- 1College of Food and Health, Jinzhou Medical University, China
- 2Liaoning Provincial Professional Technology Innovation Center of Meat Processing and Quality-Safety Control, China
Fresh-cut fruits suffer from quality deterioration and low bioaccessibility of bound polyphenols, which limit their health benefits. This study used ozone treatment (10 μL/L for 60 min) to enhance the functional properties of fresh-cut pitaya. This treatment significantly (p < 0.05) disrupted the cell wall microstructure, increasing the extractability of free and bound phenols by 16.7 and 4.9%, respectively. This structural modification enhanced polyphenol bioaccessibility by 8% after in vitro digestion. Furthermore, the ozone-treated samples exhibited stronger inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase, and in silico analyses suggested that the released polyphenols (e.g., naringin and ferulic acid) could modulate glucose metabolism via the PI3K-AKT pathway. The main advantage of this study is the direct linkage of ozone-induced microstructural changes to improved physiological functionality, positioning mild ozone treatment as a highly promising non-thermal technology that can produce health-enhanced fresh-cut fruits for the functional food market.
1 Introduction
Pitaya (dragon fruit), renowned for its vibrant color and rich nutrient profile, has gained global popularity as a functional food (1). Beyond its macronutrients, pitaya is a valuable source of bioactive compounds, particularly polyphenols, which are associated with potent antioxidant and antidiabetic activities (2). The growing consumer demand for convenient and healthy options has propelled the market for fresh-cut fruits, with pitaya being a prominent candidate owing to its appealing flesh and mild taste.
However, the fresh-cut processing industry faces several challenges. Mechanical operations such as cutting and peeling induce tissue damage and accelerate enzymatic browning, microbial spoilage, and quality deterioration (3, 4). From a nutritional standpoint, a substantial portion of polyphenols in plant foods exists in bound forms complexed with cell wall structures, such as cellulose and hemicellulose. This structural entrapment severely limits their release during human digestion, resulting in low bioaccessibility (the fraction released from the food matrix and available for intestinal absorption) and consequently diminished health benefits (5). Therefore, developing processing technologies that can preserve quality and enhance bioaccessibility of bound polyphenols is a key objective for the functional food sector.
Ozone (O₃) treatment has emerged as a promising green technology for postharvest management. Ozone, with its Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) designation, is primarily employed for its strong antimicrobial efficacy, which can effectively decontaminate fruit surfaces and extend their shelf life (6, 7). Beyond this conventional role, emerging evidence suggests that ozone also acts as a physical elicitor in plant tissues. Its oxidative properties may induce mild stress responses and, more importantly, modify the structural integrity of the cell wall matrix by breaking down polysaccharides (8). This modification presents a compelling opportunity to enhance the extractability of bound phytochemicals. Although recent studies on other crops have suggested this potential, a clear mechanistic link between ozone-induced microstructural changes, subsequent polyphenol bioaccessibility, and specific health-related functionalities in fresh-cut pitaya remains largely unexplored (7, 9, 10). Specifically, there is a notable research gap in understanding whether structural modifications caused by ozone translate into improved hypoglycemic potential—a critical health benefit of polyphenols—through enhanced bioaccessibility. However, the interplay between these factors has not been systematically investigated.
Therefore, the objectives of this study were to (1) evaluate the impact of ozone treatment on the microstructure of fresh-cut pitaya; (2) determine its effect on the extractability and in vitro bioaccessibility of free and bound polyphenols; (3) assess the subsequent changes in the in vitro hypoglycemic activity (α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition); and (4) explore the potential mechanisms of action through integrated in vitro and in silico analyses. This study aimed to establish ozone treatment not only as a preservation tool but also as a novel strategy to amplify the health-promoting value of fresh-cut pitaya.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material
Red pitaya fruit was sourced from its origin, following the procedure described in our previous study (11). Fruits of uniform maturity, size, color, and shape were selected with no signs of insect infestation or mechanical damage. The peel was manually removed, and the fruit was cut into quarters (approximately 1 cm thick). The segments were randomly distributed in polypropylene containers (15 × 10 × 4 cm), with each container containing approximately 150 g of sample. The samples were subsequently subjected to ozone fumigation and stored at 8 ± 2 °C for up to 72 h. During the storage period, samples were collected at regular intervals, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C until further analysis.
2.2 Ozone treatment
Ozone was generated using a corona-discharge ozone generator (12). Dry oxygen was introduced into the corona discharge tube to produce pure gaseous ozone. Ozone gas was delivered to a sealed treatment chamber equipped with an inlet, outlet, and ozone concentration detector. The ozone concentration in the chamber was regulated by adjusting the flow rate of the ozone generator and monitored in real time using a gas detector. Fresh-cut pitaya samples were fumigated with ozone at a concentration of 10 μL·L−1 for 60 min. Fresh-cut pitaya fruit that did not receive ozone treatment served as the control group.
2.3 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
The samples were designated as follows: control group on day 0 (CKD0, fresh-cut pitaya without ozone treatment) and treatment group on day 0 (TD0, fresh-cut pitaya with ozone treatment); the control and treated samples after 2 days of storage were labeled as CKD2 and TD2, respectively.
For SEM analysis, the samples were mounted on a specimen stub using adhesive tape and were sputter-coated with a conductive layer. Observations were performed using a field-emission scanning electron microscope (Hitachi S4800, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 2.00 kV. Images were captured at a magnification of 500 × under high-vacuum conditions (13).
FTIR analysis was performed using an FTIR spectrometer (Nicolet 6,700; Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States). The powdered sample was mixed with potassium bromide (KBr) at a ratio of 1:100 (w/w) and pressed into a transparent pellet. Spectra were acquired in the range of 4,000–400 cm−1 with 32 scans at a resolution of 4 cm−1. Peak identification and spectral processing were performed using the instrument software (13).
2.4 Effects of ozone treatment on phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut pitaya fruit
2.4.1 Polyphenol extraction
Free phenolic compounds were extracted using a slightly modified version of the method described by Ding and Morozova et al. (5). Briefly, 1 g of each sample was homogenized with 10 mL of methanol and magnetically stirred for 40 min. The mixture was centrifuged at 4,000 × g for 10 min and the supernatant was collected. The residue was re-extracted twice under the same conditions. The combined supernatants were transferred into a brown reagent bottle and stored at 4 °C until further analysis.
The bound phenolic compounds were extracted from the remaining residue according to a modified protocol described by Ding et al. (14). The residue was hydrolyzed with 20 mL of 4 mol/L NaOH solution in the dark for 24 h. The pH of the mixture was then adjusted to 7.0 using concentrated hydrochloric acid, followed by centrifugation at 4,000 × g for 10 min. The supernatant was mixed with three volumes of 95% ethanol and stored at 4 °C for 12 h to precipitate polysaccharides and proteins. After centrifugation under the same conditions, the resulting supernatant was collected and stored in a brown bottle at 4 °C for subsequent use.
2.4.2 Determination of polyphenol content
The total phenol content was determined using the method described by Gutiérrez and Chaves et al. (9), which is consistent with the experimental method described in our previous article (11).
2.4.3 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method
The antioxidant activities of the samples were evaluated according to the methodology described by Li et al. (3). The absorbance was measured at 515 nm to calculate the antioxidant activity as follows (Equation 1):
where A0 and A1 are the absorbance values of the samples from the CK and ozone groups, respectively.
2.4.4 Ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay
The total antioxidant capacity of the samples was measured using the ferric-reducing antioxidant power analysis, as previously described by Fu and Xu et al. (15). The results were expressed as mmol Fe2+ kg−1.
2.5 Determination of α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition rate
Fresh-cut pitaya polyphenols in the control group on day 0 (CKD0) and day 2 (CKD2) and fresh-cut pitaya polyphenols with ozone treatment on day 0 (TD0) and day 2 (TD2) were evaporated by rotation at 40 °C to remove the solvent. The vacuum was then freeze-dried into a powder and set aside. According to the method described by Liu et al. (16), different concentrations of pitaya polyphenol solutions were used to study the inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase activities. Acarbose was used as a positive control. The experiment was conducted in triplicate. The formula used to calculate the inhibition rate is as follows (Equation 2):
where Asample, Acontrol, and Ablank are the absorbances of the sample, control, and blank, respectively.
The α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition effects were expressed as half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values, represented as mg/mL.
2.6 In vitro simulation of gastrointestinal digestion
Fresh-cut pitaya fruit (20 g) was extracted according to the method described in Section 2.4.1, and freeze-dried pitaya powder, free phenols, and combined phenol samples were prepared. The method of Pea-Vázquez and Dominguez-Fernández et al. (17) was used to simulate saliva, gastric fluid, and intestinal fluid. After digestion, the samples were immediately frozen at −18 °C to terminate enzymatic activity and subsequently stored at −80 °C until lyophilization. The total phenolic content of the digested samples was determined using the method outlined in Section 2.4.2. The bioaccessibility of polyphenols was calculated as the percentage of total phenolic content (TPC) in the bioaccessible fraction (the supernatant after digestion and centrifugation) relative to the TPC in the undigested sample. All calculations were based on the fresh weight of the pitaya pulp.
2.7 In silico evaluation of the hypoglycemic potential of fresh-cut pitaya polyphenols
2.7.1 Selection of active ingredients and pharmacokinetic evaluation
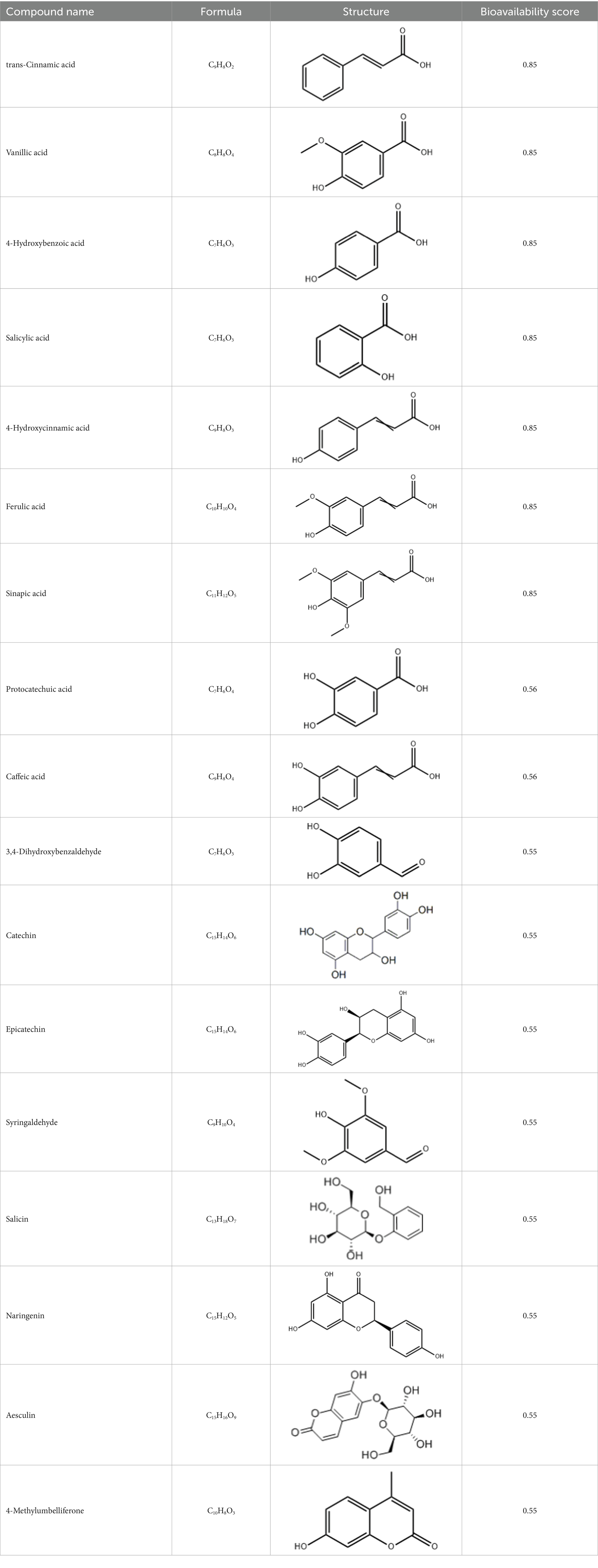
Based on our previous study, which identified 26 phenolic compounds in red pitaya fruits (11), these compounds were submitted to the SWISSADME database1 for pharmacokinetic profiling. A bioavailability score greater than 0.55 was set as the main criterion for selecting compounds with potential biological activities (18). Seventeen compounds met this criterion and were selected for further analyses (Table 1).
2.7.2 Target prediction of phenolic compounds
The putative targets of the 17 bioactive compounds were retrieved from the PubChem database.2 The SMILES notations of these compounds were submitted to SwissTargetPrediction, and the Similarity Ensemble Approach (SEA)3 was used for target prediction. A Perl script was used to remove redundant targets and standardize the target lists. Gene symbols of the resulting targets were unified using UniProt database.
2.7.3 Compilation of T2DM-related gene sets
T2DM-related genes were obtained from the GeneCards4 and OMIM5 databases. Redundant entries were removed, and the gene sets were merged and curated for further analyses.
2.7.4 Screening of compound-disease common targets
The predicted targets of pitaya polyphenols and T2DM-related genes were intersected to identify common targets. A Venn diagram was generated using the R package “VennDiagram” to visualize the overlapping targets.
2.7.5 Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network and visualization
A Perl script was used to integrate the compound–target and disease–target relationships in the network. The resulting compound–target–disease network was imported into Cytoscape for visualization and topological analysis. The PPI network of common targets was constructed using the STRING database with a confidence threshold of >0.9 and visualized in Cytoscape.
2.7.6 Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis
GO functional annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were performed on the common targets using the “clusterProfiler” R package. Significantly enriched terms (p < 0.05) were selected and visualized using bar plots and scatter plots. Key pathways related to glucose metabolism and T2DM were identified for further analysis.
2.8 Molecular docking
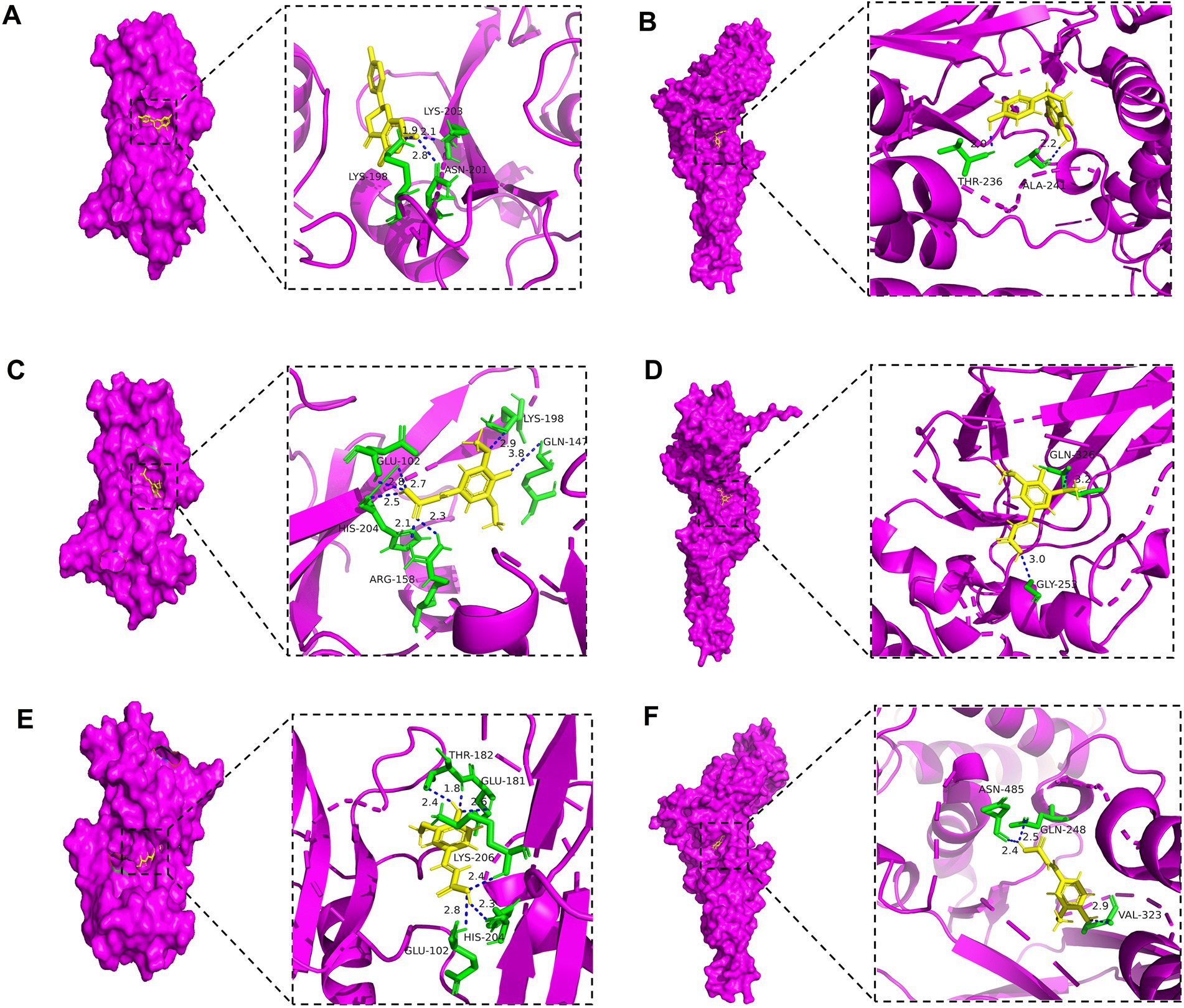
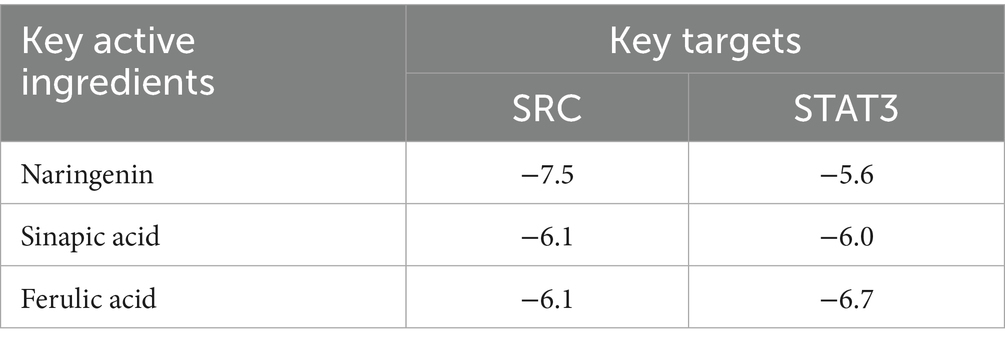
Molecular docking was performed using the SwissDock online tool. The three-dimensional structures of the target proteins (SRC and STAT3) were obtained from the RCSB PDB database.6 When multiple structures were available, the structure with the highest resolution was selected for further analysis. The protein structures were preprocessed using PyMOL to remove ligands and water molecules and then saved in the PDB format. The structures of the small-molecule ligands (naringenin, sinapic acid, and ferulic acid) were downloaded in SDF format from PubChem and converted to MOL2 format using OpenBabel. The prepared protein and ligand files were uploaded to SwissDock7 for molecular docking analysis.
2.9 Statistical analysis
The experiment was conducted using a completely randomized design. Data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States) and are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent replicates. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to determine significant differences among the treatments, with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05. Data visualization and graph generation were performed using the Origin 2021 software (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, United States).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of ozone-treated fresh-cut pitaya
The microstructural alterations in fresh-cut pitaya pulp, as visualized by SEM, provide direct evidence of the primary mechanism underlying the enhanced polyphenol extractability following ozone treatment. A comparative analysis of the control and ozone-treated groups on days 0 and 2 revealed significant differences in cell wall integrity and surface morphology.
As shown in Figures 1A,B, the cellular structure of the control samples remained relatively intact throughout the 2-day storage period. The cells were plump with smooth surfaces and the cell walls were tightly connected, forming a continuous non-porous matrix. This dense structure inherently limits the diffusion and release of intracellular components, including bound polyphenols.
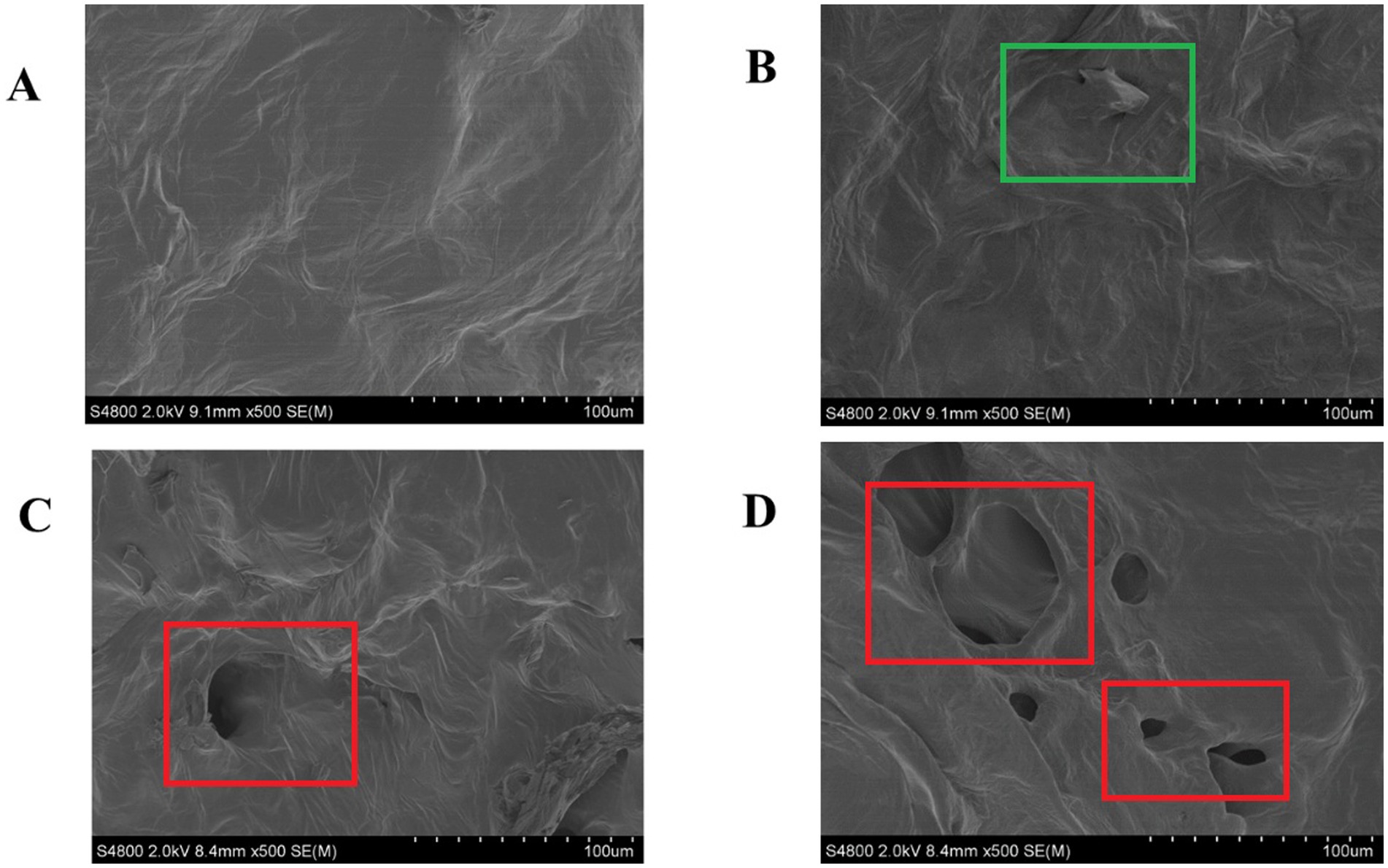
Figure 1. SEM images of the control group on day 0 (A) and day 2 (B) and ozone treatment on day 0 (C) and day 2 (D).
In stark contrast, the microstructures of the ozone-treated samples exhibited profound changes immediately after treatment (Figure 1C). The cell surfaces appeared eroded and rough, and visible pores and microfissures were formed. This disruptive effect became even more pronounced after 2 days of storage (Figure 1D), showing extensive cell wall disintegration, collapsed cellular regions, and a notably more porous and fragmented network.
To objectively quantify these morphological changes, SEM micrographs were analyzed using the ImageJ software. The data clearly demonstrated that ozone treatment significantly (p < 0.05) increased the porosity and average pore size of pitaya tissue. The porosity of the ozone-treated group on day 0 (12.7%) was approximately 6 times greater than that of the control group on day 0 (2.1%). This difference increased as storage progressed.
Our findings align with studies on other fruits, where non-thermal treatments, such as ultrasound and pulsed electric fields, have been shown to mechanically disrupt cells and enhance polyphenol yield (19, 20). However, this study specifically elucidated the role of ozone as a chemical elicitor of microstructural porosity. This finding establishes that the enhancement of polyphenol extractability by ozone is not coincidental but is fundamentally driven by the targeted modifications of the physical architecture of plant tissue.
3.2 FTIR analysis of ozone-treated fresh-cut pitaya
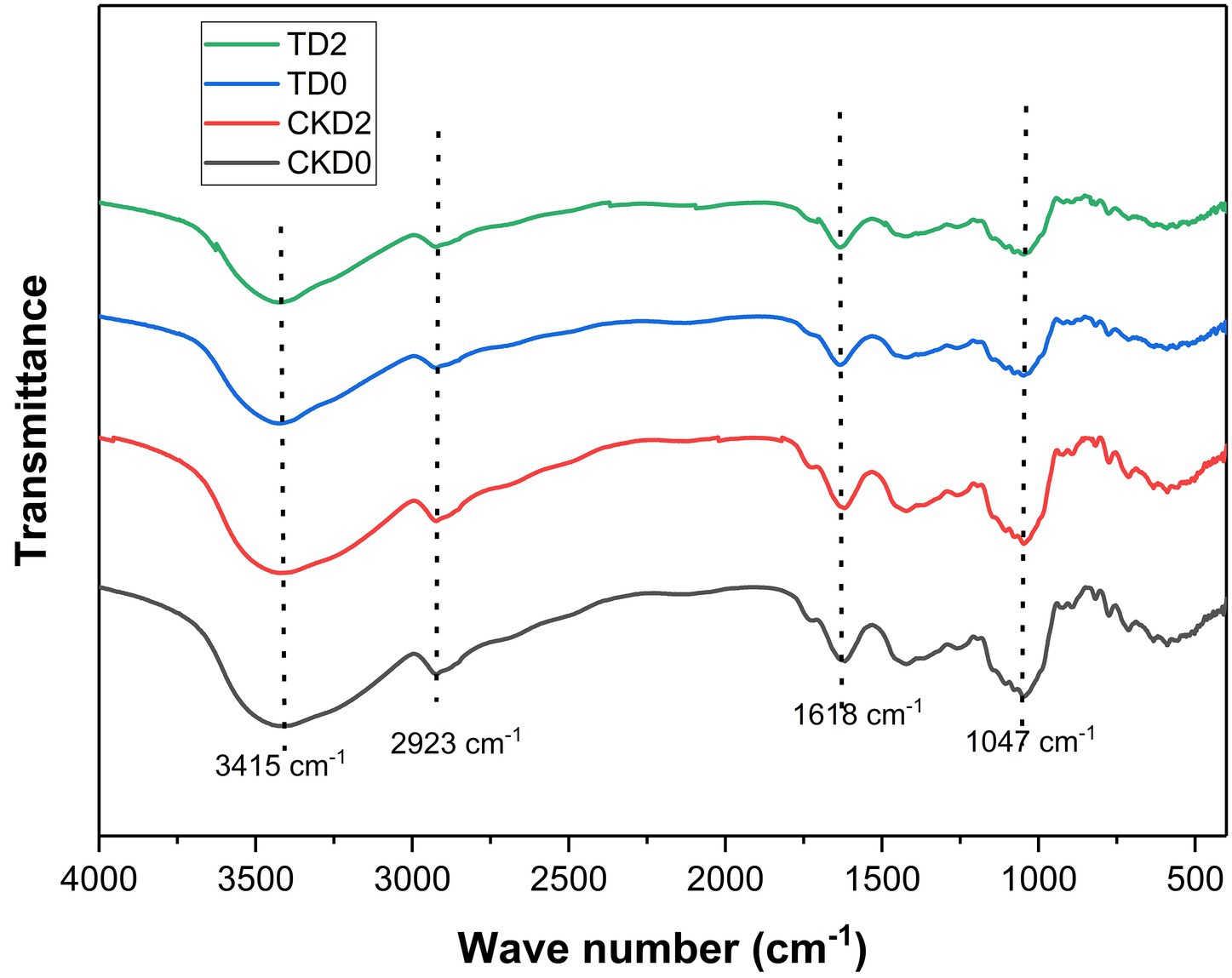
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was used to investigate the chemical alterations in the cell wall matrix of ozone-treated fresh-cut pitaya induced by ozone treatment. The comparative spectra of the control and ozone-treated groups (Figure 2) revealed consistent band profiles; however, notable changes were observed in transmittance intensity and subtle peak shifts, indicating significant modifications in the molecular structures of key components.
The broad, intense band centered at approximately 3415.81 cm−1 is attributed to O-H stretching vibrations, primarily from carbohydrates and water (21). The increased transmittance of the ozone-treated sample suggests a decrease in hydrogen bonding, which is likely due to the breakdown of the hydrated polysaccharide network in the cell wall. This is a direct consequence of the oxidative cleavage of the polymeric chains, which reduces the number of available hydroxyl groups for the intermolecular bonding.
A critical change was observed in the region between 1800 and 1,500 cm−1. The peak at approximately 1618.59 cm−1, assigned to the C=O stretching of esterified pectins (carboxylate groups) and possibly the aromatic C=C in some phenolics, showed altered intensity (22). The oxidative power of ozone is known to attack glycosidic linkages and break down pectin chains, leading to de-esterification and the formation of smaller and more soluble fragments. This degradation of the pectin matrix was directly correlated with the microstructural disintegration observed via SEM and facilitated the release of bound polyphenols. Similar ozone-induced depolymerization of pectin has been reported in other fruits, including apples and tomatoes.
The most pronounced changes occurred in the “fingerprint region” below 1,200 cm−1. The strong band at 1047.47 cm−1 is characteristic of C-O-C and C-O-H stretching vibrations in cellulose, hemicellulose, and glycosidic linkages (23). The significant increase in transmittance at this wavelength in the ozone-treated group strongly indicates the scission of these bonds. Ozone actively oxidizes the pyranose rings in cellulose and hemicellulose, leading to chain cleavage and a decrease in the overall polysaccharide content of the material. This results in a less dense and more fragmented cell wall, which mechanically explains the improved polyphenol extractability. The weakening of the 1,047 cm−1 band aligns with the findings of Dos Santos et al. (24), who observed analogous FTIR changes in ozone-treated plant tissues and linked them to the enhanced bioaccessibility of bioactives.
Furthermore, the band near 2,923 cm−1, corresponding to the C-H stretching in the CH₂ and CH₃ groups of carbohydrates, also showed increased transmittance. This further supports the premise of carbohydrate depolymerization, as the breakdown of polymer chains reduces the density of aliphatic C-H bonds.
In conclusion, the FTIR spectral data provide direct chemical evidence that ozone treatment induces the oxidative degradation of key structural polysaccharides—pectin, cellulose, and hemicellulose—in the cell wall of fresh-cut pitaya. This chemical breakdown, which manifested as the rupture of glycosidic linkages and weakening of the hydrogen-bonded network, was the fundamental mechanism behind the observed microstructural porosity and subsequent enhancement of polyphenol extractability and bioaccessibility.
3.3 Effect of ozone on phenolic content and antioxidant activity
3.3.1 Phenolic content
The effect of ozone treatment on the phenolic compound profile and resultant antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut pitaya is shown in Figure 3. Ozone treatment elicited a significant and dynamic response in both free and bound phenolic fractions. Although the content of both phenolic forms gradually declined in the control group during storage, the ozone-treated fruits exhibited a marked increase, reaching a peak at 36 h (Figures 3A,B).
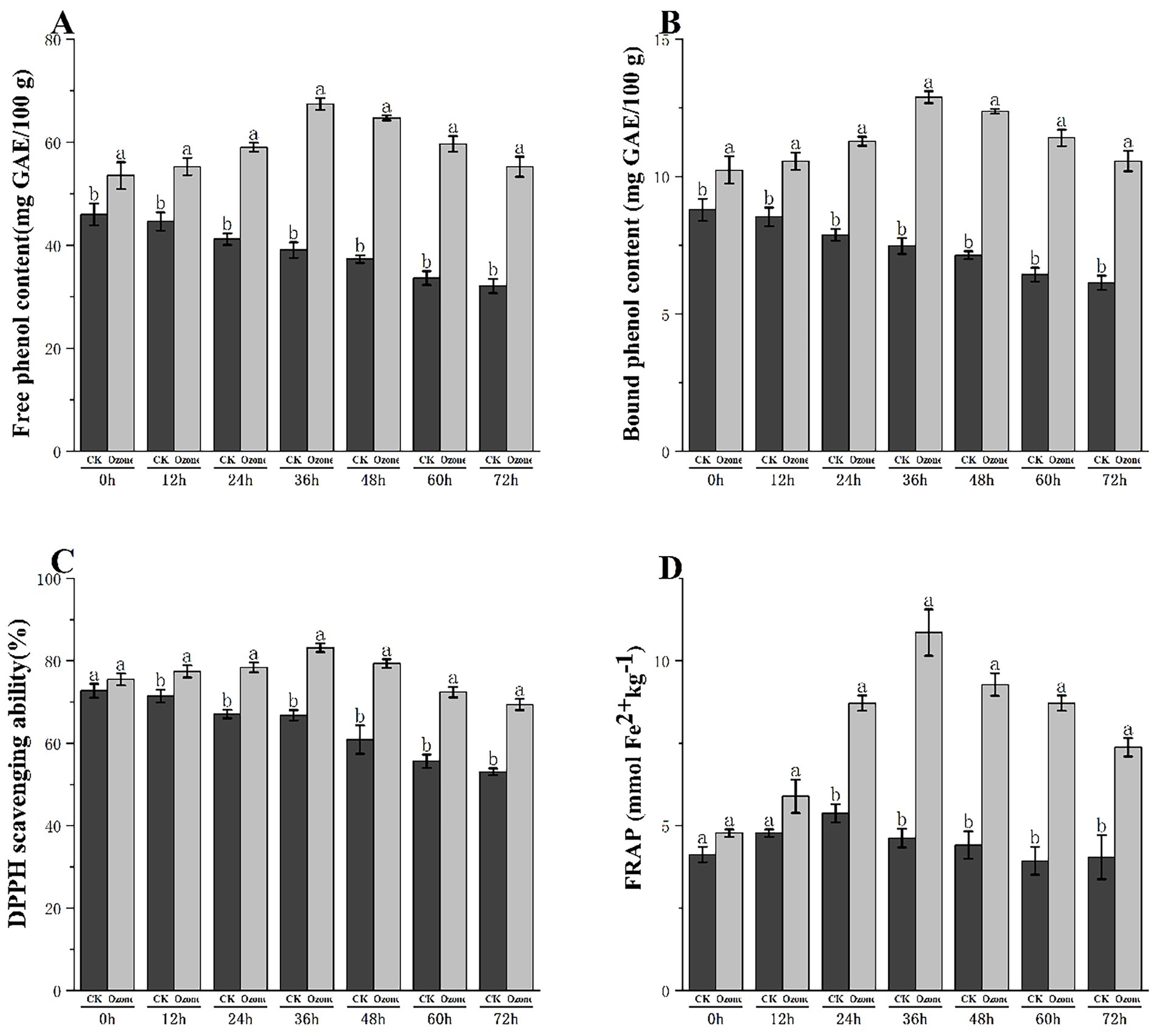
Figure 3. Free phenol content (A), bound phenol content (B), DPPH scavenging capacity (C) and FRAP (D) of fresh-cut Pitaya fruit in ozone treated group and control group.
In the control group (CK), the free phenolic content decreased gradually over 72 h, from 45.2 mg GAE/100 g at 0 h to 32.1 mg GAE/100 g at 72 h. In contrast, the ozone-treated group showed a significant increase, peaking at 36 h (68.5 mg GAE/100 g) and 48 h (65.3 mg GAE/100 g), and remained substantially higher than that of the control throughout storage.
The bound phenolic content of the control group decreased slightly from 8.2 mg GAE/100 g (0 h) to 6.8 mg GAE/100 g (72 h). Meanwhile, the ozone-treated group exhibited consistently higher levels of bound phenolics, peaking at 36 h (12.3 mg GAE/100 g) and maintaining elevated levels during storage.
These results confirmed that ozone treatment enhanced the extractability of both free and bound phenolics and delayed their degradation during storage. The increase in bound phenolics was not due to de novo synthesis but rather to the release of phenolics from cell wall conjugates, as supported by our SEM (cell wall porosity/disruption) and FTIR (polysaccharide C-O-C bond degradation) analyses.
3.3.2 Antioxidant activity
The DPPH scavenging ability of the control group decreased from 75.2% (0 h) to 52.8% (72 h). In contrast, the ozone-treated group showed a remarkable increase, peaking at 36 h (85.1%) and 48 h (82.3%) and remaining significantly higher than that of the control throughout the storage period (Figure 3C).
The FRAP value of the control group decreased from 3.2 μmol Fe2+/g (0 h) to 2.1 μmol Fe2/g (72 h). The ozone-treated group peaked at 36 h (10.5 μmol Fe2+/g) and maintained higher values during storage, consistent with the trend of phenolic content (Figure 3D).
Our results are consistent with those of other ozone-treated fruits, such as blueberries and mangoes, in which a similar elicitation of phenolic metabolism and enhancement of antioxidant activity have been documented.
Ozone treatment significantly improved the content of free and bound phenolics in fresh-cut pitaya by disrupting cell wall structures, thereby enhancing the antioxidant activity. This effect was sustained for over 72 h of storage, positioning ozone treatment as a promising technology for preserving and enhancing the nutritional quality of fresh-cut pitaya.
3.4 In vitro hypoglycemic activity
The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC₅₀) was used to evaluate the inhibitory activity of fresh-cut pitaya extracts against carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase), with a lower IC₅₀ value indicates stronger enzyme inhibition. Acarbose, a commercial antidiabetic drug, was used as the positive control in this study (see Figure 4).
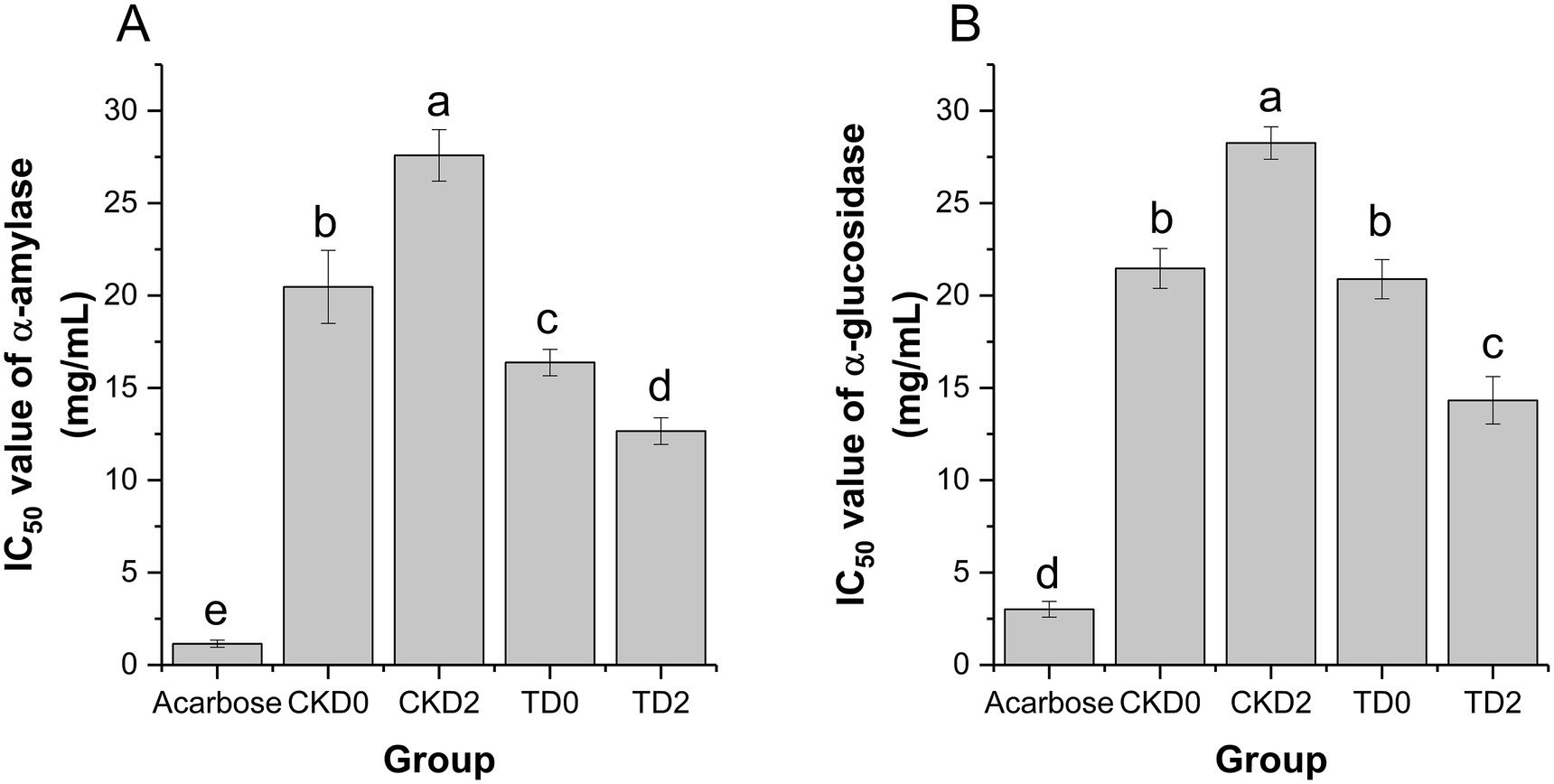
Figure 4. Inhibition rates of α-amylase (A) and α-glucosidase (B) in fresh-cut pitaya fruit on day 0 and day 2 in control group and ozone treatment group.
Acarbose exhibited the strongest α-amylase inhibition (IC₅₀ ≈ 0.8 mg/mL), serving as a benchmark for potent enzyme inhibition. In the control groups, CKD2 (control, stored for 2 days) showed a significantly higher IC₅₀ value (27.59 ± 1.40 mg/mL) than CKD0 (control, stored for 0 days) (20.47 ± 1.97 mg/mL), indicating that storage alone reduced α-amylase inhibitory activity (Figure 4A). In contrast, the ozone-treated groups demonstrated superior inhibition: TD0 (ozone, stored for 0 days) had an IC₅₀ of 16.37 ± 0.72 mg/mL, and TD2 (ozone, stored for 2 days) further decreased to 12.66 ± 0.72 mg/mL. Both values were significantly lower than those of their respective control counterparts (CKD0 and CKD2), confirming that ozone treatment enhanced α-amylase activity inhibition.
Acarbose also exhibited the strongest α-glucosidase inhibition (IC₅₀ ≈ 2.5 mg/mL). In the control groups, CKD2 (28.21 ± 1.53 mg/mL) had a higher IC₅₀ than CKD0 (21.35 ± 1.22 mg/mL), reflecting a diminished α-glucosidase inhibitory capacity after storage (Figure 4A). The ozone-treated groups exhibited robust inhibition: TD0 had an IC₅₀ of 20.86 ± 1.05 mg/mL, and TD2 decreased to 14.52 ± 0.98 mg/mL, both significantly lower than those of CKD0 and CKD2, respectively.
These findings are consistent with those of previous studies on phenol-rich foods. For example, it was reported that ozone treatment enhanced α-glucosidase inhibition in blueberry extracts by increasing free phenolic bioaccessibility (25), which is consistent with our observations in pitaya. Additionally, the structural diversity of polyphenols (e.g., number and position of hydroxyl groups) contributes to their enzyme-inhibitory efficacy. Thus, the ozone-induced release of specific polyphenolic compounds in pitaya may further explain the potent hypoglycemic activity observed.
In summary, ozone treatment improved the in vitro hypoglycemic potential of fresh-cut pitaya by strengthening the inhibition against α-amylase and α-glucosidase. This effect is primarily mediated by increased polyphenol bioaccessibility and preserved structural integrity during storage, positioning ozone-treated fresh-cut pitaya as a promising functional food for managing postprandial blood glucose levels.
3.5 Bioaccessibility of polyphenols after in vitro digestion
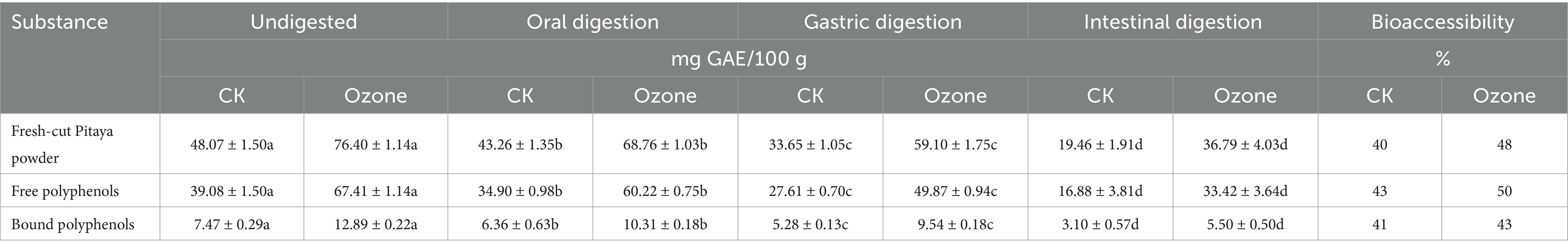
The stability and release of polyphenols throughout the simulated gastrointestinal tract were quantitatively assessed to determine their bioaccessibility, a critical factor in predicting their potential health benefits. As detailed in Table 2, ozone treatment markedly enhanced the polyphenol content at every stage of digestion and significantly improved the overall bioaccessibility.
The initial total phenolic content in the undigested pitaya powder was 48.07 mg GAE/100 g in the control (CK) and 76.40 mg GAE/100 g in the ozone-treated group, confirming the enhanced extractability reported previously. This superior starting point was maintained throughout the digestive process. After the intestinal phase, the final concentrations of bioaccessible polyphenols were 19.46 mg GAE/100 g for CK and 36.79 mg GAE/100 g for the ozone group. Consequently, the overall bioaccessibility of the total polyphenols increased from 40% in the control to 48% in the ozone-treated samples.
A more detailed analysis of the phenolic forms revealed that both free and bound polyphenols benefited from this treatment. The bioaccessibility of free polyphenols increased from 43% (CK) to 50% (Ozone), whereas that of bound polyphenols increased from 41 to 43%. Notably, the free polyphenols consistently exhibited higher bioaccessibility than the bound fraction in both groups, and the absolute amount of bioaccessible free phenolics in the ozone group (33.42 mg GAE/100 g) after digestion was nearly double that of the control (16.88 mg GAE/100 g).
A progressive decline in polyphenol content from the oral to intestinal phase is expected, as the harsh conditions of the gut (e.g., alkaline pH, digestive enzymes, and bile salts) can degrade sensitive phenolic compounds. However, the ozone-treated samples demonstrated not only higher initial levels but also greater resilience during this process.
The primary reason for the enhanced bioaccessibility is directly linked to the ozone-induced microstructural modifications. As demonstrated by SEM and FTIR, the breakdown of the cell wall matrix created a more porous structure, which likely allowed for a more efficient and complete release of polyphenols during digestion. Once liberated from the dense cellular matrix, these compounds are more readily available to enter the bioaccessible fraction. Furthermore, oxidative treatment may have broken down some larger, complex polyphenol-polyaccharide conjugates into smaller, more stable molecules that are less susceptible to degradation in the gastrointestinal environment.
The higher bioaccessibility of free polyphenols aligns with their chemical nature; as they are less tightly bound to the cell wall, they are more easily solubilized and released into digestive chyme. The modest but significant improvement in the bioaccessibility of bound polyphenols is particularly noteworthy. This suggests that ozone treatment partially predigests the cell wall, facilitating the release of this otherwise recalcitrant fraction, which is typically excluded from the bioaccessible pool (26).
Our findings are consistent with the growing body of evidence that physical and chemical pretreatments can enhance the bioaccessibility of bioactive plant compounds. Rinaldi, M., et al. (27) reported that ohmic heating, another cell-disrupting technology, improved the bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds in pineapple waste. The present study established ozone as an effective technology for fresh-cut pitaya.
In conclusion, by structurally priming plant tissues, ozone treatment ensured that a greater proportion of the extracted polyphenols survived the digestive process and remained available for potential intestinal absorption, thereby significantly increasing the functional food value of the plant.
3.6 In silico prediction of hypoglycemic potential
To elucidate the potential molecular mechanisms underlying the observed in vitro hypoglycemic activity, an integrated network pharmacology approach was used. The analysis identified 181 common targets shared between the identified pitaya polyphenols and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (Figure 5A), suggesting a multi-target modulatory potential. The compound-target network (Figure 5B) highlighted the key bioactive compounds, including naringenin, ferulic acid, and sinapic acid, as the central players that interact with numerous targets. Subsequent protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis of these common targets (Figure 5C) identified several core hub genes, such as SRC, STAT3, MAPK1, and EGFR, which are known to be critically involved in insulin signaling and inflammation pathways.
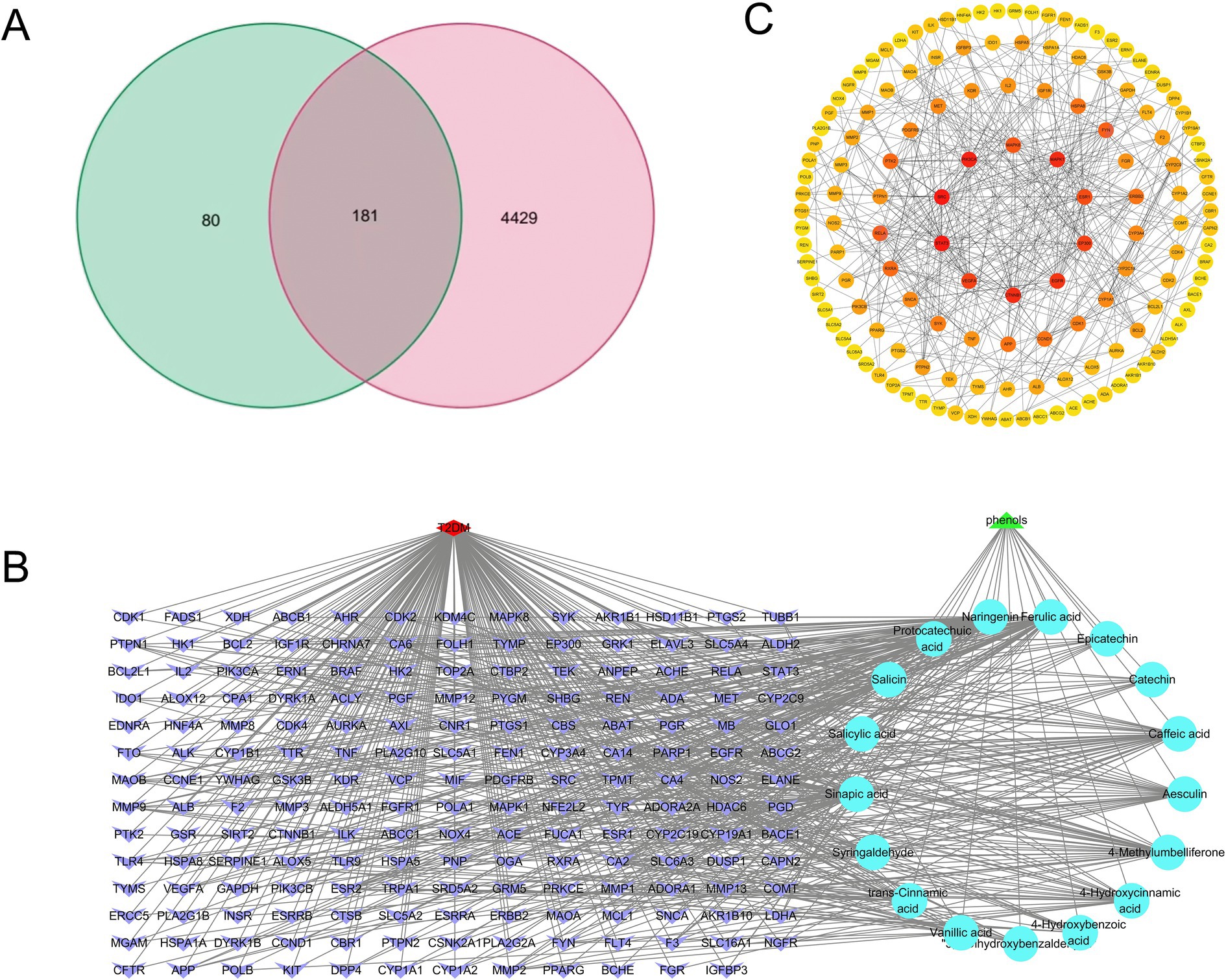
Figure 5. Venn diagram of polyphenols and disease targets (A); fresh-cut pitaya polyphenols - components - common targets (B); mutual mapping of common target PPI (C).
Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis provided insight into the biological functions of these common targets (Figure 6). The results were highly significant, revealing a strong association between the response to oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species metabolic processes (Biological Process), underscoring the potential of these polyphenols to ameliorate oxidative damage, a key pathological factor in insulin resistance. Notably, the top Molecular Functions were transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity and protein tyrosine kinase activity, which are directly implicated in the initial steps of insulin receptor signaling. This suggests that polyphenols potentiate insulin activity by interacting with and modulating these kinases.
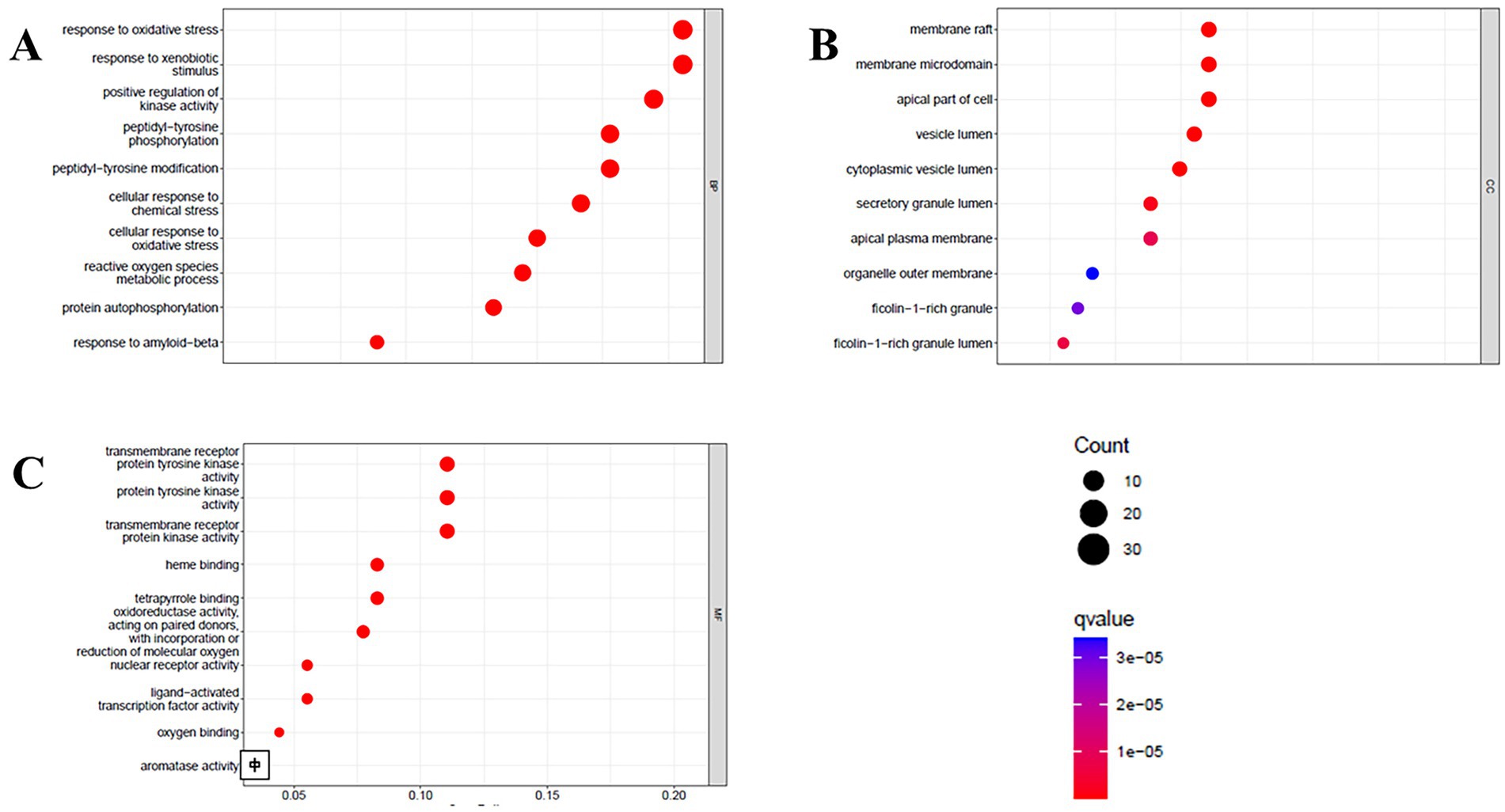
Figure 6. Biological processes (A), cell component (B), and molecular function (C) of GO enrichment analysis.
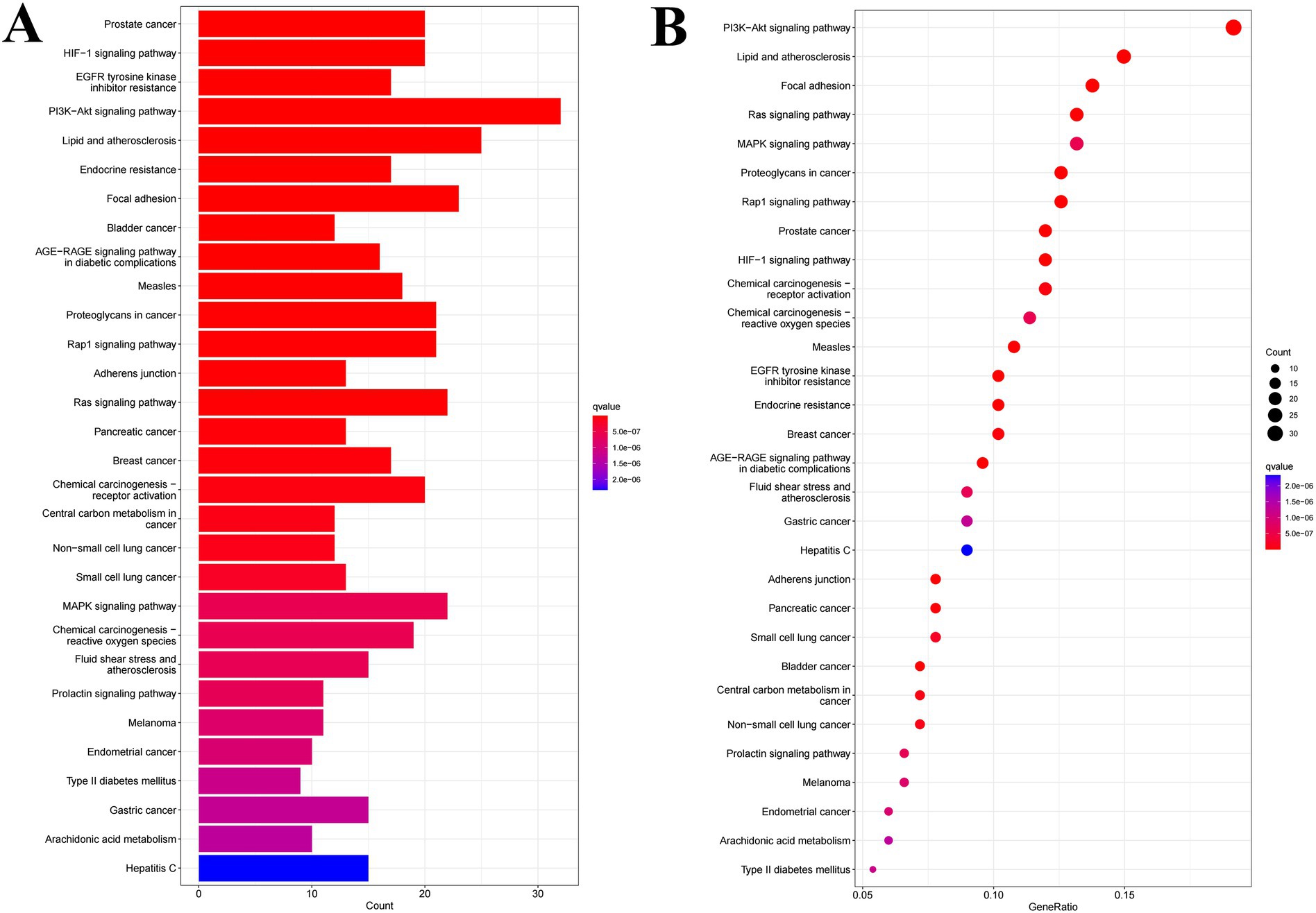
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis confirmed the hypothesized mechanisms (Figure 7). The most significantly enriched pathways in diabetic complications were the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, endocrine resistance, and AGE-RAGE signaling pathway. The enrichment of the PI3K-Akt pathway is of paramount importance because it is the primary intracellular pathway that transduces the metabolic effects of insulin, including glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis. The hub genes identified in the PPI network, such as SRC and STAT3, are known to be upstream regulators and effectors of this pathway. Furthermore, the enrichment of the AGE-RAGE pathway suggests an additional protective role, potentially inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products and associated chronic inflammation that exacerbates diabetes.
3.7 Molecular docking
The in silico molecular docking results (Figure 8 and Table 3) provided direct binding evidence, showing that key compounds such as naringenin and ferulic acid exhibited strong binding affinities (energy < −5.0 kcal/mol) with the hub targets SRC and STAT3. This computationally predicted interaction provides a structural basis for the proposed modulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway.
In summary, in silico analyses predicted that the hypoglycemic effect of ozone-treated pitaya polyphenols is not a singular event but a synergistic outcome of multi-target regulation. The proposed mechanism involves (1) the direct inhibition of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes (α-glucosidase/α-amylase), as confirmed in vitro; it also involves (2) the potential activation of the insulin-sensitive PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and mitigation of diabetic complications via interaction with core targets such as SRC and STAT3, while reducing oxidative stress. This systems-level explanation significantly enhances the scientific depth of our findings and provides a robust theoretical foundation for future in vivo studies.
4 Conclusion
In summary, this study demonstrated that ozone treatment is an effective postharvest strategy for enhancing the functional value of fresh-cut pitayas. The key mechanism was identified as the disruption of the fruit cell wall microstructure, which facilitated the release of bound polyphenols. This improved extractability significantly increased polyphenol bioaccessibility after in vitro digestion. Consequently, the ozone-treated samples exhibited markedly stronger in vitro hypoglycemic activity, as evidenced by their superior inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes.
Furthermore, our integrated approach, which combines in silico and in vitro analyses, provides deeper mechanistic insights. Molecular docking identified naringin, erucic acid, ferulic acid, and caffeic acid as key bioactive compounds, with SRC, STAT3, and PIK3CA emerging as potential targets. This suggests that the hypoglycemic effect of ozone-treated pitaya polyphenols is not only a result of enzyme inhibition but may also involve modulation of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, indicating a potential multi-target mechanism for regulating glucose metabolism.
Based on these findings, future research should prioritize in vivo studies to validate the physiological hypoglycemic effects of these compounds and further elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the modulation of the PI3K-AKT pathway. This study demonstrates the potential of ozone treatment as a clean-label technology for producing fresh-cut fruits with enhanced health benefits.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
CL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Investigation, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JF: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. QD: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft. HD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was funded by Joint Program of Science and Technology Plan of Liaoning Province, China (2024-BSLH-071); The Youth Talent Support Program of Jinzhou Medical University (JYQT202406).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Li, C, Wang, S, Tao, J, Wang, J, and Wu, Z. Monitoring quality parameters and antioxidant potential of fresh-cut red pitaya fruit treated with gaseous ozone using kinetic models. J Food Meas Charact. (2023) 17:4208–24. doi: 10.1007/s11694-023-01927-3
2. Yu, Q, Li, T, and Li, S. Interaction between wheat starch and hawthorn seed polysaccharide and its influence on starch properties and in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. (2025) 485:144610. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.144610
3. Li, X, Li, M, Ji, N, Jin, P, Zhang, J, Zheng, Y, et al. Cold plasma treatment induces phenolic accumulation and enhances antioxidant activity in fresh-cut pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) fruit. LWT. (2019) 115:108447. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108447
4. Li, X, Li, M, Wang, L, Wang, J, Jin, P, and Zheng, Y. Methyl jasmonate primes defense responses against wounding stress and enhances phenolic accumulation in fresh-cut pitaya fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2018) 145:101–7. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.07.001
5. Ding, Y, Morozova, K, Angeli, L, Gasparini, A, Ferrentino, G, and Scampicchio, M. Effect of extraction treatments on the functional properties of free and bound phenols in apple seeds. Food Biosci. (2023) 53:102602. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102602
6. Gavahian, M. Valorized pineapple waste by conventional and energy-saving ohmic extraction: potentially toxic elements and mycotoxin contamination. Qual Assur Saf Crops Foods. (2023) 15:11–20. doi: 10.15586/qas.v15i4.1361
7. Piechowiak, T, Skóra, B, and Balawejder, M. Ozone treatment induces changes in antioxidative defense system in blueberry fruit during storage. Food Bioprocess Technol. (2020) 13:1240–5. doi: 10.1007/s11947-020-02450-9
8. Geyik, ÖG, Tekin-Cakmak, ZH, and Shamanin, VP. Effects of phenolic compounds of colored wheats on colorectal cancer cell lines. Qual Assur Saf Crops Foods. (2023). doi: 10.15586/qas.v15i4.1354
9. Gutiérrez, DR, Chaves, AR, and Rodríguez, SDC. UV-C and ozone treatment influences on the antioxidant capacity and antioxidant system of minimally processed rocket (Eruca sativa mill.). Postharvest Biol Technol. (2018) 138:107–13. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2017.12.014
10. Onopiuk, A, Półtorak, A, Moczkowska, M, Szpicer, A, and Wierzbicka, A. The impact of ozone on health-promoting, microbiological, and colour properties of Rubus ideaus raspberries. CyTA-J Food. (2017) 15:563–73. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2017.1317669
11. Li, C, Wang, S, Wang, J, Wu, Z, Xu, Y, and Wu, Z. Ozone treatment promotes physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut red pitaya based on phenolic metabolism. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1016607. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1016607
12. Wang, J, Wang, S, Sun, Y, Li, C, Li, Y, Zhang, Q, et al. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and naturally present microbes on fresh-cut lettuce using lactic acid and aqueous ozone. RSC Adv. (2019) 9:22636–43. doi: 10.1039/C9RA03544C
13. Zheng, CC, Li, T, Tang, YY, Lu, T, Wu, MK, Sun, J, et al. Structural and functional investigation on stem and peel polysaccharides from different varieties of pitaya. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 259:129172.
14. Ding, X, Ma, J, Liu, S, Dong, X, Pan, X, and Dong, B. Acid electrolytic water treatment improves the quality of fresh-cut red pitaya fruit by regulating ROS metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway. Postharvest Biol Technol. (2024) 207:112636. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2023.112636
15. Fu, L, Xu, BT, Xu, XR, Gan, RY, Zhang, Y, Xia, EQ, et al. Antioxidant capacities and total phenolic contents of 62 fruits. Food Chem. (2011) 129:345–50. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.04.079
16. Liu, Z, Zhang, J, Lu, S, Tang, W, Zhou, Y, and Quek, SY. Effects of different drying methods on phenolic components and in vitro hypoglycemic activities of pulp extracts from two Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. Et Zucc.) cultivars. Food Sci Human Wellness. (2022) 11:366–73. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.11.014
17. Peña-Vázquez, GI, Dominguez-Fernández, MT, Camacho-Zamora, BD, Hernández-Salazar, M, Urías-Orona, V, de Peña, MP, et al. In vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion impacts bioaccessibility and bioactivity of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) phenolic compounds. J Funct Foods. (2022) 88:104891. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104891
18. Zahra, N, Mushtaq, I, Rehman, A, Fatima, S, Khalid, A, Sarwar, A, et al. In-vivo and in-silico analysis of the anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic activities of methanolic fruit extracts of Carica papaya. Ital J Food Sci. (2024) 36:120–35. doi: 10.15586/ijfs.v36i4.2742
19. Nithya, C, Sudheer, KP, Abdullah, S, and Jayachandran, LE. Enhancing juice yield and bioactive compounds in red dragon fruit juice through pulsed electric field and ultrasonic pre-treatments: process optimization and comparative evaluation. Food Chem. (2025) 496:146709. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.146709
20. Uslu, N, and Özcan, MM. The effect of ultrasound-vacuum-assisted extraction on bioactive properties of pitaya (Hylocereus undatus). Int J Food Sci Technol. (2021) 56:6618–25. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.15364
21. Solikhin, A, Hadi, YS, Massijaya, MY, and Nikmatin, S. Production of microfibrillated cellulose by novel continuous steam explosion assisted chemo-mechanical methods and its characterizations. Waste Biomass Valor. (2019) 10:275–86. doi: 10.1007/s12649-017-0066-z
22. Wang, J, Zhang, X, Liu, J, Li, R, Zhou, J, Li, M, et al. Steam explosion improves extractability, antioxidant activity and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of the constituents of Java tea (Clerodendranthus spicatus). Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. (2023) 86:103350. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2023.103350
23. Khatun, MHA, Wang, L, and Chen, H. High solids all-inclusive polysaccharide hydrolysis of steam-exploded corn pericarp by periodic peristalsis. Carbohydr Polym. (2020) 246:116483. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116483
24. Dos Santos, A.L., Santos, André Leonardodos, Morais, Rômulo Alves, Soares, Camila Mariane da Silva, Vellano, Patrícia Oliveira, Martins, Glêndara Aparecida de Souza, et al. Effect of gamma irradiation on the physicochemical, functional and bioactive properties of red pitaya (Hylocereus costaricensis) bark flour Radiat Phys Chem 2022 199:110371 doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2022.110371
25. Kaur, K, Pandiselvam, R, Kothakota, A, Padma Ishwarya, S, Zalpouri, R, and Mahanti, NK. Impact of ozone treatment on food polyphenols–a comprehensive review. Food Control. (2022) 142:109207. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109207
26. Khan, I, Shahid Afridi, M, Ahmad, J, Johnson, SK, Al-Rizeiqi, MH, and Almajwal, AM. Effect of adding fenugreek and Nigella sativa to white rice on postprandial glycemic and appetite responses in healthy individuals. Ital J Food Sci. (2024) 36:301–8. doi: 10.15586/ijfs.v36i3.2564
27. Rinaldi, M, Littardi, P, Ganino, T, Aldini, A, Rodolfi, M, Barbanti, D, et al. Comparison of physical, microstructural, antioxidant and enzymatic properties of pineapple cubes treated with conventional heating, ohmic heating and high-pressure processing. LWT. (2020) 134:110207. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110207
Keywords: fresh-cut pitaya, ozone, phenolic compounds, bioaccessibility, α-glucosidase, α-amylase
Citation: Li C, Hu Y, Fang J, Du Q and Ding H (2025) Ozone treatment improved the extractability, bioaccessibility, and hypoglycemic potential of fresh-cut pitaya polyphenols. Front. Nutr. 12:1707700. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1707700
Edited by:
Yingtong Zhang, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences (JAAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Bikash Kumar, Amity University, IndiaKhashayar Sarabandi, Research Institute of Food Science and Technology (RIFST), Iran
Lihui Zhang, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Hu, Fang, Du and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chen Li, bGljaGVuOTQwMzI5QDE2My5jb20=
 Chen Li
Chen Li Yishuang Hu1,2
Yishuang Hu1,2