- 1State Key Laboratory of Technologies for Chinese Medicine Pharmaceutical Process Control and Intelligent Manufacture, Department of Pharmacy, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China
- 2School of Food Science, Nanjing Xiaozhuang University, Nanjing, China
- 3School of Food Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China
by Tang, C.-F., Li, F., Ma, L.-H., Wang, Q.-N., Xie, P.-F., Xiang, L., Zhu, Y.-J., Wang, Y.-Y., Zhang, Y.-Z., Shi, J.-J., Li, S.-J., and Li, J.-M. (2025). Front. Nutr. 12:1652968. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1652968
There was a mistake in Figure 5 as published. The images for CTL and Flouxetine groups in the CA2 region were incorrect during the preparation. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
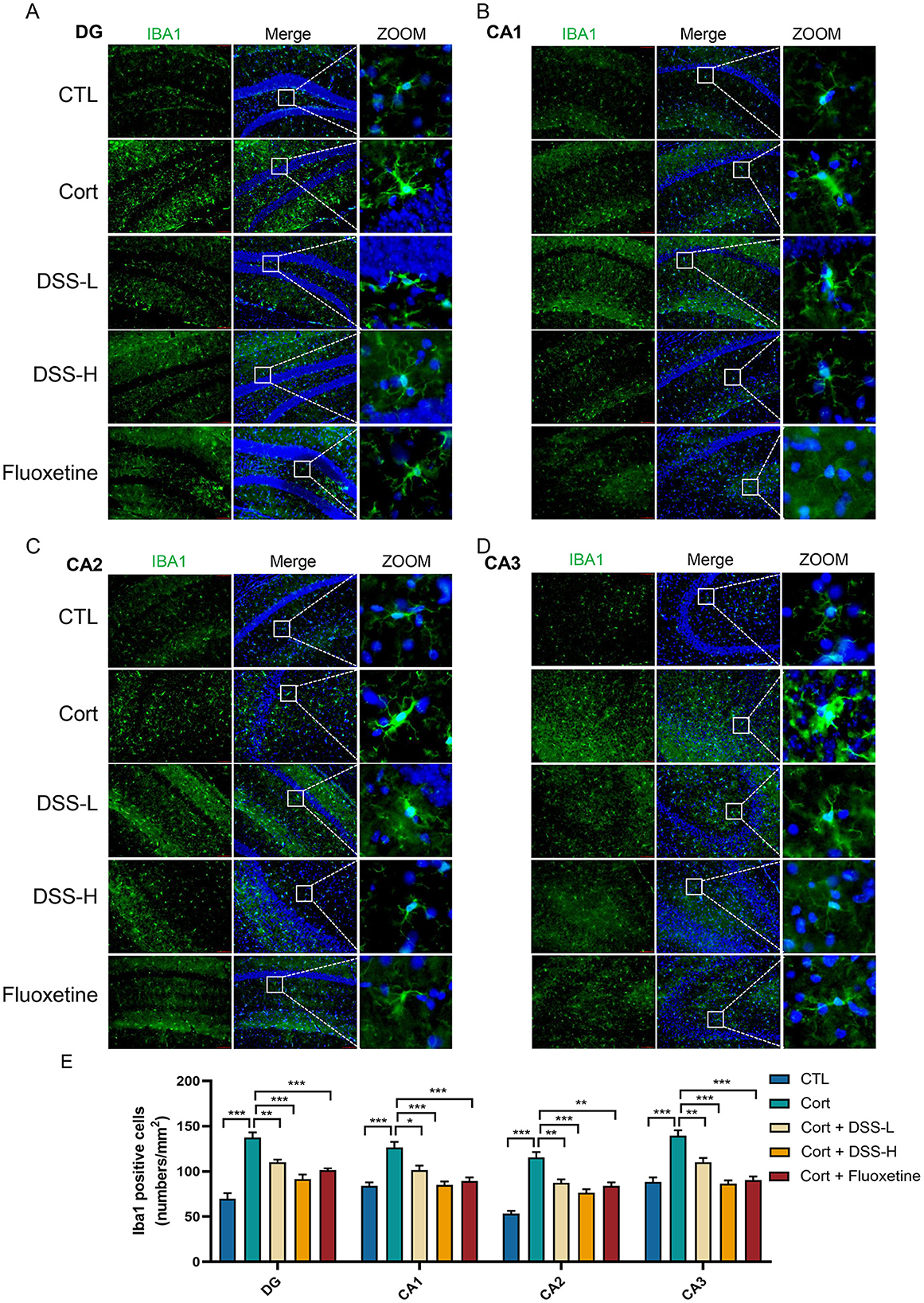
Figure 5. DSS suppresses hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice. (A) Staining using coronal section of mouse, representative images labeled with IBA1 was shown in the dentate gyrus (DG) region of the mice's hippocampus. (B) Representative images of IBA1 labeling in the CA1 region of the mouse hippocampus. (C) Representative images of IBA1 labeling in the CA2 region of the mouse hippocampus. (D) Representative images of IBA1 labeling in the CA3 region of the mouse hippocampus. (E) Quantification of microglia labeled with IBA1 in the mouse hippocampus. Data are expressed as Mean ± SEM, n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
An incorrect number was provided for the grant Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province. The incorrect number was written as, “012071002966, C-FT”. The correct number is “BK20250770, C-FT”.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Generative AI statement
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: DSS, depression, hippocampal neurogenesis, hippocampal inflammation, TLR4/NF-κB p65, JAK2/STAT3 and AKT-GSK3β signaling pathways
Citation: Tang C-F, Li F, Ma L-H, Wang Q-N, Xie P-F, Xiang L, Zhu Y-J, Wang Y-Y, Zhang Y-Z, Shi J-J, Li S-J and Li J-M (2026) Correction: Danggui Shaoyao San attenuates depressive-like behaviors in mice via TLR4/NF-κB p65/JAK-STAT3/AKT-GSK3β signaling pathways: modulation of hippocampal neurogenesis and neuroinflammation. Front. Nutr. 12:1761855. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1761855
Received: 06 December 2025; Revised: 06 December 2025;
Accepted: 09 December 2025; Published: 05 January 2026.
Edited and reviewed by: Jia Zhao, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2026 Tang, Li, Ma, Wang, Xie, Xiang, Zhu, Wang, Zhang, Shi, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chuan-Feng Tang, dGFuZ2NodWFuZmVuZ0BuanVjbS5lZHUuY24=; Jian-Mei Li, bGlqaWFubWVpQG5qbnUuZWR1LmNu; Sheng-Jie Li, bGlzaGVuZ2ppZUBuanh6Yy5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Chuan-Feng Tang
Chuan-Feng Tang Fan Li2,3†
Fan Li2,3† Jun-Jie Shi
Jun-Jie Shi Sheng-Jie Li
Sheng-Jie Li Jian-Mei Li
Jian-Mei Li