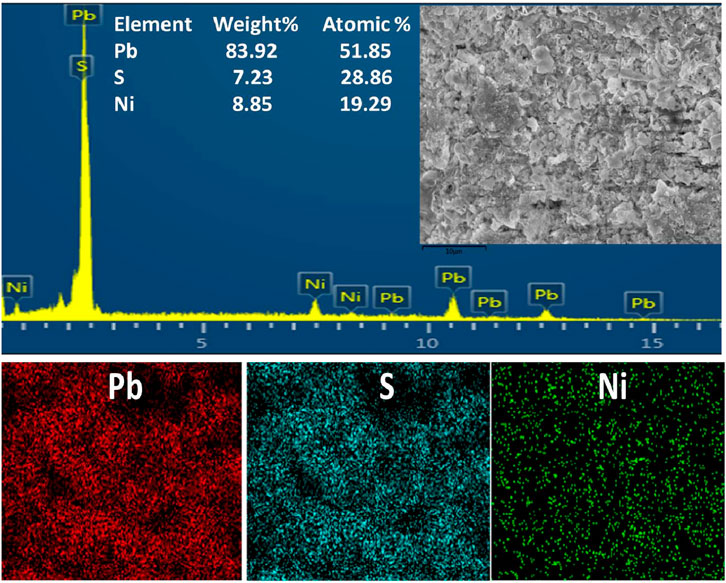
Figure 4. EDX spectrum and mapping for Ni–PbS nanoparticles confirming the presence of Pb, S, and Ni elements.
Figure 5a displays the whole XPS survey spectrum of Ni–PbS, highlighting the distinctive peaks of Pb4f, S2p, Ni2p, and O1s. The S2p peak is clearly seen in the proper binding energy range (158–174 eV) after the apparent mismatch in the survey scan has been fixed. The Ni-doped PbS sample’s elemental valence states and chemical makeup were thoroughly examined. Pb2+ in PbS is characterised by two distinct peaks at ∼138.0 eV (Pb 4f7/2) and ∼142.9 eV (Pb 4f5/2) in the high-resolution Pb 4f spectrum (Figure 5b). Deconvoluting the S2p spectrum (Figure 5c) revealed two primary components: a broader pattern at ∼168.5 eV assigned to surface-oxidized sulphate (S–O) species, and a doublet at ∼161.0 eV corresponding to S2- in PbS (Saraidarov et al., 2007). A Ni 2p3/2 peak at ∼855.5 eV with a corresponding shake-up satellite is visible in the Ni2p region (Figure 5d), indicating the Ni2+ oxidation state and the successful incorporation of Ni into the PbS lattice (Ohno, 2007).
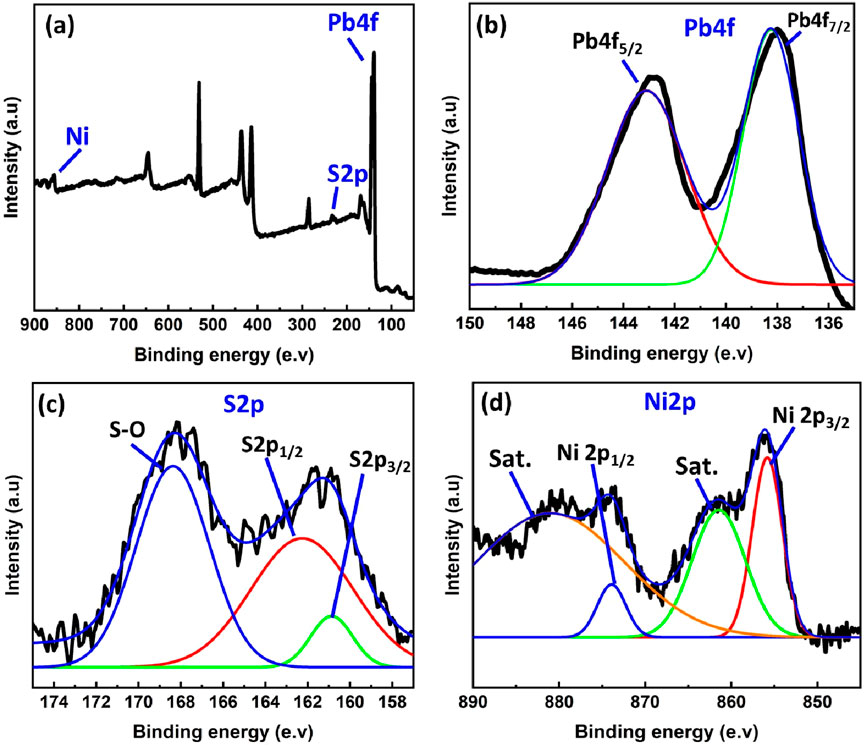
Figure 5. (a) Full XPS spectrum for Ni-PbS and deconvoluted XPS spectrum for (b) Pb 4f, (c) S2p and (d) Ni2p.
The optical properties of the Ni-doped PbS (Ni-PbS) sample were investigated using UV-Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS). The absorbance spectrum, shown in Figure 6a, reveals that the material exhibits strong and broad optical absorption across the entire visible light region (400–700 nm), which is characteristic of a narrow band gap semiconductor. To determine the optical band gap (Eg) from this data, the Tauc relation was employed. Figure 6b shows the Tauc plot, where (αhν)^1/2 is plotted against the photon energy (hν). The use of the exponent 1/2 indicates that the optical transition in the Ni-PbS material is an indirect allowed transition. By extrapolating the linear portion of the curve to the energy axis (where (αhν)^1/2 = 0), the optical band gap of the sample is determined. As indicated on the plot, the band gap (Eg) for the Ni-PbS nanoparticles was found to be 2.2 eV. This value is significantly larger than that of bulk PbS (∼0.41 eV), a phenomenon known as a “blue shift,” which is attributed to the quantum confinement effect in the nanoparticles and the influence of Ni doping on the electronic structure of PbS (Maharaz et al., 2018).
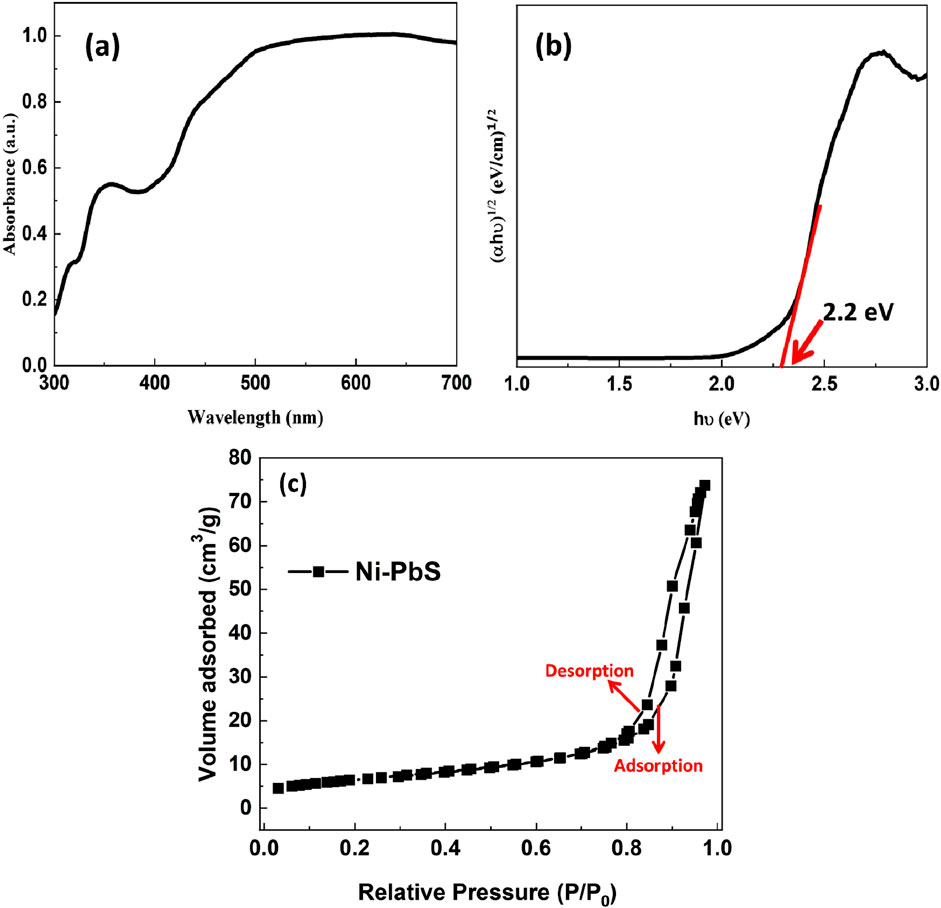
Figure 6. UV–Vis absorption spectra of PbS and Ni–PbS nanoparticles (a) and Tauc plot (b) of Ni-PbS and (c) N2 sorption isotherms for Ni-PbS.
The mesoporous structure of the material is confirmed by the nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm of Ni-PbS nanoparticles, as shown in Figure 6C. The isotherm displays a typical type IV curve with a discernible H3 hysteresis loop in the relative pressure range of 0.8–1.0. This clearly signifies the mesoporous nature of the material. The significant increase in adsorption volume at higher relative pressures is caused by capillary condensation inside mesopores. A significant number of active sites for catalytic processes are provided by Ni-PbS, which has an estimated BET surface area of 23.3 m2/g. The parallel adsorption and desorption branches further demonstrate the existence of slit-like pores, which are commonly associated with nanoparticle agglomerates. Such surface area is advantageous for photocatalytic applications as it enhances light absorption. It also permits easy diffusion of reactants and enables effective charge separation. These factors collectively improve the degradation process.
3.2 Photocatalytic activity
Figure 7A shows the UV-Visible spectrum for the TMX removal using Ni-PbS at different time intervals. This figure displays the time-dependent UV-Vis absorption spectra of the TMX solution during the photocatalytic process using the Ni-PbS catalyst. The spectra, recorded at intervals from 0 to 210 min, show a characteristic absorption peak for TMX at approximately 254 nm. As the reaction progresses under light irradiation, the intensity of this peak systematically decreases. This reduction in absorbance is a direct indication of the diminishing concentration of TMX in the solution, signifying that its molecular structure, particularly the chromophore responsible for UV absorption, is being broken down. The consistent decrease over time provides clear qualitative evidence of the successful and continuous degradation of the pesticide by the Ni-PbS photocatalyst. The absorbance peaks decrease with the treatment time of the TM solution under visible light, which shows the effective degradation of TMX using Ni-PbS.
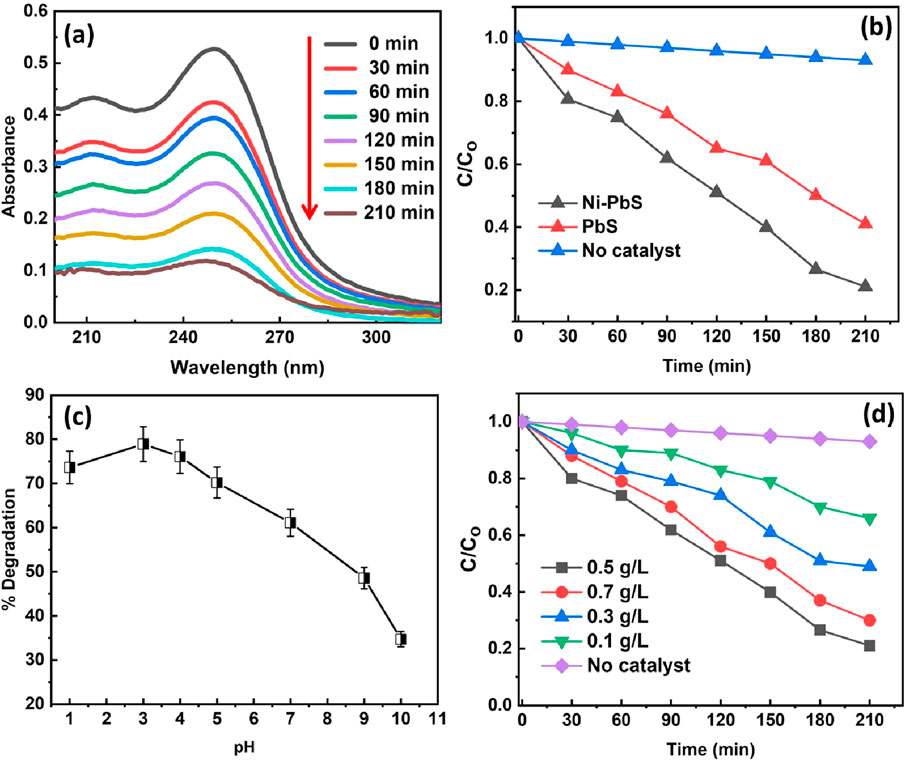
Figure 7. (a) UV-visible spectrum, (b) degradation rate using different samples (c) effect of pH and (d) catalyst amount on the photodegradation of TMX (experimental conditions: catalyst loading-0.5 g/L, pH 3, Temperature- Room temp).
The photocatalytic efficiency of Ni-doped PbS against pure PbS and a control experiment with no catalyst (photolysis) is illustrated in Figure 7b. The plot of normalised concentration (C/C0) versus time shows that in the absence of a catalyst, TMX undergoes negligible degradation, indicating its stability against direct photolysis. While pure PbS shows moderate photocatalytic activity, achieving approximately 58.63% degradation (C/C0 ≈ 0.4) after 210 min, the Ni-PbS sample demonstrates significantly superior performance, degrading about 78.93% of the TMX (C/C0 ≈ 0.2) in the same period. The improved performance is likely due to nickel helping to separate charges more effectively, reducing recombination and boosting photocatalytic activity (Cui et al., 2024; Yao and Zhou, 2024). This improved charge separation leads to a higher quantum yield and, consequently, a more efficient degradation process (M’Bra et al., 2019).
Figure 7c illustrates the profound impact of the initial solution pH on the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of TMX. The plot reveals that the process is highly pH-dependent, with optimal performance occurring in acidic conditions. The degradation percentage is low at pH 1, increases dramatically to a maximum of nearly 78.93% at an optimal pH of 3, and then steadily declines as the solution becomes less acidic and more alkaline. The low performance at pH 1 could be due to excessive protonation, which may suppress radical formation or reduce TMX adsorption. This behaviour is governed by the surface charge of the photocatalyst and the speciation of the pollutant. At the optimal pH, the electrostatic interaction between the catalyst surface and the TMX molecules is most favourable, maximising adsorption onto the catalyst’s active sites. Deviations from this optimal pH likely led to repulsive forces or changes in the catalyst’s surface chemistry, hindering the reaction rate (Krishnan et al., 2021).
The effect of the catalyst amount from 0.1 to 0.7 g/L on the photodegradation of TMX can be seen in Figure 7d. The highest degradation% (78.93%) was obtained by using a 0.5 g/L catalyst amount. However, the degradation decreases by increasing the catalyst amount to 0.7 g/L. This may be due to the agglomeration of catalyst particles by increasing the catalyst amount. It provides a limited surface area and fewer active sites during the photodegradation reaction, which decreases the photocatalytic degradation (Mohagheghian et al., 2015).
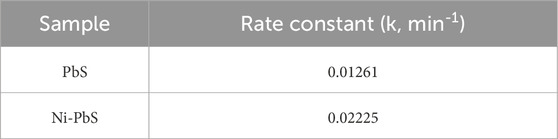
The pseudo-first-order kinetic model, represented as ln(C0/Ct) vs. time in Figure 8, was used to analyse the photocatalytic degradation kinetics of TMX over catalysts. The degradation process follows first-order kinetics, as confirmed by the linear fitting of the experimental data, which had strong correlation with regression coefficients (R2) of 0.987 for Ni-PbS and 0.971 for PbS. Ni doping effectively improves the charge separation and lowers recombination. It also produces more reactive species, as evidenced by the steeper slope seen for Ni-PbS. This indicates a larger rate constant compared to PbS. Ni-PbS shows the highest rate constant of 0.02225 min−1, whereas undoped PbS exhibits 0.01261 min−1 (Table 1). The higher photocatalytic efficiency of Ni–PbS over undoped PbS is further supported by this enhanced kinetic performance.
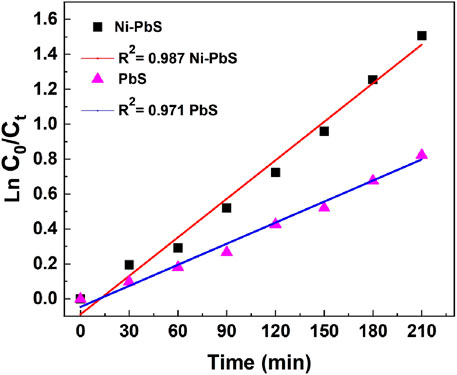
Figure 8. Rate constant assessment for TMX degradation by catalysts based on pseudo-first-order kinetics.
The rate constant associated with each individual catalyst may be computed through the employment of the following equation:
Here Co and C are the concentrations of the TMX at t = 0 and at a selected time (t, min).
Figure 9a illustrates the stability and reusability of the Ni-PbS photocatalyst over five consecutive degradation cycles. The results demonstrate excellent operational stability, which is a critical factor for the practical and economic viability of a photocatalyst. In the first cycle, the catalyst exhibited its highest efficiency, achieving approximately 79% degradation of the target pollutant. In subsequent cycles, there is a very slight and gradual decrease in performance, with the degradation efficiency dropping to approximately 71% by the fifth cycle. This minor loss of activity (less than 10% over five runs) can be attributed to factors such as the inevitable loss of a small amount of catalyst mass during the recovery and washing process between cycles, or minor surface deactivation (Ajibade et al., 2021). Overall, the ability of the catalyst to maintain high efficiency over repeated uses confirms that Ni-PbS is a robust and highly reusable material, promising for sustainable water treatment applications.
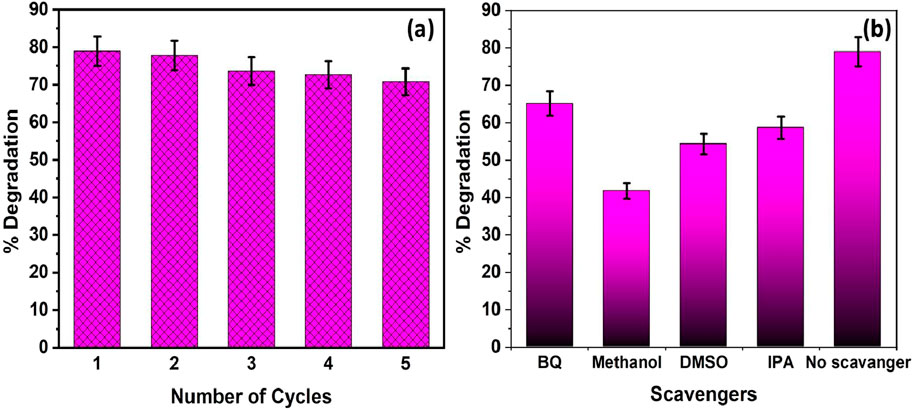
Figure 9. (a) Reusability studies for five consecutive cycles and (b) effect of scavengers on the TM degradation efficiency using Ni-PbS catalyst (experimental conditions: catalyst loading-0.5 g/L, pH 3, Temperature- Room temp).
Figure 9b presents the results of scavenger experiments designed to identify the primary reactive oxygen species (ROS) responsible for the degradation of TMX. The dominant degradation mechanism can be elucidated by introducing specific chemical scavengers that selectively quench different ROS. The control experiment with no scavenger shows the maximum degradation of 78.93%. Introducing Benzoquinone (BQ), a scavenger for superoxide radicals (O2•−), causes a moderate drop in efficiency to ∼65%. A more significant decrease to ∼59% is observed with Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA), a well-known scavenger of hydroxyl radicals (•OH). The most drastic inhibition occurs with the addition of Methanol, which reduces the degradation to ∼42%. Methanol is an efficient scavenger of photogenerated valence band holes (h+) (Mureithi et al., 2022). These results suggest that while multiple species are involved, the degradation of TMX is primarily driven by direct oxidation via valence band holes (h+), followed by attack from hydroxyl radicals (•OH). Superoxide radicals (O2•−) also play a role, but to a lesser extent. Therefore, it can be concluded that the valence band holes (h+) are the most dominant reactive species responsible for TMX degradation under visible light irradiation.
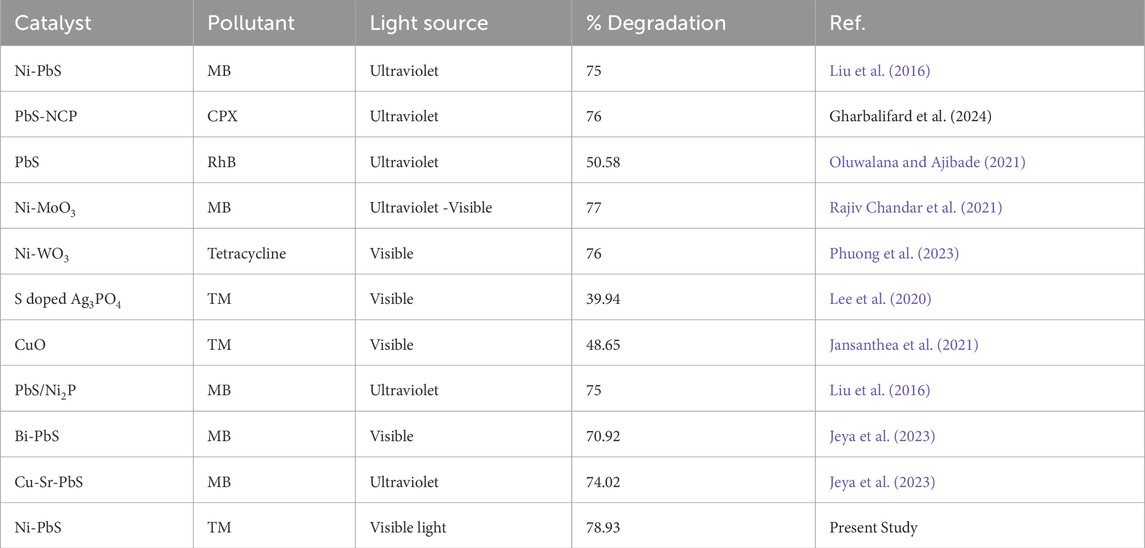
Table 2 shows the comparison of the catalytic activity of synthesized Ni-PbS with other reported catalysts for the removal of pollutants in aqueous solution. It has been seen that very few studies contain the degradation of colourless pollutants using catalysts. In the present study, Ni-PbS shows the maximum degradation of 78.93% in visible light for colourless pollutant, i.e., TMX.
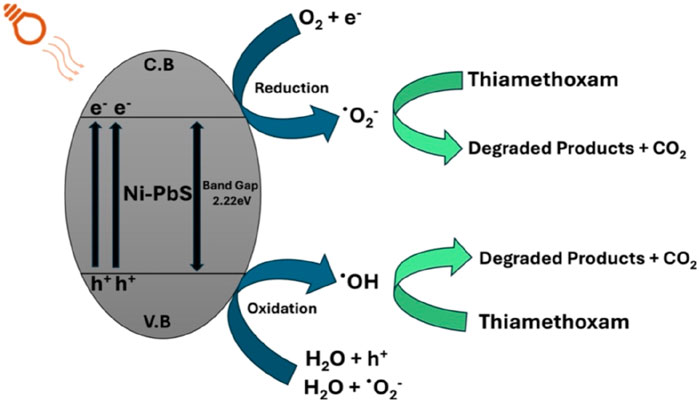
A mechanism for TMX degradation across Ni–PbS (Eg ≈ 2.22 eV) is proposed in Figure 10. When exposed to visible light, Ni–PbS produces e− (CB) and h+ (VB). While holes oxidise adsorbed H2O/OH− to create hydroxyl radicals (•OH) or directly oxidise adsorbed TMX, photogenerated electrons go to the surface and reduce O2 to make superoxide radicals (O2•-). The gradual cleavage of TMX into intermediates and ultimate mineralisation is facilitated by both direct hole oxidation and radical species. Crucially, XRD and XPS data show that Ni is incorporated into the PbS lattice as Ni2+. This incorporation probably adds defect/charge-transfer sites that help trap electrons and transfer electrons across the interface to O2, which inhibits bulk e−/h+ recombination and increases the production of ROS. Benzoquinone produces moderate inhibition, indicating O2•- is involved but less critical; IPA (•OH scavenger) produces significant inhibition, indicating a major role for •OH; and methanol (hole scavenger) produces the greatest inhibition, confirming h+−driven oxidation is dominant, according to scavenger experiments. Ni-induced charge separation and increased surface ROS flux work together to explain how Ni-PbS performs better photocatalytic than undoped PbS.
4 Conclusion
Cost-effective chemical method was used to produce innovative and efficient Ni- PbS nanoparticles. Multiple methods, including XRD, EDX, SEM, and XPS, were employed to characterise the materials. PbS production and Ni2+ inclusion into the crystal lattice were verified by XRD. The elemental makeup and chemical states of Pb, Ni, S, and O were examined using XPS. Under visible light, the maximum degradation efficiency of 78.93% for TMX was attained in 210 min at pH 3. Additionally, the catalyst demonstrated exceptional reusability after five cycles of deterioration. All things considered, combining Ni and PbS in a photocatalyst system shows a lot of promise for treating insecticide contamination in water and providing an efficient and long-lasting way to clean up the environment.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
RF: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MS: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JS: Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. AM: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
AcknowledgementsWe are thankful Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF), Lovely Professional University for availing characterization facilities. The financial support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 739566 is acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmad, N. (2025). Photocatalytic removal of pollutants from water using graphitic carbon nitride-based photocatalysts. Doctoral dissertation, Memorial University of Newfoundland.
Ahmad, T., and Niaz, N. (2014). Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped PbS nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 117 (4), 2217–2224.
Ajibade, P. A., Mbuyazi, T. B., and Oluwalana, A. E. (2021). Lead sulphide nanoparticles as photocatalyst for the degradation of methylene blue: effects of pH, time, adsorption kinetics and recyclability studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31 (5), 2197–2208. doi:10.1007/s10904-021-01957-8
Ayare, S., and Gogate, P. Sonochemical, Photocatalytic and sonophotocatalytic oxidation of flonicamid pesticide solution using different catalysts. Chem. Eng. Process. doi:10.1016/j.cep.2020.108040
Azim, M. B., Tanim, I. A., Rezaul, R. M., Tareq, R., Rahul, A. H., Kurny, A. S., et al. (2018). Degradation of methylene blue using graphene oxide-tin oxide nanocomposite as photocatalyst. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1806.06481. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1806.06481
Banerjee, K., Patil, S., Dasgupta, S., Oulkar, D., and Adsule, P. (2008). Sorption of thiamethoxam in three Indian soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part. B, Pesticides, Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 43, 151–156. doi:10.1080/03601230701795130
Baskar, A. V., Bolan, N., Hoang, S. A., Sooriyakumar, P., Kumar, M., Singh, L., et al. (2022). Recovery, regeneration and sustainable management of spent adsorbents from wastewater treatment streams: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 822, 153555. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153555
Bayram, Ü., Özer, Ç., and Yilmaz, E. (2025). Comparison of photocatalytic and adsorption properties of ZnS@ZnO, CdS@ZnO, and pbs@zno nanocomposites to select the best material for the bifunctional removal of Methylene Blue. ACS Omega 10 (10), 9986–10003. doi:10.1021/acsomega.4c07910
Bhattacherjee, A. K., and Dikshit, A. (2016). Dissipation kinetics and risk assessment of thiamethoxam and dimethoate in mango. Environ. Monit. Assess. 188 (3), 165. doi:10.1007/s10661-016-5160-3
Cui, S., Lv, J., Hough, R., Fu, Q., An, L., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024). Recent advances and prospects of neonicotinoid insecticides removal from aquatic environments using biochar: adsorption and degradation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 939, 173509. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173509
de Freitas, D. A., Barbosa, J. A., Labuto, G., Nocelli, R. C. F., and Carrilho, E. N. V. M. (2022). Removal of the pesticide thiamethoxam from sugarcane juice by magnetic nanomodified activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 79855–79865. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-18484-1
Díez, A., Sanromán, M., and Pazos, M. (2019). New approaches on the agrochemicals degradation by UV oxidation processes. J. Chem. Eng. 376, 120026. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.187
Finnegan, M. C., Baxter, L. R., Maul, J. D., Hanson, M. L., and Hoekstra, P. F. (2017). Comprehensive characterization of the acute and chronic toxicity of the neonicotinoid insecticide thiamethoxam to a suite of aquatic primary producers, invertebrates, and fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 36 (10), 2838–2848. doi:10.1002/etc.3846
García-Segura, S. (2022). Electrochemical processes used to degrade thiamethoxam in commercial actara®. Processes 10 (5), 887.
Horoz, S., Ekinci, A., and Sahin, O. (2018). Synthesis of PbS and Ni-doped PbS thin films by CBD method and investigation of their structural, optical and photovoltaic properties. J. Ovonic Res. 14 (3), 201–208.
Jansanthea, P., Saovakon, C., Chomkitichai, W., Ketwaraporn, J., Maneepong, S., Chaiwong, N., et al. (2021). Thiamethoxam insecticide degradation with a leaf-like cupric oxide monoclinic structure synthesized via the microwave method. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 66 (5), 667–678. doi:10.1134/s0036023621050089
Jeya, P., Keerthana, S. P., Kungumadevi, L., Rathinam, Y., Ganesan, R., Kandasami, A., et al. (2023). γ-Ray-Induced photocatalytic activity of Bi-Doped PbS toward organic dye removal under sunlight. ACS omega 8 (50), 47427–47439. doi:10.1021/acsomega.3c02855
Kourkoumelis, N. (2021). Photocatalytic removal of Thiamethoxam and flonicamid pesticides from water effluents of the fruit industry. Catalysts 11 (3), 516.
Krishnan, S., Jaiganesh, P. S., Karunakaran, A., Kumarasamy, K., and Lin, M. C. (2021). The effect of pH on the photocatalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes using polyazomethine/ZnO and polyazomethine/TiO2 nanocomposites. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 18 (5), 1–8. doi:10.6703/ijase.202109_18(5).008
Kumar, K. C., Pasha, S. K., Muhammad, G. S., Chidambaram, K., and Deshmukh, K. (2016). Influence of nickel on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of PbS thin films synthesized by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method. Mater. Lett. 164, 108–110. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.120
Kuppan, M., Kaleemulla, S., MadhusudhanaRao, N., SaiKrishna, N., RiganaBegam, M., and SreekanthaReddy, D. (2014). Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped SnO2 thin films prepared by flash evaporation technique. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 6 (3), 1933–1935.
Lee, Y.-J., Kang, J.-K., Park, S.-J., Lee, C.-Gu, Moon, J.-K., and Pedro, J. J. A. (2020). Photocatalytic degradation of neonicotinoid insecticides using sulfate-doped Ag3PO4 with enhanced visible light activity. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 126183. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126183
Li, W., Lv, L., Wang, Y., and Zhu, Y. C. (2023). Mixture effects of thiamethoxam and seven pesticides with different modes of action on honey bees (Aplis mellifera). Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 2679. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-29837-w
Liu, S., Han, L., and Liu, H. (2016). Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic performance of PbS/Ni2P flowers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 387, 393–398. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.123
Maharaz, M. N., Halimah, M. K., Paiman, S., Saiden, N. M., and Alibe, I. M. (2018). Influence of solvents and irradiation time on structural and optical properties of cubic PbS nanoparticles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13 (10), 9317–9332. doi:10.20964/2018.10.37
Mohagheghian, A., Karimi, S. A., Yang, J. K., and Shirzad-Siboni, M. (2015). Photocatalytic degradation of a textile dye by illuminated tungsten oxide nanopowder. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 18 (1), 61–68. doi:10.1515/jaots-2015-0108
Mohamed, H. I. K., Elkhateeb, S. A., Naguib, D. M., Moawed, A., Shaheen, M. A., and Sabik, L. M. An overview of thiamethoxam toxicity.
Mohammed, G. H., Aziz, S. B., and Abdullah, O. G. (2018). Physical properties of prepared PbS thin films by chemical bath deposition at different deposition time. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29 (15), 13241–13248.
Mureithi, A. W., Sun, Y., Mani, T., Howell, A. R., and Zhao, J. (2022). Impact of hole scavengers on photocatalytic reduction of nitrobenzene using cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 3 (5), 100889. doi:10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.100889
M’Bra, I. C., Atheba, G. P., Robert, D., Drogui, P., and Trokourey, A. (2019). Photocatalytic degradation of paraquat herbicide using a fixed bed reactor containing TiO2 nanoparticles coated onto β-SiC alveolar foams. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 10 (05), 171–184. doi:10.4236/ajac.2019.105015
Nam, M., Park, J., Kim, S. W., and Lee, K. (2014). Broadband-absorbing hybrid solar cells with efficiency greater than 3% based on a bulk heterojunction of PbS quantum dots and a low-bandgap polymer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2 (11), 3978–3985. doi:10.1039/c3ta15055k
Nayak, S., Farooq, R., Singh, R., Saxena, P., Mehta, A., and Singh, J. (2024). Photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants from aqueous solution using centimetre-scale iron (III) oxide monolith.
Ohno, Y. (2007). “Nano-scale materials with the framework of layered transition-metal dichalcogenides,” in New research on solid State chemistry ed. by james. BV.
Oluwalana, A. E., and Ajibade, P. A. (2021). Structural, optical and photocatalytic studies of oleylamine capped PbS nanoparticles. Opt. Quantum Electron. 53, 2–13. doi:10.1007/s11082-020-02636-7
Parveen, A., Agrawal, S., and Azam, A. (2018). Band gap tuning and fluorescence properties of lead sulfide Pb0. 9A0. 1S (A: fe, Co, and Ni) nanoparticles by transition metal doping. Opt. Mater. 76, 21–27. doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2017.12.015
Phuong, D. M., Duong, T. A., Huong, N. T., Khoa, N. V., Nguyen, T. H., Phuong, N. M., et al. (2023) Synthesis and characterization of Ni doped Wo3 photocatalysts applying for advanced removal of tetracycline under visible light.
Qamar, W., Shahid, M., Irfan, M., Abbas, M., Faraz, A., Hussain, M., et al. (2023). Thiamethoxam toxicity: a review in one-health perspective. Kafkas Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Derg. 29 (4), 563–570. doi:10.9775/kvfd.2023.30161
Rajiv Chandar, N., Agilan, S., Thangarasu, R., Muthukumarasamy, N., Chandrasekaran, J., Arunachalam, S., et al. (2021). Elucidation of efficient dual performance in photodegradation and antibacterial activity by a promising candidate Ni-doped MoO 3 nanostructure. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 100, 451–465. doi:10.1007/s10971-020-05382-0
Rani, M., and Shanker, U. (2018). Removal of chlorpyrifos, thiamethoxam, and tebuconazole from water using green synthesized metal hexacyanoferrate nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25 (11), 10878–10893. doi:10.1007/s11356-018-1346-2
Reddy, B. K. K., and Paul, A. (2021). Residues of thiamethoxam 12.6% + lambda cyhalothrin 9.5% ZC in vegetable cowpea. Indian J. Entomology 83 (1), 676–679. doi:10.5958/0974-8172.2020.00223.0
Sahoo, P. K., and Patra, A. K. (2023). Distribution and risk assessment of pesticide pollution in small streams of Odisha, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 195 (2), 1–14.
Salavati-Niasari, M., Dabir-Mofarah, S., and Davar, F. (2008). Synthesis and characterization of lead sulfide nanostructures via a novel lead(II) complex. J. Alloys Compd. 466 (1-2), 402–407.
Saraidarov, T., Reisfeld, R., Sashchiuk, A., and Lifshitz, E. (2007). Synthesis and characterization of PbS nanorods and nanowires. Phys. E Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostructures 37 (1-2), 173–177. doi:10.1016/j.physe.2006.07.015
She, H., Sun, Y., Li, S., Huang, J., Wang, L., Zhu, G., et al. (2019). Synthesis of non-noble metal nickel doped sulfide solid solution for improved photocatalytic performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 245, 439–447. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.002
Singh, J., and Basu, S. (2020). Synthesis of mesoporous magnetic Fe2O3/g-C3N4 monoliths for Rhodamine B removal. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 303, 110299. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110299
Singh, J., Arora, A., and Basu, S. (2019). Synthesis of coral-like WO3/g-C3N4 nanocomposites for the removal of hazardous dyes under visible light. J. Alloys Compd. 808, 151734. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151734
Singh, G. P., Aman, A. K., Singh, R. K., and Roy, M. K. (2020). Effect of low Co-doping on structural, optical, and magnetic performance of ZnO nanoparticles. Optik 203, 163966. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163966
Singh, J., Mehta, A., and Basu, S. (2024). N-doped nano-casted carbon monolith for Pb (II) removal and photocatalytic degradation of thiamethoxam from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 1–14. doi:10.1007/s11356-024-34490-5
Suganya, M., Balu, A. R., Anitha, S., Prabha, D., Balamurugan, S., Priyanka, B., et al. (2018). PbS-NiO nanocomposite material with enhanced magnetic, photocatalytic and antifungal properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 229, 118–125. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2017.12.031
Ubale, A. U. (2012). Structural and optical properties of Ni doped PbS thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 513, 417–421.
Yao, B., and Zhou, Y. (2024). Removal of neonicotinoid insecticides from water in various treatment processes: a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54 (18), 1307–1339. doi:10.1080/10643389.2024.2309845
Yi, L., Zhang, S., Chen, X., Wang, T., Yi, X., Yeerkenbieke, G., et al. (2023). Evaluation of the risk of human exposure to thiamethoxam by extrapolation from a toxicokinetic experiment in rats and literature data. Environ. Int. 173, 107823. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2023.107823
Keywords: PBS, Ni doping, photocatalysis, visible light, insecticide
Citation: Farooq R, Singh M, Singh J and Mehta A (2025) Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of toxic insecticide thiamethoxam using Ni-doped PbS nanoparticles under visible light irradiation. Front. Mater. 12:1677416. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1677416
Received: 31 July 2025; Accepted: 29 October 2025;
Published: 20 November 2025.
Edited by:
Daniela Šojić Merkulov, University of Novi Sad, SerbiaReviewed by:
Karanpal Singh, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, IndiaAadil Bathla, Vysoka skola banska-Technicka univerzita Ostrava Fakulta stavebni, Czechia
Copyright © 2025 Farooq, Singh, Singh and Mehta. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jasminder Singh, amFzbWluZGVyLnNpbmdoOTFAZ21haWwuY29t
 Rehana Farooq1
Rehana Farooq1 Jasminder Singh
Jasminder Singh Akansha Mehta
Akansha Mehta