- 1 Hamdi Mango Center for Scientific Research, The University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan
- 2 Allied Sciences Department, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Al-Ahliyya Amman University, Amman, Jordan
- 3 Chemical Engineering Department, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
- 4 Institute of Nanotechnology, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Al Ramtha, Jordan
- 5 Basic Pharmaceutical Science Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Middle East University, Amman, Jordan
- 6 Department of Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy, Isra University, Amman, Jordan
The global push for sustainability has sped up the shift from petroleum-based polymers to green polymer nanocomposites (GPNCs). These materials combine bio-based or biodegradable polymers with nanoscale reinforcements to boost performance and lessen environmental impact. This review discusses synthesis methods, structure–property relationships, and industrial uses of GPNCs. Natural polymers like starch, cellulose, chitosan, and alginate, along with bioplastics such as PLA, PHA, PBS, and PCL, offer biodegradability but have limited mechanical strength. This issue can be significantly addressed by adding nanofillers, like nanoclays, CNCs, nanofibers, biochar, and carbon materials. For example, the addition of nanofillers increased the modulus by (60-70)%, while surface-functionalized nanofillers enhanced interfacial bonding, and hybrid fillers blend stiffness with flexibility, resulting in a 200% increase in elongation at break. Some metal nanoparticles offer antimicrobial properties in which cell viability went down to less than 10% upon addition of nanofillers, or photocatalytic benefits, achieving 100% photocatalytic efficiency, with safety carefully evaluated. Advances in fabrication methods, including solution casting, melt compounding, in situ polymerization, electrospinning, and 3D printing, improve scalability and nanofiller distribution. Including nanofillers boosts mechanical and thermal properties for high-performance packaging. GPNCs are increasingly important in sectors: in packaging, for improved film strength; in automotive and aerospace, for lightweight designs; in construction, for coatings and structural parts; in water treatment, via enhanced membranes; and in biomedical devices, due to biocompatibility. GPNCs promote sustainability by utilizing waste, reducing energy use, and enabling recyclability or biodegradability, supporting circular economy goals. They meet regulatory defmands like the European Green Deal and EPR. Challenges include higher costs of bio-polymers and nanofillers, processing complexity, need for standardized testing, and toxicity concerns for certain nanomaterials. Despite these, green nanocomposites blend innovation and environmental responsibility, crucial for a sustainable future, with ongoing research promising broader industrial adoption.
1 Introduction
The urgent global environmental crisis is largely driven by petroleum-based plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene. These strong, durable, and inexpensive materials are non-renewable and non-biodegradable, taking centuries to decompose. Their use contributes to landfill expansion, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the need for sustainable alternatives (Jain, 2017; Singh and Walker, 2024; Arrieta et al., 2014).
Global production of plastics has exceeded 400 million metric tons every year and is estimated to reach 600 million metric tons by 2050 (Mahajan et al., 2023). Improper plastic disposal contaminates the environment, harms wildlife, and contributes to microplastic pollution. Burning plastic releases toxic chemicals, worsening air pollution and health risks like cancer and respiratory issues. Traditional recycling is costly and energy-intensive, complicating the treatment of mixed plastics and reducing its eco-friendliness (Kumar et al., 2020; Royer et al., 2018).
In a bid to address these limitations, green polymer nanocomposites (GPNCs) have been labeled as an optimistic solution that embodies material innovation coupled with environmental stewardship. GPNCs are hybrid composites made of biodegradable or bio-based polymer matrices reinforced by eco-friendly nanofillers (Harun-Ur-Rashid et al., 2023). These products are designed to match or exceed conventional plastics while lowering environmental impact. The use of nanofillers in bio-based matrices enhances their mechanical strength, thermal resistance, barrier properties, antimicrobial effects, and UV stability, making them suitable for packaging, automotive, aerospace, construction, biomedical, and water treatment applications (Harun-Ur-Rashid et al., 2023; Sunday et al., 2012; Saha, 2023; Hopewell et al., 2009).
GPNCs are made from biodegradable materials like starch, cellulose, chitosan, alginatepolylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), polybutylene succinate (PBS), and polycaprolactone (PCL). While eco-friendly, some may lack the strength for demanding applications. To enhance performance, nanofillers such as nanoclays, cellulose nanocrystals, biochar, carbon nanotubes, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and silver are added, improving strength along with gas barrier, antimicrobial, and photocatalytic properties (Mahajan et al., 2023; Harun-Ur-Rashid et al., 2023; Sunday et al., 2012; Saha, 2023; Bhawani et al., 2018). The high surface area and strong interfacial adhesion of nanoscale fillers enable significant property improvements at low loadings, allowing for reduced matrix use and the creation of lighter, high-performance polymer nanocomposites. Advanced processing techniques like solution casting, melt compounding, and 3D printing allow precise control over nanofiller mixing and properties for targeted applications (Iqbal et al., 2024). GPNCs are increasingly important in various industries. Starch or PLA-based nanocomposites with nanoclays strengthen packaging and improve moisture barriers. In automotive and aerospace, they create lightweight parts that reduce fuel use and emissions. In construction, GPNCs aid green building through coatings and insulation. They enhance filtration in water treatment and are biocompatible, making them suitable for tissue engineering, wound care, and drug delivery in biomedical applications (Avolio et al., 2018; Malucelli and Kausar, 2022; Reddy et al., 2013).
GPNCs support environmental and regulatory goals by utilizing recycled agricultural and industrial waste, such as rice husk ash, lignin, fly ash, or waste glass powder, fostering a circular economy. Their biodegradable or recyclable properties reduce landfill use. They also align with sustainability initiatives like the European Green Deal, Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for cleaner production practices (Mohanty et al., 2002; Rujnic Havstad and Pilipović, 2017).
Despite their potential, GPNCs face challenges in commercialization. Bio-based polymers and high-performance nanofillers are often more expensive than traditional plastics. Achieving uniform dispersion and effective bonding demands advanced processing technologies. Current biodegradability, toxicity, and durability testing methods are still being developed, hindering material comparisons and regulatory approvals. Additionally, some nanomaterials, like metal oxides and carbon nanotubes, pose toxicity and environmental persistence concerns, necessitating comprehensive life cycle assessments and risk analyses (Saha, 2023; Ramakoti et al., 2023).
This review explores green polymer nanocomposites (GPNCs) fundamental components, diverse preparation techniques, and a wide array of applications across various industries. It provides a detailed analysis of the environmental benefits these innovative materials offer, while also addressing their limitations. By synthesizing insights from materials science, nanotechnology, and sustainability studies, the review illustrates how GPNCs leverage renewable resources, such as biodegradable polymers and bio-based nanofillers, to significantly reduce the ecological footprint associated with conventional polymer products. Furthermore, it highlights recent breakthroughs in the field, outlining the persistent challenges that researchers and manufacturers face, as well as the promising future research directions that could lead to enhanced performance and wider adoption. This review serves as a crucial resource for guiding academic inquiries and informing industrial practices aimed at fostering a circular and sustainable materials economy.
2 Components of green polymer nanocomposites
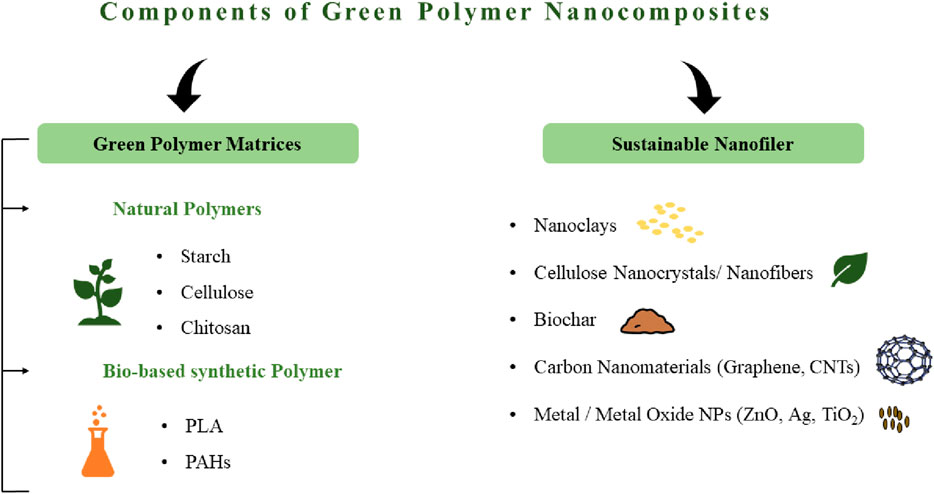
A green polymer nanocomposite mainly consists of a green polymer matrix and a sustainable nanofiller. An overview of these components is presented in Figure 1, followed by a detailed explanation in Sections 2.1 and 2.2.
2.1 Green polymer matrices
2.1.1 Natural polymers: biodegradable, abundant, renewable
Natural polymers are popular for green nanocomposites because they’re biodegradable, renewable, and eco-friendly. Sourced from plants, marine life, and microbes, they provide a sustainable alternative to petroleum plastics. Their use helps tackle plastic pollution, resource depletion, and waste problems (Rosli et al., 2021).
One of the most studied natural polymers is starch, a thermoplastic polysaccharide from wheat, potatoes, and corn, is an affordable, biodegradable matrix for biocomposites. However, its brittleness and sensitivity to water limit its mechanical performance, necessitating modification or blending with other materials for improved durability and resistance (Demirbaş, 2007).
Cellulose, the most abundant natural polymer of the Earth, is a linear plant biomass-derived polysaccharide. It is more resistant to mechanical stress, stiffness, and chemicals. It is biodegradable and renewable, but its crystallinity and limited solubility in common solvents make it challenging to process. Nevertheless, cellulose derivatives and nanocellulose materials such as cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) or nanofibers (CNFs) are increasingly being utilized as reinforcement for green polymer matrices (Mohanty et al., 2000).
Chitosan, derived from deacetylated chitin in crustacean shells, is biocompatible and antimicrobial, making it valuable in medicine and food packaging. However, its poor mechanical properties and water sensitivity require reinforcement or blending with other biodegradable polymers for enhanced performance (Pillai et al., 2009).
Alginate, a polysaccharide derived from the brown seaweed, is hydrophilic, gelling-forming, and biocompatible. Alginate is becoming more and more relevant to environmental and biomedical disciplines, especially drug delivery and wastewater treatment. As with chitosan and starch, alginate’s mechanical limitations have to be addressed by preparing composite materials (Rehm, 2009).
Though they have inherent disadvantages in the native state, such as poor mechanical toughness or sensitivity to moisture, these biopolymers are still a valuable foundation for green material design in an environmentally friendly way. With the incorporation of reinforcing nanofillers, their properties are significantly upgraded, which renders them suitable for high-performance and industrially relevant green polymer nanocomposites.
2.1.2 Bio-based synthetic polymers: derived from renewable sources, tunable properties
Synthetic biopolymers are valuable for green composite construction due to their flexibility and renewable origins. Engineered for specific properties, common types include polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), polybutylene succinate (PBS), and polycaprolactone (PCL). PLA, made from lactic acid via carbohydrate fermentation, is transparent and compostable but has issues with brittleness and barrier properties, often needing reinforcement for high-performance use (Pielichowska, 2022; Mahajan et al., 2023).
PHAs, particularly polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), are produced via microbial fermentation with microbes like Cupriavidus necator and Pseudomonas spp. They exhibit mechanical properties similar to polypropylene and are fully degradable, making them suitable for medical and packaging uses. However, high production costs hinder mass commercialization (Chen, 2003; Sudesh et al., 2000). Advances in bacterial strain optimization, substrate selection, and fermentation efficiency remain under investigation to maximize economic feasibility (Mahajan et al., 2023).
PBS, which is produced from succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, offers a fair balance between flexibility, biodegradability, and heat stability. Its inherent crystallinity of about 35% and break elongation make it highly suitable for food packaging applications, especially when nanofillers such as clays or cellulose nanocrystals are incorporated as reinforcement (Wong and Shanks, 2009; Heydari and Eghbalifam, 2022). Similarly, PCL, a biocompatible semi-crystalline aliphatic polyester, with its low melting point, slow degradation rate, and good miscibility with other polymers, is used in biomedical applications such as drug delivery and tissue engineering scaffolds (Hartley et al., 2022).
Nanocomposite technology can overcome the limitations of bio-based polymers, such as low mechanical strength and water sensitivity. By integrating nanoparticles (e.g., nanoclays, metal oxides), these materials gain enhanced thermal stability, barrier properties, and antimicrobial effectiveness, enabling innovative applications in packaging, construction, electronics, and medicine (Bari et al., 2016). In response to the worldwide transformation to a circular economy, bio-based synthetic polymers are critical in reducing dependence on fossil resources, greenhouse gas emissions, and the environmental compatibility of polymeric materials.
2.2 Sustainable nanofillers
2.2.1 Nanoclays
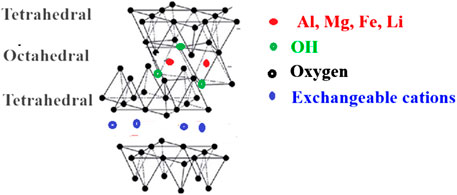
Nanoclays are powerful materials, layered aluminosilicates (Figure 2), that have been developed and utilized in numerous industrial applications (Undabeytia et al., 2021). They occur naturally in freshwater and can be synthesized. The tetrahedral silicate and octahedral aluminate arrangement allows for ion trapping, imparting unique mechanical, thermal, structural, barrier, and morphological properties (Jacquet et al., 2018).
A biodegradable and eco-friendly polymer is combined with nanoclay to produce polymer-nanoclay nanocomposites that possess remarkable thermal stability, UV resistance, diffusional barrier, and mechanical robustness (Kumar et al., 2022; Korukonda et al., 2024). Layered silicates are hydrophilic, making their interaction with polymer chains difficult. To enhance nanoclay hydrophobicity and form polymer nanocomposites, methods such as melt mixing, Sol-Gel, in situ polymerization, and solutions with surfactants or organic molecules are used (Rafiee and Shahzadi, 2019; Li et al., 2004; Polverejan et al., 2000).
Halloysite clay nanotubes was used as a natural reinforcement for polymers. Using methods like in situ polymerization and solution casting, they found that a 5% addition of halloysite enhanced composite adhesivity, increased polymer strength by 30%–70%, and introduced functions such as self-healing, antimicrobial properties, and flame retardance (Lvov and Abdullayev, 2013). Halloysite clay nanotubes were incorporated as a nanofiller into a polymer, and the resulting nanocomposite was used as sustained drug release and effective drug encapsulation due to the improvement in tensile strength, and elasticity (Liu et al., 2014). In another study, it was found that the addition of 7% of halloysite clay nanotubes to the polymer matrix improves the thermal stability, tensile strength, and elasticity (Gaaz et al., 2017).
An in situ polymerization process was used to create polymer nanoclay nanocomposites. Functionalized clay with tosyl groups was used to enhance the thermal stability of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)/clay nanocomposites (Ozkose et al., 2017). In another study fluorinated methacrylate/clay nanocomposite was synthesized and found that the they exhibits higher thermal stability, surface properties, and hydrophobicity, which are suitable for many applications, such as lithium batteries, fuel cells, and in automotive, textile, aerospace, and electronic, that use fluoropolymers (Karamane et al., 2017).
Intercalated polyaniline-clay nanocomposite (PANC) was synthesized using supercritical CO2 in a high-pressure reactor. It exhibits high conductivity and excellent thermal, mechanical, barrier, and anticorrosive properties, making it suitable for various applications (Abdelraheem et al., 2018).
A composite using bentonite clay as an adsorbent and Moringa oleifera as a coagulant was developed to remove heavy metals from water, demonstrating effective removal of cadmium, chromium, and lead (Ravikumar and Janardhanan, 2020). The solution intercalation method was developed to synthesize polymer/clay-based composites. The composite was found to display not only better thermal insulation, but also it be an eco-friendly insulator for the construction industry (Ghyati et al., 2022).
The main challenge with green polymer nanoclay nanocomposites is their biodegradability, despite enhancements from low nanofiller loading. However, they are used in tissue engineering, drug delivery, wound healing, and eco-friendly materials like packaging and membranes (Kausar et al., 2022b).
2.2.2 Cellulose nanocrystals/nanofibers
Cellulose is an abundant, renewable, and sustainable polymer, prized for its thermal stability, mechanical strength, biocompatibility, lightweight nature, eco-friendliness, and affordability (Jiwanti et al., 2022; Klemm et al., 2005). Nanocellulose (NC) consists of three types: cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), cellulose nanofiber (CNF), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) (Kumar et al., 2020). CNCs are highly crystalline, needle-shaped, with an average diameter of 3–35 nm, and a length of 100–1000 nm. CNFs wrapped up cellulose fibers, contain amorphous and crystalline forms, are flexible, and have a 10–100 nm diameter. BNCs have twisted ribbon-like fibers, with average diameters of 20–100 nm, lengths in micrometers, and are secreted by aerobic bacteria (Kumar et al., 2020). They possess significant properties like transparency, low thermal expansion coefficient, settled reinforcing potential, stability, and extraordinary Young’s modulus (Kim et al., 2015; Moon et al., 2011).
Extracting nanocellulose (NC) from natural resources is challenging due to strong hydrogen bonds in cellulose. It requires a multi-stage approach involving mechanical methods, chemical treatments, and processes like mechanical cleansing, disruption of water-soaked pulp with liquid nitrogen, and homogenization (Bhatnagar and Sain, 2005).
Kondo et al. (2014) developed a rapid novel method to break down the natural cellulose to cellulose nanofibers (CNF) via aqueous counter collision using only water without any chemical treatment, and they concluded that this method can also be applied to other polymeric materials with hierarchical structure (Kondo et al., 2014). CNC with a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) polymer in a poly (vinyl acetate) (PVAc) matrix showed a significant modulus increase, creating a versatile nanocomposite for biomedicine (Cudjoe et al., 2017).
The electrospinning method efficiently prepares CNC and CNF. Alvarado et al. created CNC-CNF with an antimicrobial agent, leading to improved thermal and mechanical properties for food packaging (Alvarado et al., 2018). Dutta et al. fabricated and characterized poly(ε-caprolactone)/cellulose nanocrystals-nanofibers derived from rice husk. The resulting nanocomposite showed that it can be a good replacement as a biomaterial for tissue engineering (Dutta et al., 2019). CNC and CNF were developed through electrospinning with cellulose acetate to evaluate their efficiency for the removal of methylene blue (MB). The adsorption capacity was found to be 50% by 1000 ppm of MB initial concentration, a double adsorption capacity compared to cellulose acetate (Khatri et al., 2024).
Different natural and microbial resources have been demonstrated to extract CNC and CNF, such as oil palm trunk (Lamaming et al., 2015), tomato peels (Jiang and Hsieh, 2015), chili leftovers (Nagalakshmaiah et al., 2016), sugarcane bagasse (El Achaby et al., 2017), sugar monomers converted to NC by the enzymes and proteins of bacteria (Moniri et al., 2017), wood and hemp biomass (Beluns et al., 2021), and lignocellulosic biomass (Saeed Qureshi et al., 2024).
In other research, CNC and CNF were developed with other materials for different applications. Hosseinpour et al. implemented multilayer membranes with CNC to enhance the performance of direct methanol fuel cells (Hosseinpour et al., 2019) different flexible functional groups were used on cellulose and CNC, then used to produce intelligent electronics (Zhao D. et al., 2021), dye adsorption (Rana, 2023), and CNC and CNF were maintained to enhance the recovery of crude oil (Rana et al., 2024).
The melt processing method, which is mostly applied for polymer-based CNCs, is a green method with no solvent needed (Dufresne, 2017; Ansar et al., 2024). Zhou et al. used the melt processing method to incorporate CNFs and corn starch to prepare a polymer-based CNF composite. The results showed that the composite gained better mechanical properties (Zhou et al., 2021).
A. A. Singh et al. developed a green approach for the preparation of polylactic acid and CNFs. They used an aqueous solvent of polyethylene oxide at the functionalization of CNFs, followed by extrusion with the solvent to get a significant enhancement in mechanical and chemical properties for different applications (Singh et al., 2020).
Many factors can affect the efficiency of utilization of CNC and CNF in different applications, such as charge distribution, ionic strength, rheology, nanocellulose shape, surface functionalization approach, additives, and post-treatment procedures, etc. (Rana et al., 2024). CNC and CNF have extraordinary applications in the industry, but still lack specific surface characterization, structural homogeneity, high preparation-functionalization costs, and need enhancement in adsorption capacity (Rana et al., 2024).
2.2.3 Carbon nanomaterials
Carbon materials, consisting of carbon atoms, are utilized in various technical fields due to their low density and high thermal conductivity. Naturally, carbon is found as coal and graphite in large quantities and as diamond in smaller amounts. Synthetic forms include cokes, carbon black, carbon fibers, and synthetic graphite. The discovery of the C60 molecule (fullerene) notably enhanced interest in carbon science (Khan et al., 2016).
In conjunction with the rapid development in nanoscience, a huge interest has emerged in nanocarbon materials (Kawamoto et al., 2017). Nanocarbon materials, such as fullerene, nanodiamond, graphene, graphite, and carbon nanotubes (CNTs), have been tested for numerous industrial, medical, and pharmaceutical applications due to their extraordinary mechanical, physical, chemical, and electrical properties (Jiwanti et al., 2022). Polymer-based carbon nanomaterials nanocomposites show superior enhancement in aspect ratio, thermal stability, flexibility, thermal conductivity, surface area, thermo-physical properties, tensile strength, tensile modulus, and mechanical properties (Zhang and Park, 2018; Shah et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2018; Tarfaoui et al., 2016). They were prepared by different procedures for various applications according to the type of nanocarbon and the polymer, such as ball milling, shear mixing, ultrasonication, extrusion, roll milling, calendaring, etc. (Abbasi et al., 2019). Y. Li and Ye discussed the enhancement of using polymer-based nanocarbon in lithium batteries; the flexibility of the polymer avoids the assembly of electrode materials, the nanocarbon framework offers a highly conductive medium of charge/discharge process for lithium ions, the polymer conductivity is considered a coating material of cathode or anode, and it is considered a protecting material of the battery (Li and Ye, 2018). Al-Saleh reviewed that using nanocarbon fillers in polymer composites significantly reduces the energy loss in energy storage systems due to the continuous conductivity framework in the polymer-based nanocarbon materials (Al-Saleh, 2019). Luceño Sánchez et al. used functionalized graphene oxide (GO) to be a powerful material in thermoelectric devices, solar energy tools, and flexible electronics (Luceño Sánchez et al., 2018). Other applications, which are based on the superior properties of polymer-based nanocarbons, were conducted, such as epoxy resins (Giovannelli et al., 2017), electronic devices (Zhang and Park, 2018), electric tools (Zhang and Park, 2018), antenna technology (Trukhanov et al., 2022), fire alarm applications (Xia et al., 2022), supercapacitors (Ding et al., 2019), aerospace applications (Kausar et al., 2023), organic solar cells (Gayathri Mohan et al., 2024), etc.
Extremely toxic and hazardous substances are used in modifying and preparing carbon nanomaterials. These include concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids, hydrazine, and organic solvents like DMF and NMP in chemical processes. Additionally, flammable or toxic gases such as methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and ammonia, along with metal catalysts like nickel and cobalt, are used in physical methods.
Carbon nanomaterials can be synthesized using green methods. One study synthesized carbon nanoparticles from tomato extract, precipitated and calcined at 60 °C under atmospheric pressure, the lowest reported temperature, advancing greener methods (Arízaga et al., 2022). Another created fluorescent nitrogen-enriched carbon nanoparticles (N-CNPs) from seaweed extract and ethylene diamine via hydrothermal treatment at 160 °C for 12.0 h (Singh et al., 2022). In addition, developing eco-friendly approaches to get the carbon nanomaterials and combine them with the polymers is a great challenge (Kawamoto et al., 2017). The green preparation of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) in a dispersion of graphene oxide (GO)/carbon nanotube (CNT) complexes to produce nanocomposite films significantly enhanced the Young’s modulus and the tensile strength due to the strong π-π surface interactions between CNTs and CMC polymer (Son and Park, 2018). X. Zhao et al. used tannic acid, which is eco-friendly, as a reducer in the synthesis of polyaniline/reduced graphite oxide (Zhao et al., 2019). Green polymer-nanocarbon nanocomposites have been synthesized in a green approach to be applied as supercapacitors (Kausar et al., 2022a). Mirzapour et al. developed a green and easy method to prepare epoxy/carbon-based nanoparticles nanocomposites. They did not use any harmful surfactants or solvents, and the resulting polymer-based nanocarbon nanocomposite gained a higher toughness, tensile strength, and modulus (Mirzapour et al., 2024).
Some drawbacks should be studied in the future. The agglomeration of nanocarbon materials among the layers occurs because of the resulting high surface area, which may weaken the connection between the nanocarbon materials and the polymer. Moreover, inadequate exfoliation and dispersion of graphite reduce its effectiveness as a filler and lead to tiny graphene sheets sliding past one another under applied loads in lightweight materials (Velmurugan et al., 2023; Lligadas et al., 2013; Tang et al., 2012).
2.2.4 Metal/metal oxide NPs
Polymer-based metals and metal oxides nanofillers have superior biocompatibility, low aggregation, and better dispersion compared to other polymer-based materials due to the great strength, toughness, and electrical conductivity (Khan et al., 2016). The insertion of metals, such as Ag, Ti, Si, Al, Zr, etc., or metal oxides such as TiO2, ZnO, and ZrO2, not only enhances the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties but also exhibits extra benefits like antimicrobial functions, drug-delivery carriers, and photocatalytic properties (Wang and Sun, 2021; Ding et al., 2019; Yadav et al., 2019; Melinte et al., 2019).
Different challenges arise with the use of metals and/or metal oxides as impeded or filler materials, including their metallurgical, chemical, environmental toxicity, and thermal properties (Rajendran et al., 2023). Green-synthesized ZnO-polymer was evaluated as a supercapacitor (Chakraborty et al., 2020). Cu-doped ZnO-based polymer nanocomposite was prepared via a novel green method, and then the prepared nanocomposite was evaluated in its efficiency as an antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory material (Al-Rajhi et al., 2022). Yao et al. discussed the main approaches for the synthesis of polymer-based metal/metal oxide materials, and then they illustrated their green method, polymer surface buckling-enabled exfoliation (PSBEE). Their method is cost-effective, simple, and eco-friendly (Yao et al., 2024).
Many metals and/or metal oxides were examined as polymer-metal/metal oxide-based nanocomposites for different purposes. Silver-based polymer was developed for antimicrobial coating for biomedical applications in different forms, such as hydrogels, multilayer structures, thin films, fibers, etc. (Dhiman et al., 2019). Copper-decorated graphene was used to improve the fireproof effectiveness of epoxy resin. The research showed that using Cu2+ gives a better efficiency due to its higher ability to oxidize carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide (Ye et al., 2019). TiO2-polymer was prepared, and its photoactivity was evaluated (Sadowski et al., 2019). For wound healing, silver was introduced to a natural polymer, such as polysaccharides, due to its availability and antimicrobial effects (Rahimi et al., 2020). The cold press method was developed to prepare the sugar palm fiber (SPF) hybrid with polyester (PET) yarn-reinforced epoxy composite, with the addition of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) at different doses. The results showed that the higher the Mg(OH)2 dose, the higher the fire retardant of the composite, and the other evaluated physical properties results confirmed that the prepared magnesium oxide polymer is suitable for other applications, such as the aerospace industry, automotive tools, and building products (Suriani et al., 2021). Thin-film nanocomposites and thin-film membranes were prepared by the vapor-phase interfacial polymerization method by using TiO2 nanoparticles as nanofillers to remove heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions (Karki and Ingole, 2022).
Polymer-based-metal/metal oxide nanocomposites have a great interest due to their wide applications in all fields. However, challenges related to these nanocomposites, such as long-term stability, cytotoxicity, and immune response, which require systematic enhancement studies in the synthesis approaches, functionalization of the surface, and biocompatibility evaluation (Harun-Ur-Rashid et al., 2025).
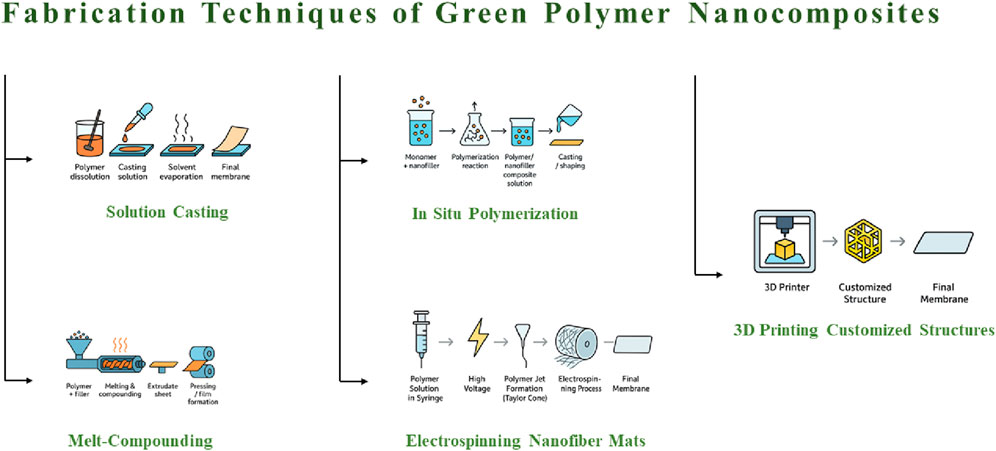
3 Fabrication techniques for GPNCs
Different methods are used to prepare GPNCs. Figure 3 summarizes fabrication techniques, with detailed descriptions in the following sections.
3.1 Solution casting
The solution casting method operates based on Stokes’ law. In this approach, the polymer and prepolymer are uniformly mixed and dissolved in a suitable solvent. The polymer, serving as the matrix phase, dissolves readily in the chosen solvent, while the nanoparticles are dispersed either in the same solvent or a separate one. Ultimately, both components are combined to form a homogeneous mixture. It is one of the most commonly used methods in our research on mixed matrix membranes for water treatment (Abu-Zurayk et al., 2025b; Abu-Zurayk et al., 2025a; Abu-Zurayk et al., 2024; Alnairat et al., 2021).
Solution casting is a technique for fabricating polymer blends by dissolving polymers in a solvent, then casting films and removing the solvent through drying. This method is suitable for small-scale production and depends on solvent selection and its interaction with the polymers. In composite membranes, micro-stirring or ultrasonic treatment is often used to ensure uniform dispersion of polymer composites and nanomaterials in the solution (Rehghunadhan et al., 2024; Deshmukh et al., 2023). The resulting films are then dried in a hot-air oven for 12–24 h or more, depending on the composition. As the solvent evaporates, thin composite membranes are formed, consisting of a polymer matrix integrated with nanomaterials (Rhim et al., 2006). Alternatively, the phase inversion technique can be used to transform the casting solution into a solid membrane (Reuvers and Smolders, 1987). It is one of the most widely employed methods for fabricating porous polymer membranes with well-defined structural morphology (Marchese et al., 2003).
3.1.1 Lab-friendly
Solution casting of polymers can be made more lab-friendly and environmentally sustainable by using bio-based polymers (Pielichowska et al., 2024). Selecting polymers from renewable sources like cellulose or starch, and using greener solvents such as water or low-toxicity alternatives, significantly improves the process. Implementing solvent recovery and reuse further minimizes waste and promotes sustainability (Cai et al., 2025). Adopting sustainable processing techniques (Gupta et al., 2022) and enhancing biodegradability through the incorporation of biodegradable additives (Cai et al., 2025) or the use of biodegradable composites (Cai et al., 2025) further supports this green approach. Overall, this strategy focuses on utilizing renewable materials, reducing hazardous substances, and improving the end-of-life performance of polymer products (Pielichowska et al., 2024).
3.1.2 Good dispersion
Solution casting is an effective method for achieving uniform dispersion of polymers and nanoparticles by ensuring a homogeneous distribution of all components in the final film or material. This method begins with selecting a suitable solvent capable of dissolving both the polymer and the nanoparticles (Jouault et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2021; Senthilkumar et al., 2018; Deshmukh et al., 2023) a step critical to achieving uniform distribution. Various mixing techniques, such as magnetic stirring, ultrasonication, or high-shear mixing, are employed to disperse nanoparticles thoroughly within the polymer solution (Senthilkumar et al., 2018; Wypych, 2016). Co-dissolving the components in a single solvent, especially when coupled with controlled precipitation and drying, further improves the dispersion quality (Jouault et al., 2014). The method enhances homogeneous mixing and reduces nanoparticle aggregation during film formation, especially when drying conditions are carefully controlled (Jouault et al., 2014; Senthilkumar et al., 2018; Deshmukh et al., 2023). Additional strategies, such as polymer adsorption onto nanoparticle surfaces, introduce steric stabilization that further prevents aggregation (Kim et al., 2021). In general, when each step of solution preparation, mixing, casting, and drying is carefully adjusted, solution casting becomes an effective technique for manufacturing well-dispersed, high-performance polymer nanoparticle composites.
Effective fiber dispersion within a polymer matrix is also essential for achieving good interfacial bonding, which significantly enhances the mechanical performance of composites. This dispersion is influenced by factors such as fiber length. Whether short or long, and processing conditions like pressure and temperature (Pickering et al., 2016; Semlali Aouragh Hassani et al., 2019).
3.1.3 Limited scalability
Solution casting is a practical and widely used technique for preparing polymer-based materials at the laboratory scale, where specific control over composition and nanoparticle dispersion is essential. Despite its advantages in lab-scale research settings, this method faces major obstacles when scaled up. It depends on large amounts of solvent, which require advanced and costly recovery systems to minimize waste and emissions (Griffin et al., 2022; Felton, 2013; Rehghunadhan et al., 2024). The evaporation process is inherently slow, limiting rates of production and extending processing durations (Rehghunadhan et al., 2024). As the production scale increases, achieving consistent film quality becomes more challenging, with a higher risk of defects like cracking or uneven thickness (Griffin et al., 2022; Rehghunadhan et al., 2024; Yao et al., 2019; Abdelhamed et al., 2025). Additionally, the use of hazardous or volatile solvents introduces environmental concerns and strict regulatory requirements that complicate industrial implementation (Griffin et al., 2022; Felton, 2013; Rehghunadhan et al., 2024; Hendeniya et al., 2023). Lastly, because solution casting is a batch-based technique, it does not readily align with the continuous, automated processes typically favored in large-scale manufacturing environments.
In summary, solution casting is a common technique for lab-scale synthesis of GPNCs, offering simplicity and uniform dispersion of bio-based polymers and nanomaterials. However, its scalability is hindered by high solvent use, slow processing rates, and environmental concerns, highlighting the need for greener, more effective fabrication methods for sustainable nanocomposites.
3.2 Melt compounding
Melt compounding, also known as melt blending, is a straightforward and commonly applied technique in polymer synthesis, particularly effective for integrating nanomaterials into a viscous polymer melt (Kausar, 2021a). Its advantages include preventing filler re-aggregation, eliminating the need for chemical surface modifications, and enabling immediate filler dispersion. This eco-friendly method is suitable for large-scale production of polymer nanocomposites and integrates well into industrial processes (Kausar, 2021a; Diez-Pascual, 2022).
Melt compounding is an eco-friendly and cost-effective method for creating composites from insoluble thermoplastic polymers. Polymer pellets are melted and mixed with additives under shear forces for uniform dispersion, then cooled to solidify. This widely used approach is effective for adding functional fillers to a viscous polymer matrix (Kausar, 2021a; Ali Z. et al., 2024). This technique is considered green because it uses molten polymers and nanofillers instead of toxic solvents, minimizing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and making it suitable for eco-friendly, industrial-scale production (Tanahashi, 2010; Li et al., 2010; Bhawal et al., 2019).
3.2.1 Industrial scalability
Melt compounding is widely recognized as the most industrially scalable method for producing polymer nanocomposites, providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly route for large-scale manufacturing. Its continuous processing capability and lack of solvents make it especially attractive to industry, ensuring compatibility with existing extrusion and compounding equipment. Although challenges occur at high filler loadings, where increased melt viscosity complicates processing (Khan et al., 2020), these issues can be addressed through careful adjustment of twin-screw parameters, optimized screw design, or the addition of compatibilizers. Importantly, the scalability of melt compounding makes it the preferred method for creating polymer nanocomposites that aim to improve multifunctional properties without sacrificing mechanical performance (Alvaredo-Atienza et al., 2020).
3.2.2 Limited dispersion
Getting appropriate nanofiller dispersion and minimizing thermal degradation through processing continues to be challenging in melt compounding. Various approaches, including surface modification of nanofillers and reactive melt mixing, are being investigated to enhance the scalability and performance of melt-compounded green polymer nanocomposites (Vidakis et al., 2024; Tran et al., 2025; Sessini et al., 2020). Moreover, the intense shear forces generated during melt compounding promote uniform dispersion of nanofillers within the polymer matrix, effectively fragmenting agglomerates into well-distributed, smaller domains (Wang et al., 2020; Meng et al., 2014; Darwish et al., 2022; Bachs-Herrera et al., 2021; Prataviera et al., 2021; Brandenburg et al., 2017). One of the advantages of melt compounding enables in-situ nanoparticle synthesis, which can enhance the dispersion and properties of the final nanocomposite (Vidakis et al., 2024; Cailloux et al., 2019).
3.3 In situ polymerization
In situ polymerization is a synthesis method in polymer chemistry conducted within the polymerization mixture, resulting in polymer nanocomposites with nanoparticles. It generates unstable oligomers for various applications and consists of an initiation step followed by polymerization reactions, forming a hybrid structure of polymer chains integrated with nanoparticles (Talreja, 2023). This was applied (Abu-Dalo et al., 2023), using interfacial polymerization to create ultra-thin, defect-free selective layers, improving membrane performance for water treatment.
3.3.1 Superior nanoparticle dispersion
In situ polymerization disperses nanomaterials in a liquid monomer with an initiator or catalyst to form nanocomposites. Low molecular weight monomers disperse via sonication, then polymerization is triggered by heat or organic initiators through chain transfer, radical, anionic, or ring-opening metathesis processes in the nanomaterial layers. This allows small monomers to intercalate, resulting in high nanomaterial loading, dispersibility, and compatibility. Filtering produces a nanocomposite with attached polymer molecules, enabling the creation of diverse nanostructures with high quality and improved chemical properties (Manopriya and Hareesh, 2021; Gao, 2012).
3.3.2 Enhanced interfacial adhesion
Nanoparticles generated in situ tend to nucleate on the growing polymer chains, resulting in strong adhesion and a high degree of compatibility between the filler and the matrix by promoting direct interactions. This improvement results from covalent grafting of polymer chains onto fillers, formation of interfacial crystallization zones for mechanical interlocking, and the development of chemical bonds that strengthen the polymer-filler interface (Ning et al., 2012; Ding et al., 2004; Tan et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2020; Bailly et al., 2010).
3.3.3 Health and environmental concerns
While in situ polymerization can yield nanocomposites with enhanced uniformity and strong interfacial bonding, the monomers involved are often hazardous chemicals that can be toxic, volatile, and environmentally persistent (Zotti et al., 2022). Furthermore, complete polymerization is rarely achieved, leaving residual unreacted monomers in the final product that may leach out during use or disposal. These residual monomers, including styrene, acrylonitrile, and vinyl chloride, are known for their carcinogenic, mutagenic, and ecotoxic effects, posing serious health and environmental risks (Lithner et al., 2011; Araujo et al., 2002). Such issues not only hinder the environmental sustainability of the process but also pose challenges for regulatory approval and large-scale implementation application.
3.4 Advanced methods
3.4.1 Electrospinning
Electrospinning is a technique that uses a high-voltage electric field to produce ultrafine fibers from a polymer solution or melt. This broad definition encompasses the diverse range of submicron-diameter fibers typically generated through the process (Subbiah et al., 2005). A polymer is dissolved in a volatile solvent and extruded from a syringe at a steady rate. An electrostatic force causes charge separation within the liquid, resulting in a charged polymer droplet forming at the tip of the needle (Subbiah et al., 2005; Xue et al., 2019). Electrospun nanofiber membranes offer key advantages such as high porosity, tunable pore size, and extremely fine fiber diameters, making them a promising platform for innovative developments in medical protective equipment (Vitchuli et al., 2011). Recently, an increasing number of biomedical products made from electrospun nanofibers have received approval for clinical use (Li et al., 2019). The combination of high surface area and controllable porosity makes these mats ideal for tissue engineering (Jiang et al., 2015), controlled drug release (Luraghi et al., 2021), and high-efficiency air filtration (Arefin et al., 2021).
3.4.2 3D printing
Polymer 3D printing represents an emerging technology that is rapidly transitioning from research to industrial applications, especially in the medical sector. This manufacturing approach offers distinct advantages, including cost-effective production of functional components with customizable properties and capabilities (Arefin et al., 2021).
3D printing enables the fabrication of highly customized and functional structures by allowing the integration of complex geometries and internal architectures that are challenging to produce using conventional manufacturing techniques (Liu and Wang, 2020; Ligon et al., 2017; Anwajler et al., 2024; Forward and Kim, 2023; Pugliese et al., 2021). This technology supports the use of multiple materials within a single build, enabling the creation of components with tailored mechanical properties, such as graded stiffness or flexibility (Liu and Wang, 2020; Ligon et al., 2017; Pugliese et al., 2021; Bandyopadhyay and Heer, 2018). Moreover, functional additives like sensors or catalysts can be directly embedded into the polymer matrix during the printing process, expanding the application range of printed materials across advanced fields such as smart devices and responsive systems (Liu and Wang, 2020; Rossi et al., 2017; Ambrosi and Pumera, 2018; Islam and Zeng, 2024).
3D printing offers a powerful approach for achieving precise filler distribution in polymer composites by enabling controlled deposition of both the polymer matrix and filler materials (Arora et al., 2024; Bernagozzi et al., 2024; Rooney et al., 2024; Markandan and Lai, 2023; Xu W. et al., 2021). Advanced techniques like material extrusion, vat polymerization, and powder bed fusion enable selective placement of materials at micro- and nanoscale resolutions. Design strategies such as hierarchical material distribution optimize component placement to enhance mechanical and functional performance (Arefin et al., 2021; Xu W. et al., 2021). Additionally, the properties of the printing materials, such as ink or filament viscosity, droplet velocity in inkjet printing, and substrate surface energy, significantly influence filler dispersion (Bekas et al., 2019). Post-processing methods, including post-curing, sintering, and surface treatments, can also be employed to refine filler alignment and distribution (Arora et al., 2024; Bekas et al., 2019; Bănică et al., 2024).
4 Enhanced properties of GPNCs
Green Polymer Nanocomposites (GPNCs) provide an important combination that enhances material’s functionality, innovation, and its environmental protective ability (Kausar, 2021b). Incorporating nanomaterials like cellulose nanocrystals, graphene oxide, or metal oxides into bio-based polymers allows GPNCs to outperform conventional biopolymers (Musa et al., 2025). These enhancements improve material characteristics such as mechanical durability, thermal stability, barrier resistance, and functional responsiveness, all while maintaining biodegradability (Zhang et al., 2019). For example, incorporation with nanofillers not only increases tensile stiffness and strength but also enhance toughness, stability, and resistance, thereby expanding the applications of sustainable polymers (Jagadeesh et al., 2021). Beyond structural reinforcement, GPNCs exhibit multi-functionality, setting them as promising materials for next-generation technologies (Losetty et al., 2025). Also it owns many advanced properties such as antimicrobial activity, photocatalytic activity, UV protection, and electrical conduction, GPNCs play an efficient role in smart packaging, biomedical devices and bioremediation (Singh et al., 2025). At the same time, GPNCs contribute in reducing environmental impacts through improving gas and vapor barrier properties copper (Peretz Damari et al., 2019; Alsoud et al., 2024), enhancing thermal degradation thresholds (Guan et al., 2018), and lowering energy processing hallmarks (Liu and Yabu, 2024). These collaborative enhancements spot GPNCs’ role in bridging high-performance material design with the urgent demand for eco-conscious industrial practices, signaling their pivotal role in advancing the circular bio-economy (Clement et al., 2025).
4.1 Mechanical properties
Green polymer nanocomposites (GPNCs) represent a transformative class of materials in which nanoscale reinforcements are distributed within bio-based polymer or biodegradable matrices to significantly improve mechanical behavior (Velmurugan et al., 2023). Embedding of nanofillers such as carbon-based nanomaterials, nanoclays, or cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), will enhance material’s load-bearing capacity through increasing interfacial surface area and mechanical interconnection (Rashid et al., 2024). Polymer chain mobility restriction, and stress transfer facilitation due to these nanofillers will result in enhancing tensile strength and stiffness (Chan et al., 2021). For instance, Improvement for more than 22.3% and 64.17%, was achieved in tensile strength and modulus respectively for 1 wt% CNC-reinforced PLA compared to neat PLA (Trivedi and Gupta, 2025).
Stiffness enhancement is particularly obvious when using high-aspect-ratio fibers or layered silicates in glass fiber reinforced composites (GFRP) fabrication (Daud et al., 2009). These nanofillers create interconnected networks uniformly distribute stress throughout the matrix (Lin et al., 2019)
In a study using montmorillonite (MMT) with potato starch, to produce nanocomposite film used in food packaging and drug delivery systems it exhibited more than double the elastic modulus, and indicate effective reinforcement at minimal nanofiller loadings (Oleyaei et al., 2016). Furthermore, surface functionalization of nanofillers, such as grafting with compatible groups, boost interfacial adhesion, which amplifies mechanical integrity (Kumar et al., 2025). Another study developed biodegradable polymer blend (PLA-co-polyester) nanocomposites using carvacrol as an antimicrobial agent and nanoclay as a filler. Four blown film samples were created: BF (no fillers), BF-C (5wt% carvacrol), BF-D (5wt% nanoclay), and BF-C-D (5wt% of both). This hybrid loading improved mechanical properties, resulting in increases of up to +70% in elastic modulus and +200% in elongation at break, as shown in Figure 4 (Scaffaro et al., 2020).
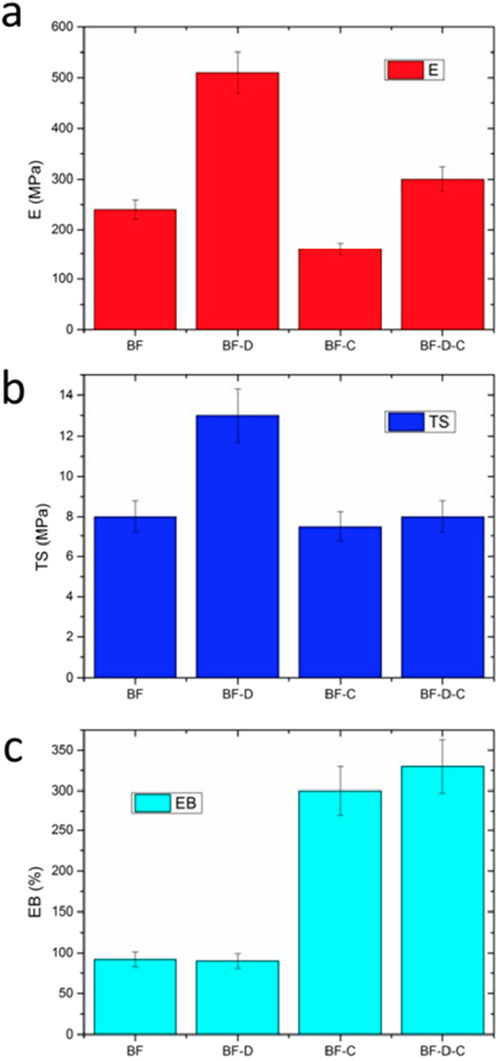
Figure 4. (a) Elastic modulus (E), (b) tensile strength (TS), and (c) elongation at break (EB) of each the four samples investigated (Scaffaro et al., 2020).
Toughness, a critical property for impact resistance, is also significantly improved in GPNCs (Zhang et al., 2024; Cui et al., 2022). Polymers like PLA are fragile in nature, the addition of flexible nanofillers such as cellulose nanofibers or graphene oxide (GO) provide energy dissipation mechanisms that prevent crack propagation (Musa et al., 2025). These fillers act as crack preventers, which increase the energy required for fracture. Moreover, hybrid nanofillers, combining organics and inorganics, have been shown to enhance both stiffness and toughness (Mousavi et al., 2022).
GPNCs are mechanically improved not only in tensile or impact strength but also extended to fatigue resistance and dimensional stability (Zhang et al., 2024; Mukhopadhyay and Mishra, 2024). Under frequent loading or long-term mechanical stress, nanocomposites show infiltration reduction and durability enhancement due to nanofiller’s restriction effect on polymer chain movement (Das et al., 2021). This makes GPNCs ideal for use in long lasting goods, medical implants, and structural applications where longevity is essential (Kumar et al., 2024).
GPNCs offer a promising alternative to conventional composites by enhancing mechanical properties. With careful design of nanofiller morphology, concentration, and interfacial compatibility, they can meet mechanical demands while ensuring biodegradability and environmental compliance (Kumar et al., 2024).
4.2 Thermal properties
A remarkable improvement of GPNCs thermal behavior achieved by nanofiller incorporation, which changes the heat flow and degradation kinetics of the polymer matrix (Sahu et al., 2023). One of the most noticeable enhancements is the increment in thermal degradation temperature (Feng et al., 2014). Graphene, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and nanoclays as examples on nanofillers act as thermal barriers that obstruct the movement of degradation byproducts, thereby delaying the decomposition emerging (Kausar, 2020). Also cold crystallization of PLA reinforced with exfoliated montmorillonite (MMT) has been delayed to a higher temperature compared with the one of pure PLA (Piekarska et al., 2015). Nanofillers nucleating ability is the reason behind the cold-crystallization behavior of the hybrid nanocomposites, this prove that materials thermal stability has been improved when using exfoliated MMT (Piekarska et al., 2015; Cailloux et al., 2016), also the polymer matrix properties (mechanical, barrier, thermal stability and flame retardancy) can be considerably enhanced by well-exfoliation and well-dispersion of 2D single- or few-layer nanosheets (Cailloux et al., 2016). Formation of tortuous diffusion pathways within the polymer is one reason behind the thermal resistance of GPNCs matrix (Wei et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022). These pathways obstruct volatile degradation products from escaping, thereby increasing thermal stability (Borucka et al., 2019). In addition, fillers well-dispersion will improve char formation during thermal decomposition, which contributes to flame retardancy and heat shielding (Wang Z. et al., 2023). This is mainly valuable for packaging and electronic casing applications where thermal protection is essential (Wang Z. et al., 2023; Wang X. et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2021).
A study on the green synthesis of new bionanocomposites made of starch, chitosan, and graphene oxide (GO) found that GO influences the thermal resistance of the composite films. However, this effect is only significant at the highest GO concentration as seen in Figure 5 (Krystyjan et al., 2021).
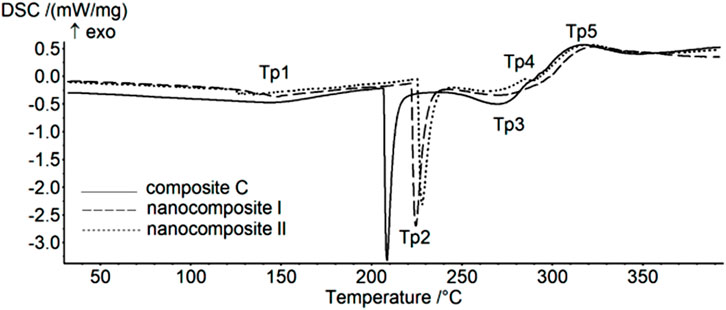
Figure 5. DSC curves of composite and nanocomposites (Krystyjan et al., 2021).
Nanofillers improve the thermal conductivity of GPNCs. Adding conductive materials like graphene or CNTs enhances the thermal transport of bio-based polymers (Liu et al., 2024). This allows GPNCs to be engineered either for insulation or for efficient heat dissipation depending on the application—ranging from thermal packaging to heat sinks in green electronics (Chen et al., 2025).
Thermal dimensional stability is another critical attribute enhanced in GPNCs. Reinforced composites exhibit lower coefficients of thermal expansion, minimizing deformation under temperature fluctuations (Madhu, 2025). This is vital in applications such as automotive interiors or outdoor construction materials where temperature variability is significant (Madhu, 2025; Eliza et al., 2025). Ultimately, the improved thermal behavior of GPNCs contributes to their performance and safety in high-temperature environments (Eliza et al., 2025). Through nanofiller selection and processing techniques, it is possible to finely tune thermal degradation profiles and thermal conductivity, ensuring the composites can meet the rigorous demands of modern sustainable industries (Musa et al., 2025; Jagadeesh et al., 2021).
4.3 Barrier properties
GPNCs provide significant advances in barrier properties, particularly in the reduction of gases and vapors permeability through polymer films (Losetty et al., 2025). The insertion of nanofillers like nanoclays, layered silicates, and graphene oxide creates a highly tortuous pathway that disrupts the diffusion of small gas molecules like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor (Kumar et al., 2025). This is known as the tortuosity effect, and it plays a central role in enhancing packaging materials barrier performance (Edo et al., 2025).
The incorporation of nanoparticles (silver, zinc oxide, and titanium dioxide) with Nano-films composed from biocompatible biopolymers like chitosan, cellulose, and alginate often form a protective, semipermeable barrier that regulates both moisture and gas exchange, slows respiration rates, and reduces microbial growth on product surfaces (Janeni and Adassooriya, 2021). In food packaging, regulation of moisture and gas exchange are major factors affecting shelf life (Sharma et al., 2025).
Likewise, CNCs integrated into chitosan or cellulose matrices have reduced moisture vapor transmission by forming hydrogen-bonded networks that restrict molecular mobility. These features make GPNCs promising alternatives to synthetic multilayer films (Marquis et al., 2011).
Induction of nanofiller nucleation stands behind barrier improvement through enhancing polymer crystallinity, which leads to denser polymer structure, thus reducing free volume and molecular transport (Singha and Hedenqvist, 2020). GPNCs maintain their barrier integrity even under mechanical stress (Tripathi et al., 2020). Under flexing, conventional films will form microcracks unlike nanocomposites which exhibit resilience due to nanofiller’s reinforcing effect, which prevent crack propagation and preserve film continuity (Hassan et al., 2021; Das et al., 2021; Zanoaga and Tanasa, 2016). This is critical for flexible packaging, wearable electronics, food industries and other dynamic applications (Kausar, 2020; Liu et al., 2019).
In conclusion, GPNCs provide multifunctional barrier solutions that utilize both physical and chemical mechanisms to block gas and vapor transmission. These improvements come in accordance with global efforts to reduce food waste and material use, providing sustainable high-performance alternatives in all sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and others.
4.4 Functional properties
GPNCs are distinguished by their structural performance and also by their ability to exhibit advanced functional properties (Barbaros et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2022). One of those functions is their antimicrobial activity, which is applicable in food packaging, medical devices, and wound healing applications (Deng et al., 2022; Shineh et al., 2023). Biopolymers incorporated with nanoparticles like silver (Ag), copper oxide (CuO) or zinc oxide (ZnO) exhibit bactericidal effects through microbial cell wall disruption and reactive oxygen species generation (Guan et al., 2021; Vieira et al., 2022; Abuamr et al., 2024) anaerobic. For instance, Chitosan/ZnO nanocomposites have strong inhibition activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (Ali S. et al., 2024; Youssef and El-Sayed, 2018; Alkhrissat and Matarneh, 2025). Furthermore, a CS-functionalized iron (II) oxide nanocomposite (CS/FeO NC) was synthesized using Sida acuta leaf extract through a simple, eco-friendly green chemistry method. The nanocomposite demonstrated notable bactericidal activity against pathogens such as Escherichia coli, B. subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus (Figure 6) (Bharathi et al., 2022).
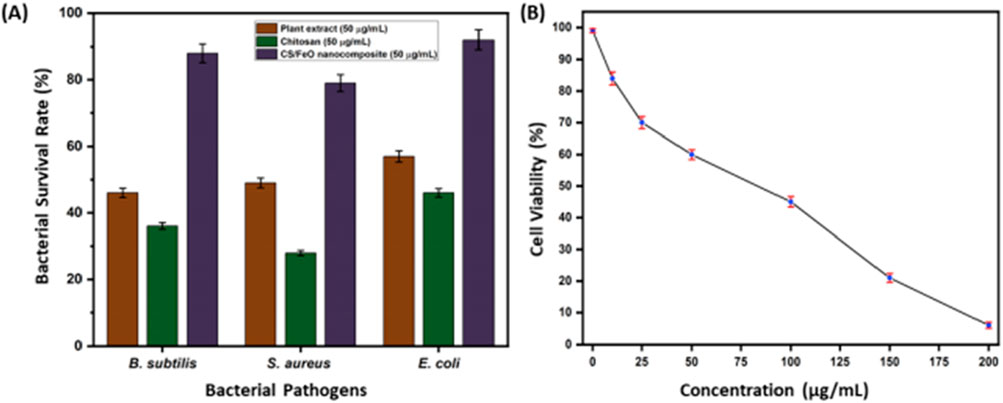
Figure 6. (A) Antibacterial activity of against B. subtilis, S. aureus, and E. coli. (B) In vitro antiproliferative activity of nanocomposite against A549 cells (Bharathi et al., 2022).
UV shielding is another functional property acquired through the inclusion of nanofillers such as TiO2, GO, or ZnO (Muzata et al., 2023; Cazan et al., 2021). Incorporation of NPs with polymers have shown an outstanding photostability especially UV stabilization effect via different mechanisms like absorption, reflection, scattering, and radicals scavenging, which prevent the polymer’s photodegradation and enhance its application in various fields, particularly in packaging, which result in extending the functional lifespan of products exposed to sunlight (Anwer et al., 2024). Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) is considered the most promising biobased substitute for fossil-derived polymers due to its good thermomechanical properties, biocompatibility, compostability, and renewability (Morais et al., 2024; Bikiaris et al., 2023). Incorporation of PLA with Graphene oxide has shown significant UV-blocking capability while maintaining transparency, an ideal property for cosmetic and pharmaceutical packaging (Bikiaris et al., 2023).
Embedding of conductive nanofillers like carbon nanotubes or graphene in GPNCs will enhance their electrical conductivity (Salari et al., 2023; Kausar and Taherian, 2019; Bilisik and Akter, 2022). These nanofillers create conductive networks within the polymer, enabling its applications in sensors, flexible electronics, and antistatic packaging (Lin et al., 2023; Shahid et al., 2025). The percolation threshold of these systems is often low, allowing for high conductivity without affecting their mechanical or environmental performance (Munawar and Schubert, 2021; Marsden et al., 2018).
Photocatalytic degradation is another promising property of GPNCs, which is considered as a powerful and sustainable method for environmental pollutants elimination, especially organic contaminants in both water and air (Gamelas et al., 2023). This process involves the light excitation (UV or visible) of a semiconductor photocatalyst (TiO2, ZnO, etc.) which results in the generation of electron-hole pairs (Tuama et al., 2024). The reaction of these charge carriers with oxygen and water molecules will form reactive oxygen species (ROS) like (hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and superoxide anions (•O2 −)), which begin the oxidative degradation of pollutants into nontoxic end-products such as CO2 and H2O (Mohd and Khan, 2024). Green polymer nanocomposites integrated with nanofillers (e.g., TiO2, ZnO, g-C3N4, or doped metal oxides…) chosen based on their high surface area, light absorption capacity, and photocatalytic efficiency (Mahesh et al., 2025). The synergy between the polymer matrix and the photocatalyst is key to enhance GPNCs performance (Gaddam et al., 2020; Li et al., 2025), TiO2 nanoparticles have remarkable photocatalytic activity; they break down organic pollutants under both UV and visible light (Amin et al., 2025).
The incorporation of functional groups (e.g., amine or hydroxyl groups from the polymer) can further enhance the adsorption of target molecules, providing a dual-function system where pollutants are both captured and degraded efficiently (Song et al., 2024). For instance, magnesium aluminide layered double hydroxide (MgAl LDH)- Chitosan/Serpentine nanocomposites have demonstrated as a promising, cost-effective and sustainable adsorbent for degradation of Methylene blue (MB) as a cationic dye and pharmaceutical residues from industrial water (Gamal et al., 2025).
5 Industrial applications
5.1 Packaging
When food is not consumed immediately after production, it must be protected in a package that serves several functions, such as protecting the food from dirt or dust, oxygen, light, pathogenic microorganisms, and moisture. The packaging must also be safe during conditions of use, cheap, light, inert, easy to dispose of or reuse, able to withstand different conditions during processing, storage, and transport (Duncan, 2011). Food packaging includes everything that surrounds or holds food, including boxes, bags, straws, plates, cups, and wraps (Hussaini et al., 2025). The shelf life of fruits and vegetables is short due to molding and decay during transportation and storage, leading to spoilage. Current food packaging trends focus on extending shelf life to improve food quality and safety.
Common polymers for food packaging include polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polystyrene (PS), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). However, these materials have drawbacks, such as gas permeability and non-biodegradability (Duncan, 2011).
To meet the demand for environmental safety, research is focused on biodegradable food packaging materials. While these eco-friendly green polymers support ecosystem health, they typically have poor barrier and mechanical properties, leading to a short shelf life. However, studies show that incorporating additives and fillers can enhance these characteristics, improving the packaging’s overall performance (El-Sayed and Youssef, 2023; Tabassum et al., 2024). Due to their instinctive eco-friendliness, biodegradable green polymer reinforced composites have become increasingly popular and have a lower carbon footprint. Some examples of natural and biodegradable polymers matrix used for packaging are cellulose, starch, chitosan, collagen, gelatin, and xanthan gum, and Poly (lactic acid) (El-Sayed and Youssef, 2023; Bikiaris et al., 2023).
Poly (lactic acid) (PLA), the most commonly used biopolymer in comparison with other biopolymers, due to its easy processability and rigidity. It is a thermoplastic biopolymer produced by fermentation of different foods rich in carbohydrates, such as corn, potato, sugar beet, or sugar cane (Bikiaris et al., 2023; Robledo-Ortíz et al., 2019).
Another highly promising alternative biopolymer for petroleum-based polymers is Nanocellulose (NC). Nanocellulose is prepared by breaking down cellulose fibers to less than 100 nm in diameter, with length in micrometer. It is a highly promising biopolymer due to its superior mechanical properties (strength 2–3 GPa), low density (1.6 g cm-3), high specific surface area (200–300 m2g-1), biodegradability, renewability, eco-friendliness, nontoxicity, and low thermal expansion coefficient (1 ppm K−1) (Trache et al., 2020; Xu T. et al., 2021). Different structures of NC have been used in food packaging applications, such as cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), cellulose nanofibrils (CNFBs), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) (Bikiaris et al., 2023). Currently, different research has investigated NC as a reinforcing agent for various biopolymers, such as PLA, for the preparation of GPNCs.
Nanoclay is vital in the packaging industry for enhancing the mechanical properties of biopolymer-based materials. When added to injection-grade poly(lactic acid) (PLA), 1.44P, 1.34 MN, and Cloisite 15A nanoclays improved tensile and flexural modulus. Notably, 5 wt% of 1.44P nanoclay significantly increased impact strength compared to the other nanoclays and pure PLA (Robledo-Ortíz et al., 2019).
Trifol et al. (2016) reduced the oxygen transmission rate by up to 90% using nanoclay (Cloisite C30B) and nanocellulose in a Poly (lactic acid) matrix. Their PLA/CNF/C30B nanocomposite also lowered water vapor transmission by 76% and enhanced thermomechanical resistance compared to standard PLA films, resulting in better protection and extended shelf life for packaged goods (Trifol et al., 2016).
Hasan et al. (2024) developed chitosan nanoparticle-based bio-nanocomposite films with different concentrations of butterfly pea extract (0%, 5%, 10%, and 15%) for sustainable packaging. The addition of 15% anthocyanin enhanced UV barrier properties and antioxidant activity but slightly increased water vapor permeability, with minimal change in water uptake compared to pure chitosan (Hasan et al., 2024).
Faraj et al. (2022) explored the gas barrier properties of polylactide/cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) nanocomposites, examining concentrations ranging from 5 to 50 wt%. They found that modifying CNC with various functionalities enhances the interaction with PLA, resulting in improved homogeneity and dispersibility. All PLA/CNC combinations displayed superior oxygen transmission compared to pure PLA, showing no significant preference for the modified or unmodified CNC. This research opens up promising possibilities for advancing materials with enhanced barrier properties (Faraj et al., 2022).
A study examined the incorporation of surfactant-modified cellulose nanocrystals (s-CNC) and silver (Ag) nanoparticles into a polylactic acid (PLA) matrix. The addition of Ag nanoparticles significantly improved the antibacterial properties of the ternary PLA/s-CNC + Ag nanocomposite compared to the PLA/s-CNC composite. This enhancement makes the system suitable for food packaging and sanitary applications that require a sustained antibacterial effect (Fortunati et al., 2012).
Other researchers have studied the influence of Nanocellulose ratio on the barrier properties, they found that cellulose nanospheres, nanocrystals (CNCs) significantly enhanced barrier properties. While cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) provided the highest mechanical strength, achieving a 350% increase in Young’s modulus due to their higher aspect ratio and percolating network (Islam et al., 2025).
5.2 Automotive and aerospace
Green biopolymer nanocomposites are popular in automotive and aerospace for their sustainability and performance. They serve as lightweight alternatives to plastics, reducing vehicle weight and emissions while improving fuel efficiency. In automotive applications, these materials are used in dashboards, door panels, body panels, and chassis components. Biopolymers like polylactic acid (PLA) and Polybutylene succinate (PBS) are notable for their biodegradability and compatibility, and they can be enhanced with nanofillers for better performance (Bouzouita, 2016).
The interior car door panel serves as an interface between the interior of the car and the inner workings of the door. Incorporating kenaf fiber into PLA bio reinforced composite can absorb higher maximum von-Mises stress (214.13 MPa) if compared to acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (211.26 MPa) car door panel. Also, it shows lower maximum total deformation (12.012 mm) if compared to ABS (42.501 mm) (Fatchurrohman et al., 2021).
In aerospace applications, materials must offer high thermal stability, lightweight properties, and excellent mechanical strength. Polymer nanocomposites reinforced with nanofillers like nanotubes, nanoclay, or graphene meet these needs effectively.
As sustainability becomes a priority, the aerospace industry is developing eco-friendly materials, including those for aircraft interiors that require strong barrier properties and thermal resistance.
The polymer structure significantly affects mechanical and thermal performance. The arrangement of long polymer chains determines whether they are flexible and transparent or strong and stiff, allowing for customized components with specific characteristic (Alami et al., 2023).
Some performance of biopolymers such as thermal and hydrolysis resistance, ductility, impact strength and crystallization rate have to be improved to compete with conventionally used polymers in automotive applications (Arjmandi et al., 2017). PLA properties like thermal stability, stiffness, rigidity, and crystallization for automotive applications have been enhanced using various nanofillers. Foaming technology enables lightweight parts for automotive and aerospace use. Long chain branching (LCB) of PLA, achieved with multifunctional chain extenders, reduces weight by 30%, improving fuel efficiency. LCB-PLAs show increased viscosity, shear sensitivity, and longer relaxation times compared to linear PLA (Giammaria et al., 2024).
5.3 Construction
Construction materials are vital in the building industry, utilizing natural resources like clay, wood, and rocks, as well as synthetic materials such as concrete and steel. Biopolymers and their nanocomposites are crucial for sustainability, as they reduce carbon emissions and waste. Biopolymer coatings enhance durability by protecting against moisture, UV radiation, oxygen, and microbial growth, supporting eco-friendly construction practices (Rezić Meštrović et al., 2025).
Wood and engineered wood materials are popular in construction for their durability and lower environmental impact, but their flammability and susceptibility to insects and mold limit exterior use. Biopolymers are increasingly recognized as effective coatings to enhance these materials due to their compatibility with wood (Patachia and Croitoru, 2016).
Biopolymer-based coatings effectively protect wood from environmental conditions. They can be directly applied or formed through chemical reactions, using materials like chitin, chitosan, proteins, PLA, and polyurethane (Patachia and Croitoru, 2016; Song et al., 2020).
While there is considerable research on biopolymers, their application and limitations as building cladding materials remain under-explored. Cladding protects buildings from weather conditions, helping to preserve structural integrity (Nazrun et al., 2024). Polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), Starch based polymers (SBP), cellulose based polymers (CBP), polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT), polybutylene succinate (PBS), and polycaprolactone (PCL) are all biopolymers currently used in cladding for outer building. The limitation of those polymer opens the door for the nanocomposite application for the enhancement of performance properties in cladding (Nazrun et al., 2024; Farah et al., 2016; Naser et al., 2021).
PLA is a strong biopolymer with a tensile strength of 50–70 MPa, but its brittleness can be improved by blending it with materials like PBAT, PBS, or PCL, or by adding nanofillers (Farah et al., 2016; Nofar et al., 2019). The hydrogen bonding within the CBP chain enhances its tensile strength to 305 MPa, exceeding that of other biopolymers (Eichhorn and Young, 2001). The high tensile strength makes them a potential choice to be used as additives with other biopolymers for mechanical property enhancement, can improve the general toughness, adaptability, and other desirable properties of diverse biopolymers (Nazrun et al., 2024).
Poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) is a polyester biopolymer commonly used in construction materials due to its high elongation at break. However, its slow biodegradation is a drawback. Researchers have addressed this by incorporating starch into the PBAT matrix with up to 1% organoclay to improve tensile modulus and strength (Ghafari, 2025).
All biopolymers are biodegradable and compost at different rates depending on their types and environmental conditions, such as temperature. For example, PLA takes about 1 year to compost at 20 °C but only around 3 months at 25 °C (Rudnik and Briassoulis, 2011). Instead of degradation, some polymers can be mechanically recycled and gain a new life such as PBS and PBAT (McKeown and Jones, 2020).
5.4 Water treatment
Water desalination treatment is considered an alternative source for fresh water in some areas of the world. Which somehow provides water of good quality for daily life use, commercial use, and agriculture irrigation to try to fill the need for an alternative fresh water source (Lew et al., 2014).
Membrane treatment methods are cost-effective and require less maintenance and fewer chemicals than traditional techniques like ion-exchange and filtration. However, fouling remains a challenge, causing reduced flux and shorter membrane lifespans. Eco-friendly biopolymers such as cellulose acetate, chitosan, and alginate offer sustainable alternatives to toxic chemicals due to their biodegradability and low cost. Cellulose acetate is derived from plant cellulose and can be sourced from materials like wood pulp and cotton linters Cellulose acetate (CA) has several drawbacks, including low mechanical strength, poor long-term stability, and susceptibility to hydrolysis in a pH range of 4–6. It also has a low oxidation temperature of 30 °C and is brittle, shrinking after drying (Khaparde, 2017; Khaparde, 2017). Addressing these issues is crucial for improving flux and membrane efficiency. Introducing nanoparticles into the membrane’s polymer matrix can enhance its surface properties and performance.
Freshwater scarcity, driven by population growth and industrial pollution, is a global issue. Desalination technologies like reverse osmosis (RO) efficiently convert saline water to fresh water using semi-permeable membranes. Cellulose acetate (CA) and nanofiltration (NF) membranes are effective for desalinating seawater and wastewater. CA membranes are valued for their low cost, biodegradability, and chlorine tolerance, but need enhancements in mechanical strength and salt rejection to compete with thin film composite membranes (Islam et al., 2023).
Heidari et al. (2023) used graphene oxide (GO) with poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers for the modification of cellulose acetate polymer. Using 1.00 wt% was sufficient for the improvement of membrane porosity (74%), antifouling (88%), reversible fouling ratio (45.71%), salt rejection (98.40% for Na2SO4), (52% for NaCl), (57% for MgCl2), addition of the GO and PAMAM filler enhance the permeability and rejection compared with neat cellulose acetate membrane (Heidari et al., 2023).
El-Noss et al. (2020) enhanced cellulose acetate forward osmosis membranes with ZnO nanoparticles, resulting in increased hydrophilicity (47.6° ± 2° contact angle vs. 63.85° ± 2° for neat CA) and improved salt rejection (99.5% for Na+, 100% for Cl-, 99.6% for Mg2+). The nanocomposite also showed a 23% increase in surface area and 20% in pore volume, leading to a 37% rise in water flux (El-Noss et al., 2020).
Chitosan’s amino groups make it effective for adsorbing metal ions and dyes, while tannic acid enhances this capacity. Recent studies show that graphene/chitosan/magnetite (Gr/CS/Fe3O4) nanocomposites remove dyes more efficiently than chitosan/magnetite (CS/Fe3O4) alone, achieving 100% photocatalytic efficiency in eliminating rhodamine B in 40 min, bromothymol blue in 60 min, methylene blue in 80 min, and methyl orange in 100 min (Maruthupandy et al., 2020). In another study, chitosan/tannic acid modified biopolymer showed up to 92.15 mg/g adsorption capacity of lead ion. Congo red and methylene blue dye were removed from solution using tannic acid acidified and carboxylated chitosan nanofibers. The removal capacity for Congo red was 589 mg/g, and it was 633 mg/g for methylene blue dye (Zhao S. et al., 2021). Chitin whisker/Ag3PO4 nanoparticles composite showed enhanced photocatalytic degradation activity of rhodamine B (RhB) compared to Ag3PO4 due to the enhancement of visible-light absorption and an increase in active sites for adsorption (Zhang and Liu, 2017). Sodium alginate/ZnO photocatalytic nanocomposite was used to study the potential of ZnO in Triclosan (TCS)compound degradation. TCS compound is used in personal care products, found in the environment at low concentrations and it is difficult to degrade by conventional water treatment processes the free ZnO and Sodium alginate/ZnO nanocomposite showed high efficiency of TCS degradation (greater than 90%) using free and immobilized catalyst in only 20 min of reaction.
5.5 Biomedical applications
GPNCs can also be used in medical applications, such as Scaffolds for tissue engineering, wound dressing, and drug delivery systems. In a recent study (Grande-Tovar et al., 2023), prepared a hybrid GPNC based on polycaprolactone (PCL) and polylactic acid (PLA) incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) and tea tree essential oil (TTEO). The developed PCL/PLA/ZnO-NPs/Gly/TTEO membranes showed a promising potential application in tissue engineering, due to increased and accelerated resorption and the absence of an aggressive inflammatory response based on subdermal implantation in Wistar rats.
In another study, a PLA/ZnO nanocomposite was developed for bone implants, where ZnO enhanced the antibacterial properties of the nanocomposite. The mechanical fatigue test showed that the nanocomposite had a higher storage modulus and withstands up to 3600 cycles, compared to neat PLA, which failed after an average of 1768 cycles (Nonato et al., 2022).
Biopolymer-based drug delivery systems use various routes like oral, ophthalmic, transdermal, nasal, and vaginal for targeted, sustained release. Chitosan is a key material in biomedical applications such as drug delivery, bone and tissue regeneration, and wound healing (Desai et al., 2023).
Biopolymers, such as alginate, chitosan, cellulose, collagen, and hyaluronic acid, are frequently used in wound healing materials, which accelerate the rate of cell proliferation and tissue regeneration activity and improve the rate of wound healing (Jaiswal and Sherje, 2024).
Biopolymers provide advantages in biomedical implants due to their complex structures, degradability, and biocompatibility. They replace damaged body parts like in the heart and bones while avoiding issues like immune rejection and harmful byproducts associated with traditional materials (Rebelo et al., 2017).
PLA-PGA copolymers are used in orthopedic implants and cartilage scaffolds. They serve as compression-molded plates or screws for fractures and bone defects. Their adjustable degradation rates and biocompatibility make them preferable to pure PLA or PGA (Rebelo et al., 2017).
6 Sustainability and environmental benefits
6.1 Waste-derived nanocomposites reduce landfill and add value
The use of traditional polymers in industry has raised environmental concerns (Aysa and Shalan, 2022). In response, polymer nanocomposites from renewable sources have emerged as a viable solution for environmental sustainability, gaining attention in the past 2 decades due to urgent environmental concerns and the limited supply of fossil resources (Avella et al., 2009).
A key benefit of renewable-source polymer composites, compared to those from synthetic origins, is their potential to mitigate the environmental impact of plastic waste (Bari et al., 2016). These materials promote sustainable technological advancement by integrating ecological responsibility with cost-effectiveness (Sinha Ray and Bousmina, 2006).
Notably, using agricultural waste and by-products in polymer composite synthesis has gained significant interest (Sinha Ray and Bousmina, 2006). These biopolymer blends, derived from natural sources, offer advantages like affordability, abundant availability, biodegradability, and ease of processing, making them ideal for the sustainable production of advanced polymer nanocomposites (Sinha Ray and Bousmina, 2006). For instance, Kaushik et al. (El-Sayed and Youssef, 2023) demonstrated the fabrication of green nanocomposites from agro-waste cellulose fibers and natural polymers. Their study reported superior mechanical and thermal properties, with the highest tensile modulus (∼220 MPa) and yield strength at 15% fiber content.
In addition to environmental benefits, bio-based composites support economic growth, particularly in rural and agricultural regions of developing countries. By creating non-food commercial applications for underutilized biomass, they add value to the farming sector (Kaushik et al., 2010). The adoption of biopolymer composites is also driven by their renewable nature and growing global environmental awareness (Majeed et al., 2012).
Green nanocomposites from biodegradable polymers are promising for food packaging, providing barriers against contaminants while preserving food quality. Those reinforced with nanoclays like montmorillonite (MMT) offer excellent gas barrier performance, durability, and environmental safety (Diacono et al., 2019; Ammala et al., 2011; Kumanayaka et al., 2010; Shah and Paul, 2006; Qin et al., 2003; Zhong et al., 2007). These materials are also non-toxic and suitable for direct food contact, enhancing their appeal for packaging. Compared to conventional synthetic materials, bio-based polymers offer greater sustainability, recyclability, and cost-efficiency (Choudalakis and Gotsis, 2009; Nguyen et al., 2023).
In summary, waste-derived nanofillers address environmental and economic challenges by transforming agricultural waste into biodegradable composites, reducing landfill use and emissions while supporting rural development.
6.2 Biodegradability or recyclability supports circular economy
In recent years, biodegradable polymers derived from renewable resources have garnered increasing attention from both academic researchers and industry professionals (Fomin and Guzeev, 2001). These materials provide an eco-friendly alternative to conventional petrochemical-based plastics, aligning with global goals of environmental conservation and economic sustainability. Advances in biodegradable polymer technology contribute to preserving fossil fuel reserves, enabling complete material breakdown, minimizing waste, improving compostability, and lowering CO2 emissions—all of which are vital in addressing climate change (Mohanty et al., 2003).
Green polymers are considered environmentally friendly because of their biodegradability, recyclability, and other sustainable properties renewability. Biodegradation refers to the breakdown of a polymer’s chemical structure into non-toxic byproducts that benefit the environment. In contrast, conventional polymers and composites offer limited degradation capabilities (Iranpour Anaraki and Poursalehi, 2015; Kausar, 2016d; Kausar and Hussain, 2013; Kausar, 2016c; Kausar, 2016a). Green polymers, however, exhibit unique degradation behaviors that distinguish them from their synthetic counterparts (Kausar, 2017b; Kausar and Ur Rahman, 2016; Kausar, 2016b; Kausar, 2015).
These biodegradable materials can be sourced directly from nature—such as polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), polylactic acid (PLA), cellulose, starch, and lignin—or synthetically produced from compounds like polyolefins, poly(vinyl alcohol), and specific polyesters, provided they meet criteria for renewability and biodegradability (Kausar, 2017a; Kausar, 2014). Such materials are often incorporated into green nanocomposites, which are increasingly viewed as the future of sustainable materials (Dicker et al., 2014). Furthermore, integrating agricultural by-products and waste materials into composite production enhances both environmental benefits and the economic development of rural communities (Avella et al., 2009).
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a widely cited example of a biodegradable polymer produced from fermented plant starch. Under suitable environmental or composting conditions, PLA breaks down into carbon dioxide, water, and methane within a period ranging from a few months to 2 years. Technological advancements have significantly enhanced PLA’s mechanical performance, expanding its application in both structural and packaging sectors (Costa et al., 2023).
Polysaccharide-based bioplastics, made from starch, cellulose, and alginate, present promising renewable alternatives to petroleum-based plastics. While they offer environmental benefits, their commercial viability is influenced by raw material costs, processing efficiency, market demand, and scalability (Hossain et al., 2024). Starch is ideal for large-scale production of bioplastics because it is affordable and widely available. In contrast, while cellulose is abundant, it involves more complex and costly processing methods (Hossain et al., 2024).
It is worth mentioning that biopolymers do not have to fully degrade during use; their performance can be customized through reinforcement, blending, and surface protection. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications mentioned earlier like lightweight automotive interiors, aerospace non-structural or temporary components, and construction materials such as insulation, composites, and disposable formworks, all while maintaining sustainability at the end of their lifecycle.
Recyclability, beyond just biodegradability, is vital in prolonging the lifespan of green composites. Mechanical and chemical recycling methods enable the recovery and reuse of polymer materials, significantly cutting down on energy consumption and raw material use. One study explored recycling polylactic acid (PLA) and PLA-based natural fiber-reinforced composites (NFRCs) using a conical twin screw extrusion (CTSE) process for up to six cycles. The recycled materials, containing 90% PLA and either basalt fibers (BFs) or halloysite nanotubes (HNTs), were injection-molded into standard test specimens for impact and tensile analysis. Recycling caused discoloration and increased crystallinity in PLA. Impact strength remained stable through six cycles, but tensile properties declined for PLA/BF NFRCs after three cycles, likely due to fiber length reduction. SEM analysis showed decreased fiber length and poor interfacial adhesion with recycling (Finnerty et al., 2023). Another study produced 3D printing filaments from hemp hurd fibre-reinforced PLA composites. Hemp microfibres were used to create composites with 20–40 wt% fibre for fused deposition modelling. Tensile testing showed Young’s modulus increased with fibre content, reaching 7.1 GPa at 40 wt%, doubling that of neat PLA. Tensile strength only improved at 20 wt%, increasing by 8%. Fibre addition significantly enhanced thermo-mechanical properties. Recycled filaments were tested, showing they retained comparable mechanical properties and printability after three cycles (Beg et al., 2024). Moreover, an alginate biopolymer composites were filled waste from the food industry like seagrass, apple pomace, and lignocellulosic side streams from brewing. The composite processed via extrusion, producing a stiff, high-performing material with a Young’s modulus of 4 GPa and tensile strength of 103 MPa—surpassing some traditional plastics. Lignocellulosic fillers reduced shrinkage by 28% and density by 7% without sacrificing stiffness. Additionally, the materials were recyclable up to four times without losing mechanical integrity when the plasticizer was reintroduced into the formulation (Rech et al., 2023).
Achieving complete recyclability is still difficult. Certain biodegradable polymers might break down too early during recycling or generate microplastics if not processed correctly. It is crucial to balance the rate of biodegradation with recyclability to preserve material quality and promote environmental advantages. Incorporating nanostructured reinforcements can enhance this balance by increasing durability during use and ensuring that the material biodegrades under controlled conditions.
Altogether, the combined qualities of biodegradability, recyclability, and renewability in green polymers and composites form the cornerstone of a circular economy. These materials not only reduce dependence on finite resources but also facilitate a closed-loop system that promotes sustainable production and responsible consumption.
6.3 Positive life cycle assessment (LCA) outcomes
Life cycle assessment (LCA) is crucial for evaluating the environmental benefits of biopolymer nanocomposites (PNCs), as it analyzes impacts and resource use from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling (Finnveden et al., 2009). This method, when applied rigorously, prevents misleading conclusions and supports sustainable material choices. Notably, nine of the fifteen reviewed LCA studies focus on biobased plastics, generally viewed as more environmentally friendly than petroleum-derived ones. For example, Pietrini et al. compared the LCA of poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and polypropylene (PP) nanocomposites, both reinforced with organo-modified clays, for use in CRT monitor housings and automotive panels (Pietrini et al., 2007). Using previously established methodologies (Roes et al., 2007), they observed that PHB’s higher density and lower Young’s modulus necessitate more material per unit application. The lower resource inputs for PHB synthesis make it more environmentally preferable to PP from cradle-to-factory gate and perform better in cradle-to-grave assessments for CRT applications. However, these findings are limited by insufficient industrial-scale data on PHB production.
This review evaluates the environmental performance of polymer nanocomposites (PNCs) made from bioplastics and recycled plastics, providing insights to support sustainable material development and processing methods.
7 Challenges and limitations
7.1 Economic challenges
A key obstacle to the broad commercialization of green biopolymers is their higher production costs relative to petroleum-based plastics. Producing bioplastics can be two to four times more expensive than synthetic plastics, mainly because of the cheaper, well-established infrastructure for petroleum refining versus renewable biomass processing (Kumari et al., 2023). For instance, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) offer excellent barrier properties compared to other biopolymers, but their high manufacturing costs limit their use (Lamberti et al., 2020). Similarly, bacterial cellulose (BC), which requires only mild purification steps and does not depend on plant biomass, is still limited in production due to costly nutrient-rich substrates and low yields (Westlake et al., 2023). Although these costs hinder scaling beyond labs, growing market interest is expected to drive industrial growth, technological advances, and economies of scale, eventually lowering costs. Over time, performance and sustainability benefits might outweigh expense considerations, especially when biopolymers can effectively compete with traditional plastics in packaging and other sectors (Westlake et al., 2023).
The scalability of nanomaterials remains a major challenge, as industrial manufacturing faces hurdles from initial design to large-scale deployment, including concerns about reproducibility, safety, and environmental impact (Hachhach et al., 2025). While some nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes (CNTs) provide excellent strength, low weight, and a high aspect ratio—making them appealing for advanced uses—their high production costs and complex processing limit their widespread adoption (Rashid et al., 2024). At the same time, developing cost-effective and reliable methods for large-scale biogenic synthesis, such as for silver nanoparticles, is crucial to support broader industrial use (Gacem and Abd-Elsalam, 2022).
7.2 Technical challenges
The development of nanomaterials depends on manufacturing methods that are reliable, reproducible, and scalable, supported by thorough research data, with a focus on creating cost-effective and consistent synthetic processes (Bi et al., 2025). However, many traditional synthesis methods lack precise control over experimental conditions, which often results in nanoparticles with varied sizes and notable batch-to-batch differences (Niculescu et al., 2021). Additionally, ensuring uniform nanoparticle dispersion within polymer matrices is essential for optimal performance. Yet, scaling from laboratory to industrial production while maintaining this uniformity and consistent properties remains challenging, with persistent reproducibility problems in large-scale manufacturing (Rahman et al., 2025).
7.3 Health and environmental concerns
The production and handling of nanomaterials pose potential health and environmental risks, as workers may be exposed during post-synthesis tasks like opening reaction chambers, drying, powder handling, or cleaning equipment, which can release nanoparticles into the air or waste streams (2018). These particles can enter the human body through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact, then travel via the bloodstream to various organs, where they might interact with biological and chemical systems at the molecular level, though these interactions are still not fully understood in complex human biology (Fond and Meyer, 2007). Some nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), are particularly concerning due to their similarity to asbestos, indicating a significant potential for human toxicity (Awasthi and Sharma, 2022). Additionally, the increased production scale heightens the risk of environmental release, with nanoparticle persistence and reactivity possibly disrupting ecosystems, underscoring the urgent need for thorough toxicological and ecotoxicological evaluations.
8 Conclusion and future perspectives
Green polymer nanocomposites (GPNCs) are emerging as innovative materials that blend sustainability with advanced functionalities. They reduce reliance on fossil-based polymers and enhance biodegradability or recyclability, making them suitable for packaging, automotive, construction, water treatment, and biomedical applications. Incorporating eco-friendly nanofillers like cellulose nanocrystals, biochar, nanoclays, and specific metal oxides further boosts their mechanical, thermal, and barrier performances, while also adding features such as antimicrobial effects and UV protection. These advancements position GPNCs as crucial materials for fostering a circular economy and decreasing carbon footprints in various sectors. Despite significant progress, several obstacles still hinder the large-scale implementation of GPNCs. First, standardization issues arise because there are no universal protocols for assessing biodegradability, nanotoxicity, and environmental effects in practical settings. Second, there is a lack of durability and performance data. Long-term studies on degradation and stability remain limited, especially for use in harsh environments. Another concern involves regulatory and safety issues. Clear guidelines for safe handling, disposal, and certification of nano-enabled green composites are still missing.
To speed up the transition of GPNCs from research to industry, it is crucial to focus on strategies like reducing costs and enhancing scalability. Developing cost-effective methods for synthesizing bio-based polymers and waste-derived nanofillers and implementing energy-efficient processing techniques is needed. Moreover, advanced fabrication techniques should be employed, leveraging optimization of 3D printing, electrospinning, and AI-based design to achieve precise control over material properties and performance. For multifunctionality, GPNCs should incorporate features like self-healing, antimicrobial, UV-blocking, or energy-harvesting capabilities aimed at high-value applications. Additionally, integrating GPNCs within the circular economy involves promoting closed-loop recycling, renewable energy-powered manufacturing, and valorizing agricultural and industrial byproducts. Lastly, establishing robust policy and regulatory frameworks is vital, including the development of international standards, support for green certifications, and comprehensive risk assessments for human health and the environment.
Through ongoing innovation, collaborative multidisciplinary efforts, and strong policy support, GPNCs can transition from promising laboratory materials to large-scale industrial solutions that balance performance with sustainability. These advancements will play a crucial role in shaping the future of green manufacturing, fostering a low-carbon, resource-efficient economy where materials innovation drives both environmental responsibility and economic growth.
Author contributions
RA-Z: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AK: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. NA: Writing – original draft. HW: Writing – original draft. AB: Writing – original draft. DA-D: Writing – original draft. MR: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Grammarly was used for the enhancement of the readability of the manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbasi, H., Antunes, M., and Velasco, J. I. (2019). Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Prog. Mater. Sci. 103, 319–373. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2019.02.003
Abdelhamed, A. H., Thien, G. S., Lee, C.-L., Au, B. W., Tan, K. B., Murthy, H. C. A., et al. (2025). Solution casting effect of PMMA-based polymer electrolyte on the performances of solid-state electrochromic devices. Polymers 17, 99. doi:10.3390/polym17010099
Abdelraheem, A., El-Shazly, A., and Elkady, M. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of intercalated polyaniline-clay nanocomposite using supercritical CO2. AIP Conf. Proc. 1968, 020027. doi:10.1063/1.5039186
Abu-Dalo, M., Bozeya, A., Sawalmeh, Z., Albiss, B., Alnairat, N., and Abu-Zurayk, R. (2023). Antifouling polymeric nanocomposite membrane based on interfacial polymerization of polyamide enhanced with green TiO2 nanoparticles for water desalination. PeerJ Anal. Chem. 5, e26. doi:10.7717/peerj-achem.26
Abu-Zurayk, R., Alnairat, N., Bozeya, A., Khalaf, A., and Abu-Dalo, D. (2024). Enhanced properties of PVDF membranes using green Ag-nanoclay composite nanoarchitectonics. Mater. Res. Express 11, 045007. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/ad4101
Abu-Zurayk, R., Alnairat, N., Waleed, H., Al-Khaial, M. Q., Khalaf, A., Bozeya, A., et al. (2025a). Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and nanoclay composites’ mixed-matrix membranes: exploring structure, properties, and performance relationships. Polymers 17, 1120. doi:10.3390/polym17081120
Abu-Zurayk, R., Alnairat, N., Waleed, H., Khalaf, A., Abu-Dalo, D., Bozeya, A., et al. (2025b). Dual-mode integration of a composite nanoparticle in PES membranes: enhanced performance and photocatalytic potential. Nanomaterials. [Online] 15, 1055. doi:10.3390/nano15141055
Abuamr, A. M., Mousa, M. S., Al-Bashaish, S. R., Madanat, M. A., Alsoud, A., Jaber, A. M. D., et al. (2024). Characterization of field emission from oxidized copper emitters. Phys. Scr. 99, 105029. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/ad7232
Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Yahya, R., Bakri, M. M., Yahya, R., and Abdelghany, T. M. (2022). In situ green synthesis of Cu-doped ZnO based polymers nanocomposite with studying antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Appl. Biol. Chem. 65, 35. doi:10.1186/s13765-022-00702-0
Al-Saleh, M. H. (2019). Carbon-based polymer nanocomposites as dielectric energy storage materials. Nanotechnology 30, 062001. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/aaf12c
Alami, A. H., Ghani Olabi, A., Alashkar, A., Alasad, S., Aljaghoub, H., Rezk, H., et al. (2023). Additive manufacturing in the aerospace and automotive industries: recent trends and role in achieving sustainable development goals. Ain Shams Eng. J. 14, 102516. doi:10.1016/j.asej.2023.102516
Ali, S., Ali, E., Hamdy, G., Badawy, M., Ismail, A., El-Sabbagh, I., et al. (2024a). Enhancing physical characteristics and antibacterial efficacy of chitosan through investigation of microwave-assisted chemically formulated chitosan-coated ZnO and chitosan/ZnO physical composite. Sci. Rep. 14, 9348. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-58862-6
Ali, Z., Yaqoob, S., Yu, J., and D'amore, A. (2024b). Critical review on the characterization, preparation, and enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of carbon nanotubes and their hybrid filler polymer composites for various applications. Compos. Part C. Open Access 13, 100434. doi:10.1016/j.jcomc.2024.100434
Alkhrissat, T., and Matarneh, S. (2025). Impact of anaerobic co-digestion of ryegrass (RG) and cow manure (CM) on methane production and kinetic analysis. Results Eng. 25, 104028. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2025.104028
Alnairat, N., Abu Dalo, M., Abu-Zurayk, R., Abu Mallouh, S., Odeh, F., and Al Bawab, A. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles as an effective antibiofouling material for polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane. Polymers 13, 3683. doi:10.3390/polym13213683
Alsoud, A., Daradkeh, S. I., Al-Bashaish, S. R., Shaheen, A. A., Jaber, A. M. D., Abuamr, A. M., et al. (2024). Electrical characterization of epoxy nanocomposite under high DC voltage. Polymers 16, 963. doi:10.3390/polym16070963
Alvarado, N., Romero, J., Torres, A., López De Dicastillo, C., Rojas, A., Galotto, M. J., et al. (2018). Supercritical impregnation of thymol in poly(lactic acid) filled with electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)-cellulose nanocrystals nanofibers: development an active food packaging material. J. Food Eng. 217, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.08.008
Alvaredo-Atienza, A., Fernández-Blázquez, J. P., Castell, P., and De Villoria, R. G. (2020). Production of graphene nanoplate/polyetheretherketone composites by semi-industrial melt-compounding. Heliyon 6 (4), e03740. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03740
Ambrosi, A., and Pumera, M. (2018). Self-contained polymer/metal 3D printed electrochemical platform for tailored water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1700655. doi:10.1002/adfm.201700655
Amin, H., Tayyab, A., Umair, M., Naveed, M., Yaseen, H., Qasim, M., et al. (2025). Recent progress in wastewater treatment: exploring the roles of zero-valent iron and titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Indus J. Biosci. Res. 3, 97–107. doi:10.70749/ijbr.v3i4.1141
Ammala, A., Bateman, S., Dean, K., Petinakis, E., Sangwan, P., Wong, S., et al. (2011). An overview of degradable and biodegradable polyolefins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 36, 1015–1049. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.12.002
Ansar, E. N., Biutty, M. N., Kim, K.-S., Yoo, S., Huh, P., and Yoo, S. I. (2024). Sustainable polyamide composites reinforced with nanocellulose via melt mixing process. J. Compos. Sci. 8, 419. doi:10.3390/jcs8100419
Anwajler, B., Zielińska, S., and Witek-Krowiak, A. (2024). Innovative cellular insulation barrier on the basis of voronoi tessellation—influence of internal structure optimization on thermal performance. Materials [Online] 17, 1578. doi:10.3390/ma17071578
Anwer, M., Al-Mashhadani, M., Alsayed, R., Mohammed, A., Alshareef, S., Alhuwaymil, Z., et al. (2024). Optimizing PVC photostability and UV blocking capability through nanoparticles incorporation: a comprehensive review. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 31, 259–278. doi:10.1002/vnl.22172
Araujo, P. H. H. D., Sayer, C., Giudici, R., and Poço, J. G. R. (2002). Techniques for reducing residual monomer content in polymers: a review. Polym. Eng. and Sci. 42 (7), 1442–1468. doi:10.1002/pen.11043
Arefin, A. M. E., Khatri, N. R., Kulkarni, N., and Egan, P. F. (2021). Polymer 3D printing review: materials, process, and design strategies for medical applications. Polymers 13, 1499. doi:10.3390/polym13091499
Arízaga, G. G. C., Galván, J. G. Q., Bail, A., González, A. L. P., Nuñez, C. P., and Álvarez, M. Á. L. (2022). Green approach to synthesize functional carbon nanoparticles at low temperature. Sustain. Chem. Clim. Action 1, 100002. doi:10.1016/j.scca.2022.100002
Arjmandi, R., Hassan, A., and Zakaria, Z. (2017). “Polylactic acid green nanocomposites for automotive applications,” in Green biocomposites: design and applications. Editors M. Jawaid, M. S. Salit, and O. Y. Alothman (Cham: Springer International Publishing).
Arora, N., Dua, S., Singh, V. K., Singh, S. K., and Senthilkumar, T. (2024). A comprehensive review on fillers and mechanical properties of 3D printed polymer composites. Mater. Today Commun. 40, 109617. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.109617
Arrieta, M., López, J., Hernández, A., and Rayón, E. (2014). Ternary PLA-PHB-Limonene blends intended for biodegradable food packaging applications. Eur. Polym. J. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.11.009
Avella, M., Buzarovska, A., Errico, M. E., Gentile, G., and Grozdanov, A. (2009). Eco-challenges of bio-based polymer composites. Materials 2, 911–925. doi:10.3390/ma2030911
Avolio, R., Castaldo, R., Avella, M., Cocca, M., Gentile, G., Fiori, S., et al. (2018). PLA-Based plasticized nanocomposites: effect of polymer/plasticizer/filler interactions on the time evolution of properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 152, 267–274. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.07.011
Awasthi, S., and Sharma, J. (2022). Toxicity and challenges of nanomaterials and their impact on the environment. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 21, 643–650. doi:10.46488/nept.2022.v21i02.023
Aysa, N. H., and Shalan, A. E. (2022). “Green nanocomposites: magical solution for environmental pollution problems,” in Advances in nanocomposite materials for environmental and energy harvesting applications. Editors A. E. Shalan, A. S. Hamdy Makhlouf, and S. Lanceros-Méndez (Cham: Springer International Publishing).
Bachs-Herrera, A., Yousefzade, O., Del Valle, L. J., and Puiggali, J. (2021). Melt electrospinning of polymers: blends, nanocomposites, additives and applications. Appl. Sci. 11, 1808. doi:10.3390/app11041808
Bailly, M., Kontopoulou, M., and El Mabrouk, K. (2010). Effect of polymer/filler interactions on the structure and rheological properties of ethylene-octene copolymer/nanosilica composites. Polymer 51, 5506–5515. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2010.09.051
Bandyopadhyay, A., and Heer, B. (2018). Additive manufacturing of multi-material structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 129, 1–16. doi:10.1016/j.mser.2018.04.001
Bănică, C.-F., Sover, A., and Anghel, D.-C. (2024). Printing the future layer by layer: a comprehensive exploration of additive manufacturing in the era of industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 14, 9919. doi:10.3390/app14219919
Barbaros, I., Yang, Y., Safaei, B., Yang, Z., Qin, Z., and Asmael, M. (2022). State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 11, 321–371. doi:10.1515/ntrev-2022-0017
Bari, S., Chatterjee, A., and Mishra, S. (2016). Biodegradable polymer nanocomposites – an overview. Polym. Rev. 56, 287–328. doi:10.1080/15583724.2015.1118123
Beg, M. D. H., Pickering, K. L., Akindoyo, J. O., and Gauss, C. (2024). Recyclable hemp hurd fibre-reinforced PLA composites for 3D printing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 33, 4439–4447. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.10.082
Bekas, D. G., Hou, Y., Liu, Y., and Panesar, A. (2019). 3D printing to enable multifunctionality in polymer-based composites: a review. Compos. Part B Eng. 179, 107540. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107540
Beluns, S., Gaidukovs, S., Platnieks, O., Gaidukova, G., Mierina, I., Grase, L., et al. (2021). From wood and hemp biomass wastes to sustainable nanocellulose foams. Industrial Crops Prod. 170, 113780. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113780
Bernagozzi, G., Arrigo, R., and Frache, A. (2024). Evolution of the microstructure of PP-LDHs nanocomposites during melt compounding: a simulation approach. Polymers 16, 70. doi:10.3390/polym16010070
Bharathi, D., Rajamani, R., Sibuh, B. Z., Pandit, S., Agrawal, S., Mishra, N., et al. (2022). Biogenic preparation, characterization, and biomedical applications of chitosan functionalized iron oxide nanocomposite. J. Compos. Sci. 6 (5), 120. doi:10.3390/jcs6050120
Bhatnagar, A., and Sain, M. (2005). Processing of cellulose nanofiber-reinforced composites. J. Reinf. Plastics Compos. 24, 1259–1268. doi:10.1177/0731684405049864
Bhawal, P., Ganguly, S., Das, T. K., Mondal, S., Nayak, L., and Das, N. C. (2019). A comparative study of physico-mechanical and electrical properties of polymer-carbon nanofiber in wet and melt mixing methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 245, 95–106. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2019.05.020
Bhawani, S., Bhat, A. H., Ahmad, F., and Ibrahim, M. (2018). Green polymer nanocomposites and their environmental applications. Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications, 617–633. doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-102262-7.00023-4
Bi, Y., Xie, S., Li, Z., Dong, S., and Teng, L. (2025). Precise nanoscale fabrication technologies, the “last mile” of medicinal development. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 15, 2372–2401. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2025.03.040
Bikiaris, N. D., Koumentakou, I., Samiotaki, C., Meimaroglou, D., Varytimidou, D., Karatza, A., et al. (2023). Recent advances in the investigation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) nanocomposites: incorporation of various nanofillers and their properties and applications. Polymers 15, 1196. doi:10.3390/polym15051196
Bilisik, K., and Akter, M. (2022). Polymer nanocomposites based on graphite nanoplatelets (GNPs): a review on thermal-electrical conductivity, mechanical and barrier properties. J. Mater. Sci. 57, 7425–7480. doi:10.1007/s10853-022-07092-0
Borucka, M., Celiński, M., Salasinska, K., and Gajek, A. (2019). Identification of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds emitted during thermal degradation and combustion of triadimenol. J. Therm. Analysis Calorim. 139, 1493–1506. doi:10.1007/s10973-019-08531-y
Bouzouita, A. (2016). Elaboration of polylactide-based materials for automotive application: study of structure-process-properties interactions.
Brandenburg, R., Lepienski, C., Becker, D., and Coelho, L. (2017). Influence of mixing methods on the properties of high density polyethylene nanocomposites with different carbon nanoparticles. Matéria, 22. doi:10.1590/s1517-707620170004.0222
Cai, J., Han, Z., Sun, Y., Chen, H., Li, H., Wang, R., et al. (2025). A novel, green method for the preparation of biodegradable PLA membranes without pore-forming agent. J. Water Process Eng. 74, 107841. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2025.107841
Cailloux, J., Hakim, R. N., Santana Perez, O., Bou, J., Abt, T., Sanchez-Soto, M., et al. (2016). Reactive extrusion: a useful process to manufacture structurally modified PLA/o-MMT composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 88, 106–115. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.05.024
Cailloux, J., Raquez, J.-M., Lo Re, G., Santana Perez, O., Bonnaud, L., Dubois, P., et al. (2019). Melt-processing of cellulose nanofibril/polylactide bionanocomposites via a sustainable polyethylene glycol-based carrier system. Carbohydr. Polym. 224, 115188. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115188
Cazan, C., Enesca, A., and Andronic, L. (2021). Synergic effect of TiO2 filler on the mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Polymers 13, 2017. doi:10.3390/polym13122017
Chakraborty, S., Raj, M. A., and Mary, N. L. (2020). Biocompatible supercapacitor electrodes using green synthesised ZnO/Polymer nanocomposites for efficient energy storage applications. J. Energy Storage 28, 101275. doi:10.1016/j.est.2020.101275
Chan, J. X., Wong, J. F., Petrů, M., Hassan, A., Nirmal, U., Othman, N., et al. (2021). Effect of nanofillers on tribological properties of polymer nanocomposites: a review on recent development. Polymers. [Online] 13, 2867. doi:10.3390/polym13172867
Chen, G. Q. (2003). “Production and Applications of Microbial Polyhydroxyalkanoates,” in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics. Editors E. Chiellini, and R. Solaro (Boston, MA, United States: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-9240-6_11
Chen, B., Qiao, G., Hou, D., Wang, M., and Li, Z. (2020). Cement-based material modified by in-situ polymerization: from experiments to molecular dynamics investigation. Compos. Part B Eng. 194, 108036. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108036
Chen, J., Tian, T., Gu, C., Zeng, H., Hou, F., Zhang, G., et al. (2025). Review of inorganic non-metallic materials in power electronics packaging application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 40, 10509–10530. doi:10.1109/tpel.2025.3550882
Choudalakis, G., and Gotsis, A. D. (2009). Permeability of polymer/clay nanocomposites: a review. Eur. Polym. J. 45, 967–984. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2009.01.027
Clement, O., Olaniyan, A., Babalola, R., Oyefeso, B., and Jaiyeoba, K. (2025). “Processing Techniques for Bio-based Products in the Global South,” in Sustainable Bioeconomy Development in the Global South, 39–65. doi:10.1007/978-981-96-0305-3_2
Costa, A., Encarnação, T., Tavares, R., Todo Bom, T., Mateus, A., de Almeida, Y. M. B., et al. (2023). Tailoring PLA/ABS blends compatibilized with SEBS-g-MA through annealing heat treatment. Bioplastics Innovation Green Transition. Polym. 15, 3434. doi:10.3390/polym15163434
Cudjoe, E., Khani, S., Way, A. E., Hore, M. J. A., Maia, J., and Rowan, S. J. (2017). Biomimetic reversible heat-stiffening polymer nanocomposites. ACS Central Sci. 3, 886–894. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.7b00215
Cui, E., Zhao, J., Wang, X., and Sun, Z. (2022). Improved fracture resistance and toughening mechanisms of GNPs reinforced ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 48, 24687–24694. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.115
Darwish, M. S. A., Mostafa, M. H., and Al-Harbi, L. M. (2022). Polymeric nanocomposites for environmental and industrial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 1023. doi:10.3390/ijms23031023
Das, P. P., Chaudhary, V., Ahmad, F., and Manral, A. (2021). Effect of nanotoxicity and enhancement in performance of polymer composites using nanofillers: a state-of-the-art review. Polym. Compos. 42, 2152–2170. doi:10.1002/pc.25968
Daud, W., Bersee, H. E. N., Picken, S. J., and Beukers, A. (2009). Layered silicates nanocomposite matrix for improved fiber reinforced composites properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69, 2285–2292. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.01.009
Demirbaş, A. (2007). Biodegradable plastics from renewable resources. Energy Sources, Part A 29, 419–424. doi:10.1080/009083190965820
Deng, X., Gould, M., and Ali, M. (2022). A review of current advancements for wound healing: biomaterial applications and medical devices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomaterials 110, 2542–2573. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.35086
Desai, N., Rana, D., Salave, S., Gupta, R., Patel, P., Karunakaran, B., et al. (2023). Chitosan: a potential biopolymer in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics 15, 1313. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15041313
Deshmukh, R. K., Kumar, L., and Gaikwad, K. K. (2023). Halloysite nanotubes for food packaging application: a review. Appl. Clay Sci. 234, 106856. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2023.106856
Dhiman, N. K., Agnihotri, S., and Shukla, R. (2019). “Silver-based polymeric nanocomposites as antimicrobial coatings for biomedical applications,” in Nanotechnology in modern animal biotechnology: recent trends and future perspectives. Editors S. Singh, and P. K. Maurya (Singapore: Springer Singapore).
Diacono, M., Persiani, A., Testani, E., Montemurro, F., and Ciaccia, C. (2019). Recycling agricultural wastes and By-products in organic farming: biofertilizer production, yield performance and carbon footprint analysis. Sustainability 11, 3824. doi:10.3390/su11143824
Dicker, M. P. M., Duckworth, P. F., Baker, A. B., Francois, G., Hazzard, M. K., and Weaver, P. M. (2014). Green composites: a review of material attributes and complementary applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 56, 280–289. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.10.014
Diez-Pascual, A. (2022). Carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for high-performance applications II. Polymers 14, 870. doi:10.3390/polym14050870
Ding, X., Zhao, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., and Wang, Z. (2004). Silica nanoparticles encapsulated by polystyrene via surface grafting and in situ emulsion polymerization. Mater. Lett. 58, 3126–3130. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2004.06.003
Ding, X., Wang, A., Tong, W., and Xu, F.-J. (2019). Biodegradable antibacterial polymeric nanosystems: a new hope to cope with multidrug-resistant bacteria. Small 15, 1900999. doi:10.1002/smll.201900999
Dufresne, A. (2017). Cellulose nanomaterials as green nanoreinforcements for polymer nanocomposites. Philosophical Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 376, 20170040. doi:10.1098/rsta.2017.0040
Duncan, T. V. (2011). Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: barrier materials, antimicrobials and sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 363, 1–24. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.017
Dutta, S., Seo, Y.-R., Park, C.-W., Lee, S.-H., Kim, J.-W., Kim, J., et al. (2019). In vitro biocompatibility of electrospun poly(ε -Caprolactone)/Cellulose nanocrystals-nanofibers for tissue engineering. J. Nanomater. 2019, 1–11. doi:10.1155/2019/2061545
Edo, G., Mafe, A., Ali, A., Akpoghelie, P., Yousif, E., Isoje, E., et al. (2025). Advancing sustainable food packaging: the role of green nanomaterials in enhancing barrier properties. Food Eng. Rev. 17, 573–607. doi:10.1007/s12393-025-09407-8
Eichhorn, S. J., and Young, R. J. (2001). The Young's modulus of a microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose 8, 197–207. doi:10.1023/a:1013181804540
El Achaby, M., El Miri, N., Aboulkas, A., Zahouily, M., Bilal, E., Barakat, A., et al. (2017). Processing and properties of eco-friendly bio-nanocomposite films filled with cellulose nanocrystals from sugarcane bagasse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 96, 340–352. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.040
El-Noss, M., Isawi, H., Shawky, H. A., Gomaa, M. A., and Abdel-Mottaleb, M. S. A. (2020). Improvement of cellulose acetate forward osmosis membrane performance using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Desalination Water Treat. 193, 19–33. doi:10.5004/dwt.2020.25677
El-Sayed, S. M., and Youssef, A. M. (2023). Eco-friendly biodegradable nanocomposite materials and their recent use in food packaging applications: a review. Sustain. Food Technol. 1, 215–227. doi:10.1039/d2fb00021k
Eliza, C., Gheorghe, V., Costiuc, J., and Costiuc, L. (2025). The effect of thermal conductivity for buildings’ composite panels including used materials on heat variation and energy consumption. Buildings 15, 1599. doi:10.3390/buildings15101599
Farah, S., Anderson, D. G., and Langer, R. (2016). Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications — a comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 107, 367–392. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.06.012
Faraj, H., Follain, N., Sollogoub, C., Almeida, G., Chappey, C., Marais, S., et al. (2022). Gas barrier properties of polylactide/cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 113, 107683. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2022.107683
Fatchurrohman, N., Jun, H. X., Muhida, R., and Adelino, M. I. (2021). “Performance simulation of bio-reinforced composite car door panel using finite element analysis,” in 2021 international conference on computer science and engineering (IC2SE), 1–5.
Felton, L. A. (2013). Mechanisms of polymeric film formation. Int. J. Pharm. 457, 423–427. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.12.027
Feng, Y., Wang, B., Wang, F., Zhao, Y., Liu, C., Chen, J., et al. (2014). Thermal degradation mechanism and kinetics of polycarbonate/silica nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 107, 129–138. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.05.012
Finnerty, J., Rowe, S., Howard, T., Connolly, S., Doran, C., Devine, D. M., et al. (2023). Effect of mechanical recycling on the mechanical properties of PLA-Based natural fiber-reinforced composites. J. Compos. Sci. 7 (4), 141. doi:10.3390/jcs7040141
Finnveden, G., Hauschild, M. Z., Ekvall, T., Guinée, J., Heijungs, R., Hellweg, S., et al. (2009). Recent developments in life cycle assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 91, 1–21. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.06.018
Fomin, V. A., and Guzeev, V. V. (2001). Biodegradable polymers, their present state and future prospects. Prog. Rubber Plastics Technol. 17, 186–204. doi:10.1177/147776060101700303
Fond, A. M., and Meyer, G. J. (2007). Biotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnologies Life Sci. doi:10.1002/9783527610419.ntls0048
Fortunati, E., Armentano, I., Zhou, Q., Iannoni, A., Saino, E., Visai, L., et al. (2012). Multifunctional bionanocomposite films of poly(lactic acid), cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 1596–1605. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.066
Forward, C., and Kim, I. Y. (2023). Layered fiber orientation optimization for continuous fiber reinforced polymer additive manufacturing using multi-material topology optimization. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 8, 1665–1676. doi:10.1007/s40964-023-00434-7
Gaaz, T. S., Sulong, A. B., Kadhum, A. A. H., Al-Amiery, A. A., Nassir, M. H., and Jaaz, A. H. (2017). The impact of halloysite on the thermo-mechanical properties of polymer composites. Molecules 22, 838. doi:10.3390/molecules22050838
Gacem, M. A., and Abd-Elsalam, K. A. (2022). “Chapter 27 - strategies for scaling up of green-synthesized nanomaterials: challenges and future trends,” in Green synthesis of silver nanomaterials. Editor K. A. Abd-Elsalam (Elsevier).
Gaddam, S. K., Pothu, R., and Boddula, R. (2020). Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) reinforced polymer nanocomposite systems—A review. Polym. Compos. 41, 430–442. doi:10.1002/pc.25410
Gamal, D., Abd-Elkhalek, A., Shaban, M., Al-Saeedi, S. I., Elbasiony, A. M., El-Aziz, G. H. A., et al. (2025). Insights into the structure and removal performance of cationic dyes by adsorption onto MgAl LDH-Chitosan/Serpentine nanocomposite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. doi:10.1007/s10904-025-03917-y
Gamelas, S. R. D., Tomé, J. P. C., Tomé, A. C., and Lourenço, L. M. O. (2023). Advances in photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters: harnessing the power of phthalocyanines and phthalocyanine-containing materials. RSC Adv. 13, 33957–33993. doi:10.1039/d3ra06598g
Gayathri Mohan, K. V., George, J., and Balachandran, M. (2024). Polymer-nanocarbon composites: a promising strategy for enhanced performance of organic solar cells. Emergent Mater. 7, 17–33. doi:10.1007/s42247-023-00604-x
Ghafari, R. (2025). Development and application of biodegradable polymers for sustainable construction: a comprehensive study on environmental and mechanical performance.
Ghyati, S., Kassou, S., El Jai, M., El Kinani, E. H., Benhamou, M., and Chang, S. H. (2022). Thermal properties of clay containing polymeric reinforcement as an eco-friendly bio-insulation composite for buildings. J. Therm. Analysis Calorim. 147, 7213–7228. doi:10.1007/s10973-021-11015-7
Giammaria, V., Capretti, M., Del Bianco, G., Boria, S., and Santulli, C. (2024). Application of poly(lactic acid) composites in the automotive sector: a critical review. Polymers 16, 3059. doi:10.3390/polym16213059
Giovannelli, A., Di Maio, D., and Scarpa, F. (2017). Industrial-graded epoxy nanocomposites with mechanically dispersed multi-walled carbon nanotubes: static and damping properties. Materials 10, 1222. doi:10.3390/ma10101222
Grande-Tovar, C. D., Castro, J. I., Valencia Llano, C. H., Tenorio, D. L., Saavedra, M., Zapata, P. A., et al. (2023). Polycaprolactone (PCL)-polylactic acid (PLA)-Glycerol (Gly) composites incorporated with zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) and Tea Tree Essential Oil (TTEO) for tissue engineering applications. Pharmaceutics 15, 43. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15010043
Griffin, A., Guo, Y., Hu, Z., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., and Qiang, Z. (2022). Scalable methods for directional assembly of fillers in polymer composites: creating pathways for improving material properties. Polym. Compos. 43, 5747–5766. doi:10.1002/pc.26905
Guan, L., Zhao, L., Wan, Y.-J., and Tang, L. C. (2018). Three-dimensional graphene-based polymer nanocomposites: preparation, property and application. Nanoscale 10. doi:10.1039/C8NR03044H
Guan, G., Zhang, L., Zhu, J., Wu, H., Li, W., and Sun, Q. (2021). Antibacterial properties and mechanism of biopolymer-based films functionalized by CuO/ZnO nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Hazard. Mater. 402, 123542. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123542
Gupta, N., Mahur, B. K., Izrayeel, A. M. D., Ahuja, A., and Rastogi, V. K. (2022). Biomass conversion of agricultural waste residues for different applications: a comprehensive review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 73622–73647. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-22802-6
Hachhach, M., Bayou, S., El Kasmi, A., Saidi, M. Z., Akram, H., Hanafi, M., et al. (2025). Towards sustainable Scaling-Up of nanomaterials fabrication: current situation, challenges, and future perspectives. Eng. [Online] 6, 149. doi:10.3390/eng6070149
Hartley, A., Moon, H., and Neves, A. (2022). Biodegradable synthetic polymers for tissue engineering: a mini-review. Reinvention Int. J. Undergrad. Res. 15. doi:10.31273/reinvention.v15i1.801
Harun-Ur-Rashid, M., Imran, A. B., and Susan, M. A. B. H. (2023). Green polymer nanocomposites in automotive and packaging industries. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 24. doi:10.2174/1389201023666220506111027
Harun-Ur-Rashid, M., Foyez, T., Krishna, S. B. N., Poda, S., and Imran, A. B. (2025). Recent advances of silver nanoparticle-based polymer nanocomposites for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 15, 8480–8505. doi:10.1039/d4ra08220f
Hasan, M., Utami, A., Purma, R., Syahrial, S., Rahmayani, R. F. I., and Zulfadli, Z. (2024). Development of environmentally friendly and intelligent food packaging bio-nanocomposite films. Ecol. Eng. and Environ. Technol. 25, 155–164. doi:10.12912/27197050/178388
Hassan, T., Salam, A., Khan, A., Khan, S. U., Wasim, M., Khan, M., et al. (2021). Functional nanocomposites and their potential applications: a review. J. Polym. Res. 28, 36. doi:10.1007/s10965-021-02408-1
Heidari, Y., Noroozian, E., and Maghsoudi, S. (2023). Improvement of salt rejection efficiency of cellulose acetate membrane through modification by poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-functionalized graphene oxide. Heliyon 9, e19171. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19171
Hendeniya, N., Hillery, K., and Chang, B. S. (2023). Processive pathways to metastability in block copolymer thin films. Polymers 15, 498. doi:10.3390/polym15030498
Heydari, A., and Eghbalifam, N. (2022). “Nanocomposite biodegradable polymers for food packaging,” in Biodegradable Polymer-Based Food Packaging, 227–244. doi:10.1007/978-981-19-5743-7_12
Hopewell, J., Dvorak, R., and Kosior, E. (2009). Plastics recycling: challenges and opportunities. Philosophical Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B, Biol. Sci. 364, 2115–2126. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0311
Hossain, M. T., Shahid, M. A., Akter, S., Ferdous, J., Afroz, K., Refat, K. R. I., et al. (2024). Cellulose and starch-based bioplastics: a review of advances and challenges for sustainability. Polymer-Plastics Technol. Mater. 63, 1329–1349. doi:10.1080/25740881.2024.2329980
Hosseinpour, M., Sahoo, M., Perez-Page, M., Baylis, S. R., Patel, F., and Holmes, S. M. (2019). Improving the performance of direct methanol fuel cells by implementing multilayer membranes blended with cellulose nanocrystals. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 30409–30419. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.194
Hussaini, A., Abdulrasheed, A., Raji, Y., Mohammed, J., Salis, A., and Mohammed, A. (2025). Green polymer composite films for sustainable food packaging: a review. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 21, 70–84. doi:10.4314/njtd.v21i4.2883
Iqbal, A., Harcen, C., and Haque, M. (2024). Graphene (GNP) reinforced 3D printing nanocomposites: an advanced structural perspective. Heliyon 10, e28771. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28771
Iranpour Anaraki, N., and Poursalehi, R. (2015). Shielding effectiveness of polymeric nanocomposites filled with Iron/Wüstite nanoparticles. Procedia Mater. Sci. 11, 700–705. doi:10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.041
Islam, F., and Zeng, Q. (2024). Advances in organosulfur-based polymers for drug delivery systems. Polymers 16, 1207. doi:10.3390/polym16091207
Islam, M. D., Uddin, F. J., Rashid, T. U., and Shahruzzaman, M. (2023). Cellulose acetate-based membrane for wastewater treatment—A state-of-the-art review. Mater. Adv. 4, 4054–4102. doi:10.1039/d3ma00255a
Islam, M. S., Elahee, G. M. F., Fang, Y., Yu, X., Advincula, R. C., and Cao, C. (2025). Polylactic acid (PLA)-based multifunctional and biodegradable nanocomposites and their applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 306, 112842. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2025.112842
Jacquet, A., Geatches, D. L., Clark, S. J., and Greenwell, H. C. (2018). Understanding cationic polymer adsorption on mineral surfaces: kaolinite in cement aggregates. Minerals 8, 130. doi:10.3390/min8040130
Jagadeesh, P., Puttegowda, M., Mavinkere Rangappa, S., and Siengchin, S. (2021). Influence of nanofillers on biodegradable composites: a comprehensive review. Polym. Compos. 42, 5691–5711. doi:10.1002/pc.26291
Jain, P. (2017). Effect of biodegradation and non degradable substances in environment. Int. J. Life Sci., 50–55. doi:10.21744/ijls.v1i1.24
Jaiswal, R., and Sherje, A. P. (2024). Recent advances in biopolymer-based smart hydrogel for wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 99, 105990. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105990
Janeni, J., and Adassooriya, N. (2021). “Nanocellulose biopolymer based biofilms: applications and challenges,” Biopolymer-Based Nano Films, 43–62. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-823381-8.00011-9
Jiang, F., and Hsieh, Y.-L. (2015). Cellulose nanocrystal isolation from tomato peels and assembled nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 122, 60–68. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.12.064
Jiang, T., Carbone, E. J., Lo, K. W. H., and Laurencin, C. T. (2015). Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers for tissue regeneration. Prog. Polym. Sci. 46, 1–24. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2014.12.001
Jiwanti, P. K., Wardhana, B. Y., Sutanto, L. G., Dewi, D. M., Putri, I. Z., and Savitri, I. N. (2022). Recent development of nano-carbon material in pharmaceutical application: a review. Molecules 27, 7578. doi:10.3390/molecules27217578
Jouault, N., Zhao, D., and Kumar, S. K. (2014). Role of casting solvent on nanoparticle dispersion in polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 47, 5246–5255. doi:10.1021/ma500619g
Karamane, M., Raihane, M., Tasdelen, M. A., Uyar, T., Lahcini, M., Ilsouk, M., et al. (2017). Preparation of fluorinated methacrylate/clay nanocomposite via in-situ polymerization: characterization, structure, and properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 55, 411–418. doi:10.1002/pola.28403
Karki, S., and Ingole, P. G. (2022). Development of polymer-based new high performance thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes by vapor phase interfacial polymerization for the removal of heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 446, 137303. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.137303
Kausar, A. (2014). Polyamide-grafted-multi-walled carbon nanotube electrospun nanofibers/epoxy composites. Fibers Polym. 15, 2564–2571. doi:10.1007/s12221-014-2564-y
Kausar, A. (2015). Investigation on self-assembled blend membranes of polyethylene-block-poly(ethylene glycol)-block-polcaprolactone and poly(styrene-block-methyl methacrylate) with Polymer/gold nanocomposite particles. Polymer-Plastics Technol. Eng. 54, 1794–1802. doi:10.1080/03602559.2015.1050511
Kausar, A. (2016a). Bucky papers of Poly(Methyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid)/Polyamide 6 and graphene oxide-montmorillonite. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 37, 66–72. doi:10.1080/01932691.2015.1027908
Kausar, A. (2016b). Estimation of thermo-mechanical and fire resistance profile of epoxy coated polyurethane/fullerene composite films. Fullerenes, Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 24, 391–399. doi:10.1080/1536383x.2016.1172067
Kausar, A. (2016c). Self-Assembled tri-block terpolymer blend membranes reinforced with Poly(Methyl methacrylate) coated gold nanoparticles obtained via phase inversion technique. Int. J. Polym. Analysis Charact. 21. doi:10.1080/1023666X.2016.1192325
Kausar, A. (2016d). Waterborne polyurethane-coated polyamide/fullerene composite films: mechanical, thermal, and flammability properties. Int. J. Polym. Analysis Charact. 21, 275–285. doi:10.1080/1023666x.2016.1147729
Kausar, A. (2017a). Carbon nano onion as versatile contender in polymer compositing and advance application. Fullerenes, Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 25, 109–123. doi:10.1080/1536383x.2016.1265513
Kausar, A. (2017b). Polyamide 1010/Polythioamide blend reinforced with graphene nanoplatelet for automotive part application. Adv. Mater. Sci. 17, 24–36. doi:10.1515/adms-2017-0013
Kausar, A. (2020). A review of high performance polymer nanocomposites for packaging applications in electronics and food industries. J. Plastic Film and Sheeting 36, 94–112. doi:10.1177/8756087919849459
Kausar, A. (2021a). Conducting Polymer-Based Nanocomposites: Fundamentals and Applications. Elsevier.
Kausar, A. (2021b). Progress in green nanocomposites for high-performance applications. Mater. Res. Innovations 25, 53–65. doi:10.1080/14328917.2020.1728489
Kausar, A., and Hussain, S. (2013). High performance heteroaromatic poly(azo-ester)s and their miscible blends: thermomechanical and conductivity profile. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 55, 556–565. doi:10.1134/s1560090413090042
Kausar, A., and Taherian, R. (2019). “Electrical conductivity behavior of polymer nanocomposite with carbon nanofillers,” Electrical Conductivity in Polymer-Based Composites: Experiments, Modelling and Applications, 41–72. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-812541-0.00003-3
Kausar, A., and Ur Rahman, A. (2016). Effect of graphene nanoplatelet addition on properties of thermo-responsive shape memory polyurethane-based nanocomposite. Fullerenes, Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 24, 235–242. doi:10.1080/1536383x.2016.1144592
Kausar, A., Ahmad, I., Maaza, M., and Eisa, M. H. (2022a). State-of-the-Art nanoclay reinforcement in green polymeric nanocomposite: from design to new opportunities. Minerals [Online] 12, 1495. doi:10.3390/min12121495
Kausar, A., Ahmad, I., Maaza, M., Eisa, M. H., and Bocchetta, P. (2022b). Cutting-Edge green Polymer/Nanocarbon nanocomposite for Supercapacitor—State-of-the-art. J. Compos. Sci. 6, 376. doi:10.3390/jcs6120376
Kausar, A., Ahmad, I., and Zhao, T. (2023). Corrosion-Resisting nanocarbon nanocomposites for aerospace application: an up-to-date account. Appl. Nano 4, 138–158. doi:10.3390/applnano4020008
Kaushik, A., Singh, M., and Verma, G. (2010). Green nanocomposites based on thermoplastic starch and steam exploded cellulose nanofibrils from wheat straw. Carbohydr. Polym. 82, 337–345. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.04.063
Kawamoto, M., He, P., and Ito, Y. (2017). Green processing of carbon nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 29, 1602423. doi:10.1002/adma.201602423
Khan, Z. U., Kausar, A., and Ullah, H. (2016). A review on composite papers of graphene oxide, carbon Nanotube, Polymer/GO, and Polymer/CNT: Processing strategies, properties, and relevance. Polymer-Plastics Technol. Eng. 55, 559–581. doi:10.1080/03602559.2015.1098693
Khan, J., Momin, S. A., and Mariatti, M. (2020). A review on advanced carbon-based thermal interface materials for electronic devices. Carbon 168, 65–112. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2020.06.012
Khaparde, D. (2017). Preparation and prediction of physical properties of cellulose acetate and polyamide polymer blend. Carbohydr. Polym. 173, 338–343. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.052
Khatri, M., Ahmed, F. E., Al-Juboori, R. A., Khanzada, N. K., and Hilal, N. (2024). Reusable environmentally friendly electrospun cellulose acetate/cellulose nanocrystals nanofibers for methylene blue removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 111788. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2023.111788
Kim, J., Zhai, L., Mun, S., Ko, H.-U., and Yun, Y.-M. (2015). Cellulose nanocrystals, nanofibers, and their composites as renewable smart materials. Proc. SPIE - Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9434, 94340G. doi:10.1117/12.2084996
Kim, S., Oh, S. M., Kim, S. Y., and Park, J. D. (2021). Role of adsorbed polymers on nanoparticle dispersion in drying polymer nanocomposite films. Polymers, 13. doi:10.3390/polym13172960
Klemm, D., Heublein, B., Fink, H.-P., and Bohn, A. (2005). Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 3358–3393. doi:10.1002/anie.200460587
Kondo, T., Kose, R., Naito, H., and Kasai, W. (2014). Aqueous counter collision using paired water jets as a novel means of preparing bio-nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 112, 284–290. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.064
Korukonda, J. R., Korumilli, T., Kumar T, S., Srujana, T. L., and Abdullahi, A. (2024). “Nanoclay-based green polymeric composites: preparation and properties,” Nanoclay-Based Sustainable Materials, 271–300. doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-13390-9.00013-8
Krystyjan, M., Khachatryan, G., Grabacka, M., Krzan, M., Witczak, M., Grzyb, J., et al. (2021). Physicochemical, bacteriostatic, and biological properties of starch/chitosan polymer composites modified by graphene oxide, designed as new bionanomaterials. Polymers 13 (14), 2327. doi:10.3390/polym13142327
Kumanayaka, T. O., Parthasarathy, R., and Jollands, M. (2010). Accelerating effect of montmorillonite on oxidative degradation of polyethylene nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 95, 672–676. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.11.036
Kumar, A., Tripathi, R., and Kumar, A. (2025). “Nanoparticle and nanofillers: a review on types, properties, application, and toxicological impact,” in Handbook of Nanofillers. Editors S. Mallakpour, and C.M. Hussain (Singapore: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-981-96-2407-2_159
Kumar, V., Pathak, P., and Bhardwaj, N. K. (2020). Waste paper: an underutilized but promising source for nanocellulose mining. Waste Manag. 102, 281–303. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2019.10.041
Kumar, J., Jatoi, A., Mazari, S., Ali, E., Hossain, N., Abro, R., et al. (2022). Advanced green nanocomposite materials for wastewater treatment. Sustainable Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation, 297–321. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-824547-7.00015-1
Kumar, E., Meher, A., Kumar, V., and Panda, D. S. (2024). “Application of functionally graded nano- and microstructures in biomedical devices,” Advances in Modelling and Analysis of Functionally Graded Micro- and Nanostructures, 9-1-12. doi:10.1088/978-0-7503-6024-1ch9
Kumar, A., Tripathi, R., and Kumar, A. (2025). Nanoparticle and nanofillers: a review on types, properties, application, and toxicological impact.
Kumari, S., Rao, A., Kaur, M., and Dhania, G. (2023). Petroleum-Based plastics versus bio-based plastics: a review. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 22, 1111–1124. doi:10.46488/nept.2023.v22i03.003
Lamaming, J., Hashim, R., Sulaiman, O., Leh, C. P., Sugimoto, T., and Nordin, N. A. (2015). Cellulose nanocrystals isolated from oil palm trunk. Carbohydr. Polym. 127, 202–208. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.03.043
Lamberti, F., Román-Ramírez, L., and Wood, J. (2020). Recycling of bioplastics: routes and benefits. J. Polym. Environ. 28, 2551–2571. doi:10.1007/s10924-020-01795-8
Lew, B., Trachtengertz, L., Ratsin, S., Oron, G., and Bick, A. (2014). Brackish groundwater membrane system design for sustainable irrigation: optimal configuration selection using analytic hierarchy process and multi-dimension scaling. Front. Environ. Sci. 2. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2014.00056
Li, Y., and Ye, D. (2018). “21 - carbon-based polymer nanocomposite for lithium-ion batteries,” in Carbon-Based polymer nanocomposites for environmental and energy applications. Editors A. F. Ismail, and P. S. Goh (Elsevier).
Li, A., Wang, A., and Chen, J. (2004). Studies on poly(acrylic acid)/Attapulgite superabsorbent composites. II. Swelling behaviors of superabsorbent composites in saline solutions and hydrophilic Solvent– water mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 94, 1869–1876. doi:10.1002/app.20850
Li, S., Meng Lin, M., Toprak, M. S., Kim, D. K., and Muhammed, M. (2010). Nanocomposites of polymer and inorganic nanoparticles for optical and magnetic applications. Nano Rev. 1, 5214. doi:10.3402/nano.v1i0.5214
Li, T., Tian, L., Liao, S., Ding, X., Irvine, S. A., and Ramakrishna, S. (2019). Fabrication, mechanical property and in vitro evaluation of poly (L-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone) core-shell nanofiber scaffold for tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 98, 48–57. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.06.003
Li, X.-P., Hu, C., Yan, X., Li, L., Ming, Z., Yao, H., et al. (2025). Tree-like 3D GNP-rPN composite structure for solar-thermal evaporation and photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 358, 130260. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.130260
Ligon, S. C., Liska, R., Stampfl, J., Gurr, M., and Mülhaupt, R. (2017). Polymers for 3D printing and customized additive manufacturing. Chem. Rev. 117, 10212–10290. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00074
Lin, S., You, W., Yu, W., and Wang, X. (2019). Key factors in mechanical reinforcement by double percolation network: particle migration and shear stability of filler network. Polymer 182, 121820. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121820
Lin, J.-C., Liatsis, P., and Alexandridis, P. (2023). Flexible and stretchable electrically conductive polymer materials for physical sensing applications. Polym. Rev. 63, 67–126. doi:10.1080/15583724.2022.2059673
Lithner, D., Larsson, Å., and Dave, G. (2011). Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 409 (18), 3309–3324. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.038
Liu, F., and Wang, X. (2020). Synthetic polymers for organ 3D printing. Polymers 12, 1765. doi:10.3390/polym12081765
Liu, T., and Yabu, H. (2024). Biomass-Derived electrocatalysts: Low-Cost, robust materials for sustainable electrochemical energy conversion. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 5, 2470001. doi:10.1002/aesr.202470001
Liu, M., Jia, Z., Jia, D., and Zhou, C. (2014). Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes-polymer nanocomposite. Prog. Polym. Sci. 39, 1498–1525. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2014.04.004
Liu, H., Jian, R., Chen, H., Tian, X., Sun, C., Zhu, J., et al. (2019). Application of biodegradable and biocompatible nanocomposites in electronics: current status and future directions. Nanomaterials 9, 950. doi:10.3390/nano9070950
Liu, L., Wang, X., Jin, H., Wang, J., and Li, Q. (2024). Carbon nanotube-derived materials for smart thermal management. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 9, 2400757. doi:10.1002/adsu.202400757
Lligadas, G., Ronda, J. C., Galià, M., and Cádiz, V. (2013). Renewable polymeric materials from vegetable oils: a perspective. Mater. Today 16, 337–343. doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2013.08.016
Losetty, V., Lakkaboyana, S. K., Chappidi, H. Y., Venkateswarlu, K., Trilaksana, H., Koduru, J. R., et al. (2025). Transformative applications of polymer-based metal oxide nanocomposites in medicine, industry, and environmental remediation: a review. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. doi:10.1007/s10904-025-03707-6
Luceño Sánchez, J. A., Peña Capilla, R., and Díez-Pascual, A. M. (2018). High-Performance PEDOT:PSS/Hexamethylene diisocyanate-functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposites: preparation and properties. Polymers 10, 1169. doi:10.3390/polym10101169
Luraghi, A., Peri, F., and Moroni, L. (2021). Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: a review. J. Control. Release 334, 463–484. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.033
Lvov, Y., and Abdullayev, E. (2013). Functional polymer–clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38, 1690–1719. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.05.009
Madhu, P. (2025). Eco-friendly composites: exploring the potential of natural fiber reinforcement. Discov. Appl. Sci. 7, 401. doi:10.1007/s42452-025-06981-8
Mahajan, M., Murugesan, K. T. G. N., Gokilalakshmi, S., Pugazh, S., Balasubramanian, B., and Balavaishnavi, B. (2023). Biodegradable polymers – research and applications. Phys. Sci. Rev. 9, 949–972. doi:10.1515/psr-2022-0217
Mahesh, N., Balakumar, S., Kamaraj, M., Palanisamy, S., and Aravind, J. (2025). Sustainable innovative approaches on catalytic-carbon nanocomposites for environmental remediation. Environ. Qual. Manag. 35, e70126. doi:10.1002/tqem.70126
Majeed, K., Jawaid, M., Hassan, A., Abu Bakar, A., Abdul Khalil, H. P. S., Salema, A., Inuwa, I., et al. (2012). Potential materials for food packaging from nanoclay/natural fibres filled hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 46, 391–410. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2012.10.044
Malucelli, G., and Kausar, A. (2022). Green composites and nanocomposites for aerospace applications.
Manopriya, S., and Hareesh, K. (2021). The prospects and challenges of solar electrochemical capacitors. J. Energy Storage 35, 102294. doi:10.1016/j.est.2021.102294
Marchese, J., Ponce, M., Ochoa, N. A., Prádanos, P., Palacio, L., and Hernández, A. (2003). Fouling behaviour of polyethersulfone UF membranes made with different PVP. J. Membr. Sci. 211, 1–11. doi:10.1016/s0376-7388(02)00260-0
Markandan, K., and Lai, C. Q. (2023). Fabrication, properties and applications of polymer composites additively manufactured with filler alignment control: a review. Compos. Part B Eng. 256, 110661. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110661
Marquis, D., Guillaume, E., and Chivas-Joly, C. (2011). “Properties of Nanofillers in Polymer,” in Nanocomposites and Polymers with Analytical Methods. doi:10.5772/21694
Marsden, A. J., Papageorgiou, D. G., Vallés, C., Liscio, A., Palermo, V., Bissett, M. A., et al. (2018). Electrical percolation in graphene–polymer composites. 2D Mater. 5, 032003. doi:10.1088/2053-1583/aac055
Maruthupandy, M., Muneeswaran, T., Anand, M., and Quero, F. (2020). Highly efficient multifunctional graphene/chitosan/magnetite nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of important dye molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 153, 736–746. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.045
Mckeown, P., and Jones, M. D. (2020). The chemical recycling of PLA: a review. Sustain. Chem. [Online] 1, 1–22. doi:10.3390/suschem1010001
Melinte, V., Stroea, L., and Chibac-Scutaru, A. L. (2019). Polymer nanocomposites for photocatalytic applications. Catalysts 9, 986. doi:10.3390/catal9120986
Meng, Q., Kuan, H.-C., Araby, S., Kawashima, N., Saber, N., Wang, C., et al. (2014). Effect of interface modification on PMMA/graphene nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 5838–5849. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8278-0
Mirzapour, M., Cousin, P., Robert, M., and Benmokrane, B. (2024). Dispersion characteristics, the mechanical, thermal stability, and durability properties of epoxy nanocomposites reinforced with carbon nanotubes, graphene, or graphene oxide. Polymers [Online] 16, 1836. doi:10.3390/polym16131836
Mohanty, A., Misra, M., and Hinrichsen, G. (2000). Biofibres, biodegradable polymers and biocomposites: an overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 276-277, 1–24. doi:10.1002/(sici)1439-2054(20000301)276:1<1::aid-mame1>3.0.co;2-w
Mohanty, A., Misra, M., and Drzal, L. (2002). Sustainable bio-composites from renewable resources: opportunities and challenges in the green materials world. J. Polym. Environ. 10, 19–26. doi:10.1023/a:1021013921916
Mohanty, A., Drzal, L., and Misra, M. (2003). Nano-reinforcement of bio-based polymers-the hope and reality. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 88, 60–61.
Moniri, M., Boroumandmoghaddam, A., Azizi, S., Rahim, R., Ariff, A., Saad, W., et al. (2017). Production and Status of Bacterial Cellulose in Biomedical Engineering. Nanomaterials (Basel) 7 (9), 257. doi:10.3390/nano7090257
Moon, R. J., Martini, A., Nairn, J., Simonsen, J., and Youngblood, J. (2011). Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 3941–3994. doi:10.1039/c0cs00108b
Morais, A. M. M. B., Morais, R., and Lackner, M. (2024). “Biodegradable bio-based plastics toward climate change mitigation,” Handbook of Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation, 1–48. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6431-0_91-3
Mousavi, S. R., Estaji, S., Paydayesh, A., Arjmand, M., Jafari, S. H., Nouranian, S., et al. (2022). A review of recent progress in improving the fracture toughness of epoxy-based composites using carbonaceous nanofillers. Polym. Compos. 43, 1871–1886. doi:10.1002/pc.26518
Mukhopadhyay, A., and Mishra, D. (2024). Deformation and fracture in materials: advances in experimental and numerical studies.
Munawar, M. A., and Schubert, D. W. (2021). Highly oriented electrospun conductive nanofibers of biodegradable polymers-revealing the electrical percolation thresholds. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 3, 2889–2901. doi:10.1021/acsapm.0c01332
Musa, A. A., Bello, A., Adams, S. M., Onwualu, A. P., Anye, V. C., Bello, K. A., et al. (2025). Nano-Enhanced polymer composite materials: a review of Current advancements and challenges. Polymers 17, 893. doi:10.3390/polym17070893
Muzata, T. S., Gebrekrstos, A., Orasugh, J. T., and Ray, S. S. (2023). An overview of recent advances in polymer composites with improved UV-shielding properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 140, e53693. doi:10.1002/app.53693
Nagalakshmaiah, M., Kissi, N. E., Mortha, G., and Dufresne, A. (2016). Structural investigation of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from chili leftover and their reinforcement in cariflex-IR rubber latex. Carbohydr. Polym. 136, 945–954. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.096
Naser, A. Z., Deiab, I., and Darras, B. M. (2021). Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: a review. RSC Adv. 11, 17151–17196. doi:10.1039/d1ra02390j
Nazrun, T., Hassan, M. K., Hossain, M. D., Ahmed, B., Hasnat, M. R., and Saha, S. (2024). Application of biopolymers as sustainable cladding materials: a review. Sustainability 16, 27.
Nguyen, N., Nguyen, H., Vo, T., Thảo, T., Khanh, N., Pham, C., et al. (2023). Isolation and characterization of Rhizobium spp. and Bradyrhizobium spp. from legume nodules, 12, 70–98.
Niculescu, A.-G., Chircov, C., Bîrcă, A. C., and Grumezescu, A. M. (2021). Nanomaterials synthesis through microfluidic methods: an updated overview. Nanomater. 11, 864. doi:10.3390/nano11040864
Ning, N., Fu, S., Zhang, W., Chen, F., Wang, K., Deng, H., et al. (2012). Realizing the enhancement of interfacial interaction in semicrystalline polymer/filler composites via interfacial crystallization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 37, 1425–1455. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.12.005
Nofar, M., Sacligil, D., Carreau, P. J., Kamal, M. R., and Heuzey, M.-C. (2019). Poly (lactic acid) blends: processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 125, 307–360. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.002
Nonato, R. C., Mei, L. H. I., Bonse, B. C., Leal, C. V., Levy, C. E., Oliveira, F. A., et al. (2022). Nanocomposites of PLA/ZnO nanofibers for medical applications: antimicrobial effect, thermal, and mechanical behavior under cyclic stress. Polym. Eng. and Sci. 62, 1147–1155. doi:10.1002/pen.25913
Oleyaei, S. A., Almasi, H., Ghanbarzadeh, B., and Moayedi, A. A. (2016). Synergistic reinforcing effect of TiO2 and montmorillonite on potato starch nanocomposite films: thermal, mechanical and barrier properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 152, 253–262. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.040
Ozkose, U. U., Altinkok, C., Yilmaz, O., Alpturk, O., and Tasdelen, M. A. (2017). In-situ preparation of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)/clay nanocomposites via living cationic ring-opening polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 88, 586–593. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.07.004
Patachia, S., and Croitoru, C. (2016). Biopolymers for wood preservation, 305, 332. doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-100214-8.00014-2
Peretz Damari, S., Cullari, L., Laredo, D., Nadiv, R., Ruse, E., Sripada, R., et al. (2019). Graphene and boron nitride nanoplatelets for improving vapor barrier properties in epoxy nanocomposites. Prog. Org. Coatings 136, 105207. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.06.053
Pickering, K. L., Efendy, M. G. A., and Le, T. M. (2016). A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 83, 98–112. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.038
Piekarska, K., Sowiński, P., Piorkowska, E., Haque, M., and Pracella, M. (2015). Structure and properties of hybrid PLA nanocomposites with inorganic nanofillers and cellulose fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 82. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.11.019
Pielichowska, K. (2022). Polymer nanocomposites: preparation, characterisation and applications. Nanomaterials 12, 1900. doi:10.3390/nano12111900
Pielichowska, K., Nowicka-Dunal, K., and Pielichowski, K. (2024). Bio-Based polymers for environmentally friendly phase change materials. Polymers 16, 328. doi:10.3390/polym16030328
Pietrini, M., Roes, L., Patel, M. K., and Chiellini, E. (2007). Comparative life cycle studies on Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-Based composites as potential replacement for conventional petrochemical plastics. Biomacromolecules 8, 2210–2218. doi:10.1021/bm0700892
Pillai, C., Paul, W., and Sharma, C. P. (2009). Chitin and chitosan polymers: chemistry, solubility and fiber Formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 34, 641–678. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.04.001
Polverejan, M., Pauly, T., and Pinnavaia, T. (2000). Acidic Porous Clay Heterostructures (PCH): Intragallery Assembly of mesoporous silica in synthetic saponite clays. Chem. Mater. 12, 2698–2704. doi:10.1021/cm0002618
Prataviera, R., Pollet, E., Bretas, R. E. S., Avérous, L., and De Almeida Lucas, A. (2021). Melt processing of nanocomposites of cellulose nanocrystals with biobased thermoplastic polyurethane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 138, 50343. doi:10.1002/app.50343
Pugliese, R., Beltrami, B., Regondi, S., and Lunetta, C. (2021). Polymeric biomaterials for 3D printing in medicine: an overview. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2, 100011. doi:10.1016/j.stlm.2021.100011
Qin, H., Zhao, C., Zhang, S., Chen, G., and Yang, M. (2003). Photo-oxidative degradation of polyethylene/montmorillonite nanocomposite. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 81, 497–500. doi:10.1016/s0141-3910(03)00136-8
Rafiee, R., and Shahzadi, R. (2019). Mechanical properties of nanoclay and nanoclay reinforced polymers: a review. Polym. Compos. 40, 431–445. doi:10.1002/pc.24725
Rahimi, M., Noruzi, E. B., Sheykhsaran, E., Ebadi, B., Kariminezhad, Z., Molaparast, M., et al. (2020). Carbohydrate polymer-based silver nanocomposites: recent progress in the antimicrobial wound dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 231, 115696. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115696
Rahman, M. M., Khan, K. H., Parvez, M. M., Irizarry, N., and Uddin, M. N. (2025). Polymer nanocomposites with optimized nanoparticle dispersion and enhanced functionalities for industrial applications. Processes [Online] 13, 994. doi:10.3390/pr13040994
Rajendran, S., Palani, G., Kanakaraj, A., Shanmugam, V., Veerasimman, A., Gądek, S., et al. (2023). Metal and polymer based composites manufactured using additive Manufacturing—A brief review. Polymers 15, 2564. doi:10.3390/polym15112564
Ramakoti, I., Panda, A., and GoudA, N. (2023). A brief review on polymer nanocomposites: current trends and prospects. J. Polym. Eng. 43, 651–679. doi:10.1515/polyeng-2023-0103
Rana, A. (2023). Nanocellulose-based hydrogels: preparation strategies, dye adsorption and factors impacting. Nanofabrication 8. doi:10.37819/nanofab.8.1757
Rana, A. K., Thakur, M. K., Gupta, V. K., and Thakur, V. K. (2024). Exploring the role of nanocellulose as potential sustainable material for enhanced oil recovery: new paradigm for a circular economy. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 183, 1198–1222. doi:10.1016/j.psep.2024.01.085
Rashid, A., Haque, M., Islam, S. M. M., and Labib, K. M. (2024). Nanotechnology-enhanced fiber-reinforced polymer composites: recent advancements on processing techniques and applications. Heliyon 10, e24692. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24692
Ravikumar, K., and Janardhanan, D. (2020). Preparation and characterisation of green clay-polymer nanocomposite for heavy metals removal. Chem. Ecol. 36, 270–291. doi:10.1080/02757540.2020.1723559
Rebelo, R., Fernandes, M., and Fangueiro, R. (2017). Biopolymers in medical implants: a brief review. Procedia Eng. 200, 236–243. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2017.07.034
Rech, A., Siamos, E., Nicholas, P., and Daugaard, A. E. (2023). Recyclable extrudable biopolymer composites from alginate and lignocellulosic biomass waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. and Eng. 11 (24), 8939–8947. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c01119
Reddy, M., Vivekanandhan, S., Misra, M., Bhatia, S., and Mohanty, A. (2013). Biobased plastics and bionanocomposites: current status and future opportunities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38, 1653–1689. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.05.006
Rehghunadhan, A., Hafusa, A., A R, A., Chandran, N., Nair, S., Maria, H., et al. (2024). Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) from rubber-plastic blends. Advances in Thermoplastic Elastomers, 291–314. doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-91758-2.00008-8
Reuvers, A. J., and Smolders, C. A. (1987). Formation of membranes by means of immersion precipitation: part II. the mechanism of formation of membranes prepared from the system cellulose acetate-acetone-water. J. Membr. Sci. 34, 67–86. doi:10.1016/s0376-7388(00)80021-6
Rezić Meštrović, I., Somogyi Škoc, M., Dragun, D. D., Glagolić, P., and Meštrović, E. (2025). Sustainable solutions for producing advanced biopolymer Membranes—From net-zero technology to zero waste. Polymers 17, 1432. doi:10.3390/polym17111432
Rhim, J.-W., Mohanty, A., Singh, S., and Ng, P. (2006). Effect of the processing methods on the performance of polylactide films: thermocompression versus solvent casting. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 101, 3736–3742. doi:10.1002/app.23403
Robledo-Ortíz, J., Martín Del Campo, A., López-Naranjo, E., Arellano, M., Jasso-Gastinel, C., González-Núñez, R., et al. (2019). Effect of low nanoclay content on the physico-mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 27, 43–54. doi:10.1177/0967391118816393
Roes, A. L., Pietrini, M., Chiellini, E., and Patel, M. (2007). Environmental life cycle studies of poly(hydroxybutyrate)- and polypropylene-based composites, 3.
Rooney, K., Dong, Y., Basak, A. K., and Pramanik, A. (2024). Prediction of mechanical properties of 3D printed particle-reinforced resin composites. J. Compos. Sci. 8, 416. doi:10.3390/jcs8100416
Rosli, N. A., Karamanlioglu, M., Kargarzadeh, H., and Ahmad, I. (2021). Comprehensive exploration of natural degradation of poly(lactic acid) blends in various degradation media: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 187, 732–741. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.196
Rossi, S., Puglisi, A., and Benaglia, M. (2017). Additive manufacturing technologies: 3D printing in organic synthesis. ChemCatChem 10, 1512–1525. doi:10.1002/cctc.201701619
Royer, S.-J., Ferrón, S., Wilson, S., and Karl, D. (2018). Production of methane and ethylene from plastic in the environment. PLOS ONE 13, e0200574. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0200574
Rudnik, E., and Briassoulis, D. (2011). Degradation behaviour of poly(lactic acid) films and fibres in soil under Mediterranean field conditions and laboratory simulations testing. Industrial Crops Prod. 33, 648–658. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.12.031
Rujnić-Sokele, M., and Pilipović, A. (2017). Challenges and opportunities of biodegradable plastics: a mini review. Waste Manag. and Res. 35 (2), 132–140. doi:10.1177/0734242X16683272
Sadowski, R., Wach, A., Buchalska, M., Kuśtrowski, P., and Macyk, W. (2019). Photosensitized TiO2 films on polymers – Titania-polymer interactions and visible light induced photoactivity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 475, 710–719. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.286
Saeed Qureshi, S., Sabzoi, N., Xu, J., Vancov, T., and Chen, C. (2024). Cellulose nanocrystals from agriculture and forestry biomass: synthesis methods, characterization and industrial applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 58745–58778. doi:10.1007/s11356-024-35127-3
Saha, A. (2023). Polymer nanocomposites: a review on recent advances in the field of green polymer nanocomposites. Curr. Nanosci. 20, 706–716. doi:10.2174/0115734137274950231113050300
Sahu, S., Vasavi, B., and Sreekanth, P. S. (2023). Improvements in the mechanical and thermal characteristics of polymer matrix composites reinforced with various nanofillers: a brief review. Mater. Today Proc., 113. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2023.07.032
Salari, M., Habibpour, S., Hamidinejad, M., Mohseni Taromsari, S., Naguib, H., Yu, A., et al. (2023). Enhanced electrical properties of microcellular polymer nanocomposites via Nanocarbon geometrical alteration: a comparison of graphene Nanoribbon and its parent multiwalled carbon nanotube. Mater. Horizons 10. doi:10.1039/D2MH01303G
Scaffaro, R., Maio, A., Gulino, E. F., Morreale, M., and La, M. F. P. (2020). The effects of nanoclay on the mechanical properties, Carvacrol release and degradation of a PLA/PBAT blend. Materials 13, 983. doi:10.3390/ma13040983
Semlali Aouragh Hassani, F.-Z., Ouarhim, W., Nadia, Z., Bouhfid, R., and Qaiss, A. (2019). 4. Natural fiber-based biocomposites: effect of orientation on mechanical properties, 49, 80. doi:10.1515/9783110603699-004
Senthilkumar, K., Saba, N., Rajini, N., Chandrasekar, M., Jawaid, M., Siengchin, S., et al. (2018). Mechanical properties evaluation of sisal fibre reinforced polymer composites: a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 174, 713–729. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.143
Sessini, V., Haseeb, B., Boldizar, A., and Lo Re, G. (2020). Sustainable pathway towards large Scale melt processing of the new generation of renewable cellulose-polyamide composites. RSC Adv. 11, 637–656. doi:10.1039/d0ra07141b
Shah, R. K., and Paul, D. R. (2006). Organoclay degradation in melt processed polyethylene nanocomposites. Polymer 47, 4075–4084. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2006.02.031
Shah, R., Kausar, A., Muhammad, B., and Shah, S. (2015). Progression from graphene and graphene oxide to high performance polymer-based nanocomposite: a review. Polymer-Plastics Technol. Eng. 54, 173–183. doi:10.1080/03602559.2014.955202
Shahid, M. A., Rahman, M. M., Hossain, M. T., Hossain, I., Sheikh, M. S., Rahman, M. S., et al. (2025). Advances in conductive polymer-based flexible electronics for multifunctional applications. J. Compos. Sci. 9, 42. doi:10.3390/jcs9010042
Sharma, N., Ahlawat, Y. K., Sharma, A. J., Sharma, P., Thakur, A., Malik, A., et al. (2025). Nano-films as a sustainable, biopolymer-based solution for post-harvest losses and improved shelf life of horticultural crops: a comprehensive review. J. Coatings Technol. Res. doi:10.1007/s11998-025-01121-8
Shineh, G., Mobaraki, M., Perves Bappy, M. J., and Mills, D. K. (2023). Biofilm Formation, and related impacts on healthcare, food processing and packaging, industrial manufacturing, marine industries, and Sanitation–A review. Appl. Microbiol. 3, 629–665. doi:10.3390/applmicrobiol3030044
Singh, N., and Walker, T. (2024). Plastic recycling: a panacea or environmental pollution problem. npj Mater. Sustain. 2, 17. doi:10.1038/s44296-024-00024-w
Singh, A. A., Genovese, M. E., Mancini, G., Marini, L., and Athanassiou, A. (2020). Green processing route for polylactic acid–cellulose fiber biocomposites. ACS Sustain. Chem. and Eng. 8, 4128–4136. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06760
Singh, V., Gorbel, B., Chatterjee, S., Sen, P., and Verma, V. (2022). Green, economical synthesis of nitrogen enriched carbon nanoparticles from seaweed extract and their application as invisible ink and fluorescent film. Mater. Lett. 309, 131446. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131446
Singh, A., Kaur, S., Thakur, H., Kashyap, S., Lyudmila, A., and Mudgal, G. (2025). “Unveiling the transformative power of smart cellulosic nanomaterials: revisiting potential promises to sustainable future,” in Functionalized cellulose materials: sustainable manufacturing and applications. Editors K. K. Kesari, C. Prakash, M. Khalid, and A. Negi (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland).
Singha, S., and Hedenqvist, M. (2020). A review on barrier properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Clay nanocomposites. Polymers 12, 1095. doi:10.3390/polym12051095
Sinha Ray, S., and Bousmina, M. (2006). Biodegradable polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites. Polym. Nanocomposites, 57–129. doi:10.1533/9781845691127.1.57
Son, Y.-R., and Park, S.-J. (2018). Green preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes-loaded carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 8, 17601. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-35984-2
Song, J., Winkeljann, B., and Lieleg, O. (2020). Biopolymer-Based coatings: promising strategies to improve the biocompatibility and functionality of materials used in biomedical engineering. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 7, 2000850. doi:10.1002/admi.202000850
Song, J., Zhu, L., Yu, S., Li, G., and Wang, D. (2024). The synergistic effect of adsorption and Fenton oxidation for organic pollutants in water remediation: an overview. RSC Adv. 14, 33489–33511. doi:10.1039/d4ra03050h
Subbiah, T., Bhat, G. S., Tock, R. W., Parameswaran, S., and Ramkumar, S. S. (2005). Electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 96, 557–569. doi:10.1002/app.21481
Sudesh, K., Abe, H., and Doi, Y. (2000). Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: biological polyesters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 25, 1503–1555. doi:10.1016/s0079-6700(00)00035-6
Sunday, A., Balogun, S., and Akpan, E. (2012). Review of green polymer nanocomposites. J. Minerals Mater. Charact. Eng. 11, 385–416. doi:10.4236/jmmce.2012.114028
Suriani, M., Sapuan, S., Ruzaidi, C., Nair, D., and Ilyas, R. (2021). Flammability, morphological and mechanical properties of sugar palm fiber/polyester yarn-reinforced epoxy hybrid biocomposites with magnesium hydroxide flame retardant filler. Text. Res. J. 91, 2600–2611. doi:10.1177/00405175211008615
Tabassum, Z., Girdhar, M., Malik, T., Kumar, A., and Mohan, A. (2024). Advancing sustainability: a novel biopolymer-based degradable nanoclay composite film for next-generation packaging. Mater. Adv. 5, 8060–8073. doi:10.1039/d4ma00476k
Talreja, R. (2023). “Manufacturing methods for polymer matrix composites (PMCs),” in Failure Analysis of Composite Materials with Manufacturing Defects 4, 26. doi:10.1201/9781003225737-2
Tan, L. J., Zhu, W., and Zhou, K. (2020). Recent progress on polymer materials for additive manufacturing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2003062. doi:10.1002/adfm.202003062
Tanahashi, M. (2010). Development of fabrication methods of Filler/Polymer nanocomposites: with focus on simple melt-compounding-based approach without surface modification of nanofillers. Materials 3, 1593–1619. doi:10.3390/ma3031593
Tang, Z., Kang, H., Shen, Z., Guo, B., Zhang, L., and Jia, D. (2012). Grafting of polyester onto graphene for electrically and thermally conductive composites. Macromolecules 45, 3444–3451. doi:10.1021/ma300450t
Tarfaoui, M., Lafdi, K., and El Moumen, A. (2016). Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes based polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 103, 113–121. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.08.016
Trache, D., Tarchoun, A. F., Derradji, M., Hamidon, T. S., Masruchin, N., Brosse, N., et al. (2020). Nanocellulose: from fundamentals to advanced applications. Front. Chem., 8. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00392
Tran, L. C., Su, X., Nguyen, H., La, L. B. T., Adu, P., Jia, Q., et al. (2025). Advancing polymer nanocomposites through mechanochemical approaches. Adv. Nanocomposites 2, 86–107. doi:10.1016/j.adna.2025.03.002
Trifol, J., Plackett, D., Sillard, C., Szabo, P., Bras, J., and Daugaard, A. (2016). Hybrid poly(lactic acid)/nanocellulose/nanoclay composites with synergistically enhanced barrier properties and improved thermomechanical resistance. Polym. Int. 65, 988–995. doi:10.1002/pi.5154
Tripathi, D., Sarkar, S., Meher, M., and Poluri, K. M. (2020). “Limitations in commercialization of green polymeric nanocomposites and avenues for rectification,” Green Polymeric Nanocomposites, 281–312. doi:10.1201/9781351045155-10
Trivedi, A. K., and Gupta, M. K. (2025). 3D printed PLA based bionanocomposites with improved mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties: effect of varying CNC reinforcements. Cellulose 32, 2303–2319. doi:10.1007/s10570-025-06432-y
Trukhanov, A. V., Tishkevich, D. I., Podgornaya, S. V., Kaniukov, E., Darwish, M. A., Zubar, T. I., et al. (2022). Impact of the nanocarbon on magnetic and electrodynamic properties of the Ferrite/Polymer composites. Nanomaterials 12, 868. doi:10.3390/nano12050868
Tuama, A. N., Alzubaidi, L. H., Jameel, M. H., Abass, K. H., Bin Mayzan, M. Z. H., and Salman, Z. N. (2024). Impact of electron–hole recombination mechanism on the photocatalytic performance of ZnO in water treatment: a review. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 110, 792–806. doi:10.1007/s10971-024-06385-x
Undabeytia, T., Shuali, U., Nir, S., and Rubin, B. (2021). Applications of chemically modified clay minerals and clays to water purification and slow release formulations of herbicides. Minerals [Online] 11, 9. doi:10.3390/min11010009
Velmurugan, G., Shankar, V. S., Shree, S. G., Abarna, M., and Rupa, B. (2023). “Review and challenges of green polymer-based nanocomposite materials,” in Recent Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2023//2023 Singapore. Editors B. Sethuraman, P. Jain, and M. Gupta (Nature Singapore: Springer), 613–624.
Vidakis, N., Michailidis, N., Papadakis, V., Argyros, A., Spiridaki, M., Mountakis, N., et al. (2024). Industrially scalable reactive melt mixing of polypropylene/silver nitrate/polyethylene glycol nanocomposite filaments: antibacterial, thermal, rheological, and engineering response in MEX 3D-printing. Mater. and Des. 242, 113032. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2024.113032
Vieira, I. R., Carvalho, A. P., and Conte Junior, C. (2022). Recent advances in biobased and biodegradable polymer nanocomposites, nanoparticles, and natural antioxidants for antibacterial and antioxidant food packaging applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 21, 3673–3716. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12990
Vitchuli, N., Shi, Q., Nowak, J., Kay, K., Caldwell, J., Breidt, F., et al. (2011). Multifunctional ZnO/Nylon 6 nanofiber mats by an electrospinning–electrospraying hybrid process for use in protective applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 12, 055004. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/12/5/055004
Wang, Y., and Sun, H. (2021). Polymeric nanomaterials for efficient delivery of antimicrobial agents. Pharmaceutics 13, 2108. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13122108
Wang, R., Kuan, H.-C., Qiu, A., Su, X., and Ma, J. (2020). A Facile approach to the scalable preparation of Thermoplastic/Carbon nanotube composites. Nanotechnology 31, 195706. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/ab5a28
Wang, X., Li, Y., Meng, D., Gu, X., Sun, J., Hu, Y., et al. (2023). A review on flame-retardant polyvinyl alcohol: additives and technologies. Polym. Rev. 63 (2), 324–364. doi:10.1080/15583724.2022.2076694
Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Weng, L., Ge, S., Jiang, D., Huang, M., et al. (2023). A roadmap review of thermally conductive polymer composites: critical factors, progress, and prospects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2301549. doi:10.1002/adfm.202301549
Wei, X., Wang, Z., Tian, Z., and Luo, T. (2021). Thermal transport in polymers: a review. J. Heat Transf. 143, 072101. doi:10.1115/1.4050557
Westlake, J. R., Tran, M. W., Jiang, Y., Zhang, X., Burrows, A. D., and Xie, M. (2023). Biodegradable biopolymers for active packaging: demand, development and directions. Sustain. Food Technol. 1, 50–72. doi:10.1039/d2fb00004k
Wong, S., and Shanks, R. (2009). Biodegradable polymer blends and composites from renewable resources.
Wu, S., Li, H., Futaba, D., Chen, G., Chen, C., Zhou, K., et al. (2022). Structural design and fabrication of multifunctional nanocarbon materials for extreme environmental applications. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201046. doi:10.1002/adma.202201046
Xia, L., Lv, Y., Miao, Z., Luo, L., Luo, W., Xu, Y., et al. (2022). A flame retardant fabric nanocoating based on nanocarbon black particles@polymer composite and its fire-alarm application. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 133501. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.133501
Xu, T., Du, H., Liu, H., Liu, W., Zhang, X., Si, C., et al. (2021a). Advanced nanocellulose-based composites for flexible functional energy storage devices. Adv. Mater. 33, 2101368. doi:10.1002/adma.202101368
Xu, W., Jambhulkar, S., Zhu, Y., Ravichandran, D., Kakarla, M., Vernon, B., et al. (2021b). 3D printing for polymer/particle-based processing: a review. Compos. Part B Eng. 223, 109102. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109102
Xue, J., Wu, T., Dai, Y., and Xia, Y. (2019). Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 119, 5298–5415. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00593
Yadav, H. K. S., Almokdad, A. A., Shaluf, S. I. M., and Debe, M. S. (2019). “Chapter 17 - polymer-based nanomaterials for drug-delivery carriers,” in Nanocarriers for drug delivery. Editors S. S. Mohapatra, S. Ranjan, N. Dasgupta, R. K. Mishra, and S. Thomas (Elsevier).
Yao, Z.-F., Zheng, Y.-Q., Li, Q.-Y., Lei, T., Zhang, S., Zou, L., et al. (2019). Wafer-Scale fabrication of high-performance n-Type polymer monolayer transistors using a multi-level self-assembly strategy. Adv. Mater. 31, 1806747. doi:10.1002/adma.201806747
Yao, Y., Zhu, W., Teng, Y., Li, C., and Yang, Y. (2024). Polymer-Based fabrication of 2D metallic and ceramic nanomaterials. Accounts Mater. Res. 5, 944–957. doi:10.1021/accountsmr.4c00122
Ye, T.-P., Liao, S.-F., Zhang, Y., Chen, M.-J., Xiao, Y., Liu, X.-Y., et al. (2019). Cu(0) and Cu(II) decorated graphene hybrid on improving fireproof efficiency of intumescent flame-retardant epoxy resins. Compos. Part B Eng. 175, 107189. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107189
Youssef, A. M., and El-Sayed, S. M. (2018). Bionanocomposites materials for food packaging applications: concepts and future outlook. Carbohydr. Polym. 193, 19–27. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.088
Zanoaga, M., and Tanasa, F. (2016). “Photochemical behavior of synthetic polymeric multicomponent materials composites and nanocomposites,” Photochemical Behavior of Multicomponent Polymeric-based Materials, 109–164. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-25196-7_5
Zhang, C., and Liu, J. (2017). Stable chitin whisker/Ag3PO4 composite photocatalyst with enhanced visible light induced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 196, 91–94. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2017.02.120
Zhang, Y., and Park, S.-J. (2018). In situ shear-induced mercapto group-activated graphite nanoplatelets for fabricating mechanically strong and thermally conductive elastomer composites for thermal management applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 112, 40–48. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.06.004
Zhang, Y., Choi, J. R., and Park, S.-J. (2018). Interlayer polymerization in amine-terminated macromolecular chain-grafted expanded graphite for fabricating highly thermal conductive and physically strong thermoset composites for thermal management applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 109, 498–506. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.04.001
Zhang, X., Liu, W., Yang, D., and Qiu, X. (2019). Biomimetic supertough and strong biodegradable polymeric materials with improved thermal properties and excellent UV-Blocking performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1806912. doi:10.1002/adfm.201806912
Zhang, J., Qian, M., Zhang, X., Li, A., and Geng, L. (2024). Enhancing strength and toughness of GNS/Al nanocomposites via a hybridization strategy. Mater. and Des. 244, 113099. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2024.113099
Zhao, X., Gnanaseelan, M., Jehnichen, D., Simon, F., and Pionteck, J. (2019). Green and facile synthesis of polyaniline/tannic acid/rGO composites for supercapacitor purpose. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 10809–10824. doi:10.1007/s10853-019-03654-x
Zhao, D., Zhu, Y., Cheng, W., Chen, W., Wu, Y., and Yu, H. (2021a). Cellulose-Based flexible functional materials for emerging intelligent electronics. Adv. Mater. 33, 2000619. doi:10.1002/adma.202000619
Zhao, S., Zhan, Y., Feng, Q., Yang, W., Dong, H., Sun, A., et al. (2021b). Easy-handling carbon nanotubes decorated poly(arylene ether nitrile)@tannic acid/carboxylated chitosan nanofibrous composite absorbent for efficient removal of methylene blue and Congo red. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 626, 127069. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127069
Zhong, Y., Janes, D., Zheng, Y., Hetzer, M., and De Kee, D. (2007). Mechanical and oxygen barrier properties of organoclay-polyethylene nanocomposite films. Polym. Eng. and Sci. 47, 1101–1107. doi:10.1002/pen.20792
Zhou, P., Luo, Y., Lv, Z., Sun, X., Tian, Y., and Zhang, X. (2021). Melt-processed poly (vinyl alcohol)/corn starch/nanocellulose composites with improved mechanical properties. Int. J. of Biol. Macromol. 183, 1903–1910. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.011
Keywords: biodegradable polymers, nanofillers, sustainability, water treatment, industrial applications
Citation: Abu-Zurayk R, Khalaf A, Alnairat N, Waleed H, Bozeya A, Abu-Dalo D and Rabba’a M (2025) Green polymer nanocomposites: bridging material innovation with sustainable industrial practices. Front. Mater. 12:1701086. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1701086
Received: 08 September 2025; Accepted: 23 October 2025;
Published: 20 November 2025.
Edited by:
Madhu Puttegowda, Malnad College of Engineering, IndiaReviewed by:
Sathickbasha K, B. S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, IndiaLin Feng Ng, University of Technology Malaysia, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Abu-Zurayk, Khalaf, Alnairat, Waleed, Bozeya, Abu-Dalo and Rabba’a. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rund Abu-Zurayk, ci5hYnV6dXJheWtAanUuZWR1Lmpv
 Rund Abu-Zurayk
Rund Abu-Zurayk Aya Khalaf
Aya Khalaf Nour Alnairat
Nour Alnairat Haneen Waleed
Haneen Waleed Ayat Bozeya
Ayat Bozeya Duaa Abu-Dalo
Duaa Abu-Dalo Manar Rabba’a
Manar Rabba’a