- 1China Jingye Engineering Co. Ltd., Central Research Institute of Building and Construction Co. Ltd., Beijing, China
- 2School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin, China
- 3CNPC East China Design Institute Co. Ltd., Qingdao, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Technology and Equipment of Tianjin Urban Air Transportation System, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin, China
Asphalt mixture stands as one of the extensively utilized materials within the realm of road engineering. Fibers have the remarkable ability to substantially enhance the road performance of asphalt mixtures. The influence of fibers on the physical and mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures, along with the microscopic strengthening mechanism, has drawn the attention of numerous scholars. In this research, the basalt fiber reinforced asphalt mixture (BFRAM) was selected as the subject of study. A series of material tests on the BFRAM were conducted to investigate the impact of basalt fibers on the physical and mechanical properties of the asphalt mixture, including bulk density, stability, flow value, and compressive strength. Based on the discrete element method, the entire process of crack formation, development, and failure of the asphalt mixture under uniaxial compression was simulated. This simulation served to uncover the microscopic strengthening mechanism of the BFRAM. The results indicated that as the fiber content increased, the bulk density and voids filled with asphalt with 6 mm and 9 mm fiber content first decreased, then increased, and finally decreased again. For 12 mm fiber content, the bulk density and voids filled with asphalt first increased and then decreased. Conversely, the void content of asphalt mixture and the asphalt-aggregate ratio showed an opposite trend, while Marshall stability consistently increased. The compressive strength of the asphalt mixture initially rises and then falls. When the fiber content reached 0.3%, the stability and compressive strength of the asphalt mixture increased by 23.6% and 43.3% respectively, in comparison to the asphalt mixture without fiber. From the perspective of microscopic mechanism analysis, the adhesion between asphalt aggregates was significantly strengthened after the addition of fibers. When the fiber content was less than 0.3%, the number of cracks, crack width, and damage degree of the asphalt mixture were notably improved. However, when the fiber content exceeded 0.3%, fiber agglomeration occurred. This phenomenon reduced the number of contacts within the mixtures, leading to a decrease in the compressive strength of the BFRAM.
1 Introduction
As a crucial material for airport pavements, asphalt mixture boasts advantages such as low take-off and landing noise, convenient maintenance, and recyclability. With the rapid economic development in China, the traffic volume on airport pavements has been continuously increasing, posing extremely severe challenges to the pavement performance of airport asphalt mixture pavements. To reduce the early damage of asphalt pavements, adding fibers to the asphalt mixture has emerged as an effective way to enhance its performance (Wang et al., 2019). From asbestos fibers to lignin fibers, and now commonly used polymer fibers, glass fibers, and basalt fibers (Taherkhani and Afroozi, 2017; Hosseinian et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2024). Among them, basalt fiber is an emerging material with excellent properties and low cost, which can improve the high-temperature and low-temperature performance as well as water stability of asphalt mixtures and prevent reflective cracking. In recent years, the application of basalt fiber in asphalt mixtures and the related research on pavement performance have gradually become a popular research direction in the field of asphalt pavements.
In recent years, scholars had found that different types and contents of fibers have significantly different effects on the performance improvement of asphalt mixtures. Zhao et al. (2020) evaluated the road performance of asphalt mixtures containing varying amounts of basalt fibers. The results indicated that when the incorporation ratio of basalt fibers was 0.3%, the asphalt mixture exhibited the optimal road performance. Alfalah et al. (2021) investigated the influences of fiber type, fiber content, and binder content on the volumetric characteristics and laboratory performance of asphalt mixtures. The results showed that without additional asphalt, the crack resistance of the asphalt mixture containing 0.3% carbon fibers was enhanced. Li et al. (2023) conducted high temperature stability tests, cracking resistance tests, water stability tests, and dynamic modulus tests to explore the improvement effect of basalt fiber on asphalt mixture. Yan et al. (2025) discussed the reinforcement of concrete structures, asphalt pavements, and chopped basalt fiber-reinforced cementitious composites using basalt fiber-reinforced polymer (BFRP) plates, BFRP rebars, or grids. Compared to non-reinforced structures, the load-bearing capacity of the reinforced structures was found to increase by up to 60%. Concrete structures reinforced with BFRP could achieve a service life of at least 50 years under harsh environmental conditions—significantly longer than that of conventional reinforced concrete structures. Moreover, the use of basalt fibers was shown to improve the fatigue crack resistance of asphalt by up to 600%.
In addition, fiber length also had a significant impact on the performance of asphalt mixtures. Jiao et al. (2020) evaluated the enhancement effect of basalt and steel fiber on the fracture resistance of asphalt mixture using low temperature indirect tensile test. The results revealed that the asphalt mixture with 12 mm basalt fiber had good ductility in the final failure stage. Xie and Wang (2023) utilized basalt fibers of three lengths (3, 6, and 9 mm) and four proportions (0%, 3%, 6%, and 9% of the asphalt mass). Dynamic shear and bending beam rheometer tests were conducted to evaluate their rheological properties. The experimental results demonstrated that basalt fibers enhanced the stiffness, rutting resistance, and cracking potential of asphalt binders, while reducing the fatigue performance of asphalt binders. Ashith et al. (2023) investigated the effect of fiber length on the mechanical performance of asphalt mixture with 3 mm, 6 mm, and 24 mm carbon fiber. The results of indirect tension cracking test indicated that the 6 mm carbon fiber presented the most improvement in mechanical performance of the mixture. Aboutalebi and Namavar (2018) evaluated the effects of various para-fiber lengths on the mechanical properties of hot mix asphalt (HMA) through tests including Marshall stability, indirect tensile strength, and resilient modulus. In this study, 0.5% of fibers with lengths of 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and 18 mm were incorporated into HMA specimens, which were subsequently subjected to the aforementioned mechanical tests. The results demonstrated that the addition of fibers significantly enhanced the mechanical performance of the asphalt mixtures. Furthermore, it was observed that as fiber length increased, a higher fiber content may be required to ensure an adequate presence of fibers within the mixture to effectively inhibit crack initiation and propagation. Laib et al. (2025) utilized brick waste powder (BWP) as an alternative to conventional limestone powder (LS) filler, and simultaneously incorporated three different lengths of polyester fiber (PF)—3 mm, 8 mm, and 15 mm—into the mix. The experimental design and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were carried out using the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) to evaluate the influence of BWP and PF on the performance characteristics of asphalt concrete (AC) mixtures. The results indicated that the combined use of PF and BWP significantly enhanced the moisture resistance and mechanical properties of the AC mixtures, thereby achieving superior overall performance. Ultimately, a PF length of 5 mm in combination with BWP was identified as the optimal configuration to achieve the best AC performance.
In addition to macroscopic research methods, numerical simulation can also be used to further explore the mechanical properties of basalt fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures from a microscopic perspective. Zhang et al. (2023) conducted X-ray computed tomography and discrete element simulations to obtain the morphological parameters of BFRAM related to fiber length distribution. Dan et al. (2018) investigated the cracking mechanism of asphalt mixtures by establishing a three-dimensional discrete element model. The research results indicated that cracks initially appeared near the loading rod. Cheng et al. (2022) utilized ABAQUS to construct three-dimensional fiber reinforced asphalt mixture beam models with diverse distribution patterns. The simulation outcomes demonstrated that the addition of fibers enhanced the tensile performance of the asphalt mixture beam model. Stukhlyak et al. (2015) investigated the shock fracture mechanisms of epoxy composite materials from different structural scales. The findings demonstrated that pronounced heterogeneity in epoxy composites across structural scales governed their physical and mechanical properties.
To enhance the road performance of asphalt mixtures, a series of material performance tests were conducted, including the BFRAM test, Marshall test, and uniaxial compression test. These tests demonstrated the influence of the content and length of basalt fibers on the physical and mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures, such as bulk density, asphalt-aggregate ratio, stability, and compressive strength. Based on the test results, a discrete element model of the BFRAM was constructed using the Particle Flow Code (PFC) software. This model was employed to investigate the entire stress-strain process and the microscopic mechanism of the fiber asphalt mixture under axial pressure. The influence mechanism of basalt fibers on the deformation mechanical behavior of the reinforced mixture was comprehensively analyzed from both macroscopic and microscopic perspectives.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Properties of raw materials
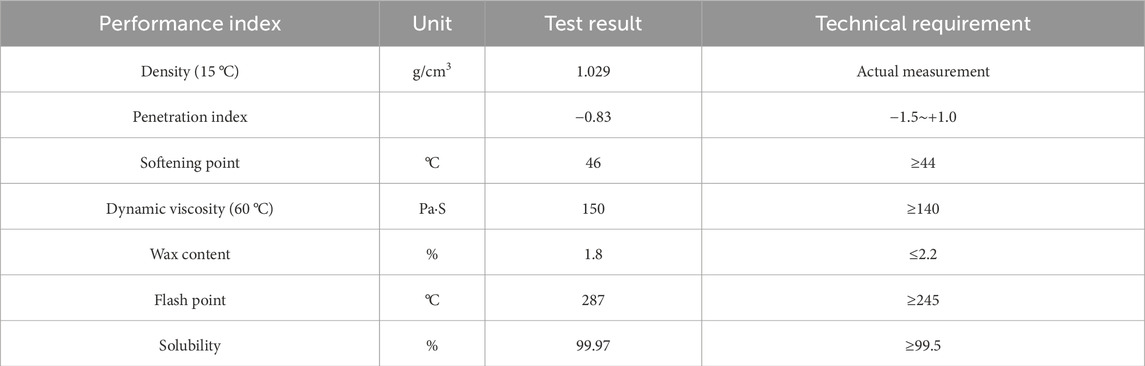
The asphalt of grade 70A was used in the tests, which was produced by Huate Company in China. Table 1 showed performance indexes of the asphalt. It could be concluded from Table 1 that the properties of asphalt satisfied the requirements of the test.
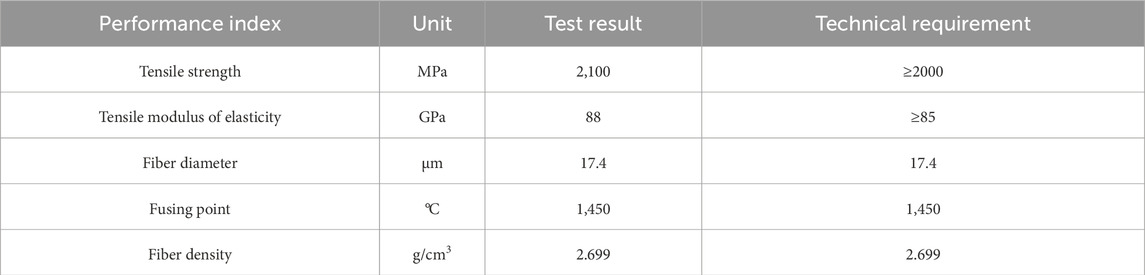
Compared with other fiber materials, basalt fiber had the advantages of high strength, better heat resistance and corrosion resistance, which could improve the mechanical properties of asphalt mixture. In this study, the basalt fiber of length of 6 mm, 9 mm and 12 mm were adopted, and the performance indexes were illustrated in Table 2.
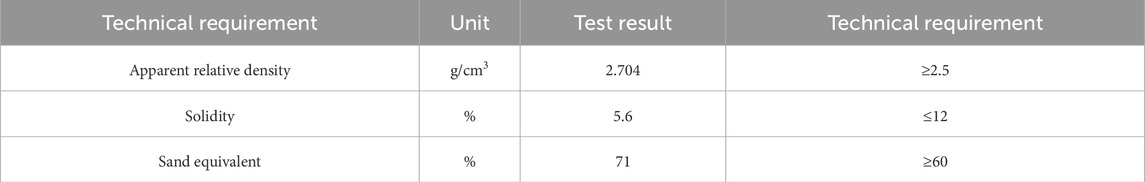
In the asphalt mixture, the aggregate with particle size greater than 2.36 mm was defined as the coarse aggregate, and that with particle size less than 2.36 mm was the fine aggregate. In this study, both coarse aggregate and fine aggregate were limestone, and the properties of the aggregate were demonstrated in Table 3 and 4.
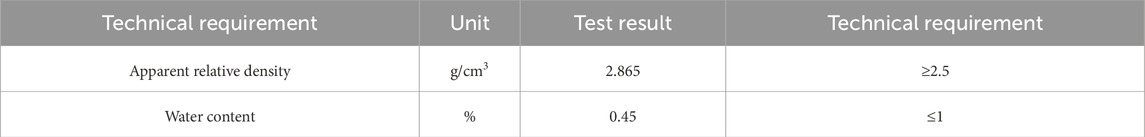
The filler adopted in the test was mineral powder of class S105 that was obtained from grinding limestone. The technical requirements and test results were illustrated in Table 5.
2.2 Aggregate grading
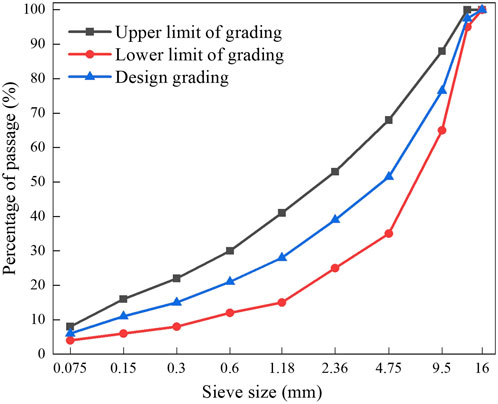
According to the specifications (Civil Aviation Administration of China, 2017), asphalt mixture of type AC-13 was selected as the research object. The aggregate grading limits of AC-13 asphalt mixture and the designed grading were demonstrated in Figure 1. The curves of three colors could be seen from the figure, where the black curve was the upper limit of the aggregate grading of the mixture, the red curve was the lower limit, and the blue curve was the grading designed in this paper.
2.3 The optimum oil-to-stone ratio for asphalt mixture
Ascertaining the optimal oil-to-stone ratio for asphalt mixtures was a crucial step in the mixture design process. The Marshall test approach was employed to gauge the stability, flow value, and density of the specimens. Subsequently, the air void content (VV), voids filled with asphalt (VFA), and voids in mineral aggregate (VMA) of the mixture were computed to identify the optimal oil-to-stone ratio of asphalt mixtures with varying fiber contents.
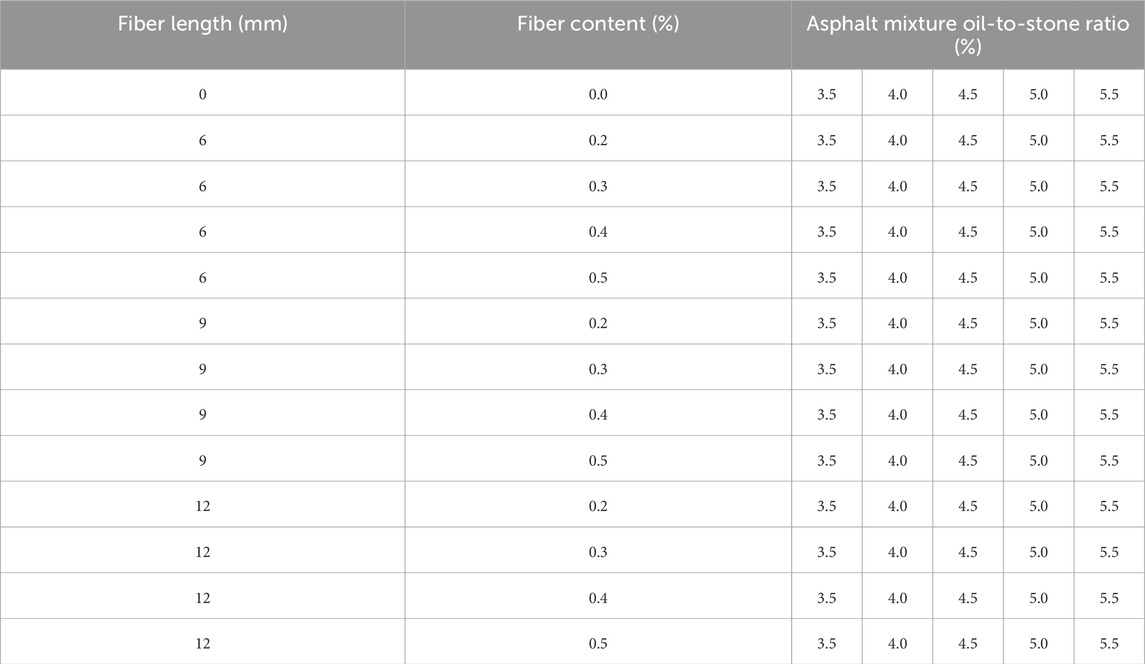
The Marshall specimen took the form of a cylinder, featuring a diameter of 101.6 mm and a height of 63.5 mm. The density of the specimen was determined using the net-basket method. The specimen was immersed in a constant-temperature water tank maintained at 60 °C for 30 min. After removing the surface water, it was promptly placed on the Marshall stability test equipment. The sample was subjected to a uniform load at a rate of 50 mm/min until the specimen failed, and the stability and flow value were recorded by the equipment. In the Marshall test, 3 fiber lengths, 5 oil-to-stone ratios, and 5 fiber contents were taken into account. This resulted in a total of 75 test conditions. Each test condition involved 4 specimens for repeated testing. The specific test conditions were presented in Table 6.
2.4 Mechanical properties test of asphalt mixture
Uniaxial compression tests were carried out on asphalt mixtures to investigate the influence rules of the length and content of basalt fiber on the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures. In the test, the cylindrical specimen (100 mm in diameter × 100 mm in height) was prepared by the compaction method. Testing was conducted at 20 °C under displacement-controlled axial loading at a rate of 2 mm/min until significant failure occurred.
The experiments were performed using the controlled-variable method. The oil-to-stone ratio of the asphalt mixture was selected as the optimal ratio in the absence of basalt fiber. The basalt fiber content was set at 0%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5%, and the fiber lengths were 6 mm, 9 mm and 12 mm, resulting in a total of 13 test conditions. For each test condition, 4 parallel specimens were employed.
3 Test results and analysis
3.1 Influence of basalt fiber on the physical properties of asphalt mixture
Figure 2 depicted the variations of bulk density, VV, VFA, and VMA in relation to the fiber content. Specifically, Figure 2A illustrated the variation of the bulk density of BFRAM as a function of fiber content. As could be observed from Figure 2A, when the fiber length was 12 mm, the bulk density of the asphalt mixture initially increased and subsequently decreased with the increasing fiber content. In contrast, when the fiber lengths were 6 mm and 9 mm, the bulk density of the asphalt mixture first decreased, then increased, and finally decreased again as the fiber content increased. Moreover, a maximum density was identified in these cases. When the fiber length was 12 mm, the maximum bulk density was achieved at a fiber content of 0.2%, and that was attained at a fiber content of 0.3% for fiber length of 6 mm and 9 mm.
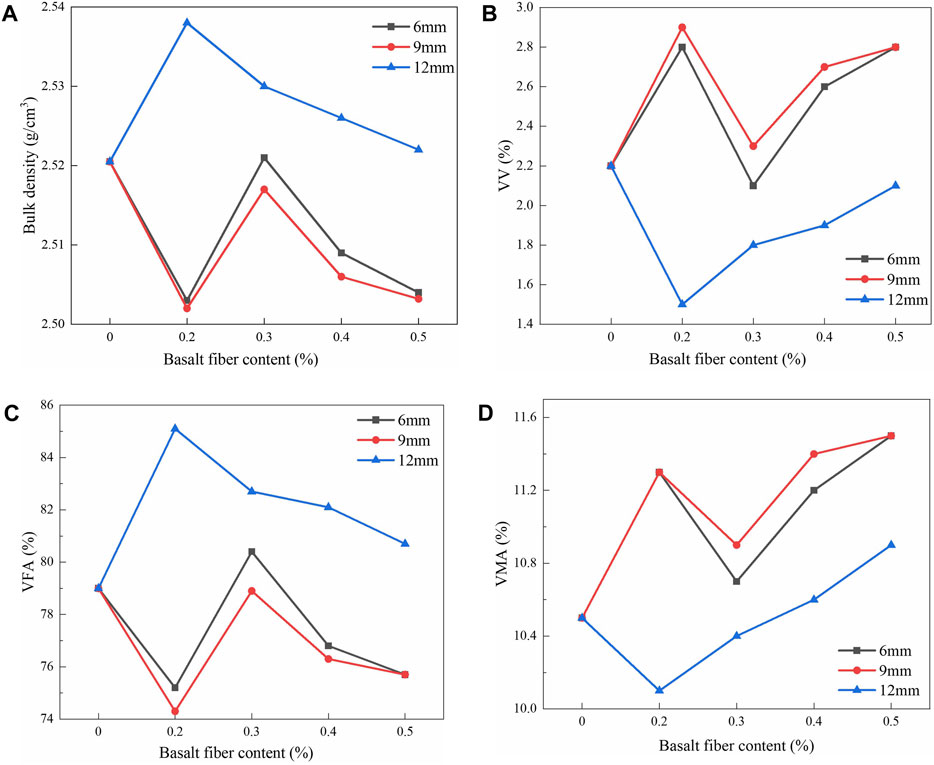
Figure 2. The variation of the physical properties of asphalt mixtures: (A) Bulk density; (B) VV; (C) VFA; (D) VMA.
Figure 2B illustrated the variation in the VV of BFRAM as a function of fiber content. As could be observed from Figure 2B, for fiber length of 12 mm, the VV initially decreased and subsequently increased with the increasing fiber content. In the cases where the fiber lengths were 6 mm and 9 mm, the VV first increased, then decreased, and finally increased again. Specifically, the maximum increase percentages of the VV for the 6 mm and 9 mm BFRAM were 27.3% and 31.8%, respectively. In comparison to the non-fiber asphalt mixture, the maximum increase percentage of the VV for the 12 mm BFRAM was 4.5%, indicating nearly negligible change. It was evident from Figure 2B that as the fiber content rose, the VV of the BFRAM increased. Consequently, this increase in VV lead to a reduction in the bulk density of the mixture.
Figure 2C showed the variation pattern of the VFA in relation to the fiber content within the BFRAM. As could be observed from Figure 2C, when the fiber length was set at 12 mm, the VFA of the asphalt mixture initially exhibited an upward trend and subsequently declined with increasing fiber content. When the fiber lengths were 6 mm and 9 mm, the VFA of the asphalt mixture first decreased, then increased, and finally decreased again. Moreover, the VFA values of the mixtures with fiber lengths of 6 mm and 9 mm were 4.8% and 5.9% lower, respectively, compared to the mixture without fiber. With the increment of fiber content, the basalt fibers adsorbed a greater amount of asphalt. This adsorption phenomenon led to a reduction in the asphalt distribution within the mixture, consequently resulting in a decrease in the VFA.
Figure 2D illustrated the VMA changing with fiber content. As could be observed from Figure 2D, when the fiber length was 12 mm, with the increase in fiber content, the VMA of the asphalt mixture initially decreased and subsequently increased. When the fiber lengths were 6 mm and 9 mm, the VMA of the asphalt mixture first increased, then decreased, and finally increased again. When the fiber content was 0.5%, compared to the asphalt mixture without fiber, the VMA of the asphalt mixtures with fiber lengths of 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm increased by 9.5%, 9.5%, and 3.8% respectively.
As could be seen from the above, the trends of bulk density and VFA with fiber content were basically consistent, and the trends of VV and VMA changes were also basically consistent. It could be concluded that added fibers formed a certain spatial structure within the asphalt mixture, increasing its porosity and thus reducing its bulk density. Adding different amounts of fibers results in increments of VV and VMA not exceeding 10%, which was attributed to the small amount of fiber, having a minor impact.
3.2 Influence of basalt fiber on the mechanical properties of asphalt mixture
3.2.1 Marshall test
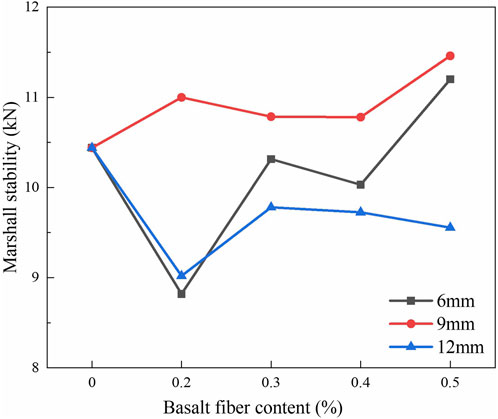
Figure 3 presented the variation of Marshall stability of BFRAM with the fiber content. It could be obtained from Figure 3 that the Marshall stability of asphalt mixture first decreased and then increased with the increase of fiber content for different fiber lengths, indicating that the maximum failure load of specimens changed with the increase of fiber content. When the fiber content was 0.5%, the stability of the asphalt mixture with 6 mm and 9 mm fiber reached the maximum value, and the stability of the mixture increased by 7.3% and 9.8%, respectively, compared with that without fiber. The stability of asphalt mixture with 9 mm fiber was higher than that with other length of fiber. For specimen of 12 mm fiber, the maximum stability of asphalt mixture appeared when the fiber content was 0.3%, and the stability of asphalt mixture with 12 mm fiber was smaller than that without fiber. The suitable content of basalt fiber could bridge the aggregates in the asphalt mixture and form a network structure, contributing to an improvement of the strength of the mixture. At the same time, the fiber could enhance the interaction between the particles of the mixture, and the increase of cohesion and adhesion helped to reduce the movement and separation of the particles in the mixture, and improved the overall stability of the mixture.
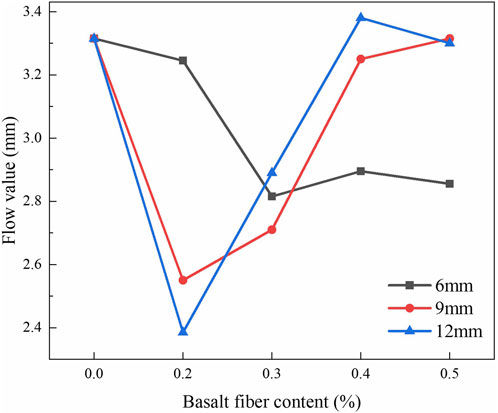
Figure 4 illustrated the variation of the flow value in the Marshall test of BFRAM with respect to the fiber content. Figure 4 revealed that the flow value of the asphalt mixture initially decreased and subsequently increased as the fiber content rose. As the fiber content increased, the minimum flow values of asphalt mixtures containing 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm fiber specimens decreased by 15.1%, 23.1%, and 28.1%, respectively, in comparison to the mixture without fiber. The flow value represented the deformation of the mixture under the maximum load, which reflected the free asphalt content and the deformation resistance of the asphalt mixture. The fiber exerted an influence on both the free asphalt content and the deformation resistance of the asphalt mixture. On one hand, the adsorption of asphalt by the fiber reduced the free asphalt content within the mixture. On the other hand, the bridging effect between the fiber and the aggregate could enhance the deformation resistance of the mixture. The effects of the fiber on the free asphalt content and the deformation resistance were opposite, which lead to the increase and decrease of the flow value.
3.2.2 Uniaxial compression test
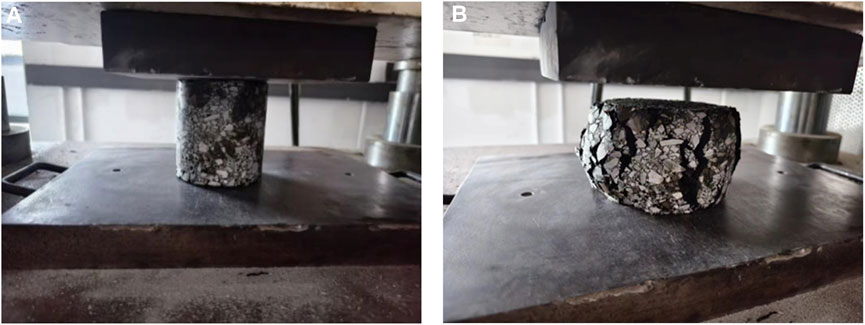
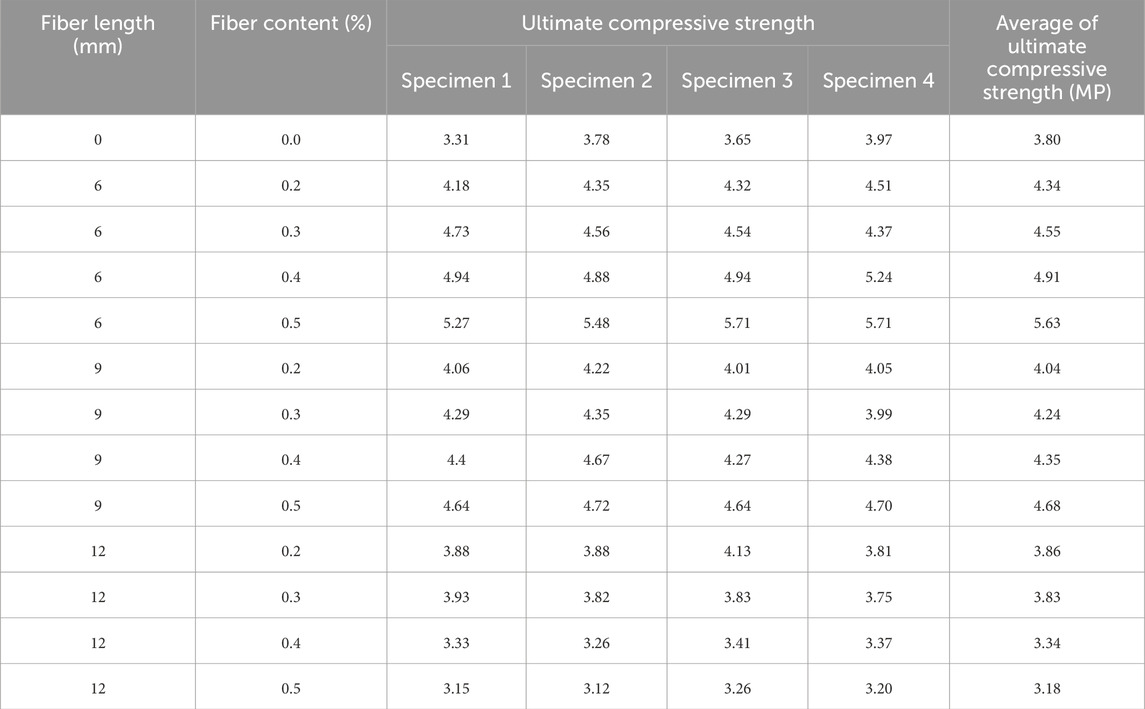
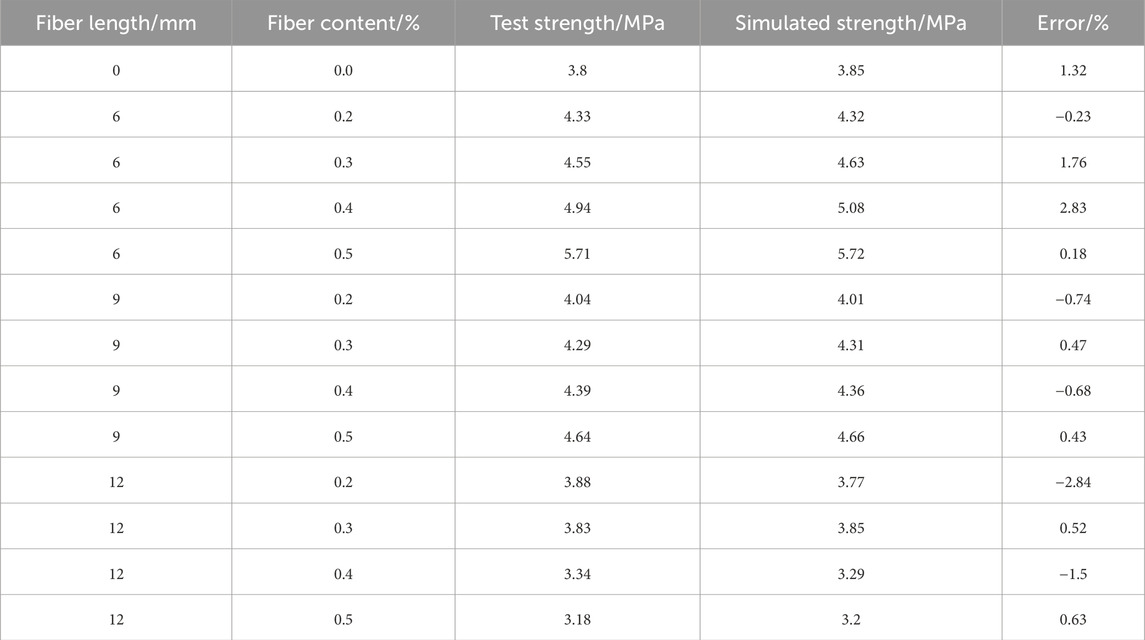
Uniaxial compression test of asphalt mixture was used to measure the compressive strength of asphalt mixture. Figure 5 showed the view of specimens before test and the typical failure mode of the specimen. The compressive strength under different fiber content and length were showed in Table 7.
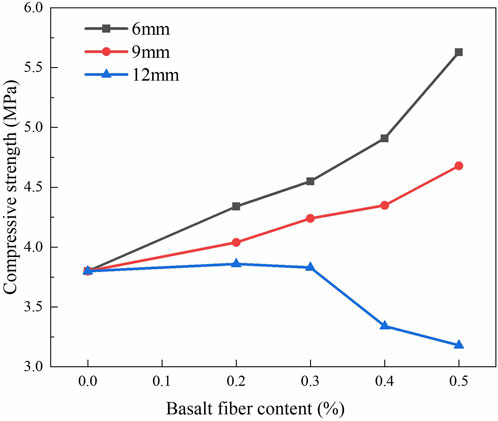
Figure 6 demonstrated the variation in the ultimate compressive strength of BFRAM in relation to the fiber content. From Figure 6, it could be deduced that as the fiber content increased, the ultimate compressive strength of asphalt mixtures containing 6 mm and 9 mm fibers exhibited an upward trend. In contrast, the ultimate compressive strength of the asphalt mixture with 12 mm fibers initially rose and then declined. The maximum compressive strengths of the asphalt mixtures with 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm fibers occurred at fiber contents of 0.5%, 0.5%, and 0.2%, respectively. Compared to the asphalt mixture without fiber, these maximum compressive strengths showed increases of 48.2%, 23.2%, and 1.6%, respectively. By comparing the ultimate compressive strengths of asphalt mixtures with different fiber lengths, it was evident that the compressive strength of asphalt mixtures decreased as the fiber length increased.
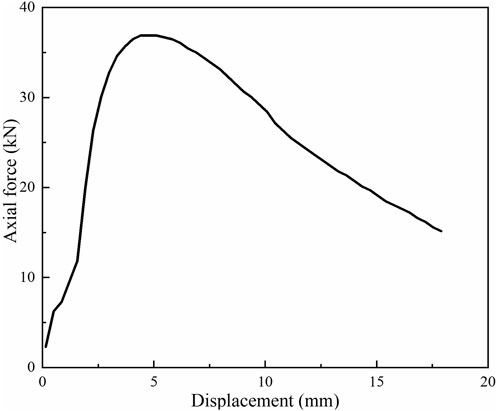
Figure 7 depicted the curve representing the relationship between the axial force and displacement of the asphalt mixture in the uniaxial compression test, with a fiber length of 9 mm and a fiber content of 0.5%. This curve could be partitioned into three distinct stages. In the first stage, the specimen undergoes compaction under the action of the axial force, during which the voids within the specimen are eliminated. The elastic modulus at this stage was comparatively low. During the second stage, as the mixture became void-free, the elastic modulus of the specimen exhibited a significant increase. The displacement increased in tandem with the increase in the axial force until the ultimate axial load was reached. Concurrently, the specimen started to crack, and the width of the crack gradually expanded. In the third stage, as the internal structure of the mixture was damaged, the displacement continues to increase while the force decreased. The width of the crack kept growing until the specimen was completely destroyed.
4 Discrete element analysis of the asphalt mixture
4.1 Discrete element model
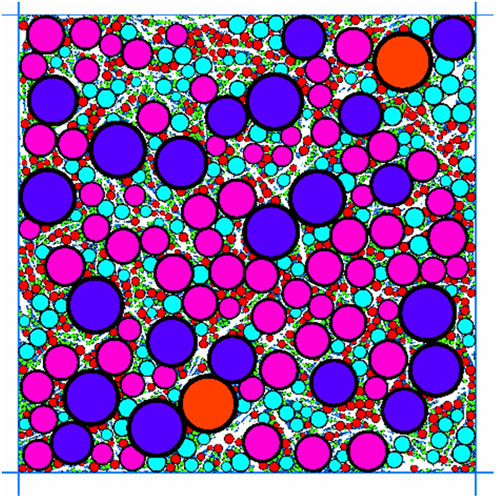
The discrete element software was employed to construct the numerical models of BFRAM. Spherical elements were utilized to mimic the aggregates with a particle size larger than 2.36 mm in the asphalt mixture. The contact model was implemented to simulate the asphalt mortar, which consisted of aggregates with a particle size smaller than 2.36 mm and matrix asphalt. The discrete element model was randomly generated by two-dimensional particles, and the dimensions of the asphalt mixture model were consistent with those of the specimen in the uniaxial compression test. The detailed modeling process is presented as follows.
1. Particle Generation. The mass percentages of aggregates with various particle sizes were transformed into volume percentages to mimic the grading composition. Subsequently, particles of different sizes were generated within the specified model scope to construct a particle system.
2. Fiber Establishment. By utilizing the FISH language to define particle boundaries, multiple spherical particles having the same diameter as basalt fibers were bonded together to create flexible clusters, which were employed to simulate the basalt fibers.
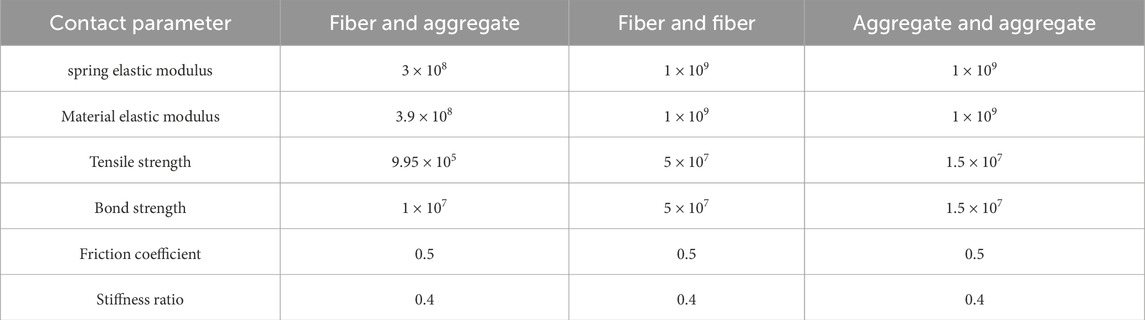
3. Contact Model Setting. The contacts within the model were classified into three categories: the contact between aggregates, the contact between aggregates and fibers, and the contact between fibers. A parallel bonding model was chosen for all contact models based on the study of Shi et al. (2024) and Liu et al., 2023, and the contact parameters were calibrated based on the outcomes of the uniaxial compression test.
4. Pre-pressing. A specific speed was assigned to the wall to compress the particle sphere and form a cylindrical specimen. As depicted in Figure 8, the two-dimensional discrete element model of BFRAM consisted of 7 types of aggregates with different particle sizes and clusters of fiber particles, amounting to a total of 14,245 particles.
Note that a two-dimensional model was applied to represent the three-dimensional specimen to improve the computational efficiency, which was verified to be practicable in reference (Yao et al., 2022).
4.2 Model verification and parameter calibration
The stress and displacement of the upper and lower walls of the model were monitored and documented using the FISH function. Subsequently, the stress-strain curve of the uniaxial compression test for the asphalt mixture model could be plotted. Drawing upon the parameter selection experience from literature (Ye et al., 2020) and making a comparison with the uniaxial compression test results presented in Section 3.2, the parameters of the model were calibrated. The contact parameters of the model were detailed in Table 8.
Table 9 presented a comparison between the test results and simulation results of BFRAM with different fiber lengths and different fiber contents. Figure 9 depicted the comparison of the stress-strain curves between the test results of the asphalt mixture containing 6 mm fibers and the corresponding simulation results. As showed in Table 9, there was a small error in the compressive strength between the simulation results and the test results, with the maximum error being 2.84%. Figure 9 indicated that under different fiber contents, the stress-strain curve of the test results aligns well with that of the simulation results. The above findings validated the prediction accuracy of the discrete element model for BFRAM.
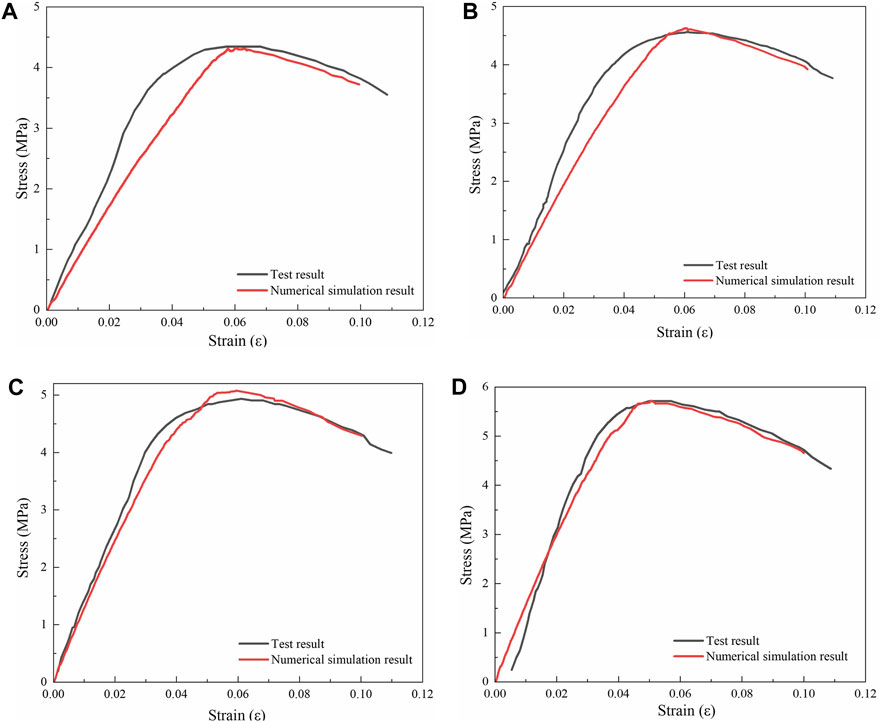
Figure 9. Stress-strain curve of test and simulation results: (A) Fiber content of 0.2%; (B) Fiber content of 0.3%; (C) Fiber content of 0.4%; (D) Fiber content of 0.5%.
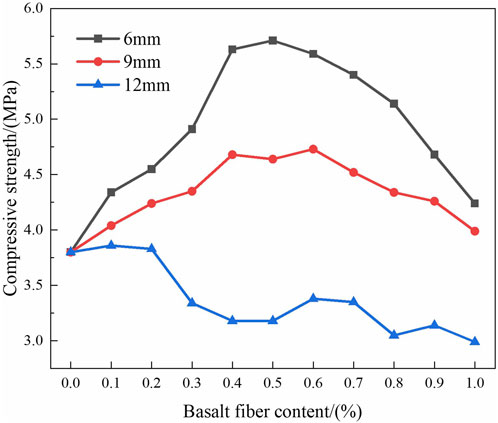
4.3 Variation of uniaxial compressive strength
To comprehensively uncover the impact of basalt fiber content on the uniaxial compressive strength of asphalt mixtures, the range of basalt fiber content was extended to 0%–1%. The variations in the compressive strength and strain of BFRAM under different fiber lengths and fiber contents were investigated. Figure 10 presented the variation of the ultimate compressive strength of the asphalt mixture with fiber content through the established discrete element model. As depicted in Figure 10, the fiber content could notably influence the axial compressive properties of the asphalt mixture. When the fiber content was 0.5%, 0.6%, and 0.2%, the compressive strengths of the asphalt mixtures with 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm fibers reached peak values of 5.71 MPa, 4.73 MPa, and 3.83 MPa, respectively. When the fiber lengths were 6 mm and 9 mm, the compressive strength of the asphalt mixture initially increased and then decreased as the basalt fiber content increased, and this strength was higher than that of the non-fiber asphalt mixture. The underlying reason was that when the fiber content was appropriate, the fibers were well-distributed within the mixture. The bridging effect was significant, which could effectively impede crack propagation and enhance the strength of the mixture. However, when an excessive amount of fiber was added, the fibers would agglomerate, and the bonding between the fibers and asphalt became weaker, leading to a reduction in the overall strength. When the fiber length was 12 mm, the compressive strength of the asphalt mixture exhibited a downward trend. This might be attributed to the fact that the overly long fibers had a negative effect on the bonding between the asphalt and the aggregates.
4.4 Microscopic mechanism analysis
4.4.1 The microscopic mechanism of different fiber contents
Figure 11 presented the strain-fracture cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture containing 6 mm fibers at four typical fiber contents, namely, 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.5%, and 1.0%. From Figure 11, it could be deduced that as the fiber content increased, the small strain area represented by the red particle region increased notably. It evolved from an unconnected small-strain state to a continuous one. Meanwhile, the breakage phenomenon became less prominent, and the number and width of cracks in the specimen decreased. This was consistent with Stukhlyak et al. (2015) that the microscale mechanisms dominated the start of a main crack. By comparing the particle strain distributions in the figure, it could be inferred that the addition of basalt fibers significantly mitigated the edge stripping phenomenon of the specimen. Figures 11C,D illustrated that when the fiber content was excessive, the lower right edge of the specimen experienced breakage. Moreover, the width of the cracks expanded, while the number of cracks in the specimen reduced.
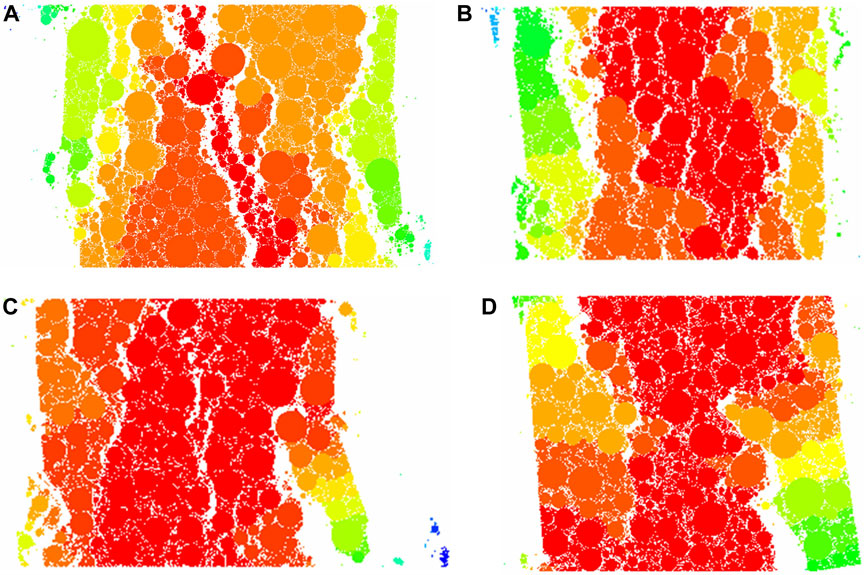
Figure 11. Strain-fracture cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture: (A) No fiber; (B) Fiber content of 0.1%; (C) Fiber content of 0.5%; (D) Fiber content of 1.0%.
Figure 12 depicted the contact force chain cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture at four typical fiber contents, namely, 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.5%, and 1.0%. In the diagram, the green color represented the contact between fibers and aggregates, the red color represented the contact between fibers, and the blue color represented the contact between aggregates. By analyzing the distribution, quantity, and thickness of different types of contact force chains in the figure, it could be deduced that fibers could remarkably enhance the contact quantity between particles. Specifically, the contact quantity at a fiber content of 1.0% was 2.61 times that at a fiber content of 0.0%. Upon comparing Figures 12C,D, it was evident that when an excessive amount of fiber was added, the contact between fibers and aggregates increased, while the contact between aggregates decreased and the force chains became thinner. Consequently, this led to a reduction in the compressive strength of the asphalt mixture.
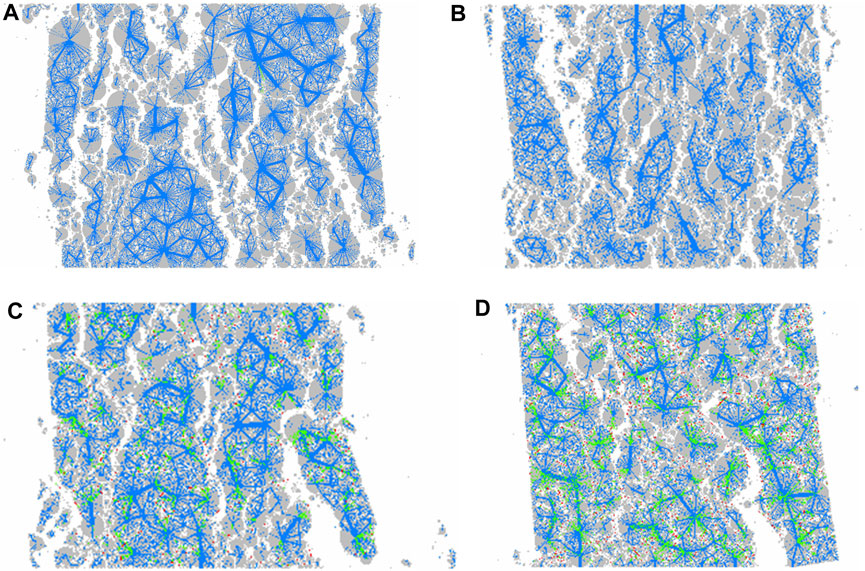
Figure 12. Contact cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture: (A) No fiber; (B) Fiber content of 0.1%; (C) Fiber content of 0.5%; (D) Fiber content of 1.0%.
Figure 13 showed the cracks in the asphalt mixture corresponding to four typical fiber contents, namely, 0.0%, 0.1%, 0.5%, and 1.0%. In the figure, the black cracks represented tensile cracks, while the red ones denoted shearing cracks. By comparing the quantity and type of cracks in the figure, it was evident that the number of tensile cracks exhibited a significant decline as the fiber content increased. When the fiber content reached 0.5%, a substantial number of shearing cracks emerged. This phenomenon led to a notable enhancement in the compressive strength, which was significantly higher than that of the asphalt mixture without fiber or with a fiber content of 0.1%. This was consistent with Stukhlyak et al. (2015) that microcracks developed due to shear strain.
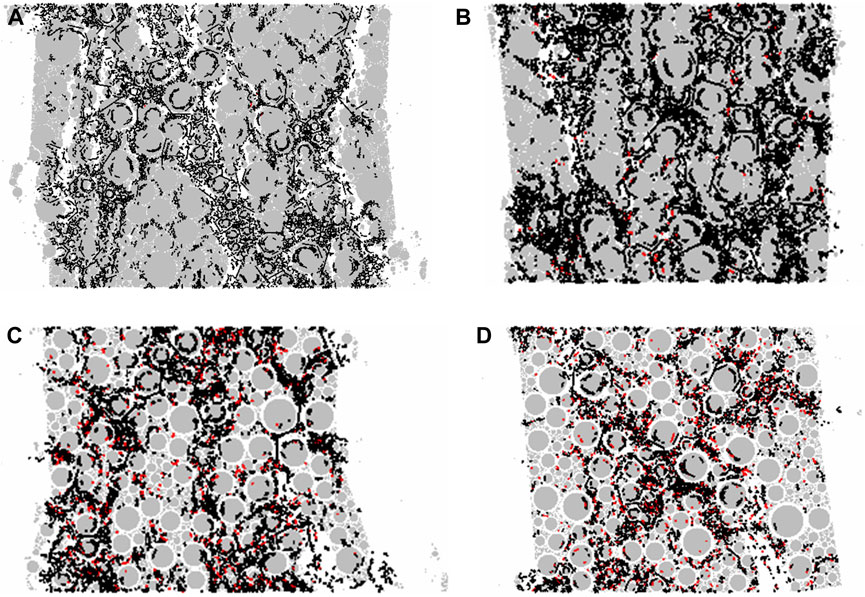
Figure 13. Crack distribution of the asphalt mixture: (A) No fiber; (B) Fiber content of 0.1%; (C) Fiber content of 0.5%; (D) Fiber content of 1.0%.
4.4.2 The microscopic mechanism of different fiber lengths
In order to uncover the microscopic mechanism underlying the influence of basalt fiber length on the mechanical properties of asphalt mixture, the particle strain-fracture cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture with a fiber content of 0.6% was presented in Figure 14. As depicted in Figure 14, in comparison to the asphalt mixture without fibers, the small strain area of the asphalt mixtures containing fibers of different lengths expanded, and the edge stripping phenomenon of the specimens significantly diminished. By comparing Figures 14B,D, it was clearly showed that as the fiber length increased, the fracture degree and crack width of the specimen decreased, and the large strain area at the edge reduced.
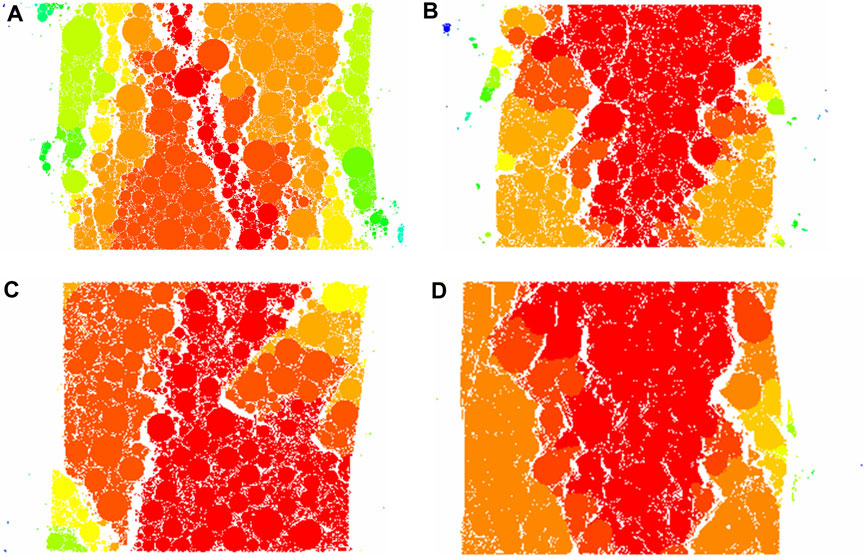
Figure 14. Strain-fracture cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture: (A) No fiber; (B) Fiber length of 6 mm; (C) Fiber length of 9 mm; (D) Fiber length of 12 mm.
Figure 15 presented the contact force chain cloud diagram of asphalt mixtures without fiber, and those containing 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm fibers. By comparing the distribution, quantity, and thickness of the contact force chains in the figure, it was evident that as the fiber length increased, the number of green contacts between the fiber and the aggregate significantly rose. Specifically, the contact quantities of the asphalt mixtures with 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm fibers were 1.98, 2.09, and 2.42 times that of the mixture without fiber, respectively. A comparison between the specimens with and without fiber revealed that the ultimate compressive strength of the specimens increased. This increase could be attributed to the augmented contacts between the fiber and the aggregate, as well as those between the aggregate and the fiber, after the addition of fibers.
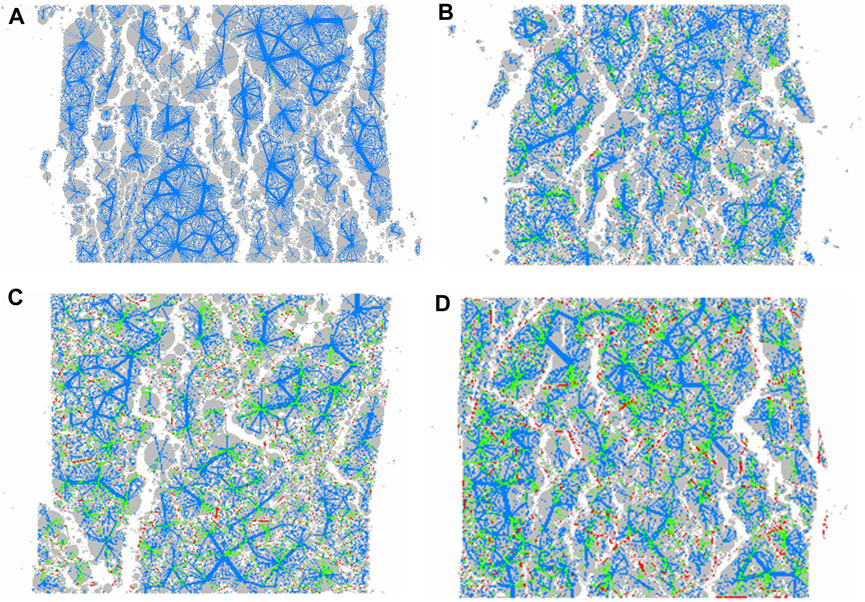
Figure 15. Contact cloud diagram of the asphalt mixture: (A) No fiber; (B) Fiber length of 6 mm; (C) Fiber length of 9 mm; (D) Fiber length of 12 mm.
Figure 16 depicted the cracks in asphalt mixtures without fiber, and those with 6 mm, 9 mm, and 12 mm fibers. As showed in Figure 16, red shear cracks emerged after the addition of fibers. Moreover, the number of shear cracks in the mixture with 6 mm fibers was greater than that in the mixture with 9 mm fibers. This implied that the 6 mm basalt fibers offered more shear resistance during the uniaxial compression test of the asphalt mixture, thereby enhancing the compressive strength of the specimen. Among these mixtures, the asphalt mixture with 12 mm fibers exhibited the largest total number of cracks and the highest number of red shear cracks. The reason could be that longer fibers were more prone to aggregating, which hindered the bonding between the asphalt and the aggregate, resulting in a greater number of cracks in the mixture compared with that without fiber.
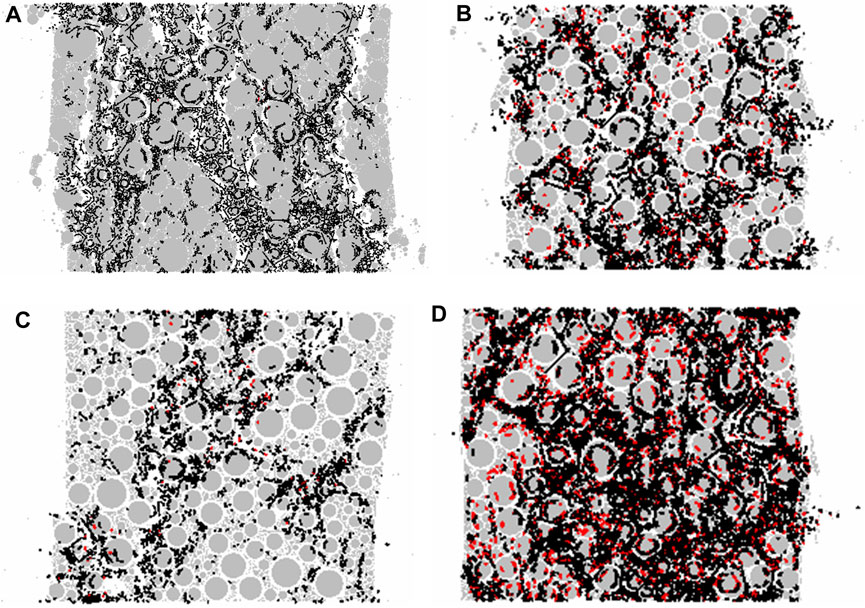
Figure 16. Crack distribution of the asphalt mixture: (A) No fiber; (B) Fiber length of 6 mm; (C) Fiber length of 9 mm; (D) Fiber length of 12 mm.
5 Conclusion and discussion
5.1 Conclusion
To enhance the road performance of asphalt mixture, material tests were conducted to investigate the impacts of basalt fiber content and length on the physical and mechanical properties of asphalt mixture, including the bulk density, stability, flow value, and compressive strength. Based on the test outcomes, a discrete element model of BFRAM was developed. Subsequently, the entire stress-strain process and the microscopic mechanism of the fiber asphalt mixture under axial force were explored. The influence mechanism of basalt fiber on the permanent deformation mechanical behavior of asphalt mixture was discussed from both macroscopic and microscopic perspectives. The primary conclusions are as follows.
1. The basalt fiber has significant influence on the physical and mechanical properties of asphalt mixture. It increases the VV and compressive strength of asphalt mixtures by up to 31.8% and 48.2%.
2. The developed discrete element model of asphalt mixture could accurately simulate the microscopic mechanism of the internal interactions within the asphalt mixture. As the basalt fiber content increased, the failure phenomena and the number of cracks at the edge of the asphalt mixture were significantly reduced, while the number of contacts between particles increased remarkably. The cracks development law and microscopic reinforced mechanism of BFRAM is revealed.
3. For the asphalt mixture used in this study, the optimal fiber content and length are 0.3% and 6 mm respectively. The results suggest to add the basalt fiber in the asphalt mixture to enhance its road performance.
5.2 Limitations and future work
The authors acknowledge several limitations in this study, which also highlight important directions for future research. These are summarized as follows.
1. Due to the limitations of the test conditions, only the Marshall test and uniaxial compression test of BFRAM are carried out in this study. Subsequently, further research can be conducted in aspects such as freeze-thaw splitting test, bending test and shear strength test of asphalt mixture.
2. Due to the limited computing power of computers, the discrete element model of the asphalt mixture established in this study is a two-dimensional model. Subsequently, a three-dimensional discrete element model can be established for further analysis.
3. The effect of asphalt and filler is simulated with contact model rather than establishing the discrete particles, neglecting the low-temperature stress buildup in bitumen and the behavior of asphalt film-aggregate interface. Future efforts will explore discrete particle modeling of binder-filler systems.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZX: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. SF: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LX: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. JM: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. MW: Validation, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. BS: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. KW: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Tianjin Municipal Education Commission (2021KJ055).
Conflict of interest
Authors ZX and SF were employed by China Jingye Engineering Co. Ltd., Central Research Institute of Building and Construction Co. Ltd. Author JM was employed by CNPC East China Design Institute Co. Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2025.1704032/full#supplementary-material
References
Aboutalebi, E. M., and Namavar, J. M. (2018). Optimum parafibre length according to mechanical properties in hot mix asphalt. Road. Mater. Pavement 21 (3), 683–700. doi:10.1080/14680629.2018.1527240
Alfalah, A., Offenbacker, D., Ali, A., Mehta, Y., Elshaer, M., and Decarlo, C. (2021). Evaluating the impact of fiber type and dosage rate on laboratory performance of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 310, 125217. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125217
Ashith, M., Ahmed, S., Ayman, A., Yusuf, M., Mohamed, E., and Christopher, D. (2023). Laboratory evaluation of the electrical resistivity and mechanical performance of electrically conductive asphalt mixtures. Transp. Res. Rec. 2677 (12), 255–266. doi:10.1177/03611981231167423
Cheng, P. J., Yi, J. Y., Guo, S. H., Pei, Z. S., and Feng, D. C. (2022). Influence of fiber dispersion and distribution on flexural tensile properties of asphalt mixture based on finite element simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 352, 128939. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128939
Civil Aviation Administration of China (2017). Specifications for asphalt pavement of civil airports. Dongcheng, Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China.
Dan, H. C., Zhang, Z., Chen, J. Q., and Wang, H. (2018). Numerical simulation of an indirect tensile test for asphalt mixtures using discrete element method software. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 30 (5), 04018067. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002252
Hosseinian, S. M., Najafi, M. G. V., Mehraban, J. P., and Arabani, M. (2020). Investigation of moisture sensitivity and conductivity properties of inductive asphalt mixtures containing steel wool fiber. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020 (1), 8890814. doi:10.1155/2020/8890814
Jiao, Y. B., Zhang, L. D., Guo, Q. L., Guo, M., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Acoustic emission-based reinforcement evaluation of basalt and steel fibers on low-temperature fracture resistance of asphalt concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 32 (5), 04020104. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003118
Laib, S., Nafa, Z., Merdas, A., Chetbani, Y., Tayeh, B. A., and Tang, Y. (2025). Experimental and statistical evaluations of recycled waste materials and polyester fibers in enhancing asphalt concrete performance. Buildings 15 (15), 2747. doi:10.3390/buildings15152747
Li, B., Zhang, Y., Xiao, P., Wang, Y., Kang, A. H., and Zhang, Y. (2023). Comparative performance evaluation of basalt fiber–modified hot in-place (HIP) recycling asphalt mixtures: site mixture versus lab mixture. Front. Mater. 10, 1332168. doi:10.3389/fmats.2023.1332168
Liu, G., Zhu, C., Han, D., and Zhao, Y. (2023). Asphalt mixture force chains morphological characteristics and bearing capacities investigation using discrete element method. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 24 (1), 2168660. doi:10.1080/10298436.2023.2168660
Shi, C., Qian, G., Yu, H., Zhu, X., Yuan, M., Dai, W., et al. (2024). Research on the evolution of aggregate skeleton characteristics of asphalt mixture under uniaxial compression loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 413, 134769. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134769
Stukhlyak, P. D., Buketov, A. V., Panin, S. V., Maruschak, P. O., Moroz, K. M., Poltaranin, M. A., et al. (2015). Structural fracture scales in shock-loaded epoxy composites. Phys. Mesomech. 18, 58–74. doi:10.1134/s1029959915010075
Taherkhani, H., and Afroozi, S. (2017). Creep behavior of nylon fiber-reinforced asphalt concrete. Iran. Polym. J. 26 (5), 365–376. doi:10.1007/s13726-017-0526-0
Xie, T. T., and Wang, L. B. (2023). Optimize the design by evaluating the performance of asphalt mastic reinforced with different basalt fiber lengths and contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 363, 129698. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129698
Yan, W. L., Shi, J. Z., Cao, X. Y., Zhang, M., Li, L., and Jiang, J. Y. (2025). A review on the applications of basalt fibers and their composites in infrastructures. Buildings 15 (14), 2525. doi:10.3390/buildings15142525
Yang, W. D., Liu, H. X., and Wang, H. S. (2024). Experimental study on mechanical properties of basalt fiber reinforced nano-SiO2 concrete after high temperature. Front. Mater. 11, 1415144. doi:10.3389/fmats.2024.1415144
Yao, H., Xu, M., Li, J., and You, Z. (2022). Literature review on the discrete element method in asphalt mixtures. Front. Mater. 9, 87924. doi:10.3389/fmats.2022.879245
Ye, Y. L., Sun, Y. Z., Gao, L., Ma, Z., and Xue, X. W. (2020). Study on creep behavior of asphalt mixture based on discrete element method. Balt. J. Road. Bridge E. 15 (4), 174–195. doi:10.7250/bjrbe.2020-15.500
Wang, S., Kang, A. H., Xiao, P., Li, B., and Fu, W. L. (2019). Investigating the effects of chopped basalt fiber on the performance of Porous asphalt mixture. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019 (1), 1–12. doi:10.1155/2019/2323761
Zhang, Y., Sang, T. Y., Kang, A. H., Wang, B. S., Wang, X., and Zhao, Y. (2023). Investigation of fiber length distribution on crack resistance mechanism of basalt fiber asphalt mixture based on digital image processing technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 401, 132753. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132753
Keywords: basalt fiber, asphalt mixture, material test, discrete element method, microscopic mechanism analysis
Citation: Xue Z, Fang S, Xiong L, Ma J, Wang M, Sun B and Wu K (2025) Experimental-numerical investigation on the performance of basalt fiber reinforced asphalt mixture. Front. Mater. 12:1704032. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1704032
Received: 12 September 2025; Accepted: 03 October 2025;
Published: 15 October 2025.
Edited by:
Jie Xu, Tianjin University, ChinaReviewed by:
Pavlo Maruschak, Ternopil Ivan Pului National Technical University, UkraineWentong Wang, Shandong University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Xue, Fang, Xiong, Ma, Wang, Sun and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kun Wu, a193dUBjYXVjLmVkdS5jbg==
 Zizhou Xue1
Zizhou Xue1 Bowei Sun
Bowei Sun Kun Wu
Kun Wu